Are you getting started with Python? Learning how to create a password generator can be the perfect project to learn or review basic Python concepts.
To create a password generator in Python you can use a for loop that randomly selects alphanumeric characters, digits, and punctuation characters to generate the password string. You can set the password length that defines the number of loop iterations. Also, by using a nested for loop you can improve the password generator to generate multiple passwords.
We will start with a simple password generator and then we will refactor the code to make it more flexible.
Are you ready?
We will start by generating a random string of 12 characters. To do that we will use the function random.choice() that returns a random character from a sequence.
We will do the following:
- Import the random module.
- Set the password length to 12.
- Define a list of characters that we will use to generate the random password. In this first version of the program, we will use just a few letters and numbers.
- Create an empty string called password.
- Write a for loop that executes 12 iterations and that at every iteration selects a random character from the string characters and appends it to the password string.
- Print the password we have generated.
import random
password_length = 12
characters = "abcde12345"
password = ""
for index in range(password_length):
password = password + random.choice(characters)
print("Password generated: {}".format(password))And here is an example of a password generated with this code:
Password generated: dcb4a2c4aac5
As you can see the password is not strong considering that we have used a limited number of characters and numbers.
In the next section, we will make it more secure.
How to Generate a Password Using All Alphanumeric Characters
Let’s improve the complexity of the password by using all alphanumeric characters.
To do that we could simply update the value of the characters string to include all letters and numbers but it would be time-consuming and prone to errors.
What can we do instead?
We can import the Python string module that provides a few constants that we can use in the generation of a password.
Here are a few examples:
>>> import string
>>> string.ascii_lowercase
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
>>> string.ascii_uppercase
'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
>>> string.ascii_letters
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
>>> string.digits
'0123456789'
>>> string.punctuation
'!"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~'We won’t use string.ascii_lowercase or string.ascii_uppercase considering that they are both included instring.ascii_letters.
In our password generator we will use the following three sets of characters:
- string.ascii_letters
- string.digits
- string.punctuation
We will use the + symbol to concatenate the three sets of characters to create a single string that we will assign to the characters variable.
This is what you get if you concatenate the three sets of characters in the Python shell:
>>> string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789!"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~'Let’s update our program…
import random, string
password_length = 12
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
password = ""
for index in range(password_length):
password = password + random.choice(characters)
print("Password generated: {}".format(password))Here are three examples of passwords generated with the updated program:
Password generated: iE%g.JqurkB0 Password generated: |>J+qbZ<Vl7$ Password generated: c94,JRgshz#g
Update the Password Generator to Receive the Password Length as User Input
Let’s make our password generator a bit more flexible.
We will allow the user to provide the password length instead of hardcoding it in our program. To do that we will use the input function.
import random, string
password_length = int(input("Provide the password length: "))
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
password = ""
for index in range(password_length):
password = password + random.choice(characters)
print("Password generated: {}".format(password))Notice that we have converted the value returned by the input function into an integer considering that when using Python 3 the input function returns a string.
The program works fine.
Confirm it works on your machine too before continuing with this tutorial.
Provide the password length: 12 Password generated: ]"c_ga%M^iOd
If you don’t convert the output of the input function into an integer you get the following error when you use the variable password_length in the for loop.
Provide the password length: 12
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "password_generator.py", line 9, in <module>
for index in range(password_length):
TypeError: 'str' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
How to Create a Python Password Generator that Generates Multiple Passwords
In this section, we will enhance our password generator to generate a custom number of passwords.
The approach will be very similar to the one we have used to get the password length from the user with the input function.
We will do the following:
- Get the number_of passwords using the input function.
- Add a for loop to generate multiple passwords based on the value of the variable number_of passwords provided by the user.
import random, string
number_of_passwords = int(input("How many passwords do you want to generate? "))
password_length = int(input("Provide the password length: "))
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
for password_index in range(number_of_passwords):
password = ""
for index in range(password_length):
password = password + random.choice(characters)
print("Password {} generated: {}".format(password_index, password))Note: make sure you use the correct indentation as shown in the code above.
Let’s test our code:
How many passwords do you want to generate? 3 Provide the password length: 8 Password 0 generated: 2B.1&=~k Password 1 generated: Wt$@1vi' Password 2 generated: ,aOXN_@$
It works, nice!
How to Generate Strong Passwords in Python
Before completing this tutorial let’s find out how we can enforce a set of rules to make sure the passwords we generate are strong enough.
We will make sure passwords contain at least:
- three digits
- two punctuation characters
To do that we will use two integers that define the number of digits and punctuation characters. Then we will use multiple nested for loops.
import random, string
number_of_digits = 3
number_of_punctuation_characters = 2
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
number_of_passwords = int(input("How many passwords do you want to generate? "))
password_length = int(input("Provide the password length: "))
for password_index in range(number_of_passwords):
password = ""
for digits_index in range(number_of_digits):
password = password + random.choice(string.digits)
for punctuation_index in range(number_of_punctuation_characters):
password = password + random.choice(string.punctuation)
for index in range(password_length - number_of_digits - number_of_punctuation_characters):
password = password + random.choice(string.ascii_letters)
print("Password {} generated: {}".format(password_index, password))Let’s have a look at a few passwords generated with this program:
How many passwords do you want to generate? 3 Provide the password length: 10 Password 0 generated: 738<>ZKwMA Password 1 generated: 332|(SlZDT Password 2 generated: 756%#NFWHs
They look fine but to make them stronger we have to avoid having digits and punctuation characters always in the same position of the password string.
To shuffle characters in the password string we will use the random.shuffle() function.
We will create a specific function that does the shuffling.
def randomize_password(password):
password_list = list(password)
random.shuffle(password_list)
return "".join(password_list)This function converts the password string into a list before applying random.shuffle. Then it returns a string using the string join method.
Then update the last print statement to call therandomize_password function.
print("Password {} generated: {}".format(password_index, randomize_password(password)))And the output is…
How many passwords do you want to generate? 3 Provide the password length: 10 Password 0 generated: X1+dT)4U1q Password 1 generated: 2T7g+OQ-B4 Password 2 generated: g3n0<3O>if
The password is a lot stronger now that digits and punctuation characters are in random positions.
In the video below I cover what we went through in this tutorial:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned how to create a password generator in Python and how to update its logic to increase the strength of the passwords.
We have covered a few Python core concepts:
- importing modules.
- defining functions.
- using the input function to read user input.
- nested for loops.
- selecting random characters from a string and shuffling a string.
- using the string format method.
Well done for completing this tutorial!
Related posts:
I’m a Tech Lead, Software Engineer and Programming Coach. I want to help you in your journey to become a Super Developer!
-
#2
Тема не новая, генераторов существует множество, однако такой простой код и глазу приятен, и место не занимает.
Для начала вставим в шапку кодировку и версию питона. Импортируем модуль random для генерации случайной последовательности. Зададим переменную chars и вобьём буквы в разном регистре, цифры и какие-нибудь спецсимволы для получения максимально взломостойкого пароля.
Python:
# -*- coding:utf -8 -*- #!/usr/bin/python3 import random chars = '+-/*!&$#?=@<>abcdefghijklnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890'Чтобы программа тупо не генерила один пароль или строго заданное количество, разрешим пользователю самому решать сколько паролей он хочет сгенерировать. Кроме этого дадим возможность определять и длину пароля.
Python:
number = input('количество паролей?'+ "n") length = input('длина пароля?'+ "n") number = int(number) length = int(length)Осталось добавить самое главное — цикл случайной генерации символов, букв и цифр из нашей переменной, согласно параметрам введённым пользователем.
Python:
for n in range(number): password ='' for i in range(length): password += random.choice(chars) print(password)Вот собственно и всё — простой генератор сложных паролей готов.
Код полностью:Python:
# -*- coding:utf -8 -*- #!/usr/bin/python3 import random chars = '+-/*!&$#?=@<>abcdefghijklnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890' number = input('количество паролей?'+ "n") length = input('длина пароля?'+ "n") number = int(number) length = int(length) for n in range(number): password ='' for i in range(length): password += random.choice(chars) print(password)Результат работы:
Посмотреть вложение 21790Не нужно искать сложных путей, если есть простые решения
С меня плюсик. И еще, во избежания лишних строк кода — советую:
Python:
number = input('количество паролей?'+ "n")
length = input('длина пароля?'+ "n")
number = int(number)
length = int(length)Заменить на:
Python:
number = int(input('количество паролей?'+ "n"))
length = int(input('длина пароля?'+ "n"))
Не нужно искать сложных путей, если есть простые решения
Последнее редактирование: 01.09.2018
-
#3
Можно еще написать пребор по таким паролям…те сначала набираеться словарь до указаного пользователем количества паролей и сразу же брут им через гидру…
-
#4
Заменить на:
Python:
number = int(input('количество паролей?'+ "n")) length = int(input('длина пароля?'+ "n"))
Согласен,
Можно еще написать пребор по таким паролям…те сначала набираеться словарь до указаного пользователем количества паролей и сразу же брут им через гидру…
Конечно. Пилить любой скрипт можно бесконечно. И чтобы сделать мега-программу многофункциональную, нужно сначала наклепать небольщих скриптиков, наподобие этого. Ну и потом скрестить, разумеется они должны быть одной направленности, чтобы дополнять друг друга. Иначе получится смесь бульдога с носорогом )
-
#5
Чего-то сегодня под вечер на меня нашло, и я решил переписать эту утилиту с оконным интерфейсом. Так гораздо удобнее, можно сразу в одном окне набить паролей разной длины.
В общем пошаманил, и получил следующий код на выходе:
Python:
# -*- coding:utf -8 -*-
#!/usr/bin/python3
from tkinter import *
import random
import string
root = Tk()
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
root.title("Генератор паролей")
root.geometry("420x338+300+300")
calculated_text = Text(root,height=15, width=50)
def erase():
calculated_text.delete('1.0', END)
chars = '+-/*!&$#?=@<>abcdefghijklnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890'
def password():
for n in range(int(number_entry.get())):
password =''
for i in range(int(length_entry.get())):
password += random.choice(chars)
calculated_text.insert(END, password + "n")
display_button = Button(text="Сгенерить", command=password)
erase_button = Button(text="Очистить", command=erase)
number_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER)
length_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER)
number_entry.insert(0, "8")
length_entry.insert(0, "25")
number_label = Label(text=" Количество паролей")
length_label = Label(text=" Длина пароля")
number_label.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w")
length_label.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="w")
number_entry.grid(row=0,column=1, padx=1, pady=5)
length_entry.grid(row=1,column=1, padx=1, pady=5)
display_button.grid(row=2, column=0, padx=5, pady=5, sticky="e")
erase_button.grid(row=2, column=2, padx=15, pady=5, sticky="w")
calculated_text.grid(row=4, column=0, sticky='nsew', columnspan=3)
scrollb = Scrollbar(root, command=calculated_text.yview)
scrollb.grid(row=4, column=4, sticky='nsew')
calculated_text.configure(yscrollcommand=scrollb.set)
root.mainloop()Выглядит так:
В копилку GUI
Valkiria
-
#6
Количество паролей — 5
Количество символов — 18.
А получилась какая-то каша.
Это тест на внимательность ?
-
#7
Количество паролей — 5
Количество символов — 18.
А получилась какая-то каша.Это тест на внимательность ?
Ну если тест на внимательность — то внимательнее читать нужно ))) ВЫше написано — можно сразу в одном окне набить паролей разной длины. Что на скрине и видно, сначала 25 знаков, потом 18. Чтобы каши не было, есть кнопка «очистить».
-
#8
Советую добавить немного отступов, и ещё добавить типо:
Пароль 1 — 7377283891
Пароль 2 — hsjsjaklaji28
Так все будет намного понятней
-
#9
Советую добавить немного отступов, и ещё добавить типо:
Пароль 1 — 7377283891
Пароль 2 — hsjsjaklaji28Так все будет намного понятней
Любые разделители можно по желанию поставить отредактировав строку 23. Пронумеровать тоже можно, но тогда нумерация будет повторяться с каждым новым циклом.
-
#10
а вот мой вариант )
Bash:
┌─╼[~]
└────╼ cat /bin/passgen
read -p "Длинна пароля: " number
echo
pwgen -sncB -1 "$number" 10
echo
-
#11
а почему не добавить при каждой новой генерации очистку предыдущей?
-
#12
а почему не добавить при каждой новой генерации очистку предыдущей?
Я так задумал просто, чтобы именно разной длины набить сразу в окно можно было. А если это не понадобится, то сделал кнопку «очистить».
Все мы по разному воспринимаем и мыслим
А так кучу всего другого можно туда добавить — например отправку в текстовый файл, чтобы ручками не копипастить и т.д.
-
#13
Решил написать свой вариант:
Код:
import datetime
import base64
import random
def Revers(string):
string = string[::-1]
return string
def CorrectPass(password):
for x in password:
password = password.replace(x,"")
if len(password) == passwordlen:
break
return password
#Get data
timer = datetime.datetime.now()
#Morph str
timer = str(timer)
timer = timer.replace('-','')
timer = timer.replace(' ','')
timer = timer.replace(':','')
timer = timer.replace('.','')
#Revers or not
realrandom = random.choice([1,2])
if realrandom == 1:
timer = Revers(timer)
#Encode str
timer = base64.b64encode(bytes(timer, "utf-8"))
#Morph
timer = str(timer)
timer = timer.replace("b'","")
timer = timer.replace("='","")
#Len
passwordlen = 15 #Change this
if passwordlen != len(timer):
timer = CorrectPass(timer)
#Check
while True: #Если в выводе ничего не получили, то запустите скрипт еще раз, до тех пор пока не получите.
if timer == '':
timer = CorrectPass(timer)
break
print (timer)
-
#14
Решил написать свой вариант
Я уж было обрадовался, что кто-то ещё свои творения выкладывает, но к сожалению консольный скрипт получился длиннющий, не всегда срабатывает, и длина пароля жёстко задана, и выдаёт в 1 экземпляре….
-
#15
сделал своё творение немного приятней глазу
Bash:
┌─╼[~]
└────╼ cat /bin/passgen
#!/bin/bash
# Скрипт генератор паролей pwgen + параметры запуска
echo
echo Генератор паролей pwgen с параметрами запуска
echo
echo ∗ Генерировать полностью случайные пароли
echo ∗ Включить хотя бы один номер в пароле
echo ∗ Включить хотя бы одну заглавную букву в пароле
echo ∗ Не включать двусмысленные символы в пароле
echo
read -p "⏵ Введите кол-во символов для пароля: " number
echo ──────────────────────╼
pwgen -1sncB "$number" 10
echo ──────────────────────╼
-
#16
Я уж было обрадовался, что кто-то ещё свои творения выкладывает, но к сожалению консольный скрипт получился длиннющий, не всегда срабатывает, и длина пароля жёстко задана, и выдаёт в 1 экземпляре….
Длину пароля можно поменять(там комментарий измени меня), а размер скрипта имеет значение(это глупо сравнить качество по количеству строк в коде)? Мне лень было фиксить эту проблему(не всегда срабатывает).
-
#17
Ну раз я сам заикнулся о варианте с сохранением в файл, то решил добавить эту функцию в программу. Теперь можно сгенерированные списки паролей сохранять.
Python:
# -*- coding:utf -8 -*-
#!/usr/bin/python3
__version__ = 'Version: 1.1'
from tkinter import *
import random
import string
from tkinter import filedialog as fd
root = Tk()
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
root.title("Генератор паролей " +str(__version__))
root.geometry("450x324+300+300")
calculated_text = Text(root,height=14, width=50)
def erase():
calculated_text.delete('1.0', END)
chars = '+-/*!&$#?=@<>abcdefghijklnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890'
def password():
for n in range(int(number_entry.get())):
password =''
for i in range(int(length_entry.get())):
password += random.choice(chars)
calculated_text.insert(END, password + "n")
def savepass():
file_name = fd.asksaveasfilename(filetypes=(("TXT files", "*.txt"),
("All files", "*.*")),defaultextension='')
f = open(file_name, 'w')
s = calculated_text.get(1.0, END)
f.write(s)
f.close()
display_button = Button(text="Сгенерить", command=password)
erase_button = Button(text="Очистить", command=erase)
save = Button(text="Сохранить", command=savepass)
number_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER)
length_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER)
number_entry.insert(0, "8")
length_entry.insert(0, "25")
number_label = Label(text=" Количество паролей")
length_label = Label(text=" Длина пароля")
number_label.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w")
length_label.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="w")
number_entry.grid(row=0,column=1, padx=1, pady=5)
length_entry.grid(row=1,column=1, padx=1, pady=5)
save.grid(row=3, column=2, padx=50, pady=5, sticky="w")
display_button.grid(row=3, column=0, padx=30, pady=5, sticky="e")
erase_button.grid(row=3, column=1, padx=30, pady=5, sticky="e")
scrollb = Scrollbar(root, command=calculated_text.yview)
scrollb.grid(row=4, column=3, sticky='nsew')
calculated_text.grid(row=4, column=0, sticky='nsew', columnspan=3)
calculated_text.configure(yscrollcommand=scrollb.set)
root.mainloop()
-
#18
Ну раз я сам заикнулся о варианте с сохранением в файл, то решил добавить эту функцию в программу. Теперь можно сгенерированные списки паролей сохранять.
Python:
# -*- coding:utf -8 -*- #!/usr/bin/python3 __version__ = 'Version: 1.1' from tkinter import * import random import string from tkinter import filedialog as fd root = Tk() root.resizable(width=False, height=False) root.title("Генератор паролей " +str(__version__)) root.geometry("450x324+300+300") calculated_text = Text(root,height=14, width=50) def erase(): calculated_text.delete('1.0', END) chars = '+-/*!&$#?=@<>abcdefghijklnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890' def password(): for n in range(int(number_entry.get())): password ='' for i in range(int(length_entry.get())): password += random.choice(chars) calculated_text.insert(END, password + "n") def savepass(): file_name = fd.asksaveasfilename(filetypes=(("TXT files", "*.txt"), ("All files", "*.*")),defaultextension='') f = open(file_name, 'w') s = calculated_text.get(1.0, END) f.write(s) f.close() display_button = Button(text="Сгенерить", command=password) erase_button = Button(text="Очистить", command=erase) save = Button(text="Сохранить", command=savepass) number_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER) length_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER) number_entry.insert(0, "8") length_entry.insert(0, "25") number_label = Label(text=" Количество паролей") length_label = Label(text=" Длина пароля") number_label.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w") length_label.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="w") number_entry.grid(row=0,column=1, padx=1, pady=5) length_entry.grid(row=1,column=1, padx=1, pady=5) save.grid(row=3, column=2, padx=50, pady=5, sticky="w") display_button.grid(row=3, column=0, padx=30, pady=5, sticky="e") erase_button.grid(row=3, column=1, padx=30, pady=5, sticky="e") scrollb = Scrollbar(root, command=calculated_text.yview) scrollb.grid(row=4, column=3, sticky='nsew') calculated_text.grid(row=4, column=0, sticky='nsew', columnspan=3) calculated_text.configure(yscrollcommand=scrollb.set) root.mainloop()Посмотреть вложение 22189
тебя уже не остановить ))))
-
#19
тебя уже не остановить ))))
Ну так ))) Сегодня вернулся из дальней поездки и сразу за дело.
Советую добавить немного отступов, и ещё добавить типо:
Пароль 1 — 7377283891
Пароль 2 — hsjsjaklaji28Так все будет намного понятней
Добавил сиё предложение, сделал отступы, и кроме того цикл не сбрасывает счётчик при многократной генерации паролей. Набил пароли разной длины — всё чётко и красиво
Python:
# -*- coding:utf -8 -*-
#!/usr/bin/python3
__version__ = 'Version: 2'
from tkinter import *
import random
import string
from tkinter import filedialog as fd
root = Tk()
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
root.title("Генератор паролей " +str(__version__))
root.geometry("450x324+300+300")
calculated_text = Text(root,height=14, width=50)
def erase():
calculated_text.delete('1.0', END)
chars = '+-/*!&$#?=@<>abcdefghijklnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890'
x = 0
def password():
for n in range(int(number_entry.get())):
password =''
global x
x += 1
for i in range(int(length_entry.get())):
password += random.choice(chars)
if x<=9:
calculated_text.insert(END,"Пароль" + ' ' + str(x) + ': ' + password + "n")
else:
calculated_text.insert(END,"Пароль" + ' ' + str(x) + ': ' + password + "n")
def savepass():
file_name = fd.asksaveasfilename(filetypes=(("TXT files", "*.txt"),
("All files", "*.*")),defaultextension='')
f = open(file_name, 'w')
s = calculated_text.get(1.0, END)
f.write(s)
f.close()
display_button = Button(text="Сгенерить", command=password)
erase_button = Button(text="Очистить", command=erase)
save = Button(text="Сохранить", command=savepass)
number_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER)
length_entry = Entry(width=10, justify=CENTER)
number_entry.insert(0, "8")
length_entry.insert(0, "25")
number_label = Label(text=" Количество паролей")
length_label = Label(text=" Длина пароля")
number_label.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w")
length_label.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky="w")
number_entry.grid(row=0,column=1, padx=1, pady=5)
length_entry.grid(row=1,column=1, padx=1, pady=5)
save.grid(row=3, column=2, padx=50, pady=5, sticky="w")
display_button.grid(row=3, column=0, padx=30, pady=5, sticky="e")
erase_button.grid(row=3, column=1, padx=30, pady=5, sticky="e")
scrollb = Scrollbar(root, command=calculated_text.yview)
scrollb.grid(row=4, column=3, sticky='nsew')
calculated_text.grid(row=4, column=0, sticky='nsew', columnspan=3)
calculated_text.configure(yscrollcommand=scrollb.set)
root.mainloop()
-
#20
Хотел спросить.
Почему используется
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
, а не
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
?
In this tutorial, we’ll build a password generator to enable us rapidly generate random and secure passwords.
What is the Purpose of a Password Generator?
We can’t instantaneously come up with new password patterns.
Computers, on the other hand, are not the same. In a matter of seconds, computers can create random and strong passwords depending on our preferences. There are several password generators on the market.
Is it possible to make our own with the adjustments we want?
Yes, we can certainly put one together. And we’ll teach you how to do it right now.
Let’s start by making a password generator.
Generator of Passwords
The nicest part about making our own password generator is that we can make it exactly as we want it.
First, we’ll make a password generator that asks for the password length and then produces a random password including numbers, alphabets, and special characters.
We’ll next enhance it by asking how many of each sort of character there are, such as numerals, alphabets, and special characters.
So, without further ado, let’s look at how to make a Python password generator.
Steps
- Make a list of all the characters. We may type all of them or utilize Python’s string module.
- Request that the user provide the password length.
- Using the random.shuffle technique, shuffle the characters.
- To save the password, create an empty list.
- Make a loop that iterates for the duration of time.
- Using the random.choice technique, choose a random character from all the characters.
- Toss in a random character at the end of the password.
- To make the final password list more random, shuffle it.
- Using the join technique, convert the password list to a string.
- The password should be printed.
Try to write code using the procedures shown above. Don’t worry if you can’t write the code yourself. Take a look at the code below.
Basic Code
import string
import random
## characters to generate password from
characters = list(string.ascii_letters + string.digits + "!@#$%^&*()")
def generate_random_password():
## length of password from the user
length = int(input("Enter password length: "))
## shuffling the characters
random.shuffle(characters)
## picking random characters from the list
password = []
for i in range(length):
password.append(random.choice(characters))
## shuffling the resultant password
random.shuffle(password)
## converting the list to string
## printing the list
print("".join(password))
## invoking the function
generate_random_password()The code in the example above is self-explanatory. To write code, we simply followed the procedures outlined. If you follow the procedures, you should have no trouble comprehending the code.
Run the code now to create a password. The following is an example of the output.
Enter password length: 10
d&amIzK%d)Take note of the password in the output above. Is there a digit somewhere? No. Because there’s no way of knowing whether or not the software will have digits.
Next, we ask the user to specify the amount of numbers, alphabets, and special characters they want, in order to ensure that the software will contain them.
The application will include the appropriate number of character kinds in the password when the user specifies the number of characters for each type.
Let’s have a look at the code that takes the amount of characters for each category and creates the password.
Random Password Generator in Python Source Code
import string
import random
## characters to generate password from
alphabets = list(string.ascii_letters)
digits = list(string.digits)
special_characters = list("!@#$%^&*()")
characters = list(string.ascii_letters + string.digits + "!@#$%^&*()")
def generate_random_password():
## length of password from the user
length = int(input("Enter password length: "))
## number of character types
alphabets_count = int(input("Enter alphabets count in password: "))
digits_count = int(input("Enter digits count in password: "))
special_characters_count = int(input("Enter special characters count in password: "))
characters_count = alphabets_count + digits_count + special_characters_count
## check the total length with characters sum count
## print not valid if the sum is greater than length
if characters_count > length:
print("Characters total count is greater than the password length")
return
## initializing the password
password = []
## picking random alphabets
for i in range(alphabets_count):
password.append(random.choice(alphabets))
## picking random digits
for i in range(digits_count):
password.append(random.choice(digits))
## picking random alphabets
for i in range(special_characters_count):
password.append(random.choice(special_characters))
## if the total characters count is less than the password length
## add random characters to make it equal to the length
if characters_count < length:
random.shuffle(characters)
for i in range(length - characters_count):
password.append(random.choice(characters))
## shuffling the resultant password
random.shuffle(password)
## converting the list to string
## printing the list
print("".join(password))
## invoking the function
generate_random_password()So, what’s the difference between this code and the one before it?
-
To add the characters to the password, we created separate loops for each kind of character.
-
There are two conditional checks to ensure that the total number of characters in the password matches the length of the password.
We’ve added some more code. The pattern, however, is identical to that of the prior code. As a result, you won’t have any trouble comprehending it.
Now it’s time to run the code and examine the results. Take a look at the following example of a test run.
Enter password length: 10
Enter alphabets count in password: 3
Enter digits count in password: 2
Enter special characters count in password: 3
V2(&#XlQq1If you look at the password that was created this time, you’ll see that it contains the minimal amount of characters that the user requested. In addition, the computer has added two extra random characters to make the password length equal to the length entered by the user.
Hurray! We offer a full-featured, secure password generator.
Conclusion
We’ve shown how to build a password generator from the ground up. Is it possible to add additional features to it? Yes, we are free to add as many as we like. However, be certain that the resulting password is sufficiently strong.
Make a password generator using the code and use it for your next online account.
In this tutorial, we’ll build a password generator to enable us rapidly generate random and secure passwords.
What is the Purpose of a Password Generator?
We can’t instantaneously come up with new password patterns.
Computers, on the other hand, are not the same. In a matter of seconds, computers can create random and strong passwords depending on our preferences. There are several password generators on the market.
Is it possible to make our own with the adjustments we want?
Yes, we can certainly put one together. And we’ll teach you how to do it right now.
Let’s start by making a password generator.
Generator of Passwords
The nicest part about making our own password generator is that we can make it exactly as we want it.
First, we’ll make a password generator that asks for the password length and then produces a random password including numbers, alphabets, and special characters.
We’ll next enhance it by asking how many of each sort of character there are, such as numerals, alphabets, and special characters.
So, without further ado, let’s look at how to make a Python password generator.
Steps
- Make a list of all the characters. We may type all of them or utilize Python’s string module.
- Request that the user provide the password length.
- Using the random.shuffle technique, shuffle the characters.
- To save the password, create an empty list.
- Make a loop that iterates for the duration of time.
- Using the random.choice technique, choose a random character from all the characters.
- Toss in a random character at the end of the password.
- To make the final password list more random, shuffle it.
- Using the join technique, convert the password list to a string.
- The password should be printed.
Try to write code using the procedures shown above. Don’t worry if you can’t write the code yourself. Take a look at the code below.
Basic Code
import string
import random
## characters to generate password from
characters = list(string.ascii_letters + string.digits + "!@#$%^&*()")
def generate_random_password():
## length of password from the user
length = int(input("Enter password length: "))
## shuffling the characters
random.shuffle(characters)
## picking random characters from the list
password = []
for i in range(length):
password.append(random.choice(characters))
## shuffling the resultant password
random.shuffle(password)
## converting the list to string
## printing the list
print("".join(password))
## invoking the function
generate_random_password()The code in the example above is self-explanatory. To write code, we simply followed the procedures outlined. If you follow the procedures, you should have no trouble comprehending the code.
Run the code now to create a password. The following is an example of the output.
Enter password length: 10
d&amIzK%d)Take note of the password in the output above. Is there a digit somewhere? No. Because there’s no way of knowing whether or not the software will have digits.
Next, we ask the user to specify the amount of numbers, alphabets, and special characters they want, in order to ensure that the software will contain them.
The application will include the appropriate number of character kinds in the password when the user specifies the number of characters for each type.
Let’s have a look at the code that takes the amount of characters for each category and creates the password.
Random Password Generator in Python Source Code
import string
import random
## characters to generate password from
alphabets = list(string.ascii_letters)
digits = list(string.digits)
special_characters = list("!@#$%^&*()")
characters = list(string.ascii_letters + string.digits + "!@#$%^&*()")
def generate_random_password():
## length of password from the user
length = int(input("Enter password length: "))
## number of character types
alphabets_count = int(input("Enter alphabets count in password: "))
digits_count = int(input("Enter digits count in password: "))
special_characters_count = int(input("Enter special characters count in password: "))
characters_count = alphabets_count + digits_count + special_characters_count
## check the total length with characters sum count
## print not valid if the sum is greater than length
if characters_count > length:
print("Characters total count is greater than the password length")
return
## initializing the password
password = []
## picking random alphabets
for i in range(alphabets_count):
password.append(random.choice(alphabets))
## picking random digits
for i in range(digits_count):
password.append(random.choice(digits))
## picking random alphabets
for i in range(special_characters_count):
password.append(random.choice(special_characters))
## if the total characters count is less than the password length
## add random characters to make it equal to the length
if characters_count < length:
random.shuffle(characters)
for i in range(length - characters_count):
password.append(random.choice(characters))
## shuffling the resultant password
random.shuffle(password)
## converting the list to string
## printing the list
print("".join(password))
## invoking the function
generate_random_password()So, what’s the difference between this code and the one before it?
-
To add the characters to the password, we created separate loops for each kind of character.
-
There are two conditional checks to ensure that the total number of characters in the password matches the length of the password.
We’ve added some more code. The pattern, however, is identical to that of the prior code. As a result, you won’t have any trouble comprehending it.
Now it’s time to run the code and examine the results. Take a look at the following example of a test run.
Enter password length: 10
Enter alphabets count in password: 3
Enter digits count in password: 2
Enter special characters count in password: 3
V2(&#XlQq1If you look at the password that was created this time, you’ll see that it contains the minimal amount of characters that the user requested. In addition, the computer has added two extra random characters to make the password length equal to the length entered by the user.
Hurray! We offer a full-featured, secure password generator.
Conclusion
We’ve shown how to build a password generator from the ground up. Is it possible to add additional features to it? Yes, we are free to add as many as we like. However, be certain that the resulting password is sufficiently strong.
Make a password generator using the code and use it for your next online account.
Yet another one-liner:
python -c "import random;print(''.join([random.choice(random.choice([['a','e','f','g','h','m','n','t','y'],['A','B','E','F','G','H','J','K','L','M','N','Q','R','T','X','Y'],['2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'],['/','*','+','~','@','#','%','^','&','//']])) for i in range(16)]));"
Samples:
L+f##Q~H88NBe6Ny
&7@M7gt4J^///gH3e
5e2455hgn2h^//ffh
Advantage:
Change char list explicitly, exclude similar chars(etc. i 1 l I, 0 o O).(Just add/del in the list)
Change password length from 16 to whatever you want.
Disadvantage:
Readability.
PS. readable version:
python -c "import random;
print(''.join([random.choice(random.choice(
[
['a','e','f','g','h','m','n','t','y'],
['A','B','E','F','G','H','J','K','L','M','N','Q','R','T','X','Y'],
['2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'],
['/','*','+','~','@','#','%','^','&','//']
]))
for i in range(16)]));"
Python-Password-Generator
Created a random password generator in Python.
We know that passwords are a real security threat. To keep your account safe and prevent your password from being hacked you have to make your password hard enough that nobody can guess.
The Password generator tool creates a random and customized password for users that helps them to create a strong password which provides greater security.
The project
The objective of this project is to create a password generator using python. The password generator project will be build using python modules like Tkinter, random, string, pyperclip.
In this project, the user has to select the password length and then click on the “Generate Password” button. It will show the generated password below. If the user clicks on the “Copy To Clipboard” button, then it will copy the password automatically.
Project Prerequisites
To build this project we will use the basic concept of python and libraries – Tkinter, pyperclip, random, string.
- Tkinter is a standard GUI library and is one of the easiest ways to build a GUI application.
- pyperclip module allows us to copy and paste text to and from the clipboard to your computer
- The random module can generate random numbers
- string module contains a number of functions to process the standard python string.
To install the libraries we can use pip installer from the command line:
1. pip install tkinter
2. pip install pyperclip
3. pip install random
4. pip install strings
Steps to create random password generator
1. Import Libraries
The first step is to import libraries
from tkinter import *
import random, string
import pyperclip
2. Initialize Window
root =Tk()
root.geometry("400x400")
root.resizable(0,0)
root.title("BeRito - PASSWORD GENERATOR")
- Tk() initialized tkinter which means window created
- geometry() set the width and height of the window
- resizable(0,0) set the fixed size of the window
- title() set the title of the window
3. Select Password Length
pass_label = Label(root, text = 'PASSWORD LENGTH', font = 'arial 10 bold').pack()
pass_len = IntVar()
length = Spinbox(root, from_ = 8, to_ = 32 , textvariable = pass_len , width = 15).pack()
- pass_len is an integer type variable that stores the length of a password.
- To select the password length we use Spinbox() widget.
- Spinbox() widget is used to select from a fixed number of values. Here the value from 8 to 32
4. Function to Generate Password
pass_str = StringVar()
def Generator():
password = ''
for x in range (0,4):
password = random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase) + random.choice(string.ascii_lowercase) + random.choice(string.digits) + random.choice(string.punctuation)
for y in range(pass_len.get()- 4):
password = password + random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits + string.punctuation)
pass_str.set(password)
- pass_str is a string type variable that stores the generated password
- password = “” is the empty string
- First loop will generate a string of length 4 which is a combination of an uppercase letter, a lowercase letter, digits, and a special symbol and that string will store in password variable.
- The second loop will generate a random string of length entered by the user – 4 and add to the password variable. Here we minus 4 to the length of the user because we already generate the string of length 4.
We have done this because we want a password which must contain an uppercase, a lowercase, a digit, and a special symbol.
Now the password is set to the pass_str() variable.
5. Function to Copy Password
def Copy_password():
pyperclip.copy(pass_str.get())
Button(root, text = 'COPY TO CLIPBOARD', command = Copy_password).pack(pady=5)
pyperclip.copy() used to copy the text to clipboard
Python Password Generator Output
Summary
With these steps, we have successfully created a random password generator project using python. We used popular tkinter library to rendering graphics in our display window and we also learned about pyperclip and random library.
We learned how to create buttons, input textfield, labels, and spinbox. In this way, we successfully created our password generator python project. Hope you enjoyed it.
In this article, we will see how to create a random password generator using Python.
Passwords are a means by which a user proves that they are authorized to use a device. It is important that passwords must be long and complex. It should contain at least more than ten characters with a combination of characters such as percent (%), commas(,), and parentheses, as well as lower-case and upper-case alphabets and numbers. Here we will create a random password using Python code.
Example of a weak password : password123
Example of a strong password : &gj5hj&*178a1
Modules needed
string – For accessing string constants. The ones we would need are –
- string.ascii_letters: ASCII is a system that is used to represent characters digitally, every ASCII character has its own unique code. string.ascii_letters is a string constant which contains all the letters in ASCII ranging from A to Z and a to z. Its value is non-locale dependent and it is just a concatenation of ascii_uppercase and ascii_lowercase. Thus it provides us the whole letter set as a string that can be used as desired.
- string.digits: This is a pre-initialized string that contains all the digits in the Arabic numeral system i.e. 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. It should be kept in mind that even though these are digits, the type is still a string constant, and all digits are concatenated like this – “0123456789”. If we want to access specific numbers then we can do so using slicing.
- string.punctuation: Apart from letters and digits, python also provides us all the special characters in a pre-initialized string constant. These include various kinds of braces, logical operators, comparison operators, arithmetical operators as well as punctuation marks like commas, inverted commas, periods, exclamations marks, and question marks. The whole string is – !”#$%&'()*+, -./:;<=>?@[]^_`{|}~
random – The python random module helps a user to generate pseudo-random numbers. Inside the module, there are various functions that just depend on the function “random()”. This function generates a random float uniformly in the semi-open range [0.0, 1.0) i.e. it generates a decimal number greater than or equal to 0 and strictly less than one. Other functions use this number in their own ways. These functions can be used for bytes, integers, and sequences. for our task, we are interested in sequences. There are functions random. choices that take in a sequence as its argument and return a random element from that sequence.
Code Implementation:
First, take the length of the password as input. Then we can display a prompt about the possible list of characters that a user wants to include in the password –
- For including letters in the character set append string.ascii_letters in the character list.
- For including letters in the character set append string.digits in the character list.
- For including letters in character set append string.punctuation in the character list.
Run a for loop till the length of the password and in each iteration choose a random character using random.choice() from characterList. Finally, print the password.
Python3
import string
import random
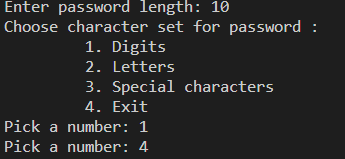
length = int(input("Enter password length: "))
print(
)
characterList = ""
while(True):
choice = int(input("Pick a number "))
if(choice == 1):
characterList += string.ascii_letters
elif(choice == 2):
characterList += string.digits
elif(choice == 3):
characterList += string.punctuation
elif(choice == 4):
break
else:
print("Please pick a valid option!")
password = []
for i in range(length):
randomchar = random.choice(characterList)
password.append(randomchar)
print("The random password is " + "".join(password))
Output:
Input 1: Taking only letters in the character set
Output
Input 1: Taking letters and numbers both
Output
Input 3: Taking letters numbers as well as special characters
Output
Strong Password Generator Only by entering the size of password
Implementation
Python3
import string
import random
s1 = list(string.ascii_lowercase)
s2 = list(string.ascii_uppercase)
s3 = list(string.digits)
s4 = list(string.punctuation)
user_input = input("How many characters do you want in your password? ")
while True:
try:
characters_number = int(user_input)
if characters_number < 8:
print("Your number should be at least 8.")
user_input = input("Please, Enter your number again: ")
else:
break
except:
print("Please, Enter numbers only.")
user_input = input("How many characters do you want in your password? ")
random.shuffle(s1)
random.shuffle(s2)
random.shuffle(s3)
random.shuffle(s4)
part1 = round(characters_number * (30/100))
part2 = round(characters_number * (20/100))
result = []
for x in range(part1):
result.append(s1[x])
result.append(s2[x])
for x in range(part2):
result.append(s3[x])
result.append(s4[x])
random.shuffle(result)
password = "".join(result)
print("Strong Password: ", password)
Output:
Output