This article is about the country. It is not to be confused with Great Britain, its largest island, or England, its largest constituent country.
|
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
|---|---|
|
Flag Coat of arms |
|
| Anthem: «God Save the King»[a] | |
Royal coat of arms in Scotland: |
|
|
Location of the United Kingdom (dark green) in Europe (dark grey) |
|
| Capital
and largest city |
London 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.500°N 0.117°W |
| Official language and national language |
English (de facto) |
| Regional and minority languages[b] |
|
| Ethnic groups
(2011) |
|
| Religion
(2011)[4][5] |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Constituent countries |
|
| Government | Unitary[e] parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch |
Charles III |
|
• Prime Minister |
Rishi Sunak |
| Legislature | Parliament |
|
• Upper house |
House of Lords |
|
• Lower house |
House of Commons |
| Formation | |
|
• Laws in Wales Acts |
1535 and 1542 |
|
• Union of the Crowns |
24 March 1603 |
|
• Treaty of Union |
22 July 1706 |
|
• Acts of Union of England and Scotland |
1 May 1707 |
|
• Acts of Union of Great Britain and Ireland |
1 January 1801 |
|
• Irish Free State Constitution Act |
5 December 1922 |
| Area | |
|
• Total |
242,495 km2 (93,628 sq mi)[9] (78th) |
|
• Water (%) |
1.51 (2015)[10] |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 estimate |
67,791,400[11] (22nd) |
|
• 2011 census |
63,182,178[12] (22nd) |
|
• Density |
270.7/km2 (701.1/sq mi) (50th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2021) | very high · 18th |
| Currency | Pound sterling[f] (GBP) |
| Time zone | UTC (Greenwich Mean Time, WET) |
|
• Summer (DST) |
UTC+1 (British Summer Time, WEST) |
| [g] | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy yyyy—mm—dd (AD) |
| Driving side | left[h] |
| Calling code | +44[i] |
| ISO 3166 code | GB |
| Internet TLD | .uk[j] |
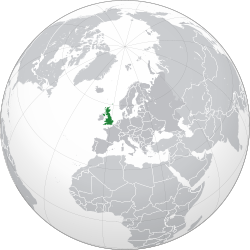
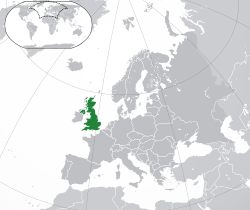
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain,[k][16] is a sovereign state and country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland.[17] It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[18] The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles.[19] Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242,495 square kilometres (93,628 sq mi), with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people.[20]
The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 1707 formed the Kingdom of Great Britain. Its union in 1801 with the Kingdom of Ireland created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Most of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922, leaving the present United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, which formally adopted that name in 1927.[l] The nearby Isle of Man, Guernsey and Jersey are not part of the UK, being Crown Dependencies, but the British Government is responsible for their defence and international representation.[21] There are also 14 British Overseas Territories,[22] the last remnants of the British Empire which, at its height in the 1920s, encompassed almost a quarter of the world’s landmass and a third of the world’s population, and was the largest empire in history. British influence can be observed in the language, culture and the legal and political systems of many of its former colonies.[23][24]
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.[m][26] The capital and largest city is London, a global city and financial centre with a metropolitan area population of over 14 million. Other major cities include Birmingham, Liverpool, Sheffield, Bristol and Glasgow.[27] Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments, each with varying powers.[28] The UK became the world’s first industrialised country and was the world’s foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries, during a period of unchallenged global hegemony known as «Pax Britannica».[29][30][31][32] In the 21st century, the UK remains a great power[33][34][35][36] and has significant economic, cultural, military, scientific, technological and political influence internationally.[37] The United Kingdom has the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the eighth-largest by purchasing power parity. It has a high-income economy and a very high Human Development Index rating, ranking 18th in the world. It also performs well in international rankings of education, healthcare, and life expectancy.[38] It is a recognised nuclear state and is ranked fourth globally in military expenditure.[39] It has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since its first session in 1946.
The United Kingdom is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Council of Europe, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, Five Eyes, the United Nations, NATO, AUKUS, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Interpol, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). The UK is also considered a part of the «Big Four», or G4, an unofficial grouping of important European nations.[40] It was a member state of the European Communities (EC) and its successor, the European Union (EU), from its accession in 1973 until its withdrawal in 2020 following a 2016 referendum.
Etymology and terminology
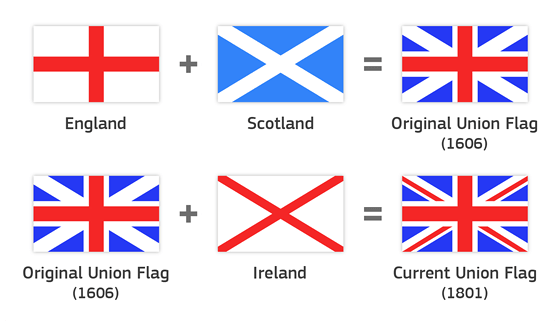
In 43 AD, Britannia referred to the Roman province that encompassed modern day England and Wales. Great Britain encompassed the whole island, taking in the land north of the River Forth known to the Romans as Caledonia in modern Scotland (i.e. «greater» Britain).[41] In the Middle Ages, the name «Britain» was also applied to a small part of France now known as Brittany. As a result, Great Britain (likely from the French «Grande Bretagne«) came into use to refer specifically to the island, with Brittany often referred to as «Little Britain».[42] However, that name had no official significance until 1707, when the island’s kingdoms of England and Scotland were united as the Kingdom of Great Britain.[43]
The Acts of Union 1707 declared that the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland were «United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain».[n][44] The term «United Kingdom» has occasionally been used as a description for the former Kingdom of Great Britain, although its official name from 1707 to 1800 was simply «Great Britain».[45] The Acts of Union 1800 united the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801, forming the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Following the partition of Ireland and the independence of the Irish Free State in 1922, which left Northern Ireland as the only part of the island of Ireland within the United Kingdom, the name was changed to the «United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland».[46]
Although the United Kingdom is a sovereign country, England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are also widely referred to as countries.[47] The UK Prime Minister’s website has used the phrase «countries within a country» to describe the United Kingdom.[18] Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as «regions».[48] Northern Ireland is also referred to as a «province».[49] With regard to Northern Ireland, the descriptive name used «can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one’s political preferences».[50]
The term «Great Britain» conventionally refers to the island of Great Britain, or politically to England, Scotland and Wales in combination.[51] It is sometimes used as a loose synonym for the United Kingdom as a whole.[52] The word England is occasionally used incorrectly to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole, a mistake principally made by people from outside the UK.[53]
The term «Britain» is used both as a synonym for Great Britain,[54][55] and as a synonym for the United Kingdom.[56][55] Usage is mixed: the UK Government prefers to use the term «UK» rather than «Britain» or «British» on its own website (except when referring to embassies),[57] while acknowledging that both terms refer to the United Kingdom and that elsewhere «British government» is used at least as frequently as «United Kingdom government».[58] The UK Permanent Committee on Geographical Names recognises «United Kingdom», «UK» and «U.K.» as shortened and abbreviated geopolitical terms for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in its toponymic guidelines; it does not list «Britain» but notes that «it is only the one specific nominal term ‘Great Britain’ which invariably excludes Northern Ireland».[58] The BBC historically preferred to use «Britain» as shorthand only for Great Britain, though the present style guide does not take a position except that «Great Britain» excludes Northern Ireland.[59]
The adjective «British» is commonly used to refer to matters relating to the United Kingdom and is used in law to refer to United Kingdom citizenship and matters to do with nationality.[60] People of the United Kingdom use several different terms to describe their national identity and may identify themselves as being British, English, Scottish, Welsh, Northern Irish, or Irish;[61] or as having a combination of different national identities.[62] The official designation for a citizen of the United Kingdom is «British citizen».[58]
History
Prior to the Treaty of Union
Stonehenge in Wiltshire is a ring of stones, each about 4 m (13 ft) high, 2 m (7 ft) wide and 25 tonnes, erected 2400–2200 BC.
Settlement by anatomically modern humans of what was to become the United Kingdom occurred in waves beginning by about 30,000 years ago.[63] By the end of the region’s prehistoric period, the population is thought to have belonged, in the main, to a culture termed Insular Celtic, comprising Brittonic Britain and Gaelic Ireland.[64]
The Roman conquest, beginning in 43 AD, and the 400-year rule of southern Britain, was followed by an invasion by Germanic Anglo-Saxon settlers, reducing the Brittonic area mainly to what was to become Wales, Cornwall and, until the latter stages of the Anglo-Saxon settlement, the Hen Ogledd (northern England and parts of southern Scotland).[65] Most of the region settled by the Anglo-Saxons became unified as the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.[66] Meanwhile, Gaelic-speakers in north-west Britain (with connections to the north-east of Ireland and traditionally supposed to have migrated from there in the 5th century)[67] united with the Picts to create the Kingdom of Scotland in the 9th century.[68]
In 1066, the Normans invaded England from northern France. After conquering England, they seized large parts of Wales, conquered much of Ireland and were invited to settle in Scotland, bringing to each country feudalism on the Northern French model and Norman-French culture.[69] The Anglo-Norman ruling class greatly influenced, but eventually assimilated with, each of the local cultures.[70] Subsequent medieval English kings completed the conquest of Wales and made unsuccessful attempts to annex Scotland. Asserting its independence in the 1320 Declaration of Arbroath, Scotland maintained its independence thereafter, albeit in near-constant conflict with England.
The English monarchs, through inheritance of substantial territories in France and claims to the French crown, were also heavily involved in conflicts in France, most notably the Hundred Years’ War, while the Kings of Scots were in an alliance with the French during this period.[71]
Early modern Britain saw religious conflict resulting from the Reformation and the introduction of Protestant state churches in each country.[72] Wales was fully incorporated into the Kingdom of England,[73] and Ireland was constituted as a kingdom in personal union with the English crown.[74] In what was to become Northern Ireland, the lands of the independent Catholic Gaelic nobility were confiscated and given to Protestant settlers from England and Scotland.[75]
The English Reformation ushered in political, constitutional, social and cultural change in the 16th century. Moreover, it defined a national identity for England and slowly, but profoundly, changed people’s religious beliefs and established the Church of England.[76]
In 1603, the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots, inherited the crowns of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal, and religious institutions.[77]
In the mid-17th century, all three kingdoms were involved in a series of connected wars (including the English Civil War) which led to the temporary overthrow of the monarchy, with the execution of King Charles I, and the establishment of the short-lived unitary republic of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.[78]
Although the monarchy was restored, the Interregnum along with the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689 in England and Claim of Right Act 1689 in Scotland ensured that, unlike much of the rest of Europe, royal absolutism would not prevail, and a professed Catholic could never accede to the throne. The British constitution would develop on the basis of constitutional monarchy and the parliamentary system.[79] With the founding of the Royal Society in 1660, science was greatly encouraged. During this period, particularly in England, the development of naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean.[80]
Though previous attempts at uniting the two kingdoms within Great Britain in 1606, 1667, and 1689 had proved unsuccessful, the attempt initiated in 1705 led to the Treaty of Union of 1706 being agreed and ratified by both parliaments.
Kingdom of Great Britain
On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union 1707 being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706 Treaty of Union and so unite the two kingdoms.[81]
In the 18th century, cabinet government developed under Robert Walpole, in practice the first prime minister (1721–1742). A series of Jacobite Uprisings sought to remove the Protestant House of Hanover from the British throne and restore the Catholic House of Stuart. The Jacobites were finally defeated at the Battle of Culloden in 1746, after which the Scottish Highlanders were brutally suppressed. The British colonies in North America that broke away from Britain in the American War of Independence became the United States of America, recognised by Britain in 1783. British imperial ambition turned towards Asia, particularly to India.[82]
Britain played a leading part in the Atlantic slave trade, mainly between 1662 and 1807 when British or British-colonial Slave ships transported nearly 3.3 million slaves from Africa.[83] The slaves were taken to work on plantations in British possessions, principally in the Caribbean but also North America.[84] Slavery coupled with the Caribbean sugar industry had a significant role in strengthening and developing the British economy in the 18th century.[85] However, Parliament banned the trade in 1807, banned slavery in the British Empire in 1833, and Britain took a role in the movement to abolish slavery worldwide through the blockade of Africa and pressing other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties.[86]
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The term «United Kingdom» became official in 1801 when the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland each passed an Act of Union, uniting the two kingdoms and creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.[87]
After the defeat of France at the end of the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815), the United Kingdom emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century (with London the largest city in the world from about 1830).[88] Unchallenged at sea, British dominance was later described as Pax Britannica («British Peace»), a period of relative peace among the Great Powers (1815–1914) during which the British Empire became the global hegemon and adopted the role of global policeman.[89] By the time of the Great Exhibition of 1851, Britain was described as the «workshop of the world».[90] From 1853 to 1856, Britain took part in the Crimean War, allied with the Ottoman Empire in the fight against the Russian Empire,[91] participating in the naval battles of the Baltic Sea known as the Åland War in the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland, among others.[92] The British Empire was expanded to include India, large parts of Africa and many other territories throughout the world. Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, British dominance of much of world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many regions, such as Asia and Latin America.[93]
Political attitudes favoured free trade and laissez-faire policies and a gradual widening of the voting franchise. During the century, the population increased at a dramatic rate, accompanied by rapid urbanisation, causing significant social and economic stresses.[94] To seek new markets and sources of raw materials, the Conservative Party under Disraeli launched a period of imperialist expansion in Egypt, South Africa, and elsewhere. Canada, Australia and New Zealand became self-governing dominions.[95] After the turn of the century, Britain’s industrial dominance was challenged by Germany and the United States.[96] Social reform and home rule for Ireland were important domestic issues after 1900. The Labour Party emerged from an alliance of trade unions and small socialist groups in 1900, and suffragettes campaigned from before 1914 for women’s right to vote.[97]
World wars and partition of Ireland
Britain was one of the principal Allies that fought against the Central Powers in the First World War (1914–1918). Alongside their French, Russian and (after 1917) American counterparts,[98] British armed forces were engaged across much of the British Empire and in several regions of Europe, particularly on the Western Front.[99] The high fatalities of trench warfare caused the loss of much of a generation of men, with lasting social effects in the nation and a great disruption in the social order. After the war, Britain became a permanent member of the Executive Council of the League of Nations and received a mandate over a number of former German and Ottoman colonies. The British Empire reached its greatest extent, covering a fifth of the world’s land surface and a quarter of its population.[100] Britain had suffered 2.5 million casualties and finished the war with a huge national debt.[99] The consequences of the war persuaded the government to expand the right to vote in national and local elections with the Representation of the People Act 1918.[citation needed]
By the mid-1920s, most of the British population could listen to BBC radio programmes.[101][102] Experimental television broadcasts began in 1929 and the first scheduled BBC Television Service commenced in 1936.[103] The rise of Irish nationalism, and disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish Home Rule, led eventually to the partition of the island in 1921.[104] The Irish Free State became independent, initially with Dominion status in 1922, and unambiguously independent in 1931. Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom.[105] The 1928 Equal Franchise Act gave women electoral equality with men in national elections. A wave of strikes in the mid-1920s culminated in the General Strike of 1926. Britain had still not recovered from the effects of the First World War when the Great Depression (1929–1932) occurred. This led to considerable unemployment and hardship in the old industrial areas, as well as political and social unrest in the 1930s, with rising membership in communist and socialist parties. A coalition government was formed in 1931.[106]
Nonetheless, «Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system.»[107] After Nazi Germany invaded Poland, Britain entered the Second World War by declaring war on Germany in 1939. Winston Churchill became prime minister and head of a coalition government in 1940. Despite the defeat of its European allies in the first year of the war, Britain and its Empire continued the war against Germany. Churchill engaged industry, scientists and engineers to advise and support the government and the military in the prosecution of the war effort.[107] In 1940, the Royal Air Force defeated the German Luftwaffe in a struggle for control of the skies in the Battle of Britain. Urban areas suffered heavy bombing during the Blitz. The Grand Alliance of Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union formed in 1941, leading the Allies against the Axis powers. There were eventual hard-fought victories in the Battle of the Atlantic, the North Africa campaign and the Italian campaign. British forces played an important role in the Normandy landings of 1944 and the liberation of Europe, achieved with its allies the United States, the Soviet Union and other Allied countries. The British Army led the Burma campaign against Japan, and the British Pacific Fleet fought Japan at sea. British scientists contributed to the Manhattan Project to design a nuclear weapon,[108] which led to the surrender of Japan.
Postwar 20th century
During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world;[109] it was an original signatory to the Declaration by United Nations. After the war, the UK became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and worked closely with the United States to establish the IMF, World Bank and NATO.[110] The war left the UK severely weakened and financially dependent on the Marshall Plan,[111] but it was spared the total war that devastated eastern Europe.[112] In the immediate post-war years, the Labour government initiated a radical programme of reforms, which had a significant effect on British society in the following decades.[113] Major industries and public utilities were nationalised, a welfare state was established, and a comprehensive, publicly funded healthcare system, the National Health Service, was created.[114] The rise of nationalism in the colonies coincided with Britain’s now much-diminished economic position, so that a policy of decolonisation was unavoidable. Independence was granted to India and Pakistan in 1947.[115] Over the next three decades, most colonies of the British Empire gained their independence, with all those that sought independence supported by the UK, during both the transition period and afterwards. Many became members of the Commonwealth of Nations.[116]
The UK was the third country to develop a nuclear weapons arsenal (with its first atomic bomb test, Operation Hurricane, in 1952), but the new post-war limits of Britain’s international role were illustrated by the Suez Crisis of 1956. The international spread of the English language ensured the continuing international influence of its literature and culture.[117][118] As a result of a shortage of workers in the 1950s, the government encouraged immigration from Commonwealth countries. In the following decades, the UK became a more multi-ethnic society than before.[119] Despite rising living standards in the late 1950s and 1960s, the UK’s economic performance was less successful than many of its main competitors such as France, West Germany and Japan.
Leaders of EU states in 2007. The UK entered the EEC in 1973. In a 1975 referendum 67% voted to stay in it;[120] in 2016 52% voted to leave the EU.[121]
In the decades-long process of European integration, the UK was a founding member of the alliance called the Western European Union, established with the London and Paris Conferences in 1954. In 1960 the UK was one of the seven founding members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), but in 1973 it left to join the European Communities (EC). When the EC became the European Union (EU) in 1992, the UK was one of the 12 founding member states. The Treaty of Lisbon, signed in 2007, forms the constitutional basis of the European Union since then.
From the late 1960s, Northern Ireland suffered communal and paramilitary violence (sometimes affecting other parts of the UK) conventionally known as the Troubles. It is usually considered to have ended with the Belfast «Good Friday» Agreement of 1998.[122]
Following a period of widespread economic slowdown and industrial strife in the 1970s, the Conservative government of the 1980s under Margaret Thatcher initiated a radical policy of monetarism, deregulation, particularly of the financial sector (for example, the Big Bang in 1986) and labour markets, the sale of state-owned companies (privatisation), and the withdrawal of subsidies to others.[123]
In 1982, Argentina invaded the British territories of South Georgia and the Falkland Islands. The occupation provoked a military response from the United Kingdom leading to the Falklands War which lasted for 10 weeks. Argentine forces were defeated and surrendered to British troops. The inhabitants of the islands are predominantly descendants of British settlers, and strongly favour British sovereignty, as shown by a 2013 referendum. From 1984, the UK economy was helped by the inflow of substantial North Sea oil revenues.[124]
Around the end of the 20th century, there were major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved administrations for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[125] The statutory incorporation followed acceptance of the European Convention on Human Rights. The UK remained a Great Power with global diplomatic and military influence and a leading role in the United Nations and NATO.[126]
21st century
2 billion doses of Oxford University- AstraZeneca vaccine have been sent to more than 170 countries (Nov 21)[127]
The UK broadly supported the United States’ approach to the «war on terror» in the early years of the 21st century.[128] Controversy surrounded some of Britain’s overseas military deployments, particularly in Afghanistan and Iraq.[129]
The 2008 global financial crisis severely affected the UK economy. The Cameron–Clegg coalition government of 2010 introduced austerity measures intended to tackle the substantial public deficits which resulted.[130] The devolved Scottish Government and UK Government agreed for a referendum to be held on Scottish independence in 2014.[131] This referendum resulted in the electorate in Scotland voting by 55.3 to 44.7% for Scotland to remain part of the United Kingdom.[132]
In 2016, 51.9 per cent of voters in the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union.[133] The UK left the EU on 31 January 2020 and completed its withdrawal in full at the end of that year.[134]
The COVID-19 pandemic had a severe impact on the UK’s economy, caused major disruptions to education and had far-reaching impacts on society and politics in 2020 and 2021.[135][136][137] The United Kingdom was the first country in the world to use an approved COVID-19 vaccine, they also developed their own vaccine between Oxford University and AstraZeneca which allowed them to roll-out the vaccine nationwide quickly.[138][139]
On 8 September 2022, Elizabeth II, the longest-living and longest-reigning British monarch, died at the age of 96.[140] Upon the Queen’s death, her eldest child Charles, Prince of Wales, acceded to the British throne as King Charles III.[141]
Geography
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately 244,820 square kilometres (94,530 sq mi). The country occupies the major part of the British Isles[142] archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland and some smaller surrounding islands. It lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea with the southeast coast coming within 22 miles (35 km) of the coast of northern France, from which it is separated by the English Channel.[143]
In 1993 10 per cent of the UK was forested, 46 per cent used for pastures and 25 per cent cultivated for agriculture.[144] The Royal Greenwich Observatory in London was chosen as the defining point of the Prime Meridian[145] in Washington, DC, in 1884, although due to more accurate modern measurement the meridian actually lies 100 metres to the east of the observatory.[146]
The United Kingdom lies between latitudes 49° and 61° N, and longitudes 9° W and 2° E. Northern Ireland shares a 224-mile (360 km) land boundary with the Republic of Ireland.[143] The coastline of Great Britain is 11,073 miles (17,820 km) long.[147] It is connected to continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel, which at 31 miles (50 km) (24 miles (38 km) underwater) is the longest underwater tunnel in the world.[148]
The UK contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Celtic broadleaf forests, English Lowlands beech forests, North Atlantic moist mixed forests, and Caledon conifer forests.[149] The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 1.65/10, ranking it 161th globally out of 172 countries.[150]
Climate
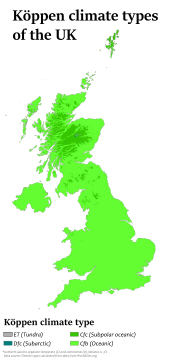
Most of the United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round.[143] The temperature varies with the seasons seldom dropping below 0 °C (32 °F) or rising above 30 °C (86 °F).[151] Some parts, away from the coast, of upland England, Wales, Northern Ireland and most of Scotland, experience a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc). Higher elevations in Scotland experience a continental subarctic climate (Dfc) and the mountains experience a tundra climate (ET).[152]
The prevailing wind is from the southwest and bears frequent spells of mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean,[143] although the eastern parts are mostly sheltered from this wind since the majority of the rain falls over the western regions the eastern parts are therefore the driest. Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters; especially in the west where winters are wet and even more so over high ground. Summers are warmest in the southeast of England and coolest in the north. Heavy snowfall can occur in winter and early spring on high ground, and occasionally settles to great depth away from the hills.[153]
The average total annual sunshine in the United Kingdom is 1339.7 hours, which is just under 30% of the maximum possible (The maximum hours of sunshine possible in one year is approximately 4476 hours).[154] The hours of sunshine vary from 1200 to about 1580 hours per year, and since 1996 the UK has been and still is receiving above the 1981 to 2010 average hours of sunshine[155]
United Kingdom is ranked 4 out of 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index.[156] A law has been passed that UK greenhouse gas emissions will be net zero by 2050.[157]
Topography
England accounts for just over half (53 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 130,395 square kilometres (50,350 sq mi).[158] Most of the country consists of lowland terrain,[144] with more upland and some mountainous terrain northwest of the Tees–Exe line; including the Lake District, the Pennines, Exmoor and Dartmoor. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber. England’s highest mountain is Scafell Pike (978 metres (3,209 ft)) in the Lake District.
Scotland accounts for just under one-third (32 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 78,772 square kilometres (30,410 sq mi).[159] This includes nearly 800 islands,[160] predominantly west and north of the mainland; notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its topography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault – a geological rock fracture – which traverses Scotland from Arran in the west to Stonehaven in the east.[161] The fault separates two distinctively different regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the Lowlands to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland’s mountainous land, including Ben Nevis which at 1,345 metres (4,413 ft)[162] is the highest point in the British Isles.[163] Lowland areas – especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth known as the Central Belt – are flatter and home to most of the population including Glasgow, Scotland’s largest city, and Edinburgh, its capital and political centre, although upland and mountainous terrain lies within the Southern Uplands.
Wales accounts for less than one-tenth (9 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 20,779 square kilometres (8,020 sq mi).[164] Wales is mostly mountainous, though South Wales is less mountainous than North and mid Wales. The main population and industrial areas are in South Wales, consisting of the coastal cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, and the South Wales Valleys to their north. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia and include Snowdon (Welsh: Yr Wyddfa) which, at 1,085 metres (3,560 ft), is the highest peak in Wales.[144] Wales has over 2,704 kilometres (1,680 miles) of coastline.[147] Several islands lie off the Welsh mainland, the largest of which is Anglesey (Ynys Môn) in the north-west.
Northern Ireland, separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea and North Channel, has an area of 14,160 square kilometres (5,470 sq mi) and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh which, at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), is the largest lake in the British Isles by area.[165] The highest peak in Northern Ireland is Slieve Donard in the Mourne Mountains at 852 metres (2,795 ft).[144]
Government and politics
Constitutional principles
The Constitution of the United Kingdom is uncodified and consists mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statutes, judge-made case law and international treaties, together with constitutional conventions.[166] Nevertheless, the Supreme Court recognises a number of principles underlying the British constitution, such as parliamentary sovereignty, the rule of law, democracy, and upholding international law.[167]
The Supreme Court also recognises that some acts of Parliament have special constitutional status, and are therefore part of the constitution.[168] These include Magna Carta, which in 1215 required the King to call a «common counsel» (now called Parliament) to represent people, to hold courts in a fixed place, to guarantee fair trials, to guarantee free movement of people, to free the church from the state, and to guarantee rights of «common» people to use the land.[169] (Most of Magna Carta is no longer in force; those principles it established that still exist are mostly protected by other enactments.) After the Wars of the Three Kingdoms and the Glorious Revolution, the Bill of Rights 1689 and the Claim of Right Act 1689 cemented Parliament’s position as the supreme law-making body, and said that the «election of members of Parliament ought to be free».
In accordance with the principle of parliamentary sovereignty, the UK Parliament can carry out constitutional reform through acts of Parliament, and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. No sitting parliament can pass laws that future parliaments cannot change.[170]
The sovereign
The United Kingdom is a unitary state under a constitutional monarchy. King Charles III is the monarch and head of state of the UK, as well as 14 other independent countries. These 15 countries are sometimes referred to as «Commonwealth realms». The monarch is formally vested with all executive authority as the personal embodiment of the Crown. The disposition of such powers however, including those belonging to the royal prerogative, is generally exercised only on the advice of ministers of the Crown responsible to Parliament and thence to the electorate. Nevertheless, in the performance of executive duties, the monarch has «the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, and the right to warn».[171] In addition, the monarch has a number of reserve powers at his disposal in order to uphold responsible government and prevent constitutional crises.[172] These reserve powers are particularly relevant to the appointment of a prime minister, preventing unconstitutional use of the British Armed Forces, the prorogation and dissolution of Parliament, the enactment of legislation, and conferring state honours.[173][174][175][176][177][178]
Parliament
The UK is a parliamentary democracy operating under the Westminster system, otherwise known as a «democratic parliamentary monarchy».[179] The Parliament of the United Kingdom is sovereign.[180] It is made up of the House of Commons, the House of Lords and the Crown.[181] The main business of parliament takes place in the two houses,[181] but royal assent is required for a bill to become an act of parliament (law).[182]
For general elections (elections to the House of Commons), the UK is divided into 650 constituencies, each of which is represented by a member of Parliament (MP).[183] MPs hold office for up to five years and are always up for re-election in general elections.[183] The Conservative Party, Labour Party and Scottish National Party are, respectively, the current first, second and third largest parties (by number of MPs) in the House of Commons.[184]
Prime minister
The prime minister is the head of government in the United Kingdom.[185] Nearly all prime ministers have served concurrently as First Lord of the Treasury[186] and all prime ministers have continuously served as First Lord of the Treasury since 1905,[187] Minister for the Civil Service since 1968[188] and Minister for the Union since 2019.[189] In modern times, the prime minister is, by constitutional convention, an MP.[190] The prime minister is appointed by the monarch[191] and their appointment is governed by constitutional conventions.[183] However, they are normally the leader of the political party with the most seats in the House of Commons[192] and hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons.[190]
The prime minister not only has statutory functions (alongside other ministers),[193] but is the monarch’s principal adviser[194] and it is for them to advise the monarch on the exercise of the royal prerogative in relation to government.[190] In particular, the prime minister recommends the appointment of ministers[190] and chairs the Cabinet.[195]
Administrative divisions
The geographical division of the United Kingdom into counties or shires began in England and Scotland in the early Middle Ages, and was completed throughout Great Britain and Ireland by the early Modern Period.[196] Administrative arrangements were developed separately in each country of the United Kingdom, with origins that often predated the formation of the United Kingdom. Modern local government by elected councils, partly based on the ancient counties, was established by separate Acts of Parliament: in England and Wales in 1888, Scotland in 1889 and Ireland in 1898, meaning there is no consistent system of administrative or geographic demarcation across the UK.[197]
Until the 19th century there was little change to those arrangements, but there has since been a constant evolution of role and function.[198]
The organisation of local government in England is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to local arrangements. The upper-tier subdivisions of England are the nine regions, now used primarily for statistical purposes.[199] One of the regions, Greater London, has had a directly elected assembly and mayor since 2000 following popular support for the proposal in a 1998 referendum.[200] It was intended that other regions would also be given their own elected regional assemblies, but a proposed assembly in the North East region was rejected by a referendum in 2004.[201] Since 2011, ten combined authorities have been established in England. Eight of these have elected mayors, elections for which first took place in May 2017.[202] Below the regional tier, some parts of England have county councils and district councils, and others have unitary authorities, while London consists of 32 London boroughs and the City of London. Councillors are elected by the first-past-the-post system in single-member wards or by the multi-member plurality system in multi-member wards.[203]
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 council areas with a wide variation in both size and population. The cities of Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen and Dundee are separate council areas, as is the Highland Council, which includes a third of Scotland’s area but only just over 200,000 people. Local councils are made up of elected councillors, of whom there are 1,223;[204] they are paid a part-time salary. Elections are conducted by single transferable vote in multi-member wards that elect either three or four councillors. Each council elects a Provost, or Convenor, to chair meetings of the council and to act as a figurehead for the area.
Local government in Wales consists of 22 unitary authorities, each led by a leader and cabinet elected by the council itself. These include the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, which are unitary authorities in their own right.[205] Elections are held every four years under the first-past-the-post system.[205]
Since 1973, local government in Northern Ireland has been organised into 26 district councils, each elected by single transferable vote. Their powers are limited to services such as waste collection, dog control, and maintaining parks and cemeteries.[206] In 2008 the executive agreed on proposals to create 11 new councils and replace the present system.[207]
Devolved governments
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a first minister (or, in the case of Northern Ireland, a diarchal first minister and deputy first minister), and a devolved unicameral legislature. England, the largest country of the United Kingdom, has no devolved executive or legislature and is administered and legislated for directly by the UK’s government and parliament on all issues. This situation has given rise to the so-called West Lothian question, which concerns the fact that members of parliament from Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland can vote, sometimes decisively,[208] on matters that affect only England.[209] The 2013 McKay Commission on this recommended that laws affecting only England should need support from a majority of English members of parliament.[210]
The Scottish Government and Parliament have wide-ranging powers over any matter that has not been specifically reserved to the UK Parliament, including education, healthcare, Scots law and local government.[211] Their power over economic issues is significantly constrained by an act of the UK parliament passed in 2020.[219]
The Welsh Government and the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; formerly the National Assembly for Wales)[220] have more limited powers than those devolved to Scotland.[221] The Senedd is able to legislate on any matter not specifically reserved to the UK Parliament through Acts of Senedd Cymru.
The Northern Ireland Executive and Assembly have powers similar to those devolved to Scotland. The Executive is led by a diarchy representing unionist and nationalist members of the Assembly.[222] Devolution to Northern Ireland is contingent on participation by the Northern Ireland administration in the North-South Ministerial Council, where the Northern Ireland Executive cooperates and develops joint and shared policies with the Government of Ireland. The British and Irish governments co-operate on non-devolved matters affecting Northern Ireland through the British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference, which assumes the responsibilities of the Northern Ireland administration in the event of its non-operation.[citation needed]
The UK does not have a codified constitution and constitutional matters are not among the powers devolved to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. Under the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty, the UK Parliament could, in theory, therefore, abolish the Scottish Parliament, Senedd or Northern Ireland Assembly.[223] Indeed, in 1972, the UK Parliament unilaterally prorogued the Parliament of Northern Ireland, setting a precedent relevant to contemporary devolved institutions.[224] In practice, it would be politically difficult for the UK Parliament to abolish devolution to the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd, given the political entrenchment created by referendum decisions.[225] The political constraints placed upon the UK Parliament’s power to interfere with devolution in Northern Ireland are even greater than in relation to Scotland and Wales, given that devolution in Northern Ireland rests upon an international agreement with the Government of Ireland.[226] The UK Parliament restricts the three devolved parliaments’ legislative competence in economic areas through an Act passed in 2020.[219]
Dependencies
The United Kingdom, the 14 British Overseas Territories[22] and the three Crown Dependencies[229] form ‘one undivided Realm’.[230][231] All parts of the realm are under the sovereignty of the British Crown, but the Territories and Dependencies are not part of the UK. This is distinct from the status of Commonwealth realms, who have separate monarchies, but share the same monarch.[231]
The 14 British Overseas Territories are remnants of the British Empire: Anguilla; Bermuda; the British Antarctic Territory; the British Indian Ocean Territory; the British Virgin Islands; the Cayman Islands; the Falkland Islands; Gibraltar; Montserrat; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; the Turks and Caicos Islands; the Pitcairn Islands; South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and Akrotiri and Dhekelia on the island of Cyprus.[232] British claims in Antarctica have limited international recognition.[233] Collectively Britain’s overseas territories encompass an approximate land area of 480,000 square nautical miles (640,000 sq mi; 1,600,000 km2),[234] with a total population of approximately 250,000.[235] The overseas territories also give the UK the world’s fifth largest exclusive economic zone at 6,805,586 km2 (2,627,651 sq mi).[236][better source needed] A 1999 UK government white paper stated that: «[The] Overseas Territories are British for as long as they wish to remain British. Britain has willingly granted independence where it has been requested; and we will continue to do so where this is an option.»[237] Self-determination is also enshrined in the constitutions of several overseas territories and three have specifically voted to remain under British sovereignty (Bermuda in 1995,[238] Gibraltar in 2002[239] and the Falkland Islands in 2013).[240]
The Crown Dependencies are possessions of the Crown, as opposed to territories of the UK.[241] They comprise three independently administered jurisdictions: the Bailiwicks of Jersey and of Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea. By mutual agreement, the British Government manages the islands’ foreign affairs and defence and the UK Parliament has the authority to legislate on their behalf. Internationally, they are regarded as «territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible».[242] The power to pass legislation affecting the islands ultimately rests with their own respective legislative assemblies, with the assent of the Crown (Privy Council or, in the case of the Isle of Man, in certain circumstances the Lieutenant-Governor).[243] Since 2005 each Crown dependency has had a Chief Minister as its head of government.[244]
Law and criminal justice
The Supreme Court is the final court of appeal for England, Wales, Northern Ireland and civil cases in Scotland
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland’s separate legal system.[245] Today the UK has three distinct systems of law: English law, Northern Ireland law and Scots law. A new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom came into being in October 2009 to replace the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords.[246] The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, including the same members as the Supreme Court, is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the British Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies.[247]
Both English law, which applies in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland law are based on common-law principles.[248] The essence of common law is that, subject to statute, the law is developed by judges in courts, applying statute, precedent and common sense to the facts before them to give explanatory judgements of the relevant legal principles, which are reported and binding in future similar cases (stare decisis).[249] The courts of England and Wales are headed by the Senior Courts of England and Wales, consisting of the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land for both criminal and civil appeal cases in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and any decision it makes is binding on every other court in the same jurisdiction, often having a persuasive effect in other jurisdictions.[250]
Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases,[251] and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases.[252] The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom serves as the highest court of appeal for civil cases under Scots law.[253] Sheriff courts deal with most civil and criminal cases including conducting criminal trials with a jury, known as sheriff solemn court, or with a sheriff and no jury, known as sheriff summary Court.[254] The Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdicts for a criminal trial: «guilty», «not guilty» and «not proven». Both «not guilty» and «not proven» result in an acquittal.[255]
Crime in England and Wales increased in the period between 1981 and 1995, though since that peak there has been an overall fall of 66 per cent in recorded crime from 1995 to 2015,[256] according to crime statistics. The prison population of England and Wales has increased to 86,000, giving England and Wales the highest rate of incarceration in Western Europe at 148 per 100,000.[257] His Majesty’s Prison Service, which reports to the Ministry of Justice, manages most of the prisons within England and Wales. The murder rate in England and Wales has stabilised in the first half of the 2010s with a murder rate around 1 per 100,000 which is half the peak in 2002 and similar to the rate in the 1980s[258] Crime in Scotland fell slightly in 2014–2015 to its lowest level in 39 years in with 59 killings for a murder rate of 1.1 per 100,000. Scotland’s prisons are overcrowded but the prison population is shrinking.[259]
Foreign relations
The UK is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of NATO, AUKUS, the Commonwealth of Nations, the G7 finance ministers, the G7 forum, the G20, the OECD, the WTO, the Council of Europe and the OSCE.[260] The UK has the British Council which is a British organisation based in over 100 countries specialising in international cultural and educational opportunities. The UK is said to have a «Special Relationship» with the United States and a close partnership with France – the «Entente cordiale» – and shares nuclear weapons technology with both countries;[261] the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance is considered to be the oldest binding military alliance in the world. The UK is also closely linked with the Republic of Ireland; the two countries share a Common Travel Area and co-operate through the British-Irish Intergovernmental Conference and the British-Irish Council. Britain’s global presence and influence is further amplified through its trading relations, foreign investments, official development assistance and military engagements.[262] Canada, Australia and New Zealand, all of which are former colonies of the British Empire which share King Charles as their head of state, are the most favourably viewed countries in the world by British people.[263]
Military
HMS Queen Elizabeth and HMS Prince of Wales
Royal Air Force Typhoon Jet
His Majesty’s Armed Forces consist of three professional service branches: the Royal Navy and Royal Marines (forming the Naval Service), the British Army and the Royal Air Force.[264] The armed forces of the United Kingdom are managed by the Ministry of Defence and controlled by the Defence Council, chaired by the Secretary of State for Defence. The Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch, to whom members of the forces swear an oath of allegiance.[265] The Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK’s global security interests and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in NATO, including the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps, the Five Power Defence Arrangements, RIMPAC and other worldwide coalition operations. Overseas garrisons and facilities are maintained in Ascension Island, Bahrain, Belize, Brunei, Canada, Cyprus, Diego Garcia, the Falkland Islands, Germany, Gibraltar, Kenya, Oman, Qatar and Singapore.[266]
The British armed forces played a key role in establishing the British Empire as the dominant world power in the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. By emerging victorious from conflicts, Britain has often been able to decisively influence world events. Since the end of the British Empire, the UK has remained a major military power. Following the end of the Cold War, defence policy has a stated assumption that «the most demanding operations» will be undertaken as part of a coalition.[267]
According to sources which include the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute and the International Institute for Strategic Studies, the UK has either the fourth- or the fifth-highest military expenditure. Total defence spending amounts to 2.0 per cent of national GDP.[268]
Economy
Overview
The United Kingdom uses the pound sterling which is the world’s oldest currency that is still in use and that has been in continuous use since its inception.[270] It is currently the fourth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market and is the world’s fourth-largest reserve currency (after the Dollar, Euro, and Yen).[271] London is the world capital for foreign exchange trading, with a global market share of 38.1% in 2022[272] of the daily $7.5 trillion global turnover.[273] Since 1997 the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England, has been responsible for setting interest rates at the level necessary to achieve the overall inflation target for the economy that is set by the Chancellor each year.[274] Lloyd’s of London is the worlds largest insurance and reinsurance market and is located in London, UK.[275]
The UK has a partially regulated market economy.[276] Based on market exchange rates, the UK is today the fifth-largest economy in the world and the second-largest in Europe after Germany. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government’s public finance policy and economic policy. The Bank of England is the UK’s central bank and is responsible for issuing notes and coins in the nation’s currency, the pound sterling. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover their issue.
The service sector made up around 80% of the UK’s GVA in 2021.[277] London is one of the world’s largest financial centres, ranking second in the world, behind New York City, in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[278] London also has the largest city GDP in Europe.[279] Edinburgh ranks 17th in the world, and sixth in Western Europe in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[278] Tourism is very important to the British economy; with over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom was ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world.[280] The creative industries accounted for 5.9% of the UK’s GVA in 2019, having grown by 43.6% in real terms from 2010.[281] Creative industries contributed more than £111bn to the UK economy in 2018, growth in the sector is more than five times larger than growth across the UK economy as a whole as reported in 2018.[282] WPP plc, the world’s biggest advertising company, is also based in the UK.
Following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union, the functioning of the UK internal economic market is enshrined by the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020 which ensures trade in goods and services continues without internal barriers across the four countries of the United Kingdom.[283]
The Industrial Revolution started in Britain with an initial concentration on the textile industry,[284] followed by other heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining and steelmaking.[285] British merchants, shippers and bankers developed overwhelming advantage over those of other nations allowing the UK to dominate international trade in the 19th century.[286] As other nations industrialised, coupled with economic decline after two world wars, the United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined, by degrees, throughout the 20th century. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy but accounted for only 16.7 per cent of national output in 2003.[287]
The automotive industry employs around 800,000 people, with a turnover in 2015 of £70 billion, generating £34.6 billion of exports (11.8 per cent of the UK’s total export goods). In 2015, the UK produced around 1.6 million passenger vehicles and 94,500 commercial vehicles including luxury cars such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley and Range Rover. The UK is a major centre for engine manufacturing: in 2015 around 2.4 million engines were produced. The UK motorsport industry employs more than 40,000 people, comprises around 4,300 companies and has an annual turnover of around £10 billion.[288]
7 of the 10 Formula One teams are based in the UK, with their technology being used in supercars and hypercars from McLaren, Aston Martin and Lotus.
The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry in the world depending upon the method of measurement and has an annual turnover of around £30 billion.[289]
BAE Systems plays a critical role in some of the world’s biggest defence aerospace projects. In the UK, the company makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter and assembles the aircraft for the Royal Air Force, the plane was based on the British Aerospace EAP design which first flew in 1986.[290][291] BAE Systems is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Joint Strike Fighter – the world’s largest single defence project – for which it designs and manufactures a range of components. It also manufactures the Hawk, the world’s most successful[clarification needed] jet training aircraft.[292] Airbus UK also manufactures the wings for the A400M military transporter. Rolls-Royce is the world’s second-largest aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft and it has more than 30,000 engines in service in the civil and defence sectors.
The UK space industry was worth £16.5bn in 2019/20 and employed 47,000 people. Since 2012, the number of space organisations has grown on average nearly 21% per year, with 1,293 organisations reported in 2021.[293] In 2013, the British Government pledged £60 m to the Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a «crucial stage» to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE engine to be built.
The pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.[294]
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing about 60 per cent of food needs with less than 1.6 per cent of the labour force (535,000 workers).[295] Around two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. The UK retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. It is also rich in a variety of natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica and an abundance of arable land.[296] In 2020, coronavirus lockdown measures caused the UK economy to suffer its biggest slump on record, shrinking by 20.4 per cent between April and June compared to the first three months of the year, to push it officially into recession for the first time in 11 years.[297]
The UK Government debt was £2,436.7 billion at the end of Quarter 2 (Apr to June) 2022. The UK has the 2nd best debt-to-GDP ratio out of the G7 countries.[298] The UK annual GDP output is estimated to have grown by 4.1% in 2022.[299]
Science and technology
England and Scotland were leading centres of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century.[301] The United Kingdom led the Industrial Revolution from the 18th century,[284] and has continued to produce scientists and engineers credited with important advances.[302] Major theorists from the 17th and 18th centuries include Isaac Newton, whose laws of motion and illumination of gravity have been seen as a keystone of modern science;[303] from the 19th century Charles Darwin, whose theory of evolution by natural selection was fundamental to the development of modern biology, and James Clerk Maxwell, who formulated classical electromagnetic theory; and more recently Stephen Hawking, who advanced major theories in the fields of cosmology, quantum gravity and the investigation of black holes.[304]
Major scientific discoveries from the 18th century include hydrogen by Henry Cavendish;[305] from the 20th century penicillin by Alexander Fleming,[306] and the structure of DNA, by Francis Crick and others.[307] Famous British engineers and inventors of the Industrial Revolution include James Watt, George Stephenson, Richard Arkwright, Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel.[308] Other major engineering projects and applications by people from the UK include the steam locomotive, developed by Richard Trevithick and Andrew Vivian;[309] from the 19th century the electric motor by Michael Faraday, the first computer designed by Charles Babbage,[310] the first commercial electrical telegraph by William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone,[311] the incandescent light bulb by Joseph Swan,[312] and the first practical telephone, patented by Alexander Graham Bell;[313] and in the 20th century the world’s first working television system by John Logie Baird and others,[314] the jet engine by Frank Whittle, the basis of the modern computer by Alan Turing, and the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee.[315]
Scientific research and development remains important in British universities, with many establishing science parks to facilitate production and co-operation with industry.[316] Between 2004 and 2008 the UK produced 7 per cent of the world’s scientific research papers and had an 8 per cent share of scientific citations, the third and second-highest in the world (after the United States and China, respectively).[317] Scientific journals produced in the UK include publications by the Royal Society, Nature, the British Medical Journal and The Lancet.[318] The United Kingdom was ranked fourth in the Global Innovation Index 2020, 2021 and 2022. [319]
Transport
A radial road network totals 29,145 miles (46,904 km) of main roads, 2,173 miles (3,497 km) of motorways and 213,750 miles (344,000 km) of paved roads.[143] The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world.[320] In 2022 there were a total of 40.8 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.[321]
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the West Coast, East Coast, Midland, Great Western and Great Eastern), which radiate from London to the rest of the country, augmented by regional rail lines and dense commuter networks within the major cities. High Speed 1 is operationally separate from the rest of the network. The world’s first passenger railway running on steam was the Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened in 1825. Just under five years later the world’s first intercity railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, designed by George Stephenson. The network grew rapidly as a patchwork of hundreds of separate companies during the Victorian era.[322]
Red double-decker buses in London
The UK has a railway network of 10,072 miles (16,209 km) in Great Britain and 189 miles (304 km) in Northern Ireland. Railways in Northern Ireland are operated by NI Railways, a subsidiary of state-owned Translink. In Great Britain, the British Rail network was privatised between 1994 and 1997, which was followed by a rapid rise in passenger numbers. The UK was ranked eighth among national European rail systems in the 2017 European Railway Performance Index assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety.[323] HS2 is a new high speed railway under construction linking up London, the Midlands, the North and Scotland serving over 25 stations, including eight of Britain’s 10 largest cities and connecting around 30 million people, capable of speeds of up to 225mph.[324][325] Crossrail, which was renamed the Elizabeth line in 2016, in honour of Queen Elizabeth II, opened in 2022, it was Europe’s largest construction project at the time and will bring in an estimated £42 billion to the UK economy.[326][327][328][329]
Great British Railways is a planned state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. In 2014, there were 5.2 billion bus journeys in the UK, 2.4 billion of which were in London.[330] The red double-decker bus has entered popular culture as an internationally recognised icon of England.[331] The London bus network is extensive, with over 6,800 scheduled services every weekday carrying about six million passengers on over 700 different routes making it one of the most extensive bus systems in the world and the largest in Europe.[332]
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers.[333] In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport (65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport (31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport (18.9 million passengers).[333] London Heathrow Airport, located 15 miles (24 km) west of the capital, is the world’s second busiest airport by international passenger traffic and has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world;[334] it is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways, as well as Virgin Atlantic.[335]
Energy
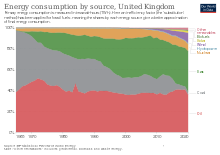
Energy mix of the United Kingdom over time
In 2021, the UK was the world’s 14th-largest consumer of energy and the 22nd-largest producer.[336] The UK is home to many large energy companies, including two of the six major oil and gas companies – BP and Shell.[337]
The total of all renewable electricity sources provided 38.9 per cent of the electricity generated in the UK in the third quarter of 2019, producing 28.8TWh of electricity.[338] The UK is one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind power production is the country’s fastest-growing supply; in 2019, almost 20 per cent of the UK’s total electricity was generated by wind power.[339]
In 2023, the UK had 9 nuclear reactors normally generating about 15 per cent of the UK’s electricity.[340] Unlike Germany and Japan, there are currently two reactors under construction and more planned.[341][342]In the late 1990s, nuclear power plants contributed around 25 per cent of the total annual electricity generation in the UK, but this has gradually declined as old plants have been shut down. The UK government is investing in Small Modular Reactors and Advanced Modular Reactors research and development.
In 2021, the UK produced 935 thousand barrels per day (bbl/d) of oil (and other liquids) and consumed 1,258 thousand bbl/d.[343] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of oil since 2005.[344] In 2020, the UK had around 2 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves.[344]
In 2021, the UK was the 21th-largest producer of natural gas in the world.[345] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of natural gas since 2004.[345]
In 2020, the UK produced 1.8 million tonnes of coal falling 91% in 10 years.[346] In 2020 it had proven recoverable coal reserves of 26 million tonnes.[346] The UK Coal Authority has stated that there is a potential to produce between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes of coal through underground coal gasification (UCG) or ‘fracking’,[347] and based on current UK coal consumption, such reserves could last between 200 and 400 years.[348] Environmental and social concerns have been raised over chemicals contaminating groundwater and minor earthquakes damaging homes.[349]
Water supply and sanitation
Access to improved water supply and sanitation in the UK is universal. It is estimated that 96.7 per cent of households are connected to the sewer network.[350] According to the Environment Agency, total water abstraction for public water supply in the UK was 16,406 megalitres per day in 2007.[351]
In England and Wales water and sewerage services are provided by 10 private regional water and sewerage companies and 13 mostly smaller private «water only» companies. In Scotland, water and sewerage services are provided by a single public company, Scottish Water. In Northern Ireland water and sewerage services are also provided by a single public entity, Northern Ireland Water.[352]
Demographics
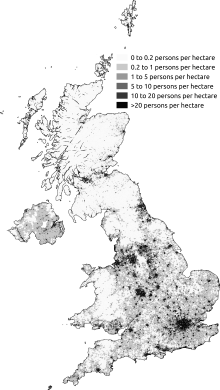
Map of population density in the UK as at the 2011 census
A census is taken simultaneously in all parts of the UK every 10 years.[353] In the 2011 census the total population of the United Kingdom was 63,181,775.[354] It is the fourth-largest in Europe (after Russia, Germany and France), the fifth-largest in the Commonwealth and the 22nd-largest in the world. In mid-2014 and mid-2015 net long-term international migration contributed more to population growth. In mid-2012 and mid-2013 natural change contributed the most to population growth.[355] Between 2001 and 2011 the population increased by an average annual rate of approximately 0.7 per cent.[354] This compares to 0.3 per cent per year in the period 1991 to 2001 and 0.2 per cent in the decade 1981 to 1991.[356] The 2011 census also showed that, over the previous 100 years, the proportion of the population aged 0–14 fell from 31 per cent to 18 per cent, and the proportion of people aged 65 and over rose from 5 to 16 per cent.[354] In 2018 the median age of the UK population was 41.7 years.[357]
England’s population in 2011 was 53 million, representing some 84 per cent of the UK total.[358] It is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with 420 people resident per square kilometre in mid-2015,[355] with a particular concentration in London and the south-east.[359] The 2011 census put Scotland’s population at 5.3 million,[360] Wales at 3.06 million and Northern Ireland at 1.81 million.[358]
In 2017 the average total fertility rate (TFR) across the UK was 1.74 children born per woman.[361] While a rising birth rate is contributing to population growth, it remains considerably below the baby boom peak of 2.95 children per woman in 1964,[362] or the high of 6.02 children born per woman in 1815,[363] below the replacement rate of 2.1, but higher than the 2001 record low of 1.63.[364] In 2011, 47.3 per cent of births in the UK were to unmarried women.[365] The Office for National Statistics published a bulletin in 2015 showing that, out of the UK population aged 16 and over, 1.7 per cent identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual (2.0 per cent of males and 1.5 per cent of females); 4.5 per cent of respondents responded with «other», «I don’t know», or did not respond.[366] The number of transgender people in the UK was estimated to be between 65,000 and 300,000 by research between 2001 and 2008.[367]
Largest urban areas of the United Kingdom (England and Wales: 2011 census built-up area;[368] Scotland: 2016 estimates settlement;[369] Northern Ireland: 2001 census urban area)[370] |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | |
 Greater London
|
1 | Greater London | 9,787,426 | London | 11 | Bristol | 617,280 | Bristol |
| 2 | West Midlands | 2,440,986 | Birmingham | 12 | Edinburgh | 512,150 | Edinburgh | |
| 3 | Greater Manchester | 2,553,379 | Manchester | 13 | Leicester | 508,916 | Leicester | |
| 4 | West Yorkshire | 1,777,934 | Leeds | 14 | Belfast | 483,418 | Belfast | |
| 5 | Greater Glasgow | 985,290 | Glasgow | 15 | Brighton & Hove | 474,485 | Brighton & Hove | |
| 6 | Liverpool | 864,122 | Liverpool | 16 | Bournemouth/ Poole | 466,266 | Bournemouth | |
| 7 | South Hampshire | 855,569 | Southampton | 17 | Cardiff | 390,214 | Cardiff | |
| 8 | Tyneside | 774,891 | Newcastle | 18 | Teesside | 376,633 | Middlesbrough | |
| 9 | Nottingham | 729,977 | Nottingham | 19 | Stoke-on-Trent | 372,775 | Stoke | |
| 10 | Sheffield | 685,368 | Sheffield | 20 | Coventry | 359,262 | Coventry |
Ethnic groups
Historically, indigenous British people were thought to be descended from the various ethnic groups that settled there before the 12th century: the Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Norse and the Normans. Welsh people could be the oldest ethnic group in the UK.[371] A 2006 genetic study shows that more than 50 per cent of England’s gene pool contains Germanic Y chromosomes.[372] Another 2005 genetic analysis indicates that «about 75 per cent of the traceable ancestors of the modern British population had arrived in the British isles by about 6,200 years ago, at the start of the British Neolithic or Stone Age», and that the British broadly share a common ancestry with the Basque people.[373][needs update] The UK has a history of non-white immigration with Liverpool having the oldest Black population in the country dating back to at least the 1730s during the period of the African slave trade. During this period it is estimated the Afro-Caribbean population of Great Britain was 10,000 to 15,000[374] which later declined due to the abolition of slavery.[375] The UK also has the oldest Chinese community in Europe, dating to the arrival of Chinese seamen in the 19th century.[376] In 1950 there were probably fewer than 20,000 non-white residents in Britain, almost all born overseas.[377] In 1951 there were an estimated 94,500 people living in Britain who had been born in South Asia, China, Africa and the Caribbean, just under 0.2 per cent of the UK population. By 1961 this number had more than quadrupled to 384,000, just over 0.7 per cent of the United Kingdom population.[378]
Since 1948 substantial immigration from Africa, the Caribbean and South Asia has been a legacy of ties forged by the British Empire.[379] Migration from new EU member states in Central and Eastern Europe since 2004 has resulted in growth in these population groups, although some of this migration has been temporary.[380] Since the 1990s, there has been substantial diversification of the immigrant population, with migrants to the UK coming from a much wider range of countries than previous waves, which tended to involve larger numbers of migrants coming from a relatively small number of countries.[381]
Academics have argued that the ethnicity categories employed in British national statistics, which were first introduced in the 1991 census, involve confusion between the concepts of ethnicity and race.[382] In 2011, 87.2 per cent of the UK population identified themselves as white, meaning 12.8 per cent of the UK population identify themselves as of one of number of ethnic minority groups.[383] In the 2001 census, this figure was 7.9 per cent of the UK population.[384] Because of differences in the wording of the census forms used in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, data on the Other White group is not available for the UK as a whole, but in England and Wales this was the fastest-growing group between the 2001 and 2011 censuses, increasing by 1.1 million (1.8 percentage points).[385] Amongst groups for which comparable data is available for all parts of the UK level, the Other Asian category increased from 0.4 per cent to 1.4 per cent of the population between 2001 and 2011, while the Mixed category rose from 1.2 per cent to 2 per cent.[383]
Ethnic diversity varies significantly across the UK. 30.4 per cent of London’s population and 37.4 per cent of Leicester’s was estimated to be non-white in 2005,[386] whereas less than 5 per cent of the populations of North East England, Wales and the South West were from ethnic minorities, according to the 2001 census.[387] In 2016, 31.4 per cent of primary and 27.9 per cent of secondary pupils at state schools in England were members of an ethnic minority.[388] The 1991 census was the first UK census to have a question on ethnic group. In the 1991 UK census 94.1 per cent of people reported themselves as being White British, White Irish or White Other with 5.9 per cent of people reporting themselves as coming from other minority groups.[389]
| Ethnic group | Population (absolute) | Population (per cent) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2011 | 2001[390] | 2011[383] | ||
| White | 54,153,898 | 55,010,359 | 92.1% | 87.1% | |
| White: Gypsy, Traveller and Irish Traveller[o] | – | 63,193 | – | 0.1% | |
| Asian and Asian British | Indian | 1,053,411 | 1,451,862 | 1.8% | 2.3% |
| Pakistani | 747,285 | 1,174,983 | 1.3% | 1.9% | |
| Bangladeshi | 283,063 | 451,529 | 0.5% | 0.7% | |
| Chinese | 247,403 | 433,150 | 0.4% | 0.7% | |
| other Asian | 247,664 | 861,815 | 0.4% | 1.4% | |
| Black, African, Caribbean and Black British[p] | 1,148,738 | 1,904,684 | 2.0% | 3.0% | |
| mixed or multiple ethnic groups | 677,117 | 1,250,229 | 1.2% | 2.0% | |
| other ethnic group | 230,615 | 580,374 | 0.4% | 0.9% | |
| Total | 58,789,194 | 63,182,178 | 100.0% | 100.0% |
Languages
The English language is the official and most spoken language of the United Kingdom that originated from England.[393][394]The United Kingdom proactively promotes the language globally to build connections, understanding and trust between people in the UK and countries worldwide.[395][396] It is estimated that 95 per cent of the UK’s population are monolingual English speakers.[397] 5.5 per cent of the population are estimated to speak languages brought to the UK as a result of relatively recent immigration.[397] South Asian languages are the largest grouping which includes Punjabi, Urdu, Bengali, Sylheti, Hindi and Gujarati.[398] According to the 2011 census, Polish has become the second-largest language spoken in England and has 546,000 speakers.[399] In 2019, some three quarters of a million people spoke little or no English.[400]
Three indigenous Celtic languages are spoken in the UK: Welsh, Irish and Scottish Gaelic. Cornish, which became extinct as a first language in the late 18th century, is subject to revival efforts and has a small group of second language speakers.[401][2] According to the 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 people (17.8 per cent).[402] In addition, it is estimated that about 200,000 Welsh speakers live in England.[403] In the 2011 census in Northern Ireland 167,487 people (10.4 per cent) stated that they had «some knowledge of Irish» (see Irish language in Northern Ireland), almost exclusively in the nationalist (mainly Catholic) population. Over 92,000 people in Scotland (just under 2 per cent of the population) had some Gaelic language ability, including 72 per cent of those living in the Outer Hebrides.[404] The number of children being taught either Welsh or Scottish Gaelic is increasing.[405] Among emigrant-descended populations some Scottish Gaelic is still spoken in Canada (principally Nova Scotia and Cape Breton Island),[406] and Welsh in Patagonia, Argentina.[407]
Scots, a language descended from early northern Middle English, has limited recognition alongside its regional variant, Ulster Scots in Northern Ireland, without specific commitments to protection and promotion.[2][408]
As of April 2020, there are said to be around 151,000 users of British Sign Language (BSL), a sign language used by deaf people, in the UK.[409] BSL was recognised as a language of England, Scotland and Wales in law in 2022.[410] It is compulsory for pupils to study a second language from the age of seven in England.[411] French and Spanish are the two most commonly taught second languages in the United Kingdom.[412] All pupils in Wales are either taught Welsh as a second language up to age 16, or are taught in Welsh as a first language.[413] Welsh was recognised as having official status in Wales in 2011.[414] Irish was recognised as having official status in Northern Ireland in 2022.[415]
Religion
Religion (2011 census)[4][5]
Other religions (0.4%)
Not stated (7.2%)
Forms of Christianity have dominated religious life in what is now the United Kingdom for more than 1,400 years.[416] Although a majority of citizens still identify with Christianity in many surveys, regular church attendance has fallen dramatically since the middle of the 20th century,[417] while immigration and demographic change have contributed to the growth of other faiths, most notably Islam.[418] This has led some commentators to variously describe the UK as a multi-faith,[419] secularised,[420] or post-Christian society.[421]
In the 2001 census, 71.6 per cent of all respondents indicated that they were Christians, with the next largest faiths being Islam (2.8 per cent), Hinduism (1.0 per cent), Sikhism (0.6 per cent), Judaism (0.5 per cent), Buddhism (0.3 per cent) and all other religions (0.3 per cent).[422] Of the respondents, 15 per cent stated that they had no religion and a further 7 per cent did not state a religious preference.[423] A Tearfund survey in 2007 showed that only one in ten Britons actually attend church weekly.[424] Between the 2001 and 2011 census, there was a 12 per cent decrease in the number of people who identified as Christian, whilst the percentage of those reporting no religious affiliation doubled. This contrasted with growth in the other main religious group categories, with the number of Muslims increasing by the most substantial margin to a total of about 5 per cent.[425] The Muslim population has increased from 1.6 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2011, making it the second-largest religious group in the UK.[426]
In a 2016 survey conducted by BSA (British Social Attitudes) on religious affiliation, 53 per cent of respondents indicated ‘no religion’, 41 per cent indicated they were Christians, followed by 6 per cent who affiliated with other religions (e.g. Islam, Hinduism, Judaism, etc.).[427] Among Christians, adherents to the Church of England constituted 15 per cent, to the Catholic Church 9 per cent, and other Christians (including Presbyterians, Methodists, other Protestants, as well as Eastern Orthodox) constituted 17 per cent.[427] Of the young people aged 18 to 24 that responded, 71 per cent said they had no religion.[427]
The Church of England is the established church in England.[428] It retains a representation in the UK Parliament, and the British monarch is its Supreme Governor.[429] In Scotland, the Church of Scotland is recognised as the national church. It is not subject to state control, and the British monarch is an ordinary member, required to swear an oath to «maintain and preserve the Protestant Religion and Presbyterian Church Government» upon his or her accession.[430][2][431] The Church in Wales was disestablished in 1920 and, because the Church of Ireland was disestablished in 1870 before the partition of Ireland, there is no established church in Northern Ireland.[432] Although there are no UK-wide data in the 2001 census on adherence to individual Christian denominations, it has been estimated that 62 per cent of Christians are Anglican, 13.5 per cent Catholic, 6 per cent Presbyterian, and 3.4 per cent Methodist, with small numbers of other Protestant denominations such as Plymouth Brethren, and Orthodox churches.[433]
In the 2021 UK census, less than half the English and Welsh population were Christian; 46.2% of the people of England and Wales said they were Christian, 37.2% that they had no religion, and 6.5% said they were Muslim.[434]
Migration
Estimated foreign-born population by country of birth from April 2007 to March 2008
| Year | Foreign born population of England and Wales | Total population [435][436][437] [438][439] |
Irish born population | Percentage of total population that was born abroad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1851 | 100,000 | 17,900,000 | 520,000 | 0.6 |
| 1861 | 150,000 | 20,100,000 | 600,000 | 0.7 |
| 1871 | 200,000 | 22,700,000 | 565,000 | 0.9 |
| 1881 | 275,000 | 26,000,000 | 560,000 | 1.1 |
| 1891 | 350,000 | 29,000,000 | 460,000 | 1.2 |
| 1901 | 475,000 | 32,500,000 | 425,000 | 1.5 |
| 1911 | 900,000 | 32,500,000 | 375,000 | 2.5 |
| 1921 | 750,000 | 37,900,000 | 365,000 | 2 |
| 1931 | 1,080,000 | 40,000,000 | 380,000 | 2.7 |
| 1951 | 1,875,000 | 43,700,000 | 470,000 | 4.3 |
| 1961 | 2,290,000 | 46,000,000 | 645,000 | 5.0 |
| 1971 | 3,100,000 | 48,700,000 | 585,000 | 6.4 |
| 1981 | 3,220,000 | 48,500,000 | 580,000 | 6.6 |
| 1991 | 3,625,000 | 49,900,000 | 570,000 | 7.3 |
| 2001 | 4,600,000 | 52,500,000 | 475,000 | 8.8 |
| 2011 | 7,500,000 | 56,000,000 | 400,000 | 13.4 |
| 2021 | 10,000,000 | 59,600,000 | 325,000 | 16.8 |
The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain.[440] Throughout the 19th century, a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to Russian Jews.[441] After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2 million left the Russian Empire by 1914. Around 120,000 settled permanently in Britain, becoming the largest ethnic minority from outside the British Isles,[442] and by 1938 this population had increased to 370,000.[443] Unable to return to Poland at the end of the Second World War, over 120,000 Polish veterans remained in the UK permanently.[444] After the war, many people immigrated from colonies and former colonies in the Caribbean and Indian subcontinent, as a legacy of empire or driven by labour shortages.[445] In 1841, only 0.25 per cent of the population of England and Wales was born in a foreign country, increasing to 1.5 per cent by 1901,[437] 2.6 per cent by 1931 and 4.4 per cent in 1951.[435]
In 2014, the immigration net increase was 318,000: immigration was at 641,000, up from 526,000 in 2013, while the number of emigrants leaving for over a year was 323,000.[446] A recent migration trend has been the arrival of workers from the new EU member states in Eastern Europe, known as the A8 countries.[380] In 2011, citizens of new EU member states made up 13 per cent of immigrants.[447] The UK applied temporary restrictions to citizens of Romania and Bulgaria, both of which joined the EU in January 2007.[448] Research conducted by the Migration Policy Institute for the Equality and Human Rights Commission suggests that, between May 2004 and September 2009, 1.5 million workers migrated from the new EU member states to the UK, most of them Polish. Many subsequently returned home, resulting in a net increase in the number of nationals of the new member states in the UK.[449] The late-2000s recession in the UK reduced the economic incentive for Poles to migrate to the UK,[450] making migration temporary and circular.[451] The proportion of foreign-born people in the UK remains slightly below that of many other European countries.[452]
Immigration is now contributing to a rising UK population,[453] with arrivals and UK-born children of migrants accounting for about half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001. According to official statistics released in 2015, 27 per cent of UK live births in 2014 were to mothers born outside the UK.[454] The ONS reported that net migration rose from 2009 to 2010 by 21 per cent to 239,000.[455]
In 2013, approximately 208,000 foreign nationals were naturalised as British citizens, the highest number since 1962. This figure fell to around 125,800 in 2014. Between 2009 and 2013, the average number of British citizenships granted annually was 195,800. The most common previous nationalities of those naturalised in 2014 were Indian, Pakistani, Filipino, Nigerian, Bangladeshi, Nepali, Chinese, South African, Polish and Somali.[456] The total number of grants of settlement, which confer permanent residence in the UK but not citizenship,[457] was approximately 154,700 in 2013, higher than the previous two years.[456]
Estimated number of British citizens living overseas by country in 2006
In 2008, the British Government introduced a points-based immigration system for immigration from outside the European Economic Area to replace former schemes, including the Scottish Government’s Fresh Talent Initiative.[458] In June 2010, a temporary limit on immigration from outside the EU was introduced, aiming to discourage applications before a permanent cap was imposed in April 2011.[459]
Emigration was an important feature of British society in the 19th century. Between 1815 and 1930, around 11.4 million people emigrated from Britain and 7.3 million from Ireland. Estimates show that by the end of the 20th century, some 300 million people of British and Irish descent were permanently settled around the globe.[460] Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad,[461][462] mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States and Canada.[461][463]
Education
Education in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter, with each country having a separate education system.
Considering the four systems together, about 38 per cent of the United Kingdom population has a university or college degree, which is the highest percentage in Europe, and among the highest percentages in the world.[464] The United Kingdom has some of the best universities in the world with Oxford University and Cambridge University often competing for the number 1 position on global rankings. [465][466]
A government commission’s report in 2014 found that privately educated people comprise 7 per cent of the general population of the UK but much larger percentages of the top professions, the most extreme case quoted being 71 per cent of senior judges.[467]
England
Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of local authorities.[468] Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944.[469] Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18.[470] In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science.[471] The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools,[472] while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.[473]
Scotland
Education in Scotland is the responsibility of the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Lifelong Learning, with day-to-day administration and funding of state schools the responsibility of Local Authorities. Two non-departmental public bodies have key roles in Scottish education. The Scottish Qualifications Authority is responsible for the development, accreditation, assessment and certification of qualifications other than degrees which are delivered at secondary schools, post-secondary colleges of further education and other centres.[474] Learning and Teaching Scotland provides advice, resources and staff development to education professionals.[475] Scotland first legislated for compulsory education in 1496.[476] The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4 per cent in 2016, but it has been falling slowly in recent years.[477] Scottish students who attend Scottish universities pay neither tuition fees nor graduate endowment charges, as fees were abolished in 2001 and the graduate endowment scheme was abolished in 2008.[478]
Wales
The Welsh Government’s Minister for Education has responsibility for education in Wales.[479] State funded education is available to children from the age of three whilst the legal obligation for parents to have their children educated, usually at school, begins at age five.[480] A sizeable minority of pupils are educated in Welsh whilst the rest are obliged to study the language until the age of 16.[481] Wales’ performance in Pisa testing, which compares the academic performance of adolescents around the world, has improved in recent years but remains lower than other parts of the UK.[482] In 2019, just under 60% of entrants passed their main English and Maths GCSEs.[483] The obligation to receive education in Wales ends at the age of 16. In 2017 and 2018, just under 80% of 16 to 18 and just under 40% of 19 to 24-year-olds were in some kind of education or training.[484]
Northern Ireland
Education in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Minister of Education, although responsibility at a local level is administered by the Education Authority which is further sub-divided into five geographical areas. The Council for the Curriculum, Examinations & Assessment (CCEA) is the body responsible for advising the government on what should be taught in Northern Ireland’s schools, monitoring standards and awarding qualifications.[485]
Healthcare
Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter and each country has its own system of private and publicly funded healthcare. Public healthcare is provided to all UK permanent residents and is mostly free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. The World Health Organization, in 2000, ranked the provision of healthcare in the United Kingdom as fifteenth best in Europe and eighteenth in the world.[486]
Since 1979 expenditure on healthcare has been increased significantly.[487] The 2018 OECD data, which incorporates in health a chunk of what in the UK is classified as social care, has the UK spending £3,121 per head.[488] In 2017 the UK spent £2,989 per person on healthcare, around the median for members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.[489]
Regulatory bodies are organised on a UK-wide basis such as the General Medical Council, the Nursing and Midwifery Council and non-governmental-based, such as the Royal Colleges. Political and operational responsibility for healthcare lies with four national executives; healthcare in England is the responsibility of the UK Government; healthcare in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Northern Ireland Executive; healthcare in Scotland is the responsibility of the Scottish Government; and healthcare in Wales is the responsibility of the Welsh Government. Each National Health Service has different policies and priorities, resulting in contrasts.[490]
Culture
The culture of the United Kingdom has been influenced by many factors including: the nation’s island status; its history as a western liberal democracy and a major power; as well as being a political union of four countries with each preserving elements of distinctive traditions, customs and symbolism. As a result of the British Empire, British influence can be observed in the language, culture and legal systems of many of its former colonies including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa and the United States; a common culture coined today as the Anglosphere. The substantial cultural influence of the United Kingdom has led to it being described as a «cultural superpower».[117][118] A global opinion poll for the BBC saw the United Kingdom ranked the third most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany and Canada) in 2013 and 2014.[491]
Literature
«British literature» refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Most British literature is in the English language. In 2005, some 206,000 books were published in the United Kingdom and in 2006 it was the largest publisher of books in the world.[492]
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest dramatist of all time.[493] The 20th-century English crime writer Agatha Christie is the best-selling novelist of all time.[494] Twelve of the top 25 of 100 novels by British writers chosen by a BBC poll of global critics were written by women; these included works by George Eliot, Virginia Woolf, Charlotte and Emily Brontë, Mary Shelley, Jane Austen, Doris Lessing and Zadie Smith.[495]
Scotland’s contributions include Arthur Conan Doyle (the creator of Sherlock Holmes), Sir Walter Scott, J. M. Barrie, Robert Louis Stevenson and the poet Robert Burns. More recently Hugh MacDiarmid and Neil M. Gunn contributed to the Scottish Renaissance, with grimmer works from Ian Rankin and Iain Banks. Scotland’s capital, Edinburgh, was UNESCO’s first worldwide City of Literature.[496]
Welsh literature includes Britain’s oldest known poem, Y Gododdin, which was composed most likely in the late 6th century. It was written in Cumbric or Old Welsh and contains the earliest known reference to King Arthur.[497] The Arthurian legend was further developed by Geoffrey of Monmouth.[498] Poet Dafydd ap Gwilym (fl. 1320–1370) is regarded as one of the greatest European poets of his age.[499] Daniel Owen is credited as the first Welsh-language novelist, publishing Rhys Lewis in 1885. The best-known of the Anglo-Welsh poets are Dylan Thomas and R. S. Thomas, the latter nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1996. Leading Welsh novelists of the twentieth century include Richard Llewellyn and Kate Roberts.[500][501]
Irish writers, living at a time when all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom, include Oscar Wilde,[502] Bram Stoker[503] and George Bernard Shaw.[504] There have been many authors whose origins were from outside the United Kingdom but who moved to the UK. These include Joseph Conrad,[505] T. S. Eliot,[506] Kazuo Ishiguro,[507] Sir Salman Rushdie[508] and Ezra Pound.[509]
Philosophy
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of ‘British Empiricism’, a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and ‘Scottish Philosophy’, sometimes referred to as the ‘Scottish School of Common Sense’.[510] The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley[q] and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish «common sense» school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work Utilitarianism.[511]
Music
Various styles of music have become popular in the UK, including the indigenous folk music of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Historically, there has been exceptional Renaissance music from the Tudor period, with masses, madrigals and lute music by Thomas Tallis, John Taverner, William Byrd, Orlando Gibbons and John Dowland. After the Stuart Restoration, an English tradition of dramatic masques, anthems and airs became established, led by Henry Purcell, followed by Thomas Arne and others. The German-born composer George Frideric Handel became a naturalised British citizen in 1727, when he composed the anthem Zadok the Priest for the coronation of George II; it became the traditional ceremonial music for anointing all future monarchs. Handel’s many oratorios, such as his famous Messiah, were written in the English language.[512] Ceremonial music is also performed to mark Remembrance Sunday across the UK, including the Traditional Music played at the Cenotaph.[513] In the second half of the 19th century, as Arthur Sullivan and his librettist W. S. Gilbert wrote their popular Savoy operas, Edward Elgar’s wide range of music rivalled that of his contemporaries on the continent. Increasingly, however, composers became inspired by the English countryside and its folk music, notably Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten, a pioneer of modern British opera. Among the many post-war composers, some of the most notable have made their own personal choice of musical identity: Peter Maxwell Davies (Orkney), Harrison Birtwistle (mythological), and John Tavener (religious).[514]
The Beatles are the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed band in popular music, selling over a billion records.[515][516][517]
According to the website of The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, the term «pop music» originated in Britain in the mid-1950s to describe rock and roll’s fusion with the «new youth music».[518] The Oxford Dictionary of Music states that artists such as The Beatles and The Rolling Stones drove pop music to the forefront of popular music in the early 1960s.[519] In the following years, Britain widely occupied a part in the development of rock music, with British acts pioneering hard rock;[520] raga rock; heavy metal;[521] space rock; glam rock;[522] Gothic rock,[523] and ska punk. In addition, British acts developed psychedelic rock;[524] and punk rock.[525] Besides rock music, British acts also developed neo soul and created dubstep.[526] Pop remains the most popular music genre by sales and streams of singles, with 33.4 per cent of that market in 2016, followed by hip-hop and R&B at 24.5 per cent.[527] Rock is not far behind, at 22.6 per cent.[527] The modern UK is known to produce some of the most prominent English-speaking rappers along with the United States, including Stormzy, Kano, Yxng Bane, Ramz, Little Simz and Skepta.[528]
The Beatles have international sales of over 1 billion units and are the biggest-selling and most influential band in the history of popular music.[515][516][517][529] Other prominent British contributors to have influenced popular music over the last 50 years include The Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen, Led Zeppelin, the Bee Gees, and Elton John, all of whom have worldwide record sales of 200 million or more.[530] The Brit Awards are the BPI’s annual music awards, and some of the British recipients of the Outstanding Contribution to Music award include; The Who, David Bowie, Eric Clapton, Rod Stewart, The Police, and Fleetwood Mac (who are a British-American band).[531] More recent UK music acts that have had international success include George Michael, Oasis, Spice Girls, Radiohead, Coldplay, Arctic Monkeys, Robbie Williams, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Ed Sheeran, One Direction and Harry Styles.[532]
A number of UK cities are known for their music. Acts from Liverpool have had 54 UK chart number 1 hit singles, more per capita than any other city worldwide.[533] Glasgow’s contribution to music was recognised in 2008 when it was named a UNESCO City of Music.[534] Manchester played a role in the spread of dance music such as acid house, and from the mid-1990s, Britpop. London and Bristol are closely associated with the origins of electronic music sub-genres such as drum and bass and trip hop.[535] Birmingham became known as the birthplace of heavy metal, with the band Black Sabbath starting there in the 1960s.[536]
Visual art
The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language;[537] the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the «Young British Artists»: Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).[538]
Cinema
Alfred Hitchcock has been ranked as one of the greatest and most influential British filmmakers of all time.[539]
The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film Vertigo is considered by some critics as the best film of all time,[540] and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time.[541] Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the highest-grossing film franchises (Harry Potter and James Bond).[542] Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.[543]
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom.[544] UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions.[544] The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.[545]
Cuisine
British cuisine developed from various influences reflective of its land, settlements, arrivals of new settlers and immigrants, trade and colonialism. Celtic agriculture and animal breeding produced a wide variety of foodstuffs for indigenous Celts and Britons. Anglo-Saxon England developed meat and savoury herb stewing techniques before the practice became common in Europe. The Norman conquest introduced exotic spices into England in the Middle Ages.[546] The British Empire facilitated a knowledge of Indian cuisine with its «strong, penetrating spices and herbs». British cuisine has absorbed the cultural influence of those who have settled in Britain, producing hybrid dishes, such as chicken tikka masala.[547] Vegan and vegetarian diets have increased in Britain in recent years. In 2021, a survey found that 8% of British respondents eat a plant-based diet and 36% of respondents have a favourable view of plant-based diets.[548]
Media
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK’s publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world.[549][550][551] It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the television licence.[552] The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world’s largest of any kind.[553] It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.[554]
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV Network,[555] and Sky.[556] Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include The Times, The Guardian, The Observer, The Economist, and the Financial Times.[557] Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include Nature, New Scientist, The Spectator, Prospect, NME, Radio Times, and The Economist.
London dominates the media sector in the UK: national newspapers and television and radio are largely based there, although Manchester is also a significant national media centre. Edinburgh and Glasgow, and Cardiff, are important centres of newspaper and broadcasting production in Scotland and Wales, respectively.[558] The UK publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover of around £20 billion and employs around 167,000 people.[559] In 2015, the UK published 2,710 book titles per million inhabitants, more than any other country, much of this being exported to other Anglophone countries.[560]
In 2009, it was estimated that individuals viewed a mean of 3.75 hours of television per day and 2.81 hours of radio. In that year the main BBC public service broadcasting channels accounted for an estimated 28.4 per cent of all television viewing; the three main independent channels accounted for 29.5 per cent and the increasingly important other satellite and digital channels for the remaining 42.1 per cent.[561] Sales of newspapers have fallen since the 1970s and in 2010 41 per cent of people reported reading a daily national newspaper.[562] In 2010, 82.5 per cent of the UK population were Internet users, the highest proportion amongst the 20 countries with the largest total number of users in that year.[563]
Symbols
Union Jack flags in London
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack).[564] It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick’s Flag.[565] Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out.[566] The national anthem of the United Kingdom is «God Save the King», with «King» replaced with «Queen» in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain.[567] Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon’s three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside the lion and the unicorn and the dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill’s defiance of Nazi Germany.[568] A now rare personification is a character originating in the 18th century, John Bull, a portly country gentleman dressed in a top hat and tailcoat with a Union Jack waistcoat, often accompanied by a bulldog.[569]
The floral emblems of the three kingdoms are the Tudor rose for England, the thistle for Scotland and the shamrock for Northern Ireland; they are sometimes shown intertwined to represent unity.[570] The daffodil and the leek are the symbols of Wales.[571] Alternatives include the Royal Oak for England and the flax flower for Northern Ireland.[570]
Sport
Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, billiards, darts, rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in late 19th-century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, «This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum».[573][574]
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the UK.[575] England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and the Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley.[576] Each of the Home Nations (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland) has its own football association, national team and league system, and each is individually a governing member of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world.[577] The first international football match was contested by England and Scotland on 30 November 1872.[578] England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.[579]
In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK.[575] The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England and Scotland.[580][581] England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship, which is the premier international rugby union tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sports governing bodies in England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland organise and regulate the game separately.[582] Every four years, the Home Nations make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions which tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788.[583] The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board,[584] and the Ireland cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales has fielded its own national cricket team in the past. Scottish players have played for England because the Scotland cricket team does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals.[585] Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, which England won in 2019. There is a professional league championship that consists of clubs representing 17 English counties and one Welsh county.[586]
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s before spreading around the world.[587] The world’s oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, was first held in 1877 and today takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.[588]
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more drivers’ and constructors’ titles in the F1 World Championship than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone, where the British Grand Prix is held each year in July.[589]
St Andrews, Scotland, the home of golf. The standard 18 hole golf course was created at St Andrews in 1764.[590]
Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport’s home course,[591] the world’s oldest golf course is in fact Musselburgh Links’ Old Golf Course.[592] In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes.[590] The British Open—the oldest golf tournament in the world and the first major championship in golf—is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.[593]
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England.[594] A single ‘Great Britain Lions’ team competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games before 2008 when England, Scotland and Ireland began to compete as separate league nations.[595] Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.[596]
The ‘Queensberry rules’, the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing.[597] Snooker is another of the UK’s popular sporting exports, with the world championship held annually in Sheffield.[598] Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports in Northern Ireland, both in terms of participation and spectatorship, and both sports are played by Irish expatriates in the UK and the United States.[599] Shinty (or camanachd) is popular in the Scottish Highlands.[600] Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and Celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.[601]
The United Kingdom hosted the Summer Olympic Games in 1908, 1948 and 2012, with London acting as the host city on all three occasions. Birmingham hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games, the seventh time the UK has hosted the Commonwealth Games.
See also
- Outline of the United Kingdom
- Outline of England
- Outline of Northern Ireland
- Outline of Scotland
- Outline of Wales
- Index of United Kingdom-related articles
- International rankings of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the British Empire
- United Kingdom–Crown Dependencies Customs Union
Notes
- ^ There is no authorised version of the national anthem as the words are a matter of tradition; only the first verse is usually sung.[1] No statute has been enacted designating «God Save the King» as the official anthem. In the English tradition, such laws are not necessary; proclamation and usage are sufficient to make it the national anthem. «God Save the King» also serves as the Royal anthem for certain Commonwealth realms. The words King, he, him, his, used at present, are replaced by Queen, she, her when the monarch is female.
- ^ Scots, Ulster Scots, Welsh, Cornish, Scottish Gaelic and Irish are classed as regional or minority languages under the Council of Europe’s European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.[2] These include defined obligations to promote those languages.[3] See also Languages of the United Kingdom. Welsh has limited de jure official status in Wales, as well as in the provision of national government services provided for Wales.
- ^ «This category could include Polish responses from the country specific question for Scotland which would have been outputted to ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK. ‘White Africans’ may also have been recorded under ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK.»
- ^ 83.6% are White British/Irish.
- ^ Although the United Kingdom has traditionally been seen as a unitary state, an alternative description of the UK as a «union state», put forward by, among others, Vernon Bogdanor,[6] has become increasingly influential since the adoption of devolution in the 1990s.[7] A union state is considered to differ from a unitary state in that while it maintains a central authority it also recognises the authority of historic rights and infrastructures of its component parts.[8]
- ^ Some of the devolved countries, Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories issue their own sterling banknotes or currencies, or use another nation’s currency. See List of British currencies for more information.
- ^ Also observed by the Crown Dependencies, and in the two British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (though in the latter, without daylight saving time). For further information, see Time in the United Kingdom#British territories.
- ^ Except two overseas territories: Gibraltar and the British Indian Ocean Territory
- ^ Excludes most overseas territories
- ^ The .gb domain is also reserved for the UK, but has been little used.
- ^ Usage is mixed. The Guardian and Telegraph use Britain as a synonym for the United Kingdom. Some prefer to use Britain as shorthand for Great Britain. The British Cabinet Office’s Government Digital Service style guide for use on gov.uk recommends: «Use UK and United Kingdom in preference to Britain and British (UK business, UK foreign policy, ambassador and high commissioner). But British embassy, not UK embassy.»
- ^ The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty resolved the Irish War of Independence. When it took effect one year later, it established the Irish Free State as a separate dominion within the Commonwealth of Nations. In 1927 the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 changed the name of the UK to reflect this.
- ^ The United Kingdom does not have a codified constitution but an unwritten one formed of Acts of Parliament, court judgments, traditions, and conventions.[25]
- ^ Compare to section 1 of both of the 1800 Acts of Union which reads: the Kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland shall…be united into one Kingdom, by the Name of «The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland».
- ^ The 2011 Census recorded Gypsies and Travellers as a separate ethnic group for the first time.
- ^ In the 2011 Census, for the purpose of harmonising results to make them comparable across the UK, the ONS includes individuals in Scotland who classified themselves in the «African» category (29,638 people), which in the Scottish version of the census is separate from «Caribbean or Black» (6,540 people),[391] in this «Black or Black British» category. The ONS note that «the African categories used in Scotland could potentially capture White/Asian/Other African in addition to Black identities».[392]
- ^ Berkeley is in fact Irish but was called a ‘British empiricist’ due to the territory of what is now known as the Republic of Ireland being in the UK at the time.
References
- ^ Berry, Ciara (15 January 2016). «National Anthem». The Royal Family. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d «List of declarations made with respect to treaty No. 148». Council of Europe. Retrieved 12 December 2013.
- ^ «Welsh language on GOV.UK – Content design: planning, writing and managing content – Guidance». www.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ a b Weller, Paul (2016). «Balancing within Three Dimensions: Christianity, Secularity, and Religious Plurality in Social Policy and Theology». Studies in Interreligious Dialogue. 26 (2): 131–146. doi:10.2143/SID.26.2.3200411.
- ^ a b Cusick, Edmund; Storry, Mike (2017). «Religion». In Storry, Mike; Childs, Peter (eds.). British Cultural Identities (5th ed.). London: Routledge. pp. 239–266. ISBN 9781315440590.
- ^ Bradbury, Jonathan (2021). Constitutional Policy and Territorial Politics in the UK: Volume 1: Union and Devolution 1997–2012. Policy Press. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-5292-0588-6.
- ^ Leith, Murray Stewart (2012). Political Discourse and National Identity in Scotland. Edinburgh University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7486-8862-3.
- ^ Gagnon, Alain-G.; Tully, James (2001). Multinational Democracies. Cambridge University Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-521-80473-8.; Bogdanor, Vernon (1998). «Devolution: the Constitutional Aspects». In Beatson, Jack (ed.). Constitutional Reform in the United Kingdom: Practice and Principles. Oxford: Hart Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-901362-84-8.
- ^ Demographic Yearbook – Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density (PDF) (Report). United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ «Surface water and surface water change». Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ «United Kingdom». The World Factbook (2023 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- ^ «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d «World Economic Outlook database: October 2022». International Monetary Fund. October 2022.
- ^ «Inequality – Income inequality». us.oecd.org. OECD. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ «Human Development Report 2021/2022» (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «Great Britain | island, Europe». Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ United Kingdom Permanent Committee on Geographical Names (May 2017). «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». GOV.UK. 10.2 Definitions.
usually shortened to United Kingdom … The abbreviation is UK or U.K.
; «United Kingdom». Encyclopedia Britannica. - ^ a b «Countries within a country». Prime Minister’s Office. 10 January 2003. Archived from the original on 9 September 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Definition of Great Britain in English». Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
Great Britain is the name for the island that comprises England, Scotland and Wales, although the term is also used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.
- ^ «Office for National Statistics». ons.gov.uk.
- ^ «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
The full title of this country is ‘the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland’. Great Britain is made up of England, Scotland and Wales. The United Kingdom (UK) is made up of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. ‘Britain’ is used informally, usually meaning the United Kingdom.
The Channel Islands and the Isle of Man are not part of the UK. - ^ a b «Supporting the Overseas Territories». Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Julian Go (2007). «A Globalizing Constitutionalism?, Views from the Postcolony, 1945–2000». In Arjomand, Saïd Amir (ed.). Constitutionalism and political reconstruction. Brill. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-90-04-15174-1.
- ^ Ferguson 2004, p. 307.
- ^ What is the UK Constitution?, The Constitution Unit of UCL, 9 August 2018, retrieved 6 February 2020
- ^ The British Monarchy, «What is constitutional monarchy?». Retrieved 17 July 2013; «United Kingdom» CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 17 July 2013
- ^ «Population of Cities in United Kingdom 2023». World Population Review. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «Devolution of powers to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland». United Kingdom Government. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
In a similar way to how the government is formed from members from the two Houses of Parliament, members of the devolved legislatures nominate ministers from among themselves to comprise executives, known as the devolved administrations…
; «Country Overviews: United Kingdom». Transport Research Knowledge Centre. Archived from the original on 4 April 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010. - ^ «Britain’s Imperial Century: What Was the Pax Britannica?». History Hit. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Mathias, P. (2001). The First Industrial Nation: the Economic History of Britain, 1700–1914. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-26672-7.; Ferguson, Niall (2004). Empire: The rise and demise of the British world order and the lessons for global power. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-02328-8.
- ^ «20th-century international relations». www.britannica.com. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ «Pax Britannica | Encyclopedia.com». www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Allison, George (18 May 2018). «Study ranks Britain ‘second most powerful country in the world’«. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Thorp, James; James (26 March 2021). «Size does not matter: the UK’s continuing great power status » Wavell Room». Wavell Room. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Tombs, Robert (13 May 2022). «Britain’s future is to be Europe’s only great power, not a satellite of Macron’s continental empire». The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ «European researchers determine UK is second most powerful country in the world». Conservative Post. 24 March 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ T.V. Paul; James J. Wirtz; Michel Fortmann (2005). «Great+power» Balance of Power. State University of New York Press. pp. 59, 282. ISBN 978-0-7914-6401-4. Accordingly, the great powers after the Cold War are Britain, China, France, Germany, Japan, Russia and the United States p. 59; McCourt, David (2014). Britain and World Power Since 1945: Constructing a Nation’s Role in International Politics. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07221-7.
- ^ «World Population Prospects – The 2006 Revision» (PDF). UN. Retrieved 27 April 2010.; Professor Arne Björnberg, Ph.D (29 January 2018). «Euro Health Consumer Index 2017» (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ^ «IISS Military Balance 2021». The Military Balance. 121 (1): 23–29. January 2021. doi:10.1080/04597222.2021.1868791. S2CID 232050862. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ «EU’s ‘big four’ speak as one ahead of G7 in Tokyo». POLITICO. 30 January 2008. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ «Volume 10 — History of Greater Britain, as well England as Scotland — Series 1 — National Library of Scotland». digital.nls.uk.
- ^ Payne, Malcolm; Shardlow, Steven (2002). Social Work in the British Isles. UK: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. p. 247. ISBN 978-1-8530-2833-5.
- ^ Richmond, Ian Archibald; Millett, Martin J. Millett (2012), «Caledonia», in Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Antony; Eidinow, Esther (eds.), The Oxford Classical Dictionary (4th ed.), Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/acref/9780199545568.001.0001, ISBN 978-0-19-954556-8, retrieved 14 February 2021; «What’s the Difference Between Great Britain and the United Kingdom? | Britannica». www.britannica.com.
- ^ «Treaty of Union, 1706». Scots History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; Barnett, Hilaire; Jago, Robert (2011). Constitutional & Administrative Law (8th ed.). Abingdon: Routledge. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-415-56301-7.
- ^ «After the political union of England and Scotland in 1707, the nation’s official name became ‘Great Britain'», The American Pageant, Volume 1, Cengage Learning (2012).; «From 1707 until 1801 Great Britain was the official designation of the kingdoms of England and Scotland». The Standard Reference Work: For the Home, School and Library, Volume 3, Harold Melvin Stanford (1921); «In 1707, on the union with Scotland, ‘Great Britain’ became the official name of the British Kingdom, and so continued until the union with Ireland in 1801». United States Congressional serial set, Issue 10; Issue 3265 (1895).; Gascoigne, Bamber. «History of Great Britain (from 1707)». History World. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Cottrell, P. (2008). The Irish Civil War 1922–23. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-84603-270-7.
- ^ S. Dunn; H. Dawson (2000), An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict, Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press,
One specific problem – in both general and particular senses – is to know what to call Northern Ireland itself: in the general sense, it is not a country, or a province, or a state – although some refer to it contemptuously as a statelet: the least controversial word appears to be jurisdiction, but this might change.
; «Changes in the list of subdivision names and code elements» (PDF). ISO 3166-2. International Organization for Standardization. 15 December 2011. Retrieved 28 May 2012. - ^ «Statistical bulletin: Regional Labour Market Statistics». Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.; «13.4% Fall In Earnings Value During Recession». Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- ^ Dunn, Seamus; Dawson, Helen (2000). An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict. Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press. ISBN 978-0-7734-7711-7.; Murphy, Dervla (1979). A Place Apart. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-005030-1.
- ^ Whyte, John; FitzGerald, Garret (1991). Interpreting Northern Ireland. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-827380-6.
- ^ «Guardian Unlimited Style Guide». London: Guardian News and Media Limited. 19 December 2008. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «BBC style guide (Great Britain)». BBC News. 19 August 2002. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Government, citizens and rights. HM Government. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ New Oxford American Dictionary: «Great Britain: England, Wales, and Scotland considered as a unit. The name is also often used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.»
- ^ «When people say England, they sometimes mean Great Britain, sometimes the United Kingdom, sometimes the British Isles — but never England.» — George Mikes (1946), How To Be An Alien, Penguin ISBN 0-582-41686-8; «England OR United Kingdom (UK)? | Vocabulary | EnglishClub». www.englishclub.com. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ «Britain Meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary». dictionary.cambridge.org.; «Definition of Britain in English by Oxford Dictionaries». Oxford Dictionaries – English. Archived from the original on 26 September 2016.
- ^ a b «Britain definition and meaning». www.collinsdictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary.
- ^ «Britain – Definition for English-Language Learners». learnersdictionary.com. Merriam-Webster’s Learner’s Dictionary.
- ^ «A to Z – Style guide». www.gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ a b c Permanent Committee on Geographical Names. «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ «BBC News style guide – Names». BBC Academy. BBC. Archived from the original on 10 November 2019. Retrieved 9 November 2019.; «Alphabetical checklist». BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 26 March 2018. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ^ Bradley, Anthony Wilfred; Ewing, Keith D. (2007). Constitutional and administrative law. Vol. 1 (14th ed.). Harlow: Pearson Longman. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-4058-1207-8.
- ^ «Which of these best describes the way you think of yourself?». Northern Ireland Life and Times Survey 2010. ARK – Access Research Knowledge. 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 25 June 2020.; Schrijver, Frans (2006). Regionalism after regionalisation: Spain, France and the United Kingdom. Amsterdam University Press. pp. 275–277. ISBN 978-90-5629-428-1.
- ^ «Ancient skeleton was ‘even older'». BBC News. 30 October 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: A historical encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 973. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ Davies, John; Jenkins, Nigel; Baines, Menna; Lynch, Peredur I., eds. (2008). The Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales. Cardiff: University of Wales Press. p. 915. ISBN 978-0-7083-1953-6.
- ^ «Short Athelstan biography». BBC History. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ Mackie, J.D. (1991). A History of Scotland. London: Penguin. pp. 18–19. ISBN 978-0-14-013649-4.; Campbell, Ewan (1999). Saints and Sea-kings: The First Kingdom of the Scots. Edinburgh: Canongate. pp. 8–15. ISBN 978-0-86241-874-8.
- ^ Haigh, Christopher (1990). The Cambridge Historical Encyclopedia of Great Britain and Ireland. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-521-39552-6.
- ^ Ganshof, F.L. (1996). Feudalism. University of Toronto. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-8020-7158-3.
- ^ Chibnall, Marjorie (1999). The Debate on the Norman Conquest. Manchester University Press. pp. 115–122. ISBN 978-0-7190-4913-2.
- ^ Keen, Maurice. «The Hundred Years’ War». BBC History.
- ^ The Reformation in England and Scotland and Ireland: The Reformation Period & Ireland under Elizabeth I, Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ «British History in Depth – Wales under the Tudors». BBC History. 5 November 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- ^ Nicholls, Mark (1999). A history of the modern British Isles, 1529–1603: The two kingdoms. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 171–172. ISBN 978-0-631-19334-0.
- ^ Canny, Nicholas P. (2003). Making Ireland British, 1580–1650. Oxford University Press. pp. 189–200. ISBN 978-0-19-925905-2.
- ^ «English Reformation c1527-1590». The National Archives. Retrieved 20 January 2023.
- ^ Ross, D. (2002). Chronology of Scottish History. Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-85534-380-1; Hearn, J. (2002). Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture. Edinburgh University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-902930-16-9
- ^ «English Civil Wars». Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 28 April 2013.; «Scotland and the Commonwealth: 1651–1660». Archontology.org. 14 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Lodge, Richard (2007) [1910]. The History of England – From the Restoration to the Death of William III (1660–1702). Read Books. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-4067-0897-4.
- ^ «Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy». Royal Navy History. Institute of Naval History. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Canny, Nicholas (1998). The Origins of Empire, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924676-2.
- ^ «Articles of Union with Scotland 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 19 October 2008.; «Acts of Union 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 6 January 2011.; «Treaty (act) of Union 1706». Scottish History online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ^ Library of Congress, The Impact of the American Revolution Abroad, p. 73.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. OUP Oxford. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-19-923899-6.
- ^ Sailing against slavery. BBC Devon. 2007.; Lovejoy, Paul E. (2000). Transformations in Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-521-78012-4.
- ^ «The Act of Union». Act of Union Virtual Library. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Tellier, L.-N. (2009). Urban World History: an Economic and Geographical Perspective. Quebec: PUQ. p. 463. ISBN 978-2-7605-1588-8.
- ^ Johnston, pp. 508–510.; Porter, p. 332.; Sondhaus, L. (2004). Navies in Modern World History. London: Reaktion Books. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-86189-202-7.; Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.
- ^ «The Workshop of the World». BBC History. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Benn, David Wedgwood (March 2012). «The Crimean War and its lessons for today». International Affairs. Oxford University Press. 88 (2): 387–391. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2346.2012.01078.x. JSTOR 41428613.
- ^ Nordisk familjebok (1913), s. 435 (in Swedish)
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.; Marshall, P.J. (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7.
- ^ Tompson, Richard S. (2003). Great Britain: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present. New York: Facts on File. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-8160-4474-0.
- ^ Hosch, William L. (2009). World War I: People, Politics, and Power. America at War. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-61530-048-8.
- ^ Zarembka, Paul (2013). Contradictions: Finance, Greed, and Labor Unequally Paid. Emerald Group Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78190-670-5.
- ^ Sophia A. Van Wingerden, The women’s suffrage movement in Britain, 1866–1928 (1999) ch 1.
- ^ Turner, John (1988). Britain and the First World War. London: Unwin Hyman. pp. 22–35. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ a b Westwell, I.; Cove, D. (eds) (2002). History of World War I, Volume 3. London: Marshall Cavendish. pp. 698 and 705. ISBN 978-0-7614-7231-5.
- ^ Turner, J. (1988). Britain and the First World War. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ «100 years of radio since Marconi’s big breakthrough». Ofcom. 15 June 2020. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ Linfoot, Matthew. «History of the BBC: The origins of BBC Local Radio». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ «History of the BBC: 1920s». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ SR&O 1921, No. 533 of 3 May 1921.
- ^ «The Anglo-Irish Treaty, 6 December 1921». CAIN Web Service. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Rubinstein, W.D. (2004). Capitalism, Culture, and Decline in Britain, 1750–1990. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-415-03719-8.
- ^ a b Edgerton, David (2012). Britain’s War Machine. www.penguin.co.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2020; «Britain’s War Machine: Weapons, Resources and Experts in the Second World War». Reviews in History. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Septimus H. Paul (2000). Nuclear Rivals: Anglo-American Atomic Relations, 1941–1952. Ohio State U.P. pp. 1–5. ISBN 9780814208526.
- ^ Doenecke, Justus D.; Stoler, Mark A. (2005). Debating Franklin D. Roosevelt’s foreign policies, 1933–1945. ISBN 978-0-8476-9416-7. Retrieved 19 March 2016.; Kelly, Brian. The Four Policemen and Postwar Planning, 1943–1945: The Collision of Realist and Idealist Perspectives. Indiana University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ «The «Special Relationship» between Great Britain and the United States Began with FDR». Roosevelt Institute. 22 July 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
and the joint efforts of both powers to create a new post-war strategic and economic order through the drafting of the Atlantic Charter; the establishment of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; and the creation of the United Nations.
; «Remarks by the President Obama and Prime Minister Cameron in Joint Press Conference» (Press release). The White House. 22 April 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2018.That’s what we built after World War II. The United States and the UK designed a set of institutions – whether it was the United Nations, or the Bretton Woods structure, IMF, World Bank, NATO, across the board.
- ^ «Britain to make its final payment on World War II loan from U.S.» The New York Times. 28 December 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ Reynolds, David (17 April 2011). «Britain’s War Machine by David Edgerton – review». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Francis, Martin (1997). Ideas and policies under Labour, 1945–1951: Building a new Britain. Manchester University Press. pp. 225–233. ISBN 978-0-7190-4833-3.
- ^ Lee, Stephen J. (1996). Aspects of British political history, 1914–1995. London; New York: Routledge. pp. 173–199. ISBN 978-0-415-13103-2.
- ^ Larres, Klaus (2009). A companion to Europe since 1945. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 118. ISBN 978-1-4051-0612-2.
- ^ «Country List». Commonwealth Secretariat. 19 March 2009. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ a b «The cultural superpower: British cultural projection abroad» (PDF). British Politics Review. Norway: British Politics Society. 6 (1). Winter 2011. ISSN 1890-4505. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2018.
- ^ a b Sheridan, Greg (15 May 2010). «Cameron has chance to make UK great again». The Australian. Sydney. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ Julios, Christina (2008). Contemporary British identity: English language, migrants, and public discourse. Studies in migration and diaspora. Aldershot: Ashgate. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-7546-7158-9.
- ^ «1975: UK embraces Europe in referendum». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Wheeler, Brian; Hunt, Alex (17 December 2018). «The UK’s EU referendum: All you need to know». BBC News.
- ^ Aughey, Arthur (2005). The Politics of Northern Ireland: Beyond the Belfast Agreement. London: Routledge. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-415-32788-6.; «The troubles were over, but the killing continued. Some of the heirs to Ireland’s violent traditions refused to give up their inheritance.» Holland, Jack (1999). Hope against History: The Course of Conflict in Northern Ireland. New York: Henry Holt. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-8050-6087-4.; Elliot, Marianne (2007). The Long Road to Peace in Northern Ireland: Peace Lectures from the Institute of Irish Studies at Liverpool University. University of Liverpool Institute of Irish Studies, Liverpool University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-84631-065-2.
- ^ Dorey, Peter (1995). British politics since 1945. Making contemporary Britain. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 164–223. ISBN 978-0-631-19075-2.
- ^ Griffiths, Alan; Wall, Stuart (2007). Applied Economics (PDF) (11th ed.). Harlow: Financial Times Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-273-70822-3. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Keating, Michael (1 January 1998). «Reforging the Union: Devolution and Constitutional Change in the United Kingdom». Publius: The Journal of Federalism. 28 (1): 217–234. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubjof.a029948.
- ^ McCourt, David (2014). Britain and World Power Since 1945: Constructing a Nation’s Role in International Politics. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07221-7.
- ^ «The story behind the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine success». UK Research and Innovation. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ McSmith, Andy (5 July 2016). «The inside story of how Tony Blair led Britain to war in Iraq». The Independent. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Jackson, Mike (3 April 2011). «Military action alone will not save Libya». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 27 August 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom country profile». BBC News. 24 January 2013. Archived from the original on 8 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Black, Andrew (15 October 2012). «Scottish independence: Cameron and Salmond strike referendum deal». BBC News. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Scottish independence referendum – Results – BBC News». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «In stunning decision, Britain votes to leave the E.U.» The Washington Post. 24 June 2016. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- ^ «Brexit: New era for UK as it completes separation from European Union». BBC News. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Coronavirus (COVID-19) in the UK». gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 14 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus and the impact on output in the UK economy: April 2020». ons.gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Walker, Andrew (10 June 2020). «Coronavirus: UK economy could be among worst hit of leading nations, says OECD». BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Landmark moment as first NHS patient receives COVID-19 vaccination». NHS. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Oxford University/AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine approved». UK Government. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Queen Elizabeth II has died». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «King Charles III, the new monarch». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary: «British Isles: a geographical term for the islands comprising Great Britain and Ireland with all their offshore islands including the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.»
- ^ a b c d e «United Kingdom». The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ a b c d Latimer Clarke Corporation Pty Ltd. «United Kingdom – Atlapedia Online». Atlapedia.com. Retrieved 26 October 2010.
- ^ ROG Learning Team (23 August 2002). «The Prime Meridian at Greenwich». Royal Museums Greenwich. Royal Museums Greenwich. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Greenwich Royal Observatory: How the Prime Meridian line is actually 100 metres away from where it was believed to be». The Independent. London. 13 August 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b Darkes, Giles (January 2008). «How long is the UK coastline?». The British Cartographic Society. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ «The Channel Tunnel». Eurotunnel. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). «An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm». BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). «Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ «Hottest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.; «Coldest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.
- ^ «English: A map of Köppen climate types in the United Kingdom (SVG version)». 9 August 2016.
- ^ «Atlantic Ocean Circulation (Gulf Stream)». UK Climate Projections. Met Office. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «UK 1971–2000 averages». Met Office. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 4 August 2007.
- ^ «UK temperature, rainfall and sunshine time series». Met Office.
- ^ «2020 EPI Results». Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «UK net zero target». Institute for Government. 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «England – Profile». BBC News. 11 February 2010.
- ^ «Scotland Facts». Scotland Online Gateway. Archived from the original on 21 June 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ Winter, Jon (1 June 2000). «The complete guide to the … Scottish Islands». The Independent. London. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Overview of Highland Boundary Fault». Gazetteer for Scotland. University of Edinburgh. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ «Great Britain’s tallest mountain is taller». Ordnance Survey. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ «Ben Nevis Weather». Ben Nevis Weather. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Profile: Wales». BBC News. 9 June 2010. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ «Geography of Northern Ireland». University of Ulster. Retrieved 22 May 2006.
- ^ Carter, Sarah. «A Guide To the UK Legal System». University of Kent at Canterbury. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2006.
- ^ See R (Miller) v Prime Minister [2019] UKSC 41 (Parliamentary sovereignty), R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor [2017] UKSC 51, [67] ff (rule of law), R (Animal Defenders International) v Secretary of State for Culture Media and Sport [2008] UKHL 15, [48] (democracy), R v Lyons [2002] UKHL 44, [27] (international law).
- ^ R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport [2014] UKSC 3, [207]
- ^ Magna Carta 1215 clauses 1 («the English church shall be free»), 12 and 14 (no tax «unless by common counsel of our kingdom»), 17 («Common pleas shall … be held in some fixed place»), 39–40 («To no one will we sell, to no one will we refuse or delay, right or justice»), 41 («merchants shall have safe and secure exit from England, and entry to England»), and 47–48 (land taken by the King «shall forthwith be disafforested»).
- ^ «Parliament’s authority». UK Parliament. n.d. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ Bagehot, Walter (1867). The English Constitution. London: Chapman and Hall. p. 103.
- ^ «Victorian Electronic Democracy, Final Report – Glossary». 28 July 2005. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 14 December 2007.
- ^ The Cabinet Manual (PDF) (Report). Cabinet Office. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Richard Knight (2 December 2008). «Whose hand is on the button?». BBC Radio 4. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ R (Miller) v The Prime Minister and Cherry v Advocate General for Scotland (Report). Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Richard Kelly. «Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Bill 2021-22» (PDF). House of Commons Library. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ «A Guide to Prorogation». BBC News. 7 November 2006. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ «The Honours System of the United Kingdom». Cabinet Office. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Stepan, Alfred; Linz, Juan J.; Minoves, Juli F. (2014). «Democratic Parliamentary Monarchies». Journal of Democracy. 25 (2): 35–36. doi:10.1353/jod.2014.0032. ISSN 1086-3214. S2CID 154555066.
- ^ «Parliamentary Sovereignty». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b «Parliament». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «Royal Assent». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c «General elections». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «State of the parties». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Government, Prime Minister and Cabinet». Public services all in one place. Directgov. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (1 January 2012). «The Institution of Prime Minister – History of government». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Brown, Jack (2020). Dale, Iain (ed.). The Prime Ministers. Hodder & Stoughton. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-5293-1214-0.
- ^ «Minister for the Civil Service». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Woodcock, Andrew (26 July 2021). «Boris Johnson accused of ‘cynical rebranding’ after appointing himself ‘Minister for the Union’«. The Independent. Retrieved 19 July 2021.; «Minister for the Union». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 21. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 7. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (2010). Premiership: The Development, Nature and Power of the Office of the British Prime Minister. Imprint Academic. pp. 116–7. ISBN 978-1-84540-168-9.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 31. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Hackwood Frederick William: The Story of the Shire, Being the Lore, History and Evolution of English County Institutions (1851)
- ^ United Nations Economic and Social Council (August 2007). «Ninth UN Conference on the standardization of Geographical Names» (PDF). UN Statistics Division. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 December 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Barlow, I.M. (1991). Metropolitan Government. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-02099-2.
- ^ «Welcome to the national site of the Government Office Network». Government Offices. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ «A short history of London government». Greater London Authority. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- ^ Sherman, Jill; Norfolk, Andrew (5 November 2004). «Prescott’s dream in tatters as North East rejects assembly». The Times Online. Archived from the original on 25 May 2010. Retrieved 15 February 2008.
The Government is now expected to tear up its twelve-year-old plan to create eight or nine regional assemblies in England to mirror devolution in Scotland and Wales.
- ^ «Elections 2017 results: Who are the new metro mayors?». BBC News. 5 May 2017. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^ «Local Authority Elections». Local Government Association. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «STV in Scotland: Local Government Elections 2007» (PDF). Political Studies Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b «Unitary authorities». Welsh Government. 2014. Archived from the original on 10 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Devenport, Mark (18 November 2005). «NI local government set for shake-up». BBC News. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ «Foster announces the future shape of local government» (Press release). Northern Ireland Executive. 13 March 2008. Archived from the original on 25 July 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ «Scots MPs attacked over fees vote». BBC News. 27 January 2004. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Taylor, Brian (1 June 1998). «Talking Politics: The West Lothian Question». BBC News. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «England-only laws ‘need majority from English MPs’«. BBC News. 25 March 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Scotland’s Parliament – powers and structures». BBC News. 8 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Keating, Michael (2 February 2021). «Taking back control? Brexit and the territorial constitution of the United Kingdom». Journal of European Public Policy. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis. 28 (4): 6–7. doi:10.1080/13501763.2021.1876156. hdl:1814/70296. S2CID 234066376.
The UK Internal Market Act gives ministers sweeping powers to enforce mutual recognition and non-discrimination across the four jurisdictions. Existing differences and some social and health matters are exempted but these are much less extensive than the exemptions permitted under the EU Internal Market provisions. Only after an amendment in the House of Lords, the Bill was amended to provide a weak and non-binding consent mechanism for amendments (equivalent to the Sewel Convention) to the list of exemptions. The result is that, while the devolved governments retain regulatory competences, these are undermined by the fact that goods and services originating in, or imported into, England can be marketed anywhere.
- ^ Kenny, Michael; McEwen, Nicola (1 March 2021). «Intergovernmental Relations and the Crisis of the Union». Political Insight. SAGE Publishing. 12 (1): 12–15. doi:10.1177/20419058211000996. S2CID 232050477.
That phase of joint working was significantly damaged by the UK Internal Market Act, pushed through by the Johnson government in December 2020…the Act diminishes the authority of the devolved institutions, and was vehemently opposed by them.
- ^ Wolffe, W James (7 April 2021). «Devolution and the Statute Book». Statute Law Review. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/slr/hmab003. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
the Internal Market Bill—a Bill that contains provisions which, if enacted, would significantly constrain, both legally and as a matter of practicality, the exercise by the devolved legislatures of their legislative competence; provisions that would be significantly more restrictive of the powers of the Scottish Parliament than either EU law or Articles 4 and 6 of the Acts of the Union…The UK Parliament passed the European Union (Withdrawal Agreement) Act 2020 and the Internal Market Act 2020 notwithstanding that, in each case, all three of the devolved legislatures had withheld consent.
- ^ Wincott, Daniel; Murray, C. R. G.; Davies, Gregory (17 May 2021). «The Anglo-British imaginary and the rebuilding of the UK’s territorial constitution after Brexit: unitary state or union state?». Territory, Politics, Governance. Abingdon/Brighton: Taylor & Francis; Regional Studies Association. 10 (5): 696–713. doi:10.1080/21622671.2021.1921613.
Taken as a whole, the Internal Market Act imposes greater restrictions upon the competences of the devolved institutions than the provisions of the EU Single Market which it replaced, in spite of pledges to use common frameworks to address these issues. Lord Hope, responsible for many of the leading judgments relating to the first two decades of devolution, regarded the legislation’s terms as deliberately confrontational: ‘this Parliament can do what it likes, but a different approach is essential if the union is to hold together’.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hayward, Katy; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen; Wincott, Daniel (2020). UK and the Internal Market, Devolution and the Union. Centre on Constitutional Change (Report). University of Edinburgh; University of Aberdeen. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 16 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael (2020). Briefing Paper. United Kingdom Internal Market Bill: Implications for Devolution (PDF) (Report). Liverpool: University of Liverpool. pp. 4–5. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen (2022). «Sleeping with an Elephant: Devolution and the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020». Law Quarterly Review. London: Sweet & Maxwell. ISSN 0023-933X. SSRN 4018581. Retrieved 4 March 2022 – via Durham Research Online.
The Act has restrictive – and potentially damaging – consequences for the regulatory capacity of the devolved legislatures…This was not the first time since the Brexit referendum that the Convention had been set aside, but it was especially notable given that the primary purpose of the legislation was to constrain the capacity of the devolved institutions to use their regulatory autonomy…in practice, it constrains the ability of the devolved institutions to make effective regulatory choices for their territories in ways that do not apply to the choices made by the UK government and parliament for the English market.
- ^ a b [212][213][214][215][216][217][218]
- ^ «Welsh assembly renamed Senedd Cymru/Welsh Parliament», BBC News, 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020
- ^ «Structure and powers of the Assembly». BBC News. 9 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «Your Executive». Northern Ireland Executive. 25 September 2015.
- ^ Burrows, N. (1999). «Unfinished Business: The Scotland Act 1998». The Modern Law Review. 62 (2): 241–260 [p. 249]. doi:10.1111/1468-2230.00203.
The UK Parliament is sovereign and the Scottish Parliament is subordinate. The White Paper had indicated that this was to be the approach taken in the legislation. The Scottish Parliament is not to be seen as a reflection of the settled will of the people of Scotland or of popular sovereignty but as a reflection of its subordination to a higher legal authority. Following the logic of this argument, the power of the Scottish Parliament to legislate can be withdrawn or overridden…
; Elliot, M. (2004). «United Kingdom: Parliamentary sovereignty under pressure». International Journal of Constitutional Law. 2 (3): 545–627, 553–554. doi:10.1093/icon/2.3.545.Notwithstanding substantial differences among the schemes, an important common factor is that the UK Parliament has not renounced legislative sovereignty in relation to the three nations concerned. For example, the Scottish Parliament is empowered to enact primary legislation on all matters, save those in relation to which competence is explicitly denied … but this power to legislate on what may be termed «devolved matters» is concurrent with the Westminster Parliament’s general power to legislate for Scotland on any matter at all, including devolved matters … In theory, therefore, Westminster may legislate on Scottish devolved matters whenever it chooses…
- ^ Walker, G. (2010). «Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Devolution, 1945–1979». Journal of British Studies. 39 (1): 117–142. doi:10.1086/644536.
- ^ Gamble, A. (2006). «The Constitutional Revolution in the United Kingdom». Publius. 36 (1): 19–35 [p. 29]. doi:10.1093/publius/pjj011.
The British parliament has the power to abolish the Scottish parliament and the Welsh assembly by a simple majority vote in both houses, but since both were sanctioned by referenda, it would be politically difficult to abolish them without the sanction of a further vote by the people. In this way, several of the constitutional measures introduced by the Blair government appear to be entrenched and not subject to a simple exercise of parliamentary sovereignty at Westminster.
- ^ Meehan, E. (1999). «The Belfast Agreement – Its Distinctiveness and Points of Cross-Fertilization in the UK’s Devolution Programme». Parliamentary Affairs. 52 (1): 19–31 [p. 23]. doi:10.1093/pa/52.1.19.
[T]he distinctive involvement of two governments in the Northern Irish problem means that Northern Ireland’s new arrangements rest upon an intergovernmental agreement. If this can be equated with a treaty, it could be argued that the forthcoming distribution of power between Westminster and Belfast has similarities with divisions specified in the written constitutions of federal states…Although the Agreement makes the general proviso that Westminster’s ‘powers to make legislation for Northern Ireland’ remains ‘unaffected’, without an explicit categorical reference to reserved matters, it may be more difficult than in Scotland or Wales for devolved powers to be repatriated. The retraction of devolved powers would not merely entail consultation in Northern Ireland backed implicitly by the absolute power of parliamentary sovereignty but also the renegotiation of an intergovernmental agreement.
- ^ «CIBC PWM Global – Introduction to The Cayman Islands». Cibc.com. 11 July 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ Rappeport, Laurie. «Cayman Islands Tourism». Washington, D.C.: USA Today Travel Tips. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Background briefing on the Crown Dependencies: Jersey, Guernsey and the Isle of Man» (PDF). Ministry of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Bosque, Maria Mut (2022). «Questioning the current status of the British Crown Dependencies». Small States & Territories. 5 (1): 55–70 – via University of Malta.
- ^ a b Loft, Philip (1 November 2022). The separation of powers in the UK’s Overseas Territories (Report). House of Commons Library.
- ^ «Overseas Territories». Gov.uk. Foreign & Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ «The World Factbook». CIA. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Overseas Territories The Ministry of Defence’s Contribution. Ministry of Defence. 1 March 2012. p. 1. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ Global Britain and the British Overseas Territories: Resetting the relationship (PDF). House of Commons Foreign Affairs Committee. 13 February 2019. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ «Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity». www.seaaroundus.org. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ^ «Partnership for Progress and Prosperity» (PDF). UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ Davison, Phil (18 August 1995). «Bermudians vote to stay British». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Gibraltar referendum result in quotes». BBC News. 8 November 2002.
- ^ «Falklands: Cameron says Argentina should respect vote». BBC News. 12 March 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons. «House of Commons – Crown Dependencies – Justice Committee». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ Fact sheet on the UK’s relationship with the Crown Dependencies – gov.uk, Ministry of Justice. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ «Profile of Jersey». States of Jersey. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2008.
The legislature passes primary legislation, which requires approval by The Queen in Council, and enacts subordinate legislation in many areas without any requirement for Royal Sanction and under powers conferred by primary legislation.
- ^ «Chief Minister to meet Channel Islands counterparts – Isle of Man Public Services» (Press release). Isle of Man Government. 29 May 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The Treaty (act) of the Union of Parliament 1706». Scottish History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ «UK Supreme Court judges sworn in». BBC News. 1 October 2009.; «Constitutional reform: A Supreme Court for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Constitutional Affairs. July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- ^ «Role of the JCPC». Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Bainham, Andrew (1998). The international survey of family law: 1996. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff. p. 298. ISBN 978-90-411-0573-8.
- ^ Adeleye, Gabriel; Acquah-Dadzie, Kofi; Sienkewicz, Thomas; McDonough, James (1999). World dictionary of foreign expressions. Waucojnda, IL: Bolchazy-Carducci. p. 371. ISBN 978-0-86516-423-9.
- ^ «The Australian courts and comparative law». Australian Law Postgraduate Network. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Court of Session – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 31 July 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «High Court of Justiciary – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 12 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «House of Lords – Practice Directions on Permission to Appeal». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 1 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Samuel Bray (2005). «Not proven: introducing a third verdict». The University of Chicago Law Review. 72 (4): 1299–1329. JSTOR 4495530.
- ^ «Crime in England and Wales, Year Ending June 2015» (PDF).
- ^ «UK prison population figures». British Government. Retrieved 10 November 2015.; Highest to Lowest. World Prison Brief. International Centre for Prison Studies.
- ^ «• England & Wales: Recorded homicides 2002–2015 – UK Statistics». Statista.
- ^ «Scottish homicide figures fall to another record low». BBC News. 29 September 2015.
- ^ «Prime Minister’s letter to Donald Tusk triggering Article 50». GOV.UK.
- ^ Swaine, Jon (13 January 2009). «Barack Obama presidency will strengthen special relationship, says Gordon Brown». The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 3 May 2011.; Kirchner, E.J.; Sperling, J. (2007). Global Security Governance: Competing Perceptions of Security in the 21st century. London: Taylor & Francis. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-415-39162-7
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons (19 February 2009). «DFID’s expenditure on development assistance». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sharp Drop in World Views of US, UK: Global Poll – GlobeScan». 4 July 2017.; «From the Outside In: G20 views of the UK before and after the EU referendum’» (PDF). British Council.; «New Zealand is Britons’ favourite country». 26 October 2020.
- ^ «Ministry of Defence». Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- ^ «Speaker addresses Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II». UK Parliament. 30 March 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «House of Commons Hansard». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2008.; «House of Commons Hansard Written Answers for 17 Jun 2013 (pt 0002)». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ UK 2005: The Official Yearbook of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Office for National Statistics. p. 89.
- ^ «Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2016» (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ «Leading European cities by gross domestic product in 2017/18». Statista. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ Rendall, Alasdair (12 November 2007). «Economic terms explained». BBC News. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ «IMF Data – Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserve – At a Glance». Data.imf.org. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ «BIS Triennial Survey of Foreign Exchange and Over-The-Counter Interest Rate Derivatives Markets in April 2022 – UK Data». Bank of England. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «Global FX trading hits record $7.5 trln a day — BIS survey». Reuters. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «More About the Bank». Bank of England. n.d. Archived from the original on 12 March 2008.
- ^ «Lloyd’s of London — value proposition». Lloyd’s of London. Archived from the original on 27 February 2023.
- ^ «Principles for Economic Regulation». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. April 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ Hutton, Georgina (6 December 2022). «Industries in the UK». UK Paliament: House of Commons Library. Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- ^ a b «GFCI 27 Rank – Long Finance». www.longfinance.net. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025». PricewaterhouseCoopers. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «UNWTO Tourism Highlights, Edition 2005» (PDF). World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.;
- ^ «DCMS Economic Estimates 2019 (provisional): Gross Value Added». gov.uk. Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- ^ «UK’s Creative Industries contributes almost £13 million to the UK economy every hour». UK Government. 2020. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «UK Internal Market Bill». Institute for Government. 9 September 2020.; «UK Internal Market Bill becomes law». gov.uk.
- ^ a b «European Countries – United Kingdom». Europa (web portal). Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ^ Harrington, James W.; Warf, Barney (1995). Industrial location: Principles, practices, and policy. London: Routledge. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-415-10479-1.; Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2008). Western Civilization: Alternative Volume: Since 1300. Belmont, CA: Thomson Wadsworth. ISBN 978-0-495-55528-5.
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6. Retrieved 22 July 2009.; Marshall, PJ (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Hewitt, Patricia (15 July 2004). «TUC Manufacturing Conference». Department of Trade and Industry. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «UK motorsport industry in pole position for F1’s 70th anniversary». UK Government. 2020. Retrieved 19 February 2023.
- ^ Tovey, Alan (29 June 2016). «Britain’s aerospace sector soars amid fears Brexit could clip its wings». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022.
- ^ «British Aerospace EAP (Paris Airshow 1987 — Complete Demonstration) Video». YouTube. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Photographs from British Aerospace — Experimental Aircraft Programme (EAP) 1985». Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ Robertson, David (9 January 2009). «The Aerospace industry has thousands of jobs in peril». The Times. London. Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2011.(subscription required)
- ^ «Size and Health of the UK Space Industry 2021». UK Government. 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «The Pharmaceutical sector in the UK». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «Ministerial Industry Strategy Group – Pharmaceutical Industry: Competitiveness and Performance Indicators» (PDF). Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Agriculture in the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Coal». BGS Minerals UK. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ «UK officially in recession for first time in 11 years». BBC. 12 August 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ UK government debt and deficit: June 2022 «Archived copy». Archived from the original on 4 February 2023. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (last checked 2023-02-21) - ^ GDP monthly estimate, UK: December 2022 «Archived copy». Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) (last checked 2023-02-21) - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hatt2006p46was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Gascoin, J. «A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution», in Lindberg, David C. and Westman, Robert S., eds (1990), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution. Cambridge University Press. p. 248. ISBN 978-0-521-34804-1.
- ^ Reynolds, E.E.; Brasher, N.H. (1966). Britain in the Twentieth Century, 1900–1964. Cambridge University Press. p. 336. OCLC 474197910
- ^ Burtt, E.A. (2003) 1924.The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science. Mineola, NY: Courier Dover. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-486-42551-1.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. pp. 16, 30 and 46. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Jungnickel, C.; McCormmach, R. (1996). Cavendish. American Philosophical Society. ISBN 978-0-87169-220-7.
- ^ «The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1945: Sir Alexander Fleming, Ernst B. Chain, Sir Howard Florey». The Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Wilson, Arthur (1994). The Living Rock: The Story of Metals Since Earliest Times and Their Impact on Civilization. p. 203. Woodhead Publishing.
- ^ James, I. (2010). Remarkable Engineers: From Riquet to Shannon. Cambridge University Press. pp. 33–36. ISBN 978-0-521-73165-2.
- ^ Newman, M.H.A. (1948). «General Principles of the Design of All-Purpose Computing Machines». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A. 195 (1042): 271–274. Bibcode:1948RSPSA.195..271N. doi:10.1098/rspa.1948.0129.
- ^ Hubbard, Geoffrey (1965) Cooke and Wheatstone and the Invention of the Electric Telegraph, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London p. 78
- ^ Bova, Ben (2002) 1932. The Story of Light. Naperville, IL: Sourcebooks. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-4022-0009-0.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922)». Nature. 159 (4035): 297. 1947. Bibcode:1947Natur.159Q.297.. doi:10.1038/159297a0.
- ^ «John Logie Baird (1888–1946)». BBC History. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011). Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-59884-302-6.
- ^ Castells, M.; Hall, P.; Hall, P.G. (2004). Technopoles of the World: the Making of Twenty-First-Century Industrial Complexes. London: Routledge. pp. 98–100. ISBN 978-0-415-10015-1.
- ^ «Knowledge, networks and nations: scientific collaborations in the twenty-first century» (PDF). Royal Society. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2011.
- ^ McCook, Alison (2006). «Is peer review broken?». The Scientist. 20 (2): 26. Archived from the original on 16 August 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ^ WIPO (2022). Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition. www.wipo.int. Global Innovation Index. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 9789280534320. Retrieved 16 November 2022.; «Global Innovation Index 2021». World Intellectual Property Organization. United Nations. Retrieved 5 March 2022.; «Release of the Global Innovation Index 2020: Who Will Finance Innovation?». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «Global Innovation Index 2019». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «RTD – Item». ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ Moran, Joe (16 November 2005). Reading the Everyday. Routledge. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-134-37216-4.
- ^ Wilkinson, Freddie. «RAC foundation traffic stats».
- ^ «German Railway Financing» (PDF). Deutschebahn.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Efficiency indicators of Railways in France» (PDF). Internationaltransportforum.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Rail industry financial information 2014–15» (PDF). Orr.gov.uk.
- ^ Sylvain Duranton; Agnès Audier; Joël Hazan; Mads Peter Langhorn; Vincent Gauche (18 April 2017). «The 2017 European Railway Performance Index». Boston Consulting Group.
- ^ «What is HS2». HS2.
- ^ «HS2 Trains». HS2.
- ^ «Crossrail’s giant tunnelling machines unveiled». BBC News. 2 January 2012.; Leftly, Mark (29 August 2010). «Crossrail delayed to save £1bn». The Independent on Sunday. London.
- ^ «Crossrail update, 10 December 2018». UK Government. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Crossrail to become the Elizabeth line in honour of Her Majesty the Queen». Transport for London. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Opening the Elizabeth Line». The Royal Family. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Bus statistics». GOV.UK.
- ^ «Our Collection». icons.org.uk. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
- ^ London Buses, Transport for London. Accessed 10 May 2007.
- ^ a b «Size of Reporting Airports October 2009 – September 2010» (PDF). Civil Aviation Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ «Heathrow ‘needs a third runway’«. BBC News. 25 June 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.; «Statistics: Top 30 World airports» (PDF) (Press release). Airports Council International. July 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ «BMI being taken over by Lufthansa». BBC News. 29 October 2008. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ^ «United Kingdom Energy Profile». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ Mason, Rowena (24 October 2009). «Let the battle begin over black gold». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 26 November 2010.; Heath, Michael (26 November 2010). «RBA Says Currency Containing Prices, Rate Level ‘Appropriate’ in Near Term». Bloomberg. New York. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ «UK Renewables Q3 2019» (PDF).
- ^ Wilson, Grant; Staffell, Iain; Godfrey, Noah (7 January 2020). «2019 saw the rise of wind power and the collapse of coal». The Independent. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. April 2013. Archived from the original on 14 February 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Nuclear energy: What you need to know». UK Government. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ «United Kingdom Energy Profile». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Oil». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Natural Gas». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 16 April 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ a b «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ «Coal Reserves in the United Kingdom» (PDF). The Coal Authority. 10 April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Expert predicts ‘coal revolution’«. BBC News. 16 October 2007. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ Watts, Susan (20 March 2012). «Fracking: Concerns over gas extraction regulations». BBC News. Retrieved 9 April 2013.; «Quit fracking aboot». Friends of the Earth Scotland. Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «WHO / UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme: 404 error».[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Environment Agency». Archived from the original on 25 November 2009.
- ^ «About Us». niwater.com. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Census Geography». Office for National Statistics. 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Population Estimates for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 27 March 2011. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ a b «Population Estimates for UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, Mid-2015». Office for National Statistics. 23 June 2016.
- ^ «Annual Mid-year Population Estimates, 2010» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ «World Factbook EUROPE: United Kingdom», The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- ^ a b «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Khan, Urmee (16 September 2008). «England is most crowded country in Europe». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 18 September 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ Carrell, Severin (17 December 2012). «Scotland’s population at record high». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Vital statistics: population and health reference tables». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Boseley, Sarah (14 July 2008). «The question: What’s behind the baby boom?». The Guardian. London. p. 3. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Max Roser (2014), «Total Fertility Rate around the world over the last centuries», Our World In Data, Gapminder Foundation, archived from the original on 5 July 2019, retrieved 10 December 2019
- ^ «Vital Statistics: Population and Health Reference Tables (February 2014 Update): Annual Time Series Data». ONS. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table. Eurostat (26 February 2013). Retrieved 12 July 2013.
- ^ «Sexual identity, UK: 2015 – Experimental Official Statistics on sexual identity in the UK in 2015 by region, sex, age, marital status, ethnicity and NS-SEC». Office for National Statistics. 5 October 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- ^ «Research report 27: Trans research review». equalityhumanrights.com. p. v.
- ^ «2011 Census — Built-up areas». ONS. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ «NRS – Background Information Settlements and Localities» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- ^ The UK’s major urban areas Office for National Statistics (Urban area of Belfast and connected settlements, Table 3.1, page 47)
- ^ «Welsh people could be most ancient in UK, DNA suggests». BBC News. 19 June 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Thomas, Mark G.; et al. (October 2006). «Evidence for a segregated social structure in early Anglo-Saxon England». Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 273 (1601): 2651–2657. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3627. PMC 1635457. PMID 17002951.
- ^ Owen, James (19 July 2005). «Review of ‘The Tribes of Britain'». National Geographic (Washington, D.C.).; Oppenheimer, Stephen (October 2006).«Myths of British ancestry». Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link). Prospect (London). Retrieved 5 November 2010; Henderson, Mark (23 October 2009). «Scientist – Griffin hijacked my work to make race claim about ‘British aborigines’«. The Times. London. Retrieved 26 October 2009. (subscription required) - ^ «Victoria and Albert Museum Black Presence». 13 January 2011.
- ^ Winder, Robert (2010). Bloody Foreigners: The Story of Immigration to Britain. ISBN 978-0-7481-2396-4.; Costello, Ray (2001). Black Liverpool: The Early History of Britain’s Oldest Black Community 1730–1918. Liverpool: Picton Press. ISBN 978-1-873245-07-1.
- ^ «Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – Chinese Community». Chambré Hardman Trust. Archived from the original on 24 July 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Coleman, David; Compton, Paul; Salt, John (2002). «The demographic characteristics of immigrant populations», Council of Europe, p. 505. ISBN 978-92-871-4974-9.
- ^ Roger Ballard Centre for Applied South Asian Studies. «Britain’s visible minorities: a demographic overview» (PDF).
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ a b Vargas-Silva, Carlos (10 April 2014). «Migration Flows of A8 and other EU Migrants to and from the UK». Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Vertovec, Steven (2007). «Super-diversity and its implications». Ethnic and Racial Studies. 30 (6): 1024–1054. doi:10.1080/01419870701599465. S2CID 143674657. Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 3 April 2019.; Vertovec, Steven (20 September 2005). «Opinion: Super-diversity revealed». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Aspinall, Peter J (2012). «Answer Formats in British Census and Survey Ethnicity Questions: Does Open Response Better Capture ‘Superdiversity’?». Sociology. 46 (2): 354–364. doi:10.1177/0038038511419195. S2CID 144841712.
- ^ Ballard, Roger (1996). «Negotiating race and ethnicity: Exploring the implications of the 1991 census» (PDF). Patterns of Prejudice. 30 (3): 3–33. doi:10.1080/0031322X.1996.9970192.; Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (2002). «Censuses, identity formation, and the struggle for political power». In Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (eds.). Census and Identity: The Politics of Race, Ethnicity, and Language in National Censuses. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–42.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in the United Kingdom». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2013. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ «Population Size: 7.9 per cent from a minority ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 13 February 2003. Archived from the original on 31 July 2003. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales 2011» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): London». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 23 June 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.; «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): Leicester». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ «Census 2001 – Ethnicity and religion in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ Schools, pupils and their characteristics: January 2016 (PDF) (Report). Department for Education. 28 June 2016. p. 8. SFR 20/2016.
- ^ M.S (11 December 2012). «Britain’s amazing technicolour dreamcoat». The Economist.
- ^ «Population size: 7.9 per cent from a non-White ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 8 January 2004. Archived from the original on 19 June 2004.
- ^ «Table KS201SC – Ethnic group: All people» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ «Ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ «English language – Government, citizens and rights». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 23 August 2011.
- ^ Mac Sithigh, Daithí (17 May 2018). «Official status of languages in the UK and Ireland» (PDF). Common Law World Review. Queen’s University, Belfast. 47 (1): 77–102. doi:10.1177/1473779518773642. S2CID 219987922.
- ^ British Council «British Council | the UK’s international culture and education organisation». Archived from the original on 1 February 2023. Retrieved 5 December 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (last checked 2023-02-06) - ^ BBC Learning English, BBC World Service «BBC Learning English — About BBC Learning English». Archived from the original on 4 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (last checked 2023-02-04) - ^ a b «Languages across Europe: United Kingdom». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 4 February 2013.
- ^ Carl Skutsch (2013). Encyclopedia of the World’s Minorities. pp.1261. Routledge. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ Booth, Robert (30 January 2013). «Polish becomes England’s second language». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^ «The teenagers who translate for their parents». BBC News. 23 April 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ Track, Robert Lawrence; Stockwell, Peter (2007). Language and Linguistics: The Key Concepts. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-415-41358-9. Retrieved 4 August 2019.; «Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, Strasbourg, 1.II.1995». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh language in Wales (Census 2021)». gov.wales. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ Wynn Thomas, Peter (March 2007). «Welsh today». Voices. BBC. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Scotland’s Census 2001 – Gaelic Report». General Register Office for Scotland. Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Local UK languages ‘taking off’«. BBC News. 12 February 2009.
- ^ Edwards, John R. (2010). Minority languages and group identity: cases and categories. John Benjamins. pp. 150–158. ISBN 978-90-272-1866-7. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 696. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ «Language Data – Scots». European Bureau for Lesser-Used Languages. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ Brown, Hannah (23 April 2020). «‘People are dying because of this’: Calls for UK Gov to follow Scotland with sign language interpreter at Covid-19 briefing». The Scotsman. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ «British Sign Language Act 2022, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ «Fall in compulsory language lessons». BBC News. 4 November 2004.
- ^ «GCSE results day 2021: Spanish has biggest increase in entries, but German plummets». i (newspaper). 12 August 2021.
- ^ «The School Gate for parents in Wales». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ Ainsworth, Paul (6 December 2022). «‘Historic milestone’ passed as Irish language legislation becomes law». The Irish News. Retrieved 10 December 2022.
- ^ Cannon, John, ed. (2nd edn., 2009). A Dictionary of British History. Oxford University Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-19-955037-1.
- ^ Field, Clive D. (November 2009). «British religion in numbers». BRIN Discussion Series on Religious Statistics, Discussion Paper 001. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Yilmaz, Ihsan (2005). Muslim Laws, Politics and Society in Modern Nation States: Dynamic Legal Pluralisms in England, Turkey, and Pakistan. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-0-7546-4389-0.
- ^ Brown, Callum G. (2006). Religion and Society in Twentieth-Century Britain. Harlow: Pearson Education. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-582-47289-1.
- ^ Norris, Pippa; Inglehart, Ronald (2004). Sacred and Secular: Religion and Politics Worldwide. Cambridge University Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-521-83984-6.
- ^ Fergusson, David (2004). Church, State and Civil Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-521-52959-4.
- ^ «UK Census 2001». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 22 April 2007.
- ^ «Religious Populations». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2004. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom: New Report Finds Only One in 10 Attend Church». News.adventist.org. 4 April 2007. Archived from the original on 13 December 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Philby, Charlotte (12 December 2012). «Less religious and more ethnically diverse: Census reveals a picture of Britain today». The Independent. London.
- ^ «The percentage of the population with no religion has increased in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. 4 April 2013.
- ^ a b c «British Social Attitudes: Record number of Brits with no religion». NatCen.ac.uk. 4 September 2017.
- ^ «The History of the Church of England». The Church of England. 2004. Archived from the original on 15 April 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ «Queen and Church of England». British Monarchy Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 October 2006. Retrieved 5 June 2010.
- ^ «Queen and the Church». The British Monarchy (Official Website). Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- ^ «Our structure». churchofscotland.org.uk. 22 February 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2020.
- ^ Weller, Paul (2005). Time for a Change: Reconfiguring Religion, State, and Society. London: Continuum. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-0-567-08487-3.
- ^ Peach, Ceri, «United Kingdom, a major transformation of the religious landscape», in H. Knippenberg. ed. (2005). The Changing Religious Landscape of Europe. Amsterdam: Het Spinhuis. pp. 44–58. ISBN 978-90-5589-248-8.
- ^ Russell, Rachel; Farley, Harry (29 November 2022). «Less than half of England and Wales population Christian, Census 2021 shows». BBC News.
- ^ a b Coleman, David (17 April 2013). «Immigration, Population and Ethnicity: The UK in International Perspective». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The National Archives | Exhibitions | 1901 Census | Events». www.nationalarchives.gov.uk.
- ^ a b Green, Lord Andrew. «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migration Watch UK.
- ^ «UK 2011 Census Data». National Archives. 11 December 2012. Archived from the original on 12 April 2013.; National Archives (17 December 2013). «Non-UK Born Population of England and Wales Quadrupled Between 1951 and 2011». Archived from the original on 5 January 2016.; «2011 Census analysis: Immigration Patterns of Non-UK Born Populations in England and Wales in 2011». Office for National Statistics. 17 December 2013.
- ^ «International migration, England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 8 November 2022.
- ^ Richards, Eric (2004). Britannia’s children: Emigration from England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland since 1600. London: Hambledon, p. 143. ISBN 978-1-85285-441-6.
- ^ P. Panayi (1906). P. Panayi, ‘German Immigrants in Britain, 1815–1914’ in Germans in Britain since 1500, ed P. Panayi, (London: Hambledon Press, 1996). pp. 73–112. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.
- ^ Panayi, Panikos (1996). Germans in Britain Since 1500. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.; «East End Jews». BBC.
- ^ Jews in Britain: Origin and Growth of Anglo-Jewry. p. 7.; «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migrationwatch UK.; «The Jews». Victoria County History, London, 1969 – via British History Online.
- ^ Gibney, Matthew J.; Hansen, Randall (2005). Immigration and asylum: from 1900 to the present, ABC-CLIO, p. 630. ISBN 978-1-57607-796-2
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. 2005. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2015». Office for National Statistics. 21 May 2015.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2012». Office for National Statistics. 24 May 2012.
- ^ Doward, Jamie; Temko, Ned (23 September 2007). «Home Office shuts the door on Bulgaria and Romania». The Observer. London. p. 2. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- ^ Sumption, Madeleine; Somerville, Will (January 2010). The UK’s new Europeans: Progress and challenges five years after accession (PDF). Policy Report. London: Equality and Human Rights Commission. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-84206-252-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Doward, Jamie; Rogers, Sam (17 January 2010). «Young, self-reliant, educated: portrait of UK’s eastern European migrants». The Observer. London. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ^ Hopkirk, Elizabeth (20 October 2008). «Packing up for home: Poles hit by UK’s economic downturn». London Evening Standard.
- ^ «Recession moves migration patterns». BBC News. 8 September 2009. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ Muenz, Rainer (June 2006). «Europe: Population and Migration in 2005». Migration Policy Institute. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 2 April 2007.
- ^ «Immigration and births to non-British mothers pushes British population to record high». London Evening Standard. 21 August 2008.
- ^ «Births in England and Wales: 2014». Office for National Statistics. 15 July 2015.
- ^ Travis, Alan (25 August 2011). «UK net migration rises 21 per cent». The Guardian. London.
- ^ a b Blinder, Scott (27 March 2015). «Naturalisation as a British Citizen: Concepts and Trends» (PDF). The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ Blinder, Scott (11 June 2014). «Settlement in the UK». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ «Fresh Talent: Working in Scotland». London: UK Border Agency. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Boxell, James (28 June 2010). «Tories begin consultation on cap for migrants». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ Richards (2004), pp. 6–7.
- ^ a b Sriskandarajah, Dhananjayan; Drew, Catherine (11 December 2006). «Brits Abroad: Mapping the scale and nature of British emigration». Institute for Public Policy Research. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: world overview». BBC. Retrieved 20 April 2007.; Casciani, Dominic (11 December 2006). «5.5 m Britons ‘opt to live abroad’«. BBC News. Retrieved 20 April 2007.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: Country-by-country». BBC News. 11 December 2006.
- ^ «The Most Educated Countries in the World». Yahoo Finance. 24 September 2012. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2016.; «And the World’s Most Educated Country Is…». Time. New York. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «The Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2023». Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ^ «QS World University Rankings». Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ^ «Elitist Britain?» (PDF). Social Mobility and Child Poverty Commission. 28 August 2014.; Arnett, George (28 August 2014). «Elitism in Britain – breakdown by profession». The Guardian: Datablog.
- ^ «Local Authorities». Department for Children, Schools and Families. Archived from the original on 30 December 2008. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ Gordon, J.C.B. (1981). Verbal Deficit: A Critique. London: Croom Helm. p. 44 note 18. ISBN 978-0-85664-990-5.; Section 8 (‘Duty of local education authorities to secure provision of primary and secondary schools’), Sections 35–40 (‘Compulsory attendance at Primary and Secondary Schools’) and Section 61 (‘Prohibition of fees in schools maintained by local education authorities …’), Education Act 1944.
- ^ «School leaving age». UK Government. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «England’s pupils in global top 10». BBC News. 10 December 2008.
- ^ Frankel, Hannah (3 September 2010). «Is Oxbridge still a preserve of the posh?». TES. London. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ MacLeod, Donald (9 November 2007). «Private school pupil numbers in decline». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Independent Schools Council Research». Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «About SQA». Scottish Qualifications Authority. 10 April 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «About Learning and Teaching Scotland». Learning and Teaching Scotland. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Brain drain in reverse». Scotland Online Gateway. July 2002. Archived from the original on 4 December 2007.
- ^ «Facts and Figures». SCIS. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ «MSPs vote to scrap endowment fee». BBC News. 28 February 2008.
- ^ «Education System». Welsh Government. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Nursery education for 3 and 4 year olds in Wales» (PDF). 2019.; «Compulsory school age». Practical Law. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Comisiynydd: Nifer y plant mewn addysg Gymraeg yn ‘sioc’«. BBC Cymru Fyw (in Welsh). BBC. 4 August 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.; «Welsh in education: Action Plan 2017–2021» (PDF). Welsh Government. 2017. p. 16.
- ^ «Pisa education tests: Wales improves performance». BBC News. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ Wightwick, Abbie (22 August 2019). «GCSE results 2019: Extreme concern at drop in English language results». WalesOnline. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Participation of young people in education and the labour market 2017 and 2018 (provisional)» (PDF). Welsh Government. 21 August 2019.
- ^ CCEA. «About Us – What we do». Council for the Curriculum Examinations & Assessment. Archived from the original on 5 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Haden, Angela; Campanini, Barbara, eds. (2000). The world health report 2000 – Health systems: improving performance. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156198-3. Retrieved 5 July 2011.; World Health Organization. «Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries» (PDF). New York University. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ Fisher, Peter. «The NHS from Thatcher to Blair». NHS Consultants Association. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
The Budget … was even more generous to the NHS than had been expected amounting to an annual rise of 7.4 per cent above the rate of inflation for the next five years. This would take us to 9.4 per cent of GDP spent on health ie around EU average.
- ^ «Swindells: They aren’t ‘your’ patients». Health Service Journal. 24 September 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
- ^ «How does UK healthcare spending compare with other countries?». Office of National Statistics. 29 August 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- ^ «‘Huge contrasts’ in devolved NHS». BBC News. 28 August 2008.; Triggle, Nick (2 January 2008). «NHS now four different systems». BBC News.
- ^ «BBC poll: Germany most popular country in the world». BBC. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 20 February 2018.; «World Service Global Poll: Negative views of Russia on the rise». BBC.co.uk. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ Goldfarb, Jeffrey (10 May 2006). «Bookish Britain overtakes America as top publisher». RedOrbit. Texas. Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008.
- ^ «William Shakespeare (English author)». Britannica Online encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; MSN Encarta Encyclopedia article on Shakespeare. Archived from the original on 9 February 2006. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; William Shakespeare. Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.
- ^ «Mystery of Christie’s success is solved». The Daily Telegraph. London. 19 December 2005. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ Ciabattari, Jane (December 2015). «The 25 greatest British novels». BBC Culture. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ «Edinburgh, United Kingdom, UNESCO City of Literature». Unesco. 2004. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Early Welsh poetry». BBC Wales. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ Lang, Andrew (2003) [1913]. History of English Literature from Beowulf to Swinburne. Holicong, PA: Wildside Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-8095-3229-2.
- ^ «Dafydd ap Gwilym». Academi.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
Dafydd ap Gwilym is widely regarded as one of the greatest Welsh poets of all time, and amongst the leading European poets of the Middle Ages.
- ^ «True birthplace of Wales’s literary hero». BBC News. 5 December 1999. Archived from the original on 16 March 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ «Kate Roberts: Biography». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 24 July 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ^ Varty, Anne (2014). A Preface to Oscar Wilde. Routledge. pp. 231–232. ISBN 978-1-317-89231-1.; «Oscar Wilde». Encyclopedia.com. Cengage. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Moss, Joyce (2001). British and Irish Literature and Its Times: The Victorian Era to the Present (1837–). Gale Group. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-7876-3729-3.
- ^ Holroyd, Michael (1989). Bernard Shaw, Volume 2: 1898–1918: The Pursuit of Power. Chatto & Windus. p. 384. ISBN 978-0-7011-3350-4.; «G B Shaw». Discovering Literature: 20th century. British Library. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Middleton, Tim (2006). Joseph Conrad. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-415-26851-6.
- ^ Cooper, John Xiros (2006). The Cambridge Introduction to T. S. Eliot. Cambridge University Press. p. 111. ISBN 978-1-139-45790-3.
- ^ Sim, Wai-chew (2009). Kazuo Ishiguro. Routledge. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-135-19867-1.
- ^ «Salman Rushdie». Oxford Reference. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Campbell, James (17 May 2008). «Home from home». The Guardian. Retrieved 10 December 2019.; Nadel, Ira (2004). Ezra Pound: A Literary Life. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-230-37881-0.
- ^ Fieser, James, ed. (2000). A bibliography of Scottish common sense philosophy: Sources and origins (PDF). Bristol: Thoemmes Press. Retrieved 17 December 2010.
- ^ Palmer, Michael (1999). Moral Problems in Medicine: A Practical Coursebook. Cambridge: Lutterworth Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-7188-2978-0.; Scarre, Geoffrey (1995). Utilitarianism. London: Routledge. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-415-12197-2.
- ^ «British Citizen by Act of Parliament: George Frideric Handel». UK Parliament. 20 July 2009. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Andrews, John (14 April 2006). «Handel all’inglese». Playbill. New York. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ^ «Remembrance Sunday». Department for Culture Media and Sport. Retrieved 19 April 2022.; Richards, Jeffrey (2001). Imperialism and Music: Britain 1876–1953. Manchester University Press. pp. 155–156. ISBN 0-7190-4506-1.
- ^ Iemperley, Nicholas (2002). «Great Britain». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Banfield, Stephen; Russell, Ian (2001). «England (i)». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Lewis, Geraint; Davies, Lyn; Kinney, Phyllis (2001). «Wales». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Elliott, Kenneth; Collinson, Francis; Duesenberry, Peggy (2001). «Scotland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; White, Harry; Carolan, Nicholas (2011). «Ireland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; «British 20th century composers». BBC. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ a b «1960–1969». EMI Group. Archived from the original on 25 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «Paul At Fifty». Time. New York. 8 June 1992. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009.
- ^ a b Most Successful Group The Guinness Book of Records 1999, p. 230. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ R. Middleton, et al., «Pop», Grove music online, retrieved 14 March 2010. (subscription required) Archived 13 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Pop», The Oxford Dictionary of Music, retrieved 9 March 2010.(subscription required) Archived 12 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «The Rolling Stones | Biography & History». AllMusic. Retrieved 22 July 2020.
- ^ Tom Larson (2004). History of Rock and Roll. Kendall/Hunt Pub. pp. 183–187. ISBN 978-0-7872-9969-9.
- ^ «Glam Rock». Encarta. Archived from the original on 28 August 2009. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ «NME Originals: Goth». NME. 2004. Archived from the original on 26 January 2008. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ^ «Pop/Rock » Psychedelic/Garage». AllMusic. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ «The Sex Pistols». RollingStone.com. 2001. Archived from the original on 1 February 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ Henderson, Alex (1 August 2003). British Soul. Allmusic. Retrieved 6 March 2011.; AllMusic – Dubstep Archived 23 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine «Absorbed and transfigured elements of techno, drum’n’ bass and dub»; Goldman, Vivien (31 January 2012). «Local Groove Does Good: The Story Of Trip-Hop’s Rise From Bristol». NPR.
- ^ a b «UK music single sales: genre breakdown 2016 | Statistic». Statista. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «5 U.K. Rappers Primed to Take Over America in 2018». Billboard. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «Beatles a big hit with downloads». Belfast Telegraph. 25 November 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- ^ «British rock legends get their own music title for PlayStation3 and PlayStation2» (Press release). EMI. 2 February 2009. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Khan, Urmee (17 July 2008). «Sir Elton John honoured in Ben and Jerry ice cream». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 30 July 2008.; Alleyne, Richard (19 April 2008). «Rock group Led Zeppelin to reunite». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Floyd ‘true to Barrett’s legacy’«. BBC News. 11 July 2006.; Holton, Kate (17 January 2008). «Rolling Stones sign Universal album deal». Reuters. Retrieved 26 October 2008.; Walker, Tim (12 May 2008). «Jive talkin’: Why Robin Gibb wants more respect for the Bee Gees». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2011. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Brit awards winners list 2012: every winner since 1977». The Guardian (London). Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ «Harry Styles Has Weathered the Post-Boy Band Storm Better Than Most». Consequence of Sound. 12 January 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; «10 Years of One Direction: The Story of the World’s Biggest Boy Band, Told With the Fans Who Made It Happen». Billboard. 16 July 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; Corner, Lewis (16 February 2012). «Adele, Coldplay biggest-selling UK artists worldwide in 2011». Digital Spy. Retrieved 22 March 2012.; Magliola, Anna Sky (30 November 2022). «Ed Sheeran’s career journey: From street busker to global superstar». PlanetRadio.co.uk. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ Hughes, Mark (14 January 2008). «A tale of two cities of culture: Liverpool vs Stavanger». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Glasgow gets city of music honour». BBC News. 20 August 2008. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Out of the melting pot: The origins and evolution of drum’n’bass». Red Bull. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ «Birmingham, England … the unlikely birthplace of heavy metal». www.cnn.com. Retrieved 28 February 2022.; Bentley, David (4 June 2013). «Midlands rocks! How Birmingham’s industrial heritage made it the birthplace of heavy metal». Birmingham Post. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ Tate. «Art & Language – Art Term | Tate». Tate. Retrieved 8 September 2018.
- ^ Bayley, Stephen (24 April 2010). «The startling success of Tate Modern». The Times. London. Retrieved 19 January 2011. (subscription required)
- ^ «The top 21 British directors of all time». The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ «Vertigo is named ‘greatest film of all time’«. BBC News. 2 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ «The Directors’ Top Ten Directors». British Film Institute. Archived from the original on 17 May 2012.
- ^ «Harry Potter becomes highest-grossing film franchise». The Guardian. London. 11 September 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- ^ «History of Ealing Studios». Ealing Studios. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «UK film – the vital statistics». UK Film Council. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Baftas fuel Oscars race». BBC News. 26 February 2001. Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- ^ Spencer, Colin (2003). British Food: An Extraordinary Thousand Years of History. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-13110-0.[pages needed]
- ^ «Robin Cook’s chicken tikka masala speech». The Guardian. London. 19 April 2001. Retrieved 7 September 2021.; BBC E-Cyclopedia (20 April 2001). «Chicken tikka masala: Spice and easy does it». BBC. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ «No meat please, we’re British: now a third of us approve of vegan diet». The Guardian. London. 25 December 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ a b «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 5 October 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ a b «Digital license». Prospect. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «About the BBC – What is the BBC». BBC Online. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Newswire7 (13 August 2009). «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.; «TV Licence Fee: facts & figures». BBC Press Office. April 2010. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft Word – The Work of the BBC World Service 2008–09 HC 334 FINAL.doc» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- ^ «News in your language – BBC News». Bbc.co.uk.; «BBC World Service». Facebook.com.
- ^ «Publications & Policies: The History of ITV». ITV.com. Archived from the original on 11 April 2011.
- ^ «Direct Broadcast Satellite Television». News Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «ABCs: National daily newspaper circulation September 2008». The Guardian. UK. 10 October 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ William, D. (2010). UK Cities: A Look at Life and Major Cities in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Eastbourne: Gardners Books. ISBN 978-9987-16-021-1, pp. 22, 46, 109 and 145.
- ^ «Publishing». Department of Culture, Media and Sport. Archived from the original on 5 May 2011.
- ^ «Annual Report 2015-2016» (PDF). www.internationalpublishers.org. International Publishers Association. 2016. p. 16. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Ofcom «Communication Market Report 2010», 19 August 2010, pp. 97, 164 and 191
- ^ «Social Trends 41: Lifestyles and social participation» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 24 February 2011.
- ^ «Top 20 countries with the highest number of Internet users». Internet World Stats. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- ^ «Union Jack or Union Flag?». The Flag Institute. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- ^ «college-of-arms.gov.uk». The College of Arms. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ «Welsh dragon call for Union flag». BBC News. 27 November 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Britannia on British Coins». Chard. Retrieved 25 June 2006.
- ^ Baker, Steve (2001). Picturing the Beast. University of Illinois Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-252-07030-3.
- ^ «Who is John Bull». www.loc.gov. The Library of Congress. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ a b Van Wie, Paul D. (1999). Image, History, and Politics: The Coinage of Modern Europe. New York: University Press of America. pp. 63–64. ISBN 978-0761812227.
- ^ Cleene, Marcel (2002). Compendium of Symbolic and Ritual Plants in Europe: Volume II Herbs. Ghent: Mens & Cultuur Uitgevers N.V. p. 211. ISBN 978-9077135044.
- ^ Ponsford, Matthew (19 January 2016). «Los Angeles to build world’s most expensive stadium complex». CNN. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
- ^ «Opening Ceremony of the Games of the XXX Olympiad» (PDF). Olympic.org. 27 July 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mehaffey, John. «Unparalleled Sporting History». Reuters. London. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ a b «Rugby Union ‘Britain’s Second Most Popular Sport’«. Ipsos-Mori. 22 December 2003. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Rudd, Alyson (7 April 2008). «The father of football deserves much more». The Times. London. Retrieved 29 January 2015.; «Sheffield FC: 150 years of history». FIFA. 24 October 2007. Archived from the original on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Ebner, Sarah (2 July 2013). «History and time are key to power of football, says Premier League chief». The Times. London. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mitchell, Paul (November 2005). «The first international football match». BBC Sport Scotland. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- ^ «Why is there no GB Olympics football team?». BBC Sport. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ «Six ways the town of Rugby helped change the world». BBC News. 1 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Godwin, Terry; Rhys, Chris (1981). The Guinness Book of Rugby Facts & Feats. Guinness Superlatives. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-85112214-4.
- ^ Louw, Jaco; Nesbit, Derrick (2008). The Girlfriends Guide to Rugby. Johannesburg: South Publishers. ISBN 978-0-620-39541-0.
- ^ Colin White (2010). «Projectile Dynamics in Sport: Principles and Applications». p. 222. Routledge
- ^ «About ECB». England and Wales Cricket Board. n.d. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ McLaughlin, Martyn (4 August 2009). «Howzat happen? England fields a Gaelic-speaking Scotsman in Ashes». The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Retrieved 30 December 2010.; «Uncapped Joyce wins Ashes call up». BBC Sport. 15 November 2006. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «Glamorgan». BBC South East Wales. August 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «History of Tennis». ITFtennis.com. Archived from the original on 22 March 2010. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ Morley, Gary (22 June 2011). «125 years of Wimbledon: From birth of lawn tennis to modern marvels». CNN. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «The History of British Motorsport and Motor Racing at Silverstone – The 1950s». Silverstone.co.uk. Archived from the original on 4 October 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ a b Forrest L. Richardson (2002). «Routing the Golf Course: The Art & Science That Forms the Golf Journey». p. 46. John Wiley & Sons
- ^ «Tracking the Field» (PDF). Ipsos MORI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Links plays into the record books». BBC News. 17 March 2009.
- ^ «The Open Championship – More Scottish than British». PGA Tour. Archived from the original on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Ardener, Shirley (2007). Professional identities: policy and practice in business and bureaucracy. New York: Berghahn. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-84545-054-0.
- ^ «Official Website of Rugby League World Cup 2008». Archived from the original on 16 October 2007.
- ^ Baker, Andrew (20 August 1995). «100 years of rugby league: From the great divide to the Super era». The Independent. London. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ «Encyclopædia Britannica (2006).ŷ Queensbury Rules, Britannica».
- ^ Chowdhury, Saj (22 January 2007). «China in Ding’s hands». BBC Sport. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ Gould, Joe (10 April 2007). «The ancient Irish sport of hurling catches on in America». Columbia News Service. Columbia Journalism School. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ «Shinty». Scottish Sport. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sport in Scotland». Scotland.org. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
External links
Government
- Official website of HM Government
- Official website of the British Monarchy
- The official site of the British Prime Minister’s Office
General information
Travel
- Official tourist guide to Britain
Coordinates: 55°N 3°W / 55°N 3°W
This article is about the country. It is not to be confused with Great Britain, its largest island, or England, its largest constituent country.
|
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
|---|---|
|
Flag Coat of arms |
|
| Anthem: «God Save the King»[a] | |
Royal coat of arms in Scotland: |
|
|
Location of the United Kingdom (dark green) in Europe (dark grey) |
|
| Capital
and largest city |
London 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.500°N 0.117°W |
| Official language and national language |
English (de facto) |
| Regional and minority languages[b] |
|
| Ethnic groups
(2011) |
|
| Religion
(2011)[4][5] |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Constituent countries |
|
| Government | Unitary[e] parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch |
Charles III |
|
• Prime Minister |
Rishi Sunak |
| Legislature | Parliament |
|
• Upper house |
House of Lords |
|
• Lower house |
House of Commons |
| Formation | |
|
• Laws in Wales Acts |
1535 and 1542 |
|
• Union of the Crowns |
24 March 1603 |
|
• Treaty of Union |
22 July 1706 |
|
• Acts of Union of England and Scotland |
1 May 1707 |
|
• Acts of Union of Great Britain and Ireland |
1 January 1801 |
|
• Irish Free State Constitution Act |
5 December 1922 |
| Area | |
|
• Total |
242,495 km2 (93,628 sq mi)[9] (78th) |
|
• Water (%) |
1.51 (2015)[10] |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 estimate |
67,791,400[11] (22nd) |
|
• 2011 census |
63,182,178[12] (22nd) |
|
• Density |
270.7/km2 (701.1/sq mi) (50th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2021) | very high · 18th |
| Currency | Pound sterling[f] (GBP) |
| Time zone | UTC (Greenwich Mean Time, WET) |
|
• Summer (DST) |
UTC+1 (British Summer Time, WEST) |
| [g] | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy yyyy—mm—dd (AD) |
| Driving side | left[h] |
| Calling code | +44[i] |
| ISO 3166 code | GB |
| Internet TLD | .uk[j] |
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain,[k][16] is a sovereign state and country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland.[17] It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[18] The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles.[19] Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242,495 square kilometres (93,628 sq mi), with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people.[20]
The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 1707 formed the Kingdom of Great Britain. Its union in 1801 with the Kingdom of Ireland created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Most of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922, leaving the present United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, which formally adopted that name in 1927.[l] The nearby Isle of Man, Guernsey and Jersey are not part of the UK, being Crown Dependencies, but the British Government is responsible for their defence and international representation.[21] There are also 14 British Overseas Territories,[22] the last remnants of the British Empire which, at its height in the 1920s, encompassed almost a quarter of the world’s landmass and a third of the world’s population, and was the largest empire in history. British influence can be observed in the language, culture and the legal and political systems of many of its former colonies.[23][24]
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.[m][26] The capital and largest city is London, a global city and financial centre with a metropolitan area population of over 14 million. Other major cities include Birmingham, Liverpool, Sheffield, Bristol and Glasgow.[27] Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments, each with varying powers.[28] The UK became the world’s first industrialised country and was the world’s foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries, during a period of unchallenged global hegemony known as «Pax Britannica».[29][30][31][32] In the 21st century, the UK remains a great power[33][34][35][36] and has significant economic, cultural, military, scientific, technological and political influence internationally.[37] The United Kingdom has the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the eighth-largest by purchasing power parity. It has a high-income economy and a very high Human Development Index rating, ranking 18th in the world. It also performs well in international rankings of education, healthcare, and life expectancy.[38] It is a recognised nuclear state and is ranked fourth globally in military expenditure.[39] It has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since its first session in 1946.
The United Kingdom is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Council of Europe, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, Five Eyes, the United Nations, NATO, AUKUS, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Interpol, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). The UK is also considered a part of the «Big Four», or G4, an unofficial grouping of important European nations.[40] It was a member state of the European Communities (EC) and its successor, the European Union (EU), from its accession in 1973 until its withdrawal in 2020 following a 2016 referendum.
Etymology and terminology
In 43 AD, Britannia referred to the Roman province that encompassed modern day England and Wales. Great Britain encompassed the whole island, taking in the land north of the River Forth known to the Romans as Caledonia in modern Scotland (i.e. «greater» Britain).[41] In the Middle Ages, the name «Britain» was also applied to a small part of France now known as Brittany. As a result, Great Britain (likely from the French «Grande Bretagne«) came into use to refer specifically to the island, with Brittany often referred to as «Little Britain».[42] However, that name had no official significance until 1707, when the island’s kingdoms of England and Scotland were united as the Kingdom of Great Britain.[43]
The Acts of Union 1707 declared that the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland were «United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain».[n][44] The term «United Kingdom» has occasionally been used as a description for the former Kingdom of Great Britain, although its official name from 1707 to 1800 was simply «Great Britain».[45] The Acts of Union 1800 united the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801, forming the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Following the partition of Ireland and the independence of the Irish Free State in 1922, which left Northern Ireland as the only part of the island of Ireland within the United Kingdom, the name was changed to the «United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland».[46]
Although the United Kingdom is a sovereign country, England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are also widely referred to as countries.[47] The UK Prime Minister’s website has used the phrase «countries within a country» to describe the United Kingdom.[18] Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as «regions».[48] Northern Ireland is also referred to as a «province».[49] With regard to Northern Ireland, the descriptive name used «can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one’s political preferences».[50]
The term «Great Britain» conventionally refers to the island of Great Britain, or politically to England, Scotland and Wales in combination.[51] It is sometimes used as a loose synonym for the United Kingdom as a whole.[52] The word England is occasionally used incorrectly to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole, a mistake principally made by people from outside the UK.[53]
The term «Britain» is used both as a synonym for Great Britain,[54][55] and as a synonym for the United Kingdom.[56][55] Usage is mixed: the UK Government prefers to use the term «UK» rather than «Britain» or «British» on its own website (except when referring to embassies),[57] while acknowledging that both terms refer to the United Kingdom and that elsewhere «British government» is used at least as frequently as «United Kingdom government».[58] The UK Permanent Committee on Geographical Names recognises «United Kingdom», «UK» and «U.K.» as shortened and abbreviated geopolitical terms for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in its toponymic guidelines; it does not list «Britain» but notes that «it is only the one specific nominal term ‘Great Britain’ which invariably excludes Northern Ireland».[58] The BBC historically preferred to use «Britain» as shorthand only for Great Britain, though the present style guide does not take a position except that «Great Britain» excludes Northern Ireland.[59]
The adjective «British» is commonly used to refer to matters relating to the United Kingdom and is used in law to refer to United Kingdom citizenship and matters to do with nationality.[60] People of the United Kingdom use several different terms to describe their national identity and may identify themselves as being British, English, Scottish, Welsh, Northern Irish, or Irish;[61] or as having a combination of different national identities.[62] The official designation for a citizen of the United Kingdom is «British citizen».[58]
History
Prior to the Treaty of Union
Stonehenge in Wiltshire is a ring of stones, each about 4 m (13 ft) high, 2 m (7 ft) wide and 25 tonnes, erected 2400–2200 BC.
Settlement by anatomically modern humans of what was to become the United Kingdom occurred in waves beginning by about 30,000 years ago.[63] By the end of the region’s prehistoric period, the population is thought to have belonged, in the main, to a culture termed Insular Celtic, comprising Brittonic Britain and Gaelic Ireland.[64]
The Roman conquest, beginning in 43 AD, and the 400-year rule of southern Britain, was followed by an invasion by Germanic Anglo-Saxon settlers, reducing the Brittonic area mainly to what was to become Wales, Cornwall and, until the latter stages of the Anglo-Saxon settlement, the Hen Ogledd (northern England and parts of southern Scotland).[65] Most of the region settled by the Anglo-Saxons became unified as the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.[66] Meanwhile, Gaelic-speakers in north-west Britain (with connections to the north-east of Ireland and traditionally supposed to have migrated from there in the 5th century)[67] united with the Picts to create the Kingdom of Scotland in the 9th century.[68]
In 1066, the Normans invaded England from northern France. After conquering England, they seized large parts of Wales, conquered much of Ireland and were invited to settle in Scotland, bringing to each country feudalism on the Northern French model and Norman-French culture.[69] The Anglo-Norman ruling class greatly influenced, but eventually assimilated with, each of the local cultures.[70] Subsequent medieval English kings completed the conquest of Wales and made unsuccessful attempts to annex Scotland. Asserting its independence in the 1320 Declaration of Arbroath, Scotland maintained its independence thereafter, albeit in near-constant conflict with England.
The English monarchs, through inheritance of substantial territories in France and claims to the French crown, were also heavily involved in conflicts in France, most notably the Hundred Years’ War, while the Kings of Scots were in an alliance with the French during this period.[71]
Early modern Britain saw religious conflict resulting from the Reformation and the introduction of Protestant state churches in each country.[72] Wales was fully incorporated into the Kingdom of England,[73] and Ireland was constituted as a kingdom in personal union with the English crown.[74] In what was to become Northern Ireland, the lands of the independent Catholic Gaelic nobility were confiscated and given to Protestant settlers from England and Scotland.[75]
The English Reformation ushered in political, constitutional, social and cultural change in the 16th century. Moreover, it defined a national identity for England and slowly, but profoundly, changed people’s religious beliefs and established the Church of England.[76]
In 1603, the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots, inherited the crowns of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal, and religious institutions.[77]
In the mid-17th century, all three kingdoms were involved in a series of connected wars (including the English Civil War) which led to the temporary overthrow of the monarchy, with the execution of King Charles I, and the establishment of the short-lived unitary republic of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.[78]
Although the monarchy was restored, the Interregnum along with the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689 in England and Claim of Right Act 1689 in Scotland ensured that, unlike much of the rest of Europe, royal absolutism would not prevail, and a professed Catholic could never accede to the throne. The British constitution would develop on the basis of constitutional monarchy and the parliamentary system.[79] With the founding of the Royal Society in 1660, science was greatly encouraged. During this period, particularly in England, the development of naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean.[80]
Though previous attempts at uniting the two kingdoms within Great Britain in 1606, 1667, and 1689 had proved unsuccessful, the attempt initiated in 1705 led to the Treaty of Union of 1706 being agreed and ratified by both parliaments.
Kingdom of Great Britain
On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union 1707 being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706 Treaty of Union and so unite the two kingdoms.[81]
In the 18th century, cabinet government developed under Robert Walpole, in practice the first prime minister (1721–1742). A series of Jacobite Uprisings sought to remove the Protestant House of Hanover from the British throne and restore the Catholic House of Stuart. The Jacobites were finally defeated at the Battle of Culloden in 1746, after which the Scottish Highlanders were brutally suppressed. The British colonies in North America that broke away from Britain in the American War of Independence became the United States of America, recognised by Britain in 1783. British imperial ambition turned towards Asia, particularly to India.[82]
Britain played a leading part in the Atlantic slave trade, mainly between 1662 and 1807 when British or British-colonial Slave ships transported nearly 3.3 million slaves from Africa.[83] The slaves were taken to work on plantations in British possessions, principally in the Caribbean but also North America.[84] Slavery coupled with the Caribbean sugar industry had a significant role in strengthening and developing the British economy in the 18th century.[85] However, Parliament banned the trade in 1807, banned slavery in the British Empire in 1833, and Britain took a role in the movement to abolish slavery worldwide through the blockade of Africa and pressing other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties.[86]
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The term «United Kingdom» became official in 1801 when the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland each passed an Act of Union, uniting the two kingdoms and creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.[87]
After the defeat of France at the end of the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815), the United Kingdom emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century (with London the largest city in the world from about 1830).[88] Unchallenged at sea, British dominance was later described as Pax Britannica («British Peace»), a period of relative peace among the Great Powers (1815–1914) during which the British Empire became the global hegemon and adopted the role of global policeman.[89] By the time of the Great Exhibition of 1851, Britain was described as the «workshop of the world».[90] From 1853 to 1856, Britain took part in the Crimean War, allied with the Ottoman Empire in the fight against the Russian Empire,[91] participating in the naval battles of the Baltic Sea known as the Åland War in the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland, among others.[92] The British Empire was expanded to include India, large parts of Africa and many other territories throughout the world. Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, British dominance of much of world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many regions, such as Asia and Latin America.[93]
Political attitudes favoured free trade and laissez-faire policies and a gradual widening of the voting franchise. During the century, the population increased at a dramatic rate, accompanied by rapid urbanisation, causing significant social and economic stresses.[94] To seek new markets and sources of raw materials, the Conservative Party under Disraeli launched a period of imperialist expansion in Egypt, South Africa, and elsewhere. Canada, Australia and New Zealand became self-governing dominions.[95] After the turn of the century, Britain’s industrial dominance was challenged by Germany and the United States.[96] Social reform and home rule for Ireland were important domestic issues after 1900. The Labour Party emerged from an alliance of trade unions and small socialist groups in 1900, and suffragettes campaigned from before 1914 for women’s right to vote.[97]
World wars and partition of Ireland
Britain was one of the principal Allies that fought against the Central Powers in the First World War (1914–1918). Alongside their French, Russian and (after 1917) American counterparts,[98] British armed forces were engaged across much of the British Empire and in several regions of Europe, particularly on the Western Front.[99] The high fatalities of trench warfare caused the loss of much of a generation of men, with lasting social effects in the nation and a great disruption in the social order. After the war, Britain became a permanent member of the Executive Council of the League of Nations and received a mandate over a number of former German and Ottoman colonies. The British Empire reached its greatest extent, covering a fifth of the world’s land surface and a quarter of its population.[100] Britain had suffered 2.5 million casualties and finished the war with a huge national debt.[99] The consequences of the war persuaded the government to expand the right to vote in national and local elections with the Representation of the People Act 1918.[citation needed]
By the mid-1920s, most of the British population could listen to BBC radio programmes.[101][102] Experimental television broadcasts began in 1929 and the first scheduled BBC Television Service commenced in 1936.[103] The rise of Irish nationalism, and disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish Home Rule, led eventually to the partition of the island in 1921.[104] The Irish Free State became independent, initially with Dominion status in 1922, and unambiguously independent in 1931. Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom.[105] The 1928 Equal Franchise Act gave women electoral equality with men in national elections. A wave of strikes in the mid-1920s culminated in the General Strike of 1926. Britain had still not recovered from the effects of the First World War when the Great Depression (1929–1932) occurred. This led to considerable unemployment and hardship in the old industrial areas, as well as political and social unrest in the 1930s, with rising membership in communist and socialist parties. A coalition government was formed in 1931.[106]
Nonetheless, «Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system.»[107] After Nazi Germany invaded Poland, Britain entered the Second World War by declaring war on Germany in 1939. Winston Churchill became prime minister and head of a coalition government in 1940. Despite the defeat of its European allies in the first year of the war, Britain and its Empire continued the war against Germany. Churchill engaged industry, scientists and engineers to advise and support the government and the military in the prosecution of the war effort.[107] In 1940, the Royal Air Force defeated the German Luftwaffe in a struggle for control of the skies in the Battle of Britain. Urban areas suffered heavy bombing during the Blitz. The Grand Alliance of Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union formed in 1941, leading the Allies against the Axis powers. There were eventual hard-fought victories in the Battle of the Atlantic, the North Africa campaign and the Italian campaign. British forces played an important role in the Normandy landings of 1944 and the liberation of Europe, achieved with its allies the United States, the Soviet Union and other Allied countries. The British Army led the Burma campaign against Japan, and the British Pacific Fleet fought Japan at sea. British scientists contributed to the Manhattan Project to design a nuclear weapon,[108] which led to the surrender of Japan.
Postwar 20th century
During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world;[109] it was an original signatory to the Declaration by United Nations. After the war, the UK became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and worked closely with the United States to establish the IMF, World Bank and NATO.[110] The war left the UK severely weakened and financially dependent on the Marshall Plan,[111] but it was spared the total war that devastated eastern Europe.[112] In the immediate post-war years, the Labour government initiated a radical programme of reforms, which had a significant effect on British society in the following decades.[113] Major industries and public utilities were nationalised, a welfare state was established, and a comprehensive, publicly funded healthcare system, the National Health Service, was created.[114] The rise of nationalism in the colonies coincided with Britain’s now much-diminished economic position, so that a policy of decolonisation was unavoidable. Independence was granted to India and Pakistan in 1947.[115] Over the next three decades, most colonies of the British Empire gained their independence, with all those that sought independence supported by the UK, during both the transition period and afterwards. Many became members of the Commonwealth of Nations.[116]
The UK was the third country to develop a nuclear weapons arsenal (with its first atomic bomb test, Operation Hurricane, in 1952), but the new post-war limits of Britain’s international role were illustrated by the Suez Crisis of 1956. The international spread of the English language ensured the continuing international influence of its literature and culture.[117][118] As a result of a shortage of workers in the 1950s, the government encouraged immigration from Commonwealth countries. In the following decades, the UK became a more multi-ethnic society than before.[119] Despite rising living standards in the late 1950s and 1960s, the UK’s economic performance was less successful than many of its main competitors such as France, West Germany and Japan.
Leaders of EU states in 2007. The UK entered the EEC in 1973. In a 1975 referendum 67% voted to stay in it;[120] in 2016 52% voted to leave the EU.[121]
In the decades-long process of European integration, the UK was a founding member of the alliance called the Western European Union, established with the London and Paris Conferences in 1954. In 1960 the UK was one of the seven founding members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), but in 1973 it left to join the European Communities (EC). When the EC became the European Union (EU) in 1992, the UK was one of the 12 founding member states. The Treaty of Lisbon, signed in 2007, forms the constitutional basis of the European Union since then.
From the late 1960s, Northern Ireland suffered communal and paramilitary violence (sometimes affecting other parts of the UK) conventionally known as the Troubles. It is usually considered to have ended with the Belfast «Good Friday» Agreement of 1998.[122]
Following a period of widespread economic slowdown and industrial strife in the 1970s, the Conservative government of the 1980s under Margaret Thatcher initiated a radical policy of monetarism, deregulation, particularly of the financial sector (for example, the Big Bang in 1986) and labour markets, the sale of state-owned companies (privatisation), and the withdrawal of subsidies to others.[123]
In 1982, Argentina invaded the British territories of South Georgia and the Falkland Islands. The occupation provoked a military response from the United Kingdom leading to the Falklands War which lasted for 10 weeks. Argentine forces were defeated and surrendered to British troops. The inhabitants of the islands are predominantly descendants of British settlers, and strongly favour British sovereignty, as shown by a 2013 referendum. From 1984, the UK economy was helped by the inflow of substantial North Sea oil revenues.[124]
Around the end of the 20th century, there were major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved administrations for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[125] The statutory incorporation followed acceptance of the European Convention on Human Rights. The UK remained a Great Power with global diplomatic and military influence and a leading role in the United Nations and NATO.[126]
21st century
2 billion doses of Oxford University- AstraZeneca vaccine have been sent to more than 170 countries (Nov 21)[127]
The UK broadly supported the United States’ approach to the «war on terror» in the early years of the 21st century.[128] Controversy surrounded some of Britain’s overseas military deployments, particularly in Afghanistan and Iraq.[129]
The 2008 global financial crisis severely affected the UK economy. The Cameron–Clegg coalition government of 2010 introduced austerity measures intended to tackle the substantial public deficits which resulted.[130] The devolved Scottish Government and UK Government agreed for a referendum to be held on Scottish independence in 2014.[131] This referendum resulted in the electorate in Scotland voting by 55.3 to 44.7% for Scotland to remain part of the United Kingdom.[132]
In 2016, 51.9 per cent of voters in the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union.[133] The UK left the EU on 31 January 2020 and completed its withdrawal in full at the end of that year.[134]
The COVID-19 pandemic had a severe impact on the UK’s economy, caused major disruptions to education and had far-reaching impacts on society and politics in 2020 and 2021.[135][136][137] The United Kingdom was the first country in the world to use an approved COVID-19 vaccine, they also developed their own vaccine between Oxford University and AstraZeneca which allowed them to roll-out the vaccine nationwide quickly.[138][139]
On 8 September 2022, Elizabeth II, the longest-living and longest-reigning British monarch, died at the age of 96.[140] Upon the Queen’s death, her eldest child Charles, Prince of Wales, acceded to the British throne as King Charles III.[141]
Geography
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately 244,820 square kilometres (94,530 sq mi). The country occupies the major part of the British Isles[142] archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland and some smaller surrounding islands. It lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea with the southeast coast coming within 22 miles (35 km) of the coast of northern France, from which it is separated by the English Channel.[143]
In 1993 10 per cent of the UK was forested, 46 per cent used for pastures and 25 per cent cultivated for agriculture.[144] The Royal Greenwich Observatory in London was chosen as the defining point of the Prime Meridian[145] in Washington, DC, in 1884, although due to more accurate modern measurement the meridian actually lies 100 metres to the east of the observatory.[146]
The United Kingdom lies between latitudes 49° and 61° N, and longitudes 9° W and 2° E. Northern Ireland shares a 224-mile (360 km) land boundary with the Republic of Ireland.[143] The coastline of Great Britain is 11,073 miles (17,820 km) long.[147] It is connected to continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel, which at 31 miles (50 km) (24 miles (38 km) underwater) is the longest underwater tunnel in the world.[148]
The UK contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Celtic broadleaf forests, English Lowlands beech forests, North Atlantic moist mixed forests, and Caledon conifer forests.[149] The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 1.65/10, ranking it 161th globally out of 172 countries.[150]
Climate
Most of the United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round.[143] The temperature varies with the seasons seldom dropping below 0 °C (32 °F) or rising above 30 °C (86 °F).[151] Some parts, away from the coast, of upland England, Wales, Northern Ireland and most of Scotland, experience a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc). Higher elevations in Scotland experience a continental subarctic climate (Dfc) and the mountains experience a tundra climate (ET).[152]
The prevailing wind is from the southwest and bears frequent spells of mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean,[143] although the eastern parts are mostly sheltered from this wind since the majority of the rain falls over the western regions the eastern parts are therefore the driest. Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters; especially in the west where winters are wet and even more so over high ground. Summers are warmest in the southeast of England and coolest in the north. Heavy snowfall can occur in winter and early spring on high ground, and occasionally settles to great depth away from the hills.[153]
The average total annual sunshine in the United Kingdom is 1339.7 hours, which is just under 30% of the maximum possible (The maximum hours of sunshine possible in one year is approximately 4476 hours).[154] The hours of sunshine vary from 1200 to about 1580 hours per year, and since 1996 the UK has been and still is receiving above the 1981 to 2010 average hours of sunshine[155]
United Kingdom is ranked 4 out of 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index.[156] A law has been passed that UK greenhouse gas emissions will be net zero by 2050.[157]
Topography
England accounts for just over half (53 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 130,395 square kilometres (50,350 sq mi).[158] Most of the country consists of lowland terrain,[144] with more upland and some mountainous terrain northwest of the Tees–Exe line; including the Lake District, the Pennines, Exmoor and Dartmoor. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber. England’s highest mountain is Scafell Pike (978 metres (3,209 ft)) in the Lake District.
Scotland accounts for just under one-third (32 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 78,772 square kilometres (30,410 sq mi).[159] This includes nearly 800 islands,[160] predominantly west and north of the mainland; notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its topography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault – a geological rock fracture – which traverses Scotland from Arran in the west to Stonehaven in the east.[161] The fault separates two distinctively different regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the Lowlands to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland’s mountainous land, including Ben Nevis which at 1,345 metres (4,413 ft)[162] is the highest point in the British Isles.[163] Lowland areas – especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth known as the Central Belt – are flatter and home to most of the population including Glasgow, Scotland’s largest city, and Edinburgh, its capital and political centre, although upland and mountainous terrain lies within the Southern Uplands.
Wales accounts for less than one-tenth (9 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 20,779 square kilometres (8,020 sq mi).[164] Wales is mostly mountainous, though South Wales is less mountainous than North and mid Wales. The main population and industrial areas are in South Wales, consisting of the coastal cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, and the South Wales Valleys to their north. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia and include Snowdon (Welsh: Yr Wyddfa) which, at 1,085 metres (3,560 ft), is the highest peak in Wales.[144] Wales has over 2,704 kilometres (1,680 miles) of coastline.[147] Several islands lie off the Welsh mainland, the largest of which is Anglesey (Ynys Môn) in the north-west.
Northern Ireland, separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea and North Channel, has an area of 14,160 square kilometres (5,470 sq mi) and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh which, at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), is the largest lake in the British Isles by area.[165] The highest peak in Northern Ireland is Slieve Donard in the Mourne Mountains at 852 metres (2,795 ft).[144]
Government and politics
Constitutional principles
The Constitution of the United Kingdom is uncodified and consists mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statutes, judge-made case law and international treaties, together with constitutional conventions.[166] Nevertheless, the Supreme Court recognises a number of principles underlying the British constitution, such as parliamentary sovereignty, the rule of law, democracy, and upholding international law.[167]
The Supreme Court also recognises that some acts of Parliament have special constitutional status, and are therefore part of the constitution.[168] These include Magna Carta, which in 1215 required the King to call a «common counsel» (now called Parliament) to represent people, to hold courts in a fixed place, to guarantee fair trials, to guarantee free movement of people, to free the church from the state, and to guarantee rights of «common» people to use the land.[169] (Most of Magna Carta is no longer in force; those principles it established that still exist are mostly protected by other enactments.) After the Wars of the Three Kingdoms and the Glorious Revolution, the Bill of Rights 1689 and the Claim of Right Act 1689 cemented Parliament’s position as the supreme law-making body, and said that the «election of members of Parliament ought to be free».
In accordance with the principle of parliamentary sovereignty, the UK Parliament can carry out constitutional reform through acts of Parliament, and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. No sitting parliament can pass laws that future parliaments cannot change.[170]
The sovereign
The United Kingdom is a unitary state under a constitutional monarchy. King Charles III is the monarch and head of state of the UK, as well as 14 other independent countries. These 15 countries are sometimes referred to as «Commonwealth realms». The monarch is formally vested with all executive authority as the personal embodiment of the Crown. The disposition of such powers however, including those belonging to the royal prerogative, is generally exercised only on the advice of ministers of the Crown responsible to Parliament and thence to the electorate. Nevertheless, in the performance of executive duties, the monarch has «the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, and the right to warn».[171] In addition, the monarch has a number of reserve powers at his disposal in order to uphold responsible government and prevent constitutional crises.[172] These reserve powers are particularly relevant to the appointment of a prime minister, preventing unconstitutional use of the British Armed Forces, the prorogation and dissolution of Parliament, the enactment of legislation, and conferring state honours.[173][174][175][176][177][178]
Parliament
The UK is a parliamentary democracy operating under the Westminster system, otherwise known as a «democratic parliamentary monarchy».[179] The Parliament of the United Kingdom is sovereign.[180] It is made up of the House of Commons, the House of Lords and the Crown.[181] The main business of parliament takes place in the two houses,[181] but royal assent is required for a bill to become an act of parliament (law).[182]
For general elections (elections to the House of Commons), the UK is divided into 650 constituencies, each of which is represented by a member of Parliament (MP).[183] MPs hold office for up to five years and are always up for re-election in general elections.[183] The Conservative Party, Labour Party and Scottish National Party are, respectively, the current first, second and third largest parties (by number of MPs) in the House of Commons.[184]
Prime minister
The prime minister is the head of government in the United Kingdom.[185] Nearly all prime ministers have served concurrently as First Lord of the Treasury[186] and all prime ministers have continuously served as First Lord of the Treasury since 1905,[187] Minister for the Civil Service since 1968[188] and Minister for the Union since 2019.[189] In modern times, the prime minister is, by constitutional convention, an MP.[190] The prime minister is appointed by the monarch[191] and their appointment is governed by constitutional conventions.[183] However, they are normally the leader of the political party with the most seats in the House of Commons[192] and hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons.[190]
The prime minister not only has statutory functions (alongside other ministers),[193] but is the monarch’s principal adviser[194] and it is for them to advise the monarch on the exercise of the royal prerogative in relation to government.[190] In particular, the prime minister recommends the appointment of ministers[190] and chairs the Cabinet.[195]
Administrative divisions
The geographical division of the United Kingdom into counties or shires began in England and Scotland in the early Middle Ages, and was completed throughout Great Britain and Ireland by the early Modern Period.[196] Administrative arrangements were developed separately in each country of the United Kingdom, with origins that often predated the formation of the United Kingdom. Modern local government by elected councils, partly based on the ancient counties, was established by separate Acts of Parliament: in England and Wales in 1888, Scotland in 1889 and Ireland in 1898, meaning there is no consistent system of administrative or geographic demarcation across the UK.[197]
Until the 19th century there was little change to those arrangements, but there has since been a constant evolution of role and function.[198]
The organisation of local government in England is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to local arrangements. The upper-tier subdivisions of England are the nine regions, now used primarily for statistical purposes.[199] One of the regions, Greater London, has had a directly elected assembly and mayor since 2000 following popular support for the proposal in a 1998 referendum.[200] It was intended that other regions would also be given their own elected regional assemblies, but a proposed assembly in the North East region was rejected by a referendum in 2004.[201] Since 2011, ten combined authorities have been established in England. Eight of these have elected mayors, elections for which first took place in May 2017.[202] Below the regional tier, some parts of England have county councils and district councils, and others have unitary authorities, while London consists of 32 London boroughs and the City of London. Councillors are elected by the first-past-the-post system in single-member wards or by the multi-member plurality system in multi-member wards.[203]
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 council areas with a wide variation in both size and population. The cities of Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen and Dundee are separate council areas, as is the Highland Council, which includes a third of Scotland’s area but only just over 200,000 people. Local councils are made up of elected councillors, of whom there are 1,223;[204] they are paid a part-time salary. Elections are conducted by single transferable vote in multi-member wards that elect either three or four councillors. Each council elects a Provost, or Convenor, to chair meetings of the council and to act as a figurehead for the area.
Local government in Wales consists of 22 unitary authorities, each led by a leader and cabinet elected by the council itself. These include the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, which are unitary authorities in their own right.[205] Elections are held every four years under the first-past-the-post system.[205]
Since 1973, local government in Northern Ireland has been organised into 26 district councils, each elected by single transferable vote. Their powers are limited to services such as waste collection, dog control, and maintaining parks and cemeteries.[206] In 2008 the executive agreed on proposals to create 11 new councils and replace the present system.[207]
Devolved governments
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a first minister (or, in the case of Northern Ireland, a diarchal first minister and deputy first minister), and a devolved unicameral legislature. England, the largest country of the United Kingdom, has no devolved executive or legislature and is administered and legislated for directly by the UK’s government and parliament on all issues. This situation has given rise to the so-called West Lothian question, which concerns the fact that members of parliament from Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland can vote, sometimes decisively,[208] on matters that affect only England.[209] The 2013 McKay Commission on this recommended that laws affecting only England should need support from a majority of English members of parliament.[210]
The Scottish Government and Parliament have wide-ranging powers over any matter that has not been specifically reserved to the UK Parliament, including education, healthcare, Scots law and local government.[211] Their power over economic issues is significantly constrained by an act of the UK parliament passed in 2020.[219]
The Welsh Government and the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; formerly the National Assembly for Wales)[220] have more limited powers than those devolved to Scotland.[221] The Senedd is able to legislate on any matter not specifically reserved to the UK Parliament through Acts of Senedd Cymru.
The Northern Ireland Executive and Assembly have powers similar to those devolved to Scotland. The Executive is led by a diarchy representing unionist and nationalist members of the Assembly.[222] Devolution to Northern Ireland is contingent on participation by the Northern Ireland administration in the North-South Ministerial Council, where the Northern Ireland Executive cooperates and develops joint and shared policies with the Government of Ireland. The British and Irish governments co-operate on non-devolved matters affecting Northern Ireland through the British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference, which assumes the responsibilities of the Northern Ireland administration in the event of its non-operation.[citation needed]
The UK does not have a codified constitution and constitutional matters are not among the powers devolved to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. Under the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty, the UK Parliament could, in theory, therefore, abolish the Scottish Parliament, Senedd or Northern Ireland Assembly.[223] Indeed, in 1972, the UK Parliament unilaterally prorogued the Parliament of Northern Ireland, setting a precedent relevant to contemporary devolved institutions.[224] In practice, it would be politically difficult for the UK Parliament to abolish devolution to the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd, given the political entrenchment created by referendum decisions.[225] The political constraints placed upon the UK Parliament’s power to interfere with devolution in Northern Ireland are even greater than in relation to Scotland and Wales, given that devolution in Northern Ireland rests upon an international agreement with the Government of Ireland.[226] The UK Parliament restricts the three devolved parliaments’ legislative competence in economic areas through an Act passed in 2020.[219]
Dependencies
The United Kingdom, the 14 British Overseas Territories[22] and the three Crown Dependencies[229] form ‘one undivided Realm’.[230][231] All parts of the realm are under the sovereignty of the British Crown, but the Territories and Dependencies are not part of the UK. This is distinct from the status of Commonwealth realms, who have separate monarchies, but share the same monarch.[231]
The 14 British Overseas Territories are remnants of the British Empire: Anguilla; Bermuda; the British Antarctic Territory; the British Indian Ocean Territory; the British Virgin Islands; the Cayman Islands; the Falkland Islands; Gibraltar; Montserrat; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; the Turks and Caicos Islands; the Pitcairn Islands; South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and Akrotiri and Dhekelia on the island of Cyprus.[232] British claims in Antarctica have limited international recognition.[233] Collectively Britain’s overseas territories encompass an approximate land area of 480,000 square nautical miles (640,000 sq mi; 1,600,000 km2),[234] with a total population of approximately 250,000.[235] The overseas territories also give the UK the world’s fifth largest exclusive economic zone at 6,805,586 km2 (2,627,651 sq mi).[236][better source needed] A 1999 UK government white paper stated that: «[The] Overseas Territories are British for as long as they wish to remain British. Britain has willingly granted independence where it has been requested; and we will continue to do so where this is an option.»[237] Self-determination is also enshrined in the constitutions of several overseas territories and three have specifically voted to remain under British sovereignty (Bermuda in 1995,[238] Gibraltar in 2002[239] and the Falkland Islands in 2013).[240]
The Crown Dependencies are possessions of the Crown, as opposed to territories of the UK.[241] They comprise three independently administered jurisdictions: the Bailiwicks of Jersey and of Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea. By mutual agreement, the British Government manages the islands’ foreign affairs and defence and the UK Parliament has the authority to legislate on their behalf. Internationally, they are regarded as «territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible».[242] The power to pass legislation affecting the islands ultimately rests with their own respective legislative assemblies, with the assent of the Crown (Privy Council or, in the case of the Isle of Man, in certain circumstances the Lieutenant-Governor).[243] Since 2005 each Crown dependency has had a Chief Minister as its head of government.[244]
Law and criminal justice
The Supreme Court is the final court of appeal for England, Wales, Northern Ireland and civil cases in Scotland
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland’s separate legal system.[245] Today the UK has three distinct systems of law: English law, Northern Ireland law and Scots law. A new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom came into being in October 2009 to replace the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords.[246] The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, including the same members as the Supreme Court, is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the British Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies.[247]
Both English law, which applies in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland law are based on common-law principles.[248] The essence of common law is that, subject to statute, the law is developed by judges in courts, applying statute, precedent and common sense to the facts before them to give explanatory judgements of the relevant legal principles, which are reported and binding in future similar cases (stare decisis).[249] The courts of England and Wales are headed by the Senior Courts of England and Wales, consisting of the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land for both criminal and civil appeal cases in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and any decision it makes is binding on every other court in the same jurisdiction, often having a persuasive effect in other jurisdictions.[250]
Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases,[251] and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases.[252] The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom serves as the highest court of appeal for civil cases under Scots law.[253] Sheriff courts deal with most civil and criminal cases including conducting criminal trials with a jury, known as sheriff solemn court, or with a sheriff and no jury, known as sheriff summary Court.[254] The Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdicts for a criminal trial: «guilty», «not guilty» and «not proven». Both «not guilty» and «not proven» result in an acquittal.[255]
Crime in England and Wales increased in the period between 1981 and 1995, though since that peak there has been an overall fall of 66 per cent in recorded crime from 1995 to 2015,[256] according to crime statistics. The prison population of England and Wales has increased to 86,000, giving England and Wales the highest rate of incarceration in Western Europe at 148 per 100,000.[257] His Majesty’s Prison Service, which reports to the Ministry of Justice, manages most of the prisons within England and Wales. The murder rate in England and Wales has stabilised in the first half of the 2010s with a murder rate around 1 per 100,000 which is half the peak in 2002 and similar to the rate in the 1980s[258] Crime in Scotland fell slightly in 2014–2015 to its lowest level in 39 years in with 59 killings for a murder rate of 1.1 per 100,000. Scotland’s prisons are overcrowded but the prison population is shrinking.[259]
Foreign relations
The UK is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of NATO, AUKUS, the Commonwealth of Nations, the G7 finance ministers, the G7 forum, the G20, the OECD, the WTO, the Council of Europe and the OSCE.[260] The UK has the British Council which is a British organisation based in over 100 countries specialising in international cultural and educational opportunities. The UK is said to have a «Special Relationship» with the United States and a close partnership with France – the «Entente cordiale» – and shares nuclear weapons technology with both countries;[261] the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance is considered to be the oldest binding military alliance in the world. The UK is also closely linked with the Republic of Ireland; the two countries share a Common Travel Area and co-operate through the British-Irish Intergovernmental Conference and the British-Irish Council. Britain’s global presence and influence is further amplified through its trading relations, foreign investments, official development assistance and military engagements.[262] Canada, Australia and New Zealand, all of which are former colonies of the British Empire which share King Charles as their head of state, are the most favourably viewed countries in the world by British people.[263]
Military
HMS Queen Elizabeth and HMS Prince of Wales
Royal Air Force Typhoon Jet
His Majesty’s Armed Forces consist of three professional service branches: the Royal Navy and Royal Marines (forming the Naval Service), the British Army and the Royal Air Force.[264] The armed forces of the United Kingdom are managed by the Ministry of Defence and controlled by the Defence Council, chaired by the Secretary of State for Defence. The Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch, to whom members of the forces swear an oath of allegiance.[265] The Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK’s global security interests and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in NATO, including the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps, the Five Power Defence Arrangements, RIMPAC and other worldwide coalition operations. Overseas garrisons and facilities are maintained in Ascension Island, Bahrain, Belize, Brunei, Canada, Cyprus, Diego Garcia, the Falkland Islands, Germany, Gibraltar, Kenya, Oman, Qatar and Singapore.[266]
The British armed forces played a key role in establishing the British Empire as the dominant world power in the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. By emerging victorious from conflicts, Britain has often been able to decisively influence world events. Since the end of the British Empire, the UK has remained a major military power. Following the end of the Cold War, defence policy has a stated assumption that «the most demanding operations» will be undertaken as part of a coalition.[267]
According to sources which include the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute and the International Institute for Strategic Studies, the UK has either the fourth- or the fifth-highest military expenditure. Total defence spending amounts to 2.0 per cent of national GDP.[268]
Economy
Overview
The United Kingdom uses the pound sterling which is the world’s oldest currency that is still in use and that has been in continuous use since its inception.[270] It is currently the fourth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market and is the world’s fourth-largest reserve currency (after the Dollar, Euro, and Yen).[271] London is the world capital for foreign exchange trading, with a global market share of 38.1% in 2022[272] of the daily $7.5 trillion global turnover.[273] Since 1997 the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England, has been responsible for setting interest rates at the level necessary to achieve the overall inflation target for the economy that is set by the Chancellor each year.[274] Lloyd’s of London is the worlds largest insurance and reinsurance market and is located in London, UK.[275]
The UK has a partially regulated market economy.[276] Based on market exchange rates, the UK is today the fifth-largest economy in the world and the second-largest in Europe after Germany. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government’s public finance policy and economic policy. The Bank of England is the UK’s central bank and is responsible for issuing notes and coins in the nation’s currency, the pound sterling. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover their issue.
The service sector made up around 80% of the UK’s GVA in 2021.[277] London is one of the world’s largest financial centres, ranking second in the world, behind New York City, in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[278] London also has the largest city GDP in Europe.[279] Edinburgh ranks 17th in the world, and sixth in Western Europe in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[278] Tourism is very important to the British economy; with over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom was ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world.[280] The creative industries accounted for 5.9% of the UK’s GVA in 2019, having grown by 43.6% in real terms from 2010.[281] Creative industries contributed more than £111bn to the UK economy in 2018, growth in the sector is more than five times larger than growth across the UK economy as a whole as reported in 2018.[282] WPP plc, the world’s biggest advertising company, is also based in the UK.
Following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union, the functioning of the UK internal economic market is enshrined by the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020 which ensures trade in goods and services continues without internal barriers across the four countries of the United Kingdom.[283]
The Industrial Revolution started in Britain with an initial concentration on the textile industry,[284] followed by other heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining and steelmaking.[285] British merchants, shippers and bankers developed overwhelming advantage over those of other nations allowing the UK to dominate international trade in the 19th century.[286] As other nations industrialised, coupled with economic decline after two world wars, the United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined, by degrees, throughout the 20th century. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy but accounted for only 16.7 per cent of national output in 2003.[287]
The automotive industry employs around 800,000 people, with a turnover in 2015 of £70 billion, generating £34.6 billion of exports (11.8 per cent of the UK’s total export goods). In 2015, the UK produced around 1.6 million passenger vehicles and 94,500 commercial vehicles including luxury cars such as Rolls-Royce, Bentley and Range Rover. The UK is a major centre for engine manufacturing: in 2015 around 2.4 million engines were produced. The UK motorsport industry employs more than 40,000 people, comprises around 4,300 companies and has an annual turnover of around £10 billion.[288]
7 of the 10 Formula One teams are based in the UK, with their technology being used in supercars and hypercars from McLaren, Aston Martin and Lotus.
The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry in the world depending upon the method of measurement and has an annual turnover of around £30 billion.[289]
BAE Systems plays a critical role in some of the world’s biggest defence aerospace projects. In the UK, the company makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter and assembles the aircraft for the Royal Air Force, the plane was based on the British Aerospace EAP design which first flew in 1986.[290][291] BAE Systems is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Joint Strike Fighter – the world’s largest single defence project – for which it designs and manufactures a range of components. It also manufactures the Hawk, the world’s most successful[clarification needed] jet training aircraft.[292] Airbus UK also manufactures the wings for the A400M military transporter. Rolls-Royce is the world’s second-largest aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft and it has more than 30,000 engines in service in the civil and defence sectors.
The UK space industry was worth £16.5bn in 2019/20 and employed 47,000 people. Since 2012, the number of space organisations has grown on average nearly 21% per year, with 1,293 organisations reported in 2021.[293] In 2013, the British Government pledged £60 m to the Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a «crucial stage» to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE engine to be built.
The pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.[294]
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing about 60 per cent of food needs with less than 1.6 per cent of the labour force (535,000 workers).[295] Around two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. The UK retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. It is also rich in a variety of natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica and an abundance of arable land.[296] In 2020, coronavirus lockdown measures caused the UK economy to suffer its biggest slump on record, shrinking by 20.4 per cent between April and June compared to the first three months of the year, to push it officially into recession for the first time in 11 years.[297]
The UK Government debt was £2,436.7 billion at the end of Quarter 2 (Apr to June) 2022. The UK has the 2nd best debt-to-GDP ratio out of the G7 countries.[298] The UK annual GDP output is estimated to have grown by 4.1% in 2022.[299]
Science and technology
England and Scotland were leading centres of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century.[301] The United Kingdom led the Industrial Revolution from the 18th century,[284] and has continued to produce scientists and engineers credited with important advances.[302] Major theorists from the 17th and 18th centuries include Isaac Newton, whose laws of motion and illumination of gravity have been seen as a keystone of modern science;[303] from the 19th century Charles Darwin, whose theory of evolution by natural selection was fundamental to the development of modern biology, and James Clerk Maxwell, who formulated classical electromagnetic theory; and more recently Stephen Hawking, who advanced major theories in the fields of cosmology, quantum gravity and the investigation of black holes.[304]
Major scientific discoveries from the 18th century include hydrogen by Henry Cavendish;[305] from the 20th century penicillin by Alexander Fleming,[306] and the structure of DNA, by Francis Crick and others.[307] Famous British engineers and inventors of the Industrial Revolution include James Watt, George Stephenson, Richard Arkwright, Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel.[308] Other major engineering projects and applications by people from the UK include the steam locomotive, developed by Richard Trevithick and Andrew Vivian;[309] from the 19th century the electric motor by Michael Faraday, the first computer designed by Charles Babbage,[310] the first commercial electrical telegraph by William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone,[311] the incandescent light bulb by Joseph Swan,[312] and the first practical telephone, patented by Alexander Graham Bell;[313] and in the 20th century the world’s first working television system by John Logie Baird and others,[314] the jet engine by Frank Whittle, the basis of the modern computer by Alan Turing, and the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee.[315]
Scientific research and development remains important in British universities, with many establishing science parks to facilitate production and co-operation with industry.[316] Between 2004 and 2008 the UK produced 7 per cent of the world’s scientific research papers and had an 8 per cent share of scientific citations, the third and second-highest in the world (after the United States and China, respectively).[317] Scientific journals produced in the UK include publications by the Royal Society, Nature, the British Medical Journal and The Lancet.[318] The United Kingdom was ranked fourth in the Global Innovation Index 2020, 2021 and 2022. [319]
Transport
A radial road network totals 29,145 miles (46,904 km) of main roads, 2,173 miles (3,497 km) of motorways and 213,750 miles (344,000 km) of paved roads.[143] The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world.[320] In 2022 there were a total of 40.8 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.[321]
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the West Coast, East Coast, Midland, Great Western and Great Eastern), which radiate from London to the rest of the country, augmented by regional rail lines and dense commuter networks within the major cities. High Speed 1 is operationally separate from the rest of the network. The world’s first passenger railway running on steam was the Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened in 1825. Just under five years later the world’s first intercity railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, designed by George Stephenson. The network grew rapidly as a patchwork of hundreds of separate companies during the Victorian era.[322]
Red double-decker buses in London
The UK has a railway network of 10,072 miles (16,209 km) in Great Britain and 189 miles (304 km) in Northern Ireland. Railways in Northern Ireland are operated by NI Railways, a subsidiary of state-owned Translink. In Great Britain, the British Rail network was privatised between 1994 and 1997, which was followed by a rapid rise in passenger numbers. The UK was ranked eighth among national European rail systems in the 2017 European Railway Performance Index assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety.[323] HS2 is a new high speed railway under construction linking up London, the Midlands, the North and Scotland serving over 25 stations, including eight of Britain’s 10 largest cities and connecting around 30 million people, capable of speeds of up to 225mph.[324][325] Crossrail, which was renamed the Elizabeth line in 2016, in honour of Queen Elizabeth II, opened in 2022, it was Europe’s largest construction project at the time and will bring in an estimated £42 billion to the UK economy.[326][327][328][329]
Great British Railways is a planned state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. In 2014, there were 5.2 billion bus journeys in the UK, 2.4 billion of which were in London.[330] The red double-decker bus has entered popular culture as an internationally recognised icon of England.[331] The London bus network is extensive, with over 6,800 scheduled services every weekday carrying about six million passengers on over 700 different routes making it one of the most extensive bus systems in the world and the largest in Europe.[332]
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers.[333] In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport (65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport (31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport (18.9 million passengers).[333] London Heathrow Airport, located 15 miles (24 km) west of the capital, is the world’s second busiest airport by international passenger traffic and has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world;[334] it is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways, as well as Virgin Atlantic.[335]
Energy
Energy mix of the United Kingdom over time
In 2021, the UK was the world’s 14th-largest consumer of energy and the 22nd-largest producer.[336] The UK is home to many large energy companies, including two of the six major oil and gas companies – BP and Shell.[337]
The total of all renewable electricity sources provided 38.9 per cent of the electricity generated in the UK in the third quarter of 2019, producing 28.8TWh of electricity.[338] The UK is one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind power production is the country’s fastest-growing supply; in 2019, almost 20 per cent of the UK’s total electricity was generated by wind power.[339]
In 2023, the UK had 9 nuclear reactors normally generating about 15 per cent of the UK’s electricity.[340] Unlike Germany and Japan, there are currently two reactors under construction and more planned.[341][342]In the late 1990s, nuclear power plants contributed around 25 per cent of the total annual electricity generation in the UK, but this has gradually declined as old plants have been shut down. The UK government is investing in Small Modular Reactors and Advanced Modular Reactors research and development.
In 2021, the UK produced 935 thousand barrels per day (bbl/d) of oil (and other liquids) and consumed 1,258 thousand bbl/d.[343] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of oil since 2005.[344] In 2020, the UK had around 2 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves.[344]
In 2021, the UK was the 21th-largest producer of natural gas in the world.[345] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of natural gas since 2004.[345]
In 2020, the UK produced 1.8 million tonnes of coal falling 91% in 10 years.[346] In 2020 it had proven recoverable coal reserves of 26 million tonnes.[346] The UK Coal Authority has stated that there is a potential to produce between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes of coal through underground coal gasification (UCG) or ‘fracking’,[347] and based on current UK coal consumption, such reserves could last between 200 and 400 years.[348] Environmental and social concerns have been raised over chemicals contaminating groundwater and minor earthquakes damaging homes.[349]
Water supply and sanitation
Access to improved water supply and sanitation in the UK is universal. It is estimated that 96.7 per cent of households are connected to the sewer network.[350] According to the Environment Agency, total water abstraction for public water supply in the UK was 16,406 megalitres per day in 2007.[351]
In England and Wales water and sewerage services are provided by 10 private regional water and sewerage companies and 13 mostly smaller private «water only» companies. In Scotland, water and sewerage services are provided by a single public company, Scottish Water. In Northern Ireland water and sewerage services are also provided by a single public entity, Northern Ireland Water.[352]
Demographics
Map of population density in the UK as at the 2011 census
A census is taken simultaneously in all parts of the UK every 10 years.[353] In the 2011 census the total population of the United Kingdom was 63,181,775.[354] It is the fourth-largest in Europe (after Russia, Germany and France), the fifth-largest in the Commonwealth and the 22nd-largest in the world. In mid-2014 and mid-2015 net long-term international migration contributed more to population growth. In mid-2012 and mid-2013 natural change contributed the most to population growth.[355] Between 2001 and 2011 the population increased by an average annual rate of approximately 0.7 per cent.[354] This compares to 0.3 per cent per year in the period 1991 to 2001 and 0.2 per cent in the decade 1981 to 1991.[356] The 2011 census also showed that, over the previous 100 years, the proportion of the population aged 0–14 fell from 31 per cent to 18 per cent, and the proportion of people aged 65 and over rose from 5 to 16 per cent.[354] In 2018 the median age of the UK population was 41.7 years.[357]
England’s population in 2011 was 53 million, representing some 84 per cent of the UK total.[358] It is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with 420 people resident per square kilometre in mid-2015,[355] with a particular concentration in London and the south-east.[359] The 2011 census put Scotland’s population at 5.3 million,[360] Wales at 3.06 million and Northern Ireland at 1.81 million.[358]
In 2017 the average total fertility rate (TFR) across the UK was 1.74 children born per woman.[361] While a rising birth rate is contributing to population growth, it remains considerably below the baby boom peak of 2.95 children per woman in 1964,[362] or the high of 6.02 children born per woman in 1815,[363] below the replacement rate of 2.1, but higher than the 2001 record low of 1.63.[364] In 2011, 47.3 per cent of births in the UK were to unmarried women.[365] The Office for National Statistics published a bulletin in 2015 showing that, out of the UK population aged 16 and over, 1.7 per cent identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual (2.0 per cent of males and 1.5 per cent of females); 4.5 per cent of respondents responded with «other», «I don’t know», or did not respond.[366] The number of transgender people in the UK was estimated to be between 65,000 and 300,000 by research between 2001 and 2008.[367]
Largest urban areas of the United Kingdom (England and Wales: 2011 census built-up area;[368] Scotland: 2016 estimates settlement;[369] Northern Ireland: 2001 census urban area)[370] |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | |
 Greater London
|
1 | Greater London | 9,787,426 | London | 11 | Bristol | 617,280 | Bristol |
| 2 | West Midlands | 2,440,986 | Birmingham | 12 | Edinburgh | 512,150 | Edinburgh | |
| 3 | Greater Manchester | 2,553,379 | Manchester | 13 | Leicester | 508,916 | Leicester | |
| 4 | West Yorkshire | 1,777,934 | Leeds | 14 | Belfast | 483,418 | Belfast | |
| 5 | Greater Glasgow | 985,290 | Glasgow | 15 | Brighton & Hove | 474,485 | Brighton & Hove | |
| 6 | Liverpool | 864,122 | Liverpool | 16 | Bournemouth/ Poole | 466,266 | Bournemouth | |
| 7 | South Hampshire | 855,569 | Southampton | 17 | Cardiff | 390,214 | Cardiff | |
| 8 | Tyneside | 774,891 | Newcastle | 18 | Teesside | 376,633 | Middlesbrough | |
| 9 | Nottingham | 729,977 | Nottingham | 19 | Stoke-on-Trent | 372,775 | Stoke | |
| 10 | Sheffield | 685,368 | Sheffield | 20 | Coventry | 359,262 | Coventry |
Ethnic groups
Historically, indigenous British people were thought to be descended from the various ethnic groups that settled there before the 12th century: the Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Norse and the Normans. Welsh people could be the oldest ethnic group in the UK.[371] A 2006 genetic study shows that more than 50 per cent of England’s gene pool contains Germanic Y chromosomes.[372] Another 2005 genetic analysis indicates that «about 75 per cent of the traceable ancestors of the modern British population had arrived in the British isles by about 6,200 years ago, at the start of the British Neolithic or Stone Age», and that the British broadly share a common ancestry with the Basque people.[373][needs update] The UK has a history of non-white immigration with Liverpool having the oldest Black population in the country dating back to at least the 1730s during the period of the African slave trade. During this period it is estimated the Afro-Caribbean population of Great Britain was 10,000 to 15,000[374] which later declined due to the abolition of slavery.[375] The UK also has the oldest Chinese community in Europe, dating to the arrival of Chinese seamen in the 19th century.[376] In 1950 there were probably fewer than 20,000 non-white residents in Britain, almost all born overseas.[377] In 1951 there were an estimated 94,500 people living in Britain who had been born in South Asia, China, Africa and the Caribbean, just under 0.2 per cent of the UK population. By 1961 this number had more than quadrupled to 384,000, just over 0.7 per cent of the United Kingdom population.[378]
Since 1948 substantial immigration from Africa, the Caribbean and South Asia has been a legacy of ties forged by the British Empire.[379] Migration from new EU member states in Central and Eastern Europe since 2004 has resulted in growth in these population groups, although some of this migration has been temporary.[380] Since the 1990s, there has been substantial diversification of the immigrant population, with migrants to the UK coming from a much wider range of countries than previous waves, which tended to involve larger numbers of migrants coming from a relatively small number of countries.[381]
Academics have argued that the ethnicity categories employed in British national statistics, which were first introduced in the 1991 census, involve confusion between the concepts of ethnicity and race.[382] In 2011, 87.2 per cent of the UK population identified themselves as white, meaning 12.8 per cent of the UK population identify themselves as of one of number of ethnic minority groups.[383] In the 2001 census, this figure was 7.9 per cent of the UK population.[384] Because of differences in the wording of the census forms used in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, data on the Other White group is not available for the UK as a whole, but in England and Wales this was the fastest-growing group between the 2001 and 2011 censuses, increasing by 1.1 million (1.8 percentage points).[385] Amongst groups for which comparable data is available for all parts of the UK level, the Other Asian category increased from 0.4 per cent to 1.4 per cent of the population between 2001 and 2011, while the Mixed category rose from 1.2 per cent to 2 per cent.[383]
Ethnic diversity varies significantly across the UK. 30.4 per cent of London’s population and 37.4 per cent of Leicester’s was estimated to be non-white in 2005,[386] whereas less than 5 per cent of the populations of North East England, Wales and the South West were from ethnic minorities, according to the 2001 census.[387] In 2016, 31.4 per cent of primary and 27.9 per cent of secondary pupils at state schools in England were members of an ethnic minority.[388] The 1991 census was the first UK census to have a question on ethnic group. In the 1991 UK census 94.1 per cent of people reported themselves as being White British, White Irish or White Other with 5.9 per cent of people reporting themselves as coming from other minority groups.[389]
| Ethnic group | Population (absolute) | Population (per cent) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2011 | 2001[390] | 2011[383] | ||
| White | 54,153,898 | 55,010,359 | 92.1% | 87.1% | |
| White: Gypsy, Traveller and Irish Traveller[o] | – | 63,193 | – | 0.1% | |
| Asian and Asian British | Indian | 1,053,411 | 1,451,862 | 1.8% | 2.3% |
| Pakistani | 747,285 | 1,174,983 | 1.3% | 1.9% | |
| Bangladeshi | 283,063 | 451,529 | 0.5% | 0.7% | |
| Chinese | 247,403 | 433,150 | 0.4% | 0.7% | |
| other Asian | 247,664 | 861,815 | 0.4% | 1.4% | |
| Black, African, Caribbean and Black British[p] | 1,148,738 | 1,904,684 | 2.0% | 3.0% | |
| mixed or multiple ethnic groups | 677,117 | 1,250,229 | 1.2% | 2.0% | |
| other ethnic group | 230,615 | 580,374 | 0.4% | 0.9% | |
| Total | 58,789,194 | 63,182,178 | 100.0% | 100.0% |
Languages
The English language is the official and most spoken language of the United Kingdom that originated from England.[393][394]The United Kingdom proactively promotes the language globally to build connections, understanding and trust between people in the UK and countries worldwide.[395][396] It is estimated that 95 per cent of the UK’s population are monolingual English speakers.[397] 5.5 per cent of the population are estimated to speak languages brought to the UK as a result of relatively recent immigration.[397] South Asian languages are the largest grouping which includes Punjabi, Urdu, Bengali, Sylheti, Hindi and Gujarati.[398] According to the 2011 census, Polish has become the second-largest language spoken in England and has 546,000 speakers.[399] In 2019, some three quarters of a million people spoke little or no English.[400]
Three indigenous Celtic languages are spoken in the UK: Welsh, Irish and Scottish Gaelic. Cornish, which became extinct as a first language in the late 18th century, is subject to revival efforts and has a small group of second language speakers.[401][2] According to the 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 people (17.8 per cent).[402] In addition, it is estimated that about 200,000 Welsh speakers live in England.[403] In the 2011 census in Northern Ireland 167,487 people (10.4 per cent) stated that they had «some knowledge of Irish» (see Irish language in Northern Ireland), almost exclusively in the nationalist (mainly Catholic) population. Over 92,000 people in Scotland (just under 2 per cent of the population) had some Gaelic language ability, including 72 per cent of those living in the Outer Hebrides.[404] The number of children being taught either Welsh or Scottish Gaelic is increasing.[405] Among emigrant-descended populations some Scottish Gaelic is still spoken in Canada (principally Nova Scotia and Cape Breton Island),[406] and Welsh in Patagonia, Argentina.[407]
Scots, a language descended from early northern Middle English, has limited recognition alongside its regional variant, Ulster Scots in Northern Ireland, without specific commitments to protection and promotion.[2][408]
As of April 2020, there are said to be around 151,000 users of British Sign Language (BSL), a sign language used by deaf people, in the UK.[409] BSL was recognised as a language of England, Scotland and Wales in law in 2022.[410] It is compulsory for pupils to study a second language from the age of seven in England.[411] French and Spanish are the two most commonly taught second languages in the United Kingdom.[412] All pupils in Wales are either taught Welsh as a second language up to age 16, or are taught in Welsh as a first language.[413] Welsh was recognised as having official status in Wales in 2011.[414] Irish was recognised as having official status in Northern Ireland in 2022.[415]
Religion
Religion (2011 census)[4][5]
Other religions (0.4%)
Not stated (7.2%)
Forms of Christianity have dominated religious life in what is now the United Kingdom for more than 1,400 years.[416] Although a majority of citizens still identify with Christianity in many surveys, regular church attendance has fallen dramatically since the middle of the 20th century,[417] while immigration and demographic change have contributed to the growth of other faiths, most notably Islam.[418] This has led some commentators to variously describe the UK as a multi-faith,[419] secularised,[420] or post-Christian society.[421]
In the 2001 census, 71.6 per cent of all respondents indicated that they were Christians, with the next largest faiths being Islam (2.8 per cent), Hinduism (1.0 per cent), Sikhism (0.6 per cent), Judaism (0.5 per cent), Buddhism (0.3 per cent) and all other religions (0.3 per cent).[422] Of the respondents, 15 per cent stated that they had no religion and a further 7 per cent did not state a religious preference.[423] A Tearfund survey in 2007 showed that only one in ten Britons actually attend church weekly.[424] Between the 2001 and 2011 census, there was a 12 per cent decrease in the number of people who identified as Christian, whilst the percentage of those reporting no religious affiliation doubled. This contrasted with growth in the other main religious group categories, with the number of Muslims increasing by the most substantial margin to a total of about 5 per cent.[425] The Muslim population has increased from 1.6 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2011, making it the second-largest religious group in the UK.[426]
In a 2016 survey conducted by BSA (British Social Attitudes) on religious affiliation, 53 per cent of respondents indicated ‘no religion’, 41 per cent indicated they were Christians, followed by 6 per cent who affiliated with other religions (e.g. Islam, Hinduism, Judaism, etc.).[427] Among Christians, adherents to the Church of England constituted 15 per cent, to the Catholic Church 9 per cent, and other Christians (including Presbyterians, Methodists, other Protestants, as well as Eastern Orthodox) constituted 17 per cent.[427] Of the young people aged 18 to 24 that responded, 71 per cent said they had no religion.[427]
The Church of England is the established church in England.[428] It retains a representation in the UK Parliament, and the British monarch is its Supreme Governor.[429] In Scotland, the Church of Scotland is recognised as the national church. It is not subject to state control, and the British monarch is an ordinary member, required to swear an oath to «maintain and preserve the Protestant Religion and Presbyterian Church Government» upon his or her accession.[430][2][431] The Church in Wales was disestablished in 1920 and, because the Church of Ireland was disestablished in 1870 before the partition of Ireland, there is no established church in Northern Ireland.[432] Although there are no UK-wide data in the 2001 census on adherence to individual Christian denominations, it has been estimated that 62 per cent of Christians are Anglican, 13.5 per cent Catholic, 6 per cent Presbyterian, and 3.4 per cent Methodist, with small numbers of other Protestant denominations such as Plymouth Brethren, and Orthodox churches.[433]
In the 2021 UK census, less than half the English and Welsh population were Christian; 46.2% of the people of England and Wales said they were Christian, 37.2% that they had no religion, and 6.5% said they were Muslim.[434]
Migration
Estimated foreign-born population by country of birth from April 2007 to March 2008
| Year | Foreign born population of England and Wales | Total population [435][436][437] [438][439] |
Irish born population | Percentage of total population that was born abroad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1851 | 100,000 | 17,900,000 | 520,000 | 0.6 |
| 1861 | 150,000 | 20,100,000 | 600,000 | 0.7 |
| 1871 | 200,000 | 22,700,000 | 565,000 | 0.9 |
| 1881 | 275,000 | 26,000,000 | 560,000 | 1.1 |
| 1891 | 350,000 | 29,000,000 | 460,000 | 1.2 |
| 1901 | 475,000 | 32,500,000 | 425,000 | 1.5 |
| 1911 | 900,000 | 32,500,000 | 375,000 | 2.5 |
| 1921 | 750,000 | 37,900,000 | 365,000 | 2 |
| 1931 | 1,080,000 | 40,000,000 | 380,000 | 2.7 |
| 1951 | 1,875,000 | 43,700,000 | 470,000 | 4.3 |
| 1961 | 2,290,000 | 46,000,000 | 645,000 | 5.0 |
| 1971 | 3,100,000 | 48,700,000 | 585,000 | 6.4 |
| 1981 | 3,220,000 | 48,500,000 | 580,000 | 6.6 |
| 1991 | 3,625,000 | 49,900,000 | 570,000 | 7.3 |
| 2001 | 4,600,000 | 52,500,000 | 475,000 | 8.8 |
| 2011 | 7,500,000 | 56,000,000 | 400,000 | 13.4 |
| 2021 | 10,000,000 | 59,600,000 | 325,000 | 16.8 |
The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain.[440] Throughout the 19th century, a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to Russian Jews.[441] After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2 million left the Russian Empire by 1914. Around 120,000 settled permanently in Britain, becoming the largest ethnic minority from outside the British Isles,[442] and by 1938 this population had increased to 370,000.[443] Unable to return to Poland at the end of the Second World War, over 120,000 Polish veterans remained in the UK permanently.[444] After the war, many people immigrated from colonies and former colonies in the Caribbean and Indian subcontinent, as a legacy of empire or driven by labour shortages.[445] In 1841, only 0.25 per cent of the population of England and Wales was born in a foreign country, increasing to 1.5 per cent by 1901,[437] 2.6 per cent by 1931 and 4.4 per cent in 1951.[435]
In 2014, the immigration net increase was 318,000: immigration was at 641,000, up from 526,000 in 2013, while the number of emigrants leaving for over a year was 323,000.[446] A recent migration trend has been the arrival of workers from the new EU member states in Eastern Europe, known as the A8 countries.[380] In 2011, citizens of new EU member states made up 13 per cent of immigrants.[447] The UK applied temporary restrictions to citizens of Romania and Bulgaria, both of which joined the EU in January 2007.[448] Research conducted by the Migration Policy Institute for the Equality and Human Rights Commission suggests that, between May 2004 and September 2009, 1.5 million workers migrated from the new EU member states to the UK, most of them Polish. Many subsequently returned home, resulting in a net increase in the number of nationals of the new member states in the UK.[449] The late-2000s recession in the UK reduced the economic incentive for Poles to migrate to the UK,[450] making migration temporary and circular.[451] The proportion of foreign-born people in the UK remains slightly below that of many other European countries.[452]
Immigration is now contributing to a rising UK population,[453] with arrivals and UK-born children of migrants accounting for about half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001. According to official statistics released in 2015, 27 per cent of UK live births in 2014 were to mothers born outside the UK.[454] The ONS reported that net migration rose from 2009 to 2010 by 21 per cent to 239,000.[455]
In 2013, approximately 208,000 foreign nationals were naturalised as British citizens, the highest number since 1962. This figure fell to around 125,800 in 2014. Between 2009 and 2013, the average number of British citizenships granted annually was 195,800. The most common previous nationalities of those naturalised in 2014 were Indian, Pakistani, Filipino, Nigerian, Bangladeshi, Nepali, Chinese, South African, Polish and Somali.[456] The total number of grants of settlement, which confer permanent residence in the UK but not citizenship,[457] was approximately 154,700 in 2013, higher than the previous two years.[456]
Estimated number of British citizens living overseas by country in 2006
In 2008, the British Government introduced a points-based immigration system for immigration from outside the European Economic Area to replace former schemes, including the Scottish Government’s Fresh Talent Initiative.[458] In June 2010, a temporary limit on immigration from outside the EU was introduced, aiming to discourage applications before a permanent cap was imposed in April 2011.[459]
Emigration was an important feature of British society in the 19th century. Between 1815 and 1930, around 11.4 million people emigrated from Britain and 7.3 million from Ireland. Estimates show that by the end of the 20th century, some 300 million people of British and Irish descent were permanently settled around the globe.[460] Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad,[461][462] mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States and Canada.[461][463]
Education
Education in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter, with each country having a separate education system.
Considering the four systems together, about 38 per cent of the United Kingdom population has a university or college degree, which is the highest percentage in Europe, and among the highest percentages in the world.[464] The United Kingdom has some of the best universities in the world with Oxford University and Cambridge University often competing for the number 1 position on global rankings. [465][466]
A government commission’s report in 2014 found that privately educated people comprise 7 per cent of the general population of the UK but much larger percentages of the top professions, the most extreme case quoted being 71 per cent of senior judges.[467]
England
Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of local authorities.[468] Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944.[469] Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18.[470] In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science.[471] The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools,[472] while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.[473]
Scotland
Education in Scotland is the responsibility of the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Lifelong Learning, with day-to-day administration and funding of state schools the responsibility of Local Authorities. Two non-departmental public bodies have key roles in Scottish education. The Scottish Qualifications Authority is responsible for the development, accreditation, assessment and certification of qualifications other than degrees which are delivered at secondary schools, post-secondary colleges of further education and other centres.[474] Learning and Teaching Scotland provides advice, resources and staff development to education professionals.[475] Scotland first legislated for compulsory education in 1496.[476] The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4 per cent in 2016, but it has been falling slowly in recent years.[477] Scottish students who attend Scottish universities pay neither tuition fees nor graduate endowment charges, as fees were abolished in 2001 and the graduate endowment scheme was abolished in 2008.[478]
Wales
The Welsh Government’s Minister for Education has responsibility for education in Wales.[479] State funded education is available to children from the age of three whilst the legal obligation for parents to have their children educated, usually at school, begins at age five.[480] A sizeable minority of pupils are educated in Welsh whilst the rest are obliged to study the language until the age of 16.[481] Wales’ performance in Pisa testing, which compares the academic performance of adolescents around the world, has improved in recent years but remains lower than other parts of the UK.[482] In 2019, just under 60% of entrants passed their main English and Maths GCSEs.[483] The obligation to receive education in Wales ends at the age of 16. In 2017 and 2018, just under 80% of 16 to 18 and just under 40% of 19 to 24-year-olds were in some kind of education or training.[484]
Northern Ireland
Education in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Minister of Education, although responsibility at a local level is administered by the Education Authority which is further sub-divided into five geographical areas. The Council for the Curriculum, Examinations & Assessment (CCEA) is the body responsible for advising the government on what should be taught in Northern Ireland’s schools, monitoring standards and awarding qualifications.[485]
Healthcare
Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter and each country has its own system of private and publicly funded healthcare. Public healthcare is provided to all UK permanent residents and is mostly free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. The World Health Organization, in 2000, ranked the provision of healthcare in the United Kingdom as fifteenth best in Europe and eighteenth in the world.[486]
Since 1979 expenditure on healthcare has been increased significantly.[487] The 2018 OECD data, which incorporates in health a chunk of what in the UK is classified as social care, has the UK spending £3,121 per head.[488] In 2017 the UK spent £2,989 per person on healthcare, around the median for members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.[489]
Regulatory bodies are organised on a UK-wide basis such as the General Medical Council, the Nursing and Midwifery Council and non-governmental-based, such as the Royal Colleges. Political and operational responsibility for healthcare lies with four national executives; healthcare in England is the responsibility of the UK Government; healthcare in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Northern Ireland Executive; healthcare in Scotland is the responsibility of the Scottish Government; and healthcare in Wales is the responsibility of the Welsh Government. Each National Health Service has different policies and priorities, resulting in contrasts.[490]
Culture
The culture of the United Kingdom has been influenced by many factors including: the nation’s island status; its history as a western liberal democracy and a major power; as well as being a political union of four countries with each preserving elements of distinctive traditions, customs and symbolism. As a result of the British Empire, British influence can be observed in the language, culture and legal systems of many of its former colonies including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa and the United States; a common culture coined today as the Anglosphere. The substantial cultural influence of the United Kingdom has led to it being described as a «cultural superpower».[117][118] A global opinion poll for the BBC saw the United Kingdom ranked the third most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany and Canada) in 2013 and 2014.[491]
Literature
«British literature» refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Most British literature is in the English language. In 2005, some 206,000 books were published in the United Kingdom and in 2006 it was the largest publisher of books in the world.[492]
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest dramatist of all time.[493] The 20th-century English crime writer Agatha Christie is the best-selling novelist of all time.[494] Twelve of the top 25 of 100 novels by British writers chosen by a BBC poll of global critics were written by women; these included works by George Eliot, Virginia Woolf, Charlotte and Emily Brontë, Mary Shelley, Jane Austen, Doris Lessing and Zadie Smith.[495]
Scotland’s contributions include Arthur Conan Doyle (the creator of Sherlock Holmes), Sir Walter Scott, J. M. Barrie, Robert Louis Stevenson and the poet Robert Burns. More recently Hugh MacDiarmid and Neil M. Gunn contributed to the Scottish Renaissance, with grimmer works from Ian Rankin and Iain Banks. Scotland’s capital, Edinburgh, was UNESCO’s first worldwide City of Literature.[496]
Welsh literature includes Britain’s oldest known poem, Y Gododdin, which was composed most likely in the late 6th century. It was written in Cumbric or Old Welsh and contains the earliest known reference to King Arthur.[497] The Arthurian legend was further developed by Geoffrey of Monmouth.[498] Poet Dafydd ap Gwilym (fl. 1320–1370) is regarded as one of the greatest European poets of his age.[499] Daniel Owen is credited as the first Welsh-language novelist, publishing Rhys Lewis in 1885. The best-known of the Anglo-Welsh poets are Dylan Thomas and R. S. Thomas, the latter nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1996. Leading Welsh novelists of the twentieth century include Richard Llewellyn and Kate Roberts.[500][501]
Irish writers, living at a time when all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom, include Oscar Wilde,[502] Bram Stoker[503] and George Bernard Shaw.[504] There have been many authors whose origins were from outside the United Kingdom but who moved to the UK. These include Joseph Conrad,[505] T. S. Eliot,[506] Kazuo Ishiguro,[507] Sir Salman Rushdie[508] and Ezra Pound.[509]
Philosophy
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of ‘British Empiricism’, a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and ‘Scottish Philosophy’, sometimes referred to as the ‘Scottish School of Common Sense’.[510] The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley[q] and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish «common sense» school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work Utilitarianism.[511]
Music
Various styles of music have become popular in the UK, including the indigenous folk music of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Historically, there has been exceptional Renaissance music from the Tudor period, with masses, madrigals and lute music by Thomas Tallis, John Taverner, William Byrd, Orlando Gibbons and John Dowland. After the Stuart Restoration, an English tradition of dramatic masques, anthems and airs became established, led by Henry Purcell, followed by Thomas Arne and others. The German-born composer George Frideric Handel became a naturalised British citizen in 1727, when he composed the anthem Zadok the Priest for the coronation of George II; it became the traditional ceremonial music for anointing all future monarchs. Handel’s many oratorios, such as his famous Messiah, were written in the English language.[512] Ceremonial music is also performed to mark Remembrance Sunday across the UK, including the Traditional Music played at the Cenotaph.[513] In the second half of the 19th century, as Arthur Sullivan and his librettist W. S. Gilbert wrote their popular Savoy operas, Edward Elgar’s wide range of music rivalled that of his contemporaries on the continent. Increasingly, however, composers became inspired by the English countryside and its folk music, notably Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten, a pioneer of modern British opera. Among the many post-war composers, some of the most notable have made their own personal choice of musical identity: Peter Maxwell Davies (Orkney), Harrison Birtwistle (mythological), and John Tavener (religious).[514]
The Beatles are the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed band in popular music, selling over a billion records.[515][516][517]
According to the website of The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, the term «pop music» originated in Britain in the mid-1950s to describe rock and roll’s fusion with the «new youth music».[518] The Oxford Dictionary of Music states that artists such as The Beatles and The Rolling Stones drove pop music to the forefront of popular music in the early 1960s.[519] In the following years, Britain widely occupied a part in the development of rock music, with British acts pioneering hard rock;[520] raga rock; heavy metal;[521] space rock; glam rock;[522] Gothic rock,[523] and ska punk. In addition, British acts developed psychedelic rock;[524] and punk rock.[525] Besides rock music, British acts also developed neo soul and created dubstep.[526] Pop remains the most popular music genre by sales and streams of singles, with 33.4 per cent of that market in 2016, followed by hip-hop and R&B at 24.5 per cent.[527] Rock is not far behind, at 22.6 per cent.[527] The modern UK is known to produce some of the most prominent English-speaking rappers along with the United States, including Stormzy, Kano, Yxng Bane, Ramz, Little Simz and Skepta.[528]
The Beatles have international sales of over 1 billion units and are the biggest-selling and most influential band in the history of popular music.[515][516][517][529] Other prominent British contributors to have influenced popular music over the last 50 years include The Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen, Led Zeppelin, the Bee Gees, and Elton John, all of whom have worldwide record sales of 200 million or more.[530] The Brit Awards are the BPI’s annual music awards, and some of the British recipients of the Outstanding Contribution to Music award include; The Who, David Bowie, Eric Clapton, Rod Stewart, The Police, and Fleetwood Mac (who are a British-American band).[531] More recent UK music acts that have had international success include George Michael, Oasis, Spice Girls, Radiohead, Coldplay, Arctic Monkeys, Robbie Williams, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Ed Sheeran, One Direction and Harry Styles.[532]
A number of UK cities are known for their music. Acts from Liverpool have had 54 UK chart number 1 hit singles, more per capita than any other city worldwide.[533] Glasgow’s contribution to music was recognised in 2008 when it was named a UNESCO City of Music.[534] Manchester played a role in the spread of dance music such as acid house, and from the mid-1990s, Britpop. London and Bristol are closely associated with the origins of electronic music sub-genres such as drum and bass and trip hop.[535] Birmingham became known as the birthplace of heavy metal, with the band Black Sabbath starting there in the 1960s.[536]
Visual art
The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language;[537] the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the «Young British Artists»: Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).[538]
Cinema
Alfred Hitchcock has been ranked as one of the greatest and most influential British filmmakers of all time.[539]
The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film Vertigo is considered by some critics as the best film of all time,[540] and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time.[541] Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the highest-grossing film franchises (Harry Potter and James Bond).[542] Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.[543]
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom.[544] UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions.[544] The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.[545]
Cuisine
British cuisine developed from various influences reflective of its land, settlements, arrivals of new settlers and immigrants, trade and colonialism. Celtic agriculture and animal breeding produced a wide variety of foodstuffs for indigenous Celts and Britons. Anglo-Saxon England developed meat and savoury herb stewing techniques before the practice became common in Europe. The Norman conquest introduced exotic spices into England in the Middle Ages.[546] The British Empire facilitated a knowledge of Indian cuisine with its «strong, penetrating spices and herbs». British cuisine has absorbed the cultural influence of those who have settled in Britain, producing hybrid dishes, such as chicken tikka masala.[547] Vegan and vegetarian diets have increased in Britain in recent years. In 2021, a survey found that 8% of British respondents eat a plant-based diet and 36% of respondents have a favourable view of plant-based diets.[548]
Media
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK’s publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world.[549][550][551] It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the television licence.[552] The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world’s largest of any kind.[553] It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.[554]
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV Network,[555] and Sky.[556] Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include The Times, The Guardian, The Observer, The Economist, and the Financial Times.[557] Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include Nature, New Scientist, The Spectator, Prospect, NME, Radio Times, and The Economist.
London dominates the media sector in the UK: national newspapers and television and radio are largely based there, although Manchester is also a significant national media centre. Edinburgh and Glasgow, and Cardiff, are important centres of newspaper and broadcasting production in Scotland and Wales, respectively.[558] The UK publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover of around £20 billion and employs around 167,000 people.[559] In 2015, the UK published 2,710 book titles per million inhabitants, more than any other country, much of this being exported to other Anglophone countries.[560]
In 2009, it was estimated that individuals viewed a mean of 3.75 hours of television per day and 2.81 hours of radio. In that year the main BBC public service broadcasting channels accounted for an estimated 28.4 per cent of all television viewing; the three main independent channels accounted for 29.5 per cent and the increasingly important other satellite and digital channels for the remaining 42.1 per cent.[561] Sales of newspapers have fallen since the 1970s and in 2010 41 per cent of people reported reading a daily national newspaper.[562] In 2010, 82.5 per cent of the UK population were Internet users, the highest proportion amongst the 20 countries with the largest total number of users in that year.[563]
Symbols
Union Jack flags in London
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack).[564] It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick’s Flag.[565] Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out.[566] The national anthem of the United Kingdom is «God Save the King», with «King» replaced with «Queen» in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain.[567] Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon’s three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside the lion and the unicorn and the dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill’s defiance of Nazi Germany.[568] A now rare personification is a character originating in the 18th century, John Bull, a portly country gentleman dressed in a top hat and tailcoat with a Union Jack waistcoat, often accompanied by a bulldog.[569]
The floral emblems of the three kingdoms are the Tudor rose for England, the thistle for Scotland and the shamrock for Northern Ireland; they are sometimes shown intertwined to represent unity.[570] The daffodil and the leek are the symbols of Wales.[571] Alternatives include the Royal Oak for England and the flax flower for Northern Ireland.[570]
Sport
Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, billiards, darts, rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in late 19th-century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, «This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum».[573][574]
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the UK.[575] England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and the Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley.[576] Each of the Home Nations (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland) has its own football association, national team and league system, and each is individually a governing member of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world.[577] The first international football match was contested by England and Scotland on 30 November 1872.[578] England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.[579]
In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK.[575] The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England and Scotland.[580][581] England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship, which is the premier international rugby union tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sports governing bodies in England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland organise and regulate the game separately.[582] Every four years, the Home Nations make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions which tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788.[583] The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board,[584] and the Ireland cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales has fielded its own national cricket team in the past. Scottish players have played for England because the Scotland cricket team does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals.[585] Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, which England won in 2019. There is a professional league championship that consists of clubs representing 17 English counties and one Welsh county.[586]
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s before spreading around the world.[587] The world’s oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, was first held in 1877 and today takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.[588]
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more drivers’ and constructors’ titles in the F1 World Championship than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone, where the British Grand Prix is held each year in July.[589]
St Andrews, Scotland, the home of golf. The standard 18 hole golf course was created at St Andrews in 1764.[590]
Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport’s home course,[591] the world’s oldest golf course is in fact Musselburgh Links’ Old Golf Course.[592] In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes.[590] The British Open—the oldest golf tournament in the world and the first major championship in golf—is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.[593]
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England.[594] A single ‘Great Britain Lions’ team competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games before 2008 when England, Scotland and Ireland began to compete as separate league nations.[595] Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.[596]
The ‘Queensberry rules’, the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing.[597] Snooker is another of the UK’s popular sporting exports, with the world championship held annually in Sheffield.[598] Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports in Northern Ireland, both in terms of participation and spectatorship, and both sports are played by Irish expatriates in the UK and the United States.[599] Shinty (or camanachd) is popular in the Scottish Highlands.[600] Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and Celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.[601]
The United Kingdom hosted the Summer Olympic Games in 1908, 1948 and 2012, with London acting as the host city on all three occasions. Birmingham hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games, the seventh time the UK has hosted the Commonwealth Games.
See also
- Outline of the United Kingdom
- Outline of England
- Outline of Northern Ireland
- Outline of Scotland
- Outline of Wales
- Index of United Kingdom-related articles
- International rankings of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the British Empire
- United Kingdom–Crown Dependencies Customs Union
Notes
- ^ There is no authorised version of the national anthem as the words are a matter of tradition; only the first verse is usually sung.[1] No statute has been enacted designating «God Save the King» as the official anthem. In the English tradition, such laws are not necessary; proclamation and usage are sufficient to make it the national anthem. «God Save the King» also serves as the Royal anthem for certain Commonwealth realms. The words King, he, him, his, used at present, are replaced by Queen, she, her when the monarch is female.
- ^ Scots, Ulster Scots, Welsh, Cornish, Scottish Gaelic and Irish are classed as regional or minority languages under the Council of Europe’s European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.[2] These include defined obligations to promote those languages.[3] See also Languages of the United Kingdom. Welsh has limited de jure official status in Wales, as well as in the provision of national government services provided for Wales.
- ^ «This category could include Polish responses from the country specific question for Scotland which would have been outputted to ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK. ‘White Africans’ may also have been recorded under ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK.»
- ^ 83.6% are White British/Irish.
- ^ Although the United Kingdom has traditionally been seen as a unitary state, an alternative description of the UK as a «union state», put forward by, among others, Vernon Bogdanor,[6] has become increasingly influential since the adoption of devolution in the 1990s.[7] A union state is considered to differ from a unitary state in that while it maintains a central authority it also recognises the authority of historic rights and infrastructures of its component parts.[8]
- ^ Some of the devolved countries, Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories issue their own sterling banknotes or currencies, or use another nation’s currency. See List of British currencies for more information.
- ^ Also observed by the Crown Dependencies, and in the two British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (though in the latter, without daylight saving time). For further information, see Time in the United Kingdom#British territories.
- ^ Except two overseas territories: Gibraltar and the British Indian Ocean Territory
- ^ Excludes most overseas territories
- ^ The .gb domain is also reserved for the UK, but has been little used.
- ^ Usage is mixed. The Guardian and Telegraph use Britain as a synonym for the United Kingdom. Some prefer to use Britain as shorthand for Great Britain. The British Cabinet Office’s Government Digital Service style guide for use on gov.uk recommends: «Use UK and United Kingdom in preference to Britain and British (UK business, UK foreign policy, ambassador and high commissioner). But British embassy, not UK embassy.»
- ^ The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty resolved the Irish War of Independence. When it took effect one year later, it established the Irish Free State as a separate dominion within the Commonwealth of Nations. In 1927 the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 changed the name of the UK to reflect this.
- ^ The United Kingdom does not have a codified constitution but an unwritten one formed of Acts of Parliament, court judgments, traditions, and conventions.[25]
- ^ Compare to section 1 of both of the 1800 Acts of Union which reads: the Kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland shall…be united into one Kingdom, by the Name of «The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland».
- ^ The 2011 Census recorded Gypsies and Travellers as a separate ethnic group for the first time.
- ^ In the 2011 Census, for the purpose of harmonising results to make them comparable across the UK, the ONS includes individuals in Scotland who classified themselves in the «African» category (29,638 people), which in the Scottish version of the census is separate from «Caribbean or Black» (6,540 people),[391] in this «Black or Black British» category. The ONS note that «the African categories used in Scotland could potentially capture White/Asian/Other African in addition to Black identities».[392]
- ^ Berkeley is in fact Irish but was called a ‘British empiricist’ due to the territory of what is now known as the Republic of Ireland being in the UK at the time.
References
- ^ Berry, Ciara (15 January 2016). «National Anthem». The Royal Family. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d «List of declarations made with respect to treaty No. 148». Council of Europe. Retrieved 12 December 2013.
- ^ «Welsh language on GOV.UK – Content design: planning, writing and managing content – Guidance». www.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ a b Weller, Paul (2016). «Balancing within Three Dimensions: Christianity, Secularity, and Religious Plurality in Social Policy and Theology». Studies in Interreligious Dialogue. 26 (2): 131–146. doi:10.2143/SID.26.2.3200411.
- ^ a b Cusick, Edmund; Storry, Mike (2017). «Religion». In Storry, Mike; Childs, Peter (eds.). British Cultural Identities (5th ed.). London: Routledge. pp. 239–266. ISBN 9781315440590.
- ^ Bradbury, Jonathan (2021). Constitutional Policy and Territorial Politics in the UK: Volume 1: Union and Devolution 1997–2012. Policy Press. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-5292-0588-6.
- ^ Leith, Murray Stewart (2012). Political Discourse and National Identity in Scotland. Edinburgh University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7486-8862-3.
- ^ Gagnon, Alain-G.; Tully, James (2001). Multinational Democracies. Cambridge University Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-521-80473-8.; Bogdanor, Vernon (1998). «Devolution: the Constitutional Aspects». In Beatson, Jack (ed.). Constitutional Reform in the United Kingdom: Practice and Principles. Oxford: Hart Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-901362-84-8.
- ^ Demographic Yearbook – Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density (PDF) (Report). United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ «Surface water and surface water change». Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ «United Kingdom». The World Factbook (2023 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- ^ «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d «World Economic Outlook database: October 2022». International Monetary Fund. October 2022.
- ^ «Inequality – Income inequality». us.oecd.org. OECD. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ «Human Development Report 2021/2022» (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «Great Britain | island, Europe». Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ United Kingdom Permanent Committee on Geographical Names (May 2017). «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». GOV.UK. 10.2 Definitions.
usually shortened to United Kingdom … The abbreviation is UK or U.K.
; «United Kingdom». Encyclopedia Britannica. - ^ a b «Countries within a country». Prime Minister’s Office. 10 January 2003. Archived from the original on 9 September 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Definition of Great Britain in English». Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
Great Britain is the name for the island that comprises England, Scotland and Wales, although the term is also used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.
- ^ «Office for National Statistics». ons.gov.uk.
- ^ «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
The full title of this country is ‘the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland’. Great Britain is made up of England, Scotland and Wales. The United Kingdom (UK) is made up of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. ‘Britain’ is used informally, usually meaning the United Kingdom.
The Channel Islands and the Isle of Man are not part of the UK. - ^ a b «Supporting the Overseas Territories». Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Julian Go (2007). «A Globalizing Constitutionalism?, Views from the Postcolony, 1945–2000». In Arjomand, Saïd Amir (ed.). Constitutionalism and political reconstruction. Brill. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-90-04-15174-1.
- ^ Ferguson 2004, p. 307.
- ^ What is the UK Constitution?, The Constitution Unit of UCL, 9 August 2018, retrieved 6 February 2020
- ^ The British Monarchy, «What is constitutional monarchy?». Retrieved 17 July 2013; «United Kingdom» CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 17 July 2013
- ^ «Population of Cities in United Kingdom 2023». World Population Review. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «Devolution of powers to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland». United Kingdom Government. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
In a similar way to how the government is formed from members from the two Houses of Parliament, members of the devolved legislatures nominate ministers from among themselves to comprise executives, known as the devolved administrations…
; «Country Overviews: United Kingdom». Transport Research Knowledge Centre. Archived from the original on 4 April 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010. - ^ «Britain’s Imperial Century: What Was the Pax Britannica?». History Hit. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Mathias, P. (2001). The First Industrial Nation: the Economic History of Britain, 1700–1914. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-26672-7.; Ferguson, Niall (2004). Empire: The rise and demise of the British world order and the lessons for global power. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-02328-8.
- ^ «20th-century international relations». www.britannica.com. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ «Pax Britannica | Encyclopedia.com». www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Allison, George (18 May 2018). «Study ranks Britain ‘second most powerful country in the world’«. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Thorp, James; James (26 March 2021). «Size does not matter: the UK’s continuing great power status » Wavell Room». Wavell Room. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Tombs, Robert (13 May 2022). «Britain’s future is to be Europe’s only great power, not a satellite of Macron’s continental empire». The Telegraph. London. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ «European researchers determine UK is second most powerful country in the world». Conservative Post. 24 March 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ T.V. Paul; James J. Wirtz; Michel Fortmann (2005). «Great+power» Balance of Power. State University of New York Press. pp. 59, 282. ISBN 978-0-7914-6401-4. Accordingly, the great powers after the Cold War are Britain, China, France, Germany, Japan, Russia and the United States p. 59; McCourt, David (2014). Britain and World Power Since 1945: Constructing a Nation’s Role in International Politics. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07221-7.
- ^ «World Population Prospects – The 2006 Revision» (PDF). UN. Retrieved 27 April 2010.; Professor Arne Björnberg, Ph.D (29 January 2018). «Euro Health Consumer Index 2017» (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ^ «IISS Military Balance 2021». The Military Balance. 121 (1): 23–29. January 2021. doi:10.1080/04597222.2021.1868791. S2CID 232050862. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ «EU’s ‘big four’ speak as one ahead of G7 in Tokyo». POLITICO. 30 January 2008. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ «Volume 10 — History of Greater Britain, as well England as Scotland — Series 1 — National Library of Scotland». digital.nls.uk.
- ^ Payne, Malcolm; Shardlow, Steven (2002). Social Work in the British Isles. UK: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. p. 247. ISBN 978-1-8530-2833-5.
- ^ Richmond, Ian Archibald; Millett, Martin J. Millett (2012), «Caledonia», in Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Antony; Eidinow, Esther (eds.), The Oxford Classical Dictionary (4th ed.), Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/acref/9780199545568.001.0001, ISBN 978-0-19-954556-8, retrieved 14 February 2021; «What’s the Difference Between Great Britain and the United Kingdom? | Britannica». www.britannica.com.
- ^ «Treaty of Union, 1706». Scots History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; Barnett, Hilaire; Jago, Robert (2011). Constitutional & Administrative Law (8th ed.). Abingdon: Routledge. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-415-56301-7.
- ^ «After the political union of England and Scotland in 1707, the nation’s official name became ‘Great Britain'», The American Pageant, Volume 1, Cengage Learning (2012).; «From 1707 until 1801 Great Britain was the official designation of the kingdoms of England and Scotland». The Standard Reference Work: For the Home, School and Library, Volume 3, Harold Melvin Stanford (1921); «In 1707, on the union with Scotland, ‘Great Britain’ became the official name of the British Kingdom, and so continued until the union with Ireland in 1801». United States Congressional serial set, Issue 10; Issue 3265 (1895).; Gascoigne, Bamber. «History of Great Britain (from 1707)». History World. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Cottrell, P. (2008). The Irish Civil War 1922–23. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-84603-270-7.
- ^ S. Dunn; H. Dawson (2000), An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict, Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press,
One specific problem – in both general and particular senses – is to know what to call Northern Ireland itself: in the general sense, it is not a country, or a province, or a state – although some refer to it contemptuously as a statelet: the least controversial word appears to be jurisdiction, but this might change.
; «Changes in the list of subdivision names and code elements» (PDF). ISO 3166-2. International Organization for Standardization. 15 December 2011. Retrieved 28 May 2012. - ^ «Statistical bulletin: Regional Labour Market Statistics». Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.; «13.4% Fall In Earnings Value During Recession». Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- ^ Dunn, Seamus; Dawson, Helen (2000). An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict. Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press. ISBN 978-0-7734-7711-7.; Murphy, Dervla (1979). A Place Apart. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-005030-1.
- ^ Whyte, John; FitzGerald, Garret (1991). Interpreting Northern Ireland. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-827380-6.
- ^ «Guardian Unlimited Style Guide». London: Guardian News and Media Limited. 19 December 2008. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «BBC style guide (Great Britain)». BBC News. 19 August 2002. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Government, citizens and rights. HM Government. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ New Oxford American Dictionary: «Great Britain: England, Wales, and Scotland considered as a unit. The name is also often used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.»
- ^ «When people say England, they sometimes mean Great Britain, sometimes the United Kingdom, sometimes the British Isles — but never England.» — George Mikes (1946), How To Be An Alien, Penguin ISBN 0-582-41686-8; «England OR United Kingdom (UK)? | Vocabulary | EnglishClub». www.englishclub.com. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ «Britain Meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary». dictionary.cambridge.org.; «Definition of Britain in English by Oxford Dictionaries». Oxford Dictionaries – English. Archived from the original on 26 September 2016.
- ^ a b «Britain definition and meaning». www.collinsdictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary.
- ^ «Britain – Definition for English-Language Learners». learnersdictionary.com. Merriam-Webster’s Learner’s Dictionary.
- ^ «A to Z – Style guide». www.gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ a b c Permanent Committee on Geographical Names. «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ «BBC News style guide – Names». BBC Academy. BBC. Archived from the original on 10 November 2019. Retrieved 9 November 2019.; «Alphabetical checklist». BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 26 March 2018. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ^ Bradley, Anthony Wilfred; Ewing, Keith D. (2007). Constitutional and administrative law. Vol. 1 (14th ed.). Harlow: Pearson Longman. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-4058-1207-8.
- ^ «Which of these best describes the way you think of yourself?». Northern Ireland Life and Times Survey 2010. ARK – Access Research Knowledge. 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 25 June 2020.; Schrijver, Frans (2006). Regionalism after regionalisation: Spain, France and the United Kingdom. Amsterdam University Press. pp. 275–277. ISBN 978-90-5629-428-1.
- ^ «Ancient skeleton was ‘even older'». BBC News. 30 October 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: A historical encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 973. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ Davies, John; Jenkins, Nigel; Baines, Menna; Lynch, Peredur I., eds. (2008). The Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales. Cardiff: University of Wales Press. p. 915. ISBN 978-0-7083-1953-6.
- ^ «Short Athelstan biography». BBC History. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ Mackie, J.D. (1991). A History of Scotland. London: Penguin. pp. 18–19. ISBN 978-0-14-013649-4.; Campbell, Ewan (1999). Saints and Sea-kings: The First Kingdom of the Scots. Edinburgh: Canongate. pp. 8–15. ISBN 978-0-86241-874-8.
- ^ Haigh, Christopher (1990). The Cambridge Historical Encyclopedia of Great Britain and Ireland. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-521-39552-6.
- ^ Ganshof, F.L. (1996). Feudalism. University of Toronto. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-8020-7158-3.
- ^ Chibnall, Marjorie (1999). The Debate on the Norman Conquest. Manchester University Press. pp. 115–122. ISBN 978-0-7190-4913-2.
- ^ Keen, Maurice. «The Hundred Years’ War». BBC History.
- ^ The Reformation in England and Scotland and Ireland: The Reformation Period & Ireland under Elizabeth I, Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ «British History in Depth – Wales under the Tudors». BBC History. 5 November 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- ^ Nicholls, Mark (1999). A history of the modern British Isles, 1529–1603: The two kingdoms. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 171–172. ISBN 978-0-631-19334-0.
- ^ Canny, Nicholas P. (2003). Making Ireland British, 1580–1650. Oxford University Press. pp. 189–200. ISBN 978-0-19-925905-2.
- ^ «English Reformation c1527-1590». The National Archives. Retrieved 20 January 2023.
- ^ Ross, D. (2002). Chronology of Scottish History. Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-85534-380-1; Hearn, J. (2002). Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture. Edinburgh University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-902930-16-9
- ^ «English Civil Wars». Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 28 April 2013.; «Scotland and the Commonwealth: 1651–1660». Archontology.org. 14 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Lodge, Richard (2007) [1910]. The History of England – From the Restoration to the Death of William III (1660–1702). Read Books. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-4067-0897-4.
- ^ «Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy». Royal Navy History. Institute of Naval History. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Canny, Nicholas (1998). The Origins of Empire, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924676-2.
- ^ «Articles of Union with Scotland 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 19 October 2008.; «Acts of Union 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 6 January 2011.; «Treaty (act) of Union 1706». Scottish History online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ^ Library of Congress, The Impact of the American Revolution Abroad, p. 73.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. OUP Oxford. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-19-923899-6.
- ^ Sailing against slavery. BBC Devon. 2007.; Lovejoy, Paul E. (2000). Transformations in Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-521-78012-4.
- ^ «The Act of Union». Act of Union Virtual Library. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Tellier, L.-N. (2009). Urban World History: an Economic and Geographical Perspective. Quebec: PUQ. p. 463. ISBN 978-2-7605-1588-8.
- ^ Johnston, pp. 508–510.; Porter, p. 332.; Sondhaus, L. (2004). Navies in Modern World History. London: Reaktion Books. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-86189-202-7.; Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.
- ^ «The Workshop of the World». BBC History. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Benn, David Wedgwood (March 2012). «The Crimean War and its lessons for today». International Affairs. Oxford University Press. 88 (2): 387–391. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2346.2012.01078.x. JSTOR 41428613.
- ^ Nordisk familjebok (1913), s. 435 (in Swedish)
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.; Marshall, P.J. (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7.
- ^ Tompson, Richard S. (2003). Great Britain: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present. New York: Facts on File. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-8160-4474-0.
- ^ Hosch, William L. (2009). World War I: People, Politics, and Power. America at War. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-61530-048-8.
- ^ Zarembka, Paul (2013). Contradictions: Finance, Greed, and Labor Unequally Paid. Emerald Group Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78190-670-5.
- ^ Sophia A. Van Wingerden, The women’s suffrage movement in Britain, 1866–1928 (1999) ch 1.
- ^ Turner, John (1988). Britain and the First World War. London: Unwin Hyman. pp. 22–35. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ a b Westwell, I.; Cove, D. (eds) (2002). History of World War I, Volume 3. London: Marshall Cavendish. pp. 698 and 705. ISBN 978-0-7614-7231-5.
- ^ Turner, J. (1988). Britain and the First World War. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ «100 years of radio since Marconi’s big breakthrough». Ofcom. 15 June 2020. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
- ^ Linfoot, Matthew. «History of the BBC: The origins of BBC Local Radio». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ «History of the BBC: 1920s». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ SR&O 1921, No. 533 of 3 May 1921.
- ^ «The Anglo-Irish Treaty, 6 December 1921». CAIN Web Service. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Rubinstein, W.D. (2004). Capitalism, Culture, and Decline in Britain, 1750–1990. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-415-03719-8.
- ^ a b Edgerton, David (2012). Britain’s War Machine. www.penguin.co.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2020; «Britain’s War Machine: Weapons, Resources and Experts in the Second World War». Reviews in History. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Septimus H. Paul (2000). Nuclear Rivals: Anglo-American Atomic Relations, 1941–1952. Ohio State U.P. pp. 1–5. ISBN 9780814208526.
- ^ Doenecke, Justus D.; Stoler, Mark A. (2005). Debating Franklin D. Roosevelt’s foreign policies, 1933–1945. ISBN 978-0-8476-9416-7. Retrieved 19 March 2016.; Kelly, Brian. The Four Policemen and Postwar Planning, 1943–1945: The Collision of Realist and Idealist Perspectives. Indiana University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ «The «Special Relationship» between Great Britain and the United States Began with FDR». Roosevelt Institute. 22 July 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
and the joint efforts of both powers to create a new post-war strategic and economic order through the drafting of the Atlantic Charter; the establishment of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; and the creation of the United Nations.
; «Remarks by the President Obama and Prime Minister Cameron in Joint Press Conference» (Press release). The White House. 22 April 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2018.That’s what we built after World War II. The United States and the UK designed a set of institutions – whether it was the United Nations, or the Bretton Woods structure, IMF, World Bank, NATO, across the board.
- ^ «Britain to make its final payment on World War II loan from U.S.» The New York Times. 28 December 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ Reynolds, David (17 April 2011). «Britain’s War Machine by David Edgerton – review». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Francis, Martin (1997). Ideas and policies under Labour, 1945–1951: Building a new Britain. Manchester University Press. pp. 225–233. ISBN 978-0-7190-4833-3.
- ^ Lee, Stephen J. (1996). Aspects of British political history, 1914–1995. London; New York: Routledge. pp. 173–199. ISBN 978-0-415-13103-2.
- ^ Larres, Klaus (2009). A companion to Europe since 1945. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 118. ISBN 978-1-4051-0612-2.
- ^ «Country List». Commonwealth Secretariat. 19 March 2009. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ a b «The cultural superpower: British cultural projection abroad» (PDF). British Politics Review. Norway: British Politics Society. 6 (1). Winter 2011. ISSN 1890-4505. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2018.
- ^ a b Sheridan, Greg (15 May 2010). «Cameron has chance to make UK great again». The Australian. Sydney. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ Julios, Christina (2008). Contemporary British identity: English language, migrants, and public discourse. Studies in migration and diaspora. Aldershot: Ashgate. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-7546-7158-9.
- ^ «1975: UK embraces Europe in referendum». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Wheeler, Brian; Hunt, Alex (17 December 2018). «The UK’s EU referendum: All you need to know». BBC News.
- ^ Aughey, Arthur (2005). The Politics of Northern Ireland: Beyond the Belfast Agreement. London: Routledge. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-415-32788-6.; «The troubles were over, but the killing continued. Some of the heirs to Ireland’s violent traditions refused to give up their inheritance.» Holland, Jack (1999). Hope against History: The Course of Conflict in Northern Ireland. New York: Henry Holt. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-8050-6087-4.; Elliot, Marianne (2007). The Long Road to Peace in Northern Ireland: Peace Lectures from the Institute of Irish Studies at Liverpool University. University of Liverpool Institute of Irish Studies, Liverpool University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-84631-065-2.
- ^ Dorey, Peter (1995). British politics since 1945. Making contemporary Britain. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 164–223. ISBN 978-0-631-19075-2.
- ^ Griffiths, Alan; Wall, Stuart (2007). Applied Economics (PDF) (11th ed.). Harlow: Financial Times Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-273-70822-3. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Keating, Michael (1 January 1998). «Reforging the Union: Devolution and Constitutional Change in the United Kingdom». Publius: The Journal of Federalism. 28 (1): 217–234. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubjof.a029948.
- ^ McCourt, David (2014). Britain and World Power Since 1945: Constructing a Nation’s Role in International Politics. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07221-7.
- ^ «The story behind the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine success». UK Research and Innovation. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ McSmith, Andy (5 July 2016). «The inside story of how Tony Blair led Britain to war in Iraq». The Independent. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Jackson, Mike (3 April 2011). «Military action alone will not save Libya». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 27 August 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom country profile». BBC News. 24 January 2013. Archived from the original on 8 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Black, Andrew (15 October 2012). «Scottish independence: Cameron and Salmond strike referendum deal». BBC News. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Scottish independence referendum – Results – BBC News». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «In stunning decision, Britain votes to leave the E.U.» The Washington Post. 24 June 2016. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- ^ «Brexit: New era for UK as it completes separation from European Union». BBC News. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Coronavirus (COVID-19) in the UK». gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 14 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus and the impact on output in the UK economy: April 2020». ons.gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Walker, Andrew (10 June 2020). «Coronavirus: UK economy could be among worst hit of leading nations, says OECD». BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Landmark moment as first NHS patient receives COVID-19 vaccination». NHS. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Oxford University/AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine approved». UK Government. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Queen Elizabeth II has died». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «King Charles III, the new monarch». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary: «British Isles: a geographical term for the islands comprising Great Britain and Ireland with all their offshore islands including the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.»
- ^ a b c d e «United Kingdom». The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ a b c d Latimer Clarke Corporation Pty Ltd. «United Kingdom – Atlapedia Online». Atlapedia.com. Retrieved 26 October 2010.
- ^ ROG Learning Team (23 August 2002). «The Prime Meridian at Greenwich». Royal Museums Greenwich. Royal Museums Greenwich. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Greenwich Royal Observatory: How the Prime Meridian line is actually 100 metres away from where it was believed to be». The Independent. London. 13 August 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b Darkes, Giles (January 2008). «How long is the UK coastline?». The British Cartographic Society. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ «The Channel Tunnel». Eurotunnel. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). «An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm». BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). «Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ «Hottest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.; «Coldest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.
- ^ «English: A map of Köppen climate types in the United Kingdom (SVG version)». 9 August 2016.
- ^ «Atlantic Ocean Circulation (Gulf Stream)». UK Climate Projections. Met Office. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «UK 1971–2000 averages». Met Office. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 4 August 2007.
- ^ «UK temperature, rainfall and sunshine time series». Met Office.
- ^ «2020 EPI Results». Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «UK net zero target». Institute for Government. 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «England – Profile». BBC News. 11 February 2010.
- ^ «Scotland Facts». Scotland Online Gateway. Archived from the original on 21 June 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ Winter, Jon (1 June 2000). «The complete guide to the … Scottish Islands». The Independent. London. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Overview of Highland Boundary Fault». Gazetteer for Scotland. University of Edinburgh. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ «Great Britain’s tallest mountain is taller». Ordnance Survey. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ «Ben Nevis Weather». Ben Nevis Weather. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Profile: Wales». BBC News. 9 June 2010. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ «Geography of Northern Ireland». University of Ulster. Retrieved 22 May 2006.
- ^ Carter, Sarah. «A Guide To the UK Legal System». University of Kent at Canterbury. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2006.
- ^ See R (Miller) v Prime Minister [2019] UKSC 41 (Parliamentary sovereignty), R (UNISON) v Lord Chancellor [2017] UKSC 51, [67] ff (rule of law), R (Animal Defenders International) v Secretary of State for Culture Media and Sport [2008] UKHL 15, [48] (democracy), R v Lyons [2002] UKHL 44, [27] (international law).
- ^ R (HS2 Action Alliance Ltd) v Secretary of State for Transport [2014] UKSC 3, [207]
- ^ Magna Carta 1215 clauses 1 («the English church shall be free»), 12 and 14 (no tax «unless by common counsel of our kingdom»), 17 («Common pleas shall … be held in some fixed place»), 39–40 («To no one will we sell, to no one will we refuse or delay, right or justice»), 41 («merchants shall have safe and secure exit from England, and entry to England»), and 47–48 (land taken by the King «shall forthwith be disafforested»).
- ^ «Parliament’s authority». UK Parliament. n.d. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ Bagehot, Walter (1867). The English Constitution. London: Chapman and Hall. p. 103.
- ^ «Victorian Electronic Democracy, Final Report – Glossary». 28 July 2005. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 14 December 2007.
- ^ The Cabinet Manual (PDF) (Report). Cabinet Office. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Richard Knight (2 December 2008). «Whose hand is on the button?». BBC Radio 4. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ R (Miller) v The Prime Minister and Cherry v Advocate General for Scotland (Report). Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Richard Kelly. «Dissolution and Calling of Parliament Bill 2021-22» (PDF). House of Commons Library. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ «A Guide to Prorogation». BBC News. 7 November 2006. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ «The Honours System of the United Kingdom». Cabinet Office. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Stepan, Alfred; Linz, Juan J.; Minoves, Juli F. (2014). «Democratic Parliamentary Monarchies». Journal of Democracy. 25 (2): 35–36. doi:10.1353/jod.2014.0032. ISSN 1086-3214. S2CID 154555066.
- ^ «Parliamentary Sovereignty». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b «Parliament». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «Royal Assent». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c «General elections». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «State of the parties». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Government, Prime Minister and Cabinet». Public services all in one place. Directgov. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (1 January 2012). «The Institution of Prime Minister – History of government». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Brown, Jack (2020). Dale, Iain (ed.). The Prime Ministers. Hodder & Stoughton. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-5293-1214-0.
- ^ «Minister for the Civil Service». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Woodcock, Andrew (26 July 2021). «Boris Johnson accused of ‘cynical rebranding’ after appointing himself ‘Minister for the Union’«. The Independent. Retrieved 19 July 2021.; «Minister for the Union». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 21. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 7. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (2010). Premiership: The Development, Nature and Power of the Office of the British Prime Minister. Imprint Academic. pp. 116–7. ISBN 978-1-84540-168-9.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 31. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Hackwood Frederick William: The Story of the Shire, Being the Lore, History and Evolution of English County Institutions (1851)
- ^ United Nations Economic and Social Council (August 2007). «Ninth UN Conference on the standardization of Geographical Names» (PDF). UN Statistics Division. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 December 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Barlow, I.M. (1991). Metropolitan Government. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-02099-2.
- ^ «Welcome to the national site of the Government Office Network». Government Offices. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ «A short history of London government». Greater London Authority. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- ^ Sherman, Jill; Norfolk, Andrew (5 November 2004). «Prescott’s dream in tatters as North East rejects assembly». The Times Online. Archived from the original on 25 May 2010. Retrieved 15 February 2008.
The Government is now expected to tear up its twelve-year-old plan to create eight or nine regional assemblies in England to mirror devolution in Scotland and Wales.
- ^ «Elections 2017 results: Who are the new metro mayors?». BBC News. 5 May 2017. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^ «Local Authority Elections». Local Government Association. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «STV in Scotland: Local Government Elections 2007» (PDF). Political Studies Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b «Unitary authorities». Welsh Government. 2014. Archived from the original on 10 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Devenport, Mark (18 November 2005). «NI local government set for shake-up». BBC News. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ «Foster announces the future shape of local government» (Press release). Northern Ireland Executive. 13 March 2008. Archived from the original on 25 July 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ «Scots MPs attacked over fees vote». BBC News. 27 January 2004. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Taylor, Brian (1 June 1998). «Talking Politics: The West Lothian Question». BBC News. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «England-only laws ‘need majority from English MPs’«. BBC News. 25 March 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Scotland’s Parliament – powers and structures». BBC News. 8 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Keating, Michael (2 February 2021). «Taking back control? Brexit and the territorial constitution of the United Kingdom». Journal of European Public Policy. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis. 28 (4): 6–7. doi:10.1080/13501763.2021.1876156. hdl:1814/70296. S2CID 234066376.
The UK Internal Market Act gives ministers sweeping powers to enforce mutual recognition and non-discrimination across the four jurisdictions. Existing differences and some social and health matters are exempted but these are much less extensive than the exemptions permitted under the EU Internal Market provisions. Only after an amendment in the House of Lords, the Bill was amended to provide a weak and non-binding consent mechanism for amendments (equivalent to the Sewel Convention) to the list of exemptions. The result is that, while the devolved governments retain regulatory competences, these are undermined by the fact that goods and services originating in, or imported into, England can be marketed anywhere.
- ^ Kenny, Michael; McEwen, Nicola (1 March 2021). «Intergovernmental Relations and the Crisis of the Union». Political Insight. SAGE Publishing. 12 (1): 12–15. doi:10.1177/20419058211000996. S2CID 232050477.
That phase of joint working was significantly damaged by the UK Internal Market Act, pushed through by the Johnson government in December 2020…the Act diminishes the authority of the devolved institutions, and was vehemently opposed by them.
- ^ Wolffe, W James (7 April 2021). «Devolution and the Statute Book». Statute Law Review. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/slr/hmab003. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
the Internal Market Bill—a Bill that contains provisions which, if enacted, would significantly constrain, both legally and as a matter of practicality, the exercise by the devolved legislatures of their legislative competence; provisions that would be significantly more restrictive of the powers of the Scottish Parliament than either EU law or Articles 4 and 6 of the Acts of the Union…The UK Parliament passed the European Union (Withdrawal Agreement) Act 2020 and the Internal Market Act 2020 notwithstanding that, in each case, all three of the devolved legislatures had withheld consent.
- ^ Wincott, Daniel; Murray, C. R. G.; Davies, Gregory (17 May 2021). «The Anglo-British imaginary and the rebuilding of the UK’s territorial constitution after Brexit: unitary state or union state?». Territory, Politics, Governance. Abingdon/Brighton: Taylor & Francis; Regional Studies Association. 10 (5): 696–713. doi:10.1080/21622671.2021.1921613.
Taken as a whole, the Internal Market Act imposes greater restrictions upon the competences of the devolved institutions than the provisions of the EU Single Market which it replaced, in spite of pledges to use common frameworks to address these issues. Lord Hope, responsible for many of the leading judgments relating to the first two decades of devolution, regarded the legislation’s terms as deliberately confrontational: ‘this Parliament can do what it likes, but a different approach is essential if the union is to hold together’.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hayward, Katy; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen; Wincott, Daniel (2020). UK and the Internal Market, Devolution and the Union. Centre on Constitutional Change (Report). University of Edinburgh; University of Aberdeen. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 16 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael (2020). Briefing Paper. United Kingdom Internal Market Bill: Implications for Devolution (PDF) (Report). Liverpool: University of Liverpool. pp. 4–5. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen (2022). «Sleeping with an Elephant: Devolution and the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020». Law Quarterly Review. London: Sweet & Maxwell. ISSN 0023-933X. SSRN 4018581. Retrieved 4 March 2022 – via Durham Research Online.
The Act has restrictive – and potentially damaging – consequences for the regulatory capacity of the devolved legislatures…This was not the first time since the Brexit referendum that the Convention had been set aside, but it was especially notable given that the primary purpose of the legislation was to constrain the capacity of the devolved institutions to use their regulatory autonomy…in practice, it constrains the ability of the devolved institutions to make effective regulatory choices for their territories in ways that do not apply to the choices made by the UK government and parliament for the English market.
- ^ a b [212][213][214][215][216][217][218]
- ^ «Welsh assembly renamed Senedd Cymru/Welsh Parliament», BBC News, 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020
- ^ «Structure and powers of the Assembly». BBC News. 9 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «Your Executive». Northern Ireland Executive. 25 September 2015.
- ^ Burrows, N. (1999). «Unfinished Business: The Scotland Act 1998». The Modern Law Review. 62 (2): 241–260 [p. 249]. doi:10.1111/1468-2230.00203.
The UK Parliament is sovereign and the Scottish Parliament is subordinate. The White Paper had indicated that this was to be the approach taken in the legislation. The Scottish Parliament is not to be seen as a reflection of the settled will of the people of Scotland or of popular sovereignty but as a reflection of its subordination to a higher legal authority. Following the logic of this argument, the power of the Scottish Parliament to legislate can be withdrawn or overridden…
; Elliot, M. (2004). «United Kingdom: Parliamentary sovereignty under pressure». International Journal of Constitutional Law. 2 (3): 545–627, 553–554. doi:10.1093/icon/2.3.545.Notwithstanding substantial differences among the schemes, an important common factor is that the UK Parliament has not renounced legislative sovereignty in relation to the three nations concerned. For example, the Scottish Parliament is empowered to enact primary legislation on all matters, save those in relation to which competence is explicitly denied … but this power to legislate on what may be termed «devolved matters» is concurrent with the Westminster Parliament’s general power to legislate for Scotland on any matter at all, including devolved matters … In theory, therefore, Westminster may legislate on Scottish devolved matters whenever it chooses…
- ^ Walker, G. (2010). «Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Devolution, 1945–1979». Journal of British Studies. 39 (1): 117–142. doi:10.1086/644536.
- ^ Gamble, A. (2006). «The Constitutional Revolution in the United Kingdom». Publius. 36 (1): 19–35 [p. 29]. doi:10.1093/publius/pjj011.
The British parliament has the power to abolish the Scottish parliament and the Welsh assembly by a simple majority vote in both houses, but since both were sanctioned by referenda, it would be politically difficult to abolish them without the sanction of a further vote by the people. In this way, several of the constitutional measures introduced by the Blair government appear to be entrenched and not subject to a simple exercise of parliamentary sovereignty at Westminster.
- ^ Meehan, E. (1999). «The Belfast Agreement – Its Distinctiveness and Points of Cross-Fertilization in the UK’s Devolution Programme». Parliamentary Affairs. 52 (1): 19–31 [p. 23]. doi:10.1093/pa/52.1.19.
[T]he distinctive involvement of two governments in the Northern Irish problem means that Northern Ireland’s new arrangements rest upon an intergovernmental agreement. If this can be equated with a treaty, it could be argued that the forthcoming distribution of power between Westminster and Belfast has similarities with divisions specified in the written constitutions of federal states…Although the Agreement makes the general proviso that Westminster’s ‘powers to make legislation for Northern Ireland’ remains ‘unaffected’, without an explicit categorical reference to reserved matters, it may be more difficult than in Scotland or Wales for devolved powers to be repatriated. The retraction of devolved powers would not merely entail consultation in Northern Ireland backed implicitly by the absolute power of parliamentary sovereignty but also the renegotiation of an intergovernmental agreement.
- ^ «CIBC PWM Global – Introduction to The Cayman Islands». Cibc.com. 11 July 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ Rappeport, Laurie. «Cayman Islands Tourism». Washington, D.C.: USA Today Travel Tips. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Background briefing on the Crown Dependencies: Jersey, Guernsey and the Isle of Man» (PDF). Ministry of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Bosque, Maria Mut (2022). «Questioning the current status of the British Crown Dependencies». Small States & Territories. 5 (1): 55–70 – via University of Malta.
- ^ a b Loft, Philip (1 November 2022). The separation of powers in the UK’s Overseas Territories (Report). House of Commons Library.
- ^ «Overseas Territories». Gov.uk. Foreign & Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ «The World Factbook». CIA. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Overseas Territories The Ministry of Defence’s Contribution. Ministry of Defence. 1 March 2012. p. 1. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ Global Britain and the British Overseas Territories: Resetting the relationship (PDF). House of Commons Foreign Affairs Committee. 13 February 2019. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ «Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity». www.seaaroundus.org. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ^ «Partnership for Progress and Prosperity» (PDF). UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ Davison, Phil (18 August 1995). «Bermudians vote to stay British». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Gibraltar referendum result in quotes». BBC News. 8 November 2002.
- ^ «Falklands: Cameron says Argentina should respect vote». BBC News. 12 March 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons. «House of Commons – Crown Dependencies – Justice Committee». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ Fact sheet on the UK’s relationship with the Crown Dependencies – gov.uk, Ministry of Justice. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ «Profile of Jersey». States of Jersey. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2008.
The legislature passes primary legislation, which requires approval by The Queen in Council, and enacts subordinate legislation in many areas without any requirement for Royal Sanction and under powers conferred by primary legislation.
- ^ «Chief Minister to meet Channel Islands counterparts – Isle of Man Public Services» (Press release). Isle of Man Government. 29 May 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The Treaty (act) of the Union of Parliament 1706». Scottish History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ «UK Supreme Court judges sworn in». BBC News. 1 October 2009.; «Constitutional reform: A Supreme Court for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Constitutional Affairs. July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- ^ «Role of the JCPC». Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Bainham, Andrew (1998). The international survey of family law: 1996. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff. p. 298. ISBN 978-90-411-0573-8.
- ^ Adeleye, Gabriel; Acquah-Dadzie, Kofi; Sienkewicz, Thomas; McDonough, James (1999). World dictionary of foreign expressions. Waucojnda, IL: Bolchazy-Carducci. p. 371. ISBN 978-0-86516-423-9.
- ^ «The Australian courts and comparative law». Australian Law Postgraduate Network. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Court of Session – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 31 July 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «High Court of Justiciary – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 12 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «House of Lords – Practice Directions on Permission to Appeal». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 1 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Samuel Bray (2005). «Not proven: introducing a third verdict». The University of Chicago Law Review. 72 (4): 1299–1329. JSTOR 4495530.
- ^ «Crime in England and Wales, Year Ending June 2015» (PDF).
- ^ «UK prison population figures». British Government. Retrieved 10 November 2015.; Highest to Lowest. World Prison Brief. International Centre for Prison Studies.
- ^ «• England & Wales: Recorded homicides 2002–2015 – UK Statistics». Statista.
- ^ «Scottish homicide figures fall to another record low». BBC News. 29 September 2015.
- ^ «Prime Minister’s letter to Donald Tusk triggering Article 50». GOV.UK.
- ^ Swaine, Jon (13 January 2009). «Barack Obama presidency will strengthen special relationship, says Gordon Brown». The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 3 May 2011.; Kirchner, E.J.; Sperling, J. (2007). Global Security Governance: Competing Perceptions of Security in the 21st century. London: Taylor & Francis. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-415-39162-7
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons (19 February 2009). «DFID’s expenditure on development assistance». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sharp Drop in World Views of US, UK: Global Poll – GlobeScan». 4 July 2017.; «From the Outside In: G20 views of the UK before and after the EU referendum’» (PDF). British Council.; «New Zealand is Britons’ favourite country». 26 October 2020.
- ^ «Ministry of Defence». Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- ^ «Speaker addresses Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II». UK Parliament. 30 March 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «House of Commons Hansard». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2008.; «House of Commons Hansard Written Answers for 17 Jun 2013 (pt 0002)». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ UK 2005: The Official Yearbook of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Office for National Statistics. p. 89.
- ^ «Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2016» (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ «Leading European cities by gross domestic product in 2017/18». Statista. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ Rendall, Alasdair (12 November 2007). «Economic terms explained». BBC News. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ «IMF Data – Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserve – At a Glance». Data.imf.org. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ «BIS Triennial Survey of Foreign Exchange and Over-The-Counter Interest Rate Derivatives Markets in April 2022 – UK Data». Bank of England. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «Global FX trading hits record $7.5 trln a day — BIS survey». Reuters. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «More About the Bank». Bank of England. n.d. Archived from the original on 12 March 2008.
- ^ «Lloyd’s of London — value proposition». Lloyd’s of London. Archived from the original on 27 February 2023.
- ^ «Principles for Economic Regulation». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. April 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ Hutton, Georgina (6 December 2022). «Industries in the UK». UK Paliament: House of Commons Library. Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- ^ a b «GFCI 27 Rank – Long Finance». www.longfinance.net. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025». PricewaterhouseCoopers. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «UNWTO Tourism Highlights, Edition 2005» (PDF). World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.;
- ^ «DCMS Economic Estimates 2019 (provisional): Gross Value Added». gov.uk. Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- ^ «UK’s Creative Industries contributes almost £13 million to the UK economy every hour». UK Government. 2020. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «UK Internal Market Bill». Institute for Government. 9 September 2020.; «UK Internal Market Bill becomes law». gov.uk.
- ^ a b «European Countries – United Kingdom». Europa (web portal). Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ^ Harrington, James W.; Warf, Barney (1995). Industrial location: Principles, practices, and policy. London: Routledge. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-415-10479-1.; Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2008). Western Civilization: Alternative Volume: Since 1300. Belmont, CA: Thomson Wadsworth. ISBN 978-0-495-55528-5.
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6. Retrieved 22 July 2009.; Marshall, PJ (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Hewitt, Patricia (15 July 2004). «TUC Manufacturing Conference». Department of Trade and Industry. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «UK motorsport industry in pole position for F1’s 70th anniversary». UK Government. 2020. Retrieved 19 February 2023.
- ^ Tovey, Alan (29 June 2016). «Britain’s aerospace sector soars amid fears Brexit could clip its wings». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022.
- ^ «British Aerospace EAP (Paris Airshow 1987 — Complete Demonstration) Video». YouTube. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Photographs from British Aerospace — Experimental Aircraft Programme (EAP) 1985». Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ Robertson, David (9 January 2009). «The Aerospace industry has thousands of jobs in peril». The Times. London. Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2011.(subscription required)
- ^ «Size and Health of the UK Space Industry 2021». UK Government. 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ «The Pharmaceutical sector in the UK». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «Ministerial Industry Strategy Group – Pharmaceutical Industry: Competitiveness and Performance Indicators» (PDF). Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Agriculture in the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Coal». BGS Minerals UK. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ «UK officially in recession for first time in 11 years». BBC. 12 August 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ UK government debt and deficit: June 2022 «Archived copy». Archived from the original on 4 February 2023. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (last checked 2023-02-21) - ^ GDP monthly estimate, UK: December 2022 «Archived copy». Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) (last checked 2023-02-21) - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hatt2006p46was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Gascoin, J. «A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution», in Lindberg, David C. and Westman, Robert S., eds (1990), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution. Cambridge University Press. p. 248. ISBN 978-0-521-34804-1.
- ^ Reynolds, E.E.; Brasher, N.H. (1966). Britain in the Twentieth Century, 1900–1964. Cambridge University Press. p. 336. OCLC 474197910
- ^ Burtt, E.A. (2003) 1924.The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science. Mineola, NY: Courier Dover. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-486-42551-1.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. pp. 16, 30 and 46. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Jungnickel, C.; McCormmach, R. (1996). Cavendish. American Philosophical Society. ISBN 978-0-87169-220-7.
- ^ «The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1945: Sir Alexander Fleming, Ernst B. Chain, Sir Howard Florey». The Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Wilson, Arthur (1994). The Living Rock: The Story of Metals Since Earliest Times and Their Impact on Civilization. p. 203. Woodhead Publishing.
- ^ James, I. (2010). Remarkable Engineers: From Riquet to Shannon. Cambridge University Press. pp. 33–36. ISBN 978-0-521-73165-2.
- ^ Newman, M.H.A. (1948). «General Principles of the Design of All-Purpose Computing Machines». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A. 195 (1042): 271–274. Bibcode:1948RSPSA.195..271N. doi:10.1098/rspa.1948.0129.
- ^ Hubbard, Geoffrey (1965) Cooke and Wheatstone and the Invention of the Electric Telegraph, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London p. 78
- ^ Bova, Ben (2002) 1932. The Story of Light. Naperville, IL: Sourcebooks. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-4022-0009-0.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922)». Nature. 159 (4035): 297. 1947. Bibcode:1947Natur.159Q.297.. doi:10.1038/159297a0.
- ^ «John Logie Baird (1888–1946)». BBC History. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011). Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-59884-302-6.
- ^ Castells, M.; Hall, P.; Hall, P.G. (2004). Technopoles of the World: the Making of Twenty-First-Century Industrial Complexes. London: Routledge. pp. 98–100. ISBN 978-0-415-10015-1.
- ^ «Knowledge, networks and nations: scientific collaborations in the twenty-first century» (PDF). Royal Society. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2011.
- ^ McCook, Alison (2006). «Is peer review broken?». The Scientist. 20 (2): 26. Archived from the original on 16 August 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ^ WIPO (2022). Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition. www.wipo.int. Global Innovation Index. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 9789280534320. Retrieved 16 November 2022.; «Global Innovation Index 2021». World Intellectual Property Organization. United Nations. Retrieved 5 March 2022.; «Release of the Global Innovation Index 2020: Who Will Finance Innovation?». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «Global Innovation Index 2019». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «RTD – Item». ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ Moran, Joe (16 November 2005). Reading the Everyday. Routledge. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-134-37216-4.
- ^ Wilkinson, Freddie. «RAC foundation traffic stats».
- ^ «German Railway Financing» (PDF). Deutschebahn.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Efficiency indicators of Railways in France» (PDF). Internationaltransportforum.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Rail industry financial information 2014–15» (PDF). Orr.gov.uk.
- ^ Sylvain Duranton; Agnès Audier; Joël Hazan; Mads Peter Langhorn; Vincent Gauche (18 April 2017). «The 2017 European Railway Performance Index». Boston Consulting Group.
- ^ «What is HS2». HS2.
- ^ «HS2 Trains». HS2.
- ^ «Crossrail’s giant tunnelling machines unveiled». BBC News. 2 January 2012.; Leftly, Mark (29 August 2010). «Crossrail delayed to save £1bn». The Independent on Sunday. London.
- ^ «Crossrail update, 10 December 2018». UK Government. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Crossrail to become the Elizabeth line in honour of Her Majesty the Queen». Transport for London. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Opening the Elizabeth Line». The Royal Family. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023.
- ^ «Bus statistics». GOV.UK.
- ^ «Our Collection». icons.org.uk. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
- ^ London Buses, Transport for London. Accessed 10 May 2007.
- ^ a b «Size of Reporting Airports October 2009 – September 2010» (PDF). Civil Aviation Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ «Heathrow ‘needs a third runway’«. BBC News. 25 June 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.; «Statistics: Top 30 World airports» (PDF) (Press release). Airports Council International. July 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ «BMI being taken over by Lufthansa». BBC News. 29 October 2008. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ^ «United Kingdom Energy Profile». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ Mason, Rowena (24 October 2009). «Let the battle begin over black gold». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 26 November 2010.; Heath, Michael (26 November 2010). «RBA Says Currency Containing Prices, Rate Level ‘Appropriate’ in Near Term». Bloomberg. New York. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ «UK Renewables Q3 2019» (PDF).
- ^ Wilson, Grant; Staffell, Iain; Godfrey, Noah (7 January 2020). «2019 saw the rise of wind power and the collapse of coal». The Independent. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. April 2013. Archived from the original on 14 February 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Nuclear energy: What you need to know». UK Government. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ «United Kingdom Energy Profile». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Oil». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Natural Gas». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 16 April 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ a b «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. Archived from the original on 28 February 2023. Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ «Coal Reserves in the United Kingdom» (PDF). The Coal Authority. 10 April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Expert predicts ‘coal revolution’«. BBC News. 16 October 2007. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ Watts, Susan (20 March 2012). «Fracking: Concerns over gas extraction regulations». BBC News. Retrieved 9 April 2013.; «Quit fracking aboot». Friends of the Earth Scotland. Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «WHO / UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme: 404 error».[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Environment Agency». Archived from the original on 25 November 2009.
- ^ «About Us». niwater.com. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Census Geography». Office for National Statistics. 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Population Estimates for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 27 March 2011. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ a b «Population Estimates for UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, Mid-2015». Office for National Statistics. 23 June 2016.
- ^ «Annual Mid-year Population Estimates, 2010» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ «World Factbook EUROPE: United Kingdom», The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- ^ a b «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Khan, Urmee (16 September 2008). «England is most crowded country in Europe». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 18 September 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ Carrell, Severin (17 December 2012). «Scotland’s population at record high». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Vital statistics: population and health reference tables». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Boseley, Sarah (14 July 2008). «The question: What’s behind the baby boom?». The Guardian. London. p. 3. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Max Roser (2014), «Total Fertility Rate around the world over the last centuries», Our World In Data, Gapminder Foundation, archived from the original on 5 July 2019, retrieved 10 December 2019
- ^ «Vital Statistics: Population and Health Reference Tables (February 2014 Update): Annual Time Series Data». ONS. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table. Eurostat (26 February 2013). Retrieved 12 July 2013.
- ^ «Sexual identity, UK: 2015 – Experimental Official Statistics on sexual identity in the UK in 2015 by region, sex, age, marital status, ethnicity and NS-SEC». Office for National Statistics. 5 October 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- ^ «Research report 27: Trans research review». equalityhumanrights.com. p. v.
- ^ «2011 Census — Built-up areas». ONS. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ «NRS – Background Information Settlements and Localities» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- ^ The UK’s major urban areas Office for National Statistics (Urban area of Belfast and connected settlements, Table 3.1, page 47)
- ^ «Welsh people could be most ancient in UK, DNA suggests». BBC News. 19 June 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Thomas, Mark G.; et al. (October 2006). «Evidence for a segregated social structure in early Anglo-Saxon England». Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 273 (1601): 2651–2657. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3627. PMC 1635457. PMID 17002951.
- ^ Owen, James (19 July 2005). «Review of ‘The Tribes of Britain'». National Geographic (Washington, D.C.).; Oppenheimer, Stephen (October 2006).«Myths of British ancestry». Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link). Prospect (London). Retrieved 5 November 2010; Henderson, Mark (23 October 2009). «Scientist – Griffin hijacked my work to make race claim about ‘British aborigines’«. The Times. London. Retrieved 26 October 2009. (subscription required) - ^ «Victoria and Albert Museum Black Presence». 13 January 2011.
- ^ Winder, Robert (2010). Bloody Foreigners: The Story of Immigration to Britain. ISBN 978-0-7481-2396-4.; Costello, Ray (2001). Black Liverpool: The Early History of Britain’s Oldest Black Community 1730–1918. Liverpool: Picton Press. ISBN 978-1-873245-07-1.
- ^ «Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – Chinese Community». Chambré Hardman Trust. Archived from the original on 24 July 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Coleman, David; Compton, Paul; Salt, John (2002). «The demographic characteristics of immigrant populations», Council of Europe, p. 505. ISBN 978-92-871-4974-9.
- ^ Roger Ballard Centre for Applied South Asian Studies. «Britain’s visible minorities: a demographic overview» (PDF).
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ a b Vargas-Silva, Carlos (10 April 2014). «Migration Flows of A8 and other EU Migrants to and from the UK». Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Vertovec, Steven (2007). «Super-diversity and its implications». Ethnic and Racial Studies. 30 (6): 1024–1054. doi:10.1080/01419870701599465. S2CID 143674657. Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 3 April 2019.; Vertovec, Steven (20 September 2005). «Opinion: Super-diversity revealed». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Aspinall, Peter J (2012). «Answer Formats in British Census and Survey Ethnicity Questions: Does Open Response Better Capture ‘Superdiversity’?». Sociology. 46 (2): 354–364. doi:10.1177/0038038511419195. S2CID 144841712.
- ^ Ballard, Roger (1996). «Negotiating race and ethnicity: Exploring the implications of the 1991 census» (PDF). Patterns of Prejudice. 30 (3): 3–33. doi:10.1080/0031322X.1996.9970192.; Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (2002). «Censuses, identity formation, and the struggle for political power». In Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (eds.). Census and Identity: The Politics of Race, Ethnicity, and Language in National Censuses. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–42.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in the United Kingdom». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2013. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ «Population Size: 7.9 per cent from a minority ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 13 February 2003. Archived from the original on 31 July 2003. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales 2011» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): London». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 23 June 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.; «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): Leicester». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ «Census 2001 – Ethnicity and religion in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ Schools, pupils and their characteristics: January 2016 (PDF) (Report). Department for Education. 28 June 2016. p. 8. SFR 20/2016.
- ^ M.S (11 December 2012). «Britain’s amazing technicolour dreamcoat». The Economist.
- ^ «Population size: 7.9 per cent from a non-White ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 8 January 2004. Archived from the original on 19 June 2004.
- ^ «Table KS201SC – Ethnic group: All people» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ «Ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ «English language – Government, citizens and rights». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 23 August 2011.
- ^ Mac Sithigh, Daithí (17 May 2018). «Official status of languages in the UK and Ireland» (PDF). Common Law World Review. Queen’s University, Belfast. 47 (1): 77–102. doi:10.1177/1473779518773642. S2CID 219987922.
- ^ British Council «British Council | the UK’s international culture and education organisation». Archived from the original on 1 February 2023. Retrieved 5 December 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (last checked 2023-02-06) - ^ BBC Learning English, BBC World Service «BBC Learning English — About BBC Learning English». Archived from the original on 4 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) (last checked 2023-02-04) - ^ a b «Languages across Europe: United Kingdom». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 4 February 2013.
- ^ Carl Skutsch (2013). Encyclopedia of the World’s Minorities. pp.1261. Routledge. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ Booth, Robert (30 January 2013). «Polish becomes England’s second language». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^ «The teenagers who translate for their parents». BBC News. 23 April 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ Track, Robert Lawrence; Stockwell, Peter (2007). Language and Linguistics: The Key Concepts. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-415-41358-9. Retrieved 4 August 2019.; «Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, Strasbourg, 1.II.1995». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh language in Wales (Census 2021)». gov.wales. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ Wynn Thomas, Peter (March 2007). «Welsh today». Voices. BBC. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Scotland’s Census 2001 – Gaelic Report». General Register Office for Scotland. Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Local UK languages ‘taking off’«. BBC News. 12 February 2009.
- ^ Edwards, John R. (2010). Minority languages and group identity: cases and categories. John Benjamins. pp. 150–158. ISBN 978-90-272-1866-7. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 696. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ «Language Data – Scots». European Bureau for Lesser-Used Languages. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ Brown, Hannah (23 April 2020). «‘People are dying because of this’: Calls for UK Gov to follow Scotland with sign language interpreter at Covid-19 briefing». The Scotsman. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ «British Sign Language Act 2022, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ «Fall in compulsory language lessons». BBC News. 4 November 2004.
- ^ «GCSE results day 2021: Spanish has biggest increase in entries, but German plummets». i (newspaper). 12 August 2021.
- ^ «The School Gate for parents in Wales». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ Ainsworth, Paul (6 December 2022). «‘Historic milestone’ passed as Irish language legislation becomes law». The Irish News. Retrieved 10 December 2022.
- ^ Cannon, John, ed. (2nd edn., 2009). A Dictionary of British History. Oxford University Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-19-955037-1.
- ^ Field, Clive D. (November 2009). «British religion in numbers». BRIN Discussion Series on Religious Statistics, Discussion Paper 001. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Yilmaz, Ihsan (2005). Muslim Laws, Politics and Society in Modern Nation States: Dynamic Legal Pluralisms in England, Turkey, and Pakistan. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-0-7546-4389-0.
- ^ Brown, Callum G. (2006). Religion and Society in Twentieth-Century Britain. Harlow: Pearson Education. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-582-47289-1.
- ^ Norris, Pippa; Inglehart, Ronald (2004). Sacred and Secular: Religion and Politics Worldwide. Cambridge University Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-521-83984-6.
- ^ Fergusson, David (2004). Church, State and Civil Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-521-52959-4.
- ^ «UK Census 2001». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 22 April 2007.
- ^ «Religious Populations». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2004. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom: New Report Finds Only One in 10 Attend Church». News.adventist.org. 4 April 2007. Archived from the original on 13 December 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Philby, Charlotte (12 December 2012). «Less religious and more ethnically diverse: Census reveals a picture of Britain today». The Independent. London.
- ^ «The percentage of the population with no religion has increased in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. 4 April 2013.
- ^ a b c «British Social Attitudes: Record number of Brits with no religion». NatCen.ac.uk. 4 September 2017.
- ^ «The History of the Church of England». The Church of England. 2004. Archived from the original on 15 April 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ «Queen and Church of England». British Monarchy Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 October 2006. Retrieved 5 June 2010.
- ^ «Queen and the Church». The British Monarchy (Official Website). Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- ^ «Our structure». churchofscotland.org.uk. 22 February 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2020.
- ^ Weller, Paul (2005). Time for a Change: Reconfiguring Religion, State, and Society. London: Continuum. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-0-567-08487-3.
- ^ Peach, Ceri, «United Kingdom, a major transformation of the religious landscape», in H. Knippenberg. ed. (2005). The Changing Religious Landscape of Europe. Amsterdam: Het Spinhuis. pp. 44–58. ISBN 978-90-5589-248-8.
- ^ Russell, Rachel; Farley, Harry (29 November 2022). «Less than half of England and Wales population Christian, Census 2021 shows». BBC News.
- ^ a b Coleman, David (17 April 2013). «Immigration, Population and Ethnicity: The UK in International Perspective». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The National Archives | Exhibitions | 1901 Census | Events». www.nationalarchives.gov.uk.
- ^ a b Green, Lord Andrew. «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migration Watch UK.
- ^ «UK 2011 Census Data». National Archives. 11 December 2012. Archived from the original on 12 April 2013.; National Archives (17 December 2013). «Non-UK Born Population of England and Wales Quadrupled Between 1951 and 2011». Archived from the original on 5 January 2016.; «2011 Census analysis: Immigration Patterns of Non-UK Born Populations in England and Wales in 2011». Office for National Statistics. 17 December 2013.
- ^ «International migration, England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 8 November 2022.
- ^ Richards, Eric (2004). Britannia’s children: Emigration from England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland since 1600. London: Hambledon, p. 143. ISBN 978-1-85285-441-6.
- ^ P. Panayi (1906). P. Panayi, ‘German Immigrants in Britain, 1815–1914’ in Germans in Britain since 1500, ed P. Panayi, (London: Hambledon Press, 1996). pp. 73–112. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.
- ^ Panayi, Panikos (1996). Germans in Britain Since 1500. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.; «East End Jews». BBC.
- ^ Jews in Britain: Origin and Growth of Anglo-Jewry. p. 7.; «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migrationwatch UK.; «The Jews». Victoria County History, London, 1969 – via British History Online.
- ^ Gibney, Matthew J.; Hansen, Randall (2005). Immigration and asylum: from 1900 to the present, ABC-CLIO, p. 630. ISBN 978-1-57607-796-2
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. 2005. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2015». Office for National Statistics. 21 May 2015.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2012». Office for National Statistics. 24 May 2012.
- ^ Doward, Jamie; Temko, Ned (23 September 2007). «Home Office shuts the door on Bulgaria and Romania». The Observer. London. p. 2. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- ^ Sumption, Madeleine; Somerville, Will (January 2010). The UK’s new Europeans: Progress and challenges five years after accession (PDF). Policy Report. London: Equality and Human Rights Commission. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-84206-252-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Doward, Jamie; Rogers, Sam (17 January 2010). «Young, self-reliant, educated: portrait of UK’s eastern European migrants». The Observer. London. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ^ Hopkirk, Elizabeth (20 October 2008). «Packing up for home: Poles hit by UK’s economic downturn». London Evening Standard.
- ^ «Recession moves migration patterns». BBC News. 8 September 2009. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ Muenz, Rainer (June 2006). «Europe: Population and Migration in 2005». Migration Policy Institute. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 2 April 2007.
- ^ «Immigration and births to non-British mothers pushes British population to record high». London Evening Standard. 21 August 2008.
- ^ «Births in England and Wales: 2014». Office for National Statistics. 15 July 2015.
- ^ Travis, Alan (25 August 2011). «UK net migration rises 21 per cent». The Guardian. London.
- ^ a b Blinder, Scott (27 March 2015). «Naturalisation as a British Citizen: Concepts and Trends» (PDF). The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ Blinder, Scott (11 June 2014). «Settlement in the UK». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ «Fresh Talent: Working in Scotland». London: UK Border Agency. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Boxell, James (28 June 2010). «Tories begin consultation on cap for migrants». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ Richards (2004), pp. 6–7.
- ^ a b Sriskandarajah, Dhananjayan; Drew, Catherine (11 December 2006). «Brits Abroad: Mapping the scale and nature of British emigration». Institute for Public Policy Research. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: world overview». BBC. Retrieved 20 April 2007.; Casciani, Dominic (11 December 2006). «5.5 m Britons ‘opt to live abroad’«. BBC News. Retrieved 20 April 2007.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: Country-by-country». BBC News. 11 December 2006.
- ^ «The Most Educated Countries in the World». Yahoo Finance. 24 September 2012. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2016.; «And the World’s Most Educated Country Is…». Time. New York. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «The Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2023». Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ^ «QS World University Rankings». Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ^ «Elitist Britain?» (PDF). Social Mobility and Child Poverty Commission. 28 August 2014.; Arnett, George (28 August 2014). «Elitism in Britain – breakdown by profession». The Guardian: Datablog.
- ^ «Local Authorities». Department for Children, Schools and Families. Archived from the original on 30 December 2008. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ Gordon, J.C.B. (1981). Verbal Deficit: A Critique. London: Croom Helm. p. 44 note 18. ISBN 978-0-85664-990-5.; Section 8 (‘Duty of local education authorities to secure provision of primary and secondary schools’), Sections 35–40 (‘Compulsory attendance at Primary and Secondary Schools’) and Section 61 (‘Prohibition of fees in schools maintained by local education authorities …’), Education Act 1944.
- ^ «School leaving age». UK Government. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «England’s pupils in global top 10». BBC News. 10 December 2008.
- ^ Frankel, Hannah (3 September 2010). «Is Oxbridge still a preserve of the posh?». TES. London. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ MacLeod, Donald (9 November 2007). «Private school pupil numbers in decline». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Independent Schools Council Research». Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «About SQA». Scottish Qualifications Authority. 10 April 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «About Learning and Teaching Scotland». Learning and Teaching Scotland. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Brain drain in reverse». Scotland Online Gateway. July 2002. Archived from the original on 4 December 2007.
- ^ «Facts and Figures». SCIS. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ «MSPs vote to scrap endowment fee». BBC News. 28 February 2008.
- ^ «Education System». Welsh Government. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Nursery education for 3 and 4 year olds in Wales» (PDF). 2019.; «Compulsory school age». Practical Law. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Comisiynydd: Nifer y plant mewn addysg Gymraeg yn ‘sioc’«. BBC Cymru Fyw (in Welsh). BBC. 4 August 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.; «Welsh in education: Action Plan 2017–2021» (PDF). Welsh Government. 2017. p. 16.
- ^ «Pisa education tests: Wales improves performance». BBC News. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ Wightwick, Abbie (22 August 2019). «GCSE results 2019: Extreme concern at drop in English language results». WalesOnline. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Participation of young people in education and the labour market 2017 and 2018 (provisional)» (PDF). Welsh Government. 21 August 2019.
- ^ CCEA. «About Us – What we do». Council for the Curriculum Examinations & Assessment. Archived from the original on 5 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Haden, Angela; Campanini, Barbara, eds. (2000). The world health report 2000 – Health systems: improving performance. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156198-3. Retrieved 5 July 2011.; World Health Organization. «Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries» (PDF). New York University. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ Fisher, Peter. «The NHS from Thatcher to Blair». NHS Consultants Association. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
The Budget … was even more generous to the NHS than had been expected amounting to an annual rise of 7.4 per cent above the rate of inflation for the next five years. This would take us to 9.4 per cent of GDP spent on health ie around EU average.
- ^ «Swindells: They aren’t ‘your’ patients». Health Service Journal. 24 September 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
- ^ «How does UK healthcare spending compare with other countries?». Office of National Statistics. 29 August 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- ^ «‘Huge contrasts’ in devolved NHS». BBC News. 28 August 2008.; Triggle, Nick (2 January 2008). «NHS now four different systems». BBC News.
- ^ «BBC poll: Germany most popular country in the world». BBC. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 20 February 2018.; «World Service Global Poll: Negative views of Russia on the rise». BBC.co.uk. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ Goldfarb, Jeffrey (10 May 2006). «Bookish Britain overtakes America as top publisher». RedOrbit. Texas. Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008.
- ^ «William Shakespeare (English author)». Britannica Online encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; MSN Encarta Encyclopedia article on Shakespeare. Archived from the original on 9 February 2006. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; William Shakespeare. Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.
- ^ «Mystery of Christie’s success is solved». The Daily Telegraph. London. 19 December 2005. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ Ciabattari, Jane (December 2015). «The 25 greatest British novels». BBC Culture. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ «Edinburgh, United Kingdom, UNESCO City of Literature». Unesco. 2004. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Early Welsh poetry». BBC Wales. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ Lang, Andrew (2003) [1913]. History of English Literature from Beowulf to Swinburne. Holicong, PA: Wildside Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-8095-3229-2.
- ^ «Dafydd ap Gwilym». Academi.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
Dafydd ap Gwilym is widely regarded as one of the greatest Welsh poets of all time, and amongst the leading European poets of the Middle Ages.
- ^ «True birthplace of Wales’s literary hero». BBC News. 5 December 1999. Archived from the original on 16 March 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ «Kate Roberts: Biography». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 24 July 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ^ Varty, Anne (2014). A Preface to Oscar Wilde. Routledge. pp. 231–232. ISBN 978-1-317-89231-1.; «Oscar Wilde». Encyclopedia.com. Cengage. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Moss, Joyce (2001). British and Irish Literature and Its Times: The Victorian Era to the Present (1837–). Gale Group. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-7876-3729-3.
- ^ Holroyd, Michael (1989). Bernard Shaw, Volume 2: 1898–1918: The Pursuit of Power. Chatto & Windus. p. 384. ISBN 978-0-7011-3350-4.; «G B Shaw». Discovering Literature: 20th century. British Library. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Middleton, Tim (2006). Joseph Conrad. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-415-26851-6.
- ^ Cooper, John Xiros (2006). The Cambridge Introduction to T. S. Eliot. Cambridge University Press. p. 111. ISBN 978-1-139-45790-3.
- ^ Sim, Wai-chew (2009). Kazuo Ishiguro. Routledge. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-135-19867-1.
- ^ «Salman Rushdie». Oxford Reference. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Campbell, James (17 May 2008). «Home from home». The Guardian. Retrieved 10 December 2019.; Nadel, Ira (2004). Ezra Pound: A Literary Life. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-230-37881-0.
- ^ Fieser, James, ed. (2000). A bibliography of Scottish common sense philosophy: Sources and origins (PDF). Bristol: Thoemmes Press. Retrieved 17 December 2010.
- ^ Palmer, Michael (1999). Moral Problems in Medicine: A Practical Coursebook. Cambridge: Lutterworth Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-7188-2978-0.; Scarre, Geoffrey (1995). Utilitarianism. London: Routledge. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-415-12197-2.
- ^ «British Citizen by Act of Parliament: George Frideric Handel». UK Parliament. 20 July 2009. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Andrews, John (14 April 2006). «Handel all’inglese». Playbill. New York. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ^ «Remembrance Sunday». Department for Culture Media and Sport. Retrieved 19 April 2022.; Richards, Jeffrey (2001). Imperialism and Music: Britain 1876–1953. Manchester University Press. pp. 155–156. ISBN 0-7190-4506-1.
- ^ Iemperley, Nicholas (2002). «Great Britain». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Banfield, Stephen; Russell, Ian (2001). «England (i)». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Lewis, Geraint; Davies, Lyn; Kinney, Phyllis (2001). «Wales». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Elliott, Kenneth; Collinson, Francis; Duesenberry, Peggy (2001). «Scotland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; White, Harry; Carolan, Nicholas (2011). «Ireland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; «British 20th century composers». BBC. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ a b «1960–1969». EMI Group. Archived from the original on 25 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «Paul At Fifty». Time. New York. 8 June 1992. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009.
- ^ a b Most Successful Group The Guinness Book of Records 1999, p. 230. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ R. Middleton, et al., «Pop», Grove music online, retrieved 14 March 2010. (subscription required) Archived 13 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Pop», The Oxford Dictionary of Music, retrieved 9 March 2010.(subscription required) Archived 12 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «The Rolling Stones | Biography & History». AllMusic. Retrieved 22 July 2020.
- ^ Tom Larson (2004). History of Rock and Roll. Kendall/Hunt Pub. pp. 183–187. ISBN 978-0-7872-9969-9.
- ^ «Glam Rock». Encarta. Archived from the original on 28 August 2009. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ «NME Originals: Goth». NME. 2004. Archived from the original on 26 January 2008. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ^ «Pop/Rock » Psychedelic/Garage». AllMusic. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ «The Sex Pistols». RollingStone.com. 2001. Archived from the original on 1 February 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ Henderson, Alex (1 August 2003). British Soul. Allmusic. Retrieved 6 March 2011.; AllMusic – Dubstep Archived 23 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine «Absorbed and transfigured elements of techno, drum’n’ bass and dub»; Goldman, Vivien (31 January 2012). «Local Groove Does Good: The Story Of Trip-Hop’s Rise From Bristol». NPR.
- ^ a b «UK music single sales: genre breakdown 2016 | Statistic». Statista. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «5 U.K. Rappers Primed to Take Over America in 2018». Billboard. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «Beatles a big hit with downloads». Belfast Telegraph. 25 November 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- ^ «British rock legends get their own music title for PlayStation3 and PlayStation2» (Press release). EMI. 2 February 2009. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Khan, Urmee (17 July 2008). «Sir Elton John honoured in Ben and Jerry ice cream». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 30 July 2008.; Alleyne, Richard (19 April 2008). «Rock group Led Zeppelin to reunite». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Floyd ‘true to Barrett’s legacy’«. BBC News. 11 July 2006.; Holton, Kate (17 January 2008). «Rolling Stones sign Universal album deal». Reuters. Retrieved 26 October 2008.; Walker, Tim (12 May 2008). «Jive talkin’: Why Robin Gibb wants more respect for the Bee Gees». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2011. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Brit awards winners list 2012: every winner since 1977». The Guardian (London). Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ «Harry Styles Has Weathered the Post-Boy Band Storm Better Than Most». Consequence of Sound. 12 January 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; «10 Years of One Direction: The Story of the World’s Biggest Boy Band, Told With the Fans Who Made It Happen». Billboard. 16 July 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; Corner, Lewis (16 February 2012). «Adele, Coldplay biggest-selling UK artists worldwide in 2011». Digital Spy. Retrieved 22 March 2012.; Magliola, Anna Sky (30 November 2022). «Ed Sheeran’s career journey: From street busker to global superstar». PlanetRadio.co.uk. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ Hughes, Mark (14 January 2008). «A tale of two cities of culture: Liverpool vs Stavanger». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Glasgow gets city of music honour». BBC News. 20 August 2008. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Out of the melting pot: The origins and evolution of drum’n’bass». Red Bull. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ «Birmingham, England … the unlikely birthplace of heavy metal». www.cnn.com. Retrieved 28 February 2022.; Bentley, David (4 June 2013). «Midlands rocks! How Birmingham’s industrial heritage made it the birthplace of heavy metal». Birmingham Post. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ Tate. «Art & Language – Art Term | Tate». Tate. Retrieved 8 September 2018.
- ^ Bayley, Stephen (24 April 2010). «The startling success of Tate Modern». The Times. London. Retrieved 19 January 2011. (subscription required)
- ^ «The top 21 British directors of all time». The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ «Vertigo is named ‘greatest film of all time’«. BBC News. 2 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ «The Directors’ Top Ten Directors». British Film Institute. Archived from the original on 17 May 2012.
- ^ «Harry Potter becomes highest-grossing film franchise». The Guardian. London. 11 September 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- ^ «History of Ealing Studios». Ealing Studios. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «UK film – the vital statistics». UK Film Council. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Baftas fuel Oscars race». BBC News. 26 February 2001. Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- ^ Spencer, Colin (2003). British Food: An Extraordinary Thousand Years of History. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-13110-0.[pages needed]
- ^ «Robin Cook’s chicken tikka masala speech». The Guardian. London. 19 April 2001. Retrieved 7 September 2021.; BBC E-Cyclopedia (20 April 2001). «Chicken tikka masala: Spice and easy does it». BBC. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ «No meat please, we’re British: now a third of us approve of vegan diet». The Guardian. London. 25 December 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ a b «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 5 October 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ a b «Digital license». Prospect. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «About the BBC – What is the BBC». BBC Online. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Newswire7 (13 August 2009). «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.; «TV Licence Fee: facts & figures». BBC Press Office. April 2010. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft Word – The Work of the BBC World Service 2008–09 HC 334 FINAL.doc» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- ^ «News in your language – BBC News». Bbc.co.uk.; «BBC World Service». Facebook.com.
- ^ «Publications & Policies: The History of ITV». ITV.com. Archived from the original on 11 April 2011.
- ^ «Direct Broadcast Satellite Television». News Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «ABCs: National daily newspaper circulation September 2008». The Guardian. UK. 10 October 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ William, D. (2010). UK Cities: A Look at Life and Major Cities in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Eastbourne: Gardners Books. ISBN 978-9987-16-021-1, pp. 22, 46, 109 and 145.
- ^ «Publishing». Department of Culture, Media and Sport. Archived from the original on 5 May 2011.
- ^ «Annual Report 2015-2016» (PDF). www.internationalpublishers.org. International Publishers Association. 2016. p. 16. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Ofcom «Communication Market Report 2010», 19 August 2010, pp. 97, 164 and 191
- ^ «Social Trends 41: Lifestyles and social participation» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 24 February 2011.
- ^ «Top 20 countries with the highest number of Internet users». Internet World Stats. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- ^ «Union Jack or Union Flag?». The Flag Institute. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- ^ «college-of-arms.gov.uk». The College of Arms. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ «Welsh dragon call for Union flag». BBC News. 27 November 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Britannia on British Coins». Chard. Retrieved 25 June 2006.
- ^ Baker, Steve (2001). Picturing the Beast. University of Illinois Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-252-07030-3.
- ^ «Who is John Bull». www.loc.gov. The Library of Congress. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ a b Van Wie, Paul D. (1999). Image, History, and Politics: The Coinage of Modern Europe. New York: University Press of America. pp. 63–64. ISBN 978-0761812227.
- ^ Cleene, Marcel (2002). Compendium of Symbolic and Ritual Plants in Europe: Volume II Herbs. Ghent: Mens & Cultuur Uitgevers N.V. p. 211. ISBN 978-9077135044.
- ^ Ponsford, Matthew (19 January 2016). «Los Angeles to build world’s most expensive stadium complex». CNN. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
- ^ «Opening Ceremony of the Games of the XXX Olympiad» (PDF). Olympic.org. 27 July 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mehaffey, John. «Unparalleled Sporting History». Reuters. London. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ a b «Rugby Union ‘Britain’s Second Most Popular Sport’«. Ipsos-Mori. 22 December 2003. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Rudd, Alyson (7 April 2008). «The father of football deserves much more». The Times. London. Retrieved 29 January 2015.; «Sheffield FC: 150 years of history». FIFA. 24 October 2007. Archived from the original on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Ebner, Sarah (2 July 2013). «History and time are key to power of football, says Premier League chief». The Times. London. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mitchell, Paul (November 2005). «The first international football match». BBC Sport Scotland. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- ^ «Why is there no GB Olympics football team?». BBC Sport. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ «Six ways the town of Rugby helped change the world». BBC News. 1 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Godwin, Terry; Rhys, Chris (1981). The Guinness Book of Rugby Facts & Feats. Guinness Superlatives. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-85112214-4.
- ^ Louw, Jaco; Nesbit, Derrick (2008). The Girlfriends Guide to Rugby. Johannesburg: South Publishers. ISBN 978-0-620-39541-0.
- ^ Colin White (2010). «Projectile Dynamics in Sport: Principles and Applications». p. 222. Routledge
- ^ «About ECB». England and Wales Cricket Board. n.d. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ McLaughlin, Martyn (4 August 2009). «Howzat happen? England fields a Gaelic-speaking Scotsman in Ashes». The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Retrieved 30 December 2010.; «Uncapped Joyce wins Ashes call up». BBC Sport. 15 November 2006. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «Glamorgan». BBC South East Wales. August 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «History of Tennis». ITFtennis.com. Archived from the original on 22 March 2010. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ Morley, Gary (22 June 2011). «125 years of Wimbledon: From birth of lawn tennis to modern marvels». CNN. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «The History of British Motorsport and Motor Racing at Silverstone – The 1950s». Silverstone.co.uk. Archived from the original on 4 October 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ a b Forrest L. Richardson (2002). «Routing the Golf Course: The Art & Science That Forms the Golf Journey». p. 46. John Wiley & Sons
- ^ «Tracking the Field» (PDF). Ipsos MORI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Links plays into the record books». BBC News. 17 March 2009.
- ^ «The Open Championship – More Scottish than British». PGA Tour. Archived from the original on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Ardener, Shirley (2007). Professional identities: policy and practice in business and bureaucracy. New York: Berghahn. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-84545-054-0.
- ^ «Official Website of Rugby League World Cup 2008». Archived from the original on 16 October 2007.
- ^ Baker, Andrew (20 August 1995). «100 years of rugby league: From the great divide to the Super era». The Independent. London. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ «Encyclopædia Britannica (2006).ŷ Queensbury Rules, Britannica».
- ^ Chowdhury, Saj (22 January 2007). «China in Ding’s hands». BBC Sport. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ Gould, Joe (10 April 2007). «The ancient Irish sport of hurling catches on in America». Columbia News Service. Columbia Journalism School. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ «Shinty». Scottish Sport. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sport in Scotland». Scotland.org. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
External links
Government
- Official website of HM Government
- Official website of the British Monarchy
- The official site of the British Prime Minister’s Office
General information
Travel
- Official tourist guide to Britain
Coordinates: 55°N 3°W / 55°N 3°W
|
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
|---|---|
|
Flag Coat of arms |
|
| Anthem: «God Save the King»[a] | |
Royal coat of arms in Scotland: |
|
|
Location of the United Kingdom (dark green) in Europe (dark grey) |
|
| Capital
and largest city |
London 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.500°N 0.117°W |
| Official language and national language |
English (de facto) |
| Regional and minority languages[b] |
|
| Ethnic groups
(2011) |
|
| Religion
(2021) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Constituent countries |
|
| Government | Unitary[e] parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch |
Charles III |
|
• Prime Minister |
Rishi Sunak |
| Legislature | Parliament |
|
• Upper house |
House of Lords |
|
• Lower house |
House of Commons |
| Formation | |
|
• Laws in Wales Acts |
1535 and 1542 |
|
• Union of the Crowns |
24 March 1603 |
|
• Treaty of Union |
22 July 1706 |
|
• Acts of Union of England and Scotland |
1 May 1707 |
|
• Acts of Union of Great Britain and Ireland |
1 January 1801 |
|
• Irish Free State Constitution Act |
5 December 1922 |
| Area | |
|
• Total |
242,495 km2 (93,628 sq mi)[7] (78th) |
|
• Water (%) |
1.51 (2015)[8] |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 estimate |
67,791,400[9] (22nd) |
|
• 2011 census |
63,182,178[10] (22nd) |
|
• Density |
270.7/km2 (701.1/sq mi) (50th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2021) | very high · 18th |
| Currency | Pound sterling[f] (GBP) |
| Time zone | UTC (Greenwich Mean Time, WET) |
|
• Summer (DST) |
UTC+1 (British Summer Time, WEST) |
| [g] | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy yyyy—mm—dd (AD) |
| Driving side | left[h] |
| Calling code | +44[i] |
| ISO 3166 code | GB |
| Internet TLD | .uk[j] |
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain,[k][14] is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland.[15] It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[16] The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles.[17] Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242,495 square kilometres (93,628 sq mi), with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people.[18]
The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 1707 formed the Kingdom of Great Britain. Its union in 1801 with the Kingdom of Ireland created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Most of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922, leaving the present United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, which formally adopted that name in 1927.[l] The nearby Isle of Man, Guernsey and Jersey are not part of the UK, being Crown Dependencies with the British Government responsible for defence and international representation.[19] There are also 14 British Overseas Territories,[20] the last remnants of the British Empire which, at its height in the 1920s, encompassed almost a quarter of the world’s landmass and a third of the world’s population, and was the largest empire in history. British influence can be observed in the language, culture and the legal and political systems of many of its former colonies.[21][22]
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.[m][24] The capital and largest city is London, a global city and financial centre with a metropolitan area population of over 14 million. Other major cities include Birmingham, Manchester, Glasgow, Liverpool and Leeds.[25] Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments, each with varying powers.[26] The UK became the world’s first industrialised country and was the world’s foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries.[27] In the 21st century, the UK retains considerable economic, cultural, military, scientific, technological and political influence.[28] The United Kingdom has the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the eighth-largest by purchasing power parity. It has a high-income economy and a very high Human Development Index rating, ranking 18th in the world. It also performs well in international rankings of education, healthcare, life expectancy and human development.[29] It is a recognised nuclear state and is ranked fourth globally in military expenditure.[30] It has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since its first session in 1946.
The United Kingdom is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Council of Europe, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, Five Eyes, the United Nations, NATO, AUKUS, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Interpol, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). It was a member state of the European Communities (EC) and its successor, the European Union (EU), from its accession in 1973 until its withdrawal in 2020 following a referendum held in 2016.
Etymology and terminology
In 43 AD, Britannia referred to the Roman province that encompassed modern day England and Wales. Great Britain encompassed the whole island, taking in the land north of the River Forth known to the Romans as Caledonia in modern Scotland (i.e. «greater» Britain).[31] In the Middle Ages, the name «Britain» was also applied to a small part of France now known as Brittany. As a result, Great Britain (likely from the French «Grande Bretagne«) came into use to refer specifically to the island, with Brittany often referred to as «Little Britain».[32] However, that name had no official significance until 1707, when the island’s kingdoms of England and Scotland were united as the Kingdom of Great Britain.[33]
The Acts of Union 1707 declared that the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland were «United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain».[n][34] The term «United Kingdom» has occasionally been used as a description for the former Kingdom of Great Britain, although its official name from 1707 to 1800 was simply «Great Britain».[35] The Acts of Union 1800 united the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801, forming the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Following the partition of Ireland and the independence of the Irish Free State in 1922, which left Northern Ireland as the only part of the island of Ireland within the United Kingdom, the name was changed to the «United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland».[36]
Although the United Kingdom is a sovereign country, England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are also widely referred to as countries.[37] The UK Prime Minister’s website has used the phrase «countries within a country» to describe the United Kingdom.[16] Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as «regions».[38] Northern Ireland is also referred to as a «province».[39] With regard to Northern Ireland, the descriptive name used «can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one’s political preferences».[40]
The term «Great Britain» conventionally refers to the island of Great Britain, or politically to England, Scotland and Wales in combination.[41] It is sometimes used as a loose synonym for the United Kingdom as a whole.[42] The word England is occasionally used incorrectly to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole, a mistake principally made by people from outside the UK.[43]
The term «Britain» is used both as a synonym for Great Britain,[44][45] and as a synonym for the United Kingdom.[46][45] Usage is mixed: the UK Government prefers to use the term «UK» rather than «Britain» or «British» on its own website (except when referring to embassies),[47] while acknowledging that both terms refer to the United Kingdom and that elsewhere «British government» is used at least as frequently as «United Kingdom government».[48] The UK Permanent Committee on Geographical Names recognises «United Kingdom», «UK» and «U.K.» as shortened and abbreviated geopolitical terms for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in its toponymic guidelines; it does not list «Britain» but notes that «it is only the one specific nominal term ‘Great Britain’ which invariably excludes Northern Ireland».[48] The BBC historically preferred to use «Britain» as shorthand only for Great Britain, though the present style guide does not take a position except that «Great Britain» excludes Northern Ireland.[49]
The adjective «British» is commonly used to refer to matters relating to the United Kingdom and is used in law to refer to United Kingdom citizenship and matters to do with nationality.[50] People of the United Kingdom use several different terms to describe their national identity and may identify themselves as being British, English, Scottish, Welsh, Northern Irish, or Irish;[51] or as having a combination of different national identities.[52] The official designation for a citizen of the United Kingdom is «British citizen».[48]
History
Prior to the Treaty of Union
Stonehenge in Wiltshire is a ring of stones, each about 4 m (13 ft) high, 2 m (7 ft) wide and 25 tonnes, erected 2400–2200 BC.
Settlement by anatomically modern humans of what was to become the United Kingdom occurred in waves beginning by about 30,000 years ago.[53] By the end of the region’s prehistoric period, the population is thought to have belonged, in the main, to a culture termed Insular Celtic, comprising Brittonic Britain and Gaelic Ireland.[54]
The Roman conquest, beginning in 43 AD, and the 400-year rule of southern Britain, was followed by an invasion by Germanic Anglo-Saxon settlers, reducing the Brittonic area mainly to what was to become Wales, Cornwall and, until the latter stages of the Anglo-Saxon settlement, the Hen Ogledd (northern England and parts of southern Scotland).[55] Most of the region settled by the Anglo-Saxons became unified as the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.[56] Meanwhile, Gaelic-speakers in north-west Britain (with connections to the north-east of Ireland and traditionally supposed to have migrated from there in the 5th century)[57] united with the Picts to create the Kingdom of Scotland in the 9th century.[58]
In 1066, the Normans invaded England from northern France. After conquering England, they seized large parts of Wales, conquered much of Ireland and were invited to settle in Scotland, bringing to each country feudalism on the Northern French model and Norman-French culture.[59] The Anglo-Norman ruling class greatly influenced, but eventually assimilated with, each of the local cultures.[60] Subsequent medieval English kings completed the conquest of Wales and made unsuccessful attempts to annex Scotland. Asserting its independence in the 1320 Declaration of Arbroath, Scotland maintained its independence thereafter, albeit in near-constant conflict with England.
The English monarchs, through inheritance of substantial territories in France and claims to the French crown, were also heavily involved in conflicts in France, most notably the Hundred Years’ War, while the Kings of Scots were in an alliance with the French during this period.[61]
Early modern Britain saw religious conflict resulting from the Reformation and the introduction of Protestant state churches in each country.[62] Wales was fully incorporated into the Kingdom of England,[63] and Ireland was constituted as a kingdom in personal union with the English crown.[64] In what was to become Northern Ireland, the lands of the independent Catholic Gaelic nobility were confiscated and given to Protestant settlers from England and Scotland.[65]
In 1603, the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots, inherited the crowns of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal, and religious institutions.[66]
In the mid-17th century, all three kingdoms were involved in a series of connected wars (including the English Civil War) which led to the temporary overthrow of the monarchy, with the execution of King Charles I, and the establishment of the short-lived unitary republic of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.[67]
Although the monarchy was restored, the Interregnum along with the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689 in England and Claim of Right Act 1689 in Scotland ensured that, unlike much of the rest of Europe, royal absolutism would not prevail, and a professed Catholic could never accede to the throne. The British constitution would develop on the basis of constitutional monarchy and the parliamentary system.[68] With the founding of the Royal Society in 1660, science was greatly encouraged. During this period, particularly in England, the development of naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean.[69]
Though previous attempts at uniting the two kingdoms within Great Britain in 1606, 1667, and 1689 had proved unsuccessful, the attempt initiated in 1705 led to the Treaty of Union of 1706 being agreed and ratified by both parliaments.
Kingdom of Great Britain
On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706 Treaty of Union and so unite the two kingdoms.[70]
In the 18th century, cabinet government developed under Robert Walpole, in practice the first prime minister (1721–1742). A series of Jacobite Uprisings sought to remove the Protestant House of Hanover from the British throne and restore the Catholic House of Stuart. The Jacobites were finally defeated at the Battle of Culloden in 1746, after which the Scottish Highlanders were brutally suppressed. The British colonies in North America that broke away from Britain in the American War of Independence became the United States of America, recognised by Britain in 1783. British imperial ambition turned towards Asia, particularly to India.[71]
Britain played a leading part in the Atlantic slave trade, mainly between 1662 and 1807 when British or British-colonial Slave ships transported nearly 3.3 million slaves from Africa.[72] The slaves were taken to work on plantations in British possessions, principally in the Caribbean but also North America.[73] Slavery coupled with the Caribbean sugar industry had a significant role in strengthening and developing the British economy in the 18th century.[74] However, Parliament banned the trade in 1807, banned slavery in the British Empire in 1833, and Britain took a role in the movement to abolish slavery worldwide through the blockade of Africa and pressing other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties. [75]
Union with Ireland
The term «United Kingdom» became official in 1801 when the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland each passed an Act of Union, uniting the two kingdoms and creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.[76]
After the defeat of France at the end of the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815), the United Kingdom emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century (with London the largest city in the world from about 1830).[77] Unchallenged at sea, British dominance was later described as Pax Britannica («British Peace»), a period of relative peace among the Great Powers (1815–1914) during which the British Empire became the global hegemon and adopted the role of global policeman.[78] By the time of the Great Exhibition of 1851, Britain was described as the «workshop of the world».[79] From 1853 to 1856, Britain took part in the Crimean War, allied with the Ottoman Empire in the fight against the Russian Empire,[80] participating in the naval battles of the Baltic Sea known as the Åland War in the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland, among others.[81] The British Empire was expanded to include India, large parts of Africa and many other territories throughout the world. Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, British dominance of much of world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many regions, such as Asia and Latin America.[82]
Domestically, political attitudes favoured free trade and laissez-faire policies and a gradual widening of the voting franchise. During the century, the population increased at a dramatic rate, accompanied by rapid urbanisation, causing significant social and economic stresses.[83] To seek new markets and sources of raw materials, the Conservative Party under Disraeli launched a period of imperialist expansion in Egypt, South Africa, and elsewhere. Canada, Australia and New Zealand became self-governing dominions.[84] After the turn of the century, Britain’s industrial dominance was challenged by Germany and the United States.[85] Social reform and home rule for Ireland were important domestic issues after 1900. The Labour Party emerged from an alliance of trade unions and small socialist groups in 1900, and suffragettes campaigned from before 1914 for women’s right to vote.[86]
World Wars and Partition of Ireland
Britain fought alongside France, Russia and (after 1917) the United States, against Germany and its allies in the First World War (1914–1918).[87] British armed forces were engaged across much of the British Empire and in several regions of Europe, particularly on the Western front.[88] The high fatalities of trench warfare caused the loss of much of a generation of men, with lasting social effects in the nation and a great disruption in the social order. After the war, Britain received the League of Nations mandate over a number of former German and Ottoman colonies. The British Empire reached its greatest extent, covering a fifth of the world’s land surface and a quarter of its population.[89] Britain had suffered 2.5 million casualties and finished the war with a huge national debt.[88]
By the mid-1920s most of the British population could listen to BBC radio programmes.[90] Experimental television broadcasts began in 1929 and the first scheduled BBC Television Service commenced in 1936.[91] The rise of Irish nationalism, and disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish Home Rule, led eventually to the partition of the island in 1921.[92] The Irish Free State became independent, initially with Dominion status in 1922, and unambiguously independent in 1931. Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom.[93] The 1928 Act widened suffrage by giving women electoral equality with men. A wave of strikes in the mid-1920s culminated in the General Strike of 1926. Britain had still not recovered from the effects of the war when the Great Depression (1929–1932) occurred. This led to considerable unemployment and hardship in the old industrial areas, as well as political and social unrest in the 1930s, with rising membership in communist and socialist parties. A coalition government was formed in 1931.[94]
Nonetheless, «Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system.»[95] After Nazi Germany invaded Poland, Britain entered the Second World War by declaring war on Germany in 1939. Winston Churchill became prime minister and head of a coalition government in 1940. Despite the defeat of its European allies in the first year of the war, Britain and its Empire continued the fight alone against Germany. Churchill engaged industry, scientists, and engineers to advise and support the government and the military in the prosecution of the war effort.[95] In 1940, the Royal Air Force defeated the German Luftwaffe in a struggle for control of the skies in the Battle of Britain. Urban areas suffered heavy bombing during the Blitz. The Grand Alliance of Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union formed in 1941 leading the Allies against the Axis powers. There were eventual hard-fought victories in the Battle of the Atlantic, the North Africa campaign and the Italian campaign. British forces played an important role in the Normandy landings of 1944 and the liberation of Europe, achieved with its allies the United States, the Soviet Union and other Allied countries. The British Army led the Burma campaign against Japan and the British Pacific Fleet fought Japan at sea. British scientists contributed to the Manhattan Project which led to the surrender of Japan.
Postwar 20th century
During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world;[96] it was an original signatory to the Declaration by United Nations. After the war, the UK became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and worked closely with the United States to establish the IMF, World Bank and NATO.[97] The war left the UK severely weakened and financially dependent on the Marshall Plan,[98] but it was spared the total war that devastated eastern Europe.[99] In the immediate post-war years, the Labour government initiated a radical programme of reforms, which had a significant effect on British society in the following decades.[100] Major industries and public utilities were nationalised, a welfare state was established, and a comprehensive, publicly funded healthcare system, the National Health Service, was created.[101] The rise of nationalism in the colonies coincided with Britain’s now much-diminished economic position, so that a policy of decolonisation was unavoidable. Independence was granted to India and Pakistan in 1947.[102] Over the next three decades, most colonies of the British Empire gained their independence, with all those that sought independence supported by the UK, during both the transition period and afterwards. Many became members of the Commonwealth of Nations.[103]
The UK was the third country to develop a nuclear weapons arsenal (with its first atomic bomb test, Operation Hurricane, in 1952), but the new post-war limits of Britain’s international role were illustrated by the Suez Crisis of 1956. The international spread of the English language ensured the continuing international influence of its literature and culture.[104][105] As a result of a shortage of workers in the 1950s, the government encouraged immigration from Commonwealth countries. In the following decades, the UK became a more multi-ethnic society than before.[106] Despite rising living standards in the late 1950s and 1960s, the UK’s economic performance was less successful than many of its main competitors such as France, West Germany and Japan.
Leaders of EU states in 2007. The UK entered the EEC in 1973. In a 1975 referendum 67% voted to stay in it;[107] in 2016 52% voted to leave the EU.[108]
In the decades-long process of European integration, the UK was a founding member of the alliance called the Western European Union, established with the London and Paris Conferences in 1954. In 1960 the UK was one of the seven founding members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), but in 1973 it left to join the European Communities (EC). When the EC became the European Union (EU) in 1992, the UK was one of the 12 founding member states. The Treaty of Lisbon, signed in 2007, forms the constitutional basis of the European Union since then.
From the late 1960s, Northern Ireland suffered communal and paramilitary violence (sometimes affecting other parts of the UK) conventionally known as the Troubles. It is usually considered to have ended with the Belfast «Good Friday» Agreement of 1998.[109]
Following a period of widespread economic slowdown and industrial strife in the 1970s, the Conservative government of the 1980s under Margaret Thatcher initiated a radical policy of monetarism, deregulation, particularly of the financial sector (for example, the Big Bang in 1986) and labour markets, the sale of state-owned companies (privatisation), and the withdrawal of subsidies to others.[110] From 1984, the economy was helped by the inflow of substantial North Sea oil revenues.[111]
Around the end of the 20th century, there were major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved administrations for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[112] The statutory incorporation followed acceptance of the European Convention on Human Rights. The UK is still a key global player diplomatically and militarily. It plays leading roles in the UN and NATO.
21st century
The UK broadly supported the United States’ approach to the «war on terror» in the early years of the 21st century.[113] Controversy surrounded some of Britain’s overseas military deployments, particularly in Afghanistan and Iraq.[114]
The 2008 global financial crisis severely affected the UK economy. The Cameron–Clegg coalition government of 2010 introduced austerity measures intended to tackle the substantial public deficits which resulted.[115] The devolved Scottish Government and UK Government agreed for a referendum to be held on Scottish independence in 2014.[116] This referendum resulted in the electorate in Scotland voting by 55.3 to 44.7% for Scotland to remain part of the United Kingdom.[117]
In 2016, 51.9 per cent of voters in the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union.[118] The UK left the EU on 31 January 2020 and completed its withdrawal in full at the end of that year.[119]
The COVID-19 pandemic had a severe impact on the UK’s economy, caused major disruptions to education and had far-reaching impacts on society and politics in 2020 and 2021.[120][121][122]
On 8 September 2022, Elizabeth II, the longest-living and longest-reigning British monarch, died at the age of 96.[123] Upon the Queen’s death, her eldest child Charles, Prince of Wales, immediately acceded to the British throne as King Charles III.[124]
Geography
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately 244,820 square kilometres (94,530 sq mi). The country occupies the major part of the British Isles[125] archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland and some smaller surrounding islands. It lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea with the southeast coast coming within 22 miles (35 km) of the coast of northern France, from which it is separated by the English Channel.[126]
In 1993 10 per cent of the UK was forested, 46 per cent used for pastures and 25 per cent cultivated for agriculture.[127] The Royal Greenwich Observatory in London was chosen as the defining point of the Prime Meridian[128] in Washington, DC, in 1884, although due to more accurate modern measurement the meridian actually lies 100 metres to the east of the observatory.[129]
The United Kingdom lies between latitudes 49° and 61° N, and longitudes 9° W and 2° E. Northern Ireland shares a 224-mile (360 km) land boundary with the Republic of Ireland.[126] The coastline of Great Britain is 11,073 miles (17,820 km) long.[130] It is connected to continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel, which at 31 miles (50 km) (24 miles (38 km) underwater) is the longest underwater tunnel in the world.[131]
The UK contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Celtic broadleaf forests, English Lowlands beech forests, North Atlantic moist mixed forests, and Caledon conifer forests.[132] The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 1.65/10, ranking it 161th globally out of 172 countries.[133]
Climate
Most of the United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round.[126] The temperature varies with the seasons seldom dropping below 0 °C (32 °F) or rising above 30 °C (86 °F).[134] Some parts, away from the coast, of upland England, Wales, Northern Ireland and most of Scotland, experience a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc). Higher elevations in Scotland experience a continental subarctic climate (Dfc) and the mountains experience a tundra climate (ET).[135]
The prevailing wind is from the southwest and bears frequent spells of mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean,[126] although the eastern parts are mostly sheltered from this wind since the majority of the rain falls over the western regions the eastern parts are therefore the driest. Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters; especially in the west where winters are wet and even more so over high ground. Summers are warmest in the southeast of England and coolest in the north. Heavy snowfall can occur in winter and early spring on high ground, and occasionally settles to great depth away from the hills.[136]
The average total annual sunshine in the United Kingdom is 1339.7 hours, which is just under 30% of the maximum possible (The maximum hours of sunshine possible in one year is approximately 4476 hours).[137] The hours of sunshine vary from 1200 to about 1580 hours per year, and since 1996 the UK has been and still is receiving above the 1981 to 2010 average hours of sunshine[138]
United Kingdom is ranked 4 out of 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index.[139] A law has been passed that UK greenhouse gas emissions will be net zero by 2050.[140]
Topography
England accounts for just over half (53 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 130,395 square kilometres (50,350 sq mi).[141] Most of the country consists of lowland terrain,[127] with more upland and some mountainous terrain northwest of the Tees–Exe line; including the Lake District, the Pennines, Exmoor and Dartmoor. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber. England’s highest mountain is Scafell Pike (978 metres (3,209 ft)) in the Lake District.
Scotland accounts for just under one-third (32 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 78,772 square kilometres (30,410 sq mi).[142] This includes nearly 800 islands,[143] predominantly west and north of the mainland; notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its topography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault – a geological rock fracture – which traverses Scotland from Arran in the west to Stonehaven in the east.[144] The fault separates two distinctively different regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the Lowlands to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland’s mountainous land, including Ben Nevis which at 1,345 metres (4,413 ft)[145] is the highest point in the British Isles.[146] Lowland areas – especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth known as the Central Belt – are flatter and home to most of the population including Glasgow, Scotland’s largest city, and Edinburgh, its capital and political centre, although upland and mountainous terrain lies within the Southern Uplands.
Wales accounts for less than one-tenth (9 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 20,779 square kilometres (8,020 sq mi).[147] Wales is mostly mountainous, though South Wales is less mountainous than North and mid Wales. The main population and industrial areas are in South Wales, consisting of the coastal cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, and the South Wales Valleys to their north. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia and include Snowdon (Welsh: Yr Wyddfa) which, at 1,085 metres (3,560 ft), is the highest peak in Wales.[127] Wales has over 2,704 kilometres (1,680 miles) of coastline.[130] Several islands lie off the Welsh mainland, the largest of which is Anglesey (Ynys Môn) in the north-west.
Northern Ireland, separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea and North Channel, has an area of 14,160 square kilometres (5,470 sq mi) and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh which, at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), is the largest lake in the British Isles by area.[148] The highest peak in Northern Ireland is Slieve Donard in the Mourne Mountains at 852 metres (2,795 ft).[127]
Government and politics
The United Kingdom is a unitary state under a constitutional monarchy. King Charles III is the monarch and head of state of the UK, as well as 14 other independent countries. These 15 countries are sometimes referred to as «Commonwealth realms». The monarch has «the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, and the right to warn».[149] The Constitution of the United Kingdom is uncodified and consists mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statutes, judge-made case law and international treaties, together with constitutional conventions.[150] The UK Parliament can carry out constitutional reform by passing acts of parliament, and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. No sitting parliament can pass laws that future parliaments cannot change.[151]
The UK is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy.[152] The Parliament of the United Kingdom is sovereign.[153] It is made up of the House of Commons, the House of Lords and the Crown.[154] The main business of parliament takes place in the two houses,[154] but royal assent is required for a bill to become an act of parliament (law).[155]
For general elections (elections to the House of Commons), the UK is divided into 650 constituencies, each of which is represented by a member of Parliament (MP).[156] MPs hold office for up to five years and are always up for re-election in general elections.[156] The Conservative Party, Labour Party and Scottish National Party are, respectively, the current first, second and third largest parties (by number of MPs) in the House of Commons.[157]
The prime minister is the head of government in the United Kingdom.[158] Nearly all prime ministers have served as First Lord of the Treasury[159] and all prime ministers have continuously served as First Lord of the Treasury since 1905,[160] Minister for the Civil Service since 1968[161] and Minister for the Union since 2019.[162] In modern times, the prime minister is, by constitutional convention, an MP.[163] The prime minister is appointed by the monarch[164] and their appointment is governed by constitutional conventions.[156] However, they are normally the leader of the political party with the most seats in the House of Commons[165] and hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons.[163]
The prime minister not only has statutory functions (alongside other ministers),[166] but is the monarch’s principal adviser[167] and it is for them to advise the monarch on the exercise of the royal prerogative in relation to government.[163] In particular, the prime minister recommends the appointment of ministers[163] and chairs the Cabinet.[168]
Administrative divisions
The geographical division of the United Kingdom into counties or shires began in England and Scotland in the early Middle Ages and was complete throughout Great Britain and Ireland by the early Modern Period.[169] Administrative arrangements were developed separately in each country of the United Kingdom, with origins which often predated the formation of the United Kingdom. Modern local government by elected councils, partly based on the ancient counties, was introduced separately: in England and Wales in a 1888 act, Scotland in a 1889 act and Ireland in a 1898 act, meaning there is no consistent system of administrative or geographic demarcation across the United Kingdom.[170]
Until the 19th century there was little change to those arrangements, but there has since been a constant evolution of role and function.[171]
The organisation of local government in England is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to local arrangements. The upper-tier subdivisions of England are the nine regions, now used primarily for statistical purposes.[172] One region, Greater London, has had a directly elected assembly and mayor since 2000 following popular support for the proposal in a referendum.[173] It was intended that other regions would also be given their own elected regional assemblies, but a proposed assembly in the North East region was rejected by a referendum in 2004.[174] Since 2011, ten combined authorities have been established in England. Eight of these have elected mayors, the first elections for which took place on 4 May 2017.[175] Below the regional tier, some parts of England have county councils and district councils and others have unitary authorities, while London consists of 32 London boroughs and the City of London. Councillors are elected by the first-past-the-post system in single-member wards or by the multi-member plurality system in multi-member wards.[176]
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 council areas, with wide variation in both size and population. The cities of Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen and Dundee are separate council areas, as is the Highland Council, which includes a third of Scotland’s area but only just over 200,000 people. Local councils are made up of elected councillors, of whom there are 1,223;[177] they are paid a part-time salary. Elections are conducted by single transferable vote in multi-member wards that elect either three or four councillors. Each council elects a Provost, or Convenor, to chair meetings of the council and to act as a figurehead for the area.
Local government in Wales consists of 22 unitary authorities. All unitary authorities are led by a leader and cabinet elected by the council itself. These include the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, which are unitary authorities in their own right.[178] Elections are held every four years under the first-past-the-post system.[178]
Local government in Northern Ireland has since 1973 been organised into 26 district councils, each elected by single transferable vote. Their powers are limited to services such as collecting waste, controlling dogs and maintaining parks and cemeteries.[179] In 2008 the executive agreed on proposals to create 11 new councils and replace the present system.[180]
Devolved governments
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a first minister (or, in the case of Northern Ireland, a diarchal first minister and deputy first minister), and a devolved unicameral legislature. England, the largest country of the United Kingdom, has no devolved executive or legislature and is administered and legislated for directly by the UK’s government and parliament on all issues. This situation has given rise to the so-called West Lothian question, which concerns the fact that members of parliament from Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland can vote, sometimes decisively,[181] on matters that affect only England.[182] The 2013 McKay Commission on this recommended that laws affecting only England should need support from a majority of English members of parliament.[183]
The Scottish Government and Parliament have wide-ranging powers over any matter that has not been specifically reserved to the UK Parliament, including education, healthcare, Scots law and local government.[184] Their power over economic issues is significantly constrained by an act of the UK parliament passed in 2020.[192]
The Welsh Government and the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; formerly the National Assembly for Wales)[193] have more limited powers than those devolved to Scotland.[194] The Senedd is able to legislate on any matter not specifically reserved to the UK Parliament through Acts of Senedd Cymru.
The Northern Ireland Executive and Assembly have powers similar to those devolved to Scotland. The Executive is led by a diarchy representing unionist and nationalist members of the Assembly.[195] Devolution to Northern Ireland is contingent on participation by the Northern Ireland administration in the North-South Ministerial Council, where the Northern Ireland Executive cooperates and develops joint and shared policies with the Government of Ireland. The British and Irish governments co-operate on non-devolved matters affecting Northern Ireland through the British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference, which assumes the responsibilities of the Northern Ireland administration in the event of its non-operation.[citation needed]
The UK does not have a codified constitution and constitutional matters are not among the powers devolved to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. Under the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty, the UK Parliament could, in theory, therefore, abolish the Scottish Parliament, Senedd or Northern Ireland Assembly.[196] Indeed, in 1972, the UK Parliament unilaterally prorogued the Parliament of Northern Ireland, setting a precedent relevant to contemporary devolved institutions.[197] In practice, it would be politically difficult for the UK Parliament to abolish devolution to the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd, given the political entrenchment created by referendum decisions.[198] The political constraints placed upon the UK Parliament’s power to interfere with devolution in Northern Ireland are even greater than in relation to Scotland and Wales, given that devolution in Northern Ireland rests upon an international agreement with the Government of Ireland.[199] The UK Parliament restricts the three devolved parliaments’ legislative competence in economic areas through an Act passed in 2020.[192]
Dependencies
The United Kingdom, the 14 British Overseas Territories[20] and the three Crown Dependencies[202] form ‘one undivided Realm’.[203][204] All parts of the realm are under the sovereignty of the British Crown, but the Territories and Dependencies are not part of the UK. This is distinct from the status of Commonwealth realms, who have separate monarchies, but share the same monarch.[204]
The 14 British Overseas Territories are remnants of the British Empire: Anguilla; Bermuda; the British Antarctic Territory; the British Indian Ocean Territory; the British Virgin Islands; the Cayman Islands; the Falkland Islands; Gibraltar; Montserrat; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; the Turks and Caicos Islands; the Pitcairn Islands; South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and Akrotiri and Dhekelia on the island of Cyprus.[205] British claims in Antarctica have limited international recognition.[206] Collectively Britain’s overseas territories encompass an approximate land area of 480,000 square nautical miles (640,000 sq mi; 1,600,000 km2),[207] with a total population of approximately 250,000.[208] The overseas territories also give the UK the world’s fifth largest exclusive economic zone at 6,805,586 km2 (2,627,651 sq mi).[209][better source needed] A 1999 UK government white paper stated that: «[The] Overseas Territories are British for as long as they wish to remain British. Britain has willingly granted independence where it has been requested; and we will continue to do so where this is an option.»[210] Self-determination is also enshrined in the constitutions of several overseas territories and three have specifically voted to remain under British sovereignty (Bermuda in 1995,[211] Gibraltar in 2002[212] and the Falkland Islands in 2013).[213]
The Crown Dependencies are possessions of the Crown, as opposed to territories of the UK.[214] They comprise three independently administered jurisdictions: the Bailiwicks of Jersey and of Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea. By mutual agreement, the British Government manages the islands’ foreign affairs and defence and the UK Parliament has the authority to legislate on their behalf. Internationally, they are regarded as «territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible».[215] The power to pass legislation affecting the islands ultimately rests with their own respective legislative assemblies, with the assent of the Crown (Privy Council or, in the case of the Isle of Man, in certain circumstances the Lieutenant-Governor).[216] Since 2005 each Crown dependency has had a Chief Minister as its head of government.[217]
Law and criminal justice
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland’s separate legal system.[218] Today the UK has three distinct systems of law: English law, Northern Ireland law and Scots law. A new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom came into being in October 2009 to replace the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords.[219] The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, including the same members as the Supreme Court, is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the British Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies.[220]
Both English law, which applies in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland law are based on common-law principles.[221] The essence of common law is that, subject to statute, the law is developed by judges in courts, applying statute, precedent and common sense to the facts before them to give explanatory judgements of the relevant legal principles, which are reported and binding in future similar cases (stare decisis).[222] The courts of England and Wales are headed by the Senior Courts of England and Wales, consisting of the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land for both criminal and civil appeal cases in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and any decision it makes is binding on every other court in the same jurisdiction, often having a persuasive effect in other jurisdictions.[223]
Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases,[224] and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases.[225] The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom serves as the highest court of appeal for civil cases under Scots law.[226] Sheriff courts deal with most civil and criminal cases including conducting criminal trials with a jury, known as sheriff solemn court, or with a sheriff and no jury, known as sheriff summary Court.[227] The Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdicts for a criminal trial: «guilty», «not guilty» and «not proven». Both «not guilty» and «not proven» result in an acquittal.[228]
Crime in England and Wales increased in the period between 1981 and 1995, though since that peak there has been an overall fall of 66 per cent in recorded crime from 1995 to 2015,[229] according to crime statistics. The prison population of England and Wales has increased to 86,000, giving England and Wales the highest rate of incarceration in Western Europe at 148 per 100,000.[230] His Majesty’s Prison Service, which reports to the Ministry of Justice, manages most of the prisons within England and Wales. The murder rate in England and Wales has stabilised in the first half of the 2010s with a murder rate around 1 per 100,000 which is half the peak in 2002 and similar to the rate in the 1980s[231] Crime in Scotland fell slightly in 2014–2015 to its lowest level in 39 years in with 59 killings for a murder rate of 1.1 per 100,000. Scotland’s prisons are overcrowded but the prison population is shrinking.[232]
Foreign relations
The UK is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of NATO, AUKUS, the Commonwealth of Nations, the G7 finance ministers, the G7 forum, the G20, the OECD, the WTO, the Council of Europe and the OSCE.[233] The UK is said to have a «Special Relationship» with the United States and a close partnership with France – the «Entente cordiale» – and shares nuclear weapons technology with both countries;[234] the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance is considered to be the oldest binding military alliance in the world. The UK is also closely linked with the Republic of Ireland; the two countries share a Common Travel Area and co-operate through the British-Irish Intergovernmental Conference and the British-Irish Council. Britain’s global presence and influence is further amplified through its trading relations, foreign investments, official development assistance and military engagements.[235] Canada, Australia and New Zealand, all of which are former colonies of the British Empire which share King Charles as their head of state, are the most favourably viewed countries in the world by British people.[236]
Military
His Majesty’s Armed Forces consist of three professional service branches: the Royal Navy and Royal Marines (forming the Naval Service), the British Army and the Royal Air Force.[237] The armed forces of the United Kingdom are managed by the Ministry of Defence and controlled by the Defence Council, chaired by the Secretary of State for Defence. The Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch, to whom members of the forces swear an oath of allegiance.[238] The Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK’s global security interests and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in NATO, including the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps, the Five Power Defence Arrangements, RIMPAC and other worldwide coalition operations. Overseas garrisons and facilities are maintained in Ascension Island, Bahrain, Belize, Brunei, Canada, Cyprus, Diego Garcia, the Falkland Islands, Germany, Gibraltar, Kenya, Oman, Qatar and Singapore.[239]
The British armed forces played a key role in establishing the British Empire as the dominant world power in the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. By emerging victorious from conflicts, Britain has often been able to decisively influence world events. Since the end of the British Empire, the UK has remained a major military power. Following the end of the Cold War, defence policy has a stated assumption that «the most demanding operations» will be undertaken as part of a coalition.[240]
According to sources which include the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute and the International Institute for Strategic Studies, the UK has either the fourth- or the fifth-highest military expenditure. Total defence spending amounts to 2.0 per cent of national GDP.[241]
Economy
Overview
The UK has a partially regulated market economy.[243] Based on market exchange rates, the UK is today the fifth-largest economy in the world and the second-largest in Europe after Germany. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government’s public finance policy and economic policy. The Bank of England is the UK’s central bank and is responsible for issuing notes and coins in the nation’s currency, the pound sterling. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover their issue. The pound sterling is the world’s fourth-largest reserve currency (after the US dollar, euro, and Japanese Yen).[244] Since 1997 the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England, has been responsible for setting interest rates at the level necessary to achieve the overall inflation target for the economy that is set by the Chancellor each year.[245]
The UK service sector makes up around 79 per cent of GDP.[246] London is one of the world’s largest financial centres, ranking second in the world, behind New York City, in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[247] London also has the largest city GDP in Europe.[248] Edinburgh ranks 17th in the world, and sixth in Western Europe in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[247] Tourism is very important to the British economy; with over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom is ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world and London has the most international visitors of any city in the world.[249] The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.[250]
Following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union, the functioning of the UK internal economic market is enshrined by the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020 which ensures trade in goods and services continues without internal barriers across the four countries of the United Kingdom.[251]
The Industrial Revolution started in Britain with an initial concentration on the textile industry,[252] followed by other heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining and steelmaking.[253] British merchants, shippers and bankers developed overwhelming advantage over those of other nations allowing the UK to dominate international trade in the 19th century.[254] As other nations industrialised, coupled with economic decline after two world wars, the United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined, by degrees, throughout the 20th century. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy but accounted for only 16.7 per cent of national output in 2003.[255]
The automotive industry employs around 800,000 people, with a turnover in 2015 of £70 billion, generating £34.6 billion of exports (11.8 per cent of the UK’s total export goods). In 2015, the UK produced around 1.6 million passenger vehicles and 94,500 commercial vehicles. The UK is a major centre for engine manufacturing: in 2015 around 2.4 million engines were produced. The UK motorsport industry employs around 41,000 people, comprises around 4,500 companies and has an annual turnover of around £6 billion.[256]
The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry in the world depending upon the method of measurement and has an annual turnover of around £30 billion.[257]
BAE Systems plays a critical role in some of the world’s biggest defence aerospace projects. In the UK, the company makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter and assembles the aircraft for the Royal Air Force. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Joint Strike Fighter – the world’s largest single defence project – for which it designs and manufactures a range of components. It also manufactures the Hawk, the world’s most successful[clarification needed] jet training aircraft.[258] Airbus UK also manufactures the wings for the A400M military transporter. Rolls-Royce is the world’s second-largest aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft and it has more than 30,000 engines in service in the civil and defence sectors.
The UK space industry was worth £9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency. In 2013, the British Government pledged £60 m to the Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a «crucial stage» to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE engine to be built.
The pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.[259]
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing about 60 per cent of food needs with less than 1.6 per cent of the labour force (535,000 workers).[260] Around two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. The UK retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. It is also rich in a variety of natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica and an abundance of arable land.[261] In 2020, coronavirus lockdown measures caused the UK economy to suffer its biggest slump on record, shrinking by 20.4 per cent between April and June compared to the first three months of the year, to push it officially into recession for the first time in 11 years.[262]
The UK has an external debt of $9.6 trillion dollars,[when?] which is the second-highest in the world after the US. As a percentage of GDP, external debt is 408 per cent, which is the third-highest in the world after Luxembourg and Iceland.[263]
Science and technology
England and Scotland were leading centres of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century.[264] The United Kingdom led the Industrial Revolution from the 18th century,[252] and has continued to produce scientists and engineers credited with important advances.[265] Major theorists from the 17th and 18th centuries include Isaac Newton, whose laws of motion and illumination of gravity have been seen as a keystone of modern science;[266] from the 19th century Charles Darwin, whose theory of evolution by natural selection was fundamental to the development of modern biology, and James Clerk Maxwell, who formulated classical electromagnetic theory; and more recently Stephen Hawking, who advanced major theories in the fields of cosmology, quantum gravity and the investigation of black holes.[267]
Major scientific discoveries from the 18th century include hydrogen by Henry Cavendish;[268] from the 20th century penicillin by Alexander Fleming,[269] and the structure of DNA, by Francis Crick and others.[270] Famous British engineers and inventors of the Industrial Revolution include James Watt, George Stephenson, Richard Arkwright, Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel.[271] Other major engineering projects and applications by people from the UK include the steam locomotive, developed by Richard Trevithick and Andrew Vivian;[272] from the 19th century the electric motor by Michael Faraday, the first computer designed by Charles Babbage,[273] the first commercial electrical telegraph by William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone,[274] the incandescent light bulb by Joseph Swan,[275] and the first practical telephone, patented by Alexander Graham Bell;[276] and in the 20th century the world’s first working television system by John Logie Baird and others,[277] the jet engine by Frank Whittle, the basis of the modern computer by Alan Turing, and the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee.[278]
Scientific research and development remains important in British universities, with many establishing science parks to facilitate production and co-operation with industry.[279] Between 2004 and 2008 the UK produced 7 per cent of the world’s scientific research papers and had an 8 per cent share of scientific citations, the third and second-highest in the world (after the United States and China, respectively).[280] Scientific journals produced in the UK include Nature, the British Medical Journal and The Lancet.[281] The United Kingdom was ranked fourth in the Global Innovation Index 2020, 2021 and 2022. [282]
Transport
A radial road network totals 29,145 miles (46,904 km) of main roads, 2,173 miles (3,497 km) of motorways and 213,750 miles (344,000 km) of paved roads.[126] The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world.[283] In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.[284]
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the West Coast, East Coast, Midland, Great Western and Great Eastern), which radiate from London to the rest of the country, augmented by regional rail lines and dense commuter networks within the major cities. High Speed 1 is operationally separate from the rest of the network. The world’s first passenger railway running on steam was the Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened in 1825. Just under five years later the world’s first intercity railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, designed by George Stephenson. The network grew rapidly as a patchwork of hundreds of separate companies during the Victorian era.[285]
The UK has a railway network of 10,072 miles (16,209 km) in Great Britain and 189 miles (304 km) in Northern Ireland. Railways in Northern Ireland are operated by NI Railways, a subsidiary of state-owned Translink. In Great Britain, the British Rail network was privatised between 1994 and 1997, which was followed by a rapid rise in passenger numbers. The UK was ranked eighth among national European rail systems in the 2017 European Railway Performance Index assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety.[286] HS2 is a new high speed railway under construction linking up London, the Midlands, the North and Scotland serving over 25 stations, including eight of Britain’s 10 largest cities and connecting around 30 million.[287] Crossrail, opened in 2022, was Europe’s largest construction project with a £15 billion projected cost.[288]
Great British Railways is a planned state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. In 2014, there were 5.2 billion bus journeys in the UK, 2.4 billion of which were in London.[289] The red double-decker bus has entered popular culture as an internationally recognised icon of England.[290] The London bus network is extensive, with over 6,800 scheduled services every weekday carrying about six million passengers on over 700 different routes making it one of the most extensive bus systems in the world and the largest in Europe.[291]
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers.[292] In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport (65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport (31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport (18.9 million passengers).[292] London Heathrow Airport, located 15 miles (24 km) west of the capital, has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world[293] and is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways, as well as Virgin Atlantic.[294]
Energy
Energy mix of the United Kingdom over time
In 2006, the UK was the world’s ninth-largest consumer of energy and the 15th-largest producer.[295] The UK is home to many large energy companies, including two of the six oil and gas «supermajors» – BP and Shell.[296]
In 2013, the UK produced 914 thousand barrels per day (bbl/d) of oil and consumed 1,507 thousand bbl/d.[297] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of oil since 2005.[298] In 2010, the UK had around 3.1 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves, the largest of any EU member state.[298]
In 2009, the UK was the 13th-largest producer of natural gas in the world and the largest producer in the EU.[299] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of natural gas since 2004.[299]
Coal production played a key role in the UK economy in the 19th and 20th centuries. In the mid-1970s, 130 million tonnes of coal were produced annually, not falling below 100 million tonnes until the early 1980s. The coal industry was scaled back considerably during the 1980s and 1990s. In 2011, the UK produced 18.3 million tonnes of coal.[300] In 2005 it had proven recoverable coal reserves of 171 million tonnes.[300] The UK Coal Authority has stated that there is a potential to produce between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes of coal through underground coal gasification (UCG) or ‘fracking’,[301] and based on current UK coal consumption, such reserves could last between 200 and 400 years.[302] Environmental and social concerns have been raised over chemicals contaminating groundwater and minor earthquakes damaging homes.[303]
In the late 1990s, nuclear power plants contributed around 25 per cent of the total annual electricity generation in the UK, but this has gradually declined as old plants have been shut down and plant availability is impacted by ageing-related problems. In 2012, the UK had 16 reactors normally generating about 19 per cent of the UK’s electricity. All but one of the reactors will be retired by 2023. Unlike Germany and Japan, the UK intends to build a new generation of nuclear power plants from about 2018.[304]
The total of all renewable electricity sources provided for 38.9 per cent of the electricity generated in the UK in the third quarter of 2019, producing 28.8TWh of electricity.[305] The UK is one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind power production is the country’s fastest-growing supply; in 2019, almost 20 per cent of the UK’s total electricity was generated by wind power.[306]
Water supply and sanitation
Access to improved water supply and sanitation in the UK is universal. It is estimated that 96.7 per cent of households are connected to the sewer network.[307] According to the Environment Agency, total water abstraction for public water supply in the UK was 16,406 megalitres per day in 2007.[308]
In England and Wales water and sewerage services are provided by 10 private regional water and sewerage companies and 13 mostly smaller private «water only» companies. In Scotland, water and sewerage services are provided by a single public company, Scottish Water. In Northern Ireland water and sewerage services are also provided by a single public entity, Northern Ireland Water.[309]
Demographics
Map of population density in the UK as at the 2011 census
A census is taken simultaneously in all parts of the UK every 10 years.[310] In the 2011 census the total population of the United Kingdom was 63,181,775.[311] It is the fourth-largest in Europe (after Russia, Germany and France), the fifth-largest in the Commonwealth and the 22nd-largest in the world. In mid-2014 and mid-2015 net long-term international migration contributed more to population growth. In mid-2012 and mid-2013 natural change contributed the most to population growth.[312] Between 2001 and 2011 the population increased by an average annual rate of approximately 0.7 per cent.[311] This compares to 0.3 per cent per year in the period 1991 to 2001 and 0.2 per cent in the decade 1981 to 1991.[313] The 2011 census also showed that, over the previous 100 years, the proportion of the population aged 0–14 fell from 31 per cent to 18 per cent, and the proportion of people aged 65 and over rose from 5 to 16 per cent.[311] In 2018 the median age of the UK population was 41.7 years.[314]
England’s population in 2011 was 53 million, representing some 84 per cent of the UK total.[315] It is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with 420 people resident per square kilometre in mid-2015,[312] with a particular concentration in London and the south-east.[316] The 2011 census put Scotland’s population at 5.3 million,[317] Wales at 3.06 million and Northern Ireland at 1.81 million.[315]
In 2017 the average total fertility rate (TFR) across the UK was 1.74 children born per woman.[318] While a rising birth rate is contributing to population growth, it remains considerably below the baby boom peak of 2.95 children per woman in 1964,[319] or the high of 6.02 children born per woman in 1815,[320] below the replacement rate of 2.1, but higher than the 2001 record low of 1.63.[321] In 2011, 47.3 per cent of births in the UK were to unmarried women.[322] The Office for National Statistics published a bulletin in 2015 showing that, out of the UK population aged 16 and over, 1.7 per cent identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual (2.0 per cent of males and 1.5 per cent of females); 4.5 per cent of respondents responded with «other», «I don’t know», or did not respond.[323] The number of transgender people in the UK was estimated to be between 65,000 and 300,000 by research between 2001 and 2008.[324]
Largest urban areas of the United Kingdom (England and Wales: 2011 census built-up area;[325] Scotland: 2016 estimates settlement;[326] Northern Ireland: 2001 census urban area)[327] |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | |
 Greater London
|
1 | Greater London | 9,787,426 | London | 11 | Bristol | 617,280 | Bristol |
| 2 | West Midlands | 2,440,986 | Birmingham | 12 | Edinburgh | 512,150 | Edinburgh | |
| 3 | Greater Manchester | 2,553,379 | Manchester | 13 | Leicester | 508,916 | Leicester | |
| 4 | West Yorkshire | 1,777,934 | Leeds | 14 | Belfast | 483,418 | Belfast | |
| 5 | Greater Glasgow | 985,290 | Glasgow | 15 | Brighton & Hove | 474,485 | Brighton & Hove | |
| 6 | Liverpool | 864,122 | Liverpool | 16 | Bournemouth/ Poole | 466,266 | Bournemouth | |
| 7 | South Hampshire | 855,569 | Southampton | 17 | Cardiff | 390,214 | Cardiff | |
| 8 | Tyneside | 774,891 | Newcastle | 18 | Teesside | 376,633 | Middlesbrough | |
| 9 | Nottingham | 729,977 | Nottingham | 19 | Stoke-on-Trent | 372,775 | Stoke | |
| 10 | Sheffield | 685,368 | Sheffield | 20 | Coventry | 359,262 | Coventry |
Ethnic groups
Historically, indigenous British people were thought to be descended from the various ethnic groups that settled there before the 12th century: the Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Norse and the Normans. Welsh people could be the oldest ethnic group in the UK.[328] A 2006 genetic study shows that more than 50 per cent of England’s gene pool contains Germanic Y chromosomes.[329] Another 2005 genetic analysis indicates that «about 75 per cent of the traceable ancestors of the modern British population had arrived in the British isles by about 6,200 years ago, at the start of the British Neolithic or Stone Age», and that the British broadly share a common ancestry with the Basque people.[330][needs update] The UK has a history of non-white immigration with Liverpool having the oldest Black population in the country dating back to at least the 1730s during the period of the African slave trade. During this period it is estimated the Afro-Caribbean population of Great Britain was 10,000 to 15,000[331] which later declined due to the abolition of slavery.[332] The UK also has the oldest Chinese community in Europe, dating to the arrival of Chinese seamen in the 19th century.[333] In 1950 there were probably fewer than 20,000 non-white residents in Britain, almost all born overseas.[334] In 1951 there were an estimated 94,500 people living in Britain who had been born in South Asia, China, Africa and the Caribbean, just under 0.2 per cent of the UK population. By 1961 this number had more than quadrupled to 384,000, just over 0.7 per cent of the United Kingdom population.[335]
Since 1948 substantial immigration from Africa, the Caribbean and South Asia has been a legacy of ties forged by the British Empire.[336] Migration from new EU member states in Central and Eastern Europe since 2004 has resulted in growth in these population groups, although some of this migration has been temporary.[337] Since the 1990s, there has been substantial diversification of the immigrant population, with migrants to the UK coming from a much wider range of countries than previous waves, which tended to involve larger numbers of migrants coming from a relatively small number of countries.[338]
Academics have argued that the ethnicity categories employed in British national statistics, which were first introduced in the 1991 census, involve confusion between the concepts of ethnicity and race.[339] In 2011, 87.2 per cent of the UK population identified themselves as white, meaning 12.8 per cent of the UK population identify themselves as of one of number of ethnic minority groups.[340] In the 2001 census, this figure was 7.9 per cent of the UK population.[341] Because of differences in the wording of the census forms used in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, data on the Other White group is not available for the UK as a whole, but in England and Wales this was the fastest-growing group between the 2001 and 2011 censuses, increasing by 1.1 million (1.8 percentage points).[342] Amongst groups for which comparable data is available for all parts of the UK level, the Other Asian category increased from 0.4 per cent to 1.4 per cent of the population between 2001 and 2011, while the Mixed category rose from 1.2 per cent to 2 per cent.[340]
Ethnic diversity varies significantly across the UK. 30.4 per cent of London’s population and 37.4 per cent of Leicester’s was estimated to be non-white in 2005,[343] whereas less than 5 per cent of the populations of North East England, Wales and the South West were from ethnic minorities, according to the 2001 census.[344] In 2016, 31.4 per cent of primary and 27.9 per cent of secondary pupils at state schools in England were members of an ethnic minority.[345] The 1991 census was the first UK census to have a question on ethnic group. In the 1991 UK census 94.1 per cent of people reported themselves as being White British, White Irish or White Other with 5.9 per cent of people reporting themselves as coming from other minority groups.[346]
| Ethnic group | Population (absolute) | Population (per cent) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2011 | 2001[347] | 2011[340] | ||
| White | 54,153,898 | 55,010,359 | 92.1% | 87.1% | |
| White: Gypsy, Traveller and Irish Traveller[o] | – | 63,193 | – | 0.1% | |
| Asian and Asian British | Indian | 1,053,411 | 1,451,862 | 1.8% | 2.3% |
| Pakistani | 747,285 | 1,174,983 | 1.3% | 1.9% | |
| Bangladeshi | 283,063 | 451,529 | 0.5% | 0.7% | |
| Chinese | 247,403 | 433,150 | 0.4% | 0.7% | |
| other Asian | 247,664 | 861,815 | 0.4% | 1.4% | |
| Black, African, Caribbean and Black British[p] | 1,148,738 | 1,904,684 | 2.0% | 3.0% | |
| mixed or multiple ethnic groups | 677,117 | 1,250,229 | 1.2% | 2.0% | |
| other ethnic group | 230,615 | 580,374 | 0.4% | 0.9% | |
| Total | 58,789,194 | 63,182,178 | 100.0% | 100.0% |
Languages
The UK’s de facto official language is English.[350][351] It is estimated that 95 per cent of the UK’s population are monolingual English speakers.[352] 5.5 per cent of the population are estimated to speak languages brought to the UK as a result of relatively recent immigration.[352] South Asian languages are the largest grouping which includes Punjabi, Urdu, Bengali, Sylheti, Hindi and Gujarati.[353] According to the 2011 census, Polish has become the second-largest language spoken in England and has 546,000 speakers.[354] In 2019, some three quarters of a million people spoke little or no English.[355]
Three indigenous Celtic languages are spoken in the UK: Welsh, Irish and Scottish Gaelic. Cornish, which became extinct as a first language in the late 18th century, is subject to revival efforts and has a small group of second language speakers.[356][2] According to the 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 people (17.8 per cent).[357] In addition, it is estimated that about 200,000 Welsh speakers live in England.[358] In the 2011 census in Northern Ireland 167,487 people (10.4 per cent) stated that they had «some knowledge of Irish» (see Irish language in Northern Ireland), almost exclusively in the nationalist (mainly Catholic) population. Over 92,000 people in Scotland (just under 2 per cent of the population) had some Gaelic language ability, including 72 per cent of those living in the Outer Hebrides.[359] The number of children being taught either Welsh or Scottish Gaelic is increasing.[360] Among emigrant-descended populations some Scottish Gaelic is still spoken in Canada (principally Nova Scotia and Cape Breton Island),[361] and Welsh in Patagonia, Argentina.[362]
Scots, a language descended from early northern Middle English, has limited recognition alongside its regional variant, Ulster Scots in Northern Ireland, without specific commitments to protection and promotion.[2][363]
As of April 2020, there are said to be around 151,000 users of British Sign Language (BSL), a sign language used by deaf people, in the UK.[364] BSL was recognised as a language of England, Scotland and Wales in law in 2022.[365] It is compulsory for pupils to study a second language from the age of seven in England.[366] French and Spanish are the two most commonly taught second languages in the United Kingdom.[367] All pupils in Wales are either taught Welsh as a second language up to age 16, or are taught in Welsh as a first language.[368] Welsh was recognised as having official status in Wales in 2011.[369] Irish was recognised as having official status in Northern Ireland in 2022.[370]
Religion
Religion in England and Wales (2021 census)[371]
Other religions (0.6%)
Not stated (6.0%)
Forms of Christianity have dominated religious life in what is now the United Kingdom for more than 1,400 years.[372] Although a majority of citizens still identify with Christianity in many surveys, regular church attendance has fallen dramatically since the middle of the 20th century,[373] while immigration and demographic change have contributed to the growth of other faiths, most notably Islam.[374] This has led some commentators to variously describe the UK as a multi-faith,[375] secularised,[376] or post-Christian society.[377]
In the 2001 census, 71.6 per cent of all respondents indicated that they were Christians, with the next largest faiths being Islam (2.8 per cent), Hinduism (1.0 per cent), Sikhism (0.6 per cent), Judaism (0.5 per cent), Buddhism (0.3 per cent) and all other religions (0.3 per cent).[378] Of the respondents, 15 per cent stated that they had no religion and a further 7 per cent did not state a religious preference.[379] A Tearfund survey in 2007 showed that only one in ten Britons actually attend church weekly.[380] Between the 2001 and 2011 census, there was a 12 per cent decrease in the number of people who identified as Christian, whilst the percentage of those reporting no religious affiliation doubled. This contrasted with growth in the other main religious group categories, with the number of Muslims increasing by the most substantial margin to a total of about 5 per cent.[381] The Muslim population has increased from 1.6 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2011, making it the second-largest religious group in the UK.[382]
In a 2016 survey conducted by BSA (British Social Attitudes) on religious affiliation, 53 per cent of respondents indicated ‘no religion’, 41 per cent indicated they were Christians, followed by 6 per cent who affiliated with other religions (e.g. Islam, Hinduism, Judaism, etc.).[383] Among Christians, adherents to the Church of England constituted 15 per cent, to the Catholic Church 9 per cent, and other Christians (including Presbyterians, Methodists, other Protestants, as well as Eastern Orthodox) constituted 17 per cent.[383] Of the young people aged 18 to 24 that responded, 71 per cent said they had no religion.[383]
The Church of England is the established church in England.[384] It retains a representation in the UK Parliament, and the British monarch is its Supreme Governor.[385] In Scotland, the Church of Scotland is recognised as the national church. It is not subject to state control, and the British monarch is an ordinary member, required to swear an oath to «maintain and preserve the Protestant Religion and Presbyterian Church Government» upon his or her accession.[386][2][387] The Church in Wales was disestablished in 1920 and, because the Church of Ireland was disestablished in 1870 before the partition of Ireland, there is no established church in Northern Ireland.[388] Although there are no UK-wide data in the 2001 census on adherence to individual Christian denominations, it has been estimated that 62 per cent of Christians are Anglican, 13.5 per cent Catholic, 6 per cent Presbyterian, and 3.4 per cent Methodist, with small numbers of other Protestant denominations such as Plymouth Brethren, and Orthodox churches.[389]
In the 2021 UK census, less than half the English and Welsh population were Christian; 46.2% of the people of England and Wales said they were Christian, 37.2% that they had no religion, and 6.5% said they were Muslim.[390]
Migration
Estimated foreign-born population by country of birth from April 2007 to March 2008
| Year | Foreign born population of England and Wales | Total population [391][392][393] [394][395] |
Irish born population | Percentage of total population that was born abroad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1851 | 100,000 | 17,900,000 | 520,000 | 0.6 |
| 1861 | 150,000 | 20,100,000 | 600,000 | 0.7 |
| 1871 | 200,000 | 22,700,000 | 565,000 | 0.9 |
| 1881 | 275,000 | 26,000,000 | 560,000 | 1.1 |
| 1891 | 350,000 | 29,000,000 | 460,000 | 1.2 |
| 1901 | 475,000 | 32,500,000 | 425,000 | 1.5 |
| 1911 | 900,000 | 32,500,000 | 375,000 | 2.5 |
| 1921 | 750,000 | 37,900,000 | 365,000 | 2 |
| 1931 | 1,080,000 | 40,000,000 | 380,000 | 2.7 |
| 1951 | 1,875,000 | 43,700,000 | 470,000 | 4.3 |
| 1961 | 2,290,000 | 46,000,000 | 645,000 | 5.0 |
| 1971 | 3,100,000 | 48,700,000 | 585,000 | 6.4 |
| 1981 | 3,220,000 | 48,500,000 | 580,000 | 6.6 |
| 1991 | 3,625,000 | 49,900,000 | 570,000 | 7.3 |
| 2001 | 4,600,000 | 52,500,000 | 475,000 | 8.8 |
| 2011 | 7,500,000 | 56,000,000 | 400,000 | 13.4 |
| 2021 | 10,000,000 | 59,600,000 | 325,000 | 16.8 |
The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain.[396] Throughout the 19th century, a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to Russian Jews.[397] After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2 million left the Russian Empire by 1914. Around 120,000 settled permanently in Britain, becoming the largest ethnic minority from outside the British Isles,[398] and by 1938 this population had increased to 370,000.[399] Unable to return to Poland at the end of the Second World War, over 120,000 Polish veterans remained in the UK permanently.[400] After the war, many people immigrated from colonies and former colonies in the Caribbean and Indian subcontinent, as a legacy of empire or driven by labour shortages.[401] In 1841, only 0.25 per cent of the population of England and Wales was born in a foreign country, increasing to 1.5 per cent by 1901,[393] 2.6 per cent by 1931 and 4.4 per cent in 1951.[391]
In 2014, the immigration net increase was 318,000: immigration was at 641,000, up from 526,000 in 2013, while the number of emigrants leaving for over a year was 323,000.[402] A recent migration trend has been the arrival of workers from the new EU member states in Eastern Europe, known as the A8 countries.[337] In 2011, citizens of new EU member states made up 13 per cent of immigrants.[403] The UK applied temporary restrictions to citizens of Romania and Bulgaria, both of which joined the EU in January 2007.[404] Research conducted by the Migration Policy Institute for the Equality and Human Rights Commission suggests that, between May 2004 and September 2009, 1.5 million workers migrated from the new EU member states to the UK, most of them Polish. Many subsequently returned home, resulting in a net increase in the number of nationals of the new member states in the UK.[405] The late-2000s recession in the UK reduced the economic incentive for Poles to migrate to the UK,[406] making migration temporary and circular.[407] The proportion of foreign-born people in the UK remains slightly below that of many other European countries.[408]
Immigration is now contributing to a rising UK population,[409] with arrivals and UK-born children of migrants accounting for about half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001. According to official statistics released in 2015, 27 per cent of UK live births in 2014 were to mothers born outside the UK.[410] The ONS reported that net migration rose from 2009 to 2010 by 21 per cent to 239,000.[411]
In 2013, approximately 208,000 foreign nationals were naturalised as British citizens, the highest number since 1962. This figure fell to around 125,800 in 2014. Between 2009 and 2013, the average number of British citizenships granted annually was 195,800. The most common previous nationalities of those naturalised in 2014 were Indian, Pakistani, Filipino, Nigerian, Bangladeshi, Nepali, Chinese, South African, Polish and Somali.[412] The total number of grants of settlement, which confer permanent residence in the UK but not citizenship,[413] was approximately 154,700 in 2013, higher than the previous two years.[412]
Estimated number of British citizens living overseas by country in 2006
In 2008, the British Government introduced a points-based immigration system for immigration from outside the European Economic Area to replace former schemes, including the Scottish Government’s Fresh Talent Initiative.[414] In June 2010, a temporary limit on immigration from outside the EU was introduced, aiming to discourage applications before a permanent cap was imposed in April 2011.[415]
Emigration was an important feature of British society in the 19th century. Between 1815 and 1930, around 11.4 million people emigrated from Britain and 7.3 million from Ireland. Estimates show that by the end of the 20th century, some 300 million people of British and Irish descent were permanently settled around the globe.[416] Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad,[417][418] mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States and Canada.[417][419]
Education
Education in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter, with each country having a separate education system.
Considering the four systems together, about 38 per cent of the United Kingdom population has a university or college degree, which is the highest percentage in Europe, and among the highest percentages in the world.[420] The United Kingdom trails only the United States in terms of representation on lists of top 100 universities.[421]
A government commission’s report in 2014 found that privately educated people comprise 7 per cent of the general population of the UK but much larger percentages of the top professions, the most extreme case quoted being 71 per cent of senior judges.[422]
England
Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of local authorities.[423] Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944.[424] Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18.[425] In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science.[426] The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools,[427] while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.[428]
Scotland
Education in Scotland is the responsibility of the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Lifelong Learning, with day-to-day administration and funding of state schools the responsibility of Local Authorities. Two non-departmental public bodies have key roles in Scottish education. The Scottish Qualifications Authority is responsible for the development, accreditation, assessment and certification of qualifications other than degrees which are delivered at secondary schools, post-secondary colleges of further education and other centres.[429] Learning and Teaching Scotland provides advice, resources and staff development to education professionals.[430] Scotland first legislated for compulsory education in 1496.[431] The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4 per cent in 2016, but it has been falling slowly in recent years.[432] Scottish students who attend Scottish universities pay neither tuition fees nor graduate endowment charges, as fees were abolished in 2001 and the graduate endowment scheme was abolished in 2008.[433]
Wales
The Welsh Government’s Minister for Education has responsibility for education in Wales.[434] State funded education is available to children from the age of three whilst the legal obligation for parents to have their children educated, usually at school, begins at age five.[435] A sizeable minority of pupils are educated in Welsh whilst the rest are obliged to study the language until the age of 16.[436] Wales’ performance in Pisa testing, which compares the academic performance of adolescents around the world, has improved in recent years but remains lower than other parts of the UK.[437] In 2019, just under 60% of entrants passed their main English and math GCSEs.[438] The obligation to receive education in Wales ends at the age of 16. In 2017 and 2018, just under 80% of 16 to 18 and just under 40% of 19 to 24-year-olds were in some kind of education or training.[439]
Northern Ireland
Education in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Minister of Education, although responsibility at a local level is administered by the Education Authority which is further sub-divided into five geographical areas. The Council for the Curriculum, Examinations & Assessment (CCEA) is the body responsible for advising the government on what should be taught in Northern Ireland’s schools, monitoring standards and awarding qualifications.[440]
Healthcare
Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter and each country has its own system of private and publicly funded healthcare. Public healthcare is provided to all UK permanent residents and is mostly free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. The World Health Organization, in 2000, ranked the provision of healthcare in the United Kingdom as fifteenth best in Europe and eighteenth in the world.[441]
Since 1979 expenditure on healthcare has been increased significantly.[442] The 2018 OECD data, which incorporates in health a chunk of what in the UK is classified as social care, has the UK spending £3,121 per head.[443] In 2017 the UK spent £2,989 per person on healthcare, around the median for members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.[444]
Regulatory bodies are organised on a UK-wide basis such as the General Medical Council, the Nursing and Midwifery Council and non-governmental-based, such as the Royal Colleges. Political and operational responsibility for healthcare lies with four national executives; healthcare in England is the responsibility of the UK Government; healthcare in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Northern Ireland Executive; healthcare in Scotland is the responsibility of the Scottish Government; and healthcare in Wales is the responsibility of the Welsh Government. Each National Health Service has different policies and priorities, resulting in contrasts.[445]
Culture
The culture of the United Kingdom has been influenced by many factors including: the nation’s island status; its history as a western liberal democracy and a major power; as well as being a political union of four countries with each preserving elements of distinctive traditions, customs and symbolism. As a result of the British Empire, British influence can be observed in the language, culture and legal systems of many of its former colonies including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa and the United States; a common culture coined today as the Anglosphere. The substantial cultural influence of the United Kingdom has led to it being described as a «cultural superpower».[104][105] A global opinion poll for the BBC saw the United Kingdom ranked the third most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany and Canada) in 2013 and 2014.[446]
Literature
«British literature» refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Most British literature is in the English language. In 2005, some 206,000 books were published in the United Kingdom and in 2006 it was the largest publisher of books in the world.[447]
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest dramatist of all time.[448] The 20th-century English crime writer Agatha Christie is the best-selling novelist of all time.[449] Twelve of the top 25 of 100 novels by British writers chosen by a BBC poll of global critics were written by women; these included works by George Eliot, Virginia Woolf, Charlotte and Emily Brontë, Mary Shelley, Jane Austen, Doris Lessing and Zadie Smith.[450]
Scotland’s contributions include Arthur Conan Doyle (the creator of Sherlock Holmes), Sir Walter Scott, J. M. Barrie, Robert Louis Stevenson and the poet Robert Burns. More recently Hugh MacDiarmid and Neil M. Gunn contributed to the Scottish Renaissance, with grimmer works from Ian Rankin and Iain Banks. Scotland’s capital, Edinburgh, was UNESCO’s first worldwide City of Literature.[451]
Britain’s oldest known poem, Y Gododdin, was composed most likely in the late 6th century. It was written in Cumbric or Old Welsh and contains the earliest known reference to King Arthur.[452] The Arthurian legend was further developed by Geoffrey of Monmouth.[453] Poet Dafydd ap Gwilym (fl. 1320–1370) is regarded as one of the greatest European poets of his age.[454] Daniel Owen is credited as the first Welsh-language novelist, publishing Rhys Lewis in 1885. The best-known of the Anglo-Welsh poets are Dylan Thomas and R. S. Thomas, the latter nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1996. Leading Welsh novelists of the twentieth century include Richard Llewellyn and Kate Roberts.[455][456]
Irish writers, living at a time when all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom, include Oscar Wilde,[457] Bram Stoker[458] and George Bernard Shaw.[459] There have been many authors whose origins were from outside the United Kingdom but who moved to the UK. These include Joseph Conrad,[460] T. S. Eliot,[461] Kazuo Ishiguro,[462] Sir Salman Rushdie[463] and Ezra Pound.[464]
Philosophy
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of ‘British Empiricism’, a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and ‘Scottish Philosophy’, sometimes referred to as the ‘Scottish School of Common Sense’.[465] The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley[q] and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish «common sense» school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work Utilitarianism.[466]
Music
Various styles of music have become popular in the UK, including the indigenous folk music of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Historically, there has been exceptional Renaissance music from the Tudor period, with masses, madrigals and lute music by Thomas Tallis, John Taverner, William Byrd, Orlando Gibbons and John Dowland. After the Stuart Restoration, an English tradition of dramatic masques, anthems and airs became established, led by Henry Purcell, followed by Thomas Arne and others. The German-born composer George Frideric Handel became a naturalised British citizen in 1727, when he composed the anthem Zadok the Priest for the coronation of George II; it became the traditional ceremonial music for anointing all future monarchs. Handel’s many oratorios, such as his famous Messiah, were written in the English language.[467] Ceremonial music is also performed to mark Remembrance Sunday across the UK, including the Traditional Music played at the Cenotaph.[468] In the second half of the 19th century, as Arthur Sullivan and his librettist W. S. Gilbert wrote their popular Savoy operas, Edward Elgar’s wide range of music rivalled that of his contemporaries on the continent. Increasingly, however, composers became inspired by the English countryside and its folk music, notably Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten, a pioneer of modern British opera. Among the many post-war composers, some of the most notable have made their own personal choice of musical identity: Peter Maxwell Davies (Orkney), Harrison Birtwistle (mythological), and John Tavener (religious).[469]
The Beatles are the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed band in popular music, selling over a billion records.[470][471][472]
According to the website of The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, the term «pop music» originated in Britain in the mid-1950s to describe rock and roll’s fusion with the «new youth music».[473] The Oxford Dictionary of Music states that artists such as The Beatles and The Rolling Stones drove pop music to the forefront of popular music in the early 1960s.[474] In the following years, Britain widely occupied a part in the development of rock music, with British acts pioneering hard rock;[475] raga rock; heavy metal;[476] space rock; glam rock;[477] Gothic rock,[478] and ska punk. In addition, British acts developed psychedelic rock;[479] and punk rock.[480] Besides rock music, British acts also developed neo soul and created dubstep.[481] Pop remains the most popular music genre by sales and streams of singles, with 33.4 per cent of that market in 2016, followed by hip-hop and R&B at 24.5 per cent.[482] Rock is not far behind, at 22.6 per cent.[482] The modern UK is known to produce some of the most prominent English-speaking rappers along with the United States, including Stormzy, Kano, Yxng Bane, Ramz, Little Simz and Skepta.[483]
The Beatles have international sales of over 1 billion units and are the biggest-selling and most influential band in the history of popular music.[470][471][472][484] Other prominent British contributors to have influenced popular music over the last 50 years include The Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen, Led Zeppelin, the Bee Gees, and Elton John, all of whom have worldwide record sales of 200 million or more.[485] The Brit Awards are the BPI’s annual music awards, and some of the British recipients of the Outstanding Contribution to Music award include; The Who, David Bowie, Eric Clapton, Rod Stewart, The Police, and Fleetwood Mac (who are a British-American band).[486] More recent UK music acts that have had international success include George Michael, Oasis, Spice Girls, Radiohead, Coldplay, Arctic Monkeys, Robbie Williams, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Ed Sheeran, One Direction and Harry Styles.[487]
A number of UK cities are known for their music. Acts from Liverpool have had 54 UK chart number 1 hit singles, more per capita than any other city worldwide.[488] Glasgow’s contribution to music was recognised in 2008 when it was named a UNESCO City of Music.[489] Manchester played a role in the spread of dance music such as acid house, and from the mid-1990s, Britpop. London and Bristol are closely associated with the origins of electronic music sub-genres such as drum and bass and trip hop.[490] Birmingham became known as the birthplace of heavy metal, with the band Black Sabbath starting there in the 1960s.[491]
Visual art
The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language;[492] the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the «Young British Artists»: Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).[493]
Cinema
Alfred Hitchcock has been ranked as one of the greatest and most influential British filmmakers of all time.[494]
The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film Vertigo is considered by some critics as the best film of all time,[495] and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time.[496] Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the highest-grossing film franchises (Harry Potter and James Bond).[497] Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.[498]
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom.[499] UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions.[499] The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.[500]
Cuisine
British cuisine developed from various influences reflective of its land, settlements, arrivals of new settlers and immigrants, trade and colonialism. Celtic agriculture and animal breeding produced a wide variety of foodstuffs for indigenous Celts and Britons. Anglo-Saxon England developed meat and savoury herb stewing techniques before the practice became common in Europe. The Norman conquest introduced exotic spices into England in the Middle Ages.[501] The British Empire facilitated a knowledge of Indian cuisine with its «strong, penetrating spices and herbs». British cuisine has absorbed the cultural influence of those who have settled in Britain, producing hybrid dishes, such as chicken tikka masala.[502] Vegan and vegetarian diets have increased in Britain in recent years. In 2021, a survey found that 8% of British respondents eat a plant-based diet and 36% of respondents have a favourable view of plant-based diets.[503]
Media
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK’s publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world.[504][505][506] It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the television licence.[507] The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world’s largest of any kind.[508] It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.[509]
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV Network,[510] and Sky.[511] Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include The Times, The Guardian, The Observer, The Economist, and the Financial Times.[512] Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include Nature, New Scientist, The Spectator, Prospect, NME, Radio Times, and The Economist.
London dominates the media sector in the UK: national newspapers and television and radio are largely based there, although Manchester is also a significant national media centre. Edinburgh and Glasgow, and Cardiff, are important centres of newspaper and broadcasting production in Scotland and Wales, respectively.[513] The UK publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover of around £20 billion and employs around 167,000 people.[514] In 2015, the UK published 2,710 book titles per million inhabitants, more than any other country, much of this being exported to other Anglophone countries.[515]
In 2009, it was estimated that individuals viewed a mean of 3.75 hours of television per day and 2.81 hours of radio. In that year the main BBC public service broadcasting channels accounted for an estimated 28.4 per cent of all television viewing; the three main independent channels accounted for 29.5 per cent and the increasingly important other satellite and digital channels for the remaining 42.1 per cent.[516] Sales of newspapers have fallen since the 1970s and in 2010 41 per cent of people reported reading a daily national newspaper.[517] In 2010, 82.5 per cent of the UK population were Internet users, the highest proportion amongst the 20 countries with the largest total number of users in that year.[518]
Symbols
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack).[519] It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick’s Flag.[520] Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out.[521] The national anthem of the United Kingdom is «God Save the King», with «King» replaced with «Queen» in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain.[522] Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon’s three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside the lion and the unicorn and the dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill’s defiance of Nazi Germany.[523] A now rare personification is a character originating in the 18th century, John Bull, a portly country gentleman dressed in a top hat and tailcoat with a Union Jack waistcoat, often accompanied by a bulldog.[524]
The floral emblems of the three kingdoms are the Tudor rose for England, the thistle for Scotland and the shamrock for Northern Ireland; they are sometimes shown intertwined to represent unity.[525] The daffodil and the leek are the symbols of Wales.[526] Alternatives include the Royal Oak for England and the flax flower for Northern Ireland.[525]
Sport
Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, billiards, darts, rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in late 19th-century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, «This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum».[528][529]
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the UK.[530] England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and the Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley.[531] Each of the Home Nations (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland) has its own football association, national team and league system, and each is individually a governing member of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world.[532] The first international football match was contested by England and Scotland on 30 November 1872.[533] England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.[534]
In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK.[530] The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England and Scotland.[535][536] England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship, which is the premier international rugby union tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sports governing bodies in England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland organise and regulate the game separately.[537] Every four years, the Home Nations make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions which tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788.[538] The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board,[539] and the Ireland cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales has fielded its own national cricket team in the past. Scottish players have played for England because the Scotland cricket team does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals.[540] Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, which England won in 2019. There is a professional league championship that consists of clubs representing 17 English counties and one Welsh county.[541]
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s before spreading around the world.[542] The world’s oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, was first held in 1877 and today takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.[543]
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more drivers’ and constructors’ titles in the F1 World Championship than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone, where the British Grand Prix is held each year in July.[544]
St Andrews, Scotland, the home of golf. The standard 18 hole golf course was created at St Andrews in 1764.[545]
Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport’s home course,[546] the world’s oldest golf course is in fact Musselburgh Links’ Old Golf Course.[547] In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes.[545] The British Open—the oldest golf tournament in the world and the first major championship in golf—is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.[548]
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England.[549] A single ‘Great Britain Lions’ team competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games before 2008 when England, Scotland and Ireland began to compete as separate league nations.[550] Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.[551]
The ‘Queensberry rules’, the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing.[552] Snooker is another of the UK’s popular sporting exports, with the world championship held annually in Sheffield.[553] Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports in Northern Ireland, both in terms of participation and spectatorship, and both sports are played by Irish expatriates in the UK and the United States.[554] Shinty (or camanachd) is popular in the Scottish Highlands.[555] Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and Celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.[556]
The United Kingdom hosted the Summer Olympic Games in 1908, 1948 and 2012, with London acting as the host city on all three occasions. Birmingham hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games, the seventh time the UK has hosted the Commonwealth Games.
See also
- Outline of the United Kingdom
- Outline of England
- Outline of Northern Ireland
- Outline of Scotland
- Outline of Wales
- Index of United Kingdom-related articles
- International rankings of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the British Empire
- United Kingdom–Crown Dependencies Customs Union
Notes
- ^ There is no authorised version of the national anthem as the words are a matter of tradition; only the first verse is usually sung.[1] No statute has been enacted designating «God Save the King» as the official anthem. In the English tradition, such laws are not necessary; proclamation and usage are sufficient to make it the national anthem. «God Save the King» also serves as the Royal anthem for certain Commonwealth realms. The words King, he, him, his, used at present, are replaced by Queen, she, her when the monarch is female.
- ^ Scots, Ulster Scots, Welsh, Cornish, Scottish Gaelic and Irish are classed as regional or minority languages under the Council of Europe’s European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.[2] These include defined obligations to promote those languages.[3] See also Languages of the United Kingdom. Welsh has limited de jure official status in Wales, as well as in the provision of national government services provided for Wales.
- ^ «This category could include Polish responses from the country specific question for Scotland which would have been outputted to ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK. ‘White Africans’ may also have been recorded under ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK.»
- ^ 83.6% are White British/Irish.
- ^ Although the United Kingdom has traditionally been seen as a unitary state, an alternative description of the UK as a «union state», put forward by, among others, Vernon Bogdanor,[4] has become increasingly influential since the adoption of devolution in the 1990s.[5] A union state is considered to differ from a unitary state in that while it maintains a central authority it also recognises the authority of historic rights and infrastructures of its component parts.[6]
- ^ Some of the devolved countries, Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories issue their own sterling banknotes or currencies, or use another nation’s currency. See List of British currencies for more information.
- ^ Also in observed by the Crown Dependencies, and in the two British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (though in the latter, without daylight saving time). For further information, see Time in the United Kingdom#British territories.
- ^ Except two overseas territories: Gibraltar and the British Indian Ocean Territory
- ^ Excludes most overseas territories
- ^ The .gb domain is also reserved for the UK, but has been little used.
- ^ Usage is mixed. The Guardian and Telegraph use Britain as a synonym for the United Kingdom. Some prefer to use Britain as shorthand for Great Britain. The British Cabinet Office’s Government Digital Service style guide for use on gov.uk recommends: «Use UK and United Kingdom in preference to Britain and British (UK business, UK foreign policy, ambassador and high commissioner). But British embassy, not UK embassy.»
- ^ The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty resolved the Irish War of Independence. When it took effect one year later, it established the Irish Free State as a separate dominion within the Commonwealth of Nations. In 1927 the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 changed the name of the UK to reflect this.
- ^ The United Kingdom does not have a codified constitution but an unwritten one formed of Acts of Parliament, court judgments, traditions, and conventions.[23]
- ^ Compare to section 1 of both of the 1800 Acts of Union which reads: the Kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland shall…be united into one Kingdom, by the Name of «The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland».
- ^ The 2011 Census recorded Gypsies and Travellers as a separate ethnic group for the first time.
- ^ In the 2011 Census, for the purpose of harmonising results to make them comparable across the UK, the ONS includes individuals in Scotland who classified themselves in the «African» category (29,638 people), which in the Scottish version of the census is separate from «Caribbean or Black» (6,540 people),[348] in this «Black or Black British» category. The ONS note that «the African categories used in Scotland could potentially capture White/Asian/Other African in addition to Black identities».[349]
- ^ Berkeley is in fact Irish but was called a ‘British empiricist’ due to the territory of what is now known as the Republic of Ireland being in the UK at the time.
References
- ^ Berry, Ciara (15 January 2016). «National Anthem». The Royal Family. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d «List of declarations made with respect to treaty No. 148». Council of Europe. Retrieved 12 December 2013.
- ^ «Welsh language on GOV.UK – Content design: planning, writing and managing content – Guidance». www.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ Bradbury, Jonathan (2021). Constitutional Policy and Territorial Politics in the UK: Volume 1: Union and Devolution 1997–2012. Policy Press. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-5292-0588-6.
- ^ Leith, Murray Stewart (2012). Political Discourse and National Identity in Scotland. Edinburgh University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7486-8862-3.
- ^ Gagnon, Alain-G.; Tully, James (2001). Multinational Democracies. Cambridge University Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-521-80473-8.; Bogdanor, Vernon (1998). «Devolution: the Constitutional Aspects». In Beatson, Jack (ed.). Constitutional Reform in the United Kingdom: Practice and Principles. Oxford: Hart Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-901362-84-8.
- ^ Demographic Yearbook – Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density (PDF) (Report). United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ «Surface water and surface water change». Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ «United Kingdom». The World Factbook (2023 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- ^ «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d «World Economic Outlook database: October 2022». International Monetary Fund. October 2022.
- ^ «Inequality – Income inequality». us.oecd.org. OECD. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ «Human Development Report 2021/2022» (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «Great Britain | island, Europe». Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ United Kingdom Permanent Committee on Geographical Names (May 2017). «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». GOV.UK. 10.2 Definitions.
usually shortened to United Kingdom … The abbreviation is UK or U.K.
; «United Kingdom». Encyclopedia Britannica. - ^ a b «Countries within a country». Prime Minister’s Office. 10 January 2003. Archived from the original on 9 September 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Definition of Great Britain in English». Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
Great Britain is the name for the island that comprises England, Scotland and Wales, although the term is also used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.
- ^ «Office for National Statistics». ons.gov.uk.
- ^ «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
The full title of this country is ‘the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland’. Great Britain is made up of England, Scotland and Wales. The United Kingdom (UK) is made up of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. ‘Britain’ is used informally, usually meaning the United Kingdom.
The Channel Islands and the Isle of Man are not part of the UK. - ^ a b «Supporting the Overseas Territories». Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Julian Go (2007). «A Globalizing Constitutionalism?, Views from the Postcolony, 1945–2000». In Arjomand, Saïd Amir (ed.). Constitutionalism and political reconstruction. Brill. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-90-04-15174-1.
- ^ Ferguson 2004, p. 307.
- ^ What is the UK Constitution?, The Constitution Unit of UCL, 9 August 2018, retrieved 6 February 2020
- ^ The British Monarchy, «What is constitutional monarchy?». Retrieved 17 July 2013; «United Kingdom» CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 17 July 2013
- ^ D. Clark (17 January 2022). «Largest UK cities 2020». Statista. Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- ^ «Devolution of powers to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland». United Kingdom Government. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
In a similar way to how the government is formed from members from the two Houses of Parliament, members of the devolved legislatures nominate ministers from among themselves to comprise executives, known as the devolved administrations…
; «Country Overviews: United Kingdom». Transport Research Knowledge Centre. Archived from the original on 4 April 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010. - ^ Mathias, P. (2001). The First Industrial Nation: the Economic History of Britain, 1700–1914. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-26672-7.; Ferguson, Niall (2004). Empire: The rise and demise of the British world order and the lessons for global power. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-02328-8.
- ^ T.V. Paul; James J. Wirtz; Michel Fortmann (2005). «Great+power» Balance of Power. State University of New York Press. pp. 59, 282. ISBN 978-0-7914-6401-4. Accordingly, the great powers after the Cold War are Britain, China, France, Germany, Japan, Russia and the United States p. 59; McCourt, David (2014). Britain and World Power Since 1945: Constructing a Nation’s Role in International Politics. United States: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07221-7.
- ^ «World Population Prospects – The 2006 Revision» (PDF). UN. Retrieved 27 April 2010.; Professor Arne Björnberg, Ph.D (29 January 2018). «Euro Health Consumer Index 2017» (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ^ «IISS Military Balance 2021». The Military Balance. 121 (1): 23–29. January 2021. doi:10.1080/04597222.2021.1868791. S2CID 232050862. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ «Volume 10 — History of Greater Britain, as well England as Scotland — Series 1 — National Library of Scotland». digital.nls.uk.
- ^ Payne, Malcolm; Shardlow, Steven (2002). Social Work in the British Isles. UK: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. p. 247. ISBN 978-1-8530-2833-5.
- ^ Richmond, Ian Archibald; Millett, Martin J. Millett (2012), «Caledonia», in Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Antony; Eidinow, Esther (eds.), The Oxford Classical Dictionary (4th ed.), Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/acref/9780199545568.001.0001, ISBN 978-0-19-954556-8, retrieved 14 February 2021; «What’s the Difference Between Great Britain and the United Kingdom? | Britannica». www.britannica.com.
- ^ «Treaty of Union, 1706». Scots History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; Barnett, Hilaire; Jago, Robert (2011). Constitutional & Administrative Law (8th ed.). Abingdon: Routledge. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-415-56301-7.
- ^ «After the political union of England and Scotland in 1707, the nation’s official name became ‘Great Britain’», The American Pageant, Volume 1, Cengage Learning (2012).; «From 1707 until 1801 Great Britain was the official designation of the kingdoms of England and Scotland». The Standard Reference Work: For the Home, School and Library, Volume 3, Harold Melvin Stanford (1921); «In 1707, on the union with Scotland, ‘Great Britain’ became the official name of the British Kingdom, and so continued until the union with Ireland in 1801». United States Congressional serial set, Issue 10; Issue 3265 (1895).; Gascoigne, Bamber. «History of Great Britain (from 1707)». History World. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Cottrell, P. (2008). The Irish Civil War 1922–23. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-84603-270-7.
- ^ S. Dunn; H. Dawson (2000), An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict, Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press,
One specific problem – in both general and particular senses – is to know what to call Northern Ireland itself: in the general sense, it is not a country, or a province, or a state – although some refer to it contemptuously as a statelet: the least controversial word appears to be jurisdiction, but this might change.
; «Changes in the list of subdivision names and code elements» (PDF). ISO 3166-2. International Organization for Standardization. 15 December 2011. Retrieved 28 May 2012. - ^ «Statistical bulletin: Regional Labour Market Statistics». Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.; «13.4% Fall In Earnings Value During Recession». Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- ^ Dunn, Seamus; Dawson, Helen (2000). An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict. Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press. ISBN 978-0-7734-7711-7.; Murphy, Dervla (1979). A Place Apart. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-005030-1.
- ^ Whyte, John; FitzGerald, Garret (1991). Interpreting Northern Ireland. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-827380-6.
- ^ «Guardian Unlimited Style Guide». London: Guardian News and Media Limited. 19 December 2008. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «BBC style guide (Great Britain)». BBC News. 19 August 2002. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Government, citizens and rights. HM Government. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ New Oxford American Dictionary: «Great Britain: England, Wales, and Scotland considered as a unit. The name is also often used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.»
- ^ «When people say England, they sometimes mean Great Britain, sometimes the United Kingdom, sometimes the British Isles — but never England.» — George Mikes (1946), How To Be An Alien, Penguin ISBN 0-582-41686-8; «England OR United Kingdom (UK)? | Vocabulary | EnglishClub». www.englishclub.com. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ «Britain Meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary». dictionary.cambridge.org.; «Definition of Britain in English by Oxford Dictionaries». Oxford Dictionaries – English. Archived from the original on 26 September 2016.
- ^ a b «Britain definition and meaning». www.collinsdictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary.
- ^ «Britain – Definition for English-Language Learners». learnersdictionary.com. Merriam-Webster’s Learner’s Dictionary.
- ^ «A to Z – Style guide». www.gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ a b c Permanent Committee on Geographical Names. «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ «BBC News style guide – Names». BBC Academy. BBC. Archived from the original on 10 November 2019. Retrieved 9 November 2019.; «Alphabetical checklist». BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 26 March 2018. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ^ Bradley, Anthony Wilfred; Ewing, Keith D. (2007). Constitutional and administrative law. Vol. 1 (14th ed.). Harlow: Pearson Longman. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-4058-1207-8.
- ^ «Which of these best describes the way you think of yourself?». Northern Ireland Life and Times Survey 2010. ARK – Access Research Knowledge. 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 25 June 2020.; Schrijver, Frans (2006). Regionalism after regionalisation: Spain, France and the United Kingdom. Amsterdam University Press. pp. 275–277. ISBN 978-90-5629-428-1.
- ^ «Ancient skeleton was ‘even older’». BBC News. 30 October 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: A historical encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 973. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ Davies, John; Jenkins, Nigel; Baines, Menna; Lynch, Peredur I., eds. (2008). The Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales. Cardiff: University of Wales Press. p. 915. ISBN 978-0-7083-1953-6.
- ^ «Short Athelstan biography». BBC History. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ Mackie, J.D. (1991). A History of Scotland. London: Penguin. pp. 18–19. ISBN 978-0-14-013649-4.; Campbell, Ewan (1999). Saints and Sea-kings: The First Kingdom of the Scots. Edinburgh: Canongate. pp. 8–15. ISBN 978-0-86241-874-8.
- ^ Haigh, Christopher (1990). The Cambridge Historical Encyclopedia of Great Britain and Ireland. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-521-39552-6.
- ^ Ganshof, F.L. (1996). Feudalism. University of Toronto. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-8020-7158-3.
- ^ Chibnall, Marjorie (1999). The Debate on the Norman Conquest. Manchester University Press. pp. 115–122. ISBN 978-0-7190-4913-2.
- ^ Keen, Maurice. «The Hundred Years’ War». BBC History.
- ^ The Reformation in England and Scotland and Ireland: The Reformation Period & Ireland under Elizabeth I, Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ «British History in Depth – Wales under the Tudors». BBC History. 5 November 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- ^ Nicholls, Mark (1999). A history of the modern British Isles, 1529–1603: The two kingdoms. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 171–172. ISBN 978-0-631-19334-0.
- ^ Canny, Nicholas P. (2003). Making Ireland British, 1580–1650. Oxford University Press. pp. 189–200. ISBN 978-0-19-925905-2.
- ^ Ross, D. (2002). Chronology of Scottish History. Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-85534-380-1; Hearn, J. (2002). Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture. Edinburgh University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-902930-16-9
- ^ «English Civil Wars». Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 28 April 2013.; «Scotland and the Commonwealth: 1651–1660». Archontology.org. 14 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Lodge, Richard (2007) [1910]. The History of England – From the Restoration to the Death of William III (1660–1702). Read Books. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-4067-0897-4.
- ^ «Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy». Royal Navy History. Institute of Naval History. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Canny, Nicholas (1998). The Origins of Empire, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924676-2.
- ^ «Articles of Union with Scotland 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 19 October 2008.; «Acts of Union 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 6 January 2011.; «Treaty (act) of Union 1706». Scottish History online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ^ Library of Congress, The Impact of the American Revolution Abroad, p. 73.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. OUP Oxford. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-19-923899-6.
- ^ Sailing against slavery. BBC Devon. 2007.; Lovejoy, Paul E. (2000). Transformations in Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-521-78012-4.
- ^ «The Act of Union». Act of Union Virtual Library. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Tellier, L.-N. (2009). Urban World History: an Economic and Geographical Perspective. Quebec: PUQ. p. 463. ISBN 978-2-7605-1588-8.
- ^ Johnston, pp. 508–510.; Porter, p. 332.; Sondhaus, L. (2004). Navies in Modern World History. London: Reaktion Books. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-86189-202-7.; Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.
- ^ «The Workshop of the World». BBC History. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Benn, David Wedgwood (March 2012). «The Crimean War and its lessons for today». International Affairs. Oxford University Press. 88 (2): 387–391. JSTOR 41428613.
- ^ Nordisk familjebok (1913), s. 435 (in Swedish)
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.; Marshall, P.J. (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7.
- ^ Tompson, Richard S. (2003). Great Britain: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present. New York: Facts on File. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-8160-4474-0.
- ^ Hosch, William L. (2009). World War I: People, Politics, and Power. America at War. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-61530-048-8.
- ^ Zarembka, Paul (2013). Contradictions: Finance, Greed, and Labor Unequally Paid. Emerald Group Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78190-670-5.
- ^ Sophia A. Van Wingerden, The women’s suffrage movement in Britain, 1866–1928 (1999) ch 1.
- ^ Turner, John (1988). Britain and the First World War. London: Unwin Hyman. pp. 22–35. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ a b Westwell, I.; Cove, D. (eds) (2002). History of World War I, Volume 3. London: Marshall Cavendish. pp. 698 and 705. ISBN 978-0-7614-7231-5.
- ^ Turner, J. (1988). Britain and the First World War. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ «100 years of radio since Marconi’s big breakthrough». Ofcom. 15 June 2020. Retrieved 17 November 2020.; «The origins of BBC Local Radio». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ «1920s». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ SR&O 1921, No. 533 of 3 May 1921.
- ^ «The Anglo-Irish Treaty, 6 December 1921». CAIN. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Rubinstein, W.D. (2004). Capitalism, Culture, and Decline in Britain, 1750–1990. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-415-03719-8.
- ^ a b Edgerton, David (2012). Britain’s War Machine. www.penguin.co.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2020; «Britain’s War Machine: Weapons, Resources and Experts in the Second World War». Reviews in History. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Doenecke, Justus D.; Stoler, Mark A. (2005). Debating Franklin D. Roosevelt’s foreign policies, 1933–1945. ISBN 978-0-8476-9416-7. Retrieved 19 March 2016.; Kelly, Brian. The Four Policemen and Postwar Planning, 1943–1945: The Collision of Realist and Idealist Perspectives. Indiana University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ «The «Special Relationship» between Great Britain and the United States Began with FDR». Roosevelt Institute. 22 July 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
and the joint efforts of both powers to create a new post-war strategic and economic order through the drafting of the Atlantic Charter; the establishment of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; and the creation of the United Nations.
; «Remarks by the President Obama and Prime Minister Cameron in Joint Press Conference» (Press release). The White House. 22 April 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2018.That’s what we built after World War II. The United States and the UK designed a set of institutions – whether it was the United Nations, or the Bretton Woods structure, IMF, World Bank, NATO, across the board.
- ^ «Britain to make its final payment on World War II loan from U.S.» The New York Times. 28 December 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ Reynolds, David (17 April 2011). «Britain’s War Machine by David Edgerton – review». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Francis, Martin (1997). Ideas and policies under Labour, 1945–1951: Building a new Britain. Manchester University Press. pp. 225–233. ISBN 978-0-7190-4833-3.
- ^ Lee, Stephen J. (1996). Aspects of British political history, 1914–1995. London; New York: Routledge. pp. 173–199. ISBN 978-0-415-13103-2.
- ^ Larres, Klaus (2009). A companion to Europe since 1945. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 118. ISBN 978-1-4051-0612-2.
- ^ «Country List». Commonwealth Secretariat. 19 March 2009. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ a b «The cultural superpower: British cultural projection abroad» (PDF). British Politics Review. Norway: British Politics Society. 6 (1). Winter 2011. ISSN 1890-4505. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2018.
- ^ a b Sheridan, Greg (15 May 2010). «Cameron has chance to make UK great again». The Australian. Sydney. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ Julios, Christina (2008). Contemporary British identity: English language, migrants, and public discourse. Studies in migration and diaspora. Aldershot: Ashgate. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-7546-7158-9.
- ^ «1975: UK embraces Europe in referendum». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Wheeler, Brian; Hunt, Alex (17 December 2018). «The UK’s EU referendum: All you need to know». BBC News.
- ^ Aughey, Arthur (2005). The Politics of Northern Ireland: Beyond the Belfast Agreement. London: Routledge. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-415-32788-6.; «The troubles were over, but the killing continued. Some of the heirs to Ireland’s violent traditions refused to give up their inheritance.» Holland, Jack (1999). Hope against History: The Course of Conflict in Northern Ireland. New York: Henry Holt. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-8050-6087-4.; Elliot, Marianne (2007). The Long Road to Peace in Northern Ireland: Peace Lectures from the Institute of Irish Studies at Liverpool University. University of Liverpool Institute of Irish Studies, Liverpool University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-84631-065-2.
- ^ Dorey, Peter (1995). British politics since 1945. Making contemporary Britain. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 164–223. ISBN 978-0-631-19075-2.
- ^ Griffiths, Alan; Wall, Stuart (2007). Applied Economics (PDF) (11th ed.). Harlow: Financial Times Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-273-70822-3. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Keating, Michael (1 January 1998). «Reforging the Union: Devolution and Constitutional Change in the United Kingdom». Publius: The Journal of Federalism. 28 (1): 217–234. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubjof.a029948.
- ^ McSmith, Andy (5 July 2016). «The inside story of how Tony Blair led Britain to war in Iraq». The Independent. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Jackson, Mike (3 April 2011). «Military action alone will not save Libya». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 27 August 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom country profile». BBC News. 24 January 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ Black, Andrew (15 October 2012). «Scottish independence: Cameron and Salmond strike referendum deal». BBC News. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Scottish independence referendum – Results – BBC News». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «In stunning decision, Britain votes to leave the E.U.» The Washington Post. 24 June 2016. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- ^ «Brexit: New era for UK as it completes separation from European Union». BBC News. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Coronavirus (COVID-19) in the UK». gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 14 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus and the impact on output in the UK economy: April 2020». ons.gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Walker, Andrew (10 June 2020). «Coronavirus: UK economy could be among worst hit of leading nations, says OECD». BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Queen Elizabeth II has died». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «King Charles III, the new monarch». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary: «British Isles: a geographical term for the islands comprising Great Britain and Ireland with all their offshore islands including the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.»
- ^ a b c d e «United Kingdom». The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ a b c d Latimer Clarke Corporation Pty Ltd. «United Kingdom – Atlapedia Online». Atlapedia.com. Retrieved 26 October 2010.
- ^ ROG Learning Team (23 August 2002). «The Prime Meridian at Greenwich». Royal Museums Greenwich. Royal Museums Greenwich. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Greenwich Royal Observatory: How the Prime Meridian line is actually 100 metres away from where it was believed to be». The Independent. London. 13 August 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b Darkes, Giles (January 2008). «How long is the UK coastline?». The British Cartographic Society. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ «The Channel Tunnel». Eurotunnel. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). «An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm». BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). «Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ «Hottest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.; «Coldest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.
- ^ «English: A map of Köppen climate types in the United Kingdom (SVG version)». 9 August 2016.
- ^ «Atlantic Ocean Circulation (Gulf Stream)». UK Climate Projections. Met Office. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «UK 1971–2000 averages». Met Office. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 4 August 2007.
- ^ «UK temperature, rainfall and sunshine time series». Met Office.
- ^ «2020 EPI Results». Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «UK net zero target». Institute for Government. 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «England – Profile». BBC News. 11 February 2010.
- ^ «Scotland Facts». Scotland Online Gateway. Archived from the original on 21 June 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ Winter, Jon (1 June 2000). «The complete guide to the … Scottish Islands». The Independent. London. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Overview of Highland Boundary Fault». Gazetteer for Scotland. University of Edinburgh. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ «Great Britain’s tallest mountain is taller». Ordnance Survey. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ «Ben Nevis Weather». Ben Nevis Weather. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Profile: Wales». BBC News. 9 June 2010. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ «Geography of Northern Ireland». University of Ulster. Retrieved 22 May 2006.
- ^ Bagehot, Walter (1867). The English Constitution. London: Chapman and Hall. p. 103.
- ^ Carter, Sarah. «A Guide To the UK Legal System». University of Kent at Canterbury. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2006.
- ^ «Parliament’s authority». UK Parliament. n.d. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ «United Kingdom – Government». Commonwealth Network. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «Parliamentary Sovereignty». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b «Parliament». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «Royal Assent». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c «General elections». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «State of the parties». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Government, Prime Minister and Cabinet». Public services all in one place. Directgov. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (1 January 2012). «The Institution of Prime Minister – History of government». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Brown, Jack (2020). Dale, Iain (ed.). The Prime Ministers. Hodder & Stoughton. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-5293-1214-0.
- ^ «Minister for the Civil Service». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Woodcock, Andrew (26 July 2021). «Boris Johnson accused of ‘cynical rebranding’ after appointing himself ‘Minister for the Union’«. The Independent. Retrieved 19 July 2021.; «Minister for the Union». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 21. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 7. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (2010). Premiership: The Development, Nature and Power of the Office of the British Prime Minister. Imprint Academic. pp. 116–7. ISBN 978-1-84540-168-9.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 31. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Hackwood Frederick William: The Story of the Shire, Being the Lore, History and Evolution of English County Institutions (1851)
- ^ United Nations Economic and Social Council (August 2007). «Ninth UN Conference on the standardization of Geographical Names» (PDF). UN Statistics Division. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 December 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Barlow, I.M. (1991). Metropolitan Government. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-02099-2.
- ^ «Welcome to the national site of the Government Office Network». Government Offices. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ «A short history of London government». Greater London Authority. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- ^ Sherman, Jill; Norfolk, Andrew (5 November 2004). «Prescott’s dream in tatters as North East rejects assembly». The Times. London. Retrieved 15 February 2008.
The Government is now expected to tear up its twelve-year-old plan to create eight or nine regional assemblies in England to mirror devolution in Scotland and Wales.
(subscription required) - ^ «Elections 2017 results: Who are the new metro mayors?». BBC News. 5 May 2017. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^ «Local Authority Elections». Local Government Association. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «STV in Scotland: Local Government Elections 2007» (PDF). Political Studies Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b «Unitary authorities». Welsh Government. 2014. Archived from the original on 10 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Devenport, Mark (18 November 2005). «NI local government set for shake-up». BBC News. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ «Foster announces the future shape of local government» (Press release). Northern Ireland Executive. 13 March 2008. Archived from the original on 25 July 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ «Scots MPs attacked over fees vote». BBC News. 27 January 2004. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Taylor, Brian (1 June 1998). «Talking Politics: The West Lothian Question». BBC News. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «England-only laws ‘need majority from English MPs’«. BBC News. 25 March 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Scotland’s Parliament – powers and structures». BBC News. 8 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Keating, Michael (2 February 2021). «Taking back control? Brexit and the territorial constitution of the United Kingdom». Journal of European Public Policy. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis. 28 (4): 6–7. doi:10.1080/13501763.2021.1876156. hdl:1814/70296. S2CID 234066376.
The UK Internal Market Act gives ministers sweeping powers to enforce mutual recognition and non-discrimination across the four jurisdictions. Existing differences and some social and health matters are exempted but these are much less extensive than the exemptions permitted under the EU Internal Market provisions. Only after an amendment in the House of Lords, the Bill was amended to provide a weak and non-binding consent mechanism for amendments (equivalent to the Sewel Convention) to the list of exemptions. The result is that, while the devolved governments retain regulatory competences, these are undermined by the fact that goods and services originating in, or imported into, England can be marketed anywhere.
- ^ Kenny, Michael; McEwen, Nicola (1 March 2021). «Intergovernmental Relations and the Crisis of the Union». Political Insight. SAGE Publishing. 12 (1): 12–15. doi:10.1177/20419058211000996. S2CID 232050477.
That phase of joint working was significantly damaged by the UK Internal Market Act, pushed through by the Johnson government in December 2020…the Act diminishes the authority of the devolved institutions, and was vehemently opposed by them.
- ^ Wolffe, W James (7 April 2021). «Devolution and the Statute Book». Statute Law Review. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/slr/hmab003. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
the Internal Market Bill—a Bill that contains provisions which, if enacted, would significantly constrain, both legally and as a matter of practicality, the exercise by the devolved legislatures of their legislative competence; provisions that would be significantly more restrictive of the powers of the Scottish Parliament than either EU law or Articles 4 and 6 of the Acts of the Union…The UK Parliament passed the European Union (Withdrawal Agreement) Act 2020 and the Internal Market Act 2020 notwithstanding that, in each case, all three of the devolved legislatures had withheld consent.
- ^ Wincott, Daniel; Murray, C. R. G.; Davies, Gregory (17 May 2021). «The Anglo-British imaginary and the rebuilding of the UK’s territorial constitution after Brexit: unitary state or union state?». Territory, Politics, Governance. Abingdon/Brighton: Taylor & Francis; Regional Studies Association. 10 (5): 696–713. doi:10.1080/21622671.2021.1921613.
Taken as a whole, the Internal Market Act imposes greater restrictions upon the competences of the devolved institutions than the provisions of the EU Single Market which it replaced, in spite of pledges to use common frameworks to address these issues. Lord Hope, responsible for many of the leading judgments relating to the first two decades of devolution, regarded the legislation’s terms as deliberately confrontational: ‘this Parliament can do what it likes, but a different approach is essential if the union is to hold together’.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hayward, Katy; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen; Wincott, Daniel (2020). UK and the Internal Market, Devolution and the Union. Centre on Constitutional Change (Report). University of Edinburgh; University of Aberdeen. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 16 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael (2020). Briefing Paper. United Kingdom Internal Market Bill: Implications for Devolution (PDF) (Report). Liverpool: University of Liverpool. pp. 4–5. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen (2022). «Sleeping with an Elephant: Devolution and the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020». Law Quarterly Review. London: Sweet & Maxwell. ISSN 0023-933X. SSRN 4018581. Retrieved 4 March 2022 – via Durham Research Online.
The Act has restrictive – and potentially damaging – consequences for the regulatory capacity of the devolved legislatures…This was not the first time since the Brexit referendum that the Convention had been set aside, but it was especially notable given that the primary purpose of the legislation was to constrain the capacity of the devolved institutions to use their regulatory autonomy…in practice, it constrains the ability of the devolved institutions to make effective regulatory choices for their territories in ways that do not apply to the choices made by the UK government and parliament for the English market.
- ^ a b [185][186][187][188][189][190][191]
- ^ «Welsh assembly renamed Senedd Cymru/Welsh Parliament», BBC News, 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020
- ^ «Structure and powers of the Assembly». BBC News. 9 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «Your Executive». Northern Ireland Executive. 25 September 2015.
- ^ Burrows, N. (1999). «Unfinished Business: The Scotland Act 1998». The Modern Law Review. 62 (2): 241–260 [p. 249]. doi:10.1111/1468-2230.00203.
The UK Parliament is sovereign and the Scottish Parliament is subordinate. The White Paper had indicated that this was to be the approach taken in the legislation. The Scottish Parliament is not to be seen as a reflection of the settled will of the people of Scotland or of popular sovereignty but as a reflection of its subordination to a higher legal authority. Following the logic of this argument, the power of the Scottish Parliament to legislate can be withdrawn or overridden…
; Elliot, M. (2004). «United Kingdom: Parliamentary sovereignty under pressure». International Journal of Constitutional Law. 2 (3): 545–627, 553–554. doi:10.1093/icon/2.3.545.Notwithstanding substantial differences among the schemes, an important common factor is that the UK Parliament has not renounced legislative sovereignty in relation to the three nations concerned. For example, the Scottish Parliament is empowered to enact primary legislation on all matters, save those in relation to which competence is explicitly denied … but this power to legislate on what may be termed «devolved matters» is concurrent with the Westminster Parliament’s general power to legislate for Scotland on any matter at all, including devolved matters … In theory, therefore, Westminster may legislate on Scottish devolved matters whenever it chooses…
- ^ Walker, G. (2010). «Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Devolution, 1945–1979». Journal of British Studies. 39 (1): 117–142. doi:10.1086/644536.
- ^ Gamble, A. (2006). «The Constitutional Revolution in the United Kingdom». Publius. 36 (1): 19–35 [p. 29]. doi:10.1093/publius/pjj011.
The British parliament has the power to abolish the Scottish parliament and the Welsh assembly by a simple majority vote in both houses, but since both were sanctioned by referenda, it would be politically difficult to abolish them without the sanction of a further vote by the people. In this way, several of the constitutional measures introduced by the Blair government appear to be entrenched and not subject to a simple exercise of parliamentary sovereignty at Westminster.
- ^ Meehan, E. (1999). «The Belfast Agreement – Its Distinctiveness and Points of Cross-Fertilization in the UK’s Devolution Programme». Parliamentary Affairs. 52 (1): 19–31 [p. 23]. doi:10.1093/pa/52.1.19.
[T]he distinctive involvement of two governments in the Northern Irish problem means that Northern Ireland’s new arrangements rest upon an intergovernmental agreement. If this can be equated with a treaty, it could be argued that the forthcoming distribution of power between Westminster and Belfast has similarities with divisions specified in the written constitutions of federal states…Although the Agreement makes the general proviso that Westminster’s ‘powers to make legislation for Northern Ireland’ remains ‘unaffected’, without an explicit categorical reference to reserved matters, it may be more difficult than in Scotland or Wales for devolved powers to be repatriated. The retraction of devolved powers would not merely entail consultation in Northern Ireland backed implicitly by the absolute power of parliamentary sovereignty but also the renegotiation of an intergovernmental agreement.
- ^ «CIBC PWM Global – Introduction to The Cayman Islands». Cibc.com. 11 July 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ Rappeport, Laurie. «Cayman Islands Tourism». Washington, D.C.: USA Today Travel Tips. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Background briefing on the Crown Dependencies: Jersey, Guernsey and the Isle of Man» (PDF). Ministry of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Bosque, Maria Mut (2022). «Questioning the current status of the British Crown Dependencies». Small States & Territories. 5 (1): 55–70 – via University of Malta.
- ^ a b Loft, Philip (1 November 2022). The separation of powers in the UK’s Overseas Territories (Report). House of Commons Library.
- ^ «Overseas Territories». Gov.uk. Foreign & Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ «The World Factbook». CIA. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Overseas Territories The Ministry of Defence’s Contribution. Ministry of Defence. 1 March 2012. p. 1. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ Global Britain and the British Overseas Territories: Resetting the relationship (PDF). House of Commons Foreign Affairs Committee. 13 February 2019. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ «Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity». www.seaaroundus.org. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ^ «Partnership for Progress and Prosperity» (PDF). UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ Davison, Phil (18 August 1995). «Bermudians vote to stay British». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Gibraltar referendum result in quotes». BBC News. 8 November 2002.
- ^ «Falklands: Cameron says Argentina should respect vote». BBC News. 12 March 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons. «House of Commons – Crown Dependencies – Justice Committee». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ Fact sheet on the UK’s relationship with the Crown Dependencies – gov.uk, Ministry of Justice. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ «Profile of Jersey». States of Jersey. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2008.
The legislature passes primary legislation, which requires approval by The Queen in Council, and enacts subordinate legislation in many areas without any requirement for Royal Sanction and under powers conferred by primary legislation.
- ^ «Chief Minister to meet Channel Islands counterparts – Isle of Man Public Services» (Press release). Isle of Man Government. 29 May 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The Treaty (act) of the Union of Parliament 1706». Scottish History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ «UK Supreme Court judges sworn in». BBC News. 1 October 2009.; «Constitutional reform: A Supreme Court for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Constitutional Affairs. July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- ^ «Role of the JCPC». Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Bainham, Andrew (1998). The international survey of family law: 1996. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff. p. 298. ISBN 978-90-411-0573-8.
- ^ Adeleye, Gabriel; Acquah-Dadzie, Kofi; Sienkewicz, Thomas; McDonough, James (1999). World dictionary of foreign expressions. Waucojnda, IL: Bolchazy-Carducci. p. 371. ISBN 978-0-86516-423-9.
- ^ «The Australian courts and comparative law». Australian Law Postgraduate Network. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Court of Session – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 31 July 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «High Court of Justiciary – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 12 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «House of Lords – Practice Directions on Permission to Appeal». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 1 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Samuel Bray (2005). «Not proven: introducing a third verdict». The University of Chicago Law Review. 72 (4): 1299–1329. JSTOR 4495530.
- ^ «Crime in England and Wales, Year Ending June 2015» (PDF).
- ^ «UK prison population figures». British Government. Retrieved 10 November 2015.; Highest to Lowest. World Prison Brief. International Centre for Prison Studies.
- ^ «• England & Wales: Recorded homicides 2002–2015 – UK Statistics». Statista.
- ^ «Scottish homicide figures fall to another record low». BBC News. 29 September 2015.
- ^ «Prime Minister’s letter to Donald Tusk triggering Article 50». GOV.UK.
- ^ Swaine, Jon (13 January 2009). «Barack Obama presidency will strengthen special relationship, says Gordon Brown». The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 3 May 2011.; Kirchner, E.J.; Sperling, J. (2007). Global Security Governance: Competing Perceptions of Security in the 21st century. London: Taylor & Francis. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-415-39162-7
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons (19 February 2009). «DFID’s expenditure on development assistance». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sharp Drop in World Views of US, UK: Global Poll – GlobeScan». 4 July 2017.; «From the Outside In: G20 views of the UK before and after the EU referendum’» (PDF). British Council.; «New Zealand is Britons’ favourite country». 26 October 2020.
- ^ «Ministry of Defence». Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- ^ «Speaker addresses Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II». UK Parliament. 30 March 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «House of Commons Hansard». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2008.; «House of Commons Hansard Written Answers for 17 Jun 2013 (pt 0002)». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ UK 2005: The Official Yearbook of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Office for National Statistics. p. 89.
- ^ «Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2016» (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ «Leading European cities by gross domestic product in 2017/18». Statista. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ «Principles for Economic Regulation». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. April 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ «IMF Data – Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserve – At a Glance». Data.imf.org. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ «More About the Bank». Bank of England. n.d. Archived from the original on 12 March 2008.
- ^ «UK index of services: October 2017». Office for National Statistics. 22 December 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ a b «GFCI 27 Rank – Long Finance». www.longfinance.net. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025». PricewaterhouseCoopers. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «UNWTO Tourism Highlights, Edition 2005» (PDF). World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Bremner, Caroline (10 January 2010). «Euromonitor International’s Top City Destination Ranking». Euromonitor International. Archived from the original on 5 March 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ^ «From the Margins to the Mainstream – Government unveils new action plan for the creative industries». DCMS. 9 March 2007. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «UK Internal Market Bill». Institute for Government. 9 September 2020.; «UK Internal Market Bill becomes law». gov.uk.
- ^ a b «European Countries – United Kingdom». Europa (web portal). Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ^ Harrington, James W.; Warf, Barney (1995). Industrial location: Principles, practices, and policy. London: Routledge. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-415-10479-1.; Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2008). Western Civilization: Alternative Volume: Since 1300. Belmont, CA: Thomson Wadsworth. ISBN 978-0-495-55528-5.
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6. Retrieved 22 July 2009.; Marshall, PJ (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Hewitt, Patricia (15 July 2004). «TUC Manufacturing Conference». Department of Trade and Industry. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Motor Industry Facts 2016» (PDF). Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders. 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 October 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ Tovey, Alan (29 June 2016). «Britain’s aerospace sector soars amid fears Brexit could clip its wings». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022.
- ^ Robertson, David (9 January 2009). «The Aerospace industry has thousands of jobs in peril». The Times. London. Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2011.(subscription required)
- ^ «The Pharmaceutical sector in the UK». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «Ministerial Industry Strategy Group – Pharmaceutical Industry: Competitiveness and Performance Indicators» (PDF). Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Agriculture in the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Coal». BGS Minerals UK. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ «UK officially in recession for first time in 11 years». BBC. 12 August 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ World Development Indicators, World Bank. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for Bermuda, Chad, Cyprus, Eritrea, Greenland, Federated States of Micronesia, Monaco, Netherlands, New Caledonia and Turkmenistan.; Total Midyear Population Archived 12 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Census Bureau, International Data Base. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for Aruba, Cayman Islands, Cook Islands, Cuba, North Korea, Marshall Islands, Montenegro, Samoa, Somalia, Trinidad and Tobago and West Bank.; The World Factbook – European Union, Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 29 June 2011.; World Economic Outlook Database, April 2011, International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for the rest of the countries.; GDP (official exchange rate) Archived 24 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine, The World Factbook, United States Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for the rest of the countries.
- ^ Gascoin, J. «A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution», in Lindberg, David C. and Westman, Robert S., eds (1990), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution. Cambridge University Press. p. 248. ISBN 978-0-521-34804-1.
- ^ Reynolds, E.E.; Brasher, N.H. (1966). Britain in the Twentieth Century, 1900–1964. Cambridge University Press. p. 336. OCLC 474197910
- ^ Burtt, E.A. (2003) 1924.The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science. Mineola, NY: Courier Dover. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-486-42551-1.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. pp. 16, 30 and 46. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Jungnickel, C.; McCormmach, R. (1996). Cavendish. American Philosophical Society. ISBN 978-0-87169-220-7.
- ^ «The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1945: Sir Alexander Fleming, Ernst B. Chain, Sir Howard Florey». The Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Wilson, Arthur (1994). The Living Rock: The Story of Metals Since Earliest Times and Their Impact on Civilization. p. 203. Woodhead Publishing.
- ^ James, I. (2010). Remarkable Engineers: From Riquet to Shannon. Cambridge University Press. pp. 33–36. ISBN 978-0-521-73165-2.
- ^ Newman, M.H.A. (1948). «General Principles of the Design of All-Purpose Computing Machines». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A. 195 (1042): 271–274. Bibcode:1948RSPSA.195..271N. doi:10.1098/rspa.1948.0129.
- ^ Hubbard, Geoffrey (1965) Cooke and Wheatstone and the Invention of the Electric Telegraph, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London p. 78
- ^ Bova, Ben (2002) 1932. The Story of Light. Naperville, IL: Sourcebooks. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-4022-0009-0.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922)». Nature. 159 (4035): 297. 1947. Bibcode:1947Natur.159Q.297.. doi:10.1038/159297a0.
- ^ «John Logie Baird (1888–1946)». BBC History. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011). Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-59884-302-6.
- ^ Castells, M.; Hall, P.; Hall, P.G. (2004). Technopoles of the World: the Making of Twenty-First-Century Industrial Complexes. London: Routledge. pp. 98–100. ISBN 978-0-415-10015-1.
- ^ «Knowledge, networks and nations: scientific collaborations in the twenty-first century» (PDF). Royal Society. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2011.
- ^ McCook, Alison (2006). «Is peer review broken?». The Scientist. 20 (2): 26. Archived from the original on 16 August 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ^ WIPO. «Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition». www.wipo.int. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. Retrieved 16 November 2022.; «Global Innovation Index 2021». World Intellectual Property Organization. United Nations. Retrieved 5 March 2022.; «Release of the Global Innovation Index 2020: Who Will Finance Innovation?». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «Global Innovation Index 2019». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «RTD – Item». ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ Moran, Joe (16 November 2005). Reading the Everyday. Routledge. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-134-37216-4.
- ^ «Transport Statistics Great Britain: 2010» (PDF). Department for Transport. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 December 2010.
- ^ «German Railway Financing» (PDF). Deutschebahn.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Efficiency indicators of Railways in France» (PDF). Internationaltransportforum.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Rail industry financial information 2014–15» (PDF). Orr.gov.uk.
- ^ Sylvain Duranton; Agnès Audier; Joël Hazan; Mads Peter Langhorn; Vincent Gauche (18 April 2017). «The 2017 European Railway Performance Index». Boston Consulting Group.
- ^ «What is HS2». HS2.
- ^ «Crossrail’s giant tunnelling machines unveiled». BBC News. 2 January 2012.; Leftly, Mark (29 August 2010). «Crossrail delayed to save £1bn». The Independent on Sunday. London.
- ^ «Bus statistics». GOV.UK.
- ^ «Our Collection». icons.org.uk. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
- ^ London Buses, Transport for London. Accessed 10 May 2007.
- ^ a b «Size of Reporting Airports October 2009 – September 2010» (PDF). Civil Aviation Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ «Heathrow ‘needs a third runway’«. BBC News. 25 June 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.; «Statistics: Top 30 World airports» (PDF) (Press release). Airports Council International. July 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ «BMI being taken over by Lufthansa». BBC News. 29 October 2008. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ^ «United Kingdom Energy Profile». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 2 January 2009. Retrieved 4 November 2010.
- ^ Mason, Rowena (24 October 2009). «Let the battle begin over black gold». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 26 November 2010.; Heath, Michael (26 November 2010). «RBA Says Currency Containing Prices, Rate Level ‘Appropriate’ in Near Term». Bloomberg. New York. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ «International – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)». www.eia.gov.; «United Kingdom Crude Oil Consumption by Year (Thousand Barrels per Day)». indexmundi.com.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Oil». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Natural Gas». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 16 April 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Quick Facts Energy Overview». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Coal Reserves in the United Kingdom» (PDF). The Coal Authority. 10 April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Expert predicts ‘coal revolution’«. BBC News. 16 October 2007. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ Watts, Susan (20 March 2012). «Fracking: Concerns over gas extraction regulations». BBC News. Retrieved 9 April 2013.; «Quit fracking aboot». Friends of the Earth Scotland. Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. April 2013. Archived from the original on 14 February 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «UK Renewables Q3 2019» (PDF).
- ^ Wilson, Grant; Staffell, Iain; Godfrey, Noah (7 January 2020). «2019 saw the rise of wind power and the collapse of coal». The Independent. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ «WHO / UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme: 404 error».[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Environment Agency». Archived from the original on 25 November 2009.
- ^ «About Us». niwater.com. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Census Geography». Office for National Statistics. 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Population Estimates for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 27 March 2011. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ a b «Population Estimates for UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, Mid-2015». Office for National Statistics. 23 June 2016.
- ^ «Annual Mid-year Population Estimates, 2010» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ «World Factbook EUROPE: United Kingdom», The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- ^ a b «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Khan, Urmee (16 September 2008). «England is most crowded country in Europe». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 18 September 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ Carrell, Severin (17 December 2012). «Scotland’s population at record high». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Vital statistics: population and health reference tables». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Boseley, Sarah (14 July 2008). «The question: What’s behind the baby boom?». The Guardian. London. p. 3. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Max Roser (2014), «Total Fertility Rate around the world over the last centuries», Our World In Data, Gapminder Foundation, archived from the original on 5 July 2019, retrieved 10 December 2019
- ^ «Vital Statistics: Population and Health Reference Tables (February 2014 Update): Annual Time Series Data». ONS. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table. Eurostat (26 February 2013). Retrieved 12 July 2013.
- ^ «Sexual identity, UK: 2015 – Experimental Official Statistics on sexual identity in the UK in 2015 by region, sex, age, marital status, ethnicity and NS-SEC». Office for National Statistics. 5 October 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- ^ «Research report 27: Trans research review». equalityhumanrights.com. p. v.
- ^ «2011 Census — Built-up areas». ONS. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ «NRS – Background Information Settlements and Localities» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- ^ The UK’s major urban areas Office for National Statistics (Urban area of Belfast and connected settlements, Table 3.1, page 47)
- ^ «Welsh people could be most ancient in UK, DNA suggests». BBC News. 19 June 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Thomas, Mark G.; et al. (October 2006). «Evidence for a segregated social structure in early Anglo-Saxon England». Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 273 (1601): 2651–2657. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3627. PMC 1635457. PMID 17002951.
- ^ Owen, James (19 July 2005). «Review of ‘The Tribes of Britain’». National Geographic (Washington, D.C.).; Oppenheimer, Stephen (October 2006).«Myths of British ancestry». Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link). Prospect (London). Retrieved 5 November 2010; Henderson, Mark (23 October 2009). «Scientist – Griffin hijacked my work to make race claim about ‘British aborigines’«. The Times. London. Retrieved 26 October 2009. (subscription required) - ^ «Victoria and Albert Museum Black Presence». 13 January 2011.
- ^ Winder, Robert (2010). Bloody Foreigners: The Story of Immigration to Britain. ISBN 978-0-7481-2396-4.; Costello, Ray (2001). Black Liverpool: The Early History of Britain’s Oldest Black Community 1730–1918. Liverpool: Picton Press. ISBN 978-1-873245-07-1.
- ^ «Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – Chinese Community». Chambré Hardman Trust. Archived from the original on 24 July 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Coleman, David; Compton, Paul; Salt, John (2002). «The demographic characteristics of immigrant populations», Council of Europe, p. 505. ISBN 978-92-871-4974-9.
- ^ Roger Ballard Centre for Applied South Asian Studies. «Britain’s visible minorities: a demographic overview» (PDF).
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ a b Vargas-Silva, Carlos (10 April 2014). «Migration Flows of A8 and other EU Migrants to and from the UK». Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Vertovec, Steven (2007). «Super-diversity and its implications». Ethnic and Racial Studies. 30 (6): 1024–1054. doi:10.1080/01419870701599465. S2CID 143674657. Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 3 April 2019.; Vertovec, Steven (20 September 2005). «Opinion: Super-diversity revealed». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Aspinall, Peter J (2012). «Answer Formats in British Census and Survey Ethnicity Questions: Does Open Response Better Capture ‘Superdiversity’?». Sociology. 46 (2): 354–364. doi:10.1177/0038038511419195. S2CID 144841712.
- ^ Ballard, Roger (1996). «Negotiating race and ethnicity: Exploring the implications of the 1991 census» (PDF). Patterns of Prejudice. 30 (3): 3–33. doi:10.1080/0031322X.1996.9970192.; Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (2002). «Censuses, identity formation, and the struggle for political power». In Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (eds.). Census and Identity: The Politics of Race, Ethnicity, and Language in National Censuses. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–42.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in the United Kingdom». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2013. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ «Population Size: 7.9 per cent from a minority ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 13 February 2003. Archived from the original on 31 July 2003. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales 2011» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): London». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 23 June 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.; «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): Leicester». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ «Census 2001 – Ethnicity and religion in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ Schools, pupils and their characteristics: January 2016 (PDF) (Report). Department for Education. 28 June 2016. p. 8. SFR 20/2016.
- ^ M.S (11 December 2012). «Britain’s amazing technicolour dreamcoat». The Economist.
- ^ «Population size: 7.9 per cent from a non-White ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 8 January 2004. Archived from the original on 19 June 2004.
- ^ «Table KS201SC – Ethnic group: All people» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ «Ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ «English language – Government, citizens and rights». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 23 August 2011.
- ^ Mac Sithigh, Daithí (17 May 2018). «Official status of languages in the UK and Ireland» (PDF). Common Law World Review. Queen’s University, Belfast. 47 (1): 77–102. doi:10.1177/1473779518773642.
- ^ a b «Languages across Europe: United Kingdom». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 4 February 2013.
- ^ Carl Skutsch (2013). Encyclopedia of the World’s Minorities. pp.1261. Routledge. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ Booth, Robert (30 January 2013). «Polish becomes England’s second language». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^ «The teenagers who translate for their parents». BBC News. 23 April 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ Track, Robert Lawrence; Stockwell, Peter (2007). Language and Linguistics: The Key Concepts. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-415-41358-9. Retrieved 4 August 2019.; «Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, Strasbourg, 1.II.1995». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh language in Wales (Census 2021)». gov.wales. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ Wynn Thomas, Peter (March 2007). «Welsh today». Voices. BBC. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Scotland’s Census 2001 – Gaelic Report». General Register Office for Scotland. Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Local UK languages ‘taking off’«. BBC News. 12 February 2009.
- ^ Edwards, John R. (2010). Minority languages and group identity: cases and categories. John Benjamins. pp. 150–158. ISBN 978-90-272-1866-7. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 696. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ «Language Data – Scots». European Bureau for Lesser-Used Languages. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ Brown, Hannah (23 April 2020). «‘People are dying because of this’: Calls for UK Gov to follow Scotland with sign language interpreter at Covid-19 briefing». The Scotsman. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ «British Sign Language Act 2022, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ «Fall in compulsory language lessons». BBC News. 4 November 2004.
- ^ «GCSE results day 2021: Spanish has biggest increase in entries, but German plummets». i (newspaper). 12 August 2021.
- ^ «The School Gate for parents in Wales». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ Ainsworth, Paul (6 December 2022). «‘Historic milestone’ passed as Irish language legislation becomes law». The Irish News. Retrieved 10 December 2022.
- ^ «Religion, England and Wales: Census 2021». ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ Cannon, John, ed. (2nd edn., 2009). A Dictionary of British History. Oxford University Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-19-955037-1.
- ^ Field, Clive D. (November 2009). «British religion in numbers». BRIN Discussion Series on Religious Statistics, Discussion Paper 001. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Yilmaz, Ihsan (2005). Muslim Laws, Politics and Society in Modern Nation States: Dynamic Legal Pluralisms in England, Turkey, and Pakistan. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-0-7546-4389-0.
- ^ Brown, Callum G. (2006). Religion and Society in Twentieth-Century Britain. Harlow: Pearson Education. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-582-47289-1.
- ^ Norris, Pippa; Inglehart, Ronald (2004). Sacred and Secular: Religion and Politics Worldwide. Cambridge University Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-521-83984-6.
- ^ Fergusson, David (2004). Church, State and Civil Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-521-52959-4.
- ^ «UK Census 2001». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 22 April 2007.
- ^ «Religious Populations». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2004. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom: New Report Finds Only One in 10 Attend Church». News.adventist.org. 4 April 2007. Archived from the original on 13 December 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Philby, Charlotte (12 December 2012). «Less religious and more ethnically diverse: Census reveals a picture of Britain today». The Independent. London.
- ^ «The percentage of the population with no religion has increased in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. 4 April 2013.
- ^ a b c «British Social Attitudes: Record number of Brits with no religion». NatCen.ac.uk. 4 September 2017.
- ^ «The History of the Church of England». The Church of England. 2004. Archived from the original on 15 April 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ «Queen and Church of England». British Monarchy Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 October 2006. Retrieved 5 June 2010.
- ^ «Queen and the Church». The British Monarchy (Official Website). Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- ^ «Our structure». churchofscotland.org.uk. 22 February 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2020.
- ^ Weller, Paul (2005). Time for a Change: Reconfiguring Religion, State, and Society. London: Continuum. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-0-567-08487-3.
- ^ Peach, Ceri, «United Kingdom, a major transformation of the religious landscape», in H. Knippenberg. ed. (2005). The Changing Religious Landscape of Europe. Amsterdam: Het Spinhuis. pp. 44–58. ISBN 978-90-5589-248-8.
- ^ Russell, Rachel; Farley, Harry (29 November 2022). «Less than half of England and Wales population Christian, Census 2021 shows». BBC News.
- ^ a b Coleman, David (17 April 2013). «Immigration, Population and Ethnicity: The UK in International Perspective». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The National Archives | Exhibitions | 1901 Census | Events». www.nationalarchives.gov.uk.
- ^ a b Green, Lord Andrew. «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migration Watch UK.
- ^ «UK 2011 Census Data». National Archives. 11 December 2012. Archived from the original on 12 April 2013.; National Archives (17 December 2013). «Non-UK Born Population of England and Wales Quadrupled Between 1951 and 2011». Archived from the original on 5 January 2016.; «2011 Census analysis: Immigration Patterns of Non-UK Born Populations in England and Wales in 2011». Office for National Statistics. 17 December 2013.
- ^ «International migration, England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 8 November 2022.
- ^ Richards, Eric (2004). Britannia’s children: Emigration from England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland since 1600. London: Hambledon, p. 143. ISBN 978-1-85285-441-6.
- ^ P. Panayi (1906). P. Panayi, ‘German Immigrants in Britain, 1815–1914’ in Germans in Britain since 1500, ed P. Panayi, (London: Hambledon Press, 1996). pp. 73–112. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.
- ^ Panayi, Panikos (1996). Germans in Britain Since 1500. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.; «East End Jews». BBC.
- ^ Jews in Britain: Origin and Growth of Anglo-Jewry. p. 7.; «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migrationwatch UK.; «The Jews». Victoria County History, London, 1969 – via British History Online.
- ^ Gibney, Matthew J.; Hansen, Randall (2005). Immigration and asylum: from 1900 to the present, ABC-CLIO, p. 630. ISBN 978-1-57607-796-2
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. 2005. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2015». Office for National Statistics. 21 May 2015.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2012». Office for National Statistics. 24 May 2012.
- ^ Doward, Jamie; Temko, Ned (23 September 2007). «Home Office shuts the door on Bulgaria and Romania». The Observer. London. p. 2. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- ^ Sumption, Madeleine; Somerville, Will (January 2010). The UK’s new Europeans: Progress and challenges five years after accession (PDF). Policy Report. London: Equality and Human Rights Commission. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-84206-252-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Doward, Jamie; Rogers, Sam (17 January 2010). «Young, self-reliant, educated: portrait of UK’s eastern European migrants». The Observer. London. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ^ Hopkirk, Elizabeth (20 October 2008). «Packing up for home: Poles hit by UK’s economic downturn». London Evening Standard.
- ^ «Recession moves migration patterns». BBC News. 8 September 2009. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ Muenz, Rainer (June 2006). «Europe: Population and Migration in 2005». Migration Policy Institute. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 2 April 2007.
- ^ «Immigration and births to non-British mothers pushes British population to record high». London Evening Standard. 21 August 2008.
- ^ «Births in England and Wales: 2014». Office for National Statistics. 15 July 2015.
- ^ Travis, Alan (25 August 2011). «UK net migration rises 21 per cent». The Guardian. London.
- ^ a b Blinder, Scott (27 March 2015). «Naturalisation as a British Citizen: Concepts and Trends» (PDF). The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ Blinder, Scott (11 June 2014). «Settlement in the UK». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ «Fresh Talent: Working in Scotland». London: UK Border Agency. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Boxell, James (28 June 2010). «Tories begin consultation on cap for migrants». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ Richards (2004), pp. 6–7.
- ^ a b Sriskandarajah, Dhananjayan; Drew, Catherine (11 December 2006). «Brits Abroad: Mapping the scale and nature of British emigration». Institute for Public Policy Research. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: world overview». BBC. Retrieved 20 April 2007.; Casciani, Dominic (11 December 2006). «5.5 m Britons ‘opt to live abroad’«. BBC News. Retrieved 20 April 2007.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: Country-by-country». BBC News. 11 December 2006.
- ^ «The Most Educated Countries in the World». Yahoo Finance. 24 September 2012. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2016.; «And the World’s Most Educated Country Is…». Time. New York. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «Academic Ranking of World Universities 2015». Shanghai. 2015. Archived from the original on 30 October 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.; Quacquarelli Symonds Limited (2015). «QS World University Rankings 2015/16». London. Retrieved 21 October 2015.; «World University Rankings 2015–16». Times Higher Education. London. 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.; «Best Global Universities Rankings 2016». U.S. News & World Report. Washington, D.C. 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ «Elitist Britain?» (PDF). Social Mobility and Child Poverty Commission. 28 August 2014.; Arnett, George (28 August 2014). «Elitism in Britain – breakdown by profession». The Guardian: Datablog.
- ^ «Local Authorities». Department for Children, Schools and Families. Archived from the original on 30 December 2008. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ Gordon, J.C.B. (1981). Verbal Deficit: A Critique. London: Croom Helm. p. 44 note 18. ISBN 978-0-85664-990-5.; Section 8 (‘Duty of local education authorities to secure provision of primary and secondary schools’), Sections 35–40 (‘Compulsory attendance at Primary and Secondary Schools’) and Section 61 (‘Prohibition of fees in schools maintained by local education authorities …’), Education Act 1944.
- ^ «School leaving age». UK Government. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «England’s pupils in global top 10». BBC News. 10 December 2008.
- ^ Frankel, Hannah (3 September 2010). «Is Oxbridge still a preserve of the posh?». TES. London. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ MacLeod, Donald (9 November 2007). «Private school pupil numbers in decline». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Independent Schools Council Research». Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «About SQA». Scottish Qualifications Authority. 10 April 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «About Learning and Teaching Scotland». Learning and Teaching Scotland. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Brain drain in reverse». Scotland Online Gateway. July 2002. Archived from the original on 4 December 2007.
- ^ «Facts and Figures». SCIS. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ «MSPs vote to scrap endowment fee». BBC News. 28 February 2008.
- ^ «Education System». Welsh Government. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Nursery education for 3 and 4 year olds in Wales» (PDF). 2019.; «Compulsory school age». Practical Law. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Comisiynydd: Nifer y plant mewn addysg Gymraeg yn ‘sioc’«. BBC Cymru Fyw (in Welsh). BBC. 4 August 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.; «Welsh in education: Action Plan 2017–2021» (PDF). Welsh Government. 2017. p. 16.
- ^ «Pisa education tests: Wales improves performance». BBC News. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ Wightwick, Abbie (22 August 2019). «GCSE results 2019: Extreme concern at drop in English language results». WalesOnline. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Participation of young people in education and the labour market 2017 and 2018 (provisional)» (PDF). Welsh Government. 21 August 2019.
- ^ CCEA. «About Us – What we do». Council for the Curriculum Examinations & Assessment. Archived from the original on 5 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Haden, Angela; Campanini, Barbara, eds. (2000). The world health report 2000 – Health systems: improving performance. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156198-3. Retrieved 5 July 2011.; World Health Organization. «Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries» (PDF). New York University. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ Fisher, Peter. «The NHS from Thatcher to Blair». NHS Consultants Association. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
The Budget … was even more generous to the NHS than had been expected amounting to an annual rise of 7.4 per cent above the rate of inflation for the next five years. This would take us to 9.4 per cent of GDP spent on health ie around EU average.
- ^ «Swindells: They aren’t ‘your’ patients». Health Service Journal. 24 September 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
- ^ «How does UK healthcare spending compare with other countries?». Office of National Statistics. 29 August 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- ^ «‘Huge contrasts’ in devolved NHS». BBC News. 28 August 2008.; Triggle, Nick (2 January 2008). «NHS now four different systems». BBC News.
- ^ «BBC poll: Germany most popular country in the world». BBC. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 20 February 2018.; «World Service Global Poll: Negative views of Russia on the rise». BBC.co.uk. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ Goldfarb, Jeffrey (10 May 2006). «Bookish Britain overtakes America as top publisher». RedOrbit. Texas. Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008.
- ^ «William Shakespeare (English author)». Britannica Online encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; MSN Encarta Encyclopedia article on Shakespeare. Archived from the original on 9 February 2006. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; William Shakespeare. Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.
- ^ «Mystery of Christie’s success is solved». The Daily Telegraph. London. 19 December 2005. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ Ciabattari, Jane (December 2015). «The 25 greatest British novels». BBC Culture. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ «Edinburgh, United Kingdom, UNESCO City of Literature». Unesco. 2004. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Early Welsh poetry». BBC Wales. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ Lang, Andrew (2003) [1913]. History of English Literature from Beowulf to Swinburne. Holicong, PA: Wildside Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-8095-3229-2.
- ^ «Dafydd ap Gwilym». Academi.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
Dafydd ap Gwilym is widely regarded as one of the greatest Welsh poets of all time, and amongst the leading European poets of the Middle Ages.
- ^ «True birthplace of Wales’s literary hero». BBC News. 5 December 1999. Archived from the original on 16 March 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ «Kate Roberts: Biography». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 24 July 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ^ Varty, Anne (2014). A Preface to Oscar Wilde. Routledge. pp. 231–232. ISBN 978-1-317-89231-1.; «Oscar Wilde». Encyclopedia.com. Cengage. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Moss, Joyce (2001). British and Irish Literature and Its Times: The Victorian Era to the Present (1837–). Gale Group. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-7876-3729-3.
- ^ Holroyd, Michael (1989). Bernard Shaw, Volume 2: 1898–1918: The Pursuit of Power. Chatto & Windus. p. 384. ISBN 978-0-7011-3350-4.; «G B Shaw». Discovering Literature: 20th century. British Library. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Middleton, Tim (2006). Joseph Conrad. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-415-26851-6.
- ^ Cooper, John Xiros (2006). The Cambridge Introduction to T. S. Eliot. Cambridge University Press. p. 111. ISBN 978-1-139-45790-3.
- ^ Sim, Wai-chew (2009). Kazuo Ishiguro. Routledge. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-135-19867-1.
- ^ «Salman Rushdie». Oxford Reference. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Campbell, James (17 May 2008). «Home from home». The Guardian. Retrieved 10 December 2019.; Nadel, Ira (2004). Ezra Pound: A Literary Life. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-230-37881-0.
- ^ Fieser, James, ed. (2000). A bibliography of Scottish common sense philosophy: Sources and origins (PDF). Bristol: Thoemmes Press. Retrieved 17 December 2010.
- ^ Palmer, Michael (1999). Moral Problems in Medicine: A Practical Coursebook. Cambridge: Lutterworth Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-7188-2978-0.; Scarre, Geoffrey (1995). Utilitarianism. London: Routledge. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-415-12197-2.
- ^ «British Citizen by Act of Parliament: George Frideric Handel». UK Parliament. 20 July 2009. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Andrews, John (14 April 2006). «Handel all’inglese». Playbill. New York. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ^ «Remembrance Sunday». Department for Culture Media and Sport. Retrieved 19 April 2022.; Richards, Jeffrey (2001). Imperialism and Music: Britain 1876–1953. Manchester University Press. pp. 155–156. ISBN 0-7190-4506-1.
- ^ Iemperley, Nicholas (2002). «Great Britain». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Banfield, Stephen; Russell, Ian (2001). «England (i)». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Lewis, Geraint; Davies, Lyn; Kinney, Phyllis (2001). «Wales». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Elliott, Kenneth; Collinson, Francis; Duesenberry, Peggy (2001). «Scotland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; White, Harry; Carolan, Nicholas (2011). «Ireland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; «British 20th century composers». BBC. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ a b «1960–1969». EMI Group. Archived from the original on 25 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «Paul At Fifty». Time. New York. 8 June 1992. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009.
- ^ a b Most Successful Group The Guinness Book of Records 1999, p. 230. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ R. Middleton, et al., «Pop», Grove music online, retrieved 14 March 2010. (subscription required) Archived 13 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Pop», The Oxford Dictionary of Music, retrieved 9 March 2010.(subscription required) Archived 12 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «The Rolling Stones | Biography & History». AllMusic. Retrieved 22 July 2020.
- ^ Tom Larson (2004). History of Rock and Roll. Kendall/Hunt Pub. pp. 183–187. ISBN 978-0-7872-9969-9.
- ^ «Glam Rock». Encarta. Archived from the original on 28 August 2009. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ «NME Originals: Goth». NME. 2004. Archived from the original on 26 January 2008. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ^ «Pop/Rock » Psychedelic/Garage». AllMusic. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ «The Sex Pistols». RollingStone.com. 2001. Archived from the original on 1 February 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ Henderson, Alex (1 August 2003). British Soul. Allmusic. Retrieved 6 March 2011.; AllMusic – Dubstep Archived 23 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine «Absorbed and transfigured elements of techno, drum’n’ bass and dub»; Goldman, Vivien (31 January 2012). «Local Groove Does Good: The Story Of Trip-Hop’s Rise From Bristol». NPR.
- ^ a b «UK music single sales: genre breakdown 2016 | Statistic». Statista. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «5 U.K. Rappers Primed to Take Over America in 2018». Billboard. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «Beatles a big hit with downloads». Belfast Telegraph. 25 November 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- ^ «British rock legends get their own music title for PlayStation3 and PlayStation2» (Press release). EMI. 2 February 2009. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Khan, Urmee (17 July 2008). «Sir Elton John honoured in Ben and Jerry ice cream». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 30 July 2008.; Alleyne, Richard (19 April 2008). «Rock group Led Zeppelin to reunite». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Floyd ‘true to Barrett’s legacy’«. BBC News. 11 July 2006.; Holton, Kate (17 January 2008). «Rolling Stones sign Universal album deal». Reuters. Retrieved 26 October 2008.; Walker, Tim (12 May 2008). «Jive talkin’: Why Robin Gibb wants more respect for the Bee Gees». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2011. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Brit awards winners list 2012: every winner since 1977». The Guardian (London). Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ «Harry Styles Has Weathered the Post-Boy Band Storm Better Than Most». Consequence of Sound. 12 January 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; «10 Years of One Direction: The Story of the World’s Biggest Boy Band, Told With the Fans Who Made It Happen». Billboard. 16 July 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; Corner, Lewis (16 February 2012). «Adele, Coldplay biggest-selling UK artists worldwide in 2011». Digital Spy. Retrieved 22 March 2012.; Magliola, Anna Sky (30 November 2022). «Ed Sheeran’s career journey: From street busker to global superstar». PlanetRadio.co.uk. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ Hughes, Mark (14 January 2008). «A tale of two cities of culture: Liverpool vs Stavanger». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Glasgow gets city of music honour». BBC News. 20 August 2008. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Out of the melting pot: The origins and evolution of drum’n’bass». Red Bull. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ «Birmingham, England … the unlikely birthplace of heavy metal». www.cnn.com. Retrieved 28 February 2022.; Bentley, David (4 June 2013). «Midlands rocks! How Birmingham’s industrial heritage made it the birthplace of heavy metal». Birmingham Post. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ Tate. «Art & Language – Art Term | Tate». Tate. Retrieved 8 September 2018.
- ^ Bayley, Stephen (24 April 2010). «The startling success of Tate Modern». The Times. London. Retrieved 19 January 2011. (subscription required)
- ^ «The top 21 British directors of all time». The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ «Vertigo is named ‘greatest film of all time’«. BBC News. 2 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ «The Directors’ Top Ten Directors». British Film Institute. Archived from the original on 17 May 2012.
- ^ «Harry Potter becomes highest-grossing film franchise». The Guardian. London. 11 September 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- ^ «History of Ealing Studios». Ealing Studios. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «UK film – the vital statistics». UK Film Council. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Baftas fuel Oscars race». BBC News. 26 February 2001. Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- ^ Spencer, Colin (2003). British Food: An Extraordinary Thousand Years of History. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-13110-0.[pages needed]
- ^ «Robin Cook’s chicken tikka masala speech». The Guardian. London. 19 April 2001. Retrieved 7 September 2021.; BBC E-Cyclopedia (20 April 2001). «Chicken tikka masala: Spice and easy does it». BBC. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ «No meat please, we’re British: now a third of us approve of vegan diet». The Guardian. London. 25 December 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ a b «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 5 October 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ a b «Digital license». Prospect. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «About the BBC – What is the BBC». BBC Online. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Newswire7 (13 August 2009). «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.; «TV Licence Fee: facts & figures». BBC Press Office. April 2010. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft Word – The Work of the BBC World Service 2008–09 HC 334 FINAL.doc» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- ^ «News in your language – BBC News». Bbc.co.uk.; «BBC World Service». Facebook.com.
- ^ «Publications & Policies: The History of ITV». ITV.com. Archived from the original on 11 April 2011.
- ^ «Direct Broadcast Satellite Television». News Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «ABCs: National daily newspaper circulation September 2008». The Guardian. UK. 10 October 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ William, D. (2010). UK Cities: A Look at Life and Major Cities in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Eastbourne: Gardners Books. ISBN 978-9987-16-021-1, pp. 22, 46, 109 and 145.
- ^ «Publishing». Department of Culture, Media and Sport. Archived from the original on 5 May 2011.
- ^ «Annual Report 2015-2016» (PDF). www.internationalpublishers.org. International Publishers Association. 2016. p. 16. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Ofcom «Communication Market Report 2010», 19 August 2010, pp. 97, 164 and 191
- ^ «Social Trends 41: Lifestyles and social participation» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 24 February 2011.
- ^ «Top 20 countries with the highest number of Internet users». Internet World Stats. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- ^ «Union Jack or Union Flag?». The Flag Institute. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- ^ «college-of-arms.gov.uk». The College of Arms. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ «Welsh dragon call for Union flag». BBC News. 27 November 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Britannia on British Coins». Chard. Retrieved 25 June 2006.
- ^ Baker, Steve (2001). Picturing the Beast. University of Illinois Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-252-07030-3.
- ^ «Who is John Bull». www.loc.gov. The Library of Congress. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ a b Van Wie, Paul D. (1999). Image, History, and Politics: The Coinage of Modern Europe. New York: University Press of America. pp. 63–64. ISBN 978-0761812227.
- ^ Cleene, Marcel (2002). Compendium of Symbolic and Ritual Plants in Europe: Volume II Herbs. Ghent: Mens & Cultuur Uitgevers N.V. p. 211. ISBN 978-9077135044.
- ^ Ponsford, Matthew (19 January 2016). «Los Angeles to build world’s most expensive stadium complex». CNN. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
- ^ «Opening Ceremony of the Games of the XXX Olympiad» (PDF). Olympic.org. 27 July 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mehaffey, John. «Unparalleled Sporting History». Reuters. London. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ a b «Rugby Union ‘Britain’s Second Most Popular Sport’«. Ipsos-Mori. 22 December 2003. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Rudd, Alyson (7 April 2008). «The father of football deserves much more». The Times. London. Retrieved 29 January 2015.; «Sheffield FC: 150 years of history». FIFA. 24 October 2007. Archived from the original on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Ebner, Sarah (2 July 2013). «History and time are key to power of football, says Premier League chief». The Times. London. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mitchell, Paul (November 2005). «The first international football match». BBC Sport Scotland. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- ^ «Why is there no GB Olympics football team?». BBC Sport. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ «Six ways the town of Rugby helped change the world». BBC News. 1 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Godwin, Terry; Rhys, Chris (1981). The Guinness Book of Rugby Facts & Feats. Guinness Superlatives. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-85112214-4.
- ^ Louw, Jaco; Nesbit, Derrick (2008). The Girlfriends Guide to Rugby. Johannesburg: South Publishers. ISBN 978-0-620-39541-0.
- ^ Colin White (2010). «Projectile Dynamics in Sport: Principles and Applications». p. 222. Routledge
- ^ «About ECB». England and Wales Cricket Board. n.d. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ McLaughlin, Martyn (4 August 2009). «Howzat happen? England fields a Gaelic-speaking Scotsman in Ashes». The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Retrieved 30 December 2010.; «Uncapped Joyce wins Ashes call up». BBC Sport. 15 November 2006. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «Glamorgan». BBC South East Wales. August 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «History of Tennis». ITFtennis.com. Archived from the original on 22 March 2010. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ Morley, Gary (22 June 2011). «125 years of Wimbledon: From birth of lawn tennis to modern marvels». CNN. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «The History of British Motorsport and Motor Racing at Silverstone – The 1950s». Silverstone.co.uk. Archived from the original on 4 October 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ a b Forrest L. Richardson (2002). «Routing the Golf Course: The Art & Science That Forms the Golf Journey». p. 46. John Wiley & Sons
- ^ «Tracking the Field» (PDF). Ipsos MORI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Links plays into the record books». BBC News. 17 March 2009.
- ^ «The Open Championship – More Scottish than British». PGA Tour. Archived from the original on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Ardener, Shirley (2007). Professional identities: policy and practice in business and bureaucracy. New York: Berghahn. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-84545-054-0.
- ^ «Official Website of Rugby League World Cup 2008». Archived from the original on 16 October 2007.
- ^ Baker, Andrew (20 August 1995). «100 years of rugby league: From the great divide to the Super era». The Independent. London. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ «Encyclopædia Britannica (2006).ŷ Queensbury Rules, Britannica».
- ^ Chowdhury, Saj (22 January 2007). «China in Ding’s hands». BBC Sport. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ Gould, Joe (10 April 2007). «The ancient Irish sport of hurling catches on in America». Columbia News Service. Columbia Journalism School. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ «Shinty». Scottish Sport. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sport in Scotland». Scotland.org. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
External links
Government
- Official website of HM Government
- Official website of the British Monarchy
- The official site of the British Prime Minister’s Office
General information
Travel
- Official tourist guide to Britain
Coordinates: 55°N 3°W / 55°N 3°W
|
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|
|---|---|
|
Flag Coat of arms |
|
| Anthem: «God Save the King»[a] | |
Royal coat of arms in Scotland: |
|
|
Location of the United Kingdom (dark green) in Europe (dark grey) |
|
| Capital
and largest city |
London 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.500°N 0.117°W |
| Official language and national language |
English (de facto) |
| Regional and minority languages[b] |
|
| Ethnic groups
(2011) |
|
| Religion
(2021) |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Constituent countries |
|
| Government | Unitary[e] parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch |
Charles III |
|
• Prime Minister |
Rishi Sunak |
| Legislature | Parliament |
|
• Upper house |
House of Lords |
|
• Lower house |
House of Commons |
| Formation | |
|
• Laws in Wales Acts |
1535 and 1542 |
|
• Union of the Crowns |
24 March 1603 |
|
• Treaty of Union |
22 July 1706 |
|
• Acts of Union of England and Scotland |
1 May 1707 |
|
• Acts of Union of Great Britain and Ireland |
1 January 1801 |
|
• Irish Free State Constitution Act |
5 December 1922 |
| Area | |
|
• Total |
242,495 km2 (93,628 sq mi)[7] (78th) |
|
• Water (%) |
1.51 (2015)[8] |
| Population | |
|
• 2022 estimate |
67,791,400[9] (22nd) |
|
• 2011 census |
63,182,178[10] (22nd) |
|
• Density |
270.7/km2 (701.1/sq mi) (50th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total |
|
|
• Per capita |
|
| Gini (2019) | medium |
| HDI (2021) | very high · 18th |
| Currency | Pound sterling[f] (GBP) |
| Time zone | UTC (Greenwich Mean Time, WET) |
|
• Summer (DST) |
UTC+1 (British Summer Time, WEST) |
| [g] | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy yyyy—mm—dd (AD) |
| Driving side | left[h] |
| Calling code | +44[i] |
| ISO 3166 code | GB |
| Internet TLD | .uk[j] |
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain,[k][14] is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland.[15] It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[16] The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles.[17] Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242,495 square kilometres (93,628 sq mi), with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people.[18]
The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 1707 formed the Kingdom of Great Britain. Its union in 1801 with the Kingdom of Ireland created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Most of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922, leaving the present United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, which formally adopted that name in 1927.[l] The nearby Isle of Man, Guernsey and Jersey are not part of the UK, being Crown Dependencies with the British Government responsible for defence and international representation.[19] There are also 14 British Overseas Territories,[20] the last remnants of the British Empire which, at its height in the 1920s, encompassed almost a quarter of the world’s landmass and a third of the world’s population, and was the largest empire in history. British influence can be observed in the language, culture and the legal and political systems of many of its former colonies.[21][22]
The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy.[m][24] The capital and largest city is London, a global city and financial centre with a metropolitan area population of over 14 million. Other major cities include Birmingham, Manchester, Glasgow, Liverpool and Leeds.[25] Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland have their own devolved governments, each with varying powers.[26] The UK became the world’s first industrialised country and was the world’s foremost power during the 19th and early 20th centuries.[27] In the 21st century, the UK retains considerable economic, cultural, military, scientific, technological and political influence.[28] The United Kingdom has the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the eighth-largest by purchasing power parity. It has a high-income economy and a very high Human Development Index rating, ranking 18th in the world. It also performs well in international rankings of education, healthcare, life expectancy and human development.[29] It is a recognised nuclear state and is ranked fourth globally in military expenditure.[30] It has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since its first session in 1946.
The United Kingdom is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Council of Europe, the G7, the Group of Ten, the G20, Five Eyes, the United Nations, NATO, AUKUS, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Interpol, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). It was a member state of the European Communities (EC) and its successor, the European Union (EU), from its accession in 1973 until its withdrawal in 2020 following a referendum held in 2016.
Etymology and terminology
In 43 AD, Britannia referred to the Roman province that encompassed modern day England and Wales. Great Britain encompassed the whole island, taking in the land north of the River Forth known to the Romans as Caledonia in modern Scotland (i.e. «greater» Britain).[31] In the Middle Ages, the name «Britain» was also applied to a small part of France now known as Brittany. As a result, Great Britain (likely from the French «Grande Bretagne«) came into use to refer specifically to the island, with Brittany often referred to as «Little Britain».[32] However, that name had no official significance until 1707, when the island’s kingdoms of England and Scotland were united as the Kingdom of Great Britain.[33]
The Acts of Union 1707 declared that the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland were «United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain».[n][34] The term «United Kingdom» has occasionally been used as a description for the former Kingdom of Great Britain, although its official name from 1707 to 1800 was simply «Great Britain».[35] The Acts of Union 1800 united the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801, forming the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Following the partition of Ireland and the independence of the Irish Free State in 1922, which left Northern Ireland as the only part of the island of Ireland within the United Kingdom, the name was changed to the «United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland».[36]
Although the United Kingdom is a sovereign country, England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland are also widely referred to as countries.[37] The UK Prime Minister’s website has used the phrase «countries within a country» to describe the United Kingdom.[16] Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as «regions».[38] Northern Ireland is also referred to as a «province».[39] With regard to Northern Ireland, the descriptive name used «can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one’s political preferences».[40]
The term «Great Britain» conventionally refers to the island of Great Britain, or politically to England, Scotland and Wales in combination.[41] It is sometimes used as a loose synonym for the United Kingdom as a whole.[42] The word England is occasionally used incorrectly to refer to the United Kingdom as a whole, a mistake principally made by people from outside the UK.[43]
The term «Britain» is used both as a synonym for Great Britain,[44][45] and as a synonym for the United Kingdom.[46][45] Usage is mixed: the UK Government prefers to use the term «UK» rather than «Britain» or «British» on its own website (except when referring to embassies),[47] while acknowledging that both terms refer to the United Kingdom and that elsewhere «British government» is used at least as frequently as «United Kingdom government».[48] The UK Permanent Committee on Geographical Names recognises «United Kingdom», «UK» and «U.K.» as shortened and abbreviated geopolitical terms for the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in its toponymic guidelines; it does not list «Britain» but notes that «it is only the one specific nominal term ‘Great Britain’ which invariably excludes Northern Ireland».[48] The BBC historically preferred to use «Britain» as shorthand only for Great Britain, though the present style guide does not take a position except that «Great Britain» excludes Northern Ireland.[49]
The adjective «British» is commonly used to refer to matters relating to the United Kingdom and is used in law to refer to United Kingdom citizenship and matters to do with nationality.[50] People of the United Kingdom use several different terms to describe their national identity and may identify themselves as being British, English, Scottish, Welsh, Northern Irish, or Irish;[51] or as having a combination of different national identities.[52] The official designation for a citizen of the United Kingdom is «British citizen».[48]
History
Prior to the Treaty of Union
Stonehenge in Wiltshire is a ring of stones, each about 4 m (13 ft) high, 2 m (7 ft) wide and 25 tonnes, erected 2400–2200 BC.
Settlement by anatomically modern humans of what was to become the United Kingdom occurred in waves beginning by about 30,000 years ago.[53] By the end of the region’s prehistoric period, the population is thought to have belonged, in the main, to a culture termed Insular Celtic, comprising Brittonic Britain and Gaelic Ireland.[54]
The Roman conquest, beginning in 43 AD, and the 400-year rule of southern Britain, was followed by an invasion by Germanic Anglo-Saxon settlers, reducing the Brittonic area mainly to what was to become Wales, Cornwall and, until the latter stages of the Anglo-Saxon settlement, the Hen Ogledd (northern England and parts of southern Scotland).[55] Most of the region settled by the Anglo-Saxons became unified as the Kingdom of England in the 10th century.[56] Meanwhile, Gaelic-speakers in north-west Britain (with connections to the north-east of Ireland and traditionally supposed to have migrated from there in the 5th century)[57] united with the Picts to create the Kingdom of Scotland in the 9th century.[58]
In 1066, the Normans invaded England from northern France. After conquering England, they seized large parts of Wales, conquered much of Ireland and were invited to settle in Scotland, bringing to each country feudalism on the Northern French model and Norman-French culture.[59] The Anglo-Norman ruling class greatly influenced, but eventually assimilated with, each of the local cultures.[60] Subsequent medieval English kings completed the conquest of Wales and made unsuccessful attempts to annex Scotland. Asserting its independence in the 1320 Declaration of Arbroath, Scotland maintained its independence thereafter, albeit in near-constant conflict with England.
The English monarchs, through inheritance of substantial territories in France and claims to the French crown, were also heavily involved in conflicts in France, most notably the Hundred Years’ War, while the Kings of Scots were in an alliance with the French during this period.[61]
Early modern Britain saw religious conflict resulting from the Reformation and the introduction of Protestant state churches in each country.[62] Wales was fully incorporated into the Kingdom of England,[63] and Ireland was constituted as a kingdom in personal union with the English crown.[64] In what was to become Northern Ireland, the lands of the independent Catholic Gaelic nobility were confiscated and given to Protestant settlers from England and Scotland.[65]
In 1603, the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland were united in a personal union when James VI, King of Scots, inherited the crowns of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London; each country nevertheless remained a separate political entity and retained its separate political, legal, and religious institutions.[66]
In the mid-17th century, all three kingdoms were involved in a series of connected wars (including the English Civil War) which led to the temporary overthrow of the monarchy, with the execution of King Charles I, and the establishment of the short-lived unitary republic of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland.[67]
Although the monarchy was restored, the Interregnum along with the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and the subsequent Bill of Rights 1689 in England and Claim of Right Act 1689 in Scotland ensured that, unlike much of the rest of Europe, royal absolutism would not prevail, and a professed Catholic could never accede to the throne. The British constitution would develop on the basis of constitutional monarchy and the parliamentary system.[68] With the founding of the Royal Society in 1660, science was greatly encouraged. During this period, particularly in England, the development of naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean.[69]
Though previous attempts at uniting the two kingdoms within Great Britain in 1606, 1667, and 1689 had proved unsuccessful, the attempt initiated in 1705 led to the Treaty of Union of 1706 being agreed and ratified by both parliaments.
Kingdom of Great Britain
On 1 May 1707, the Kingdom of Great Britain was formed, the result of Acts of Union being passed by the parliaments of England and Scotland to ratify the 1706 Treaty of Union and so unite the two kingdoms.[70]
In the 18th century, cabinet government developed under Robert Walpole, in practice the first prime minister (1721–1742). A series of Jacobite Uprisings sought to remove the Protestant House of Hanover from the British throne and restore the Catholic House of Stuart. The Jacobites were finally defeated at the Battle of Culloden in 1746, after which the Scottish Highlanders were brutally suppressed. The British colonies in North America that broke away from Britain in the American War of Independence became the United States of America, recognised by Britain in 1783. British imperial ambition turned towards Asia, particularly to India.[71]
Britain played a leading part in the Atlantic slave trade, mainly between 1662 and 1807 when British or British-colonial Slave ships transported nearly 3.3 million slaves from Africa.[72] The slaves were taken to work on plantations in British possessions, principally in the Caribbean but also North America.[73] Slavery coupled with the Caribbean sugar industry had a significant role in strengthening and developing the British economy in the 18th century.[74] However, Parliament banned the trade in 1807, banned slavery in the British Empire in 1833, and Britain took a role in the movement to abolish slavery worldwide through the blockade of Africa and pressing other nations to end their trade with a series of treaties. [75]
Union with Ireland
The term «United Kingdom» became official in 1801 when the parliaments of Great Britain and Ireland each passed an Act of Union, uniting the two kingdoms and creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.[76]
After the defeat of France at the end of the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815), the United Kingdom emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century (with London the largest city in the world from about 1830).[77] Unchallenged at sea, British dominance was later described as Pax Britannica («British Peace»), a period of relative peace among the Great Powers (1815–1914) during which the British Empire became the global hegemon and adopted the role of global policeman.[78] By the time of the Great Exhibition of 1851, Britain was described as the «workshop of the world».[79] From 1853 to 1856, Britain took part in the Crimean War, allied with the Ottoman Empire in the fight against the Russian Empire,[80] participating in the naval battles of the Baltic Sea known as the Åland War in the Gulf of Bothnia and the Gulf of Finland, among others.[81] The British Empire was expanded to include India, large parts of Africa and many other territories throughout the world. Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, British dominance of much of world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many regions, such as Asia and Latin America.[82]
Domestically, political attitudes favoured free trade and laissez-faire policies and a gradual widening of the voting franchise. During the century, the population increased at a dramatic rate, accompanied by rapid urbanisation, causing significant social and economic stresses.[83] To seek new markets and sources of raw materials, the Conservative Party under Disraeli launched a period of imperialist expansion in Egypt, South Africa, and elsewhere. Canada, Australia and New Zealand became self-governing dominions.[84] After the turn of the century, Britain’s industrial dominance was challenged by Germany and the United States.[85] Social reform and home rule for Ireland were important domestic issues after 1900. The Labour Party emerged from an alliance of trade unions and small socialist groups in 1900, and suffragettes campaigned from before 1914 for women’s right to vote.[86]
World Wars and Partition of Ireland
Britain fought alongside France, Russia and (after 1917) the United States, against Germany and its allies in the First World War (1914–1918).[87] British armed forces were engaged across much of the British Empire and in several regions of Europe, particularly on the Western front.[88] The high fatalities of trench warfare caused the loss of much of a generation of men, with lasting social effects in the nation and a great disruption in the social order. After the war, Britain received the League of Nations mandate over a number of former German and Ottoman colonies. The British Empire reached its greatest extent, covering a fifth of the world’s land surface and a quarter of its population.[89] Britain had suffered 2.5 million casualties and finished the war with a huge national debt.[88]
By the mid-1920s most of the British population could listen to BBC radio programmes.[90] Experimental television broadcasts began in 1929 and the first scheduled BBC Television Service commenced in 1936.[91] The rise of Irish nationalism, and disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish Home Rule, led eventually to the partition of the island in 1921.[92] The Irish Free State became independent, initially with Dominion status in 1922, and unambiguously independent in 1931. Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom.[93] The 1928 Act widened suffrage by giving women electoral equality with men. A wave of strikes in the mid-1920s culminated in the General Strike of 1926. Britain had still not recovered from the effects of the war when the Great Depression (1929–1932) occurred. This led to considerable unemployment and hardship in the old industrial areas, as well as political and social unrest in the 1930s, with rising membership in communist and socialist parties. A coalition government was formed in 1931.[94]
Nonetheless, «Britain was a very wealthy country, formidable in arms, ruthless in pursuit of its interests and sitting at the heart of a global production system.»[95] After Nazi Germany invaded Poland, Britain entered the Second World War by declaring war on Germany in 1939. Winston Churchill became prime minister and head of a coalition government in 1940. Despite the defeat of its European allies in the first year of the war, Britain and its Empire continued the fight alone against Germany. Churchill engaged industry, scientists, and engineers to advise and support the government and the military in the prosecution of the war effort.[95] In 1940, the Royal Air Force defeated the German Luftwaffe in a struggle for control of the skies in the Battle of Britain. Urban areas suffered heavy bombing during the Blitz. The Grand Alliance of Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union formed in 1941 leading the Allies against the Axis powers. There were eventual hard-fought victories in the Battle of the Atlantic, the North Africa campaign and the Italian campaign. British forces played an important role in the Normandy landings of 1944 and the liberation of Europe, achieved with its allies the United States, the Soviet Union and other Allied countries. The British Army led the Burma campaign against Japan and the British Pacific Fleet fought Japan at sea. British scientists contributed to the Manhattan Project which led to the surrender of Japan.
Postwar 20th century
During the Second World War, the UK was one of the Big Three powers (along with the U.S. and the Soviet Union) who met to plan the post-war world;[96] it was an original signatory to the Declaration by United Nations. After the war, the UK became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council and worked closely with the United States to establish the IMF, World Bank and NATO.[97] The war left the UK severely weakened and financially dependent on the Marshall Plan,[98] but it was spared the total war that devastated eastern Europe.[99] In the immediate post-war years, the Labour government initiated a radical programme of reforms, which had a significant effect on British society in the following decades.[100] Major industries and public utilities were nationalised, a welfare state was established, and a comprehensive, publicly funded healthcare system, the National Health Service, was created.[101] The rise of nationalism in the colonies coincided with Britain’s now much-diminished economic position, so that a policy of decolonisation was unavoidable. Independence was granted to India and Pakistan in 1947.[102] Over the next three decades, most colonies of the British Empire gained their independence, with all those that sought independence supported by the UK, during both the transition period and afterwards. Many became members of the Commonwealth of Nations.[103]
The UK was the third country to develop a nuclear weapons arsenal (with its first atomic bomb test, Operation Hurricane, in 1952), but the new post-war limits of Britain’s international role were illustrated by the Suez Crisis of 1956. The international spread of the English language ensured the continuing international influence of its literature and culture.[104][105] As a result of a shortage of workers in the 1950s, the government encouraged immigration from Commonwealth countries. In the following decades, the UK became a more multi-ethnic society than before.[106] Despite rising living standards in the late 1950s and 1960s, the UK’s economic performance was less successful than many of its main competitors such as France, West Germany and Japan.
Leaders of EU states in 2007. The UK entered the EEC in 1973. In a 1975 referendum 67% voted to stay in it;[107] in 2016 52% voted to leave the EU.[108]
In the decades-long process of European integration, the UK was a founding member of the alliance called the Western European Union, established with the London and Paris Conferences in 1954. In 1960 the UK was one of the seven founding members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), but in 1973 it left to join the European Communities (EC). When the EC became the European Union (EU) in 1992, the UK was one of the 12 founding member states. The Treaty of Lisbon, signed in 2007, forms the constitutional basis of the European Union since then.
From the late 1960s, Northern Ireland suffered communal and paramilitary violence (sometimes affecting other parts of the UK) conventionally known as the Troubles. It is usually considered to have ended with the Belfast «Good Friday» Agreement of 1998.[109]
Following a period of widespread economic slowdown and industrial strife in the 1970s, the Conservative government of the 1980s under Margaret Thatcher initiated a radical policy of monetarism, deregulation, particularly of the financial sector (for example, the Big Bang in 1986) and labour markets, the sale of state-owned companies (privatisation), and the withdrawal of subsidies to others.[110] From 1984, the economy was helped by the inflow of substantial North Sea oil revenues.[111]
Around the end of the 20th century, there were major changes to the governance of the UK with the establishment of devolved administrations for Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.[112] The statutory incorporation followed acceptance of the European Convention on Human Rights. The UK is still a key global player diplomatically and militarily. It plays leading roles in the UN and NATO.
21st century
The UK broadly supported the United States’ approach to the «war on terror» in the early years of the 21st century.[113] Controversy surrounded some of Britain’s overseas military deployments, particularly in Afghanistan and Iraq.[114]
The 2008 global financial crisis severely affected the UK economy. The Cameron–Clegg coalition government of 2010 introduced austerity measures intended to tackle the substantial public deficits which resulted.[115] The devolved Scottish Government and UK Government agreed for a referendum to be held on Scottish independence in 2014.[116] This referendum resulted in the electorate in Scotland voting by 55.3 to 44.7% for Scotland to remain part of the United Kingdom.[117]
In 2016, 51.9 per cent of voters in the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union.[118] The UK left the EU on 31 January 2020 and completed its withdrawal in full at the end of that year.[119]
The COVID-19 pandemic had a severe impact on the UK’s economy, caused major disruptions to education and had far-reaching impacts on society and politics in 2020 and 2021.[120][121][122]
On 8 September 2022, Elizabeth II, the longest-living and longest-reigning British monarch, died at the age of 96.[123] Upon the Queen’s death, her eldest child Charles, Prince of Wales, immediately acceded to the British throne as King Charles III.[124]
Geography
The total area of the United Kingdom is approximately 244,820 square kilometres (94,530 sq mi). The country occupies the major part of the British Isles[125] archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland and some smaller surrounding islands. It lies between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea with the southeast coast coming within 22 miles (35 km) of the coast of northern France, from which it is separated by the English Channel.[126]
In 1993 10 per cent of the UK was forested, 46 per cent used for pastures and 25 per cent cultivated for agriculture.[127] The Royal Greenwich Observatory in London was chosen as the defining point of the Prime Meridian[128] in Washington, DC, in 1884, although due to more accurate modern measurement the meridian actually lies 100 metres to the east of the observatory.[129]
The United Kingdom lies between latitudes 49° and 61° N, and longitudes 9° W and 2° E. Northern Ireland shares a 224-mile (360 km) land boundary with the Republic of Ireland.[126] The coastline of Great Britain is 11,073 miles (17,820 km) long.[130] It is connected to continental Europe by the Channel Tunnel, which at 31 miles (50 km) (24 miles (38 km) underwater) is the longest underwater tunnel in the world.[131]
The UK contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Celtic broadleaf forests, English Lowlands beech forests, North Atlantic moist mixed forests, and Caledon conifer forests.[132] The country had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 1.65/10, ranking it 161th globally out of 172 countries.[133]
Climate
Most of the United Kingdom has a temperate climate, with generally cool temperatures and plentiful rainfall all year round.[126] The temperature varies with the seasons seldom dropping below 0 °C (32 °F) or rising above 30 °C (86 °F).[134] Some parts, away from the coast, of upland England, Wales, Northern Ireland and most of Scotland, experience a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc). Higher elevations in Scotland experience a continental subarctic climate (Dfc) and the mountains experience a tundra climate (ET).[135]
The prevailing wind is from the southwest and bears frequent spells of mild and wet weather from the Atlantic Ocean,[126] although the eastern parts are mostly sheltered from this wind since the majority of the rain falls over the western regions the eastern parts are therefore the driest. Atlantic currents, warmed by the Gulf Stream, bring mild winters; especially in the west where winters are wet and even more so over high ground. Summers are warmest in the southeast of England and coolest in the north. Heavy snowfall can occur in winter and early spring on high ground, and occasionally settles to great depth away from the hills.[136]
The average total annual sunshine in the United Kingdom is 1339.7 hours, which is just under 30% of the maximum possible (The maximum hours of sunshine possible in one year is approximately 4476 hours).[137] The hours of sunshine vary from 1200 to about 1580 hours per year, and since 1996 the UK has been and still is receiving above the 1981 to 2010 average hours of sunshine[138]
United Kingdom is ranked 4 out of 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index.[139] A law has been passed that UK greenhouse gas emissions will be net zero by 2050.[140]
Topography
England accounts for just over half (53 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 130,395 square kilometres (50,350 sq mi).[141] Most of the country consists of lowland terrain,[127] with more upland and some mountainous terrain northwest of the Tees–Exe line; including the Lake District, the Pennines, Exmoor and Dartmoor. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber. England’s highest mountain is Scafell Pike (978 metres (3,209 ft)) in the Lake District.
Scotland accounts for just under one-third (32 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 78,772 square kilometres (30,410 sq mi).[142] This includes nearly 800 islands,[143] predominantly west and north of the mainland; notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its topography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault – a geological rock fracture – which traverses Scotland from Arran in the west to Stonehaven in the east.[144] The fault separates two distinctively different regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the Lowlands to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland’s mountainous land, including Ben Nevis which at 1,345 metres (4,413 ft)[145] is the highest point in the British Isles.[146] Lowland areas – especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth known as the Central Belt – are flatter and home to most of the population including Glasgow, Scotland’s largest city, and Edinburgh, its capital and political centre, although upland and mountainous terrain lies within the Southern Uplands.
Wales accounts for less than one-tenth (9 per cent) of the total area of the UK, covering 20,779 square kilometres (8,020 sq mi).[147] Wales is mostly mountainous, though South Wales is less mountainous than North and mid Wales. The main population and industrial areas are in South Wales, consisting of the coastal cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, and the South Wales Valleys to their north. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia and include Snowdon (Welsh: Yr Wyddfa) which, at 1,085 metres (3,560 ft), is the highest peak in Wales.[127] Wales has over 2,704 kilometres (1,680 miles) of coastline.[130] Several islands lie off the Welsh mainland, the largest of which is Anglesey (Ynys Môn) in the north-west.
Northern Ireland, separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea and North Channel, has an area of 14,160 square kilometres (5,470 sq mi) and is mostly hilly. It includes Lough Neagh which, at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), is the largest lake in the British Isles by area.[148] The highest peak in Northern Ireland is Slieve Donard in the Mourne Mountains at 852 metres (2,795 ft).[127]
Government and politics
The United Kingdom is a unitary state under a constitutional monarchy. King Charles III is the monarch and head of state of the UK, as well as 14 other independent countries. These 15 countries are sometimes referred to as «Commonwealth realms». The monarch has «the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, and the right to warn».[149] The Constitution of the United Kingdom is uncodified and consists mostly of a collection of disparate written sources, including statutes, judge-made case law and international treaties, together with constitutional conventions.[150] The UK Parliament can carry out constitutional reform by passing acts of parliament, and thus has the political power to change or abolish almost any written or unwritten element of the constitution. No sitting parliament can pass laws that future parliaments cannot change.[151]
The UK is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy.[152] The Parliament of the United Kingdom is sovereign.[153] It is made up of the House of Commons, the House of Lords and the Crown.[154] The main business of parliament takes place in the two houses,[154] but royal assent is required for a bill to become an act of parliament (law).[155]
For general elections (elections to the House of Commons), the UK is divided into 650 constituencies, each of which is represented by a member of Parliament (MP).[156] MPs hold office for up to five years and are always up for re-election in general elections.[156] The Conservative Party, Labour Party and Scottish National Party are, respectively, the current first, second and third largest parties (by number of MPs) in the House of Commons.[157]
The prime minister is the head of government in the United Kingdom.[158] Nearly all prime ministers have served as First Lord of the Treasury[159] and all prime ministers have continuously served as First Lord of the Treasury since 1905,[160] Minister for the Civil Service since 1968[161] and Minister for the Union since 2019.[162] In modern times, the prime minister is, by constitutional convention, an MP.[163] The prime minister is appointed by the monarch[164] and their appointment is governed by constitutional conventions.[156] However, they are normally the leader of the political party with the most seats in the House of Commons[165] and hold office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the House of Commons.[163]
The prime minister not only has statutory functions (alongside other ministers),[166] but is the monarch’s principal adviser[167] and it is for them to advise the monarch on the exercise of the royal prerogative in relation to government.[163] In particular, the prime minister recommends the appointment of ministers[163] and chairs the Cabinet.[168]
Administrative divisions
The geographical division of the United Kingdom into counties or shires began in England and Scotland in the early Middle Ages and was complete throughout Great Britain and Ireland by the early Modern Period.[169] Administrative arrangements were developed separately in each country of the United Kingdom, with origins which often predated the formation of the United Kingdom. Modern local government by elected councils, partly based on the ancient counties, was introduced separately: in England and Wales in a 1888 act, Scotland in a 1889 act and Ireland in a 1898 act, meaning there is no consistent system of administrative or geographic demarcation across the United Kingdom.[170]
Until the 19th century there was little change to those arrangements, but there has since been a constant evolution of role and function.[171]
The organisation of local government in England is complex, with the distribution of functions varying according to local arrangements. The upper-tier subdivisions of England are the nine regions, now used primarily for statistical purposes.[172] One region, Greater London, has had a directly elected assembly and mayor since 2000 following popular support for the proposal in a referendum.[173] It was intended that other regions would also be given their own elected regional assemblies, but a proposed assembly in the North East region was rejected by a referendum in 2004.[174] Since 2011, ten combined authorities have been established in England. Eight of these have elected mayors, the first elections for which took place on 4 May 2017.[175] Below the regional tier, some parts of England have county councils and district councils and others have unitary authorities, while London consists of 32 London boroughs and the City of London. Councillors are elected by the first-past-the-post system in single-member wards or by the multi-member plurality system in multi-member wards.[176]
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 council areas, with wide variation in both size and population. The cities of Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen and Dundee are separate council areas, as is the Highland Council, which includes a third of Scotland’s area but only just over 200,000 people. Local councils are made up of elected councillors, of whom there are 1,223;[177] they are paid a part-time salary. Elections are conducted by single transferable vote in multi-member wards that elect either three or four councillors. Each council elects a Provost, or Convenor, to chair meetings of the council and to act as a figurehead for the area.
Local government in Wales consists of 22 unitary authorities. All unitary authorities are led by a leader and cabinet elected by the council itself. These include the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport, which are unitary authorities in their own right.[178] Elections are held every four years under the first-past-the-post system.[178]
Local government in Northern Ireland has since 1973 been organised into 26 district councils, each elected by single transferable vote. Their powers are limited to services such as collecting waste, controlling dogs and maintaining parks and cemeteries.[179] In 2008 the executive agreed on proposals to create 11 new councils and replace the present system.[180]
Devolved governments
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each have their own government or executive, led by a first minister (or, in the case of Northern Ireland, a diarchal first minister and deputy first minister), and a devolved unicameral legislature. England, the largest country of the United Kingdom, has no devolved executive or legislature and is administered and legislated for directly by the UK’s government and parliament on all issues. This situation has given rise to the so-called West Lothian question, which concerns the fact that members of parliament from Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland can vote, sometimes decisively,[181] on matters that affect only England.[182] The 2013 McKay Commission on this recommended that laws affecting only England should need support from a majority of English members of parliament.[183]
The Scottish Government and Parliament have wide-ranging powers over any matter that has not been specifically reserved to the UK Parliament, including education, healthcare, Scots law and local government.[184] Their power over economic issues is significantly constrained by an act of the UK parliament passed in 2020.[192]
The Welsh Government and the Senedd (Welsh Parliament; formerly the National Assembly for Wales)[193] have more limited powers than those devolved to Scotland.[194] The Senedd is able to legislate on any matter not specifically reserved to the UK Parliament through Acts of Senedd Cymru.
The Northern Ireland Executive and Assembly have powers similar to those devolved to Scotland. The Executive is led by a diarchy representing unionist and nationalist members of the Assembly.[195] Devolution to Northern Ireland is contingent on participation by the Northern Ireland administration in the North-South Ministerial Council, where the Northern Ireland Executive cooperates and develops joint and shared policies with the Government of Ireland. The British and Irish governments co-operate on non-devolved matters affecting Northern Ireland through the British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference, which assumes the responsibilities of the Northern Ireland administration in the event of its non-operation.[citation needed]
The UK does not have a codified constitution and constitutional matters are not among the powers devolved to Scotland, Wales or Northern Ireland. Under the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty, the UK Parliament could, in theory, therefore, abolish the Scottish Parliament, Senedd or Northern Ireland Assembly.[196] Indeed, in 1972, the UK Parliament unilaterally prorogued the Parliament of Northern Ireland, setting a precedent relevant to contemporary devolved institutions.[197] In practice, it would be politically difficult for the UK Parliament to abolish devolution to the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd, given the political entrenchment created by referendum decisions.[198] The political constraints placed upon the UK Parliament’s power to interfere with devolution in Northern Ireland are even greater than in relation to Scotland and Wales, given that devolution in Northern Ireland rests upon an international agreement with the Government of Ireland.[199] The UK Parliament restricts the three devolved parliaments’ legislative competence in economic areas through an Act passed in 2020.[192]
Dependencies
The United Kingdom, the 14 British Overseas Territories[20] and the three Crown Dependencies[202] form ‘one undivided Realm’.[203][204] All parts of the realm are under the sovereignty of the British Crown, but the Territories and Dependencies are not part of the UK. This is distinct from the status of Commonwealth realms, who have separate monarchies, but share the same monarch.[204]
The 14 British Overseas Territories are remnants of the British Empire: Anguilla; Bermuda; the British Antarctic Territory; the British Indian Ocean Territory; the British Virgin Islands; the Cayman Islands; the Falkland Islands; Gibraltar; Montserrat; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; the Turks and Caicos Islands; the Pitcairn Islands; South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and Akrotiri and Dhekelia on the island of Cyprus.[205] British claims in Antarctica have limited international recognition.[206] Collectively Britain’s overseas territories encompass an approximate land area of 480,000 square nautical miles (640,000 sq mi; 1,600,000 km2),[207] with a total population of approximately 250,000.[208] The overseas territories also give the UK the world’s fifth largest exclusive economic zone at 6,805,586 km2 (2,627,651 sq mi).[209][better source needed] A 1999 UK government white paper stated that: «[The] Overseas Territories are British for as long as they wish to remain British. Britain has willingly granted independence where it has been requested; and we will continue to do so where this is an option.»[210] Self-determination is also enshrined in the constitutions of several overseas territories and three have specifically voted to remain under British sovereignty (Bermuda in 1995,[211] Gibraltar in 2002[212] and the Falkland Islands in 2013).[213]
The Crown Dependencies are possessions of the Crown, as opposed to territories of the UK.[214] They comprise three independently administered jurisdictions: the Bailiwicks of Jersey and of Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea. By mutual agreement, the British Government manages the islands’ foreign affairs and defence and the UK Parliament has the authority to legislate on their behalf. Internationally, they are regarded as «territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible».[215] The power to pass legislation affecting the islands ultimately rests with their own respective legislative assemblies, with the assent of the Crown (Privy Council or, in the case of the Isle of Man, in certain circumstances the Lieutenant-Governor).[216] Since 2005 each Crown dependency has had a Chief Minister as its head of government.[217]
Law and criminal justice
The United Kingdom does not have a single legal system as Article 19 of the 1706 Treaty of Union provided for the continuation of Scotland’s separate legal system.[218] Today the UK has three distinct systems of law: English law, Northern Ireland law and Scots law. A new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom came into being in October 2009 to replace the Appellate Committee of the House of Lords.[219] The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, including the same members as the Supreme Court, is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the British Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies.[220]
Both English law, which applies in England and Wales, and Northern Ireland law are based on common-law principles.[221] The essence of common law is that, subject to statute, the law is developed by judges in courts, applying statute, precedent and common sense to the facts before them to give explanatory judgements of the relevant legal principles, which are reported and binding in future similar cases (stare decisis).[222] The courts of England and Wales are headed by the Senior Courts of England and Wales, consisting of the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). The Supreme Court is the highest court in the land for both criminal and civil appeal cases in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and any decision it makes is binding on every other court in the same jurisdiction, often having a persuasive effect in other jurisdictions.[223]
Scots law is a hybrid system based on both common-law and civil-law principles. The chief courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases,[224] and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases.[225] The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom serves as the highest court of appeal for civil cases under Scots law.[226] Sheriff courts deal with most civil and criminal cases including conducting criminal trials with a jury, known as sheriff solemn court, or with a sheriff and no jury, known as sheriff summary Court.[227] The Scots legal system is unique in having three possible verdicts for a criminal trial: «guilty», «not guilty» and «not proven». Both «not guilty» and «not proven» result in an acquittal.[228]
Crime in England and Wales increased in the period between 1981 and 1995, though since that peak there has been an overall fall of 66 per cent in recorded crime from 1995 to 2015,[229] according to crime statistics. The prison population of England and Wales has increased to 86,000, giving England and Wales the highest rate of incarceration in Western Europe at 148 per 100,000.[230] His Majesty’s Prison Service, which reports to the Ministry of Justice, manages most of the prisons within England and Wales. The murder rate in England and Wales has stabilised in the first half of the 2010s with a murder rate around 1 per 100,000 which is half the peak in 2002 and similar to the rate in the 1980s[231] Crime in Scotland fell slightly in 2014–2015 to its lowest level in 39 years in with 59 killings for a murder rate of 1.1 per 100,000. Scotland’s prisons are overcrowded but the prison population is shrinking.[232]
Foreign relations
The UK is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, a member of NATO, AUKUS, the Commonwealth of Nations, the G7 finance ministers, the G7 forum, the G20, the OECD, the WTO, the Council of Europe and the OSCE.[233] The UK is said to have a «Special Relationship» with the United States and a close partnership with France – the «Entente cordiale» – and shares nuclear weapons technology with both countries;[234] the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance is considered to be the oldest binding military alliance in the world. The UK is also closely linked with the Republic of Ireland; the two countries share a Common Travel Area and co-operate through the British-Irish Intergovernmental Conference and the British-Irish Council. Britain’s global presence and influence is further amplified through its trading relations, foreign investments, official development assistance and military engagements.[235] Canada, Australia and New Zealand, all of which are former colonies of the British Empire which share King Charles as their head of state, are the most favourably viewed countries in the world by British people.[236]
Military
His Majesty’s Armed Forces consist of three professional service branches: the Royal Navy and Royal Marines (forming the Naval Service), the British Army and the Royal Air Force.[237] The armed forces of the United Kingdom are managed by the Ministry of Defence and controlled by the Defence Council, chaired by the Secretary of State for Defence. The Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch, to whom members of the forces swear an oath of allegiance.[238] The Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK’s global security interests and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in NATO, including the Allied Rapid Reaction Corps, the Five Power Defence Arrangements, RIMPAC and other worldwide coalition operations. Overseas garrisons and facilities are maintained in Ascension Island, Bahrain, Belize, Brunei, Canada, Cyprus, Diego Garcia, the Falkland Islands, Germany, Gibraltar, Kenya, Oman, Qatar and Singapore.[239]
The British armed forces played a key role in establishing the British Empire as the dominant world power in the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. By emerging victorious from conflicts, Britain has often been able to decisively influence world events. Since the end of the British Empire, the UK has remained a major military power. Following the end of the Cold War, defence policy has a stated assumption that «the most demanding operations» will be undertaken as part of a coalition.[240]
According to sources which include the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute and the International Institute for Strategic Studies, the UK has either the fourth- or the fifth-highest military expenditure. Total defence spending amounts to 2.0 per cent of national GDP.[241]
Economy
Overview
The UK has a partially regulated market economy.[243] Based on market exchange rates, the UK is today the fifth-largest economy in the world and the second-largest in Europe after Germany. HM Treasury, led by the Chancellor of the Exchequer, is responsible for developing and executing the government’s public finance policy and economic policy. The Bank of England is the UK’s central bank and is responsible for issuing notes and coins in the nation’s currency, the pound sterling. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover their issue. The pound sterling is the world’s fourth-largest reserve currency (after the US dollar, euro, and Japanese Yen).[244] Since 1997 the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England, has been responsible for setting interest rates at the level necessary to achieve the overall inflation target for the economy that is set by the Chancellor each year.[245]
The UK service sector makes up around 79 per cent of GDP.[246] London is one of the world’s largest financial centres, ranking second in the world, behind New York City, in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[247] London also has the largest city GDP in Europe.[248] Edinburgh ranks 17th in the world, and sixth in Western Europe in the Global Financial Centres Index in 2020.[247] Tourism is very important to the British economy; with over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom is ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world and London has the most international visitors of any city in the world.[249] The creative industries accounted for 7 per cent GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6 per cent per annum between 1997 and 2005.[250]
Following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union, the functioning of the UK internal economic market is enshrined by the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020 which ensures trade in goods and services continues without internal barriers across the four countries of the United Kingdom.[251]
The Industrial Revolution started in Britain with an initial concentration on the textile industry,[252] followed by other heavy industries such as shipbuilding, coal mining and steelmaking.[253] British merchants, shippers and bankers developed overwhelming advantage over those of other nations allowing the UK to dominate international trade in the 19th century.[254] As other nations industrialised, coupled with economic decline after two world wars, the United Kingdom began to lose its competitive advantage and heavy industry declined, by degrees, throughout the 20th century. Manufacturing remains a significant part of the economy but accounted for only 16.7 per cent of national output in 2003.[255]
The automotive industry employs around 800,000 people, with a turnover in 2015 of £70 billion, generating £34.6 billion of exports (11.8 per cent of the UK’s total export goods). In 2015, the UK produced around 1.6 million passenger vehicles and 94,500 commercial vehicles. The UK is a major centre for engine manufacturing: in 2015 around 2.4 million engines were produced. The UK motorsport industry employs around 41,000 people, comprises around 4,500 companies and has an annual turnover of around £6 billion.[256]
The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry in the world depending upon the method of measurement and has an annual turnover of around £30 billion.[257]
BAE Systems plays a critical role in some of the world’s biggest defence aerospace projects. In the UK, the company makes large sections of the Typhoon Eurofighter and assembles the aircraft for the Royal Air Force. It is also a principal subcontractor on the F35 Joint Strike Fighter – the world’s largest single defence project – for which it designs and manufactures a range of components. It also manufactures the Hawk, the world’s most successful[clarification needed] jet training aircraft.[258] Airbus UK also manufactures the wings for the A400M military transporter. Rolls-Royce is the world’s second-largest aero-engine manufacturer. Its engines power more than 30 types of commercial aircraft and it has more than 30,000 engines in service in the civil and defence sectors.
The UK space industry was worth £9.1bn in 2011 and employed 29,000 people. It is growing at a rate of 7.5 per cent annually, according to its umbrella organisation, the UK Space Agency. In 2013, the British Government pledged £60 m to the Skylon project: this investment will provide support at a «crucial stage» to allow a full-scale prototype of the SABRE engine to be built.
The pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures.[259]
Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised and efficient by European standards, producing about 60 per cent of food needs with less than 1.6 per cent of the labour force (535,000 workers).[260] Around two-thirds of production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. The UK retains a significant, though much reduced fishing industry. It is also rich in a variety of natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica and an abundance of arable land.[261] In 2020, coronavirus lockdown measures caused the UK economy to suffer its biggest slump on record, shrinking by 20.4 per cent between April and June compared to the first three months of the year, to push it officially into recession for the first time in 11 years.[262]
The UK has an external debt of $9.6 trillion dollars,[when?] which is the second-highest in the world after the US. As a percentage of GDP, external debt is 408 per cent, which is the third-highest in the world after Luxembourg and Iceland.[263]
Science and technology
England and Scotland were leading centres of the Scientific Revolution from the 17th century.[264] The United Kingdom led the Industrial Revolution from the 18th century,[252] and has continued to produce scientists and engineers credited with important advances.[265] Major theorists from the 17th and 18th centuries include Isaac Newton, whose laws of motion and illumination of gravity have been seen as a keystone of modern science;[266] from the 19th century Charles Darwin, whose theory of evolution by natural selection was fundamental to the development of modern biology, and James Clerk Maxwell, who formulated classical electromagnetic theory; and more recently Stephen Hawking, who advanced major theories in the fields of cosmology, quantum gravity and the investigation of black holes.[267]
Major scientific discoveries from the 18th century include hydrogen by Henry Cavendish;[268] from the 20th century penicillin by Alexander Fleming,[269] and the structure of DNA, by Francis Crick and others.[270] Famous British engineers and inventors of the Industrial Revolution include James Watt, George Stephenson, Richard Arkwright, Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel.[271] Other major engineering projects and applications by people from the UK include the steam locomotive, developed by Richard Trevithick and Andrew Vivian;[272] from the 19th century the electric motor by Michael Faraday, the first computer designed by Charles Babbage,[273] the first commercial electrical telegraph by William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone,[274] the incandescent light bulb by Joseph Swan,[275] and the first practical telephone, patented by Alexander Graham Bell;[276] and in the 20th century the world’s first working television system by John Logie Baird and others,[277] the jet engine by Frank Whittle, the basis of the modern computer by Alan Turing, and the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee.[278]
Scientific research and development remains important in British universities, with many establishing science parks to facilitate production and co-operation with industry.[279] Between 2004 and 2008 the UK produced 7 per cent of the world’s scientific research papers and had an 8 per cent share of scientific citations, the third and second-highest in the world (after the United States and China, respectively).[280] Scientific journals produced in the UK include Nature, the British Medical Journal and The Lancet.[281] The United Kingdom was ranked fourth in the Global Innovation Index 2020, 2021 and 2022. [282]
Transport
A radial road network totals 29,145 miles (46,904 km) of main roads, 2,173 miles (3,497 km) of motorways and 213,750 miles (344,000 km) of paved roads.[126] The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world.[283] In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.[284]
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the West Coast, East Coast, Midland, Great Western and Great Eastern), which radiate from London to the rest of the country, augmented by regional rail lines and dense commuter networks within the major cities. High Speed 1 is operationally separate from the rest of the network. The world’s first passenger railway running on steam was the Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened in 1825. Just under five years later the world’s first intercity railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, designed by George Stephenson. The network grew rapidly as a patchwork of hundreds of separate companies during the Victorian era.[285]
The UK has a railway network of 10,072 miles (16,209 km) in Great Britain and 189 miles (304 km) in Northern Ireland. Railways in Northern Ireland are operated by NI Railways, a subsidiary of state-owned Translink. In Great Britain, the British Rail network was privatised between 1994 and 1997, which was followed by a rapid rise in passenger numbers. The UK was ranked eighth among national European rail systems in the 2017 European Railway Performance Index assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety.[286] HS2 is a new high speed railway under construction linking up London, the Midlands, the North and Scotland serving over 25 stations, including eight of Britain’s 10 largest cities and connecting around 30 million.[287] Crossrail, opened in 2022, was Europe’s largest construction project with a £15 billion projected cost.[288]
Great British Railways is a planned state-owned public body that will oversee rail transport in Great Britain from 2023. In 2014, there were 5.2 billion bus journeys in the UK, 2.4 billion of which were in London.[289] The red double-decker bus has entered popular culture as an internationally recognised icon of England.[290] The London bus network is extensive, with over 6,800 scheduled services every weekday carrying about six million passengers on over 700 different routes making it one of the most extensive bus systems in the world and the largest in Europe.[291]
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers.[292] In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport (65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport (31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport (18.9 million passengers).[292] London Heathrow Airport, located 15 miles (24 km) west of the capital, has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world[293] and is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways, as well as Virgin Atlantic.[294]
Energy
Energy mix of the United Kingdom over time
In 2006, the UK was the world’s ninth-largest consumer of energy and the 15th-largest producer.[295] The UK is home to many large energy companies, including two of the six oil and gas «supermajors» – BP and Shell.[296]
In 2013, the UK produced 914 thousand barrels per day (bbl/d) of oil and consumed 1,507 thousand bbl/d.[297] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of oil since 2005.[298] In 2010, the UK had around 3.1 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves, the largest of any EU member state.[298]
In 2009, the UK was the 13th-largest producer of natural gas in the world and the largest producer in the EU.[299] Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of natural gas since 2004.[299]
Coal production played a key role in the UK economy in the 19th and 20th centuries. In the mid-1970s, 130 million tonnes of coal were produced annually, not falling below 100 million tonnes until the early 1980s. The coal industry was scaled back considerably during the 1980s and 1990s. In 2011, the UK produced 18.3 million tonnes of coal.[300] In 2005 it had proven recoverable coal reserves of 171 million tonnes.[300] The UK Coal Authority has stated that there is a potential to produce between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes of coal through underground coal gasification (UCG) or ‘fracking’,[301] and based on current UK coal consumption, such reserves could last between 200 and 400 years.[302] Environmental and social concerns have been raised over chemicals contaminating groundwater and minor earthquakes damaging homes.[303]
In the late 1990s, nuclear power plants contributed around 25 per cent of the total annual electricity generation in the UK, but this has gradually declined as old plants have been shut down and plant availability is impacted by ageing-related problems. In 2012, the UK had 16 reactors normally generating about 19 per cent of the UK’s electricity. All but one of the reactors will be retired by 2023. Unlike Germany and Japan, the UK intends to build a new generation of nuclear power plants from about 2018.[304]
The total of all renewable electricity sources provided for 38.9 per cent of the electricity generated in the UK in the third quarter of 2019, producing 28.8TWh of electricity.[305] The UK is one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind power production is the country’s fastest-growing supply; in 2019, almost 20 per cent of the UK’s total electricity was generated by wind power.[306]
Water supply and sanitation
Access to improved water supply and sanitation in the UK is universal. It is estimated that 96.7 per cent of households are connected to the sewer network.[307] According to the Environment Agency, total water abstraction for public water supply in the UK was 16,406 megalitres per day in 2007.[308]
In England and Wales water and sewerage services are provided by 10 private regional water and sewerage companies and 13 mostly smaller private «water only» companies. In Scotland, water and sewerage services are provided by a single public company, Scottish Water. In Northern Ireland water and sewerage services are also provided by a single public entity, Northern Ireland Water.[309]
Demographics
Map of population density in the UK as at the 2011 census
A census is taken simultaneously in all parts of the UK every 10 years.[310] In the 2011 census the total population of the United Kingdom was 63,181,775.[311] It is the fourth-largest in Europe (after Russia, Germany and France), the fifth-largest in the Commonwealth and the 22nd-largest in the world. In mid-2014 and mid-2015 net long-term international migration contributed more to population growth. In mid-2012 and mid-2013 natural change contributed the most to population growth.[312] Between 2001 and 2011 the population increased by an average annual rate of approximately 0.7 per cent.[311] This compares to 0.3 per cent per year in the period 1991 to 2001 and 0.2 per cent in the decade 1981 to 1991.[313] The 2011 census also showed that, over the previous 100 years, the proportion of the population aged 0–14 fell from 31 per cent to 18 per cent, and the proportion of people aged 65 and over rose from 5 to 16 per cent.[311] In 2018 the median age of the UK population was 41.7 years.[314]
England’s population in 2011 was 53 million, representing some 84 per cent of the UK total.[315] It is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with 420 people resident per square kilometre in mid-2015,[312] with a particular concentration in London and the south-east.[316] The 2011 census put Scotland’s population at 5.3 million,[317] Wales at 3.06 million and Northern Ireland at 1.81 million.[315]
In 2017 the average total fertility rate (TFR) across the UK was 1.74 children born per woman.[318] While a rising birth rate is contributing to population growth, it remains considerably below the baby boom peak of 2.95 children per woman in 1964,[319] or the high of 6.02 children born per woman in 1815,[320] below the replacement rate of 2.1, but higher than the 2001 record low of 1.63.[321] In 2011, 47.3 per cent of births in the UK were to unmarried women.[322] The Office for National Statistics published a bulletin in 2015 showing that, out of the UK population aged 16 and over, 1.7 per cent identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual (2.0 per cent of males and 1.5 per cent of females); 4.5 per cent of respondents responded with «other», «I don’t know», or did not respond.[323] The number of transgender people in the UK was estimated to be between 65,000 and 300,000 by research between 2001 and 2008.[324]
Largest urban areas of the United Kingdom (England and Wales: 2011 census built-up area;[325] Scotland: 2016 estimates settlement;[326] Northern Ireland: 2001 census urban area)[327] |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | Rank | Urban area | Pop. | Principal settlement | |
 Greater London
|
1 | Greater London | 9,787,426 | London | 11 | Bristol | 617,280 | Bristol |
| 2 | West Midlands | 2,440,986 | Birmingham | 12 | Edinburgh | 512,150 | Edinburgh | |
| 3 | Greater Manchester | 2,553,379 | Manchester | 13 | Leicester | 508,916 | Leicester | |
| 4 | West Yorkshire | 1,777,934 | Leeds | 14 | Belfast | 483,418 | Belfast | |
| 5 | Greater Glasgow | 985,290 | Glasgow | 15 | Brighton & Hove | 474,485 | Brighton & Hove | |
| 6 | Liverpool | 864,122 | Liverpool | 16 | Bournemouth/ Poole | 466,266 | Bournemouth | |
| 7 | South Hampshire | 855,569 | Southampton | 17 | Cardiff | 390,214 | Cardiff | |
| 8 | Tyneside | 774,891 | Newcastle | 18 | Teesside | 376,633 | Middlesbrough | |
| 9 | Nottingham | 729,977 | Nottingham | 19 | Stoke-on-Trent | 372,775 | Stoke | |
| 10 | Sheffield | 685,368 | Sheffield | 20 | Coventry | 359,262 | Coventry |
Ethnic groups
Historically, indigenous British people were thought to be descended from the various ethnic groups that settled there before the 12th century: the Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Norse and the Normans. Welsh people could be the oldest ethnic group in the UK.[328] A 2006 genetic study shows that more than 50 per cent of England’s gene pool contains Germanic Y chromosomes.[329] Another 2005 genetic analysis indicates that «about 75 per cent of the traceable ancestors of the modern British population had arrived in the British isles by about 6,200 years ago, at the start of the British Neolithic or Stone Age», and that the British broadly share a common ancestry with the Basque people.[330][needs update] The UK has a history of non-white immigration with Liverpool having the oldest Black population in the country dating back to at least the 1730s during the period of the African slave trade. During this period it is estimated the Afro-Caribbean population of Great Britain was 10,000 to 15,000[331] which later declined due to the abolition of slavery.[332] The UK also has the oldest Chinese community in Europe, dating to the arrival of Chinese seamen in the 19th century.[333] In 1950 there were probably fewer than 20,000 non-white residents in Britain, almost all born overseas.[334] In 1951 there were an estimated 94,500 people living in Britain who had been born in South Asia, China, Africa and the Caribbean, just under 0.2 per cent of the UK population. By 1961 this number had more than quadrupled to 384,000, just over 0.7 per cent of the United Kingdom population.[335]
Since 1948 substantial immigration from Africa, the Caribbean and South Asia has been a legacy of ties forged by the British Empire.[336] Migration from new EU member states in Central and Eastern Europe since 2004 has resulted in growth in these population groups, although some of this migration has been temporary.[337] Since the 1990s, there has been substantial diversification of the immigrant population, with migrants to the UK coming from a much wider range of countries than previous waves, which tended to involve larger numbers of migrants coming from a relatively small number of countries.[338]
Academics have argued that the ethnicity categories employed in British national statistics, which were first introduced in the 1991 census, involve confusion between the concepts of ethnicity and race.[339] In 2011, 87.2 per cent of the UK population identified themselves as white, meaning 12.8 per cent of the UK population identify themselves as of one of number of ethnic minority groups.[340] In the 2001 census, this figure was 7.9 per cent of the UK population.[341] Because of differences in the wording of the census forms used in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, data on the Other White group is not available for the UK as a whole, but in England and Wales this was the fastest-growing group between the 2001 and 2011 censuses, increasing by 1.1 million (1.8 percentage points).[342] Amongst groups for which comparable data is available for all parts of the UK level, the Other Asian category increased from 0.4 per cent to 1.4 per cent of the population between 2001 and 2011, while the Mixed category rose from 1.2 per cent to 2 per cent.[340]
Ethnic diversity varies significantly across the UK. 30.4 per cent of London’s population and 37.4 per cent of Leicester’s was estimated to be non-white in 2005,[343] whereas less than 5 per cent of the populations of North East England, Wales and the South West were from ethnic minorities, according to the 2001 census.[344] In 2016, 31.4 per cent of primary and 27.9 per cent of secondary pupils at state schools in England were members of an ethnic minority.[345] The 1991 census was the first UK census to have a question on ethnic group. In the 1991 UK census 94.1 per cent of people reported themselves as being White British, White Irish or White Other with 5.9 per cent of people reporting themselves as coming from other minority groups.[346]
| Ethnic group | Population (absolute) | Population (per cent) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2011 | 2001[347] | 2011[340] | ||
| White | 54,153,898 | 55,010,359 | 92.1% | 87.1% | |
| White: Gypsy, Traveller and Irish Traveller[o] | – | 63,193 | – | 0.1% | |
| Asian and Asian British | Indian | 1,053,411 | 1,451,862 | 1.8% | 2.3% |
| Pakistani | 747,285 | 1,174,983 | 1.3% | 1.9% | |
| Bangladeshi | 283,063 | 451,529 | 0.5% | 0.7% | |
| Chinese | 247,403 | 433,150 | 0.4% | 0.7% | |
| other Asian | 247,664 | 861,815 | 0.4% | 1.4% | |
| Black, African, Caribbean and Black British[p] | 1,148,738 | 1,904,684 | 2.0% | 3.0% | |
| mixed or multiple ethnic groups | 677,117 | 1,250,229 | 1.2% | 2.0% | |
| other ethnic group | 230,615 | 580,374 | 0.4% | 0.9% | |
| Total | 58,789,194 | 63,182,178 | 100.0% | 100.0% |
Languages
The UK’s de facto official language is English.[350][351] It is estimated that 95 per cent of the UK’s population are monolingual English speakers.[352] 5.5 per cent of the population are estimated to speak languages brought to the UK as a result of relatively recent immigration.[352] South Asian languages are the largest grouping which includes Punjabi, Urdu, Bengali, Sylheti, Hindi and Gujarati.[353] According to the 2011 census, Polish has become the second-largest language spoken in England and has 546,000 speakers.[354] In 2019, some three quarters of a million people spoke little or no English.[355]
Three indigenous Celtic languages are spoken in the UK: Welsh, Irish and Scottish Gaelic. Cornish, which became extinct as a first language in the late 18th century, is subject to revival efforts and has a small group of second language speakers.[356][2] According to the 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 538,300 people (17.8 per cent).[357] In addition, it is estimated that about 200,000 Welsh speakers live in England.[358] In the 2011 census in Northern Ireland 167,487 people (10.4 per cent) stated that they had «some knowledge of Irish» (see Irish language in Northern Ireland), almost exclusively in the nationalist (mainly Catholic) population. Over 92,000 people in Scotland (just under 2 per cent of the population) had some Gaelic language ability, including 72 per cent of those living in the Outer Hebrides.[359] The number of children being taught either Welsh or Scottish Gaelic is increasing.[360] Among emigrant-descended populations some Scottish Gaelic is still spoken in Canada (principally Nova Scotia and Cape Breton Island),[361] and Welsh in Patagonia, Argentina.[362]
Scots, a language descended from early northern Middle English, has limited recognition alongside its regional variant, Ulster Scots in Northern Ireland, without specific commitments to protection and promotion.[2][363]
As of April 2020, there are said to be around 151,000 users of British Sign Language (BSL), a sign language used by deaf people, in the UK.[364] BSL was recognised as a language of England, Scotland and Wales in law in 2022.[365] It is compulsory for pupils to study a second language from the age of seven in England.[366] French and Spanish are the two most commonly taught second languages in the United Kingdom.[367] All pupils in Wales are either taught Welsh as a second language up to age 16, or are taught in Welsh as a first language.[368] Welsh was recognised as having official status in Wales in 2011.[369] Irish was recognised as having official status in Northern Ireland in 2022.[370]
Religion
Religion in England and Wales (2021 census)[371]
Other religions (0.6%)
Not stated (6.0%)
Forms of Christianity have dominated religious life in what is now the United Kingdom for more than 1,400 years.[372] Although a majority of citizens still identify with Christianity in many surveys, regular church attendance has fallen dramatically since the middle of the 20th century,[373] while immigration and demographic change have contributed to the growth of other faiths, most notably Islam.[374] This has led some commentators to variously describe the UK as a multi-faith,[375] secularised,[376] or post-Christian society.[377]
In the 2001 census, 71.6 per cent of all respondents indicated that they were Christians, with the next largest faiths being Islam (2.8 per cent), Hinduism (1.0 per cent), Sikhism (0.6 per cent), Judaism (0.5 per cent), Buddhism (0.3 per cent) and all other religions (0.3 per cent).[378] Of the respondents, 15 per cent stated that they had no religion and a further 7 per cent did not state a religious preference.[379] A Tearfund survey in 2007 showed that only one in ten Britons actually attend church weekly.[380] Between the 2001 and 2011 census, there was a 12 per cent decrease in the number of people who identified as Christian, whilst the percentage of those reporting no religious affiliation doubled. This contrasted with growth in the other main religious group categories, with the number of Muslims increasing by the most substantial margin to a total of about 5 per cent.[381] The Muslim population has increased from 1.6 million in 2001 to 2.7 million in 2011, making it the second-largest religious group in the UK.[382]
In a 2016 survey conducted by BSA (British Social Attitudes) on religious affiliation, 53 per cent of respondents indicated ‘no religion’, 41 per cent indicated they were Christians, followed by 6 per cent who affiliated with other religions (e.g. Islam, Hinduism, Judaism, etc.).[383] Among Christians, adherents to the Church of England constituted 15 per cent, to the Catholic Church 9 per cent, and other Christians (including Presbyterians, Methodists, other Protestants, as well as Eastern Orthodox) constituted 17 per cent.[383] Of the young people aged 18 to 24 that responded, 71 per cent said they had no religion.[383]
The Church of England is the established church in England.[384] It retains a representation in the UK Parliament, and the British monarch is its Supreme Governor.[385] In Scotland, the Church of Scotland is recognised as the national church. It is not subject to state control, and the British monarch is an ordinary member, required to swear an oath to «maintain and preserve the Protestant Religion and Presbyterian Church Government» upon his or her accession.[386][2][387] The Church in Wales was disestablished in 1920 and, because the Church of Ireland was disestablished in 1870 before the partition of Ireland, there is no established church in Northern Ireland.[388] Although there are no UK-wide data in the 2001 census on adherence to individual Christian denominations, it has been estimated that 62 per cent of Christians are Anglican, 13.5 per cent Catholic, 6 per cent Presbyterian, and 3.4 per cent Methodist, with small numbers of other Protestant denominations such as Plymouth Brethren, and Orthodox churches.[389]
In the 2021 UK census, less than half the English and Welsh population were Christian; 46.2% of the people of England and Wales said they were Christian, 37.2% that they had no religion, and 6.5% said they were Muslim.[390]
Migration
Estimated foreign-born population by country of birth from April 2007 to March 2008
| Year | Foreign born population of England and Wales | Total population [391][392][393] [394][395] |
Irish born population | Percentage of total population that was born abroad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1851 | 100,000 | 17,900,000 | 520,000 | 0.6 |
| 1861 | 150,000 | 20,100,000 | 600,000 | 0.7 |
| 1871 | 200,000 | 22,700,000 | 565,000 | 0.9 |
| 1881 | 275,000 | 26,000,000 | 560,000 | 1.1 |
| 1891 | 350,000 | 29,000,000 | 460,000 | 1.2 |
| 1901 | 475,000 | 32,500,000 | 425,000 | 1.5 |
| 1911 | 900,000 | 32,500,000 | 375,000 | 2.5 |
| 1921 | 750,000 | 37,900,000 | 365,000 | 2 |
| 1931 | 1,080,000 | 40,000,000 | 380,000 | 2.7 |
| 1951 | 1,875,000 | 43,700,000 | 470,000 | 4.3 |
| 1961 | 2,290,000 | 46,000,000 | 645,000 | 5.0 |
| 1971 | 3,100,000 | 48,700,000 | 585,000 | 6.4 |
| 1981 | 3,220,000 | 48,500,000 | 580,000 | 6.6 |
| 1991 | 3,625,000 | 49,900,000 | 570,000 | 7.3 |
| 2001 | 4,600,000 | 52,500,000 | 475,000 | 8.8 |
| 2011 | 7,500,000 | 56,000,000 | 400,000 | 13.4 |
| 2021 | 10,000,000 | 59,600,000 | 325,000 | 16.8 |
The United Kingdom has experienced successive waves of migration. The Great Famine in Ireland, then part of the United Kingdom, resulted in perhaps a million people migrating to Great Britain.[396] Throughout the 19th century, a small population of 28,644 German immigrants built up in England and Wales. London held around half of this population, and other small communities existed in Manchester, Bradford and elsewhere. The German immigrant community was the largest group until 1891, when it became second to Russian Jews.[397] After 1881, Russian Jews suffered bitter persecutions and 2 million left the Russian Empire by 1914. Around 120,000 settled permanently in Britain, becoming the largest ethnic minority from outside the British Isles,[398] and by 1938 this population had increased to 370,000.[399] Unable to return to Poland at the end of the Second World War, over 120,000 Polish veterans remained in the UK permanently.[400] After the war, many people immigrated from colonies and former colonies in the Caribbean and Indian subcontinent, as a legacy of empire or driven by labour shortages.[401] In 1841, only 0.25 per cent of the population of England and Wales was born in a foreign country, increasing to 1.5 per cent by 1901,[393] 2.6 per cent by 1931 and 4.4 per cent in 1951.[391]
In 2014, the immigration net increase was 318,000: immigration was at 641,000, up from 526,000 in 2013, while the number of emigrants leaving for over a year was 323,000.[402] A recent migration trend has been the arrival of workers from the new EU member states in Eastern Europe, known as the A8 countries.[337] In 2011, citizens of new EU member states made up 13 per cent of immigrants.[403] The UK applied temporary restrictions to citizens of Romania and Bulgaria, both of which joined the EU in January 2007.[404] Research conducted by the Migration Policy Institute for the Equality and Human Rights Commission suggests that, between May 2004 and September 2009, 1.5 million workers migrated from the new EU member states to the UK, most of them Polish. Many subsequently returned home, resulting in a net increase in the number of nationals of the new member states in the UK.[405] The late-2000s recession in the UK reduced the economic incentive for Poles to migrate to the UK,[406] making migration temporary and circular.[407] The proportion of foreign-born people in the UK remains slightly below that of many other European countries.[408]
Immigration is now contributing to a rising UK population,[409] with arrivals and UK-born children of migrants accounting for about half of the population increase between 1991 and 2001. According to official statistics released in 2015, 27 per cent of UK live births in 2014 were to mothers born outside the UK.[410] The ONS reported that net migration rose from 2009 to 2010 by 21 per cent to 239,000.[411]
In 2013, approximately 208,000 foreign nationals were naturalised as British citizens, the highest number since 1962. This figure fell to around 125,800 in 2014. Between 2009 and 2013, the average number of British citizenships granted annually was 195,800. The most common previous nationalities of those naturalised in 2014 were Indian, Pakistani, Filipino, Nigerian, Bangladeshi, Nepali, Chinese, South African, Polish and Somali.[412] The total number of grants of settlement, which confer permanent residence in the UK but not citizenship,[413] was approximately 154,700 in 2013, higher than the previous two years.[412]
Estimated number of British citizens living overseas by country in 2006
In 2008, the British Government introduced a points-based immigration system for immigration from outside the European Economic Area to replace former schemes, including the Scottish Government’s Fresh Talent Initiative.[414] In June 2010, a temporary limit on immigration from outside the EU was introduced, aiming to discourage applications before a permanent cap was imposed in April 2011.[415]
Emigration was an important feature of British society in the 19th century. Between 1815 and 1930, around 11.4 million people emigrated from Britain and 7.3 million from Ireland. Estimates show that by the end of the 20th century, some 300 million people of British and Irish descent were permanently settled around the globe.[416] Today, at least 5.5 million UK-born people live abroad,[417][418] mainly in Australia, Spain, the United States and Canada.[417][419]
Education
Education in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter, with each country having a separate education system.
Considering the four systems together, about 38 per cent of the United Kingdom population has a university or college degree, which is the highest percentage in Europe, and among the highest percentages in the world.[420] The United Kingdom trails only the United States in terms of representation on lists of top 100 universities.[421]
A government commission’s report in 2014 found that privately educated people comprise 7 per cent of the general population of the UK but much larger percentages of the top professions, the most extreme case quoted being 71 per cent of senior judges.[422]
England
Whilst education in England is the responsibility of the Secretary of State for Education, the day-to-day administration and funding of state schools is the responsibility of local authorities.[423] Universally free of charge state education was introduced piecemeal between 1870 and 1944.[424] Education is now mandatory from ages 5 to 16, and in England youngsters must stay in education or training until they are 18.[425] In 2011, the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) rated 13–14-year-old pupils in England and Wales tenth in the world for maths and ninth for science.[426] The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools, a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Two of the top 10 performing schools in terms of GCSE results in 2006 were state-run grammar schools. In 2010, over half of places at the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge were taken by students from state schools,[427] while the proportion of children in England attending private schools is around 7 per cent.[428]
Scotland
Education in Scotland is the responsibility of the Cabinet Secretary for Education and Lifelong Learning, with day-to-day administration and funding of state schools the responsibility of Local Authorities. Two non-departmental public bodies have key roles in Scottish education. The Scottish Qualifications Authority is responsible for the development, accreditation, assessment and certification of qualifications other than degrees which are delivered at secondary schools, post-secondary colleges of further education and other centres.[429] Learning and Teaching Scotland provides advice, resources and staff development to education professionals.[430] Scotland first legislated for compulsory education in 1496.[431] The proportion of children in Scotland attending private schools is just over 4 per cent in 2016, but it has been falling slowly in recent years.[432] Scottish students who attend Scottish universities pay neither tuition fees nor graduate endowment charges, as fees were abolished in 2001 and the graduate endowment scheme was abolished in 2008.[433]
Wales
The Welsh Government’s Minister for Education has responsibility for education in Wales.[434] State funded education is available to children from the age of three whilst the legal obligation for parents to have their children educated, usually at school, begins at age five.[435] A sizeable minority of pupils are educated in Welsh whilst the rest are obliged to study the language until the age of 16.[436] Wales’ performance in Pisa testing, which compares the academic performance of adolescents around the world, has improved in recent years but remains lower than other parts of the UK.[437] In 2019, just under 60% of entrants passed their main English and math GCSEs.[438] The obligation to receive education in Wales ends at the age of 16. In 2017 and 2018, just under 80% of 16 to 18 and just under 40% of 19 to 24-year-olds were in some kind of education or training.[439]
Northern Ireland
Education in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Minister of Education, although responsibility at a local level is administered by the Education Authority which is further sub-divided into five geographical areas. The Council for the Curriculum, Examinations & Assessment (CCEA) is the body responsible for advising the government on what should be taught in Northern Ireland’s schools, monitoring standards and awarding qualifications.[440]
Healthcare
Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter and each country has its own system of private and publicly funded healthcare. Public healthcare is provided to all UK permanent residents and is mostly free at the point of need, being paid for from general taxation. The World Health Organization, in 2000, ranked the provision of healthcare in the United Kingdom as fifteenth best in Europe and eighteenth in the world.[441]
Since 1979 expenditure on healthcare has been increased significantly.[442] The 2018 OECD data, which incorporates in health a chunk of what in the UK is classified as social care, has the UK spending £3,121 per head.[443] In 2017 the UK spent £2,989 per person on healthcare, around the median for members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.[444]
Regulatory bodies are organised on a UK-wide basis such as the General Medical Council, the Nursing and Midwifery Council and non-governmental-based, such as the Royal Colleges. Political and operational responsibility for healthcare lies with four national executives; healthcare in England is the responsibility of the UK Government; healthcare in Northern Ireland is the responsibility of the Northern Ireland Executive; healthcare in Scotland is the responsibility of the Scottish Government; and healthcare in Wales is the responsibility of the Welsh Government. Each National Health Service has different policies and priorities, resulting in contrasts.[445]
Culture
The culture of the United Kingdom has been influenced by many factors including: the nation’s island status; its history as a western liberal democracy and a major power; as well as being a political union of four countries with each preserving elements of distinctive traditions, customs and symbolism. As a result of the British Empire, British influence can be observed in the language, culture and legal systems of many of its former colonies including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa and the United States; a common culture coined today as the Anglosphere. The substantial cultural influence of the United Kingdom has led to it being described as a «cultural superpower».[104][105] A global opinion poll for the BBC saw the United Kingdom ranked the third most positively viewed nation in the world (behind Germany and Canada) in 2013 and 2014.[446]
Literature
«British literature» refers to literature associated with the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Most British literature is in the English language. In 2005, some 206,000 books were published in the United Kingdom and in 2006 it was the largest publisher of books in the world.[447]
The English playwright and poet William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest dramatist of all time.[448] The 20th-century English crime writer Agatha Christie is the best-selling novelist of all time.[449] Twelve of the top 25 of 100 novels by British writers chosen by a BBC poll of global critics were written by women; these included works by George Eliot, Virginia Woolf, Charlotte and Emily Brontë, Mary Shelley, Jane Austen, Doris Lessing and Zadie Smith.[450]
Scotland’s contributions include Arthur Conan Doyle (the creator of Sherlock Holmes), Sir Walter Scott, J. M. Barrie, Robert Louis Stevenson and the poet Robert Burns. More recently Hugh MacDiarmid and Neil M. Gunn contributed to the Scottish Renaissance, with grimmer works from Ian Rankin and Iain Banks. Scotland’s capital, Edinburgh, was UNESCO’s first worldwide City of Literature.[451]
Britain’s oldest known poem, Y Gododdin, was composed most likely in the late 6th century. It was written in Cumbric or Old Welsh and contains the earliest known reference to King Arthur.[452] The Arthurian legend was further developed by Geoffrey of Monmouth.[453] Poet Dafydd ap Gwilym (fl. 1320–1370) is regarded as one of the greatest European poets of his age.[454] Daniel Owen is credited as the first Welsh-language novelist, publishing Rhys Lewis in 1885. The best-known of the Anglo-Welsh poets are Dylan Thomas and R. S. Thomas, the latter nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1996. Leading Welsh novelists of the twentieth century include Richard Llewellyn and Kate Roberts.[455][456]
Irish writers, living at a time when all of Ireland was part of the United Kingdom, include Oscar Wilde,[457] Bram Stoker[458] and George Bernard Shaw.[459] There have been many authors whose origins were from outside the United Kingdom but who moved to the UK. These include Joseph Conrad,[460] T. S. Eliot,[461] Kazuo Ishiguro,[462] Sir Salman Rushdie[463] and Ezra Pound.[464]
Philosophy
The United Kingdom is famous for the tradition of ‘British Empiricism’, a branch of the philosophy of knowledge that states that only knowledge verified by experience is valid, and ‘Scottish Philosophy’, sometimes referred to as the ‘Scottish School of Common Sense’.[465] The most famous philosophers of British Empiricism are John Locke, George Berkeley[q] and David Hume; while Dugald Stewart, Thomas Reid and William Hamilton were major exponents of the Scottish «common sense» school. Two Britons are also notable for the ethical theory of utilitarianism, a moral philosophy first used by Jeremy Bentham and later by John Stuart Mill in his short work Utilitarianism.[466]
Music
Various styles of music have become popular in the UK, including the indigenous folk music of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Historically, there has been exceptional Renaissance music from the Tudor period, with masses, madrigals and lute music by Thomas Tallis, John Taverner, William Byrd, Orlando Gibbons and John Dowland. After the Stuart Restoration, an English tradition of dramatic masques, anthems and airs became established, led by Henry Purcell, followed by Thomas Arne and others. The German-born composer George Frideric Handel became a naturalised British citizen in 1727, when he composed the anthem Zadok the Priest for the coronation of George II; it became the traditional ceremonial music for anointing all future monarchs. Handel’s many oratorios, such as his famous Messiah, were written in the English language.[467] Ceremonial music is also performed to mark Remembrance Sunday across the UK, including the Traditional Music played at the Cenotaph.[468] In the second half of the 19th century, as Arthur Sullivan and his librettist W. S. Gilbert wrote their popular Savoy operas, Edward Elgar’s wide range of music rivalled that of his contemporaries on the continent. Increasingly, however, composers became inspired by the English countryside and its folk music, notably Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten, a pioneer of modern British opera. Among the many post-war composers, some of the most notable have made their own personal choice of musical identity: Peter Maxwell Davies (Orkney), Harrison Birtwistle (mythological), and John Tavener (religious).[469]
The Beatles are the most commercially successful and critically acclaimed band in popular music, selling over a billion records.[470][471][472]
According to the website of The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, the term «pop music» originated in Britain in the mid-1950s to describe rock and roll’s fusion with the «new youth music».[473] The Oxford Dictionary of Music states that artists such as The Beatles and The Rolling Stones drove pop music to the forefront of popular music in the early 1960s.[474] In the following years, Britain widely occupied a part in the development of rock music, with British acts pioneering hard rock;[475] raga rock; heavy metal;[476] space rock; glam rock;[477] Gothic rock,[478] and ska punk. In addition, British acts developed psychedelic rock;[479] and punk rock.[480] Besides rock music, British acts also developed neo soul and created dubstep.[481] Pop remains the most popular music genre by sales and streams of singles, with 33.4 per cent of that market in 2016, followed by hip-hop and R&B at 24.5 per cent.[482] Rock is not far behind, at 22.6 per cent.[482] The modern UK is known to produce some of the most prominent English-speaking rappers along with the United States, including Stormzy, Kano, Yxng Bane, Ramz, Little Simz and Skepta.[483]
The Beatles have international sales of over 1 billion units and are the biggest-selling and most influential band in the history of popular music.[470][471][472][484] Other prominent British contributors to have influenced popular music over the last 50 years include The Rolling Stones, Pink Floyd, Queen, Led Zeppelin, the Bee Gees, and Elton John, all of whom have worldwide record sales of 200 million or more.[485] The Brit Awards are the BPI’s annual music awards, and some of the British recipients of the Outstanding Contribution to Music award include; The Who, David Bowie, Eric Clapton, Rod Stewart, The Police, and Fleetwood Mac (who are a British-American band).[486] More recent UK music acts that have had international success include George Michael, Oasis, Spice Girls, Radiohead, Coldplay, Arctic Monkeys, Robbie Williams, Amy Winehouse, Adele, Ed Sheeran, One Direction and Harry Styles.[487]
A number of UK cities are known for their music. Acts from Liverpool have had 54 UK chart number 1 hit singles, more per capita than any other city worldwide.[488] Glasgow’s contribution to music was recognised in 2008 when it was named a UNESCO City of Music.[489] Manchester played a role in the spread of dance music such as acid house, and from the mid-1990s, Britpop. London and Bristol are closely associated with the origins of electronic music sub-genres such as drum and bass and trip hop.[490] Birmingham became known as the birthplace of heavy metal, with the band Black Sabbath starting there in the 1960s.[491]
Visual art
The history of British visual art forms part of western art history. Major British artists include: the Romantics William Blake, John Constable, Samuel Palmer and J.M.W. Turner; the portrait painters Sir Joshua Reynolds and Lucian Freud; the landscape artists Thomas Gainsborough and L. S. Lowry; the pioneer of the Arts and Crafts Movement William Morris; the figurative painter Francis Bacon; the Pop artists Peter Blake, Richard Hamilton and David Hockney; the pioneers of Conceptual art movement Art & Language;[492] the collaborative duo Gilbert and George; the abstract artist Howard Hodgkin; and the sculptors Antony Gormley, Anish Kapoor and Henry Moore. During the late 1980s and 1990s the Saatchi Gallery in London helped to bring to public attention a group of multi-genre artists who would become known as the «Young British Artists»: Damien Hirst, Chris Ofili, Rachel Whiteread, Tracey Emin, Mark Wallinger, Steve McQueen, Sam Taylor-Wood and the Chapman Brothers are among the better-known members of this loosely affiliated movement.
The Royal Academy in London is a key organisation for the promotion of the visual arts in the United Kingdom. Major schools of art in the UK include: the six-school University of the Arts London, which includes the Central Saint Martins College of Art and Design and Chelsea College of Art and Design; Goldsmiths, University of London; the Slade School of Fine Art (part of University College London); the Glasgow School of Art; the Royal College of Art; and The Ruskin School of Drawing and Fine Art (part of the University of Oxford). The Courtauld Institute of Art is a leading centre for the teaching of the history of art. Important art galleries in the United Kingdom include the National Gallery, National Portrait Gallery, Tate Britain and Tate Modern (the most-visited modern art gallery in the world, with around 4.7 million visitors per year).[493]
Cinema
Alfred Hitchcock has been ranked as one of the greatest and most influential British filmmakers of all time.[494]
The United Kingdom has had a considerable influence on the history of the cinema. The British directors Alfred Hitchcock, whose film Vertigo is considered by some critics as the best film of all time,[495] and David Lean are among the most critically acclaimed of all time.[496] Many British actors have achieved international fame and critical success. Some of the most commercially successful films of all time have been produced in the United Kingdom, including two of the highest-grossing film franchises (Harry Potter and James Bond).[497] Ealing Studios has a claim to being the oldest continuously working film studio in the world.[498]
In 2009, British films grossed around $2 billion worldwide and achieved a market share of around 7 per cent globally and 17 per cent in the United Kingdom.[499] UK box-office takings totalled £944 million in 2009, with around 173 million admissions.[499] The annual British Academy Film Awards are hosted by the British Academy of Film and Television Arts.[500]
Cuisine
British cuisine developed from various influences reflective of its land, settlements, arrivals of new settlers and immigrants, trade and colonialism. Celtic agriculture and animal breeding produced a wide variety of foodstuffs for indigenous Celts and Britons. Anglo-Saxon England developed meat and savoury herb stewing techniques before the practice became common in Europe. The Norman conquest introduced exotic spices into England in the Middle Ages.[501] The British Empire facilitated a knowledge of Indian cuisine with its «strong, penetrating spices and herbs». British cuisine has absorbed the cultural influence of those who have settled in Britain, producing hybrid dishes, such as chicken tikka masala.[502] Vegan and vegetarian diets have increased in Britain in recent years. In 2021, a survey found that 8% of British respondents eat a plant-based diet and 36% of respondents have a favourable view of plant-based diets.[503]
Media
The BBC, founded in 1922, is the UK’s publicly funded radio, television and Internet broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest and largest broadcaster in the world.[504][505][506] It operates numerous television and radio stations in the UK and abroad and its domestic services are funded by the television licence.[507] The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world’s largest of any kind.[508] It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages.[509]
Other major players in the UK media include ITV plc, which operates 11 of the 15 regional television broadcasters that make up the ITV Network,[510] and Sky.[511] Newspapers produced in the United Kingdom include The Times, The Guardian, The Observer, The Economist, and the Financial Times.[512] Magazines and journals published in the United Kingdom that have achieved worldwide circulation include Nature, New Scientist, The Spectator, Prospect, NME, Radio Times, and The Economist.
London dominates the media sector in the UK: national newspapers and television and radio are largely based there, although Manchester is also a significant national media centre. Edinburgh and Glasgow, and Cardiff, are important centres of newspaper and broadcasting production in Scotland and Wales, respectively.[513] The UK publishing sector, including books, directories and databases, journals, magazines and business media, newspapers and news agencies, has a combined turnover of around £20 billion and employs around 167,000 people.[514] In 2015, the UK published 2,710 book titles per million inhabitants, more than any other country, much of this being exported to other Anglophone countries.[515]
In 2009, it was estimated that individuals viewed a mean of 3.75 hours of television per day and 2.81 hours of radio. In that year the main BBC public service broadcasting channels accounted for an estimated 28.4 per cent of all television viewing; the three main independent channels accounted for 29.5 per cent and the increasingly important other satellite and digital channels for the remaining 42.1 per cent.[516] Sales of newspapers have fallen since the 1970s and in 2010 41 per cent of people reported reading a daily national newspaper.[517] In 2010, 82.5 per cent of the UK population were Internet users, the highest proportion amongst the 20 countries with the largest total number of users in that year.[518]
Symbols
The flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Flag (also referred to as the Union Jack).[519] It was created in 1606 by the superimposition of the Flag of England, representing Saint George, on the Flag of Scotland, representing Saint Andrew, and was updated in 1801 with the addition of Saint Patrick’s Flag.[520] Wales is not represented in the Union Flag, as Wales had been conquered and annexed to England prior to the formation of the United Kingdom. The possibility of redesigning the Union Flag to include representation of Wales has not been completely ruled out.[521] The national anthem of the United Kingdom is «God Save the King», with «King» replaced with «Queen» in the lyrics whenever the monarch is a woman.
Britannia is a national personification of the United Kingdom, originating from Roman Britain.[522] Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon’s three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag.
Beside the lion and the unicorn and the dragon of heraldry, the bulldog is an iconic animal and commonly represented with the Union Jack. It has been associated with Winston Churchill’s defiance of Nazi Germany.[523] A now rare personification is a character originating in the 18th century, John Bull, a portly country gentleman dressed in a top hat and tailcoat with a Union Jack waistcoat, often accompanied by a bulldog.[524]
The floral emblems of the three kingdoms are the Tudor rose for England, the thistle for Scotland and the shamrock for Northern Ireland; they are sometimes shown intertwined to represent unity.[525] The daffodil and the leek are the symbols of Wales.[526] Alternatives include the Royal Oak for England and the flax flower for Northern Ireland.[525]
Sport
Association football, tennis, table tennis, badminton, rugby union, rugby league, rugby sevens, golf, boxing, netball, water polo, field hockey, billiards, darts, rowing, rounders and cricket originated or were substantially developed in the UK, with the rules and codes of many modern sports invented and codified in late 19th-century Victorian Britain. In 2012, the President of the IOC, Jacques Rogge, stated, «This great, sports-loving country is widely recognised as the birthplace of modern sport. It was here that the concepts of sportsmanship and fair play were first codified into clear rules and regulations. It was here that sport was included as an educational tool in the school curriculum».[528][529]
A 2003 poll found that football is the most popular sport in the UK.[530] England is recognised by FIFA as the birthplace of club football, and the Football Association is the oldest of its kind, with the rules of football first drafted in 1863 by Ebenezer Cobb Morley.[531] Each of the Home Nations (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland) has its own football association, national team and league system, and each is individually a governing member of the International Football Association Board alongside FIFA. The English top division, the Premier League, is the most watched football league in the world.[532] The first international football match was contested by England and Scotland on 30 November 1872.[533] England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland usually compete as separate countries in international competitions.[534]
In 2003, rugby union was ranked the second most popular sport in the UK.[530] The sport was created in Rugby School, Warwickshire, and the first rugby international took place on 27 March 1871 between England and Scotland.[535][536] England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, France and Italy compete in the Six Nations Championship, which is the premier international rugby union tournament in the northern hemisphere. Sports governing bodies in England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland organise and regulate the game separately.[537] Every four years, the Home Nations make a combined team known as the British and Irish Lions which tours Australia, New Zealand and South Africa.
Cricket was invented in England, and its laws were established by the Marylebone Cricket Club in 1788.[538] The England cricket team, controlled by the England and Wales Cricket Board,[539] and the Ireland cricket team, controlled by Cricket Ireland are the only national teams in the UK with Test status. Team members are drawn from the main county sides, and include both English and Welsh players. Cricket is distinct from football and rugby where Wales and England field separate national teams, although Wales has fielded its own national cricket team in the past. Scottish players have played for England because the Scotland cricket team does not have Test status and has only recently started to play in One Day Internationals.[540] Scotland, England (and Wales), and Ireland (including Northern Ireland) have competed at the Cricket World Cup, which England won in 2019. There is a professional league championship that consists of clubs representing 17 English counties and one Welsh county.[541]
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the 1860s before spreading around the world.[542] The world’s oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon championships, was first held in 1877 and today takes place over two weeks in late June and early July.[543]
The UK is closely associated with motorsport. Many teams and drivers in Formula One (F1) are based in the UK, and the country has won more drivers’ and constructors’ titles in the F1 World Championship than any other. The UK hosted the first F1 Grand Prix in 1950 at Silverstone, where the British Grand Prix is held each year in July.[544]
St Andrews, Scotland, the home of golf. The standard 18 hole golf course was created at St Andrews in 1764.[545]
Golf is the sixth most popular sport, by participation, in the UK. Although The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews in Scotland is the sport’s home course,[546] the world’s oldest golf course is in fact Musselburgh Links’ Old Golf Course.[547] In 1764, the standard 18-hole golf course was created at St Andrews when members modified the course from 22 to 18 holes.[545] The British Open—the oldest golf tournament in the world and the first major championship in golf—is played annually on the weekend of the third Friday in July.[548]
Rugby league originated in Huddersfield, West Yorkshire, in 1895 and is generally played in Northern England.[549] A single ‘Great Britain Lions’ team competed in the Rugby League World Cup and Test match games before 2008 when England, Scotland and Ireland began to compete as separate league nations.[550] Great Britain is still retained as the full national team. Super League is the highest level of professional rugby league in the UK and Europe. It consists of 11 teams from Northern England, and one each from London, Wales and France.[551]
The ‘Queensberry rules’, the code of general rules in boxing, was named after John Douglas, 9th Marquess of Queensberry in 1867, and formed the basis of modern boxing.[552] Snooker is another of the UK’s popular sporting exports, with the world championship held annually in Sheffield.[553] Gaelic football and hurling are popular team sports in Northern Ireland, both in terms of participation and spectatorship, and both sports are played by Irish expatriates in the UK and the United States.[554] Shinty (or camanachd) is popular in the Scottish Highlands.[555] Highland games are held in spring and summer in Scotland, celebrating Scottish and Celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands.[556]
The United Kingdom hosted the Summer Olympic Games in 1908, 1948 and 2012, with London acting as the host city on all three occasions. Birmingham hosted the 2022 Commonwealth Games, the seventh time the UK has hosted the Commonwealth Games.
See also
- Outline of the United Kingdom
- Outline of England
- Outline of Northern Ireland
- Outline of Scotland
- Outline of Wales
- Index of United Kingdom-related articles
- International rankings of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the United Kingdom
- Historiography of the British Empire
- United Kingdom–Crown Dependencies Customs Union
Notes
- ^ There is no authorised version of the national anthem as the words are a matter of tradition; only the first verse is usually sung.[1] No statute has been enacted designating «God Save the King» as the official anthem. In the English tradition, such laws are not necessary; proclamation and usage are sufficient to make it the national anthem. «God Save the King» also serves as the Royal anthem for certain Commonwealth realms. The words King, he, him, his, used at present, are replaced by Queen, she, her when the monarch is female.
- ^ Scots, Ulster Scots, Welsh, Cornish, Scottish Gaelic and Irish are classed as regional or minority languages under the Council of Europe’s European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.[2] These include defined obligations to promote those languages.[3] See also Languages of the United Kingdom. Welsh has limited de jure official status in Wales, as well as in the provision of national government services provided for Wales.
- ^ «This category could include Polish responses from the country specific question for Scotland which would have been outputted to ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK. ‘White Africans’ may also have been recorded under ‘Other White’ and then included under ‘White’ for UK.»
- ^ 83.6% are White British/Irish.
- ^ Although the United Kingdom has traditionally been seen as a unitary state, an alternative description of the UK as a «union state», put forward by, among others, Vernon Bogdanor,[4] has become increasingly influential since the adoption of devolution in the 1990s.[5] A union state is considered to differ from a unitary state in that while it maintains a central authority it also recognises the authority of historic rights and infrastructures of its component parts.[6]
- ^ Some of the devolved countries, Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories issue their own sterling banknotes or currencies, or use another nation’s currency. See List of British currencies for more information.
- ^ Also in observed by the Crown Dependencies, and in the two British Overseas Territories of Gibraltar and Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (though in the latter, without daylight saving time). For further information, see Time in the United Kingdom#British territories.
- ^ Except two overseas territories: Gibraltar and the British Indian Ocean Territory
- ^ Excludes most overseas territories
- ^ The .gb domain is also reserved for the UK, but has been little used.
- ^ Usage is mixed. The Guardian and Telegraph use Britain as a synonym for the United Kingdom. Some prefer to use Britain as shorthand for Great Britain. The British Cabinet Office’s Government Digital Service style guide for use on gov.uk recommends: «Use UK and United Kingdom in preference to Britain and British (UK business, UK foreign policy, ambassador and high commissioner). But British embassy, not UK embassy.»
- ^ The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty resolved the Irish War of Independence. When it took effect one year later, it established the Irish Free State as a separate dominion within the Commonwealth of Nations. In 1927 the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 changed the name of the UK to reflect this.
- ^ The United Kingdom does not have a codified constitution but an unwritten one formed of Acts of Parliament, court judgments, traditions, and conventions.[23]
- ^ Compare to section 1 of both of the 1800 Acts of Union which reads: the Kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland shall…be united into one Kingdom, by the Name of «The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland».
- ^ The 2011 Census recorded Gypsies and Travellers as a separate ethnic group for the first time.
- ^ In the 2011 Census, for the purpose of harmonising results to make them comparable across the UK, the ONS includes individuals in Scotland who classified themselves in the «African» category (29,638 people), which in the Scottish version of the census is separate from «Caribbean or Black» (6,540 people),[348] in this «Black or Black British» category. The ONS note that «the African categories used in Scotland could potentially capture White/Asian/Other African in addition to Black identities».[349]
- ^ Berkeley is in fact Irish but was called a ‘British empiricist’ due to the territory of what is now known as the Republic of Ireland being in the UK at the time.
References
- ^ Berry, Ciara (15 January 2016). «National Anthem». The Royal Family. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- ^ a b c d «List of declarations made with respect to treaty No. 148». Council of Europe. Retrieved 12 December 2013.
- ^ «Welsh language on GOV.UK – Content design: planning, writing and managing content – Guidance». www.gov.uk. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.; «Welsh language scheme». GOV.UK. Retrieved 3 August 2018.
- ^ Bradbury, Jonathan (2021). Constitutional Policy and Territorial Politics in the UK: Volume 1: Union and Devolution 1997–2012. Policy Press. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-5292-0588-6.
- ^ Leith, Murray Stewart (2012). Political Discourse and National Identity in Scotland. Edinburgh University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7486-8862-3.
- ^ Gagnon, Alain-G.; Tully, James (2001). Multinational Democracies. Cambridge University Press. p. 47. ISBN 978-0-521-80473-8.; Bogdanor, Vernon (1998). «Devolution: the Constitutional Aspects». In Beatson, Jack (ed.). Constitutional Reform in the United Kingdom: Practice and Principles. Oxford: Hart Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-901362-84-8.
- ^ Demographic Yearbook – Table 3: Population by sex, rate of population increase, surface area and density (PDF) (Report). United Nations Statistics Division. 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ «Surface water and surface water change». Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ «United Kingdom». The World Factbook (2023 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
- ^ «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ a b c d «World Economic Outlook database: October 2022». International Monetary Fund. October 2022.
- ^ «Inequality – Income inequality». us.oecd.org. OECD. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ «Human Development Report 2021/2022» (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «Great Britain | island, Europe». Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ United Kingdom Permanent Committee on Geographical Names (May 2017). «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». GOV.UK. 10.2 Definitions.
usually shortened to United Kingdom … The abbreviation is UK or U.K.
; «United Kingdom». Encyclopedia Britannica. - ^ a b «Countries within a country». Prime Minister’s Office. 10 January 2003. Archived from the original on 9 September 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Definition of Great Britain in English». Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
Great Britain is the name for the island that comprises England, Scotland and Wales, although the term is also used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.
- ^ «Office for National Statistics». ons.gov.uk.
- ^ «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
The full title of this country is ‘the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland’. Great Britain is made up of England, Scotland and Wales. The United Kingdom (UK) is made up of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. ‘Britain’ is used informally, usually meaning the United Kingdom.
The Channel Islands and the Isle of Man are not part of the UK. - ^ a b «Supporting the Overseas Territories». Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Julian Go (2007). «A Globalizing Constitutionalism?, Views from the Postcolony, 1945–2000». In Arjomand, Saïd Amir (ed.). Constitutionalism and political reconstruction. Brill. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-90-04-15174-1.
- ^ Ferguson 2004, p. 307.
- ^ What is the UK Constitution?, The Constitution Unit of UCL, 9 August 2018, retrieved 6 February 2020
- ^ The British Monarchy, «What is constitutional monarchy?». Retrieved 17 July 2013; «United Kingdom» CIA The World Factbook. Retrieved 17 July 2013
- ^ D. Clark (17 January 2022). «Largest UK cities 2020». Statista. Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- ^ «Devolution of powers to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland». United Kingdom Government. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
In a similar way to how the government is formed from members from the two Houses of Parliament, members of the devolved legislatures nominate ministers from among themselves to comprise executives, known as the devolved administrations…
; «Country Overviews: United Kingdom». Transport Research Knowledge Centre. Archived from the original on 4 April 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010. - ^ Mathias, P. (2001). The First Industrial Nation: the Economic History of Britain, 1700–1914. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-26672-7.; Ferguson, Niall (2004). Empire: The rise and demise of the British world order and the lessons for global power. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-02328-8.
- ^ T.V. Paul; James J. Wirtz; Michel Fortmann (2005). «Great+power» Balance of Power. State University of New York Press. pp. 59, 282. ISBN 978-0-7914-6401-4. Accordingly, the great powers after the Cold War are Britain, China, France, Germany, Japan, Russia and the United States p. 59; McCourt, David (2014). Britain and World Power Since 1945: Constructing a Nation’s Role in International Politics. United States: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-07221-7.
- ^ «World Population Prospects – The 2006 Revision» (PDF). UN. Retrieved 27 April 2010.; Professor Arne Björnberg, Ph.D (29 January 2018). «Euro Health Consumer Index 2017» (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ^ «IISS Military Balance 2021». The Military Balance. 121 (1): 23–29. January 2021. doi:10.1080/04597222.2021.1868791. S2CID 232050862. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ «Volume 10 — History of Greater Britain, as well England as Scotland — Series 1 — National Library of Scotland». digital.nls.uk.
- ^ Payne, Malcolm; Shardlow, Steven (2002). Social Work in the British Isles. UK: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. p. 247. ISBN 978-1-8530-2833-5.
- ^ Richmond, Ian Archibald; Millett, Martin J. Millett (2012), «Caledonia», in Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Antony; Eidinow, Esther (eds.), The Oxford Classical Dictionary (4th ed.), Oxford University Press, doi:10.1093/acref/9780199545568.001.0001, ISBN 978-0-19-954556-8, retrieved 14 February 2021; «What’s the Difference Between Great Britain and the United Kingdom? | Britannica». www.britannica.com.
- ^ «Treaty of Union, 1706». Scots History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; Barnett, Hilaire; Jago, Robert (2011). Constitutional & Administrative Law (8th ed.). Abingdon: Routledge. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-415-56301-7.
- ^ «After the political union of England and Scotland in 1707, the nation’s official name became ‘Great Britain’», The American Pageant, Volume 1, Cengage Learning (2012).; «From 1707 until 1801 Great Britain was the official designation of the kingdoms of England and Scotland». The Standard Reference Work: For the Home, School and Library, Volume 3, Harold Melvin Stanford (1921); «In 1707, on the union with Scotland, ‘Great Britain’ became the official name of the British Kingdom, and so continued until the union with Ireland in 1801». United States Congressional serial set, Issue 10; Issue 3265 (1895).; Gascoigne, Bamber. «History of Great Britain (from 1707)». History World. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Cottrell, P. (2008). The Irish Civil War 1922–23. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-84603-270-7.
- ^ S. Dunn; H. Dawson (2000), An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict, Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press,
One specific problem – in both general and particular senses – is to know what to call Northern Ireland itself: in the general sense, it is not a country, or a province, or a state – although some refer to it contemptuously as a statelet: the least controversial word appears to be jurisdiction, but this might change.
; «Changes in the list of subdivision names and code elements» (PDF). ISO 3166-2. International Organization for Standardization. 15 December 2011. Retrieved 28 May 2012. - ^ «Statistical bulletin: Regional Labour Market Statistics». Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.; «13.4% Fall In Earnings Value During Recession». Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- ^ Dunn, Seamus; Dawson, Helen (2000). An Alphabetical Listing of Word, Name and Place in Northern Ireland and the Living Language of Conflict. Lewiston, New York: Edwin Mellen Press. ISBN 978-0-7734-7711-7.; Murphy, Dervla (1979). A Place Apart. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-005030-1.
- ^ Whyte, John; FitzGerald, Garret (1991). Interpreting Northern Ireland. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-827380-6.
- ^ «Guardian Unlimited Style Guide». London: Guardian News and Media Limited. 19 December 2008. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «BBC style guide (Great Britain)». BBC News. 19 August 2002. Retrieved 23 August 2011.; «Key facts about the United Kingdom». Government, citizens and rights. HM Government. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ New Oxford American Dictionary: «Great Britain: England, Wales, and Scotland considered as a unit. The name is also often used loosely to refer to the United Kingdom.»
- ^ «When people say England, they sometimes mean Great Britain, sometimes the United Kingdom, sometimes the British Isles — but never England.» — George Mikes (1946), How To Be An Alien, Penguin ISBN 0-582-41686-8; «England OR United Kingdom (UK)? | Vocabulary | EnglishClub». www.englishclub.com. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ «Britain Meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary». dictionary.cambridge.org.; «Definition of Britain in English by Oxford Dictionaries». Oxford Dictionaries – English. Archived from the original on 26 September 2016.
- ^ a b «Britain definition and meaning». www.collinsdictionary.com. Collins English Dictionary.
- ^ «Britain – Definition for English-Language Learners». learnersdictionary.com. Merriam-Webster’s Learner’s Dictionary.
- ^ «A to Z – Style guide». www.gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ a b c Permanent Committee on Geographical Names. «Toponymic guidelines for the United Kingdom». gov.uk. UK Government.
- ^ «BBC News style guide – Names». BBC Academy. BBC. Archived from the original on 10 November 2019. Retrieved 9 November 2019.; «Alphabetical checklist». BBC News. BBC. Archived from the original on 26 March 2018. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ^ Bradley, Anthony Wilfred; Ewing, Keith D. (2007). Constitutional and administrative law. Vol. 1 (14th ed.). Harlow: Pearson Longman. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-4058-1207-8.
- ^ «Which of these best describes the way you think of yourself?». Northern Ireland Life and Times Survey 2010. ARK – Access Research Knowledge. 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 25 June 2020.; Schrijver, Frans (2006). Regionalism after regionalisation: Spain, France and the United Kingdom. Amsterdam University Press. pp. 275–277. ISBN 978-90-5629-428-1.
- ^ «Ancient skeleton was ‘even older’». BBC News. 30 October 2007. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: A historical encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 973. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ Davies, John; Jenkins, Nigel; Baines, Menna; Lynch, Peredur I., eds. (2008). The Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales. Cardiff: University of Wales Press. p. 915. ISBN 978-0-7083-1953-6.
- ^ «Short Athelstan biography». BBC History. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ Mackie, J.D. (1991). A History of Scotland. London: Penguin. pp. 18–19. ISBN 978-0-14-013649-4.; Campbell, Ewan (1999). Saints and Sea-kings: The First Kingdom of the Scots. Edinburgh: Canongate. pp. 8–15. ISBN 978-0-86241-874-8.
- ^ Haigh, Christopher (1990). The Cambridge Historical Encyclopedia of Great Britain and Ireland. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-521-39552-6.
- ^ Ganshof, F.L. (1996). Feudalism. University of Toronto. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-8020-7158-3.
- ^ Chibnall, Marjorie (1999). The Debate on the Norman Conquest. Manchester University Press. pp. 115–122. ISBN 978-0-7190-4913-2.
- ^ Keen, Maurice. «The Hundred Years’ War». BBC History.
- ^ The Reformation in England and Scotland and Ireland: The Reformation Period & Ireland under Elizabeth I, Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ «British History in Depth – Wales under the Tudors». BBC History. 5 November 2009. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- ^ Nicholls, Mark (1999). A history of the modern British Isles, 1529–1603: The two kingdoms. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 171–172. ISBN 978-0-631-19334-0.
- ^ Canny, Nicholas P. (2003). Making Ireland British, 1580–1650. Oxford University Press. pp. 189–200. ISBN 978-0-19-925905-2.
- ^ Ross, D. (2002). Chronology of Scottish History. Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset. p. 56. ISBN 978-1-85534-380-1; Hearn, J. (2002). Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture. Edinburgh University Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-1-902930-16-9
- ^ «English Civil Wars». Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 28 April 2013.; «Scotland and the Commonwealth: 1651–1660». Archontology.org. 14 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Lodge, Richard (2007) [1910]. The History of England – From the Restoration to the Death of William III (1660–1702). Read Books. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-4067-0897-4.
- ^ «Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy». Royal Navy History. Institute of Naval History. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Canny, Nicholas (1998). The Origins of Empire, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924676-2.
- ^ «Articles of Union with Scotland 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 19 October 2008.; «Acts of Union 1707». UK Parliament. Retrieved 6 January 2011.; «Treaty (act) of Union 1706». Scottish History online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ^ Library of Congress, The Impact of the American Revolution Abroad, p. 73.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-19-156627-1.
- ^ Morgan, Kenneth (2007). Slavery and the British Empire: From Africa to America. OUP Oxford. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-19-923899-6.
- ^ Sailing against slavery. BBC Devon. 2007.; Lovejoy, Paul E. (2000). Transformations in Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa (2nd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 290. ISBN 978-0-521-78012-4.
- ^ «The Act of Union». Act of Union Virtual Library. Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Tellier, L.-N. (2009). Urban World History: an Economic and Geographical Perspective. Quebec: PUQ. p. 463. ISBN 978-2-7605-1588-8.
- ^ Johnston, pp. 508–510.; Porter, p. 332.; Sondhaus, L. (2004). Navies in Modern World History. London: Reaktion Books. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-86189-202-7.; Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.
- ^ «The Workshop of the World». BBC History. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Benn, David Wedgwood (March 2012). «The Crimean War and its lessons for today». International Affairs. Oxford University Press. 88 (2): 387–391. JSTOR 41428613.
- ^ Nordisk familjebok (1913), s. 435 (in Swedish)
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6.; Marshall, P.J. (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7.
- ^ Tompson, Richard S. (2003). Great Britain: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present. New York: Facts on File. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-8160-4474-0.
- ^ Hosch, William L. (2009). World War I: People, Politics, and Power. America at War. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-61530-048-8.
- ^ Zarembka, Paul (2013). Contradictions: Finance, Greed, and Labor Unequally Paid. Emerald Group Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78190-670-5.
- ^ Sophia A. Van Wingerden, The women’s suffrage movement in Britain, 1866–1928 (1999) ch 1.
- ^ Turner, John (1988). Britain and the First World War. London: Unwin Hyman. pp. 22–35. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ a b Westwell, I.; Cove, D. (eds) (2002). History of World War I, Volume 3. London: Marshall Cavendish. pp. 698 and 705. ISBN 978-0-7614-7231-5.
- ^ Turner, J. (1988). Britain and the First World War. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-04-445109-9.
- ^ «100 years of radio since Marconi’s big breakthrough». Ofcom. 15 June 2020. Retrieved 17 November 2020.; «The origins of BBC Local Radio». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ «1920s». bbc.com. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ SR&O 1921, No. 533 of 3 May 1921.
- ^ «The Anglo-Irish Treaty, 6 December 1921». CAIN. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ^ Rubinstein, W.D. (2004). Capitalism, Culture, and Decline in Britain, 1750–1990. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-415-03719-8.
- ^ a b Edgerton, David (2012). Britain’s War Machine. www.penguin.co.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2020; «Britain’s War Machine: Weapons, Resources and Experts in the Second World War». Reviews in History. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Doenecke, Justus D.; Stoler, Mark A. (2005). Debating Franklin D. Roosevelt’s foreign policies, 1933–1945. ISBN 978-0-8476-9416-7. Retrieved 19 March 2016.; Kelly, Brian. The Four Policemen and Postwar Planning, 1943–1945: The Collision of Realist and Idealist Perspectives. Indiana University of Pennsylvania. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ «The «Special Relationship» between Great Britain and the United States Began with FDR». Roosevelt Institute. 22 July 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
and the joint efforts of both powers to create a new post-war strategic and economic order through the drafting of the Atlantic Charter; the establishment of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; and the creation of the United Nations.
; «Remarks by the President Obama and Prime Minister Cameron in Joint Press Conference» (Press release). The White House. 22 April 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2018.That’s what we built after World War II. The United States and the UK designed a set of institutions – whether it was the United Nations, or the Bretton Woods structure, IMF, World Bank, NATO, across the board.
- ^ «Britain to make its final payment on World War II loan from U.S.» The New York Times. 28 December 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ Reynolds, David (17 April 2011). «Britain’s War Machine by David Edgerton – review». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ Francis, Martin (1997). Ideas and policies under Labour, 1945–1951: Building a new Britain. Manchester University Press. pp. 225–233. ISBN 978-0-7190-4833-3.
- ^ Lee, Stephen J. (1996). Aspects of British political history, 1914–1995. London; New York: Routledge. pp. 173–199. ISBN 978-0-415-13103-2.
- ^ Larres, Klaus (2009). A companion to Europe since 1945. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 118. ISBN 978-1-4051-0612-2.
- ^ «Country List». Commonwealth Secretariat. 19 March 2009. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ a b «The cultural superpower: British cultural projection abroad» (PDF). British Politics Review. Norway: British Politics Society. 6 (1). Winter 2011. ISSN 1890-4505. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2018.
- ^ a b Sheridan, Greg (15 May 2010). «Cameron has chance to make UK great again». The Australian. Sydney. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
- ^ Julios, Christina (2008). Contemporary British identity: English language, migrants, and public discourse. Studies in migration and diaspora. Aldershot: Ashgate. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-7546-7158-9.
- ^ «1975: UK embraces Europe in referendum». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Wheeler, Brian; Hunt, Alex (17 December 2018). «The UK’s EU referendum: All you need to know». BBC News.
- ^ Aughey, Arthur (2005). The Politics of Northern Ireland: Beyond the Belfast Agreement. London: Routledge. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-415-32788-6.; «The troubles were over, but the killing continued. Some of the heirs to Ireland’s violent traditions refused to give up their inheritance.» Holland, Jack (1999). Hope against History: The Course of Conflict in Northern Ireland. New York: Henry Holt. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-8050-6087-4.; Elliot, Marianne (2007). The Long Road to Peace in Northern Ireland: Peace Lectures from the Institute of Irish Studies at Liverpool University. University of Liverpool Institute of Irish Studies, Liverpool University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-84631-065-2.
- ^ Dorey, Peter (1995). British politics since 1945. Making contemporary Britain. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 164–223. ISBN 978-0-631-19075-2.
- ^ Griffiths, Alan; Wall, Stuart (2007). Applied Economics (PDF) (11th ed.). Harlow: Financial Times Press. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-273-70822-3. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Keating, Michael (1 January 1998). «Reforging the Union: Devolution and Constitutional Change in the United Kingdom». Publius: The Journal of Federalism. 28 (1): 217–234. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubjof.a029948.
- ^ McSmith, Andy (5 July 2016). «The inside story of how Tony Blair led Britain to war in Iraq». The Independent. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ Jackson, Mike (3 April 2011). «Military action alone will not save Libya». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 27 August 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom country profile». BBC News. 24 January 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ Black, Andrew (15 October 2012). «Scottish independence: Cameron and Salmond strike referendum deal». BBC News. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Scottish independence referendum – Results – BBC News». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «In stunning decision, Britain votes to leave the E.U.» The Washington Post. 24 June 2016. Retrieved 24 June 2016.
- ^ «Brexit: New era for UK as it completes separation from European Union». BBC News. 1 January 2021. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ «Coronavirus (COVID-19) in the UK». gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 14 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ «Coronavirus and the impact on output in the UK economy: April 2020». ons.gov.uk. Government of the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Walker, Andrew (10 June 2020). «Coronavirus: UK economy could be among worst hit of leading nations, says OECD». BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Queen Elizabeth II has died». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Archived from the original on 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ «King Charles III, the new monarch». BBC News. 8 September 2022. Retrieved 8 September 2022.
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary: «British Isles: a geographical term for the islands comprising Great Britain and Ireland with all their offshore islands including the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands.»
- ^ a b c d e «United Kingdom». The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ a b c d Latimer Clarke Corporation Pty Ltd. «United Kingdom – Atlapedia Online». Atlapedia.com. Retrieved 26 October 2010.
- ^ ROG Learning Team (23 August 2002). «The Prime Meridian at Greenwich». Royal Museums Greenwich. Royal Museums Greenwich. Archived from the original on 7 November 2015. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Greenwich Royal Observatory: How the Prime Meridian line is actually 100 metres away from where it was believed to be». The Independent. London. 13 August 2015. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ a b Darkes, Giles (January 2008). «How long is the UK coastline?». The British Cartographic Society. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ «The Channel Tunnel». Eurotunnel. Archived from the original on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). «An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm». BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). «Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material». Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ «Hottest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.; «Coldest day of each year from 1900». www.trevorharley.com.
- ^ «English: A map of Köppen climate types in the United Kingdom (SVG version)». 9 August 2016.
- ^ «Atlantic Ocean Circulation (Gulf Stream)». UK Climate Projections. Met Office. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «UK 1971–2000 averages». Met Office. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 4 August 2007.
- ^ «UK temperature, rainfall and sunshine time series». Met Office.
- ^ «2020 EPI Results». Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «UK net zero target». Institute for Government. 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ «England – Profile». BBC News. 11 February 2010.
- ^ «Scotland Facts». Scotland Online Gateway. Archived from the original on 21 June 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ Winter, Jon (1 June 2000). «The complete guide to the … Scottish Islands». The Independent. London. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Overview of Highland Boundary Fault». Gazetteer for Scotland. University of Edinburgh. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ «Great Britain’s tallest mountain is taller». Ordnance Survey. 18 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ «Ben Nevis Weather». Ben Nevis Weather. Archived from the original on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Profile: Wales». BBC News. 9 June 2010. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ «Geography of Northern Ireland». University of Ulster. Retrieved 22 May 2006.
- ^ Bagehot, Walter (1867). The English Constitution. London: Chapman and Hall. p. 103.
- ^ Carter, Sarah. «A Guide To the UK Legal System». University of Kent at Canterbury. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2006.
- ^ «Parliament’s authority». UK Parliament. n.d. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ «United Kingdom – Government». Commonwealth Network. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «Parliamentary Sovereignty». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b «Parliament». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «Royal Assent». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c «General elections». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «State of the parties». parliament.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Government, Prime Minister and Cabinet». Public services all in one place. Directgov. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (1 January 2012). «The Institution of Prime Minister – History of government». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Brown, Jack (2020). Dale, Iain (ed.). The Prime Ministers. Hodder & Stoughton. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-5293-1214-0.
- ^ «Minister for the Civil Service». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Woodcock, Andrew (26 July 2021). «Boris Johnson accused of ‘cynical rebranding’ after appointing himself ‘Minister for the Union’«. The Independent. Retrieved 19 July 2021.; «Minister for the Union». gov.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 21. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 7. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ Blick, Andrew; Jones, George (2010). Premiership: The Development, Nature and Power of the Office of the British Prime Minister. Imprint Academic. pp. 116–7. ISBN 978-1-84540-168-9.
- ^ Norton, Philip (2020). Governing Britain: Parliament, Ministers and Our Ambiguous Constitution. Manchester University Press. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-5261-4545-1.
- ^ «The Cabinet Manual» (PDF). gov.uk. October 2011. p. 31. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Hackwood Frederick William: The Story of the Shire, Being the Lore, History and Evolution of English County Institutions (1851)
- ^ United Nations Economic and Social Council (August 2007). «Ninth UN Conference on the standardization of Geographical Names» (PDF). UN Statistics Division. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 December 2009. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Barlow, I.M. (1991). Metropolitan Government. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-02099-2.
- ^ «Welcome to the national site of the Government Office Network». Government Offices. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ «A short history of London government». Greater London Authority. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- ^ Sherman, Jill; Norfolk, Andrew (5 November 2004). «Prescott’s dream in tatters as North East rejects assembly». The Times. London. Retrieved 15 February 2008.
The Government is now expected to tear up its twelve-year-old plan to create eight or nine regional assemblies in England to mirror devolution in Scotland and Wales.
(subscription required) - ^ «Elections 2017 results: Who are the new metro mayors?». BBC News. 5 May 2017. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^ «Local Authority Elections». Local Government Association. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «STV in Scotland: Local Government Elections 2007» (PDF). Political Studies Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
- ^ a b «Unitary authorities». Welsh Government. 2014. Archived from the original on 10 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Devenport, Mark (18 November 2005). «NI local government set for shake-up». BBC News. Retrieved 15 November 2008.
- ^ «Foster announces the future shape of local government» (Press release). Northern Ireland Executive. 13 March 2008. Archived from the original on 25 July 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ «Scots MPs attacked over fees vote». BBC News. 27 January 2004. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Taylor, Brian (1 June 1998). «Talking Politics: The West Lothian Question». BBC News. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «England-only laws ‘need majority from English MPs’«. BBC News. 25 March 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Scotland’s Parliament – powers and structures». BBC News. 8 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ Keating, Michael (2 February 2021). «Taking back control? Brexit and the territorial constitution of the United Kingdom». Journal of European Public Policy. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis. 28 (4): 6–7. doi:10.1080/13501763.2021.1876156. hdl:1814/70296. S2CID 234066376.
The UK Internal Market Act gives ministers sweeping powers to enforce mutual recognition and non-discrimination across the four jurisdictions. Existing differences and some social and health matters are exempted but these are much less extensive than the exemptions permitted under the EU Internal Market provisions. Only after an amendment in the House of Lords, the Bill was amended to provide a weak and non-binding consent mechanism for amendments (equivalent to the Sewel Convention) to the list of exemptions. The result is that, while the devolved governments retain regulatory competences, these are undermined by the fact that goods and services originating in, or imported into, England can be marketed anywhere.
- ^ Kenny, Michael; McEwen, Nicola (1 March 2021). «Intergovernmental Relations and the Crisis of the Union». Political Insight. SAGE Publishing. 12 (1): 12–15. doi:10.1177/20419058211000996. S2CID 232050477.
That phase of joint working was significantly damaged by the UK Internal Market Act, pushed through by the Johnson government in December 2020…the Act diminishes the authority of the devolved institutions, and was vehemently opposed by them.
- ^ Wolffe, W James (7 April 2021). «Devolution and the Statute Book». Statute Law Review. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/slr/hmab003. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
the Internal Market Bill—a Bill that contains provisions which, if enacted, would significantly constrain, both legally and as a matter of practicality, the exercise by the devolved legislatures of their legislative competence; provisions that would be significantly more restrictive of the powers of the Scottish Parliament than either EU law or Articles 4 and 6 of the Acts of the Union…The UK Parliament passed the European Union (Withdrawal Agreement) Act 2020 and the Internal Market Act 2020 notwithstanding that, in each case, all three of the devolved legislatures had withheld consent.
- ^ Wincott, Daniel; Murray, C. R. G.; Davies, Gregory (17 May 2021). «The Anglo-British imaginary and the rebuilding of the UK’s territorial constitution after Brexit: unitary state or union state?». Territory, Politics, Governance. Abingdon/Brighton: Taylor & Francis; Regional Studies Association. 10 (5): 696–713. doi:10.1080/21622671.2021.1921613.
Taken as a whole, the Internal Market Act imposes greater restrictions upon the competences of the devolved institutions than the provisions of the EU Single Market which it replaced, in spite of pledges to use common frameworks to address these issues. Lord Hope, responsible for many of the leading judgments relating to the first two decades of devolution, regarded the legislation’s terms as deliberately confrontational: ‘this Parliament can do what it likes, but a different approach is essential if the union is to hold together’.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hayward, Katy; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen; Wincott, Daniel (2020). UK and the Internal Market, Devolution and the Union. Centre on Constitutional Change (Report). University of Edinburgh; University of Aberdeen. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 16 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael (2020). Briefing Paper. United Kingdom Internal Market Bill: Implications for Devolution (PDF) (Report). Liverpool: University of Liverpool. pp. 4–5. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Dougan, Michael; Hunt, Jo; McEwen, Nicola; McHarg, Aileen (2022). «Sleeping with an Elephant: Devolution and the United Kingdom Internal Market Act 2020». Law Quarterly Review. London: Sweet & Maxwell. ISSN 0023-933X. SSRN 4018581. Retrieved 4 March 2022 – via Durham Research Online.
The Act has restrictive – and potentially damaging – consequences for the regulatory capacity of the devolved legislatures…This was not the first time since the Brexit referendum that the Convention had been set aside, but it was especially notable given that the primary purpose of the legislation was to constrain the capacity of the devolved institutions to use their regulatory autonomy…in practice, it constrains the ability of the devolved institutions to make effective regulatory choices for their territories in ways that do not apply to the choices made by the UK government and parliament for the English market.
- ^ a b [185][186][187][188][189][190][191]
- ^ «Welsh assembly renamed Senedd Cymru/Welsh Parliament», BBC News, 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020
- ^ «Structure and powers of the Assembly». BBC News. 9 April 1999. Retrieved 21 October 2008.
- ^ «Your Executive». Northern Ireland Executive. 25 September 2015.
- ^ Burrows, N. (1999). «Unfinished Business: The Scotland Act 1998». The Modern Law Review. 62 (2): 241–260 [p. 249]. doi:10.1111/1468-2230.00203.
The UK Parliament is sovereign and the Scottish Parliament is subordinate. The White Paper had indicated that this was to be the approach taken in the legislation. The Scottish Parliament is not to be seen as a reflection of the settled will of the people of Scotland or of popular sovereignty but as a reflection of its subordination to a higher legal authority. Following the logic of this argument, the power of the Scottish Parliament to legislate can be withdrawn or overridden…
; Elliot, M. (2004). «United Kingdom: Parliamentary sovereignty under pressure». International Journal of Constitutional Law. 2 (3): 545–627, 553–554. doi:10.1093/icon/2.3.545.Notwithstanding substantial differences among the schemes, an important common factor is that the UK Parliament has not renounced legislative sovereignty in relation to the three nations concerned. For example, the Scottish Parliament is empowered to enact primary legislation on all matters, save those in relation to which competence is explicitly denied … but this power to legislate on what may be termed «devolved matters» is concurrent with the Westminster Parliament’s general power to legislate for Scotland on any matter at all, including devolved matters … In theory, therefore, Westminster may legislate on Scottish devolved matters whenever it chooses…
- ^ Walker, G. (2010). «Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Devolution, 1945–1979». Journal of British Studies. 39 (1): 117–142. doi:10.1086/644536.
- ^ Gamble, A. (2006). «The Constitutional Revolution in the United Kingdom». Publius. 36 (1): 19–35 [p. 29]. doi:10.1093/publius/pjj011.
The British parliament has the power to abolish the Scottish parliament and the Welsh assembly by a simple majority vote in both houses, but since both were sanctioned by referenda, it would be politically difficult to abolish them without the sanction of a further vote by the people. In this way, several of the constitutional measures introduced by the Blair government appear to be entrenched and not subject to a simple exercise of parliamentary sovereignty at Westminster.
- ^ Meehan, E. (1999). «The Belfast Agreement – Its Distinctiveness and Points of Cross-Fertilization in the UK’s Devolution Programme». Parliamentary Affairs. 52 (1): 19–31 [p. 23]. doi:10.1093/pa/52.1.19.
[T]he distinctive involvement of two governments in the Northern Irish problem means that Northern Ireland’s new arrangements rest upon an intergovernmental agreement. If this can be equated with a treaty, it could be argued that the forthcoming distribution of power between Westminster and Belfast has similarities with divisions specified in the written constitutions of federal states…Although the Agreement makes the general proviso that Westminster’s ‘powers to make legislation for Northern Ireland’ remains ‘unaffected’, without an explicit categorical reference to reserved matters, it may be more difficult than in Scotland or Wales for devolved powers to be repatriated. The retraction of devolved powers would not merely entail consultation in Northern Ireland backed implicitly by the absolute power of parliamentary sovereignty but also the renegotiation of an intergovernmental agreement.
- ^ «CIBC PWM Global – Introduction to The Cayman Islands». Cibc.com. 11 July 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ Rappeport, Laurie. «Cayman Islands Tourism». Washington, D.C.: USA Today Travel Tips. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Background briefing on the Crown Dependencies: Jersey, Guernsey and the Isle of Man» (PDF). Ministry of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Bosque, Maria Mut (2022). «Questioning the current status of the British Crown Dependencies». Small States & Territories. 5 (1): 55–70 – via University of Malta.
- ^ a b Loft, Philip (1 November 2022). The separation of powers in the UK’s Overseas Territories (Report). House of Commons Library.
- ^ «Overseas Territories». Gov.uk. Foreign & Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ «The World Factbook». CIA. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- ^ Overseas Territories The Ministry of Defence’s Contribution. Ministry of Defence. 1 March 2012. p. 1. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ Global Britain and the British Overseas Territories: Resetting the relationship (PDF). House of Commons Foreign Affairs Committee. 13 February 2019. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ «Sea Around Us | Fisheries, Ecosystems and Biodiversity». www.seaaroundus.org. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ^ «Partnership for Progress and Prosperity» (PDF). UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ Davison, Phil (18 August 1995). «Bermudians vote to stay British». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
- ^ «Gibraltar referendum result in quotes». BBC News. 8 November 2002.
- ^ «Falklands: Cameron says Argentina should respect vote». BBC News. 12 March 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons. «House of Commons – Crown Dependencies – Justice Committee». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2010.
- ^ Fact sheet on the UK’s relationship with the Crown Dependencies – gov.uk, Ministry of Justice. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ «Profile of Jersey». States of Jersey. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2008.
The legislature passes primary legislation, which requires approval by The Queen in Council, and enacts subordinate legislation in many areas without any requirement for Royal Sanction and under powers conferred by primary legislation.
- ^ «Chief Minister to meet Channel Islands counterparts – Isle of Man Public Services» (Press release). Isle of Man Government. 29 May 2012. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The Treaty (act) of the Union of Parliament 1706». Scottish History Online. Archived from the original on 27 May 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2008.
- ^ «UK Supreme Court judges sworn in». BBC News. 1 October 2009.; «Constitutional reform: A Supreme Court for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Constitutional Affairs. July 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 January 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- ^ «Role of the JCPC». Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Bainham, Andrew (1998). The international survey of family law: 1996. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff. p. 298. ISBN 978-90-411-0573-8.
- ^ Adeleye, Gabriel; Acquah-Dadzie, Kofi; Sienkewicz, Thomas; McDonough, James (1999). World dictionary of foreign expressions. Waucojnda, IL: Bolchazy-Carducci. p. 371. ISBN 978-0-86516-423-9.
- ^ «The Australian courts and comparative law». Australian Law Postgraduate Network. Archived from the original on 14 April 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Court of Session – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 31 July 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «High Court of Justiciary – Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 12 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «House of Lords – Practice Directions on Permission to Appeal». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «Introduction». Scottish Courts. Archived from the original on 1 September 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Samuel Bray (2005). «Not proven: introducing a third verdict». The University of Chicago Law Review. 72 (4): 1299–1329. JSTOR 4495530.
- ^ «Crime in England and Wales, Year Ending June 2015» (PDF).
- ^ «UK prison population figures». British Government. Retrieved 10 November 2015.; Highest to Lowest. World Prison Brief. International Centre for Prison Studies.
- ^ «• England & Wales: Recorded homicides 2002–2015 – UK Statistics». Statista.
- ^ «Scottish homicide figures fall to another record low». BBC News. 29 September 2015.
- ^ «Prime Minister’s letter to Donald Tusk triggering Article 50». GOV.UK.
- ^ Swaine, Jon (13 January 2009). «Barack Obama presidency will strengthen special relationship, says Gordon Brown». The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 3 May 2011.; Kirchner, E.J.; Sperling, J. (2007). Global Security Governance: Competing Perceptions of Security in the 21st century. London: Taylor & Francis. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-415-39162-7
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons (19 February 2009). «DFID’s expenditure on development assistance». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 12 January 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sharp Drop in World Views of US, UK: Global Poll – GlobeScan». 4 July 2017.; «From the Outside In: G20 views of the UK before and after the EU referendum’» (PDF). British Council.; «New Zealand is Britons’ favourite country». 26 October 2020.
- ^ «Ministry of Defence». Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- ^ «Speaker addresses Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II». UK Parliament. 30 March 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «House of Commons Hansard». UK Parliament. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2008.; «House of Commons Hansard Written Answers for 17 Jun 2013 (pt 0002)». Publications.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ UK 2005: The Official Yearbook of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Office for National Statistics. p. 89.
- ^ «Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2016» (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ «Leading European cities by gross domestic product in 2017/18». Statista. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ «Principles for Economic Regulation». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. April 2011. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ «IMF Data – Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserve – At a Glance». Data.imf.org. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ «More About the Bank». Bank of England. n.d. Archived from the original on 12 March 2008.
- ^ «UK index of services: October 2017». Office for National Statistics. 22 December 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ a b «GFCI 27 Rank – Long Finance». www.longfinance.net. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025». PricewaterhouseCoopers. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ «UNWTO Tourism Highlights, Edition 2005» (PDF). World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Bremner, Caroline (10 January 2010). «Euromonitor International’s Top City Destination Ranking». Euromonitor International. Archived from the original on 5 March 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ^ «From the Margins to the Mainstream – Government unveils new action plan for the creative industries». DCMS. 9 March 2007. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «UK Internal Market Bill». Institute for Government. 9 September 2020.; «UK Internal Market Bill becomes law». gov.uk.
- ^ a b «European Countries – United Kingdom». Europa (web portal). Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ^ Harrington, James W.; Warf, Barney (1995). Industrial location: Principles, practices, and policy. London: Routledge. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-415-10479-1.; Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2008). Western Civilization: Alternative Volume: Since 1300. Belmont, CA: Thomson Wadsworth. ISBN 978-0-495-55528-5.
- ^ Porter, Andrew (1998). The Nineteenth Century, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume III. Oxford University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-19-924678-6. Retrieved 22 July 2009.; Marshall, PJ (1996). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the British Empire. Cambridge University Press. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-0-521-00254-7. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Hewitt, Patricia (15 July 2004). «TUC Manufacturing Conference». Department of Trade and Industry. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Motor Industry Facts 2016» (PDF). Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders. 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 October 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ Tovey, Alan (29 June 2016). «Britain’s aerospace sector soars amid fears Brexit could clip its wings». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022.
- ^ Robertson, David (9 January 2009). «The Aerospace industry has thousands of jobs in peril». The Times. London. Archived from the original on 14 October 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2011.(subscription required)
- ^ «The Pharmaceutical sector in the UK». Department for Business, Innovation & Skills. Archived from the original on 12 December 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «Ministerial Industry Strategy Group – Pharmaceutical Industry: Competitiveness and Performance Indicators» (PDF). Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Agriculture in the United Kingdom» (PDF). Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Coal». BGS Minerals UK. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ «UK officially in recession for first time in 11 years». BBC. 12 August 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ World Development Indicators, World Bank. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for Bermuda, Chad, Cyprus, Eritrea, Greenland, Federated States of Micronesia, Monaco, Netherlands, New Caledonia and Turkmenistan.; Total Midyear Population Archived 12 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Census Bureau, International Data Base. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for Aruba, Cayman Islands, Cook Islands, Cuba, North Korea, Marshall Islands, Montenegro, Samoa, Somalia, Trinidad and Tobago and West Bank.; The World Factbook – European Union, Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 29 June 2011.; World Economic Outlook Database, April 2011, International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for the rest of the countries.; GDP (official exchange rate) Archived 24 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine, The World Factbook, United States Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 29 June 2011. Note: Used for the rest of the countries.
- ^ Gascoin, J. «A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution», in Lindberg, David C. and Westman, Robert S., eds (1990), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution. Cambridge University Press. p. 248. ISBN 978-0-521-34804-1.
- ^ Reynolds, E.E.; Brasher, N.H. (1966). Britain in the Twentieth Century, 1900–1964. Cambridge University Press. p. 336. OCLC 474197910
- ^ Burtt, E.A. (2003) 1924.The Metaphysical Foundations of Modern Science. Mineola, NY: Courier Dover. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-486-42551-1.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. pp. 16, 30 and 46. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Jungnickel, C.; McCormmach, R. (1996). Cavendish. American Philosophical Society. ISBN 978-0-87169-220-7.
- ^ «The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1945: Sir Alexander Fleming, Ernst B. Chain, Sir Howard Florey». The Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Hatt, C. (2006). Scientists and Their Discoveries. London: Evans Brothers. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-237-53195-9.
- ^ Wilson, Arthur (1994). The Living Rock: The Story of Metals Since Earliest Times and Their Impact on Civilization. p. 203. Woodhead Publishing.
- ^ James, I. (2010). Remarkable Engineers: From Riquet to Shannon. Cambridge University Press. pp. 33–36. ISBN 978-0-521-73165-2.
- ^ Newman, M.H.A. (1948). «General Principles of the Design of All-Purpose Computing Machines». Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A. 195 (1042): 271–274. Bibcode:1948RSPSA.195..271N. doi:10.1098/rspa.1948.0129.
- ^ Hubbard, Geoffrey (1965) Cooke and Wheatstone and the Invention of the Electric Telegraph, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London p. 78
- ^ Bova, Ben (2002) 1932. The Story of Light. Naperville, IL: Sourcebooks. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-4022-0009-0.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922)». Nature. 159 (4035): 297. 1947. Bibcode:1947Natur.159Q.297.. doi:10.1038/159297a0.
- ^ «John Logie Baird (1888–1946)». BBC History. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011). Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-59884-302-6.
- ^ Castells, M.; Hall, P.; Hall, P.G. (2004). Technopoles of the World: the Making of Twenty-First-Century Industrial Complexes. London: Routledge. pp. 98–100. ISBN 978-0-415-10015-1.
- ^ «Knowledge, networks and nations: scientific collaborations in the twenty-first century» (PDF). Royal Society. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2011.
- ^ McCook, Alison (2006). «Is peer review broken?». The Scientist. 20 (2): 26. Archived from the original on 16 August 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ^ WIPO. «Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition». www.wipo.int. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. Retrieved 16 November 2022.; «Global Innovation Index 2021». World Intellectual Property Organization. United Nations. Retrieved 5 March 2022.; «Release of the Global Innovation Index 2020: Who Will Finance Innovation?». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «Global Innovation Index 2019». World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.; «RTD – Item». ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ Moran, Joe (16 November 2005). Reading the Everyday. Routledge. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-134-37216-4.
- ^ «Transport Statistics Great Britain: 2010» (PDF). Department for Transport. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 December 2010.
- ^ «German Railway Financing» (PDF). Deutschebahn.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Efficiency indicators of Railways in France» (PDF). Internationaltransportforum.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2018.; «Rail industry financial information 2014–15» (PDF). Orr.gov.uk.
- ^ Sylvain Duranton; Agnès Audier; Joël Hazan; Mads Peter Langhorn; Vincent Gauche (18 April 2017). «The 2017 European Railway Performance Index». Boston Consulting Group.
- ^ «What is HS2». HS2.
- ^ «Crossrail’s giant tunnelling machines unveiled». BBC News. 2 January 2012.; Leftly, Mark (29 August 2010). «Crossrail delayed to save £1bn». The Independent on Sunday. London.
- ^ «Bus statistics». GOV.UK.
- ^ «Our Collection». icons.org.uk. Retrieved 16 August 2014.
- ^ London Buses, Transport for London. Accessed 10 May 2007.
- ^ a b «Size of Reporting Airports October 2009 – September 2010» (PDF). Civil Aviation Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ «Heathrow ‘needs a third runway’«. BBC News. 25 June 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.; «Statistics: Top 30 World airports» (PDF) (Press release). Airports Council International. July 2008. Retrieved 15 October 2008.
- ^ «BMI being taken over by Lufthansa». BBC News. 29 October 2008. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ^ «United Kingdom Energy Profile». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 2 January 2009. Retrieved 4 November 2010.
- ^ Mason, Rowena (24 October 2009). «Let the battle begin over black gold». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 26 November 2010.; Heath, Michael (26 November 2010). «RBA Says Currency Containing Prices, Rate Level ‘Appropriate’ in Near Term». Bloomberg. New York. Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2010.
- ^ «International – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)». www.eia.gov.; «United Kingdom Crude Oil Consumption by Year (Thousand Barrels per Day)». indexmundi.com.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Oil». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Natural Gas». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 16 April 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ a b «United Kingdom – Quick Facts Energy Overview». U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 12 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Coal Reserves in the United Kingdom» (PDF). The Coal Authority. 10 April 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Expert predicts ‘coal revolution’«. BBC News. 16 October 2007. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ Watts, Susan (20 March 2012). «Fracking: Concerns over gas extraction regulations». BBC News. Retrieved 9 April 2013.; «Quit fracking aboot». Friends of the Earth Scotland. Archived from the original on 24 April 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «Nuclear Power in the United Kingdom». World Nuclear Association. April 2013. Archived from the original on 14 February 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ «UK Renewables Q3 2019» (PDF).
- ^ Wilson, Grant; Staffell, Iain; Godfrey, Noah (7 January 2020). «2019 saw the rise of wind power and the collapse of coal». The Independent. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ «WHO / UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme: 404 error».[permanent dead link]
- ^ «Environment Agency». Archived from the original on 25 November 2009.
- ^ «About Us». niwater.com. Retrieved 29 August 2020.
- ^ «Census Geography». Office for National Statistics. 30 October 2007. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Population Estimates for the United Kingdom» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 27 March 2011. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ a b «Population Estimates for UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, Mid-2015». Office for National Statistics. 23 June 2016.
- ^ «Annual Mid-year Population Estimates, 2010» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2012.
- ^ «World Factbook EUROPE: United Kingdom», The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- ^ a b «2011 UK censuses». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ Khan, Urmee (16 September 2008). «England is most crowded country in Europe». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 18 September 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ Carrell, Severin (17 December 2012). «Scotland’s population at record high». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ «Vital statistics: population and health reference tables». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- ^ Boseley, Sarah (14 July 2008). «The question: What’s behind the baby boom?». The Guardian. London. p. 3. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Max Roser (2014), «Total Fertility Rate around the world over the last centuries», Our World In Data, Gapminder Foundation, archived from the original on 5 July 2019, retrieved 10 December 2019
- ^ «Vital Statistics: Population and Health Reference Tables (February 2014 Update): Annual Time Series Data». ONS. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table. Eurostat (26 February 2013). Retrieved 12 July 2013.
- ^ «Sexual identity, UK: 2015 – Experimental Official Statistics on sexual identity in the UK in 2015 by region, sex, age, marital status, ethnicity and NS-SEC». Office for National Statistics. 5 October 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- ^ «Research report 27: Trans research review». equalityhumanrights.com. p. v.
- ^ «2011 Census — Built-up areas». ONS. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ «NRS – Background Information Settlements and Localities» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- ^ The UK’s major urban areas Office for National Statistics (Urban area of Belfast and connected settlements, Table 3.1, page 47)
- ^ «Welsh people could be most ancient in UK, DNA suggests». BBC News. 19 June 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Thomas, Mark G.; et al. (October 2006). «Evidence for a segregated social structure in early Anglo-Saxon England». Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 273 (1601): 2651–2657. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3627. PMC 1635457. PMID 17002951.
- ^ Owen, James (19 July 2005). «Review of ‘The Tribes of Britain’». National Geographic (Washington, D.C.).; Oppenheimer, Stephen (October 2006).«Myths of British ancestry». Archived from the original on 26 September 2006. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link). Prospect (London). Retrieved 5 November 2010; Henderson, Mark (23 October 2009). «Scientist – Griffin hijacked my work to make race claim about ‘British aborigines’«. The Times. London. Retrieved 26 October 2009. (subscription required) - ^ «Victoria and Albert Museum Black Presence». 13 January 2011.
- ^ Winder, Robert (2010). Bloody Foreigners: The Story of Immigration to Britain. ISBN 978-0-7481-2396-4.; Costello, Ray (2001). Black Liverpool: The Early History of Britain’s Oldest Black Community 1730–1918. Liverpool: Picton Press. ISBN 978-1-873245-07-1.
- ^ «Culture and Ethnicity Differences in Liverpool – Chinese Community». Chambré Hardman Trust. Archived from the original on 24 July 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Coleman, David; Compton, Paul; Salt, John (2002). «The demographic characteristics of immigrant populations», Council of Europe, p. 505. ISBN 978-92-871-4974-9.
- ^ Roger Ballard Centre for Applied South Asian Studies. «Britain’s visible minorities: a demographic overview» (PDF).
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ a b Vargas-Silva, Carlos (10 April 2014). «Migration Flows of A8 and other EU Migrants to and from the UK». Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Vertovec, Steven (2007). «Super-diversity and its implications». Ethnic and Racial Studies. 30 (6): 1024–1054. doi:10.1080/01419870701599465. S2CID 143674657. Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 3 April 2019.; Vertovec, Steven (20 September 2005). «Opinion: Super-diversity revealed». BBC News. Retrieved 8 March 2015.; Aspinall, Peter J (2012). «Answer Formats in British Census and Survey Ethnicity Questions: Does Open Response Better Capture ‘Superdiversity’?». Sociology. 46 (2): 354–364. doi:10.1177/0038038511419195. S2CID 144841712.
- ^ Ballard, Roger (1996). «Negotiating race and ethnicity: Exploring the implications of the 1991 census» (PDF). Patterns of Prejudice. 30 (3): 3–33. doi:10.1080/0031322X.1996.9970192.; Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (2002). «Censuses, identity formation, and the struggle for political power». In Kertzer, David I.; Arel, Dominique (eds.). Census and Identity: The Politics of Race, Ethnicity, and Language in National Censuses. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–42.
- ^ a b c «2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in the United Kingdom». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2013. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ «Population Size: 7.9 per cent from a minority ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 13 February 2003. Archived from the original on 31 July 2003. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ «Ethnicity and National Identity in England and Wales 2011» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): London». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 23 June 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.; «Resident population estimates by ethnic group (percentages): Leicester». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ «Census 2001 – Ethnicity and religion in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 April 2008.
- ^ Schools, pupils and their characteristics: January 2016 (PDF) (Report). Department for Education. 28 June 2016. p. 8. SFR 20/2016.
- ^ M.S (11 December 2012). «Britain’s amazing technicolour dreamcoat». The Economist.
- ^ «Population size: 7.9 per cent from a non-White ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 8 January 2004. Archived from the original on 19 June 2004.
- ^ «Table KS201SC – Ethnic group: All people» (PDF). National Records of Scotland. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ «Ethnic group». Office for National Statistics. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- ^ «English language – Government, citizens and rights». Directgov. Archived from the original on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 23 August 2011.
- ^ Mac Sithigh, Daithí (17 May 2018). «Official status of languages in the UK and Ireland» (PDF). Common Law World Review. Queen’s University, Belfast. 47 (1): 77–102. doi:10.1177/1473779518773642.
- ^ a b «Languages across Europe: United Kingdom». bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 4 February 2013.
- ^ Carl Skutsch (2013). Encyclopedia of the World’s Minorities. pp.1261. Routledge. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ Booth, Robert (30 January 2013). «Polish becomes England’s second language». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^ «The teenagers who translate for their parents». BBC News. 23 April 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ Track, Robert Lawrence; Stockwell, Peter (2007). Language and Linguistics: The Key Concepts. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-415-41358-9. Retrieved 4 August 2019.; «Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, Strasbourg, 1.II.1995». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; «European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992». Council of Europe. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh language in Wales (Census 2021)». gov.wales. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ Wynn Thomas, Peter (March 2007). «Welsh today». Voices. BBC. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ «Scotland’s Census 2001 – Gaelic Report». General Register Office for Scotland. Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Local UK languages ‘taking off’«. BBC News. 12 February 2009.
- ^ Edwards, John R. (2010). Minority languages and group identity: cases and categories. John Benjamins. pp. 150–158. ISBN 978-90-272-1866-7. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Koch, John T. (2006). Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 696. ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0.
- ^ «Language Data – Scots». European Bureau for Lesser-Used Languages. Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ Brown, Hannah (23 April 2020). «‘People are dying because of this’: Calls for UK Gov to follow Scotland with sign language interpreter at Covid-19 briefing». The Scotsman. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ «British Sign Language Act 2022, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ «Fall in compulsory language lessons». BBC News. 4 November 2004.
- ^ «GCSE results day 2021: Spanish has biggest increase in entries, but German plummets». i (newspaper). 12 August 2021.
- ^ «The School Gate for parents in Wales». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 15 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011, s 1(1)». legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ Ainsworth, Paul (6 December 2022). «‘Historic milestone’ passed as Irish language legislation becomes law». The Irish News. Retrieved 10 December 2022.
- ^ «Religion, England and Wales: Census 2021». ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ Cannon, John, ed. (2nd edn., 2009). A Dictionary of British History. Oxford University Press. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-19-955037-1.
- ^ Field, Clive D. (November 2009). «British religion in numbers». BRIN Discussion Series on Religious Statistics, Discussion Paper 001. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- ^ Yilmaz, Ihsan (2005). Muslim Laws, Politics and Society in Modern Nation States: Dynamic Legal Pluralisms in England, Turkey, and Pakistan. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-0-7546-4389-0.
- ^ Brown, Callum G. (2006). Religion and Society in Twentieth-Century Britain. Harlow: Pearson Education. p. 291. ISBN 978-0-582-47289-1.
- ^ Norris, Pippa; Inglehart, Ronald (2004). Sacred and Secular: Religion and Politics Worldwide. Cambridge University Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-521-83984-6.
- ^ Fergusson, David (2004). Church, State and Civil Society. Cambridge University Press. p. 94. ISBN 978-0-521-52959-4.
- ^ «UK Census 2001». Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 12 March 2007. Retrieved 22 April 2007.
- ^ «Religious Populations». Office for National Statistics. 11 October 2004. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «United Kingdom: New Report Finds Only One in 10 Attend Church». News.adventist.org. 4 April 2007. Archived from the original on 13 December 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Philby, Charlotte (12 December 2012). «Less religious and more ethnically diverse: Census reveals a picture of Britain today». The Independent. London.
- ^ «The percentage of the population with no religion has increased in England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. 4 April 2013.
- ^ a b c «British Social Attitudes: Record number of Brits with no religion». NatCen.ac.uk. 4 September 2017.
- ^ «The History of the Church of England». The Church of England. 2004. Archived from the original on 15 April 2009. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ «Queen and Church of England». British Monarchy Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 October 2006. Retrieved 5 June 2010.
- ^ «Queen and the Church». The British Monarchy (Official Website). Archived from the original on 5 June 2011.
- ^ «Our structure». churchofscotland.org.uk. 22 February 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2020.
- ^ Weller, Paul (2005). Time for a Change: Reconfiguring Religion, State, and Society. London: Continuum. pp. 79–80. ISBN 978-0-567-08487-3.
- ^ Peach, Ceri, «United Kingdom, a major transformation of the religious landscape», in H. Knippenberg. ed. (2005). The Changing Religious Landscape of Europe. Amsterdam: Het Spinhuis. pp. 44–58. ISBN 978-90-5589-248-8.
- ^ Russell, Rachel; Farley, Harry (29 November 2022). «Less than half of England and Wales population Christian, Census 2021 shows». BBC News.
- ^ a b Coleman, David (17 April 2013). «Immigration, Population and Ethnicity: The UK in International Perspective». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ «The National Archives | Exhibitions | 1901 Census | Events». www.nationalarchives.gov.uk.
- ^ a b Green, Lord Andrew. «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migration Watch UK.
- ^ «UK 2011 Census Data». National Archives. 11 December 2012. Archived from the original on 12 April 2013.; National Archives (17 December 2013). «Non-UK Born Population of England and Wales Quadrupled Between 1951 and 2011». Archived from the original on 5 January 2016.; «2011 Census analysis: Immigration Patterns of Non-UK Born Populations in England and Wales in 2011». Office for National Statistics. 17 December 2013.
- ^ «International migration, England and Wales». Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 8 November 2022.
- ^ Richards, Eric (2004). Britannia’s children: Emigration from England, Scotland, Wales and Ireland since 1600. London: Hambledon, p. 143. ISBN 978-1-85285-441-6.
- ^ P. Panayi (1906). P. Panayi, ‘German Immigrants in Britain, 1815–1914’ in Germans in Britain since 1500, ed P. Panayi, (London: Hambledon Press, 1996). pp. 73–112. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.
- ^ Panayi, Panikos (1996). Germans in Britain Since 1500. ISBN 978-0-8264-2038-1.; «East End Jews». BBC.
- ^ Jews in Britain: Origin and Growth of Anglo-Jewry. p. 7.; «A summary history of immigration to Britain». Migrationwatch UK.; «The Jews». Victoria County History, London, 1969 – via British History Online.
- ^ Gibney, Matthew J.; Hansen, Randall (2005). Immigration and asylum: from 1900 to the present, ABC-CLIO, p. 630. ISBN 978-1-57607-796-2
- ^ «Short History of Immigration». BBC News. 2005. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2015». Office for National Statistics. 21 May 2015.
- ^ «Migration Statistics Quarterly Report May 2012». Office for National Statistics. 24 May 2012.
- ^ Doward, Jamie; Temko, Ned (23 September 2007). «Home Office shuts the door on Bulgaria and Romania». The Observer. London. p. 2. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- ^ Sumption, Madeleine; Somerville, Will (January 2010). The UK’s new Europeans: Progress and challenges five years after accession (PDF). Policy Report. London: Equality and Human Rights Commission. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-84206-252-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Doward, Jamie; Rogers, Sam (17 January 2010). «Young, self-reliant, educated: portrait of UK’s eastern European migrants». The Observer. London. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ^ Hopkirk, Elizabeth (20 October 2008). «Packing up for home: Poles hit by UK’s economic downturn». London Evening Standard.
- ^ «Recession moves migration patterns». BBC News. 8 September 2009. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ Muenz, Rainer (June 2006). «Europe: Population and Migration in 2005». Migration Policy Institute. Archived from the original on 9 June 2008. Retrieved 2 April 2007.
- ^ «Immigration and births to non-British mothers pushes British population to record high». London Evening Standard. 21 August 2008.
- ^ «Births in England and Wales: 2014». Office for National Statistics. 15 July 2015.
- ^ Travis, Alan (25 August 2011). «UK net migration rises 21 per cent». The Guardian. London.
- ^ a b Blinder, Scott (27 March 2015). «Naturalisation as a British Citizen: Concepts and Trends» (PDF). The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ Blinder, Scott (11 June 2014). «Settlement in the UK». The Migration Observatory, University of Oxford. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ^ «Fresh Talent: Working in Scotland». London: UK Border Agency. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Boxell, James (28 June 2010). «Tories begin consultation on cap for migrants». Financial Times. London. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ Richards (2004), pp. 6–7.
- ^ a b Sriskandarajah, Dhananjayan; Drew, Catherine (11 December 2006). «Brits Abroad: Mapping the scale and nature of British emigration». Institute for Public Policy Research. Archived from the original on 28 August 2007. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: world overview». BBC. Retrieved 20 April 2007.; Casciani, Dominic (11 December 2006). «5.5 m Britons ‘opt to live abroad’«. BBC News. Retrieved 20 April 2007.
- ^ «Brits Abroad: Country-by-country». BBC News. 11 December 2006.
- ^ «The Most Educated Countries in the World». Yahoo Finance. 24 September 2012. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2016.; «And the World’s Most Educated Country Is…». Time. New York. 27 September 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «Academic Ranking of World Universities 2015». Shanghai. 2015. Archived from the original on 30 October 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.; Quacquarelli Symonds Limited (2015). «QS World University Rankings 2015/16». London. Retrieved 21 October 2015.; «World University Rankings 2015–16». Times Higher Education. London. 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.; «Best Global Universities Rankings 2016». U.S. News & World Report. Washington, D.C. 2015. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ «Elitist Britain?» (PDF). Social Mobility and Child Poverty Commission. 28 August 2014.; Arnett, George (28 August 2014). «Elitism in Britain – breakdown by profession». The Guardian: Datablog.
- ^ «Local Authorities». Department for Children, Schools and Families. Archived from the original on 30 December 2008. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ Gordon, J.C.B. (1981). Verbal Deficit: A Critique. London: Croom Helm. p. 44 note 18. ISBN 978-0-85664-990-5.; Section 8 (‘Duty of local education authorities to secure provision of primary and secondary schools’), Sections 35–40 (‘Compulsory attendance at Primary and Secondary Schools’) and Section 61 (‘Prohibition of fees in schools maintained by local education authorities …’), Education Act 1944.
- ^ «School leaving age». UK Government. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «England’s pupils in global top 10». BBC News. 10 December 2008.
- ^ Frankel, Hannah (3 September 2010). «Is Oxbridge still a preserve of the posh?». TES. London. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ^ MacLeod, Donald (9 November 2007). «Private school pupil numbers in decline». The Guardian. London. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Independent Schools Council Research». Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ «About SQA». Scottish Qualifications Authority. 10 April 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «About Learning and Teaching Scotland». Learning and Teaching Scotland. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Brain drain in reverse». Scotland Online Gateway. July 2002. Archived from the original on 4 December 2007.
- ^ «Facts and Figures». SCIS. Retrieved 14 November 2017.
- ^ «MSPs vote to scrap endowment fee». BBC News. 28 February 2008.
- ^ «Education System». Welsh Government. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Nursery education for 3 and 4 year olds in Wales» (PDF). 2019.; «Compulsory school age». Practical Law. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Comisiynydd: Nifer y plant mewn addysg Gymraeg yn ‘sioc’«. BBC Cymru Fyw (in Welsh). BBC. 4 August 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.; «Welsh in education: Action Plan 2017–2021» (PDF). Welsh Government. 2017. p. 16.
- ^ «Pisa education tests: Wales improves performance». BBC News. 3 December 2019. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ Wightwick, Abbie (22 August 2019). «GCSE results 2019: Extreme concern at drop in English language results». WalesOnline. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ^ «Participation of young people in education and the labour market 2017 and 2018 (provisional)» (PDF). Welsh Government. 21 August 2019.
- ^ CCEA. «About Us – What we do». Council for the Curriculum Examinations & Assessment. Archived from the original on 5 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Haden, Angela; Campanini, Barbara, eds. (2000). The world health report 2000 – Health systems: improving performance. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156198-3. Retrieved 5 July 2011.; World Health Organization. «Measuring overall health system performance for 191 countries» (PDF). New York University. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
- ^ Fisher, Peter. «The NHS from Thatcher to Blair». NHS Consultants Association. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
The Budget … was even more generous to the NHS than had been expected amounting to an annual rise of 7.4 per cent above the rate of inflation for the next five years. This would take us to 9.4 per cent of GDP spent on health ie around EU average.
- ^ «Swindells: They aren’t ‘your’ patients». Health Service Journal. 24 September 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
- ^ «How does UK healthcare spending compare with other countries?». Office of National Statistics. 29 August 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- ^ «‘Huge contrasts’ in devolved NHS». BBC News. 28 August 2008.; Triggle, Nick (2 January 2008). «NHS now four different systems». BBC News.
- ^ «BBC poll: Germany most popular country in the world». BBC. 23 May 2013. Retrieved 20 February 2018.; «World Service Global Poll: Negative views of Russia on the rise». BBC.co.uk. 4 June 2014. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ Goldfarb, Jeffrey (10 May 2006). «Bookish Britain overtakes America as top publisher». RedOrbit. Texas. Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 January 2008.
- ^ «William Shakespeare (English author)». Britannica Online encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; MSN Encarta Encyclopedia article on Shakespeare. Archived from the original on 9 February 2006. Retrieved 26 February 2006.; William Shakespeare. Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 26 February 2006.
- ^ «Mystery of Christie’s success is solved». The Daily Telegraph. London. 19 December 2005. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ Ciabattari, Jane (December 2015). «The 25 greatest British novels». BBC Culture. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ «Edinburgh, United Kingdom, UNESCO City of Literature». Unesco. 2004. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Early Welsh poetry». BBC Wales. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ Lang, Andrew (2003) [1913]. History of English Literature from Beowulf to Swinburne. Holicong, PA: Wildside Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-8095-3229-2.
- ^ «Dafydd ap Gwilym». Academi.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
Dafydd ap Gwilym is widely regarded as one of the greatest Welsh poets of all time, and amongst the leading European poets of the Middle Ages.
- ^ «True birthplace of Wales’s literary hero». BBC News. 5 December 1999. Archived from the original on 16 March 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ «Kate Roberts: Biography». BBC Wales. Archived from the original on 24 July 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ^ Varty, Anne (2014). A Preface to Oscar Wilde. Routledge. pp. 231–232. ISBN 978-1-317-89231-1.; «Oscar Wilde». Encyclopedia.com. Cengage. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Moss, Joyce (2001). British and Irish Literature and Its Times: The Victorian Era to the Present (1837–). Gale Group. p. 107. ISBN 978-0-7876-3729-3.
- ^ Holroyd, Michael (1989). Bernard Shaw, Volume 2: 1898–1918: The Pursuit of Power. Chatto & Windus. p. 384. ISBN 978-0-7011-3350-4.; «G B Shaw». Discovering Literature: 20th century. British Library. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Middleton, Tim (2006). Joseph Conrad. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-415-26851-6.
- ^ Cooper, John Xiros (2006). The Cambridge Introduction to T. S. Eliot. Cambridge University Press. p. 111. ISBN 978-1-139-45790-3.
- ^ Sim, Wai-chew (2009). Kazuo Ishiguro. Routledge. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-135-19867-1.
- ^ «Salman Rushdie». Oxford Reference. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ Campbell, James (17 May 2008). «Home from home». The Guardian. Retrieved 10 December 2019.; Nadel, Ira (2004). Ezra Pound: A Literary Life. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-230-37881-0.
- ^ Fieser, James, ed. (2000). A bibliography of Scottish common sense philosophy: Sources and origins (PDF). Bristol: Thoemmes Press. Retrieved 17 December 2010.
- ^ Palmer, Michael (1999). Moral Problems in Medicine: A Practical Coursebook. Cambridge: Lutterworth Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-7188-2978-0.; Scarre, Geoffrey (1995). Utilitarianism. London: Routledge. p. 82. ISBN 978-0-415-12197-2.
- ^ «British Citizen by Act of Parliament: George Frideric Handel». UK Parliament. 20 July 2009. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Andrews, John (14 April 2006). «Handel all’inglese». Playbill. New York. Archived from the original on 16 May 2008. Retrieved 11 September 2009.
- ^ «Remembrance Sunday». Department for Culture Media and Sport. Retrieved 19 April 2022.; Richards, Jeffrey (2001). Imperialism and Music: Britain 1876–1953. Manchester University Press. pp. 155–156. ISBN 0-7190-4506-1.
- ^ Iemperley, Nicholas (2002). «Great Britain». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Banfield, Stephen; Russell, Ian (2001). «England (i)». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Lewis, Geraint; Davies, Lyn; Kinney, Phyllis (2001). «Wales». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; Elliott, Kenneth; Collinson, Francis; Duesenberry, Peggy (2001). «Scotland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; White, Harry; Carolan, Nicholas (2011). «Ireland». Grove Music Online (8th ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0.; «British 20th century composers». BBC. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ a b «1960–1969». EMI Group. Archived from the original on 25 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «Paul At Fifty». Time. New York. 8 June 1992. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009.
- ^ a b Most Successful Group The Guinness Book of Records 1999, p. 230. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ R. Middleton, et al., «Pop», Grove music online, retrieved 14 March 2010. (subscription required) Archived 13 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Pop», The Oxford Dictionary of Music, retrieved 9 March 2010.(subscription required) Archived 12 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «The Rolling Stones | Biography & History». AllMusic. Retrieved 22 July 2020.
- ^ Tom Larson (2004). History of Rock and Roll. Kendall/Hunt Pub. pp. 183–187. ISBN 978-0-7872-9969-9.
- ^ «Glam Rock». Encarta. Archived from the original on 28 August 2009. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ «NME Originals: Goth». NME. 2004. Archived from the original on 26 January 2008. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ^ «Pop/Rock » Psychedelic/Garage». AllMusic. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ «The Sex Pistols». RollingStone.com. 2001. Archived from the original on 1 February 2013. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ Henderson, Alex (1 August 2003). British Soul. Allmusic. Retrieved 6 March 2011.; AllMusic – Dubstep Archived 23 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine «Absorbed and transfigured elements of techno, drum’n’ bass and dub»; Goldman, Vivien (31 January 2012). «Local Groove Does Good: The Story Of Trip-Hop’s Rise From Bristol». NPR.
- ^ a b «UK music single sales: genre breakdown 2016 | Statistic». Statista. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «5 U.K. Rappers Primed to Take Over America in 2018». Billboard. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- ^ «Beatles a big hit with downloads». Belfast Telegraph. 25 November 2010. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
- ^ «British rock legends get their own music title for PlayStation3 and PlayStation2» (Press release). EMI. 2 February 2009. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2015.; Khan, Urmee (17 July 2008). «Sir Elton John honoured in Ben and Jerry ice cream». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 30 July 2008.; Alleyne, Richard (19 April 2008). «Rock group Led Zeppelin to reunite». The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2010.; «Floyd ‘true to Barrett’s legacy’«. BBC News. 11 July 2006.; Holton, Kate (17 January 2008). «Rolling Stones sign Universal album deal». Reuters. Retrieved 26 October 2008.; Walker, Tim (12 May 2008). «Jive talkin’: Why Robin Gibb wants more respect for the Bee Gees». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2011. Retrieved 26 October 2008.
- ^ «Brit awards winners list 2012: every winner since 1977». The Guardian (London). Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ «Harry Styles Has Weathered the Post-Boy Band Storm Better Than Most». Consequence of Sound. 12 January 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; «10 Years of One Direction: The Story of the World’s Biggest Boy Band, Told With the Fans Who Made It Happen». Billboard. 16 July 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.; Corner, Lewis (16 February 2012). «Adele, Coldplay biggest-selling UK artists worldwide in 2011». Digital Spy. Retrieved 22 March 2012.; Magliola, Anna Sky (30 November 2022). «Ed Sheeran’s career journey: From street busker to global superstar». PlanetRadio.co.uk. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ^ Hughes, Mark (14 January 2008). «A tale of two cities of culture: Liverpool vs Stavanger». The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 18 June 2018. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Glasgow gets city of music honour». BBC News. 20 August 2008. Retrieved 2 August 2009.
- ^ «Out of the melting pot: The origins and evolution of drum’n’bass». Red Bull. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- ^ «Birmingham, England … the unlikely birthplace of heavy metal». www.cnn.com. Retrieved 28 February 2022.; Bentley, David (4 June 2013). «Midlands rocks! How Birmingham’s industrial heritage made it the birthplace of heavy metal». Birmingham Post. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ Tate. «Art & Language – Art Term | Tate». Tate. Retrieved 8 September 2018.
- ^ Bayley, Stephen (24 April 2010). «The startling success of Tate Modern». The Times. London. Retrieved 19 January 2011. (subscription required)
- ^ «The top 21 British directors of all time». The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ «Vertigo is named ‘greatest film of all time’«. BBC News. 2 August 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- ^ «The Directors’ Top Ten Directors». British Film Institute. Archived from the original on 17 May 2012.
- ^ «Harry Potter becomes highest-grossing film franchise». The Guardian. London. 11 September 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- ^ «History of Ealing Studios». Ealing Studios. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «UK film – the vital statistics». UK Film Council. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ «Baftas fuel Oscars race». BBC News. 26 February 2001. Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- ^ Spencer, Colin (2003). British Food: An Extraordinary Thousand Years of History. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-13110-0.[pages needed]
- ^ «Robin Cook’s chicken tikka masala speech». The Guardian. London. 19 April 2001. Retrieved 7 September 2021.; BBC E-Cyclopedia (20 April 2001). «Chicken tikka masala: Spice and easy does it». BBC. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ «No meat please, we’re British: now a third of us approve of vegan diet». The Guardian. London. 25 December 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2022.
- ^ a b «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 5 October 2010. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ^ a b «Digital license». Prospect. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ a b «About the BBC – What is the BBC». BBC Online. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Newswire7 (13 August 2009). «BBC: World’s largest broadcaster & Most trusted media brand». Media Newsline. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.; «TV Licence Fee: facts & figures». BBC Press Office. April 2010. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft Word – The Work of the BBC World Service 2008–09 HC 334 FINAL.doc» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2011.
- ^ «News in your language – BBC News». Bbc.co.uk.; «BBC World Service». Facebook.com.
- ^ «Publications & Policies: The History of ITV». ITV.com. Archived from the original on 11 April 2011.
- ^ «Direct Broadcast Satellite Television». News Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011.
- ^ «ABCs: National daily newspaper circulation September 2008». The Guardian. UK. 10 October 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ William, D. (2010). UK Cities: A Look at Life and Major Cities in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Eastbourne: Gardners Books. ISBN 978-9987-16-021-1, pp. 22, 46, 109 and 145.
- ^ «Publishing». Department of Culture, Media and Sport. Archived from the original on 5 May 2011.
- ^ «Annual Report 2015-2016» (PDF). www.internationalpublishers.org. International Publishers Association. 2016. p. 16. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Ofcom «Communication Market Report 2010», 19 August 2010, pp. 97, 164 and 191
- ^ «Social Trends 41: Lifestyles and social participation» (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 24 February 2011.
- ^ «Top 20 countries with the highest number of Internet users». Internet World Stats. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2011.
- ^ «Union Jack or Union Flag?». The Flag Institute. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- ^ «college-of-arms.gov.uk». The College of Arms. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ «Welsh dragon call for Union flag». BBC News. 27 November 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Britannia on British Coins». Chard. Retrieved 25 June 2006.
- ^ Baker, Steve (2001). Picturing the Beast. University of Illinois Press. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-252-07030-3.
- ^ «Who is John Bull». www.loc.gov. The Library of Congress. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ a b Van Wie, Paul D. (1999). Image, History, and Politics: The Coinage of Modern Europe. New York: University Press of America. pp. 63–64. ISBN 978-0761812227.
- ^ Cleene, Marcel (2002). Compendium of Symbolic and Ritual Plants in Europe: Volume II Herbs. Ghent: Mens & Cultuur Uitgevers N.V. p. 211. ISBN 978-9077135044.
- ^ Ponsford, Matthew (19 January 2016). «Los Angeles to build world’s most expensive stadium complex». CNN. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
- ^ «Opening Ceremony of the Games of the XXX Olympiad» (PDF). Olympic.org. 27 July 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mehaffey, John. «Unparalleled Sporting History». Reuters. London. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ a b «Rugby Union ‘Britain’s Second Most Popular Sport’«. Ipsos-Mori. 22 December 2003. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ Rudd, Alyson (7 April 2008). «The father of football deserves much more». The Times. London. Retrieved 29 January 2015.; «Sheffield FC: 150 years of history». FIFA. 24 October 2007. Archived from the original on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Ebner, Sarah (2 July 2013). «History and time are key to power of football, says Premier League chief». The Times. London. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ Mitchell, Paul (November 2005). «The first international football match». BBC Sport Scotland. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- ^ «Why is there no GB Olympics football team?». BBC Sport. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2010.
- ^ «Six ways the town of Rugby helped change the world». BBC News. 1 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2015.
- ^ Godwin, Terry; Rhys, Chris (1981). The Guinness Book of Rugby Facts & Feats. Guinness Superlatives. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-85112214-4.
- ^ Louw, Jaco; Nesbit, Derrick (2008). The Girlfriends Guide to Rugby. Johannesburg: South Publishers. ISBN 978-0-620-39541-0.
- ^ Colin White (2010). «Projectile Dynamics in Sport: Principles and Applications». p. 222. Routledge
- ^ «About ECB». England and Wales Cricket Board. n.d. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ McLaughlin, Martyn (4 August 2009). «Howzat happen? England fields a Gaelic-speaking Scotsman in Ashes». The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Retrieved 30 December 2010.; «Uncapped Joyce wins Ashes call up». BBC Sport. 15 November 2006. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «Glamorgan». BBC South East Wales. August 2009. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ «History of Tennis». ITFtennis.com. Archived from the original on 22 March 2010. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ Morley, Gary (22 June 2011). «125 years of Wimbledon: From birth of lawn tennis to modern marvels». CNN. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «The History of British Motorsport and Motor Racing at Silverstone – The 1950s». Silverstone.co.uk. Archived from the original on 4 October 2009. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ a b Forrest L. Richardson (2002). «Routing the Golf Course: The Art & Science That Forms the Golf Journey». p. 46. John Wiley & Sons
- ^ «Tracking the Field» (PDF). Ipsos MORI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ «Links plays into the record books». BBC News. 17 March 2009.
- ^ «The Open Championship – More Scottish than British». PGA Tour. Archived from the original on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ^ Ardener, Shirley (2007). Professional identities: policy and practice in business and bureaucracy. New York: Berghahn. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-84545-054-0.
- ^ «Official Website of Rugby League World Cup 2008». Archived from the original on 16 October 2007.
- ^ Baker, Andrew (20 August 1995). «100 years of rugby league: From the great divide to the Super era». The Independent. London. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ «Encyclopædia Britannica (2006).ŷ Queensbury Rules, Britannica».
- ^ Chowdhury, Saj (22 January 2007). «China in Ding’s hands». BBC Sport. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ Gould, Joe (10 April 2007). «The ancient Irish sport of hurling catches on in America». Columbia News Service. Columbia Journalism School. Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ^ «Shinty». Scottish Sport. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ «Sport in Scotland». Scotland.org. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
External links
Government
- Official website of HM Government
- Official website of the British Monarchy
- The official site of the British Prime Minister’s Office
General information
Travel
- Official tourist guide to Britain
Coordinates: 55°N 3°W / 55°N 3°W
Координаты: 53°33′00″ с. ш. 2°26′00″ з. д. / 53.55° с. ш. 2.433333° з. д. (G)
Соединённое Королевство Великобритании и Северной Ирландии
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
 |
|
| Девиз: «Dieu et mon droit» «(Бог и моё право)» | |
| Гимн: «God Save the Queen» | |
| Основано | 1 января 1801 (объединение Королевства Великобритании и Королевства Ирландии) |
| Официальный язык | Английский |
| Столица | Лондон |
| Крупнейшие города | Лондон, Бирмингем, Глазго, Манчестер, Эдинбург, Ливерпуль |
| Форма правления | Парламентская монархия |
| Королева Премьер-министр |
Елизавета II Гордон Браун |
| Территория • Всего • % водной поверхн. |
76-я в мире 244 820 км² 1,3 |
| Население • Всего (2007) • Плотность |
21-е в мире 60 776 238 чел. 247 чел./км² |
| ВВП • Итого (2008) • На душу населения |
6-й в мире $2,833 трлн.[1] $46 432[1] |
| Этнохороним | Британец, Британка, Британцы |
| Валюта | Фунт стерлингов (GBP) |
| Интернет-домен | .eu (как член ЕС), |
| Телефонный код | +44 |
| Часовой пояс | UTC +0 |
Великобрита́ния (англ. United Kingdom[2]; полное название — Соединённое Короле́вство Великобрита́нии и Се́верной Ирла́ндии, англ. United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland) — островное государство в Западной Европе, форма правления — парламентская монархия. Столица — город Лондон. Название страны происходит от английского Great Britain. Британия — по этнониму племени бритты.
Государство на Британских островах (остров Великобритания и северо-восточная часть острова Ирландия, большое количество мелких островов и архипелагов, Нормандские острова), омывается Атлантическим океаном и его морями. Площадь: всего — 244 820 км², суша — 240 590 км², внутренние воды — 3 230 км². Самая высокая вершина — г. Бен-Невис (1343 м) — расположена на севере Шотландии (Грампианские горы), самая низкая точка — Фенланд (−4 м).
На севере и западе преобладает горный рельеф — Северо-Шотландское нагорье (до 1343 м), Пеннинские и Кембрийские горы; на юге и юго-востоке — холмистые равнины. Климат умеренно океанический, влажный. Средние температуры января от 3 до 7 °C, июля 11—17°C; осадков до 3000 мм в год на западе и 600—750 мм на юго-востоке. Основные реки: Темза — 334 км, Северн — 310 км, Трент, Мерси — 109 км, Клайд — 170 км. Крупнейшие озёра: Лох-Несс (пл. 56 км²), Лох-Ней (пл. 396 км²). Леса (бук, дуб, берёза) занимают около 9 % территории Великобритании.
Содержание
- 1 Административное деление
- 2 Население
- 2.1 Численность
- 2.2 Этнический состав
- 2.3 Британская нация
- 3 История
- 4 Политическая структура
- 5 Гражданство
- 6 Экономика
- 7 Культура
- 8 Религия
- 9 Вооружённые силы Великобритании
- 10 Отношения с Российской Федерацией
- 11 Устойчивые словосочетания
- 12 См. также
- 13 Примечания
- 14 Ссылки
Административное деление
Великобритания состоит из 4 административно-политических частей (исторических провинций):
- Англия (39 графств, 6 метрополитенских графств и Большой Лондон) — адм. центр Лондон
- Уэльс (22 унитарных образования: 9 графств, 3 города и 10 городов-графств) — адм. центр Кардифф
- Шотландия (12 областей: 9 округов и 3 основных территории) — адм. центр Эдинбург
- Северная Ирландия (26 округов) — адм. центр Белфаст
Зависимые территории со столицами:
- Британские острова
- Остров Мэн (Дуглас)
- Нормандские острова
- Гернси (Сент-Питер-Порт)
- Джерси (Сент-Хельер)
- Европа
- Гибралтар (Гибралтар)
- Америка
- Ангилья (Валли)
- Бермуды (Гамильтон)
- Британские Виргинские острова (Род-Таун)
- Каймановы острова (Джорджтаун)
- Остров Монтсеррат (Плимут)
- Острова Тёркс и Кайкос (Кукбурнтаун)
- Фолклендские острова (Порт-Стэнли)
- Южная Георгия и Южные Сандвичевы острова
- Атлантический океан
- Остров Святой Елены (Джеймстаун) и его зависимые территории — острова Вознесения и Тристан-да-Кунья
- Океания
- Остров Питкэрн (Адамстаун)
- Индийский океан
- Британская территория в Индийском океане — архипелаг Чагос
Население
Численность
Численность населения Великобритании с 1900 по 2007 год:
| Год | Численность (чел.) |
|---|---|
| 1900 | 35 405 900 |
| 1949 | 50 300 000 |
| 1959 | 51 900 000 |
| 1976 | 55 900 000 |
| 1998 | 59 100 000 |
| 2004 | 59 834 900 |
| 2005 | 60 441 457 |
| 2007 | 60 776 238 |
Главным образом, численность населения растет за счет трудовых иммигрантов из недавно вступивших стран в Европейский союз, которым после расширения ЕС в мае 2004 года был разрешен свободный въезд для работы на территории Великобритании. Тем не менее, рождаемость в стране по-прежнему превышает смертность, хотя естественный прирост уже не является главенствующим фактором увеличения численности британцев.[3] Общая численность населения (по данным 2008) – 61 113 205. Возрастная структура: до 14 лет – 16.7 %, 15-64 – 67.1%, от 65 и старше – 16.2%. Средний возраст мужчин – 39 лет, у женщин – 41 год. Прирост населения – 0.279%, уровень рождаемости – 10.65/1,000; уровень смертности – 10.05/1,000. Уровень чистой миграции – 2.16 мигрантов/ 1,000. 90% населения проживает в городах, с ежегодным приростом – 0.5%. В городах с числом жителей св. 100 тыс. чел. проживает почти половина населения страны. Крупнейшие по числу жителей города: Лондон (6803000 чел.), Бирмингем (935000 чел.), Глазго (654000 чел.), Шеффилд (500000 чел.), Ливерпуль (450000 чел.), Эдинбург (421000 чел.), Манчестер (398000 чел.), Белфаст (280000 чел.).
Этнический состав
Коренные жители страны составляют 92 % населения В. (2001, перепись), из них:
- англичане — 83,6 %,
- шотландцы (в основном в Шотландии) — 8,5 %,
- валлийцы (в основном в Уэльсе) — 4,9 %,
- ирландцы (в основном в Северной Ирландии, ольстерцы) — 2,9 %.
Иммигранты и их дети проживают главным образом в конурбациях Большого Лондона, Западного Мидленда и Мерсейсайда. Они составляют около 8 % населения страны, в том числе[4]:
- выходцы из Индии, Пакистана и Бангладеш — 3,6 %,
- Китая — 0,4 %,
- стран Африки — 0,8 %,
- темнокожие выходцы с островов Карибского моря — 1 %
Британская нация
1. Формирование британской нации происходило особым путем, который не сопоставим с французской моделью формирования нации (противостояние «низов» и «верхов» в Великую Французскую револицию), также и с немецкой моделью, в связи с тем, что Великобритания никогда не была раздробленным государством, как Германия до 1871 года.
2. В XIV—XV веках, в период великих географических открытий, в Великобритании огромную роль начинает играть национальная экономика, которая и сплачивала население страны.
3. Великобритания, в отличие от других европейских государств, всегда была несколько изолированна, в силу своего географического местоположения.
4. Огромную роль в консолидации британской нации сыграла и религиозная составляющая (XVII век) — была совершена революция с религиозными мотивами (противостояние католиков, протестантов).
5. Также немаловажную роль в процессе формирования британской нации можно отвести процессу огораживания, в результате которого проходила ассимиляция крестьянского населения в городах, а также освоение земли крестьянами в отдаленных уголках Великобритании.
6. В Англии Библия была переведена на английский язык раньше, чем в других европейских государствах; таким образом, возник единый универсальный для всех британцев английский язык.
7. Британцы зачастую противопоставляют себя другим этносам:
а) Британия имела самую могущественную и широкомасштабную колониальную империю в мире. Но при этом британцы демонстрировали свои различия с другими народами мира.
б) Резко отличалась и британская колониальная политика, которая в отличие от французской или испанской не пыталась ассимилировать туземцев в своих колониях, руководствуясь принципом: «Мы — англичане! Они — туземцы!» [5] [6] Однако, Распад империи привел к фундаментальному сдвигу в сознании населения: активизировались национальные движения, все больше число людей считали себя не британцами, а шотландцами, валлийцами, ирландцами. По опросам общественного мнения, даже в Англии лишь треть населения считают себя британцами. То, что в течении долгого времени объединяло жителей страны(протестантизм, патриархальность институтов власти, монархия, империя), перестало работать так же эффективно как раньше. Характерно, что с 2001 г слово ‘Британия’ в название ежегодника государственного бюро национальной статистике было заменено на Соединенное Королевство[7]
История
Британские острова завоёваны в V—VI веках англосаксами. После нормандского завоевания Англии 1066 завершился процесс феодализации, сопровождавшийся политическим объединением страны. Во 2-й половине XIII века возник английский парламент, оформилась сословная монархия. Развитие товарно-денежных отношений и борьба крестьянства (восстание Уота Тайлера 1381 и др.) привели (XV век) к почти полной ликвидации личной зависимости крестьян. В то же время крестьяне были лишены земельной собственности, что привело к их быстрой пролетаризации. В период Реформации, в 1534, создана англиканская церковь. Английская революция XVII века обеспечила утверждение капитализма. В конце XVII века оформились политические партии — тори и виги (в середине XIX века трансформировались соответственно в Консервативную и Либеральную партии). После закрепления в 1707 присоединения Шотландии (в 1649—1651 была покорена Ирландия) за объединённым королевством закрепилось название Великобритания. В конце XVIII — 1-й половине XIX веков происходил промышленный переворот. С завоевания Ост-Индской компанией богатой Бенгалии начинается создание британской колониальной империи. Около трети всех английских инвестиций этого времени имеют индийское происхождение. В 1830-е годы утвердилась фабричная система производства. В 1830 — 1840-е гг. развернулось первое массовое движение пролетариата — чартизм. В 1840-е Ирландию поражает голод, жертвами которого становится более миллиона человек. В 1868 создан Британский конгресс тред-юнионов. В 1900 основана Лейбористская партия Великобритании. В XIX веке Великобритания стала крупнейшей колониальной державой мира (Британская империя). В годы Второй мировой войны Великобритания была одним из главных участников антигитлеровской коалиции. В ходе распада Британской колониальной империи независимость получили к середине 1970-х годов почти все английские колонии. После Второй мировой войны правительства Великобритании попеременно формировали лейбористы (1945—1951, 1964—1970, 1974—1979, c 1997 по настоящее время) и консерваторы (1951—1964, 1970—1974, 1979—1997).
Политическая структура
Великобритания — парламентская монархия во главе с королевой.
Законодательный орган — двухпалатный парламент (Палата общин и Палата лордов). Парламент является высшим органом власти на всей территории, несмотря на наличие в Шотландии, Уэльсе и Северной Ирландии собственных управленческих административных структур. Правительство возглавляет премьер-министр.
Отличительной характеристикой является отсутствие какого-либо единого документа, который можно было бы назвать основным законом страны, не существует письменной Конституции, более того, не существует даже точного перечня документов, которые бы относились к Конституции. Отношения между народом и правительством регулируются законодательными актами, неписаными законами и конвенциями.
Гражданство
Начиная с 1 ноября 2005 года кандидаты на получение британского гражданства должны сдавать специальный тест «Life in the UK» на знание истории, культуры и традиций, а также основ государственного устройства Великобритании и общественной жизни этой страны.
Тест, рассчитанный на 45 минут и состоящий из 24 вопросов с вариантами ответов, является обязательным для получения подданства. Ранее Лондон ввёл обязательный тест на знание английского языка, а также систему оценки квалификации и востребованности трудовых навыков иммигрантов.
Получить необходимые для прохождения экзамена знания будущие граждане смогут на специально организованных для них курсах. По мнению разработчиков законодательства, эти знания помогут иммигрантам быстрее интегрироваться в британское общество, в том числе осознать свои права и обязанности.
В 2004 году заявления на получение гражданства Великобритании подали 140870 человек, что на 12 процентов больше, чем в 2003 году.
Экономика
Преимущества: ведущая экономика в сфере финансовых услуг, фармакологической и военной промышленности. Стабильные ТНК. Высокоточные технологии и хайтек (телекоммуникации и биотехнологии). Добыча нефти и газа из Северного моря. Инновации в разработках программного обеспечения. Гибкие условия труда. Успешно улавливает тенденции в снижении курсов валют. Низкая безработица (в 2004 г. 4 %).
Слабые стороны: с 70-х гг. производственный спад, особенно в тяжелой и автомобильной промышленности. Многие инвестиционные решения рассчитаны на быструю прибыль. Отказ от введения евро угрожает ведущей в ЕС роли привлечения иностранных инвестиций; ряд крупных инвесторов уже закрыли свои производства.
Великобритания лидер европейской торговли и крупный финансовый центр. За 2 последних десятилетия правительство сильно уменьшило долю частного сектора в экономике и расширило социальные программы. Сельское хозяйство отличается высокой интенсивностью, хорошо оборудовано и отвечает самым высоким европейским стандартам, производя 60% продуктов при использовании менее чем 2% рабочей силы. Ведущие отрасли промышленности: добыча нефти и газа, машиностроение, химическая и нефтехимическая, черная металлургия, нефтепереработка. Великобритания — высокоразвитая индустриальная страна, крупный поставщик готовой промышленной продукции на мировой рынок и крупный экспортёр капитала (преимущественно в развитые страны). ВВП на душу населения 16070 долларов в год. Занимает 13 место в мире по уровню жизни населения. Добыча нефти и природного газа (в основном на шельфе Северного моря), каменного угля. Наиболее развиты машиностроение (ориентировано на выпуск нестандартной продукции, а также различных видов и типов машин), в том числе электротехническое и электронное, транспортное (включая крупное авиаракето-, автомобиле- и судостроение), станкостроение, сельскохозяйственное, производство промышленного оборудования, подъёмно-транспортной техники и др., химическое и нефтехимическое (Великобритания занимает одно из ведущих мест в мире по производству и экспорту синтетических волокон и красителей, пластмасс, моющих средств, удобрений и др.), фармацевтическая, нефтеперерабатывающая промышленность, чёрная (качественные стали) и цветная (олово, алюминий) металлургия. Старейшая отрасль английской промышленности — текстильная — утратила прежнее значение. Крупная пищевкусовая (традиционное производство виски, пива; переработка импортного сельскохозяйственного сырья) промышленность; производство обуви, трикотажа; известен английский фарфор. В сельском хозяйстве преобладает молочное и мясо-молочное скотоводство и беконное свиноводство; мясо-шерстное овцеводство. Выращивают преимущественно ячмень, пшеницу, сахарную свёклу, овёс, картофель. Овощеводство и плодоводство (крупное парниково-тепличное хозяйство), цветоводство (нарциссы, тюльпаны).
ВВП за 2006 составлял 2.151 трилл долл; за 2007 – 2.215 трилл долл; за 2008 – 2.231 трилл долл. ВВП Великобритании в первом квартале 2009 года сократился на 1,9 процента по сравнению с предыдущим кварталом, что стало рекордным падением за последние 30 лет. В четвертом квартале 2008 года падение ВВП страны составило 1,6 процента.
Экономически активное население составляет 31.2 млн. чел. В сельском хозяйстве занято 1.4% населения, в промышленности – 18.2% населения, в сфере услуг – 80.4% населения. Уровень безработных – 5.5%. Денежная единица — фунт стерлингов = 100 пенсов.
Годовой доход бюджета составляет 1.107 трилл долл; годовой расход бюджета состаляет 1.242 трилл долл. Инвестиции в экономику составляют 16.7% от ВВП. Уровень инфляции за 2008 составил 3.8%.
Экспорт за 2008 составил 468.7 миллионов долл. Экспорт: машины и оборудование, нефть и нефтепродукты, автомобили, вооружение, химические продукты, медицинские препараты, продовольствие. Экспортные партнеры: США -14.2%, Германия – 11.1%, Франция – 8.1%, Ирландия – 8%, Нидерланды – 6.8%, Бельгия -5.3%, Испания -4.5%, Италия -4.1%. Импорт за 2008 составил 645.7 милл долл. Импорт: готовые пром товары, машины и оборудование, сырье, металлы, продукты питания. Партнеры по импорту: Германия -14.2%, США -8.6%, Китай -7.3%, Нидерланды -7.3%, Франция -6.9%, Бельгия -4.7%, Норвения -4.7%, Италия -4.2%.
Культура
Культура Соединённого Королевства богата и разнообразна. Она в значительной мере влияет на культуру в мировом масштабе. Великобритания обладает сильными культурными связями со своими бывшими колониями, особенно с теми государствами, где английский язык является государственным. Значительный вклад в британскую культуру за последние полвека внесли иммигранты с Индийского субконтинента и из стран Карибского бассейна. В процессе формирования Соединённого Королевства в его состав вошли бывшие независимые государства с отличающимися друг от друга культурами, которые следует рассматривать в отдельности.
Национальные газеты: The Times, The Guardian, The Independent, The Daily Telegraph, The Observer, The Financial Times, The Daily Express, The Sun, The Mirror, The People.
Религия
Основные религии: Христианство(42,079,000) -71,6 %, Буддизм(152,000) -0,3 %, Индуизм(559,000) -1 %, Иудаизм(267,000) -0,5 %, Ислам(1,591,000) -2,7 %, Сикхизм(336,000) -0,6 %, Другие религии(179,000) -0,3 %, Атеисты(9,104,000) -15,5 %, Воздержались от ответа(4,289,000) -7,3 %.
На территории Англии существует церковь с государственным статусом — Церковь Англии, светский глава которой — британский монарх. Церковь Англии — одна из поместных церквей, входящих в англиканское сообщество, имеющее своим духовным лидером Архиепископа Кентерберийского.
Согласно исследованиям, Соединённое Королевство — страна с преимущественно секулярным населением: лишь 38 % людей заявляют о своей вере в Бога («a God»)[8], хотя, по данным Церкви Англии на 2005 год, «72 % населения Англии указали свою религиозную принадлежность как христианскую»[9].
Согласно опубликованному в апреле 2008 года исследованию, проведённому христианским благотворительным фондом Joseph Rowntree Foundation, «преобладающим мнением» является взгляд на религию как на «социальное зло»[10].
Вооружённые силы Великобритании
Эмблема ВС Великобритании
Военные силы разделены на армию, королевский военно-морской флот, королевские военно-воздушные силы. Сухопутные войска -113 500 чел; ввс – 52 540 чел; военно-морской флот – 43 700 чел. Вооружённые силы Великобритании (англ. British Armed Forces) Главнокомандующим Британских Вооружённых сил является британский монарх, королева Елизавета II. ВС Великобритании находятся под управлением Оборонного Совета Министерства Обороны. Основной задачей Британских Вооружённых сил является защита Соединённого Королевства и его заморских территорий, продвижение интересов безопасности Великобритании и поддержка международных миротворческих усилий. Также ВС Великобритании активные и постоянные участники операций НАТО и сил коалиции в Ираке и Афганистане.
Военный бюджет составляет 2.4% от ВВП по данным за 2005 год, приблизительно 37 млрд. долл.
Отношения с Российской Федерацией
Сотрудничество России и Великобритании осуществляется в основном через структуры Европейского союза. Двустороннее сотрудничество таким образом исключает некоторые аспекты, включённые в программу ЕС-Россия, например, борьба с преступностью, военные учения и научные семинары по вопросам обороны. На уровне Россия-Великобритания рассматриваются следующие вопросы: безопасность в области энергетики, ядерных разработок, технологий и новейших конструкторских разработок. Проводятся совместные консультации по разработкам в сфере контроля на предприятиях, в госучреждениях и на улицах (тут государства выходят на особый уровень сотрудничества из-за сложности и пикантности вопроса, проводятся консультации по усовершенствованию существующих систем контроля, слежки и фиксации посещаемости, появления, проч.). Это позволяет обеим странам повышать уровень безопасности населения и государственных структур и становится приоритетным направлением в отношениях государств в области обороны и безопасности.
Так, например, происшествия с несогласием сторон по экстрадиции граждан (Лугового с территории России и Березовского из Великобритании), последовавшая высылка дипломатических лиц и прекращение сотрудничества в некоторых областях никак не сказались на совместных консультациях по предметам контроля и обеспечению безопасности. Также незатронутой политическими скандалами остаётся сфера борьбы с терроризмом, где стороны открыто высказывают заинтересованность в сотрудничестве, взаимных разработках и передаче опыта в вопросах противостояния данной угрозе. Британская сторона выделяет важность борьбы с терроризмом, как основополагающую российско-британских отношений, наиболее важную сферу сотрудничества в целом и позиционирует данную область выше «политических недоразумений». Об этом свидетельствует заявление министра Великобритании по европейским делам Джима Мерфи: «В плане противодействия терроризму мы очень тесно сотрудничаем и продолжим сотрудничество»[11].
В условиях непростого положения российско-британской дипломатии, многочисленных скандалов, невыполненных требований и претензий, нежелания идти на уступки, громких новостных репортажей и критических статей, не перестающих развивать тему задач и целей Березовского, политических убийств, причастности российских спецслужб к смерти британских подданных, разведывательной деятельности британских спецслужб на территории РФ, проч., снижается возможность эффективной кооперации, уменьшается количество двусторонних проектов[12]. К тому же, поскольку в Великобритании НАТО считают краегульном камнем национальной безопасности и активно поддерживают политику альянса, а у Москвы есть все основания полагать, что компоненты антироссийской направленности в ближайшее время не будут изъяты из натовских документов военного планирования, достижение взаимоприемлемого уровня сотрудничества представляется маловероятным.
Устойчивые словосочетания
- Туманный Альбион
- Британский лев
- Британский флот (Гранд Флит)
- Британская сдержанность
- Британский миф
- Британский футбол
- Английская королева
- Британские ученые
- Английская соль
- Английская булавка
- Английский парк
- Английский звук
- Английский юмор
- Английский рожок
- Английский замок
- Английский бульдог
- Английский мастиф
- Английский сеттер
- Уйти по-английски
- Английский пациент
- Лондонский кэб
- Лондонский туман
- Британский джентльмен
- Джон Булль
См. также
- Телекоммуникации в Великобритании
- Транспорт в Великобритании
- Международные отношения Великобритании
- Система образования Великобритании
- Список частей Соединённого Королевства, сортировка по площади
- Британские острова (терминология)
- Налогообложение в Великобритании
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 Международный валютный фонд (апрель 2008)
- ↑ Английское название United Kingdom переводится на русский как Соединённое Королевство; дословный перевод русского «Великая Британия» — Great Britain.
- ↑ http://www.demographia.ru/articles_N/index.html?idR=24&idArt=504
- ↑ «Великобритания» // Большая российская энциклопедия. Т. 5. 2006.
- ↑ Руднев В. В. Великобритания накануне XXI века. Европейский союз и процесс деволюции в Шотландии // Европа на рубеже третьего тысячелетия: народы и государства. Сб. статей. Под ред. М. Ю. Мартыновой, Н. Н. Грацианской. М., 2000
- ↑ Козлов В. И. Иммигранты и этнорасовые проблемы в Британии. М.: Наука, 1987
- ↑ Ал. А. Громыко, Великобритания эпоха реформ; М 2007
- ↑ Опрос Eurobarometer, проведённый в 2005 году
- ↑ Church Statistics 2005/6
- ↑ Robert Watts. Religion is ‘the new social evil’ The Sunday Times 20 апреля 2008 г.
- ↑ http://www.rosbalt.ru/2008/5/8/401487.html
- ↑ http://www.utro.ru/articles/2007/07/17/663915.shtml
Ссылки
- Великобритания в DMOZ
- Британия Новости Великобритании и путеводитель от Би-би-си.
Координаты: 53°33′00″ с. ш. 2°26′00″ з. д. / 53.55° с. ш. 2.433333° з. д. (G)
|
||||
 |
||||
| Девиз: «Dieu et mon droit» «(Бог и моё право)» | ||||
| Гимн: «God Save the Queen» | ||||
| Основано | 1 января 1801 (объединение Королевства Великобритании и Королевства Ирландии) |
|||
| Официальный язык | Английский | |||
| Столица | Лондон | |||
| Крупнейшие города | Лондон, Бирмингем, Глазго, Манчестер, Эдинбург, Ливерпуль | |||
| Форма правления | Парламентская монархия | |||
| Королева Премьер-министр |
Елизавета II Гордон Браун |
|||
| Территория • Всего • % водной поверхн. |
76-я в мире 244 820 км² 1,3 |
|||
| Население • Всего (2007) • Плотность |
21-е в мире 60 776 238 чел. 247 чел./км² |
|||
| ВВП • Итого (2008) • На душу населения |
6-й в мире $2,833 трлн.[1] $46 432[1] |
|||
| Этнохороним | Британец, Британка, Британцы | |||
| Валюта | Фунт стерлингов (GBP) | |||
| Интернет-домен | .eu (как член ЕС), | |||
| Телефонный код | +44 | |||
| Часовой пояс | UTC +0 |
Великобрита́ния (англ. United Kingdom[2]; полное название — Соединённое Короле́вство Великобрита́нии и Се́верной Ирла́ндии, англ. United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland) — островное государство в Западной Европе, форма правления — парламентская монархия. Столица — город Лондон. Название страны происходит от английского Great Britain. Британия — по этнониму племени бритты.
Государство на Британских островах (остров Великобритания и северо-восточная часть острова Ирландия, большое количество мелких островов и архипелагов, Нормандские острова), омывается Атлантическим океаном и его морями. Площадь: всего — 244 820 км², суша — 240 590 км², внутренние воды — 3 230 км². Самая высокая вершина — г. Бен-Невис (1343 м) — расположена на севере Шотландии (Грампианские горы), самая низкая точка — Фенланд (−4 м).
На севере и западе преобладает горный рельеф — Северо-Шотландское нагорье (до 1343 м), Пеннинские и Кембрийские горы; на юге и юго-востоке — холмистые равнины. Климат умеренно океанический, влажный. Средние температуры января от 3 до 7 °C, июля 11—17°C; осадков до 3000 мм в год на западе и 600—750 мм на юго-востоке. Основные реки: Темза — 334 км, Северн — 310 км, Трент, Мерси — 109 км, Клайд — 170 км. Крупнейшие озёра: Лох-Несс (пл. 56 км²), Лох-Ней (пл. 396 км²). Леса (бук, дуб, берёза) занимают около 9 % территории Великобритании.
Содержание
- 1 Административное деление
- 2 Население
- 2.1 Численность
- 2.2 Этнический состав
- 2.3 Британская нация
- 3 История
- 4 Политическая структура
- 5 Гражданство
- 6 Экономика
- 7 Культура
- 8 Религия
- 9 Вооружённые силы Великобритании
- 10 Отношения с Российской Федерацией
- 11 Устойчивые словосочетания
- 12 См. также
- 13 Примечания
- 14 Ссылки
Административное деление
Великобритания состоит из 4 административно-политических частей (исторических провинций):
- Англия (39 графств, 6 метрополитенских графств и Большой Лондон) — адм. центр Лондон
- Уэльс (22 унитарных образования: 9 графств, 3 города и 10 городов-графств) — адм. центр Кардифф
- Шотландия (12 областей: 9 округов и 3 основных территории) — адм. центр Эдинбург
- Северная Ирландия (26 округов) — адм. центр Белфаст
Зависимые территории со столицами:
- Британские острова
- Остров Мэн (Дуглас)
- Нормандские острова
- Гернси (Сент-Питер-Порт)
- Джерси (Сент-Хельер)
- Европа
- Гибралтар (Гибралтар)
- Америка
- Ангилья (Валли)
- Бермуды (Гамильтон)
- Британские Виргинские острова (Род-Таун)
- Каймановы острова (Джорджтаун)
- Остров Монтсеррат (Плимут)
- Острова Тёркс и Кайкос (Кукбурнтаун)
- Фолклендские острова (Порт-Стэнли)
- Южная Георгия и Южные Сандвичевы острова
- Атлантический океан
- Остров Святой Елены (Джеймстаун) и его зависимые территории — острова Вознесения и Тристан-да-Кунья
- Океания
- Остров Питкэрн (Адамстаун)
- Индийский океан
- Британская территория в Индийском океане — архипелаг Чагос
Население
Численность
Численность населения Великобритании с 1900 по 2007 год:
| Год | Численность (чел.) |
|---|---|
| 1900 | 35 405 900 |
| 1949 | 50 300 000 |
| 1959 | 51 900 000 |
| 1976 | 55 900 000 |
| 1998 | 59 100 000 |
| 2004 | 59 834 900 |
| 2005 | 60 441 457 |
| 2007 | 60 776 238 |
Главным образом, численность населения растет за счет трудовых иммигрантов из недавно вступивших стран в Европейский союз, которым после расширения ЕС в мае 2004 года был разрешен свободный въезд для работы на территории Великобритании. Тем не менее, рождаемость в стране по-прежнему превышает смертность, хотя естественный прирост уже не является главенствующим фактором увеличения численности британцев.[3] Общая численность населения (по данным 2008) – 61 113 205. Возрастная структура: до 14 лет – 16.7 %, 15-64 – 67.1%, от 65 и старше – 16.2%. Средний возраст мужчин – 39 лет, у женщин – 41 год. Прирост населения – 0.279%, уровень рождаемости – 10.65/1,000; уровень смертности – 10.05/1,000. Уровень чистой миграции – 2.16 мигрантов/ 1,000. 90% населения проживает в городах, с ежегодным приростом – 0.5%. В городах с числом жителей св. 100 тыс. чел. проживает почти половина населения страны. Крупнейшие по числу жителей города: Лондон (6803000 чел.), Бирмингем (935000 чел.), Глазго (654000 чел.), Шеффилд (500000 чел.), Ливерпуль (450000 чел.), Эдинбург (421000 чел.), Манчестер (398000 чел.), Белфаст (280000 чел.).
Этнический состав
Коренные жители страны составляют 92 % населения В. (2001, перепись), из них:
- англичане — 83,6 %,
- шотландцы (в основном в Шотландии) — 8,5 %,
- валлийцы (в основном в Уэльсе) — 4,9 %,
- ирландцы (в основном в Северной Ирландии, ольстерцы) — 2,9 %.
Иммигранты и их дети проживают главным образом в конурбациях Большого Лондона, Западного Мидленда и Мерсейсайда. Они составляют около 8 % населения страны, в том числе[4]:
- выходцы из Индии, Пакистана и Бангладеш — 3,6 %,
- Китая — 0,4 %,
- стран Африки — 0,8 %,
- темнокожие выходцы с островов Карибского моря — 1 %
Британская нация
1. Формирование британской нации происходило особым путем, который не сопоставим с французской моделью формирования нации (противостояние «низов» и «верхов» в Великую Французскую револицию), также и с немецкой моделью, в связи с тем, что Великобритания никогда не была раздробленным государством, как Германия до 1871 года.
2. В XIV—XV веках, в период великих географических открытий, в Великобритании огромную роль начинает играть национальная экономика, которая и сплачивала население страны.
3. Великобритания, в отличие от других европейских государств, всегда была несколько изолированна, в силу своего географического местоположения.
4. Огромную роль в консолидации британской нации сыграла и религиозная составляющая (XVII век) — была совершена революция с религиозными мотивами (противостояние католиков, протестантов).
5. Также немаловажную роль в процессе формирования британской нации можно отвести процессу огораживания, в результате которого проходила ассимиляция крестьянского населения в городах, а также освоение земли крестьянами в отдаленных уголках Великобритании.
6. В Англии Библия была переведена на английский язык раньше, чем в других европейских государствах; таким образом, возник единый универсальный для всех британцев английский язык.
7. Британцы зачастую противопоставляют себя другим этносам:
а) Британия имела самую могущественную и широкомасштабную колониальную империю в мире. Но при этом британцы демонстрировали свои различия с другими народами мира.
б) Резко отличалась и британская колониальная политика, которая в отличие от французской или испанской не пыталась ассимилировать туземцев в своих колониях, руководствуясь принципом: «Мы — англичане! Они — туземцы!» [5] [6] Однако, Распад империи привел к фундаментальному сдвигу в сознании населения: активизировались национальные движения, все больше число людей считали себя не британцами, а шотландцами, валлийцами, ирландцами. По опросам общественного мнения, даже в Англии лишь треть населения считают себя британцами. То, что в течении долгого времени объединяло жителей страны(протестантизм, патриархальность институтов власти, монархия, империя), перестало работать так же эффективно как раньше. Характерно, что с 2001 г слово ‘Британия’ в название ежегодника государственного бюро национальной статистике было заменено на Соединенное Королевство[7]
История
Британские острова завоёваны в V—VI веках англосаксами. После нормандского завоевания Англии 1066 завершился процесс феодализации, сопровождавшийся политическим объединением страны. Во 2-й половине XIII века возник английский парламент, оформилась сословная монархия. Развитие товарно-денежных отношений и борьба крестьянства (восстание Уота Тайлера 1381 и др.) привели (XV век) к почти полной ликвидации личной зависимости крестьян. В то же время крестьяне были лишены земельной собственности, что привело к их быстрой пролетаризации. В период Реформации, в 1534, создана англиканская церковь. Английская революция XVII века обеспечила утверждение капитализма. В конце XVII века оформились политические партии — тори и виги (в середине XIX века трансформировались соответственно в Консервативную и Либеральную партии). После закрепления в 1707 присоединения Шотландии (в 1649—1651 была покорена Ирландия) за объединённым королевством закрепилось название Великобритания. В конце XVIII — 1-й половине XIX веков происходил промышленный переворот. С завоевания Ост-Индской компанией богатой Бенгалии начинается создание британской колониальной империи. Около трети всех английских инвестиций этого времени имеют индийское происхождение. В 1830-е годы утвердилась фабричная система производства. В 1830 — 1840-е гг. развернулось первое массовое движение пролетариата — чартизм. В 1840-е Ирландию поражает голод, жертвами которого становится более миллиона человек. В 1868 создан Британский конгресс тред-юнионов. В 1900 основана Лейбористская партия Великобритании. В XIX веке Великобритания стала крупнейшей колониальной державой мира (Британская империя). В годы Второй мировой войны Великобритания была одним из главных участников антигитлеровской коалиции. В ходе распада Британской колониальной империи независимость получили к середине 1970-х годов почти все английские колонии. После Второй мировой войны правительства Великобритании попеременно формировали лейбористы (1945—1951, 1964—1970, 1974—1979, c 1997 по настоящее время) и консерваторы (1951—1964, 1970—1974, 1979—1997).
Политическая структура
Великобритания — парламентская монархия во главе с королевой.
Законодательный орган — двухпалатный парламент (Палата общин и Палата лордов). Парламент является высшим органом власти на всей территории, несмотря на наличие в Шотландии, Уэльсе и Северной Ирландии собственных управленческих административных структур. Правительство возглавляет премьер-министр.
Отличительной характеристикой является отсутствие какого-либо единого документа, который можно было бы назвать основным законом страны, не существует письменной Конституции, более того, не существует даже точного перечня документов, которые бы относились к Конституции. Отношения между народом и правительством регулируются законодательными актами, неписаными законами и конвенциями.
Гражданство
Начиная с 1 ноября 2005 года кандидаты на получение британского гражданства должны сдавать специальный тест «Life in the UK» на знание истории, культуры и традиций, а также основ государственного устройства Великобритании и общественной жизни этой страны.
Тест, рассчитанный на 45 минут и состоящий из 24 вопросов с вариантами ответов, является обязательным для получения подданства. Ранее Лондон ввёл обязательный тест на знание английского языка, а также систему оценки квалификации и востребованности трудовых навыков иммигрантов.
Получить необходимые для прохождения экзамена знания будущие граждане смогут на специально организованных для них курсах. По мнению разработчиков законодательства, эти знания помогут иммигрантам быстрее интегрироваться в британское общество, в том числе осознать свои права и обязанности.
В 2004 году заявления на получение гражданства Великобритании подали 140870 человек, что на 12 процентов больше, чем в 2003 году.
Экономика
Преимущества: ведущая экономика в сфере финансовых услуг, фармакологической и военной промышленности. Стабильные ТНК. Высокоточные технологии и хайтек (телекоммуникации и биотехнологии). Добыча нефти и газа из Северного моря. Инновации в разработках программного обеспечения. Гибкие условия труда. Успешно улавливает тенденции в снижении курсов валют. Низкая безработица (в 2004 г. 4 %).
Слабые стороны: с 70-х гг. производственный спад, особенно в тяжелой и автомобильной промышленности. Многие инвестиционные решения рассчитаны на быструю прибыль. Отказ от введения евро угрожает ведущей в ЕС роли привлечения иностранных инвестиций; ряд крупных инвесторов уже закрыли свои производства.
Великобритания лидер европейской торговли и крупный финансовый центр. За 2 последних десятилетия правительство сильно уменьшило долю частного сектора в экономике и расширило социальные программы. Сельское хозяйство отличается высокой интенсивностью, хорошо оборудовано и отвечает самым высоким европейским стандартам, производя 60% продуктов при использовании менее чем 2% рабочей силы. Ведущие отрасли промышленности: добыча нефти и газа, машиностроение, химическая и нефтехимическая, черная металлургия, нефтепереработка. Великобритания — высокоразвитая индустриальная страна, крупный поставщик готовой промышленной продукции на мировой рынок и крупный экспортёр капитала (преимущественно в развитые страны). ВВП на душу населения 16070 долларов в год. Занимает 13 место в мире по уровню жизни населения. Добыча нефти и природного газа (в основном на шельфе Северного моря), каменного угля. Наиболее развиты машиностроение (ориентировано на выпуск нестандартной продукции, а также различных видов и типов машин), в том числе электротехническое и электронное, транспортное (включая крупное авиаракето-, автомобиле- и судостроение), станкостроение, сельскохозяйственное, производство промышленного оборудования, подъёмно-транспортной техники и др., химическое и нефтехимическое (Великобритания занимает одно из ведущих мест в мире по производству и экспорту синтетических волокон и красителей, пластмасс, моющих средств, удобрений и др.), фармацевтическая, нефтеперерабатывающая промышленность, чёрная (качественные стали) и цветная (олово, алюминий) металлургия. Старейшая отрасль английской промышленности — текстильная — утратила прежнее значение. Крупная пищевкусовая (традиционное производство виски, пива; переработка импортного сельскохозяйственного сырья) промышленность; производство обуви, трикотажа; известен английский фарфор. В сельском хозяйстве преобладает молочное и мясо-молочное скотоводство и беконное свиноводство; мясо-шерстное овцеводство. Выращивают преимущественно ячмень, пшеницу, сахарную свёклу, овёс, картофель. Овощеводство и плодоводство (крупное парниково-тепличное хозяйство), цветоводство (нарциссы, тюльпаны).
ВВП за 2006 составлял 2.151 трилл долл; за 2007 – 2.215 трилл долл; за 2008 – 2.231 трилл долл. ВВП Великобритании в первом квартале 2009 года сократился на 1,9 процента по сравнению с предыдущим кварталом, что стало рекордным падением за последние 30 лет. В четвертом квартале 2008 года падение ВВП страны составило 1,6 процента.
Экономически активное население составляет 31.2 млн. чел. В сельском хозяйстве занято 1.4% населения, в промышленности – 18.2% населения, в сфере услуг – 80.4% населения. Уровень безработных – 5.5%. Денежная единица — фунт стерлингов = 100 пенсов.
Годовой доход бюджета составляет 1.107 трилл долл; годовой расход бюджета состаляет 1.242 трилл долл. Инвестиции в экономику составляют 16.7% от ВВП. Уровень инфляции за 2008 составил 3.8%.
Экспорт за 2008 составил 468.7 миллионов долл. Экспорт: машины и оборудование, нефть и нефтепродукты, автомобили, вооружение, химические продукты, медицинские препараты, продовольствие. Экспортные партнеры: США -14.2%, Германия – 11.1%, Франция – 8.1%, Ирландия – 8%, Нидерланды – 6.8%, Бельгия -5.3%, Испания -4.5%, Италия -4.1%. Импорт за 2008 составил 645.7 милл долл. Импорт: готовые пром товары, машины и оборудование, сырье, металлы, продукты питания. Партнеры по импорту: Германия -14.2%, США -8.6%, Китай -7.3%, Нидерланды -7.3%, Франция -6.9%, Бельгия -4.7%, Норвения -4.7%, Италия -4.2%.
Культура
Культура Соединённого Королевства богата и разнообразна. Она в значительной мере влияет на культуру в мировом масштабе. Великобритания обладает сильными культурными связями со своими бывшими колониями, особенно с теми государствами, где английский язык является государственным. Значительный вклад в британскую культуру за последние полвека внесли иммигранты с Индийского субконтинента и из стран Карибского бассейна. В процессе формирования Соединённого Королевства в его состав вошли бывшие независимые государства с отличающимися друг от друга культурами, которые следует рассматривать в отдельности.
Национальные газеты: The Times, The Guardian, The Independent, The Daily Telegraph, The Observer, The Financial Times, The Daily Express, The Sun, The Mirror, The People.
Религия
Основные религии: Христианство(42,079,000) -71,6 %, Буддизм(152,000) -0,3 %, Индуизм(559,000) -1 %, Иудаизм(267,000) -0,5 %, Ислам(1,591,000) -2,7 %, Сикхизм(336,000) -0,6 %, Другие религии(179,000) -0,3 %, Атеисты(9,104,000) -15,5 %, Воздержались от ответа(4,289,000) -7,3 %.
На территории Англии существует церковь с государственным статусом — Церковь Англии, светский глава которой — британский монарх. Церковь Англии — одна из поместных церквей, входящих в англиканское сообщество, имеющее своим духовным лидером Архиепископа Кентерберийского.
Согласно исследованиям, Соединённое Королевство — страна с преимущественно секулярным населением: лишь 38 % людей заявляют о своей вере в Бога («a God»)[8], хотя, по данным Церкви Англии на 2005 год, «72 % населения Англии указали свою религиозную принадлежность как христианскую»[9].
Согласно опубликованному в апреле 2008 года исследованию, проведённому христианским благотворительным фондом Joseph Rowntree Foundation, «преобладающим мнением» является взгляд на религию как на «социальное зло»[10].
Вооружённые силы Великобритании
Эмблема ВС Великобритании
Военные силы разделены на армию, королевский военно-морской флот, королевские военно-воздушные силы. Сухопутные войска -113 500 чел; ввс – 52 540 чел; военно-морской флот – 43 700 чел. Вооружённые силы Великобритании (англ. British Armed Forces) Главнокомандующим Британских Вооружённых сил является британский монарх, королева Елизавета II. ВС Великобритании находятся под управлением Оборонного Совета Министерства Обороны. Основной задачей Британских Вооружённых сил является защита Соединённого Королевства и его заморских территорий, продвижение интересов безопасности Великобритании и поддержка международных миротворческих усилий. Также ВС Великобритании активные и постоянные участники операций НАТО и сил коалиции в Ираке и Афганистане.
Военный бюджет составляет 2.4% от ВВП по данным за 2005 год, приблизительно 37 млрд. долл.
Отношения с Российской Федерацией
Сотрудничество России и Великобритании осуществляется в основном через структуры Европейского союза. Двустороннее сотрудничество таким образом исключает некоторые аспекты, включённые в программу ЕС-Россия, например, борьба с преступностью, военные учения и научные семинары по вопросам обороны. На уровне Россия-Великобритания рассматриваются следующие вопросы: безопасность в области энергетики, ядерных разработок, технологий и новейших конструкторских разработок. Проводятся совместные консультации по разработкам в сфере контроля на предприятиях, в госучреждениях и на улицах (тут государства выходят на особый уровень сотрудничества из-за сложности и пикантности вопроса, проводятся консультации по усовершенствованию существующих систем контроля, слежки и фиксации посещаемости, появления, проч.). Это позволяет обеим странам повышать уровень безопасности населения и государственных структур и становится приоритетным направлением в отношениях государств в области обороны и безопасности.
Так, например, происшествия с несогласием сторон по экстрадиции граждан (Лугового с территории России и Березовского из Великобритании), последовавшая высылка дипломатических лиц и прекращение сотрудничества в некоторых областях никак не сказались на совместных консультациях по предметам контроля и обеспечению безопасности. Также незатронутой политическими скандалами остаётся сфера борьбы с терроризмом, где стороны открыто высказывают заинтересованность в сотрудничестве, взаимных разработках и передаче опыта в вопросах противостояния данной угрозе. Британская сторона выделяет важность борьбы с терроризмом, как основополагающую российско-британских отношений, наиболее важную сферу сотрудничества в целом и позиционирует данную область выше «политических недоразумений». Об этом свидетельствует заявление министра Великобритании по европейским делам Джима Мерфи: «В плане противодействия терроризму мы очень тесно сотрудничаем и продолжим сотрудничество»[11].
В условиях непростого положения российско-британской дипломатии, многочисленных скандалов, невыполненных требований и претензий, нежелания идти на уступки, громких новостных репортажей и критических статей, не перестающих развивать тему задач и целей Березовского, политических убийств, причастности российских спецслужб к смерти британских подданных, разведывательной деятельности британских спецслужб на территории РФ, проч., снижается возможность эффективной кооперации, уменьшается количество двусторонних проектов[12]. К тому же, поскольку в Великобритании НАТО считают краегульном камнем национальной безопасности и активно поддерживают политику альянса, а у Москвы есть все основания полагать, что компоненты антироссийской направленности в ближайшее время не будут изъяты из натовских документов военного планирования, достижение взаимоприемлемого уровня сотрудничества представляется маловероятным.
Устойчивые словосочетания
- Туманный Альбион
- Британский лев
- Британский флот (Гранд Флит)
- Британская сдержанность
- Британский миф
- Британский футбол
- Английская королева
- Британские ученые
- Английская соль
- Английская булавка
- Английский парк
- Английский звук
- Английский юмор
- Английский рожок
- Английский замок
- Английский бульдог
- Английский мастиф
- Английский сеттер
- Уйти по-английски
- Английский пациент
- Лондонский кэб
- Лондонский туман
- Британский джентльмен
- Джон Булль
См. также
- Телекоммуникации в Великобритании
- Транспорт в Великобритании
- Международные отношения Великобритании
- Система образования Великобритании
- Список частей Соединённого Королевства, сортировка по площади
- Британские острова (терминология)
- Налогообложение в Великобритании
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 Международный валютный фонд (апрель 2008)
- ↑ Английское название United Kingdom переводится на русский как Соединённое Королевство; дословный перевод русского «Великая Британия» — Great Britain.
- ↑ http://www.demographia.ru/articles_N/index.html?idR=24&idArt=504
- ↑ «Великобритания» // Большая российская энциклопедия. Т. 5. 2006.
- ↑ Руднев В. В. Великобритания накануне XXI века. Европейский союз и процесс деволюции в Шотландии // Европа на рубеже третьего тысячелетия: народы и государства. Сб. статей. Под ред. М. Ю. Мартыновой, Н. Н. Грацианской. М., 2000
- ↑ Козлов В. И. Иммигранты и этнорасовые проблемы в Британии. М.: Наука, 1987
- ↑ Ал. А. Громыко, Великобритания эпоха реформ; М 2007
- ↑ Опрос Eurobarometer, проведённый в 2005 году
- ↑ Church Statistics 2005/6
- ↑ Robert Watts. Religion is ‘the new social evil’ The Sunday Times 20 апреля 2008 г.
- ↑ http://www.rosbalt.ru/2008/5/8/401487.html
- ↑ http://www.utro.ru/articles/2007/07/17/663915.shtml
Ссылки
- Великобритания в DMOZ
- Британия Новости Великобритании и путеводитель от Би-би-си.
В статье рассказали, чем отличаются термины the United Kingdom, Great Britain и England, а также, какие еще страны относятся к владениям британской монархии.
Вы когда-нибудь задумывались о том, почему англичан нередко называют британцами, профиль Елизаветы II красуется на канадских банкнотах, а над крошечным Гибралтаром, расположенным на юге Испании, развевается флаг Соединенного Королевства? На эти и другие вопросы мы постарались ответить в статье.
Вопрос географический
Государство Соединенное Королевство (the United Kingdom, UK) расположено на двух крупнейших островах ― Великобритания (Great Britain) и Ирландия (Ireland).
Великобритания ― это прежде всего географический термин, определяющий крупнейший из Британских островов (the British Isles). Ирландия ― остров, на котором расположены Северная Ирландия (Northern Ireland), что входит в состав Соединенного Королевства, и независимое государство Ирландия (Irland или Republic of Ireland). Кроме того, к Соединенному Королевству относятся острова Уайт (Isle of Wight), Силли (Isles of Scilly), Ланди (Lundy), Англси (Isle of Anglesey), Гебридские острова (Hebrides), Шетландские острова (Shetland Islands), Оркнейские острова (Orkney Islands) и остров Клайд (Islands of the Clyde).
Предлагаем посмотреть наглядное видео. Обратите внимание, в конце ролика ведущий говорит о том, что Соединенное Королевство входит в состав Европейского союза, однако в январе 2020 страна вышла из него. Также автор видео назвал остров Мэн, расположенный у берегов Великобритании, частью Соединенного Королевства. Однако здесь он допустил ошибку, потому как этот остров не входит в состав страны.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| to be located | быть расположенным |
| to include | включать в себя |
| to be surrounded | быть окруженным |
| a coastline | береговая линия |
| protection | защита |
| a rival | противник |
| integration | объединение в одно целое |
| a lowland | низменность, низина |
| coal | каменный уголь |
| an iron deposit | месторождение железа |
| a global trade | мировой рынок |
Вопрос политический
Нередко Соединенное Королевство, которое подразумевает содружество четырех независимых суверенных государств, называют Англией, что неверно. Англия ― крупнейшая и самая населенная административно-политическая часть страны, в которой расположена столица Соединенного Королевства ― Лондон (London). Отметим, столица Шотландии ― Эдинбург (Edinburgh), Уэльса ― Кардифф (Cardiff), а Северной Ирландии ― Белфаст (Belfast). В каждой из стран, входящих в состав Соединенного Королевства, есть собственные парламенты, которые могут влиять на принятие английских законов.
Современный флаг Соединенного Королевства, который называют Юнион Джек, символизирует объединение Англии (широкий красный крест), Шотландии (белый косой крест) и Ирландии (красный диагональный крест). Заметили, что среди перечисленных символов нет символа Уэльса? Вот и валлийцы недовольны тем, что на флаге Соединенного Королевства не изображен красный дракон ― национальный символ Уэльса.
Посмотрите видеоролик, в котором ведущая подробно рассказывает о национальных символах каждой из частей Соединенного Королевства.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| the political union | политическое объединение |
| to indicate | указывать |
| north | север |
| west | запад |
| east | восток |
| a cross | крест |
| a thistle | цветок чертополоха |
| a shamrock | трилистник |
| a leek | лук-порей |
| a daffodil | желтый нарцисс |
| a population | население |
| to recognise | признавать |
Всех жителей Соединенного Королевства называют британцами (the British), однако сами граждане предпочитают четкое разграничение: в Англии живут англичане (the English), в Шотландии ― шотландцы (the Scottish или the Scots), в Уэльсе ― валлийцы (the Welsh), а в Северной Ирландии ― североирландцы (могут определять себя как the Northern Irish, the Irish). Несмотря на это, все жители Соединенного Королевства получают паспорта граждан одной страны.
Во всем Соединенном Королевстве говорят на английском, однако в Уэльсе и части Англии вы можете услышать валлийский, в Шотландии и нескольких графствах Северной Ирландии ― шотландский (в горном регионе Шотландии встречается и гэльский язык), а в Северной Ирландии ― ирландский.
Жителей страны объединяет один язык, но в каждой из ее частей можно услышать свой акцент. Давайте посмотрим ролик, в котором ведущая сравнивает классический британский акцент, характерный для Англии, с акцентом Glaswegian, который чаще всего можно встретить в городе Глазго (Шотландия).
К тому же, в речи жителей разных регионов Соединенного Королевства есть и лексические отличия ― разные слова для определения одного и того же явления.
В каждой из стран, входящих в состав Соединенного Королевства, есть и сленг, о котором на YouTube-канале Vanity Fair рассказали известные актеры.
Бытует мнение, что шотландцы, валлийцы и североирландцы недолюбливают англичан, считая их напыщенными и заносчивыми колонизаторами. Англичане же полагают, что их соседи ― неисправимые провинциалы. В Соединенном Королевстве периодически возникают движения за независимость той или иной части страны.
В одной из серий третьего сезона сериала The Crown («Корона») показана неприязнь валлийцев к англичанам на примере эпизода из жизни принца Чарльза ― старшего сына Елизаветы II и наследника британского престола. В 1952 году ему был пожалован титул принца Уэльского. В конце 60-х в Уэльсе усилились национальные движения, а потому правительство порекомендовало монархии провести торжественную церемонию, которая сможет сплотить монархистов и ослабить настроения протестующих. Церемония инвеституры, в ходе которой королева возложила на голову Чарльза венец, прошла в 1969 году в Уэльсе. К этому событию принц готовился несколько месяцев: учил историю и культурные традиции Уэльса, а также валлийский язык,чтобы произнести речь на двух языках. Посмотрите ролик от Netflix, в котором ведущая поясняет, на основе каких фактов писали сценарий к серии про инвеституру Чарльза.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| a term | семестр |
| to propel | толкать вперед |
| an affection | привязанность |
| prior to something | до того как |
| an heir | наследник |
| to be in trouble | попасть в неприятную ситуацию |
| to erode | ослаблять |
| to regard | принимать во внимание |
| the native tongue | родной язык |
| to heckle | перебивать |
| to wield | орудовать |
| to go down a treat | доставлять удовольствие/радость |
| a predecessor | предшественник |
| relatable | узнаваемый, понятный |
| to convey | передавать смысл |
| to disarm | обезоруживать |
| sympathy | сочувствие, сострадание |
| to explode | взрываться |
| faultless | безупречный |
| contribution | вклад |
| rapturous | восторженный |
Содружество наций, Коронные земли и Британские заморские территории
Британская империя (the British Empire), просуществовавшая до 1997 года, когда-то занимала четверть планеты. Большинство ее колоний обрели независимость не в ходе жестоких кровопролитий, а благодаря дипломатическому договору. Эти колонии заключили договор с империей, согласно которому признали британского монарха главой своих стран, а взамен получили право на формирование собственного парламента. К таким странам относятся Канада (Canada), Австралия (Australia), Папуа-Новая Гвинея (Papua New Guinea), Новая Зеландия (New Zealand), Ямайка (Jamaica), Соломоновы Острова (Solomon Islands), Белиз (Belize), Багамские Острова (The Bahamas), Барбадос (Barbados), Сент-Люсия (Saint Lucia), Сент-Винсент и Гренадины (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines), Гренада (Grenada), Антигуа и Барбуда (Antigua and Barbuda), Сент-Киттс и Невис (Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis), Тувалу (Tuvalu). Все они имеют общее название ― Королевства Содружества (Commonwealth realms). Несмотря на то что каждая из этих стран признает британского монарха главой, они по факту независимые государства, над которыми Соединенное Королевство не имеет никакой власти.
К Коронным землям (the Crown dependencies) относят острова Мэн (Isle of Man), Джерси (Jersey) и Гернси (Bailiwick of Guernsey), расположенные вблизи островов Великобритания и Ирландия. Они не получили независимость, хоть и обладают значительной автономией. Соединенное Королевство сохраняет за собой право отменять законы, принятые местными парламентами, а жители этих территорий при рождении получают британское гражданство.
К последней группе британских владений относятся Британские заморские территории (the British Overseas Territories) ― обломки Британской империи, которые продолжают быть колониями (Crown colonies). В отличие от стран Содружества, они не стали самостоятельными государствами и до сих пор зависят от Соединенного Королевства в экономических и даже военных вопросах. Также как и жители Коронных земель, граждане Британских заморских территорий ― подданные Соединенного Королевства.
К заморским территориям относятся следующие страны: Бермудские Острова (Bermuda), Острова Кайман (Cayman Islands), Теркс и Кайкос (Turks and Caicos Islands), Гибралтар (Gibraltar), Виргинские Острова (Virgin Islands), Акротири и Декелия (Akrotiri and Dhekelia), Ангилья (Anguilla), остров Святой Елены (Saint Helena), остров Вознесения (Ascension Island), Тристан-да-Кунья (Tristan da Cunha), Монсеррат (Montserrat), Британская территория в Индийском океане (British Indian Ocean Territory), Южная Георгия и Южные Сандвичевы Острова (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands), Фолклендские Острова (Falkland Islands), Британская антарктическая территория (British Antarctic Territory) и остров Питкэрн (The Pitcairn Islands).
Посмотрите видео и насладитесь красотами тех стран, которые все еще принадлежат Соединенному Королевству.
| Слово/Словосочетание | Перевод |
|---|---|
| to be scattered | быть разбросанным |
| to erupt | извергаться |
| noisy | шумный |
| sheltered | защищенный |
| an edge | граница |
| inhabited | заселенный |
| to breed | размножаться |
| to rise | разрастаться |
| nesting | гнездование |
| a descendant | потомок |
| to bury | закапывать |
| treasure | сокровище |
Хотите свободно общаться с иностранцами и узнавать об их культуре из первых уст? Тогда записывайтесь на уроки английского к носителям языка.
Подведем итог:
Соединенное Королевство (the United Kingdom) ― страна, объединяющая Англию, Шотландию, Уэльс и Северную Ирландию
Англия (England) ― часть Соединенного Королевства
Великобритания (Great Britain) ― остров на котором расположены Англия, Уэльс и Шотландия, входящие в состав Соединенного Королевства
Содружество Наций (Commonwealth realms) ― страны, ставшие независимыми от Британской империи благодаря дипломатическому договору
Коронные земли (the Crown dependencies) ― три автономных, но зависимых от Соединенного Королевства острова
Заморские территории (the British Overseas Territories) ― государства, которые остаются колониями Соединенного Королевства.
Надеемся, теперь вы разобрались в многообразии британских политических и географических терминов.
© 2023 englex.ru, копирование материалов возможно только при указании прямой активной ссылки на первоисточник.