Часовой пояс — time zone.
Наше время впереди/позади вашего на … часов.
Our time is … hours ahead of/behind yours.
Our time is ahead of/behind yours by … hours.
Часто при международном телефонном разговоре возникает этот вопрос — а который час сейчас в вашей стране? — What time is it now in your country?
Ответ — как обычно, например: It’s 4:25 A.M. И Вашему собеседнику станет понятно, почему у Вас несколько заспанный и недовольный голос.
Следует различать астрономические часовые пояса и часовые зоны, установленные законодательно.
Часовые пояса и зоны имеют буквенные обозначения. Московское время — MSK.
Нулевой часовой пояс (Гринвичское время) — Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) или Universal Time Coordinated (UTC).
Летнее время (в тех странах, где оно используется) — Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Time zones in North America
ADT — Atlantic Daylight Time
AKDT — Alaska Daylight Time
AKST — Alaska Standard Time
AST — Atlantic Standard Time
CDT — Central Daylight Time
CST — Central Standard Time
EDT — Eastern Daylight Time
EGST — Eastern Greenland Summer Time
EGT — East Greenland Time
EST — Eastern Standard TimeHADT — Hawaii-Aleutian Daylight Time
HAST — Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time
MDT — Mountain Daylight Time
MST — Mountain Standard Time
NDT — Newfoundland Daylight Time
NST — Newfoundland Standard Time
PDT — Pacific Daylight Time
PMDT — Pierre & Miquelon Daylight Time
PMST — Pierre & Miquelon Standard Time
PST — Pacific Standard Time
WGST — Western Greenland Summer Time
WGT — West Greenland Time
Когда человек быстро перемещается из одного часового пояса в другой с большой разницей во времени, у него возникает состояние, которое называется «jet lag» — сбой суточного ритма. В той стране, куда он прилетел, все бодрствуют, а ему хочется спать, потому что в стране, из которой он улетел, сейчас ночь.
Большая Советская энциклопедия → Что такое Московское время, что означает и как правильно пишется
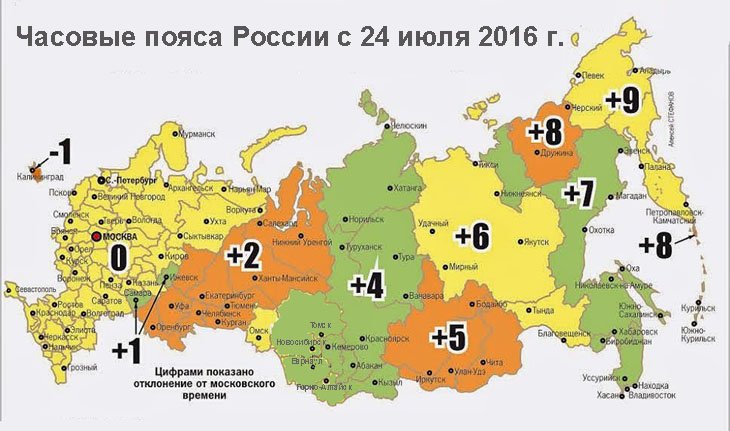
Часовые пояса России
Территория нашей страны очень велика и поэтому в России целых одиннадцать часовых поясов.
Карта часовых поясов России:
На карте часовых поясов России цифрами обозначена разница во времени с Москвой.
Каждый из нас слышал выражение, что когда москвичи просыпаются, на Дальнем Востоке уже собираются спать. Происходит это потому, что эти два города находятся в разных районах страны и живут по разным часовым поясам с максимальной разницей. Основным считается московское время – по Москве объявляют отправление поездов с вокзалов во всех городах, по московскому времени дикторы телевидения сообщают нам о демонстрации фильмов. Все остальные регионы должны высчитывать разницу между московским и местным временем самостоятельно.
Одиннадцать часовых поясов России обусловлены огромной территорией нашей страны. На вопрос: «Сколько времени?” нет определённого ответа, ведь в разных городах и странах в этот момент совершенно разное время, в зависимости от того, в каком часовом поясе находится город или страна.
Текущее время сейчас в городах России:
Существует огромное количество карт часовых поясов, они составляются для удобства людей. Посмотрев на такую карту, можно наглядно увидеть, в каком часовом поясе вы проживаете и какая разница между вашим местным временем и, например, московским. Поэтому нет необходимости держать в голове сведения о часовых поясах России или другой страны. Можно в любой момент открыть нужную страницу сайта и узнать всю информацию, которая нас интересует.
Разница во времени между городами России:
Алфавитный список часовых поясов городов России и разницей во времени с Москвой:
Часовой пояс Абакана UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Анадыря UTC +12: 00 MSK +09: 00
Часовой пояс Анапы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Ангарска UTC +08: 00 MSK +05: 00
Часовой пояс Армавира UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Архангельска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Астрахани UTC +04: 00 MSK +01: 00
Часовой пояс Барнаула UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Белгорода UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Бийска UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Биробиджана UTC +10: 00 MSK +07: 00
Часовой пояс Благовещенска UTC +09: 00 MSK +06: 00
Часовой пояс Братска UTC +08: 00 MSK +05: 00
Часовой пояс Брянска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Великого Новгорода UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Владивостока UTC +10: 00 MSK +07: 00
Часовой пояс Владикавказа UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Владимира UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Волгограда UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Волжского UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Вологды UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Воркуты UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Воронежа UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Гатчины UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Горно-Алтайска UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Грозного UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Дмитрова UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Екатеринбурга UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Ессентуки UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Иваново UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Ижевска UTC +04: 00 MSK +01: 00
Часовой пояс Иркутска UTC +08: 00 MSK +05: 00
Часовой пояс Йошкар-Олы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Казани UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Калининграда UTC +02: 00 MSK -01: 00
Часовой пояс Калуги UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Кемерово UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Кирова UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Кисловодска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Коломны UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Комсомольска-на-Амуре UTC +10: 00 MSK +07: 00
Часовой пояс Королёва UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Костромы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Краснодара UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Красноярска UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Кургана UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Курска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Кызыла UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Липецка UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Магадана UTC +11: 00 MSK +08: 00
Часовой пояс Магнитогорска UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Майкопа UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Махачкалы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Минеральных Вод UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Мирного UTC +09: 00 MSK +06: 00
Часовой пояс Москвы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Мурманска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Мурома UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Набережных Челнов UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Нальчика UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Нарьян-Мара UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Находки UTC +10: 00 MSK +07: 00
Часовой пояс Нижневартовска UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Нижнекамска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Нижнего Новгорода UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Нижнего Тагила UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Новокузнецка UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Новороссийска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Новосибирска UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Нового Уренгоя UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Норильска UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Оймякона UTC +10: 00 MSK +07: 00
Часовой пояс Омска UTC +06: 00 MSK +03: 00
Часовой пояс Оренбурга UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Орла UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Орска UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Пензы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Переславля-Залесского UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Перми UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Петрозаводска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Петропавловска-Камчатского UTC +12: 00 MSK +09: 00
Часовой пояс Пскова UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Пятигорска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Ростова Великого UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Ростова-на-Дону UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Рязани UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Салехарда UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Самары UTC +04: 00 MSK +01: 00
Часовой пояс Санкт-Петербурга UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Саранска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Саратова UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Севастополя UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Сергиева Посада UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Симферополя UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Смоленска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Сочи UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Среднеколымска UTC +11: 00 MSK +08: 00
Часовой пояс Ставрополя UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Старого Оскола UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Стерлитамака UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Суздаля UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Сургута UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Сыктывкара UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Таганрога UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Тамбова UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Твери UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Тобольска UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Тольятти UTC +04: 00 MSK +01: 00
Часовой пояс Томска UTC +07: 00 MSK +04: 00
Часовой пояс Тулы UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Тюмени UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Углича UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Улан-Удэ UTC +08: 00 MSK +05: 00
Часовой пояс Ульяновска UTC +04: 00 MSK +01: 00
Часовой пояс Уфы UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Хабаровска UTC +10: 00 MSK +07: 00
Часовой пояс Ханты-Мансийска UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Чебоксар UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Челябинска UTC +05: 00 MSK +02: 00
Часовой пояс Череповца UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Черкесска UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Читы UTC +09: 00 MSK +06: 00
Часовой пояс Элисты UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
Часовой пояс Южно-Сахалинска UTC +11: 00 MSK +08: 00
Часовой пояс Якутска UTC +09: 00 MSK +06: 00
Часовой пояс Ярославля UTC +03: 00 MSK +00: 00
См. также:
Время:
Карты:
2007 — 2018 © world-time-zones.ru
13.00 или 13:00
Комментируем ответы «Справочного бюро». Не забывайте указывать номер ответа на «Справке»!
Вернуться в Обсуждение ответов «Справки»
Кто сейчас на форуме
Сейчас этот форум просматривают: нет зарегистрированных пользователей и гости: 3
Сообщений: 8 • Страница1из1
13.00 или 13:00
Alena » 07 ноя 2014, 12:52
Вопрос № 279202
Здравствуйте.
Меня интересует вопрос оформления программы мероприятий для сайта. Например:
12.00 Обед
13.00 Выступление генерального директора компании по вопросам:
— повышение заработной платы <…>
Александра
Alexandrin88
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Лучше так:
12.00 – обед
13.00 – выступление генерального директора компании по вопросам:
<…>
_________________
А как же рекомендация время писать через двоеточие? 13:00 и т. п.Alena Сообщений:566Зарегистрирован:
12 янв 2010, 11:35
Re: 13.00 или 13:00
fililog » 07 ноя 2014, 13:12
Рекомендация писать время через двоеточие существует для технических и официальных текстов. В художественных и неофициальных (как сайт) можно писать (и часто пишут) с точкой, как рекомендовала Справка.
Вопрос № 237484
Как правильно указывать в официальных документах обозначение времени?
Например:
9:00 или 9,00 или 9.00, 9:00ч., 9ч.00м. либо другой вариант…
и еще… как обозначить, что это именно время?
Например время работы:
с 9:00 до 21:00, 9:00 — 21:00, либо другой вариант.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Возможные варианты: в 9 часов, в 9 ч., с 9 ч.
Перевод «Московскому времени» на английский
до 21 ч., с 9:00 до 21:00, 9:00 — 21:00. Варианты с двоеточием употребляются, как правило, в научно-технических документах.
fililog Сообщений: 10199Зарегистрирован:
25 окт 2013, 06:31Откуда: Москва
Re: 13.00 или 13:00
Alena » 07 ноя 2014, 15:19
fililog писал(а):Рекомендация писать время через двоеточие существует для технических и официальных текстов. В художественных и неофициальных (как сайт) можно писать (и часто пишут) с точкой, как рекомендовала Справка.
Вопрос № 237484
Как правильно указывать в официальных документах обозначение времени?
Например:
9:00 или 9,00 или 9.00, 9:00ч., 9ч.00м. либо другой вариант…
и еще… как обозначить, что это именно время?
Например время работы:
с 9:00 до 21:00, 9:00 — 21:00, либо другой вариант.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Возможные варианты: в 9 часов, в 9 ч., с 9 ч. до 21 ч., с 9:00 до 21:00, 9:00 — 21:00. Варианты с двоеточием употребляются, как правило, в научно-технических документах.
В этом ответе нет варианта 21.00Alena Сообщений:566Зарегистрирован:
12 янв 2010, 11:35
Re: 13.00 или 13:00
Марго » 07 ноя 2014, 16:47
fililog писал(а):Рекомендация писать время через двоеточие существует для технических и официальных текстов.
Так программа мероприятия и есть официальный текст.
Марго Сообщений:16211Зарегистрирован:
28 дек 2009, 16:42Откуда:Москва
Re: 13.00 или 13:00
adada » 07 ноя 2014, 17:08
А вот это попадание — в точку, в каждую точку двоеточия!
adada Сообщений:39062Зарегистрирован:
28 дек 2009, 14:00
Откуда:тупик между Доном и Сяном
Re: 13.00 или 13:00
fililog » 07 ноя 2014, 17:13
Alena писал(а):В этом ответе нет варианта 21.00
Вопрос № 213306
Написание времени цифрами, только через двуеточие или можно использовать и точку?
12:05, 12.05
Prusac Aleksandar
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Международный стандарт обозначения времени — через двоеточие. Однако второй вариант написания тоже часто встречается.
Вопрос № 259611
Здравствуйте!
Пару дней назад задавала вопрос, но так и не получила ответа.
Какое написание времени в русском языке считается верным: через точку или двоеточие? Например: 12.46 или 12:46?
Спасибо!
katjakolesina
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Для обозначения времени дня в научно-технических документах требуется постановка двоеточия: 12:46.
fililog Сообщений: 10199Зарегистрирован:
25 окт 2013, 06:31Откуда: Москва
Re: 13.00 или 13:00
adada » 07 ноя 2014, 17:20
Без двоеточия, наверно, не обойтись, когда в состав лаконичной отметки времени включаются не только часы и минуты (и секунды), но и месяцы и дни (и годы).
adada Сообщений:39062Зарегистрирован:
28 дек 2009, 14:00Откуда:тупик между Доном и Сяном
Re: 13.00 и 13:00
fililog » 07 ноя 2014, 18:56
Если в научно-популярных журналах пишут по ГОСТ ИСО 8601–2001 «Представление дат и времени. Общие требования», то в глянце можно и через точку. На сайте президента должно писаться через двоеточие, а на сайте компании можно и через точку. Ошибки в этом нет, главное — выбрать один формат для сайта или журнала и его придерживаться.
fililog Сообщений:10199Зарегистрирован:
25 окт 2013, 06:31Откуда:Москва Сообщений: 8 • Страница1из1
Иногда можно услышать, как дикторы новостей на радио или телевидении, приветствуя зрителя, называют точное время, говоря обычно что-то вроде «сейчас полдень по Москве». Что такое это самое «московское время», знают даже дети, которые уже учат географию в школе, а вот многие взрослые забывают и вспоминают, только когда надо позвонить в Красноярск или лететь в Токио.
Московское время — это главный часовой пояс, стандартное время России. Другие часовые пояса отсчитываются от него, а в расписаниях поездов московское время и вовсе используется по всей стране.
Часовой пояс: МСК+2, Мск+2 или мск+2 — Говорим и пишем правильно
Например, когда в Москве полночь, во Владивостоке — MSK+7, или семь утра, а полдень в Красноярске — это восемь утра «по Москве».
Московское время, в свою очередь, отличается от всемирного координационного времени (UTС) на четыре часа и пишется как (UTС+4). Когда Москвичи просыпаются в семь утра, чтобы успеть на работу, жители Лондона, время которого без отклонений от Гринвича, ещё спят в кроватях, так как «всего три часа ночи».
Интересно, что технически точное Московское время находится между UTС+2 и UTС+3. Сквозь Москву проходит меридиан 37°30’ восточной долготы, являющийся границей 2-го и 3-го географических часовых поясов. А если еще точнее, то с точки зрения географии московское время выглядит так: UTC+02:30:48. Так Москва и жила до 1919 года, но история не щадит даже время. Сначала в 1919 году СНК РСФСР ввёл в стране международную систему часовых поясов, и Москва была неправильно отнесена ко 2-му поясу (UTC+2).
Потом, спустя 21 год, 16 июня 1930, вместе с отменой перехода на летнее время Москва перешла на один «декретный» час вперёд, и в Москве установилось самое близкое к природному время UTC+3, но и это не навсегда. Последнее изменение произошло относительно недавно: в середине 2011 года вместе с отменой перехода на летнее время Москва одновременно перешла ещё на один час, и было установлено время UTC+4.
Долго говорили о возврате на зимнее время, и вот, наконец, 26 октября 2014 года в 02:00, в ночь с субботы на воскресенье, стрелки переводятся на час назад. Надолго ли — неизвестно, то самое «Точное Московское» вновь может измениться. Но пока об этом говорить не время.
В русском языке имена существительные имеют категорию рода: мужского, среднего, женского или общего, могут быть одушевленными или неодушевленными, собственными или нарицательными, а также изменяться по числам и падежам. Изменение падежных окончаний соответствует определенному типу склонения, в котором учитываются все перечисленные характеристики. Правописание существительного время в форме косвенных падежей подчиняется особым правилам. Знание этих правил позволит избежать ошибки в ответе на вопрос о том, как нужно писать: время или времени?
Существительное время относится к среднему роду, но в единственном числе изменяется по падежам не по II типу склонения, как, например, существительные море, окно, озеро, а по так называемому разносклоняемому типу. Он объединяет 10 существительных среднего рода, оканчивающихся на –мя: время, темя, вымя, стремя, знамя, семя, имя, пламя, племя, бремя, и одно существительное мужского рода путь. В родительном, дательном, творительном и предложном падежах, кроме устойчивых окончаний -и, -ем, они приобретают суффикс –ен-, а в именительном и винительном полностью совпадают по форме написания:
| Падеж, вопрос | Существительные на -мя | ||
| И. (что?) | время | темя | знамя |
| Р. (чего?) | времени | темени | знамени |
| Д. (чему?) | времени | темени | знамени |
| В. (что?) | время | темя | знамя |
| Т. (чем?) | временем | теменем | знаменем |
| П. (о чем?) | (о) времени | (о) темени | (о) знамени |
В зависимости от того, в каком падеже употребляется существительное время, в предложении оно может иметь только одну из трех форм: время, времени или временем.
Пришло время собирать урожай яблок. (Им. п.)
Несмотря на позднее время, все еще было светло. (Вин. п.)
Сколько времени утекло с тех пор! (Род. п.)
Надо доверять своему времени. (Дат. п.)
Тем временем в зрительном зале происходило что-то странное. (Твор. п.)
Что вспоминать о былом времени! (Пр. п.)
При выборе нужной падежной формы время или времени следует обращать внимание на вопрос, который можно поставить к слову. Вопросу что? соответствует форма время, вопросам чего? чему? о чем? – форма времени.
TheDifference.ru дает следующие рекомендации по образованию и употреблению в речи падежных форм время и времени:
- В именительном и винительном падежах правильно употреблять форму время. В родительном, дательном и предложном употребляется форма времени.
- Существительное время в предложении выступает в роли подлежащего или прямого дополнения. Форма времени может быть дополнением или обстоятельством.
- С вопросительным местоимением сколько и наречием много сочетается форма родительного падежа: сколько времени; много времени.
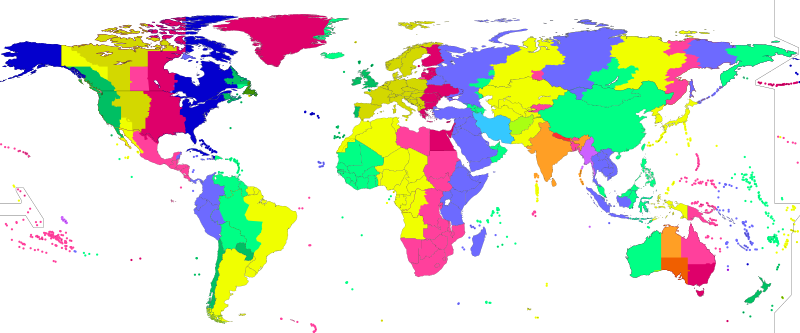
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.
All time zones are defined as offsets from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), ranging from UTC−12:00 to UTC+14:00. The offsets are usually a whole number of hours, but a few zones are offset by an additional 30 or 45 minutes, such as in India, South Australia and Nepal.
Some areas of higher latitude use daylight saving time for about half of the year, typically by adding one hour to local time during spring and summer.
List of UTC offsets
In the table below, the locations that use daylight saving time (DST) are listed in their UTC offset when DST is not in effect. When DST is in effect, approximately during spring and summer, their UTC offset is increased by one hour (except for Lord Howe Island, where it is increased by 30 minutes). For example, during the DST period California observes UTC−07:00 and the United Kingdom observes UTC+01:00.
| UTC offset | Locations that do not use DST | Locations that use DST | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTC−12:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−11:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−10:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−09:30 | ||||
| UTC−09:00 | ||||
| UTC−08:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−07:00 | ||||
| UTC−06:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC−05:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC−04:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−03:30 | ||||
| UTC−03:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−02:00 | ||||
| UTC−01:00 |
|
|||
| UTC±00:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+01:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC+02:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC+03:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+03:30 | ||||
| UTC+04:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+04:30 | ||||
| UTC+05:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+05:30 |
|
|||
| UTC+05:45 | ||||
| UTC+06:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+06:30 |
|
|||
| UTC+07:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+08:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+08:45 | ||||
| UTC+09:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+09:30 | ||||
| UTC+10:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+10:30 | ||||
| UTC+11:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+12:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+12:45 | ||||
| UTC+13:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+14:00 |
- ^ a b Observes UTC±00:00 around Ramadan.[1][2][3]
History
The apparent position of the Sun in the sky, and thus solar time, varies by location due to the spherical shape of the Earth. This variation corresponds to four minutes of time for every degree of longitude, so for example when it is solar noon in London, it is about 10 minutes before solar noon in Bristol, which is about 2.5 degrees to the west.[5]
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich, founded in 1675, established Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), the mean solar time at that location, as an aid to mariners to determine longitude at sea, providing a standard reference time while each location in England kept a different time.
Railway time
Plaque commemorating the Railway General Time Convention of 1883 in North America
In the 19th century, as transportation and telecommunications improved, it became increasingly inconvenient for each location to observe its own solar time. In November 1840, the Great Western Railway started using GMT kept by portable chronometers.[6] This practice was soon followed by other railway companies in Great Britain and became known as Railway Time.
Around August 23, 1852, time signals were first transmitted by telegraph from the Royal Observatory. By 1855, 98% of Great Britain’s public clocks were using GMT, but it was not made the island’s legal time until August 2, 1880. Some British clocks from this period have two minute hands, one for the local time and one for GMT.[7]
On November 2, 1868, the then British Colony of New Zealand officially adopted a standard time to be observed throughout the colony.[8] It was based on longitude 172°30′ east of Greenwich, that is 11 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT. This standard was known as New Zealand Mean Time.[9]
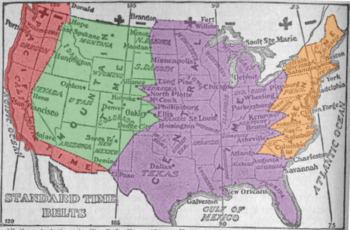
Timekeeping on North American railroads in the 19th century was complex. Each railroad used its own standard time, usually based on the local time of its headquarters or most important terminus, and the railroad’s train schedules were published using its own time. Some junctions served by several railroads had a clock for each railroad, each showing a different time.[10]
1913 time zone map of the United States, showing boundaries very different from today
Charles F. Dowd proposed a system of hourly standard time zones for North American railroads around 1863, although he published nothing on the matter at that time and did not consult railroad officials until 1869. In 1870 he proposed four ideal time zones having north–south borders, the first centered on Washington, D.C., but by 1872 the first was centered on meridian 75° west of Greenwich, with natural borders such as sections of the Appalachian Mountains. Dowd’s system was never accepted by North American railroads. Instead, U.S. and Canadian railroads implemented a version proposed by William F. Allen, the editor of the Traveler’s Official Railway Guide.[11] The borders of its time zones ran through railroad stations, often in major cities. For example, the border between its Eastern and Central time zones ran through Detroit, Buffalo, Pittsburgh, Atlanta, and Charleston. It was inaugurated on Sunday, November 18, 1883, also called «The Day of Two Noons»,[12] when each railroad station clock was reset as standard-time noon was reached within each time zone.
The North American zones were named Intercolonial, Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific. Within a year 85% of all cities with populations over 10,000 (about 200 cities) were using standard time.[13] A notable exception was Detroit (located about halfway between the meridians of Eastern and Central time), which kept local time until 1900, then tried Central Standard Time, local mean time, and Eastern Standard Time (EST) before a May 1915 ordinance settled on EST and was ratified by popular vote in August 1916. The confusion of times came to an end when standard time zones were formally adopted by the U.S. Congress in the Standard Time Act of March 19, 1918.
Worldwide time zones
Italian mathematician Quirico Filopanti introduced the idea of a worldwide system of time zones in his book Miranda!, published in 1858. He proposed 24 hourly time zones, which he called «longitudinal days», the first centred on the meridian of Rome. He also proposed a universal time to be used in astronomy and telegraphy. However, his book attracted no attention until long after his death.[14][15]
Scottish-born Canadian Sir Sandford Fleming proposed a worldwide system of time zones in 1876 — see Sandford Fleming § Inventor of worldwide standard time. The proposal divided the world into twenty-four time zones labeled A-Y (skipping J), each one covering 15 degrees of longitude. All clocks within each zone would be set to the same time as the others, but differed by one hour from those in the neighboring zones.[16] He advocated his system at several international conferences, including the International Meridian Conference, where it received some consideration. The system has not been directly adopted, but some maps divide the world into 24 time zones and assign letters to them, similarly to Fleming’s system.[17]
World map of time zones in 1928
By about 1900, almost all inhabited places on Earth had adopted a standard time zone, but only some of them used an hourly offset from GMT. Many applied the time at a local astronomical observatory to an entire country, without any reference to GMT. It took many decades before all time zones were based on some standard offset from GMT or Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). By 1929, the majority of countries had adopted hourly time zones, though some countries such as Iran, India, Myanmar and parts of Australia had time zones with a 30-minute offset. Nepal was the last country to adopt a standard offset, shifting slightly to UTC+05:45 in 1986.[18]
All nations currently use standard time zones for secular purposes, but not all of them apply the concept as originally conceived. Several countries and subdivisions use half-hour or quarter-hour deviations from standard time. Some countries, such as China and India, use a single time zone even though the extent of their territory far exceeds the ideal 15° of longitude for one hour; other countries, such as Spain and Argentina, use standard hour-based offsets, but not necessarily those that would be determined by their geographical location. The consequences, in some areas, can affect the lives of local citizens, and in extreme cases contribute to larger political issues, such as in the western reaches of China.[19] In Russia, which has 11 time zones, two time zones were removed in 2010[20][21] and reinstated in 2014.[22]
Notation
ISO 8601
ISO 8601 is a standard established by the International Organization for Standardization defining methods of representing dates and times in textual form, including specifications for representing time zones.[23]
If a time is in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), a «Z» is added directly after the time without a separating space. «Z» is the zone designator for the zero UTC offset. «09:30 UTC» is therefore represented as «09:30Z» or «0930Z». Likewise, «14:45:15 UTC» is written as «14:45:15Z» or «144515Z».[24] UTC time is also known as «Zulu» time, since «Zulu» is a phonetic alphabet code word for the letter «Z».[24]
Offsets from UTC are written in the format ±hh:mm, ±hhmm, or ±hh (either hours ahead or behind UTC). For example, if the time being described is one hour ahead of UTC (such as the time in Germany during the winter), the zone designator would be «+01:00», «+0100», or simply «+01». This numeric representation of time zones is appended to local times in the same way that alphabetic time zone abbreviations (or «Z», as above) are appended. The offset from UTC changes with daylight saving time, e.g. a time offset in Chicago, which is in the North American Central Time Zone, is «−06:00» for the winter (Central Standard Time) and «−05:00» for the summer (Central Daylight Time).[25]
Abbreviations
Time zones are often represented by alphabetic abbreviations such as «EST», «WST», and «CST», but these are not part of the international time and date standard ISO 8601. Such designations can be ambiguous; for example, «CST» can mean (North American) Central Standard Time (UTC−06:00), Cuba Standard Time (UTC−05:00) and China Standard Time (UTC+08:00), and it is also a widely used variant of ACST (Australian Central Standard Time, UTC+09:30).[26]
Conversions
Conversion between time zones obeys the relationship
- «time in zone A» − «UTC offset for zone A» = «time in zone B» − «UTC offset for zone B»,
in which each side of the equation is equivalent to UTC.
The conversion equation can be rearranged to
- «time in zone B» = «time in zone A» − «UTC offset for zone A» + «UTC offset for zone B».
For example, the New York Stock Exchange opens at 09:30 (EST, UTC offset= −05:00). In California (PST, UTC offset= −08:00) and India (IST, UTC offset= +05:30), the New York Stock Exchange opens at
- time in California = 09:30 − (−05:00) + (−08:00) = 06:30;
- time in India = 09:30 − (−05:00) + (+05:30) = 20:00.
These calculations become more complicated near the time switch to or from daylight saving time, as the UTC offset for the area becomes a function of UTC time.
The time differences may also result in different dates. For example, when it is 22:00 on Monday in Egypt (UTC+02:00), it is 01:00 on Tuesday in Pakistan (UTC+05:00).
The table «Time of day by zone» gives an overview on the time relations between different zones.
| Time of day by zone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTC offset | Monday | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| UTC−12:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 |
| UTC−11:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 |
| UTC−10:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 |
| UTC−09:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 |
| UTC−09:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 |
| UTC−08:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 |
| UTC−07:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 |
| UTC−06:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 |
| UTC−05:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 |
| UTC−04:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 |
| UTC−03:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 |
| UTC−03:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 |
| UTC−02:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 |
| UTC−02:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 |
| UTC−01:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 |
| UTC±00:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 |
| UTC+01:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 |
| UTC+02:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 |
| UTC+03:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 |
| UTC+03:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 |
| UTC+04:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 |
| UTC+04:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 |
| UTC+05:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 |
| UTC+05:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 |
| UTC+05:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 | 00:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 |
| UTC+06:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 |
| UTC+06:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 |
| UTC+07:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 |
| UTC+08:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 |
| UTC+08:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 | 00:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 |
| UTC+09:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 |
| UTC+09:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 |
| UTC+10:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 |
| UTC+10:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 |
| UTC+11:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 |
| UTC+12:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 |
| UTC+12:45 | 00:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 |
| UTC+13:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 |
| UTC+13:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 | 00:45 |
| UTC+14:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 |
| UTC offset | Tuesday | Wednesday |
Nautical time zones
Since the 1920s, a nautical standard time system has been in operation for ships on the high seas. As an ideal form of the terrestrial time zone system, nautical time zones consist of gores of 15° offset from GMT by a whole number of hours. A nautical date line follows the 180th meridian, bisecting one 15° gore into two 7.5° gores that differ from GMT by ±12 hours.[27][28][29]
However, in practice each ship may choose what time to observe at each location. Ships may decide to adjust their clocks at a convenient time, usually at night, not exactly when they cross a certain longitude.[30] Some ships simply remain on the time of the departing port during the whole trip.[31]
Skewing of time zones
Difference between sun time and clock time during daylight saving time:
| 1h ± 30 min behind | |
| 0h ± 30m | |
| 1h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 2h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 3h ± 30 m ahead |
DST observed
DST formerly observed
DST never observed
Ideal time zones, such as nautical time zones, are based on the mean solar time of a particular meridian located in the middle of that zone with boundaries located 7.5 degrees east and west of the meridian. In practice, however, many time zone boundaries are drawn much farther to the west, and some countries are located entirely outside their ideal time zones.
For example, even though the Prime Meridian (0°) passes through Spain and France, they use the mean solar time of 15 degrees east (Central European Time) rather than 0 degrees (Greenwich Mean Time). France previously used GMT, but was switched to CET (Central European Time) during the German occupation of the country during World War II and did not switch back after the war.[32] Similarly, prior to World War II, the Netherlands observed «Amsterdam Time», which was twenty minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. They were obliged to follow German time during the war, and kept it thereafter. In the mid-1970s the Netherlands, as other European states, began observing daylight saving (summer) time.
One reason to draw time zone boundaries far to the west of their ideal meridians is to allow the more efficient use of afternoon sunlight.[33] Some of these locations also use daylight saving time (DST), further increasing the difference to local solar time. As a result, in summer, solar noon in the Spanish city of Vigo occurs at 14:41 clock time. This westernmost area of continental Spain never experiences sunset before 18:00 clock time, even in winter, despite lying 42 degrees north of the equator.[34] Near the summer solstice, Vigo has sunset times after 22:00, similar to those of Stockholm, which is in the same time zone and 17 degrees farther north. Stockholm has much earlier sunrises, though.[35]
A more extreme example is Nome, Alaska, which is at 165°24′W longitude – just west of center of the idealized Samoa Time Zone (165°W). Nevertheless, Nome observes Alaska Time (135°W) with DST so it is slightly more than two hours ahead of the sun in winter and over three in summer.[36]
Kotzebue, Alaska, also near the same meridian but north of the Arctic Circle, has two sunsets on the same day in early August, one shortly after midnight at the start of the day, and the other shortly before midnight at the end of the day.[37]
China extends as far west as 73°E, but all parts of it use UTC+08:00 (120°E), so solar «noon» can occur as late as 15:00 in western portions of China such as Xinjiang.[38] The Afghanistan-China border marks the greatest terrestrial time zone difference on Earth, with a 3.5 hour difference between Afghanistan’s UTC+4:30 and China’s UTC+08:00.
A visualization of the mismatch between clock time and solar time in different locations. In blue areas, clock time lags behind solar time; in red areas, the reverse is true. The two are synchronized in the white areas.
Daylight saving time
Many countries, and sometimes just certain regions of countries, adopt daylight saving time (DST), also known as summer time, during part of the year. This typically involves advancing clocks by an hour near the start of spring and adjusting back in autumn («spring forward», «fall back»). Modern DST was first proposed in 1907 and was in widespread use in 1916 as a wartime measure aimed at conserving coal. Despite controversy, many countries have used it off and on since then; details vary by location and change occasionally. Countries around the equator usually do not observe daylight saving time, since the seasonal difference in sunlight there is minimal.
Computer systems
Many computer operating systems include the necessary support for working with all (or almost all) possible local times based on the various time zones. Internally, operating systems typically use UTC as their basic time-keeping standard, while providing services for converting local times to and from UTC, and also the ability to automatically change local time conversions at the start and end of daylight saving time in the various time zones. (See the article on daylight saving time for more details on this aspect).
Web servers presenting web pages primarily for an audience in a single time zone or a limited range of time zones typically show times as a local time, perhaps with UTC time in brackets. More internationally oriented websites may show times in UTC only or using an arbitrary time zone. For example, the international English-language version of CNN includes GMT and Hong Kong Time,[39] whereas the US version shows Eastern Time.[40] US Eastern Time and Pacific Time are also used fairly commonly on many US-based English-language websites with global readership. The format is typically based in the W3C Note «datetime».
Email systems and other messaging systems (IRC chat, etc.)[41] time-stamp messages using UTC, or else include the sender’s time zone as part of the message, allowing the receiving program to display the message’s date and time of sending in the recipient’s local time.
Database records that include a time stamp typically use UTC, especially when the database is part of a system that spans multiple time zones. The use of local time for time-stamping records is not recommended for time zones that implement daylight saving time because once a year there is a one-hour period when local times are ambiguous.
Calendar systems nowadays usually tie their time stamps to UTC, and show them differently on computers that are in different time zones. That works when having telephone or internet meetings. It works less well when travelling, because the calendar events are assumed to take place in the time zone the computer or smartphone was on when creating the event. The event can be shown at the wrong time. For example, if a New Yorker plans to meet someone in Los Angeles at 9 AM, and makes a calendar entry at 9 AM (which the computer assumes is New York time), the calendar entry will be at 6 AM if taking the computer’s time zone. There is also an option in newer versions of Microsoft Outlook to enter the time zone in which an event will happen, but often not in other calendar systems. Calendaring software must also deal with daylight saving time (DST). If, for political reasons, the begin and end dates of daylight saving time are changed, calendar entries should stay the same in local time, even though they may shift in UTC time. In Microsoft Outlook, time stamps are therefore stored and communicated without DST offsets.[42] Hence, an appointment in London at noon in the summer will be represented as 12:00 (UTC+00:00) even though the event will actually take place at 13:00 UTC. In Google Calendar, calendar events are stored in UTC (although shown in local time) and might be changed by a time-zone changes,[43] although normal daylight saving start and end are compensated for (similar to much other calendar software).
Operating systems
Unix
Most Unix-like systems, including Linux and Mac OS X, keep system time in time_t format, representing the number of seconds (excluding leap seconds) that have elapsed since 00:00:00 Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on Thursday, January 1, 1970.[44] By default the external representation is as UTC (Coordinated Universal Time), though individual processes can specify time zones using the TZ environment variable.[45] This allows users in multiple time zones to use the same computer, with their respective local times displayed correctly to each user. Time zone information most commonly comes from the IANA time zone database. In fact, many systems, including anything using the GNU C Library, can make use of this database.
Microsoft Windows
Windows-based computer systems prior to Windows 2000 used local time, but Windows 2000 and later can use UTC as the basic system time.[46] The system registry contains time zone information that includes the offset from UTC and rules that indicate the start and end dates for daylight saving in each zone. Interaction with the user normally uses local time, and application software is able to calculate the time in various zones. Terminal Servers allow remote computers to redirect their time zone settings to the Terminal Server so that users see the correct time for their time zone in their desktop/application sessions. Terminal Services uses the server base time on the Terminal Server and the client time zone information to calculate the time in the session.
Programming languages
Java
While most application software will use the underlying operating system for time zone information, the Java Platform, from version 1.3.1, has maintained its own time zone database. This database is updated whenever time zone rules change. Oracle provides an updater tool for this purpose.[47]
As an alternative to the time zone information bundled with the Java Platform, programmers may choose to use the Joda-Time library.[48] This library includes its own time zone data based on the IANA time zone database.[49]
As of Java 8 there is a new date and time API that can help with converting time zones.
Java 8 Date Time
JavaScript
Traditionally, there was very little in the way of time zone support for JavaScript. Essentially the programmer had to extract the UTC offset by instantiating a time object, getting a GMT time from it, and differencing the two. This does not provide a solution for more complex daylight saving variations, such as divergent DST directions between northern and southern hemispheres.
ECMA-402, the standard on Internationalization API for JavaScript, provides ways of formatting Time Zones.[50] However, due to size constraint, some implementations or distributions do not include it.[51]
Perl
The DateTime object in Perl supports all time zones in the Olson DB and includes the ability to get, set and convert between time zones.[52]
PHP
The DateTime objects and related functions have been compiled into the PHP core since 5.2. This includes the ability to get and set the default script time zone, and DateTime is aware of its own time zone internally. PHP.net provides extensive documentation on this.[53] As noted there, the most current time zone database can be implemented via the PECL timezonedb.
Python
The standard module datetime included with Python stores and operates on the time zone information class tzinfo. The third party pytz module provides access to the full IANA time zone database.[54] Negated time zone offset in seconds is stored time.timezone and time.altzone attributes. From Python 3.9, the zoneinfo module introduces timezone management without need for third party module.[55]
Smalltalk
Each Smalltalk dialect comes with its own built-in classes for dates, times and timestamps, only a few of which implement the DateAndTime and Duration classes as specified by the ANSI Smalltalk Standard. VisualWorks provides a TimeZone class that supports up to two annually recurring offset transitions, which are assumed to apply to all years (same behavior as Windows time zones). Squeak provides a Timezone class that does not support any offset transitions. Dolphin Smalltalk does not support time zones at all.
For full support of the tz database (zoneinfo) in a Smalltalk application (including support for any number of annually recurring offset transitions, and support for different intra-year offset transition rules in different years) the third-party, open-source, ANSI-Smalltalk-compliant Chronos Date/Time Library is available for use with any of the following Smalltalk dialects: VisualWorks, Squeak, Gemstone, or Dolphin.[56]
Time in outer space
Orbiting spacecraft may experience many sunrises and sunsets, or none, in a 24-hour period. Therefore, it is not possible to calibrate the time with respect to the Sun and still respect a 24-hour sleep/wake cycle. A common practice for space exploration is to use the Earth-based time of the launch site or mission control, synchronizing the sleeping cycles of the crew and controllers. The International Space Station normally uses Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).[57][58]
Timekeeping on Mars can be more complex, since the planet has a solar day of approximately 24 hours and 40 minutes, known as a sol. Earth controllers for some Mars missions have synchronized their sleep/wake cycles with the Martian day, because solar-powered rover activity on the surface was tied to periods of light and dark.[59]
See also
- Daylight saving time
- ISO 8601
- Jet lag
- Lists of time zones
- Metric time
- Time by country
- Time in Europe
- Time zone abolition
- World clock
- International Date Line
References
- ^ «Morocco Re-Introduces Clock Changes for Ramadan 2019». Timeanddate.com. April 19, 2019. Archived from the original on December 29, 2020.
- ^ «Time Zone in Casablanca, Morocco». Timeanddate.com. Archived from the original on March 30, 2021.
- ^ «Time Zone in El Aaiún, Western Sahara». Timeanddate.com. Archived from the original on February 14, 2021.
- ^ a b «Décret nº 2017-292 du 6 mars 2017 relatif au temps légal français» [Decree no. 2017-292 of 6 March 2017 relative to French legal time] (in French). Légifrance. March 8, 2017. Archived from the original on December 2, 2020.
- ^ «Latitude and Longitude of World Cities». Infoplease. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ «WESTMINSTER MEDICAL SOCIETY. Saturday, November 21, 1840». The Lancet. 35 (901): 383. December 1840. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(00)59842-0. ISSN 0140-6736. Archived from the original on March 30, 2021. Retrieved January 27, 2021.
- ^ «Bristol Time». GreenwichMeanTime.com. Archived from the original on June 28, 2006. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Telegraph line laid across Cook Strait». New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Archived from the original on February 18, 2020. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
- ^ «Our Time. How we got it. New Zealand’s Method. A Lead to the World». Papers Past. Evening Post. p. 10. Archived from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved October 2, 2013.
- ^ Alfred, Randy (November 18, 2010). «Nov. 18, 1883: Railroad Time Goes Coast to Coast». Wired. Archived from the original on August 19, 2018. Retrieved July 30, 2018.
- ^ «Economics of Time Zones» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 14, 2012. (1.89 MB)
- ^ «The Times Reports on «the Day of Two Noons»«. History Matters. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Resolution concerning new standard time by Chicago». Sos.state.il.us. Archived from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ Quirico Filopanti from scienzagiovane, Bologna University, Italy. Archived January 17, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gianluigi Parmeggiani (Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna),
The origin of time zones Archived August 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine - ^ Fleming, Sandford (1886). «Time-reckoning for the twentieth century». Annual Report of the Board of Regents of the Smithsonian Institution (1): 345–366. Reprinted in 1889: Time-reckoning for the twentieth century at the Internet Archive.
- ^ Stromberg, Joseph (November 18, 2011). «Sandford Fleming Sets the World’s Clock». Smithsonian Magazine.
- ^ «Time Zone & Clock Changes in Kathmandu, Nepal». www.timeanddate.com. Archived from the original on January 22, 2021. Retrieved December 1, 2020.
- ^ Schiavenza, Matt (November 5, 2013). «China Only Has One Time Zone—and That’s a Problem». The Atlantic. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «Russia Reduces Number of Time Zones». TimeAndDate.com. March 23, 2010. Archived from the original on August 9, 2020. Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- ^ «About Time: Huge country, nine time zones» (Video). BBC. March 22, 2011. Archived from the original on February 13, 2019. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- ^ «Russian clocks to retreat again in winter, 11 time zones return». Reuters. July 2014. Archived from the original on October 28, 2020. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ «In Canada, You Can Just Write the Date Whichever Way You Want». Atlas Obscura. June 8, 2015. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ a b «Z – Zulu Time Zone (Time Zone Abbreviation)». TimeAndDate.com. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «What is UTC or GMT Time?». www.nhc.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ Time Zone Abbreviations – Worldwide List Archived August 21, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com.
- ^ Bowditch, Nathaniel. American Practical Navigator. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1925, 1939, 1975.
- ^ Hill, John C., Thomas F. Utegaard, Gerard Riordan. Dutton’s Navigation and Piloting. Annapolis: United States Naval Institute, 1958.
- ^ Howse, Derek. Greenwich Time and the Discovery of the Longitude. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1980. ISBN 0-19-215948-8.
- ^ What Is Cruise Ship Time? Archived March 30, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Cruise Critic, January 8, 2020.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions Archived February 14, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Caribbean Adventures Roatan.
- ^ Poulle, Yvonne (1999). «La France à l’heure allemande» (PDF). Bibliothèque de l’École des Chartes. 157 (2): 493–502. doi:10.3406/bec.1999.450989. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 4, 2015. Retrieved January 11, 2012.
- ^ «法定时与北京时间» (in Chinese). 人民教育出版社. Archived from the original on November 14, 2006.
- ^ Vigo, Galicia, Spain – Sunrise, Sunset, and Daylength Archived November 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com.
- ^ Stockholm, Sweden – Sunrise, Sunset, and Daylength Archived February 9, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com.
- ^ O’Hara, Doug (March 11, 2007). «Alaska: daylight stealing time». Far North Science. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved May 11, 2007.
- ^ Alaskan village to get two sunsets Friday Archived October 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, United Press International, August 7, 1986.
- ^ Kashgar, Xinjiang, China – Sunrise, Sunset, and Daylength Archived November 8, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com
- ^ «International CNN». Edition.cnn.com. Archived from the original on March 10, 2018. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «United States CNN». Cnn.com. Archived from the original on September 11, 2001. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Guidelines for Ubuntu IRC Meetings». Canonical Ltd. August 6, 2008. Archived from the original on February 25, 2011. Retrieved July 13, 2009.
- ^ How time zone normalization works in Microsoft Outlook Archived October 6, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft (2015).
- ^ Use Google Calendar in different time zones Archived October 16, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Google Calendar Help (as of Oct. 2015)
- ^ «The Open Group Base Specifications Issue 7, section 4.16 Seconds Since the Epoch». The Open Group. Archived from the original on December 22, 2017. Retrieved January 22, 2017.
- ^ «tzset(3) man page from FreeBSD 12.1-RELEASE». freebsd.org. The FreeBSD project. Archived from the original on August 9, 2020. Retrieved April 21, 2020.
- ^ «GetSystemTime function (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 13, 2018. Retrieved February 13, 2018.
- ^ «Timezone Updater Tool». Java.sun.com. Archived from the original on November 24, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Joda-Time». Joda-time.sourceforge.net. Archived from the original on December 3, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «tz database». Twinsun.com. December 26, 2007. Archived from the original on June 23, 2012. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «ECMAScript 2015 Internationalization API Specification». ecma-international.org. ECMA International. June 2015. Archived from the original on October 26, 2019. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- ^ «Internationalization Support». Node.js v12.10.0 Documentation. Archived from the original on August 28, 2019. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- ^ «DateTime». METACPAN. Archived from the original on March 29, 2014. Retrieved April 14, 2014.
- ^ «DateTime». Php.net. Archived from the original on November 22, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «pytz module». Pytz.sourceforge.net. Archived from the original on November 30, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «zoneinfo module». www.python.org. Archived from the original on February 7, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Chronos Date/Time Library Archived April 5, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Ask the Crew: STS-111». National Aeronautics and Space Administration. June 19, 2002. Archived from the original on September 28, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Lu, Ed (September 8, 2003). «Day in the Life». National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Archived from the original on September 1, 2012. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ New Tricks Could Help Mars Rover Team Live on Mars Time Archived August 12, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Megan Gannon, Space.com, September 28, 2012.
Further reading
- Biswas, Soutik (February 12, 2019). «How India’s single time zone is hurting its people». BBC News. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- Maulik Jagnani, economist at Cornell University (January 15, 2019). «PoorSleep: Sunset Time and Human Capital Production» (Job Market Paper). Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- «Time Bandits: The countries rebelling against GMT» (Video). BBC News. August 14, 2015. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- «How time zones confused the world». BBC News. August 7, 2015. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- Lane, Megan (May 10, 2011). «How does a country change its time zone?». BBC News. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- «A brief history of time zones» (Video). BBC News. March 24, 2011. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- The Time Zone Information Format (TZif). doi:10.17487/RFC8536. RFC 8536.
External links
Media related to Time zones at Wikimedia Commons
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.
All time zones are defined as offsets from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), ranging from UTC−12:00 to UTC+14:00. The offsets are usually a whole number of hours, but a few zones are offset by an additional 30 or 45 minutes, such as in India, South Australia and Nepal.
Some areas of higher latitude use daylight saving time for about half of the year, typically by adding one hour to local time during spring and summer.
List of UTC offsets
In the table below, the locations that use daylight saving time (DST) are listed in their UTC offset when DST is not in effect. When DST is in effect, approximately during spring and summer, their UTC offset is increased by one hour (except for Lord Howe Island, where it is increased by 30 minutes). For example, during the DST period California observes UTC−07:00 and the United Kingdom observes UTC+01:00.
| UTC offset | Locations that do not use DST | Locations that use DST | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTC−12:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−11:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−10:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−09:30 | ||||
| UTC−09:00 | ||||
| UTC−08:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−07:00 | ||||
| UTC−06:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC−05:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC−04:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−03:30 | ||||
| UTC−03:00 |
|
|||
| UTC−02:00 | ||||
| UTC−01:00 |
|
|||
| UTC±00:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+01:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC+02:00 |
|
|
||
| UTC+03:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+03:30 | ||||
| UTC+04:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+04:30 | ||||
| UTC+05:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+05:30 |
|
|||
| UTC+05:45 | ||||
| UTC+06:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+06:30 |
|
|||
| UTC+07:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+08:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+08:45 | ||||
| UTC+09:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+09:30 | ||||
| UTC+10:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+10:30 | ||||
| UTC+11:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+12:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+12:45 | ||||
| UTC+13:00 |
|
|||
| UTC+14:00 |
- ^ a b Observes UTC±00:00 around Ramadan.[1][2][3]
History
The apparent position of the Sun in the sky, and thus solar time, varies by location due to the spherical shape of the Earth. This variation corresponds to four minutes of time for every degree of longitude, so for example when it is solar noon in London, it is about 10 minutes before solar noon in Bristol, which is about 2.5 degrees to the west.[5]
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich, founded in 1675, established Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), the mean solar time at that location, as an aid to mariners to determine longitude at sea, providing a standard reference time while each location in England kept a different time.
Railway time
Plaque commemorating the Railway General Time Convention of 1883 in North America
In the 19th century, as transportation and telecommunications improved, it became increasingly inconvenient for each location to observe its own solar time. In November 1840, the Great Western Railway started using GMT kept by portable chronometers.[6] This practice was soon followed by other railway companies in Great Britain and became known as Railway Time.
Around August 23, 1852, time signals were first transmitted by telegraph from the Royal Observatory. By 1855, 98% of Great Britain’s public clocks were using GMT, but it was not made the island’s legal time until August 2, 1880. Some British clocks from this period have two minute hands, one for the local time and one for GMT.[7]
On November 2, 1868, the then British Colony of New Zealand officially adopted a standard time to be observed throughout the colony.[8] It was based on longitude 172°30′ east of Greenwich, that is 11 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT. This standard was known as New Zealand Mean Time.[9]
Timekeeping on North American railroads in the 19th century was complex. Each railroad used its own standard time, usually based on the local time of its headquarters or most important terminus, and the railroad’s train schedules were published using its own time. Some junctions served by several railroads had a clock for each railroad, each showing a different time.[10]
1913 time zone map of the United States, showing boundaries very different from today
Charles F. Dowd proposed a system of hourly standard time zones for North American railroads around 1863, although he published nothing on the matter at that time and did not consult railroad officials until 1869. In 1870 he proposed four ideal time zones having north–south borders, the first centered on Washington, D.C., but by 1872 the first was centered on meridian 75° west of Greenwich, with natural borders such as sections of the Appalachian Mountains. Dowd’s system was never accepted by North American railroads. Instead, U.S. and Canadian railroads implemented a version proposed by William F. Allen, the editor of the Traveler’s Official Railway Guide.[11] The borders of its time zones ran through railroad stations, often in major cities. For example, the border between its Eastern and Central time zones ran through Detroit, Buffalo, Pittsburgh, Atlanta, and Charleston. It was inaugurated on Sunday, November 18, 1883, also called «The Day of Two Noons»,[12] when each railroad station clock was reset as standard-time noon was reached within each time zone.
The North American zones were named Intercolonial, Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific. Within a year 85% of all cities with populations over 10,000 (about 200 cities) were using standard time.[13] A notable exception was Detroit (located about halfway between the meridians of Eastern and Central time), which kept local time until 1900, then tried Central Standard Time, local mean time, and Eastern Standard Time (EST) before a May 1915 ordinance settled on EST and was ratified by popular vote in August 1916. The confusion of times came to an end when standard time zones were formally adopted by the U.S. Congress in the Standard Time Act of March 19, 1918.
Worldwide time zones
Italian mathematician Quirico Filopanti introduced the idea of a worldwide system of time zones in his book Miranda!, published in 1858. He proposed 24 hourly time zones, which he called «longitudinal days», the first centred on the meridian of Rome. He also proposed a universal time to be used in astronomy and telegraphy. However, his book attracted no attention until long after his death.[14][15]
Scottish-born Canadian Sir Sandford Fleming proposed a worldwide system of time zones in 1876 — see Sandford Fleming § Inventor of worldwide standard time. The proposal divided the world into twenty-four time zones labeled A-Y (skipping J), each one covering 15 degrees of longitude. All clocks within each zone would be set to the same time as the others, but differed by one hour from those in the neighboring zones.[16] He advocated his system at several international conferences, including the International Meridian Conference, where it received some consideration. The system has not been directly adopted, but some maps divide the world into 24 time zones and assign letters to them, similarly to Fleming’s system.[17]
World map of time zones in 1928
By about 1900, almost all inhabited places on Earth had adopted a standard time zone, but only some of them used an hourly offset from GMT. Many applied the time at a local astronomical observatory to an entire country, without any reference to GMT. It took many decades before all time zones were based on some standard offset from GMT or Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). By 1929, the majority of countries had adopted hourly time zones, though some countries such as Iran, India, Myanmar and parts of Australia had time zones with a 30-minute offset. Nepal was the last country to adopt a standard offset, shifting slightly to UTC+05:45 in 1986.[18]
All nations currently use standard time zones for secular purposes, but not all of them apply the concept as originally conceived. Several countries and subdivisions use half-hour or quarter-hour deviations from standard time. Some countries, such as China and India, use a single time zone even though the extent of their territory far exceeds the ideal 15° of longitude for one hour; other countries, such as Spain and Argentina, use standard hour-based offsets, but not necessarily those that would be determined by their geographical location. The consequences, in some areas, can affect the lives of local citizens, and in extreme cases contribute to larger political issues, such as in the western reaches of China.[19] In Russia, which has 11 time zones, two time zones were removed in 2010[20][21] and reinstated in 2014.[22]
Notation
ISO 8601
ISO 8601 is a standard established by the International Organization for Standardization defining methods of representing dates and times in textual form, including specifications for representing time zones.[23]
If a time is in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), a «Z» is added directly after the time without a separating space. «Z» is the zone designator for the zero UTC offset. «09:30 UTC» is therefore represented as «09:30Z» or «0930Z». Likewise, «14:45:15 UTC» is written as «14:45:15Z» or «144515Z».[24] UTC time is also known as «Zulu» time, since «Zulu» is a phonetic alphabet code word for the letter «Z».[24]
Offsets from UTC are written in the format ±hh:mm, ±hhmm, or ±hh (either hours ahead or behind UTC). For example, if the time being described is one hour ahead of UTC (such as the time in Germany during the winter), the zone designator would be «+01:00», «+0100», or simply «+01». This numeric representation of time zones is appended to local times in the same way that alphabetic time zone abbreviations (or «Z», as above) are appended. The offset from UTC changes with daylight saving time, e.g. a time offset in Chicago, which is in the North American Central Time Zone, is «−06:00» for the winter (Central Standard Time) and «−05:00» for the summer (Central Daylight Time).[25]
Abbreviations
Time zones are often represented by alphabetic abbreviations such as «EST», «WST», and «CST», but these are not part of the international time and date standard ISO 8601. Such designations can be ambiguous; for example, «CST» can mean (North American) Central Standard Time (UTC−06:00), Cuba Standard Time (UTC−05:00) and China Standard Time (UTC+08:00), and it is also a widely used variant of ACST (Australian Central Standard Time, UTC+09:30).[26]
Conversions
Conversion between time zones obeys the relationship
- «time in zone A» − «UTC offset for zone A» = «time in zone B» − «UTC offset for zone B»,
in which each side of the equation is equivalent to UTC.
The conversion equation can be rearranged to
- «time in zone B» = «time in zone A» − «UTC offset for zone A» + «UTC offset for zone B».
For example, the New York Stock Exchange opens at 09:30 (EST, UTC offset= −05:00). In California (PST, UTC offset= −08:00) and India (IST, UTC offset= +05:30), the New York Stock Exchange opens at
- time in California = 09:30 − (−05:00) + (−08:00) = 06:30;
- time in India = 09:30 − (−05:00) + (+05:30) = 20:00.
These calculations become more complicated near the time switch to or from daylight saving time, as the UTC offset for the area becomes a function of UTC time.
The time differences may also result in different dates. For example, when it is 22:00 on Monday in Egypt (UTC+02:00), it is 01:00 on Tuesday in Pakistan (UTC+05:00).
The table «Time of day by zone» gives an overview on the time relations between different zones.
| Time of day by zone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTC offset | Monday | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| UTC−12:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 |
| UTC−11:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 |
| UTC−10:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 |
| UTC−09:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 |
| UTC−09:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 |
| UTC−08:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 |
| UTC−07:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 |
| UTC−06:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 |
| UTC−05:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 |
| UTC−04:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 |
| UTC−03:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 |
| UTC−03:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 |
| UTC−02:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 |
| UTC−02:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 |
| UTC−01:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 |
| UTC±00:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 |
| UTC+01:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 |
| UTC+02:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 |
| UTC+03:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 |
| UTC+03:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 |
| UTC+04:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 |
| UTC+04:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 |
| UTC+05:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 |
| UTC+05:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 |
| UTC+05:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 | 00:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 |
| UTC+06:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 |
| UTC+06:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 |
| UTC+07:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 |
| UTC+08:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 |
| UTC+08:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 | 00:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 |
| UTC+09:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 |
| UTC+09:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 |
| UTC+10:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 |
| UTC+10:30 | 22:30 | 23:30 | 00:30 | 01:30 | 02:30 | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | 07:30 | 08:30 | 09:30 | 10:30 | 11:30 | 12:30 | 13:30 | 14:30 | 15:30 | 16:30 | 17:30 | 18:30 | 19:30 | 20:30 | 21:30 |
| UTC+11:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 |
| UTC+12:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 |
| UTC+12:45 | 00:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 |
| UTC+13:00 | 01:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 |
| UTC+13:45 | 01:45 | 02:45 | 03:45 | 04:45 | 05:45 | 06:45 | 07:45 | 08:45 | 09:45 | 10:45 | 11:45 | 12:45 | 13:45 | 14:45 | 15:45 | 16:45 | 17:45 | 18:45 | 19:45 | 20:45 | 21:45 | 22:45 | 23:45 | 00:45 |
| UTC+14:00 | 02:00 | 03:00 | 04:00 | 05:00 | 06:00 | 07:00 | 08:00 | 09:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 00:00 | 01:00 |
| UTC offset | Tuesday | Wednesday |
Nautical time zones
Since the 1920s, a nautical standard time system has been in operation for ships on the high seas. As an ideal form of the terrestrial time zone system, nautical time zones consist of gores of 15° offset from GMT by a whole number of hours. A nautical date line follows the 180th meridian, bisecting one 15° gore into two 7.5° gores that differ from GMT by ±12 hours.[27][28][29]
However, in practice each ship may choose what time to observe at each location. Ships may decide to adjust their clocks at a convenient time, usually at night, not exactly when they cross a certain longitude.[30] Some ships simply remain on the time of the departing port during the whole trip.[31]
Skewing of time zones
Difference between sun time and clock time during daylight saving time:
| 1h ± 30 min behind | |
| 0h ± 30m | |
| 1h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 2h ± 30 m ahead | |
| 3h ± 30 m ahead |
DST observed
DST formerly observed
DST never observed
Ideal time zones, such as nautical time zones, are based on the mean solar time of a particular meridian located in the middle of that zone with boundaries located 7.5 degrees east and west of the meridian. In practice, however, many time zone boundaries are drawn much farther to the west, and some countries are located entirely outside their ideal time zones.
For example, even though the Prime Meridian (0°) passes through Spain and France, they use the mean solar time of 15 degrees east (Central European Time) rather than 0 degrees (Greenwich Mean Time). France previously used GMT, but was switched to CET (Central European Time) during the German occupation of the country during World War II and did not switch back after the war.[32] Similarly, prior to World War II, the Netherlands observed «Amsterdam Time», which was twenty minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. They were obliged to follow German time during the war, and kept it thereafter. In the mid-1970s the Netherlands, as other European states, began observing daylight saving (summer) time.
One reason to draw time zone boundaries far to the west of their ideal meridians is to allow the more efficient use of afternoon sunlight.[33] Some of these locations also use daylight saving time (DST), further increasing the difference to local solar time. As a result, in summer, solar noon in the Spanish city of Vigo occurs at 14:41 clock time. This westernmost area of continental Spain never experiences sunset before 18:00 clock time, even in winter, despite lying 42 degrees north of the equator.[34] Near the summer solstice, Vigo has sunset times after 22:00, similar to those of Stockholm, which is in the same time zone and 17 degrees farther north. Stockholm has much earlier sunrises, though.[35]
A more extreme example is Nome, Alaska, which is at 165°24′W longitude – just west of center of the idealized Samoa Time Zone (165°W). Nevertheless, Nome observes Alaska Time (135°W) with DST so it is slightly more than two hours ahead of the sun in winter and over three in summer.[36]
Kotzebue, Alaska, also near the same meridian but north of the Arctic Circle, has two sunsets on the same day in early August, one shortly after midnight at the start of the day, and the other shortly before midnight at the end of the day.[37]
China extends as far west as 73°E, but all parts of it use UTC+08:00 (120°E), so solar «noon» can occur as late as 15:00 in western portions of China such as Xinjiang.[38] The Afghanistan-China border marks the greatest terrestrial time zone difference on Earth, with a 3.5 hour difference between Afghanistan’s UTC+4:30 and China’s UTC+08:00.
A visualization of the mismatch between clock time and solar time in different locations. In blue areas, clock time lags behind solar time; in red areas, the reverse is true. The two are synchronized in the white areas.
Daylight saving time
Many countries, and sometimes just certain regions of countries, adopt daylight saving time (DST), also known as summer time, during part of the year. This typically involves advancing clocks by an hour near the start of spring and adjusting back in autumn («spring forward», «fall back»). Modern DST was first proposed in 1907 and was in widespread use in 1916 as a wartime measure aimed at conserving coal. Despite controversy, many countries have used it off and on since then; details vary by location and change occasionally. Countries around the equator usually do not observe daylight saving time, since the seasonal difference in sunlight there is minimal.
Computer systems
Many computer operating systems include the necessary support for working with all (or almost all) possible local times based on the various time zones. Internally, operating systems typically use UTC as their basic time-keeping standard, while providing services for converting local times to and from UTC, and also the ability to automatically change local time conversions at the start and end of daylight saving time in the various time zones. (See the article on daylight saving time for more details on this aspect).
Web servers presenting web pages primarily for an audience in a single time zone or a limited range of time zones typically show times as a local time, perhaps with UTC time in brackets. More internationally oriented websites may show times in UTC only or using an arbitrary time zone. For example, the international English-language version of CNN includes GMT and Hong Kong Time,[39] whereas the US version shows Eastern Time.[40] US Eastern Time and Pacific Time are also used fairly commonly on many US-based English-language websites with global readership. The format is typically based in the W3C Note «datetime».
Email systems and other messaging systems (IRC chat, etc.)[41] time-stamp messages using UTC, or else include the sender’s time zone as part of the message, allowing the receiving program to display the message’s date and time of sending in the recipient’s local time.
Database records that include a time stamp typically use UTC, especially when the database is part of a system that spans multiple time zones. The use of local time for time-stamping records is not recommended for time zones that implement daylight saving time because once a year there is a one-hour period when local times are ambiguous.
Calendar systems nowadays usually tie their time stamps to UTC, and show them differently on computers that are in different time zones. That works when having telephone or internet meetings. It works less well when travelling, because the calendar events are assumed to take place in the time zone the computer or smartphone was on when creating the event. The event can be shown at the wrong time. For example, if a New Yorker plans to meet someone in Los Angeles at 9 AM, and makes a calendar entry at 9 AM (which the computer assumes is New York time), the calendar entry will be at 6 AM if taking the computer’s time zone. There is also an option in newer versions of Microsoft Outlook to enter the time zone in which an event will happen, but often not in other calendar systems. Calendaring software must also deal with daylight saving time (DST). If, for political reasons, the begin and end dates of daylight saving time are changed, calendar entries should stay the same in local time, even though they may shift in UTC time. In Microsoft Outlook, time stamps are therefore stored and communicated without DST offsets.[42] Hence, an appointment in London at noon in the summer will be represented as 12:00 (UTC+00:00) even though the event will actually take place at 13:00 UTC. In Google Calendar, calendar events are stored in UTC (although shown in local time) and might be changed by a time-zone changes,[43] although normal daylight saving start and end are compensated for (similar to much other calendar software).
Operating systems
Unix
Most Unix-like systems, including Linux and Mac OS X, keep system time in time_t format, representing the number of seconds (excluding leap seconds) that have elapsed since 00:00:00 Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) on Thursday, January 1, 1970.[44] By default the external representation is as UTC (Coordinated Universal Time), though individual processes can specify time zones using the TZ environment variable.[45] This allows users in multiple time zones to use the same computer, with their respective local times displayed correctly to each user. Time zone information most commonly comes from the IANA time zone database. In fact, many systems, including anything using the GNU C Library, can make use of this database.
Microsoft Windows
Windows-based computer systems prior to Windows 2000 used local time, but Windows 2000 and later can use UTC as the basic system time.[46] The system registry contains time zone information that includes the offset from UTC and rules that indicate the start and end dates for daylight saving in each zone. Interaction with the user normally uses local time, and application software is able to calculate the time in various zones. Terminal Servers allow remote computers to redirect their time zone settings to the Terminal Server so that users see the correct time for their time zone in their desktop/application sessions. Terminal Services uses the server base time on the Terminal Server and the client time zone information to calculate the time in the session.
Programming languages
Java
While most application software will use the underlying operating system for time zone information, the Java Platform, from version 1.3.1, has maintained its own time zone database. This database is updated whenever time zone rules change. Oracle provides an updater tool for this purpose.[47]
As an alternative to the time zone information bundled with the Java Platform, programmers may choose to use the Joda-Time library.[48] This library includes its own time zone data based on the IANA time zone database.[49]
As of Java 8 there is a new date and time API that can help with converting time zones.
Java 8 Date Time
JavaScript
Traditionally, there was very little in the way of time zone support for JavaScript. Essentially the programmer had to extract the UTC offset by instantiating a time object, getting a GMT time from it, and differencing the two. This does not provide a solution for more complex daylight saving variations, such as divergent DST directions between northern and southern hemispheres.
ECMA-402, the standard on Internationalization API for JavaScript, provides ways of formatting Time Zones.[50] However, due to size constraint, some implementations or distributions do not include it.[51]
Perl
The DateTime object in Perl supports all time zones in the Olson DB and includes the ability to get, set and convert between time zones.[52]
PHP
The DateTime objects and related functions have been compiled into the PHP core since 5.2. This includes the ability to get and set the default script time zone, and DateTime is aware of its own time zone internally. PHP.net provides extensive documentation on this.[53] As noted there, the most current time zone database can be implemented via the PECL timezonedb.
Python
The standard module datetime included with Python stores and operates on the time zone information class tzinfo. The third party pytz module provides access to the full IANA time zone database.[54] Negated time zone offset in seconds is stored time.timezone and time.altzone attributes. From Python 3.9, the zoneinfo module introduces timezone management without need for third party module.[55]
Smalltalk
Each Smalltalk dialect comes with its own built-in classes for dates, times and timestamps, only a few of which implement the DateAndTime and Duration classes as specified by the ANSI Smalltalk Standard. VisualWorks provides a TimeZone class that supports up to two annually recurring offset transitions, which are assumed to apply to all years (same behavior as Windows time zones). Squeak provides a Timezone class that does not support any offset transitions. Dolphin Smalltalk does not support time zones at all.
For full support of the tz database (zoneinfo) in a Smalltalk application (including support for any number of annually recurring offset transitions, and support for different intra-year offset transition rules in different years) the third-party, open-source, ANSI-Smalltalk-compliant Chronos Date/Time Library is available for use with any of the following Smalltalk dialects: VisualWorks, Squeak, Gemstone, or Dolphin.[56]
Time in outer space
Orbiting spacecraft may experience many sunrises and sunsets, or none, in a 24-hour period. Therefore, it is not possible to calibrate the time with respect to the Sun and still respect a 24-hour sleep/wake cycle. A common practice for space exploration is to use the Earth-based time of the launch site or mission control, synchronizing the sleeping cycles of the crew and controllers. The International Space Station normally uses Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).[57][58]
Timekeeping on Mars can be more complex, since the planet has a solar day of approximately 24 hours and 40 minutes, known as a sol. Earth controllers for some Mars missions have synchronized their sleep/wake cycles with the Martian day, because solar-powered rover activity on the surface was tied to periods of light and dark.[59]
See also
- Daylight saving time
- ISO 8601
- Jet lag
- Lists of time zones
- Metric time
- Time by country
- Time in Europe
- Time zone abolition
- World clock
- International Date Line
References
- ^ «Morocco Re-Introduces Clock Changes for Ramadan 2019». Timeanddate.com. April 19, 2019. Archived from the original on December 29, 2020.
- ^ «Time Zone in Casablanca, Morocco». Timeanddate.com. Archived from the original on March 30, 2021.
- ^ «Time Zone in El Aaiún, Western Sahara». Timeanddate.com. Archived from the original on February 14, 2021.
- ^ a b «Décret nº 2017-292 du 6 mars 2017 relatif au temps légal français» [Decree no. 2017-292 of 6 March 2017 relative to French legal time] (in French). Légifrance. March 8, 2017. Archived from the original on December 2, 2020.
- ^ «Latitude and Longitude of World Cities». Infoplease. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ «WESTMINSTER MEDICAL SOCIETY. Saturday, November 21, 1840». The Lancet. 35 (901): 383. December 1840. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(00)59842-0. ISSN 0140-6736. Archived from the original on March 30, 2021. Retrieved January 27, 2021.
- ^ «Bristol Time». GreenwichMeanTime.com. Archived from the original on June 28, 2006. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Telegraph line laid across Cook Strait». New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Archived from the original on February 18, 2020. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
- ^ «Our Time. How we got it. New Zealand’s Method. A Lead to the World». Papers Past. Evening Post. p. 10. Archived from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved October 2, 2013.
- ^ Alfred, Randy (November 18, 2010). «Nov. 18, 1883: Railroad Time Goes Coast to Coast». Wired. Archived from the original on August 19, 2018. Retrieved July 30, 2018.
- ^ «Economics of Time Zones» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 14, 2012. (1.89 MB)
- ^ «The Times Reports on «the Day of Two Noons»«. History Matters. Archived from the original on April 4, 2012. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Resolution concerning new standard time by Chicago». Sos.state.il.us. Archived from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ Quirico Filopanti from scienzagiovane, Bologna University, Italy. Archived January 17, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gianluigi Parmeggiani (Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna),
The origin of time zones Archived August 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine - ^ Fleming, Sandford (1886). «Time-reckoning for the twentieth century». Annual Report of the Board of Regents of the Smithsonian Institution (1): 345–366. Reprinted in 1889: Time-reckoning for the twentieth century at the Internet Archive.
- ^ Stromberg, Joseph (November 18, 2011). «Sandford Fleming Sets the World’s Clock». Smithsonian Magazine.
- ^ «Time Zone & Clock Changes in Kathmandu, Nepal». www.timeanddate.com. Archived from the original on January 22, 2021. Retrieved December 1, 2020.
- ^ Schiavenza, Matt (November 5, 2013). «China Only Has One Time Zone—and That’s a Problem». The Atlantic. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «Russia Reduces Number of Time Zones». TimeAndDate.com. March 23, 2010. Archived from the original on August 9, 2020. Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- ^ «About Time: Huge country, nine time zones» (Video). BBC. March 22, 2011. Archived from the original on February 13, 2019. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- ^ «Russian clocks to retreat again in winter, 11 time zones return». Reuters. July 2014. Archived from the original on October 28, 2020. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ «In Canada, You Can Just Write the Date Whichever Way You Want». Atlas Obscura. June 8, 2015. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ a b «Z – Zulu Time Zone (Time Zone Abbreviation)». TimeAndDate.com. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «What is UTC or GMT Time?». www.nhc.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on August 22, 2018. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ Time Zone Abbreviations – Worldwide List Archived August 21, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com.
- ^ Bowditch, Nathaniel. American Practical Navigator. Washington: Government Printing Office, 1925, 1939, 1975.
- ^ Hill, John C., Thomas F. Utegaard, Gerard Riordan. Dutton’s Navigation and Piloting. Annapolis: United States Naval Institute, 1958.
- ^ Howse, Derek. Greenwich Time and the Discovery of the Longitude. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1980. ISBN 0-19-215948-8.
- ^ What Is Cruise Ship Time? Archived March 30, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Cruise Critic, January 8, 2020.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions Archived February 14, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Caribbean Adventures Roatan.
- ^ Poulle, Yvonne (1999). «La France à l’heure allemande» (PDF). Bibliothèque de l’École des Chartes. 157 (2): 493–502. doi:10.3406/bec.1999.450989. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 4, 2015. Retrieved January 11, 2012.
- ^ «法定时与北京时间» (in Chinese). 人民教育出版社. Archived from the original on November 14, 2006.
- ^ Vigo, Galicia, Spain – Sunrise, Sunset, and Daylength Archived November 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com.
- ^ Stockholm, Sweden – Sunrise, Sunset, and Daylength Archived February 9, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com.
- ^ O’Hara, Doug (March 11, 2007). «Alaska: daylight stealing time». Far North Science. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved May 11, 2007.
- ^ Alaskan village to get two sunsets Friday Archived October 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, United Press International, August 7, 1986.
- ^ Kashgar, Xinjiang, China – Sunrise, Sunset, and Daylength Archived November 8, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, Timeanddate.com
- ^ «International CNN». Edition.cnn.com. Archived from the original on March 10, 2018. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «United States CNN». Cnn.com. Archived from the original on September 11, 2001. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Guidelines for Ubuntu IRC Meetings». Canonical Ltd. August 6, 2008. Archived from the original on February 25, 2011. Retrieved July 13, 2009.
- ^ How time zone normalization works in Microsoft Outlook Archived October 6, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft (2015).
- ^ Use Google Calendar in different time zones Archived October 16, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Google Calendar Help (as of Oct. 2015)
- ^ «The Open Group Base Specifications Issue 7, section 4.16 Seconds Since the Epoch». The Open Group. Archived from the original on December 22, 2017. Retrieved January 22, 2017.
- ^ «tzset(3) man page from FreeBSD 12.1-RELEASE». freebsd.org. The FreeBSD project. Archived from the original on August 9, 2020. Retrieved April 21, 2020.
- ^ «GetSystemTime function (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 13, 2018. Retrieved February 13, 2018.
- ^ «Timezone Updater Tool». Java.sun.com. Archived from the original on November 24, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «Joda-Time». Joda-time.sourceforge.net. Archived from the original on December 3, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «tz database». Twinsun.com. December 26, 2007. Archived from the original on June 23, 2012. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «ECMAScript 2015 Internationalization API Specification». ecma-international.org. ECMA International. June 2015. Archived from the original on October 26, 2019. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- ^ «Internationalization Support». Node.js v12.10.0 Documentation. Archived from the original on August 28, 2019. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- ^ «DateTime». METACPAN. Archived from the original on March 29, 2014. Retrieved April 14, 2014.
- ^ «DateTime». Php.net. Archived from the original on November 22, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «pytz module». Pytz.sourceforge.net. Archived from the original on November 30, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ «zoneinfo module». www.python.org. Archived from the original on February 7, 2021. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Chronos Date/Time Library Archived April 5, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Ask the Crew: STS-111». National Aeronautics and Space Administration. June 19, 2002. Archived from the original on September 28, 2015. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ Lu, Ed (September 8, 2003). «Day in the Life». National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Archived from the original on September 1, 2012. Retrieved September 10, 2015.
- ^ New Tricks Could Help Mars Rover Team Live on Mars Time Archived August 12, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, Megan Gannon, Space.com, September 28, 2012.
Further reading
- Biswas, Soutik (February 12, 2019). «How India’s single time zone is hurting its people». BBC News. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- Maulik Jagnani, economist at Cornell University (January 15, 2019). «PoorSleep: Sunset Time and Human Capital Production» (Job Market Paper). Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- «Time Bandits: The countries rebelling against GMT» (Video). BBC News. August 14, 2015. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- «How time zones confused the world». BBC News. August 7, 2015. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- Lane, Megan (May 10, 2011). «How does a country change its time zone?». BBC News. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- «A brief history of time zones» (Video). BBC News. March 24, 2011. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- The Time Zone Information Format (TZif). doi:10.17487/RFC8536. RFC 8536.
External links
Media related to Time zones at Wikimedia Commons
Всего найдено: 4
Здравствуйте! Как будет звучать выражение «маршрут опоясывает весь земной шар» в будущем времени? Спасибо.
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Глагол совершенного вида – опоясать: маршрут опояшет весь земной шар.
балтийское море история названия
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Есть две версии происхождения названия Балтийского моря. Согласно первой, _Балтика_ — из литов. baltas, латыш. balts ‘белый’, что может быть связано с цветом песчаных берегов этого моря. По другой версии название образовано от лат. balteus ‘пояс’ (ср. швед., дат., норв. bälte ‘пояс’), и связано это с тем, что это море продолжает цепочку морей, опоясывающих материковую Европу.
1) Когда употребляется слово «поясА», а когда «поясЫ«?
2) Употребляется ли вообще в современном русском языке слово «поясЫ«, как множественное число слова «пояс»?
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильная форма: _пояса_. Форма _поясы_ считается устаревшей.
Как правильно:
часовые поясА или часовые поясЫ? В энциклопедии пишется первый ваиант, в тестах по русскому языку федерального центра тестирования — второй.
Спасибо
Ответ справочной службы русского языка
Правильно: _часовые пояса_.
Географический часово́й по́яс — условная полоса на земной поверхности шириной ровно 15° (± 7,5° относительно среднего меридиана). Средним меридианом нулевого часового пояса считается гринвичский меридиан.
Административный часово́й по́яс — участок земной поверхности, на котором в соответствии с некоторым законом установлено определённое официальное время. Как правило, в понятие административного часового пояса включается ещё и совпадение даты — в этом случае, например, пояса UTC−10:00 и UTC+14:00 будут считаться различными, хотя в них действует одинаковое время суток.
Формирование часовых поясов (часовых зон — time zones) связано со стремлением, с одной стороны, учитывать вращение Земли вокруг своей оси, а с другой стороны, определить территории (временные зоны) с примерно одинаковым местным солнечным временем таким образом, чтобы различия по времени между ними были кратны одному часу. В результате было достигнуто решение, что должно быть 24 административных часовых пояса и каждый из них должен более или менее совпадать с географическим часовым поясом. Точкой отсчёта был принят гринвичский меридиан, нулевой меридиан, средний меридиан нулевого часового пояса.
Сейчас время устанавливается при помощи всемирного координированного времени (UTC), которое было введено взамен времени по Гринвичу (GMT). Шкала UTC базируется на равномерной шкале атомного времени (TAI) и является более удобной для гражданского использования. Часовые пояса вокруг земного шара относительно нулевого меридиана выражаются как положительное (к востоку) и отрицательное (к западу) смещение от UTC. Для территорий часового пояса, где используется перевод часов на летнее время, смещение относительно UTC на летний период меняется.
В России с 2011 года законодательно установлено понятие часовая зона.
| В Википедии есть статья «часовой пояс». |
Содержание
- 1 Русский
- 1.1 Тип и синтаксические свойства сочетания
- 1.2 Произношение
- 1.3 Семантические свойства
- 1.3.1 Значение
- 1.3.2 Синонимы
- 1.3.3 Антонимы
- 1.3.4 Гиперонимы
- 1.3.5 Гипонимы
- 1.4 Этимология
- 1.5 Перевод
Русский[править]
Тип и синтаксические свойства сочетания[править]
часовой пояс
Устойчивое сочетание (термин). Используется в качестве именной группы.
Произношение[править]
- МФА: [t͡ɕɪsɐˈvoɪ̯ ˈpo(ɪ̯)ɪs]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- регион Земли, в каждой точке которого действует одинаковое местное время ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
- —
Антонимы[править]
- —
Гиперонимы[править]
- зона
Гипонимы[править]
Этимология[править]
Перевод[править]
| Список переводов | |
|
|
|
Статья нуждается в доработке.
Это незаконченная статья. Вы можете помочь проекту, исправив и дополнив её.
(См. Общепринятые правила). |
UTC – всемирное координатное время.
Вся планета Земля разделена вертикальными линиями от северного до южного полюса. Эти линии образуют 24 часовых пояса. Каждый часовой пояс имеет свое значение от -12 до +12. Это значение показывает, на сколько часов в конкретном часовом поясе больше или меньше, чем в нулевом поясе — поясе отсчета. Нулевой пояс это Гринвичский меридиан.
Примеры
- Москва находится в UTC +3. Это значит, что в Москве на 3 часа больше, чем в Лондоне. Поэтому когда в Лондоне 08:00, то в Москве 11:00.
- Великобритания и Марокко находится в UTC +0. Поэтому в обеих странах одинаковое время, хотя страны находятся на расстоянии в несколько тысяч километров друг от друга.
Тахограф записывает на карту водителя время в UTC +0. В распечатке тахограф указывает время в этом же часовом поясе. Постоянно «в уме» пересчитывать время в свой часовой пояс утомительно.
Чтобы вам было удобнее, мы автоматически определяем ваш часовой пояс и можем показать смены водителя в вашем часовом поясе. Однако, иногда нужно взглянуть на активность водителя из другого часового пояса. К примеру, автоколонна повезла груз в город, который находится в другом часовом поясе. Для этого часовой пояс можно сменить и все показатели времени будут сразу пересчитаны.
Инструкция
1. Откройте раздел «Профиль»
2. В открывшейся вкладке «Главное» найдите пункт «Часовой пояс»
3. Снимите галочку
4. Выберите необходимый часовой пояс
5. Также вы можете перейти к изменению часового пояса, например, из вкладки «Смены»
Также вам могут быть интересны эти статьи
Можно ли считать карту с истекшим сроком?
Как долго хранятся считанные карты?
Сколько стоит GR.CARDS?
Частозадаваемые вопросы по картам водителя
Частозадаваемые вопросы по тахографам
Как разблокировать карту водителя?
Как правильно пользоваться тахографом?
Как повысить эффективность работы водителей?
Как расшифровать данные с тахографа?
Почему возникают ошибки при использовании тахографа?
Какие грозят штрафы за отсутствие тахографа и несоблюдение режима труда и отдыха
Как провести аудит установленных тахографов за 5 минут