Английская буква джи — написание и произношение
G – седьмая буква английского алфавита. Она имеет несколько вариантов написания, техника зависит от шрифта (печатный/рукописный) и типа символа (заглавная/строчная).
Техника написания
Для написания буквы «G» предпочтительно взять лист разлинованной бумаги, чтобы видеть разницу между прописными и строчными буквами.
Печатная заглавная «G»
- Написать заглавную букву «С»:
- начертить полумесяц с отверстием справа
- От нижней точки буквы «С» добавить горизонтальную линию влево, внутрь буквы наполовину
Печатная строчная «g»
- Написать строчную букву «с».
- Единственное отличие от заглавной буквы «С»: строчная меньше почти в два раза.
- От верхней точки буквы «с» провести вертикальную линию вниз, переходящую в крючок в левую сторону.
Печатная строчная «g»
- В верхней части строки изобразить букву «о» размером 7/8 от строчной буквы.
- От нижней правой точки нарисовать овальную петлю вправо и вниз.
- К верхней правой точке добавить «ушко».
Рукописная заглавная
- От левой нижней точки строки начертить наклонную линию, ведущую вправо вверх.
- Развернуть петлей влево и вниз. Вывести петлю крючком вправо до самого верха строки.
- Начертить наклонную линию, идущую влево вниз. Вывести ее крючком влево. Крючок должен пересечь первую линию (шаг 1).
- Провести горизонтальную линию вправо, внутрь наполовину буквы.
Рукописная строчная «g»
- Нарисовать о образную форму с наклоном.
- От нижней правой точки добавить наклонную линию, ведущую влево вниз.
- Развернуть ее влево петлей и вывести наверх.
Произношение буквы «G»
Буква «G» имеет два основных правила чтения и несколько второстепенных.
g = [г]
- перед гласными a, o, u.
legacy [‘legəsi] – наследство, наследие
go [gou] – идти
regulate [‘regjuleit] – регулировать
- перед любой согласной.
ingredient [in’gri:diənt] – компонент
- в конце слова.
leg [leg] – нога
g = [дж]
- перед гласными e, i, y.
page [peidʒ] – страница
giant [‘dʒaiənt] – гигант
gym [dʒim] – тренажерный зал
Исключения:
- g = [г] перед окончаниями -er и -est прилагательных и наречий.
big [big] – большой / bigger [‘bigə] – больше / biggest [‘bigəst] – самый большой
g = [г] в следующих словах:
begin – начинать(ся) anger – гнев
gift – подарок
forget – забывать
get – получать
target – цель, мишень
girl – девушка
together – вместе
give – давать
forgive – прощать
geese – гуси
finger – палец
tiger – тигр
hunger – голод
- g = [ж] в словах французского происхождения.
garage [gə’raʒ] – гараж
- gn = [-] в начале и конце слов.
gnome [noum] – гном
sign [sain] – символ; подпись
ng = [ŋ]
Язык располагается у основания нижних зубов. Рот открыт широко. Задняя часть языка прижата к опущенному мягкому нёбу, воздушная струя следует через полость носа. Для носового звука требуется не поднимать к альвеолам кончик языка.
kingdom [‘kiŋdəm] – королевство
gh = [г], [ф], [-]
Чтение слов с буквосочетанием «gh» необходимо проверять по словарю в связи с вариациями произношения и отсутствием правил.
ghost [gəust] – приведение
tough [tʌf] – жесткий
high [hai] – высоко
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the letter of the alphabet. For other uses, see G (disambiguation).
| G | |
|---|---|
| G g | |
| (See below, Typographic) | |
 |
|
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Phonetic usage |
|
| Unicode codepoint | U+0047, U+0067, U+0261 |
| Alphabetical position | 7 |
| History | |
| Development |
|
| Time period | ~-300 to present |
| Descendants |
|
| Sisters |
|
| Transliteration equivalents | C |
| Variations | (See below, Typographic) |
| Other | |
| Other letters commonly used with | gh, g(x) |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. |
G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is gee (pronounced ), plural gees.[1]
History
The letter ‘G’ was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ‘C’ to distinguish voiced /ɡ/ from voiceless /k/.
The recorded originator of ‘G’ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, who added letter G to the teaching of the Roman alphabet during the 3rd century BC:[2] he was the first Roman to open a fee-paying school, around 230 BCE. At this time, ‘K’ had fallen out of favor, and ‘C’, which had formerly represented both /ɡ/ and /k/ before open vowels, had come to express /k/ in all environments.
Ruga’s positioning of ‘G’ shows that alphabetic order related to the letters’ values as Greek numerals was a concern even in the 3rd century BC. According to some records, the original seventh letter, ‘Z’, had been purged from the Latin alphabet somewhat earlier in the 3rd century BC by the Roman censor Appius Claudius, who found it distasteful and foreign.[3] Sampson (1985) suggests that: «Evidently the order of the alphabet was felt to be such a concrete thing that a new letter could be added in the middle only if a ‘space’ was created by the dropping of an old letter.»[4]
George Hempl proposed in 1899 that there never was such a «space» in the alphabet and that in fact ‘G’ was a direct descendant of zeta. Zeta took shapes like ⊏ in some of the Old Italic scripts; the development of the monumental form ‘G’ from this shape would be exactly parallel to the development of ‘C’ from gamma. He suggests that the pronunciation /k/ > /ɡ/ was due to contamination from the also similar-looking ‘K’.[5]
Eventually, both velar consonants /k/ and /ɡ/ developed palatalized allophones before front vowels; consequently in today’s Romance languages, ⟨c⟩ and ⟨g⟩ have different sound values depending on context (known as hard and soft C and hard and soft G). Because of French influence, English language orthography shares this feature.
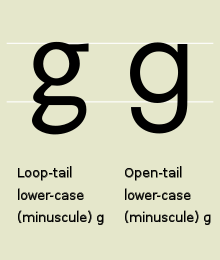
Typographic variants
The modern lowercase ‘g’ has two typographic variants: the single-storey (sometimes opentail) ‘‘ and the double-storey (sometimes looptail) ‘
‘. The single-storey form derives from the majuscule (uppercase) form by raising the serif that distinguishes it from ‘c’ to the top of the loop, thus closing the loop and extending the vertical stroke downward and to the left. The double-storey form (
) had developed similarly, except that some ornate forms then extended the tail back to the right, and to the left again, forming a closed bowl or loop. The initial extension to the left was absorbed into the upper closed bowl. The double-storey version became popular when printing switched to «Roman type» because the tail was effectively shorter, making it possible to put more lines on a page. In the double-storey version, a small top stroke in the upper-right, often terminating in an orb shape, is called an «ear».
Generally, the two forms are complementary, but occasionally the difference has been exploited to provide contrast. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, opentail ⟨ɡ⟩ has always represented a voiced velar plosive, while ⟨⟩ was distinguished from ⟨ɡ⟩ and represented a voiced velar fricative from 1895 to 1900.[6][7] In 1948, the Council of the International Phonetic Association recognized ⟨ɡ⟩ and ⟨
⟩ as typographic equivalents,[8] and this decision was reaffirmed in 1993.[9] While the 1949 Principles of the International Phonetic Association recommended the use of ⟨
⟩ for a velar plosive and ⟨ɡ⟩ for an advanced one for languages where it is preferable to distinguish the two, such as Russian,[10] this practice never caught on.[11] The 1999 Handbook of the International Phonetic Association, the successor to the Principles, abandoned the recommendation and acknowledged both shapes as acceptable variants.[12]
Wong et al. (2018) found that native English speakers have little conscious awareness of the looptail ‘g’ ().[13][14] They write: «Despite being questioned repeatedly, and despite being informed directly that G has two lowercase print forms, nearly half of the participants failed to reveal any knowledge of the looptail ‘g’, and only 1 of the 38 participants was able to write looptail ‘g’ correctly.»
In Unicode, the two appearances are generally treated as glyph variants with no semantic difference. For applications where the single-storey variant must be distinguished (such as strict IPA in a typeface where the usual g character is double-storey), the character U+0261 ɡ LATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT G is available, as well as an upper case version, U+A7AC Ɡ LATIN CAPITAL LETTER SCRIPT G.
Pronunciation and use
| Language | Dialect(s) | Pronunciation (IPA) | Environment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afrikaans | /x/ | |||
| Arabic | /ɡ/ | Latinization; corresponding to ⟨ق⟩ or ⟨ج⟩ in Arabic | ||
| Azeri | /ɟ/ | |||
| Catalan | /(d)ʒ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Danish | /ɡ/ | Word-initially | ||
| /k/ | Usually | |||
| Dutch | Standard | /ɣ/ | ||
| Southern dialects | /ɣ̟/ | |||
| Northern dialects | /χ/ | |||
| English | /dʒ/ | Before e, i, y (see exceptions below) | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i in «modern» loanwords from French | |||
| silent | Some words, initial <gn>, and word-finally before a consonant | |||
| Faroese | /j/ | soft, lenited; see Faroese phonology | ||
| /k/ | hard | |||
| /tʃ/ | soft | |||
| /v/ | after a, æ, á, e, o, ø and before u | |||
| /w/ | after ó, u, ú and before a, i, or u | |||
| silent | after a, æ, á, e, o, ø and before a | |||
| Fijian | /ŋ/ | |||
| French | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |||
| Galician | /ɡ/~/ħ/ | Usually | See Gheada for consonant variation | |
| /ʃ/ | Before e, i | obsolete spelling, replaced by the letter x | ||
| Greek | /ɡ/ | Usually | Latinization | |
| /ɟ/ | Before ai, e, i, oi, y | Latinization | ||
| Icelandic | /c/ | soft | ||
| /k/ | hard | |||
| /ɣ/ | hard, lenited; see Icelandic phonology | |||
| /j/ | soft, lenited | |||
| Irish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ɟ/ | After i or before e, i | |||
| Italian | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /dʒ/ | Before e, i | |||
| Mandarin | Standard | /k/ | Pinyin latinization | |
| Norman | /dʒ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Norwegian | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /j/ | Before ei, i, j, øy, y | |||
| Portuguese | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |||
| Romanian | /dʒ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Romansh | /dʑ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Samoan | /ŋ/ | |||
| Scottish Gaelic | /k/ | Usually | ||
| /kʲ/ | After i or before e, i | |||
| Spanish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /x/ or /h/ | Before e, i, y | Variation between velar and glottal realizations depends on dialect | ||
| Swedish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /j/ | Before ä, e, i, ö, y | |||
| Turkish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ɟ/ | Before e, i, ö, ü | |||
| Vietnamese | Standard | /ɣ/ | ||
| Northern | /z/ | Before i | ||
| Southern | /j/ | Before i |
English
In English, the letter appears either alone or in some digraphs. Alone, it represents
- a voiced velar plosive (/ɡ/ or «hard» ⟨g⟩), as in goose, gargoyle, and game;
- a voiced palato-alveolar affricate (/d͡ʒ/ or «soft» ⟨g⟩), predominates before ⟨i⟩ or ⟨e⟩, as in giant, ginger, and geology; or
- a voiced palato-alveolar sibilant (/ʒ/) in post-medieval loanwords from French, such as rouge, beige, genre (often), and margarine (rarely)
⟨g⟩ is predominantly soft before ⟨e⟩ (including the digraphs ⟨ae⟩ and ⟨oe⟩), ⟨i⟩, or ⟨y⟩, and hard otherwise. It is hard in those derivations from γυνή (gynḗ) meaning woman where initial-worded as such. Soft ⟨g⟩ is also used in many words that came into English from medieval church/academic use, French, Spanish, Italian or Portuguese – these tend to, in other ways in English, closely align to their Ancient Latin and Greek roots (such as fragile, logic or magic).
There remain widely used a few English words of non-Romance origin where ⟨g⟩ is hard followed by ⟨e⟩ or ⟨i⟩ (get, give, gift), and very few in which ⟨g⟩ is soft though followed by ⟨a⟩ such as gaol, which since the 20th century is almost always written as «jail».
The double consonant ⟨gg⟩ has the value /ɡ/ (hard ⟨g⟩) as in nugget, with very few exceptions: /d͡ʒ/ in exaggerate and veggies and dialectally /ɡd͡ʒ/ in suggest.
The digraph ⟨dg⟩ has the value /d͡ʒ/ (soft ⟨g⟩), as in badger. Non-digraph ⟨dg⟩ can also occur, in compounds like floodgate and headgear.
The digraph ⟨ng⟩ may represent:
- a velar nasal () as in length, singer
- the latter followed by hard ⟨g⟩ (/ŋɡ/) as in jungle, finger, longest
Non-digraph ⟨ng⟩ also occurs, with possible values
- /nɡ/ as in engulf, ungainly
- /nd͡ʒ/ as in sponge, angel
- /nʒ/ as in melange
The digraph ⟨gh⟩ (in many cases a replacement for the obsolete letter yogh, which took various values including /ɡ/, /ɣ/, /x/ and /j/) may represent:
- /ɡ/ as in ghost, aghast, burgher, spaghetti
- /f/ as in cough, laugh, roughage
- Ø (no sound) as in through, neighbor, night
- /x/ in ugh
- (rarely) /p/ in hiccough
- (rarely) /k/ in s’ghetti
Non-digraph ⟨gh⟩ also occurs, in compounds like foghorn, pigheaded
The digraph ⟨gn⟩ may represent:
- /n/ as in gnostic, deign, foreigner, signage
- /nj/ in loanwords like champignon, lasagna
Non-digraph ⟨gn⟩ also occurs, as in signature, agnostic
The trigraph ⟨ngh⟩ has the value /ŋ/ as in gingham or dinghy. Non-trigraph ⟨ngh⟩ also occurs, in compounds like stronghold and dunghill.
G is the tenth least frequently used letter in the English language (after Y, P, B, V, K, J, X, Q, and Z), with a frequency of about 2.02% in words.
Other languages
Most Romance languages and some Nordic languages also have two main pronunciations for ⟨g⟩, hard and soft. While the soft value of ⟨g⟩ varies in different Romance languages (/ʒ/ in French and Portuguese, [(d)ʒ] in Catalan, /d͡ʒ/ in Italian and Romanian, and /x/ in most dialects of Spanish), in all except Romanian and Italian, soft ⟨g⟩ has the same pronunciation as the ⟨j⟩.
In Italian and Romanian, ⟨gh⟩ is used to represent /ɡ/ before front vowels where ⟨g⟩ would otherwise represent a soft value. In Italian and French, ⟨gn⟩ is used to represent the palatal nasal /ɲ/, a sound somewhat similar to the ⟨ny⟩ in English canyon. In Italian, the trigraph ⟨gli⟩, when appearing before a vowel or as the article and pronoun gli, represents the palatal lateral approximant /ʎ/.
Other languages typically use ⟨g⟩ to represent /ɡ/ regardless of position.
Amongst European languages, Czech, Dutch, Estonian and Finnish are an exception as they do not have /ɡ/ in their native words. In Dutch, ⟨g⟩ represents a voiced velar fricative /ɣ/ instead, a sound that does not occur in modern English, but there is a dialectal variation: many Netherlandic dialects use a voiceless fricative ([x] or [χ]) instead, and in southern dialects it may be palatal [ʝ]. Nevertheless, word-finally it is always voiceless in all dialects, including the standard Dutch of Belgium and the Netherlands. On the other hand, some dialects (like Amelands) may have a phonemic /ɡ/.
Faroese uses ⟨g⟩ to represent /dʒ/, in addition to /ɡ/, and also uses it to indicate a glide.
In Māori, ⟨g⟩ is used in the digraph ⟨ng⟩ which represents the velar nasal /ŋ/ and is pronounced like the ⟨ng⟩ in singer.
The Samoan and Fijian languages use the letter ⟨g⟩ by itself for /ŋ/.
In older Czech and Slovak orthographies, ⟨g⟩ was used to represent /j/, while /ɡ/ was written as ⟨ǧ⟩ (⟨g⟩ with caron).
The Azerbaijani Latin alphabet uses ⟨g⟩ exclusively for the «soft» sound, namely /ɟ/. The sound /ɡ/ is written as ⟨q⟩. This leads to unusual spellings of loanwords: qram ‘gram’, qrup ‘group’, qaraj ‘garage’, qallium ‘gallium’.
Ancestors, descendants and siblings
- 𐤂 : Semitic letter Gimel, from which the following symbols originally derive
- C c : Latin letter C, from which G derives
- Γ γ : Greek letter Gamma, from which C derives in turn
- ɡ : Latin letter script small G
- ᶢ : Modifier letter small script g is used for phonetic transcription[15]
- 𝼁 : Latin small letter reversed script g, an extension to IPA for disordered speech (extIPA)[16][17]
- ᵷ : Turned g
- 𝼂 : Latin letter small capital turned g, an extension to IPA for disordered speech (extIPA)[16][17]
- Г г : Cyrillic letter Ge
- Ȝ ȝ : Latin letter Yogh
- Ɣ ɣ : Latin letter Gamma
- Ᵹ ᵹ : Insular g
- ᫌ : Combining insular g, used in the Ormulum[18]
- Ꝿ ꝿ : Turned insular g
- Ꟑ ꟑ : Closed insular g, used in the Ormulum[18]
- ɢ : Latin letter small capital G, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent a voiced uvular stop
- 𐞒 : Modifier letter small capital G, used as a superscript IPA letter[19]
- ʛ : Latin letter small capital G with hook, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent a voiced uvular implosive
- 𐞔 : Modifier letter small capital G with hook, used as a superscript IPA letter[19]
- 𐞓 : Modifier letter small g with hook, used as a superscript IPA letter[19]
- ᴳ ᵍ : Modifier letters are used in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet[20]
- ꬶ : Used for the Teuthonista phonetic transcription system[21]
- G with diacritics: Ǵ ǵ Ǥ ǥ Ĝ ĝ Ǧ ǧ Ğ ğ Ģ ģ Ɠ ɠ Ġ ġ Ḡ ḡ Ꞡ ꞡ ᶃ
- ց : Armenian alphabet Tso
Ligatures and abbreviations
- ₲ : Paraguayan guaraní
Computing codes
| Preview | G | g | Ɡ | ɡ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER G | LATIN SMALL LETTER G | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER SCRIPT G | LATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT G | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71 | U+0047 | 103 | U+0067 | 42924 | U+A7AC | 609 | U+0261 |
| UTF-8 | 71 | 47 | 103 | 67 | 234 158 172 | EA 9E AC | 201 161 | C9 A1 |
| Numeric character reference | G | G | g | g | Ɡ | Ɡ | ɡ | ɡ |
| EBCDIC family | 199 | C7 | 135 | 87 | ||||
| ASCII 1 | 71 | 47 | 103 | 67 |
- 1 Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Other representations
See also
- Carolingian G
- Hard and soft G
- Latin letters used in mathematics § Gg
References
- ^ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. 1976.
- ^ Gnanadesikan, Amalia E. (2011-09-13). The Writing Revolution: Cuneiform to the Internet. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781444359855.
- ^ Encyclopaedia Romana
- ^ Everson, Michael; Sigurðsson, Baldur; Málstöð, Íslensk. «Sorting the letter ÞORN». Evertype. ISO CEN/TC304. Archived from the original on 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2018-11-01.
- ^ Hempl, George (1899). «The Origin of the Latin Letters G and Z». Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association. The Johns Hopkins University Press. 30: 24–41. doi:10.2307/282560. JSTOR 282560.
- ^ Association phonétique internationale (January 1895). «vɔt syr l alfabɛ» [Votes sur l’alphabet]. Le Maître Phonétique. 10 (1): 16–17. JSTOR 44707535.
- ^ Association phonétique internationale (February–March 1900). «akt ɔfisjɛl» [Acte officiel]. Le Maître Phonétique. 15 (2/3): 20. JSTOR 44701257.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (July–December 1948). «desizjɔ̃ ofisjɛl» [Décisions officielles]. Le Maître Phonétique. 26 (63) (90): 28–30. JSTOR 44705217.
- ^ International Phonetic Association (1993). «Council actions on revisions of the IPA». Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 23 (1): 32–34. doi:10.1017/S002510030000476X. S2CID 249420050.
- ^ International Phonetic Association (1949). The Principles of the International Phonetic Association. Department of Phonetics, University College, London. Supplement to Le Maître Phonétique 91, January–June 1949. JSTOR i40200179.
- Reprinted in Journal of the International Phonetic Association 40 (3), December 2010, pp. 299–358, doi:10.1017/S0025100311000089.
- ^ Wells, John C. (6 November 2006). «Scenes from IPA history». John Wells’s phonetic blog. Department of Phonetics and Linguistics, University College London. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 29 March 2018.
- ^ International Phonetic Association (1999). Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A Guide to the Use of the International Phonetic Alphabet. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 19. ISBN 0-521-63751-1.
- ^ Wong, Kimberly; Wadee, Frempongma; Ellenblum, Gali; McCloskey, Michael (2 April 2018). «The Devil’s in the g-tails: Deficient letter-shape knowledge and awareness despite massive visual experience». Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. 44 (9): 1324–1335. doi:10.1037/xhp0000532. PMID 29608074. S2CID 4571477.
- ^ Dean, Signe (4 April 2018). «Most People Don’t Know What Lowercase ‘G’ Looks Like And We’re Not Even Kidding». Science Alert. Archived from the original on 8 April 2018. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- ^ Constable, Peter (2004-04-19). «L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-10-11. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ^ a b Miller, Kirk; Ball, Martin (2020-07-11). «L2/20-116R: Expansion of the extIPA and VoQS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-24.
- ^ a b Anderson, Deborah (2020-12-07). «L2/21-021: Reference doc numbers for L2/20-266R «Consolidated code chart of proposed phonetic characters» and IPA etc. code point and name changes» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-01-08.
- ^ a b Everson, Michael; West, Andrew (2020-10-05). «L2/20-268: Revised proposal to add ten characters for Middle English to the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-24.
- ^ a b c Miller, Kirk; Ashby, Michael (2020-11-08). «L2/20-252R: Unicode request for IPA modifier-letters (a), pulmonic» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-07-30.
- ^ Everson, Michael; et al. (2002-03-20). «L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-02-19. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ^ Everson, Michael; Dicklberger, Alois; Pentzlin, Karl; Wandl-Vogt, Eveline (2011-06-02). «L2/11-202: Revised proposal to encode «Teuthonista» phonetic characters in the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-10-11. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
External links
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the letter of the alphabet. For other uses, see G (disambiguation).
| G | |
|---|---|
| G g | |
| (See below, Typographic) | |
 |
|
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Phonetic usage |
|
| Unicode codepoint | U+0047, U+0067, U+0261 |
| Alphabetical position | 7 |
| History | |
| Development |
|
| Time period | ~-300 to present |
| Descendants |
|
| Sisters |
|
| Transliteration equivalents | C |
| Variations | (See below, Typographic) |
| Other | |
| Other letters commonly used with | gh, g(x) |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. |
G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is gee (pronounced ), plural gees.[1]
History
The letter ‘G’ was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ‘C’ to distinguish voiced /ɡ/ from voiceless /k/.
The recorded originator of ‘G’ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, who added letter G to the teaching of the Roman alphabet during the 3rd century BC:[2] he was the first Roman to open a fee-paying school, around 230 BCE. At this time, ‘K’ had fallen out of favor, and ‘C’, which had formerly represented both /ɡ/ and /k/ before open vowels, had come to express /k/ in all environments.
Ruga’s positioning of ‘G’ shows that alphabetic order related to the letters’ values as Greek numerals was a concern even in the 3rd century BC. According to some records, the original seventh letter, ‘Z’, had been purged from the Latin alphabet somewhat earlier in the 3rd century BC by the Roman censor Appius Claudius, who found it distasteful and foreign.[3] Sampson (1985) suggests that: «Evidently the order of the alphabet was felt to be such a concrete thing that a new letter could be added in the middle only if a ‘space’ was created by the dropping of an old letter.»[4]
George Hempl proposed in 1899 that there never was such a «space» in the alphabet and that in fact ‘G’ was a direct descendant of zeta. Zeta took shapes like ⊏ in some of the Old Italic scripts; the development of the monumental form ‘G’ from this shape would be exactly parallel to the development of ‘C’ from gamma. He suggests that the pronunciation /k/ > /ɡ/ was due to contamination from the also similar-looking ‘K’.[5]
Eventually, both velar consonants /k/ and /ɡ/ developed palatalized allophones before front vowels; consequently in today’s Romance languages, ⟨c⟩ and ⟨g⟩ have different sound values depending on context (known as hard and soft C and hard and soft G). Because of French influence, English language orthography shares this feature.
Typographic variants
The modern lowercase ‘g’ has two typographic variants: the single-storey (sometimes opentail) ‘‘ and the double-storey (sometimes looptail) ‘
‘. The single-storey form derives from the majuscule (uppercase) form by raising the serif that distinguishes it from ‘c’ to the top of the loop, thus closing the loop and extending the vertical stroke downward and to the left. The double-storey form (
) had developed similarly, except that some ornate forms then extended the tail back to the right, and to the left again, forming a closed bowl or loop. The initial extension to the left was absorbed into the upper closed bowl. The double-storey version became popular when printing switched to «Roman type» because the tail was effectively shorter, making it possible to put more lines on a page. In the double-storey version, a small top stroke in the upper-right, often terminating in an orb shape, is called an «ear».
Generally, the two forms are complementary, but occasionally the difference has been exploited to provide contrast. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, opentail ⟨ɡ⟩ has always represented a voiced velar plosive, while ⟨⟩ was distinguished from ⟨ɡ⟩ and represented a voiced velar fricative from 1895 to 1900.[6][7] In 1948, the Council of the International Phonetic Association recognized ⟨ɡ⟩ and ⟨
⟩ as typographic equivalents,[8] and this decision was reaffirmed in 1993.[9] While the 1949 Principles of the International Phonetic Association recommended the use of ⟨
⟩ for a velar plosive and ⟨ɡ⟩ for an advanced one for languages where it is preferable to distinguish the two, such as Russian,[10] this practice never caught on.[11] The 1999 Handbook of the International Phonetic Association, the successor to the Principles, abandoned the recommendation and acknowledged both shapes as acceptable variants.[12]
Wong et al. (2018) found that native English speakers have little conscious awareness of the looptail ‘g’ ().[13][14] They write: «Despite being questioned repeatedly, and despite being informed directly that G has two lowercase print forms, nearly half of the participants failed to reveal any knowledge of the looptail ‘g’, and only 1 of the 38 participants was able to write looptail ‘g’ correctly.»
In Unicode, the two appearances are generally treated as glyph variants with no semantic difference. For applications where the single-storey variant must be distinguished (such as strict IPA in a typeface where the usual g character is double-storey), the character U+0261 ɡ LATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT G is available, as well as an upper case version, U+A7AC Ɡ LATIN CAPITAL LETTER SCRIPT G.
Pronunciation and use
| Language | Dialect(s) | Pronunciation (IPA) | Environment | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afrikaans | /x/ | |||
| Arabic | /ɡ/ | Latinization; corresponding to ⟨ق⟩ or ⟨ج⟩ in Arabic | ||
| Azeri | /ɟ/ | |||
| Catalan | /(d)ʒ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Danish | /ɡ/ | Word-initially | ||
| /k/ | Usually | |||
| Dutch | Standard | /ɣ/ | ||
| Southern dialects | /ɣ̟/ | |||
| Northern dialects | /χ/ | |||
| English | /dʒ/ | Before e, i, y (see exceptions below) | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i in «modern» loanwords from French | |||
| silent | Some words, initial <gn>, and word-finally before a consonant | |||
| Faroese | /j/ | soft, lenited; see Faroese phonology | ||
| /k/ | hard | |||
| /tʃ/ | soft | |||
| /v/ | after a, æ, á, e, o, ø and before u | |||
| /w/ | after ó, u, ú and before a, i, or u | |||
| silent | after a, æ, á, e, o, ø and before a | |||
| Fijian | /ŋ/ | |||
| French | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |||
| Galician | /ɡ/~/ħ/ | Usually | See Gheada for consonant variation | |
| /ʃ/ | Before e, i | obsolete spelling, replaced by the letter x | ||
| Greek | /ɡ/ | Usually | Latinization | |
| /ɟ/ | Before ai, e, i, oi, y | Latinization | ||
| Icelandic | /c/ | soft | ||
| /k/ | hard | |||
| /ɣ/ | hard, lenited; see Icelandic phonology | |||
| /j/ | soft, lenited | |||
| Irish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ɟ/ | After i or before e, i | |||
| Italian | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /dʒ/ | Before e, i | |||
| Mandarin | Standard | /k/ | Pinyin latinization | |
| Norman | /dʒ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Norwegian | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /j/ | Before ei, i, j, øy, y | |||
| Portuguese | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |||
| Romanian | /dʒ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Romansh | /dʑ/ | Before e, i | ||
| /ɡ/ | Usually | |||
| Samoan | /ŋ/ | |||
| Scottish Gaelic | /k/ | Usually | ||
| /kʲ/ | After i or before e, i | |||
| Spanish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /x/ or /h/ | Before e, i, y | Variation between velar and glottal realizations depends on dialect | ||
| Swedish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /j/ | Before ä, e, i, ö, y | |||
| Turkish | /ɡ/ | Usually | ||
| /ɟ/ | Before e, i, ö, ü | |||
| Vietnamese | Standard | /ɣ/ | ||
| Northern | /z/ | Before i | ||
| Southern | /j/ | Before i |
English
In English, the letter appears either alone or in some digraphs. Alone, it represents
- a voiced velar plosive (/ɡ/ or «hard» ⟨g⟩), as in goose, gargoyle, and game;
- a voiced palato-alveolar affricate (/d͡ʒ/ or «soft» ⟨g⟩), predominates before ⟨i⟩ or ⟨e⟩, as in giant, ginger, and geology; or
- a voiced palato-alveolar sibilant (/ʒ/) in post-medieval loanwords from French, such as rouge, beige, genre (often), and margarine (rarely)
⟨g⟩ is predominantly soft before ⟨e⟩ (including the digraphs ⟨ae⟩ and ⟨oe⟩), ⟨i⟩, or ⟨y⟩, and hard otherwise. It is hard in those derivations from γυνή (gynḗ) meaning woman where initial-worded as such. Soft ⟨g⟩ is also used in many words that came into English from medieval church/academic use, French, Spanish, Italian or Portuguese – these tend to, in other ways in English, closely align to their Ancient Latin and Greek roots (such as fragile, logic or magic).
There remain widely used a few English words of non-Romance origin where ⟨g⟩ is hard followed by ⟨e⟩ or ⟨i⟩ (get, give, gift), and very few in which ⟨g⟩ is soft though followed by ⟨a⟩ such as gaol, which since the 20th century is almost always written as «jail».
The double consonant ⟨gg⟩ has the value /ɡ/ (hard ⟨g⟩) as in nugget, with very few exceptions: /d͡ʒ/ in exaggerate and veggies and dialectally /ɡd͡ʒ/ in suggest.
The digraph ⟨dg⟩ has the value /d͡ʒ/ (soft ⟨g⟩), as in badger. Non-digraph ⟨dg⟩ can also occur, in compounds like floodgate and headgear.
The digraph ⟨ng⟩ may represent:
- a velar nasal () as in length, singer
- the latter followed by hard ⟨g⟩ (/ŋɡ/) as in jungle, finger, longest
Non-digraph ⟨ng⟩ also occurs, with possible values
- /nɡ/ as in engulf, ungainly
- /nd͡ʒ/ as in sponge, angel
- /nʒ/ as in melange
The digraph ⟨gh⟩ (in many cases a replacement for the obsolete letter yogh, which took various values including /ɡ/, /ɣ/, /x/ and /j/) may represent:
- /ɡ/ as in ghost, aghast, burgher, spaghetti
- /f/ as in cough, laugh, roughage
- Ø (no sound) as in through, neighbor, night
- /x/ in ugh
- (rarely) /p/ in hiccough
- (rarely) /k/ in s’ghetti
Non-digraph ⟨gh⟩ also occurs, in compounds like foghorn, pigheaded
The digraph ⟨gn⟩ may represent:
- /n/ as in gnostic, deign, foreigner, signage
- /nj/ in loanwords like champignon, lasagna
Non-digraph ⟨gn⟩ also occurs, as in signature, agnostic
The trigraph ⟨ngh⟩ has the value /ŋ/ as in gingham or dinghy. Non-trigraph ⟨ngh⟩ also occurs, in compounds like stronghold and dunghill.
G is the tenth least frequently used letter in the English language (after Y, P, B, V, K, J, X, Q, and Z), with a frequency of about 2.02% in words.
Other languages
Most Romance languages and some Nordic languages also have two main pronunciations for ⟨g⟩, hard and soft. While the soft value of ⟨g⟩ varies in different Romance languages (/ʒ/ in French and Portuguese, [(d)ʒ] in Catalan, /d͡ʒ/ in Italian and Romanian, and /x/ in most dialects of Spanish), in all except Romanian and Italian, soft ⟨g⟩ has the same pronunciation as the ⟨j⟩.
In Italian and Romanian, ⟨gh⟩ is used to represent /ɡ/ before front vowels where ⟨g⟩ would otherwise represent a soft value. In Italian and French, ⟨gn⟩ is used to represent the palatal nasal /ɲ/, a sound somewhat similar to the ⟨ny⟩ in English canyon. In Italian, the trigraph ⟨gli⟩, when appearing before a vowel or as the article and pronoun gli, represents the palatal lateral approximant /ʎ/.
Other languages typically use ⟨g⟩ to represent /ɡ/ regardless of position.
Amongst European languages, Czech, Dutch, Estonian and Finnish are an exception as they do not have /ɡ/ in their native words. In Dutch, ⟨g⟩ represents a voiced velar fricative /ɣ/ instead, a sound that does not occur in modern English, but there is a dialectal variation: many Netherlandic dialects use a voiceless fricative ([x] or [χ]) instead, and in southern dialects it may be palatal [ʝ]. Nevertheless, word-finally it is always voiceless in all dialects, including the standard Dutch of Belgium and the Netherlands. On the other hand, some dialects (like Amelands) may have a phonemic /ɡ/.
Faroese uses ⟨g⟩ to represent /dʒ/, in addition to /ɡ/, and also uses it to indicate a glide.
In Māori, ⟨g⟩ is used in the digraph ⟨ng⟩ which represents the velar nasal /ŋ/ and is pronounced like the ⟨ng⟩ in singer.
The Samoan and Fijian languages use the letter ⟨g⟩ by itself for /ŋ/.
In older Czech and Slovak orthographies, ⟨g⟩ was used to represent /j/, while /ɡ/ was written as ⟨ǧ⟩ (⟨g⟩ with caron).
The Azerbaijani Latin alphabet uses ⟨g⟩ exclusively for the «soft» sound, namely /ɟ/. The sound /ɡ/ is written as ⟨q⟩. This leads to unusual spellings of loanwords: qram ‘gram’, qrup ‘group’, qaraj ‘garage’, qallium ‘gallium’.
Ancestors, descendants and siblings
- 𐤂 : Semitic letter Gimel, from which the following symbols originally derive
- C c : Latin letter C, from which G derives
- Γ γ : Greek letter Gamma, from which C derives in turn
- ɡ : Latin letter script small G
- ᶢ : Modifier letter small script g is used for phonetic transcription[15]
- 𝼁 : Latin small letter reversed script g, an extension to IPA for disordered speech (extIPA)[16][17]
- ᵷ : Turned g
- 𝼂 : Latin letter small capital turned g, an extension to IPA for disordered speech (extIPA)[16][17]
- Г г : Cyrillic letter Ge
- Ȝ ȝ : Latin letter Yogh
- Ɣ ɣ : Latin letter Gamma
- Ᵹ ᵹ : Insular g
- ᫌ : Combining insular g, used in the Ormulum[18]
- Ꝿ ꝿ : Turned insular g
- Ꟑ ꟑ : Closed insular g, used in the Ormulum[18]
- ɢ : Latin letter small capital G, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent a voiced uvular stop
- 𐞒 : Modifier letter small capital G, used as a superscript IPA letter[19]
- ʛ : Latin letter small capital G with hook, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent a voiced uvular implosive
- 𐞔 : Modifier letter small capital G with hook, used as a superscript IPA letter[19]
- 𐞓 : Modifier letter small g with hook, used as a superscript IPA letter[19]
- ᴳ ᵍ : Modifier letters are used in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet[20]
- ꬶ : Used for the Teuthonista phonetic transcription system[21]
- G with diacritics: Ǵ ǵ Ǥ ǥ Ĝ ĝ Ǧ ǧ Ğ ğ Ģ ģ Ɠ ɠ Ġ ġ Ḡ ḡ Ꞡ ꞡ ᶃ
- ց : Armenian alphabet Tso
Ligatures and abbreviations
- ₲ : Paraguayan guaraní
Computing codes
| Preview | G | g | Ɡ | ɡ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER G | LATIN SMALL LETTER G | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER SCRIPT G | LATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT G | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71 | U+0047 | 103 | U+0067 | 42924 | U+A7AC | 609 | U+0261 |
| UTF-8 | 71 | 47 | 103 | 67 | 234 158 172 | EA 9E AC | 201 161 | C9 A1 |
| Numeric character reference | G | G | g | g | Ɡ | Ɡ | ɡ | ɡ |
| EBCDIC family | 199 | C7 | 135 | 87 | ||||
| ASCII 1 | 71 | 47 | 103 | 67 |
- 1 Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Other representations
See also
- Carolingian G
- Hard and soft G
- Latin letters used in mathematics § Gg
References
- ^ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. 1976.
- ^ Gnanadesikan, Amalia E. (2011-09-13). The Writing Revolution: Cuneiform to the Internet. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781444359855.
- ^ Encyclopaedia Romana
- ^ Everson, Michael; Sigurðsson, Baldur; Málstöð, Íslensk. «Sorting the letter ÞORN». Evertype. ISO CEN/TC304. Archived from the original on 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2018-11-01.
- ^ Hempl, George (1899). «The Origin of the Latin Letters G and Z». Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association. The Johns Hopkins University Press. 30: 24–41. doi:10.2307/282560. JSTOR 282560.
- ^ Association phonétique internationale (January 1895). «vɔt syr l alfabɛ» [Votes sur l’alphabet]. Le Maître Phonétique. 10 (1): 16–17. JSTOR 44707535.
- ^ Association phonétique internationale (February–March 1900). «akt ɔfisjɛl» [Acte officiel]. Le Maître Phonétique. 15 (2/3): 20. JSTOR 44701257.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (July–December 1948). «desizjɔ̃ ofisjɛl» [Décisions officielles]. Le Maître Phonétique. 26 (63) (90): 28–30. JSTOR 44705217.
- ^ International Phonetic Association (1993). «Council actions on revisions of the IPA». Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 23 (1): 32–34. doi:10.1017/S002510030000476X. S2CID 249420050.
- ^ International Phonetic Association (1949). The Principles of the International Phonetic Association. Department of Phonetics, University College, London. Supplement to Le Maître Phonétique 91, January–June 1949. JSTOR i40200179.
- Reprinted in Journal of the International Phonetic Association 40 (3), December 2010, pp. 299–358, doi:10.1017/S0025100311000089.
- ^ Wells, John C. (6 November 2006). «Scenes from IPA history». John Wells’s phonetic blog. Department of Phonetics and Linguistics, University College London. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 29 March 2018.
- ^ International Phonetic Association (1999). Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A Guide to the Use of the International Phonetic Alphabet. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 19. ISBN 0-521-63751-1.
- ^ Wong, Kimberly; Wadee, Frempongma; Ellenblum, Gali; McCloskey, Michael (2 April 2018). «The Devil’s in the g-tails: Deficient letter-shape knowledge and awareness despite massive visual experience». Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. 44 (9): 1324–1335. doi:10.1037/xhp0000532. PMID 29608074. S2CID 4571477.
- ^ Dean, Signe (4 April 2018). «Most People Don’t Know What Lowercase ‘G’ Looks Like And We’re Not Even Kidding». Science Alert. Archived from the original on 8 April 2018. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- ^ Constable, Peter (2004-04-19). «L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-10-11. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ^ a b Miller, Kirk; Ball, Martin (2020-07-11). «L2/20-116R: Expansion of the extIPA and VoQS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-24.
- ^ a b Anderson, Deborah (2020-12-07). «L2/21-021: Reference doc numbers for L2/20-266R «Consolidated code chart of proposed phonetic characters» and IPA etc. code point and name changes» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-01-08.
- ^ a b Everson, Michael; West, Andrew (2020-10-05). «L2/20-268: Revised proposal to add ten characters for Middle English to the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-24.
- ^ a b c Miller, Kirk; Ashby, Michael (2020-11-08). «L2/20-252R: Unicode request for IPA modifier-letters (a), pulmonic» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-07-30.
- ^ Everson, Michael; et al. (2002-03-20). «L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-02-19. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ^ Everson, Michael; Dicklberger, Alois; Pentzlin, Karl; Wandl-Vogt, Eveline (2011-06-02). «L2/11-202: Revised proposal to encode «Teuthonista» phonetic characters in the UCS» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-10-11. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
External links
Печатные и прописные буквы английского алфавита начинают изучать с самого начала освоения английского языка.
Без алфавита никуда в любом языке. Сперва учат печатные буквы. А уже освоив их, приступают к изучению прописных. Могу сказать, что некоторые буквы достаточно непривычно пишутся для нас и поначалу трудно их освоить детям. Но это уже дело привычки.
Как писать? Прописными или печатными буквами?
Дочка второй год учит английский язык и пишет на смеси печатных и прописных, даже больше печатными. Так проще детям. Соответственно, как маму, меня заинтересовало, а нужно ли заставлять писать прописными или это можно оставить на второй план.
Поспрашивав не одного учителя английского языка и изучив просторы интернета пришла к выводу, что не стоит. Конечно прописи мы купили. Прописываем по одной букве в день для развития мышечной памяти и красивого почерка, но я не заостряю на этом внимания. Соответственно в рабочей тетради дочка пишет миксом. А я смотрю на правильность написания слов и предложений.
Сейчас стали больше писать печатными, чем прописными буквами даже в странах с родным английским языком. И тенденция эта пошла из США начиная с 1970-80-х годов.
А почему? Все просто: дети так плохо писали прописными, что учителям трудно было проверять тетради. И стали учить печатные буквы, постепенно переходя на прописные. Но многие так и продолжали писать печатными и во взрослом возрасте.
Существует конечно и каллиграфический вариант прописных букв, но это, как и каллиграфический русский язык. Красиво, но очень мало кто пишет. Хотя лучше бы дети уделяли больше этому внимания в школе. Я имею в виду каллиграфию. Это очень полезно для развития усидчивости и концентрации внимания. А современные дети в большинстве своём ну уж очень гиперактивные, им каллиграфия пошла бы только на пользу.
Лучшие онлайн-школы английского языка для детей (обзор) смотрите здесь.
Английский алфавит
Английский алфавит произошел от латинского алфавита. И содержит он 26 букв. Из данных букв — 6 обозначают гласные звуки, а остальные обозначают согласные звуки.
Внимание! Буква «Y» обозначает и согласный звук, и гласный. К примеру: many, yes. Звуков намного больше в английском языке, чем имеющихся букв.
Отдельно стоит сказать о букве «Z», так как она имеет 2 варианта произношения:
- Британский вариант — [zed]
- Американский вариант — [zi:]
Выучить английский алфавит помогут детские песенки, они очень легко запоминаются. А вот в написании букв, особенно это касается прописных, помогут прописи. Чем больше рука пишет, тем лучше человек запоминает.
Интересный факт. Буква «Е» в английском языке используется чаще всего, а буква «Z» используется меньше всего.
Печатные буквы английского алфавита с транскрипцией (в виде таблицы)
| Заглавная | Строчная | Транскрипция | русский вариант транскрипции |
| A | a | [ei] | эй |
| B | b | [bi:] | би |
| C | c | [si:] | си |
| D | d | [di:] | ди |
| E | e | [i:] | и |
| F | f | [ef] | эф |
| G | g | [dʒi:] | джи |
| H | h | [eitʃ] | эйч |
| I | i | [ai] | ай |
| J | j | [dʒei] | джей |
| K | k | [kei] | кэй |
| L | l | [el] | эл |
| M | m | [em] | эм |
| N | n | [en] | эн |
| O | o | [əʊ] | оу |
| P | p | [pi:] | пи |
| Q | q | [kju:] | кью |
| R | r | [a:] [a:r] | а |
| S | s | [es] | эс |
| T | t | [ti:] | ти |
| U | u | [ju:] | ю |
| V | v | [vi:] | ви |
| W | w | [`dʌblju:] | дабл-ю |
| X | x | [eks] | экс |
| Y | y | [wai] | уай |
| Z | z | [zed] [zi:] | зед |
Прописные буквы английского алфавита
Важно!!! Раньше прописную заглавную букву «А» писали так же как в русском языке заглавную букву «А». А теперь она пишется, как строчная «а», только в увеличенном размере.
Как появился английский алфавит?
Любопытно было узнать историю появления английского алфавита. Просмотрев разные источники, мы узнали, что изначально в Англии использовались англосаксонские руны (5 век н.э.).
С 7 века н.э. (под влиянием христианства) постепенно руны стали заменять буквами латинского алфавита.
Под влиянием разных исторических моментов алфавит постоянно менялся и к 16 веку уже насчитывал 23 буквы. Не было ещё букв «J»,»U»,»W». С 16 века постепенно стали появляться буквы «J» и «U». Со временем они прочно вошли в алфавит. Затем появилась буква «W», как замена сочетания двух «V».
Таким образом полностью сформировался английский алфавит к началу 18 века. Дальше уже менялась фонетика и словоформа.
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели печатные и прописные буквы английского алфавита. Нужно ли учить прописные буквы английского алфавита или нет решать Вам. Возможно стоит, но только тогда, когда хорошо уже будете знать печатные буквы.
Ждём Ваши комментарии и оценки. По желанию подписывайтесь на нас в Яндекс.Дзен и в других социальных сетях!!!)))
Значение символа
Латинская буква маленькая заглавная g. Расширения МФА.
Символ «Латинская буква маленькая заглавная g» был утвержден как часть Юникода версии 1.1 в 1993 г.
| Название в Юникоде | Latin Letter Small Capital G |
| Номер в Юникоде | |
| HTML-код | |
| CSS-код | |
| Разделы Юникода | Расширения МФА |
| Версия Юникода | 1.1 (1993) |
| Версия | 1.1 |
| Блок | Расширения МФА |
| Тип парной зеркальной скобки (bidi) | Нет |
| Композиционное исключение | Нет |
| Изменение регистра | 0262 |
| Простое изменение регистра | 0262 |
| Кодировка | hex | dec (bytes) | dec | binary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-8 | C9 A2 | 201 162 | 51618 | 11001001 10100010 |
| UTF-16BE | 02 62 | 2 98 | 610 | 00000010 01100010 |
| UTF-16LE | 62 02 | 98 2 | 25090 | 01100010 00000010 |
| UTF-32BE | 00 00 02 62 | 0 0 2 98 | 610 | 00000000 00000000 00000010 01100010 |
| UTF-32LE | 62 02 00 00 | 98 2 0 0 | 1644298240 | 01100010 00000010 00000000 00000000 |
Значение символа
Латинская буква маленькая заглавная g. Расширения МФА.
Символ «Латинская буква маленькая заглавная g» был утвержден как часть Юникода версии 1.1 в 1993 г.
| Название в Юникоде | Latin Letter Small Capital G |
| Номер в Юникоде | |
| HTML-код | |
| CSS-код | |
| Разделы Юникода | Расширения МФА |
| Версия Юникода | 1.1 (1993) |
| Версия | 1.1 |
| Блок | Расширения МФА |
| Тип парной зеркальной скобки (bidi) | Нет |
| Композиционное исключение | Нет |
| Изменение регистра | 0262 |
| Простое изменение регистра | 0262 |
| Кодировка | hex | dec (bytes) | dec | binary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-8 | C9 A2 | 201 162 | 51618 | 11001001 10100010 |
| UTF-16BE | 02 62 | 2 98 | 610 | 00000010 01100010 |
| UTF-16LE | 62 02 | 98 2 | 25090 | 01100010 00000010 |
| UTF-32BE | 00 00 02 62 | 0 0 2 98 | 610 | 00000000 00000000 00000010 01100010 |
| UTF-32LE | 62 02 00 00 | 98 2 0 0 | 1644298240 | 01100010 00000010 00000000 00000000 |
Перейти к содержанию
Как пишется буква г на английском языка
Русская буква Г является четвертой по счёту в русской алфавите. Она относится к группе тех букв, которые без особых сложностей можно передать при помощи английских литер.
Итак, если потребуется передать русскую Г на английский манер, то для этого используют английскую G (маленькая g). Читается и звучит она как «джи». Транскрипция буквы имеет такой вид — [ ʤi: ]. Если данная литера находится в конце слова или перед согласными буквами, то она произносится, как звук [ g ], если стоит перед гласными, тогда произносится, как [ ʤ ]. К примеру, имя Георгий на английском будет писаться, как Georgii.
( 5 оценок, среднее 2.6 из 5 )