From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

|
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
calcium iodide |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
CAS Number |
|
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.238 |
| EC Number |
|
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
|
InChI
|
|
|
SMILES
|
|
| Properties | |
|
Chemical formula |
CaI2 |
| Molar mass | 293.887 g/mol (anhydrous) 365.95 g/mol (tetrahydrate) |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 3.956 g/cm3 (anhydrous)[1] |
| Melting point | 779 °C (1,434 °F; 1,052 K) (anhydrous) [2] |
| Boiling point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K)[2] |
|
Solubility in water |
64.6 g/100 mL (0 °C) 66 g/100 mL (20 °C) 81 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone and alcohols |
|
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
-109.0·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Structure | |
|
Crystal structure |
Rhombohedral, hP3 |
|
Space group |
P-3m1, No. 164 |
|
Coordination geometry |
octahedral |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
2 0 1 |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions |
calcium fluoride calcium chloride calcium bromide |
|
Other cations |
beryllium iodide magnesium iodide strontium iodide barium iodide |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references |
Calcium iodide (chemical formula CaI2) is the ionic compound of calcium and iodine. This colourless deliquescent solid is a salt that is highly soluble in water. Its properties are similar to those for related salts, such as calcium chloride. It is used in photography.[1] It is also used in cat food as a source of iodine.
Reactions[edit]
Henri Moissan first isolated pure calcium in 1898 by reducing calcium iodide with pure sodium metal:[3]
- CaI2 + 2 Na → 2 NaI + Ca
Calcium iodide can be formed by treating calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, or calcium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid:[4]
- CaCO3 + 2 HI → CaI2 + H2O + CO2
Calcium iodide slowly reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air, liberating iodine, which is responsible for the faint yellow color of impure samples.[5]
- 2 CaI2 + 2 CO2 + O2 → 2 CaCO3 + 2 I2
References[edit]
- ^ a b
Turner, Jr., Francis M., ed. (1920), The Condensed Chemical Dictionary (1st ed.), New York: Chemical Catalog Co., p. 127, retrieved 2007-12-08 - ^ a b R. J. Lewis (1993), Hawley’s Condensed Chemical Dictionary 12th edition
- ^
Mellor, Joseph William (1912), Modern Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Longmans, Green, and Co, p. 334, 6909989325689, retrieved 2007-12-08 - ^
Gooch, Frank Austin; Walker, Claude Frederic (1905), Outlines of Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, p. 340, retrieved 2007-12-08 - ^ Jones, Harry Clary (1906), Principles of Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, p. 365, retrieved 2007-12-08
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

|
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
calcium iodide |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
CAS Number |
|
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.238 |
| EC Number |
|
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
|
InChI
|
|
|
SMILES
|
|
| Properties | |
|
Chemical formula |
CaI2 |
| Molar mass | 293.887 g/mol (anhydrous) 365.95 g/mol (tetrahydrate) |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 3.956 g/cm3 (anhydrous)[1] |
| Melting point | 779 °C (1,434 °F; 1,052 K) (anhydrous) [2] |
| Boiling point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K)[2] |
|
Solubility in water |
64.6 g/100 mL (0 °C) 66 g/100 mL (20 °C) 81 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in acetone and alcohols |
|
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
-109.0·10−6 cm3/mol |
| Structure | |
|
Crystal structure |
Rhombohedral, hP3 |
|
Space group |
P-3m1, No. 164 |
|
Coordination geometry |
octahedral |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
2 0 1 |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions |
calcium fluoride calcium chloride calcium bromide |
|
Other cations |
beryllium iodide magnesium iodide strontium iodide barium iodide |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references |
Calcium iodide (chemical formula CaI2) is the ionic compound of calcium and iodine. This colourless deliquescent solid is a salt that is highly soluble in water. Its properties are similar to those for related salts, such as calcium chloride. It is used in photography.[1] It is also used in cat food as a source of iodine.
Reactions[edit]
Henri Moissan first isolated pure calcium in 1898 by reducing calcium iodide with pure sodium metal:[3]
- CaI2 + 2 Na → 2 NaI + Ca
Calcium iodide can be formed by treating calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, or calcium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid:[4]
- CaCO3 + 2 HI → CaI2 + H2O + CO2
Calcium iodide slowly reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air, liberating iodine, which is responsible for the faint yellow color of impure samples.[5]
- 2 CaI2 + 2 CO2 + O2 → 2 CaCO3 + 2 I2
References[edit]
- ^ a b
Turner, Jr., Francis M., ed. (1920), The Condensed Chemical Dictionary (1st ed.), New York: Chemical Catalog Co., p. 127, retrieved 2007-12-08 - ^ a b R. J. Lewis (1993), Hawley’s Condensed Chemical Dictionary 12th edition
- ^
Mellor, Joseph William (1912), Modern Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Longmans, Green, and Co, p. 334, 6909989325689, retrieved 2007-12-08 - ^
Gooch, Frank Austin; Walker, Claude Frederic (1905), Outlines of Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, p. 340, retrieved 2007-12-08 - ^ Jones, Harry Clary (1906), Principles of Inorganic Chemistry, New York: Macmillan, p. 365, retrieved 2007-12-08
| Иодид кальция | |
 |
|
| Общие | |
|---|---|
| Систематическое наименование | иодид кальция(II) |
| Химическая формула | CaI2 |
| Физические свойства | |
| Состояние (ст. усл.) | белое вещество |
| Молярная масса | (ангидрид) 293.887 г/моль
(тетрагидрат) 365.95 г/моль |
| Плотность | 3.956 г/см³ |
| Термические свойства | |
| Температура плавления | (тетрагидрат; разлагается) 779 °C |
| Температура кипения | 1100 °C |
| Химические свойства | |
| Растворимость в воде | (0 °C) 64.6 г/100 мл
(20 °C) 66 г/100 мл (100 °C) 81 г/100 мл |
| Растворимость в остальных веществах | растворим в ацетоне и спиртах; нерастворим в эфире, диоксане г/100 мл |
| Структура | |
| Координационная геометрия | восьмигранная |
| Кристаллическая структура | тригональная, гексагональная |
| Классификация | |
| Рег. номер CAS | 10102-68-8, (тетрагидрат) 13640-62-5 |
| SMILES | [Ca+2].[I-].[I-] |
| RTECS | EV1300000 |
| Безопасность | |
| Токсичность |
0 2 1 |
Иодид кальция — это неорганическое бинарное химическое соединение из иода и кальция. Это бесцветный твердый очень растворимый в воде порошок. Его свойства аналогичны многим солям кислот, таких, например, как хлорид кальция.
Свойства
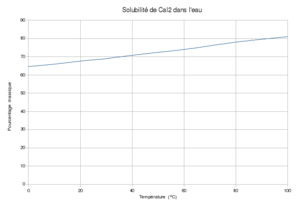
График растворимости иодида кальция в воде
Анри Муассан впервые получил чистый кальций за счет реакции кальция иодида с чистыми металлическим натрием:
- CaI2 + 2Na → 2NaI + Ca
Кальция иодид может быть сформирован путем обработки карбонатом кальция с иодоводородом:
- CaCO3 + 2HI → CaI2 + H2O + CO2
Кальций иодистый медленно реагирует с кислородом и двуокисью углерода в воздухе, освобождая иод, который придает слабый желтый цвет полученным продуктам реакции:
- 2CaI2 + 2CO2 + O2 → 2CaCO3 + I2
Использование
Используется в фотографии.
Получение
|
Растворимость кислот, оснований и солей в воде |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Calcium (Ca) is a substance that is important for living creatures, including people. It is the most plentiful mineral in the body and fundamental for good wellbeing. We want to consume a specific measure of calcium to assemble and keep up with solid bones and sound correspondence between the mind and different pieces of the body.
An iodide particle is a particle I–. Compounds with iodine in proper oxidation state -1 are called iodides. In regular daily existence, iodide is generally normally experienced as a part of iodized salt, which numerous states order. It might be a compound, medicine, and dietary enhancement. And furthermore, in radiation crises, it very well might be a medication. it is additionally familiar with safeguarding the thyroid when specific sorts of radiopharmaceuticals are utilized. Iodide might be a halide anion and monoatomic iodine.
Calcium Iodide
Calcium Iodide is an inorganic compound that is made of calcium and iodine elements. Calcium Iodide can be formed by using anyone out of calcium oxide, calcium carbonate, or calcium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid. Calcium Iodide is the compound that is used in medicines and photography. Calcium (Ca) is the component in one of the alkaline earth metals. It is the metallic component in the human body as well as the fifth most plentiful component in Earth’s covering. In any case, Calcium doesn’t happen normally in the Free State, in spite of the fact that its mixtures are generally circulated. One such calcium compound is lime for example calcium oxide, CaO.
The human body is having 2% calcium and its significant sources are milk, milk items, fish, and green verdant vegetables. Calcium Iodide is an inorganic compound. It is boring deliquescent strong and exceptionally solvent in water. Its properties are like those of comparable sorts of salts like calcium chloride. It is helpful in photography widely. It is additionally valuable in feline food as a wellspring of iodine.
Formula for Calcium Iodide
Calcium reacts with the iodine gas to produce calcium iodide compounds. This reaction takes place at a temperature of 200-400°C. Its chemical equation is:
Ca + I2 → CaI2
Structure of Calcium Iodide
The chemical formula of Calcium Iodide is CaI2. The molecular mass of CaI2 is 293.89 grams per mole.
Physical Properties of Calcium Iodide
- Its color is white.
- Its melting point is 779°C.
- It is easily soluble in acetone and alcohol.
- Its boiling point is 1100°C.
- Its acid reaction will release the hydrogen iodide. Dehydrated chemical compounds for it is CaI2. 2H2O with a molecular weight of 330.02.
- It is mostly used for the analysis of reagents, photography, and pharmaceutical industries.
Chemical properties of Calcium Iodide
- Reducing calcium iodide with pure sodium metal,
CaI2 + 2 Na → 2NaI + Ca
- Calcium iodide can be formed by combining calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, or calcium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid,
CaCO3 + 2 HI → CaI2 + H2O + CO2
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
Ca(OH)2 + 2 HI → CaI2 + 2H2O
- Calcium iodide slowly reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air, realizing iodine.
2CaI2 + 2CO2 + O2 → 2CaCO3 + 2I2
Uses of Calcium Iodide
- Calcium iodide is used in medicines like Pharma Synthesis, available in the form of white powder.
- It is used in photography.
- Calcium iodide is used as food for cats that have iodine-rich sources.
Sample Questions
Question 1: What is the molecular weight of Calcium Iodide?
Answer:
Molecular weight of CaI2 is:
= 40.078 + 2 × 126.90447
= 293.88694 gram per mole.
Thus, the molecular weight of Calcium Iodide 293.88694 gram per mole.
Question 2: What are the health hazards of Calcium Iodide?
Answer:
It might make eye disturbance and harm a few people. It might cause aggravation of the skin on contact in certain people. In the event that unreasonable centralisation s of it are breathed in, harm to the circulatory or sensory systems or kidney harm is conceivable.
Its drawn out openness might cause changes in lung work for example pneumoconiosis. Its great side effects are shortness of breath and lung shadows show on X-beam. Iodides might lead to nearby unfavourably susceptible responses, for example, hives, crack of skin veins, and agony in joints. Expanding and aggravation of the throat, bothered and enlarged eyes and lung enlarging may likewise happen. Expanding of the glottis, requiring a tracheotomy has been accounted for.
Question 3: Is calcium iodide soluble in water?
Answer:
Calcium Iodide is highly soluble in water, the colourless deliquescent is also soluble in acetones and alcohols alongwith being soluble in water. When calcium iodide is dissolved in water, it dissociates, which means, that the ions dissolve.
Question 4: How many electrons are transferred in calcium Iodide?
Answer:
Calcium iodide (CaI2) is an ionic bond, which means that electrons are transferred. In order for Ca to become the ion Ca2+, the calcium atom must lose 2 electrons. (Electrons have a negative charge, so when an atom loses 2 electrons, its ion becomes more positive.)
Question 5: What type of bond does Calcium Iodide have?
Answer:
Calcium Iodide is Ionic bond, where electrons are transferred. For
Ca to turn into the ion Ca2+, the calcium molecule should lose 2 electrons. (Electrons have a negative charge, so when a particle loses 2 electrons, its particle turns out to be more certain.) For I to turn into the particle I–, the iodine molecule should acquire 1 electron. (At the point when a particle acquires an electron, its particle will be more negative.)Now for calcium iodide is CaI2, there are 2 iodine particles present. This appears to be legit in light of the fact that the iodine particle has a charge of – 1, so two iodine particles must be available to counteract the +2 charge of the calcium particle.
Thus, the calcium particle moves 2 valence electrons, one to every iodine molecule, to shape the ionic bond.
Calcium (Ca) is a substance that is important for living creatures, including people. It is the most plentiful mineral in the body and fundamental for good wellbeing. We want to consume a specific measure of calcium to assemble and keep up with solid bones and sound correspondence between the mind and different pieces of the body.
An iodide particle is a particle I–. Compounds with iodine in proper oxidation state -1 are called iodides. In regular daily existence, iodide is generally normally experienced as a part of iodized salt, which numerous states order. It might be a compound, medicine, and dietary enhancement. And furthermore, in radiation crises, it very well might be a medication. it is additionally familiar with safeguarding the thyroid when specific sorts of radiopharmaceuticals are utilized. Iodide might be a halide anion and monoatomic iodine.
Calcium Iodide
Calcium Iodide is an inorganic compound that is made of calcium and iodine elements. Calcium Iodide can be formed by using anyone out of calcium oxide, calcium carbonate, or calcium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid. Calcium Iodide is the compound that is used in medicines and photography. Calcium (Ca) is the component in one of the alkaline earth metals. It is the metallic component in the human body as well as the fifth most plentiful component in Earth’s covering. In any case, Calcium doesn’t happen normally in the Free State, in spite of the fact that its mixtures are generally circulated. One such calcium compound is lime for example calcium oxide, CaO.
The human body is having 2% calcium and its significant sources are milk, milk items, fish, and green verdant vegetables. Calcium Iodide is an inorganic compound. It is boring deliquescent strong and exceptionally solvent in water. Its properties are like those of comparable sorts of salts like calcium chloride. It is helpful in photography widely. It is additionally valuable in feline food as a wellspring of iodine.
Formula for Calcium Iodide
Calcium reacts with the iodine gas to produce calcium iodide compounds. This reaction takes place at a temperature of 200-400°C. Its chemical equation is:
Ca + I2 → CaI2
Structure of Calcium Iodide
The chemical formula of Calcium Iodide is CaI2. The molecular mass of CaI2 is 293.89 grams per mole.
Physical Properties of Calcium Iodide
- Its color is white.
- Its melting point is 779°C.
- It is easily soluble in acetone and alcohol.
- Its boiling point is 1100°C.
- Its acid reaction will release the hydrogen iodide. Dehydrated chemical compounds for it is CaI2. 2H2O with a molecular weight of 330.02.
- It is mostly used for the analysis of reagents, photography, and pharmaceutical industries.
Chemical properties of Calcium Iodide
- Reducing calcium iodide with pure sodium metal,
CaI2 + 2 Na → 2NaI + Ca
- Calcium iodide can be formed by combining calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, or calcium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid,
CaCO3 + 2 HI → CaI2 + H2O + CO2
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
Ca(OH)2 + 2 HI → CaI2 + 2H2O
- Calcium iodide slowly reacts with oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air, realizing iodine.
2CaI2 + 2CO2 + O2 → 2CaCO3 + 2I2
Uses of Calcium Iodide
- Calcium iodide is used in medicines like Pharma Synthesis, available in the form of white powder.
- It is used in photography.
- Calcium iodide is used as food for cats that have iodine-rich sources.
Sample Questions
Question 1: What is the molecular weight of Calcium Iodide?
Answer:
Molecular weight of CaI2 is:
= 40.078 + 2 × 126.90447
= 293.88694 gram per mole.
Thus, the molecular weight of Calcium Iodide 293.88694 gram per mole.
Question 2: What are the health hazards of Calcium Iodide?
Answer:
It might make eye disturbance and harm a few people. It might cause aggravation of the skin on contact in certain people. In the event that unreasonable centralisation s of it are breathed in, harm to the circulatory or sensory systems or kidney harm is conceivable.
Its drawn out openness might cause changes in lung work for example pneumoconiosis. Its great side effects are shortness of breath and lung shadows show on X-beam. Iodides might lead to nearby unfavourably susceptible responses, for example, hives, crack of skin veins, and agony in joints. Expanding and aggravation of the throat, bothered and enlarged eyes and lung enlarging may likewise happen. Expanding of the glottis, requiring a tracheotomy has been accounted for.
Question 3: Is calcium iodide soluble in water?
Answer:
Calcium Iodide is highly soluble in water, the colourless deliquescent is also soluble in acetones and alcohols alongwith being soluble in water. When calcium iodide is dissolved in water, it dissociates, which means, that the ions dissolve.
Question 4: How many electrons are transferred in calcium Iodide?
Answer:
Calcium iodide (CaI2) is an ionic bond, which means that electrons are transferred. In order for Ca to become the ion Ca2+, the calcium atom must lose 2 electrons. (Electrons have a negative charge, so when an atom loses 2 electrons, its ion becomes more positive.)
Question 5: What type of bond does Calcium Iodide have?
Answer:
Calcium Iodide is Ionic bond, where electrons are transferred. For
Ca to turn into the ion Ca2+, the calcium molecule should lose 2 electrons. (Electrons have a negative charge, so when a particle loses 2 electrons, its particle turns out to be more certain.) For I to turn into the particle I–, the iodine molecule should acquire 1 electron. (At the point when a particle acquires an electron, its particle will be more negative.)Now for calcium iodide is CaI2, there are 2 iodine particles present. This appears to be legit in light of the fact that the iodine particle has a charge of – 1, so two iodine particles must be available to counteract the +2 charge of the calcium particle.
Thus, the calcium particle moves 2 valence electrons, one to every iodine molecule, to shape the ionic bond.
 |
|
| Имена | |
|---|---|
| Название IUPAC йодид кальция | |
| Идентификаторы | |
| Номер CAS |
|
| 3D-модель (JSmol ) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.238 |
| Номер EC |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| номер RTECS |
|
| UNII |
|
| Панель управления CompTox (EPA ) |
|
InChI
|
|
УЛЫБАЕТСЯ
|
|
| Свойства | |
| Химическая формула | CaI 2 |
| Молярная масса | 293,887 г / моль (безводный). 365,95 г / моль (тетрагидрат) |
| Внешний вид | белое твердое вещество |
| Плотность | 3,956 г / см (безводный) |
| Точка плавления | 779 ° C (1434 ° F; 1052 K) (безводный) |
| Точка кипения | 1100 ° C (2010 ° F; 1370 K) |
| Растворимость в воде | 64,6 г / 100 мл (0 ° C). 66 г / 100 мл (20 ° C). 81 г / 100 мл (100 ° C) |
| Растворимость | растворим в ацетоне и спиртах |
| Магнитная восприимчивость (χ) | -109,0 · 10 см / моль |
| Структура | |
| Кристаллическая структура | Ромбоэдрическая, hP3 |
| Пространственная группа | P-3m1, No. 164 |
| Координационная геометрия | октаэдрическая |
| Опасности | |
| NFPA 704 (огненный алмаз) |  0 2 1 0 2 1 |
| Родственные соединения | |
| Другие анионы | фторид кальция. хлорид кальция. бромид кальция |
| Другие катионы | йодид бериллия. йодид магния. йодид стронция. йодид бария |
| Если не указано иное, данные приведены для материалов в их стандартном состоянии (при 25 ° C [77 ° F], 100 кПа). | |
| Ссылки в ink | |
Йодид кальция (химическая формула CaI 2) — это ионное соединение из кальция и йода. Это бесцветное расплывающееся твердое вещество представляет собой соль, которая хорошо растворима в воде. Его свойства аналогичны свойствам родственных солей, таких как хлорид кальция. Используется в фотографии. Он также используется в корме для кошек в качестве источника йода.
Реакции
Анри Муассан впервые выделил чистый кальций в 1898 году путем восстановления йодида кальция с помощью чистый натрий металл:
- CaI 2 + 2 Na → 2 NaI + Ca
Иодид кальция может быть образован обработка карбоната кальция, оксида кальция или гидроксида кальция с помощью иодистоводородной кислоты :
- CaCO 3 + 2 HI → CaI 2+ H2O + CO2
Иодид кальция медленно реагирует с кислородом и углекислым газом в воздухе, высвобождая йод, который является причиной слабого желтого цвета загрязненных образцов..
- 2 CaI 2 + 2 CO 2 + O 2 → 2 CaCO 3 + 2 I 2
Литература
- ^ Тернер младший, Фрэнсис М., изд. (1920), The Condensed Chemical Dictionary (1-е изд.), Нью-Йорк: Chemical Catalog Co., стр. 127, получено 08 декабря 2007 г.
- ^ R. Дж. Льюис (1993), Краткий химический словарь Хоули, 12-е издание
- ^Меллор, Джозеф Уильям (1912), Современная неорганическая химия, Нью-Йорк: Longmans, Green, and Co, стр. 334, 6909989325689, получено 08.12.2007
- ^Гуч, Фрэнк Остин; Уокер, Клод Фредерик (1905), Очерки неорганической химии, Нью-Йорк: Макмиллан, стр. 340, получено 08 декабря 2007 г.
- ^Джонс, Гарри Клэри (1906), Принципы неорганической химии, Нью-Йорк: Макмиллан, стр. 365, получено 2008-12-08
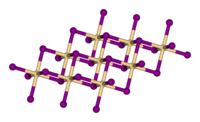
| Кристальная структура | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||
| __ Ca 2+ __ I — | |||||||||||||
| Общий | |||||||||||||
| Фамилия | Йодид кальция | ||||||||||||
| Другие названия |
|
||||||||||||
| Формула соотношения | CaI 2 | ||||||||||||
| Краткое описание |
от белого до желтоватого твердого вещества |
||||||||||||
| Внешние идентификаторы / базы данных | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| характеристики | |||||||||||||
| Молярная масса | 293,89 г моль -1 | ||||||||||||
| Физическое состояние |
твердо |
||||||||||||
| плотность |
3,956 г см −3 (20 ° С) |
||||||||||||
| Температура плавления |
740 ° С |
||||||||||||
| точка кипения |
1100 ° С |
||||||||||||
| растворимость |
легко растворим в воде |
||||||||||||
| Инструкции по технике безопасности | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Насколько это возможно и обычно, используются единицы СИ . Если не указано иное, приведенные данные относятся к стандартным условиям . |
Иодид кальция представляет собой химическое соединение из кальция и является одним из иодидов . Это белое твердое вещество, которое на воздухе медленно желтеет.
история
Восстановив йодид кальция натрием , Анри Муассану впервые удалось получить чистый кальций.
Извлечение и представление
Йодиды кальция, содержащие воду, при концентрировании кристаллизуются из водных растворов. В зависимости от концентрации образуется гекса- или тетрагидрат. Безводный йодид кальция нельзя получить путем дегидратации гидрата; вместо этого его можно получить из раствора гидроксида кальция и йода . Образуются йодид кальция и йодат кальция , которые затем восстанавливаются.
Другой возможный способ получения безводного йодида кальция — разложение оксалата кальция йодом.
характеристики
По своим свойствам безводный и водосодержащий йодид кальция существенно различаются. Различные гидраты представляют собой легко растворяющиеся кристаллические массы, которые плавятся при 42 ° C, т.е. растворяются в собственной кристаллической воде. Если гидрат йодида кальция вступает в контакт с воздухом или светом, он может поглощать углекислый газ или выделять йод и в результате становится желтым.
С другой стороны, безводный йодид кальция представляет собой тугоплавкое кристаллическое твердое вещество, которое кристаллизуется в типичной структуре слоев , гексагональной структуре йодида кадмия . В газообразном состоянии образует линейные молекулы.
использовать
Иодид кальция, как иодид калия, является отхаркивающим .
В уровне техники соединение используется в качестве сцинтилляционного кристалла и в галогенных лампах .
Индивидуальные доказательства
- ↑ Дийодид кальция на webelements.com .
- ↑ a b c d e f Технический паспорт Иодид кальция, ультра сухой, 99,999% (на основе металлов) в AlfaAesar, по состоянию на 7 декабря 2019 г. ( PDF )(Требуется JavaScript) .
- ↑ Ален Трессо: Анри Муассан: Нобелевская премия по химии в 1906 году. В: Angewandte Chemie . 2006, 118, стр 6946-6950,. Дои : 10.1002 / anie.200601600 .
- ^ A b Беате Блюмер-Швинум, Герман Хагер, Франц фон Бруххаузен, Э. Нюрнберг, Питер Сурман: Справочник Хагерса по фармацевтической практике, тома 1-4 . 5-е издание, Birkhäuser, 1995, ISBN 978-3-540-52688-9 , стр. 607.
- ↑ а б запись на иодиде кальция. В: Römpp Online . Георг Тиме Верлаг, по состоянию на 15 июля 2014 г.
- ^ А. Ф. Holleman , Е. Wiberg , Н. Wiberg : Учебник неорганической химии . 102-е издание. Вальтер де Грюйтер, Берлин 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , стр. 1241.
- ↑ Кеннет Л. Беккер, Джон П. Билезикян: Принципы и практика эндокринологии и метаболизма. 3-е издание, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001, ISBN 978-0-781-71750-2 , стр. 362.