| Egyptian hieroglyphs | |
|---|---|

Hieroglyphs from the tomb of Seti I (KV17), 13th century BC |
|
| Script type |
Logography usable as an abjad |
|
Time period |
c. 3200 BC[1][2][3] – AD 400[4] |
| Direction | right-to-left script, left-to-right |
| Languages | Egyptian language |
| Related scripts | |
|
Parent systems |
(Proto-writing)
|
|
Child systems |
Hieratic, Proto-Sinaitic |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Egyp (050), Egyptian hieroglyphs |
| Unicode | |
|
Unicode alias |
Egyptian Hieroglyphs |
|
Unicode range |
|
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. |
Egyptian hieroglyphs (, )[5][6] were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt, used for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with some 1,000 distinct characters.[7][8] Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet.[9] Through the Phoenician alphabet’s major child systems (the Greek and Aramaic scripts), the Egyptian hieroglyphic script is ancestral to the majority of scripts in modern use, most prominently the Latin and Cyrillic scripts (through Greek) and the Arabic script, and possibly the Brahmic family of scripts (through Aramaic, Phoenician, and Greek).[citation needed]
The use of hieroglyphic writing arose from proto-literate symbol systems in the Early Bronze Age, around the 32nd century BC (Naqada III),[2] with the first decipherable sentence written in the Egyptian language dating to the Second Dynasty (28th century BC). Egyptian hieroglyphs developed into a mature writing system used for monumental inscription in the classical language of the Middle Kingdom period; during this period, the system made use of about 900 distinct signs. The use of this writing system continued through the New Kingdom and Late Period, and on into the Persian and Ptolemaic periods. Late survivals of hieroglyphic use are found well into the Roman period, extending into the 4th century AD.[4]
With the final closing of pagan temples in the 5th century, knowledge of hieroglyphic writing was lost. Although attempts were made, the script remained undeciphered throughout the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The decipherment of hieroglyphic writing was finally accomplished in the 1820s by Jean-François Champollion, with the help of the Rosetta Stone.[10]
Etymology[edit]
The word hieroglyph comes from the Greek adjective ἱερογλυφικός (hieroglyphikos),[11] a compound of ἱερός (hierós ‘sacred’)[12] and γλύφω (glýphō ‘(Ι) carve, engrave’; see glyph)[13] meaning sacred carving.
The glyphs themselves, since the Ptolemaic period, were called τὰ ἱερογλυφικὰ [γράμματα] (tà hieroglyphikà [grámmata]) «the sacred engraved letters», the Greek counterpart to the Egyptian expression of mdw.w-nṯr «god’s words».[14] Greek ἱερόγλυφος meant «a carver of hieroglyphs».[15]
In English, hieroglyph as a noun is recorded from 1590, originally short for nominalized hieroglyphic (1580s, with a plural hieroglyphics), from adjectival use (hieroglyphic character).[16][17]
The Nag Hammadi texts written in Sahidic Coptic call the hieroglyphs «writings of the magicians, soothsayers» (Coptic: ϩⲉⲛⲥϩⲁⲓ̈ ⲛ̄ⲥⲁϩ ⲡⲣⲁⲛ︦ϣ︦).[18]
History and evolution[edit]
Origin[edit]
Paintings with symbols on Naqada II pottery (3500–3200 BCE)
Hieroglyphs may have emerged from the preliterate artistic traditions of Egypt. For example, symbols on Gerzean pottery from c. 4000 BC have been argued to resemble hieroglyphic writing.[19]
Proto-hieroglyphic symbol systems developed in the second half of the 4th millennium BC, such as the clay labels of a Predynastic ruler called «Scorpion I» (Naqada IIIA period, c. 33rd century BC) recovered at Abydos (modern Umm el-Qa’ab) in 1998 or the Narmer Palette (c. 31st century BC).[2]
The first full sentence written in mature hieroglyphs so far discovered was found on a seal impression in the tomb of Seth-Peribsen at Umm el-Qa’ab, which dates from the Second Dynasty (28th or 27th century BC). Around 800 hieroglyphs are known to date back to the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom Eras. By the Greco-Roman period, there were more than 5,000.[7]
Geoffrey Sampson stated that Egyptian hieroglyphs «came into existence a little after Sumerian script, and, probably, [were] invented under the influence of the latter»,[23] and that it is «probable that the general idea of expressing words of a language in writing was brought to Egypt from Sumerian Mesopotamia».[24][25] There are many instances of early Egypt-Mesopotamia relations, but given the lack of direct evidence for the transfer of writing, «no definitive determination has been made as to the origin of hieroglyphics in ancient Egypt».[26] Others have held that «the evidence for such direct influence remains flimsy» and that «a very credible argument can also be made for the independent development of writing in Egypt…»[27]
Since the 1990s, the above-mentioned discoveries of glyphs at Abydos, dated to between 3400 and 3200 BCE, have shed doubt on the classical notion that the Mesopotamian symbol system predates the Egyptian one. However, Egyptian writing appeared suddenly at that time, while Mesopotamia had a long evolutionary history of the usage of signs—for agricultural and accounting purposes—in tokens dating as early back to circa 8000 BC.[21] Rosalie David stated that «If Egypt did adopt the idea of writing from elsewhere, it was presumably only the concept which was taken over, since the forms of the hieroglyphs are entirely Egyptian in origin and reflect the distinctive flora, fauna and images of Egypt’s own landscape.»[28]
-
Labels with early inscriptions from the tomb of Menes (3200–3000 BCE)
-
Ivory plaque of Menes (3200–3000 BCE)
-
Ivory plaque of Menes (drawing)
-
The oldest known full sentence written in mature hieroglyphs. Seal impression of Seth-Peribsen (Second Dynasty, c. 28–27th century BCE)
Mature writing system[edit]
Hieroglyphs on stela in Louvre, circa 1321 BCE
Artist’s scaled drawing of hieroglyphs meaning «life, stability, and dominion.» The grid lines allowed the artist to draw the hieroglyphs at whatever scale was needed. ca. 1479–1458 B.C.[29]
Hieroglyphs consist of three kinds of glyphs: phonetic glyphs, including single-consonant characters that function like an alphabet; logographs, representing morphemes; and determinatives, which narrow down the meaning of logographic or phonetic words.
Late Period[edit]
As writing developed and became more widespread among the Egyptian people, simplified glyph forms developed, resulting in the hieratic (priestly) and demotic (popular) scripts. These variants were also more suited than hieroglyphs for use on papyrus. Hieroglyphic writing was not, however, eclipsed, but existed alongside the other forms, especially in monumental and other formal writing. The Rosetta Stone contains three parallel scripts – hieroglyphic, demotic, and Greek.
Late survival[edit]
Hieroglyphs continued to be used under Persian rule (intermittent in the 6th and 5th centuries BCE), and after Alexander the Great’s conquest of Egypt, during the ensuing Ptolemaic and Roman periods. It appears that the misleading quality of comments from Greek and Roman writers about hieroglyphs came about, at least in part, as a response to the changed political situation. Some believed that hieroglyphs may have functioned as a way to distinguish ‘true Egyptians’ from some of the foreign conquerors. Another reason may be the refusal to tackle a foreign culture on its own terms, which characterized Greco-Roman approaches to Egyptian culture generally.[citation needed] Having learned that hieroglyphs were sacred writing, Greco-Roman authors imagined the complex but rational system as an allegorical, even magical, system transmitting secret, mystical knowledge.[4]
By the 4th century AD, few Egyptians were capable of reading hieroglyphs, and the «myth of allegorical hieroglyphs» was ascendant.[4] Monumental use of hieroglyphs ceased after the closing of all non-Christian temples in 391 by the Roman Emperor Theodosius I; the last known inscription is from Philae, known as the Graffito of Esmet-Akhom, from 394.[4][30]
The Hieroglyphica of Horapollo (c. 5th century) appears to retain some genuine knowledge about the writing system. It offers an explanation of close to 200 signs.
Some are identified correctly, such as the «goose» hieroglyph (zꜣ) representing the word for «son».[4]
A half-dozen Demotic glyphs are still in use, added to the Greek alphabet when writing Coptic.
Decipherment[edit]
Ibn Wahshiyya’s attempt at a translation of a hieroglyphic text
Knowledge of the hieroglyphs had been lost completely in the medieval period.
Early attempts at decipherment are due to Dhul-Nun al-Misri and Ibn Wahshiyya (9th and 10th century, respectively).[31]
All medieval and early modern attempts were hampered by the fundamental assumption that hieroglyphs
recorded ideas and not the sounds of the language.
As no bilingual texts were available, any such symbolic ‘translation’ could be proposed without the possibility of verification.[32] It was not until Athanasius Kircher in the mid 17th century that scholars began to think the hieroglyphs might also represent sounds. Kircher was familiar with Coptic, and thought that it might be the key to deciphering the hieroglyphs, but was held back by a belief in the mystical nature of the symbols.[4]
The breakthrough in decipherment came only with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone by Napoleon’s troops in 1799 (during Napoleon’s Egyptian invasion).
As the stone presented a hieroglyphic and a demotic version of the same text in parallel with a Greek translation, plenty of material for falsifiable studies in translation was suddenly available. In the early 19th century, scholars such as Silvestre de Sacy, Johan David Åkerblad, and Thomas Young studied the inscriptions on the stone, and were able to make some headway. Finally, Jean-François Champollion made the complete decipherment by the 1820s. In his Lettre à M. Dacier (1822), he wrote:
It is a complex system, writing figurative, symbolic, and phonetic all at once, in the same text, the same phrase, I would almost say in the same word.[33]
Illustration from Tabula Aegyptiaca hieroglyphicis exornata published in Acta Eruditorum, 1714
Writing system[edit]
Visually, hieroglyphs are all more or less figurative: they represent real or abstract elements, sometimes stylized and simplified, but all generally perfectly recognizable in form. However, the same sign can, according to context, be interpreted in diverse ways: as a phonogram (phonetic reading), as a logogram, or as an ideogram (semagram; «determinative») (semantic reading). The determinative was not read as a phonetic constituent, but facilitated understanding by differentiating the word from its homophones.
Phonetic reading[edit]
Hieroglyphs typical of the Graeco-Roman period
Most non-determinative hieroglyphic signs are phonograms, whose meaning is determined by pronunciation, independent of visual characteristics. This follows the rebus principle where, for example, the picture of an eye could stand not only for the English word eye, but also for its phonetic equivalent, the first person pronoun I.
Phonograms formed with one consonant are called uniliteral signs; with two consonants, biliteral signs; with three, triliteral signs.
Twenty-four uniliteral signs make up the so-called hieroglyphic alphabet. Egyptian hieroglyphic writing does not normally indicate vowels, unlike cuneiform, and for that reason has been labelled by some as an abjad, i.e., an alphabet without vowels.
Thus, hieroglyphic writing representing a pintail duck is read in Egyptian as sꜣ, derived from the main consonants of the Egyptian word for this duck: ‘s’, ‘ꜣ’ and ‘t’. (Note that ꜣ or , two half-rings opening to the left, sometimes replaced by the digit ‘3’, is the Egyptian alef.)
It is also possible to use the hieroglyph of the pintail duck without a link to its meaning in order to represent the two phonemes s and ꜣ, independently of any vowels that could accompany these consonants, and in this way write the word: sꜣ, «son»; or when complemented by other signs detailed below[clarification needed] sꜣ, «keep, watch»; and sꜣṯ.w, «hard ground». For example:
– the characters sꜣ;
– the same character used only in order to signify, according to the context, «pintail duck» or, with the appropriate determinative, «son», two words having the same or similar consonants; the meaning of the little vertical stroke will be explained further on under Logograms:
– the character sꜣ as used in the word sꜣw, «keep, watch»[clarification needed]
As in the Arabic script, not all vowels were written in Egyptian hieroglyphs; it is debatable whether vowels were written at all. Possibly, as with Arabic, the semivowels /w/ and /j/ (as in English W and Y) could double as the vowels /u/ and /i/. In modern transcriptions, an e is added between consonants to aid in their pronunciation. For example, nfr «good» is typically written nefer. This does not reflect Egyptian vowels, which are obscure, but is merely a modern convention. Likewise, the ꜣ and ʾ are commonly transliterated as a, as in Ra.
Hieroglyphs are inscribed in rows of pictures arranged in horizontal lines or vertical columns.[34] Both hieroglyph lines as well as signs contained in the lines are read with upper content having precedence over content below.[34] The lines or columns, and the individual inscriptions within them, read from left to right in rare instances only and for particular reasons at that; ordinarily however, they read from right to left–the Egyptians’ preferred direction of writing (although, for convenience, modern texts are often normalized into left-to-right order).[34] The direction toward which asymmetrical hieroglyphs face indicate their proper reading order. For example, when human and animal hieroglyphs face or look toward the left, they almost always must be read from left to right, and vice versa.
As in many ancient writing systems, words are not separated by blanks or punctuation marks. However, certain hieroglyphs appear particularly common only at the end of words, making it possible to readily distinguish words.
Uniliteral signs[edit]
The Egyptian hieroglyphic script contained 24 uniliterals (symbols that stood for single consonants, much like letters in English). It would have been possible to write all Egyptian words in the manner of these signs, but the Egyptians never did so and never simplified their complex writing into a true alphabet.[35]
Each uniliteral glyph once had a unique reading, but several of these fell together as Old Egyptian developed into Middle Egyptian. For example, the folded-cloth glyph (𓋴) seems to have been originally an /s/ and the door-bolt glyph (𓊃) a /θ/ sound, but these both came to be pronounced /s/, as the /θ/ sound was lost.[clarification needed] A few uniliterals first appear in Middle Egyptian texts.
Besides the uniliteral glyphs, there are also the biliteral and triliteral signs, to represent a specific sequence of two or three consonants, consonants and vowels, and a few as vowel combinations only, in the language.
Phonetic complements[edit]
Egyptian writing is often redundant: in fact, it happens very frequently that a word is followed by several characters writing the same sounds, in order to guide the reader. For example, the word nfr, «beautiful, good, perfect», was written with a unique triliteral that was read as nfr:
However, it is considerably more common to add to that triliteral, the uniliterals for f and r. The word can thus be written as nfr+f+r, but one still reads it as merely nfr. The two alphabetic characters are adding clarity to the spelling of the preceding triliteral hieroglyph.
Redundant characters accompanying biliteral or triliteral signs are called phonetic complements (or complementaries). They can be placed in front of the sign (rarely), after the sign (as a general rule), or even framing it (appearing both before and after). Ancient Egyptian scribes consistently avoided leaving large areas of blank space in their writing and might add additional phonetic complements or sometimes even invert the order of signs if this would result in a more aesthetically pleasing appearance (good scribes attended to the artistic, and even religious, aspects of the hieroglyphs, and would not simply view them as a communication tool). Various examples of the use of phonetic complements can be seen below:
- – md +d +w (the complementary d is placed after the sign) → it reads mdw, meaning «tongue».
- – ḫ +p +ḫpr +r +j (the four complementaries frame the triliteral sign of the scarab beetle) → it reads ḫpr.j, meaning the name «Khepri», with the final glyph being the determinative for ‘ruler or god’.
Notably, phonetic complements were also used to allow the reader to differentiate between signs that are homophones, or which do not always have a unique reading. For example, the symbol of «the seat» (or chair):
– This can be read st, ws and ḥtm, according to the word in which it is found. The presence of phonetic complements—and of the suitable determinative—allows the reader to know which of the three readings to choose:
- 1st Reading: st – – st, written st+t; the last character is the determinative of «the house» or that which is found there, meaning «seat, throne, place»;
- – st (written st+t; the «egg» determinative is used for female personal names in some periods), meaning «Isis»;
- 2nd Reading: ws – – wsjr (written ws+jr, with, as a phonetic complement, «the eye», which is read jr, following the determinative of «god»), meaning «Osiris»;
- 3rd Reading: ḥtm – – ḥtm.t (written ḥ+ḥtm+m+t, with the determinative of «Anubis» or «the jackal»), meaning a kind of wild animal;
- – ḥtm (written ḥ +ḥtm +t, with the determinative of the flying bird), meaning «to disappear».
Finally, it sometimes happens that the pronunciation of words might be changed because of their connection to Ancient Egyptian: in this case, it is not rare for writing to adopt a compromise in notation, the two readings being indicated jointly. For example, the adjective bnj, «sweet», became bnr. In Middle Egyptian, one can write:
-
-
- – bnrj (written b+n+r+i, with determinative)
-
which is fully read as bnr, the j not being pronounced but retained in order to keep a written connection with the ancient word (in the same fashion as the English language words through, knife, or victuals, which are no longer pronounced the way they are written.)
Semantic reading[edit]
Comparative evolution from pictograms to abstract shapes, in cuneiform, Egyptian and Chinese characters
Besides a phonetic interpretation, characters can also be read for their meaning: in this instance, logograms are being spoken (or ideograms) and semagrams (the latter are also called determinatives).[clarification needed][36]
Logograms[edit]
A hieroglyph used as a logogram defines the object of which it is an image. Logograms are therefore the most frequently used common nouns; they are always accompanied by a mute vertical stroke indicating their status as a logogram (the usage of a vertical stroke is further explained below); in theory, all hieroglyphs would have the ability to be used as logograms. Logograms can be accompanied by phonetic complements. Here are some examples:
-
- – rꜥ, meaning «sun»;
-
- – pr, meaning «house»;
-
- – swt (sw+t), meaning «reed»;
-
- – ḏw, meaning «mountain».
In some cases, the semantic connection is indirect (metonymic or metaphoric):
-
- – nṯr, meaning «god»; the character in fact represents a temple flag (standard);
-
- – bꜣ, meaning «Bâ» (soul); the character is the traditional representation of a «bâ» (a bird with a human head);
-
- – dšr, meaning «flamingo»; the corresponding phonogram means «red» and the bird is associated by metonymy with this color.
Determinatives[edit]
Determinatives or semagrams (semantic symbols specifying meaning) are placed at the end of a word. These mute characters serve to clarify what the word is about, as homophonic glyphs are common. If a similar procedure existed in English, words with the same spelling would be followed by an indicator that would not be read, but which would fine-tune the meaning: «retort [chemistry]» and «retort [rhetoric]» would thus be distinguished.
A number of determinatives exist: divinities, humans, parts of the human body, animals, plants, etc. Certain determinatives possess a literal and a figurative meaning. For example, a roll of papyrus,
is used to define «books» but also abstract ideas. The determinative of the plural is a shortcut to signal three occurrences of the word, that is to say, its plural (since the Egyptian language had a dual, sometimes indicated by two strokes). This special character is explained below.
Here, are several examples of the use of determinatives borrowed from the book, Je lis les hiéroglyphes («I am reading hieroglyphs») by Jean Capart, which illustrate their importance:
– nfrw (w and the three strokes are the marks of the plural): [literally] «the beautiful young people», that is to say, the young military recruits. The word has a young-person determinative symbol:
– which is the determinative indicating babies and children;
– nfr.t (.t is here the suffix that forms the feminine): meaning «the nubile young woman», with
as the determinative indicating a woman;
– nfrw (the tripling of the character serving to express the plural, flexional ending w) : meaning «foundations (of a house)», with the house as a determinative,
;
– nfr : meaning «clothing» with
as the determinative for lengths of cloth;
– nfr : meaning «wine» or «beer»; with a jug
as the determinative.
All these words have a meliorative connotation: «good, beautiful, perfect». The Concise Dictionary of Middle Egyptian by Raymond A. Faulkner, gives some twenty words that are read nfr or which are formed from this word.
Additional signs[edit]
Cartouche[edit]
Rarely, the names of gods are placed within a cartouche; the two last names of the sitting king are always placed within a cartouche:
jmn-rꜥ, «Amon-Ra»;
qljwꜣpdrꜣ.t, «Cleopatra»;
Filling stroke[edit]
A filling stroke is a character indicating the end of a quadrat that would otherwise be incomplete.
Signs joined[edit]
Some signs are the contraction of several others. These signs have, however, a function and existence of their own: for example, a forearm where the hand holds a scepter is used as a determinative for words meaning «to direct, to drive» and their derivatives.
Doubling[edit]
The doubling of a sign indicates its dual; the tripling of a sign indicates its plural.
Grammatical signs[edit]
- The vertical stroke indicates that the sign is a logogram.
- Two strokes indicate the dual number, and the three strokes the plural.
- The direct notation of flexional endings, for example:
Spelling[edit]
Standard orthography—»correct» spelling—in Egyptian is much looser than in modern languages. In fact, one or several variants exist for almost every word. One finds:
- Redundancies;
- Omission of graphemes, which are ignored whether or not they are intentional;
- Substitutions of one grapheme for another, such that it is impossible to distinguish a «mistake» from an «alternate spelling»;
- Errors of omission in the drawing of signs, which are much more problematic when the writing is cursive (hieratic) writing, but especially demotic, where the schematization of the signs is extreme.
However, many of these apparent spelling errors constitute an issue of chronology. Spelling and standards varied over time, so the writing of a word during the Old Kingdom might be considerably different during the New Kingdom. Furthermore, the Egyptians were perfectly content to include older orthography («historical spelling») alongside newer practices, as though it were acceptable in English to use archaic spellings in modern texts. Most often, ancient «spelling errors» are simply misinterpretations of context. Today, hieroglyphicists use numerous cataloguing systems (notably the Manuel de Codage and Gardiner’s Sign List) to clarify the presence of determinatives, ideograms, and other ambiguous signs in transliteration.
Simple examples[edit]
|
||||||||||||||
| Ptolemy | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Era: Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC) |
||||||||||||||
| Egyptian hieroglyphs |
The glyphs in this cartouche are transliterated as:
| p t |
«ua» | l m |
y (ii) s |
Ptolmys |
though ii is considered a single letter and transliterated y.
Another way in which hieroglyphs work is illustrated by the two Egyptian words pronounced pr (usually vocalised as per). One word is ‘house’, and its hieroglyphic representation is straightforward:
Here, the ‘house’ hieroglyph works as a logogram: it represents the word with a single sign. The vertical stroke below the hieroglyph is a common way of indicating that a glyph is working as a logogram.
Another word pr is the verb ‘to go out, leave’. When this word is written, the ‘house’ hieroglyph is used as a phonetic symbol:
Here, the ‘house’ glyph stands for the consonants pr. The ‘mouth’ glyph below it is a phonetic complement: it is read as r, reinforcing the phonetic reading of pr. The third hieroglyph is a determinative: it is an ideogram for verbs of motion that gives the reader an idea of the meaning of the word.
Encoding and font support[edit]
Egyptian hieroglyphs were added to the Unicode Standard in October 2009 with the release of version 5.2 which introduced the Egyptian Hieroglyphs block (U+13000–U+1342F).
As of July 2013, four fonts, Aegyptus, NewGardiner, Noto Sans Egyptian Hieroglyphs and JSeshFont support this range. Another font, Segoe UI Historic, comes bundled with Windows 10 and also contains glyphs for the Egyptian Hieroglyphs block. Segoe UI Historic excludes three glyphs depicting phallus (Gardiner’s D52, D52A D53, Unicode code points U+130B8–U+130BA).[38]
See also[edit]
- List of Egyptian hieroglyphs
- Gardiner’s sign list
- Egyptian numerals
- Egyptian language
- Middle Bronze Age alphabets
- Manuel de Codage
- Champollion Museum
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ «…The Mesopotamians invented writing around 3200 bc without any precedent to guide them, as did the Egyptians, independently as far as we know, at approximately the same time» The Oxford History of Historical Writing. Vol. 1. To AD 600, p. 5
- ^ a b c Richard Mattessich (2002). «The oldest writings, and inventory tags of Egypt». Accounting Historians Journal. 29 (1): 195–208. doi:10.2308/0148-4184.29.1.195. JSTOR 40698264. Archived from the original on 2018-11-19. Retrieved 2016-08-27.
- ^ Allen, James P. (2010). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-1139486354.
- ^ a b c d e f g Allen, James P. (2010). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-1139486354.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (2003) [1917], Peter Roach; James Hartmann; Jane Setter (eds.), English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-3-12-539683-8
- ^ «hieroglyph». Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ^ a b There were about 1,000 graphemes in the Old Kingdom period, reduced to around 750 to 850 in the classical language of the Middle Kingdom, but inflated to the order of some 5,000 signs in the Ptolemaic period. Antonio Loprieno, Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 12.
- ^ The standard inventory of characters used in Egyptology is Gardiner’s sign list (1928–1953).
A.H. Gardiner (1928), Catalogue of the Egyptian hieroglyphic printing type, from matrices owned and controlled by Dr. Alan Gardiner, «Additions to the new hieroglyphic fount (1928)», in The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology 15 (1929), p. 95; «Additions to the new hieroglyphic fount (1931)», in The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology 17 (1931), pp. 245–247; A.H. Gardiner, «Supplement to the catalogue of the Egyptian hieroglyphic printing type, showing acquisitions to December 1953» (1953).
Unicode Egyptian Hieroglyphs as of version 5.2 (2009) assigned 1,070 Unicode characters. - ^ Michael C. Howard (2012). Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies. P. 23.
- ^ Houston, Stephen; Baines, John; Cooper, Jerrold (July 2003). «Last Writing: Script Obsolescence in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Mesoamerica». Comparative Studies in Society and History. 45 (3). doi:10.1017/s0010417503000227. ISSN 0010-4175. S2CID 145542213.
- ^ ἱερογλυφικός. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- ^ ἱερός in Liddell and Scott.
- ^ γλύφω in Liddell and Scott,
- ^ Antonio Loprieno, Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 11.
- ^ ἱερόγλυφος in Liddell and Scott.
- ^ «Hieroglyphic | Definition of Hieroglyphic by Merriam-Webster». Retrieved 2016-08-27.
- ^ Harper, Douglas. «hieroglyphic». Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ The Discourse on the Eighth and Ninth, VI, 61,20; 61,30; 62,15
- ^ Joly, Marcel (2003). «Sayles, George(, Sr.)». Grove Music Online. Oxford Music Online. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.j397600.
- ^ Scarre, Chris; Fagan, Brian M. (2016). Ancient Civilizations. Routledge. p. 106. ISBN 978-1317296089.
- ^ a b «The seal impressions, from various tombs, date even further back, to 3400 B.C. These dates challenge the commonly held belief that early logographs, pictographic symbols representing a specific place, object, or quantity, first evolved into more complex phonetic symbols in Mesopotamia.»Mitchell, Larkin. «Earliest Egyptian Glyphs». Archaeology. Archaeological Institute of America. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ Conference, William Foxwell Albright Centennial (1996). The Study of the Ancient Near East in the Twenty-first Century: The William Foxwell Albright Centennial Conference. Eisenbrauns. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-0931464966.
- ^ Geoffrey Sampson (1990). Writing Systems: A Linguistic Introduction. Stanford University Press. pp. 78–. ISBN 978-0-8047-1756-4. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Geoffrey W. Bromiley (1995). The international standard Bible encyclopedia. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. pp. 1150–. ISBN 978-0-8028-3784-4. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Iorwerth Eiddon Stephen Edwards, et al., The Cambridge Ancient History (3d ed. 1970) pp. 43–44.
- ^ Robert E. Krebs; Carolyn A. Krebs (2003). Groundbreaking scientific experiments, inventions, and discoveries of the ancient world. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 91–. ISBN 978-0-313-31342-4. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Simson Najovits, Egypt, Trunk of the Tree: A Modern Survey of an Ancient Land, Algora Publishing, 2004, pp. 55–56.
- ^ David, Rosalie (2002). The Experience of Ancient Egypt. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-96799-5. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
- ^ «Artist’s Scaled Drawing of Hieroglyphs ca. 1479–1458 B.C.» metmuseum.org. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ^ The latest presently known hieroglyphic inscription date: Birthday of Osiris, year 110 [of Diocletian], dated to August 24, 394
- ^ Ahmed ibn ‘Ali ibn al Mukhtar ibn ‘Abd al Karim (called Ibn Wahshiyah) (1806). Ancient alphabets & hieroglyphic characters explained: with an account of the Egyptian priests, their classes, initiation time, & sacrifices by the aztecs and their birds, in the Arabic language. W. Bulmer & co. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Tabula Aegyptiaca hieroglyphics exornata. Acta Eruditorum. Leipzig. 1714. p. 127.
- ^ Jean-François Champollion, Letter to M. Dacier, September 27, 1822
- ^ a b c Sir Alan H. Gardiner, Egyptian Grammar, Third Edition Revised, Griffith Institute (2005), p. 25.
- ^ Gardiner, Sir Alan H. (1973). Egyptian Grammar. Griffith Institute. ISBN 978-0-900416-35-4.
- ^ Antonio Loprieno, Ancient Egyptian, A Linguistic Introduction, Cambridge University Press (1995), p. 13
- ^ Budge, Wallis (1889). Egyptian Language. pp. 38–42.
- ^ «Segoe UI Historic Phallus Microsoft Censorship – Fonts in the Spludlow Framework». www.spludlow.co.uk. Retrieved 2019-05-13.
Further reading[edit]
- Adkins, Lesley; Adkins, Roy (2000). The Keys of Egypt: The Obsession to Decipher Egyptian Hieroglyphs. HarperCollins Publishers. ISBN 978-0-06-019439-0.
- Allen, James P. (1999). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77483-3.
- Collier, Mark & Bill Manley (1998). How to Read Egyptian Hieroglyphs: a step-by-step guide to teach yourself. British Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-7141-1910-6.
- Davidson, James, «At the British Museum», London Review of Books, vol. 45, no.3 (2 February 2023), pp. 26–27.
- Selden, Daniel L. (2013). Hieroglyphic Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Literature of the Middle Kingdom. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-27546-1.
- Faulkner, Raymond O. (1962). Concise Dictionary of Middle Egyptian. Griffith Institute. ISBN 978-0-900416-32-3.
- Gardiner, Sir Alan H. (1957). Egyptian Grammar: Being an Introduction to the Study of Hieroglyphs, 3rd ed. revised. The Griffith Institute.
- Hill, Marsha (2007). Gifts for the gods: images from Egyptian temples. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 9781588392312.
- Kamrin, Janice (2004). Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphs: A Practical Guide. Harry N. Abrams, Inc. ISBN 978-0-8109-4961-4.
- McDonald, Angela. Write Your Own Egyptian Hieroglyphs. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2007 (paperback, ISBN 0-520-25235-7).
- Erman, Adolf (1894). Egyptian Grammar: with table of signs, bibliography, exercises for reading and glossary. Williams and Norgate. ISBN 978-3862882045.
External links[edit]
Look up hieroglyph in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics – Aldokkan
- Glyphs and Grammars – Resources for those interested in learning hieroglyphs, compiled by Aayko Eyma
- Hieroglyphics! – Annotated directory of popular and scholarly resources
- Egyptian Language and Writing
- Full-text of The stela of Menthu-weser
- Wikimedia’s hieroglyph writing codes
- Unicode Fonts for Ancient Scripts – Ancient scripts free software fonts
| Egyptian hieroglyphs | |
|---|---|

Hieroglyphs from the tomb of Seti I (KV17), 13th century BC |
|
| Script type |
Logography usable as an abjad |
|
Time period |
c. 3200 BC[1][2][3] – AD 400[4] |
| Direction | right-to-left script, left-to-right |
| Languages | Egyptian language |
| Related scripts | |
|
Parent systems |
(Proto-writing)
|
|
Child systems |
Hieratic, Proto-Sinaitic |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Egyp (050), Egyptian hieroglyphs |
| Unicode | |
|
Unicode alias |
Egyptian Hieroglyphs |
|
Unicode range |
|
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. |
Egyptian hieroglyphs (, )[5][6] were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt, used for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with some 1,000 distinct characters.[7][8] Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet.[9] Through the Phoenician alphabet’s major child systems (the Greek and Aramaic scripts), the Egyptian hieroglyphic script is ancestral to the majority of scripts in modern use, most prominently the Latin and Cyrillic scripts (through Greek) and the Arabic script, and possibly the Brahmic family of scripts (through Aramaic, Phoenician, and Greek).[citation needed]
The use of hieroglyphic writing arose from proto-literate symbol systems in the Early Bronze Age, around the 32nd century BC (Naqada III),[2] with the first decipherable sentence written in the Egyptian language dating to the Second Dynasty (28th century BC). Egyptian hieroglyphs developed into a mature writing system used for monumental inscription in the classical language of the Middle Kingdom period; during this period, the system made use of about 900 distinct signs. The use of this writing system continued through the New Kingdom and Late Period, and on into the Persian and Ptolemaic periods. Late survivals of hieroglyphic use are found well into the Roman period, extending into the 4th century AD.[4]
With the final closing of pagan temples in the 5th century, knowledge of hieroglyphic writing was lost. Although attempts were made, the script remained undeciphered throughout the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The decipherment of hieroglyphic writing was finally accomplished in the 1820s by Jean-François Champollion, with the help of the Rosetta Stone.[10]
Etymology[edit]
The word hieroglyph comes from the Greek adjective ἱερογλυφικός (hieroglyphikos),[11] a compound of ἱερός (hierós ‘sacred’)[12] and γλύφω (glýphō ‘(Ι) carve, engrave’; see glyph)[13] meaning sacred carving.
The glyphs themselves, since the Ptolemaic period, were called τὰ ἱερογλυφικὰ [γράμματα] (tà hieroglyphikà [grámmata]) «the sacred engraved letters», the Greek counterpart to the Egyptian expression of mdw.w-nṯr «god’s words».[14] Greek ἱερόγλυφος meant «a carver of hieroglyphs».[15]
In English, hieroglyph as a noun is recorded from 1590, originally short for nominalized hieroglyphic (1580s, with a plural hieroglyphics), from adjectival use (hieroglyphic character).[16][17]
The Nag Hammadi texts written in Sahidic Coptic call the hieroglyphs «writings of the magicians, soothsayers» (Coptic: ϩⲉⲛⲥϩⲁⲓ̈ ⲛ̄ⲥⲁϩ ⲡⲣⲁⲛ︦ϣ︦).[18]
History and evolution[edit]
Origin[edit]
Paintings with symbols on Naqada II pottery (3500–3200 BCE)
Hieroglyphs may have emerged from the preliterate artistic traditions of Egypt. For example, symbols on Gerzean pottery from c. 4000 BC have been argued to resemble hieroglyphic writing.[19]
Proto-hieroglyphic symbol systems developed in the second half of the 4th millennium BC, such as the clay labels of a Predynastic ruler called «Scorpion I» (Naqada IIIA period, c. 33rd century BC) recovered at Abydos (modern Umm el-Qa’ab) in 1998 or the Narmer Palette (c. 31st century BC).[2]
The first full sentence written in mature hieroglyphs so far discovered was found on a seal impression in the tomb of Seth-Peribsen at Umm el-Qa’ab, which dates from the Second Dynasty (28th or 27th century BC). Around 800 hieroglyphs are known to date back to the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom Eras. By the Greco-Roman period, there were more than 5,000.[7]
Geoffrey Sampson stated that Egyptian hieroglyphs «came into existence a little after Sumerian script, and, probably, [were] invented under the influence of the latter»,[23] and that it is «probable that the general idea of expressing words of a language in writing was brought to Egypt from Sumerian Mesopotamia».[24][25] There are many instances of early Egypt-Mesopotamia relations, but given the lack of direct evidence for the transfer of writing, «no definitive determination has been made as to the origin of hieroglyphics in ancient Egypt».[26] Others have held that «the evidence for such direct influence remains flimsy» and that «a very credible argument can also be made for the independent development of writing in Egypt…»[27]
Since the 1990s, the above-mentioned discoveries of glyphs at Abydos, dated to between 3400 and 3200 BCE, have shed doubt on the classical notion that the Mesopotamian symbol system predates the Egyptian one. However, Egyptian writing appeared suddenly at that time, while Mesopotamia had a long evolutionary history of the usage of signs—for agricultural and accounting purposes—in tokens dating as early back to circa 8000 BC.[21] Rosalie David stated that «If Egypt did adopt the idea of writing from elsewhere, it was presumably only the concept which was taken over, since the forms of the hieroglyphs are entirely Egyptian in origin and reflect the distinctive flora, fauna and images of Egypt’s own landscape.»[28]
-
Labels with early inscriptions from the tomb of Menes (3200–3000 BCE)
-
Ivory plaque of Menes (3200–3000 BCE)
-
Ivory plaque of Menes (drawing)
-
The oldest known full sentence written in mature hieroglyphs. Seal impression of Seth-Peribsen (Second Dynasty, c. 28–27th century BCE)
Mature writing system[edit]
Hieroglyphs on stela in Louvre, circa 1321 BCE
Artist’s scaled drawing of hieroglyphs meaning «life, stability, and dominion.» The grid lines allowed the artist to draw the hieroglyphs at whatever scale was needed. ca. 1479–1458 B.C.[29]
Hieroglyphs consist of three kinds of glyphs: phonetic glyphs, including single-consonant characters that function like an alphabet; logographs, representing morphemes; and determinatives, which narrow down the meaning of logographic or phonetic words.
Late Period[edit]
As writing developed and became more widespread among the Egyptian people, simplified glyph forms developed, resulting in the hieratic (priestly) and demotic (popular) scripts. These variants were also more suited than hieroglyphs for use on papyrus. Hieroglyphic writing was not, however, eclipsed, but existed alongside the other forms, especially in monumental and other formal writing. The Rosetta Stone contains three parallel scripts – hieroglyphic, demotic, and Greek.
Late survival[edit]
Hieroglyphs continued to be used under Persian rule (intermittent in the 6th and 5th centuries BCE), and after Alexander the Great’s conquest of Egypt, during the ensuing Ptolemaic and Roman periods. It appears that the misleading quality of comments from Greek and Roman writers about hieroglyphs came about, at least in part, as a response to the changed political situation. Some believed that hieroglyphs may have functioned as a way to distinguish ‘true Egyptians’ from some of the foreign conquerors. Another reason may be the refusal to tackle a foreign culture on its own terms, which characterized Greco-Roman approaches to Egyptian culture generally.[citation needed] Having learned that hieroglyphs were sacred writing, Greco-Roman authors imagined the complex but rational system as an allegorical, even magical, system transmitting secret, mystical knowledge.[4]
By the 4th century AD, few Egyptians were capable of reading hieroglyphs, and the «myth of allegorical hieroglyphs» was ascendant.[4] Monumental use of hieroglyphs ceased after the closing of all non-Christian temples in 391 by the Roman Emperor Theodosius I; the last known inscription is from Philae, known as the Graffito of Esmet-Akhom, from 394.[4][30]
The Hieroglyphica of Horapollo (c. 5th century) appears to retain some genuine knowledge about the writing system. It offers an explanation of close to 200 signs.
Some are identified correctly, such as the «goose» hieroglyph (zꜣ) representing the word for «son».[4]
A half-dozen Demotic glyphs are still in use, added to the Greek alphabet when writing Coptic.
Decipherment[edit]
Ibn Wahshiyya’s attempt at a translation of a hieroglyphic text
Knowledge of the hieroglyphs had been lost completely in the medieval period.
Early attempts at decipherment are due to Dhul-Nun al-Misri and Ibn Wahshiyya (9th and 10th century, respectively).[31]
All medieval and early modern attempts were hampered by the fundamental assumption that hieroglyphs
recorded ideas and not the sounds of the language.
As no bilingual texts were available, any such symbolic ‘translation’ could be proposed without the possibility of verification.[32] It was not until Athanasius Kircher in the mid 17th century that scholars began to think the hieroglyphs might also represent sounds. Kircher was familiar with Coptic, and thought that it might be the key to deciphering the hieroglyphs, but was held back by a belief in the mystical nature of the symbols.[4]
The breakthrough in decipherment came only with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone by Napoleon’s troops in 1799 (during Napoleon’s Egyptian invasion).
As the stone presented a hieroglyphic and a demotic version of the same text in parallel with a Greek translation, plenty of material for falsifiable studies in translation was suddenly available. In the early 19th century, scholars such as Silvestre de Sacy, Johan David Åkerblad, and Thomas Young studied the inscriptions on the stone, and were able to make some headway. Finally, Jean-François Champollion made the complete decipherment by the 1820s. In his Lettre à M. Dacier (1822), he wrote:
It is a complex system, writing figurative, symbolic, and phonetic all at once, in the same text, the same phrase, I would almost say in the same word.[33]
Illustration from Tabula Aegyptiaca hieroglyphicis exornata published in Acta Eruditorum, 1714
Writing system[edit]
Visually, hieroglyphs are all more or less figurative: they represent real or abstract elements, sometimes stylized and simplified, but all generally perfectly recognizable in form. However, the same sign can, according to context, be interpreted in diverse ways: as a phonogram (phonetic reading), as a logogram, or as an ideogram (semagram; «determinative») (semantic reading). The determinative was not read as a phonetic constituent, but facilitated understanding by differentiating the word from its homophones.
Phonetic reading[edit]
Hieroglyphs typical of the Graeco-Roman period
Most non-determinative hieroglyphic signs are phonograms, whose meaning is determined by pronunciation, independent of visual characteristics. This follows the rebus principle where, for example, the picture of an eye could stand not only for the English word eye, but also for its phonetic equivalent, the first person pronoun I.
Phonograms formed with one consonant are called uniliteral signs; with two consonants, biliteral signs; with three, triliteral signs.
Twenty-four uniliteral signs make up the so-called hieroglyphic alphabet. Egyptian hieroglyphic writing does not normally indicate vowels, unlike cuneiform, and for that reason has been labelled by some as an abjad, i.e., an alphabet without vowels.
Thus, hieroglyphic writing representing a pintail duck is read in Egyptian as sꜣ, derived from the main consonants of the Egyptian word for this duck: ‘s’, ‘ꜣ’ and ‘t’. (Note that ꜣ or , two half-rings opening to the left, sometimes replaced by the digit ‘3’, is the Egyptian alef.)
It is also possible to use the hieroglyph of the pintail duck without a link to its meaning in order to represent the two phonemes s and ꜣ, independently of any vowels that could accompany these consonants, and in this way write the word: sꜣ, «son»; or when complemented by other signs detailed below[clarification needed] sꜣ, «keep, watch»; and sꜣṯ.w, «hard ground». For example:
– the characters sꜣ;
– the same character used only in order to signify, according to the context, «pintail duck» or, with the appropriate determinative, «son», two words having the same or similar consonants; the meaning of the little vertical stroke will be explained further on under Logograms:
– the character sꜣ as used in the word sꜣw, «keep, watch»[clarification needed]
As in the Arabic script, not all vowels were written in Egyptian hieroglyphs; it is debatable whether vowels were written at all. Possibly, as with Arabic, the semivowels /w/ and /j/ (as in English W and Y) could double as the vowels /u/ and /i/. In modern transcriptions, an e is added between consonants to aid in their pronunciation. For example, nfr «good» is typically written nefer. This does not reflect Egyptian vowels, which are obscure, but is merely a modern convention. Likewise, the ꜣ and ʾ are commonly transliterated as a, as in Ra.
Hieroglyphs are inscribed in rows of pictures arranged in horizontal lines or vertical columns.[34] Both hieroglyph lines as well as signs contained in the lines are read with upper content having precedence over content below.[34] The lines or columns, and the individual inscriptions within them, read from left to right in rare instances only and for particular reasons at that; ordinarily however, they read from right to left–the Egyptians’ preferred direction of writing (although, for convenience, modern texts are often normalized into left-to-right order).[34] The direction toward which asymmetrical hieroglyphs face indicate their proper reading order. For example, when human and animal hieroglyphs face or look toward the left, they almost always must be read from left to right, and vice versa.
As in many ancient writing systems, words are not separated by blanks or punctuation marks. However, certain hieroglyphs appear particularly common only at the end of words, making it possible to readily distinguish words.
Uniliteral signs[edit]
The Egyptian hieroglyphic script contained 24 uniliterals (symbols that stood for single consonants, much like letters in English). It would have been possible to write all Egyptian words in the manner of these signs, but the Egyptians never did so and never simplified their complex writing into a true alphabet.[35]
Each uniliteral glyph once had a unique reading, but several of these fell together as Old Egyptian developed into Middle Egyptian. For example, the folded-cloth glyph (𓋴) seems to have been originally an /s/ and the door-bolt glyph (𓊃) a /θ/ sound, but these both came to be pronounced /s/, as the /θ/ sound was lost.[clarification needed] A few uniliterals first appear in Middle Egyptian texts.
Besides the uniliteral glyphs, there are also the biliteral and triliteral signs, to represent a specific sequence of two or three consonants, consonants and vowels, and a few as vowel combinations only, in the language.
Phonetic complements[edit]
Egyptian writing is often redundant: in fact, it happens very frequently that a word is followed by several characters writing the same sounds, in order to guide the reader. For example, the word nfr, «beautiful, good, perfect», was written with a unique triliteral that was read as nfr:
However, it is considerably more common to add to that triliteral, the uniliterals for f and r. The word can thus be written as nfr+f+r, but one still reads it as merely nfr. The two alphabetic characters are adding clarity to the spelling of the preceding triliteral hieroglyph.
Redundant characters accompanying biliteral or triliteral signs are called phonetic complements (or complementaries). They can be placed in front of the sign (rarely), after the sign (as a general rule), or even framing it (appearing both before and after). Ancient Egyptian scribes consistently avoided leaving large areas of blank space in their writing and might add additional phonetic complements or sometimes even invert the order of signs if this would result in a more aesthetically pleasing appearance (good scribes attended to the artistic, and even religious, aspects of the hieroglyphs, and would not simply view them as a communication tool). Various examples of the use of phonetic complements can be seen below:
- – md +d +w (the complementary d is placed after the sign) → it reads mdw, meaning «tongue».
- – ḫ +p +ḫpr +r +j (the four complementaries frame the triliteral sign of the scarab beetle) → it reads ḫpr.j, meaning the name «Khepri», with the final glyph being the determinative for ‘ruler or god’.
Notably, phonetic complements were also used to allow the reader to differentiate between signs that are homophones, or which do not always have a unique reading. For example, the symbol of «the seat» (or chair):
– This can be read st, ws and ḥtm, according to the word in which it is found. The presence of phonetic complements—and of the suitable determinative—allows the reader to know which of the three readings to choose:
- 1st Reading: st – – st, written st+t; the last character is the determinative of «the house» or that which is found there, meaning «seat, throne, place»;
- – st (written st+t; the «egg» determinative is used for female personal names in some periods), meaning «Isis»;
- 2nd Reading: ws – – wsjr (written ws+jr, with, as a phonetic complement, «the eye», which is read jr, following the determinative of «god»), meaning «Osiris»;
- 3rd Reading: ḥtm – – ḥtm.t (written ḥ+ḥtm+m+t, with the determinative of «Anubis» or «the jackal»), meaning a kind of wild animal;
- – ḥtm (written ḥ +ḥtm +t, with the determinative of the flying bird), meaning «to disappear».
Finally, it sometimes happens that the pronunciation of words might be changed because of their connection to Ancient Egyptian: in this case, it is not rare for writing to adopt a compromise in notation, the two readings being indicated jointly. For example, the adjective bnj, «sweet», became bnr. In Middle Egyptian, one can write:
-
-
- – bnrj (written b+n+r+i, with determinative)
-
which is fully read as bnr, the j not being pronounced but retained in order to keep a written connection with the ancient word (in the same fashion as the English language words through, knife, or victuals, which are no longer pronounced the way they are written.)
Semantic reading[edit]
Comparative evolution from pictograms to abstract shapes, in cuneiform, Egyptian and Chinese characters
Besides a phonetic interpretation, characters can also be read for their meaning: in this instance, logograms are being spoken (or ideograms) and semagrams (the latter are also called determinatives).[clarification needed][36]
Logograms[edit]
A hieroglyph used as a logogram defines the object of which it is an image. Logograms are therefore the most frequently used common nouns; they are always accompanied by a mute vertical stroke indicating their status as a logogram (the usage of a vertical stroke is further explained below); in theory, all hieroglyphs would have the ability to be used as logograms. Logograms can be accompanied by phonetic complements. Here are some examples:
-
- – rꜥ, meaning «sun»;
-
- – pr, meaning «house»;
-
- – swt (sw+t), meaning «reed»;
-
- – ḏw, meaning «mountain».
In some cases, the semantic connection is indirect (metonymic or metaphoric):
-
- – nṯr, meaning «god»; the character in fact represents a temple flag (standard);
-
- – bꜣ, meaning «Bâ» (soul); the character is the traditional representation of a «bâ» (a bird with a human head);
-
- – dšr, meaning «flamingo»; the corresponding phonogram means «red» and the bird is associated by metonymy with this color.
Determinatives[edit]
Determinatives or semagrams (semantic symbols specifying meaning) are placed at the end of a word. These mute characters serve to clarify what the word is about, as homophonic glyphs are common. If a similar procedure existed in English, words with the same spelling would be followed by an indicator that would not be read, but which would fine-tune the meaning: «retort [chemistry]» and «retort [rhetoric]» would thus be distinguished.
A number of determinatives exist: divinities, humans, parts of the human body, animals, plants, etc. Certain determinatives possess a literal and a figurative meaning. For example, a roll of papyrus,
is used to define «books» but also abstract ideas. The determinative of the plural is a shortcut to signal three occurrences of the word, that is to say, its plural (since the Egyptian language had a dual, sometimes indicated by two strokes). This special character is explained below.
Here, are several examples of the use of determinatives borrowed from the book, Je lis les hiéroglyphes («I am reading hieroglyphs») by Jean Capart, which illustrate their importance:
– nfrw (w and the three strokes are the marks of the plural): [literally] «the beautiful young people», that is to say, the young military recruits. The word has a young-person determinative symbol:
– which is the determinative indicating babies and children;
– nfr.t (.t is here the suffix that forms the feminine): meaning «the nubile young woman», with
as the determinative indicating a woman;
– nfrw (the tripling of the character serving to express the plural, flexional ending w) : meaning «foundations (of a house)», with the house as a determinative,
;
– nfr : meaning «clothing» with
as the determinative for lengths of cloth;
– nfr : meaning «wine» or «beer»; with a jug
as the determinative.
All these words have a meliorative connotation: «good, beautiful, perfect». The Concise Dictionary of Middle Egyptian by Raymond A. Faulkner, gives some twenty words that are read nfr or which are formed from this word.
Additional signs[edit]
Cartouche[edit]
Rarely, the names of gods are placed within a cartouche; the two last names of the sitting king are always placed within a cartouche:
jmn-rꜥ, «Amon-Ra»;
qljwꜣpdrꜣ.t, «Cleopatra»;
Filling stroke[edit]
A filling stroke is a character indicating the end of a quadrat that would otherwise be incomplete.
Signs joined[edit]
Some signs are the contraction of several others. These signs have, however, a function and existence of their own: for example, a forearm where the hand holds a scepter is used as a determinative for words meaning «to direct, to drive» and their derivatives.
Doubling[edit]
The doubling of a sign indicates its dual; the tripling of a sign indicates its plural.
Grammatical signs[edit]
- The vertical stroke indicates that the sign is a logogram.
- Two strokes indicate the dual number, and the three strokes the plural.
- The direct notation of flexional endings, for example:
Spelling[edit]
Standard orthography—»correct» spelling—in Egyptian is much looser than in modern languages. In fact, one or several variants exist for almost every word. One finds:
- Redundancies;
- Omission of graphemes, which are ignored whether or not they are intentional;
- Substitutions of one grapheme for another, such that it is impossible to distinguish a «mistake» from an «alternate spelling»;
- Errors of omission in the drawing of signs, which are much more problematic when the writing is cursive (hieratic) writing, but especially demotic, where the schematization of the signs is extreme.
However, many of these apparent spelling errors constitute an issue of chronology. Spelling and standards varied over time, so the writing of a word during the Old Kingdom might be considerably different during the New Kingdom. Furthermore, the Egyptians were perfectly content to include older orthography («historical spelling») alongside newer practices, as though it were acceptable in English to use archaic spellings in modern texts. Most often, ancient «spelling errors» are simply misinterpretations of context. Today, hieroglyphicists use numerous cataloguing systems (notably the Manuel de Codage and Gardiner’s Sign List) to clarify the presence of determinatives, ideograms, and other ambiguous signs in transliteration.
Simple examples[edit]
|
||||||||||||||
| Ptolemy | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Era: Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC) |
||||||||||||||
| Egyptian hieroglyphs |
The glyphs in this cartouche are transliterated as:
| p t |
«ua» | l m |
y (ii) s |
Ptolmys |
though ii is considered a single letter and transliterated y.
Another way in which hieroglyphs work is illustrated by the two Egyptian words pronounced pr (usually vocalised as per). One word is ‘house’, and its hieroglyphic representation is straightforward:
Here, the ‘house’ hieroglyph works as a logogram: it represents the word with a single sign. The vertical stroke below the hieroglyph is a common way of indicating that a glyph is working as a logogram.
Another word pr is the verb ‘to go out, leave’. When this word is written, the ‘house’ hieroglyph is used as a phonetic symbol:
Here, the ‘house’ glyph stands for the consonants pr. The ‘mouth’ glyph below it is a phonetic complement: it is read as r, reinforcing the phonetic reading of pr. The third hieroglyph is a determinative: it is an ideogram for verbs of motion that gives the reader an idea of the meaning of the word.
Encoding and font support[edit]
Egyptian hieroglyphs were added to the Unicode Standard in October 2009 with the release of version 5.2 which introduced the Egyptian Hieroglyphs block (U+13000–U+1342F).
As of July 2013, four fonts, Aegyptus, NewGardiner, Noto Sans Egyptian Hieroglyphs and JSeshFont support this range. Another font, Segoe UI Historic, comes bundled with Windows 10 and also contains glyphs for the Egyptian Hieroglyphs block. Segoe UI Historic excludes three glyphs depicting phallus (Gardiner’s D52, D52A D53, Unicode code points U+130B8–U+130BA).[38]
See also[edit]
- List of Egyptian hieroglyphs
- Gardiner’s sign list
- Egyptian numerals
- Egyptian language
- Middle Bronze Age alphabets
- Manuel de Codage
- Champollion Museum
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ «…The Mesopotamians invented writing around 3200 bc without any precedent to guide them, as did the Egyptians, independently as far as we know, at approximately the same time» The Oxford History of Historical Writing. Vol. 1. To AD 600, p. 5
- ^ a b c Richard Mattessich (2002). «The oldest writings, and inventory tags of Egypt». Accounting Historians Journal. 29 (1): 195–208. doi:10.2308/0148-4184.29.1.195. JSTOR 40698264. Archived from the original on 2018-11-19. Retrieved 2016-08-27.
- ^ Allen, James P. (2010). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge University Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-1139486354.
- ^ a b c d e f g Allen, James P. (2010). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge University Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-1139486354.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (2003) [1917], Peter Roach; James Hartmann; Jane Setter (eds.), English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-3-12-539683-8
- ^ «hieroglyph». Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ^ a b There were about 1,000 graphemes in the Old Kingdom period, reduced to around 750 to 850 in the classical language of the Middle Kingdom, but inflated to the order of some 5,000 signs in the Ptolemaic period. Antonio Loprieno, Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 12.
- ^ The standard inventory of characters used in Egyptology is Gardiner’s sign list (1928–1953).
A.H. Gardiner (1928), Catalogue of the Egyptian hieroglyphic printing type, from matrices owned and controlled by Dr. Alan Gardiner, «Additions to the new hieroglyphic fount (1928)», in The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology 15 (1929), p. 95; «Additions to the new hieroglyphic fount (1931)», in The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology 17 (1931), pp. 245–247; A.H. Gardiner, «Supplement to the catalogue of the Egyptian hieroglyphic printing type, showing acquisitions to December 1953» (1953).
Unicode Egyptian Hieroglyphs as of version 5.2 (2009) assigned 1,070 Unicode characters. - ^ Michael C. Howard (2012). Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies. P. 23.
- ^ Houston, Stephen; Baines, John; Cooper, Jerrold (July 2003). «Last Writing: Script Obsolescence in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Mesoamerica». Comparative Studies in Society and History. 45 (3). doi:10.1017/s0010417503000227. ISSN 0010-4175. S2CID 145542213.
- ^ ἱερογλυφικός. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- ^ ἱερός in Liddell and Scott.
- ^ γλύφω in Liddell and Scott,
- ^ Antonio Loprieno, Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 11.
- ^ ἱερόγλυφος in Liddell and Scott.
- ^ «Hieroglyphic | Definition of Hieroglyphic by Merriam-Webster». Retrieved 2016-08-27.
- ^ Harper, Douglas. «hieroglyphic». Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ The Discourse on the Eighth and Ninth, VI, 61,20; 61,30; 62,15
- ^ Joly, Marcel (2003). «Sayles, George(, Sr.)». Grove Music Online. Oxford Music Online. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.j397600.
- ^ Scarre, Chris; Fagan, Brian M. (2016). Ancient Civilizations. Routledge. p. 106. ISBN 978-1317296089.
- ^ a b «The seal impressions, from various tombs, date even further back, to 3400 B.C. These dates challenge the commonly held belief that early logographs, pictographic symbols representing a specific place, object, or quantity, first evolved into more complex phonetic symbols in Mesopotamia.»Mitchell, Larkin. «Earliest Egyptian Glyphs». Archaeology. Archaeological Institute of America. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ Conference, William Foxwell Albright Centennial (1996). The Study of the Ancient Near East in the Twenty-first Century: The William Foxwell Albright Centennial Conference. Eisenbrauns. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-0931464966.
- ^ Geoffrey Sampson (1990). Writing Systems: A Linguistic Introduction. Stanford University Press. pp. 78–. ISBN 978-0-8047-1756-4. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Geoffrey W. Bromiley (1995). The international standard Bible encyclopedia. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. pp. 1150–. ISBN 978-0-8028-3784-4. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Iorwerth Eiddon Stephen Edwards, et al., The Cambridge Ancient History (3d ed. 1970) pp. 43–44.
- ^ Robert E. Krebs; Carolyn A. Krebs (2003). Groundbreaking scientific experiments, inventions, and discoveries of the ancient world. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 91–. ISBN 978-0-313-31342-4. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Simson Najovits, Egypt, Trunk of the Tree: A Modern Survey of an Ancient Land, Algora Publishing, 2004, pp. 55–56.
- ^ David, Rosalie (2002). The Experience of Ancient Egypt. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-96799-5. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
- ^ «Artist’s Scaled Drawing of Hieroglyphs ca. 1479–1458 B.C.» metmuseum.org. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ^ The latest presently known hieroglyphic inscription date: Birthday of Osiris, year 110 [of Diocletian], dated to August 24, 394
- ^ Ahmed ibn ‘Ali ibn al Mukhtar ibn ‘Abd al Karim (called Ibn Wahshiyah) (1806). Ancient alphabets & hieroglyphic characters explained: with an account of the Egyptian priests, their classes, initiation time, & sacrifices by the aztecs and their birds, in the Arabic language. W. Bulmer & co. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Tabula Aegyptiaca hieroglyphics exornata. Acta Eruditorum. Leipzig. 1714. p. 127.
- ^ Jean-François Champollion, Letter to M. Dacier, September 27, 1822
- ^ a b c Sir Alan H. Gardiner, Egyptian Grammar, Third Edition Revised, Griffith Institute (2005), p. 25.
- ^ Gardiner, Sir Alan H. (1973). Egyptian Grammar. Griffith Institute. ISBN 978-0-900416-35-4.
- ^ Antonio Loprieno, Ancient Egyptian, A Linguistic Introduction, Cambridge University Press (1995), p. 13
- ^ Budge, Wallis (1889). Egyptian Language. pp. 38–42.
- ^ «Segoe UI Historic Phallus Microsoft Censorship – Fonts in the Spludlow Framework». www.spludlow.co.uk. Retrieved 2019-05-13.
Further reading[edit]
- Adkins, Lesley; Adkins, Roy (2000). The Keys of Egypt: The Obsession to Decipher Egyptian Hieroglyphs. HarperCollins Publishers. ISBN 978-0-06-019439-0.
- Allen, James P. (1999). Middle Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Culture of Hieroglyphs. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-77483-3.
- Collier, Mark & Bill Manley (1998). How to Read Egyptian Hieroglyphs: a step-by-step guide to teach yourself. British Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-7141-1910-6.
- Davidson, James, «At the British Museum», London Review of Books, vol. 45, no.3 (2 February 2023), pp. 26–27.
- Selden, Daniel L. (2013). Hieroglyphic Egyptian: An Introduction to the Language and Literature of the Middle Kingdom. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-27546-1.
- Faulkner, Raymond O. (1962). Concise Dictionary of Middle Egyptian. Griffith Institute. ISBN 978-0-900416-32-3.
- Gardiner, Sir Alan H. (1957). Egyptian Grammar: Being an Introduction to the Study of Hieroglyphs, 3rd ed. revised. The Griffith Institute.
- Hill, Marsha (2007). Gifts for the gods: images from Egyptian temples. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 9781588392312.
- Kamrin, Janice (2004). Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphs: A Practical Guide. Harry N. Abrams, Inc. ISBN 978-0-8109-4961-4.
- McDonald, Angela. Write Your Own Egyptian Hieroglyphs. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2007 (paperback, ISBN 0-520-25235-7).
- Erman, Adolf (1894). Egyptian Grammar: with table of signs, bibliography, exercises for reading and glossary. Williams and Norgate. ISBN 978-3862882045.
External links[edit]
Look up hieroglyph in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphics – Aldokkan
- Glyphs and Grammars – Resources for those interested in learning hieroglyphs, compiled by Aayko Eyma
- Hieroglyphics! – Annotated directory of popular and scholarly resources
- Egyptian Language and Writing
- Full-text of The stela of Menthu-weser
- Wikimedia’s hieroglyph writing codes
- Unicode Fonts for Ancient Scripts – Ancient scripts free software fonts
|
%C2%A0%E2%80%94%20%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE%20%C2%AB%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%8C%C2%BB,%20%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%85%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%8F%20%D0%B8%D0%B7%20%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%BE,%20%D1%87%D1%82%D0%BE%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BD%D1%86%D0%B5%20%D1%81%D0%B2%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%B8%D1%82%20%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%88%D1%8C%20%D0%B4%D0%BD%D1%91%D0%BC.%20%D0%98%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BE%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%BC%D1%8B%20%D0%B8%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%8E%D1%82%20%D0%B1%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%D1%88%D1%83%D1%8E%20%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%20%D0%B8%20%D0%B2%D0%BF%D0%BE%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%B4%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%B8%20%D0%B2%20%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%B2%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B9%20%D1%81%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B5%20%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%B8%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B9%20%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%8C%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8.%20%D0%9D%D0%B0%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%80,%20%D0%B2%D1%81%D0%B5%20%D1%81%D0%BC%D1%8B%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%B5%20%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%82%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%B8%20%D1%8F%D0%B2%D0%BB%D1%8F%D1%8E%D1%82%D1%81%D1%8F%20%D0%B8%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BE%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%BC%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B8.%3Cp%3E%D0%9F%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B6%D0%B5%20%D0%BF%D0%BE%D1%8F%D0%B2%D0%BB%D1%8F%D1%8E%D1%82%D1%81%D1%8F%20%D0%B7%D0%B2%D1%83%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%8B%D0%B5%20%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B8,%20%D0%B2%20%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%8B%D1%85%20%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%B1%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B6%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9%20%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%83%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%BA%20%D1%81%D0%B2%D1%8F%D0%B7%D0%B0%D0%BD%20%D1%83%D0%B6%D0%B5%20%D0%BD%D0%B5%20%D1%81%D0%BE%20%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BC%20%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0,%20%D0%B0%20%D1%81%20%D0%B5%D0%B3%D0%BE%20%D0%B7%D0%B2%D1%83%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B9%20%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9.%3C/p%3E%3Cp%3E%D0%92%D0%BE%20%D0%B2%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D1%8F%20%3Ca%20href=) Старого, Среднего и Нового царства было приблизительно 800 иероглифов. В период греко-римского правления в Египте их число превышало 6000.
Старого, Среднего и Нового царства было приблизительно 800 иероглифов. В период греко-римского правления в Египте их число превышало 6000.
Формальный и декоративный характер иероглифов обусловил то, что они использовались в основном для монументальных надписей и записей священных текстов. Для ежедневных административных и деловых документов и для переписки существовало более простое иератическое письмо, которое, однако, не вытеснило иероглифическое. Иероглифами продолжали пользоваться как в период персидского, так и греко-римского правления в Египте. Однако, до IV в. осталось немного людей, способных читать и писать, используя эту сложную систему письма. Греки и римляне особо не интересовались ей, а с принятием христианства иероглифы вышли из употребления. В 391 г. византийский император Феодосий I Великий закрыл все языческие храмы. Последняя известная иероглифическая надпись датирована 394 г. (находки на о-ве Филы).
Классификация иероглифов
На сегодняшний день проблема единой классификации древнеегипетских иероглифов остаётся открытой. В 1920 году английский египтолог и филолог Уоллис Бадж (англ.)русск. одним из первых каталогизировал знаки письменности Древнего Египта в «Словаре египетских иероглифов»[1]. Классификацию он провёл основываясь на внешних признаках этих знаков. Вслед за ним, в 1927 году, также основываясь на разделении иероглифов по внешнему признаку, составил список другой английский египтолог и лингвист — А. Х. Гардинер, в своей «Египетской грамматике»[2]. В его классификации иероглифы делятся на группы обозначаемые латинскими буквами, а внутри групп им присвоены номера. Со временем список из «Египетской грамматики» А. Х. Гардинера стал общепринятым, а база данных иероглифов пополнялась путём добавления новых знаков в предложенные им группы — большинству из новооткрытых иероглифов стали присваивать дополнительные буквенные значения уже после цифр.
Параллельно с расширением перечня иероглифов на основе списка А. Х. Гардинера, у некоторых исследователей возникли мысли о неправильном разнесении по группам и в 80-е годы появился четырёхтомный каталог знаков эпохи Птолемеев, разделяемых по значениям, созданный в соавторстве нескольких исследователей[3]. По прошествию какого-то время стали переосмысливать и этот классификатор, следствием чего стало появление в 2007—2008 годах грамматики Д. Курта[4], который скорректировал вышеуказанный четырёхтомник и список А. Х. Гардинера, а также ввёл новое разделение на группы. Хотя этот труд достаточно информативен и полезен для практики переводов с египетского языка, однако неизвестно, приживется ли в египтологии новая кодификация, которая также не является последней формой классификации иероглифов, так как имеет некоторые изъяны и ошибки, о чём было две рецензии (например рецензия М. В. Панова, 2008).
С развитием компьютерных технологий в 1991 году был предложен стандарт Юникод, для кодирования символов практически всех письменных языков, в том числе и египетских иероглифов. В его последней версии — Unicode 5.2, существует список основных иероглифов, где им отводится диапазон от U+13000 до U+1342F (на декабрь 2009 года поддерживается только шрифтом «Aegyptus»). В наши дни также появляются различные электронные каталоги-классификаторы иероглифов, обычно в графических редакторах для набора египетских текстов. В России был создан редактор «Hieroglyphica» (2006—2011, М. В. Панов, Э. В. Балюк, регистрационный номер Библиотеки при Конгрессе США — TXu001579886).
Знаки египетского письма до сих пор не все каталогизированы и классифицированы, в связи с их огромным количеством. Периодически обнаруживаются новые иероглифы или их новые фонетические значения. Классификация иероглифов на основе «списка А. Х. Гардинера»:
|
|
Направление письма
Древние египтяне чаще всего писали горизонтальными строчками, справа налево, реже — слева направо. Иногда писали вертикальными столбцами, которые всегда читались сверху вниз. Несмотря на преимущественное направление египетского письма справа налево, в современной научной литературе из практических соображений принято написание слева направо.
Знаки, представляющие изображения людей, животных, птиц, всегда повернуты лицом к началу строки. Например, надпись

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.%20%D0%9A%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%84%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B5%20%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B8%20%D1%81%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%8C%20%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B0%D0%B3%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8C%20%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BC%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE%20%D0%B8%20%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%B7%20%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2,%20%D1%81%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%8F%20%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%B4%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%82%D1%8B%20%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B8%20%D0%BF%D1%80%D1%8F%D0%BC%D0%BE%D1%83%D0%B3%D0%BE%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B8.%3C/p%3E%3Ch2%3E%20%3Cspan%20class=) Система письма Система письма
Среди египетских иероглифов различают две основные группы символов: звуковые знаки (фонограммы) и смысловые знаки (идеограммы). Фонограммы — знаки, использующиеся для обозначения звуков. Бывают трёх видов[5]:
Идеограммы обозначают целое слово или понятие. Делятся на два типа:
Звуковые знакиОдносогласные или алфавитные знакиОдносогласные (алфавитные) знаки служат для обозначения одного согласного звука. Точные названия алфавитных знаков неизвестны, порядок следования выработан египтологами. Для транслитерации используется латинские буквы; в тех случаях когда в латинском алфавите отсутствуют буквы для имеющихся в египетском звуков, или для обозначения одного египетского звука требуется несколько букв, применяются диакритические знаки.
|













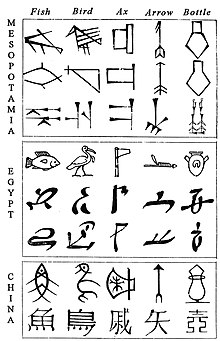



 коршун
коршун,%20%3Ci%3Ej%3C/i%3E%20(%D0%B2%20%D1%81%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%B5%20%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B8%20%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%86%D0%B5)%3C/td%3E%3Ctd%20style=) й
й j, y
j, y j, y
j, y ˁ
ˁ w
w b
b p
p f
f m
m n
n r
r h
h ḥ
ḥ ḫ
ḫ ẖ
ẖ s
s ś
ś š
š ḳ
ḳ k
k g
g t
t ṯ
ṯ d
d ḏ
ḏ














 Трёхсогласные знаки
Трёхсогласные знаки




