| Nissan Patrol | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Nissan |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (until 1984) Nissan Safari (Japan, 1980–2007) Nissan Armada (North America, 2016–present) Infiniti QX80 (2014–present) |
| Production | 1951–present (international) 1951–2007 (Japan) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Off-road vehicle/Full-size SUV |
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive (1951–present) Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive (1980–present) |
The Nissan Patrol (Japanese: 日産・パトロール, Hepburn: Nissan Patorōru) is a series of full-size SUVs manufactured by Nissan in Japan and sold throughout the world.
The Patrol has been available as either a short-wheelbase (SWB) three-door or a long-wheelbase (LWB) five-door chassis since 1951. The LWB version has been offered in pickup truck and cab chassis variants. Between 1988 and 1994, Ford Australia marketed the Patrol as the Ford Maverick. In some European countries, such as Spain, the Patrol was marketed by Ebro as the Ebro Patrol. In 1980 in Japan, it was rebadged and alternately sold at Nissan Prince Store locations as the Nissan Safari.
The Patrol is available in Australia, Central and South America, South Africa, parts of Southeast Asia, and Western Europe, as well as Iran and the Middle East. For the 2011 model year, it was made available in North America as the upscale Infiniti QX56 (later renamed as Infiniti QX80), the first time that a Patrol-based vehicle had been sold in North America since 1969, and for the 2017 model year, it would be offered in that market as the Nissan Armada.
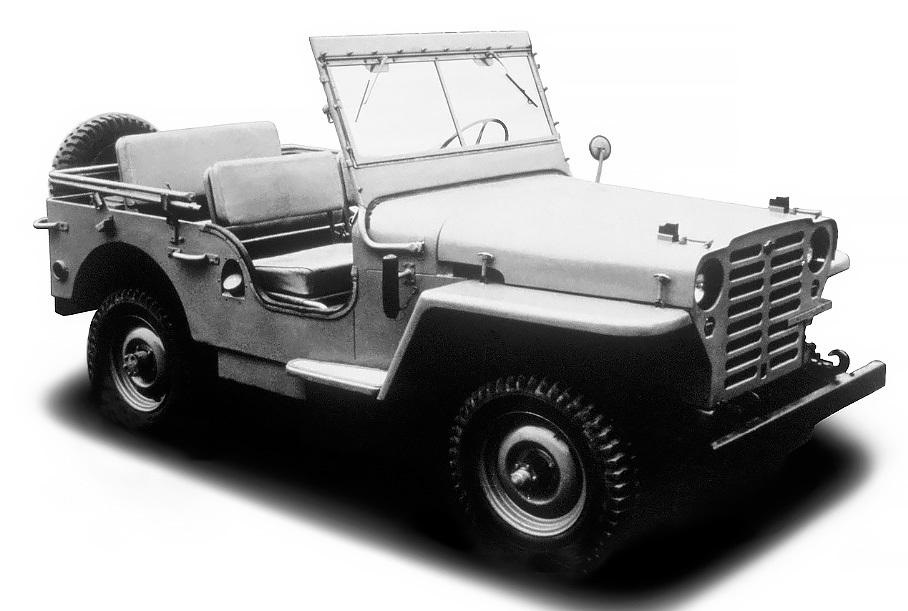
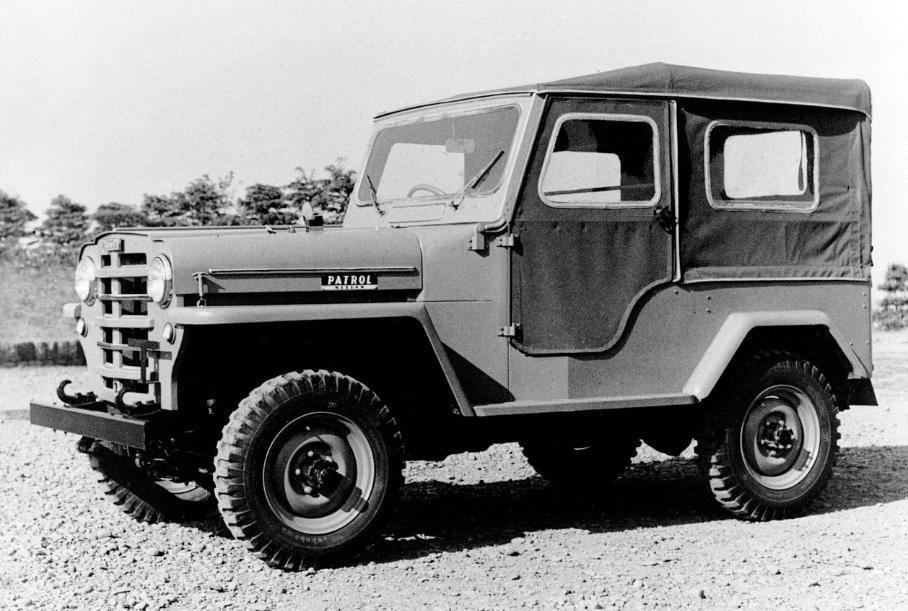
First generation (4W60; 1951)[edit]
| First generation (4W60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Jeep |
| Production | 1951–1960 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Related | Willys CJ-3B |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200 mm (86.6 in) |
| Length | 3,650 mm (143.7 in) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
| Curb weight | 1,500 kg (3,306.9 lb) |
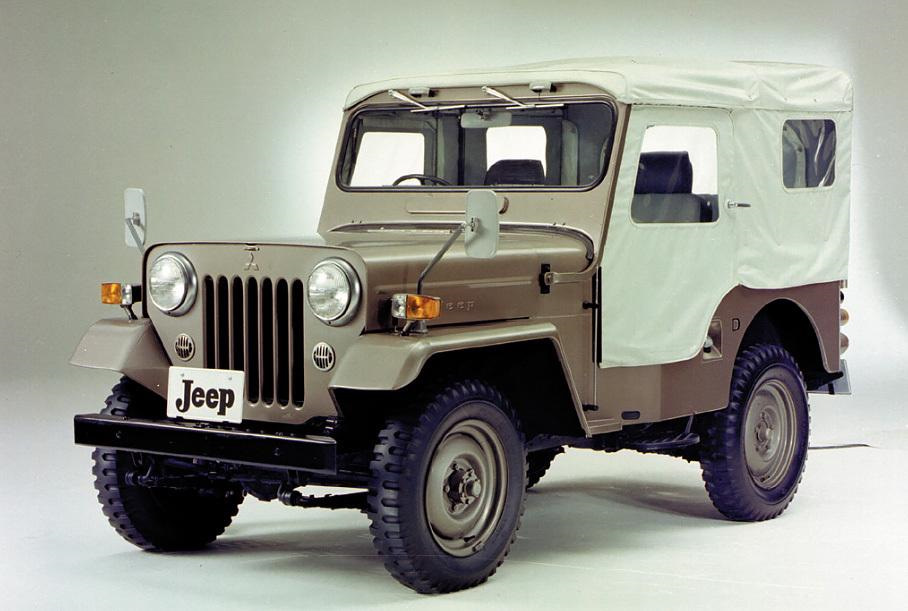
In September 1951, the 4W60 was introduced exclusively to Japanese Nissan dealerships. The overall styling was similar to the Willys Jeep. The 4W60 used the 75 PS (55 kW) 3.7 L Nissan NAK engine from the Nissan 290 bus, but with part-time four-wheel drive and a four-speed manual transmission. The grille had a pressed-steel Nissan badge. A 4W70 Carrier-based wagon was available.
The 4W61 was introduced in August 1955; it changed the grille (with some chrome bars), a one-piece windshield that sits further back when folded, chrome strips on the hood, and unequally sized seats (passenger’s side is wider than the driver’s). The other big change was the engine. The 4W61 was powered by the new 3.7 L Nissan NB engine, producing 92 PS (68 kW), and later was powered by the 105 PS (77 kW) 4.0 L Nissan NC engine. The grille badge was chrome and red and said «NISSAN».
In October 1958, the 4W65 Patrol replaced the 4W61. The 4W65 changed the grille, which now had all chrome bars and redesigned front fenders and hood. A «NISSAN» badge was on the grille and «Patrol» badges were added on the sides of the hood. An eight-seater hardtop wagon, the WG4W65, was added. The short-lived 4W66 Patrol was introduced in December 1956, powered by the 125 PS (92 kW) 4.0 L P engine. The 4W66 was discontinued in June 1960. A wagon version of the 4W66 was called the Carrier, from 1956 to 1959.
4W70 series[edit]
The Nissan 4W70 Carrier was introduced in 1950 based on the Dodge M37. The 4W70 used the M37’s chassis, but the 4W60 Patrol’s drivetrain. The grille was narrower and the front fenders changed. The 4W72 was introduced in 1955 (the 4W71 designation was skipped) with changes to the hood, grille, and headlights. Power increased to 105 hp due to the new Nissan NC engine. Modifications again to the hood, fenders, and grille and an increase in power to 145 PS (107 kW) led to the 4W73, introduced in 1959 and powered by the Nissan P engine.
| Series | Body styles | Engines (gasoline) |
|---|---|---|
| 4W60 series (later named Nissan Patrol) |
SWB: soft top (4W60/61/65/66) SWB: fire truck (F4W61/65/66) |
NAK/NB/NC/P |
| Nissan Carrier 4W70/72/73 |
Troop carrier, weapon carrier | NC/P |
Second generation (60; 1959–1980)[edit]
| Second generation (60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (Philippines) Jonga P60 (India) |
| Production | 1960–1980 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Yokohama; Zama (1965–1980) Philippines: Makati (1961–1983) India: Jabalpur (1965–1999) South Africa: Rosslyn (1959–1983) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size off-road vehicle |
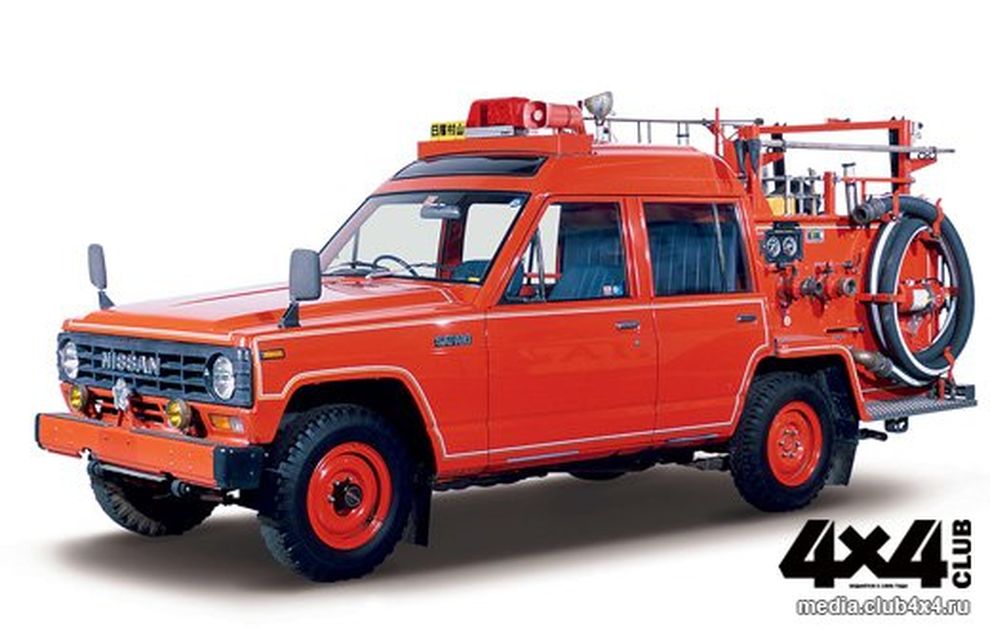
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 3-door softtop 3-door wagon/van 2-door pickup fire truck |
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 3/4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200–2,800 mm (86.6–110.2 in) |
| Length | 3,650–4,250 mm (143.7–167.3 in) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
The soft-top Nissan Patrol 60 (two-door; 2,200 mm (86.6 in) wheelbase) and G60 (two-door; 2,500 mm (98.4 in) wheelbase) were first sold in Australia in 1960. Left-hand drive L60/GL60 models were sold outside of Australia.
Canadian and American customers could get Patrols only from 1962 until 1969. Patrols were sold through Datsun dealerships, making it the only Nissan-badged vehicle sold in the USA until the early 1980s, when the Datsun marque was phased out (barring a small test batch of about 100 Nissan Cedrics that was also exported to the US in the early 60s).[1] An extra-long wheelbase version, the H60, was also available.
The 4WD Nissan Patrol 60 series was produced in short, medium, and long wheelbase versions. It had a manual transmission type-F3B83L at first with three and later with four speeds, and a two-speed transfer case with part-time four-wheel drive. The motor was the P engine, a 3,956 cc (241.4 cu in) inline overhead-valve six-cylinder, featuring bathtub-shaped combustion chambers and a fully balanced seven-bearing crank shaft. With two doors in front and one at the back and four seats (driver and companion in front, two parallel back seats), the extra-long wheelbase version (the H60) was available with eight-passenger capacity.
In 1963, the KG60 (and KGL60) hard-top models were introduced.
Nissan Australia claimed that the 60 series Patrol was the first vehicle to drive across the Simpson Desert in Australia, and built much publicity around the 50th anniversary of the event, including a re-enactment with a similar vehicle ending on 21 July 2012 to publicise the impending release of their new-generation Y62. However, a conflicting account claimed that a Toyota Land Cruiser support vehicle arrived before the Patrol.
| Series | Body styles | Engines (gasoline) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 series | 60 (SWB) | G60 (LWB) | H60 (Super LWB) | P engine |
| 60 soft top K60 hard top |
WG60 station wagon G60H-A cab/chassis 62ZG60H pickup truck |
VH60 van FH60 fire truck |
Jonga[edit]
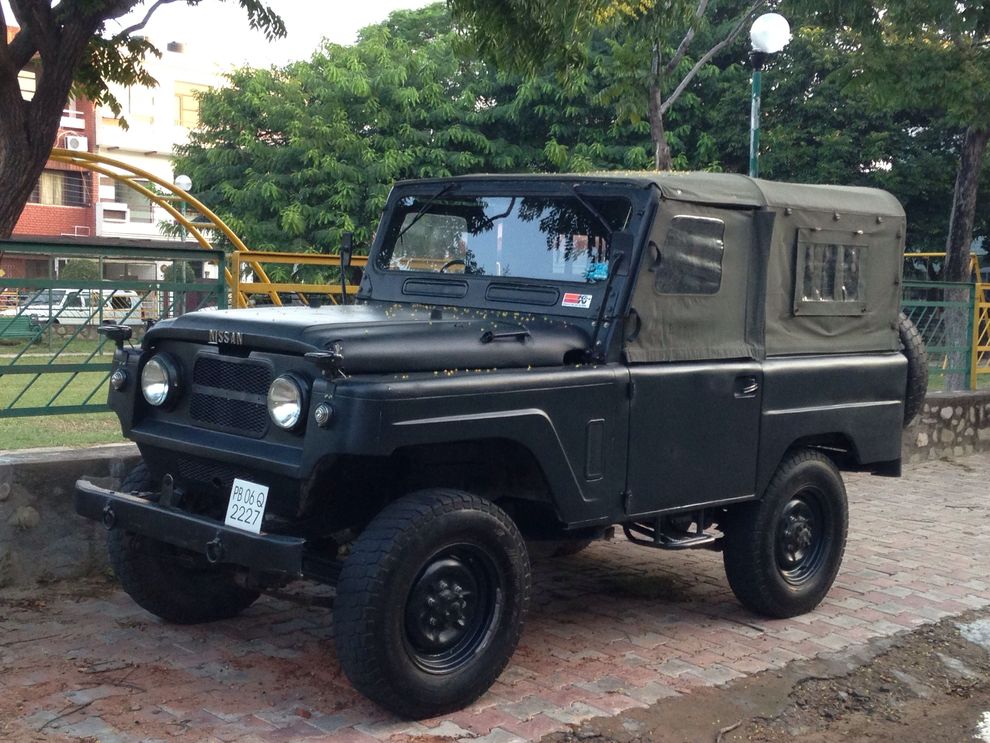
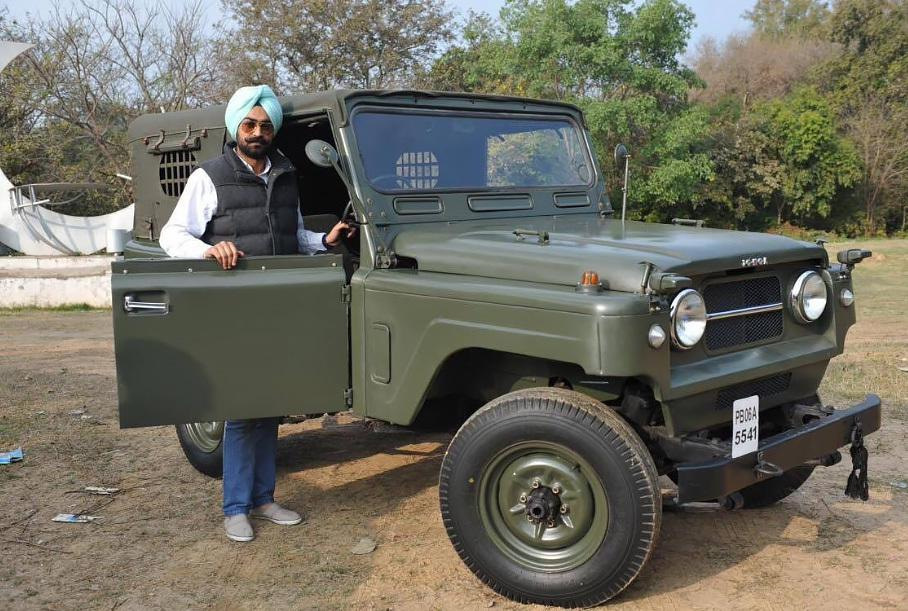
Beginning around 1969, the Indian Army’s Vehicle Factory Jabalpur began assembling the quarter-ton Nissan Patrol as the Jonga, along with the Nissan 4W73. The name as per Indian army records is an acronym for Jabalpur Ordinance aNd Guncarriage Assembly. Both the Nissan vehicles were fitted with the same engines and shared many parts. The Jonga was briefly sold to civilian customers with a 4.0-litre Hino diesel engine in 1996, but demand was low, due to an uncompetitive price, as well as unappealing looks. Less than 200 units were sold. The Jonga served faithfully until the late 1990s, when it was replaced by the lighter Mahindra and Mahindra MM550. Auctioned ex-Army Jongas, stretched and converted to people carriers, still serve in some rural areas of India.
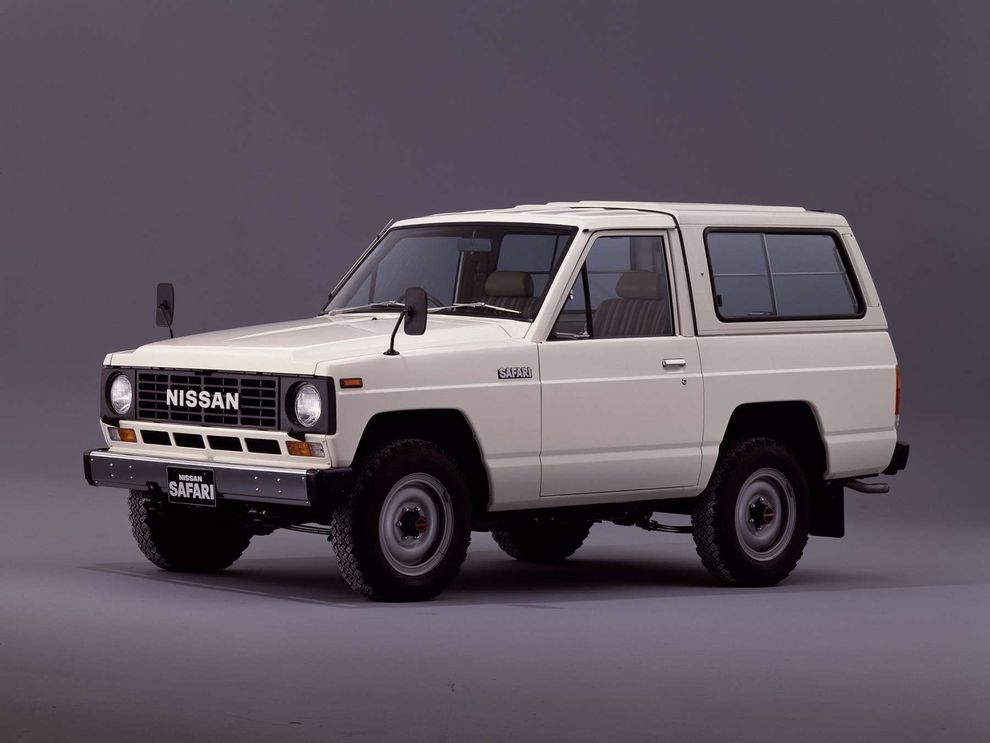
Third generation (160; 1980)[edit]
| Third generation (160) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
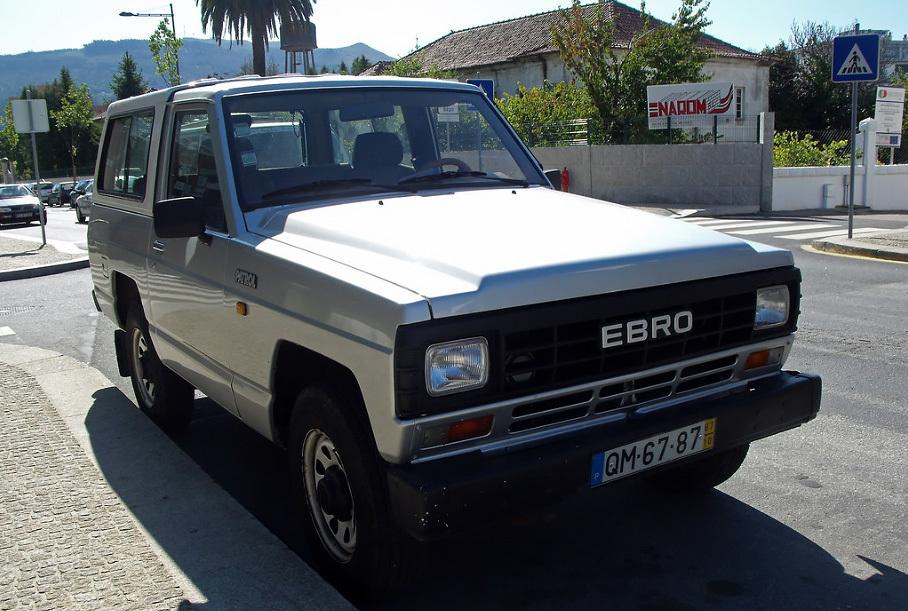
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (1980–1986) Ebro Patrol Nissan Safari (Japan) |
| Production | 1980–1989 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Kanda; Zama (1980–1987) Iran: Tehran (Pars Khodro; 1984–2003) South Africa: Rosslyn (1983–1991) Philippines: Makati (1983–1990) Spain: Barcelona (1983–1988) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 3-door softtop 5-door wagon/van 2/4-door pickup fire truck |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4/5-speed manual 3-speed 3N71 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,350 mm (92.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
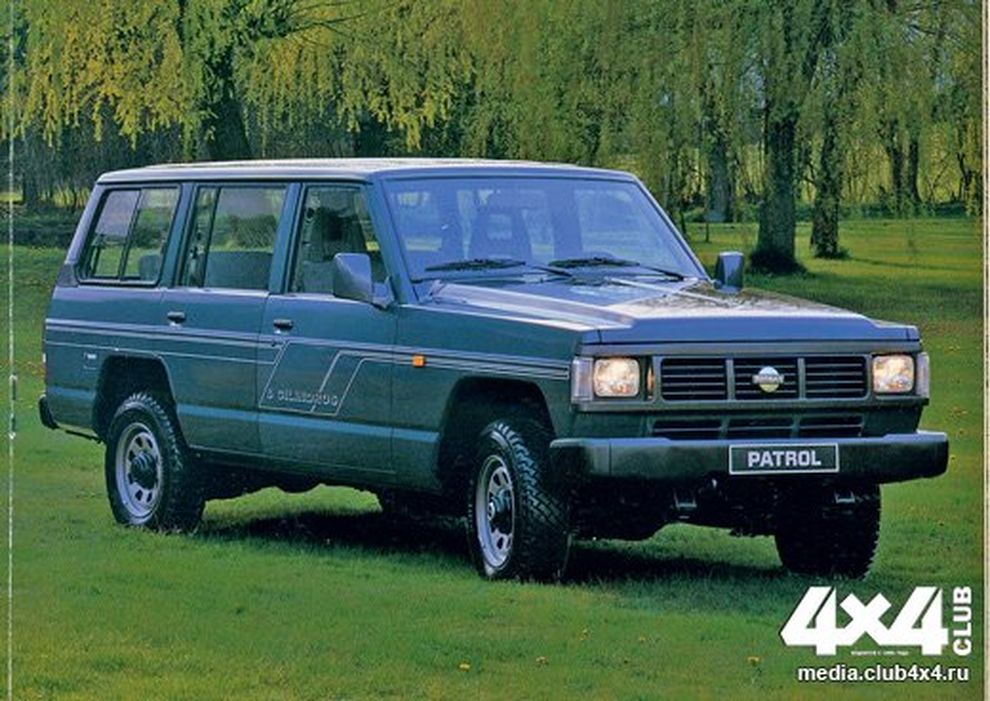
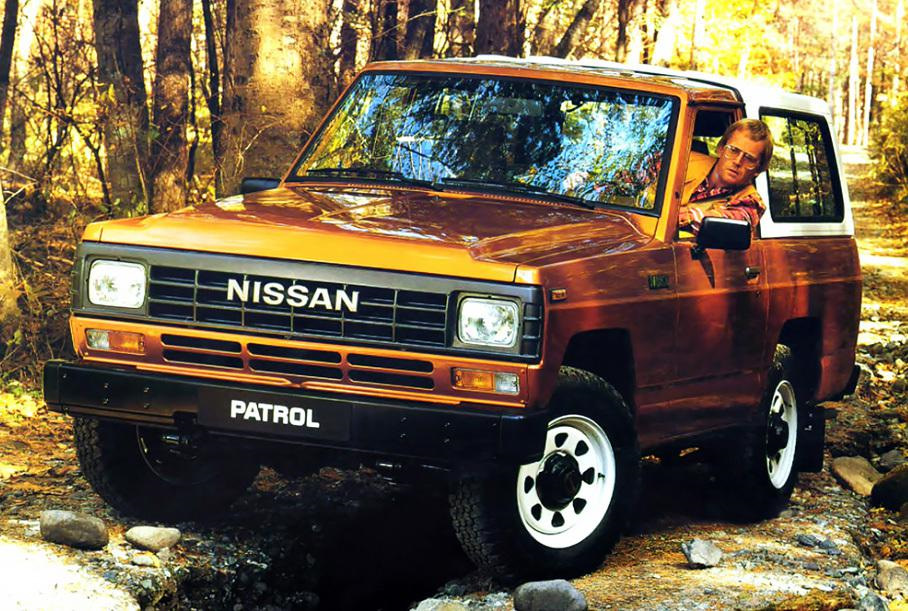
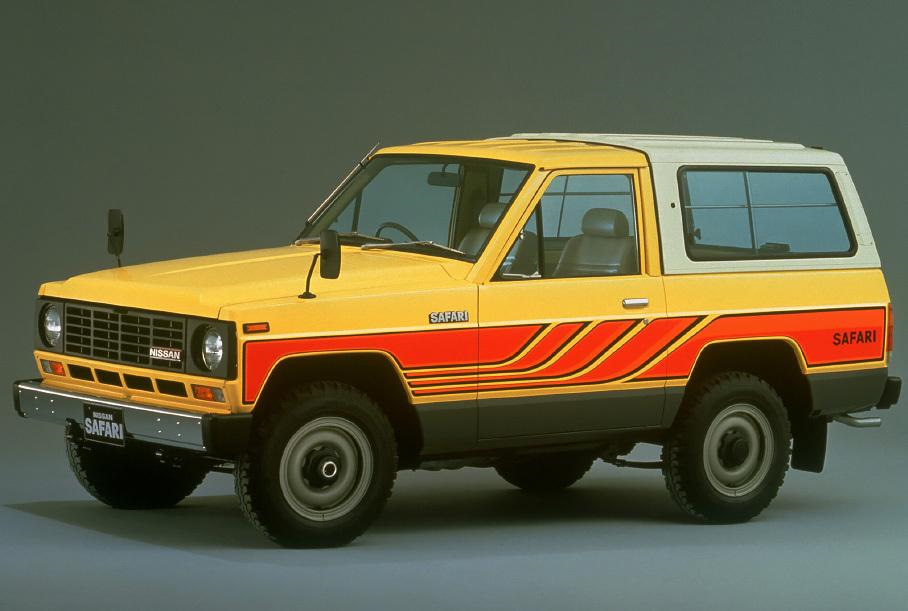
The 160 series was introduced in 1980 to replace the 60 series. In Australia, these are sold as the MQ Patrol. In 1980, the available engines were the L28, P40, and SD33. All models were available with a four-speed manual transmission, while a three-speed automatic was optional on long-wheelbase vehicles fitted with the L28 engine. All 160 series Patrols came with a two-speed offset transfer case, which featured a 1:1 high gear and a low gear.
All models had leaf -spring suspension. The SD33 vehicles feature 24-volt electronics. Different trim options and colors were available, with options including vinyl or carpet floors and blue or brown interior trim. Air conditioning and power steering were available on deluxe models.
The front differential in all models was C200. In Australia, the standard rear differential was the H233. Some versions featured limited slip differentials. A heavy-duty model rear differential was used in some pickup trucks and P40-engined wagons. This was the H260 model differential. In European markets, where less onerous off-road use was expected, the light-duty C200 rear differential was installed in some vehicles.
In 1983, the MQ was updated as MK Patrol, but this does not appear on any Nissan literature or service manuals. Nissan parts dealers do not recognise these initials. Updates included a revised front end with rectangular headlights and an upgraded front suspension. The four-speed gearbox was revised and a fifth gear was added for most models. The four-speed was still used in some lower specificationed units, presumably to run out stock. A high roof («Super Roof») version of the wagon was added at the same time along with the SD33T turbo-diesel option. With 110 PS (81 kW), the turbodiesel can reach 145 km/h (90 mph).[2]
The naturally aspirated SD33 diesel engine was updated at this time. Revisions included the use of three piston rings instead of five, piston oil squirters, and a spin-on oil filter instead of a paper cartridge type. In Australia and some other parts of the world, the SD33-engined Patrols were revised to standard 12-volt electronics. To accommodate the turbodiesel’s extra power, these models featured a larger clutch (270 versus 240 mm) and larger oil cooler (five rows versus three) than the naturally aspirated version.
These were the last Patrols to carry the Datsun brand; in line with the rest of the Nissan lineup, the Patrol lost its Datsun branding in 1984 in most markets.
Spanish production[edit]
Nissan acquired a 35.85% stake in Motor Ibérica in 1980, which was increased to 54.68% in 1982.[3] In early 1983, the first Spanish-made Nissan Patrol left the plant in Zona Franca, near Barcelona. The first year’s production, planned to be 4,000 to 5000 cars, was earmarked for Spain and Portugal.[3] Exports were to follow during 1984. Nissan Ibérica-built Patrols originally received a Spanish-made Perkins MD27 four-cylinder diesel engine and Spanish transmission to meet local content regulations.[4] Later on, this was replaced by the A428, which evolved into the A428T and then the A428II. Later yet, the RD28 and the RD28T were added to Spanish-made cars.
260 (1986–1993)[edit]
| Third generation (260) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Ebro Patrol (Spain, 1986–1993) Sanxing Desert King (China) |
| Production | 1986–2002 |
| Assembly | Spain: Barcelona |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 5-door wagon/van 2/4-door pickup |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,350 mm (92.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,230 mm (166.5 in) LWB: 4,690 mm (184.6 in) |
| Width | 1,689 mm (66.5 in) |
| Height | 1,980 mm (78.0 in) |
The 260 series was a facelifted version of the Spanish-built 160 (easily spotted by the rectangular headlamps) sold in Europe and available in SWB and LWB with L28, SD33, RD28 and RD28T engines. The SD-engined version, at least in the UK market, had a 24-volt electrical system. Nissan helped Nissan Ibérica amortize plant investments. The 260 Patrol later received a facelift with a new grille similar to that of the Y60 series which succeeded this generation elsewhere. Spanish production continued until 1994 for export and until 2002 for the Spanish domestic market.
Fourth generation (Y60; 1987)[edit]
| Fourth generation (Y60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Safari (Japan) Ford Maverick (Australia) Yunbao YB2030 (China; JV) |
| Production | 1987–1997 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Kanda; Zama (1987–1993) South Africa: Rosslyn (1991–2001) Spain: Barcelona (1988–1998) Philippines: Makati (1990–1998), Santa Rosa City (1998–2000) China: Huadu |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door wagon 5-door wagon/van 2-door pickup |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | Petrol: 3.0 L RB30S I6 4.2 L TB42S/TB42E I6 Diesel: 2.8 L RD28T I6 turbo 4.2 L TD42 I6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed RE4R03A automatic 5-speed FS5R50A manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,400 mm (94.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,285 mm (168.7 in) LWB: 4,845 mm (190.7 in) |
| Width | SWB: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) LWB: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) |
| Height | SWB: 1,810 mm (71.3 in) LWB: 1,815 mm (71.5 in) |
Pre-facelift Nissan Patrol ST
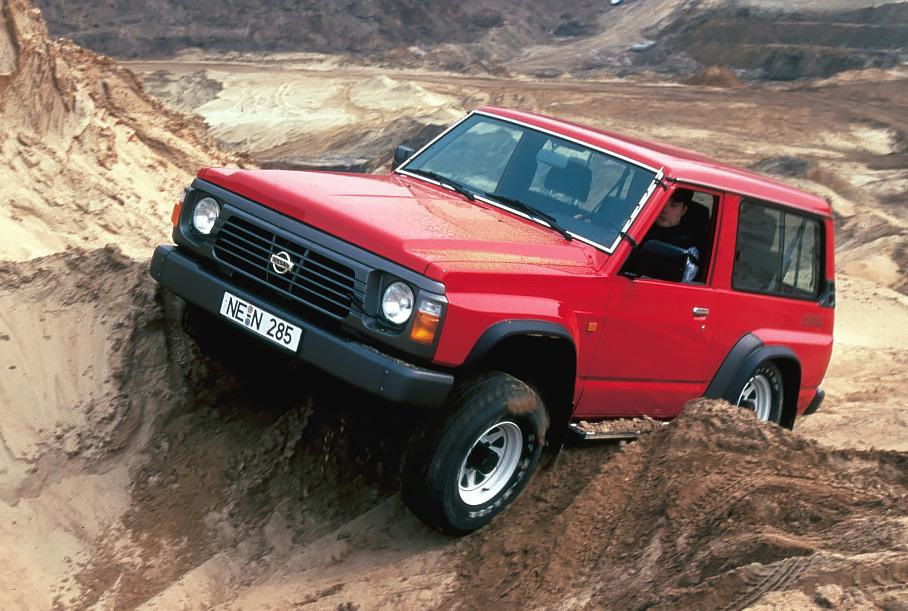
The Y60 was radically different mechanically from its predecessors, as it was the first Patrol with coil-spring suspension, increasing comfort and improving rough-ground handling. All Y60 Patrols had a three-link live axle suspension set-up at the front, with all wagons (SWB, LWB, and SWB LW) adopting a five-link set-up at the rear. The utility model was available with both a leaf-spring rear axle, and from 1994 onwards, a choice of the same coil-spring rear axle as the wagons. Sway bars were included on both front and rear coil-spring live axles. Power steering was standard. Some wagon models had front and rear disc brakes, while the utility retained rear drum brakes. The introduction of a synchromesh on reverse gear was another improvement.
The alternative model codes of GR and GQ were applied to left- and right-hand drive models, respectively.
Most models had a rear limited slip differential and some variants had a vacuum or electric solenoid-operated manual rear differential lock. A rear sway bar release mechanism appeared on some models. Some Y60s had a power take-off-driven front-mounted winch, with an in-cab control lever to the right of the gearstick.
The Patrol was also branded as Safari in Japan, depending on which Japanese dealership was offering it – Safari at Nissan Prince Shop and Patrol at Nissan Bluebird Shop. The Safari was available with an optional 24V electrical system, instead of the standard 12V. This was the first series that placed the exterior dimensions in the higher tax bracket for the wider exterior measurement as defined in Japanese Government dimension regulations and the larger engines added a higher road tax obligation for Japanese owners.
The TD42 and TB42 were available with either a five-speed manual or a four-speed automatic gearbox. The RD28T and the RB30 offered only a five-speed manual.
Trim levels in Australia included:
- DX with manual mirrors, no central locking, vinyl interior, optional AC, manual locking hubs
- RX (from 1995) with electric mirrors, central locking, carpet interior, AC, manual locking hubs
- ST with electric windows, electric mirrors, central locking, carpet interior, AC, automatic locking hubs
- Ti (from late 1989) was equipped with an electronic fuel-injected engine, electric windows, electric mirrors, central locking, velour and carpet interior, rear AC, seven-speaker sound system, alloy three-spoke wheels, and automatic locking hubs. It had a high roof design with sunroof until 1991. Leather and woodgrain trim was made standard in 1992 with the Series 2.
Several dealer-fitted accessories were available, including sunroofs, roof racks, tow bars, driving lights, cargo barriers, and side steps. The TD42 was available with an optional Safari turbocharger at some Australian dealers.
Trim levels in Europe varied by country. These include designations such as SLX, LX, LW, and many others in France. Finnish Patrols came standard with two batteries. LW (1996–1997) featured a lightweight body, reducing the weight by 50 kg (110 lb) and a special smaller body (40 mm [1.6 in]). These were produced only for extreme off-road championships. The engine and chassis remained the same.
1995–1997 Nissan Patrol (GQ II) RX wagon (Australia)
Ford Maverick wagon (Australia)
Two major updates came in Australia, one in 1992 (GQ Series 2), and one in 1995 (minor facelift). The most notable changes in 1992 were the introduction of fuel-injection on the TB42 motor, EGR valve and oil cooler on the RD28T, new seats, new trim, sound deadening, and side intrusion bars. Other 1992 Series 2 refinements included a revised transmission and suspension, and introducing bigger brakes, bigger wheels, and the standardization of limited slip differentials and auto-freewheeling hubs. This update included new seats, trim, and side intrusion bars.
In 1991, the rear indicators, tail lights, and brake lights were relocated to the bumper from the body to meet Australian Design Rules, but they stayed the same in European versions. In 1992, another set of indicators was placed on the front quarter panel.
In August 1993, the TD42 lost weight to reduce fuel consumption and increase maximum engine speed. This had the side effect of weakening the engine. The original engine can be identified by its silver rocker cover, whereas the lightened engine featured a black rocker cover. The RD28T got some extra changes, moving the vacuum pump from behind the alternator to the top of the engine. Driver-side airbags appeared in some European models.
Changes in 1995 featured a minor facelift, with a redesigned front grille and the RX model entering Australia.
Known weaknesses included vibrations from the front end (largely fixed under warranty), cracking hinges on the rear door (due to the spare tyre’s weight), and rust on rear window frames. The RD28T and TB42 engines suffered from head gasket issues when driven with a heavy foot. European five-speed gearboxes suffered from bearing failures in fifth gear at high mileages. However, the TD42 was highly reliable. Patrols are known for their strong axles and good limited slip differential (when so equipped).
From 1988 to 1994, Ford Australia rebadged the Y60 Patrol as the Ford Maverick. This was a result of the Button car plan devised by the government of Australia. The car was mechanically similar, although the Nissan version had rear disc brakes depending on vehicle grade, while the Ford mostly had drum brakes and featured different paint colours and trim levels.
All wagons had a 95-liter main fuel tank with the utility having a 90-liter tank and the option of a 95-liter second tank.
Engine specifications[edit]
| Engine code | Displacement | Bore x stroke | Power | Torque | Compression ratio | Design | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB30S | 2962 cc | 86 x
85mm |
100 kW at 4800 rpm | 224 Nm at 3000 rpm | 9.0:1 | Inline-six SOHC, petrol | Aluminum crossflow cylinder head |
| TB42S | 4169 cc | 96 x
96mm |
125 kW at 4200 rpm | 325 Nm at 2800 rpm | 8.3.1 | Inline-six Pushrod, petrol | Crossflow cylinder head, high camshaft |
| TB42E | 135 kW at 4400 rpm | 320 Nm at 3200 rpm | 8.3:1 | ||||
| RD28T | 2826 cc | 85 x
83mm |
91.9 kW at 4400 rpm | 255 Nm at 2000 rpm | 21.2:1 | Inline-six SOHC, diesel | Turbocharged |
| TD422 | 4169 cc | 96 x
96mm |
85 kW at 4000 rpm | 264 Nm at 2000 rpm | 22.7:1 | Inline-six pushrod, diesel | Crossflow cylinder head, high camshaft |
Fifth generation (Y61; 1997)[edit]
| Fifth generation (Y61) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Safari (Japan) |
| Production | October 1997 – 2016[5] 1997–present (continues in selective countries) |
| Assembly |
|
| Designer | Masato Takahashi (1994) Junichi Sakai (facelift: 2003)[6] |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,400 mm (94.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,440 mm (174.8 in) LWB: 5,080 mm (200.0 in) |
| Width | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
| Height | 1,855 mm (73.0 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,473 kg (5,452 lb) |
Cab chassis
5-door SUV
3-door SUV (facelift)
Nissan Safari (facelift)
Interior
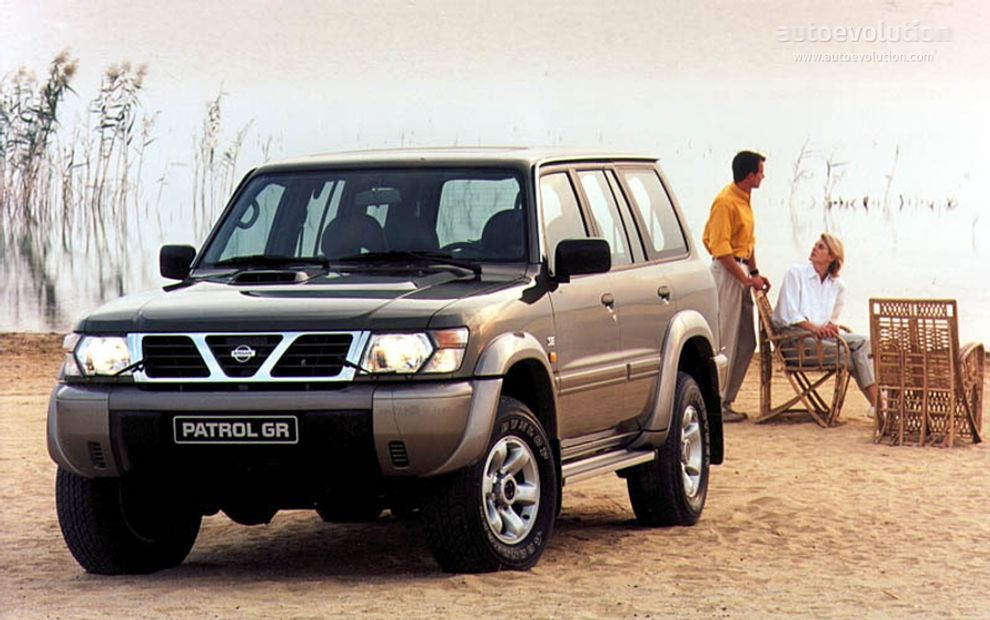
Y61 models first appeared in December 1997, available in 4.5- and 4.8-litre petrol, 2.8-, 3.0-, and 4.2-litre turbo-diesel and 4.2-litre turbo-diesel intercooler variants. The alternative model codes of GR and GU were applied to left- and right-hand drive models, respectively.
The drivetrain was changed in this model, including larger CVs and less synchros in the manual gearboxes. The differential housings were widened to fall inline with the new body shape, but centers remained the same (H233 and H260). Some petrol wagons received a coil version of the H260 differential.
Comfort levels were increased over GQ, especially in the seating and NVH areas.
GU IV onwards[edit]
For the 2005 model year a significant facelift model was released, with new headlights, box flares on each guard and larger tail lights. The troubles that plagued the ZD30 diesel around the variable turbo geometry were resolved by this refresh.
That same year, Nissan stopped selling the Safari in Japan due to poor sales. Nissan also made a two-door pickup version of the Y61 series available as cab chassis and with a style side tray in some markets. Although a new model was launched, this Y61 series still sells for offroad enthusiasts but with few options.
Its TB48DE engine is very popular among the tuning community in the middle east, especially in the UAE. The TB48DE engine is easily modifiable and is shown to be able to handle over 2,000 hp (1,500 kW) for several sand hills and sand drag challenges in the region.
As of 2014, Nissan discontinued the fifth generation model worldwide, except for South Africa, the Middle East, Paraguay, Haiti, Philippines, Nepal, Bolivia, Sri Lanka, and some African and Eastern European countries where the 4×4 competed against the Toyota Land Cruiser (J70). In Australia, the Y61 was sold until 2016, alongside the Y62.
Several special edition trims have been also been released in respective regions where the Y61 was and are currently being sold, of which some of them are The Presidential edition and 4XPRO edition (Philippines), The Legend edition (Philippines, South Africa and Australia), The ‘Special’ Super Safari edition (Middle East), The Falcon edition (Middle East), Gazelle, Gazelle Storm and Gazelle X editions (Middle East).
The Y61 is also still being produced for and used by United Nations agencies across different countries as well as some military branches and government sectors. They are mainly being used as security escorts vehicles, chief personnel carriers and off pavement patrol units.
Sixth generation (Y62; 2010)[edit]
| Sixth generation (Y62) | |
|---|---|

Pre-facelift |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Armada (2016–present) Infiniti QX56/QX80 Nissan Patrol Royale (Philippines) |
| Production | January 2010 – present |
| Assembly |
Russia: Saint-Petersburg, (SKD, 2012–2014) |
| Designer | Taiji Toyota (2007) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size SUV |
| Body style | 5-door SUV |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Y62 |
| Related | Infiniti QX56/QX80 Nissan Armada (Y62) Nissan Terra Nissan Navara (D23) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 3,075 mm (121.1 in) |
| Length | 5,165 mm (203.3 in) |
| Width | 1,995 mm (78.5 in) |
| Height | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,695–2,795 kg (5,941–6,162 lb) |
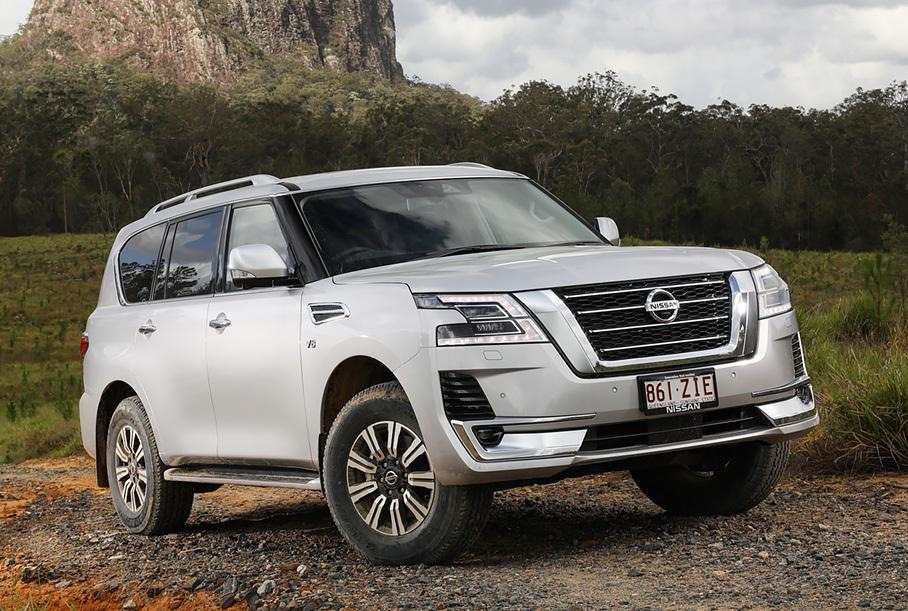
The all-new, sixth generation, Y62 series Nissan Patrol was launched on 13 February 2010 in Abu Dhabi.[9] A luxury version (Z62) was sold as the Infiniti QX56 from 2010 (the first time that a Patrol-based vehicle had been sold in North America since 1969), which was later renamed the Infiniti QX80 in 2013. The Y62 was introduced in North America under the Armada nameplate in 2016, for the 2017 model year. It was presented as a replacement for the Titan-based first generation Nissan Armada (WA60).
As of 2017, the Y62 is powered by either a 275 hp (205 kW) / 394 N⋅m (291 lb⋅ft) 4.0-litre VQ40DE V6 engine for the entry level XE and SE trims or a more powerful 400 hp (298 kW) / 560 N⋅m (410 lb⋅ft) 5.6-litre VK56VD V8 engine for the upper level trims. The NISMO edition uses a tuned version of the 5.6-litre V8 producing 28 additional horsepower. Prior to the introduction of the 4.0-litre V6, a lower output 317 hp (236 kW) / 526 N⋅m (388 lb⋅ft) 5.6-litre VK56DE V8 was designated for the entry level trims.
As of 2017, all models come with a 7-speed automatic transmission although Nissan previously offered a 5-speed automatic and also a 6-speed manual for the entry level trim. A variable 4×4 mode package allows switching between four drive modes: sand, on-road, rock and snow. A Hydraulic Body Motion Control System is available. An electronic-locking rear differential, hill start and hill descent control, as well as lane-departure warning, computer assisted braking and stability control. The Infiniti version launched in the United States in 2010, the first Patrol sold there since the 60 series. The Nissan Patrol launched in Australia in early 2013.[8]
The Nissan Patrol is offered in various different trim levels in the Middle East: XE, SE, SE-Platinum City, LE, LE-Titanium, LE-Platinum City and NISMO Edition. In Australia the Ti and Ti-L trim levels are offered.
-
Rear view (pre-facelift)
-
Interior
Facelift[edit]
In 2014, a significant facelift arrived, with revised tail lights with red elements present, globe housings and built-in LED headlights. A new tan interior was added and new sets of wheels.
Nissan introduced a limited-run Patrol Black Special Edition in 200 units. These cars offer several enhancements such as red seats, chrome detailing and a black matte exterior paint scheme.
Nissan gave a second facelift to the 2019 Patrol before it will have a new version by 2020. Changes include a new front bumper featuring a deeper apron and a traditional round housing. The vehicle will be equipped with Nissan’s Intelligent Mobility driver-assistance features like lane keeping assist, forward collision warning, automatic emergency braking for front and rear, rear cross traffic alert, and blind spot monitoring.[10]
-
First facelift
-
Rear view (first facelift)
-
Second facelift
-
Second facelift (China)
-
Rear view (second facelift)
-
Interior (second facelift)
Patrol Desert Edition[edit]
The Desert Edition comes with the 400 hp 5.6-litre (5552cc) engine, manually-adjusted cloth seats, navigation and regular suspension instead of the hydraulic body-control system.[11]
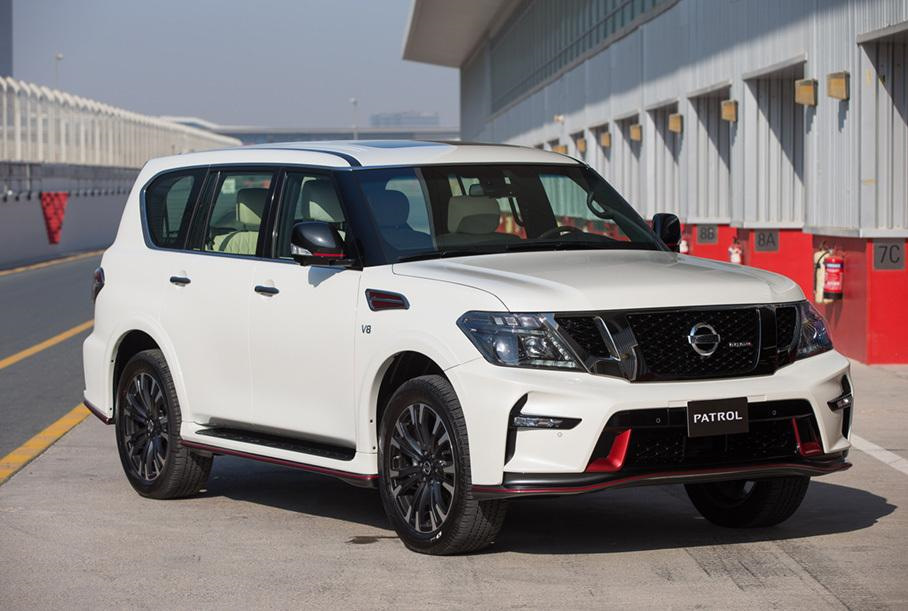
Patrol Nismo[edit]
On launching the Nismo brand in the Middle East, the Nissan Patrol Nismo was introduced at the launch event in Dubai along with the GT-R Nismo and 370Z Nismo. Unlike the standard Patrol, the Nismo version comes with (5.6-litre) V8 with 428 hp (319 kW) engine tuned by Nissan’s Takumi craftsmen. The suspensions is upgraded with Bilstein shocks and fitted with 22-inch forged-alloy wheels.[12]
-
2018 Nissan Patrol Nismo (front)
-
2018 Nissan Patrol Nismo (rear)
References[edit]
- ^ Ramey, Jay (17 September 2013). «This may be the oldest surviving Nissan in North America». Autoweek. Hearst Autos, Inc. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ^ Nissan Gamma [Nissan range] (brochure) (in Flemish), Aartselaar, Belgium: N.V. Nissan Belgium S.A., 1984, p. 1
- ^ a b Visart, Etienne, ed. (10 March 1983). «Un constructeur Japonais fabrique en Europe!» [A Japanese manufacturer builds in Europe!]. Le Moniteur de l’Automobile (in French). Brussels, Belgium: Editions Auto-Magazine. 34 (764): 24.
- ^ Walker, Alan (September 1982). Kennett, Pat (ed.). «The great European retreat». Truck. London: FF Publishing: 36.
- ^ «History». Nissan Shatai. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ «A Revitalised Design for Nissan’s 2005 Patrol». Next Car. 12 October 2004. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ Opara, Theodore (27 April 2014). «First built in Nigeria Nissan Patrol rolls off production line». Vanguard. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ a b «2013 Nissan Patrol (Y62) Australia Introduction» (PDF).
- ^ «Stunning looks coupled with unstoppable 4WD upgrades make Nissan Patrol new class-leader as Nissan’s ‘Hero of All Terrain’» (Press release). Nissan. 13 February 2010. Archived from the original on 22 April 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ «Nissan gives 2019 Patrol a (slightly) new look – Auto Industry News». AutoIndustriya.com. 8 October 2018. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- ^ «First drive: 2016 Nissan Patrol Desert Edition in Liwa UAE»
- ^ «2017 Nissan Patrol Nismo | Drive Arabia»
External links[edit]
Media related to Nissan Patrol at Wikimedia Commons
- Nissan Patrol Archived 12 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine at Nissan’s global website
- Nissanh Heritage Nissan Safari
| Nissan Patrol | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Nissan |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (until 1984) Nissan Safari (Japan, 1980–2007) Nissan Armada (North America, 2016–present) Infiniti QX80 (2014–present) |
| Production | 1951–present (international) 1951–2007 (Japan) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Off-road vehicle/Full-size SUV |
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive (1951–present) Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive (1980–present) |
The Nissan Patrol (Japanese: 日産・パトロール, Hepburn: Nissan Patorōru) is a series of full-size SUVs manufactured by Nissan in Japan and sold throughout the world.
The Patrol has been available as either a short-wheelbase (SWB) three-door or a long-wheelbase (LWB) five-door chassis since 1951. The LWB version has been offered in pickup truck and cab chassis variants. Between 1988 and 1994, Ford Australia marketed the Patrol as the Ford Maverick. In some European countries, such as Spain, the Patrol was marketed by Ebro as the Ebro Patrol. In 1980 in Japan, it was rebadged and alternately sold at Nissan Prince Store locations as the Nissan Safari.
The Patrol is available in Australia, Central and South America, South Africa, parts of Southeast Asia, and Western Europe, as well as Iran and the Middle East. For the 2011 model year, it was made available in North America as the upscale Infiniti QX56 (later renamed as Infiniti QX80), the first time that a Patrol-based vehicle had been sold in North America since 1969, and for the 2017 model year, it would be offered in that market as the Nissan Armada.
First generation (4W60; 1951)[edit]
| First generation (4W60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Jeep |
| Production | 1951–1960 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Related | Willys CJ-3B |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200 mm (86.6 in) |
| Length | 3,650 mm (143.7 in) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
| Curb weight | 1,500 kg (3,306.9 lb) |
In September 1951, the 4W60 was introduced exclusively to Japanese Nissan dealerships. The overall styling was similar to the Willys Jeep. The 4W60 used the 75 PS (55 kW) 3.7 L Nissan NAK engine from the Nissan 290 bus, but with part-time four-wheel drive and a four-speed manual transmission. The grille had a pressed-steel Nissan badge. A 4W70 Carrier-based wagon was available.
The 4W61 was introduced in August 1955; it changed the grille (with some chrome bars), a one-piece windshield that sits further back when folded, chrome strips on the hood, and unequally sized seats (passenger’s side is wider than the driver’s). The other big change was the engine. The 4W61 was powered by the new 3.7 L Nissan NB engine, producing 92 PS (68 kW), and later was powered by the 105 PS (77 kW) 4.0 L Nissan NC engine. The grille badge was chrome and red and said «NISSAN».
In October 1958, the 4W65 Patrol replaced the 4W61. The 4W65 changed the grille, which now had all chrome bars and redesigned front fenders and hood. A «NISSAN» badge was on the grille and «Patrol» badges were added on the sides of the hood. An eight-seater hardtop wagon, the WG4W65, was added. The short-lived 4W66 Patrol was introduced in December 1956, powered by the 125 PS (92 kW) 4.0 L P engine. The 4W66 was discontinued in June 1960. A wagon version of the 4W66 was called the Carrier, from 1956 to 1959.
4W70 series[edit]
The Nissan 4W70 Carrier was introduced in 1950 based on the Dodge M37. The 4W70 used the M37’s chassis, but the 4W60 Patrol’s drivetrain. The grille was narrower and the front fenders changed. The 4W72 was introduced in 1955 (the 4W71 designation was skipped) with changes to the hood, grille, and headlights. Power increased to 105 hp due to the new Nissan NC engine. Modifications again to the hood, fenders, and grille and an increase in power to 145 PS (107 kW) led to the 4W73, introduced in 1959 and powered by the Nissan P engine.
| Series | Body styles | Engines (gasoline) |
|---|---|---|
| 4W60 series (later named Nissan Patrol) |
SWB: soft top (4W60/61/65/66) SWB: fire truck (F4W61/65/66) |
NAK/NB/NC/P |
| Nissan Carrier 4W70/72/73 |
Troop carrier, weapon carrier | NC/P |
Second generation (60; 1959–1980)[edit]
| Second generation (60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (Philippines) Jonga P60 (India) |
| Production | 1960–1980 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Yokohama; Zama (1965–1980) Philippines: Makati (1961–1983) India: Jabalpur (1965–1999) South Africa: Rosslyn (1959–1983) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 3-door softtop 3-door wagon/van 2-door pickup fire truck |
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 3/4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200–2,800 mm (86.6–110.2 in) |
| Length | 3,650–4,250 mm (143.7–167.3 in) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
The soft-top Nissan Patrol 60 (two-door; 2,200 mm (86.6 in) wheelbase) and G60 (two-door; 2,500 mm (98.4 in) wheelbase) were first sold in Australia in 1960. Left-hand drive L60/GL60 models were sold outside of Australia.
Canadian and American customers could get Patrols only from 1962 until 1969. Patrols were sold through Datsun dealerships, making it the only Nissan-badged vehicle sold in the USA until the early 1980s, when the Datsun marque was phased out (barring a small test batch of about 100 Nissan Cedrics that was also exported to the US in the early 60s).[1] An extra-long wheelbase version, the H60, was also available.
The 4WD Nissan Patrol 60 series was produced in short, medium, and long wheelbase versions. It had a manual transmission type-F3B83L at first with three and later with four speeds, and a two-speed transfer case with part-time four-wheel drive. The motor was the P engine, a 3,956 cc (241.4 cu in) inline overhead-valve six-cylinder, featuring bathtub-shaped combustion chambers and a fully balanced seven-bearing crank shaft. With two doors in front and one at the back and four seats (driver and companion in front, two parallel back seats), the extra-long wheelbase version (the H60) was available with eight-passenger capacity.
In 1963, the KG60 (and KGL60) hard-top models were introduced.
Nissan Australia claimed that the 60 series Patrol was the first vehicle to drive across the Simpson Desert in Australia, and built much publicity around the 50th anniversary of the event, including a re-enactment with a similar vehicle ending on 21 July 2012 to publicise the impending release of their new-generation Y62. However, a conflicting account claimed that a Toyota Land Cruiser support vehicle arrived before the Patrol.
| Series | Body styles | Engines (gasoline) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 series | 60 (SWB) | G60 (LWB) | H60 (Super LWB) | P engine |
| 60 soft top K60 hard top |
WG60 station wagon G60H-A cab/chassis 62ZG60H pickup truck |
VH60 van FH60 fire truck |
Jonga[edit]
Beginning around 1969, the Indian Army’s Vehicle Factory Jabalpur began assembling the quarter-ton Nissan Patrol as the Jonga, along with the Nissan 4W73. The name as per Indian army records is an acronym for Jabalpur Ordinance aNd Guncarriage Assembly. Both the Nissan vehicles were fitted with the same engines and shared many parts. The Jonga was briefly sold to civilian customers with a 4.0-litre Hino diesel engine in 1996, but demand was low, due to an uncompetitive price, as well as unappealing looks. Less than 200 units were sold. The Jonga served faithfully until the late 1990s, when it was replaced by the lighter Mahindra and Mahindra MM550. Auctioned ex-Army Jongas, stretched and converted to people carriers, still serve in some rural areas of India.
Third generation (160; 1980)[edit]
| Third generation (160) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (1980–1986) Ebro Patrol Nissan Safari (Japan) |
| Production | 1980–1989 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Kanda; Zama (1980–1987) Iran: Tehran (Pars Khodro; 1984–2003) South Africa: Rosslyn (1983–1991) Philippines: Makati (1983–1990) Spain: Barcelona (1983–1988) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 3-door softtop 5-door wagon/van 2/4-door pickup fire truck |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4/5-speed manual 3-speed 3N71 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,350 mm (92.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
The 160 series was introduced in 1980 to replace the 60 series. In Australia, these are sold as the MQ Patrol. In 1980, the available engines were the L28, P40, and SD33. All models were available with a four-speed manual transmission, while a three-speed automatic was optional on long-wheelbase vehicles fitted with the L28 engine. All 160 series Patrols came with a two-speed offset transfer case, which featured a 1:1 high gear and a low gear.
All models had leaf -spring suspension. The SD33 vehicles feature 24-volt electronics. Different trim options and colors were available, with options including vinyl or carpet floors and blue or brown interior trim. Air conditioning and power steering were available on deluxe models.
The front differential in all models was C200. In Australia, the standard rear differential was the H233. Some versions featured limited slip differentials. A heavy-duty model rear differential was used in some pickup trucks and P40-engined wagons. This was the H260 model differential. In European markets, where less onerous off-road use was expected, the light-duty C200 rear differential was installed in some vehicles.
In 1983, the MQ was updated as MK Patrol, but this does not appear on any Nissan literature or service manuals. Nissan parts dealers do not recognise these initials. Updates included a revised front end with rectangular headlights and an upgraded front suspension. The four-speed gearbox was revised and a fifth gear was added for most models. The four-speed was still used in some lower specificationed units, presumably to run out stock. A high roof («Super Roof») version of the wagon was added at the same time along with the SD33T turbo-diesel option. With 110 PS (81 kW), the turbodiesel can reach 145 km/h (90 mph).[2]
The naturally aspirated SD33 diesel engine was updated at this time. Revisions included the use of three piston rings instead of five, piston oil squirters, and a spin-on oil filter instead of a paper cartridge type. In Australia and some other parts of the world, the SD33-engined Patrols were revised to standard 12-volt electronics. To accommodate the turbodiesel’s extra power, these models featured a larger clutch (270 versus 240 mm) and larger oil cooler (five rows versus three) than the naturally aspirated version.
These were the last Patrols to carry the Datsun brand; in line with the rest of the Nissan lineup, the Patrol lost its Datsun branding in 1984 in most markets.
Spanish production[edit]
Nissan acquired a 35.85% stake in Motor Ibérica in 1980, which was increased to 54.68% in 1982.[3] In early 1983, the first Spanish-made Nissan Patrol left the plant in Zona Franca, near Barcelona. The first year’s production, planned to be 4,000 to 5000 cars, was earmarked for Spain and Portugal.[3] Exports were to follow during 1984. Nissan Ibérica-built Patrols originally received a Spanish-made Perkins MD27 four-cylinder diesel engine and Spanish transmission to meet local content regulations.[4] Later on, this was replaced by the A428, which evolved into the A428T and then the A428II. Later yet, the RD28 and the RD28T were added to Spanish-made cars.
260 (1986–1993)[edit]
| Third generation (260) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Ebro Patrol (Spain, 1986–1993) Sanxing Desert King (China) |
| Production | 1986–2002 |
| Assembly | Spain: Barcelona |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 5-door wagon/van 2/4-door pickup |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,350 mm (92.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,230 mm (166.5 in) LWB: 4,690 mm (184.6 in) |
| Width | 1,689 mm (66.5 in) |
| Height | 1,980 mm (78.0 in) |
The 260 series was a facelifted version of the Spanish-built 160 (easily spotted by the rectangular headlamps) sold in Europe and available in SWB and LWB with L28, SD33, RD28 and RD28T engines. The SD-engined version, at least in the UK market, had a 24-volt electrical system. Nissan helped Nissan Ibérica amortize plant investments. The 260 Patrol later received a facelift with a new grille similar to that of the Y60 series which succeeded this generation elsewhere. Spanish production continued until 1994 for export and until 2002 for the Spanish domestic market.
Fourth generation (Y60; 1987)[edit]
| Fourth generation (Y60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Safari (Japan) Ford Maverick (Australia) Yunbao YB2030 (China; JV) |
| Production | 1987–1997 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Kanda; Zama (1987–1993) South Africa: Rosslyn (1991–2001) Spain: Barcelona (1988–1998) Philippines: Makati (1990–1998), Santa Rosa City (1998–2000) China: Huadu |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door wagon 5-door wagon/van 2-door pickup |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | Petrol: 3.0 L RB30S I6 4.2 L TB42S/TB42E I6 Diesel: 2.8 L RD28T I6 turbo 4.2 L TD42 I6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed RE4R03A automatic 5-speed FS5R50A manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,400 mm (94.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,285 mm (168.7 in) LWB: 4,845 mm (190.7 in) |
| Width | SWB: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) LWB: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) |
| Height | SWB: 1,810 mm (71.3 in) LWB: 1,815 mm (71.5 in) |
Pre-facelift Nissan Patrol ST
The Y60 was radically different mechanically from its predecessors, as it was the first Patrol with coil-spring suspension, increasing comfort and improving rough-ground handling. All Y60 Patrols had a three-link live axle suspension set-up at the front, with all wagons (SWB, LWB, and SWB LW) adopting a five-link set-up at the rear. The utility model was available with both a leaf-spring rear axle, and from 1994 onwards, a choice of the same coil-spring rear axle as the wagons. Sway bars were included on both front and rear coil-spring live axles. Power steering was standard. Some wagon models had front and rear disc brakes, while the utility retained rear drum brakes. The introduction of a synchromesh on reverse gear was another improvement.
The alternative model codes of GR and GQ were applied to left- and right-hand drive models, respectively.
Most models had a rear limited slip differential and some variants had a vacuum or electric solenoid-operated manual rear differential lock. A rear sway bar release mechanism appeared on some models. Some Y60s had a power take-off-driven front-mounted winch, with an in-cab control lever to the right of the gearstick.
The Patrol was also branded as Safari in Japan, depending on which Japanese dealership was offering it – Safari at Nissan Prince Shop and Patrol at Nissan Bluebird Shop. The Safari was available with an optional 24V electrical system, instead of the standard 12V. This was the first series that placed the exterior dimensions in the higher tax bracket for the wider exterior measurement as defined in Japanese Government dimension regulations and the larger engines added a higher road tax obligation for Japanese owners.
The TD42 and TB42 were available with either a five-speed manual or a four-speed automatic gearbox. The RD28T and the RB30 offered only a five-speed manual.
Trim levels in Australia included:
- DX with manual mirrors, no central locking, vinyl interior, optional AC, manual locking hubs
- RX (from 1995) with electric mirrors, central locking, carpet interior, AC, manual locking hubs
- ST with electric windows, electric mirrors, central locking, carpet interior, AC, automatic locking hubs
- Ti (from late 1989) was equipped with an electronic fuel-injected engine, electric windows, electric mirrors, central locking, velour and carpet interior, rear AC, seven-speaker sound system, alloy three-spoke wheels, and automatic locking hubs. It had a high roof design with sunroof until 1991. Leather and woodgrain trim was made standard in 1992 with the Series 2.
Several dealer-fitted accessories were available, including sunroofs, roof racks, tow bars, driving lights, cargo barriers, and side steps. The TD42 was available with an optional Safari turbocharger at some Australian dealers.
Trim levels in Europe varied by country. These include designations such as SLX, LX, LW, and many others in France. Finnish Patrols came standard with two batteries. LW (1996–1997) featured a lightweight body, reducing the weight by 50 kg (110 lb) and a special smaller body (40 mm [1.6 in]). These were produced only for extreme off-road championships. The engine and chassis remained the same.
1995–1997 Nissan Patrol (GQ II) RX wagon (Australia)
Ford Maverick wagon (Australia)
Two major updates came in Australia, one in 1992 (GQ Series 2), and one in 1995 (minor facelift). The most notable changes in 1992 were the introduction of fuel-injection on the TB42 motor, EGR valve and oil cooler on the RD28T, new seats, new trim, sound deadening, and side intrusion bars. Other 1992 Series 2 refinements included a revised transmission and suspension, and introducing bigger brakes, bigger wheels, and the standardization of limited slip differentials and auto-freewheeling hubs. This update included new seats, trim, and side intrusion bars.
In 1991, the rear indicators, tail lights, and brake lights were relocated to the bumper from the body to meet Australian Design Rules, but they stayed the same in European versions. In 1992, another set of indicators was placed on the front quarter panel.
In August 1993, the TD42 lost weight to reduce fuel consumption and increase maximum engine speed. This had the side effect of weakening the engine. The original engine can be identified by its silver rocker cover, whereas the lightened engine featured a black rocker cover. The RD28T got some extra changes, moving the vacuum pump from behind the alternator to the top of the engine. Driver-side airbags appeared in some European models.
Changes in 1995 featured a minor facelift, with a redesigned front grille and the RX model entering Australia.
Known weaknesses included vibrations from the front end (largely fixed under warranty), cracking hinges on the rear door (due to the spare tyre’s weight), and rust on rear window frames. The RD28T and TB42 engines suffered from head gasket issues when driven with a heavy foot. European five-speed gearboxes suffered from bearing failures in fifth gear at high mileages. However, the TD42 was highly reliable. Patrols are known for their strong axles and good limited slip differential (when so equipped).
From 1988 to 1994, Ford Australia rebadged the Y60 Patrol as the Ford Maverick. This was a result of the Button car plan devised by the government of Australia. The car was mechanically similar, although the Nissan version had rear disc brakes depending on vehicle grade, while the Ford mostly had drum brakes and featured different paint colours and trim levels.
All wagons had a 95-liter main fuel tank with the utility having a 90-liter tank and the option of a 95-liter second tank.
Engine specifications[edit]
| Engine code | Displacement | Bore x stroke | Power | Torque | Compression ratio | Design | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB30S | 2962 cc | 86 x
85mm |
100 kW at 4800 rpm | 224 Nm at 3000 rpm | 9.0:1 | Inline-six SOHC, petrol | Aluminum crossflow cylinder head |
| TB42S | 4169 cc | 96 x
96mm |
125 kW at 4200 rpm | 325 Nm at 2800 rpm | 8.3.1 | Inline-six Pushrod, petrol | Crossflow cylinder head, high camshaft |
| TB42E | 135 kW at 4400 rpm | 320 Nm at 3200 rpm | 8.3:1 | ||||
| RD28T | 2826 cc | 85 x
83mm |
91.9 kW at 4400 rpm | 255 Nm at 2000 rpm | 21.2:1 | Inline-six SOHC, diesel | Turbocharged |
| TD422 | 4169 cc | 96 x
96mm |
85 kW at 4000 rpm | 264 Nm at 2000 rpm | 22.7:1 | Inline-six pushrod, diesel | Crossflow cylinder head, high camshaft |
Fifth generation (Y61; 1997)[edit]
| Fifth generation (Y61) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Safari (Japan) |
| Production | October 1997 – 2016[5] 1997–present (continues in selective countries) |
| Assembly |
|
| Designer | Masato Takahashi (1994) Junichi Sakai (facelift: 2003)[6] |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,400 mm (94.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,440 mm (174.8 in) LWB: 5,080 mm (200.0 in) |
| Width | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
| Height | 1,855 mm (73.0 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,473 kg (5,452 lb) |
Cab chassis
5-door SUV
3-door SUV (facelift)
Nissan Safari (facelift)
Interior
Y61 models first appeared in December 1997, available in 4.5- and 4.8-litre petrol, 2.8-, 3.0-, and 4.2-litre turbo-diesel and 4.2-litre turbo-diesel intercooler variants. The alternative model codes of GR and GU were applied to left- and right-hand drive models, respectively.
The drivetrain was changed in this model, including larger CVs and less synchros in the manual gearboxes. The differential housings were widened to fall inline with the new body shape, but centers remained the same (H233 and H260). Some petrol wagons received a coil version of the H260 differential.
Comfort levels were increased over GQ, especially in the seating and NVH areas.
GU IV onwards[edit]
For the 2005 model year a significant facelift model was released, with new headlights, box flares on each guard and larger tail lights. The troubles that plagued the ZD30 diesel around the variable turbo geometry were resolved by this refresh.
That same year, Nissan stopped selling the Safari in Japan due to poor sales. Nissan also made a two-door pickup version of the Y61 series available as cab chassis and with a style side tray in some markets. Although a new model was launched, this Y61 series still sells for offroad enthusiasts but with few options.
Its TB48DE engine is very popular among the tuning community in the middle east, especially in the UAE. The TB48DE engine is easily modifiable and is shown to be able to handle over 2,000 hp (1,500 kW) for several sand hills and sand drag challenges in the region.
As of 2014, Nissan discontinued the fifth generation model worldwide, except for South Africa, the Middle East, Paraguay, Haiti, Philippines, Nepal, Bolivia, Sri Lanka, and some African and Eastern European countries where the 4×4 competed against the Toyota Land Cruiser (J70). In Australia, the Y61 was sold until 2016, alongside the Y62.
Several special edition trims have been also been released in respective regions where the Y61 was and are currently being sold, of which some of them are The Presidential edition and 4XPRO edition (Philippines), The Legend edition (Philippines, South Africa and Australia), The ‘Special’ Super Safari edition (Middle East), The Falcon edition (Middle East), Gazelle, Gazelle Storm and Gazelle X editions (Middle East).
The Y61 is also still being produced for and used by United Nations agencies across different countries as well as some military branches and government sectors. They are mainly being used as security escorts vehicles, chief personnel carriers and off pavement patrol units.
Sixth generation (Y62; 2010)[edit]
| Sixth generation (Y62) | |
|---|---|

Pre-facelift |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Armada (2016–present) Infiniti QX56/QX80 Nissan Patrol Royale (Philippines) |
| Production | January 2010 – present |
| Assembly |
Russia: Saint-Petersburg, (SKD, 2012–2014) |
| Designer | Taiji Toyota (2007) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size SUV |
| Body style | 5-door SUV |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Y62 |
| Related | Infiniti QX56/QX80 Nissan Armada (Y62) Nissan Terra Nissan Navara (D23) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 3,075 mm (121.1 in) |
| Length | 5,165 mm (203.3 in) |
| Width | 1,995 mm (78.5 in) |
| Height | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,695–2,795 kg (5,941–6,162 lb) |
The all-new, sixth generation, Y62 series Nissan Patrol was launched on 13 February 2010 in Abu Dhabi.[9] A luxury version (Z62) was sold as the Infiniti QX56 from 2010 (the first time that a Patrol-based vehicle had been sold in North America since 1969), which was later renamed the Infiniti QX80 in 2013. The Y62 was introduced in North America under the Armada nameplate in 2016, for the 2017 model year. It was presented as a replacement for the Titan-based first generation Nissan Armada (WA60).
As of 2017, the Y62 is powered by either a 275 hp (205 kW) / 394 N⋅m (291 lb⋅ft) 4.0-litre VQ40DE V6 engine for the entry level XE and SE trims or a more powerful 400 hp (298 kW) / 560 N⋅m (410 lb⋅ft) 5.6-litre VK56VD V8 engine for the upper level trims. The NISMO edition uses a tuned version of the 5.6-litre V8 producing 28 additional horsepower. Prior to the introduction of the 4.0-litre V6, a lower output 317 hp (236 kW) / 526 N⋅m (388 lb⋅ft) 5.6-litre VK56DE V8 was designated for the entry level trims.
As of 2017, all models come with a 7-speed automatic transmission although Nissan previously offered a 5-speed automatic and also a 6-speed manual for the entry level trim. A variable 4×4 mode package allows switching between four drive modes: sand, on-road, rock and snow. A Hydraulic Body Motion Control System is available. An electronic-locking rear differential, hill start and hill descent control, as well as lane-departure warning, computer assisted braking and stability control. The Infiniti version launched in the United States in 2010, the first Patrol sold there since the 60 series. The Nissan Patrol launched in Australia in early 2013.[8]
The Nissan Patrol is offered in various different trim levels in the Middle East: XE, SE, SE-Platinum City, LE, LE-Titanium, LE-Platinum City and NISMO Edition. In Australia the Ti and Ti-L trim levels are offered.
-
Rear view (pre-facelift)
-
Interior
Facelift[edit]
In 2014, a significant facelift arrived, with revised tail lights with red elements present, globe housings and built-in LED headlights. A new tan interior was added and new sets of wheels.
Nissan introduced a limited-run Patrol Black Special Edition in 200 units. These cars offer several enhancements such as red seats, chrome detailing and a black matte exterior paint scheme.
Nissan gave a second facelift to the 2019 Patrol before it will have a new version by 2020. Changes include a new front bumper featuring a deeper apron and a traditional round housing. The vehicle will be equipped with Nissan’s Intelligent Mobility driver-assistance features like lane keeping assist, forward collision warning, automatic emergency braking for front and rear, rear cross traffic alert, and blind spot monitoring.[10]
-
First facelift
-
Rear view (first facelift)
-
Second facelift
-
Second facelift (China)
-
Rear view (second facelift)
-
Interior (second facelift)
Patrol Desert Edition[edit]
The Desert Edition comes with the 400 hp 5.6-litre (5552cc) engine, manually-adjusted cloth seats, navigation and regular suspension instead of the hydraulic body-control system.[11]
Patrol Nismo[edit]
On launching the Nismo brand in the Middle East, the Nissan Patrol Nismo was introduced at the launch event in Dubai along with the GT-R Nismo and 370Z Nismo. Unlike the standard Patrol, the Nismo version comes with (5.6-litre) V8 with 428 hp (319 kW) engine tuned by Nissan’s Takumi craftsmen. The suspensions is upgraded with Bilstein shocks and fitted with 22-inch forged-alloy wheels.[12]
-
2018 Nissan Patrol Nismo (front)
-
2018 Nissan Patrol Nismo (rear)
References[edit]
- ^ Ramey, Jay (17 September 2013). «This may be the oldest surviving Nissan in North America». Autoweek. Hearst Autos, Inc. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ^ Nissan Gamma [Nissan range] (brochure) (in Flemish), Aartselaar, Belgium: N.V. Nissan Belgium S.A., 1984, p. 1
- ^ a b Visart, Etienne, ed. (10 March 1983). «Un constructeur Japonais fabrique en Europe!» [A Japanese manufacturer builds in Europe!]. Le Moniteur de l’Automobile (in French). Brussels, Belgium: Editions Auto-Magazine. 34 (764): 24.
- ^ Walker, Alan (September 1982). Kennett, Pat (ed.). «The great European retreat». Truck. London: FF Publishing: 36.
- ^ «History». Nissan Shatai. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ «A Revitalised Design for Nissan’s 2005 Patrol». Next Car. 12 October 2004. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ Opara, Theodore (27 April 2014). «First built in Nigeria Nissan Patrol rolls off production line». Vanguard. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ a b «2013 Nissan Patrol (Y62) Australia Introduction» (PDF).
- ^ «Stunning looks coupled with unstoppable 4WD upgrades make Nissan Patrol new class-leader as Nissan’s ‘Hero of All Terrain’» (Press release). Nissan. 13 February 2010. Archived from the original on 22 April 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ «Nissan gives 2019 Patrol a (slightly) new look – Auto Industry News». AutoIndustriya.com. 8 October 2018. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- ^ «First drive: 2016 Nissan Patrol Desert Edition in Liwa UAE»
- ^ «2017 Nissan Patrol Nismo | Drive Arabia»
External links[edit]
Media related to Nissan Patrol at Wikimedia Commons
- Nissan Patrol Archived 12 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine at Nissan’s global website
- Nissanh Heritage Nissan Safari
Nissan Patrol
Общие данные
| Иные обозначения: | Nissan Safari |
Характеристики
Массово-габаритные
Динамические
На рынке
Другое
Nissan Patrol — японский автомобиль повышенной проходимости, выпускаемый компанией Nissan с 1951 года. С 1980 года известен в Японии как Nissan Safari. Nissan Patrol четвёртого и пятого поколения являлись основным транспортным средством Ирландской армии. За всю свою историю принцип конструкции остался неизменным: мощная рама, неразрезные мосты (кроме Y62), тяговитый неприхотливый двигатель. Patrol отличается высокой проходимостью и надежностью даже при тяжелых условиях эксплуатации. Кузов — 3-х или 5-и дверный универсал соответственно 5-и или 7-и местный салон. Двигатели дизельные 2,8 л (116 л. с.) RD28, 2.8 л (125 л. с.) ZD30, 3.0 л (158 л. с.) TD42, 4,2 л (145 л. с.) TD42DTTI. Бензиновые 4,5 л (200 л. с.) TB45 и 4,8 л (245 л. с.) и топовая версия двигателя, доставшаяся в наследство от Infiniti QX56 — 5,6 л (405 л. с.) VK56VD. Основным, и, явным недостатком топового мотора (в сравнении с основными моделями полноразмерных внедорожников от Lexus, Cadillac и т.д.) является отсутствие особо востребованной системы отключения половины цилиндров (особенно на американском рынке — для которого и создавался данный автомобиль) двигателя, при которой снижается расход топлива (соответственно и вред наносимый окружающей среде). Коробка передач автоматическая 4/5 — диапазонная (привычная и соответствующая низкооборотистым, высокообъемным моторам V8) или механическая, 5-ступенчатая (для любителей офф-роуда). Поскольку в раздаточной коробке отсутствует межосевой дифференциал, поэтому передний мост подключается жестко по Part-time схеме. Подвеска спереди и сзади пружинно-рычажная зависимая со стабилизатором поперечной устойчивости.
Содержание
- 1 Первое поколение (1951—1960)
- 2 Второе поколение (1960—1980)
- 3 Третье поколение (1980—1988/—1994)
- 4 Четвёртое поколение (1987—1997)
- 5 Пятое поколение (1997-2010)
- 6 Шестое поколение (2010—настоящее время)
Первое поколение (1951—1960)
Первое поколение вседорожников Nissan Patrol появилось в 1951 году.
Второе поколение (1960—1980)
В 1960-м году второе поколение (Patrol 60 Series), которое выпускалось без значительных изменений в течение 20 лет.
Третье поколение (1980—1988/—1994)
Четвёртое поколение (1987—1997)
В 1988 году был запущен в производство Nissan Patrol Y60
Пятое поколение (1997-2010)
а в 1998 — Y61. В 2004 году рестайлинг модели: новая оптика, бамперы, новый бензиновый двигатель 4,8 л, 245 л. с.
Шестое поколение (2010—настоящее время)
В 2010 году на рынок выходит совершенно новый Nissan Patrol Y62, который отличается от предшественников необычайно роскошным кожаным салоном, массой электронных помощников, двигателем 405 л. с. и объемом 5.6 литра, независимой подвеской.
|
Автомобили «Nissan» с 2000-х до наших дней |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Класс | 2000-е | 2010-е | |||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
| Малый класс | Micra K11 | Micra K12 | Micra K12C | Micra K13 | |||||||
| Гольф-класс | Pulsar N16 | ||||||||||
| Almera N16 | |||||||||||
| Renault Samsung SM3 | Almera Classic B10 | ||||||||||
| Tiida C11 | |||||||||||
| Sunny B15 | Sentra B16 | ||||||||||
| Bluebird Sylphy N16 | Bluebird Sylphy G11 | ||||||||||
| LEAF | |||||||||||
| Средний класс | Avenir W11 | ||||||||||
| Altima L30 | Altima L31 | Altima L32, Altima Hybrid | |||||||||
| Primera P11 | Primera P12 | ||||||||||
| Бизнес-класс | Cedric, Gloria (Y34) | Fuga Y50 | Fuga Y51 | ||||||||
| Cefiro A33 | Teana J31 | Teana J32 | |||||||||
| Laurel C35 | |||||||||||
| Представительский класс | Cima Y33 | Cima F50 | |||||||||
| President G50 | President PGF50 | ||||||||||
| Спорткары | 300ZX | 350Z | 370Z | ||||||||
| R34 | Skyline V35 | Skyline V36 | |||||||||
| Silvia S15 | GT-R | ||||||||||
| Микровэны | Cube Z10 | Cube Z11 | Cube Z12 | ||||||||
| Note | |||||||||||
| Минивэны | Prairie | Liberty | Lafesta | ||||||||
| Caravan Elgrand E50 | Caravan Elgrand E51 | ||||||||||
| Serena C24 | Serena C25 | Serena C26 | |||||||||
| Presage U30 | Presage U31 | ||||||||||
| Универсалы | Wingroad Y11 | Wingroad Y12 | |||||||||
| Кроссоверы | Juke | ||||||||||
| Qashqai | |||||||||||
| Qashqai+2 | |||||||||||
| X-Trail T30 | X-Trail T31 | ||||||||||
| Murano Z50 | Murano Z51 | ||||||||||
| Внедорожники | Pathfinder R50 | Pathfinder R51 | |||||||||
| Mistral | |||||||||||
| Patrol Y61 | Patrol Y62 | ||||||||||
| Armada | |||||||||||
| Пикапы | Titan | ||||||||||
| Navara D21 | Navara D40 |
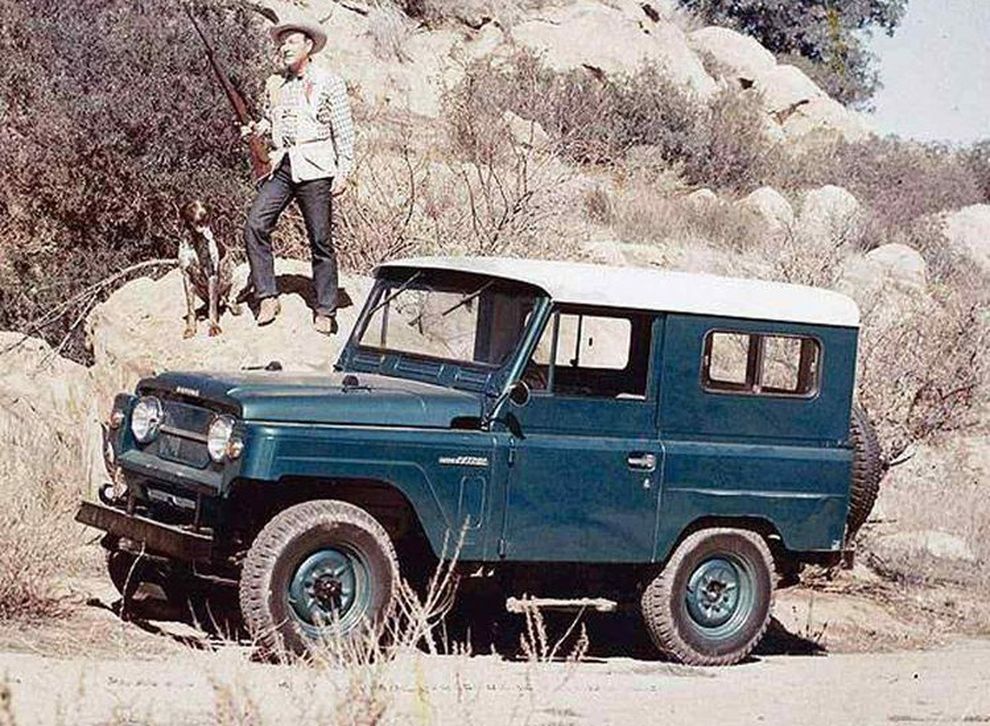
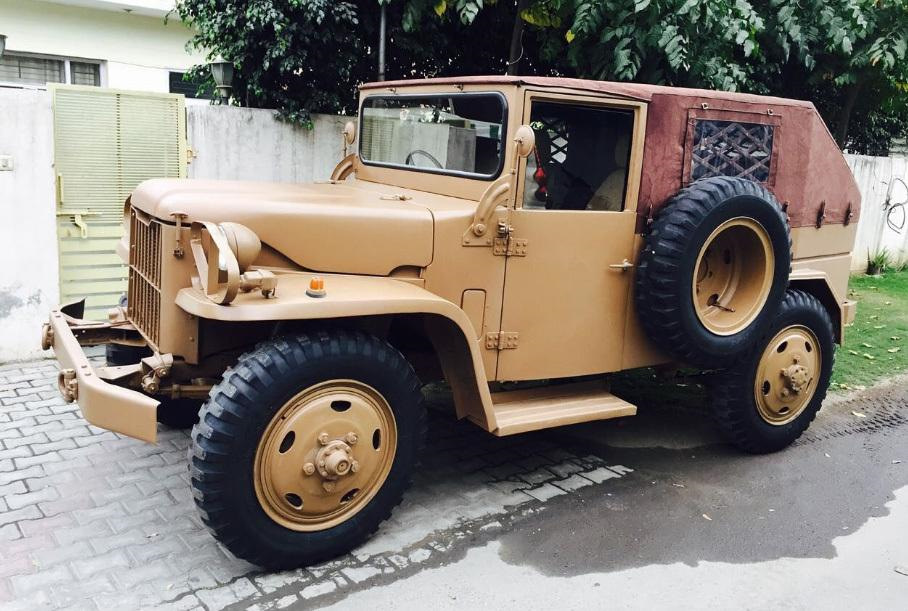
Недавно один из наших читателей написал в комментариях, что его удивил факт появления Nissan Patrol уже через шесть лет после окончания Второй мировой – в 1951 году. Мы решили раскрыть тему чуть глубже и вспомнить историю появления легендарного внедорожника.
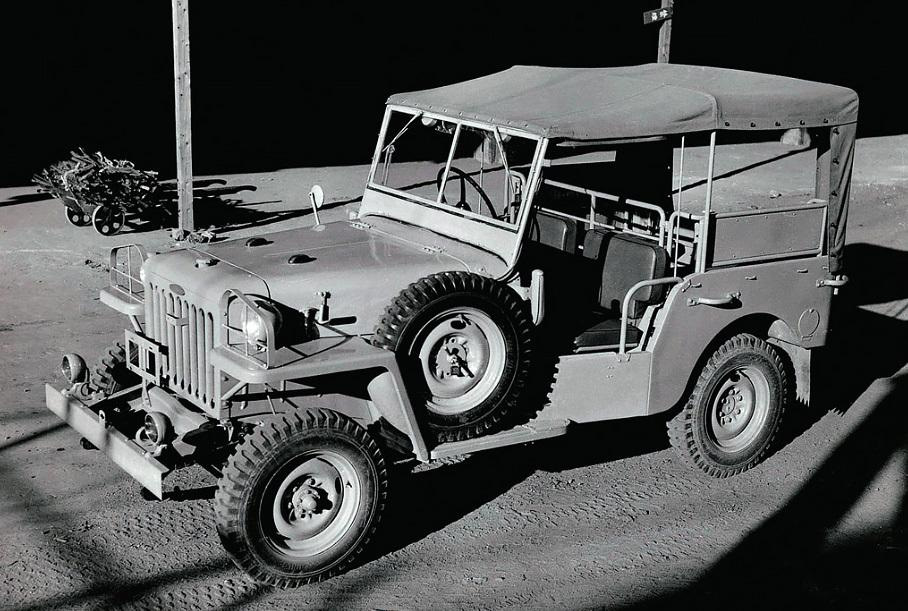
Нужно ли говорить, что после окончания Второй мировой войны японская промышленность в прямом смысле слова лежала в руинах. Предстояло начинать с нуля. Поэтому нет ничего удивительного, что у японцев возникло искушение не возиться с собственным автопромом, а покупать машины у американцев. Тем более, что в те годы автомобили родом из США по праву считались лучшими в мире. Однако, американцы сами подтолкнули японцев к возрождению национального автопрома. Началась Корейская война и армия потребовала большое количество полноприводной техники, а поскольку от Японских островов до Южной Кореи рукой подать (ну почти), вполне логично было не тащить машины из Детройта, а производить их рядом с театром боевых действий, на японских заводах – по образу и подобию.
РАННИЕ ГОДЫ
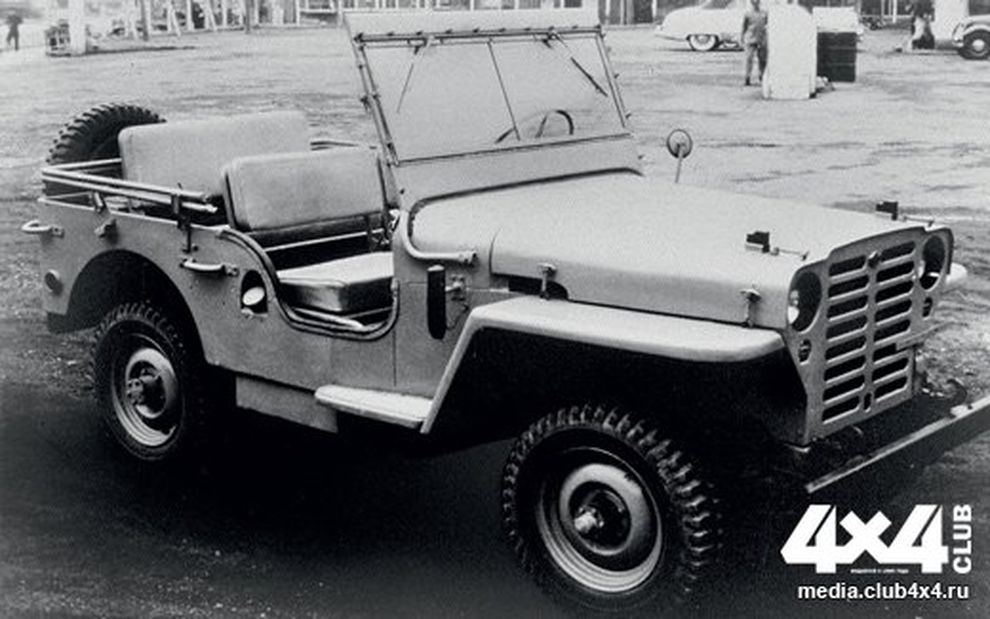
Одним из трёх производителей, получивших заказ на армейский вездеход, стала фирма Nissan. Её инженеры быстро подготовили прототип, естественно сильно напоминавший Willys MB, а в 1951 году первые Nissan Patrol серии 4W60 уже сошли с конвейера. На первый взгляд могло показаться, что новый японский внедорожник – точная копия американского Jeep времён Второй мировой, только с правым рулем. Если, конечно, не принимать во внимание характерную горизонтальную радиаторную решётку и небольшой горб на капоте. Однако, если смотреть сбоку, то оказывалось, что японская копия ощутимо длиннее американского оригинала – 3 615 мм у Patrol, при базе 2 207 мм, против соответственно 3 378 мм и 2 032 мм у MB. Причиной тому был рядный шестицилиндровый бензиновый двигатель Nissan NAK, позаимствованный у автобуса. При рабочем объёме в 3.7 литра он развивал мощность 75 л. с. и крутящий момент 206 Нм. Вес машины составлял 1,5 тонны. В остальном конструкция принципиально не отличалась от американского прототипа: коробка передач четырёхступенчатая, передний мост подключаемый (раздаточная коробка без понижающей передачи), подвеска всех колёс – зависимая рессорная, а тормоза барабанные гидравлические. Само собой разумеется, что все эти узлы и агрегаты базировались на прочной раме лестничного типа.
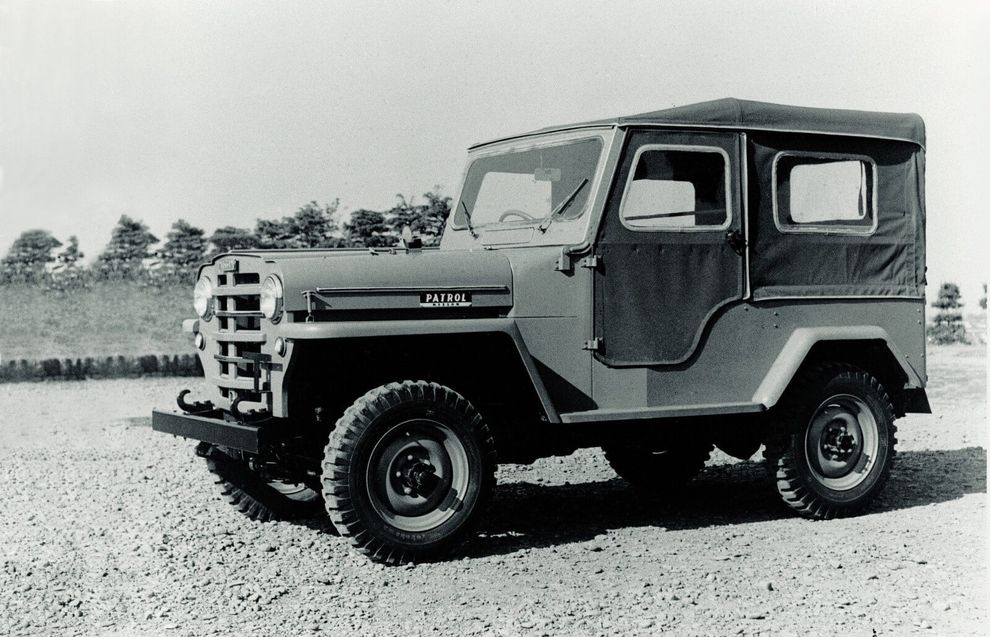
Вскоре был налажен и выпуск полностью закрытой модификации с кузовом универсал. А в 1955 году свет увидел модернизированный Patrol серии 4W61 с новым, тоже шестицилиндровым, двигателем NB объёмом 3 665 куб. см, развивавшим уже в 92 л. с. Чуть позже его сменил четырёхлитровый Nissan NC, выдававший 105 л. с. и крутящий момент 264 Нм. Потяжелевшая всего на пятьдесят килограмм машина разгонялась до 105 км/ч. Внешне она отличалась выступающими фарами в стиле Willys CJ3, цельным лобовым стеклом, и хромированным декором а-ля Willys Station Wagon. В 1958 году появляется очередная улучшенная версия – Patrol 4W65. Внешне она отличалась дополнительными хромированными полосками на радиаторной решётке и расширенной колеёй, для которой потребовались новые крылья. Любопытно, что передние были подозрительно похожи на крылья так и не пошедшего в серию Willys CJ4, а задние навевали мысли о советском ГАЗ-67Б, что, в общем-то, неудивительно. Довольно много «газиков» попадало к американцам и японцам в качестве трофеев во время Корейской войны. Кроме того, в том же году были выпущены обновлённый восьмиместный универсал WG4W65 на удлинённой до 2 500 мм базе, и пожарная версия с насосом и небольшим запасом воды (или пеногенератором). А в конце 1959 года в продажу поступил переходной 4W66 Patrol с тем же мотором, но форсированным до 125 л. с. Выпускали его недолго – до лета 1960-го, когда свет увидело второе поколение – 60-я серия.
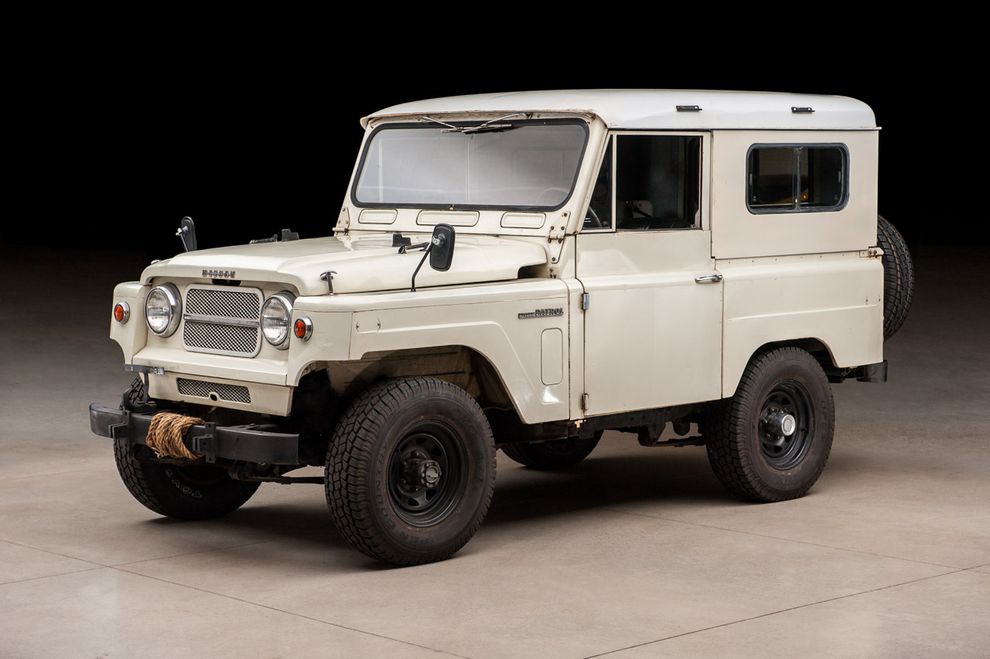
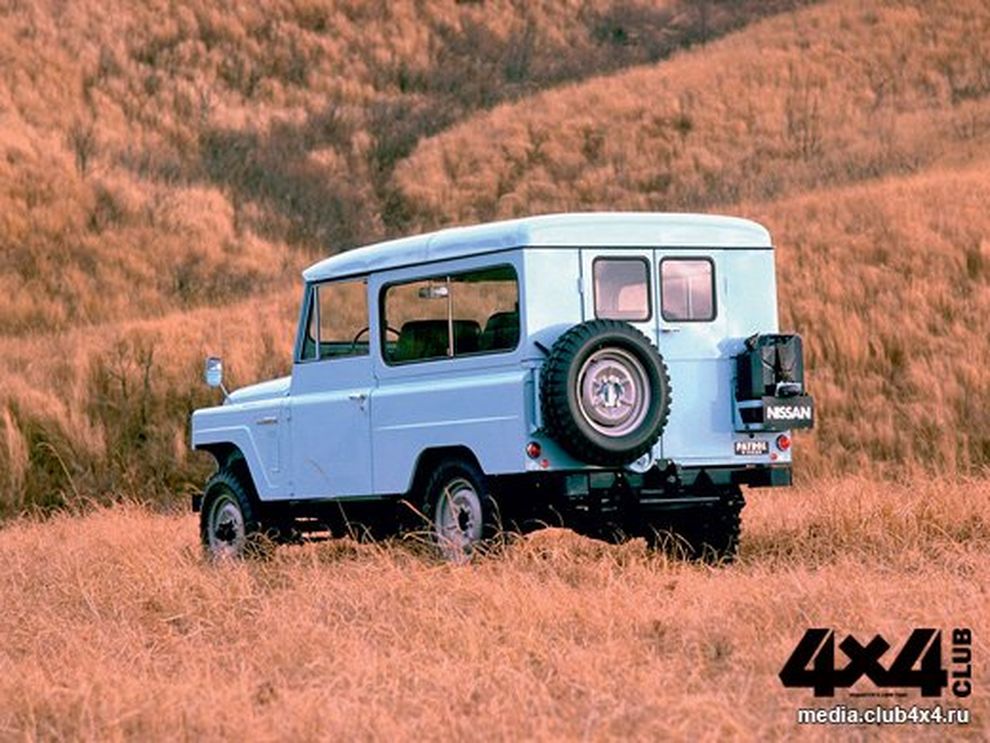
ЯПОНО-ИНДИЙСКИЙ
Главным отличием нового Nissan Patrol 60 стал кузов без выступающих крыльев, решённый в новомодном линейном дизайне. Впрочем, боролись разработчики не за стиль: при уменьшении ширины с 1 700 до 1 693 мм, им удалось существенно увеличить внутреннее пространство. Теперь на передних сиденьях (узкое водительское и широкое пассажирское) можно было сидеть втроём. При этом все без исключения Patrol комплектовали нормальными стальными дверцами (быстросъёмными) со стеклоподъёмниками. Электропроводка была полностью защищена от воды, а в качестве дополнительного оборудования предлагали лебёдку и два вала отбора мощности.
Выпускали шесть типов кузовов: кабриолет, короткий универсал L60 со съёмным стальным верхом (оба с откидным лобовым стеклом), длиннобазный трёхдверный универсал WG, пикап 62ZG60H (с конца 1960-х), шасси для спецкузовов G60H-A, и пожарный автомобиль FH60. Малыми партиями производили пятидверные универсалы (база 2 800 мм). По желанию покупателя можно было заказать кузов с откидным бортом, распашным бортом или узкой двухстворчатой задней дверью (для закрытых версий). Задние сиденья располагали либо вдоль бортов, либо традиционно – поперек машины.
ЗАВОЕВАНИЕ АМЕРИКИ
Ещё одним поводом для радикального изменения дизайна, стал запланированный на начало 1960-х выход на североамериканский рынок. Надо сказать, что Patrol 60 имел все шансы на успех хотя бы потому, что он был ощутимо мощнее всех потенциальных конкурентов. Двигатель от грузовика с клапанным механизмом OHV развивал 134 л. с. (по SAE) против 72 л. с. у Jeep CJ5 и 93 л. с. у International Scout. Коробки передач у японца были механические, трёх- или четырёхступенчатые. Специально для американцев рычаг переключения переместили на рулевую колонку. Снаряжённая масса, в зависимости от длины базы и типа кузова, колебалась в пределах 1 540-1 800 кг. Правда у него так и не появились автоматическая коробка передач и гидроусилитель (почти обязательный набор для американских внедорожников конца 1960-х), а мощность двигателя никогда не превышала 147 л. с., чего вполне хватало для того, чтобы разогнаться до 125 км/ч (с трёхскоростной КП). Но главной проблемой было вполне понятное недоверие к новой марке, тем более японской (война-то отгремела совсем недавно). Сыграла свою негативную роль и слабая рекламная поддержка. Как результат, Patrol второго поколения в Америке не пошёл. С 1961 по 1969 год было продано всего около четырёх тысяч экземпляров.
Зато машина стала популярной в Азии, Латинской Америке и частично в Африке, то есть в тех странах, где позиции Land Rover и Toyota Land Cruiser были не столь сильны. К новому Patrol проявили интерес индусы. С 1969 года на заводе Vehicle Factory Jabalpur (VFJ) начинается выпуск лицензионной копии под названием JONGA. Расшифровывалось это как Jabalpur Ordinance aNd Guncarriage Assembly («Сборка военных машин и лафетов в Джабалпуре»). Автомобиль выпускали тридцать лет (!), причём в 1996 году была предпринята попытка заинтересовать гражданских покупателей, установив под капотом дизель от японской Hino. Увы, низкое качество, а также устаревшая конструкция и дизайн не позволили добиться хоть какого-нибудь успеха.
ИСПАНЕЦ И РЕЙДЕР
В 1980 году место ветерана серии 60 занял новый Nissan Patrol серии 160. В Японии его продавали как Nissan Safari (можно отличить по «форточкам» в передних дверях), а в некоторых странах Южной Америки его запомнили под именем Samurai. От предшественника он отличался комфортабельным и наконец-то четырёхдверным кузовом (базу удлинили почти до трёх метров), решённым в духе ультрасовременного на тот момент американского «квадратного» дизайна. Длина автомобиля составляла 4 690 мм, ширина – 1 690 мм, а высота – 1 805 мм. При этом был сохранён короткобазный (2 350 мм) кабриолет, с дугой безопасности и съёмным жёстким или откидным мягким верхом, а также пожарный автомобиль. Кроме того, можно было заказать модификацию с высокой крышей (High Roof) и распашной задней дверью. В зависимости от комплектации в багажном отсеке ставили либо две откидные лавки по бортам, либо складной третий ряд сидений.
Новый Patrol обзавёлся современной пластиковой панелью приборов (вместо стальной) и мощной шумоизоляцией, с ковровым покрытием пола. В максимальной комплектации можно было насладиться кондиционированным воздухом, электростеклоподъёмниками и изящным прибором под названием «кренометр». При этом штатная магнитола на некоторых модификациях размещалась весьма необычно – вертикально, между водительским и пассажирским сиденьями.
Шасси, по просьбам трудящихся, претерпело скорее эволюционные, чем революционные изменения. Никуда не делись ни рама, ни жёсткие мосты на рессорах, ни подключаемый полный привод, ни двухступенчатая раздаточная коробка, но при этом появились автоматические муфты включения передних полуосей (был вариант с механическими), гидроусилитель руля и задний межколёсный дифференциал повышенного трения. Кроме того, Patrol 160 получил новые тормоза (спереди дисковые вентилируемые) с вакуумным усилителем.
Стандартным двигателем остался рядный карбюраторный шестицилиндровый OHV, рабочим объёмом 3 956 куб. см и мощностью 130 л. с. (крутящий момент 294 Нм). Кроме того, покупателям предлагали атмосферный дизель объёмом 3 246 куб. см, который развивал мощность в 95 л. с. и крутящий момент 294 Нм. Он не отличался особой экономичностью (12-18 литров на 100 км), зато ТНВД фирмы Kiki мог без ощутимого ущерба переваривать даже советскую солярку. Максимальная скорость, что с дизелем, что с бензином, у Patrol 160 была одинакова – 130 км/ч.
В 1983 году Patrol/Safari модернизировали и место круглых фар заняли прямоугольные. При этом несколько изменился салон, появились пятиступенчатая коробка передач (а чуть позже и трёхскоростной автомат) и быстроходные двигатели. Новая карбюраторная шестёрка при объёме в 2.8 литра развивала мощность в 134 л. с. Дизель получил турбонаддув, за счёт чего мощность увеличилась до 120 л. с. Скорость бензиновой версии выросла до 150 км/ч (чуть позже до 160 км/ч), что дало повод немецким рекламщикам называть улучшенный Patrol – Sportwagen. В том же году появилась испанская версия Ebro Patrol, которую позже переименовали в Nissan. Основное отличие – упрощённая (поначалу) комплектация и недорогой четырёхцилиндровый дизель объёмом 2.7 литра и мощностью 70 л. с. Во второй половине 1980-х производство модели 160 окончательно перебралось в Испанию. По такому случаю её переименовали в 260. При этом машина немного подросла в размерах, за счёт расширителей колёсных арок, и получила почти те же двигатели, что и японское семейство. Выпускали её вплоть до 2003 года.
В ЧЕСТЬ СЛАВНЫХ ПОБЕД
В конце 1987 года был представлен новый Nissan Patrol GR (Grand Raid), названный в честь спортивных успехов заводской раллийной команды. У него была рычажная пружинная зависимая подвеска всех колёс и расширенная колея, из-за чего кузов пришлось дополнить пухлыми подштамповками, имитирующими крылья легковых автомобилей 1930-х годов. Сходство с ними ещё более усиливалось алюминиевыми подножками. В итоге «рейдер» раздался вширь до 1 800 мм, что вкупе с новой подвеской весьма положительно сказалось на управляемости и комфорте. Поскольку автомобиль существенно потяжелел, его оснастили новыми шестицилиндровыми моторами – дизельным и бензиновым одинакового объёма 4.2 литра и мощностью соответственно 115 (турбоверсия выдавала 125) и 170 л. с. С последним двигателем GR разгонялся до 170 км/ч. Для экономных европейцев предназначался турбодизель 2.9 литра на 115 л. с.
Дизельные Patrol GR, а также испанские Patrol 260, запомнились нам как ярчайшие представители первой волны иномарок, массово завозившихся в СССР в конце 1980-х. Что интересно, первые рекламные полосы, с типичными образцами буржуазной автомобильной роскоши и излишеств, размещали не в каком-нибудь «За рулём», а в вольнодумном, но при этом страшно далёком от техники журнале «Огонёк». Советским водителям японские внедорожники казались пределом совершенства. Они были просты по конструкции, редко ломались и отличались ремонтопригодностью. При этом, за счёт самоблокирующегося дифференциала и мощных тяговитых двигателей, Patrol отличался отменной проходимостью. Позже, уже в 1990-х, он стал объектом поклонения любителей самого причудливого тюнинга, да и сейчас в определённых кругах Nissan Patrol GR вспоминается со слезами на глазах.
Текст Георгия Варфоломеева
Здравия. В этот раз хочу рассказать вам о легендарном внедорожнике, о котором наверное известно даже в отдалённых уголках мира. Предлагаю вместе узнать- чем же так прославился этот замечательный внедорожник, который находится на конвейере достаточно долго времени сменяя поколение за поколением. Имя этому внедорожнику- Nissan Patrol.
История Nissan Patrol. Внедорожник, который побеждал в Дакаре и ставил на место гиперкары.
Nissan Patrol — знаменитый вездеход с долгой славной историей. Без него Toyota Land Cruiser оставалась бы единственным полноразмерным внедорожником-иконой из Японии. Впрочем, последние годы всё выглядит именно так: «двухсотки» постоянно мелькают перед глазами, а как выглядит Patrol, мы, кажется, скоро забудем…
За причинами такой вопиющей несправедливости далеко ходить не надо — последние три года полноразмерный внедорожник Nissan у нас официально не продается. А когда продавался, то не пользовался успехом: богатая комплектация и отменная проходимость — это, конечно хорошо, но с одним только бензиновым V8 объемом 5,6 литра в России каши не сваришь. И ладно бы этот недостаток компенсировала привлекательная цена, но нет — машины поколения Y62 плыли к нам из Юкухаси, обрастая в пути налоговыми надбавками.
Фиаско последнего Патрола в России, впрочем, не разбило Nissan сердце и не подстегнуло сворачивать производство внедорожника. Patrol по-прежнему обожают на Ближнем Востоке, высоко ценят в Австралии, тепло вспоминают в Испании и, конечно же, глубоко уважают в родной Японии. Ведь именно на плечах внедорожников, как Nissan Patrol, Страна восходящего солнца смогла сотворить то самое «экономическое чудо».
Япония стала последней страной, которая вышла из Второй мировой войны, поэтому во второй половине 40-х годов инфраструктура страны находилась в упадке. Разрушены были не только здания, но и дороги, что ограничивало грузопассажирское сообщение и быструю отстройку. Поскольку правительство Японии осознавало, что на создание сети дорог уйдут годы, оно, со свойственной Востоку нестандартностью мышления, попросило своих автопроизводителей уделить внимание внедорожникам. Стране нужно было нечто простое, выносливое и неприхотливое к качеству покрытия. Что-то вроде Виллиса.
Компании радостно сказали «будет сделано»… потому что внедорожники были нужны не только родине. Японскими джипами интересовались и американцы: намечался военный конфликт в Корее и армии США нужны были компактные вездеходы в театре военных действий. После тендера, объявленного Соединенными Штатами, создание внедорожников для Nissan, Mitsubishi и Toyota выглядело еще более выгодным.
Mitsubishi Jeep
Компания Mitsubishi к кличу американцев отнеслась расслабленно, но ответственно. В 1952 году был заключен контракт с Willys Overland на мелкоузловую сборку Jeep CJ3A, который впоследствии получил японские двигатели и превратился в Mitsubishi Jeep. Но к тому времени, когда местный Jeep был готов, война в Корее близилась к своему завершению.
А вот Toyota с Nissan подошли к вопросу с большим энтузиазмом и представили вездеходы раньше.
Toyota BJ
Toyota создала новый внедорожник на шасси имеющегося на тот момент грузовика SB. Этот вездеход получил имя Toyota BJ и впоследствии стал небезызвестной Toyota Land Cruiser. Что касается Nissan, то компания пошла и путем Mitsubishi, и путем Toyota. Однако даже это не помогло выиграть Ниссану американский тендер — заказ достался Тойоте. Да, и здесь «Крузер» оказался впереди.
Первым внедорожником Nissan стал 4W70, построенный на шасси Dodge M37 в 1950 году. Фактически, 4W70 и был американским Доджем (лицензированным, что немаловажно), но с силовой установкой японского производства. Однако этот пятиметровый великан не предназначался для американского конкурса — 4W70 использовался только в японской армии для перевозки людей и боеприпасов. Машину также знали как Nissan Carrier.
Nissan 4W70
А вот автомобиль, который компания Nissan построила в соответствии с требованиями американского тендера, звали 4W60. Он, как и Toyota BJ, сильно напоминал Jeep, но технически был полностью японским: своя механическая коробка передач, своя система полного привода типа part-time и, конечно же, свой двигатель — 3,7-литровая рядная шестерка мощностью 75 лошадиных сил. Все это добро досталось 4W60 от 4W70.
Nissan 4W60
Поскольку 4W60 проиграл тендерную битву Тойоте, он отправился не в Корею воевать, а в местные дилерские центры — завоевывать сердца. И местным жителям новинка Nissan пришлась по душе. Да, внедорожник был утилитарным до безобразия (всюду голый металл, крыша — только матерчатая), но машина была надежной, выносливой и могла проехать буквально везде. Именно поэтому 4W60 взяли на вооружение не только фермеры и строители, но и пожарные, медики, военные.
Конечно, продажи нового внедорожника Nissan едва ли были сравнимы с популярностью пращура Land Cruiser, но своя доля рынка у 4W60 была. Поэтому в августе 1955 года Nissan обновил внедорожник до версии 4W61. Из самых заметных изменений — смещенное ближе к капоту цельное ветровое стекло, несимметричные передние сиденья (пассажирское было шире водительского), хромированные элементы радиаторной решетки, а также новый двигатель. Архаичный мотор NAK, доставшийся 4W60 от автобуса, уступил место NB, который при том же рабочем объеме и количестве цилиндров развивал 92 силы. Впоследствии компанию ему составил 105-сильный четырехлитровый мотор NC.
Наконец, в октябре 1958 года «звезда родилась». Обновленный во второй раз внедорожник получил имя 4W65 Patrol и, помимо шильдиков Patrol на изгибах капота, обзавелся новым оперением передка. По части техники изменений не было. В таком виде Patrol выпускался до 1960 года, пока его не сменило новое поколение.
Nissan 4W65
Поскольку внедорожники серии 4W выпускались с именем Patrol чуть больше двух лет, оригинальный Patrol 1958-1960 годов является самым малочисленным представителем рода. Найти его в продаже почти нереально: официально автомобиль продавался только в Японии, но «серыми» каналами несколько экземпляров попали в Латинскую Америку и даже Россию. Сколько из них дожили до наших дней — неизвестно.
Уже начиная со второго поколения, которое получило индекс просто 60, география Patrol расширилась. Как расширилось и число модификаций внедорожника. Помимо короткобазного Патрола (60), у которого расстояние между осями составляло 2200 миллиметров, появился удлиненный на 30 сантиметров вариант (G60), леворульные версии (L60 и GL60 соответственно), удлиненный вариант с жесткой съемной крышей (KG60), полностью закрытый универсал (WG60), сверхдлинный вариант (H60), пикап (ZG60H) и даже пожарная модификация (FH60).
Nissan Patrol 60
Но, независимо от типа кузова, вся 60-я серия оснащалась единственным мотором — четырехлитровой «шестеркой» серии Р, которая совмещалась с механической коробкой передач. На первых порах в «механике» было всего три скорости, но позже число передач было увеличено до четырех. В принципе, комбинация привычная для внедорожников той эпохи. Но едва ли универсальная.
Как уже было сказано, Patrol 60, в отличие от предшественника, официально продавался во многих странах, в том числе на Филиппинах, в США, Австралии, ЮАР. И в тех государствах, где наравне с Патролом можно было купить Land Cruiser, именно внедорожник Toyota продавался лучше. Догадайтесь с одного раза почему. Дело было не в имени — тогда ни Nissan, ни Toyota не были так известны как сейчас.
Просто LC, в отличие от Patrol, еще полвека назад предлагал не только кузовную, но и моторную альтернативу — в том числе дизельную. Что было особенно важно в годы топливного кризиса 70-х — а выпускалось второе поколение Patrol до 1980 года. Или до 1999 года, если учитывать индийские внедорожники Jonga.
Jonga Nissan Patrol
Под именем Jonga (сокращение от Jabalpur Ordinance aNd Guncarriage Assembly) с 1965 года в Индии выпускались армейские внедорожники. По факту это были лицензионные копии Nissan Carrier (4W73) и Patrol (60), оснащенные все теми же японскими двигателями. Служили они долго и усердно, пока в 1999 году не были заменены продукцией отечественной Mahindra. Хотя не факт, что индийские внедорожники были намного лучше устаревших Ниссанов.
Тем не менее, благодаря Джонге в Индии с Nissan Patrol 60 отлично знакомы. А еще Patrol второго поколения хорошо знают в Австралии. Ведь Patrol G60 второго поколения стал первым внедорожником, который без посторонней помощи пересек пустыню Симпсон.
Для понимания картины: пустыня Симпсон — это не песчаный стол. На каждый километр пути приходится по 5-6 дюн, которые образуют песчаные волны высотой до 15-30 метров. Но эти «мелочи» не остановили Регга Спригга и его семью в 1962 году. Много ли на свете людей, которые решатся пересечь одну из крупнейших и опаснейших пустынь в мире на стандартном внедорожнике — да еще и с двумя детьми на борту? Регг — парень не робкого десятка. После этого подвига продажи Nissan в Австралии существенно увеличились.
Чего не скажешь про Соединенные Штаты. Внедорожник попал в Северную Америку в 1961 году и стал первым Ниссаном, который официально продавался в США. До Патрола в Новом свете можно было купить лишь Датсуны. Внедорожник реализовывали через дилерскую сеть Datsun, но на фоне Land Cruiser FJ40 продажи были просто смешными: в период с 1961 по 1969 год было продано около 2200 машин! И это несмотря на рекламные ролики, в которых снимался знаменитый в Америке ковбой Рой Роджерс.
Поэтому, когда настала очередь выпускать третье поколение Patrol, руководство Nissan сразу отказалось от идеи поставлять его в США. Новый Patrol (серия 160) появился в 1980 году и, в теории, был лишен всех недостатков своего предшественника. У него была широкая линейка бензиновых и дизельных двигателей (как четырех-, так и шестицилиндровых), в качестве альтернативы предлагалась автоматическая трехступенчатая коробка передач, а список дополнительного оборудования включал гидроусилитель руля, кондиционер и модные в 80-е годы декоративные наклейки. Для некоторых версий предлагались самоблокирующиеся дифференциалы вместо двуступенчатой раздаточной коробки. А для японского рынка — новое имя: на родине, по какой-то причине, Patrol с третьего поколения начали называть Safari.
Nissan Patrol 160
Nissan Safari 160
В том же самом году, когда Patrol 160-й серии (или MQ, как его знали посвященные) оформил свой дебют, Nissan приобрел почти 36 процентов акций испанского предприятия Motor Ibérica, а к 1982 году доля японцев достигла 55 процентов. Фактически, это означало, что Motor Ibérica, вместе с заводом близ Барселоны, превращался в собственность Nissan. Поэтому с 1983 года на этом предприятии, расположенного в свободной экономической зоне, начался выпуск обновленного Patrol 160, который в Испании и Португалии продавался под брендом EBRO. Для других стран Европы внедорожник реализовывали преимущественно под именем Nissan.
EBRO Patrol 160
160-я серия обновилась в 1983 году и стала неофициально называться MK, хотя это обозначение не встречалось ни в официальных брошюрах, ни в сопроводительной документации. Из важных изменений — новые прямоугольные фары, усиленная передняя подвеска, появление пятиступенчатой «механики», которая почти полностью заместила четырехступенчатую, новая высокая крыша Super Roof, предлагающаяся за доплату, и новый турбодизель SD33T, который дорабатывался из года в год.
Казалось бы, на фоне второго поколения, которое успешно покорило пустыню Симпсон, жизнь третьей генерации получится довольно блеклой. Так бы и было, если бы не энтузиазм технического центра Nissan в Испании. Он настоял на постройке раллийного Patrol для легендарного марафона Париж-Дакар.
Заручившись поддержкой головного офиса и спонсорством компании Coca-Cola, инженеры приступили к работе в начале 1986 года. Уже к лету два боевых автомобиля были готовы. Перед тем, как везти машины в Дакар, их нужно было протестировать, и тут как нельзя кстати оказались Ралли Туниса, Баха Арагон и Ралли Фараонов. Во всех трех гонках Patrol одержал победу в дизельном классе, так что к Дакару команда Nissan шла настроенной на высокий результат.
Но Дакар известен своим тяжелым нравом, поэтому марафон 1987 года давался Патролу непросто. Сначала команда потеряла техничку сопровождения, а после крутого переворота сошел экипаж под номером 212, пилотируемый братьями Хорхе и Хонсе Баблерами. Тем не менее, машина с номером 211, управляемая Мигелем Прието под руководством штурмана Рамона Терменса, смогла добраться до финиша. Она не только стала быстрейшим дизельным автомобилем Дакара, но и первым внедорожником с дизельным двигателем, который вошел в Топ-10 абсолютного зачета: Patrol финишировал девятым.
После победы Nissan дизельных автомобилей в ралли Дакар становилось больше из года в год, и сейчас почти все автомобили, которые принимают участие в марафоне, работают на солярке. Ну а для Nissan Patrol своеобразная победа в Дакаре стала отличной рекламой: продажи в Испании выросли вдвое. Но ненадолго — Patrol третьего поколения готовился уйти на покой.
В Японии внедорожник перестали выпускать в 1987 году, но в Тегеране, на предприятии PARS (том самом, где до сих пор собирают Peugeot 405), Patrol 160 серии собирали вплоть до начала 2000-х.
И вот настала очередь четвертого поколения — того самого, которое хорошо знакомо автомобилистам России и постсоветского пространства. После распада СССР немало этих машин хлынуло к нам из Западной Европы, потому что харизмы у японского внедорожника было выше крыши.
Nissan Patrol Y60
Новый Patrol серии Y60 внешне напоминал предшественника, однако технически это был новый автомобиль. По-прежнему предлагающийся как в коротко-, так и длиннобазном варианте, внедорожник получил полностью новую пружинную подвеску, что было немыслимой роскошью по меркам тех лет — тогда пружины и спереди, и сзади предлагал лишь куда более дорогой Range Rover. Для некоторых утилитарных версий, впрочем, были сохранены рессоры, повышающие грузоподъемность.
Гидроусилитель руля стал базовым для всех версий, как и стабилизаторы поперечной устойчивости с дисковыми тормозами (опять-таки, если не считать коммерческие версии). Также на большинство экземпляров устанавливался задний дифференциал повышенного трения. Поэтому на бездорожье новый Patrol оказывался еще более живучим, чем предшественники. А в случае, если силенок Y60 не хватало, можно было воспользоваться лебедкой, которая предлагалась в качестве заводской опции.
В зависимости от рынка сильно отличались комплектации. Например, в Австралии, которая по-прежнему оставалась одним из ведущих рынков для модели, Patrol предлагался в четырех версиях. Самая роскошная, Ti, доступная с 1989 года, могла похвастать электростеклоподъемниками, электрозеркалами, велюровой отделкой, двумя раздельными кондиционерами (для передних пассажиров и задних), премиальной аудиосистемой с семью динамиками, а также высокой крышей. Машины для финского рынка, в свою очередь, шли с двумя аккумуляторными батареями. Но вот силовые установки от рынка к рынку были плюс минус одинаковыми. Потому что их было не так много.
В общей сложности Y60 оснащался четырьмя рядными «шестерками» — двумя бензиновыми и двумя дизельными. Причем одним из бензиновых двигателей был RB30S — родственник мотора Nissan Skyline, пускай и одновальный. Но не этот мотор прославил Patrol, а малопримечательный дизель TD42, который прослыл просто пуленепробиваемым.
Поскольку с 90-х годов мир начал меняться значительно быстрее, Patrol обновлялся понемногу чуть ли не каждый год. Пока в 1997 году не уступил место Y61.
Nissan Patrol Y61
Пожалуй, именно Y61 у нас знают и любят больше всего. Такие машины часто встречаются на триалах, становятся объектами серьезных доработок. Да и в «гражданском» виде периодически встречаются на дорогах.
Как и Land Cruiser 100, Patrol Y61 стал заметно роскошнее. Мощность моторов заметно подросла, а на вершине линейки обосновался 4,8-литровый рядный двигатель TB48DE с шестью цилиндрами. Его мощность составляла 245 лошадиных сил… пока в него не вмешивались тюнеры.
Когда Nissan Patrol Y61 выпускался для рынка России, то официальные машины попадали к нам из Арабских Эмиратов. Из тех самых Эмиратов, где любят быстрые и мощные машины.
В ОАЭ давно научились превращать Y61 в настоящих монстров для дрэга. Если речь идет о так называемом «пустынном дрэге», в котором внедорожники заезжают на бархан, то берутся длиннобазные версии Y61 с TB48DE, на который устанавливались системы впрыска метанола и монструозных размеров турбины. С таким тюнингом внедорожники развивают более 2000 лошадиных сил, а их моторы живут от силы пару заездов. Что касается традиционного дрэга на асфальте, тот тут все еще интереснее: в короткобазный Patrol устанавливаются потроха от прокачанного GT-R R35 и… В общем, результат подобных доработок вы могли видеть в шоу The Grand Tour: прокачанный Patrol уверенно обогнал Ричарда Хаммонда на Porsche 918 Spyder.
Y61 стал последним Патролом (точнее, Safari), который продавался в Японии. Y61 стал последним Патролом, который реально не боялся бездорожья — благодаря чему сотни этих автомобилей до сих пор используются наблюдательными миссиями ООН. Y61 стал последним Патролом, который можно было купить как в короткобазном, так и в длиннобазном варианте. Y61 стал последним Патролом, который выпускался в Испании. Но его история не окончена: немолодой внедорожник по-прежнему можно купить в некоторых странах Африки, где он называется Nissan Super Safari. В ОАЭ цены начинаются от 153 тысяч дирхам, что эквивалентно 4 миллионам рублей. И спрос по-прежнему есть.
Nissan Patrol (Super Safari) Y61
Потому что нынешний Patrol, который дебютировал в 2010 году и является родственником Inifiniti QX56 (QX80)… Он не то, чтобы хуже. Просто он другой. На этом трехтонном здоровяке едва ли кто-то поедет триалы. Да и кожаный салон с деревянным шпоном и продвинутой мультимедийкой пачкать как-то не комильфо. На изменение характера Patrol всячески намекает и сама компания Nissan: в Эмиратах, которые последние 10 лет являются главным рынком для модели, Patrol можно купить в версии Nismo — с аэродинамическим пакетом и спортивной подвеской.
Nissan Patrol Nismo Y62
Пускай Patrol не снискал такой популярности, как Land Cruiser, он всегда был и остается серьезным внедорожником с богатой историей и широкими возможностями.
Nissan Patrol Y62 (рестайлинг 2019-го года)
Учитывая, что недавно анонсированный Nissan Fairlady собирается вернуться к истокам, возможно, такая же судьба коснется и Patrol. А там, глядишь, и его рынок опять станет обширным, как 30 лет назад.
Источник.
Надеюсь- что вам понравился данный материал. Впереди будет ещё много интересного.
До новых встреч!
С ув.
OBITUARY-DEATH.
| Nissan Patrol | |
|---|---|
 Nissan Patrol ST-L универсал (Y62, Австралия) Nissan Patrol ST-L универсал (Y62, Австралия) |
|
| Обзор | |
| Производитель | Nissan Shatai |
| Также называется | Nissan Safari (Япония, 1980–2007 гг.). Datsun Patrol (до 1984 г.) |
| Производство | 1951– настоящее время (международный). 1951–2007 (Япония) |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Класс | Внедорожник / Полноразмерный внедорожник |
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, полный привод (с 1951 г. по настоящее время). с передним двигателем, с задним приводом (с 1980 г. по настоящее время) |
Nissan Patrol (яп.日 産 ・ パ ト ロ ー ル Nissan Patorōru) — серия полноприводных автомобилей, производимых Nissan в Японии и продаваемых по всему миру.
Patrol выпускался с 1951 года как трехдверное шасси с короткой колесной базой (SWB) или пятидверное шасси с длинной колесной базой (LWB). Версия LWB предлагалась в пикапе . и шасси с кабиной варианты. Между 1988 и 1994 годами Ford Australia продавал Patrol как Ford Maverick. В некоторых европейских странах, таких как Испания, Patrol продавался компанией Ebro как Ebro Patrol. В 1980 году в Японии он стал известен как Nissan Safari.
Патруль доступен в Австралии, Центральной и Южной Америке, Южной Африке, некоторых частях Юго-Восточной Азии и Западной Европы, а также в Иране и на Ближнем Востоке. В 2011 модельном году он был доступен в Северной Америке как высококлассный Infiniti QX56 (позже будет переименован в Infiniti QX80), впервые с 1969 года автомобиль на базе Patrol был продан в Северной Америке., а в 2017 модельном году он будет предлагаться на этом рынке как Nissan Armada.
Платформа Y61 производится как военный автомобиль в странах Азии и Ближнего Востока. Различные версии Patrol широко используются агентствами ООН. Модели Y61 производятся вместе с нынешним Y62. Патрули Y60 и Y61 были основными транспортными средствами, использовавшимися ирландской армией.
Содержание
- 1 Первое поколение (4W60; 1951–1960)
- 1.1 Серия 4W70
- 2 Второе поколение (60 ; 1959–1980)
- 2.1 Jonga
- 3 Третье поколение (1980–1989)
- 3.1 160 (1980–1989)
- 3.1.1 Испанское производство
- 3,2 260 (1986–2002)
- 3.1 160 (1980–1989)
- 4 Четвертое поколение (Y60; 1987–1997)
- 4.1 Технические характеристики двигателя
- 5 Пятое поколение (Y61; 1997 – настоящее время)
- 5.1 GU IV и новее
- 6 Шестое поколение (Y62; 2010 – настоящее время)
- 6.1 Patrol Desert Edition
- 6.2 Patrol Nismo
- 6.3 Галерея
- 7 Ссылки
- 8 Внешние ссылки
Первое поколение (4W60; 1951–1960)
| Первое поколение (4W60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется | Nissan Jeep |
| Производство | 1951–1960 |
| Сборка | Япония: Hiratsuka |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Класс | Среднего размера внедорожник |
| Тип кузова |
|
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, полный привод |
| Трансмиссия | |
| Двигатель |
|
| Трансмиссия | 4-ступенчатая механическая коробка передач |
| Размеры | |
| Колесная база | 2200 мм (86,6 дюйма) |
| Длина | 3650 мм (143,7 дюйма) |
| Ширина | 1740 мм (68,5 дюйма) |
| Высота | 1720 мм (67,7 дюйма) |
| Снаряженная масса | 1500 кг (3306,9 фунта) |
В сентябре 1951 года 4W60 был представлен исключительно японским дилерским центрам Nissan. Общий стиль был похож на Willys Jeep. В 4W60 использовался 3,7-литровый двигатель Nissan NAK мощностью 75 л.с. от автобуса Nissan 290, но с частичным полным приводом и четырехступенчатой механической коробкой передач. Решетка радиатора имела значок Nissan из штампованной стали. Доступен был универсал на базе 4W70 Carrier.
4W61 был представлен в августе 1955 года. 4W61 изменил решетку радиатора (с некоторыми хромированными планками), цельное ветровое стекло, которое в сложенном виде откидывается назад, хромированные полосы на капоте и сиденья разных размеров (со стороны пассажира). шире водительского). Другим большим изменением стал двигатель. 4W61 был оснащен новым 3,7-литровым двигателем Nissan NB мощностью 92 л.с. (69 кВт), а позже был оснащен 4,0-литровым двигателем Nissan NC мощностью 105 л.с. (78 кВт). Значок решетки радиатора был хромовым и красным с надписью «NISSAN».
В октябре 1958 года модель 4W65 Patrol пришла на смену 4W61. В 4W65 была изменена решетка радиатора, которая теперь имела все хромированные решетки, а также переработаны передние крылья и капот. Значок «NISSAN» был на решетке радиатора, а значки «Патруль» добавлены по бокам капота. Был добавлен восьмиместный универсал с жесткой крышей WG4W65. Недолговечный 4W66 Patrol был представлен в декабре 1956 года с двигателем 4,0 л P мощностью 125 л.с. Выпуск 4W66 был прекращен в июне 1960 года. С 1956 по 1959 год выпускалась универсальная версия 4W66 под названием Carrier.
Серия 4W70
Nissan 4W70 Carrier был представлен в 1950 году на основе модели <263.>Додж М37. В 4W70 использовалось шасси M37, но трансмиссия 4W60 Patrol. Решетка радиатора стала уже, а передние крылья изменились. 4W72 был представлен в 1955 году (обозначение 4W71 было пропущено) с изменениями капота, решетки радиатора и фар. Мощность увеличилась до 105 л.с. благодаря новому двигателю Nissan NC. Снова модификации капота, крыльев и решетки радиатора, а также увеличение мощности до 145 л.с. привели к появлению модели 4W73, представленной в 1959 году и оснащенной двигателем Nissan P.
| Серия | Типы кузова | Двигатели (бензин) |
|---|---|---|
| Серия 4W60. (позже названная Nissan Patrol) | SWB : мягкий верх (4W60, 61, 65,66). SWB : пожарная машина (F4W61,65,66) | //NC /P |
| Nissan Carrier. 4W70 / 72/73 | военный транспортер, | NC /P |
Второе поколение (60; 1959–1980)
| Второе поколение (60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется | Datsun Patrol (Филиппины). Jonga P60 (Индия) |
| Производство | 1960–1980 |
| Сборка | Япония: Хирацука ; Иокогама ; Зама (1965–1980). Индия: Джабалпур (1965–1999). Южная Африка: Росслин (1959–1983) |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Класс | Среднего размера внедорожник |
| Тип кузова | 3-дверная жесткая крыша. 3-дверная мягкая крыша. 3-дверный универсал / фургон. 2-дверный пикап. пожарная машина |
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, полный привод |
| Силовой агрегат | |
| Двигатель | 4,0 л P I6 (бензин) |
| Трансмиссия | 3/4-ступенчатая механическая коробка передач |
Nissan Patrol 60 с мягким верхом (двухдверный; колесная база 2200 мм (86,6 дюйма)) и G60 (двухдверный; 2500 мм (98,4 дюйма)) колесная база) были впервые проданы в Австралии в 1960 году. Леворульный Модели L60 / GL60 продавались за пределами Австралии.
Канадские и американские клиенты могли получить патрули только с 1962 по 1969 год. Патрули продавались через дилерские центры Datsun, что делало его единственным автомобилем под маркой Nissan, продаваемым в США до начала 1980-х, когда Марка Datsun была прекращена (за исключением небольшой тестовой партии из примерно 100 Nissan Cedrics, которые также экспортировались в США в начале 60-х). Также была доступна версия H60 с удлиненной колесной базой.
Полноприводные Nissan Patrol 60 серии выпускались с короткой, средней и длинной колесной базой. Он имел механическую коробку передач типа F3B83L сначала с тремя, а затем с четырьмя скоростями, двухступенчатую раздаточную коробку с частичным приводом на четыре колеса. Мотором был P-двигатель, рядный шестицилиндровый двигатель с верхним расположением клапанов объемом 3956 куб. См (241,4 куб. Дюйма), с камерами сгорания в форме ванны и полностью сбалансированным семиопорным коленчатым валом. С двумя дверями спереди и одной сзади и четырьмя сиденьями (водитель и спутник спереди, два параллельных задних сиденья) была доступна версия с удлиненной колесной базой (H60) с вместимостью восемь пассажиров.
В 1963 году были представлены модели с жестким верхом KG60 (и KGL60).
Nissan Australia заявил, что Patrol 60-й серии был первым автомобилем, проехавшим по пустыне Симпсон в Австралии, и вызвал широкую огласку к 50-летнему юбилею этого события, в том числе -законение с аналогичным автомобилем завершится 21 июля 2012 года, чтобы предать гласности предстоящий выпуск их нового поколения Y62. Однако противоречивый отчет утверждал, что автомобиль поддержки Toyota Land Cruiser прибыл раньше патруля.
| Серия | Типы кузова | Двигатели (бензин) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 серия | 60 (SWB) | G60 (LWB) | H60 (Super LWB) | P двигатель |
| 60мягкий верх. K60 жесткий верх | WG60 универсал. G60H-A кабина / шасси. 62ZG60H пикап | VH60van. FH60 пожарный автомобиль |
Jonga
Примерно с 1969 года был основан автомобильный завод индийской армии в Джабалпуре (VFJ). сборка четвертьтонного Nissan Patrol как «Jonga» вместе с Nissan 4W73. Название согласно записям индийской армии является аббревиатурой от J abalpur O rdinance a Nd Gunarriage A ssembly. Оба автомобиля Nissan были оснащены одинаковыми двигателями и имеют много общих частей. В 1996 году Jonga ненадолго продавалась гражданским покупателям с 4,0-литровым дизельным двигателем Hino, но спрос был низким из-за неконкурентоспособной цены, а также непривлекательного внешнего вида. Было продано менее двухсот единиц. Jonga верой и правдой служил до конца 1990-х годов, когда его заменили более легкие джипы Mahindra Mahindra MM550. Проданные с аукциона бывшие армейские джонги, растянутые и преобразованные в авианосцы, до сих пор служат в некоторых сельских районах Индии.
Третье поколение (1980–1989)
160 (1980–1989)
| Третье поколение (160) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется | Datsun Patrol (1980- 1986). Ebro Patrol. Nissan Safari (Япония) |
| Производство | 1980–1989 |
| Сборка | Япония: Хирацука ; Канда ; Зама (1980–1987). Иран: Тегеран (Парс Ходро ; 1984–2003). Южная Африка: Росслин (1983–1991). Испания: Барселона (1983–1988) |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Тип кузова | 3-дверная жесткая крыша. 3-дверная мягкая крыша. 5-дверный фургон. 2/4-дверный пикап. пожарная машина |
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, задний привод. Передний двигатель, полный привод |
| Силовой агрегат | |
| Двигатель |
|
| Трансмиссия | 4/5 -скоростной ручной. 3-ступенчатый 3N71 автоматический |
| Размеры | |
| Колесная база | SWB: 2350 мм (92,5 дюйма). LWB: 2970 мм (116,9 дюйма) |

Серия 160 была представлена в 1980 году и пришла на замену серии 60. В Австралии они продаются как MQ Patrol. В 1980 году доступны двигатели L28, P40 и SD33. Все модели были доступны с четырехступенчатой механической коробкой передач, а трехступенчатая автоматическая коробка передач была необязательной для автомобилей с длинной колесной базой, оснащенных двигателем L28. Все модели Patrol 160 серии поставлялись с двухступенчатой раздаточной коробкой со смещением, которая имела высокую передачу 1: 1 и низшую передачу.
Все модели имели рессорную подвеску. В автомобилях SD33 используется электроника на 24 В. Доступны различные варианты отделки и цвета, включая виниловые или ковровые покрытия, а также синюю или коричневую внутреннюю отделку. Кондиционер и гидроусилитель руля были доступны на моделях люкс.
Передний дифференциал во всех моделях был C200. В Австралии стандартным задним дифференциалом был H233. Некоторые версии имели дифференциал повышенного трения (LSD). Задний дифференциал модели для тяжелых условий эксплуатации использовался в некоторых пикапах и фургонах с двигателем P40. Это был дифференциал модели H260. На европейских рынках, где ожидалось менее обременительное использование на бездорожье, на некоторых автомобилях устанавливали легкий задний дифференциал C200.
В 1983 году MQ был обновлен. Они известны как MK Patrol, однако не упоминаются ни в какой документации или руководствах по обслуживанию Nissan. Продавцы запчастей Nissan не узнают эти инициалы. Обновления включали переработанную переднюю часть с прямоугольными фарами и модернизированную переднюю подвеску. Была переработана четырехступенчатая коробка передач, и для большинства моделей была добавлена пятая передача. Четырехступенчатая коробка передач все еще использовалась в некоторых моделях с более низкими характеристиками, предположительно для того, чтобы исчерпать запасы. Версия фургона с высокой крышей («Super Roof») была добавлена одновременно с опцией SD33T с турбодизелем. При 110 л.с. (81 кВт) турбодизель может развивать скорость 145 км / ч (90 миль / ч).
В это время был обновлен дизельный двигатель SD33 без наддува. Изменения включали использование трех поршневых колец вместо пяти, поршневых маслосборников и масляного фильтра вместо бумажного картриджа. В Австралии и некоторых других частях света патрули с двигателем SD33 были модернизированы и оснащены стандартной 12-вольтовой электроникой. Чтобы приспособиться к дополнительной мощности турбодизеля, эти модели имели более крупное сцепление (270 против 240 мм) и больший масляный радиатор (пять рядов против трех), чем у безнаддувной версии.
Это были последние модели Patrol с маркой Datsun — как и остальная часть модельного ряда Nissan, Patrol потерял свой бренд Datsun в 1984 году на большинстве рынков.
Испанское производство
Nissan приобрел 35,85% акций Motor Ibérica в 1980 году, которые были увеличены до 54,68% в 1982 году. В начале 1983 года первый Nissan Patrol испанского производства покинул завод в Зона Франка, недалеко от Барселоны. Производство в первый год, запланированное на 4-5000 автомобилей, было предназначено для Испании и Португалии. Экспорт должен был последовать в течение 1984 года. Patrols, построенные Nissan Ibérica, первоначально получили четырехцилиндровый дизельный двигатель Perkins MD27 испанского производства и испанскую трансмиссию, чтобы соответствовать требованиям местного содержания. Позже его заменил A428, который превратился в A428T, а затем в A428II. Позже к автомобилям испанского производства добавились RD28 и RD28T.
260 (1986–2002)
| Третье поколение (260) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется | Патруль Эбро (Испания, 1986–1993 гг.). Король пустыни Саньсин (Китай) |
| Производство | 1986–2002 |
| Сборка | Италия: Рим (1988–1993). Испания: Барселона |
| Тело и шасси | |
| Класс | Полноразмерный внедорожник |
| Тип кузова | 3-дверный хардтоп. 5-дверный фургон / фургон. 2/4-дверный пикап |
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, задний привод. Передний двигатель, полный привод |
| Трансмиссия | |
| Двигатель |
|
| Трансмиссия | 5-ступенчатая механическая коробка передач |
| Размеры | |
| Колесная база | SWB: 2350 мм (92,5 дюйма). LWB: 2970 мм (116,9 дюйма) |
| Длина | SWB: 4230 мм (166,5 дюйма). LWB: 4690 мм (184,6 дюйма) |
| Ширина | 1689 мм (66,5 дюйма) |
| Высота | 1980 мм (78,0 дюйма) |

Серия 260 представляла собой обновленную версию испанской 160-й модели (ее легко заметить по прямоугольным фарам.) продается в Европе и доступен в версиях SWB и LWB с двигателями L28, SD33, RD28 и RD28T. Версия с двигателем SD, по крайней мере, на рынке Великобритании, имела электрическую систему на 24 В. Nissan помог Nissan Ibérica окупить вложения в завод. Позже 260 Patrol получил фейслифтинг с новой решеткой радиатора, аналогичной решетке серии Y60, которая пришла на смену этому поколению в других местах. Производство в Испании продолжалось до 1994 г. для экспорта и до 2002 г. для внутреннего рынка Испании.
Четвертое поколение (Y60; 1987–1997)
| Четвертое поколение (Y60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется | Nissan Patrol Safari (Филиппины). Nissan Safari (Япония). Ford Maverick (Австралия) |
| Производство | 1987–1997 |
| Сборка | Япония: Хирацука ; Канда ; Зама (1987–1993). Южная Африка: Росслин (1991–2001). Испания: Барселона (1988–1998). Филиппины: Санта-Роса-Сити (1990-2000) |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Класс | Полноразмерный внедорожник |
| Кузов | 3-дверный универсал. 5-дверный универсал. 2-дверный пикап |
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, задний привод. Передний двигатель, четыре колеса привод |
| Трансмиссия | |
| Двигатель | 2,8 л RD28T I6 -T (дизель). 3,0 л RB30S I6 (бензин). 4,2 л TB42S / TB42E I6 (бензин). 4,2 л TD42 I6 (дизель) |
| Трансмиссия | 4-ступенчатая RE4R03A автомат. 5-ступенчатая FS5R50A механическая 5-ступенчатая FS5R30A механическая с Двигатель RD28T |
| Размеры | |
| Колесная база | SWB: 2400 мм (94,5 дюйма). LWB: 2970 мм (116,9 дюйма) |
| Длина | SWB: 4285 мм (168,7 дюйма). LWB: 4845 мм (190,7 дюйма) |
| Ширина | SWB: 1930 мм (76,0 дюйма). LWB: 1930 мм (76,0 дюйма) |
| Высота | SWB: 1810 мм (71,3 дюйма). LWB: 1815 мм (71,5 дюйма) |


Y60 радикально отличался механически от своих предшественников, поскольку это был первый Patrol с пружинной подвеской, повышающим комфорт и управляемость на неровностях. Все модели Y60 Patrol имели трехрычажную подвеску ведущего моста спереди, а все универсалы (SWB, LWB и SWB LW) имели пятирычажную подвеску сзади. Полезная модель была доступна как с задней осью с листовой рессорой, так и с 1994 года — с той же задней осью с винтовой пружиной, что и у универсалов. стабилизаторы поперечной устойчивости были включены как на передние, так и на задние ведущие оси с винтовой подвеской. Усилитель руля был стандартным. Некоторые модели вагонов имели передние и задние дисковые тормоза, в то время как у Ute сохранились задние барабанные тормоза. Другим усовершенствованием стало введение синхронизатора на задней передаче.
Альтернативные коды моделей GR и GQ были применены к моделям с левым и правым рулем соответственно.
Большинство моделей имели задний дифференциал повышенного трения, а некоторые варианты имели ручную блокировку заднего дифференциала с вакуумным или электрическим соленоидом. На некоторых моделях появился механизм разблокировки заднего стабилизатора поперечной устойчивости. У некоторых Y60 была передняя лебедка с приводом от ВОМ лебедка с рычагом управления в кабине справа от рычага переключения передач.
Patrol имел бренд Safari в Японии, где имел электрическую систему 24 В вместо стандартной 12 В.
TD42 и TB42 были доступны как с пятиступенчатой механической, так и с четырехступенчатой автоматической коробкой передач. RD28T и RB30 предлагали только 5-ступенчатую механическую коробку передач.
Уровни отделки салона в Австралии:
- DX с ручными зеркалами, без центрального замка, виниловый интерьер, дополнительный кондиционер, ступицы с ручным замком.
- RX (с 1995 г.) с электрическими зеркалами, центральный замок, ковровое покрытие салона, кондиционер, ступицы ручной блокировки.
- ST с электрическими стеклоподъемниками, электрическими зеркалами, центральным замком, ковровым покрытием салона, кондиционером, ступицами с автоматической блокировкой.
- Ti (с конца 1989 г.) с Электродвигатель efi и электрические стеклоподъемники, электрические зеркала, центральный замок, салон из велюра и ковра, задний кондиционер, аудиосистема с семью динамиками, легкосплавные трехспицевые колеса, ступицы с автоматической блокировкой. До 1991 года модель Ti имела высокую крышу с люком. Кожаная и деревянная отделка стала стандартной в 1992 году с Series 2.
Было доступно множество аксессуаров, устанавливаемых дилерами, включая люки на крыше, багажники на крышу, фаркоп, фары дальнего света., грузовые барьеры и подножки. TD42 был доступен с дополнительным турбонагнетателем Safari у некоторых австралийских дилеров.
Уровни отделки салона в Европе различаются в зависимости от страны. К ним относятся такие обозначения, как SLX, LX, LW и многие другие во Франции. Финские патрули стандартно поставлялись с двумя батареями. LW (1996–1997) отличался легким корпусом, уменьшившим вес на 50 кг, и специальным корпусом меньшего размера (40 миллиметров). Они выпускались только для чемпионатов по экстремальному бездорожью. Двигатель и ходовая часть остались прежними.


Два основных обновления появились в Австралии: одно в 1992 году (GQ Series 2) и одно в 1995 году ( незначительный фейслифтинг). Наиболее заметными изменениями в 1992 году были внедрение системы впрыска топлива на двигателе TB42 с впрыском топлива, клапан рециркуляции отработавших газов и маслоохладитель на RD28T, новые сиденья, новая отделка салона, звукоизоляция и боковые защитные дуги. Другие усовершенствования 1992 года Series 2 включали пересмотренную трансмиссию, подвеску, более крупные тормоза, большие колеса и стандартизацию дифференциалов повышенного трения и ступиц с автоматическим свободным ходом. Это обновление включало новые сиденья, отделку салона и боковые защитные дуги.
В 1991 году задние указатели поворота, задние фонари и стоп-сигналы были перемещены на бампер от кузова, чтобы соответствовать Австралийским правилам проектирования, однако они остались такими же в европейских версиях. В 1992 году на переднюю четверть панели разместили еще один набор индикаторов.
В августе 1993 года TD42 похудел, чтобы снизить расход топлива и увеличить обороты. Это имело побочный эффект в виде ослабления двигателя. Оригинальный двигатель можно узнать по серебристой крышке коромысла, тогда как облегченный двигатель имел черную крышку. RD28T получил некоторые дополнительные изменения, переместив вакуумный насос из-за генератора в верхнюю часть двигателя. Водительские подушки безопасности появились в некоторых европейских моделях.
1995 год ознаменовался незначительным фейслифтингом, с измененной передней решеткой и моделью RX, представленной в Австралии.
Среди известных недостатков — вибрация от передней части (в основном устраненная по гарантии), треск петель на задней двери (из-за веса запасной шины) и ржавчина на рамах заднего стекла. Мотор RD28T и мотор TB42 страдали от проблем с прокладкой головки при движении с тяжелой ногой. Европейские пятиступенчатые коробки передач страдали от отказа подшипников пятой передачи на больших пробегах. Однако TD42 отличался высокой надежностью. Патрули известны своими прочными мостами и хорошим дифференциалом повышенного трения (если таковой имеется).
С 1988 по 1994 годы Ford Australia переименовал Y60 Patrol в Ford Maverick. Это было результатом плана автомобиля Button, разработанного правительством Австралии. Автомобиль был механически похож, хотя версия Nissan имела задние дисковые тормоза в зависимости от класса автомобиля, в то время как Ford в основном имел барабанные тормоза и отличался разными цветами окраски и комплектациями.
Все вагоны имели 95-литровый основной топливный бак, а коммунальные услуги имели 90-литровый бак и опцию 95-литрового вспомогательного бака.
Технические характеристики двигателя
| Код двигателя | Рабочий объем | Диаметр цилиндра x ход | Мощность | Крутящий момент | Степень сжатия | Конструкция | Характеристики |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB30s | 2962 куб.см | 100 кВт при 4800 об / мин | 224 Нм при 3000 об / мин | 9,0 : 1 | Рядный шестицилиндровый двигатель SOHC, бензин | Алюминиевая головка цилиндров с поперечным потоком | |
| TB42S | 4169 куб.см | 96 x 96 мм | 125 кВт при 4200 об / мин | 325 Нм при 2800 об / мин | 8.3.1 | Рядный шестицилиндровый толкатель, бензин | Головка блока цилиндров с поперечным потоком, высокая распределительный вал |
| TB42E | 135 кВт при 4400 об / мин | 320 Нм при 3200 об / мин | 8,3: 1 | ||||
| RD28T | 91,9 кВт при 4400 об / мин | 255 Нм при 2000 об / мин | 21,2: 1 | рядный шестицилиндровый двигатель SOHC, дизельный | с турбонаддувом | ||
| TD42 | 4169 куб.см | 96 x 96 мм | 85 кВт при 4000 об / мин | 264 Нм при 2000 об / мин | 22,7: 1 | Рядный шестицилиндровый толкатель, дизель | Головка блока цилиндров с поперечным потоком, высокий распредвал |
Пятое поколение (Y61; 1997 – настоящее время)
| Пятое поколение (Y61) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется |
|
| Производство | октябрь 1997 — 2016. 1997 – настоящее время (продолжается в отдельных странах) |
| Сборка |
|
| Конструктор | Масато Такахаши (1994). Дзюнъити Сакаи (рестайлинг: 2003) |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Класс | Полноразмерный внедорожник |
| Тип кузова |
|
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, задний привод. Передний двигатель, полный привод |
| Трансмиссия | |
| Двигатель |
|
| Трансмиссия |
|
| Размеры | |
| Колесная база | SWB: 2400 мм (94,5 дюйма). LWB: 2970 мм (116,9 дюйма) |
| Длина | SWB: 4440 мм (174,8 дюйма). LWB: 5,080 мм (200,0 дюйма) |
| Ширина | 1,940 мм (76,4 дюйма) |
| Высота | 1855 мм (73,0 дюйма) |
| Снаряженная масса | 2473 кг (5452 фунта) |



Модели Y61 впервые появились в декабре 1997 года, доступны с бензиновым двигателем объемом 4,5 и 4,8 литра, объемом 2,8 литра. -, 3,0- и 4,2-литровый турбодизель и 4,2-литровый турбодизель варианты с промежуточным охладителем. Альтернативные коды моделей GR и GU были применены к моделям с левым и правым рулем соответственно.
В этой модели была изменена трансмиссия, в том числе увеличены CV и меньше синхронизаторов в механических коробках передач. Корпуса дифференциала были расширены, чтобы соответствовать новой форме корпуса, но центры остались прежними (H233 и H260). Некоторые бензиновые вагоны получили винтовой вариант дифференциала H260.
Уровни комфорта были увеличены по сравнению с GQ, особенно в местах для сидения и шумоизоляции.
GU IV и далее
В 2005 модельном году была выпущена значительная модификация фейслифтинга с новыми фарами, раструбом на каждой защите и большими задними фонарями. Проблемы, которые преследовали дизель ZD30, связанные с изменяемой геометрией турбонаддува, были устранены этим обновлением.
В том же году Nissan прекратил продавать Safari в Японии из-за плохих продаж. Nissan также сделал двухдверную версию пикапа серии Y61, доступную на некоторых рынках как шасси с кабиной и с боковым подносом. Несмотря на то, что была запущена новая модель, эта серия Y61 по-прежнему продается для энтузиастов бездорожья, но с некоторыми вариантами.
Его двигатель TB48DE очень популярен среди тюнингового сообщества на Ближнем Востоке, особенно в ОАЭ. Двигатель TB48DE легко модифицируется и, как было показано, способен выдерживать более 2000 л.с. (1491 кВт) для нескольких песчаных холмов и проблем с сопротивлением песку в этом регионе.
По состоянию на 2014 год Nissan прекратил выпуск модели пятого поколения во всем мире, за исключением Южной Африки, Ближнего Востока, Пакистана, Парагвая, Филиппин, Боливии, Шри-Ланки и некоторых африканских стран, где внедорожник 4×4 конкурировал с автомобилем Тойота Ленд Крузер (J70). Несколько специальных версий были также выпущены в соответствующих регионах, где Y61 продавался и в настоящее время продается, в том числе The Presidential edition (Филиппины), The Legend edition (Филиппины, Южная Африка и Австралия), The ‘Special ‘Super Safari edition (Ближний Восток), The Falcon edition (Ближний Восток), Gazelle и Gazelle X editions (Ближний Восток). 29 апреля 2016 года производство модели пятого поколения также было прекращено в Австралии и Новой Зеландии.
Шестое поколение (Y62; 2010 – настоящее время)
| Шестое поколение (Y62) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Обзор | |
| Также называется | Nissan Armada (2016 – настоящее время). Infiniti QX56 / QX80. Nissan Patrol Royale (Филиппины) |
| Производство | Январь 2010 г. — настоящее время |
| Сборка |
Россия: Санкт-Петербург, (SKD, 2012–2014) |
| Конструктор | Taiji Toyota (2007) |
| Кузов и шасси | |
| Класс | Полноразмерный Внедорожник |
| Кузов | 5-дверный Внедорожник |
| Компоновка | Передний двигатель, задний привод или полный привод |
| Платформа | Y62 / Платформа Nissan F-Alpha |
| Родственные | Infiniti QX56 / QX80. Nissan Armada Y62. Nissan Titan (второе поколение). Nissan NV. Nissan Terra. Nissan Navara (D23) |
| Трансмиссия | |
| Двигатель |
|
| Коробка передач |
|
| Размеры | |
| Колесная база | 3,075 мм (121,1 дюйма) |
| Длина | 5,165 мм (203,3 дюйма) |
| Ширина | 1,995 мм (78,5 дюйма)) |
| Высота | 1940 мм (76,4 дюйма) |
| Снаряженная масса | 2,69 5–2 795 кг (5 941–6 162 фунта) |


Совершенно новый Nissan Patrol шестого поколения серии Y62 был представлен 13 февраля 2010 года в Абу-Даби. Роскошная версия (Z62) продавалась как Infiniti QX56 с 2010 года (впервые с 1969 года в Северной Америке продавался автомобиль на базе Patrol), который позже был переименован в Infiniti QX80. в 2013 году. Y62 был представлен в Северной Америке под шильдиком Armada в 2016 году в качестве модели 2017 года. Он был представлен в качестве замены первого поколения на базе Титана Nissan Armada (WA60).
По состоянию на 2017 год Y62 оснащался мощностью 275 л.с. (205 кВт) / 394 Н · м (291 фунт-сила). футов) 4,0-литровый двигатель VQ40DE V6 для начального уровня комплектации XE и SE или более мощный 400 л.с. (298 кВт) / 560 Нм (410 фунт-фут) 5,6-литровый VK56VD Двигатель V8 для верхнего уровня отделки салона. В версии NISMO используется доработанная версия 5,6-литрового V8, производящего 28 дополнительных лошадиных сил. До появления 4,0-литрового V6, более низкая мощность 317 л.с. (236 кВт) / 526 Нм (388 lb⋅ft) 5,6-литровый VK56DE V8 предназначалась для комплектаций начального уровня.
По состоянию на 2017 год все модели поставляются с 7-ступенчатой автоматической коробкой передач, хотя ранее Nissan предлагал 5-ступенчатую автоматическую коробку передач, а также 6-ступенчатую механическую коробку передач для начального уровня отделки салона. Пакет с регулируемым режимом 4 × 4 позволяет переключаться между четырьмя режимами движения: песок, дорога, камень и снег. Доступна гидравлическая система управления движением кузова. Задний дифференциал с электронной блокировкой, управление троганием с холма и спуском с холма, а также предупреждение о выезде с полосы, торможение с помощью компьютера и контроль устойчивости. Версия Infiniti, выпущенная в США в 2010 году, стала первым Patrol, проданным там после 60-й серии. Nissan Patrol был запущен в Австралии в начале 2013 года.
На Ближнем Востоке Nissan Patrol предлагается в различных комплектациях: XE, SE, SE-Platinum City, LE, LE-Titanium, LE-Platinum City. и NISMO Edition. В Австралии предлагаются уровни отделки салона Ti и Ti-L.
В 2014 году произошел значительный фейслифтинг: обновленные задние фонари с красными элементами, шарнирные корпуса и встроенные светодиодные фары. Был добавлен новый коричневый салон и новые комплекты колес.
Nissan представил ограниченную серию Patrol Black Special Edition в количестве 200 экземпляров. Эти автомобили предлагают несколько улучшений, таких как красные сиденья, хромированные детали и черная матовая окраска кузова.
Nissan провел вторую реконструкцию Patrol 2019 года, прежде чем к 2020 году у него появится новая версия. Изменения включают новый передний бампер с более глубоким фартуком и традиционный круглый корпус. Автомобиль будет оснащен Nissan Intelligent Mobility функциями помощи водителю, такими как помощь в удержании полосы движения, предупреждение о лобовом столкновении, автоматическое экстренное торможение спереди и сзади, предупреждение о перекрестном движении сзади и мониторинг слепых зон.
Patrol Desert Edition
Desert Edition поставляется с 5,6-литровым (5552 куб. См) двигателем мощностью 400 л.с., тканевыми сиденьями с ручной регулировкой, навигацией и обычной подвеской вместо гидравлической системы управления кузовом.
Patrol Nismo
При запуске бренда Nismo на Ближнем Востоке, Nissan Patrol Nismo был представлен на презентации в Дубае вместе с GT-R Nismo и 370Z Nismo. В отличие от стандартного Patrol, версия Nismo оснащена (5,6-литровым) двигателем V8 мощностью 428 л.с. (319 кВт), настроенным мастерами Nissan Takumi. Подвески модернизированы с помощью амортизаторов Bilstein и оснащены 22-дюймовыми коваными легкосплавными дисками.
Галерея
Предварительный рестайлинг
Передняя часть
Задняя часть
Первая -стайлинг фейслифтинга
Спереди
Зад
Второй фейслифтинг
Спереди
Зад
Nissan Patrol Nismo
Nissan Armada
Спереди
Зад
Отзывы
Внешние ссылки
СМИ, связанные с Nissan Patrol на Викискладе
- Nissan Patrol на глобальном веб-сайте Nissan
- Nissanh Heritage Nissan Safari
| Nissan Patrol | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Nissan |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (until 1984) Nissan Safari (Japan, 1980–2007) Nissan Armada (North America, 2016–present) Infiniti QX80 (2014–present) |
| Production | 1951–present (international) 1951–2007 (Japan) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Off-road vehicle/Full-size SUV |
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive (1951–present) Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive (1980–present) |
The Nissan Patrol (Japanese: 日産・パトロール, Hepburn: Nissan Patorōru) is a series of full-size SUVs manufactured by Nissan in Japan and sold throughout the world.
The Patrol has been available as either a short-wheelbase (SWB) three-door or a long-wheelbase (LWB) five-door chassis since 1951. The LWB version has been offered in pickup truck and cab chassis variants. Between 1988 and 1994, Ford Australia marketed the Patrol as the Ford Maverick. In some European countries, such as Spain, the Patrol was marketed by Ebro as the Ebro Patrol. In 1980 in Japan, it was rebadged and alternately sold at Nissan Prince Store locations as the Nissan Safari.
The Patrol is available in Australia, Central and South America, South Africa, parts of Southeast Asia, and Western Europe, as well as Iran and the Middle East. For the 2011 model year, it was made available in North America as the upscale Infiniti QX56 (later renamed as Infiniti QX80), the first time that a Patrol-based vehicle had been sold in North America since 1969, and for the 2017 model year, it would be offered in that market as the Nissan Armada.
First generation (4W60; 1951)[edit]
| First generation (4W60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Jeep |
| Production | 1951–1960 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Related | Willys CJ-3B |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200 mm (86.6 in) |
| Length | 3,650 mm (143.7 in) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
| Curb weight | 1,500 kg (3,306.9 lb) |
In September 1951, the 4W60 was introduced exclusively to Japanese Nissan dealerships. The overall styling was similar to the Willys Jeep. The 4W60 used the 75 PS (55 kW) 3.7 L Nissan NAK engine from the Nissan 290 bus, but with part-time four-wheel drive and a four-speed manual transmission. The grille had a pressed-steel Nissan badge. A 4W70 Carrier-based wagon was available.
The 4W61 was introduced in August 1955; it changed the grille (with some chrome bars), a one-piece windshield that sits further back when folded, chrome strips on the hood, and unequally sized seats (passenger’s side is wider than the driver’s). The other big change was the engine. The 4W61 was powered by the new 3.7 L Nissan NB engine, producing 92 PS (68 kW), and later was powered by the 105 PS (77 kW) 4.0 L Nissan NC engine. The grille badge was chrome and red and said «NISSAN».
In October 1958, the 4W65 Patrol replaced the 4W61. The 4W65 changed the grille, which now had all chrome bars and redesigned front fenders and hood. A «NISSAN» badge was on the grille and «Patrol» badges were added on the sides of the hood. An eight-seater hardtop wagon, the WG4W65, was added. The short-lived 4W66 Patrol was introduced in December 1956, powered by the 125 PS (92 kW) 4.0 L P engine. The 4W66 was discontinued in June 1960. A wagon version of the 4W66 was called the Carrier, from 1956 to 1959.
4W70 series[edit]
The Nissan 4W70 Carrier was introduced in 1950 based on the Dodge M37. The 4W70 used the M37’s chassis, but the 4W60 Patrol’s drivetrain. The grille was narrower and the front fenders changed. The 4W72 was introduced in 1955 (the 4W71 designation was skipped) with changes to the hood, grille, and headlights. Power increased to 105 hp due to the new Nissan NC engine. Modifications again to the hood, fenders, and grille and an increase in power to 145 PS (107 kW) led to the 4W73, introduced in 1959 and powered by the Nissan P engine.
| Series | Body styles | Engines (gasoline) |
|---|---|---|
| 4W60 series (later named Nissan Patrol) |
SWB: soft top (4W60/61/65/66) SWB: fire truck (F4W61/65/66) |
NAK/NB/NC/P |
| Nissan Carrier 4W70/72/73 |
Troop carrier, weapon carrier | NC/P |
Second generation (60; 1959–1980)[edit]
| Second generation (60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (Philippines) Jonga P60 (India) |
| Production | 1960–1980 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Yokohama; Zama (1965–1980) Philippines: Makati (1961–1983) India: Jabalpur (1965–1999) South Africa: Rosslyn (1959–1983) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 3-door softtop 3-door wagon/van 2-door pickup fire truck |
| Layout | Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 3/4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200–2,800 mm (86.6–110.2 in) |
| Length | 3,650–4,250 mm (143.7–167.3 in) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
The soft-top Nissan Patrol 60 (two-door; 2,200 mm (86.6 in) wheelbase) and G60 (two-door; 2,500 mm (98.4 in) wheelbase) were first sold in Australia in 1960. Left-hand drive L60/GL60 models were sold outside of Australia.
Canadian and American customers could get Patrols only from 1962 until 1969. Patrols were sold through Datsun dealerships, making it the only Nissan-badged vehicle sold in the USA until the early 1980s, when the Datsun marque was phased out (barring a small test batch of about 100 Nissan Cedrics that was also exported to the US in the early 60s).[1] An extra-long wheelbase version, the H60, was also available.
The 4WD Nissan Patrol 60 series was produced in short, medium, and long wheelbase versions. It had a manual transmission type-F3B83L at first with three and later with four speeds, and a two-speed transfer case with part-time four-wheel drive. The motor was the P engine, a 3,956 cc (241.4 cu in) inline overhead-valve six-cylinder, featuring bathtub-shaped combustion chambers and a fully balanced seven-bearing crank shaft. With two doors in front and one at the back and four seats (driver and companion in front, two parallel back seats), the extra-long wheelbase version (the H60) was available with eight-passenger capacity.
In 1963, the KG60 (and KGL60) hard-top models were introduced.
Nissan Australia claimed that the 60 series Patrol was the first vehicle to drive across the Simpson Desert in Australia, and built much publicity around the 50th anniversary of the event, including a re-enactment with a similar vehicle ending on 21 July 2012 to publicise the impending release of their new-generation Y62. However, a conflicting account claimed that a Toyota Land Cruiser support vehicle arrived before the Patrol.
| Series | Body styles | Engines (gasoline) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 series | 60 (SWB) | G60 (LWB) | H60 (Super LWB) | P engine |
| 60 soft top K60 hard top |
WG60 station wagon G60H-A cab/chassis 62ZG60H pickup truck |
VH60 van FH60 fire truck |
Jonga[edit]
Beginning around 1969, the Indian Army’s Vehicle Factory Jabalpur began assembling the quarter-ton Nissan Patrol as the Jonga, along with the Nissan 4W73. The name as per Indian army records is an acronym for Jabalpur Ordinance aNd Guncarriage Assembly. Both the Nissan vehicles were fitted with the same engines and shared many parts. The Jonga was briefly sold to civilian customers with a 4.0-litre Hino diesel engine in 1996, but demand was low, due to an uncompetitive price, as well as unappealing looks. Less than 200 units were sold. The Jonga served faithfully until the late 1990s, when it was replaced by the lighter Mahindra and Mahindra MM550. Auctioned ex-Army Jongas, stretched and converted to people carriers, still serve in some rural areas of India.
Third generation (160; 1980)[edit]
| Third generation (160) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Datsun Patrol (1980–1986) Ebro Patrol Nissan Safari (Japan) |
| Production | 1980–1989 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Kanda; Zama (1980–1987) Iran: Tehran (Pars Khodro; 1984–2003) South Africa: Rosslyn (1983–1991) Philippines: Makati (1983–1990) Spain: Barcelona (1983–1988) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 3-door softtop 5-door wagon/van 2/4-door pickup fire truck |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4/5-speed manual 3-speed 3N71 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,350 mm (92.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
The 160 series was introduced in 1980 to replace the 60 series. In Australia, these are sold as the MQ Patrol. In 1980, the available engines were the L28, P40, and SD33. All models were available with a four-speed manual transmission, while a three-speed automatic was optional on long-wheelbase vehicles fitted with the L28 engine. All 160 series Patrols came with a two-speed offset transfer case, which featured a 1:1 high gear and a low gear.
All models had leaf -spring suspension. The SD33 vehicles feature 24-volt electronics. Different trim options and colors were available, with options including vinyl or carpet floors and blue or brown interior trim. Air conditioning and power steering were available on deluxe models.
The front differential in all models was C200. In Australia, the standard rear differential was the H233. Some versions featured limited slip differentials. A heavy-duty model rear differential was used in some pickup trucks and P40-engined wagons. This was the H260 model differential. In European markets, where less onerous off-road use was expected, the light-duty C200 rear differential was installed in some vehicles.
In 1983, the MQ was updated as MK Patrol, but this does not appear on any Nissan literature or service manuals. Nissan parts dealers do not recognise these initials. Updates included a revised front end with rectangular headlights and an upgraded front suspension. The four-speed gearbox was revised and a fifth gear was added for most models. The four-speed was still used in some lower specificationed units, presumably to run out stock. A high roof («Super Roof») version of the wagon was added at the same time along with the SD33T turbo-diesel option. With 110 PS (81 kW), the turbodiesel can reach 145 km/h (90 mph).[2]
The naturally aspirated SD33 diesel engine was updated at this time. Revisions included the use of three piston rings instead of five, piston oil squirters, and a spin-on oil filter instead of a paper cartridge type. In Australia and some other parts of the world, the SD33-engined Patrols were revised to standard 12-volt electronics. To accommodate the turbodiesel’s extra power, these models featured a larger clutch (270 versus 240 mm) and larger oil cooler (five rows versus three) than the naturally aspirated version.
These were the last Patrols to carry the Datsun brand; in line with the rest of the Nissan lineup, the Patrol lost its Datsun branding in 1984 in most markets.
Spanish production[edit]
Nissan acquired a 35.85% stake in Motor Ibérica in 1980, which was increased to 54.68% in 1982.[3] In early 1983, the first Spanish-made Nissan Patrol left the plant in Zona Franca, near Barcelona. The first year’s production, planned to be 4,000 to 5000 cars, was earmarked for Spain and Portugal.[3] Exports were to follow during 1984. Nissan Ibérica-built Patrols originally received a Spanish-made Perkins MD27 four-cylinder diesel engine and Spanish transmission to meet local content regulations.[4] Later on, this was replaced by the A428, which evolved into the A428T and then the A428II. Later yet, the RD28 and the RD28T were added to Spanish-made cars.
260 (1986–1993)[edit]
| Third generation (260) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Ebro Patrol (Spain, 1986–1993) Sanxing Desert King (China) |
| Production | 1986–2002 |
| Assembly | Spain: Barcelona |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door hardtop 5-door wagon/van 2/4-door pickup |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,350 mm (92.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,230 mm (166.5 in) LWB: 4,690 mm (184.6 in) |
| Width | 1,689 mm (66.5 in) |
| Height | 1,980 mm (78.0 in) |
The 260 series was a facelifted version of the Spanish-built 160 (easily spotted by the rectangular headlamps) sold in Europe and available in SWB and LWB with L28, SD33, RD28 and RD28T engines. The SD-engined version, at least in the UK market, had a 24-volt electrical system. Nissan helped Nissan Ibérica amortize plant investments. The 260 Patrol later received a facelift with a new grille similar to that of the Y60 series which succeeded this generation elsewhere. Spanish production continued until 1994 for export and until 2002 for the Spanish domestic market.
Fourth generation (Y60; 1987)[edit]
| Fourth generation (Y60) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Safari (Japan) Ford Maverick (Australia) Yunbao YB2030 (China; JV) |
| Production | 1987–1997 |
| Assembly | Japan: Hiratsuka; Kanda; Zama (1987–1993) South Africa: Rosslyn (1991–2001) Spain: Barcelona (1988–1998) Philippines: Makati (1990–1998), Santa Rosa City (1998–2000) China: Huadu |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off road vehicle |
| Body style | 3-door wagon 5-door wagon/van 2-door pickup |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel-drive Front-engine, four-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | Petrol: 3.0 L RB30S I6 4.2 L TB42S/TB42E I6 Diesel: 2.8 L RD28T I6 turbo 4.2 L TD42 I6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed RE4R03A automatic 5-speed FS5R50A manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,400 mm (94.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,285 mm (168.7 in) LWB: 4,845 mm (190.7 in) |
| Width | SWB: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) LWB: 1,930 mm (76.0 in) |
| Height | SWB: 1,810 mm (71.3 in) LWB: 1,815 mm (71.5 in) |
Pre-facelift Nissan Patrol ST
The Y60 was radically different mechanically from its predecessors, as it was the first Patrol with coil-spring suspension, increasing comfort and improving rough-ground handling. All Y60 Patrols had a three-link live axle suspension set-up at the front, with all wagons (SWB, LWB, and SWB LW) adopting a five-link set-up at the rear. The utility model was available with both a leaf-spring rear axle, and from 1994 onwards, a choice of the same coil-spring rear axle as the wagons. Sway bars were included on both front and rear coil-spring live axles. Power steering was standard. Some wagon models had front and rear disc brakes, while the utility retained rear drum brakes. The introduction of a synchromesh on reverse gear was another improvement.
The alternative model codes of GR and GQ were applied to left- and right-hand drive models, respectively.
Most models had a rear limited slip differential and some variants had a vacuum or electric solenoid-operated manual rear differential lock. A rear sway bar release mechanism appeared on some models. Some Y60s had a power take-off-driven front-mounted winch, with an in-cab control lever to the right of the gearstick.
The Patrol was also branded as Safari in Japan, depending on which Japanese dealership was offering it – Safari at Nissan Prince Shop and Patrol at Nissan Bluebird Shop. The Safari was available with an optional 24V electrical system, instead of the standard 12V. This was the first series that placed the exterior dimensions in the higher tax bracket for the wider exterior measurement as defined in Japanese Government dimension regulations and the larger engines added a higher road tax obligation for Japanese owners.
The TD42 and TB42 were available with either a five-speed manual or a four-speed automatic gearbox. The RD28T and the RB30 offered only a five-speed manual.
Trim levels in Australia included:
- DX with manual mirrors, no central locking, vinyl interior, optional AC, manual locking hubs
- RX (from 1995) with electric mirrors, central locking, carpet interior, AC, manual locking hubs
- ST with electric windows, electric mirrors, central locking, carpet interior, AC, automatic locking hubs
- Ti (from late 1989) was equipped with an electronic fuel-injected engine, electric windows, electric mirrors, central locking, velour and carpet interior, rear AC, seven-speaker sound system, alloy three-spoke wheels, and automatic locking hubs. It had a high roof design with sunroof until 1991. Leather and woodgrain trim was made standard in 1992 with the Series 2.
Several dealer-fitted accessories were available, including sunroofs, roof racks, tow bars, driving lights, cargo barriers, and side steps. The TD42 was available with an optional Safari turbocharger at some Australian dealers.
Trim levels in Europe varied by country. These include designations such as SLX, LX, LW, and many others in France. Finnish Patrols came standard with two batteries. LW (1996–1997) featured a lightweight body, reducing the weight by 50 kg (110 lb) and a special smaller body (40 mm [1.6 in]). These were produced only for extreme off-road championships. The engine and chassis remained the same.
1995–1997 Nissan Patrol (GQ II) RX wagon (Australia)
Ford Maverick wagon (Australia)
Two major updates came in Australia, one in 1992 (GQ Series 2), and one in 1995 (minor facelift). The most notable changes in 1992 were the introduction of fuel-injection on the TB42 motor, EGR valve and oil cooler on the RD28T, new seats, new trim, sound deadening, and side intrusion bars. Other 1992 Series 2 refinements included a revised transmission and suspension, and introducing bigger brakes, bigger wheels, and the standardization of limited slip differentials and auto-freewheeling hubs. This update included new seats, trim, and side intrusion bars.
In 1991, the rear indicators, tail lights, and brake lights were relocated to the bumper from the body to meet Australian Design Rules, but they stayed the same in European versions. In 1992, another set of indicators was placed on the front quarter panel.
In August 1993, the TD42 lost weight to reduce fuel consumption and increase maximum engine speed. This had the side effect of weakening the engine. The original engine can be identified by its silver rocker cover, whereas the lightened engine featured a black rocker cover. The RD28T got some extra changes, moving the vacuum pump from behind the alternator to the top of the engine. Driver-side airbags appeared in some European models.
Changes in 1995 featured a minor facelift, with a redesigned front grille and the RX model entering Australia.
Known weaknesses included vibrations from the front end (largely fixed under warranty), cracking hinges on the rear door (due to the spare tyre’s weight), and rust on rear window frames. The RD28T and TB42 engines suffered from head gasket issues when driven with a heavy foot. European five-speed gearboxes suffered from bearing failures in fifth gear at high mileages. However, the TD42 was highly reliable. Patrols are known for their strong axles and good limited slip differential (when so equipped).
From 1988 to 1994, Ford Australia rebadged the Y60 Patrol as the Ford Maverick. This was a result of the Button car plan devised by the government of Australia. The car was mechanically similar, although the Nissan version had rear disc brakes depending on vehicle grade, while the Ford mostly had drum brakes and featured different paint colours and trim levels.
All wagons had a 95-liter main fuel tank with the utility having a 90-liter tank and the option of a 95-liter second tank.
Engine specifications[edit]
| Engine code | Displacement | Bore x stroke | Power | Torque | Compression ratio | Design | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB30S | 2962 cc | 86 x
85mm |
100 kW at 4800 rpm | 224 Nm at 3000 rpm | 9.0:1 | Inline-six SOHC, petrol | Aluminum crossflow cylinder head |
| TB42S | 4169 cc | 96 x
96mm |
125 kW at 4200 rpm | 325 Nm at 2800 rpm | 8.3.1 | Inline-six Pushrod, petrol | Crossflow cylinder head, high camshaft |
| TB42E | 135 kW at 4400 rpm | 320 Nm at 3200 rpm | 8.3:1 | ||||
| RD28T | 2826 cc | 85 x
83mm |
91.9 kW at 4400 rpm | 255 Nm at 2000 rpm | 21.2:1 | Inline-six SOHC, diesel | Turbocharged |
| TD422 | 4169 cc | 96 x
96mm |
85 kW at 4000 rpm | 264 Nm at 2000 rpm | 22.7:1 | Inline-six pushrod, diesel | Crossflow cylinder head, high camshaft |
Fifth generation (Y61; 1997)[edit]
| Fifth generation (Y61) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Safari (Japan) |
| Production | October 1997 – 2016[5] 1997–present (continues in selective countries) |
| Assembly |
|
| Designer | Masato Takahashi (1994) Junichi Sakai (facelift: 2003)[6] |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size off-road vehicle |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 2,400 mm (94.5 in) LWB: 2,970 mm (116.9 in) |
| Length | SWB: 4,440 mm (174.8 in) LWB: 5,080 mm (200.0 in) |
| Width | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
| Height | 1,855 mm (73.0 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,473 kg (5,452 lb) |
Cab chassis
5-door SUV
3-door SUV (facelift)
Nissan Safari (facelift)
Interior
Y61 models first appeared in December 1997, available in 4.5- and 4.8-litre petrol, 2.8-, 3.0-, and 4.2-litre turbo-diesel and 4.2-litre turbo-diesel intercooler variants. The alternative model codes of GR and GU were applied to left- and right-hand drive models, respectively.
The drivetrain was changed in this model, including larger CVs and less synchros in the manual gearboxes. The differential housings were widened to fall inline with the new body shape, but centers remained the same (H233 and H260). Some petrol wagons received a coil version of the H260 differential.
Comfort levels were increased over GQ, especially in the seating and NVH areas.
GU IV onwards[edit]
For the 2005 model year a significant facelift model was released, with new headlights, box flares on each guard and larger tail lights. The troubles that plagued the ZD30 diesel around the variable turbo geometry were resolved by this refresh.
That same year, Nissan stopped selling the Safari in Japan due to poor sales. Nissan also made a two-door pickup version of the Y61 series available as cab chassis and with a style side tray in some markets. Although a new model was launched, this Y61 series still sells for offroad enthusiasts but with few options.
Its TB48DE engine is very popular among the tuning community in the middle east, especially in the UAE. The TB48DE engine is easily modifiable and is shown to be able to handle over 2,000 hp (1,500 kW) for several sand hills and sand drag challenges in the region.
As of 2014, Nissan discontinued the fifth generation model worldwide, except for South Africa, the Middle East, Paraguay, Haiti, Philippines, Nepal, Bolivia, Sri Lanka, and some African and Eastern European countries where the 4×4 competed against the Toyota Land Cruiser (J70). In Australia, the Y61 was sold until 2016, alongside the Y62.
Several special edition trims have been also been released in respective regions where the Y61 was and are currently being sold, of which some of them are The Presidential edition and 4XPRO edition (Philippines), The Legend edition (Philippines, South Africa and Australia), The ‘Special’ Super Safari edition (Middle East), The Falcon edition (Middle East), Gazelle, Gazelle Storm and Gazelle X editions (Middle East).
The Y61 is also still being produced for and used by United Nations agencies across different countries as well as some military branches and government sectors. They are mainly being used as security escorts vehicles, chief personnel carriers and off pavement patrol units.
Sixth generation (Y62; 2010)[edit]
| Sixth generation (Y62) | |
|---|---|

Pre-facelift |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Nissan Armada (2016–present) Infiniti QX56/QX80 Nissan Patrol Royale (Philippines) |
| Production | January 2010 – present |
| Assembly |
Russia: Saint-Petersburg, (SKD, 2012–2014) |
| Designer | Taiji Toyota (2007) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size SUV |
| Body style | 5-door SUV |
| Layout | Front-engine, rear-wheel drive Front-engine, four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Y62 |
| Related | Infiniti QX56/QX80 Nissan Armada (Y62) Nissan Terra Nissan Navara (D23) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 3,075 mm (121.1 in) |
| Length | 5,165 mm (203.3 in) |
| Width | 1,995 mm (78.5 in) |
| Height | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
| Curb weight | 2,695–2,795 kg (5,941–6,162 lb) |
The all-new, sixth generation, Y62 series Nissan Patrol was launched on 13 February 2010 in Abu Dhabi.[9] A luxury version (Z62) was sold as the Infiniti QX56 from 2010 (the first time that a Patrol-based vehicle had been sold in North America since 1969), which was later renamed the Infiniti QX80 in 2013. The Y62 was introduced in North America under the Armada nameplate in 2016, for the 2017 model year. It was presented as a replacement for the Titan-based first generation Nissan Armada (WA60).
As of 2017, the Y62 is powered by either a 275 hp (205 kW) / 394 N⋅m (291 lb⋅ft) 4.0-litre VQ40DE V6 engine for the entry level XE and SE trims or a more powerful 400 hp (298 kW) / 560 N⋅m (410 lb⋅ft) 5.6-litre VK56VD V8 engine for the upper level trims. The NISMO edition uses a tuned version of the 5.6-litre V8 producing 28 additional horsepower. Prior to the introduction of the 4.0-litre V6, a lower output 317 hp (236 kW) / 526 N⋅m (388 lb⋅ft) 5.6-litre VK56DE V8 was designated for the entry level trims.
As of 2017, all models come with a 7-speed automatic transmission although Nissan previously offered a 5-speed automatic and also a 6-speed manual for the entry level trim. A variable 4×4 mode package allows switching between four drive modes: sand, on-road, rock and snow. A Hydraulic Body Motion Control System is available. An electronic-locking rear differential, hill start and hill descent control, as well as lane-departure warning, computer assisted braking and stability control. The Infiniti version launched in the United States in 2010, the first Patrol sold there since the 60 series. The Nissan Patrol launched in Australia in early 2013.[8]
The Nissan Patrol is offered in various different trim levels in the Middle East: XE, SE, SE-Platinum City, LE, LE-Titanium, LE-Platinum City and NISMO Edition. In Australia the Ti and Ti-L trim levels are offered.
-
Rear view (pre-facelift)
-
Interior
Facelift[edit]
In 2014, a significant facelift arrived, with revised tail lights with red elements present, globe housings and built-in LED headlights. A new tan interior was added and new sets of wheels.
Nissan introduced a limited-run Patrol Black Special Edition in 200 units. These cars offer several enhancements such as red seats, chrome detailing and a black matte exterior paint scheme.
Nissan gave a second facelift to the 2019 Patrol before it will have a new version by 2020. Changes include a new front bumper featuring a deeper apron and a traditional round housing. The vehicle will be equipped with Nissan’s Intelligent Mobility driver-assistance features like lane keeping assist, forward collision warning, automatic emergency braking for front and rear, rear cross traffic alert, and blind spot monitoring.[10]
-
First facelift
-
Rear view (first facelift)
-
Second facelift
-
Second facelift (China)
-
Rear view (second facelift)
-
Interior (second facelift)
Patrol Desert Edition[edit]
The Desert Edition comes with the 400 hp 5.6-litre (5552cc) engine, manually-adjusted cloth seats, navigation and regular suspension instead of the hydraulic body-control system.[11]
Patrol Nismo[edit]
On launching the Nismo brand in the Middle East, the Nissan Patrol Nismo was introduced at the launch event in Dubai along with the GT-R Nismo and 370Z Nismo. Unlike the standard Patrol, the Nismo version comes with (5.6-litre) V8 with 428 hp (319 kW) engine tuned by Nissan’s Takumi craftsmen. The suspensions is upgraded with Bilstein shocks and fitted with 22-inch forged-alloy wheels.[12]
-
2018 Nissan Patrol Nismo (front)
-
2018 Nissan Patrol Nismo (rear)
References[edit]
- ^ Ramey, Jay (17 September 2013). «This may be the oldest surviving Nissan in North America». Autoweek. Hearst Autos, Inc. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ^ Nissan Gamma [Nissan range] (brochure) (in Flemish), Aartselaar, Belgium: N.V. Nissan Belgium S.A., 1984, p. 1
- ^ a b Visart, Etienne, ed. (10 March 1983). «Un constructeur Japonais fabrique en Europe!» [A Japanese manufacturer builds in Europe!]. Le Moniteur de l’Automobile (in French). Brussels, Belgium: Editions Auto-Magazine. 34 (764): 24.
- ^ Walker, Alan (September 1982). Kennett, Pat (ed.). «The great European retreat». Truck. London: FF Publishing: 36.
- ^ «History». Nissan Shatai. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ «A Revitalised Design for Nissan’s 2005 Patrol». Next Car. 12 October 2004. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ Opara, Theodore (27 April 2014). «First built in Nigeria Nissan Patrol rolls off production line». Vanguard. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ^ a b «2013 Nissan Patrol (Y62) Australia Introduction» (PDF).
- ^ «Stunning looks coupled with unstoppable 4WD upgrades make Nissan Patrol new class-leader as Nissan’s ‘Hero of All Terrain’» (Press release). Nissan. 13 February 2010. Archived from the original on 22 April 2012. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ «Nissan gives 2019 Patrol a (slightly) new look – Auto Industry News». AutoIndustriya.com. 8 October 2018. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- ^ «First drive: 2016 Nissan Patrol Desert Edition in Liwa UAE»
- ^ «2017 Nissan Patrol Nismo | Drive Arabia»
External links[edit]
Media related to Nissan Patrol at Wikimedia Commons
- Nissan Patrol Archived 12 July 2019 at the Wayback Machine at Nissan’s global website
- Nissanh Heritage Nissan Safari