Локальный хост — также называемый «адресом обратной связи» — используется для установления IP-соединения или вызова на ваш собственный компьютер или машину. Адрес обратной связи обычно используется в контексте работы в сети и предоставляет компьютеру возможность проверять стек IP.
Любой, кто имеет опыт работы или интересуется сетевыми технологиями, сочтет важным изучить и понять связанную с ним компьютерную терминологию. Localhost — один из таких терминов, который считается полезным для любого компьютерного специалиста. Понимание важности и использования localhost также является отличным местом для начала вашего путешествия по сетевой терминологии.
Не только термин, localhost также может быть доменным именем, например netflix.com или google.com, Как и любой домен, локальный хост также будет иметь свой собственный IP-адрес.
Необходимый адрес будет зависеть от используемого интернет-протокола. Вызов localhost с использованием IPv4, который является наиболее распространенным IP-адресом, будет иметь диапазон от 127.0.0.0 до 127.255.255.255, но обычно по умолчанию равен 127.0.0.1. Пользователи IPv6 могут установить петлю, введя: 1.
протокол Интернета
Интернет-протокол (IP) был введен в действие для установления стандартного метода связи компьютеров с другими устройствами в сети. Он не только управляет адресами, но и тем, как ваши данные отправляются и принимаются как в локальных сетях, так и в Интернете.
IPv4, который является интернет-протоколом версии 4, является наиболее распространенным в мире. IPv4 в значительной степени опирается на протокол управления передачей (TCP) для обработки большого объема данных, таких как доставка, последовательность и целостность данных. Этот IP был разработан как протокол без установления соединения для использования на машинах на основе Ethernet.
IPv6 начал медленно заменять IPv4. Спрос на IP-адреса вырос в геометрической прогрессии после цифрового бума. Все больше и больше устройств используют Интернет, поэтому IPv6 был разработан, чтобы учесть это увеличение и устранить некоторые фундаментальные недостатки, обнаруженные в IPv4.
Там, где IPv4 позволяет использовать около 4,3 миллиарда уникальных IP-адресов, IPv6 позволяет использовать до 340 триллионов триллионов.
Помимо цифр, IPv6 также предлагает сетевые преимущества. Это облегчает обнаружение между устройствами других сетей с поддержкой IPv6, позволяя пользователям использовать службы без необходимости действий конечного пользователя. Потребность в преобразовании сетевых адресов (NAT) также значительно снижается при использовании IPv6. NAT — это то, что позволяет клиентам IPv4 использовать один IP-адрес.
Поскольку IPv4 является наиболее распространенным из двух используемых интернет-протоколов, мы будем продолжать двигаться вперед.
Как работает 127.0.0.1
Когда вы устанавливаете соединение IPv4 с адресом обратной связи 127.0.0.1, назначается маска подсети 255.0.0.1. Таким образом, если какой-либо общедоступный коммутатор, маршрутизатор или шлюз получает пакет данных с вашим шлейфом в качестве места назначения, информация данных не будет записана.
Это означает, что если пакет данных удален за пределы локального узла, информация не будет передана другому компьютеру в сети. Это помогает поддерживать безопасность сети, предотвращая захват вашей машиной случайных пакетов данных, которые могут попытаться активировать другие службы в ответ.
Распространенное использование для Localhost
Помимо возможностей безопасности, localhost может быть полезен в нескольких других сценариях. Существует три основных цели для адреса обратной связи, который считается полезным для специалиста по компьютерным сетям.
Запуск теста скорости
Отправка запроса ping является наиболее распространенным способом использования адреса обратной связи. Используя командную строку Windows, вы можете проверить подключение и обнаружить любые проблемы с производительностью, которые могут возникнуть на вашем компьютере в данный момент.
Чтобы выполнить запрос ping к localhost:
- Откройте диалоговое окно «Выполнить» (клавиша Windows + R) и введите cmd. Нажмите Ввод.
- Вы также можете ввести cmd в поле поиска на панели задач и выбрать командную строку из списка.
- Запуск от имени администратора рекомендуется.
- Введите ping 127.0.0.1 и нажмите Enter.
Результаты будут отображены на экране. Показанные данные будут включать в себя количество отправленных, полученных, потерянных пакетов данных и приблизительное время прохождения сигнала в обоих направлениях.
Блокировка сайтов
Когда вам нужно заблокировать доступ к определенным веб-сайтам, localhost может сделать свое дело. Обратная петля может быть очень полезна для предотвращения проникновения в ваш браузер вредоносных сайтов. Чтобы справиться с этим, вам нужно знать, что представляют собой файлы хоста и их назначение в этом контексте.
Каждый раз, когда ваш компьютер пытается получить доступ к веб-сайту или удаленному компьютеру, используя имя домена, компьютер отправляет запрос на сервер доменных имен (DNS) в поисках локально сохраненного файла хоста.
Например, IPv4-адрес 127.0.0.1 будет отображаться как «localhost» в DNS. Доменное имя любого нового веб-сайта, который вы посещаете, также будет храниться в виде файла хоста. Это создает более быстрый ответ на загрузку для любых повторных посещений того же сайта.
Файл хоста также будет содержать IP-адреса всех имен доменов, которые он хранит. Вам нужно отредактировать эти IP-адреса, чтобы они соответствовали петлевому адресу 127.0.0.1, чтобы заблокировать их. Это приведет к тому, что трафик будет перенаправлен обратно на локальный хост.
Хотя это работает в крайнем случае, использование localhost в качестве метода предотвращения доступа к нежелательным веб-сайтам не является лучшим решением. Основная причина заключается в том, что если вам потребуется доступ к этим сайтам, вам придется вручную удалить запись как администратор. Только администратор, создавший исходную запись, сможет сделать это, заблокировав других, которым по той или иной причине необходимо перейти на конкретный сайт.
Тестирование новых программ или веб-приложений
Всякий раз, когда запускается петля, ваша операционная система становится имитируемым сервером. Это позволяет загружать любые необходимые файлы программы на сервер для проверки работоспособности.
В сочетании с другим программным обеспечением вы даже можете использовать обратную связь, чтобы позволить мобильным приложениям с боковой загрузкой получать доступ к компонентам настольного сервера или отправлять запросы в определенный API.
The localhost – also referred to as ‘the loopback address’ – is used to establish an IP connection or call, to your own computer or machine. The loopback address is typically used in the context of networking and provides a computer the capability to validate the IP stack.
Anyone with a background or interest in networking will find it important to learn and understand the affiliated computer terminology with the field. Localhost is one such piece of terminology seen as beneficial to any computer technician. Understanding the importance and uses of localhost is also a great place to begin your journey into networking terminology.

Not just a term, localhost can also be a domain name, like netflix.com or google.com. Just like any domain, the localhost will also have its own Internet Protocol (IP) address.
The address needed will depend on the internet protocol being used. Calling the localhost using IPv4, which is the most common IP, will have a range of 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 but will typically default to 127.0.0.1. IPv6 users can establish a loopback by entering :1.
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) was put in place to establish a standard method for computers to communicate with other devices on the network. It not only governs addresses but also how your data is sent and received for both local networks and on the internet.
IPv4, which is Internet Protocol version 4, is the one most commonly used globally. IPv4 relies heavily on the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to handle the bulk of data concerns such as delivery, sequencing, and integrity. This IP was designed as a connectionless protocol to be used on ethernet-based machines.
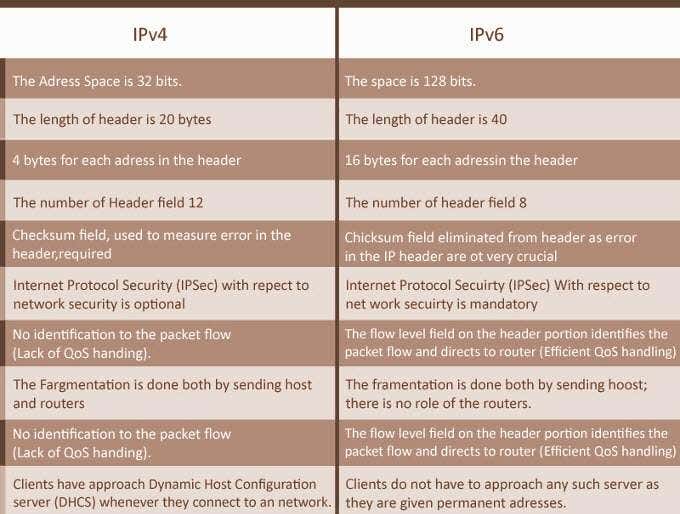
IPv6 has begun slowly replacing IPv4. The demand for IP addresses has grown exponentially in the wake of the digital boom. More and more devices are using the internet, so IPv6 was developed to accommodate the increase and address a few of the fundamental flaws found in IPv4.
Where IPv4 allows for approximately 4.3 billion unique IP addresses for use, IPv6 will permit up to 340 trillion, trillion.
Aside from numbers, IPv6 also offers networking advantages. It opens up easier detection between devices of other IPv6 enabled networks, allowing users to use services without the need for end-user action. The need for the Network Address Translation (NAT) is also significantly reduced when using IPv6. The NAT is what allows IPv4 clients to share a single IP address.
Seeing as IPv4 is the more common of the two used internet protocols, it will be our focus moving forward.

How 127.0.0.1 Works
When you establish an IPv4 connection to the 127.0.0.1 loopback address, a 255.0.0.1 subnet mask is assigned. So, if any public switch, router, or gateway receives a data packet with your loopback as its destination, the data’s information will not be logged.
This means that if a data packet is dropped off outside of the localhost, the information will not continue on to another computer on the network. This helps to maintain network security by preventing your machine from picking up stray data packets that may attempt to activate other services in response.
Common Uses For Localhost
Aside from security capabilities, localhost can be useful in a few other scenarios. There are three primary purposes for the loopback address considered useful to a computer network technician.

Running A Speed Test
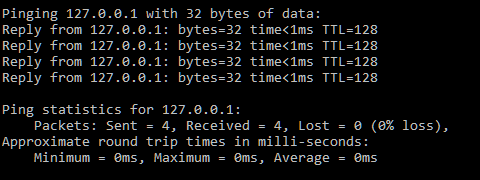
Sending a ping request is the most common use you’ll find for the loopback address. Using the Windows Command Prompt, you can test your connection and discover any performance issues your computer may currently be facing.
To perform a ping request to localhost:
- Open the Run function (Windows key + R) dialog and type cmd. Press Enter.
- You can also type cmd into the Taskbar Search box and select Command Prompt from the list.
- Running as Administrator is advised.
- Type ping 127.0.0.1 and press Enter.
The results will be displayed on the screen. The data shown will include the number of data packets sent, received, lost, and the approximate round trip time of the data transmission.
Blocking Websites
When you need to block access to certain websites, localhost can do the trick. The loopback can be quite useful in the prevention of your browser from entering malicious sites. To pull this off, you’ll need to know what host files are and the purpose they serve in this context.
Each time your computer attempts to access a website or remote computer using the domain name, the computer will send a request to the Domain Name Server (DNS) in search of a locally stored host file.
For example, the IPv4 address 127.0.0.1, will be displayed as ‘localhost’ in the DNS. The domain name of any new website you visit will also find itself stored as a host file. This creates a faster load response for any return visits to the same site.
The host file will also contain the IP addresses of all the domain names it stores. You’ll have to edit these IP addresses to match the loopback address 127.0.0.1 in order to block them. Doing so will cause traffic to be directed back to the localhost instead.
Though it works in a pinch, using localhost as a method to prevent access to undesirable websites is not the best solution. The primary reason being that if you were to need access to those sites, you would have to manually remove the entry as an administrator. Only the administrator who created the initial entry will be able to do this, locking out others who need to reach the specific site for one reason or another.
Testing New Programs Or Web Applications
Whenever a loopback is triggered, your operating system becomes a simulated server. This makes it possible to load any necessary files of a program into the server in order to test functionality.
In combination with other software, you can even use loopback to allow side-loaded mobile apps to access desktop server components or send requests to a specific API.
The localhost – also referred to as ‘the loopback address’ – is used to establish an IP connection or call, to your own computer or machine. The loopback address is typically used in the context of networking and provides a computer the capability to validate the IP stack.
Anyone with a background or interest in networking will find it important to learn and understand the affiliated computer terminology with the field. Localhost is one such piece of terminology seen as beneficial to any computer technician. Understanding the importance and uses of localhost is also a great place to begin your journey into networking terminology.

Not just a term, localhost can also be a domain name, like netflix.com or google.com. Just like any domain, the localhost will also have its own Internet Protocol (IP) address.
The address needed will depend on the internet protocol being used. Calling the localhost using IPv4, which is the most common IP, will have a range of 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 but will typically default to 127.0.0.1. IPv6 users can establish a loopback by entering :1.
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) was put in place to establish a standard method for computers to communicate with other devices on the network. It not only governs addresses but also how your data is sent and received for both local networks and on the internet.
IPv4, which is Internet Protocol version 4, is the one most commonly used globally. IPv4 relies heavily on the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to handle the bulk of data concerns such as delivery, sequencing, and integrity. This IP was designed as a connectionless protocol to be used on ethernet-based machines.

IPv6 has begun slowly replacing IPv4. The demand for IP addresses has grown exponentially in the wake of the digital boom. More and more devices are using the internet, so IPv6 was developed to accommodate the increase and address a few of the fundamental flaws found in IPv4.
Where IPv4 allows for approximately 4.3 billion unique IP addresses for use, IPv6 will permit up to 340 trillion, trillion.
Aside from numbers, IPv6 also offers networking advantages. It opens up easier detection between devices of other IPv6 enabled networks, allowing users to use services without the need for end-user action. The need for the Network Address Translation (NAT) is also significantly reduced when using IPv6. The NAT is what allows IPv4 clients to share a single IP address.
Seeing as IPv4 is the more common of the two used internet protocols, it will be our focus moving forward.

How 127.0.0.1 Works
When you establish an IPv4 connection to the 127.0.0.1 loopback address, a 255.0.0.1 subnet mask is assigned. So, if any public switch, router, or gateway receives a data packet with your loopback as its destination, the data’s information will not be logged.
This means that if a data packet is dropped off outside of the localhost, the information will not continue on to another computer on the network. This helps to maintain network security by preventing your machine from picking up stray data packets that may attempt to activate other services in response.
Common Uses For Localhost
Aside from security capabilities, localhost can be useful in a few other scenarios. There are three primary purposes for the loopback address considered useful to a computer network technician.

Running A Speed Test
Sending a ping request is the most common use you’ll find for the loopback address. Using the Windows Command Prompt, you can test your connection and discover any performance issues your computer may currently be facing.
To perform a ping request to localhost:
- Open the Run function (Windows key + R) dialog and type cmd. Press Enter.
- You can also type cmd into the Taskbar Search box and select Command Prompt from the list.
- Running as Administrator is advised.
- Type ping 127.0.0.1 and press Enter.
The results will be displayed on the screen. The data shown will include the number of data packets sent, received, lost, and the approximate round trip time of the data transmission.

Blocking Websites
When you need to block access to certain websites, localhost can do the trick. The loopback can be quite useful in the prevention of your browser from entering malicious sites. To pull this off, you’ll need to know what host files are and the purpose they serve in this context.
Each time your computer attempts to access a website or remote computer using the domain name, the computer will send a request to the Domain Name Server (DNS) in search of a locally stored host file.
For example, the IPv4 address 127.0.0.1, will be displayed as ‘localhost’ in the DNS. The domain name of any new website you visit will also find itself stored as a host file. This creates a faster load response for any return visits to the same site.

The host file will also contain the IP addresses of all the domain names it stores. You’ll have to edit these IP addresses to match the loopback address 127.0.0.1 in order to block them. Doing so will cause traffic to be directed back to the localhost instead.
Though it works in a pinch, using localhost as a method to prevent access to undesirable websites is not the best solution. The primary reason being that if you were to need access to those sites, you would have to manually remove the entry as an administrator. Only the administrator who created the initial entry will be able to do this, locking out others who need to reach the specific site for one reason or another.

Testing New Programs Or Web Applications
Whenever a loopback is triggered, your operating system becomes a simulated server. This makes it possible to load any necessary files of a program into the server in order to test functionality.
In combination with other software, you can even use loopback to allow side-loaded mobile apps to access desktop server components or send requests to a specific API.
http://localhost
Если вы хотите перейти на http://localhost, то воспользуйтесь быстрыми ссылками для входа:
- http://localhost
- http://localhost:8080
- http://localhost:8081
- http://localhost/phpmyadmin
- http://localhost/WordPress
- http://localhost:3000
- http://localhost/php
- http://localhost/index
- http://localhost/index.php
- http://localhost/server
- http://localhost/bonfire
localhost — это универсальное имя хоста, которое всегда указывает на этот же самый компьютер. Точнее говоря, это имя указывает на IP адрес 127.0.0.1, а данный IP уже является специальным адресом, всегда принадлежащий локальному компьютеру.
Если открыть адрес http://localhost в веб-браузере, то будет выполнено подключение к локальному веб-серверу. По этой причине localhost обычно ассоциируется с веб-сервером, но на самом деле localhost можно использоваться самыми разными сетевыми службами: программами для обмены данными между собой, MySQL, SSH, FTP и пр.
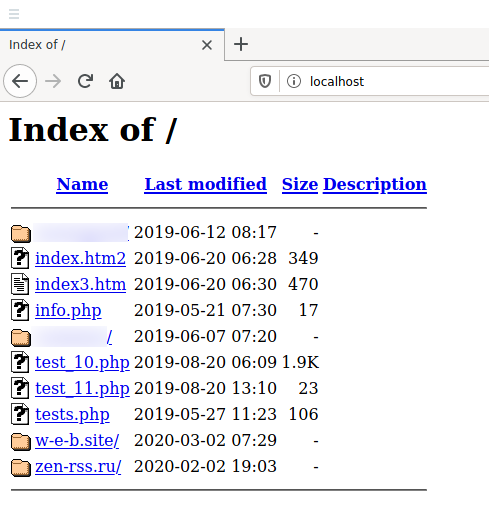
Вы можете даже пинговать localhost:
ping localhost
Пинги будут самыми лучшими из всех, какие вы когда-либо видели, поскольку проверяется соединение до этого же самого компьютера, на котором выполняется пинг.
Про loopback будет чуть ниже — на случай, если вам интересна теория, а сейчас рассмотрим, почему не работает localhost.
Как включить localhost
Возможно вы и так знали, что localhost это локальный веб-сервер, но при попытке открыть
http://localhost у вас возникает ошибка, например такая:
Не удается получить доступ к сайту
Сайт localhost не позволяет установить соединение.
Попробуйте сделать следующее:
Проверьте подключение к Интернету.
Проверьте настройки прокси-сервера и брандмауэра.
ERR_CONNECTION_REFUSED
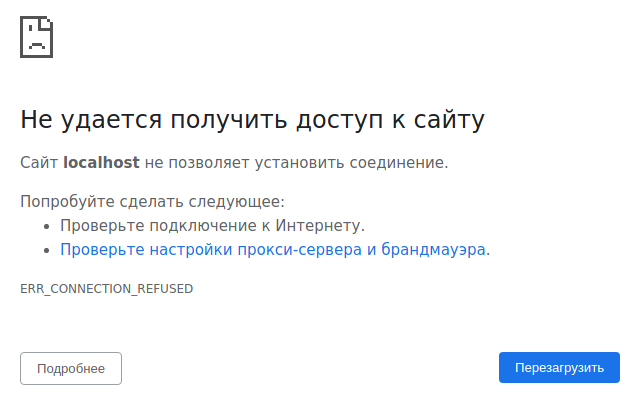
Причин может быть несколько, самая популярная — вы просто не установили веб-сервер. Если это действительно так, то переходите к инструкции «Как установить веб-сервер Apache c PHP, MySQL и phpMyAdmin на Windows».
После завершения указанной инструкции localhost заработает!
Веб-сервер установлен, но localhost не открывается
В этом случае причины могут быть следующие:
- веб-сервер установлен, но его служба не запущена (особенно если раньше работало, а после перезагрузки перестало работать) — вернитесь к инструкции по установке, запустите службу веб-сервера и добавьте её в автозагрузку;
- неправильно настроены права доступа в веб-сервере, либо ошибка в конфигурации — вернитесь к настройке веб-сервера или переустановите его.
127.0.0.1
127.0.0.1 — это специальный IP адрес, который имеет loopback интерфейс. В любой операционной системе имеется поддержка 127.0.0.1, поскольку этот специальный IP описан в протоколе.
Суть работы 127.0.0.1 (а следовательно и localhost, который является именем для указания на этот IP) состоит в том, что пакет, отправленный на адрес 127.0.0.1 на самом деле никуда не отправляется, но при этом система начинает считать, что этот пакет пришёл из сети. То есть образно можно представить так: пакет отправляется на сетевую карту компьютера, там разворачивается и возвращается с сетевой карты обратно в компьютер.
Несмотря на кажущуюся бесполезность, такой подход очень популярен и используется для взаимодействия с самыми разными программами.
http://localhost:8080
Чтобы подключиться к localhost на 8080 порту перейдите по ссылке http://localhost:8080
localhost php
Чтобы использовать PHP на своём компьютере нужно установить веб-сервер. Пошаговую инструкцию смотрите в статье «Как установить веб-сервер Apache c PHP, MySQL и phpMyAdmin на Windows».
localhost phpmyadmin
Аналогично, для получения phpMyAdmin установите веб-сервер.
localhost error
Ошибки могут возникнуть в случае неправильной установки веб-сервера или приложений. Смотрите «Ошибки при настройке и установке Apache, PHP, MySQL/MariaDB, phpMyAdmin».
Связанные статьи:
- Apache для Windows (100%)
- Как запустить Apache на Windows (100%)
- Документация по Apache на русском языке (100%)
- Как подключить PHP к Apache на Windows (100%)
- Как подключить MySQL к Apache на Windows (100%)
- Как в Windows поменять сообщения ошибок Apache (RANDOM — 100%)
Полезное
Смотреть что такое «.localhost» в других словарях:
-
Localhost — Dans le domaine des réseaux informatiques, localhost (l hôte local en français) est un nom utilisé pour se référer à l ordinateur local. On s en sert pour communiquer avec notre machine par l intermédiaire du protocole IP. Le nom localhost est… … Wikipédia en Français
-
.localhost — est un domaine de premier niveau réservé. Un domaine de premier niveau réservé est un domaine de premier niveau qui n’est pas destiné à être utilisé dans le système de nom de domaine (Domain Name System) d’Internet, mais qui est réservé à un… … Wikipédia en Français
-
Localhost — steht in der Netzwerktechnik für das momentan genutzte System oder dessen IP Adresse. Üblicherweise ist das eigene System (der local host) unter der IP Adresse 127.0.0.1 für TCP/IP Applikationen auf dieselbe Weise erreichbar, wie ein fernes… … Deutsch Wikipedia
-
Localhost — (127.0.0.1 127.255.255.255) зарезервированный диапазон IP адресов для обозначения т. н. «локального хоста», то есть для сети, состоящей только из одного компьютера. Как правило, используется всего один адрес 127.0.0.1, который… … Википедия
-
localhost — (так называемый, «локальный хост», по смыслу этот компьютер) в компьютерных сетях, стандартное, официально зарезервированное, доменное имя для частных IP адресов (в диапазоне 127.0.0.1 127.255.255.255, RFC 2606), то есть для… … Википедия
-
Localhost — In computer networking of Unix like operating systems, localhost (meaning this computer ) is the standard hostname given to the address of the loopback network interface. The name is also a reserved domain name (RFC 2606) (cf. .localhost), set… … Wikipedia
-
localhost — Dans les domaines des réseaux informatiques, localhost (l hôte local en français) est un nom utilisé pour se référer à une interface logique de l ordinateur local. On s en sert pour communiquer avec sa propre machine par l intermédiaire du… … Wikipédia en Français
-
.localhost — Infobox Top level domain name=.localhost background=#6CC introduced=1999 type=Reserved top level domain status=Reserved to prevent actual use registry=IANA sponsor=None intendeduse=Identifies the current local computer; reserved at the top level… … Wikipedia
-
localhost — Veranschaulichung der Kommunikation zwischen Browser und Webserver Software innerhalb des lokalen Rechners localhost steht in der Netzwerktechnik für das momentan genutzte System oder dessen IP Adresse. Üblicherweise ist das eigene System (der… … Deutsch Wikipedia
-
.localhost — Jeder Name einer Domain im Internet besteht aus einer Folge von durch Punkte getrennten Zeichen. Die Bezeichnung Top Level Domain (vom englischen top level domain, übersetzt Bereich oberster Ebene; Abkürzung TLD) bezeichnet dabei den letzten… … Deutsch Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer networking, localhost is a hostname that refers to the current device used to access it. It is used to access the network services that are running on the host via the loopback network interface. Using the loopback interface bypasses any local network interface
hardware.
Loopback[edit]
The local loopback mechanism may be used to run a network service on a host without requiring a physical network interface, or without making the service accessible from the networks the computer may be connected to. For example, a locally installed website may be accessed from a Web browser by the URL http://localhost to display its home page.
The name localhost normally resolves to the IPv4 loopback address 127.0.0.1, and to the IPv6 loopback address ::1.[1]
Name resolution[edit]
IPv4 network standards reserve the entire address block 127.0.0.0/8 (more than 16 million addresses) for loopback purposes.[2] That means any packet sent to any of those addresses is looped back. The address 127.0.0.1 is the standard address for IPv4 loopback traffic; the rest are not supported by all operating systems. However, they can be used to set up multiple server applications on the host, all listening on the same port number. The IPv6 standard assigns only a single address for loopback: ::1.
The resolution of the name localhost to one or more IP addresses is normally configured by the following lines in the operating system’s hosts file:
127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost
The name may also be resolved by Domain Name System (DNS) servers, but queries for this name should be resolved locally, and should not be forwarded to remote name servers.
In addition to the mapping of localhost to the loopback addresses (127.0.0.1 and ::1), localhost may also be mapped to other IPv4 (loopback) addresses and it is also possible to assign other, or additional, names to any loopback address. The mapping of localhost to addresses other than the designated loopback address range in the hosts file or in DNS is not guaranteed to have the desired effect, as applications may map the name internally.
In the Domain Name System, the name localhost is reserved as a top-level domain name, originally set aside to avoid confusion with the hostname used for loopback purposes.[3] IETF standards prohibit domain name registrars from assigning the name localhost.
IETF standards[edit]
The name localhost is reserved for loopback purposes by RFC 6761 (Special-Use Domain Names),[4] which achieved the Proposed Standard maturity level in February 2013. The standard sets forth a number of special considerations governing the use of the name in the Domain Name System:
- An IPv4 or IPv6 address query for the name localhost must always resolve to the respective loopback address, which is specified in a separate standard.
- Applications may resolve the name to a loopback address themselves, or pass it to the local name resolver mechanisms.
- When a name resolver receives an address (A or AAAA) query for localhost, it should return the appropriate loopback addresses, and negative responses for any other requested record types. Queries for localhost should not be sent to caching name servers.
- To avoid burdening the Domain Name System root servers with traffic, caching name servers should never request name server records for localhost, or forward resolution to authoritative name servers.
- DNS registrars are precluded from delegating domain names in the top-level domain localhost.
- When authoritative name servers receive queries for ‘localhost’ in spite of the provisions mentioned resolve them appropriately.
The IPv4 loopback addresses are reserved within the IPv4 address space by the IETF «Special Use IPv4 Addresses» standard (RFC 5735).[5] The reservation can be traced back to the November 1986 «Assigned Numbers» standard (RFC 990).
In contrast, the IETF «IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture» standard (RFC 4291) reserves the single IPv6 loopback address ::1 within the IPv6 address space. The standard precludes the assignment of that address to any physical interface, as well as its use as the source or destination address in any packet sent to remote hosts. Any such packet that is erroneously transmitted is not supposed to be routed, and should be dropped by all routers or hosts that receive it.
Packet processing[edit]
The processing of any packet sent to a loopback address is implemented in the link layer of the TCP/IP stack. Such packets are never passed to any network interface controller (NIC) or hardware device driver and must not appear outside of a computing system or be routed by any router. This permits software testing and local services in the absence of any hardware network interfaces.
Looped-back packets are distinguished from any other packets traversing the TCP/IP stack only by the special IP address they were addressed to. Thus, the services that ultimately receive them respond according to the specified destination. For example, an HTTP service could route packets addressed to 127.0.0.99:80 and 127.0.0.100:80 to different Web servers, or to a single server that returns different web pages. To simplify such testing, the hosts file may be configured to provide appropriate names for each address.
Packets received on a non-loopback interface with a loopback source or destination address must be dropped. Such packets are sometimes referred to as Martian packets.[6] As with any other bogus packets, they may be malicious and any problems they might cause can be avoided by applying bogon filtering.
Special cases[edit]
The releases of the MySQL database differentiate between the use of the hostname localhost and the use of the addresses 127.0.0.1 and ::1.[7] When using localhost as the destination in a client connector interface of an application, the MySQL application programming interface connects to the database using a Unix domain socket, while a TCP connection via the loopback interface requires the direct use of the explicit address.
One notable exception to the use of the 127.0.0.0/8 addresses is their use in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) traceroute error detection, in which their property of not being routable provides a convenient means to avoid delivery of faulty packets to end users.
See also[edit]
- Private network
- Reserved IP addresses
- 0.0.0.0
References[edit]
- ^ «RFC4291: IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture». IETF. Section 2.5.3.
- ^ M. Cotton; L. Vegoda; R. Bonica; B. Haberman (April 2013). Special-Purpose IP Address Registries. Internet Engineering Task Force. doi:10.17487/RFC6890. BCP 153. RFC 6890. Updated by RFC 8190.
- ^ «RFC2606: Reserved Top Level DNS Names». IETF. Section 2.
- ^ «RFC6761: Special-Use Domain Names». IETF. Section 6.3.
- ^ «RFC5735: Special Use IPv4 Addresses». IETF. Section 4.
- ^ Raymond, Eric S. «The Jargon File».
- ^ «MySQL :: MySQL 5.5 Reference Manual :: 4.1 Overview of MySQL Programs».
На чтение 2 мин Опубликовано 31.03.2022
Localhost часто считают синонимом IP-адреса 127.0.0.1.
Хотя функционально они одинаковы, между localhost и 127.0.0.1 есть существенные различия.
Читайте далее, чтобы узнать о сходствах и различиях между этими часто используемыми терминами.
В чем разница между localhost и 127.0.0.1?
Localhost – это алиас, используемый для обозначения IP-адресов, зарезервированных для loopback.
В то время как IPv4 использует последний блок адресов класса A (от 127.0.0.1 до 127.255.255), IPv6 резервирует первый (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 – или : :1, сокращенно) в качестве адреса loopback.
см. также: IPv4 против IPv6: В чем разница между IPv4 и IPv6
Localhost относится не только к 127.0.0.1, но и к целому ряду IP-адресов, зарезервированных для loopback.
Также важно отметить, что вы не всегда можете использовать 127.0.0.1 для loopback.
Cистемы IPv6 не отвечают на такие запросы, поскольку их localhost связан с адресом : :1.
Упомянутые выше адреса являются значениями по умолчанию, используемыми в большинстве систем.
Однако, настроив файл host, можно легко связать localhost с другим IP-адресом, поскольку этот файл содержит сопоставления IP-адресов с именами хостов.
На изображении выше показаны настройки по умолчанию.
Однако вы можете отредактировать файл host и назначить localhost на другой IP-адрес.
Тем не менее, это не рекомендуется, так как это может привести к сбою локальных приложений, которые полагаются на соединение localhost, и нарушить функциональность системы.
Таким образом, адрес для localhost необходимо искать или разрешать, в то время как при использовании 127.0.0.1 происходит прямой переход на этот IP-адрес.
Еще одно существенное различие между localhost и 127.0.0.1 заключается в том, как отправляется запрос.
Запрос не проходит через сетевую карту при пинге адреса loopback с помощью localhost.
С другой стороны, при запуске 127.0.0.1 запрос проходит через сетевую карту, на что могут влиять настройки и конфигурации брандмауэра.
Заключение
В этой статье вы узнали, что localhost и 127.0.0.1 часто взаимозаменяемы и дают одинаковый результат, но мы не можем сказать, что они полностью синонимичны.
- 🐳 Как опросить сокет Docker с помощью curl
- Как найти уязвимость к SQL-инъекции
- Mylg – средство мониторинга сети для командной строки для Linux-систем
Пожалуйста, не спамьте и никого не оскорбляйте.
Это поле для комментариев, а не спамбокс.
Рекламные ссылки не индексируются!





