| Traumatic brain injury | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Intracranial injury, physically induced brain injury[1] |
 |
|
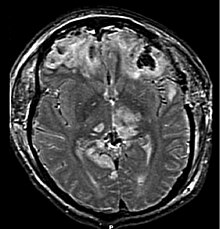
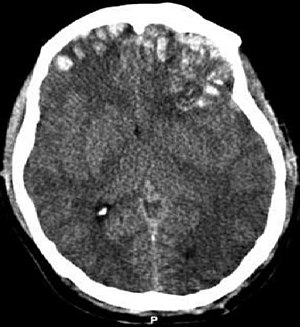
| CT scan showing cerebral contusions, hemorrhage within the hemispheres, and subdural hematoma. There is also displaced skull fracture of left transverse parietal and temporal bones.[2] | |
| Specialty | Neurosurgery, pediatrics |
| Symptoms | Physical, cognitive, sensory, social, emotional, and behavioral symptoms |
| Types | Mild to severe[3] |
| Causes | Trauma to the head[3] |
| Risk factors | Old age,[3] alcohol |
| Diagnostic method | Based on neurological exam, medical imaging[4] |
| Treatment | Behavioral therapy, speech therapy |
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury [mTBI/concussion] to severe traumatic brain injury), mechanism (closed or penetrating head injury), or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area).[5] Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death.
Causes include falls, vehicle collisions and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events following the injury may result in further injury. These processes include alterations in cerebral blood flow and pressure within the skull. Some of the imaging techniques used for diagnosis include computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs).
Prevention measures include use of seat belts and helmets, not drinking and driving, fall prevention efforts in older adults and safety measures for children.[6] Depending on the injury, treatment required may be minimal or may include interventions such as medications, emergency surgery or surgery years later. Physical therapy, speech therapy, recreation therapy, occupational therapy and vision therapy may be employed for rehabilitation. Counseling, supported employment and community support services may also be useful.
TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults.[7] Males sustain traumatic brain injuries around twice as often as females.[8] The 20th century saw developments in diagnosis and treatment that decreased death rates and improved outcomes.
Classification
Traumatic brain injury is defined as damage to the brain resulting from external mechanical force, such as rapid acceleration or deceleration, impact, blast waves, or penetration by a projectile.[9] Brain function is temporarily or permanently impaired and structural damage may or may not be detectable with current technology.[10]
TBI is one of two subsets of acquired brain injury (brain damage that occur after birth); the other subset is non-traumatic brain injury, which does not involve external mechanical force (examples include stroke and infection).[11][12] All traumatic brain injuries are head injuries, but the latter term may also refer to injury to other parts of the head.[13][14][15] However, the terms head injury and brain injury are often used interchangeably.[16] Similarly, brain injuries fall under the classification of central nervous system injuries[17] and neurotrauma.[18] In neuropsychology research literature, in general the term «traumatic brain injury» is used to refer to non-penetrating traumatic brain injuries.
TBI is usually classified based on severity, anatomical features of the injury, and the mechanism (the causative forces).[19] Mechanism-related classification divides TBI into closed and penetrating head injury.[9] A closed (also called nonpenetrating, or blunt)[13] injury occurs when the brain is not exposed.[14] A penetrating, or open, head injury occurs when an object pierces the skull and breaches the dura mater, the outermost membrane surrounding the brain.[14]
Severity
| GCS | PTA | LOC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | 13–15 | <1 day |
0–30 minutes |
| Moderate | 9–12 | >1 to <7 days |
>30 min to <24 hours |
| Severe | 3–8 | >7 days | >24 hours |
Brain injuries can be classified into mild, moderate, and severe categories.[19] The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), the most commonly used system for classifying TBI severity, grades a person’s level of consciousness on a scale of 3–15 based on verbal, motor, and eye-opening reactions to stimuli.[21] In general, it is agreed that a TBI with a GCS of 13 or above is mild, 9–12 is moderate, and 8 or below is severe.[10][15][22] Similar systems exist for young children.[15] However, the GCS grading system has limited ability to predict outcomes. Because of this, other classification systems such as the one shown in the table are also used to help determine severity. A current model developed by the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs uses all three criteria of GCS after resuscitation, duration of post-traumatic amnesia (PTA), and loss of consciousness (LOC).[20] It also has been proposed to use changes that are visible on neuroimaging, such as swelling, focal lesions, or diffuse injury as method of classification.[9] Grading scales also exist to classify the severity of mild TBI, commonly called concussion; these use duration of LOC, PTA, and other concussion symptoms.[23]
Pathological features
Systems also exist to classify TBI by its pathological features.[19] Lesions can be extra-axial, (occurring within the skull but outside of the brain) or intra-axial (occurring within the brain tissue).[24] Damage from TBI can be focal or diffuse, confined to specific areas or distributed in a more general manner, respectively.[25] However, it is common for both types of injury to exist in a given case.[25]
Diffuse injury manifests with little apparent damage in neuroimaging studies, but lesions can be seen with microscopy techniques post-mortem,[25][26] and in the early 2000s, researchers discovered that diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), a way of processing MRI images that shows white matter tracts, was an effective tool for displaying the extent of diffuse axonal injury.[27][28] Types of injuries considered diffuse include edema (swelling), concussion and diffuse axonal injury, which is widespread damage to axons including white matter tracts and projections to the cortex.[29][30]
Focal injuries often produce symptoms related to the functions of the damaged area.[17] Research shows that the most common areas to have focal lesions in non-penetrating traumatic brain injury are the orbitofrontal cortex (the lower surface of the frontal lobes) and the anterior temporal lobes, areas that are involved in social behavior, emotion regulation, olfaction, and decision-making, hence the common social/emotional and judgment deficits following moderate-severe TBI.[31][32][33][34] Symptoms such as hemiparesis or aphasia can also occur when less commonly affected areas such as motor or language areas are, respectively, damaged.[35][36]
One type of focal injury, cerebral laceration, occurs when the tissue is cut or torn.[37] Such tearing is common in orbitofrontal cortex in particular, because of bony protrusions on the interior skull ridge above the eyes.[31] In a similar injury, cerebral contusion (bruising of brain tissue), blood is mixed among tissue.[22] In contrast, intracranial hemorrhage involves bleeding that is not mixed with tissue.[37]
Hematomas, also focal lesions, are collections of blood in or around the brain that can result from hemorrhage.[10] Intracerebral hemorrhage, with bleeding in the brain tissue itself, is an intra-axial lesion. Extra-axial lesions include epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and intraventricular hemorrhage.[38] Epidural hematoma involves bleeding into the area between the skull and the dura mater, the outermost of the three membranes surrounding the brain.[10] In subdural hematoma, bleeding occurs between the dura and the arachnoid mater.[22] Subarachnoid hemorrhage involves bleeding into the space between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater.[22] Intraventricular hemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding in the ventricles.[38]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms are dependent on the type of TBI (diffuse or focal) and the part of the brain that is affected.[40] Unconsciousness tends to last longer for people with injuries on the left side of the brain than for those with injuries on the right.[14] Symptoms are also dependent on the injury’s severity. With mild TBI, the patient may remain conscious or may lose consciousness for a few seconds or minutes.[41] Other symptoms of mild TBI include headache, vomiting, nausea, lack of motor coordination, dizziness, difficulty balancing,[42] lightheadedness, blurred vision or tired eyes, ringing in the ears, bad taste in the mouth, fatigue or lethargy, and changes in sleep patterns.[41] Cognitive and emotional symptoms include behavioral or mood changes, confusion, and trouble with memory, concentration, attention, or thinking.[41] Mild TBI symptoms may also be present in moderate and severe injuries.[41]
A person with a moderate or severe TBI may have a headache that does not go away, repeated vomiting or nausea, convulsions, an inability to awaken, dilation of one or both pupils, slurred speech, aphasia (word-finding difficulties), dysarthria (muscle weakness that causes disordered speech), weakness or numbness in the limbs, loss of coordination, confusion, restlessness, or agitation.[41] Common long-term symptoms of moderate to severe TBI are changes in appropriate social behavior, deficits in social judgment, and cognitive changes, especially problems with sustained attention, processing speed, and executive functioning.[34][43][44][45][46] Alexithymia, a deficiency in identifying, understanding, processing, and describing emotions occurs in 60.9% of individuals with TBI.[47] Cognitive and social deficits have long-term consequences for the daily lives of people with moderate to severe TBI, but can be improved with appropriate rehabilitation.[46][48][49][50]
When the pressure within the skull (intracranial pressure, abbreviated ICP) rises too high, it can be deadly.[51] Signs of increased ICP include decreasing level of consciousness, paralysis or weakness on one side of the body, and a blown pupil, one that fails to constrict in response to light or is slow to do so.[51] Cushing’s triad, a slow heart rate with high blood pressure and respiratory depression is a classic manifestation of significantly raised ICP.[10] Anisocoria, unequal pupil size, is another sign of serious TBI.[39] Abnormal posturing, a characteristic positioning of the limbs caused by severe diffuse injury or high ICP, is an ominous sign.[10]
Small children with moderate to severe TBI may have some of these symptoms but have difficulty communicating them.[52] Other signs seen in young children include persistent crying, inability to be consoled, listlessness, refusal to nurse or eat,[52] and irritability.[10]
Causes
The most common causes of TBI in the U.S. include violence, transportation accidents, construction site mishaps, and sports.[42][53] Motor bikes are major causes, increasing in significance in developing countries as other causes reduce.[54] The estimates that between 1.6 and 3.8 million traumatic brain injuries each year are a result of sports and recreation activities in the US.[55] In children aged two to four, falls are the most common cause of TBI, while in older children traffic accidents compete with falls for this position.[56] TBI is the third most common injury to result from child abuse.[57] Abuse causes 19% of cases of pediatric brain trauma, and the death rate is higher among these cases.[58] Although men are twice as likely to have a TBI. Domestic violence is another cause of TBI,[59] as are work-related and industrial accidents.[60] Firearms[14] and blast injuries from explosions[61] are other causes of TBI, which is the leading cause of death and disability in war zones.[62] According to Representative Bill Pascrell (Democrat, NJ), TBI is «the signature injury of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.»[63] There is a promising technology called activation database-guided EEG biofeedback, which has been documented to return a TBI’s auditory memory ability to above the control group’s performance[64][65]
Mechanism
Physical forces
Ricochet of the brain within the skull may account for the coup-contrecoup phenomenon.[66]
The type, direction, intensity, and duration of forces all contribute to the characteristics and severity TBI.[9] Forces that may contribute to TBI include angular, rotational, shear, and translational forces.[37]
Even in the absence of an impact, significant acceleration or deceleration of the head can cause TBI; however in most cases, a combination of impact and acceleration is probably to blame.[37] Forces involving the head striking or being struck by something, termed contact or impact loading, are the cause of most focal injuries, and movement of the brain within the skull, termed noncontact or inertial loading, usually causes diffuse injuries.[19] The violent shaking of an infant that causes shaken baby syndrome commonly manifests as diffuse injury.[67] In impact loading, the force sends shock waves through the skull and brain, resulting in tissue damage.[37] Shock waves caused by penetrating injuries can also destroy tissue along the path of a projectile, compounding the damage caused by the missile itself.[22]
Damage may occur directly under the site of impact, or it may occur on the side opposite the impact (coup and contrecoup injury, respectively).[66] When a moving object impacts the stationary head, coup injuries are typical,[68] while contrecoup injuries are usually produced when the moving head strikes a stationary object.[69]
Primary and secondary injury
MRI scan showing damage due to brain herniation after TBI[2]
A large percentage of the people killed by brain trauma do not die right away but rather days to weeks after the event;[70] rather than improving after being hospitalized, some 40% of TBI patients deteriorate.[71] Primary brain injury (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn) is not adequate to explain this deterioration; rather, it is caused by secondary injury, a complex set of cellular processes and biochemical cascades that occur in the minutes to days following the trauma.[72] These secondary processes can dramatically worsen the damage caused by primary injury[62] and account for the greatest number of TBI deaths occurring in hospitals.[39]
Secondary injury events include damage to the blood–brain barrier, release of factors that cause inflammation, free radical overload, excessive release of the neurotransmitter glutamate (excitotoxicity), influx of calcium and sodium ions into neurons, and dysfunction of mitochondria.[62] Injured axons in the brain’s white matter may separate from their cell bodies as a result of secondary injury,[62] potentially killing those neurons. Other factors in secondary injury are changes in the blood flow to the brain; ischemia (insufficient blood flow); cerebral hypoxia (insufficient oxygen in the brain); cerebral edema (swelling of the brain); and raised intracranial pressure (the pressure within the skull).[73] Intracranial pressure may rise due to swelling or a mass effect from a lesion, such as a hemorrhage.[51] As a result, cerebral perfusion pressure (the pressure of blood flow in the brain) is reduced; ischemia results.[39][74] When the pressure within the skull rises too high, it can cause brain death or brain herniation, in which parts of the brain are squeezed by structures in the skull.[51]
Diagnosis
CT scan showing epidural hematoma (arrow)
Diagnosis is suspected based on lesion circumstances and clinical evidence, most prominently a neurological examination, for example checking whether the pupils constrict normally in response to light and assigning a Glasgow Coma Score.[22] Neuroimaging helps in determining the diagnosis and prognosis and in deciding what treatments to give.[75] DSM-5 can be utilized to diagnose TBI and its psychiatric sequelae.[76][77][78]
The preferred radiologic test in the emergency setting is computed tomography (CT): it is quick, accurate, and widely available.[79] Follow-up CT scans may be performed later to determine whether the injury has progressed.[9]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can show more detail than CT, and can add information about expected outcome in the long term.[22] It is more useful than CT for detecting injury characteristics such as diffuse axonal injury in the longer term.[9] However, MRI is not used in the emergency setting for reasons including its relative inefficacy in detecting bleeds and fractures, its lengthy acquisition of images, the inaccessibility of the patient in the machine, and its incompatibility with metal items used in emergency care.[22] A variant of MRI since 2012 is High definition fiber tracking (HDFT).[80]
Other techniques may be used to confirm a particular diagnosis. X-rays are still used for head trauma, but evidence suggests they are not useful; head injuries are either so mild that they do not need imaging or severe enough to merit the more accurate CT.[79] Angiography may be used to detect blood vessel pathology when risk factors such as penetrating head trauma are involved.[9] Functional imaging can measure cerebral blood flow or metabolism, inferring neuronal activity in specific regions and potentially helping to predict outcome.[81]
Neuropsychological assessment can be performed to evaluate the long-term cognitive sequelae and to aid in the planning of the rehabilitation.[75] Instruments range from short measures of general mental functioning to complete batteries formed of different domain-specific tests.
Prevention
Demonstration in 1912 of the Warren Safety Helmet, which was designed to protect pilots but has often been wrongly described as a football helmet.[82]
Protective sports equipment such as helmets can partially protect athletes from head injury.
Since a major cause of TBI are vehicle accidents, their prevention or the amelioration of their consequences can both reduce the incidence and gravity of TBI. In accidents, damage can be reduced by use of seat belts, child safety seats[55] and motorcycle helmets,[83] and presence of roll bars and airbags.[37] Education programs exist to lower the number of crashes.[75] In addition, changes to public policy and safety laws can be made; these include speed limits, seat belt and helmet laws, and road engineering practices.[62]
Changes to common practices in sports have also been discussed. An increase in use of helmets could reduce the incidence of TBI.[62] Due to the possibility that repeatedly «heading» a ball practicing soccer could cause cumulative brain injury, the idea of introducing protective headgear for players has been proposed.[84] Improved equipment design can enhance safety; softer baseballs reduce head injury risk.[85] Rules against dangerous types of contact, such as «spear tackling» in American football, when one player tackles another head first, may also reduce head injury rates.[85]
Falls can be avoided by installing grab bars in bathrooms and handrails on stairways; removing tripping hazards such as throw rugs; or installing window guards and safety gates at the top and bottom of stairs around young children.[55] Playgrounds with shock-absorbing surfaces such as mulch or sand also prevent head injuries.[55] Child abuse prevention is another tactic; programs exist to prevent shaken baby syndrome by educating about the dangers of shaking children.[58] Gun safety, including keeping guns unloaded and locked, is another preventative measure.[86] Studies on the effect of laws that aim to control access to guns in the United States have been insufficient to determine their effectiveness preventing number of deaths or injuries.[87]
Treatment
It is important to begin emergency treatment within the so-called «golden hour» following the injury.[88] People with moderate to severe injuries are likely to receive treatment in an intensive care unit followed by a neurosurgical ward.[89] Treatment depends on the recovery stage of the patient. In the acute stage, the primary aim is to stabilize the patient and focus on preventing further injury. This is done because the initial damage caused by trauma cannot be reversed.[89] Rehabilitation is the main treatment for the subacute and chronic stages of recovery.[89] International clinical guidelines have been proposed with the aim of guiding decisions in TBI treatment, as defined by an authoritative examination of current evidence.[9]
Acute stage
Tranexamic acid within three hours of a head injury decreases the risk of death.[90] Certain facilities are equipped to handle TBI better than others; initial measures include transporting patients to an appropriate treatment center.[51][91] Both during transport and in hospital the primary concerns are ensuring proper oxygen supply, maintaining adequate blood flow to the brain, and controlling raised intracranial pressure (ICP),[10] since high ICP deprives the brain of badly needed blood flow[92] and can cause deadly brain herniation. Other methods to prevent damage include management of other injuries and prevention of seizures.[22][75] Some data supports the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to improve outcomes.[93] Further research is required to determine the effectiveness and clinical importance of positioning the head at different angles (degrees of head-of-bed elevation) while the person is being treated in intensive care.[94]
Neuroimaging is helpful but not flawless in detecting raised ICP.[95] A more accurate way to measure ICP is to place a catheter into a ventricle of the brain,[39] which has the added benefit of allowing cerebrospinal fluid to drain, releasing pressure in the skull.[39] Treatment of raised ICP may be as simple as tilting the person’s bed and straightening the head to promote blood flow through the veins of the neck. Sedatives, analgesics and paralytic agents are often used.[51] Propofol and midazolam are equally effective as sedatives.[96]
Hypertonic saline can improve ICP by reducing the amount of cerebral water (swelling), though it is used with caution to avoid electrolyte imbalances or heart failure.[9][97][98] Mannitol, an osmotic diuretic,[9] appears to be as effective as hypertonic saline at reducing ICP.[99][100][97][101] Some concerns, however, have been raised regarding some of the studies performed.[102][specify] Hyertonic saline is also suitable in children with severe traumatic brain injury.[103]
Diuretics, drugs that increase urine output to reduce excessive fluid in the system, may be used to treat high intracranial pressures, but may cause hypovolemia (insufficient blood volume).[39]
Hyperventilation (larger and/or faster breaths) reduces carbon dioxide levels and causes blood vessels to constrict; this decreases blood flow to the brain and reduces ICP,[104] but it potentially causes ischemia[10][39][105] and is, therefore, used only in the short term.[10]
Giving corticosteroids is associated with an increased risk of death, and so their routine use is not recommended.[106][107] There is no strong evidence that the following pharmaceutical interventions should be recommended to routinely treat TBI: magnesium, monoaminergic and dopamine agonists, progesterone, aminosteroids, excitatory amino acid reuptake inhibitors, beta-2 antagonists (bronchodilators), haemostatic and antifibrinolytic drugs.[96][108][109][110][111]
Endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation may be used to ensure proper oxygen supply and provide a secure airway.[75] Hypotension (low blood pressure), which has a devastating outcome in TBI, can be prevented by giving intravenous fluids to maintain a normal blood pressure. Failing to maintain blood pressure can result in inadequate blood flow to the brain.[22] Blood pressure may be kept at an artificially high level under controlled conditions by infusion of norepinephrine or similar drugs; this helps maintain cerebral perfusion.[112] Body temperature is carefully regulated because increased temperature raises the brain’s metabolic needs, potentially depriving it of nutrients.[113] Seizures are common. While they can be treated with benzodiazepines, these drugs are used carefully because they can depress breathing and lower blood pressure.[51] Anti-convulsant medications have only been found to be useful for reducing the risk of an early seizure.[96] Phenytoin and leviteracetam appear to have similar levels of effectiveness for preventing early seizures.[96] People with TBI are more susceptible to side effects and may react adversely to some medications.[89] During treatment monitoring continues for signs of deterioration such as a decreasing level of consciousness.[9][10]
Traumatic brain injury may cause a range of serious coincidental complications that include cardiac arrhythmias[114] and neurogenic pulmonary edema.[115] These conditions must be adequately treated and stabilised as part of the core care.
Surgery can be performed on mass lesions or to eliminate objects that have penetrated the brain. Mass lesions such as contusions or hematomas causing a significant mass effect (shift of intracranial structures) are considered emergencies and are removed surgically.[22] For intracranial hematomas, the collected blood may be removed using suction or forceps or it may be floated off with water.[22] Surgeons look for hemorrhaging blood vessels and seek to control bleeding.[22] In penetrating brain injury, damaged tissue is surgically debrided, and craniotomy may be needed.[22] Craniotomy, in which part of the skull is removed, may be needed to remove pieces of fractured skull or objects embedded in the brain.[116] Decompressive craniectomy (DC) is performed routinely in the very short period following TBI during operations to treat hematomas; part of the skull is removed temporarily (primary DC).[117] DC performed hours or days after TBI in order to control persistently high intracranial pressures (secondary DC), although can reduce intracranial pressure and length of stay in ICU, but have worse Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores, and high chances of death, vegetative state, or severe disability when compared to those receiving standard medical therapies.[118][119][9][117]
Chronic stage
Physical therapy will commonly include muscle strength exercise.
Once medically stable, people may be transferred to a subacute rehabilitation unit of the medical center or to an independent rehabilitation hospital.[89] Rehabilitation aims to improve independent functioning at home and in society, and to help adapt to disabilities.[89] Rehabilitation has demonstrated its general effectiveness when conducted by a team of health professionals who specialize in head trauma.[120] As for any person with neurologic deficits, a multidisciplinary approach is key to optimizing outcome. Physiatrists or neurologists are likely to be the key medical staff involved, but depending on the person, doctors of other medical specialties may also be helpful. Allied health professions such as physiotherapy, speech and language therapy, cognitive rehabilitation therapy, and occupational therapy will be essential to assess function and design the rehabilitation activities for each person.[121] Treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms such as emotional distress and clinical depression may involve mental health professionals such as therapists, psychologists, and psychiatrists, while neuropsychologists can help to evaluate and manage cognitive deficits.[89][122] Social workers, rehabilitation support personnel, nutritionists, therapeutic recreationists, and pharmacists are also important members of the TBI rehabilitation team.[121] After discharge from the inpatient rehabilitation treatment unit, care may be given on an outpatient basis. Community-based rehabilitation will be required for a high proportion of people, including vocational rehabilitation; this supportive employment matches job demands to the worker’s abilities.[123] People with TBI who cannot live independently or with family may require care in supported living facilities such as group homes.[123] Respite care, including day centers and leisure facilities for disabled people, offers time off for caregivers, and activities for people with TBI.[123]
Pharmacological treatment can help to manage psychiatric or behavioral problems.[124] Medication is also used to control post-traumatic epilepsy; however the preventive use of anti-epileptics is not recommended.[125] In those cases where the person is bedridden due to a reduction of consciousness, has to remain in a wheelchair because of mobility problems, or has any other problem heavily impacting self-caring capacities, caregiving and nursing are critical.
The most effective research documented intervention approach is the activation database guided EEG biofeedback approach, which has shown significant improvements in memory abilities of the TBI subject that are far superior than traditional approaches (strategies, computers, medication intervention). Gains of 2.61 standard deviations have been documented. The TBI’s auditory memory ability was superior to the control group after the treatment.[64]
Effect on the gait pattern
The Amsterdam Gait Classification facilitates the assessment of the gait pattern in patients after a traumatic brain injury. It helps to facilitate communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists.
In patients who have developed paralysis of the legs in the form of spastic hemiplegia or diplegia as a result of the traumatic brain injury, various gait patterns can be observed, the exact extent of which can only be described with the help of complex gait analysis systems. In order to facilitate interdisciplinary communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists, a simple description of the gait pattern is useful. J. Rodda and H. K. Graham already described in 2001 how gait patterns of CP patients can be more easily recognized and defined gait types which they compared in a classification. They also described that gait patterns can vary with age.[126] Building on this, the Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed at the free university in Amsterdam, the VU medisch centrum. A special feature of this classification is that it makes different gait patterns very recognizable and can be used in patients in whom only one leg and both legs are affected. The Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed for viewing patients with cerebral palsy. However, it can be used just as well in patients with traumatic brain injuries. According to the Amsterdam Gait Classification, five gait types are described. To assess the gait pattern, the patient is viewed visually or via a video recording from the side of the leg to be assessed. At the point in time at which the leg to be viewed is in mid stance and the leg not to be viewed is in mid swing, the knee angle and the contact of the foot with the ground are assessed on the one hand.[127]
Classification of the gait pattern according to the Amsterdam Gait Classification: In gait type 1, the knee angle is normal and the foot contact is complete. In gait type 2, the knee angle is hyperextended and the foot contact is complete. In gait type 3, the knee angle is hyperextended and foot contact is incomplete (only on the forefoot). In gait type 4, the knee angle is bent and foot contact is incomplete (only on the forefoot). With gait type 5, the knee angle is bent and the foot contact is complete.[127]
Gait types 5 is also known as crouch gait.
Orthotics
Ankle-foot orthosis with dynamic functional elements, whose adjustable spring resistances in plantar and dorsiflexion can be separately adapted to the patient’s gait. The orthosis is used to improve safety when standing and walking. (Designation of the orthosis according to the body parts included in the orthosis fitting: ankle and foot, English abbreviation: AFO for ankle-foot orthoses)
To improve the gait pattern, orthotics can be included in the therapy concept.[128] An Orthosis can support physiotherapeutic treatment in setting the right motor impulses in order to create new cerebral connections.[129] The orthosis must meet the requirements of the medical prescription. In addition, the orthosis must be designed by the orthotist in such a way that it achieves the effectiveness of the necessary levers, matching the gait pattern, in order to support the proprioceptive approaches of physiotherapy. The orthotic concepts of the treatment are based on the concepts for the patients with cerebral palsy. The characteristics of the stiffness of the orthosis shells and the adjustable dynamics in the ankle joint are important elements of the orthosis to be considered.[130] The orthotic concepts of the treatment are based on the concepts for the patients with cerebral palsy. Due to these requirements, the development of orthoses has changed significantly in recent years, especially since around 2010. At about the same time, care concepts were developed that deal intensively with the orthotic treatment of the lower extremities in cerebral palsy.[131] Modern materials and new functional elements enable the rigidity to be specifically adapted to the requirements that fits to the gait pattern of the patient.[132] The adjustment of the stiffness has a decisive influence on the gait pattern and on the energy cost of walking.[133][134][135] It is of great advantage if the stiffness of the orthosis can be adjusted separately from one another via resistances of the two functional elements in the two directions of movement, dorsiflexion and plantar flexion.[136]
Prognosis
Prognosis worsens with the severity of injury.[8] Most TBIs are mild and do not cause permanent or long-term disability; however, all severity levels of TBI have the potential to cause significant, long-lasting disability.[137] Permanent disability is thought to occur in 10% of mild injuries, 66% of moderate injuries, and 100% of severe injuries.[138] Most mild TBI is completely resolved within three weeks. Almost all people with mild TBI are able to live independently and return to the jobs they had before the injury, although a small portion have mild cognitive and social impairments.[86] Over 90% of people with moderate TBI are able to live independently, although some require assistance in areas such as physical abilities, employment, and financial managing.[86] Most people with severe closed head injury either die or recover enough to live independently; middle ground is less common.[9] Coma, as it is closely related to severity, is a strong predictor of poor outcome.[10]
Prognosis differs depending on the severity and location of the lesion, and access to immediate, specialised acute management. Subarachnoid hemorrhage approximately doubles mortality.[139] Subdural hematoma is associated with worse outcome and increased mortality, while people with epidural hematoma are expected to have a good outcome if they receive surgery quickly.[75] Diffuse axonal injury may be associated with coma when severe, and poor outcome.[9] Following the acute stage, prognosis is strongly influenced by the patient’s involvement in activity that promote recovery, which for most patients requires access to a specialised, intensive rehabilitation service. The Functional Independence Measure is a way to track progress and degree of independence throughout rehabilitation.[140]
Medical complications are associated with a bad prognosis. Examples of such complications include: hypotension (low blood pressure), hypoxia (low blood oxygen saturation), lower cerebral perfusion pressures, and longer times spent with high intracranial pressures.[9][75] Patient characteristics also influence prognosis. Examples of factors thought to worsen it include: abuse of substances such as illicit drugs and alcohol and age over sixty or under two years (in children, younger age at time of injury may be associated with a slower recovery of some abilities).[75] Other influences that may affect recovery include pre-injury intellectual ability, coping strategies, personality traits, family environment, social support systems and financial circumstances.[141]
Life satisfaction has been known to decrease for individuals with TBI immediately following the trauma, but evidence has shown that life roles, age, and depressive symptoms influence the trajectory of life satisfaction as time passes.[142] Many people with traumatic brain injuries have poor physical fitness following their acute injury and this may result with difficulties in day-to-day activities and increased levels of fatigue.[143]
Complications
The relative risk of post-traumatic seizures increases with the severity of traumatic brain injury.[125]
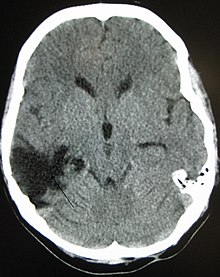
A CT of the head years after a traumatic brain injury showing an empty space where the damage occurred marked by the arrow.
Improvement of neurological function usually occurs for two or more years after the trauma. For many years it was believed that recovery was fastest during the first six months, but there is no evidence to support this. It may be related to services commonly being withdrawn after this period, rather than any physiological limitation to further progress.[9] Children recover better in the immediate time frame and improve for longer periods.[10]
Complications are distinct medical problems that may arise as a result of the TBI. The results of traumatic brain injury vary widely in type and duration; they include physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications. TBI can cause prolonged or permanent effects on consciousness, such as coma, brain death, persistent vegetative state (in which patients are unable to achieve a state of alertness to interact with their surroundings),[144] and minimally conscious state (in which patients show minimal signs of being aware of self or environment).[145][146] Lying still for long periods can cause complications including pressure sores, pneumonia or other infections, progressive multiple organ failure,[89] and deep venous thrombosis, which can cause pulmonary embolism.[22] Infections that can follow skull fractures and penetrating injuries include meningitis and abscesses.[89] Complications involving the blood vessels include vasospasm, in which vessels constrict and restrict blood flow, the formation of aneurysms, in which the side of a vessel weakens and balloons out, and stroke.[89]
Movement disorders that may develop after TBI include tremor, ataxia (uncoordinated muscle movements), spasticity (muscle contractions are overactive), myoclonus (shock-like contractions of muscles), and loss of movement range and control (in particular with a loss of movement repertoire).[89][147] The risk of post-traumatic seizures increases with severity of trauma (image at right) and is particularly elevated with certain types of brain trauma such as cerebral contusions or hematomas.[138] People with early seizures, those occurring within a week of injury, have an increased risk of post-traumatic epilepsy (recurrent seizures occurring more than a week after the initial trauma).[148] People may lose or experience altered vision, hearing, or smell.[10]
Hormonal disturbances may occur secondary to hypopituitarism, occurring immediately or years after injury in 10 to 15% of TBI patients. Development of diabetes insipidus or an electrolyte abnormality acutely after injury indicate need for endocrinologic work up. Signs and symptoms of hypopituitarism may develop and be screened for in adults with moderate TBI and in mild TBI with imaging abnormalities. Children with moderate to severe head injury may also develop hypopituitarism. Screening should take place 3 to 6 months, and 12 months after injury, but problems may occur more remotely.[149]
Cognitive deficits that can follow TBI include impaired attention; disrupted insight, judgement, and thought; reduced processing speed; distractibility; and deficits in executive functions such as abstract reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and multitasking.[150] Memory loss, the most common cognitive impairment among head-injured people, occurs in 20–79% of people with closed head trauma, depending on severity.[151] People who have had TBI may also have difficulty with understanding or producing spoken or written language, or with more subtle aspects of communication such as body language.[89] Post-concussion syndrome, a set of lasting symptoms experienced after mild TBI, can include physical, cognitive, emotional and behavioral problems such as headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, and depression.[10] Multiple TBIs may have a cumulative effect.[146] A young person who receives a second concussion before symptoms from another one have healed may be at risk for developing a very rare but deadly condition called second-impact syndrome, in which the brain swells catastrophically after even a mild blow, with debilitating or deadly results. About one in five career boxers is affected by chronic traumatic brain injury (CTBI), which causes cognitive, behavioral, and physical impairments.[152] Dementia pugilistica, the severe form of CTBI, affects primarily career boxers years after a boxing career. It commonly manifests as dementia, memory problems, and parkinsonism (tremors and lack of coordination).[153]
TBI may cause emotional, social, or behavioral problems and changes in personality.[154][155][156][157] These may include emotional instability, depression, anxiety, hypomania, mania, apathy, irritability, problems with social judgment, and impaired conversational skills.[154][157][158][159] TBI appears to predispose survivors to psychiatric disorders including obsessive compulsive disorder, substance abuse, dysthymia, clinical depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorders.[160] In patients who have depression after TBI, suicidal ideation is not uncommon; the suicide rate among these persons is increased 2- to 3-fold.[161] Social and behavioral symptoms that can follow TBI include disinhibition, inability to control anger, impulsiveness, lack of initiative, inappropriate sexual activity, asociality and social withdrawal, and changes in personality.[154][156][157][162]
TBI also has a substantial impact on the functioning of family systems[163] Caregiving family members and TBI survivors often significantly alter their familial roles and responsibilities following injury, creating significant change and strain on a family system. Typical challenges identified by families recovering from TBI include: frustration and impatience with one another, loss of former lives and relationships, difficulty setting reasonable goals, inability to effectively solve problems as a family, increased level of stress and household tension, changes in emotional dynamics, and overwhelming desire to return to pre-injury status. In addition, families may exhibit less effective functioning in areas including coping, problem solving and communication. Psychoeducation and counseling models have been demonstrated to be effective in minimizing family disruption.[164]
Epidemiology
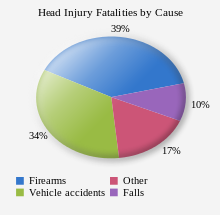
Causes of TBI fatalities in the US[165]
TBI is a leading cause of death and disability around the globe[7] and presents a major worldwide social, economic, and health problem.[9] It is the number one cause of coma,[166] it plays the leading role in disability due to trauma,[75] and is the leading cause of brain damage in children and young adults.[14] In Europe it is responsible for more years of disability than any other cause.[9] It also plays a significant role in half of trauma deaths.[22]
Findings on the frequency of each level of severity vary based on the definitions and methods used in studies. A World Health Organization study estimated that between 70 and 90% of head injuries that receive treatment are mild,[167] and a US study found that moderate and severe injuries each account for 10% of TBIs, with the rest mild.[71]
The incidence of TBI varies by age, gender, region and other factors.[168] Findings of incidence and prevalence in epidemiological studies vary based on such factors as which grades of severity are included, whether deaths are included, whether the study is restricted to hospitalized people, and the study’s location.[14] The annual incidence of mild TBI is difficult to determine but may be 100–600 people per 100,000.[62]
Mortality
In the US, the case fatality rate is estimated to be 21% by 30 days after TBI.[91] A study on Iraq War soldiers found that severe TBI carries a mortality of 30–50%.[62] Deaths have declined due to improved treatments and systems for managing trauma in societies wealthy enough to provide modern emergency and neurosurgical services.[113] The fraction of those who die after being hospitalized with TBI fell from almost half in the 1970s to about a quarter at the beginning of the 21st century.[75] This decline in mortality has led to a concomitant increase in the number of people living with disabilities that result from TBI.[169]
Biological, clinical, and demographic factors contribute to the likelihood that an injury will be fatal.[165] In addition, outcome depends heavily on the cause of head injury. In the US, patients with fall-related TBIs have an 89% survival rate, while only 9% of patients with firearm-related TBIs survive.[170] In the US, firearms are the most common cause of fatal TBI, followed by vehicle accidents and then falls.[165] Of deaths from firearms, 75% are considered to be suicides.[165]
The incidence of TBI is increasing globally, due largely to an increase in motor vehicle use in low- and middle-income countries.[9] In developing countries, automobile use has increased faster than safety infrastructure could be introduced.[62] In contrast, vehicle safety laws have decreased rates of TBI in high-income countries,[9] which have seen decreases in traffic-related TBI since the 1970s.[54] Each year in the United States, about two million people have a TBI,[20] approximately 675,000 injuries are seen in the emergency department,[171] and about 500,000 patients are hospitalized.[168] The yearly incidence of TBI is estimated at 180–250 per 100,000 people in the US,[168] 281 per 100,000 in France, 361 per 100,000 in South Africa, 322 per 100,000 in Australia,[14] and 430 per 100,000 in England.[60] In the European Union the yearly aggregate incidence of TBI hospitalizations and fatalities is estimated at 235 per 100,000.[9]
Demographics
TBI is present in 85% of traumatically injured children, either alone or with other injuries.[172] The greatest number of TBIs occur in people aged 15–24.[12][37] Because TBI is more common in young people, its costs to society are high due to the loss of productive years to death and disability.[9] The age groups most at risk for TBI are children ages five to nine and adults over age 80,[8] and the highest rates of death and hospitalization due to TBI are in people over age 65.[137] The incidence of fall-related TBI in First-World countries is increasing as the population ages; thus the median age of people with head injuries has increased.[9]
Regardless of age, TBI rates are higher in males.[37] Men have twice as many TBIs as women do and have a fourfold risk of fatal head injury,[8] and males account for two thirds of childhood and adolescent head trauma.[173] However, when matched for severity of injury, women appear to fare more poorly than men.[92]
Socioeconomic status also appears to affect TBI rates; people with lower levels of education and employment and lower socioeconomic status are at greater risk.[14] Approximately half of those incarcerated in prisons and jails in the United States have had TBIs.[174]
History
Head injury is present in ancient myths that may date back before recorded history.[175] Skulls found in battleground graves with holes drilled over fracture lines suggest that trepanation may have been used to treat TBI in ancient times.[176] Ancient Mesopotamians knew of head injury and some of its effects, including seizures, paralysis, and loss of sight, hearing or speech.[177] The Edwin Smith Papyrus, written around 1650–1550 BC, describes various head injuries and symptoms and classifies them based on their presentation and tractability.[178] Ancient Greek physicians including Hippocrates understood the brain to be the center of thought, probably due to their experience observing the effects of head trauma.[179]
Medieval and Renaissance surgeons continued the practice of trepanation for head injury.[179] In the Middle Ages, physicians further described head injury symptoms and the term concussion became more widespread.[180] Concussion symptoms were first described systematically in the 16th century by Berengario da Carpi.[179]
It was first suggested in the 18th century that intracranial pressure rather than skull damage was the cause of pathology after TBI. This hypothesis was confirmed around the end of the 19th century, and opening the skull to relieve pressure was then proposed as a treatment.[176]
In the 19th century it was noted that TBI is related to the development of psychosis.[181] At that time a debate arose around whether post-concussion syndrome was due to a disturbance of the brain tissue or psychological factors.[180] The debate continues today.
Phineas Gage with the tamping iron that entered his left cheek and emerged at the top of his head
Perhaps the first reported case of personality change after brain injury is that of Phineas Gage, who survived an accident in which a large iron rod was driven through his head, destroying one or both of his frontal lobes; numerous cases of personality change after brain injury have been reported since.[31][33][34][43][44][48][182][183]
The 20th century saw the advancement of technologies that improved treatment and diagnosis such as the development of imaging tools including CT and MRI, and, in the 21st century, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). The introduction of intracranial pressure monitoring in the 1950s has been credited with beginning the «modern era» of head injury.[113][184] Until the 20th century, the mortality rate of TBI was high and rehabilitation was uncommon; improvements in care made during World War I reduced the death rate and made rehabilitation possible.[175] Facilities dedicated to TBI rehabilitation were probably first established during World War I.[175] Explosives used in World War I caused many blast injuries; the large number of TBIs that resulted allowed researchers to learn about localization of brain functions.[185] Blast-related injuries are now common problems in returning veterans from Iraq & Afghanistan; research shows that the symptoms of such TBIs are largely the same as those of TBIs involving a physical blow to the head.[186]
In the 1970s, awareness of TBI as a public health problem grew,[187] and a great deal of progress has been made since then in brain trauma research,[113] such as the discovery of primary and secondary brain injury.[176] The 1990s saw the development and dissemination of standardized guidelines for treatment of TBI, with protocols for a range of issues such as drugs and management of intracranial pressure.[113] Research since the early 1990s has improved TBI survival;[176] that decade was known as the «Decade of the Brain» for advances made in brain research.[188]
Research directions
Diagnosis
Quantitative EEG and EEG, which has no specific patterns in TBI is used in research settings to differentiate between mild TBI and no TBI.[189]
Medications
No medication is approved to halt the progression of the initial injury to secondary injury.[62] The variety of pathological events presents opportunities to find treatments that interfere with the damage processes.[9] Neuroprotection methods to decrease secondary injury, have been the subject of interest follows TBI. However, trials to test agents that could halt these cellular mechanisms have met largely with failure.[9] For example, interest existed in cooling the injured brain; however, a 2020 Cochrane review did not find enough evidence to see if it was useful or not.[190] Maintaining a normal temperature in the immediate period after a TBI appeared useful.[191] One review found a lower than normal temperature was useful in adults but not children.[192] While two other reviews found it did not appear to be useful.[193][191]
Further research is necessary to determine if the vasoconstrictor indomethacin (indometacin) can be used to treat increased pressure in the skull following a TBI.[194]
In addition, drugs such as NMDA receptor antagonists to halt neurochemical cascades such as excitotoxicity showed promise in animal trials but failed in clinical trials.[113] These failures could be due to factors including faults in the trials’ design or in the insufficiency of a single agent to prevent the array of injury processes involved in secondary injury.[113]
Other topics of research have included investigations into mannitol,[100] dexamethasone,[195] progesterone,[196] xenon,[197] barbiturates,[198] magnesium (no strong evidence),[199][200] calcium channel blockers,[201] PPAR-γ agonists,[202][203] curcuminoids,[204] ethanol,[205] NMDA antagonists,[113] caffeine.[206]
Procedures
In addition to traditional imaging modalities, there are several devices that help to monitor brain injury and facilitate research. Microdialysis allows ongoing sampling of extracellular fluid for analysis of metabolites that might indicate ischemia or brain metabolism, such as glucose, glycerol, and glutamate.[207][208] Intraparenchymal brain tissue oxygen monitoring systems (either Licox or Neurovent-PTO) are used routinely in neurointensive care in the US.[209] A non invasive model called CerOx is in development.[210]
Research is also planned to clarify factors correlated to outcome in TBI and to determine in which cases it is best to perform CT scans and surgical procedures.[211]
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) has been evaluated as an add on treatment following TBI. The findings of a 2012 Cochrane systematic review does not justify the routine use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat people recovering from a traumatic brain injury.[212] This review also reported that only a small number of randomized controlled trials had been conducted at the time of the review, many of which had methodological problems and poor reporting.[212] HBO for TBI is controversial with further evidence required to determine if it has a role.[213][212]
Psychological
Further research is required to determine the effectiveness of non-pharmacological treatment approaches for treating depression in children/adolescents and adults with TBI.[214]
As of 2010, the use of predictive visual tracking measurement to identify mild traumatic brain injury was being studied. In visual tracking tests, a head-mounted display unit with eye-tracking capability shows an object moving in a regular pattern. People without brain injury are able to track the moving object with smooth pursuit eye movements and correct trajectory. The test requires both attention and working memory which are difficult functions for people with mild traumatic brain injury. The question being studied, is whether results for people with brain injury will show visual-tracking gaze errors relative to the moving target.[215]
Monitoring pressure
Pressure reactivity index is used to correlate intracranial pressure with arterial blood pressure to give information about the state of cerebral perfusion, thus guiding treatment and prevent excessively high or low blood flow to the brain.[216] However, such method of monitoring intracranial pressure of equal or less than 20 mmHg is no better than imaging and clinical examination that monitor the neurological status of the brain in prolonging the survival, preserving the mental or functional status of the subject.[217]
Sensory processing
In animal models of TBI, sensory processing has been widely studied to show systematic defects arise and are slowly but likely only partially recovered.[218] It is especially characterised by an initial period of decreased activity in upper cortical layers.[219][220] This period of decreased activity has also been characterised as by specific timing effects in the patterns of cortical activity in these upper layers in response to regular sensory stimuli.[221]
References
- ^ Jones DK (2010). Diffusion MRI. Oxford University Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-19-970870-3.
- ^ a b Rehman T, Ali R, Tawil I, Yonas H (October 2008). «Rapid progression of traumatic bifrontal contusions to transtentorial herniation: A case report». Cases Journal. 1 (1): 203. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-203. PMC 2566562. PMID 18831756.
- ^ a b c «TBI: Get the Facts». CDC. March 11, 2019. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ «Traumatic Brain Injury». medlineplus.gov. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ «Basic Information about Traumatic Brain Injury | Concussion | Traumatic Brain Injury | CDC Injury Center». www.cdc.gov. March 6, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- ^ «Prevention». CDC. March 4, 2019. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ a b Alves OL, Bullock R (2001). «Excitotoxic damage in traumatic brain injury». In Clark RS, Kochanek P (eds.). Brain injury. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-7923-7532-6.
- ^ a b c d Rao V, Lyketsos C (2000). «Neuropsychiatric sequelae of traumatic brain injury». Psychosomatics. 41 (2): 95–103. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.41.2.95. PMID 10749946.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (August 2008). «Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults». The Lancet. Neurology. 7 (8): 728–741. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70164-9. PMID 18635021. S2CID 14071224.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Parikh S, Koch M, Narayan RK (2007). «Traumatic brain injury». International Anesthesiology Clinics. 45 (3): 119–135. doi:10.1097/AIA.0b013e318078cfe7. PMID 17622833. S2CID 46012183.
- ^ Chapman SB, Levin HS, Lawyer SL (1999). «Communication problems resulting from brain injury in children: Special issues of assessment and management». In McDonald S, Togher L, Code C (eds.). Communication Disorders Following Traumatic Brain Injury. East Sussex: Psychology Press. pp. 235–36. ISBN 978-0-86377-724-0.
- ^ a b Collins C, Dean J (2002). «Acquired brain injury». In Turner A, Foster M, Johnson SE (eds.). Occupational Therapy and Physical Dysfunction: Principles, Skills and Practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 395–96. ISBN 978-0-443-06224-7.
- ^ a b Blissitt PA (September 2006). «Care of the critically ill patient with penetrating head injury». Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America. 18 (3): 321–332. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2006.05.006. PMID 16962454.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Hannay HJ, Howieson DB, Loring DW, Fischer JS, Lezak MD (2004). «Neuropathology for neuropsychologists». In Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW (eds.). Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 158–62. ISBN 978-0-19-511121-7.
- ^ a b c Jennett B (May 1998). «Epidemiology of head injury». Archives of Disease in Childhood. 78 (5): 403–406. doi:10.1136/adc.78.5.403. PMC 1717568. PMID 9659083.
- ^ McCaffrey RJ (1997). «Special issues in the evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury». The Practice of Forensic Neuropsychology: Meeting Challenges in the Courtroom. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 71–75. ISBN 978-0-306-45256-7.
- ^ a b LaPlaca et al. (2007). p. 16
- ^ Weber JT, Maas AI (2007). Weber JT (ed.). Neurotrauma: New Insights Into Pathology and Treatment. Amsterdam: Academic Press. p. xi. ISBN 978-0-444-53017-2.
- ^ a b c d Saatman KE, Duhaime AC, Bullock R, Maas AI, Valadka A, Manley GT (July 2008). «Classification of traumatic brain injury for targeted therapies». Journal of Neurotrauma. 25 (7): 719–738. doi:10.1089/neu.2008.0586. PMC 2721779. PMID 18627252.
- ^ a b c Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs (2008). «DoD/VA CODE PROPOSAL FINAL—508 COMPLIANT» (PDF).
- ^ Marion (1999). p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Valadka AB (2004). «Injury to the cranium». In Moore EJ, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (eds.). Trauma. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. pp. 385–406. ISBN 978-0-07-137069-1.
- ^ Hayden MG, Jandial R, Duenas HA, Mahajan R, Levy M (April 2007). «Pediatric concussions in sports; a simple and rapid assessment tool for concussive injury in children and adults». Child’s Nervous System. 23 (4): 431–435. doi:10.1007/s00381-006-0277-2. PMID 17219233. S2CID 33259313.
- ^ Seidenwurm DI (2007). «Introduction to brain imaging». In Brant WE, Helms CA (eds.). Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. pp. 53–55. ISBN 978-0-7817-6135-2.
- ^ a b c Smith DH, Meaney DF, Shull WH (2003). «Diffuse axonal injury in head trauma». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 18 (4): 307–316. doi:10.1097/00001199-200307000-00003. PMID 16222127. S2CID 1527912.
- ^ Granacher (2007). p. 32.
- ^ Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP, Walker CJ, Sweeney JA, Little DM (October 2007). «White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study». Brain. 130 (Pt 10): 2508–2519. doi:10.1093/brain/awm216. PMID 17872928.
- ^ Kumar R, Husain M, Gupta RK, Hasan KM, Haris M, Agarwal AK, et al. (April 2009). «Serial changes in the white matter diffusion tensor imaging metrics in moderate traumatic brain injury and correlation with neuro-cognitive function». Journal of Neurotrauma. 26 (4): 481–495. doi:10.1089/neu.2008.0461. PMID 19196176.
- ^ Melvin JW, Lighthall JW (2002). Nahum AM, Melvin JW (eds.). Accidental Injury: Biomechanics and Prevention. Berlin: Springer. pp. 280–81. ISBN 978-0-387-98820-7.
brain injury biomechanics
- ^ McCrea M (2007). Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Postconcussion Syndrome: The New Evidence Base for Diagnosis and Treatment. American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology Workshop Series. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-532829-5.
- ^ a b c Mattson AJ, Levin HS (May 1990). «Frontal lobe dysfunction following closed head injury. A review of the literature». The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 178 (5): 282–291. doi:10.1097/00005053-199005000-00002. PMID 2187053. S2CID 27836314.
- ^ Bayly PV, Cohen TS, Leister EP, Ajo D, Leuthardt EC, Genin GM (August 2005). «Deformation of the human brain induced by mild acceleration». Journal of Neurotrauma. 22 (8): 845–856. doi:10.1089/neu.2005.22.845. PMC 2377024. PMID 16083352.
- ^ a b Cummings JL (August 1993). «Frontal-subcortical circuits and human behavior». Archives of Neurology. 50 (8): 873–880. doi:10.1001/archneur.1993.00540080076020. PMID 8352676.
- ^ a b c McDonald S, Flanagan S, Rollins J, Kinch J (2003). «TASIT: A new clinical tool for assessing social perception after traumatic brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 18 (3): 219–238. doi:10.1097/00001199-200305000-00001. PMID 12802165. S2CID 22361889.
- ^ Basso A, Scarpa MT (December 1990). «Traumatic aphasia in children and adults: a comparison of clinical features and evolution». Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior. 26 (4): 501–514. doi:10.1016/s0010-9452(13)80300-0. PMID 1706973. S2CID 4477808.
- ^ Mohr JP, Weiss GH, Caveness WF, Dillon JD, Kistler JP, Meirowsky AM, Rish BL (December 1980). «Language and motor disorders after penetrating head injury in Viet Nam». Neurology. 30 (12): 1273–1279. doi:10.1212/wnl.30.12.1273. PMID 7192808. S2CID 25106246.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Hardman JM, Manoukian A (May 2002). «Pathology of head trauma». Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. 12 (2): 175–87, vii. doi:10.1016/S1052-5149(02)00009-6. PMID 12391630.
TBI is highest in young adults aged 15 to 24 years and higher in men than women in all age groups.
- ^ a b Barkley JM, Morales D, Hayman LA, Diaz-Marchan PJ (2006). «Static neuroimaging in the evaluation of TBI». In Zasler ND, Katz DI, Zafonte RD (eds.). Brain Injury Medicine: Principles and Practice. Demos Medical Publishing. pp. 140–43. ISBN 978-1-888799-93-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Ghajar J (September 2000). «Traumatic brain injury». Lancet. 356 (9233): 923–929. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02689-1. PMID 11036909. S2CID 45288155.
- ^ Arlinghaus KA, Shoaib AM, Price TR (2005). «Neuropsychiatric assessment». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. pp. 63–65. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ a b c d e «NINDS Traumatic Brain Injury Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. September 15, 2008. Archived from the original on December 3, 2016. Retrieved October 27, 2008.
- ^ a b Kushner D (1998). «Mild traumatic brain injury: toward understanding manifestations and treatment». Archives of Internal Medicine. 158 (15): 1617–1624. doi:10.1001/archinte.158.15.1617. PMID 9701095.
- ^ a b Stone VE, Baron-Cohen S, Knight RT (September 1998). «Frontal lobe contributions to theory of mind». Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 10 (5): 640–656. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.330.1488. doi:10.1162/089892998562942. PMID 9802997. S2CID 207724498.
- ^ a b Kim E (2002). «Agitation, aggression, and disinhibition syndromes after traumatic brain injury». NeuroRehabilitation. 17 (4): 297–310. doi:10.3233/NRE-2002-17404. PMID 12547978.
- ^ Busch RM, McBride A, Curtiss G, Vanderploeg RD (November 2005). «The components of executive functioning in traumatic brain injury». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 27 (8): 1022–1032. doi:10.1080/13803390490919263. PMID 16207623. S2CID 8840941.
- ^ a b Ponsford J, Draper K, Schönberger M (March 2008). «Functional outcome 10 years after traumatic brain injury: its relationship with demographic, injury severity, and cognitive and emotional status». Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 14 (2): 233–242. doi:10.1017/S1355617708080272. PMID 18282321.
- ^ Williams C, Wood RL (March 2010). «Alexithymia and emotional empathy following traumatic brain injury». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 32 (3): 259–267. doi:10.1080/13803390902976940. PMID 19548166. S2CID 34126700.
- ^ a b Milders M, Fuchs S, Crawford JR (April 2003). «Neuropsychological impairments and changes in emotional and social behaviour following severe traumatic brain injury». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 25 (2): 157–172. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.510.871. doi:10.1076/jcen.25.2.157.13642. PMID 12754675. S2CID 2264964.
- ^ Ownsworth T, Fleming J (2005). «The relative importance of metacognitive skills, emotional status, and executive function in psychosocial adjustment following acquired brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 20 (4): 315–332. doi:10.1097/00001199-200507000-00004. PMID 16030439. S2CID 41271134.
- ^ Dahlberg CA, Cusick CP, Hawley LA, Newman JK, Morey CE, Harrison-Felix CL, Whiteneck GG (December 2007). «Treatment efficacy of social communication skills training after traumatic brain injury: a randomized treatment and deferred treatment controlled trial». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 88 (12): 1561–1573. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.033. PMID 18047870.
- ^ a b c d e f g Salomone JP, Frame SB (2004). «Prehospital care». In Moore EJ, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (eds.). Trauma. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. pp. 117–18. ISBN 978-0-07-137069-1.
- ^ a b «Signs and Symptoms». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. July 7, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2008.
- ^ Faul M, Xu L, Wald MM, Coronado VG (2010). «Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, 2002–2006». National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved October 22, 2013.
- ^ a b Reilly P (2007). «The impact of neurotrauma on society: An international perspective». In Weber JT (ed.). Neurotrauma: New Insights Into Pathology and Treatment. Amsterdam: Academic Press. pp. 5–7. ISBN 978-0-444-53017-2.
- ^ a b c d «Traumatic brain injury». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. 2007. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Granacher (2007). p. 16.
- ^ Hunt JP, Weintraub SL, Wang YZ, Buetcher KJ (2004). «Kinematics of trauma». In Moore EJ, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (eds.). Trauma. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. p. 153. ISBN 978-0-07-137069-1.
- ^ a b Elovic E, Zafonte R (2005). «Prevention». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. p. 740. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ Bay E, McLean SA (February 2007). «Mild traumatic brain injury: an update for advanced practice nurses». The Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 39 (1): 43–51. doi:10.1097/01376517-200702000-00009. PMID 17396538. S2CID 44600297.
- ^ a b Comper P, Bisschop SM, Carnide N, Tricco A (October 2005). «A systematic review of treatments for mild traumatic brain injury». Brain Injury. 19 (11): 863–880. doi:10.1080/02699050400025042. PMID 16296570. S2CID 34912966.
- ^ Champion HR, Holcomb JB, Young LA (May 2009). «Injuries from explosions: physics, biophysics, pathology, and required research focus». The Journal of Trauma. 66 (5): 1468–77, discussion 1477. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a27e7f. PMID 19430256. Archived from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved May 16, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Park E, Bell JD, Baker AJ (April 2008). «Traumatic brain injury: can the consequences be stopped?». CMAJ. 178 (9): 1163–1170. doi:10.1503/cmaj.080282. PMC 2292762. PMID 18427091.
- ^ «Pentagon Told Congress It’s Studying Brain-Damage Therapy». ProPublica. December 23, 2010. Retrieved January 23, 2011.
Brave Americans who risked everything for their country and sustained traumatic brain injuries – the signature injury of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan – deserve cognitive rehabilitation therapy to help them secure the best futures possible. It is unacceptable that the United States has been at war for nearly a decade and there is still no plan to treat these soldiers.
- ^ a b Thornton KE, Carmody DP (June 2008). «Efficacy of traumatic brain injury rehabilitation: interventions of QEEG-guided biofeedback, computers, strategies, and medications». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 33 (2): 101–24. doi:10.1007/s10484-008-9056-z. PMID 18551365. S2CID 7262160.
- ^ Thornton KE, Carmody DP (March 2009). «Traumatic brain injury rehabilitation: QEEG biofeedback treatment protocols». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 34 (1): 59–68. doi:10.1007/s10484-009-9075-4. PMID 19199027. S2CID 7928780.
- ^ a b Shaw NA (July 2002). «The neurophysiology of concussion». Progress in Neurobiology. 67 (4): 281–344. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(02)00018-7. PMID 12207973. S2CID 46514293.
- ^ American Academy of Pediatrics: Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect (July 2001). «Shaken baby syndrome: rotational cranial injuries-technical report». Pediatrics. 108 (1): 206–210. doi:10.1542/peds.108.1.206. PMID 11433079.
- ^ Morrison AL, King TM, Korell MA, Smialek JE, Troncoso JC (June 1998). «Acceleration-deceleration injuries to the brain in blunt force trauma». The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 19 (2): 109–112. doi:10.1097/00000433-199806000-00002. PMID 9662103.
- ^ Poirier MP (2003). «Concussions: Assessment, management, and recommendations for return to activity». Clinical Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 4 (3): 179–85. doi:10.1016/S1522-8401(03)00061-2.
- ^ Sauaia A, Moore FA, Moore EE, Moser KS, Brennan R, Read RA, Pons PT (February 1995). «Epidemiology of trauma deaths: a reassessment». The Journal of Trauma. 38 (2): 185–193. doi:10.1097/00005373-199502000-00006. PMID 7869433.
- ^ a b Narayan RK, Michel ME, Ansell B, Baethmann A, Biegon A, Bracken MB, et al. (May 2002). «Clinical trials in head injury». Journal of Neurotrauma. 19 (5): 503–557. doi:10.1089/089771502753754037. PMC 1462953. PMID 12042091.
- ^ Xiong Y, Lee CP, Peterson PL (2000). «Mitochondrial dysfunction following traumatic brain injury». In Miller LP, Hayes RL, Newcomb JK (eds.). Head Trauma: Basic, Preclinical, and Clinical Directions. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. pp. 257–80. ISBN 978-0-471-36015-5.
- ^ Scalea TM (2005). «Does it matter how head injured patients are resuscitated?». In Valadka AB, Andrews BT (eds.). Neurotrauma: Evidence-based Answers to Common Questions. Thieme. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-3-13-130781-1.
- ^ Morley EJ, Zehtabchi S (September 2008). «Evidence-based emergency medicine/systematic review abstract. Mannitol for traumatic brain injury: searching for the evidence». Annals of Emergency Medicine. 52 (3): 298–300. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.10.013. PMID 18763356.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Zink BJ (March 2001). «Traumatic brain injury outcome: concepts for emergency care». Annals of Emergency Medicine. 37 (3): 318–332. doi:10.1067/mem.2001.113505. PMID 11223769.
- ^ Wortzel HS, Arciniegas DB (January 1, 2014). «The DSM-5 approach to the evaluation of traumatic brain injury and its neuropsychiatric sequelae». NeuroRehabilitation. 34 (4): 613–623. doi:10.3233/NRE-141086. PMID 24820171.
- ^ Simpson JR (June 1, 2014). «DSM-5 and neurocognitive disorders». The Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. 42 (2): 159–164. PMID 24986342.
- ^ «The DSM-5 Approach to Evaluating Traumatic Brain Injury». www.hsrd.research.va.gov. Retrieved November 5, 2019.
- ^ a b Barr RM, Gean AD, Le TH (2007). «Craniofacial trauma». In Brant WE, Helms CA (eds.). Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-7817-6135-2.
- ^ «University Times ‘ Research Notes». University of Pittsburgh. March 22, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2013.
- ^ Coles JP (July 2007). «Imaging after brain injury». British Journal of Anaesthesia. 99 (1): 49–60. doi:10.1093/bja/aem141. PMID 17573394.
- ^ From Flight magazine (1912), as described by Grothe S (March 26, 2016). «Mit dem Kopf durch die Wand (With the Head Through the Wall)». Der Spiegel (in German). Archived from the original on May 23, 2018.
- ^ Liu BC, Ivers R, Norton R, Boufous S, Blows S, Lo SK (January 2008). Liu BC (ed.). «Helmets for preventing injury in motorcycle riders». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (1): CD004333. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004333.pub3. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30009360. PMID 18254047.
- ^ McCrory PR (August 2003). «Brain injury and heading in soccer». BMJ. 327 (7411): 351–352. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7411.351. PMC 1126775. PMID 12919964.
- ^ a b McIntosh AS, McCrory P (June 2005). «Preventing head and neck injury». British Journal of Sports Medicine. 39 (6): 314–318. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2005.018200. PMC 1725244. PMID 15911597.
- ^ a b c Crooks CY, Zumsteg JM, Bell KR (November 2007). «Traumatic brain injury: a review of practice management and recent advances». Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America. 18 (4): 681–710, vi. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2007.06.005. PMID 17967360.
- ^ Hahn RA, Bilukha O, Crosby A, Fullilove MT, Liberman A, Moscicki E, et al. (February 2005). «Firearms laws and the reduction of violence: a systematic review». American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 28 (2 Suppl 1): 40–71. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2004.10.005. PMID 15698747.
- ^ Kluger, Jeffrey. «Dealing with Brain Injuries. Time Magazine, April 6, 2009, p. 57. Online: [1]. Accessed: May 1, 2009
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Office of Communications and Public Liaison (February 2002). «Traumatic brain injury: Hope through research». NIH Publication No. 02-2478. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on December 18, 2016. Retrieved August 17, 2008.
Many patients with mild to moderate head injuries who experience cognitive deficits become easily confused or distracted and have problems with concentration and attention. They also have problems with higher level, so-called executive functions, such as planning, organizing, abstract reasoning, problem solving, and making judgments, which may make it difficult to resume pre-injury work-related activities. Recovery from cognitive deficits is greatest within the first 6 months after the injury and more gradual after that.
- ^ Kawada T (2020). «Efficacy of tranexamic acid in patients with traumatic brain injury». EXCLI Journal. 19: 1547–1548. doi:10.17179/excli2020-3161. PMC 7744966. PMID 33343272.
- ^ a b Greenwald BD, Burnett DM, Miller MA (March 2003). «Congenital and acquired brain injury. 1. Brain injury: epidemiology and pathophysiology». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 84 (3 Suppl 1): S3–S7. doi:10.1053/apmr.2003.50052. PMID 12708551.
- ^ a b Moppett IK (July 2007). «Traumatic brain injury: assessment, resuscitation and early management». British Journal of Anaesthesia. 99 (1): 18–31. doi:10.1093/bja/aem128. PMID 17545555. Moppet07
- ^ Wang F, Wang Y, Sun T, Yu HL (May 2016). «Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis». Neurological Sciences. 37 (5): 693–701. doi:10.1007/s10072-015-2460-2. PMID 26746238. S2CID 10548255.
- ^ Alarcon JD, Rubiano AM, Okonkwo DO, Alarcón J, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Urrútia G, Bonfill Cosp X (December 2017). «Elevation of the head during intensive care management in people with severe traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (12): CD009986. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009986.pub2. PMC 6486002. PMID 29283434.
- ^ Gruen P (May 2002). «Surgical management of head trauma». Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. 12 (2): 339–343. doi:10.1016/S1052-5149(02)00013-8. PMID 12391640.
- ^ a b c d Gultekin R, Huang S, Clavisi O, Pattuwage L, König TC, Gruen R (March 2016). «Pharmacological interventions in traumatic brain injury: Can we rely on systematic reviews for evidence?». Injury. 47 (3): 516–524. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.10.011. PMID 26589595.
- ^ a b Burgess S, Abu-Laban RB, Slavik RS, Vu EN, Zed PJ (April 2016). «A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing Hypertonic Sodium Solutions and Mannitol for Traumatic Brain Injury: Implications for Emergency Department Management». The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 50 (4): 291–300. doi:10.1177/1060028016628893. PMID 26825644. S2CID 23859003.
- ^ Mathur A, Duke T, Kukuruzovic R, South M (2004). «Hypotonic vs isotonic saline solutions for intravenous fluid management of acute infections». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003 (2): CD004169. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004169.pub2. PMC 6986696. PMID 15106241.
- ^ Rickard AC, Smith JE, Newell P, Bailey A, Kehoe A, Mann C (August 2014). «Salt or sugar for your injured brain? A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of mannitol versus hypertonic sodium solutions to manage raised intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury». Emergency Medicine Journal. 31 (8): 679–683. doi:10.1136/emermed-2013-202679. hdl:10026.1/4537. PMID 23811861. S2CID 24947684.
- ^ a b Wakai A, McCabe A, Roberts I, Schierhout G (August 2013). «Mannitol for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 8 (8): CD001049. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001049.pub5. PMC 7050611. PMID 23918314.
- ^ Chen H, Song Z, Dennis JA (January 2020). «Hypertonic saline versus other intracranial pressure-lowering agents for people with acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD010904. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010904.pub3. PMC 6984412. PMID 31978260.
- ^ Roberts I, Smith R, Evans S (February 2007). «Doubts over head injury studies». BMJ. 334 (7590): 392–394. doi:10.1136/bmj.39118.480023.BE. PMC 1804156. PMID 17322250.
- ^ «Guidelines for the Acute Medical Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants, Children, and Adolescents-Second Edition:». Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 13: S1–S2. January 2012. doi:10.1097/PCC.0b013e31823f435c. ISSN 1529-7535.
- ^ Schierhout G, Roberts I (2000). «Hyperventilation therapy for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1997 (2): CD000566. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000566. PMC 7061354. PMID 10796728.
- ^ Curry R, Hollingworth W, Ellenbogen RG, Vavilala MS (March 2008). «Incidence of hypo- and hypercarbia in severe traumatic brain injury before and after 2003 pediatric guidelines». Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 9 (2): 141–146. doi:10.1097/PCC.0B013e318166870e. PMID 18477926. S2CID 9927553.
- ^ Alderson P, Roberts I (January 2005). «Corticosteroids for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005 (1): CD000196. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000196.pub2. PMC 7043302. PMID 15674869.
- ^ Campbell J (2018). International Trauma Life Support for Emergency Care Providers (8th Global ed.). Pearson. p. 221. ISBN 978-1292-17084-8.
- ^ Roberts I (2000). «Aminosteroids for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (4): CD001527. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001527. PMC 8406780. PMID 11034722.
- ^ Ker K, Blackhall K (January 2008). «Beta-2 receptor antagonists for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2008 (1): CD006686. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006686.pub2. PMC 7387850. PMID 18254109.
- ^ Willis C, Lybrand S, Bellamy N (2004). «Excitatory amino acid inhibitors for traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003 (1): CD003986. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003986.pub2. PMC 6984678. PMID 14974051.
- ^ Forsyth RJ, Jayamoni B, Paine TC (October 2006). «Monoaminergic agonists for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD003984. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003984.pub2. PMID 17054192.
- ^ Tasker RC (2008). «Head and spinal cord trauma». In Nichols DG (ed.). Roger’s Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care (4th ed.). PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 887–911. ISBN 978-0-7817-8275-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Marshall LF (September 2000). «Head injury: recent past, present, and future». Neurosurgery. 47 (3): 546–561. doi:10.1097/00006123-200009000-00002. PMID 10981741.
- ^ Adams JP (2010). «Non-neurological complications of brain injury». In Adams JP, Bell D, McKinlay J (eds.). Neurocritical care : a guide to practical management. London: Springer. pp. 77–88. ISBN 978-1-84882-069-2.
- ^ O’Leary R, McKinlay J (2011). «Neurogenic pulmonary oedema». Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain. 11 (3): 87–92. doi:10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkr006.
- ^ Wilkins, Lippincott Williams (2005). Strategies for Managing Multisystem Disorders. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 370. ISBN 978-1-58255-423-5.
- ^ a b Dunn IF, Ellegala DB (2008). «Decompressive hemicraniectomy in the management of severe traumatic brain injury». In Bhardwaj A, Ellegala DB, Kirsch JR (eds.). Acute Brain and Spinal Cord Injury: Evolving Paradigms and Management. Informa Health Care. pp. 1–2. ISBN 978-1-4200-4794-3.
- ^ Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, D’Urso P, Kossmann T, Ponsford J, Seppelt I, Reilly P, Wolfe R (April 2011). «Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury» (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (16): 1493–502. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102077. PMID 21434843.
- ^ Carney N, Totten AM, O’Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, Bratton SL, Chesnut R, Harris OA, Kissoon N, Rubiano AM, Shutter L, Tasker RC, Vavilala MS, Wilberger J, Wright DW, Ghajar J (January 2017). «Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition». Neurosurgery. 80 (1): 6–15. doi:10.1227/NEU.0000000000001432. PMID 27654000. S2CID 3616546.
- ^ Turner-Stokes L, Pick A, Nair A, Disler PB, Wade DT (December 2015). «Multi-disciplinary rehabilitation for acquired brain injury in adults of working age». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (12): CD004170. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004170.pub3. PMC 8629646. PMID 26694853.
- ^ a b Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation and Institut national d’excellence en santé et en services sociaux (2015). «Clinical Practice Guideline for the Rehabilitation of Adults with Modarate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury». braininjuryguidelines.org. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Soo C, Tate R (July 2007). «Psychological treatment for anxiety in people with traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD005239. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005239.pub2. PMID 17636792.
- ^ a b c McMillan TM, Oddy M (2000). «Service provision for social disability and handicap after acquired brain injury». In Wood RL, McMillan TM (eds.). Neurobehavioural Disability and Social Handicap Following Traumatic Brain Injury. East Sussex: Psychology Press. pp. 267–68. ISBN 978-0-86377-889-6.
- ^ Deb S, Crownshaw T (January 2004). «The role of pharmacotherapy in the management of behaviour disorders in traumatic brain injury patients». Brain Injury. 18 (1): 1–31. doi:10.1080/0269905031000110463. PMID 14660233. S2CID 24775120.
- ^ a b Agrawal A, Timothy J, Pandit L, Manju M (July 2006). «Post-traumatic epilepsy: an overview». Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 108 (5): 433–439. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2005.09.001. PMID 16225987. S2CID 2650670.
- ^ Rodda J, Graham HK (November 2001). «Classification of gait patterns in spastic hemiplegia and spastic diplegia: a basis for a management algorithm». European Journal of Neurology. 8 (Suppl 5): 98–108. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.2001.00042.x. PMID 11851738. S2CID 45860264.
- ^ a b Grunt S. «Geh-Orthesen bei Kindern mit Cerebralparese». Pediatrica. 18: 30–34.
- ^ Esquenazi A (2008). Hsu JD, Michael JW, Fisk JR (eds.). Assessment and orthotic management of gait dysfunction in individuals with brain injury. AAOS Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices (4 ed.). Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier. pp. 441–447. ISBN 978-0-323-03931-4.
- ^ Horst R (2005). Motorisches Strategietraining und PNF. Renata Horst. ISBN 978-3-13-151351-9.
- ^ Novacheck TF (2008). Hsu JD, Michael JW, Fisk JR (eds.). Orthoses for cerebral palsy. AAOS Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices. Philadelphia. pp. 487–500. ISBN 978-0-323-03931-4.
- ^ Muñoz S (2018). «The new generation of AFOs». The O&P EDGE. 11. Archived from the original on June 6, 2021. Retrieved October 25, 2021.
- ^ Kerkum YL, Harlaar J, Buizer AI, van den Noort JC, Becher JG, Brehm MA (May 2016). «An individual approach for optimizing ankle-foot orthoses to improve mobility in children with spastic cerebral palsy walking with excessive knee flexion». Gait & Posture. 46: 104–111. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.03.001. PMID 27131186.
- ^ Kerkum YL (2016). «The effect of ankle foot orthosis stiffness on trunk movement and walking energy cost in cerebral palsy». Gait & Posture. 49: 2. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.07.070. ISSN 0966-6362.
- ^ Meyns P, Kerkum YL, Brehm MA, Becher JG, Buizer AI, Harlaar J (May 2020). «Ankle foot orthoses in cerebral palsy: Effects of ankle stiffness on trunk kinematics, gait stability and energy cost of walking». European Journal of Paediatric Neurology. 26: 68–74. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2020.02.009. PMID 32147412. S2CID 212641072.
- ^ Waterval NF, Nollet F, Harlaar J, Brehm MA (October 2019). «Modifying ankle foot orthosis stiffness in patients with calf muscle weakness: gait responses on group and individual level». Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation. 16 (1): 120. doi:10.1186/s12984-019-0600-2. PMC 6798503. PMID 31623670.
- ^ Ploeger HE, Waterval NF, Nollet F, Bus SA, Brehm MA (2019). «Stiffness modification of two ankle-foot orthosis types to optimize gait in individuals with non-spastic calf muscle weakness — a proof-of-concept study». Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (in German). 12: 41. doi:10.1186/s13047-019-0348-8. PMC 6686412. PMID 31406508.
- ^ a b Brown AW, Elovic EP, Kothari S, Flanagan SR, Kwasnica C (March 2008). «Congenital and acquired brain injury. 1. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, prognostication, innovative treatments, and prevention». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 89 (3 Suppl 1): S3–S8. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.12.001. PMID 18295647.
- ^ a b Frey LC (2003). «Epidemiology of posttraumatic epilepsy: a critical review». Epilepsia. 44 (s10): 11–17. doi:10.1046/j.1528-1157.44.s10.4.x. PMID 14511389. S2CID 34749005.
- ^ Armin SS, Colohan AR, Zhang JH (June 2006). «Traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: our current understanding and its evolution over the past half century». Neurological Research. 28 (4): 445–452. doi:10.1179/016164106X115053. PMID 16759448. S2CID 23726077.
- ^ Chumney D, Nollinger K, Shesko K, Skop K, Spencer M, Newton RA (2010). «Ability of Functional Independence Measure to accurately predict functional outcome of stroke-specific population: systematic review». Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 47 (1): 17–29. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2009.08.0140. PMID 20437324.
- ^ Murray ED, Buttner N, Price BH (2012). «Depression and Psychosis in Neurological Practice». In Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J (eds.). Bradley’s neurology in clinical practice. Vol. 1 (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. p. 111. ISBN 978-1-4377-0434-1.
- ^ Juengst SB, Adams LM, Bogner JA, Arenth PM, O’Neil-Pirozzi TM, Dreer LE, et al. (November 2015). «Trajectories of life satisfaction after traumatic brain injury: Influence of life roles, age, cognitive disability, and depressive symptoms». Rehabilitation Psychology. 60 (4): 353–364. doi:10.1037/rep0000056. PMC 4667543. PMID 26618215.
- ^ Hassett L, Moseley AM, Harmer AR (December 2017). «Fitness training for cardiorespiratory conditioning after traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (12): CD006123. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006123.pub3. PMC 6486048. PMID 29286534.
- ^ «Persistent vegetative state» at Dorland’s Medical Dictionary.
- ^ Schiff ND, Plum F, Rezai AR (March 2002). «Developing prosthetics to treat cognitive disabilities resulting from acquired brain injuries». Neurological Research. 24 (2): 116–124. doi:10.1179/016164102101199576. PMID 11877893. S2CID 347998.
- ^ a b Kwasnica C, Brown AW, Elovic EP, Kothari S, Flanagan SR (March 2008). «Congenital and acquired brain injury. 3. Spectrum of the acquired brain injury population». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 89 (3 Suppl 1): S15–S20. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.12.006. PMID 18295644.
- ^ Synnot A, Chau M, Pitt V, O’Connor D, Gruen RL, Wasiak J, et al. (November 2017). «Interventions for managing skeletal muscle spasticity following traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD008929. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008929.pub2. PMC 6486165. PMID 29165784.
- ^ Oliveros-Juste A, Bertol V, Oliveros-Cid A (2002). «[Preventive prophylactic treatment in posttraumatic epilepsy]». Revista de Neurologia (in Spanish). 34 (5): 448–459. doi:10.33588/rn.3405.2001439. PMID 12040514.
- ^ Aimaretti G, Ghigo E (April 2007). «Should every patient with traumatic brain injury be referred to an endocrinologist?». Nature Clinical Practice. Endocrinology & Metabolism. 3 (4): 318–319. doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0460. PMID 17377615. S2CID 26338743.
- ^ Arlinghaus KA, Shoaib AM, Price TR (2005). «Neuropsychiatric assessment». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. pp. 59–62. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ Hall RC, Hall RC, Chapman MJ (2005). «Definition, diagnosis, and forensic implications of postconcussional syndrome». Psychosomatics. 46 (3): 195–202. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.46.3.195. PMID 15883140. Archived from the original on May 15, 2005.
- ^ Jordan BD (2000). «Chronic traumatic brain injury associated with boxing». Seminars in Neurology. 20 (2): 179–185. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9826. PMID 10946737.
- ^ Mendez MF (1995). «The neuropsychiatric aspects of boxing». International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine. 25 (3): 249–262. doi:10.2190/CUMK-THT1-X98M-WB4C. PMID 8567192. S2CID 20238578.
- ^ a b c Draper K, Ponsford J (October 2009). «Long-term outcome following traumatic brain injury: a comparison of subjective reports by those injured and their relatives». Neuropsychological Rehabilitation. 19 (5): 645–661. doi:10.1080/17405620802613935. PMID 19629849. S2CID 205907369.
- ^ Rutherford GW, Corrigan JD (2009). «Long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 24 (6): 421–423. doi:10.1097/HTR.0b013e3181c13439. PMID 19940674.
- ^ a b Temkin NR, Corrigan JD, Dikmen SS, Machamer J (2009). «Social functioning after traumatic brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 24 (6): 460–467. doi:10.1097/HTR.0b013e3181c13413. PMID 19940679. S2CID 43384334.
- ^ a b c Velikonja D, Warriner E, Brum C (July 2010). «Profiles of emotional and behavioral sequelae following acquired brain injury: cluster analysis of the Personality Assessment Inventory». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 32 (6): 610–621. doi:10.1080/13803390903401302. PMID 20029697. S2CID 21067999.
- ^ Hawley LA, Newman JK (2010). «Group interactive structured treatment (GIST): a social competence intervention for individuals with brain injury». Brain Injury. 24 (11): 1292–1297. doi:10.3109/02699052.2010.506866. PMID 20735320. S2CID 207447494.
- ^ Lane-Brown A, Tate R (April 2009). «Interventions for apathy after traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009 (2): CD006341. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006341.pub2. PMC 7390354. PMID 19370632.
- ^ Hesdorffer DC, Rauch SL, Tamminga CA (2009). «Long-term psychiatric outcomes following traumatic brain injury: a review of the literature». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 24 (6): 452–459. doi:10.1097/htr.0b013e3181c133fd. PMID 19940678. S2CID 205643570.
- ^ Fleminger S (2010). «Neuropsychiatric effects of traumatic brain injury». Psychiatr Times. 27 (3): 40–45.
- ^ Dockree PM, O’Keeffe FM, Moloney P, Bishara AJ, Carton S, Jacoby LL, Robertson IH (January 2006). «Capture by misleading information and its false acceptance in patients with traumatic brain injury». Brain. 129 (Pt 1): 128–140. doi:10.1093/brain/awh664. PMID 16280354.
- ^ Kreutzer JS, Stejskal TM, Ketchum JM, Marwitz JH, Taylor LA, Menzel JC (June 2009). «A preliminary investigation of the brain injury family intervention: impact on family members». Brain Injury. 23 (6): 535–547. doi:10.1080/02699050902926291. PMID 19484627. S2CID 12428952.
- ^ Kreutzer JS, Kolakowsky-Hayner SA, Demm SR, Meade MA (August 2002). «A structured approach to family intervention after brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 17 (4): 349–367. doi:10.1097/00001199-200208000-00008. PMID 12106003. S2CID 20918911.
- ^ a b c d León-Carrión J, Domínguez-Morales M, Barroso y Martín JM, Murillo-Cabezas F (2005). «Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage». Pituitary. 8 (3–4): 197–202. doi:10.1007/s11102-006-6041-5. PMID 16508717. S2CID 23713764.
- ^ «Coma» at Dorland’s Medical Dictionary.
- ^ Cassidy JD, Carroll LJ, Peloso PM, Borg J, von Holst H, Holm L, et al. (WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury) (February 2004). «Incidence, risk factors and prevention of mild traumatic brain injury: results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury». Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 36 (43 Suppl): 28–60. doi:10.1080/16501960410023732. PMID 15083870.
- ^ a b c D’Ambrosio R, Perucca E (December 2004). «Epilepsy after head injury». Current Opinion in Neurology. 17 (6): 731–735. doi:10.1097/00019052-200412000-00014. PMC 2672045. PMID 15542983.
- ^ Chesnutt RM, Eisenberg JM (1999). «Introduction and background». Rehabilitation for Traumatic Brain Injury. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7881-8376-8.
- ^
Tolias C, Sgouros S (February 4, 2005). «Initial evaluation and management of CNS injury». Medscape. Retrieved December 16, 2007. - ^ Kindermann D, Mutter R, Pines JM (May 2013). Emergency Department Transfers to Acute Care Facilities 2009 (Report). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP Statistical Brief #155. Archived from the original on December 1, 2016.
- ^ Carli P, Orliaguet G (February 2004). «Severe traumatic brain injury in children». Lancet. 363 (9409): 584–585. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15626-2. PMID 14987880. S2CID 28381295.
- ^
Necajauskaite O, Endziniene M, Jureniene K (2005). «The prevalence, course and clinical features of post-concussion syndrome in children» (PDF). Medicina. 41 (6): 457–464. PMID 15998982. - ^ «An Unrecognized Problem» (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved October 13, 2019.
- ^ a b c Boake and Diller (2005). p. 3
- ^ a b c d Granacher (2007). p. 1.
- ^ Scurlock JA, Andersen BR (2005). Diagnoses in Assyrian and Babylonian Medicine: Ancient Sources, Translations, and Modern Medical Analyses. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. p. 307. ISBN 978-0-252-02956-1.
- ^ Sanchez GM, Burridge AL (2007). «Decision making in head injury management in the Edwin Smith Papyrus». Neurosurgical Focus. 23 (1): E5. doi:10.3171/FOC-07/07/E5. PMID 17961064.
- ^ a b c Levin HS, Benton AL, Grossman R (1982). «Historical review of head injury». Neurobehavioral Consequences of Closed Head Injury. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–5. ISBN 978-0-19-503008-2.
- ^ a b Zillmer EA, Schneider J, Tinker J, Kaminaris CI (2006). «A history of sports-related concussions: A neuropsychological perspective». In Echemendia RJ (ed.). Sports Neuropsychology: Assessment and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury. New York: The Guilford Press. pp. 21–23. ISBN 978-1-57230-078-1.
- ^ Corcoran C, McAlister TW, Malaspina D (2005). «Psychotic disorders». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. p. 213. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ Eslinger PJ, Damasio AR (December 1985). «Severe disturbance of higher cognition after bilateral frontal lobe ablation: patient EVR». Neurology. 35 (12): 1731–1741. doi:10.1212/wnl.35.12.1731. PMID 4069365. S2CID 22373825.
- ^ Devinsky O, D’Esposito M (2004). Neurology of Cognitive and Behavioral Disorders. Vol. 68. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-513764-4.
- ^ Marion (1999). p. 3.
- ^ Jones E, Fear NT, Wessely S (November 2007). «Shell shock and mild traumatic brain injury: a historical review». The American Journal of Psychiatry. 164 (11): 1641–1645. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07071180. PMID 17974926.
- ^ Belanger HG, Kretzmer T, Yoash-Gantz R, Pickett T, Tupler LA (January 2009). «Cognitive sequelae of blast-related versus other mechanisms of brain trauma». Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 15 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1017/S1355617708090036. PMID 19128523. S2CID 21648436.
- ^ Boake and Diller (2005). p. 8
- ^ Bush GH (July 1990). «Project on the Decade of the Brain». Library of Congress. Retrieved October 22, 2013.
- ^ Livint Popa L, Dragos H, Pantelemon C, Verisezan Rosu O, Strilciuc S (2020). «The Role of Quantitative EEG in the Diagnosis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders». J Med Life. 13 (1): 8–15. doi:10.25122/jml-2019-0085. PMC 7175442. PMID 32341694.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lewis SR, Baker PE, Andrews PJ, Cheng A, Deol K, Hammond N, Saxena M (October 2020). «Interventions to reduce body temperature to 35 °C to 37 °C in adults and children with traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (10): CD006811. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006811.pub4. PMC 8094748. PMID 33126293.
- ^ a b Watson HI, Shepherd AA, Rhodes JK, Andrews PJ (June 2018). «Revisited: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Hypothermia for Adult Patients Following Traumatic Brain Injury». Critical Care Medicine. 46 (6): 972–979. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000003125. hdl:20.500.11820/fae8c4d4-8286-42db-b08d-1369e9092e06. PMID 29601315. S2CID 4495428.
- ^ Crompton EM, Lubomirova I, Cotlarciuc I, Han TS, Sharma SD, Sharma P (April 2017). «Meta-Analysis of Therapeutic Hypothermia for Traumatic Brain Injury in Adult and Pediatric Patients». Critical Care Medicine. 45 (4): 575–583. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002205. PMID 27941370. S2CID 19064475.
- ^ Lewis SR, Evans DJ, Butler AR, Schofield-Robinson OJ, Alderson P (September 2017). «Hypothermia for traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (9): CD001048. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001048.pub5. PMC 6483736. PMID 28933514.
- ^ Martín-Saborido C, López-Alcalde J, Ciapponi A, Sánchez Martín CE, Garcia Garcia E, Escobar Aguilar G, et al. (November 2019). «Indomethacin for intracranial hypertension secondary to severe traumatic brain injury in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (11). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011725.pub2. PMC 6872435. PMID 31752052.
- ^ Thal SC, Schaible EV, Neuhaus W, Scheffer D, Brandstetter M, Engelhard K, et al. (May 2013). «Inhibition of proteasomal glucocorticoid receptor degradation restores dexamethasone-mediated stabilization of the blood-brain barrier after traumatic brain injury». Critical Care Medicine. 41 (5): 1305–1315. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827ca494. PMID 23474678. S2CID 23399305.
- ^ Wright DW, Kellermann AL, Hertzberg VS, Clark PL, Frankel M, Goldstein FC, et al. (April 2007). «ProTECT: a randomized clinical trial of progesterone for acute traumatic brain injury». Annals of Emergency Medicine. 49 (4): 391–402. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.07.932. PMID 17011666.
- ^ Harris K, Armstrong SP, Campos-Pires R, Kiru L, Franks NP, Dickinson R (November 2013). «Neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury by xenon, but not argon, is mediated by inhibition at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor glycine site». Anesthesiology. 119 (5): 1137–1148. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182a2a265. PMID 23867231. S2CID 9756580.
- ^ Roberts I, Sydenham E (December 2012). «Barbiturates for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD000033. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000033.pub2. PMC 7061245. PMID 23235573.
- ^ Sen AP, Gulati A (January 2010). «Use of magnesium in traumatic brain injury». Neurotherapeutics. 7 (1): 91–99. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2009.10.014. PMC 5084116. PMID 20129501.
- ^ Arango MF, Bainbridge D (October 2008). «Magnesium for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD005400. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005400.pub3. PMID 18843689.
- ^ Langham J, Goldfrad C, Teasdale G, Shaw D, Rowan K (2003). «Calcium channel blockers for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD000565. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000565. PMC 7032539. PMID 14583925.
- ^ Yi JH, Park SW, Brooks N, Lang BT, Vemuganti R (December 2008). «PPARgamma agonist rosiglitazone is neuroprotective after traumatic brain injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms». Brain Research. 1244: 164–172. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.074. PMC 2603294. PMID 18948087.
- ^ Luo Y, Yin W, Signore AP, Zhang F, Hong Z, Wang S, et al. (April 2006). «Neuroprotection against focal ischemic brain injury by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist rosiglitazone». Journal of Neurochemistry. 97 (2): 435–448. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03758.x. PMID 16539667. S2CID 37759164.
- ^ Liu Y, Dargusch R, Maher P, Schubert D (May 2008). «A broadly neuroprotective derivative of curcumin». Journal of Neurochemistry. 105 (4): 1336–1345. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05236.x. PMID 18208543. S2CID 13345179.
- ^ Kelly DF, Lee SM, Pinanong PA, Hovda DA (May 1997). «Paradoxical effects of acute ethanolism in experimental brain injury». Journal of Neurosurgery. 86 (5): 876–882. doi:10.3171/jns.1997.86.5.0876. PMID 9126906.
- ^ Li W, Dai S, An J, Li P, Chen X, Xiong R, et al. (February 2008). «Chronic but not acute treatment with caffeine attenuates traumatic brain injury in the mouse cortical impact model». Neuroscience. 151 (4): 1198–1207. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.020. PMID 18207647. S2CID 29276898.
- ^ Nilsson P, Hillered L, Pontén U, Ungerstedt U (September 1990). «Changes in cortical extracellular levels of energy-related metabolites and amino acids following concussive brain injury in rats». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 10 (5): 631–637. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1990.115. PMID 2384536.
- ^ Vespa P, Bergsneider M, Hattori N, Wu HM, Huang SC, Martin NA, et al. (June 2005). «Metabolic crisis without brain ischemia is common after traumatic brain injury: a combined microdialysis and positron emission tomography study». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 25 (6): 763–774. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600073. PMC 4347944. PMID 15716852.
- ^ Dengler J, Frenzel C, Vajkoczy P, Wolf S, Horn P (November 2011). «Cerebral tissue oxygenation measured by two different probes: challenges and interpretation». Intensive Care Medicine. 37 (11): 1809–1815. doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2316-z. PMID 21809108. S2CID 23154956.
- ^ Rosenthal G, Furmanov A, Itshayek E, Shoshan Y, Singh V (April 2014). «Assessment of a noninvasive cerebral oxygenation monitor in patients with severe traumatic brain injury». Journal of Neurosurgery. 120 (4): 901–907. doi:10.3171/2013.12.JNS131089. PMID 24484228.
- ^ Yates D, Aktar R, Hill J (October 2007). «Assessment, investigation, and early management of head injury: summary of NICE guidance». BMJ. 335 (7622): 719–720. doi:10.1136/bmj.39331.702951.47. PMC 2001047. PMID 17916856.
- ^ a b c Bennett MH, Trytko B, Jonker B (December 2012). «Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the adjunctive treatment of traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD004609. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004609.pub3. PMID 23235612.
- ^ Rockswold SB, Rockswold GL, Defillo A (March 2007). «Hyperbaric oxygen in traumatic brain injury». Neurological Research. 29 (2): 162–172. doi:10.1179/016164107X181798. PMID 17439701. S2CID 35914918.
- ^ Gertler P, Tate RL, Cameron ID (December 2015). «Non-pharmacological interventions for depression in adults and children with traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (12): CD009871. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009871.pub2. PMC 8761477. PMID 26663136.
- ^ Maruta J, Lee SW, Jacobs EF, Ghajar J (October 2010). «A unified science of concussion». Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1208 (1): 58–66. Bibcode:2010NYASA1208…58M. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05695.x. PMC 3021720. PMID 20955326.
- ^ Copplestone S, Welbourne J (February 2018). «A narrative review of the clinical application of pressure reactiviy indices in the neurocritical care unit». British Journal of Neurosurgery. 32 (1): 4–12. doi:10.1080/02688697.2017.1416063. PMID 29298527. S2CID 26020481.
- ^ Chesnut RM, Temkin N, Carney N, Dikmen S, Rondina C, Videtta W, et al. (December 2012). «A trial of intracranial-pressure monitoring in traumatic brain injury». The New England Journal of Medicine. 367 (26): 2471–2481. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1207363. PMC 3565432. PMID 23234472.
- ^ Carron SF, Alwis DS, Rajan R (2016). «Traumatic Brain Injury and Neuronal Functionality Changes in Sensory Cortex». Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience. 10: 47. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2016.00047. PMC 4889613. PMID 27313514.
- ^ Alwis DS, Yan EB, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Rajan R (2012). «Sensory cortex underpinnings of traumatic brain injury deficits». PLOS ONE. 7 (12): e52169. Bibcode:2012PLoSO…752169A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052169. PMC 3528746. PMID 23284921.
- ^ Johnstone VP, Shultz SR, Yan EB, O’Brien TJ, Rajan R (November 2014). «The acute phase of mild traumatic brain injury is characterized by a distance-dependent neuronal hypoactivity». Journal of Neurotrauma. 31 (22): 1881–1895. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3343. PMC 4224042. PMID 24927383.
- ^ Burns TF (2019). Burns (2019): Temporal neuronal activity patterns in barrel cortex to simple and complex stimuli and the effects of traumatic brain injury. Monash University. Thesis. 10.26180/5b7166ad13e47 (thesis). Monash University. doi:10.26180/5b7166ad13e47.
Cited texts
- Boake C, Diller L (2005). «History of rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury». In High WM, Sander AM, Struchen MA, Hart KA (eds.). Rehabilitation for Traumatic Brain Injury. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-517355-0.
- Granacher RA (2007). Traumatic Brain Injury: Methods for Clinical & Forensic Neuropsychiatric Assessment, Second Edition. Boca Raton: CRC. ISBN 978-0-8493-8138-6.
- LaPlaca MC, Simon CM, Prado GR, Cullen DR (2007). «CNS injury biomechanics and experimental models». In Weber JT (ed.). Neurotrauma: New Insights Into Pathology and Treatment. Amsterdam: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-444-53017-2.
- Marion DW (1999). «Introduction». In Marion DW (ed.). Traumatic Brain Injury. Stuttgart: Thieme. ISBN 978-0-86577-727-9.
The original version of this article contained text from the NINDS public domain pages on TBI Archived December 18, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
External links
- Brain injury at Curlie
- The Brain Injury Hub – information and practical advice to parents and family members of children with acquired brain injury Archived October 5, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center – U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System center for traumatic brain injury Archived October 12, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
| Traumatic brain injury | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Intracranial injury, physically induced brain injury[1] |
 |
|
| CT scan showing cerebral contusions, hemorrhage within the hemispheres, and subdural hematoma. There is also displaced skull fracture of left transverse parietal and temporal bones.[2] | |
| Specialty | Neurosurgery, pediatrics |
| Symptoms | Physical, cognitive, sensory, social, emotional, and behavioral symptoms |
| Types | Mild to severe[3] |
| Causes | Trauma to the head[3] |
| Risk factors | Old age,[3] alcohol |
| Diagnostic method | Based on neurological exam, medical imaging[4] |
| Treatment | Behavioral therapy, speech therapy |
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury [mTBI/concussion] to severe traumatic brain injury), mechanism (closed or penetrating head injury), or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area).[5] Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death.
Causes include falls, vehicle collisions and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events following the injury may result in further injury. These processes include alterations in cerebral blood flow and pressure within the skull. Some of the imaging techniques used for diagnosis include computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs).
Prevention measures include use of seat belts and helmets, not drinking and driving, fall prevention efforts in older adults and safety measures for children.[6] Depending on the injury, treatment required may be minimal or may include interventions such as medications, emergency surgery or surgery years later. Physical therapy, speech therapy, recreation therapy, occupational therapy and vision therapy may be employed for rehabilitation. Counseling, supported employment and community support services may also be useful.
TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults.[7] Males sustain traumatic brain injuries around twice as often as females.[8] The 20th century saw developments in diagnosis and treatment that decreased death rates and improved outcomes.
Classification
Traumatic brain injury is defined as damage to the brain resulting from external mechanical force, such as rapid acceleration or deceleration, impact, blast waves, or penetration by a projectile.[9] Brain function is temporarily or permanently impaired and structural damage may or may not be detectable with current technology.[10]
TBI is one of two subsets of acquired brain injury (brain damage that occur after birth); the other subset is non-traumatic brain injury, which does not involve external mechanical force (examples include stroke and infection).[11][12] All traumatic brain injuries are head injuries, but the latter term may also refer to injury to other parts of the head.[13][14][15] However, the terms head injury and brain injury are often used interchangeably.[16] Similarly, brain injuries fall under the classification of central nervous system injuries[17] and neurotrauma.[18] In neuropsychology research literature, in general the term «traumatic brain injury» is used to refer to non-penetrating traumatic brain injuries.
TBI is usually classified based on severity, anatomical features of the injury, and the mechanism (the causative forces).[19] Mechanism-related classification divides TBI into closed and penetrating head injury.[9] A closed (also called nonpenetrating, or blunt)[13] injury occurs when the brain is not exposed.[14] A penetrating, or open, head injury occurs when an object pierces the skull and breaches the dura mater, the outermost membrane surrounding the brain.[14]
Severity
| GCS | PTA | LOC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | 13–15 | <1 day |
0–30 minutes |
| Moderate | 9–12 | >1 to <7 days |
>30 min to <24 hours |
| Severe | 3–8 | >7 days | >24 hours |
Brain injuries can be classified into mild, moderate, and severe categories.[19] The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), the most commonly used system for classifying TBI severity, grades a person’s level of consciousness on a scale of 3–15 based on verbal, motor, and eye-opening reactions to stimuli.[21] In general, it is agreed that a TBI with a GCS of 13 or above is mild, 9–12 is moderate, and 8 or below is severe.[10][15][22] Similar systems exist for young children.[15] However, the GCS grading system has limited ability to predict outcomes. Because of this, other classification systems such as the one shown in the table are also used to help determine severity. A current model developed by the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs uses all three criteria of GCS after resuscitation, duration of post-traumatic amnesia (PTA), and loss of consciousness (LOC).[20] It also has been proposed to use changes that are visible on neuroimaging, such as swelling, focal lesions, or diffuse injury as method of classification.[9] Grading scales also exist to classify the severity of mild TBI, commonly called concussion; these use duration of LOC, PTA, and other concussion symptoms.[23]
Pathological features
Systems also exist to classify TBI by its pathological features.[19] Lesions can be extra-axial, (occurring within the skull but outside of the brain) or intra-axial (occurring within the brain tissue).[24] Damage from TBI can be focal or diffuse, confined to specific areas or distributed in a more general manner, respectively.[25] However, it is common for both types of injury to exist in a given case.[25]
Diffuse injury manifests with little apparent damage in neuroimaging studies, but lesions can be seen with microscopy techniques post-mortem,[25][26] and in the early 2000s, researchers discovered that diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), a way of processing MRI images that shows white matter tracts, was an effective tool for displaying the extent of diffuse axonal injury.[27][28] Types of injuries considered diffuse include edema (swelling), concussion and diffuse axonal injury, which is widespread damage to axons including white matter tracts and projections to the cortex.[29][30]
Focal injuries often produce symptoms related to the functions of the damaged area.[17] Research shows that the most common areas to have focal lesions in non-penetrating traumatic brain injury are the orbitofrontal cortex (the lower surface of the frontal lobes) and the anterior temporal lobes, areas that are involved in social behavior, emotion regulation, olfaction, and decision-making, hence the common social/emotional and judgment deficits following moderate-severe TBI.[31][32][33][34] Symptoms such as hemiparesis or aphasia can also occur when less commonly affected areas such as motor or language areas are, respectively, damaged.[35][36]
One type of focal injury, cerebral laceration, occurs when the tissue is cut or torn.[37] Such tearing is common in orbitofrontal cortex in particular, because of bony protrusions on the interior skull ridge above the eyes.[31] In a similar injury, cerebral contusion (bruising of brain tissue), blood is mixed among tissue.[22] In contrast, intracranial hemorrhage involves bleeding that is not mixed with tissue.[37]
Hematomas, also focal lesions, are collections of blood in or around the brain that can result from hemorrhage.[10] Intracerebral hemorrhage, with bleeding in the brain tissue itself, is an intra-axial lesion. Extra-axial lesions include epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and intraventricular hemorrhage.[38] Epidural hematoma involves bleeding into the area between the skull and the dura mater, the outermost of the three membranes surrounding the brain.[10] In subdural hematoma, bleeding occurs between the dura and the arachnoid mater.[22] Subarachnoid hemorrhage involves bleeding into the space between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater.[22] Intraventricular hemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding in the ventricles.[38]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms are dependent on the type of TBI (diffuse or focal) and the part of the brain that is affected.[40] Unconsciousness tends to last longer for people with injuries on the left side of the brain than for those with injuries on the right.[14] Symptoms are also dependent on the injury’s severity. With mild TBI, the patient may remain conscious or may lose consciousness for a few seconds or minutes.[41] Other symptoms of mild TBI include headache, vomiting, nausea, lack of motor coordination, dizziness, difficulty balancing,[42] lightheadedness, blurred vision or tired eyes, ringing in the ears, bad taste in the mouth, fatigue or lethargy, and changes in sleep patterns.[41] Cognitive and emotional symptoms include behavioral or mood changes, confusion, and trouble with memory, concentration, attention, or thinking.[41] Mild TBI symptoms may also be present in moderate and severe injuries.[41]
A person with a moderate or severe TBI may have a headache that does not go away, repeated vomiting or nausea, convulsions, an inability to awaken, dilation of one or both pupils, slurred speech, aphasia (word-finding difficulties), dysarthria (muscle weakness that causes disordered speech), weakness or numbness in the limbs, loss of coordination, confusion, restlessness, or agitation.[41] Common long-term symptoms of moderate to severe TBI are changes in appropriate social behavior, deficits in social judgment, and cognitive changes, especially problems with sustained attention, processing speed, and executive functioning.[34][43][44][45][46] Alexithymia, a deficiency in identifying, understanding, processing, and describing emotions occurs in 60.9% of individuals with TBI.[47] Cognitive and social deficits have long-term consequences for the daily lives of people with moderate to severe TBI, but can be improved with appropriate rehabilitation.[46][48][49][50]
When the pressure within the skull (intracranial pressure, abbreviated ICP) rises too high, it can be deadly.[51] Signs of increased ICP include decreasing level of consciousness, paralysis or weakness on one side of the body, and a blown pupil, one that fails to constrict in response to light or is slow to do so.[51] Cushing’s triad, a slow heart rate with high blood pressure and respiratory depression is a classic manifestation of significantly raised ICP.[10] Anisocoria, unequal pupil size, is another sign of serious TBI.[39] Abnormal posturing, a characteristic positioning of the limbs caused by severe diffuse injury or high ICP, is an ominous sign.[10]
Small children with moderate to severe TBI may have some of these symptoms but have difficulty communicating them.[52] Other signs seen in young children include persistent crying, inability to be consoled, listlessness, refusal to nurse or eat,[52] and irritability.[10]
Causes
The most common causes of TBI in the U.S. include violence, transportation accidents, construction site mishaps, and sports.[42][53] Motor bikes are major causes, increasing in significance in developing countries as other causes reduce.[54] The estimates that between 1.6 and 3.8 million traumatic brain injuries each year are a result of sports and recreation activities in the US.[55] In children aged two to four, falls are the most common cause of TBI, while in older children traffic accidents compete with falls for this position.[56] TBI is the third most common injury to result from child abuse.[57] Abuse causes 19% of cases of pediatric brain trauma, and the death rate is higher among these cases.[58] Although men are twice as likely to have a TBI. Domestic violence is another cause of TBI,[59] as are work-related and industrial accidents.[60] Firearms[14] and blast injuries from explosions[61] are other causes of TBI, which is the leading cause of death and disability in war zones.[62] According to Representative Bill Pascrell (Democrat, NJ), TBI is «the signature injury of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.»[63] There is a promising technology called activation database-guided EEG biofeedback, which has been documented to return a TBI’s auditory memory ability to above the control group’s performance[64][65]
Mechanism
Physical forces
Ricochet of the brain within the skull may account for the coup-contrecoup phenomenon.[66]
The type, direction, intensity, and duration of forces all contribute to the characteristics and severity TBI.[9] Forces that may contribute to TBI include angular, rotational, shear, and translational forces.[37]
Even in the absence of an impact, significant acceleration or deceleration of the head can cause TBI; however in most cases, a combination of impact and acceleration is probably to blame.[37] Forces involving the head striking or being struck by something, termed contact or impact loading, are the cause of most focal injuries, and movement of the brain within the skull, termed noncontact or inertial loading, usually causes diffuse injuries.[19] The violent shaking of an infant that causes shaken baby syndrome commonly manifests as diffuse injury.[67] In impact loading, the force sends shock waves through the skull and brain, resulting in tissue damage.[37] Shock waves caused by penetrating injuries can also destroy tissue along the path of a projectile, compounding the damage caused by the missile itself.[22]
Damage may occur directly under the site of impact, or it may occur on the side opposite the impact (coup and contrecoup injury, respectively).[66] When a moving object impacts the stationary head, coup injuries are typical,[68] while contrecoup injuries are usually produced when the moving head strikes a stationary object.[69]
Primary and secondary injury
MRI scan showing damage due to brain herniation after TBI[2]
A large percentage of the people killed by brain trauma do not die right away but rather days to weeks after the event;[70] rather than improving after being hospitalized, some 40% of TBI patients deteriorate.[71] Primary brain injury (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn) is not adequate to explain this deterioration; rather, it is caused by secondary injury, a complex set of cellular processes and biochemical cascades that occur in the minutes to days following the trauma.[72] These secondary processes can dramatically worsen the damage caused by primary injury[62] and account for the greatest number of TBI deaths occurring in hospitals.[39]
Secondary injury events include damage to the blood–brain barrier, release of factors that cause inflammation, free radical overload, excessive release of the neurotransmitter glutamate (excitotoxicity), influx of calcium and sodium ions into neurons, and dysfunction of mitochondria.[62] Injured axons in the brain’s white matter may separate from their cell bodies as a result of secondary injury,[62] potentially killing those neurons. Other factors in secondary injury are changes in the blood flow to the brain; ischemia (insufficient blood flow); cerebral hypoxia (insufficient oxygen in the brain); cerebral edema (swelling of the brain); and raised intracranial pressure (the pressure within the skull).[73] Intracranial pressure may rise due to swelling or a mass effect from a lesion, such as a hemorrhage.[51] As a result, cerebral perfusion pressure (the pressure of blood flow in the brain) is reduced; ischemia results.[39][74] When the pressure within the skull rises too high, it can cause brain death or brain herniation, in which parts of the brain are squeezed by structures in the skull.[51]
Diagnosis
CT scan showing epidural hematoma (arrow)
Diagnosis is suspected based on lesion circumstances and clinical evidence, most prominently a neurological examination, for example checking whether the pupils constrict normally in response to light and assigning a Glasgow Coma Score.[22] Neuroimaging helps in determining the diagnosis and prognosis and in deciding what treatments to give.[75] DSM-5 can be utilized to diagnose TBI and its psychiatric sequelae.[76][77][78]
The preferred radiologic test in the emergency setting is computed tomography (CT): it is quick, accurate, and widely available.[79] Follow-up CT scans may be performed later to determine whether the injury has progressed.[9]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can show more detail than CT, and can add information about expected outcome in the long term.[22] It is more useful than CT for detecting injury characteristics such as diffuse axonal injury in the longer term.[9] However, MRI is not used in the emergency setting for reasons including its relative inefficacy in detecting bleeds and fractures, its lengthy acquisition of images, the inaccessibility of the patient in the machine, and its incompatibility with metal items used in emergency care.[22] A variant of MRI since 2012 is High definition fiber tracking (HDFT).[80]
Other techniques may be used to confirm a particular diagnosis. X-rays are still used for head trauma, but evidence suggests they are not useful; head injuries are either so mild that they do not need imaging or severe enough to merit the more accurate CT.[79] Angiography may be used to detect blood vessel pathology when risk factors such as penetrating head trauma are involved.[9] Functional imaging can measure cerebral blood flow or metabolism, inferring neuronal activity in specific regions and potentially helping to predict outcome.[81]
Neuropsychological assessment can be performed to evaluate the long-term cognitive sequelae and to aid in the planning of the rehabilitation.[75] Instruments range from short measures of general mental functioning to complete batteries formed of different domain-specific tests.
Prevention
Demonstration in 1912 of the Warren Safety Helmet, which was designed to protect pilots but has often been wrongly described as a football helmet.[82]
Protective sports equipment such as helmets can partially protect athletes from head injury.
Since a major cause of TBI are vehicle accidents, their prevention or the amelioration of their consequences can both reduce the incidence and gravity of TBI. In accidents, damage can be reduced by use of seat belts, child safety seats[55] and motorcycle helmets,[83] and presence of roll bars and airbags.[37] Education programs exist to lower the number of crashes.[75] In addition, changes to public policy and safety laws can be made; these include speed limits, seat belt and helmet laws, and road engineering practices.[62]
Changes to common practices in sports have also been discussed. An increase in use of helmets could reduce the incidence of TBI.[62] Due to the possibility that repeatedly «heading» a ball practicing soccer could cause cumulative brain injury, the idea of introducing protective headgear for players has been proposed.[84] Improved equipment design can enhance safety; softer baseballs reduce head injury risk.[85] Rules against dangerous types of contact, such as «spear tackling» in American football, when one player tackles another head first, may also reduce head injury rates.[85]
Falls can be avoided by installing grab bars in bathrooms and handrails on stairways; removing tripping hazards such as throw rugs; or installing window guards and safety gates at the top and bottom of stairs around young children.[55] Playgrounds with shock-absorbing surfaces such as mulch or sand also prevent head injuries.[55] Child abuse prevention is another tactic; programs exist to prevent shaken baby syndrome by educating about the dangers of shaking children.[58] Gun safety, including keeping guns unloaded and locked, is another preventative measure.[86] Studies on the effect of laws that aim to control access to guns in the United States have been insufficient to determine their effectiveness preventing number of deaths or injuries.[87]
Treatment
It is important to begin emergency treatment within the so-called «golden hour» following the injury.[88] People with moderate to severe injuries are likely to receive treatment in an intensive care unit followed by a neurosurgical ward.[89] Treatment depends on the recovery stage of the patient. In the acute stage, the primary aim is to stabilize the patient and focus on preventing further injury. This is done because the initial damage caused by trauma cannot be reversed.[89] Rehabilitation is the main treatment for the subacute and chronic stages of recovery.[89] International clinical guidelines have been proposed with the aim of guiding decisions in TBI treatment, as defined by an authoritative examination of current evidence.[9]
Acute stage
Tranexamic acid within three hours of a head injury decreases the risk of death.[90] Certain facilities are equipped to handle TBI better than others; initial measures include transporting patients to an appropriate treatment center.[51][91] Both during transport and in hospital the primary concerns are ensuring proper oxygen supply, maintaining adequate blood flow to the brain, and controlling raised intracranial pressure (ICP),[10] since high ICP deprives the brain of badly needed blood flow[92] and can cause deadly brain herniation. Other methods to prevent damage include management of other injuries and prevention of seizures.[22][75] Some data supports the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to improve outcomes.[93] Further research is required to determine the effectiveness and clinical importance of positioning the head at different angles (degrees of head-of-bed elevation) while the person is being treated in intensive care.[94]
Neuroimaging is helpful but not flawless in detecting raised ICP.[95] A more accurate way to measure ICP is to place a catheter into a ventricle of the brain,[39] which has the added benefit of allowing cerebrospinal fluid to drain, releasing pressure in the skull.[39] Treatment of raised ICP may be as simple as tilting the person’s bed and straightening the head to promote blood flow through the veins of the neck. Sedatives, analgesics and paralytic agents are often used.[51] Propofol and midazolam are equally effective as sedatives.[96]
Hypertonic saline can improve ICP by reducing the amount of cerebral water (swelling), though it is used with caution to avoid electrolyte imbalances or heart failure.[9][97][98] Mannitol, an osmotic diuretic,[9] appears to be as effective as hypertonic saline at reducing ICP.[99][100][97][101] Some concerns, however, have been raised regarding some of the studies performed.[102][specify] Hyertonic saline is also suitable in children with severe traumatic brain injury.[103]
Diuretics, drugs that increase urine output to reduce excessive fluid in the system, may be used to treat high intracranial pressures, but may cause hypovolemia (insufficient blood volume).[39]
Hyperventilation (larger and/or faster breaths) reduces carbon dioxide levels and causes blood vessels to constrict; this decreases blood flow to the brain and reduces ICP,[104] but it potentially causes ischemia[10][39][105] and is, therefore, used only in the short term.[10]
Giving corticosteroids is associated with an increased risk of death, and so their routine use is not recommended.[106][107] There is no strong evidence that the following pharmaceutical interventions should be recommended to routinely treat TBI: magnesium, monoaminergic and dopamine agonists, progesterone, aminosteroids, excitatory amino acid reuptake inhibitors, beta-2 antagonists (bronchodilators), haemostatic and antifibrinolytic drugs.[96][108][109][110][111]
Endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation may be used to ensure proper oxygen supply and provide a secure airway.[75] Hypotension (low blood pressure), which has a devastating outcome in TBI, can be prevented by giving intravenous fluids to maintain a normal blood pressure. Failing to maintain blood pressure can result in inadequate blood flow to the brain.[22] Blood pressure may be kept at an artificially high level under controlled conditions by infusion of norepinephrine or similar drugs; this helps maintain cerebral perfusion.[112] Body temperature is carefully regulated because increased temperature raises the brain’s metabolic needs, potentially depriving it of nutrients.[113] Seizures are common. While they can be treated with benzodiazepines, these drugs are used carefully because they can depress breathing and lower blood pressure.[51] Anti-convulsant medications have only been found to be useful for reducing the risk of an early seizure.[96] Phenytoin and leviteracetam appear to have similar levels of effectiveness for preventing early seizures.[96] People with TBI are more susceptible to side effects and may react adversely to some medications.[89] During treatment monitoring continues for signs of deterioration such as a decreasing level of consciousness.[9][10]
Traumatic brain injury may cause a range of serious coincidental complications that include cardiac arrhythmias[114] and neurogenic pulmonary edema.[115] These conditions must be adequately treated and stabilised as part of the core care.
Surgery can be performed on mass lesions or to eliminate objects that have penetrated the brain. Mass lesions such as contusions or hematomas causing a significant mass effect (shift of intracranial structures) are considered emergencies and are removed surgically.[22] For intracranial hematomas, the collected blood may be removed using suction or forceps or it may be floated off with water.[22] Surgeons look for hemorrhaging blood vessels and seek to control bleeding.[22] In penetrating brain injury, damaged tissue is surgically debrided, and craniotomy may be needed.[22] Craniotomy, in which part of the skull is removed, may be needed to remove pieces of fractured skull or objects embedded in the brain.[116] Decompressive craniectomy (DC) is performed routinely in the very short period following TBI during operations to treat hematomas; part of the skull is removed temporarily (primary DC).[117] DC performed hours or days after TBI in order to control persistently high intracranial pressures (secondary DC), although can reduce intracranial pressure and length of stay in ICU, but have worse Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores, and high chances of death, vegetative state, or severe disability when compared to those receiving standard medical therapies.[118][119][9][117]
Chronic stage
Physical therapy will commonly include muscle strength exercise.
Once medically stable, people may be transferred to a subacute rehabilitation unit of the medical center or to an independent rehabilitation hospital.[89] Rehabilitation aims to improve independent functioning at home and in society, and to help adapt to disabilities.[89] Rehabilitation has demonstrated its general effectiveness when conducted by a team of health professionals who specialize in head trauma.[120] As for any person with neurologic deficits, a multidisciplinary approach is key to optimizing outcome. Physiatrists or neurologists are likely to be the key medical staff involved, but depending on the person, doctors of other medical specialties may also be helpful. Allied health professions such as physiotherapy, speech and language therapy, cognitive rehabilitation therapy, and occupational therapy will be essential to assess function and design the rehabilitation activities for each person.[121] Treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms such as emotional distress and clinical depression may involve mental health professionals such as therapists, psychologists, and psychiatrists, while neuropsychologists can help to evaluate and manage cognitive deficits.[89][122] Social workers, rehabilitation support personnel, nutritionists, therapeutic recreationists, and pharmacists are also important members of the TBI rehabilitation team.[121] After discharge from the inpatient rehabilitation treatment unit, care may be given on an outpatient basis. Community-based rehabilitation will be required for a high proportion of people, including vocational rehabilitation; this supportive employment matches job demands to the worker’s abilities.[123] People with TBI who cannot live independently or with family may require care in supported living facilities such as group homes.[123] Respite care, including day centers and leisure facilities for disabled people, offers time off for caregivers, and activities for people with TBI.[123]
Pharmacological treatment can help to manage psychiatric or behavioral problems.[124] Medication is also used to control post-traumatic epilepsy; however the preventive use of anti-epileptics is not recommended.[125] In those cases where the person is bedridden due to a reduction of consciousness, has to remain in a wheelchair because of mobility problems, or has any other problem heavily impacting self-caring capacities, caregiving and nursing are critical.
The most effective research documented intervention approach is the activation database guided EEG biofeedback approach, which has shown significant improvements in memory abilities of the TBI subject that are far superior than traditional approaches (strategies, computers, medication intervention). Gains of 2.61 standard deviations have been documented. The TBI’s auditory memory ability was superior to the control group after the treatment.[64]
Effect on the gait pattern
The Amsterdam Gait Classification facilitates the assessment of the gait pattern in patients after a traumatic brain injury. It helps to facilitate communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists.
In patients who have developed paralysis of the legs in the form of spastic hemiplegia or diplegia as a result of the traumatic brain injury, various gait patterns can be observed, the exact extent of which can only be described with the help of complex gait analysis systems. In order to facilitate interdisciplinary communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists, a simple description of the gait pattern is useful. J. Rodda and H. K. Graham already described in 2001 how gait patterns of CP patients can be more easily recognized and defined gait types which they compared in a classification. They also described that gait patterns can vary with age.[126] Building on this, the Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed at the free university in Amsterdam, the VU medisch centrum. A special feature of this classification is that it makes different gait patterns very recognizable and can be used in patients in whom only one leg and both legs are affected. The Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed for viewing patients with cerebral palsy. However, it can be used just as well in patients with traumatic brain injuries. According to the Amsterdam Gait Classification, five gait types are described. To assess the gait pattern, the patient is viewed visually or via a video recording from the side of the leg to be assessed. At the point in time at which the leg to be viewed is in mid stance and the leg not to be viewed is in mid swing, the knee angle and the contact of the foot with the ground are assessed on the one hand.[127]
Classification of the gait pattern according to the Amsterdam Gait Classification: In gait type 1, the knee angle is normal and the foot contact is complete. In gait type 2, the knee angle is hyperextended and the foot contact is complete. In gait type 3, the knee angle is hyperextended and foot contact is incomplete (only on the forefoot). In gait type 4, the knee angle is bent and foot contact is incomplete (only on the forefoot). With gait type 5, the knee angle is bent and the foot contact is complete.[127]
Gait types 5 is also known as crouch gait.
Orthotics
Ankle-foot orthosis with dynamic functional elements, whose adjustable spring resistances in plantar and dorsiflexion can be separately adapted to the patient’s gait. The orthosis is used to improve safety when standing and walking. (Designation of the orthosis according to the body parts included in the orthosis fitting: ankle and foot, English abbreviation: AFO for ankle-foot orthoses)
To improve the gait pattern, orthotics can be included in the therapy concept.[128] An Orthosis can support physiotherapeutic treatment in setting the right motor impulses in order to create new cerebral connections.[129] The orthosis must meet the requirements of the medical prescription. In addition, the orthosis must be designed by the orthotist in such a way that it achieves the effectiveness of the necessary levers, matching the gait pattern, in order to support the proprioceptive approaches of physiotherapy. The orthotic concepts of the treatment are based on the concepts for the patients with cerebral palsy. The characteristics of the stiffness of the orthosis shells and the adjustable dynamics in the ankle joint are important elements of the orthosis to be considered.[130] The orthotic concepts of the treatment are based on the concepts for the patients with cerebral palsy. Due to these requirements, the development of orthoses has changed significantly in recent years, especially since around 2010. At about the same time, care concepts were developed that deal intensively with the orthotic treatment of the lower extremities in cerebral palsy.[131] Modern materials and new functional elements enable the rigidity to be specifically adapted to the requirements that fits to the gait pattern of the patient.[132] The adjustment of the stiffness has a decisive influence on the gait pattern and on the energy cost of walking.[133][134][135] It is of great advantage if the stiffness of the orthosis can be adjusted separately from one another via resistances of the two functional elements in the two directions of movement, dorsiflexion and plantar flexion.[136]
Prognosis
Prognosis worsens with the severity of injury.[8] Most TBIs are mild and do not cause permanent or long-term disability; however, all severity levels of TBI have the potential to cause significant, long-lasting disability.[137] Permanent disability is thought to occur in 10% of mild injuries, 66% of moderate injuries, and 100% of severe injuries.[138] Most mild TBI is completely resolved within three weeks. Almost all people with mild TBI are able to live independently and return to the jobs they had before the injury, although a small portion have mild cognitive and social impairments.[86] Over 90% of people with moderate TBI are able to live independently, although some require assistance in areas such as physical abilities, employment, and financial managing.[86] Most people with severe closed head injury either die or recover enough to live independently; middle ground is less common.[9] Coma, as it is closely related to severity, is a strong predictor of poor outcome.[10]
Prognosis differs depending on the severity and location of the lesion, and access to immediate, specialised acute management. Subarachnoid hemorrhage approximately doubles mortality.[139] Subdural hematoma is associated with worse outcome and increased mortality, while people with epidural hematoma are expected to have a good outcome if they receive surgery quickly.[75] Diffuse axonal injury may be associated with coma when severe, and poor outcome.[9] Following the acute stage, prognosis is strongly influenced by the patient’s involvement in activity that promote recovery, which for most patients requires access to a specialised, intensive rehabilitation service. The Functional Independence Measure is a way to track progress and degree of independence throughout rehabilitation.[140]
Medical complications are associated with a bad prognosis. Examples of such complications include: hypotension (low blood pressure), hypoxia (low blood oxygen saturation), lower cerebral perfusion pressures, and longer times spent with high intracranial pressures.[9][75] Patient characteristics also influence prognosis. Examples of factors thought to worsen it include: abuse of substances such as illicit drugs and alcohol and age over sixty or under two years (in children, younger age at time of injury may be associated with a slower recovery of some abilities).[75] Other influences that may affect recovery include pre-injury intellectual ability, coping strategies, personality traits, family environment, social support systems and financial circumstances.[141]
Life satisfaction has been known to decrease for individuals with TBI immediately following the trauma, but evidence has shown that life roles, age, and depressive symptoms influence the trajectory of life satisfaction as time passes.[142] Many people with traumatic brain injuries have poor physical fitness following their acute injury and this may result with difficulties in day-to-day activities and increased levels of fatigue.[143]
Complications
The relative risk of post-traumatic seizures increases with the severity of traumatic brain injury.[125]
A CT of the head years after a traumatic brain injury showing an empty space where the damage occurred marked by the arrow.
Improvement of neurological function usually occurs for two or more years after the trauma. For many years it was believed that recovery was fastest during the first six months, but there is no evidence to support this. It may be related to services commonly being withdrawn after this period, rather than any physiological limitation to further progress.[9] Children recover better in the immediate time frame and improve for longer periods.[10]
Complications are distinct medical problems that may arise as a result of the TBI. The results of traumatic brain injury vary widely in type and duration; they include physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications. TBI can cause prolonged or permanent effects on consciousness, such as coma, brain death, persistent vegetative state (in which patients are unable to achieve a state of alertness to interact with their surroundings),[144] and minimally conscious state (in which patients show minimal signs of being aware of self or environment).[145][146] Lying still for long periods can cause complications including pressure sores, pneumonia or other infections, progressive multiple organ failure,[89] and deep venous thrombosis, which can cause pulmonary embolism.[22] Infections that can follow skull fractures and penetrating injuries include meningitis and abscesses.[89] Complications involving the blood vessels include vasospasm, in which vessels constrict and restrict blood flow, the formation of aneurysms, in which the side of a vessel weakens and balloons out, and stroke.[89]
Movement disorders that may develop after TBI include tremor, ataxia (uncoordinated muscle movements), spasticity (muscle contractions are overactive), myoclonus (shock-like contractions of muscles), and loss of movement range and control (in particular with a loss of movement repertoire).[89][147] The risk of post-traumatic seizures increases with severity of trauma (image at right) and is particularly elevated with certain types of brain trauma such as cerebral contusions or hematomas.[138] People with early seizures, those occurring within a week of injury, have an increased risk of post-traumatic epilepsy (recurrent seizures occurring more than a week after the initial trauma).[148] People may lose or experience altered vision, hearing, or smell.[10]
Hormonal disturbances may occur secondary to hypopituitarism, occurring immediately or years after injury in 10 to 15% of TBI patients. Development of diabetes insipidus or an electrolyte abnormality acutely after injury indicate need for endocrinologic work up. Signs and symptoms of hypopituitarism may develop and be screened for in adults with moderate TBI and in mild TBI with imaging abnormalities. Children with moderate to severe head injury may also develop hypopituitarism. Screening should take place 3 to 6 months, and 12 months after injury, but problems may occur more remotely.[149]
Cognitive deficits that can follow TBI include impaired attention; disrupted insight, judgement, and thought; reduced processing speed; distractibility; and deficits in executive functions such as abstract reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and multitasking.[150] Memory loss, the most common cognitive impairment among head-injured people, occurs in 20–79% of people with closed head trauma, depending on severity.[151] People who have had TBI may also have difficulty with understanding or producing spoken or written language, or with more subtle aspects of communication such as body language.[89] Post-concussion syndrome, a set of lasting symptoms experienced after mild TBI, can include physical, cognitive, emotional and behavioral problems such as headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, and depression.[10] Multiple TBIs may have a cumulative effect.[146] A young person who receives a second concussion before symptoms from another one have healed may be at risk for developing a very rare but deadly condition called second-impact syndrome, in which the brain swells catastrophically after even a mild blow, with debilitating or deadly results. About one in five career boxers is affected by chronic traumatic brain injury (CTBI), which causes cognitive, behavioral, and physical impairments.[152] Dementia pugilistica, the severe form of CTBI, affects primarily career boxers years after a boxing career. It commonly manifests as dementia, memory problems, and parkinsonism (tremors and lack of coordination).[153]
TBI may cause emotional, social, or behavioral problems and changes in personality.[154][155][156][157] These may include emotional instability, depression, anxiety, hypomania, mania, apathy, irritability, problems with social judgment, and impaired conversational skills.[154][157][158][159] TBI appears to predispose survivors to psychiatric disorders including obsessive compulsive disorder, substance abuse, dysthymia, clinical depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorders.[160] In patients who have depression after TBI, suicidal ideation is not uncommon; the suicide rate among these persons is increased 2- to 3-fold.[161] Social and behavioral symptoms that can follow TBI include disinhibition, inability to control anger, impulsiveness, lack of initiative, inappropriate sexual activity, asociality and social withdrawal, and changes in personality.[154][156][157][162]
TBI also has a substantial impact on the functioning of family systems[163] Caregiving family members and TBI survivors often significantly alter their familial roles and responsibilities following injury, creating significant change and strain on a family system. Typical challenges identified by families recovering from TBI include: frustration and impatience with one another, loss of former lives and relationships, difficulty setting reasonable goals, inability to effectively solve problems as a family, increased level of stress and household tension, changes in emotional dynamics, and overwhelming desire to return to pre-injury status. In addition, families may exhibit less effective functioning in areas including coping, problem solving and communication. Psychoeducation and counseling models have been demonstrated to be effective in minimizing family disruption.[164]
Epidemiology
Causes of TBI fatalities in the US[165]
TBI is a leading cause of death and disability around the globe[7] and presents a major worldwide social, economic, and health problem.[9] It is the number one cause of coma,[166] it plays the leading role in disability due to trauma,[75] and is the leading cause of brain damage in children and young adults.[14] In Europe it is responsible for more years of disability than any other cause.[9] It also plays a significant role in half of trauma deaths.[22]
Findings on the frequency of each level of severity vary based on the definitions and methods used in studies. A World Health Organization study estimated that between 70 and 90% of head injuries that receive treatment are mild,[167] and a US study found that moderate and severe injuries each account for 10% of TBIs, with the rest mild.[71]
The incidence of TBI varies by age, gender, region and other factors.[168] Findings of incidence and prevalence in epidemiological studies vary based on such factors as which grades of severity are included, whether deaths are included, whether the study is restricted to hospitalized people, and the study’s location.[14] The annual incidence of mild TBI is difficult to determine but may be 100–600 people per 100,000.[62]
Mortality
In the US, the case fatality rate is estimated to be 21% by 30 days after TBI.[91] A study on Iraq War soldiers found that severe TBI carries a mortality of 30–50%.[62] Deaths have declined due to improved treatments and systems for managing trauma in societies wealthy enough to provide modern emergency and neurosurgical services.[113] The fraction of those who die after being hospitalized with TBI fell from almost half in the 1970s to about a quarter at the beginning of the 21st century.[75] This decline in mortality has led to a concomitant increase in the number of people living with disabilities that result from TBI.[169]
Biological, clinical, and demographic factors contribute to the likelihood that an injury will be fatal.[165] In addition, outcome depends heavily on the cause of head injury. In the US, patients with fall-related TBIs have an 89% survival rate, while only 9% of patients with firearm-related TBIs survive.[170] In the US, firearms are the most common cause of fatal TBI, followed by vehicle accidents and then falls.[165] Of deaths from firearms, 75% are considered to be suicides.[165]
The incidence of TBI is increasing globally, due largely to an increase in motor vehicle use in low- and middle-income countries.[9] In developing countries, automobile use has increased faster than safety infrastructure could be introduced.[62] In contrast, vehicle safety laws have decreased rates of TBI in high-income countries,[9] which have seen decreases in traffic-related TBI since the 1970s.[54] Each year in the United States, about two million people have a TBI,[20] approximately 675,000 injuries are seen in the emergency department,[171] and about 500,000 patients are hospitalized.[168] The yearly incidence of TBI is estimated at 180–250 per 100,000 people in the US,[168] 281 per 100,000 in France, 361 per 100,000 in South Africa, 322 per 100,000 in Australia,[14] and 430 per 100,000 in England.[60] In the European Union the yearly aggregate incidence of TBI hospitalizations and fatalities is estimated at 235 per 100,000.[9]
Demographics
TBI is present in 85% of traumatically injured children, either alone or with other injuries.[172] The greatest number of TBIs occur in people aged 15–24.[12][37] Because TBI is more common in young people, its costs to society are high due to the loss of productive years to death and disability.[9] The age groups most at risk for TBI are children ages five to nine and adults over age 80,[8] and the highest rates of death and hospitalization due to TBI are in people over age 65.[137] The incidence of fall-related TBI in First-World countries is increasing as the population ages; thus the median age of people with head injuries has increased.[9]
Regardless of age, TBI rates are higher in males.[37] Men have twice as many TBIs as women do and have a fourfold risk of fatal head injury,[8] and males account for two thirds of childhood and adolescent head trauma.[173] However, when matched for severity of injury, women appear to fare more poorly than men.[92]
Socioeconomic status also appears to affect TBI rates; people with lower levels of education and employment and lower socioeconomic status are at greater risk.[14] Approximately half of those incarcerated in prisons and jails in the United States have had TBIs.[174]
History
Head injury is present in ancient myths that may date back before recorded history.[175] Skulls found in battleground graves with holes drilled over fracture lines suggest that trepanation may have been used to treat TBI in ancient times.[176] Ancient Mesopotamians knew of head injury and some of its effects, including seizures, paralysis, and loss of sight, hearing or speech.[177] The Edwin Smith Papyrus, written around 1650–1550 BC, describes various head injuries and symptoms and classifies them based on their presentation and tractability.[178] Ancient Greek physicians including Hippocrates understood the brain to be the center of thought, probably due to their experience observing the effects of head trauma.[179]
Medieval and Renaissance surgeons continued the practice of trepanation for head injury.[179] In the Middle Ages, physicians further described head injury symptoms and the term concussion became more widespread.[180] Concussion symptoms were first described systematically in the 16th century by Berengario da Carpi.[179]
It was first suggested in the 18th century that intracranial pressure rather than skull damage was the cause of pathology after TBI. This hypothesis was confirmed around the end of the 19th century, and opening the skull to relieve pressure was then proposed as a treatment.[176]
In the 19th century it was noted that TBI is related to the development of psychosis.[181] At that time a debate arose around whether post-concussion syndrome was due to a disturbance of the brain tissue or psychological factors.[180] The debate continues today.
Phineas Gage with the tamping iron that entered his left cheek and emerged at the top of his head
Perhaps the first reported case of personality change after brain injury is that of Phineas Gage, who survived an accident in which a large iron rod was driven through his head, destroying one or both of his frontal lobes; numerous cases of personality change after brain injury have been reported since.[31][33][34][43][44][48][182][183]
The 20th century saw the advancement of technologies that improved treatment and diagnosis such as the development of imaging tools including CT and MRI, and, in the 21st century, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). The introduction of intracranial pressure monitoring in the 1950s has been credited with beginning the «modern era» of head injury.[113][184] Until the 20th century, the mortality rate of TBI was high and rehabilitation was uncommon; improvements in care made during World War I reduced the death rate and made rehabilitation possible.[175] Facilities dedicated to TBI rehabilitation were probably first established during World War I.[175] Explosives used in World War I caused many blast injuries; the large number of TBIs that resulted allowed researchers to learn about localization of brain functions.[185] Blast-related injuries are now common problems in returning veterans from Iraq & Afghanistan; research shows that the symptoms of such TBIs are largely the same as those of TBIs involving a physical blow to the head.[186]
In the 1970s, awareness of TBI as a public health problem grew,[187] and a great deal of progress has been made since then in brain trauma research,[113] such as the discovery of primary and secondary brain injury.[176] The 1990s saw the development and dissemination of standardized guidelines for treatment of TBI, with protocols for a range of issues such as drugs and management of intracranial pressure.[113] Research since the early 1990s has improved TBI survival;[176] that decade was known as the «Decade of the Brain» for advances made in brain research.[188]
Research directions
Diagnosis
Quantitative EEG and EEG, which has no specific patterns in TBI is used in research settings to differentiate between mild TBI and no TBI.[189]
Medications
No medication is approved to halt the progression of the initial injury to secondary injury.[62] The variety of pathological events presents opportunities to find treatments that interfere with the damage processes.[9] Neuroprotection methods to decrease secondary injury, have been the subject of interest follows TBI. However, trials to test agents that could halt these cellular mechanisms have met largely with failure.[9] For example, interest existed in cooling the injured brain; however, a 2020 Cochrane review did not find enough evidence to see if it was useful or not.[190] Maintaining a normal temperature in the immediate period after a TBI appeared useful.[191] One review found a lower than normal temperature was useful in adults but not children.[192] While two other reviews found it did not appear to be useful.[193][191]
Further research is necessary to determine if the vasoconstrictor indomethacin (indometacin) can be used to treat increased pressure in the skull following a TBI.[194]
In addition, drugs such as NMDA receptor antagonists to halt neurochemical cascades such as excitotoxicity showed promise in animal trials but failed in clinical trials.[113] These failures could be due to factors including faults in the trials’ design or in the insufficiency of a single agent to prevent the array of injury processes involved in secondary injury.[113]
Other topics of research have included investigations into mannitol,[100] dexamethasone,[195] progesterone,[196] xenon,[197] barbiturates,[198] magnesium (no strong evidence),[199][200] calcium channel blockers,[201] PPAR-γ agonists,[202][203] curcuminoids,[204] ethanol,[205] NMDA antagonists,[113] caffeine.[206]
Procedures
In addition to traditional imaging modalities, there are several devices that help to monitor brain injury and facilitate research. Microdialysis allows ongoing sampling of extracellular fluid for analysis of metabolites that might indicate ischemia or brain metabolism, such as glucose, glycerol, and glutamate.[207][208] Intraparenchymal brain tissue oxygen monitoring systems (either Licox or Neurovent-PTO) are used routinely in neurointensive care in the US.[209] A non invasive model called CerOx is in development.[210]
Research is also planned to clarify factors correlated to outcome in TBI and to determine in which cases it is best to perform CT scans and surgical procedures.[211]
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO) has been evaluated as an add on treatment following TBI. The findings of a 2012 Cochrane systematic review does not justify the routine use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat people recovering from a traumatic brain injury.[212] This review also reported that only a small number of randomized controlled trials had been conducted at the time of the review, many of which had methodological problems and poor reporting.[212] HBO for TBI is controversial with further evidence required to determine if it has a role.[213][212]
Psychological
Further research is required to determine the effectiveness of non-pharmacological treatment approaches for treating depression in children/adolescents and adults with TBI.[214]
As of 2010, the use of predictive visual tracking measurement to identify mild traumatic brain injury was being studied. In visual tracking tests, a head-mounted display unit with eye-tracking capability shows an object moving in a regular pattern. People without brain injury are able to track the moving object with smooth pursuit eye movements and correct trajectory. The test requires both attention and working memory which are difficult functions for people with mild traumatic brain injury. The question being studied, is whether results for people with brain injury will show visual-tracking gaze errors relative to the moving target.[215]
Monitoring pressure
Pressure reactivity index is used to correlate intracranial pressure with arterial blood pressure to give information about the state of cerebral perfusion, thus guiding treatment and prevent excessively high or low blood flow to the brain.[216] However, such method of monitoring intracranial pressure of equal or less than 20 mmHg is no better than imaging and clinical examination that monitor the neurological status of the brain in prolonging the survival, preserving the mental or functional status of the subject.[217]
Sensory processing
In animal models of TBI, sensory processing has been widely studied to show systematic defects arise and are slowly but likely only partially recovered.[218] It is especially characterised by an initial period of decreased activity in upper cortical layers.[219][220] This period of decreased activity has also been characterised as by specific timing effects in the patterns of cortical activity in these upper layers in response to regular sensory stimuli.[221]
References
- ^ Jones DK (2010). Diffusion MRI. Oxford University Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-19-970870-3.
- ^ a b Rehman T, Ali R, Tawil I, Yonas H (October 2008). «Rapid progression of traumatic bifrontal contusions to transtentorial herniation: A case report». Cases Journal. 1 (1): 203. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-203. PMC 2566562. PMID 18831756.
- ^ a b c «TBI: Get the Facts». CDC. March 11, 2019. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ «Traumatic Brain Injury». medlineplus.gov. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ «Basic Information about Traumatic Brain Injury | Concussion | Traumatic Brain Injury | CDC Injury Center». www.cdc.gov. March 6, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- ^ «Prevention». CDC. March 4, 2019. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ a b Alves OL, Bullock R (2001). «Excitotoxic damage in traumatic brain injury». In Clark RS, Kochanek P (eds.). Brain injury. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-7923-7532-6.
- ^ a b c d Rao V, Lyketsos C (2000). «Neuropsychiatric sequelae of traumatic brain injury». Psychosomatics. 41 (2): 95–103. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.41.2.95. PMID 10749946.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (August 2008). «Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults». The Lancet. Neurology. 7 (8): 728–741. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70164-9. PMID 18635021. S2CID 14071224.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Parikh S, Koch M, Narayan RK (2007). «Traumatic brain injury». International Anesthesiology Clinics. 45 (3): 119–135. doi:10.1097/AIA.0b013e318078cfe7. PMID 17622833. S2CID 46012183.
- ^ Chapman SB, Levin HS, Lawyer SL (1999). «Communication problems resulting from brain injury in children: Special issues of assessment and management». In McDonald S, Togher L, Code C (eds.). Communication Disorders Following Traumatic Brain Injury. East Sussex: Psychology Press. pp. 235–36. ISBN 978-0-86377-724-0.
- ^ a b Collins C, Dean J (2002). «Acquired brain injury». In Turner A, Foster M, Johnson SE (eds.). Occupational Therapy and Physical Dysfunction: Principles, Skills and Practice. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 395–96. ISBN 978-0-443-06224-7.
- ^ a b Blissitt PA (September 2006). «Care of the critically ill patient with penetrating head injury». Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America. 18 (3): 321–332. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2006.05.006. PMID 16962454.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Hannay HJ, Howieson DB, Loring DW, Fischer JS, Lezak MD (2004). «Neuropathology for neuropsychologists». In Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW (eds.). Neuropsychological Assessment. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 158–62. ISBN 978-0-19-511121-7.
- ^ a b c Jennett B (May 1998). «Epidemiology of head injury». Archives of Disease in Childhood. 78 (5): 403–406. doi:10.1136/adc.78.5.403. PMC 1717568. PMID 9659083.
- ^ McCaffrey RJ (1997). «Special issues in the evaluation of mild traumatic brain injury». The Practice of Forensic Neuropsychology: Meeting Challenges in the Courtroom. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 71–75. ISBN 978-0-306-45256-7.
- ^ a b LaPlaca et al. (2007). p. 16
- ^ Weber JT, Maas AI (2007). Weber JT (ed.). Neurotrauma: New Insights Into Pathology and Treatment. Amsterdam: Academic Press. p. xi. ISBN 978-0-444-53017-2.
- ^ a b c d Saatman KE, Duhaime AC, Bullock R, Maas AI, Valadka A, Manley GT (July 2008). «Classification of traumatic brain injury for targeted therapies». Journal of Neurotrauma. 25 (7): 719–738. doi:10.1089/neu.2008.0586. PMC 2721779. PMID 18627252.
- ^ a b c Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs (2008). «DoD/VA CODE PROPOSAL FINAL—508 COMPLIANT» (PDF).
- ^ Marion (1999). p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Valadka AB (2004). «Injury to the cranium». In Moore EJ, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (eds.). Trauma. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. pp. 385–406. ISBN 978-0-07-137069-1.
- ^ Hayden MG, Jandial R, Duenas HA, Mahajan R, Levy M (April 2007). «Pediatric concussions in sports; a simple and rapid assessment tool for concussive injury in children and adults». Child’s Nervous System. 23 (4): 431–435. doi:10.1007/s00381-006-0277-2. PMID 17219233. S2CID 33259313.
- ^ Seidenwurm DI (2007). «Introduction to brain imaging». In Brant WE, Helms CA (eds.). Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. pp. 53–55. ISBN 978-0-7817-6135-2.
- ^ a b c Smith DH, Meaney DF, Shull WH (2003). «Diffuse axonal injury in head trauma». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 18 (4): 307–316. doi:10.1097/00001199-200307000-00003. PMID 16222127. S2CID 1527912.
- ^ Granacher (2007). p. 32.
- ^ Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP, Walker CJ, Sweeney JA, Little DM (October 2007). «White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study». Brain. 130 (Pt 10): 2508–2519. doi:10.1093/brain/awm216. PMID 17872928.
- ^ Kumar R, Husain M, Gupta RK, Hasan KM, Haris M, Agarwal AK, et al. (April 2009). «Serial changes in the white matter diffusion tensor imaging metrics in moderate traumatic brain injury and correlation with neuro-cognitive function». Journal of Neurotrauma. 26 (4): 481–495. doi:10.1089/neu.2008.0461. PMID 19196176.
- ^ Melvin JW, Lighthall JW (2002). Nahum AM, Melvin JW (eds.). Accidental Injury: Biomechanics and Prevention. Berlin: Springer. pp. 280–81. ISBN 978-0-387-98820-7.
brain injury biomechanics
- ^ McCrea M (2007). Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Postconcussion Syndrome: The New Evidence Base for Diagnosis and Treatment. American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology Workshop Series. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-532829-5.
- ^ a b c Mattson AJ, Levin HS (May 1990). «Frontal lobe dysfunction following closed head injury. A review of the literature». The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease. 178 (5): 282–291. doi:10.1097/00005053-199005000-00002. PMID 2187053. S2CID 27836314.
- ^ Bayly PV, Cohen TS, Leister EP, Ajo D, Leuthardt EC, Genin GM (August 2005). «Deformation of the human brain induced by mild acceleration». Journal of Neurotrauma. 22 (8): 845–856. doi:10.1089/neu.2005.22.845. PMC 2377024. PMID 16083352.
- ^ a b Cummings JL (August 1993). «Frontal-subcortical circuits and human behavior». Archives of Neurology. 50 (8): 873–880. doi:10.1001/archneur.1993.00540080076020. PMID 8352676.
- ^ a b c McDonald S, Flanagan S, Rollins J, Kinch J (2003). «TASIT: A new clinical tool for assessing social perception after traumatic brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 18 (3): 219–238. doi:10.1097/00001199-200305000-00001. PMID 12802165. S2CID 22361889.
- ^ Basso A, Scarpa MT (December 1990). «Traumatic aphasia in children and adults: a comparison of clinical features and evolution». Cortex; A Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior. 26 (4): 501–514. doi:10.1016/s0010-9452(13)80300-0. PMID 1706973. S2CID 4477808.
- ^ Mohr JP, Weiss GH, Caveness WF, Dillon JD, Kistler JP, Meirowsky AM, Rish BL (December 1980). «Language and motor disorders after penetrating head injury in Viet Nam». Neurology. 30 (12): 1273–1279. doi:10.1212/wnl.30.12.1273. PMID 7192808. S2CID 25106246.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Hardman JM, Manoukian A (May 2002). «Pathology of head trauma». Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. 12 (2): 175–87, vii. doi:10.1016/S1052-5149(02)00009-6. PMID 12391630.
TBI is highest in young adults aged 15 to 24 years and higher in men than women in all age groups.
- ^ a b Barkley JM, Morales D, Hayman LA, Diaz-Marchan PJ (2006). «Static neuroimaging in the evaluation of TBI». In Zasler ND, Katz DI, Zafonte RD (eds.). Brain Injury Medicine: Principles and Practice. Demos Medical Publishing. pp. 140–43. ISBN 978-1-888799-93-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Ghajar J (September 2000). «Traumatic brain injury». Lancet. 356 (9233): 923–929. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02689-1. PMID 11036909. S2CID 45288155.
- ^ Arlinghaus KA, Shoaib AM, Price TR (2005). «Neuropsychiatric assessment». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. pp. 63–65. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ a b c d e «NINDS Traumatic Brain Injury Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. September 15, 2008. Archived from the original on December 3, 2016. Retrieved October 27, 2008.
- ^ a b Kushner D (1998). «Mild traumatic brain injury: toward understanding manifestations and treatment». Archives of Internal Medicine. 158 (15): 1617–1624. doi:10.1001/archinte.158.15.1617. PMID 9701095.
- ^ a b Stone VE, Baron-Cohen S, Knight RT (September 1998). «Frontal lobe contributions to theory of mind». Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 10 (5): 640–656. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.330.1488. doi:10.1162/089892998562942. PMID 9802997. S2CID 207724498.
- ^ a b Kim E (2002). «Agitation, aggression, and disinhibition syndromes after traumatic brain injury». NeuroRehabilitation. 17 (4): 297–310. doi:10.3233/NRE-2002-17404. PMID 12547978.
- ^ Busch RM, McBride A, Curtiss G, Vanderploeg RD (November 2005). «The components of executive functioning in traumatic brain injury». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 27 (8): 1022–1032. doi:10.1080/13803390490919263. PMID 16207623. S2CID 8840941.
- ^ a b Ponsford J, Draper K, Schönberger M (March 2008). «Functional outcome 10 years after traumatic brain injury: its relationship with demographic, injury severity, and cognitive and emotional status». Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 14 (2): 233–242. doi:10.1017/S1355617708080272. PMID 18282321.
- ^ Williams C, Wood RL (March 2010). «Alexithymia and emotional empathy following traumatic brain injury». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 32 (3): 259–267. doi:10.1080/13803390902976940. PMID 19548166. S2CID 34126700.
- ^ a b Milders M, Fuchs S, Crawford JR (April 2003). «Neuropsychological impairments and changes in emotional and social behaviour following severe traumatic brain injury». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 25 (2): 157–172. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.510.871. doi:10.1076/jcen.25.2.157.13642. PMID 12754675. S2CID 2264964.
- ^ Ownsworth T, Fleming J (2005). «The relative importance of metacognitive skills, emotional status, and executive function in psychosocial adjustment following acquired brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 20 (4): 315–332. doi:10.1097/00001199-200507000-00004. PMID 16030439. S2CID 41271134.
- ^ Dahlberg CA, Cusick CP, Hawley LA, Newman JK, Morey CE, Harrison-Felix CL, Whiteneck GG (December 2007). «Treatment efficacy of social communication skills training after traumatic brain injury: a randomized treatment and deferred treatment controlled trial». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 88 (12): 1561–1573. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.033. PMID 18047870.
- ^ a b c d e f g Salomone JP, Frame SB (2004). «Prehospital care». In Moore EJ, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (eds.). Trauma. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. pp. 117–18. ISBN 978-0-07-137069-1.
- ^ a b «Signs and Symptoms». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. July 7, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2008.
- ^ Faul M, Xu L, Wald MM, Coronado VG (2010). «Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths, 2002–2006». National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved October 22, 2013.
- ^ a b Reilly P (2007). «The impact of neurotrauma on society: An international perspective». In Weber JT (ed.). Neurotrauma: New Insights Into Pathology and Treatment. Amsterdam: Academic Press. pp. 5–7. ISBN 978-0-444-53017-2.
- ^ a b c d «Traumatic brain injury». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. 2007. Retrieved October 28, 2008.
- ^ Granacher (2007). p. 16.
- ^ Hunt JP, Weintraub SL, Wang YZ, Buetcher KJ (2004). «Kinematics of trauma». In Moore EJ, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (eds.). Trauma. New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. p. 153. ISBN 978-0-07-137069-1.
- ^ a b Elovic E, Zafonte R (2005). «Prevention». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. p. 740. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ Bay E, McLean SA (February 2007). «Mild traumatic brain injury: an update for advanced practice nurses». The Journal of Neuroscience Nursing. 39 (1): 43–51. doi:10.1097/01376517-200702000-00009. PMID 17396538. S2CID 44600297.
- ^ a b Comper P, Bisschop SM, Carnide N, Tricco A (October 2005). «A systematic review of treatments for mild traumatic brain injury». Brain Injury. 19 (11): 863–880. doi:10.1080/02699050400025042. PMID 16296570. S2CID 34912966.
- ^ Champion HR, Holcomb JB, Young LA (May 2009). «Injuries from explosions: physics, biophysics, pathology, and required research focus». The Journal of Trauma. 66 (5): 1468–77, discussion 1477. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a27e7f. PMID 19430256. Archived from the original on September 23, 2017. Retrieved May 16, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Park E, Bell JD, Baker AJ (April 2008). «Traumatic brain injury: can the consequences be stopped?». CMAJ. 178 (9): 1163–1170. doi:10.1503/cmaj.080282. PMC 2292762. PMID 18427091.
- ^ «Pentagon Told Congress It’s Studying Brain-Damage Therapy». ProPublica. December 23, 2010. Retrieved January 23, 2011.
Brave Americans who risked everything for their country and sustained traumatic brain injuries – the signature injury of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan – deserve cognitive rehabilitation therapy to help them secure the best futures possible. It is unacceptable that the United States has been at war for nearly a decade and there is still no plan to treat these soldiers.
- ^ a b Thornton KE, Carmody DP (June 2008). «Efficacy of traumatic brain injury rehabilitation: interventions of QEEG-guided biofeedback, computers, strategies, and medications». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 33 (2): 101–24. doi:10.1007/s10484-008-9056-z. PMID 18551365. S2CID 7262160.
- ^ Thornton KE, Carmody DP (March 2009). «Traumatic brain injury rehabilitation: QEEG biofeedback treatment protocols». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 34 (1): 59–68. doi:10.1007/s10484-009-9075-4. PMID 19199027. S2CID 7928780.
- ^ a b Shaw NA (July 2002). «The neurophysiology of concussion». Progress in Neurobiology. 67 (4): 281–344. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(02)00018-7. PMID 12207973. S2CID 46514293.
- ^ American Academy of Pediatrics: Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect (July 2001). «Shaken baby syndrome: rotational cranial injuries-technical report». Pediatrics. 108 (1): 206–210. doi:10.1542/peds.108.1.206. PMID 11433079.
- ^ Morrison AL, King TM, Korell MA, Smialek JE, Troncoso JC (June 1998). «Acceleration-deceleration injuries to the brain in blunt force trauma». The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 19 (2): 109–112. doi:10.1097/00000433-199806000-00002. PMID 9662103.
- ^ Poirier MP (2003). «Concussions: Assessment, management, and recommendations for return to activity». Clinical Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 4 (3): 179–85. doi:10.1016/S1522-8401(03)00061-2.
- ^ Sauaia A, Moore FA, Moore EE, Moser KS, Brennan R, Read RA, Pons PT (February 1995). «Epidemiology of trauma deaths: a reassessment». The Journal of Trauma. 38 (2): 185–193. doi:10.1097/00005373-199502000-00006. PMID 7869433.
- ^ a b Narayan RK, Michel ME, Ansell B, Baethmann A, Biegon A, Bracken MB, et al. (May 2002). «Clinical trials in head injury». Journal of Neurotrauma. 19 (5): 503–557. doi:10.1089/089771502753754037. PMC 1462953. PMID 12042091.
- ^ Xiong Y, Lee CP, Peterson PL (2000). «Mitochondrial dysfunction following traumatic brain injury». In Miller LP, Hayes RL, Newcomb JK (eds.). Head Trauma: Basic, Preclinical, and Clinical Directions. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. pp. 257–80. ISBN 978-0-471-36015-5.
- ^ Scalea TM (2005). «Does it matter how head injured patients are resuscitated?». In Valadka AB, Andrews BT (eds.). Neurotrauma: Evidence-based Answers to Common Questions. Thieme. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-3-13-130781-1.
- ^ Morley EJ, Zehtabchi S (September 2008). «Evidence-based emergency medicine/systematic review abstract. Mannitol for traumatic brain injury: searching for the evidence». Annals of Emergency Medicine. 52 (3): 298–300. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2007.10.013. PMID 18763356.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Zink BJ (March 2001). «Traumatic brain injury outcome: concepts for emergency care». Annals of Emergency Medicine. 37 (3): 318–332. doi:10.1067/mem.2001.113505. PMID 11223769.
- ^ Wortzel HS, Arciniegas DB (January 1, 2014). «The DSM-5 approach to the evaluation of traumatic brain injury and its neuropsychiatric sequelae». NeuroRehabilitation. 34 (4): 613–623. doi:10.3233/NRE-141086. PMID 24820171.
- ^ Simpson JR (June 1, 2014). «DSM-5 and neurocognitive disorders». The Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law. 42 (2): 159–164. PMID 24986342.
- ^ «The DSM-5 Approach to Evaluating Traumatic Brain Injury». www.hsrd.research.va.gov. Retrieved November 5, 2019.
- ^ a b Barr RM, Gean AD, Le TH (2007). «Craniofacial trauma». In Brant WE, Helms CA (eds.). Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-7817-6135-2.
- ^ «University Times ‘ Research Notes». University of Pittsburgh. March 22, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2013.
- ^ Coles JP (July 2007). «Imaging after brain injury». British Journal of Anaesthesia. 99 (1): 49–60. doi:10.1093/bja/aem141. PMID 17573394.
- ^ From Flight magazine (1912), as described by Grothe S (March 26, 2016). «Mit dem Kopf durch die Wand (With the Head Through the Wall)». Der Spiegel (in German). Archived from the original on May 23, 2018.
- ^ Liu BC, Ivers R, Norton R, Boufous S, Blows S, Lo SK (January 2008). Liu BC (ed.). «Helmets for preventing injury in motorcycle riders». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (1): CD004333. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004333.pub3. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30009360. PMID 18254047.
- ^ McCrory PR (August 2003). «Brain injury and heading in soccer». BMJ. 327 (7411): 351–352. doi:10.1136/bmj.327.7411.351. PMC 1126775. PMID 12919964.
- ^ a b McIntosh AS, McCrory P (June 2005). «Preventing head and neck injury». British Journal of Sports Medicine. 39 (6): 314–318. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2005.018200. PMC 1725244. PMID 15911597.
- ^ a b c Crooks CY, Zumsteg JM, Bell KR (November 2007). «Traumatic brain injury: a review of practice management and recent advances». Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America. 18 (4): 681–710, vi. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2007.06.005. PMID 17967360.
- ^ Hahn RA, Bilukha O, Crosby A, Fullilove MT, Liberman A, Moscicki E, et al. (February 2005). «Firearms laws and the reduction of violence: a systematic review». American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 28 (2 Suppl 1): 40–71. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2004.10.005. PMID 15698747.
- ^ Kluger, Jeffrey. «Dealing with Brain Injuries. Time Magazine, April 6, 2009, p. 57. Online: [1]. Accessed: May 1, 2009
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Office of Communications and Public Liaison (February 2002). «Traumatic brain injury: Hope through research». NIH Publication No. 02-2478. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on December 18, 2016. Retrieved August 17, 2008.
Many patients with mild to moderate head injuries who experience cognitive deficits become easily confused or distracted and have problems with concentration and attention. They also have problems with higher level, so-called executive functions, such as planning, organizing, abstract reasoning, problem solving, and making judgments, which may make it difficult to resume pre-injury work-related activities. Recovery from cognitive deficits is greatest within the first 6 months after the injury and more gradual after that.
- ^ Kawada T (2020). «Efficacy of tranexamic acid in patients with traumatic brain injury». EXCLI Journal. 19: 1547–1548. doi:10.17179/excli2020-3161. PMC 7744966. PMID 33343272.
- ^ a b Greenwald BD, Burnett DM, Miller MA (March 2003). «Congenital and acquired brain injury. 1. Brain injury: epidemiology and pathophysiology». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 84 (3 Suppl 1): S3–S7. doi:10.1053/apmr.2003.50052. PMID 12708551.
- ^ a b Moppett IK (July 2007). «Traumatic brain injury: assessment, resuscitation and early management». British Journal of Anaesthesia. 99 (1): 18–31. doi:10.1093/bja/aem128. PMID 17545555. Moppet07
- ^ Wang F, Wang Y, Sun T, Yu HL (May 2016). «Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis». Neurological Sciences. 37 (5): 693–701. doi:10.1007/s10072-015-2460-2. PMID 26746238. S2CID 10548255.
- ^ Alarcon JD, Rubiano AM, Okonkwo DO, Alarcón J, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Urrútia G, Bonfill Cosp X (December 2017). «Elevation of the head during intensive care management in people with severe traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (12): CD009986. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009986.pub2. PMC 6486002. PMID 29283434.
- ^ Gruen P (May 2002). «Surgical management of head trauma». Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. 12 (2): 339–343. doi:10.1016/S1052-5149(02)00013-8. PMID 12391640.
- ^ a b c d Gultekin R, Huang S, Clavisi O, Pattuwage L, König TC, Gruen R (March 2016). «Pharmacological interventions in traumatic brain injury: Can we rely on systematic reviews for evidence?». Injury. 47 (3): 516–524. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.10.011. PMID 26589595.
- ^ a b Burgess S, Abu-Laban RB, Slavik RS, Vu EN, Zed PJ (April 2016). «A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Comparing Hypertonic Sodium Solutions and Mannitol for Traumatic Brain Injury: Implications for Emergency Department Management». The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 50 (4): 291–300. doi:10.1177/1060028016628893. PMID 26825644. S2CID 23859003.
- ^ Mathur A, Duke T, Kukuruzovic R, South M (2004). «Hypotonic vs isotonic saline solutions for intravenous fluid management of acute infections». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003 (2): CD004169. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004169.pub2. PMC 6986696. PMID 15106241.
- ^ Rickard AC, Smith JE, Newell P, Bailey A, Kehoe A, Mann C (August 2014). «Salt or sugar for your injured brain? A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of mannitol versus hypertonic sodium solutions to manage raised intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury». Emergency Medicine Journal. 31 (8): 679–683. doi:10.1136/emermed-2013-202679. hdl:10026.1/4537. PMID 23811861. S2CID 24947684.
- ^ a b Wakai A, McCabe A, Roberts I, Schierhout G (August 2013). «Mannitol for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 8 (8): CD001049. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001049.pub5. PMC 7050611. PMID 23918314.
- ^ Chen H, Song Z, Dennis JA (January 2020). «Hypertonic saline versus other intracranial pressure-lowering agents for people with acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD010904. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010904.pub3. PMC 6984412. PMID 31978260.
- ^ Roberts I, Smith R, Evans S (February 2007). «Doubts over head injury studies». BMJ. 334 (7590): 392–394. doi:10.1136/bmj.39118.480023.BE. PMC 1804156. PMID 17322250.
- ^ «Guidelines for the Acute Medical Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants, Children, and Adolescents-Second Edition:». Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 13: S1–S2. January 2012. doi:10.1097/PCC.0b013e31823f435c. ISSN 1529-7535.
- ^ Schierhout G, Roberts I (2000). «Hyperventilation therapy for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1997 (2): CD000566. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000566. PMC 7061354. PMID 10796728.
- ^ Curry R, Hollingworth W, Ellenbogen RG, Vavilala MS (March 2008). «Incidence of hypo- and hypercarbia in severe traumatic brain injury before and after 2003 pediatric guidelines». Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 9 (2): 141–146. doi:10.1097/PCC.0B013e318166870e. PMID 18477926. S2CID 9927553.
- ^ Alderson P, Roberts I (January 2005). «Corticosteroids for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2005 (1): CD000196. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000196.pub2. PMC 7043302. PMID 15674869.
- ^ Campbell J (2018). International Trauma Life Support for Emergency Care Providers (8th Global ed.). Pearson. p. 221. ISBN 978-1292-17084-8.
- ^ Roberts I (2000). «Aminosteroids for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (4): CD001527. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001527. PMC 8406780. PMID 11034722.
- ^ Ker K, Blackhall K (January 2008). «Beta-2 receptor antagonists for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2008 (1): CD006686. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006686.pub2. PMC 7387850. PMID 18254109.
- ^ Willis C, Lybrand S, Bellamy N (2004). «Excitatory amino acid inhibitors for traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003 (1): CD003986. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003986.pub2. PMC 6984678. PMID 14974051.
- ^ Forsyth RJ, Jayamoni B, Paine TC (October 2006). «Monoaminergic agonists for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD003984. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003984.pub2. PMID 17054192.
- ^ Tasker RC (2008). «Head and spinal cord trauma». In Nichols DG (ed.). Roger’s Textbook of Pediatric Intensive Care (4th ed.). PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 887–911. ISBN 978-0-7817-8275-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Marshall LF (September 2000). «Head injury: recent past, present, and future». Neurosurgery. 47 (3): 546–561. doi:10.1097/00006123-200009000-00002. PMID 10981741.
- ^ Adams JP (2010). «Non-neurological complications of brain injury». In Adams JP, Bell D, McKinlay J (eds.). Neurocritical care : a guide to practical management. London: Springer. pp. 77–88. ISBN 978-1-84882-069-2.
- ^ O’Leary R, McKinlay J (2011). «Neurogenic pulmonary oedema». Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain. 11 (3): 87–92. doi:10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkr006.
- ^ Wilkins, Lippincott Williams (2005). Strategies for Managing Multisystem Disorders. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 370. ISBN 978-1-58255-423-5.
- ^ a b Dunn IF, Ellegala DB (2008). «Decompressive hemicraniectomy in the management of severe traumatic brain injury». In Bhardwaj A, Ellegala DB, Kirsch JR (eds.). Acute Brain and Spinal Cord Injury: Evolving Paradigms and Management. Informa Health Care. pp. 1–2. ISBN 978-1-4200-4794-3.
- ^ Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, D’Urso P, Kossmann T, Ponsford J, Seppelt I, Reilly P, Wolfe R (April 2011). «Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury» (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (16): 1493–502. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102077. PMID 21434843.
- ^ Carney N, Totten AM, O’Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, Bratton SL, Chesnut R, Harris OA, Kissoon N, Rubiano AM, Shutter L, Tasker RC, Vavilala MS, Wilberger J, Wright DW, Ghajar J (January 2017). «Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition». Neurosurgery. 80 (1): 6–15. doi:10.1227/NEU.0000000000001432. PMID 27654000. S2CID 3616546.
- ^ Turner-Stokes L, Pick A, Nair A, Disler PB, Wade DT (December 2015). «Multi-disciplinary rehabilitation for acquired brain injury in adults of working age». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (12): CD004170. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004170.pub3. PMC 8629646. PMID 26694853.
- ^ a b Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation and Institut national d’excellence en santé et en services sociaux (2015). «Clinical Practice Guideline for the Rehabilitation of Adults with Modarate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury». braininjuryguidelines.org. Retrieved April 27, 2020.
- ^ Soo C, Tate R (July 2007). «Psychological treatment for anxiety in people with traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (3): CD005239. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005239.pub2. PMID 17636792.
- ^ a b c McMillan TM, Oddy M (2000). «Service provision for social disability and handicap after acquired brain injury». In Wood RL, McMillan TM (eds.). Neurobehavioural Disability and Social Handicap Following Traumatic Brain Injury. East Sussex: Psychology Press. pp. 267–68. ISBN 978-0-86377-889-6.
- ^ Deb S, Crownshaw T (January 2004). «The role of pharmacotherapy in the management of behaviour disorders in traumatic brain injury patients». Brain Injury. 18 (1): 1–31. doi:10.1080/0269905031000110463. PMID 14660233. S2CID 24775120.
- ^ a b Agrawal A, Timothy J, Pandit L, Manju M (July 2006). «Post-traumatic epilepsy: an overview». Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 108 (5): 433–439. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2005.09.001. PMID 16225987. S2CID 2650670.
- ^ Rodda J, Graham HK (November 2001). «Classification of gait patterns in spastic hemiplegia and spastic diplegia: a basis for a management algorithm». European Journal of Neurology. 8 (Suppl 5): 98–108. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.2001.00042.x. PMID 11851738. S2CID 45860264.
- ^ a b Grunt S. «Geh-Orthesen bei Kindern mit Cerebralparese». Pediatrica. 18: 30–34.
- ^ Esquenazi A (2008). Hsu JD, Michael JW, Fisk JR (eds.). Assessment and orthotic management of gait dysfunction in individuals with brain injury. AAOS Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices (4 ed.). Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier. pp. 441–447. ISBN 978-0-323-03931-4.
- ^ Horst R (2005). Motorisches Strategietraining und PNF. Renata Horst. ISBN 978-3-13-151351-9.
- ^ Novacheck TF (2008). Hsu JD, Michael JW, Fisk JR (eds.). Orthoses for cerebral palsy. AAOS Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices. Philadelphia. pp. 487–500. ISBN 978-0-323-03931-4.
- ^ Muñoz S (2018). «The new generation of AFOs». The O&P EDGE. 11. Archived from the original on June 6, 2021. Retrieved October 25, 2021.
- ^ Kerkum YL, Harlaar J, Buizer AI, van den Noort JC, Becher JG, Brehm MA (May 2016). «An individual approach for optimizing ankle-foot orthoses to improve mobility in children with spastic cerebral palsy walking with excessive knee flexion». Gait & Posture. 46: 104–111. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.03.001. PMID 27131186.
- ^ Kerkum YL (2016). «The effect of ankle foot orthosis stiffness on trunk movement and walking energy cost in cerebral palsy». Gait & Posture. 49: 2. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.07.070. ISSN 0966-6362.
- ^ Meyns P, Kerkum YL, Brehm MA, Becher JG, Buizer AI, Harlaar J (May 2020). «Ankle foot orthoses in cerebral palsy: Effects of ankle stiffness on trunk kinematics, gait stability and energy cost of walking». European Journal of Paediatric Neurology. 26: 68–74. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2020.02.009. PMID 32147412. S2CID 212641072.
- ^ Waterval NF, Nollet F, Harlaar J, Brehm MA (October 2019). «Modifying ankle foot orthosis stiffness in patients with calf muscle weakness: gait responses on group and individual level». Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation. 16 (1): 120. doi:10.1186/s12984-019-0600-2. PMC 6798503. PMID 31623670.
- ^ Ploeger HE, Waterval NF, Nollet F, Bus SA, Brehm MA (2019). «Stiffness modification of two ankle-foot orthosis types to optimize gait in individuals with non-spastic calf muscle weakness — a proof-of-concept study». Journal of Foot and Ankle Research (in German). 12: 41. doi:10.1186/s13047-019-0348-8. PMC 6686412. PMID 31406508.
- ^ a b Brown AW, Elovic EP, Kothari S, Flanagan SR, Kwasnica C (March 2008). «Congenital and acquired brain injury. 1. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, prognostication, innovative treatments, and prevention». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 89 (3 Suppl 1): S3–S8. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.12.001. PMID 18295647.
- ^ a b Frey LC (2003). «Epidemiology of posttraumatic epilepsy: a critical review». Epilepsia. 44 (s10): 11–17. doi:10.1046/j.1528-1157.44.s10.4.x. PMID 14511389. S2CID 34749005.
- ^ Armin SS, Colohan AR, Zhang JH (June 2006). «Traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: our current understanding and its evolution over the past half century». Neurological Research. 28 (4): 445–452. doi:10.1179/016164106X115053. PMID 16759448. S2CID 23726077.
- ^ Chumney D, Nollinger K, Shesko K, Skop K, Spencer M, Newton RA (2010). «Ability of Functional Independence Measure to accurately predict functional outcome of stroke-specific population: systematic review». Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development. 47 (1): 17–29. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2009.08.0140. PMID 20437324.
- ^ Murray ED, Buttner N, Price BH (2012). «Depression and Psychosis in Neurological Practice». In Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J (eds.). Bradley’s neurology in clinical practice. Vol. 1 (6th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. p. 111. ISBN 978-1-4377-0434-1.
- ^ Juengst SB, Adams LM, Bogner JA, Arenth PM, O’Neil-Pirozzi TM, Dreer LE, et al. (November 2015). «Trajectories of life satisfaction after traumatic brain injury: Influence of life roles, age, cognitive disability, and depressive symptoms». Rehabilitation Psychology. 60 (4): 353–364. doi:10.1037/rep0000056. PMC 4667543. PMID 26618215.
- ^ Hassett L, Moseley AM, Harmer AR (December 2017). «Fitness training for cardiorespiratory conditioning after traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (12): CD006123. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006123.pub3. PMC 6486048. PMID 29286534.
- ^ «Persistent vegetative state» at Dorland’s Medical Dictionary.
- ^ Schiff ND, Plum F, Rezai AR (March 2002). «Developing prosthetics to treat cognitive disabilities resulting from acquired brain injuries». Neurological Research. 24 (2): 116–124. doi:10.1179/016164102101199576. PMID 11877893. S2CID 347998.
- ^ a b Kwasnica C, Brown AW, Elovic EP, Kothari S, Flanagan SR (March 2008). «Congenital and acquired brain injury. 3. Spectrum of the acquired brain injury population». Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 89 (3 Suppl 1): S15–S20. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.12.006. PMID 18295644.
- ^ Synnot A, Chau M, Pitt V, O’Connor D, Gruen RL, Wasiak J, et al. (November 2017). «Interventions for managing skeletal muscle spasticity following traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD008929. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008929.pub2. PMC 6486165. PMID 29165784.
- ^ Oliveros-Juste A, Bertol V, Oliveros-Cid A (2002). «[Preventive prophylactic treatment in posttraumatic epilepsy]». Revista de Neurologia (in Spanish). 34 (5): 448–459. doi:10.33588/rn.3405.2001439. PMID 12040514.
- ^ Aimaretti G, Ghigo E (April 2007). «Should every patient with traumatic brain injury be referred to an endocrinologist?». Nature Clinical Practice. Endocrinology & Metabolism. 3 (4): 318–319. doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0460. PMID 17377615. S2CID 26338743.
- ^ Arlinghaus KA, Shoaib AM, Price TR (2005). «Neuropsychiatric assessment». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. pp. 59–62. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ Hall RC, Hall RC, Chapman MJ (2005). «Definition, diagnosis, and forensic implications of postconcussional syndrome». Psychosomatics. 46 (3): 195–202. doi:10.1176/appi.psy.46.3.195. PMID 15883140. Archived from the original on May 15, 2005.
- ^ Jordan BD (2000). «Chronic traumatic brain injury associated with boxing». Seminars in Neurology. 20 (2): 179–185. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9826. PMID 10946737.
- ^ Mendez MF (1995). «The neuropsychiatric aspects of boxing». International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine. 25 (3): 249–262. doi:10.2190/CUMK-THT1-X98M-WB4C. PMID 8567192. S2CID 20238578.
- ^ a b c Draper K, Ponsford J (October 2009). «Long-term outcome following traumatic brain injury: a comparison of subjective reports by those injured and their relatives». Neuropsychological Rehabilitation. 19 (5): 645–661. doi:10.1080/17405620802613935. PMID 19629849. S2CID 205907369.
- ^ Rutherford GW, Corrigan JD (2009). «Long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 24 (6): 421–423. doi:10.1097/HTR.0b013e3181c13439. PMID 19940674.
- ^ a b Temkin NR, Corrigan JD, Dikmen SS, Machamer J (2009). «Social functioning after traumatic brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 24 (6): 460–467. doi:10.1097/HTR.0b013e3181c13413. PMID 19940679. S2CID 43384334.
- ^ a b c Velikonja D, Warriner E, Brum C (July 2010). «Profiles of emotional and behavioral sequelae following acquired brain injury: cluster analysis of the Personality Assessment Inventory». Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 32 (6): 610–621. doi:10.1080/13803390903401302. PMID 20029697. S2CID 21067999.
- ^ Hawley LA, Newman JK (2010). «Group interactive structured treatment (GIST): a social competence intervention for individuals with brain injury». Brain Injury. 24 (11): 1292–1297. doi:10.3109/02699052.2010.506866. PMID 20735320. S2CID 207447494.
- ^ Lane-Brown A, Tate R (April 2009). «Interventions for apathy after traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2009 (2): CD006341. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006341.pub2. PMC 7390354. PMID 19370632.
- ^ Hesdorffer DC, Rauch SL, Tamminga CA (2009). «Long-term psychiatric outcomes following traumatic brain injury: a review of the literature». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 24 (6): 452–459. doi:10.1097/htr.0b013e3181c133fd. PMID 19940678. S2CID 205643570.
- ^ Fleminger S (2010). «Neuropsychiatric effects of traumatic brain injury». Psychiatr Times. 27 (3): 40–45.
- ^ Dockree PM, O’Keeffe FM, Moloney P, Bishara AJ, Carton S, Jacoby LL, Robertson IH (January 2006). «Capture by misleading information and its false acceptance in patients with traumatic brain injury». Brain. 129 (Pt 1): 128–140. doi:10.1093/brain/awh664. PMID 16280354.
- ^ Kreutzer JS, Stejskal TM, Ketchum JM, Marwitz JH, Taylor LA, Menzel JC (June 2009). «A preliminary investigation of the brain injury family intervention: impact on family members». Brain Injury. 23 (6): 535–547. doi:10.1080/02699050902926291. PMID 19484627. S2CID 12428952.
- ^ Kreutzer JS, Kolakowsky-Hayner SA, Demm SR, Meade MA (August 2002). «A structured approach to family intervention after brain injury». The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 17 (4): 349–367. doi:10.1097/00001199-200208000-00008. PMID 12106003. S2CID 20918911.
- ^ a b c d León-Carrión J, Domínguez-Morales M, Barroso y Martín JM, Murillo-Cabezas F (2005). «Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage». Pituitary. 8 (3–4): 197–202. doi:10.1007/s11102-006-6041-5. PMID 16508717. S2CID 23713764.
- ^ «Coma» at Dorland’s Medical Dictionary.
- ^ Cassidy JD, Carroll LJ, Peloso PM, Borg J, von Holst H, Holm L, et al. (WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury) (February 2004). «Incidence, risk factors and prevention of mild traumatic brain injury: results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury». Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 36 (43 Suppl): 28–60. doi:10.1080/16501960410023732. PMID 15083870.
- ^ a b c D’Ambrosio R, Perucca E (December 2004). «Epilepsy after head injury». Current Opinion in Neurology. 17 (6): 731–735. doi:10.1097/00019052-200412000-00014. PMC 2672045. PMID 15542983.
- ^ Chesnutt RM, Eisenberg JM (1999). «Introduction and background». Rehabilitation for Traumatic Brain Injury. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7881-8376-8.
- ^
Tolias C, Sgouros S (February 4, 2005). «Initial evaluation and management of CNS injury». Medscape. Retrieved December 16, 2007. - ^ Kindermann D, Mutter R, Pines JM (May 2013). Emergency Department Transfers to Acute Care Facilities 2009 (Report). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP Statistical Brief #155. Archived from the original on December 1, 2016.
- ^ Carli P, Orliaguet G (February 2004). «Severe traumatic brain injury in children». Lancet. 363 (9409): 584–585. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15626-2. PMID 14987880. S2CID 28381295.
- ^
Necajauskaite O, Endziniene M, Jureniene K (2005). «The prevalence, course and clinical features of post-concussion syndrome in children» (PDF). Medicina. 41 (6): 457–464. PMID 15998982. - ^ «An Unrecognized Problem» (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved October 13, 2019.
- ^ a b c Boake and Diller (2005). p. 3
- ^ a b c d Granacher (2007). p. 1.
- ^ Scurlock JA, Andersen BR (2005). Diagnoses in Assyrian and Babylonian Medicine: Ancient Sources, Translations, and Modern Medical Analyses. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. p. 307. ISBN 978-0-252-02956-1.
- ^ Sanchez GM, Burridge AL (2007). «Decision making in head injury management in the Edwin Smith Papyrus». Neurosurgical Focus. 23 (1): E5. doi:10.3171/FOC-07/07/E5. PMID 17961064.
- ^ a b c Levin HS, Benton AL, Grossman R (1982). «Historical review of head injury». Neurobehavioral Consequences of Closed Head Injury. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–5. ISBN 978-0-19-503008-2.
- ^ a b Zillmer EA, Schneider J, Tinker J, Kaminaris CI (2006). «A history of sports-related concussions: A neuropsychological perspective». In Echemendia RJ (ed.). Sports Neuropsychology: Assessment and Management of Traumatic Brain Injury. New York: The Guilford Press. pp. 21–23. ISBN 978-1-57230-078-1.
- ^ Corcoran C, McAlister TW, Malaspina D (2005). «Psychotic disorders». In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC (eds.). Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. p. 213. ISBN 978-1-58562-105-7.
- ^ Eslinger PJ, Damasio AR (December 1985). «Severe disturbance of higher cognition after bilateral frontal lobe ablation: patient EVR». Neurology. 35 (12): 1731–1741. doi:10.1212/wnl.35.12.1731. PMID 4069365. S2CID 22373825.
- ^ Devinsky O, D’Esposito M (2004). Neurology of Cognitive and Behavioral Disorders. Vol. 68. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-513764-4.
- ^ Marion (1999). p. 3.
- ^ Jones E, Fear NT, Wessely S (November 2007). «Shell shock and mild traumatic brain injury: a historical review». The American Journal of Psychiatry. 164 (11): 1641–1645. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07071180. PMID 17974926.
- ^ Belanger HG, Kretzmer T, Yoash-Gantz R, Pickett T, Tupler LA (January 2009). «Cognitive sequelae of blast-related versus other mechanisms of brain trauma». Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 15 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1017/S1355617708090036. PMID 19128523. S2CID 21648436.
- ^ Boake and Diller (2005). p. 8
- ^ Bush GH (July 1990). «Project on the Decade of the Brain». Library of Congress. Retrieved October 22, 2013.
- ^ Livint Popa L, Dragos H, Pantelemon C, Verisezan Rosu O, Strilciuc S (2020). «The Role of Quantitative EEG in the Diagnosis of Neuropsychiatric Disorders». J Med Life. 13 (1): 8–15. doi:10.25122/jml-2019-0085. PMC 7175442. PMID 32341694.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lewis SR, Baker PE, Andrews PJ, Cheng A, Deol K, Hammond N, Saxena M (October 2020). «Interventions to reduce body temperature to 35 °C to 37 °C in adults and children with traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020 (10): CD006811. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006811.pub4. PMC 8094748. PMID 33126293.
- ^ a b Watson HI, Shepherd AA, Rhodes JK, Andrews PJ (June 2018). «Revisited: A Systematic Review of Therapeutic Hypothermia for Adult Patients Following Traumatic Brain Injury». Critical Care Medicine. 46 (6): 972–979. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000003125. hdl:20.500.11820/fae8c4d4-8286-42db-b08d-1369e9092e06. PMID 29601315. S2CID 4495428.
- ^ Crompton EM, Lubomirova I, Cotlarciuc I, Han TS, Sharma SD, Sharma P (April 2017). «Meta-Analysis of Therapeutic Hypothermia for Traumatic Brain Injury in Adult and Pediatric Patients». Critical Care Medicine. 45 (4): 575–583. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002205. PMID 27941370. S2CID 19064475.
- ^ Lewis SR, Evans DJ, Butler AR, Schofield-Robinson OJ, Alderson P (September 2017). «Hypothermia for traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (9): CD001048. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001048.pub5. PMC 6483736. PMID 28933514.
- ^ Martín-Saborido C, López-Alcalde J, Ciapponi A, Sánchez Martín CE, Garcia Garcia E, Escobar Aguilar G, et al. (November 2019). «Indomethacin for intracranial hypertension secondary to severe traumatic brain injury in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (11). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011725.pub2. PMC 6872435. PMID 31752052.
- ^ Thal SC, Schaible EV, Neuhaus W, Scheffer D, Brandstetter M, Engelhard K, et al. (May 2013). «Inhibition of proteasomal glucocorticoid receptor degradation restores dexamethasone-mediated stabilization of the blood-brain barrier after traumatic brain injury». Critical Care Medicine. 41 (5): 1305–1315. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827ca494. PMID 23474678. S2CID 23399305.
- ^ Wright DW, Kellermann AL, Hertzberg VS, Clark PL, Frankel M, Goldstein FC, et al. (April 2007). «ProTECT: a randomized clinical trial of progesterone for acute traumatic brain injury». Annals of Emergency Medicine. 49 (4): 391–402. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.07.932. PMID 17011666.
- ^ Harris K, Armstrong SP, Campos-Pires R, Kiru L, Franks NP, Dickinson R (November 2013). «Neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury by xenon, but not argon, is mediated by inhibition at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor glycine site». Anesthesiology. 119 (5): 1137–1148. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182a2a265. PMID 23867231. S2CID 9756580.
- ^ Roberts I, Sydenham E (December 2012). «Barbiturates for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD000033. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000033.pub2. PMC 7061245. PMID 23235573.
- ^ Sen AP, Gulati A (January 2010). «Use of magnesium in traumatic brain injury». Neurotherapeutics. 7 (1): 91–99. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2009.10.014. PMC 5084116. PMID 20129501.
- ^ Arango MF, Bainbridge D (October 2008). «Magnesium for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD005400. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005400.pub3. PMID 18843689.
- ^ Langham J, Goldfrad C, Teasdale G, Shaw D, Rowan K (2003). «Calcium channel blockers for acute traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD000565. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000565. PMC 7032539. PMID 14583925.
- ^ Yi JH, Park SW, Brooks N, Lang BT, Vemuganti R (December 2008). «PPARgamma agonist rosiglitazone is neuroprotective after traumatic brain injury via anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms». Brain Research. 1244: 164–172. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.074. PMC 2603294. PMID 18948087.
- ^ Luo Y, Yin W, Signore AP, Zhang F, Hong Z, Wang S, et al. (April 2006). «Neuroprotection against focal ischemic brain injury by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist rosiglitazone». Journal of Neurochemistry. 97 (2): 435–448. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03758.x. PMID 16539667. S2CID 37759164.
- ^ Liu Y, Dargusch R, Maher P, Schubert D (May 2008). «A broadly neuroprotective derivative of curcumin». Journal of Neurochemistry. 105 (4): 1336–1345. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05236.x. PMID 18208543. S2CID 13345179.
- ^ Kelly DF, Lee SM, Pinanong PA, Hovda DA (May 1997). «Paradoxical effects of acute ethanolism in experimental brain injury». Journal of Neurosurgery. 86 (5): 876–882. doi:10.3171/jns.1997.86.5.0876. PMID 9126906.
- ^ Li W, Dai S, An J, Li P, Chen X, Xiong R, et al. (February 2008). «Chronic but not acute treatment with caffeine attenuates traumatic brain injury in the mouse cortical impact model». Neuroscience. 151 (4): 1198–1207. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.020. PMID 18207647. S2CID 29276898.
- ^ Nilsson P, Hillered L, Pontén U, Ungerstedt U (September 1990). «Changes in cortical extracellular levels of energy-related metabolites and amino acids following concussive brain injury in rats». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 10 (5): 631–637. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1990.115. PMID 2384536.
- ^ Vespa P, Bergsneider M, Hattori N, Wu HM, Huang SC, Martin NA, et al. (June 2005). «Metabolic crisis without brain ischemia is common after traumatic brain injury: a combined microdialysis and positron emission tomography study». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 25 (6): 763–774. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600073. PMC 4347944. PMID 15716852.
- ^ Dengler J, Frenzel C, Vajkoczy P, Wolf S, Horn P (November 2011). «Cerebral tissue oxygenation measured by two different probes: challenges and interpretation». Intensive Care Medicine. 37 (11): 1809–1815. doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2316-z. PMID 21809108. S2CID 23154956.
- ^ Rosenthal G, Furmanov A, Itshayek E, Shoshan Y, Singh V (April 2014). «Assessment of a noninvasive cerebral oxygenation monitor in patients with severe traumatic brain injury». Journal of Neurosurgery. 120 (4): 901–907. doi:10.3171/2013.12.JNS131089. PMID 24484228.
- ^ Yates D, Aktar R, Hill J (October 2007). «Assessment, investigation, and early management of head injury: summary of NICE guidance». BMJ. 335 (7622): 719–720. doi:10.1136/bmj.39331.702951.47. PMC 2001047. PMID 17916856.
- ^ a b c Bennett MH, Trytko B, Jonker B (December 2012). «Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the adjunctive treatment of traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12: CD004609. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004609.pub3. PMID 23235612.
- ^ Rockswold SB, Rockswold GL, Defillo A (March 2007). «Hyperbaric oxygen in traumatic brain injury». Neurological Research. 29 (2): 162–172. doi:10.1179/016164107X181798. PMID 17439701. S2CID 35914918.
- ^ Gertler P, Tate RL, Cameron ID (December 2015). «Non-pharmacological interventions for depression in adults and children with traumatic brain injury». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (12): CD009871. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009871.pub2. PMC 8761477. PMID 26663136.
- ^ Maruta J, Lee SW, Jacobs EF, Ghajar J (October 2010). «A unified science of concussion». Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1208 (1): 58–66. Bibcode:2010NYASA1208…58M. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05695.x. PMC 3021720. PMID 20955326.
- ^ Copplestone S, Welbourne J (February 2018). «A narrative review of the clinical application of pressure reactiviy indices in the neurocritical care unit». British Journal of Neurosurgery. 32 (1): 4–12. doi:10.1080/02688697.2017.1416063. PMID 29298527. S2CID 26020481.
- ^ Chesnut RM, Temkin N, Carney N, Dikmen S, Rondina C, Videtta W, et al. (December 2012). «A trial of intracranial-pressure monitoring in traumatic brain injury». The New England Journal of Medicine. 367 (26): 2471–2481. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1207363. PMC 3565432. PMID 23234472.
- ^ Carron SF, Alwis DS, Rajan R (2016). «Traumatic Brain Injury and Neuronal Functionality Changes in Sensory Cortex». Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience. 10: 47. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2016.00047. PMC 4889613. PMID 27313514.
- ^ Alwis DS, Yan EB, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Rajan R (2012). «Sensory cortex underpinnings of traumatic brain injury deficits». PLOS ONE. 7 (12): e52169. Bibcode:2012PLoSO…752169A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052169. PMC 3528746. PMID 23284921.
- ^ Johnstone VP, Shultz SR, Yan EB, O’Brien TJ, Rajan R (November 2014). «The acute phase of mild traumatic brain injury is characterized by a distance-dependent neuronal hypoactivity». Journal of Neurotrauma. 31 (22): 1881–1895. doi:10.1089/neu.2014.3343. PMC 4224042. PMID 24927383.
- ^ Burns TF (2019). Burns (2019): Temporal neuronal activity patterns in barrel cortex to simple and complex stimuli and the effects of traumatic brain injury. Monash University. Thesis. 10.26180/5b7166ad13e47 (thesis). Monash University. doi:10.26180/5b7166ad13e47.
Cited texts
- Boake C, Diller L (2005). «History of rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury». In High WM, Sander AM, Struchen MA, Hart KA (eds.). Rehabilitation for Traumatic Brain Injury. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-517355-0.
- Granacher RA (2007). Traumatic Brain Injury: Methods for Clinical & Forensic Neuropsychiatric Assessment, Second Edition. Boca Raton: CRC. ISBN 978-0-8493-8138-6.
- LaPlaca MC, Simon CM, Prado GR, Cullen DR (2007). «CNS injury biomechanics and experimental models». In Weber JT (ed.). Neurotrauma: New Insights Into Pathology and Treatment. Amsterdam: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-444-53017-2.
- Marion DW (1999). «Introduction». In Marion DW (ed.). Traumatic Brain Injury. Stuttgart: Thieme. ISBN 978-0-86577-727-9.
The original version of this article contained text from the NINDS public domain pages on TBI Archived December 18, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
External links
- Brain injury at Curlie
- The Brain Injury Hub – information and practical advice to parents and family members of children with acquired brain injury Archived October 5, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center – U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System center for traumatic brain injury Archived October 12, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
Черепно-мозговая травма — это повреждение костей черепа и/или мягких тканей (мозговые оболочки, ткани мозга, нервы, сосуды). По характеру травмы различают закрытую и открытую, проникающую и непроникающую ЧМТ, а также сотрясение или ушиб головного мозга. Клиническая картина черепно-мозговой травмы зависит от ее характера и тяжести. Основными симптомами являются головная боль, головокружение, тошнота и рвота, потеря сознания, нарушение памяти. Ушиб головного мозга и внутримозговая гематома сопровождаются очаговыми симптомами. Диагностика черепно-мозговой травмы включает анамнестические данные, неврологический осмотр, рентгенографию черепа, КТ или МРТ головного мозга.
Общие сведения
Черепно-мозговая травма — собирательное понятие, включающее различные повреждения костных и мягких структур головы. Выделяют следующие клинические формы ЧМТ: сотрясение мозга, ушиб мозга, диффузное аксональное повреждение, сдавление мозга. Самая распространенная травма среди возможных черепно-мозговых (около 70% всех ЧМТ) — это сотрясение головного мозга. Ушиб головного мозга легкой степени выявляют у 10-15% пострадавших с черепно-мозговой травмой, средней степени тяжести диагностируют у 8-10% пострадавших, тяжелый ушиб — у 5-7% пострадавших.
Черепно-мозговая травма (ЧМТ)
Причины
По генезу и механизму возникновения ЧМТ бывает первичная (воздействию на мозг травмирующей механической энергии не предшествует какая-либо церебральная или внецеребральная катастрофой) и вторичная (воздействию травмирующей механической энергии на мозг предшествует церебральная или внецеребральная катастрофа). ЧМТ у одного и того же пациента может происходить впервые или повторно (дважды, трижды).
- Первичные поражения — это очаговые ушибы и размозжения мозга, диффузные аксональные повреждения, внутричерепные гематомы, разрывы ствола, множественные внутримозговые геморрагии, возникшие вследствие механической травмы головы.
- Вторичные поражения возникают в результате действия вторичных внутричерепных факторов (отсроченных гематом, нарушений ликворо- и гемоциркуляции вследствие внутрижелудочкового или субарахноидального кровоизлияния, отека мозга, гиперемии и др.) или вторичных внечерепных факторов (артериальная гипертензия, гиперкапния, гипоксемия, анемия и др.)
Классификация
Классификация ЧМТ основывается на ее биомеханике, виде, типе, характере, форме, тяжести повреждений, клинической фазе, периоде лечения, а также исходе травмы.
По биомеханике различают следующие виды ЧМТ:
- ударно-противоударная (ударная волна распространяется от места полученного удара и проходит через мозг к противоположной стороне с быстрыми перепадами давления);
- ускорения-замедления (перемещение и ротация больших полушарий по отношению к более фиксированному стволу мозга);
- сочетанная (одновременное воздействие обоих механизмов).
По виду повреждения:
- очаговые (характеризуются локальными макроструктурными повреждениями мозгового вещества за исключением участков разрушений, мелко- и крупноочаговых кровоизлияний в области удара, противоудара и ударной волны);
- диффузные (натяжение и распространение первичными и вторичными разрывами аксонов в семиовальном центре, мозолистом теле, подкорковых образованиях, стволе мозга);
- сочетанные (сочетание очаговых и диффузных повреждений головного мозга).
По своему типу ЧМТ классифицируются на:
- закрытую — повреждения, не нарушившие целостность кожных покровов головы; переломы костей свода черепа без повреждения прилежащих мягких тканей или перелом основания черепа с развившейся ликвореей и кровотечением (из уха или носа);
- открытую непроникающую ЧМТ — без повреждения твердой мозговой оболочки и открытую проникающую ЧМТ — с повреждением твердой мозговой оболочки.
Кроме этого выделяют изолированную (отсутствие каких-либо внечерепных повреждений), сочетанную (внечерепные повреждения в результате механической энергии) и комбинированную (одновременное воздействие различных энергий: механической и термической/лучевой/химической) черепно-мозговую травму.
По тяжести ЧМТ делят на 3 степени: легкую, средней тяжести и тяжелую. При соотнесении этой рубрикации со шкалой комы Глазго легкую черепно-мозговую травм оценивают в 13-15, среднетяжелую – в 9-12, тяжелую – в 8 баллов и менее. Легкая черепно-мозговая травма соответствует сотрясению и ушибу мозга легкой степени, среднетяжелая — ушибу мозга средней степени, тяжелая — ушибу мозга тяжелой степени, диффузному аксональному повреждению и острому сдавлению мозга.
Течение ЧМТ разделяется на 3 базисных периода: острый, промежуточный и отдаленный. Временная протяженность периодов течения черепно-мозговой травмы варьирует в зависимости от клинической формы ЧМТ: острый – 2-10 недель, промежуточный – 2-6 месяцев, отдаленный при клиническом выздоровлении – до 2 лет.
Сотрясение головного мозга
Симптомы
Угнетение сознания (до уровня сопора) при сотрясении мозга может продолжаться от нескольких секунд до нескольких минут, но может и отсутствовать вовсе. На непродолжительный период времени развивается ретроградная, конградная и антероградная амнезия. Непосредственно после черепно-мозговой травмы возникает однократная рвота, дыхание учащается, но вскоре приходит в норму. Также приходит в норму и артериальное давление, за исключением тех случаев, когда анамнез отягощен гипертензией. Температура тела при сотрясении мозга сохраняется в норме.
Когда пострадавший приходит в сознание, возникают жалобы на головокружение, головную боль, общую слабость, появление холодного пота, приливы крови к лицу, шум в ушах. Неврологический статус на данной стадии характеризуется мягкой асимметрией кожных и сухожильных рефлексов, мелким горизонтальным нистагмом в крайних отведениях глаз, легкими менингиальными симптомами, которые исчезают в течение первой недели. При сотрясении головного мозга в результате черепно-мозговой травмы через 1,5 – 2 недели отмечается улучшение общего состояния пациента. Возможно сохранение некоторых астенических явлений.
Диагноз
Распознавание сотрясения головного мозга — непростая задача для невролога или травматолога, так как основными критериями его диагностирования являются составляющие субъективной симптоматики в отсутствие каких-либо объективных данных. Необходимо ознакомиться с обстоятельствами травмы, используя для этого информацию, имеющуюся у свидетелей происшедшего. Большое значение имеет обследование у отоневролога, с помощью которого определяют наличие симптомов раздражения вестибулярного анализатора в отсутствие признаков выпадения.
По причине мягкой семиотики сотрясения головного мозга и возможности возникновения подобной картины в результате одной из многих дотравматических патологий, особое значение в диагностике придается динамике клинических симптомов. Обоснованием диагноза «сотрясение мозга» является исчезновение таких симптомов через 3-6 суток после получения черепно-мозговой травмы. При сотрясении мозга отсутствуют переломы костей черепа. Состав ликвора и его давление сохраняются в норме. На КТ головного мозга не определяются внутричерепные пространства.
Лечение
Если пострадавший с черепно-мозговой травмой пришел в себя, в первую очередь ему необходимо придать удобное горизонтальное положение, голова должна быть чуть приподнята. Пострадавшему с черепно-мозговой травмой, находящемуся в бессознательном состоянии, необходимо придать т. н. «спасительное» положение — уложить его на правый бок, лицо должно быть повернуто к земле, левые руку и ногу согнуть под прямым углом в локтевом и коленном суставах (если исключены переломы позвоночника и конечностей). Такое положение способствует свободному прохождению воздуха в легкие, предотвращая западение языка, попадание рвотных масс, слюны и крови в дыхательные пути. На кровоточащие раны на голове, если таковые имеются, наложить асептическую повязку.
Всех пострадавших с черепно-мозговой травмой в обязательном порядке транспортируют в стационар, где после подтверждения диагноза устанавливают им постельным режим на срок, который зависит от клинических особенностей течения заболевания. Отсутствие признаков очаговых поражений головного мозга на КТ и МРТ головного мозга, а также состояние пациента, позволяющее воздержаться от активного медикаментозного лечения, позволяют решить вопрос в пользу выписки пациента на амбулаторное лечение.
При сотрясении головного мозга не применяют чрезмерно активного медикаментозного лечения. Его основные цели — нормализация функционального состояние головного мозга, купирование головной боли, нормализация сна. Для этого используют анальгетики, седативные средства (как правило, таблетированных форм).
Ушиб головного мозга
Симптомы
Для ушиба мозга легкой степени характерна утрата сознания после травмы до нескольких десятков минут. После восстановления сознания появляются жалобы на головную боль, головокружение, тошноту. Отмечают ретроградную, конградную, антероградную амнезию. Возможна рвота, иногда с повторами. Жизненно важные функции, как правило, сохраняются. Наблюдается умеренная тахикардия или брадикардия, иногда повышение артериального давления. Температура тела и дыхание без существенных отклонений. Мягко выраженные неврологические симптомы регрессируют через 2-3 недели.
Утрата сознания при ушибе мозга средней степени может длиться от 10-30 минут до 5-7 часов. Сильно выражена ретроградная, конградная и антероградная амнезия. Возможна многократная рвота и сильная головная боль. Нарушены некоторые жизненно важные функции. Определяется брадикардия или тахикардия, повышение АД, тахипноэ без нарушения дыхания, повышение температуры тела до субфебрильной. Возможно проявление оболочечных признаков, а также стволовых симптомов: двусторонние пирамидные признаки, нистагм, диссоциация менингеальных симптомов по оси тела. Выраженные очаговые признаки: глазодвигательные и зрачковые нарушения, парезы конечностей, расстройства речи и чувствительности. Они регрессируют через 4-5 недель.
Ушиб мозга тяжелой степени сопровождается потерей сознания от нескольких часов до 1-2 недель. Нередко он сочетается с переломами костей основания и свода черепа, обильным субарахноидальным кровоизлиянием. Отмечаются расстройства жизненно важных функций: нарушение дыхательного ритма, резко повышенное (иногда пониженное) давление, тахи- или брадиаритмия. Возможна блокировка проходимости дыхательных путей, интенсивная гипертермия.
Очаговые симптомы поражения полушарий зачастую маскируются за выходящей на первый план стволовой симптоматикой (нистагм, парез взора, дисфагия, птоз, мидриаз, децеребрационная ригидность, изменение сухожильных рефлексов, появление патологических стопных рефлексов). Могут определяться симптомы орального автоматизма, парезы, фокальные или генерализованные эпиприступы. Восстановление утраченных функций идет тяжело. В большинстве случаев сохраняются грубые остаточные двигательные нарушения и расстройства психической сферы.
Диагноз
Методом выбора при диагностике ушиба головного мозга является КТ головного мозга. На КТ определяют ограниченную зону пониженной плотности, возможны переломы костей свода черепа, субарахноидальное кровоизлияние. При ушибе мозга средней степени тяжести на КТ или спиральной КТ в большинстве случаев выявляют очаговые изменения (некомпактно расположенные зоны пониженной плотности с небольшими участками повышенной плотности).
При ушибе тяжелой степени на КТ определяются зоны неоднородного повышения плотности (чередование участков повышенной и пониженной плотности). Перифокальный отек головного мозга сильно выражен. Формируется гиподенсивная дорожка в область ближайшего отдела бокового желудочка. Через нее происходит сброс жидкости с продуктами распада крови и мозговой ткани.
Диффузное аксональное повреждение головного мозга
Симптомы
Для диффузного аксонального повреждения головного мозга типично длительное коматозное состояние после черепно-мозговой травмы, а также ярко выраженные стволовые симптомы. Коме сопутствует симметричная либо асимметричная децеребрация или декортикация как спонтанными, так и легко провоцируемыми раздражениями (например, болевыми). Изменения мышечного тонуса весьма вариабельны (горметония или диффузная гипотония). Типично проявление пирамидно-экстрапирамидных парезов конечностей, в том числе асимметричные тетрапарезы.
Кроме грубых нарушений ритма и частоты дыхания проявляются и вегетативные расстройства: повышение температуры тела и артериального давления, гипергидроз и др. Характерной особенностью клинического течения диффузного аксонального повреждения мозга является трансформация состояния пациента из продолжительной комы в транзиторное вегетативное состояние. О наступлении такого состояния свидетельствует спонтанное открывание глаз (при этом отсутствуют признаки слежения и фиксации взора).
Диагноз
КТ-картина диффузного аксонального поражения мозга характеризуется увеличением объема мозга, в результате которого под сдавлением находятся боковые и III желудочки, субарахноидальные конвекситальные пространства, а также цистерны основания мозга. Нередко выявляют наличие мелкоочаговых геморрагий в белом веществе полушарий мозга, мозолистом теле, подкорковых и стволовых структурах.
Сдавление головного мозга
Симптомы
Сдавление головного мозга развивается более чем в 55% случаев черепно-мозговой травмы. Чаще всего причиной сдавления головного мозга становится внутричерепная гематома (внутримозговая, эпи- или субдуральная). Опасность для жизни пострадавшего представляют стремительно нарастающие очаговые, стволовые и общемозговые симптомы. Наличие и продолжительность т. н. «светлого промежутка» — развернутого или стертого — зависит от степени тяжести состояния пострадавшего.
Диагноз
На КТ определяют двояковыпуклую, реже плоско-выпуклую ограниченною зону повышенной плотности, которая примыкает к своду черепа и локализируется в пределах одной или двух долей. Однако, если источников кровотечения несколько, зона повышенной плотности может быть значительного размера и иметь серповидной форму.
Диагностика
При поступлении в реанимационное отделение пациента с черепно-мозговой травмой необходимо провести следующие мероприятия:
- Осмотр тела пострадавшего, во время которого обнаруживают либо исключают ссадины, кровоподтеки, деформации суставов, изменения формы живота и грудной клетки, крово- и/или ликворотечение из ушей и носа, кровотечение из прямой кишки и/или уретры, специфический запах изо рта.
- Всестороннее рентгеновское исследование: череп в 2-х проекциях, шейный, грудной и поясничный отдел позвоночника, грудная клетка, кости таза, верхних и нижних конечностей.
- УЗИ грудной клетки, УЗИ брюшной полости и забрюшинного пространства.
- Лабораторные исследования: общий клинический анализ крови и мочи, биохимический анализ крови (креатинин, мочевина, билирубин и т. д.), сахар крови, электролиты. Данные лабораторные исследования необходимо проводить и в дальнейшем, ежедневно.
- ЭКГ (три стандартных и шесть грудных отведений).
- Исследование мочи и крови на содержание алкоголя. В случае необходимости проводят консультацию токсиколога.
- Консультации нейрохирурга, хирурга, травматолога.
Обязательным методом обследования пострадавших с черепно-мозговой травмой является компьютерная томография. Относительными противопоказаниями к ее проведению могут служить геморрагический или травматический шок, а также нестабильная гемодинамика. С помощью КТ определяют патологический очаг и его расположение, количество и объем гипер- и гиподенсивных зон, положение и степень смещения срединных структур головного мозга, состояние и степень повреждения головного мозга и черепа.
При подозрении на менингит показано проведение люмбальной пункции и динамического исследования ликвора, которое позволяет контролировать изменения воспалительного характера его составе.
Неврологический осмотр пациента с черепно-мозговой травмой следует проводить каждые 4 часа. Для определения степени нарушения сознания используют шкалу комы Глазго (состояние речи, реакция на боль и способность открывать/закрывать глаза). Кроме того, определяют уровень очаговых, глазодвигательных, зрачковых и бульбарных расстройств.
Лечение черепно-мозговой травмы
Консервативная терапия
Пострадавшему с нарушением сознания 8 баллов и менее по шкале Глазго показана интубация трахеи, благодаря которой поддерживается нормальная оксигенация. Угнетение сознания до уровня сопора или комы — показание к проведению вспомогательной или контролируемой ИВЛ (не менее 50% кислорода). С ее помощью поддерживается оптимальная церебральная оксигенация.
Пациенты с тяжелой черепно-мозговой травмой (выявленные на КТ гематомы, отек мозга и т. д.) нуждаются в мониторинге внутричерепного давления, которое необходимо поддерживать на уровне ниже 20 мм рт.ст. Для этого назначают маннитол, гипервентиляцию, иногда — барбитураты.
Для профилактики септических осложнений применяют эскалационную или деэскалационную антибактериальную терапию. Для лечения посттравматических менингитов используют современные противомикробные препараты, разрешенные для эндолюмбального введения (ванкомицин).
Питание пациентов начинают не позже 3 трех суток после ЧМТ. Его объем увеличивают постепенно и в конце первой недели, прошедшей со дня получения черепно-мозговой травмы, он должен обеспечивать 100% калорическую потребность пациента. Способ питания может быть энтеральным или парентеральным. Для купирования эпилептических приступов назначают противосудорожные препараты с минимальным титрованием дозы (леветирацетам, вальпроаты).
Хирургическое лечение
Показанием к операции служит эпидуральная гематома объемом свыше 30 см³. Доказано, что метод, обеспечивающий максимально полную эвакуацию гематомы — транскраниальное удаление. Острая субдуральная гематома толщиной свыше 10 мм также подлежит хирургическому лечению. Пациентам в коме удаляют острую субдуральную гематому с помощью краниотомии, сохраняя или удаляя костный лоскут. Эпидуральная гематома объемом более 25 см³ также подлежит обязательному хирургическому лечению.
Прогноз
Сотрясение головного мозга — преимущественно обратимая клиническая форма черепно-мозговой травмы. Поэтому более чем в 90% случаев сотрясения головного мозга исходом заболевания становится выздоровление пострадавшего с полным восстановлением трудоспособности. У части пациентов по прошествии острого периода сотрясения головного мозга отмечают те или иные проявления посткоммоционного синдрома: нарушения когнитивных функций, настроения, физического благополучия и поведения. Через 5-12 месяцев после черепно-мозговой травмы эти симптомы исчезают или существенно сглаживаются.
Прогностическую оценку при тяжелой черепно-мозговой травме проводят при помощи шкалы исходов Глазго. Уменьшение общего кол-ва баллов по шкале Глазго повышает вероятность неблагоприятного исхода заболевания. Анализируя прогностическую значимость возрастного фактора, можно сделать вывод о его существенном влиянии как на инвалидизацию, так и на летальность. Сочетание гипоксии и артериальной гипертензии является неблагоприятным фактором прогноза.
В России частота ЧМТ составляет примерно 4 случая на 1000 населения или 400 тыс. пострадавших в год. Около 10% из них погибают и ещё столько же становятся инвалидами. По оценке разных авторов ЧМТ является наиболее частой причиной смерти и тяжелой инвалидности в группе лиц не старше 35 лет. При этом мужчины получают ЧМТ в 2-3 раза чаще, чем женщины .
Наиболее частой причиной ЧМТ являются дорожно-транспортные происшествия . Второй наиболее значительной причиной ЧМТ (от 20% до 30%) являются падения, особенно среди молодых и пожилых лиц. Наибольший риск ЧМТ отмечается в возрасте от 15 до 24 лет и после 70 лет, причем у последних ЧМТ связана в основном с падениями производственные, спортивные и бытовые травмы.
Черепно-мозговые травмы делят на две основные группы: открытые и закрытые.
Открытая черепно-мозговая травма характеризуется наличием одновременного повреждения мягких покровов головы и черепных костей, создающих угрозу инфицирования головного мозга и его оболочек. Открытую травму в свою очередь подразделяют на непроникающую и проникающую в зависимости от целостности твердой оболочки головного мозга.
К закрытой травме относят черепно-мозговые травмы без нарушения целостности покровов головы.
В патогенезе ЧМТ помимо непосредственного повреждения мозга, играет роль механическая деформация черепа и мозга с ушибом последнего о костные выступы внутренней поверхности черепа (по механизму противоудара). Кроме того, в патогенезе ЧМТ ведущую роль играют нарушения основных нейродинамических процессов в центральной нервной системе, обуславливающие сосудистые, ликвородинамические и эндокринно-гуморальные нарушения. Реакция сосудистой системы мозга проявляются распространенным спазмом сосудов с последующей гиперемией мозга и венозным застоем. Расстройства ликвороциркуляции связаны с развитием ликворной гипо- и гипертензии, нарушениями проницаемости гематоэнцефалического барьера. Ослабление регуляторных функций гипоталамо-гипофизарной системы приводит к нарушениям гормонального баланса в организме, расстройствам водного и солевого обмена, нарушениям кровообращения с развитием гипоксии головного мозга и явлений отека-набухания мозговой ткани.
Как при закрытой, так и при открытой черепно-мозговой травме по характеру и тяжести повреждения мозга выделяют следующие основные клинические формы:
сотрясение головного мозга, ушиб головного мозга (лёгкой, средней и тяжёлой степени), тяжелое диффузное аксональное повреждение, сдавление головного мозга.
Сотрясение головного мозга характеризуется кратковременной потерей сознания в момент травмы, рвотой (чаще однократной), головной болью, головокружением, слабостью, болезненностью движений глаз и др. В неврологическом статусе очаговая симптоматика отсутствует. КТ не обнаруживает отклонений в состоянии вещества мозга и ликворных внутричерепных пространствах.
Ушиб – очаг травматического размозжения мозговой ткани, часто сопровождающийся кровоизлиянием, может локализоваться в месте удара или противоудара, но особенно часто формируется в базальных отделах лобной и передних отделах височной долей, которые тесно соприкасаются с выступающим костным рельефом.
Выделяют 3 степени тяжести ушиба головного мозга (легкая, средняя и тяжелая), различающиеся между собой по продолжительности выключения сознания (от нескольких минут до нескольких недель), выраженности антероградной амнезии на события, которые непосредственно предшествовали травме или произошли сразу после нее (общая продолжительность амнезированного периода не превышает 1 ч),, степени расстройств жизненно важных функций, выраженности симптомов, выраженности изменений при КТ исследовании.
Диффузное аксональное повреждение – результат вращательного или линейного ускорения в момент травмы, вызывающего закручивание массивных больших полушарий относительно жестко фиксированного ствола. Аксональное повреждение развивается в течение 12 – 24 часов, что оставляет «терапевтическое окно» для воздействия на этот процесс.
У 3-5% пострадавших встречается сдавление головного мозга, которое характеризуется нарастанием общемозговых, очаговых и дислокационных симптомов через некоторый промежуток времени после травмы. Сдавление головного мозга развивается при вдавленных переломах черепа, нарастании внутричерепной гематомы, при массивных ушибах, сопровождающихся отеком-набуханием мозга. При этом состоянии показаны неотложные оперативные вмешательства.
Проводя обследование больного с ЧМТ, особенно тяжелой, нужно придерживаться определенного плана.
1. Вначале следует обратить внимание на проходимость дыхательных путей, частоту и ритмичность дыхания, состояние гемодинамики.
2. Следует быстро осмотреть грудную клетку и живот, чтобы исключить гемо- или пневмоторакс , абдоминальное кровотечение.
3. Оценить состояние сознания. При легкой ЧМТ важно оценить ориентацию в месте, времени, собственной личности, внимание, попросив больного назвать месяцы года в обратном порядке или последовательно отнимать от 40 по 3, памяти, попросив запомнить 3 слова и проверив, сможет ли больной назвать их через 5 мин.
4. Осмотреть голову, туловище, конечности, обращая внимание на внешние признаки травмы (ранения,ушибы, кровоподтеки, переломы).
5. Важное значение имеет выявление признаков перелома основания черепа: истечение цереброспинальной жидкости из носа (в отличие от обычной слизи ликвор содержит глюкозу), симптом очков (отставленное появление двустороннего кровоподтека в периорбитальной области, ограниченного краями орбиты), истечение крови и ликвора из уха (кровотечение из уха может быть связано и с повреждением наружного слухового прохода или барабанной перепонки), а также кровоподтек за ушной раковиной в области сосцевидного отростка, появляющийся через 24—48 ч после травмы.
6. Собирая анамнез у больного или сопровождающих его лиц, следует обратить внимание на обстоятельства травмы (травма может спровоцировать инсульт, эпилептический припадок), употребление алкоголя или лекарственных средств.
7. Выясняя длительность утраты сознания, важно учитывать, что для внешнего наблюдателя сознание возвращается в тот момент, когда больной открывает глаза, для самого же больного сознание возвращается в тот момент, когда возвращается способность запоминать.
8. Появление менингеальных симптомов указывает на субарахноидальное кровоизлияние или менингит , однако ригидность шейных мышц можно проверить лишь в том случае, когда исключена травма шейного отдела.
9. Всем больным с ЧМТ проводится рентгенография черепа в двух проекциях, которая может выявить вдавленные переломы , линейные переломы в области средней черепной ямки или на основании черепа, уровень жидкости в решетчатой пазухе, пневмоцефалию (наличие воздуха в полости черепа). При линейном переломе свода черепа следует обратить внимание, не пересекает ли линия перелома борозду, в которой проходит средняя менингеальная артерия. Ее повреждение — самая частая причина эпидуральной гематомы.
10. Большинству больных (даже при минимальных признаках повреждения шейного отдела позвоночника или ссадине на лбу) следует назначить рентгенографию шейного отдела (по крайней мере в боковой проекции, при этом нужно получить изображение всех шейных позвонков).
13. При наличии спутанности или угнетения сознания, очаговых неврологических симптомов, эпилептического припадка, менингеальных симптомов, признаков перелома основания черепа, оскольчатом или вдавленном переломе свода черепа необходима срочная консультация нейрохирурга. Особая настороженность в отношении гематомы необходима у лиц пожилого возраста, больных, страдающих алкоголизмом или принимающих антикоагулянты.
Основными клиническими факторами, определяющими степень тяжести ЧМТ как при очаговом, так и при диффузном повреждении, являются (Штульман Д.Р., Левин О.С., 2002):
- продолжительность утраты сознания (от 0-10 мин при легкой степени до более 1 часа при тяжелой степени ЧМТ);
- продолжительность посттравматической (антероградной) амнезии;
- степень угнетения сознания на момент первичного осмотра или госпитализации (степень тяжести комы); продолжительность и глубина комы является наиболее важным предиктором восстановления. Считается, что кома продолжительностью более 6 часов может рассматриваться как предиктор плохого восстановления нормальной жизнедеятельности
- выраженность очаговой неврологической симптоматики, прежде всего, связанной с повреждением диэнцефально-стволовых структур;
- наличие субарахноидального кровоизлияния;
- выраженность системных осложнений.
По тяжести, отражающей степень изменения морфологического субстрата головного мозга), ЧМТ подразделяют на лёгкую, средней тяжести и тяжёлую. К лёгкой ЧМТ относят сотрясение и ушиб мозга лёгкой степени, к средней тяжести ЧМТ — ушиб мозга средней степени, к тяжёлой — ушиб мозга тяжёлой степени, диффузное аксональное повреждение, сдавление мозга в остром периоде.
Во многом прогноз при черепно-мозговой травме определяются возрастом пострадавшего (Полищук Н.Е., 1999). Так среди переживших кому после тяжелой ЧМТ длительностью 2 и более суток и обнаруживших через 2 года после травмы исходы I и II по шкале Глазго две трети составили дети, и не было ни одного больного в возрасте старше 50 лет (Доброхотова Т.А, 1999).
Для построения реабилитационной программы, определения её объёма и продолжительности очень важным является знание характера течения острейшего периода травмы.
Черепно-мозговая травма — динамический процесс, требующий постоянного контроля за состоянием сознания, неврологическим и психическим статусом. В течение первых суток неврологический статус, прежде всего состояние сознания нужно оценивать каждый час, воздерживаясь по возможности от назначения седативных средств (если больной засыпает, то следует периодически его будить).В течение ЧМТ выделяют следующие периоды:
- острый – от момента травмы до стабилизации нарушенных функций (от 2 до 10 недель);
- промежуточный период – от момента стабилизации функций до их полного или частичного восстановления или устойчивой компенсации (при легкой ЧМТ – до 2 –х месяцев, при среднетяжелой – до 4 мес, при тяжелой – до 6 мес.);
- отдаленный период – клинического выздоровления или максимально возможного восстановления нарушенных функций, либо возникновения или прогрессирования новых, вызванных ЧМТ, патологических состояний. Длительность отдаленного периода при клиническом выздоровлении до 2 лет, при прогредиентом течении – не ограничено.
К лёгкой ЧМТ относят сотрясение и ушиб мозга лёгкой степени. Клинически легкая ЧМТ характеризуется кратковременной (несколько секунд или минут) потерей сознания. После восстановления сознания могут появиться амнезия (не более 1 часа), головная боль, нарушение сна, вегетативные нарушения (изменение зрачковые реакций, колебания АД, лабильность пульса, рвота, бледность, гипергидроз), мышечная гипотония, асимметрия рефлексов, анизокория, вестибулярные нарушения, атаксия и другие очаговые симптомы, которые спонтанно регрессируют в течение нескольких дней.
При ушибе головы легкой степени в отличие от сотрясения головного мозга может выявляться более стойкая очаговая симптоматика, сохраняющаяся в течение 1-3 недель, а иногда и более выраженные общемозговые симптомы (дезориентация и спутанность сознания). Нередко выявляется линейный перелом свода черепа. При КТ исследовании обнаруживается ограниченный очаг пониженной плотности, который в последующем полностью регрессирует.
Считается, что больные с легкой ЧМТ в специальной реабилитации не нуждаются, но иногда при наличии неблагоприятного преморбидного фона, предрасполагающего к развитию клинически значимых последствий ЧМТ, восстановительные мероприятия могут проводиться и больным с легкой ЧМТ (Белова А.Н., 2000).
Большинство больных с легкой степенью ЧМТ полностью выздоравливают, хотя у многих из них ещё в течение нескольких недель может наблюдаться снижение внимания, нарушения памяти, нарушения настроения и некоторые другие симптомы (Levin et al., 1989), которые могут свидетельствовать о развитии у таких больных посткоммоционного синдрома. Для посткоммоционного синдрома характерны: общая слабость, головная боль, головокружение, снижение внимания и памяти, замедленность психической деятельности, быстрая утомляемость, нарушение сна, раздражительность, тревога, депрессия, аффективная лабильность, апатия, вегетативная дисфункция Эти изменения могут регрессировать в течение нескольких месяцев. Большинство больных возвращаются к нормальной деятельности через 3-6 месяцев, хотя некоторые могут иметь постоянные изменения.
У этой группы больных широко применяют ноотропные препараты ( пирацетам, церебролизин, энцефабол, мемантин, меклофеноксат (ацефен), а также противоастенические препараты (когитум,бемитил, цитруллин). При посттравматической мигрени применяют бета-блокаторы (пропранолол), антидепрессанты (амитриптилин), НПВС, антагонисты кальция (верапамил), вальпроевую кислоту. Для лечения посттравматической головной боли напряжения используют антидепрессанты (амитриптилин), НПВС, миорелаксанты (тизанидин). При затылочной невралгии и цервикогенной головной боли применяют НПВС, антидепрессанты, миорелаксанты.
При лечении легкой ЧМТ, особенно при наличии в клинической картине посткоммоционного синдрома, важное значение имеют немедикаментозные методы лечения такие как:
- Лечебная гимнастика; общеукрепляющую лечебную гимнастику с элементами вестибулярной гимнастики. Кроме того, включают упражнения на координацию движений.
- Постизометрическая релаксация; направлена на релаксацию мышц головы, шеи, верхнего плечевого пояса.
- Массаж воротниковой зоны; для улучшения кровоснабжения головного мозга и улучшения венозного оттока.
- Физиотерапия; электрофорез веществ, улучшающих обменные процессы в мозге
- Рефлексотерапия; для уменьшения выраженности головной боли, повышения общего тонуса и активности.
Среднетяжелая и тяжелая ЧМТ в остром периоде характеризуется продолжительной потерей сознания, амнезией, стойкими когнитивными нарушениями, очаговыми неврологическими симптомами что обусловлено контузией мозга, диффузным аксональным повреждением, внутричерепной гипертензией, повреждением ствола, субарахноидальным кровоизлиянием, внутричерепной гематомой.
При средней тяжести ЧМТ (при средней степени ушиба) острый период может продолжаться до 4-5 недель.
При тяжелой степени ЧМТ (тяжелом ушибе мозга, диффузном аксональном повреждении, сдавлении мозга) – от 6 до 10 недель.
Медикаментозная терапия в остром периоде тяжелых ЧМТ направлена на предупреждение гипоксии, стабилизацию гемодинамики (коррекция гиповолемии, введение вазопрессоров, гипотензивных средств), снижение ВЧД (применение осмотических диуретиков, в наиболее тяжелых случаях – возможно применение барбитуратов), купирование психомоторного возбуждения при исключении возможности развития внутричерепной гематомы (реланиум, оксибутират натрия, мидазолам, галоперидол), профилактику эпилептических припадков (карбамазепин, дефинин в течение не более 1-2 недели
Кроме того, используют нейропротекторные средства (блокаторы кальциевых каналов, антиоксиданты, антигипоксанты, антагонисты возбуждающих аминокислот). Целесообразность применения ноотропов в острейшем периоде ЧМТ вызывает сомнение, особенно у больных с психомоторным возбуждением.
Однако в промежуточном и отдаленном периодах ЧМТ ноотропы применяют для стимуляции восстановительных процессов
В реабилитации больных с тяжелыми ЧМТ особенно велика роль так называемой мультидисциплинарной реабилитационной команды: центральной фигурой которой является больной и его семья. В эту команду входят врач-реабилитолог, который осуществляет общее руководство этой командой, реабилитационная сестра, инструктуры и методисты ЛФК, нейрохирург, физиотерапевт, специалист по бытовой реабилитации (occupational therapist), логопед (speech и language pathologist), клинический психолог, нейропсихолог, социальный работник и консультант.
Реабилитационные мероприятия у больных с тяжелыми ЧМТ должны начинаться как можно раньше, но лишь после того, как минует угроза для жизни пациента и при отсутствии витальных нарушений. Продолжительность ранней реабилитации среднетяжелой и тяжелой ЧМТ может продолжаться от 1 до 3 месяцев.
Основные задачи реабилитации в остром периоде среднетяжелой и тяжелой ЧМТ заключаются в следующем (Карасева Т.А., 1994; McMillan, Greenwood, 1993):
- Создание максимально благоприятных условий для течения восстановительно-компенсаторных процессов в головном мозге;
- Профилактика и лечение осложнений со стороны дыхательной и сердечно-сосудистой системы;
- Профилактика пролежней, контрактур паретичных конечностей.
С этой целью, прежде всего, применяется тщательный уход за пациентом, который заключается в предупреждении пролежней и гипостатической пневмонии (поворачивание больного в постели, массаж, туалет кожи, банки, горчичники, отсасывание слюны и слизи из полости рта, санация трахеи). С целью улучшения венозного оттока из полости черепа и предупреждения внутричерепной гипертензии изголовье приподнимают до 30о . При этом голова больного должна находится в одной плоскости с телом, чтобы избежать сдавления яремных вен.
Больные с травмой головы часто поступают на реабилитацию с различной степенью кахексии, подтверждая тем самым, что их потребности в питании часто недооценены. После серьёзной травмы головы, многие больные имеют гиперпирексию и повышенную потливость, обусловленные нарушением вегетативной иннервации. Повышенная потеря веса может увеличивать заболеваемость и смертность, нарушить заживление тканей и привести к развитию пролежней и других осложнений. Обычно питание начинают на 2-й день после травмы. При нормальной работе кишечника питание осуществляют через гибкий назогастральный зонд. Суточная калорийность должна быть не менее 2500-4000 ккал/сутки.
Реабилитационные мероприятия, направленные на профилактику и лечение пролежней.
Для профилактики пролежней кожа больного постоянно протирается 3% раствором камфорного спирта, а ссадины смазываются 1% раствором бриллиантовой зелени или 3% раствором настойки йода, больного через каждые 2 часа переворачивают, под костные выступы подкладывают резиновые или ватно-марлевые круги, используют противопролежневые матрасы.
Кроме того, для профилактики пролежней применяют ультрафиолетовое облучение (УФО) поясницы, крестца, ягодиц и пяток в субэритемных дозах.
Реабилитационные мероприятия, направленные на профилактику контрактур.
Лечение положением с использованием лонгет, ортезов, валиков, которое обеспечивает правильное положение конечности, применяют как для отдельных мышечных групп, так и для всего корпуса (Найдин В.П., 1972). Варианты укладок зависят от характера двигательных нарушений. Так, при спастических парезах используют укладку, такую же, как при постинсультных гемипарезах. При преобладании экстрапирамидных нарушений с ригидностью, при которых характерно развитии флексорных контрактур, особенно в коленных суставах, рекомендуется фиксация разгибательного положения в пораженных суставах. При гипотонии рекомендуется среднефизиологическое расположение конечностей с валиками под коленными суставами и упором для стоп.
Пассивные упражнения в виде движений в полном объеме для всех суставов следует проводить ежедневно, начинают с мелких дистальных суставов конечностей с небольшой амплитуды и скорости, затем переходят к проксимальным участкам, постепенно увеличивая объем и скорость движений.
Массаж легкий конечностей для улучшения кровообращения в мышцах, для уменьшения отека, снижения спастичности.
Физические методы, направленных на уменьшение болевого синдрома и отека, улучшение кровообращения в тканях (диадинамические токи; синусоидальные модулированные токи; электрофорез анальгина, новокаина, диметилсульфоксида, тримекаина, а также различных противоалгических смесей поперечно на пораженный сустав; УЗ или ультрафонофорез (трилон Б, тиодин, гидрокортизон с новокаином) на пораженный сустав; низкочастотная магнитотерапия).
Реабилитационные мероприятия, направленные на профилактику осложнений со стороны дыхательной и сердечно-сосудистой системы.
Дыхательные упражнения в остром периоде тяжелой ЧМТ должны начинаться как можно раньше при отсутствии противопоказаний, с первых суток после травмы (Найдина В.П., 1972). Целью дыхательных упражнений в остром периоде является предотвращение образования секрета, возможности инфекции и ухудшения дыхания и повышение насыщения кислородом мозга.
Противопоказанием к проведению дыхательных упражнений являются:
- грубые сердечно-сосудистые расстройства;
- значительная неустойчивость артериального давления;
- выраженная сердечная недостаточность.
При угнетении сознания начинают применять пассивные дыхательные упражнения, выполняемые методистом и направленные на стимуляцию выдоха и вдоха. Вначале руки методиста пассивно следуют за дыхательными экскурсиями грудной клетки, подстраиваясь под ритм дыхания больного. Во время выдоха методист производит с минимальным усилием вибрирующее сдавление грудной клетки больного, увеличивая это усилие с каждым дальнейшим выдохом. При вдохе методист оказывает легкое сопротивление расширяющейся грудной клетке. Через каждые 2-3 дыхательных упражнения методист меняет место приложения рук (различные участки грудной клетки, область реберного угла, область живота).
По мере восстановления сознания и активности больного переходят к пассивно-активным упражнениям, при которых в дополнении к описанным выше пассивным упражнениям, выполняемом только методистом, больной начинает активно ему помогать, форсируя выдох втягиванием мышц живота, а вдох – одновременным расширением грудной клетки и выпячиванием живота
Затем переходят к активно-пассивным дыхательным упражнениям, направленным на преимущественную вентиляцию нижней доли правого и левого легкого, используя для этого специальную укладку больного и локальное сопротивление движению ребер во время вдоха. По мере улучшения состояния больного начинают проводить дыхательные упражнения динамического характера с активным движением рук и корпуса. Для достижения более полноценной вентиляции легких дыхание производится ртом, без натуживания и длительной задержки дыхания на вдохе.
Массаж используют методику общего массажа для нормализации дыхательной и сердечно-сосудистой функции.
Реабилитация в промежуточном и отдаленном периодах тяжелой ЧМТ.
В промежуточном и отдаленном периодах ЧМТ могут формироваться различные её последствия, морфологической основой которых являются тканевые изменения в мозге (атрофия, рубцы, дефекты черепа, остит), ликворные нарушения (гидроцефалия, гигромы, кисты, пневмоцефалия), сосудистые нарушения (ишемия, аневризмы, хронические гематомы).
К числу основных клинических последствий ЧМТ: относятся дефицитарные синдромы (параличи и парезы, экстрапирамидные и мозжечковые расстройства, нарушения функции черепных нервов); синдромы психических дисфункций (неврозоподобные синдромы – астенический, ипохондрический, депрессивный, неврастенический, психопатоподобный синдром); посттравматическая эпилепсия; вегетативная дисрегуляция (вегетососудистые, вегетовисцеральные, обменно-эндокринные синдромы).
Продолжительность реабилитационных мероприятий в промежуточном и отдаленном периодах тяжелых ЧМТ зависит от возраста больных, тяжести травмы, выраженности функциональных, двигательных, когнитивных нарушений и может продолжаться от 1 года до 2 лет
В этом периоде, также как в остром периоде по-прежнему чрезвычайно актуальным является применение активных дыхательных упражнений, направленных на увеличение экскурсии легких, обучение больных откашливанию там, где это возможно (Ellis, 1990; Hough, 1991).Программа медикаментозной терапии применяется с учетом ведущего клинического синдрома и направлена на:
- нормализацию мозгового и системного кровообращения (кавинтон, сермион, циннаризин);
- улучшение метаболизма ткани мозга (ноотропил, церебролизин, актовегин),
- купирование ликвородинамических нарушений,
- предупреждение образования спаек оболочек головного мозга (биогенные стимуляторы — алоэ, фибс, стекловидное тело; лидаза);
- борьбу с иммунопатологическими процессами (иммунокорректоры),
- коррекцию психопатологических проявлений.
Программа коррекции постуральных нарушений.
Поддержание постурального контроля одна из важнейших задач реабилитации больных с тяжелой ЧМТ
Лечение положением. У многих больных с серьезной ЧМТ в положении лежа имеется асимметрия позы, характерная для децеребрации и эти больные не в состоянии лежать, плотно прижавших к постели. В результате этого у больных развиваются контрактуры суставов, пролежни и осложнения со стороны дыхания. Патологическая поза может быть скорректирована путем применения дополнительных поддерживающих устройств и предметов (подушек, Т-образного валика и распорок), которые обеспечивают стабилизацию сегментов тела.
При сидении у больных с выраженными двигательными нарушениями после тяжелой ЧМТ могут наблюдаться три основные позы:
- Флексорная поза, выражающаяся в кифозе всех отделов позвоночника, резком сгибании головы в шейном отделе, сгибании рук во всех суставах;
- Дугообразная поза, при которой тело выгибается дугой назад от копчика с чрезмерным поясничным лордозом, при этом ноги имеют тенденцию к сгибанию и руки к разгибанию;
- Асимметричная поза, при которой таз наклонен в сторону и ротирован, туловище и голова также наклонены и ротированы.
У больного может наблюдаться комбинация этих поз. Если больной не в состоянии сам поддерживать позу в положении сидя, ему необходимо обеспечить приспособления для стабильной, сбалансированной и симметричной позы при сидении. Для этого предложены специальные устройства для сидения
Стояние больного с тяжелыми постуральными нарушениями обеспечивается специальными вертикальными столами или рамами для стояния, когда объем движений в суставах нижних конечностей позволяет этой процедуре быть безопасной и выполнимой.
Активная лечебная гимнастика, направленная на улучшение постурального контроля.
Метод биоуправления по статокинезиграмме Данный метод позволяет обучать больного в ходе специальных компьютерных стабилографических игр (КСИ) произвольному перемещению центра давления (ЦД) с различной амплитудой, скоростью, степенью точности и направления движения без потери равновесия. Программа тренировки строится в зависимости от степени нарушения постурального контроля и общего состояния больного. Использование этого метода возможно только у больных без грубых зрительных и когнитивных нарушений.
Программа коррекции двигательных нарушений.
Лечебная гимнастика. Для больных с тяжелой ЧМТ характерна комбинация пирамидных, экстрапирамидных, стволо-мозжечковых и вестибулярных нарушений, проявляющихся в самых различных сочетаниях и формах взамодействия (Найдин В.П., 1972). В связи с этим при построении лечебно-гимнастических программ у этих больных используются приемы различных подходов кинезитерапии (
Нервно-мышечная электростимуляция.
Применяют электростимуляцию антагонистов спастических мышц СМТ. Один электрод (катод) размещают на двигательной точке мышцы, а другой (анод) – в области перехода мышцы в сухожилие.
Новые технологии.
В настоящее время также как и у больных, перенесших инсульт, для восстановления двигательных функций у больных с последствиями тяжелых ЧМТ широко применяются новые технологии, основанные на виртуальной реальности
использование робототехнических устройств для обучения двигательным навыкам в паретичной руке (the MIT-Manus and Mirror-Image Motion Enabler Robot) и системы Lokomat для обучения ходьбе (Hesse S, et al., 2003).
Программа лечения спастичности, контрактур и гетеротопической оссификации.
ЧМТ часто ассоциируются с очень выраженной спастичностью, которая обычно развивается после нескольких дней или в течение первых нескольких недель после травмы. Спастичность может быть определена как увеличение сопротивления на пассивное растяжение мышцы, сочетающееся с повышением сухожильных рефлексов
Спастичность, в свою очередь, способствует изменению вязко-эластических свойств самой мышцы, то есть приводит к развитию так называемой гипержесткости мягких тканей. Спастичность и гипержесткость часто усиливают выраженность двигательных нарушений, препятствует восстановлению двигательных навыков и имеют тенденцию к нарастанию в течение первых месяцев после травмы, часто приводя к развитию контрактур.
Для уменьшения спастичности и улучшения вязко-эластических свойств мышц применяют:
- лечение положением,
- специальные лечебно-гимнастические приемы на расслабление,
- избирательный и точечный массаж по тормозной методике,массаж,
- физиотерапию (магнитотерапия)
- термотерапию (парафино-, озокеритотерапия или криотерапия),
- гидротерапия (вихревые ванны),
- прием миорелаксантов,
- локальное введение в спазмированные мышцы ботулинового токсина типа А (особенно эффективен в улучшении положения головы, уменьшении спастичности в верхних и нижних конечностях на ранних стадиях восстановления после ЧМТ),
- интратекальное введение баклофена,
- Блокада нерва с помощью инъекций спирта или фенола может быть полезной для снятия спастичности в отдаленном периоде, когда нет надежды на восстановление.
В промежуточном и отдаленном периодах тяжелой ЧМТ у больных часто наблюдаются разгибательные или флексорные контрактуры в конечностях.
Для лечения контрактур применяют лечение положением, кинезитерапию, физиотерапию, гидрокинезитерапию, механотерапию.
Лечение положением осуществляется с помощью ортезов и шин. При коррекции контрактур необходимо применение непрерывной силы, лежащей ниже «болевого порога раздражения», наращиваемой постепенно, «капельным» способом, и потому до известных пределов почти не ощутимой для больного. Увеличение силы растяжения достигается изменением углов между плечами ортезов или шин . Если таким способом устранить или уменьшить контрактуру не удается, то применяют лечение этапными гипсовыми повязками (Гайдар Б.В.с соавтр., 1997).
Очень эффективно проведение таких упражнений в теплой воде, или после тепловых процедур (горячее укутывание, парафиновые или озокеритовые аппликации, грязелечение). Активные упражнения используются с целью укрепления растянутых мышц (антагонистов мышц, находящихся в сокращенном виде).
Эффективным средством снижения спастичности является лечение холодом (криотерапия), при которой спастичные мышцы предварительно согревают компрессами или ванночками с водой температурой 37-38°С в течение 5-10 мин. Затем к этим мышцам прикладывают пакет или грелку со льдом на 20-30-60 с. Время воздействия холода постепенно увеличивают от 20 до 60 с. После снятия пакета или грелки конечность заворачивают в сухое полотенце и согревают в течение 60 с. Затем процедуру повторяют от 5 до 10 раз. Курс лечения состоит из 10-15 процедур.
В случае неэффективности консервативной терапии контрактур применяют оперативное лечение, которое заключается в различных пластических операциях на мягких тканях и костях (разновидности кожной пластики, миотенолиз, тенотомия, капсулотомия, артролиз и др.) (Новиков
Другим осложнением тяжелых ЧМТ является гетеротопическая оссификация (ГО), представляющее собой образование зрелой костной ткани в мягких тканях организма, чаще всего в области тканей крупных суставов (Garland DE et al., 1981). ГО наблюдается часто при травме головного мозга, сопровождающейся длительной комой. ГО не выявляются при рентгенологическом обследовании раньше, чем через месяц после травмы и может прогрессировать в течение года или более, прежде чем окончательно сформируется. Причина ГО остается неясной. Лечение ГО заключается в лечебной гимнастике, направленной на сохранение в суставах должного объема движений, препаратах этидроновой кислоты – отечественный препарат Ксидифон (первые 6-9 месяцев в дозе 20 мг/кг/день, следующие 3-6 месяцев в дозе 10 мг/кг/день). Для уменьшения болей и воспалительных реакций применяются нестероидные противоспалительные препараты (индометацин, найз и др.). Оперативное вмешательство выполняется не ранее чем через 2 года после травмы (Белова А.Н., 2000; Collin C, Daly G., 1998).Посттравматическое вегетативное состояние.
Наконец, необходимо остановится на одном из неблагоприятных исходов тяжелой ЧМТ – посттравматическом вегетативном статусе (ВС), который определяется как состояние, наблюдающееся у больных с тяжелой ЧМТ после длительной комы и характеризующееся относительной стабилизацией вегетативных процессов при отсутствии признаков сознании Клинически ВС проявляется следующим образом:
- Больной лежит с открытыми глазами или открывает их на болевые раздражения.
- На внешние стимулы, особенно словесные обращения, он не реагирует.
- Глазные яблоки неподвижны или совершают плавающие движения.
- Нарушен цикл сна и бодрствования.
- Краткие периоды бодрствования сменяются более длительными периодами сна.
- Характерны декортикационная поза, примитивные двигательные феномены (оральный гиперкинез).
- Возможны хаотические движения в ответ на болевые раздражения.
В связи с увеличением частоты ЧМТ, успехами реаниматологии в последние годы отмечается рост числа больных с ВС.
В стадии ВС сенсорная стимуляция направлена на вызывание у больного возможно более разнообразных элементарных ощущений. Для этого применяют стимулы (невербальные – тактильные, слуховые, зрительные), разные по силе, по направленности на различные анализаторы, по местонахождению источника воздействия, по эмоциональной окраске, используют сочетание знакомых и незнакомых раздражителей. Эмоциональному оживлению способствует присутствие рядом с больными родных и близких, что необходимо обеспечить как можно раньше. Психостимулотерапия должна проводится не только медперсоналом (сестрами, психологами), но и родственниками больных.
Вместе с тем, Lombardi F. с соавтр.(2001), проведя анализ исследований, посвященных применению мультисенсорной стимуляции при коме и ВС, делают заключение, что пока не получено достоверных результатов эффективности этой технологии при этих состояниях.
В заключении необходимо подчеркнуть, что больные, перенесшие ЧМТ, относятся к одному из самых тяжелых контингентов больных, нуждающихся в реабилитационном лечении. Использование своевременной реабилитационной помощи таким больным позволяет улучшить адаптационные возможности и способность их к социальной интеграции в общество.
Через 4 месяца после закрытой ЧМТ и через 6 месяцев после открытой ЧМТ показано санаторно-курортное лечение в местных неврологических санаториях и на бальнеологических курортах
26 сентября 2018 г.
Закрытая черепно-мозговая травма (сотрясение головного мозга, ушиб головного мозга, внутричерепные гематомы и т.д.)
Утратил силу — Архив
Также:
E-008
Версия: Архив — Клинические протоколы МЗ РК — 2007 (Приказ №764)
Категории МКБ:
Другие внутричерепные травмы (S06.8)
Общая информация
Краткое описание
Закрытая черепно-мозговая травма (ЗЧМТ) — повреждение черепа и мозга, которое не сопровождается нарушением целостности мягких тканей головы и/или апоневротическим растяжением черепа.
К открытой ЧМТ относятся повреждения, которые сопровождаются нарушением целостности мягких тканей головы и апоневротического шлема черепа и/или
соответствуют зоне перелома.
К проникающим повреждениям относят такую ЧМТ, которая сопровождается переломами костей черепа и повреждением твердой мозговой оболочки мозга с возникновением ликворных свищей (ликвореей).
Код протокола: E-008 «Закрытая черепно-мозговая травма (сотрясение головного мозга, ушиб головного мозга, внутричерепные гематомы и т.д.)»
Профиль: скорая медицинская помощь
Цель этапа: восстановление функций всех жизненно важных систем и органов
Код (коды) по МКБ-10-10:
S06.0 Сотрясение головного мозга
S06.1 Травматический отек головного мозга
S06.2 Диффузная травма головного мозга
S06.3 Очаговая травма головного мозга
S06.4 Эпидуральное кровоизлияние
S06.5 Травматическое субдуральное кровоизлияние
S06.6 Травматическое субарахноидальное кровоизлияние
S06.7 Внутричерепная травма с продолжительным коматозным состоянием
S06.8 Другие внутричерепные травмы
S06.9 Внутричерепная травма неуточненная
Облачная МИС «МедЭлемент»
Облачная МИС «МедЭлемент»

Автоматизация клиники: быстро и недорого!
- Подключено 300 клиник из 4 стран
- 1 место — 800 RUB / 5500 KZT / 27 BYN в месяц
Классификация
По патофизиологии ЧМТ:
1. Первичные – повреждения обусловлены непосредственным воздействием травмирующих сил на кости черепа, мозговые оболочки и мозговую ткань, сосуды мозга и ликворную систему.
2. Вторичные – повреждения не связаны с непосредственным повреждением мозга, но обусловлены последствиями первичного повреждения мозга и развиваются в основном по типу вторичных ишемических изменений мозговой ткани (внутричерепные и системные).
Внутричерепные – цереброваскулярные изменения, нарушения ликвороциркуляции, отек мозга, изменения внутричерепного давления, дислокационный синдром.
Системные – артериальная гипотензия, гипоксия, гипер- и гипокапния, гипер- и гипонатриемия, гипертермия, нарушение углеводного обмена, ДВС-синдром.
По тяжести состояния больных с ЧМТ – основывается на оценке степени угнетения сознания пострадавшего, наличии и выраженности неврологических симптомов, наличии или отсутствии повреждения других органов. Наибольшее распространение получила шкала комы Глазго (предложенная G. Teasdale и B. Jennet 1974г.). Состояние пострадавших оценивают при первом контакте с больным, через 12 и 24 часа по трем параметрам: открыванию глаз, речевому ответу и двигательной реакции в ответ на внешнее раздражение.
Выделяют классификацию нарушений сознания при ЧМТ, основанную на качественной оценке степени угнетения сознания, где существуют следующие градации состояния сознания:
— ясное;
— умеренное оглушение;
— глубокое оглушение;
— сопор;
— умеренная кома;
— глубокая кома;
— запредельная кома;
К легким ЗЧМТ относят сотрясение головного мозга и ушиб головного мозга легкой степени.
ЗЧМТ средней степени тяжести – ушиб головного мозга средней тяжести.
К тяжелой ЗЧМТ относят ушиб головного мозга тяжелой степени и все виды сдавления головного мозга.
Выделяют 5 градаций состояния больных с ЧМТ:
— удовлетворительное;
— средней тяжести;
— тяжелое;
— крайне тяжелое;
— терминальное.
Критериями удовлетворительного состояния являются:
— ясное сознание;
— отсутствие нарушений витальных функций;
— отсутствие вторичной (дислокационной) неврологической симптоматики, отсутствие или нерезкая выраженность первичных полушарных и краниобазальных симптомов. Угроза для жизни отсутствует, прогноз восстановления трудоспособности обычно хороший.
Критериями состояния средней тяжести являются:
— ясное сознание или умеренное оглушение;
— витальные функции не нарушены (возможна лишь брадикардия);
— очаговые симптомы – могут быть выражены те или иные полушарные и краниобазальные симптомы. Иногда наблюдаются единичные, мягко выраженные стволовые симптомы (спонтанный нистагм и др.).
Для констатации состояния средней степени тяжести достаточно иметь один из указанных параметров. Угроза для жизни незначительная, прогноз восстановления трудоспособности чаще благоприятный.
Критерии тяжелого состояния (15-60 мин.):
— изменение сознания до глубокого оглушения или сопора;
— нарушение витальных функций (умеренное по одному-двум показателям);
— очаговые симптомы – стволовые умеренно выражены (анизокория, легкое ограничение взора вверх, спонтанный нистагм, контралатеральная пирамидная недостаточность, диссоциация менингеальных симптомов по оси тела и др.); могут быть резко выражены полушарные и краниобазальные симптомы, в том числе эпилептические припадки, парезы и параличи.
Для констатации тяжелого состояния допустимо иметь указанные нарушения хотя бы по одному из параметров. Угроза для жизни значительная, во многом зависит от длительности тяжелого состояния, прогноз восстановления трудоспособности чаще неблагоприятный.
Критериями крайне тяжелого состояния являются (6-12 часов):
— нарушение сознания до умеренной или глубокой комы;
— резко выраженное нарушение витальных функций по нескольким параметрам;
— очаговые симптомы – стволовые выражены четко (парез взора вверх, выраженная анизокория, дивергенция глаз по вертикали или горизонтали, тонический спонтанный нистагм, ослабление реакции зрачков на свет, двусторонние патологические рефлексы, децеребрационная ригидность и др.); полушарные и краниобазальные симптомы резко выражены (вплоть до двусторонних и множественных парезов).
При констатации крайне тяжелого состояния необходимо иметь выраженные нарушения по всем параметрам, причем по одному из них обязательно предельное, угроза для жизни максимальная. Прогноз восстановления трудоспособности чаще неблагоприятный.
Критерии терминального состояния следующие:
— нарушение сознания до уровня запредельной комы;
— критическое нарушение витальных функций;
— очаговые симптомы – стволовые в виде предельного двустороннего мидриаза, отсутствие роговичных и зрачковых реакций; полушарные и краниобазальные обычно перекрыты общемозговыми и стволовыми нарушениями. Прогноз выживания больного неблагоприятный.
1. Изолированная.
2. Сочетанная.
3. Комбинированная.
4. Повторная.
Черепно-мозговую травму разделяют на:
1. Закрытую.
2. Открытую:
— непроникающую;
— проникающую.
По видам повреждений мозга различают:
1. Сотрясение головного мозга – состояние, возникающее чаще вследствие воздействия небольшой травмирующей силы. Встречается почти у 70% пострадавших с ЧМТ. Сотрясение характеризуется отсутствием утраты сознания или кратковременной утратой сознания после травмы: от 1-2 до 10-15 минут. Больные жалуются на головные боли, тошноту, реже — рвоту, головокружение, слабость, болезненность при движении глазных яблок.
Может быть легкая асимметрия сухожильных рефлексов. Ретроградная амнезия (если она возникает) кратковременна. Антероретроградной амнезии не бывает. При сотрясении мозга указанные явления вызваны функциональным поражением головного мозга и по прошествии 5-8 дней проходят. Для установления диагноза необязательно наличие всех указанных симптомов. Сотрясение головного мозга является единой формой и не подразделяется на степени тяжести.
2. Ушиб головного мозга – это повреждение в виде макроструктурной деструкции вещества мозга, чаще с геморрагическим компонентом, возникшим в момент приложения травмирующей силы. По клиническому течению и выраженности повреждения мозговой ткани, ушибы мозга разделяют на ушибы легкой, средней и тяжелой степени.
3. Ушиб мозга легкой степени (10-15% пострадавших). После травмы отмечается утрата сознания от нескольких минут до 40 мин. У большинства имеется ретроградная амнезия на период до 30 мин. Если возникает антероретроградная амнезия, то она непродолжительна. После восстановления сознания пострадавший жалуется на головную боль, тошноту, рвоту (часто повторную), головокружение, ослабление внимания, памяти.
Могут выявляться — нистагм (чаще горизонтальный), анизорефлексия, иногда легкий гемипарез. Иногда появляются патологические рефлексы. Вследствие субарахноидального кровоизлияния может выявляться легко выраженный менингеальный синдром. Может наблюдаться бради- и тахикардия, транзиторное увеличение артериального давления на 10-15 мм рт. ст. Симптоматика регрессирует обычно в течение 1-3 недель после травмы. Ушиб головного мозга легкой степени тяжести может сопровождаться переломами костей черепа.
4. Ушиб головного мозга средней степени тяжести. Утрата сознания длится от нескольких десятков минут до 2-4 часов. Угнетение сознания до уровня умеренного или глубокого оглушения может сохраняться в течение нескольких часов или суток. Наблюдается выраженная головная боль, часто повторная рвота. Горизонтальный нистагм, ослабление реакции зрачков на свет, возможно нарушение конвергенции.
Отмечаются диссоциация сухожильных рефлексов, иногда умеренно выраженный гемипарез и патологические рефлексы. Могут быть нарушения чувствительности, речевые расстройства. Менингеальный синдром умеренно выражен, а ликворное давление умеренно повышено (за исключением пострадавших, у которых имеется ликворея).
Имеется тахи- или брадикардия. Нарушения дыхания в виде умеренного тахипноэ без нарушения ритма и не требует аппаратной коррекции. Температура субфебрильная. В 1-е сутки могут быть — психомоторное возбуждение, иногда судорожные припадки. Имеется ретро- и антероретроградная амнезия.
5. Ушиб мозга тяжелой степени. Утрата сознания длится от нескольких часов до нескольких суток (у части больных с переходом в апаллический синдром или акинетический мутизм). Угнетение сознания до сопора или комы. Может быть выраженное психомоторное возбуждение, сменяющееся атонией.
Выражены стволовые симптомы – плавающие движения глазных яблок, разностояние глазных яблок по вертикальной оси, фиксация взора вниз, анизокория. Реакция зрачков на свет и роговичные рефлексы угнетены. Глотание нарушено. Иногда развивается горметония на болевые раздражения или спонтанно. Двусторонние патологические стопные рефлексы. Имеются изменения мышечного тонуса, часто – гемипарез, анизорефлексия. Могут быть судорожные припадки.
Нарушение дыхания – по центральному или периферическому типу (тахи- или брадипноэ). Артериальное давление или повышено, или снижено (может быть нормальным), а при атонической коме нестабильно и требует постоянной медикаментозной поддержки. Выражен менингеальный синдром.
К особой форме ушибов мозга относится диффузное аксональное повреждение мозга. Его клинические признаки включают нарушение функции мозгового ствола – угнетение сознания до глубокой комы, резко выраженное нарушение витальных функций, которые требуют обязательной медикаментозной и аппаратной коррекции.
Летальность при диффузном аксональном повреждении мозга очень высока и достигает 80-90%, а у выживших развивается апаллический синдром. Диффузно аксональное повреждение может сопровождаться образованием внутричерепных гематом.
6. Сдавление мозга (нарастающее и ненарастающее) – происходит за счет уменьшения внутричерепного пространства объемными образованиями. Следует иметь в виду, что любое «ненарастающее» сдавление при ЧМТ может стать нарастающим и привести к выраженной компрессии и дислокации мозга. К ненарастающим сдавлениям относят сдавление отломками костей черепа при вдавленных переломах, давление на мозг другими инородными телами. В этих случаях само сдавливающее мозг образование не увеличивается в объеме.
В генезе сдавления мозга ведущую роль играют вторичные внутричерепные механизмы. К нарастающим сдавлениям относятся все виды внутричерепных гематом и ушибы мозга, сопровождающиеся масс-эффектом.
— эпидуральные;
— субдуральные;
— внутримозговые;
— внутрижелудочковые;
— множественные подоболочечные гематомы;
— субдуральные гидромы.
Гематомы могут быть: острыми (первые 3 суток), подострыми (4 сут.-3 недель) и хроническими (позже 3 недель).
Классическая клиническая картина внутричерепных гематом включает наличие светлого промежутка, анизокорию, гемипарез, брадикардию, которая встречается реже. Классическая клиника характерна для гематом без сопутствующего ушиба мозга. У пострадавших с гематомами в сочетании с ушибом головного мозга уже с первых часов ЧМТ имеются признаки первичного повреждения мозга и симптомы сдавления и дислокации мозга, обусловленные ушибом мозговой ткани.
Факторы и группы риска
1. Алкогольное опьянение (70%).
2. ЧМТ в результате возникшего эпилептического приступа.
Ведущие причины ЧМТ:
1. Автодорожный травматизм.
2. Бытовая травма.
3. Падение и спортивная травма.
Диагностика
Диагностические критерии
Обращают внимание на наличие видимых повреждений кожных покровов головы.
Периорбитальная гематома («симптом очков», «глаза енота») свидетельствует о переломе дна передней черепной ямки.
Гематома в области сосцевидного отростка (симптом Баттла) сопутствует перелому пирамиды височной кости.
Гемотимпанум или разрыв барабанной перепонки может соответствовать перелому основания черепа.
Носовая или ушная ликворея свидетельствует о переломе основания черепа и проникающей ЧМТ.
Звук «треснувшего горшка» при перкуссии черепа может возникать при переломах костей свода черепа.
Экзофтальм с отеком конъюнктивы может указывать на формирование каротидно-кавернозного соустья или на образовавшуюся ретробульбарную гематому.
Гематома мягких тканей в затылочно-шейной области может сопутствовать перелому затылочной кости и (или) ушибу полюсов и базальных отделов лобных долей и полюсов височной долей.
Несомненно, обязательным является оценка уровня сознания, наличия менингеальных симптомов, состояния зрачков и их реакция на свет, функции черепных нервов и двигательных функций, неврологических симптомов, повышение внутричерепного давления, дислокация мозга, развитие острой ликворной окклюзии.
Лечение
Тактика оказания медицинской помощи
Выбор тактики лечения пострадавших определяют характером повреждения головного мозга, костей свода и основания черепа, сопутствующей внечерепной травмой и развитием осложнений вследствие травмы.
Основная задача при оказании первой помощи пострадавшим с ЧМТ – не допустить развития артериальной гипотензии, гиповентиляции, гипоксии, гиперкапнии, так как эти осложнения приводят к тяжелым ишемическим поражениям мозга и сопровождаются высокой летальностью.
В связи с этим в первые минуты и часы после травмы все лечебные мероприятия должны быть подчинены правилу «АВС»:
А (аirway) – обеспечение проходимости дыхательных путей.
В (breathing) – восстановление адекватного дыхания: устранение обструкции дыхательных путей, дренирование плевральной полости при пневмо-, гемотораксе, ИВЛ (по показаниям).
С (circulation) – контроль за деятельностью сердечно-сосудистой системы: быстрое восстановление ОЦК (переливание растворов кристаллоидов и коллоидов), при недостаточности миокарда – введение инотропных препаратов (допамин, добутамин) или вазопрессоров (адреналин, норадреналин, мезатон). Необходимо помнить, что без нормализации массы циркулирующей крови введение вазопрессоров опасно.
Показанием к интубации трахеи и проведению ИВЛ являются апноэ и гипоапноэ, наличие цианоза кожи и слизистых оболочек. Интубация через нос имеет ряд преимуществ, т.к. при ЧМТ не исключается вероятность шейно-спинальной травмы (и поэтому же всем пострадавшим до уточнения характера травмы на догоспитальном этапе необходимо фиксировать шейный отдел позвоночника, накладывая специальные шейные воротники). Для нормализации артериовенозной разницы по кислороду у пострадавших с ЧМТ целесообразно применение кислородно-воздушной смеси с содержанием кислорода до 35-50%.
Обязательным компонентом лечения тяжелой ЧМТ является устранение гиповолемии, и с этой целью обычно жидкость вводят в объеме 30-35 мл/кг в сутки. Исключением являются больные с острым окклюзионным синдромом, у которых темп продукции ЦСЖ напрямую зависит от водного баланса, поэтому у них оправдана дегидратация, позволяющая снижать ВЧД.
Для профилактики внутричерепной гипертензии и ее повреждающих головной мозг последствий на догоспитальном этапе применяют глюкокортикоидные гормоны и салуретики.
Глюкокортикоидные гормоны предупреждают развитие внутричерепной гипертензии за счет стабилизации проницаемости гематоэнцефалического барьера и уменьшения транссудации жидкости в ткань мозга.
Они способствуют спадению перифокального отека в области травмы.
На догоспитальном этапе целесообразно внутривенное или внутримышечное введение преднизолона в дозе 30 мг.
Однако следует иметь в виду, что из-за сопутствующего минералокортикоидного эффекта преднизолон способен задерживать в организме натрий и усиливать элиминацию калия, что неблагоприятно сказывается на общем состоянии больных с ЧМТ.
Поэтому предпочтительнее использование дексаметазона в дозе 4-8 мг который практически не обладает минералокортикоидными свойствами.
При отсутствии нарушений кровообращения одновременно с глюкокортикоидными гормонами для дегидратации мозга возможно назначение быстродействующих салуретиков, например, лазикса в дозе 20-40 мг (2-4 мл 1% раствора).
Ганглиоблокирующие препараты при высокой степени внутричерепной гипертензии противопоказаны, так как при снижении системного кровяного давления может развиться полная блокада мозгового кровотока за счет сдавления капилляров мозга отечной мозговой тканью.
Для снижения внутричерепного давления — как на догоспитальном этапе, так и в стационаре — не следует пользоваться осмотически активными веществами (маннит), ибо при поврежденном гематоэнцефалическом барьере создать градиент их концентрации между веществом мозга и сосудистым руслом не удается и вероятно ухудшение состояния больного из-за быстрого вторичного повышения внутричерепного давления.
Исключение — угроза дислокации головного мозга, сопровождающаяся тяжелыми нарушениями дыхания и кровообращения.
В этом случае целесообразно внутривенное введение маннита (маннитола) из расчета 0,5 г/кг массы тела в виде 20% раствора.
Последовательность мер оказания неотложной помощи на догоспитальном этапе
При сотрясении головного мозга неотложная помощь не требуется.
При психомоторном возбуждении:
1. 2-4 мл 0,5% раствора седуксена (реланиум, сибазон) внутривенно.
2. Транспортировка в стационар (в неврологическое отделение).
При ушибе и сдавлении головного мозга:
1. Обеспечить доступ к вене.
2. При развитии терминального состояния произвести сердечную реанимацию.
3. При декомпенсации кровообращения:
— реополиглюкин, кристаллоидные растворы внутривенно капельно;
— при необходимости допамин 200 мг в 400 мл изотонического раствора натрия хлорида или любого другого кристаллоидного раствора внутривенно со скоростью, обеспечивающей поддержание АД на уровне 120-140 мм рт. ст.
4. При бессознательном состоянии:
— осмотр и механическая очистка полости рта;
— применение приема Селлика;
— выполнение прямой ларингоскопии;
Позвоночник в шейном отделе не разгибать!
— стабилизация шейного отдела позвоночника (легкое вытягивание руками);
— интубирование трахеи (без миорелаксантов!), вне зависимости от того, будет проводиться ИВЛ или нет; миорелаксанты (сукцинилхолин хлорид— дицилин, листенон в дозе 1-2 мг/кг; инъекции осуществляют только врачи реанимационно-хирургических бригад).
При неэффективности самостоятельного дыхания показана искусственная вентиляция легких в режиме умеренной гипервентиляции (12-14 л/мин. для больного с массой тела 75-80 кг).
5. При психомоторном возбуждении, судорогах и в качестве премедикации:
— 0,5-1,0 мл 0,1% раствора атропина подкожно;
— внутривенно пропофол 1-2 мг/кг, или тиопентал натрия 3-5 мг/кг, или 2-4 мл 0,5% раствора седуксена, или 15-20 мл 20 % раствора натрия оксибутирата, или дормикум 0,1-0,2 мг/кг;
— при транспортировке необходим контроль дыхательного ритма.
6. При внутричерепном гипертензионном синдроме:
— 2-4 мл 1 % раствора фуросемида (лазикса) внутривенно (при декомпенсированной кровопотере вследствие сочетанной травмы лазикс не вводить!);
— искусственная гипервентиляция легких.
7. При болевом синдроме: внутримышечно (или внутривенно медленно) 30 мг-1,0 кеторолака и 2 мл 1-2 % раствора димедрола и (или) 2-4 мл (200-400 мг) 0,5 % раствора трамала или другой ненаркотический анальгетик в соответствующих дозах.
Опиаты не вводить!
8. При ранах головы и наружных кровотечениях из них:
— туалет раны с обработкой краев антисептиком (см. гл. 15).
9. Транспортировка в стационар, где имеется нейрохирургическая служба; при критическом состоянии — в реанимационное отделение.
Перечень основных медикаментов:
1. *Допамин 4% по 5 мл; амп.
2. Добутамин раствор для инфузий 5 мг/мл
3. *Дексаметазон 4 мг/мл, амп.
4. *Преднизолон 25 мг 1 мл, амп.
5. *Диазепам 10 мг/2 мл; амп.
6. *Декстран 70 — 400 мл; фл.
7. *Натрия оксибат 20% 5 мл, амп.
8. *Магния сульфат 25% 5,0, амп.
9. *Маннитол 15% 200 мл, фл.
10. *Фуросемид 1% 2,0, амп.
11. Мезатон 1% — 1,0; амп.
Перечень дополнительных медикаментов:
1. *Атропина сульфат 0,1% — 1,0, амп.
2. *Бетаметазон 1 мл, амп.
3. *Эпинефрин 0,18 % — 1 мл; амп.
4. *Дестран 70 400,0; фл.
5. *Дифенгидрамин 1% — 1,0, амп.
6. * Кеторолак 30 мг — 1,0; амп.
* – препараты, входящие в список основных (жизненно важных) лекарственных средств.
Информация
Источники и литература
-
Протоколы диагностики и лечения заболеваний МЗ РК (Приказ №764 от 28.12.2007)
- 1. «Болезни нервной системы» /Руководство для врачей /Под редакцией Н.Н. Яхно,
Д.Р. Штульмана – 3-е издание, 2003г.
2. В.А. Михайлович, А.Г. Мирошниченко. Руководство для врачей скорой
медицинской помощи. 2001г.
3. Рекомендации по оказанию скорой медицинской помощи в РФ / 2-е издание, под
редакцией проф. А.Г. Мирошниченко, проф. В.В. Руксина. 2006 г.
4. Биртанов Е.А., Новиков С.В., Акшалова Д.З. Разработка клинических руководств
и протоколов диагностики и лечения с учетом современных требования. Методические рекомендации. Алматы, 2006, 44 с.
5. Приказ Министра Здравоохранения Республики Казахстан от 22 декабря 2004 года № 883 «Об утверждении Списка основных (жизненно важных) лекарственных средств».
6. Приказ Министра Здравоохранения Республики Казахстан от 30 ноября 2005 года
№542 «О внесении изменений и дополнений в приказ МЗ РК от 7 декабря 2004 года № 854 «Об утверждении Инструкции по формированию Списка основных (жизненно важных) лекарственных средств».
- 1. «Болезни нервной системы» /Руководство для врачей /Под редакцией Н.Н. Яхно,
Информация
Заведующий кафедрой скорой и неотложной медицинской помощи, внутренних болезней №2 Казахского национального медицинского университета им. С.Д. Асфендиярова — д.м.н., профессор Турланов К.М.
Сотрудники кафедры скорой и неотложной медицинской помощи, внутренних болезней №2 Казахского национального медицинского университета им. С.Д. Асфендиярова: к.м.н, доцент Воднев В.П.; к.м.н., доцент Дюсембаев Б.К.; к.м.н., доцент Ахметова Г.Д.; к.м.н., доцент Бедельбаева Г.Г.; Альмухамбетов М.К.; Ложкин А.А.; Маденов Н.Н.
Заведующий кафедрой неотложной медицины Алматинского государственного института усовершенствования врачей – к.м.н., доцент Рахимбаев Р.С.
Сотрудники кафедры неотложной медицины Алматинского государственного института усовершенствования врачей: к.м.н., доцент Силачев Ю.Я.; Волкова Н.В.; Хайрулин Р.З.; Седенко В.А.
Прикреплённые файлы
Мобильное приложение «MedElement»

- Профессиональные медицинские справочники. Стандарты лечения
- Коммуникация с пациентами: онлайн-консультация, отзывы, запись на приём
Скачать приложение для ANDROID / для iOS
Мобильное приложение «MedElement»

- Профессиональные медицинские справочники
- Коммуникация с пациентами: онлайн-консультация, отзывы, запись на приём
Скачать приложение для ANDROID / для iOS
Внимание!
Если вы не являетесь медицинским специалистом:
-
Занимаясь самолечением, вы можете нанести непоправимый вред своему здоровью.
-
Информация, размещенная на сайте MedElement и в мобильных приложениях «MedElement (МедЭлемент)», «Lekar Pro»,
«Dariger Pro», «Заболевания: справочник терапевта», не может и не должна заменять очную консультацию врача.
Обязательно
обращайтесь в медицинские учреждения при наличии каких-либо заболеваний или беспокоящих вас симптомов.
-
Выбор лекарственных средств и их дозировки, должен быть оговорен со специалистом. Только врач может
назначить
нужное лекарство и его дозировку с учетом заболевания и состояния организма больного.
-
Сайт MedElement и мобильные приложения «MedElement (МедЭлемент)», «Lekar Pro»,
«Dariger Pro», «Заболевания: справочник терапевта» являются исключительно информационно-справочными ресурсами.
Информация, размещенная на данном
сайте, не должна использоваться для самовольного изменения предписаний врача.
-
Редакция MedElement не несет ответственности за какой-либо ущерб здоровью или материальный ущерб, возникший
в
результате использования данного сайта.
Черепно-мозговая травма
причины, симптомы, методы лечения и профилактики
Черепно-мозговая травма — повреждение костей черепа, мозга и его оболочек. Причина заключается в любом механическом воздействии. Заболевание требует консультации у травматолога, при наличии осложнений рекомендуется обратиться к неврологу.
Симптомы черепно-мозговой травмы
Признаки заболевания зависят от разновидности травмы. Сотрясение характеризуется следующими симптомами:
- потеря сознания до 10 минут;
- небольшая оглушенность;
- затруднения в ориентации в пространстве;
- больной не помнит несколько часов жизни после травмы;
- возможно моторное возбуждение;
- приступы головокружения;
- головные боли;
- тошнота, в тяжелых случаях рвота;
- слабость мышечных тканей;
- повышение или снижение артериального давления;
- кончики пальцев приобретают синий оттенок;
- тахикардия;
- образование гематомы;
- гипергидроз;
- бесконтрольные колебания глаз.
Симптоматика исчезает в течение 3 дней. Ушибы сопровождаются следующими признаками:
- обморок, в тяжелых случаях до 3 недель;
- головные боли;
- приступы головокружения, рвота;
- нарушение ритма сердца;
- в некоторых случаях гипертензия артериального типа;
- пробелы в памяти;
- гипертермия;
- моторное возбуждение;
- судороги;
- параличи верхних или нижних конечностей;
- гипертонус мышечных тканей.
Сдавление имеет следующую симптоматику:
- расстройства общемозгового типа;
- очаговые признаки;
- нарушения сознания.
Статью проверил
Кученков А.В.
Ортопед • Травматолог • Хирург • Флеболог • Спортивный врач • стаж 25 лет
Дата публикации: 24 Марта 2021 года
Дата проверки: 23 Февраля 2023 года
Содержание статьи
Причины
ЧМТ происходит при физическом повреждении. Тяжесть зависит от силы воздействия. Чаще диагностируется в следующих ситуациях:
- дорожно-транспортное происшествие;
- попытка суицида;
- падение с большой высоты;
- травмы на производстве;
- у профессиональных спортсменов, занимающихся боевыми искусствами.
Стадии развития черепно-мозговой травмы
Выделяют несколько стадий:
- острая, от момента получения травмы до стабилизации нейротических функций головного мозга. Длится около 2,5 месяцев;
- промежуточная, характеризуется восстановлением функционирования нервной системы, длительность зависит от тяжести травмы, длится до 12 месяцев;
- отдаленная, характеризуется завершением процессов восстановления или развитием дегенеративных нарушений, длится на протяжении нескольких лет.
Разновидности
В зависимости от характера травмирования выделяют следующие виды:
- закрытый, характеризуется сохранением кожных покровов;
- открытый, чаще сопровождается повреждением кожных покровов и переломами свода черепа;
- проникающий, подразумевает нарушение мозговой оболочки, повреждение основания органа.
Выделяют несколько степеней тяжести повреждения:
- удовлетворительная степень подразумевает ясное сознание, отсутствие нарушений жизненно-важных функций и неврологических симптомов. При своевременно оказанной первой помощи признаки болезни быстро исчезают, у больного полностью восстанавливается работоспособность;
- черепно-мозговая травма средней тяжести подразумевает некоторую приглушенность сознания, основные функции организма не нарушены, однако возможно учащение сердечного ритма. Присутствуют признаки очагового поражения и кровоизлияния. Угроза для жизни больного минимальна при своевременной помощи;
- тяжелая степень характеризуется выраженным оглушением или угнетением сознания. Отличается утратой произвольной деятельности, при этом остается рефлекторная. Врачи отмечают нарушения кровообмена и дыхания, имеются признаки неврологии. Возможен паралич или судороги. Имеется серьезная угроза для жизни пострадавшего;
- очень тяжелое состояние подразумевает кому, жизненно-важные функции человека нарушены, имеется первичная и вторичная неврологическая картина. Больным редко удается полностью восстановиться после травмы;
- терминальная степень характеризуется критической дисфункцией важных органов, стволовым нарушением. Отличается высокой вероятностью смертельного исхода.
Диагностика
Диагностика затрудняется алкогольным опьянением, в котором поступают большинство пострадавших. Постановка диагноза также затрудняется при остром нарушении кровообмена мозгового отдела. Для определения разновидности и тяжести черепно-мозговой травмы используют следующие методы: компьютерная томография, МРТ, рентгенография черепной коробки, клинический анализ крови и мочи. В сети клиник ЦМРТ рекомендуют прохождение следующих процедур:
К какому врачу обратиться
Для диагностики степени повреждения мозга при черепно-мозговой травмы в сети клиник ЦМРТ используют следующие методы исследования:
Лечение черепно-мозговой травмы
Курс лечения имеет комплексный характер, зависит от разновидности и тяжести травмы. Терапия легких повреждений подразумевает нахождение в травматологическом отделении. Тяжелые степени заболевания требуют госпитализации в реанимацию. Средний срок лечения в больничных условиях — 10 дней. Избавиться от боли удастся при помощи лекарственных препаратов. Также проводят восстановление проходимости дыхательных путей при их нарушении. Врач назначает процедуры для предупреждения гипотонии артериального типа. Лекарства снижают риск септических осложнений. Вылечить поможет противосудорожная терапия. В тяжелых случаях назначается оперативное вмешательство. В сети клиник ЦМРТ для лечения черепно-мозговой травмы используют следующие методы:
Осложнения
Если своевременно не оказать помощь больному, повышается вероятность остаться инвалидом. Объясняется это нарушением речевого аппарата, памяти, психики, развитием эпилепсии посттравматического типа.
Черепно-мозговые травмы отражаются на когнитивных функциях — у больного ухудшается концентрация внимания. При тяжелых травмах имеется риск амнезии, нарушений работы зрительного аппарата, паралича верхних конечностей. Возможна полная утрата речи, хронический болевой синдром на протяжении всей жизни. У перенесших черепно-мозговую травму отмечают апатию и раздражительность.
Профилактика черепно-мозговой травмы
Для снижения риска получения травмы и уменьшения вероятности развития последствий рекомендуется:
- соблюдать правила дорожного движения;
- соблюдать технику безопасности на производстве и во время поездки на транспортном средстве;
- после получения травмы требуется обратиться к врачу.