Оплачивать любые покупки, не используя при этом наличных денег, сегодня проще, чем когда-либо. Для этого даже необязательно доставать свою кредитку из кошелька. Система NFC позволяет сделать это, не прикасаясь к терминалу, а просто поднеся карточку, смартфон, часы или другое устройство на определенное расстояние от него. Уникальная методика стремительно набирает популярность во всем мире, поскольку выводит приобретение товаров на совершенно новый по удобству уровень. При этом остаются вопросы, связанные с безопасностью ее использования. В этой статье мы расскажем о бесконтактной технологии оплаты банковскими картами, объясним, что это такое и как правильно ее использовать.

Что это за способ
Суть такого платежа заключается в том, что не требуется прямого использования кредитки, для того чтобы списать с нее деньги. Если раньше проведение сделки сопровождалось вставкой средств в терминал или передачей через него магнитной полосой, то теперь достаточно держать его на близком расстоянии от банковского оборудования.
Устройство считает информацию, а затем передаст ее в эквайринговый центр, который разрешит или отменит операцию. Особенно важно, что использование карты для бесконтактной системы оплаты возможно с посторонних технических средств: смартфона, часов, браслета, к которым привязывается платежный инструмент. Собственно карточка при этом может оставаться дома.
Кредитки, которым доступен расчет без прямого контакта, как и торговое оборудование, принимающее их, имеют специальную маркировку – PayWave или PayPass, а также дополнительную эмблему-рисунок. Увидев такой знак в магазине можно быть уверенным, что такой способ доступен в этой точке.
Как называется система

Технология бесконтактных платежей известна как NFC — Near field communication. Перевод – «ближняя связь без контакта». Разберем каждое слово, чтобы лучше понять как устроена технология.
Термин «ближняя» означает, что обмен данными может происходить на небольшом расстоянии технических устройств друг от друга. Оно не превышает четырех сантиметров.
Значение слова «без контакта» заключается в том, что взаимосвязь не требует прямого воздействия карточки на торговый терминал. Считывание данных происходит с помощью индукции магнитного поля. Слово «связь» тоже весьма понятно и логично и обозначает взаимодействие между двумя техническими средствами.
Таким образом, получается, что система NFC – это обмен данными между 2 устройствами, происходящий с использованием принципа магнитного воздействия. Это определение не раскрывает всю сущность технологии, но демонстрирует главные ее черты.
Методика бесконтактной оплаты
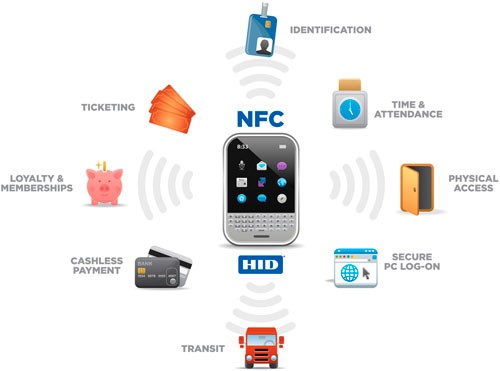
Сама по себе идея использования беспроводной передачи данных не нова. Первый стандарт пластиковых карт, способных производить расчет без прямого взаимодействия с торговым оборудованием, появился еще в 2004 году. Главная особенность системы кроется в объединении интерфейса смарт-карты и небольшого считывателя в одно устройство. Свою основу она взяла у метода радиочастотной идентификации RFID, которая дает возможность передачи данных по радиоканалу.
Раньше подобную методику использовали для приема платежей в транспортных средствах, а сегодня она перешла на работу с банками. Преимущественно для этого используются современные смартфоны и планшеты. Они могут обеспечить достаточную безопасность денежным средствам, поскольку оснащены хорошими системами защиты данных. Но чип NFC может быть помещен куда угодно: в браслет, электронные часы, удостоверение личности.
Готовые решения для всех направлений
Ускорь работу сотрудников склада при помощи мобильной автоматизации. Навсегда устраните ошибки при приёмке, отгрузке, инвентаризации и перемещении товара.
Узнать больше
Мобильность, точность и скорость пересчёта товара в торговом зале и на складе, позволят вам не потерять дни продаж во время проведения инвентаризации и при приёмке товара.
Узнать больше
Обязательная маркировка товаров — это возможность для каждой организации на 100% исключить приёмку на свой склад контрафактного товара и отследить цепочку поставок от производителя.
Узнать больше
Скорость, точность приёмки и отгрузки товаров на складе — краеугольный камень в E-commerce бизнесе. Начни использовать современные, более эффективные мобильные инструменты.
Узнать больше
Повысь точность учета имущества организации, уровень контроля сохранности и перемещения каждой единицы. Мобильный учет снизит вероятность краж и естественных потерь.
Узнать больше
Повысь эффективность деятельности производственного предприятия за счет внедрения мобильной автоматизации для учёта товарно-материальных ценностей.
Узнать больше
Первое в России готовое решение для учёта товара по RFID-меткам на каждом из этапов цепочки поставок.
Узнать больше
Исключи ошибки сопоставления и считывания акцизных марок алкогольной продукции при помощи мобильных инструментов учёта.
Узнать больше
Получение сертифицированного статуса партнёра «Клеверенс» позволит вашей компании выйти на новый уровень решения задач на предприятиях ваших клиентов..
Узнать больше
Используй современные мобильные инструменты для проведения инвентаризации товара. Повысь скорость и точность бизнес-процесса.
Узнать больше
Показать все решения по автоматизации
Функция бесконтактной оплаты на картах

Как уже говорилось ранее, возможности использования технологии практически безграничны. Функционал становится доступным клиентам платежных систем MasterCard, Visa и некоторым категориям карточек «Мир».
В последние пару лет NFC-система устанавливается в «пластик» по умолчанию, так что нет необходимости заказывать ее в виде дополнительной функции. Речь идет только об именных дебетовых и кредитных картах. Моментально выдаваемые платежные инструменты, не имеющие указанного имени владельца на лицевой стороне, позволяют оплачивать покупки только прежними способами: с помощью магнитной ленты или простого чипа.
Преимущества и недостатки бесконтактных платежей
Достоинств у технологии очень много, иначе она не стала бы так активно развиваться и распространяться. Среди прочего ее ценят за:
-
Возможность быстрого проведения операций.
-
Отсутствие необходимости давать свою карту в руки чужого человека.
-
Высокую технологичность.
-
Удобство и комфорт при совершении покупок.
Минусы тоже есть, но со временем их становится все меньше. Самым важным из них можно считать небольшое количество торговых точек, чье оборудование поддерживает NFC. С этим недостатком борются сами финансовые учреждения, являющиеся эквайерами для магазинов. Постепенно они заменяют терминалы на новое оборудование, в котором с легкостью можно пользоваться услугой.
Еще одной проблемой, с которой реально столкнуться, является достаточно высокая цена на торговое оборудование, поддерживающее бесконтактные карточки. Особенно сильно это мешает владельцам небольших предприятий торговли. Но и они при более тщательном рассмотрении вопроса нередко меняют свое мнение.
Как работает система

В общих чертах схема работы уже была представлена выше. В кредитки встраивается внутренний чип, излучающий радиоволны через антенну, те самые, которые распознаются технологией RFID. Сам терминал при этом оснащается считывателем, улавливающим данные.
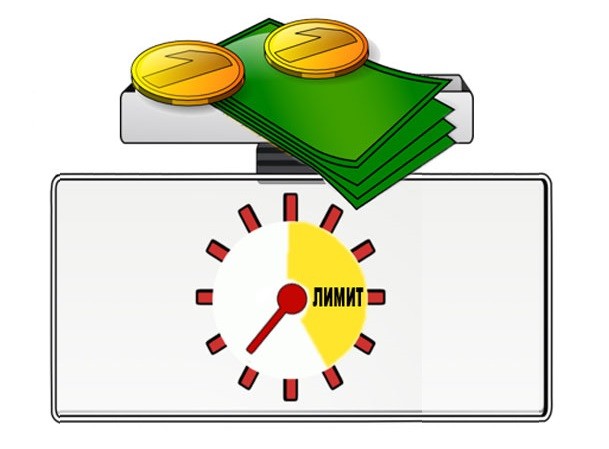
Когда клиент подносит свой «пластик» к торговому оборудованию на небольшое расстояние, сигнал с носителя считывается, и обрабатываются идентификационные данные. При этом маленькие суммы покупки не требуют, вообще, никакое дополнительное подтверждение, для крупных необходимо вводить пин-код.
Держать карточку у банковского терминала нужно в течение пары секунд. Этого времени оказывается достаточно, чтобы получить все необходимые сведения и передать их в эквайринговый центр. Чтобы покупатель точно знал, когда можно убирать платежный инструмент, устройство издает звуковой сигнал.
Способы бесконтактной оплаты картой
Ранее уже указывалось, что для совершения платежей без реального контакта могут быть использованы методики PayWave или PayPass. Первая активно задействуется системой Visa, вторая – MasterCard. Есть и иные варианты, разработанные специально для American Express, UnionPay и других операторов. Но все они строятся на одном и том же принципе работы, так что назвать их сильно отличающимися и, тем более, уникальными нельзя.
При таком раскладе способ для проведения платежей всегда один и тот же: чтобы совершить покупку необходимо поднести свой платежный инструмент к терминалу, способному уловить радиочастоту, на которой передает сведения чип. Более того, ровно такой же вариант можно использовать, если вместо собственно кредитки подносить к оборудованию другое техническое средство (смартфон, часы, фитнес-трекер). Разница, зависящая исключительно от банка и страны, прослеживается только в сумме, которую можно переводить без введения пин-кода.
Как пользоваться бесконтактной оплатой
Научиться делать покупки, используя систему NFC очень легко. Для этого не требуется никаких особых действий. Общая схема выглядит следующим образом:
-
Кассир вносит необходимые сведения в свой кассовый аппарат или банковское оборудование.
-
Покупатель проверяет на дисплее терминала корректность введенной суммы.
-
Платежный инструмент подносится к считывателю на расстояние, не превышающее 10 см, иногда его следует сократить до 4-х см.
-
После получения звукового сигнала карточку можно убирать.
-
При запросе дополнительно вводится пин-код. Это происходит, если превышен лимит траты без специального контроля. В России сумма составляет 999 рублей, все, что стоит дороже, должно подтверждаться паролем.
На всю процедуру уходит несколько секунд, после чего распечатывается чек, подтверждающий списывание денежных средств. Оплатить товар таким образом можно как в небольшом магазинчике, так и в представителе крупной федеральной сети.
Как настроить NFC для оплаты телефоном

Большинство современных мобильных устройств поддерживает эту систему расчета, но требует проведения специальной подготовительной процедуры. Каждый производитель предлагает выполнить ряд незначительно отличающихся действий, но в самом общем виде схема выглядит так:
-
Сначала необходимо открыть основные настройки смартфона.
-
Далее, следует найти вкладку «Беспроводные сети» и нажать на кнопку «Еще».
-
В выпавшем списке поищите функцию бесконтактной оплаты и дайте разрешение на ее использование.
-
Далее, следует привязать свою пластиковую карту к аккаунту на Google Pay.
После совершения всех действий можно начать использовать техническое средство для рассчета. Представленная схема касается устройств, работающих на базе операционной системы Android. Аппараты, использующие iOS с момента покупки настроены должным образом. К ним достаточно привязать кредитку.
Безопасность
Многих клиентов, кроме вопроса, как работает бесконтактная оплата банковской картой, волнует также тема безопасности ее использования. Не получится ли мошенникам списать средства, просто находясь рядом с сумкой, в которой лежит карточка? Как защитить свои деньги? В действительности, риск при правильном использовании технологии минимален.
Чтобы максимально сократить возможность неправомерных действий в отношении своих денежных средств, достаточно соблюдать 2 простых правила:
-
Снизить максимальный порог платежей, разрешенных без подтверждения пин-кодом.
-
Установить определенный лимит на количество операций, который совершаются с использованием NFC.
Еще одним способом, повышающим безопасность, может стать расчет с применением смартфона. Они сами по себе требуют дополнительной идентификации, чем исключают возможность совершения мошеннических действий. Снизить риск поможет и подключенное смс-информирование о покупках.
Готовые решения для всех направлений
Ускорь работу сотрудников склада при помощи мобильной автоматизации. Навсегда устраните ошибки при приёмке, отгрузке, инвентаризации и перемещении товара.
Узнать больше
Мобильность, точность и скорость пересчёта товара в торговом зале и на складе, позволят вам не потерять дни продаж во время проведения инвентаризации и при приёмке товара.
Узнать больше
Обязательная маркировка товаров — это возможность для каждой организации на 100% исключить приёмку на свой склад контрафактного товара и отследить цепочку поставок от производителя.
Узнать больше
Скорость, точность приёмки и отгрузки товаров на складе — краеугольный камень в E-commerce бизнесе. Начни использовать современные, более эффективные мобильные инструменты.
Узнать больше
Повысь точность учета имущества организации, уровень контроля сохранности и перемещения каждой единицы. Мобильный учет снизит вероятность краж и естественных потерь.
Узнать больше
Повысь эффективность деятельности производственного предприятия за счет внедрения мобильной автоматизации для учёта товарно-материальных ценностей.
Узнать больше
Первое в России готовое решение для учёта товара по RFID-меткам на каждом из этапов цепочки поставок.
Узнать больше
Исключи ошибки сопоставления и считывания акцизных марок алкогольной продукции при помощи мобильных инструментов учёта.
Узнать больше
Получение сертифицированного статуса партнёра «Клеверенс» позволит вашей компании выйти на новый уровень решения задач на предприятиях ваших клиентов..
Узнать больше
Используй современные мобильные инструменты для проведения инвентаризации товара. Повысь скорость и точность бизнес-процесса.
Узнать больше
Показать все решения по автоматизации
Насколько популярны дистанционные платежи

Распространенность системы NFC в сфере торговли и услуг растет с каждым днем. Если 3 года назад общая сумма покупок, совершенных с использованием бесконтактной оплаты, составляла не более двух миллиардов рублей, то буквально пару лет назад она возросла в 2 раза. Прогрессия увеличивается каждый месяц, а технология из крупных городов перекочевала в небольшие населенные пункты.
По статистике особенной популярностью это пользуется при совершении платежей в адрес сферы услуг, будь то ресторан, клуб или парк аттракционов. Его же предпочитают пассажиры общественного транспорта. Оно и понятно, никому не хочется возиться с мелкой наличкой в автобусной давке. Правда, здесь есть и другая сторона вопроса: сами представители организаций очень неохотно меняют уже установленное банковское оборудование на новое и более дорогостоящее. Так что, можно сказать, частота использования бесконтактных платежей в данный момент зависит только от предпринимателей. Покупатели готовы к их использованию.
Организация дистанционной оплаты
Сегодня практически в каждой торговой точке уже установлены POS-терминалы, дающие возможность безналичного расчета. В некоторых из них встроена бесконтактная система. Новичкам, которые только открывают свой бизнес, и тем представителям торговли, которые располагают старым оборудованием, действовать следует по одной схеме:
-
Изучите предложения банков, обеспечивающих эквайринг. Важна каждая деталь: тарифы, предоставляемые устройства и условия их обслуживания.
-
Выберите один вариант и подайте заявление о необходимости подключения оборудования, поддерживающего NFC.
-
Обеспечьте специалистам доступ к рабочему месту продавца для монтажа и настройки терминала.
После этого можно начинать активно использовать этот способ приема платежей в своем магазине. Покупатели отметят этот вариант, как очень удобный и эффективный, а значит уровень продаж увеличится.
Обзор софта «Курьер»

Это программное обеспечение от компании «Клеверенс» идеально подходит для работы в интернет-магазине, использующем мобильный POS-терминал. Если раньше таким организациям был доступен только один способ оплаты (непосредственно на сайте в момент покупки), то сегодня за укомплектованный и доставленный курьером товар можно заплатить у себя дома, в момент его передачи. При этом продажа будет сопровождаться выдачей реального чека, как того и требуют последние нововведения в законодательстве.
Весь процесс автоматизирован и не занимает много времени. Схема выглядит следующим образом:
-
Клиент оформляет заказ и принимает решение о выборе удобного для себя способа расчета.
-
Интернет-магазин обрабатывает заявку и отправляет по указанному адресу доставки.
-
Во время передачи покупки поставщик использует мобильный терминал, на который установлено ПО Mobile SMARTS: «Курьер».
-
Сведения отправляются в эквайринговый центр, распечатывается чек, подтверждающий совершение сделки.
-
Сведения перенаправляются оператору фискальных данных, а оттуда в налоговую службу.
Весь процесс занимает считанные секунды и является абсолютно безопасным для всех сторон. Кроме собственно терминала, софт можно использовать на смартфоне, планшете или ТСД, что значительно расширяет возможности продавца.
Заключение
Уровень конкуренции в торговле сегодня настолько высок, что в борьбе за каждого покупателя необходимо создавать самые комфортные условия, постоянно идти в ногу со временем. Оперативная оплата без контакта становится обязательным инструментом для достижения своих целей. Она позволяет работать быстро, качественно и безопасно, а главное – максимально удобно. Скорость проведения операций возрастает, а значит продавец имеет возможность обслуживать больше клиентов каждую рабочую схему.
В статье мы поговорили о системе бесконтактного платежа картой, выяснили, как называется такая оплата, как пользоваться платежным оборудованием и как оно работает.
Количество показов: 84018
EMV contactless symbol used on compatible payment terminals
Contactless payment systems are credit cards and debit cards, key fobs, smart cards, or other devices, including smartphones and other mobile devices, that use radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near-field communication (NFC, e.g. Samsung Pay, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Fitbit Pay, or any bank mobile application that supports contactless) for making secure payments. The embedded integrated circuit chip and antenna enable consumers to wave their card, fob, or handheld device over a reader at the point of sale terminal. Contactless payments are made in close physical proximity, unlike other types of mobile payments which use broad-area cellular or WiFi networks and do not involve close physical proximity.
EMV is a common standard used by major credit card and smartphone companies for use in general commerce. Contactless smart cards that function as stored-value cards are becoming popular for use as transit system farecards, such as the Oyster card or RioCard. These can often store non-currency value (such as monthly passes), in additional to fare value purchased with cash or electronic payment.
Tokenisation is a newer concept of encapsulating a card issuers details within a hardware device application such as via Apple Pay app on iPhones.
Some suppliers claim that transactions can be almost twice as fast as a conventional cash, credit, or debit card purchase. Because no signature or PIN verification is typically required, contactless purchases are usually limited to small value sales. Lack of authentication provides a window during which fraudulent purchases can be made while the card owner is unaware of the card’s loss.
Major financial institutions and multinational corporations now offer contactless payment systems to customers as contactless credit cards have become widespread in the U.S., U.K., Japan, Germany, Canada, Australia, France, the Netherlands, etc., as consumers are likely to spend more money using their cards due to the ease of small transactions. With contactless cards growing in numbers and percentages of adoption, the number of payments by this method had increased significantly since the spending limit was raised.[when?] Purchases made by card now surpass those made by cash and account for approximately one-third of all card transactions in countries like the UK.[citation needed] Contactless payments specifically have become increasingly popular, accounting for 4 out of 5 point-of-sale purchases in Australia as of 2019.[1] Card issuers indicate that they will increase the availability of contactless cards to consumers. There are over 58 million contactless-enabled cards and over 147,000 terminals in use in the UK alone,[citation needed] VISA estimated that there would be 300 million contactless cards issued in the US by the end of 2020, up from the predicted 100 million at the end of 2019.[citation needed]
Image of Contactless Card, opened up
History[edit]
1990s—2000s[edit]
Mobil was one of the most notable early adopters of a similar technology, and offered their «Speedpass» contactless payment system for participating Mobil gas stations as early as 1997. Although Mobil has since merged with Exxon, the service is still offered at many of ExxonMobil’s stations. Freedompay also had early wins in the contactless space with Bank of America[2] and McDonald’s.[3]
In 2002, Philips teamed up with Sony to elaborate the NFC standard.[4][5] Then Philips Semiconductors applied for the six fundamental patents of NFC, invented by the Austrian and French engineers Franz Amtmann and Philippe Maugars who received the European Inventor Award in 2015.[6]
In July 2004, Sony, who had implemented the contactless RFID smart card FeliCa in Japan, introduced the Osaifu-Keitai (おサイフケータイ) system (literal translation: «wallet-phone») developed with the mobile phone operator NTT DoCoMo on multiple FeliCa systems such as Edy and, on 28 January 2006, on Mobile Suica used primarily on the railway networks owned by JR East.[7]
In May 2005, after some experimentation in the Netherlands, the contactless deferred payment at the end of each month, after the registration of the trips aboard with a contactless mobile phone on the client’s account, was first experimented in Germany during 6 months on the tramways and bus of Hanau with the Nokia 3220 using the NFC standard of Philips and Sony.[8]
In October 2005, the immediate contactless payment was first experimented in France in Caen during 6 months with a Samsung NFC smartphone by Orange in collaboration with Philips Semiconductors in the Cofinoga shops (Galeries Lafayette, Monoprix) and Vinci parkings. For the first time, thanks to «Fly Tag», the system allowed to receive as well audiovisual informations, like bus timetables or cinema trailers from the concerned services.[7][5] In June 2007, the payment with a contactless bank card was tested at the FNAC of La Défense in Paris and from 19 November 2007 to 2009 in some shops of Caen and Strasbourg, this time with smartphones NFC, provided by four operators (Orange, Bouygues Telecom, SFR and NRJ Mobile).[5] On 5 November 2007, Orange and the transport societies SNCF and Keolis associated themselves for a 2 months experimentation with smartphones in Rennes in the metro, bus and TER trains.[9][5]
The first contactless cards in the UK were issued by Barclaycard in September 2007.[10] PayPass trialed the world’s first NFC-enabled phone, the Nokia 6131 NFC, in New York in 2007.[11]
In March 2008, Eat became the first restaurant chain to adopt contactless.[12]
On 19 January 2009, NFC is used in transports for the first time in the world by China Unicom and Yucheng Transportation Card with Changhong DG28 and F4 mobile phones in the tramways and bus of Chongqing in China.[13]
2010s[edit]
In January 2010, Barclaycard partnered with mobile phone firm Orange, to launch a contactless credit card in the UK.[14] Orange and Barclaycard also announced in 2009 that they would be launching a mobile phone with contactless technology.[15]
After a test conducted from October 2005 to November 2006 with 27 users,[16] on 21 May 2010, the transport authority of Nice Régie Lignes d’Azur was the first public transport provider in Europe to add definitely to its own offer a contactless payment on its tramways and bus network either with a NFC bank card or smartphone application notably on Samsung Player One (with the same mobile phone operators than in Caen and Strasbourg in 2007), as well as the validation aboard with them of the transport titles and the loading of these titles onto the smartphone, in addition to the season tickets contactless card.[17] This service was as well experimented then respectively implemented for NFC smartphones on 18 and 25 June 2013 in the tramways and bus of Caen[18][19] and Strasbourg.,[20][21] after the contactless payment on the 765 pay and display parking machines of Strasbourg was made available in October 2011. In the Paris transport network, after a 4 months testing from November 2006 with Bouygues Telecom and 43 persons[16] and finally with 8,000 users from July 2018, the contactless mobile payment and direct validation on the turnstile readers with a smartphone was adopted on 25 September 2019[22][23][24] in collaboration with the societies Orange, Samsung, Wizway Solutions, Worldline and Conduent.
NFC is used in Seoul[25] after its introduction in Korea by the discount retailer Homeplus in March 2010[26] and in Tokyo it is tested then adopted or added to the existing systems, like the mobile wallet Osaifu-Keitai, from May 2010 to end of 2012.[27][28] The NFC standard is implemented for the first time in a metro network, by China Unicom in Beijing on 31 December 2010.[29]
In October 2011, the first mobile phones with Mastercard PayPass and/or Visa payWave certification appeared. A PayPass or payWave account can be assigned to the embedded secure element and/or SIM card within the phones.
In October 2013, Citi Enterprise Payments and 3 Hong Kong, the mobile operation of Hutchison Telecommunications Hong Kong Holdings Limited (SEHK: 215), jointly announced the launch of ‘3 Citi Wallet.’ Using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, the ‘3 Citi Wallet’ was a multi-purpose mobile wallet service that included mobile payment, transaction history, a location-based special offer service and a search function that directed customers to the best deals within their vicinity. The 3Citi wallet was compatible with a wide range of designated smartphones, from Samsung, Sony, HTC, LG and iPhone. Over 9,000 Visa payWave readers across Hong Kong were able to accept contactless payments on Day 1.[30]
In February 2014, Mastercard announced that it would partner with Weve, which is a joint venture between EE, Telefónica UK, and Vodafone UK, to focus on mobile payments. The partnership will promote the development of «contactless mobile payment systems» by creating a universal platform in Europe for it.[31]
On 9 September 2014, Apple Inc. announced Apple Pay, a proprietary form of contactless payment integrated with its smartphones, with the release of the iPhone 6.[32]
In September 2014, Transport for London’s Tube began accepting contactless payment. TFL are claiming that they pushed the banking industry to develop the contactless system. See the tv programme Secrets of the London Underground Series 2 Episode 9 (around minute 58).The number of completed contactless journeys has now exceeded 300m. On Friday 18 December, the busiest single day in 2015, a record 1.24m journeys were completed by over 500k unique contactless cards.[33]
In 2016 Erste Group launched an NFC-only debit card implemented as a sticker in Austria. It can be used at any NFC supporting terminal for transactions of unlimited amount however for transactions over the floor limit of €25 a PIN is required to confirm the transaction.[34]
In 2016, contactless payments start to become even broader with wearable technology devices also offering this payment feature.
2020s[edit]
A Transport for London bus stop advertisement recommending contactless payment as safe during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic,[35] several banks raised their contactless payment limits.[36][37] In the United Kingdom, the limit was increased from £30 to £45 in March 2020.[38] Contactless payments were recommended as a safer payment method compared to Chip and PIN card payments and cash transactions.[39] It was later raised to £100. [40]
Adoption and usage[edit]
Google Pay is an application for devices running Google’s Android OS, which allows users to make purchases using NFC, which initially required a physical secure element but this was replaced by host card emulation which was introduced in Android 4.4 (KitKat). Softcard (formerly known as Isis mobile wallet), Cityzi and Quick Tap wallets for example, use a secure SIM card to store encrypted personal information. Contactless payments with enabled mobile phones still occur on a small scale, but every month an increasing number of mobile phones are certified.[41]
In 2012, Mastercard Advisors wrote that consumers are likely to spend more money using their cards due to the ease of small transactions.[42] Mastercard Canada says it has seen «about 25 percent» higher spending by users of its Mastercard Contactless-brand RFID credit cards.[43]
As of December 2014, there were approximately 58 million contactless-enabled cards in use in the UK, and over 147,000 terminals in use.[44][45] By June 2017 purchases made by card surpassed those made by cash. This was reported to have been driven by the rise in contactless payments, which accounted for approximately one third of all card transactions in the UK. The number of payments by this method had increased significantly since the spending limit was raised from £20 to £30.[46] In 2018, contactless payments made up around 19% of transactions in the UK.[47]
In 2018, the Westpac Banking Corporation in Australia revealed contactless payment statistics from 2017 and claimed in the report that contactless payments approached saturation point by being used in over 90% of purchases. The Australian St.George Bank reported 94.6% usage for the same period.[48]
Recent statements by Visa and other US card issuers indicate that they will increase the availability of contactless cards to US consumers in the near future. Visa estimates there will be 300 million contactless cards issued in the US by the end of 2020, up from the predicted 100 million at the end of 2019 as announced on its 2018 Q4 earnings call.[49]
Telecom operators are starting to get involved in contactless payments via the use of NFC-enabled phones. Belgacom’s Pingping, for example, has a stored value account and via a partnership with Alcatel-Lucent’s Touchatag provides contactless payment functionalities.
Major financial entities now offering contactless payment systems include Mastercard, China UnionPay, Citibank, JPMorgan Chase, American Express, KeyBank, Barclays, Barclaycard, HSBC, Lloyds Banking Group, FreedomPay, RuPay, The Co-operative Bank, Nationwide Building Society and NatWest Group. Visa payWave, American Express Expresspay, and Mastercard Contactless are examples of contactless credit cards which have become widespread in the U.S. and U.K.
Technology[edit]
There are two main standard usages for contactless payments adopted throughout payment terminals with the EMV standard.
EMV Chip
On issued bank cards a smart chip or cryptographic chip is placed on the card known as a smart card which allows wireless payments to be made from the EMV chip in range of a payment terminal using RFID technology following the EMVCo standard. When the smart card is tapped against a payment terminal that authenticates the card issuer’s details through a series of PIN interactions the payment for the interaction will succeed.
Tokenisation
A newer approach to smart card technology is achieved by linking a smart card to a hardware device, such as through the Apple Pay application on an iPhone mobile phone, thereby allowing mobile devices the ability to make payments using RFID technology against a payment terminal on behalf of a smart card using a token generated by the card issuer, a process known as tokenisation. A Device Account Number (DAN) similar to a Private Account Number (PAN) in traditional payment stripe and chip cards, is generated along with a private key and sent to the card issuer during initial setup of the smart card on the hardware device. When payments are made via the respective approved application on the hardware device the DAN and relevant details such as expiry date and CVV are sent to the card issuer via a payment terminal for cryptography where the associated private key is then used to authorise the transaction.
NFC
The near field communication (NFC, compliant with ISO/IEC 14443[50] standard) technology in contactless cards uses a 13.56Mhz radio frequency technology that only transmits digital data within a concise range.
Typically the optimum distance is 4 centimetres or less — beyond, the signal is rapidly decreasing and can never exceed 10 centimetres.
Security[edit]
In 2006 security researchers found that the cardholder’s name, credit card number, and expiration date may be transmitted by contactless payment cards without encryption. They were able to use information leaked from a contactless credit card to make a purchase online, without opening the envelope in which the card was sent.[51]
Depending on the economic space, there may be a payment limit on single transactions without the need to input the PIN, and some contactless cards can only be used a certain number of times before customers are asked for their PIN.[52] Contactless debit and credit transactions use the same chip and PIN network as older cards and are protected by the same fraud guarantees. Where PIN is supported, the contactless part of the card may remain non-functional until a standard chip and PIN transaction has been executed.[53] This provides some verification that the card was delivered to the actual cardholder.
Under fraud guarantee standards, U.S. banks are liable for any fraudulent transactions charged to the contactless cards.
CVM limit[edit]
Because no signature or PIN verification is typically required, contactless purchases are often limited to a maximum amount per transaction, known as a Cardholder Verification Limit (CVM limit). Limits vary between banks. For transactions over the defined CVM limit a verification is usually required (e.g. PIN, signature, or biometric authentication).
Transactions under the floor limit, in addition to not requiring consumer authentication, are also accepted without sending the transaction online for verification by the acquiring host.
Note that these limits typically do not apply when CDCVM verification (such as in Apple Pay) is used.
| Economic space | CVM limit | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | $200 | For transactions over A$200 a PIN or biometric authentication is required.[54][55] |
| Austria | €25 | For transactions exceeding €25 a PIN is required. Additionally for cards produced before 2017 only five transactions can be made without a PIN.[56] Cards issued after December 2016 need a PIN code for transactions over €25 or a contactless total of €125. |
| Azerbaijan | ₼100 | For transactions of ₼100 and above using a physical card a PIN is required. There’s no mandatory PIN requirement when CDCVM (Apply Pay, Garmin Pay, or Google Pay) is used. |
| Bahrain | 20 BHD | |
| Bangladesh | BDT3000.00 | For transactions over BDT3000.00 a PIN is required. |
| Belgium | €50 | Since the COVID crisis, transaction limits in Belgium were increased. For transactions over €50 a PIN is required. When several contactless payments in a row reach the amount of €125, the PIN is required. |
| Brazil | R$200 | For transactions over R$200,00 a PIN is required.[57] |
| Bulgaria | 50 BGN | For transactions over 50 BGN (~€25) a PIN is required. 25 BGN (~€12) until April 12, 2019. |
| Canada | No limit | Limits are completely at the discretion of the merchant’s acquiring bank and the consumer’s bank. There is no law limiting the amounts. However, in practice, financial institutions limit contactless payments to $CA100. Some merchants may accept higher amounts subject to signature verification. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, MasterCard, Visa, and American Express increased their limits to $250.[58][59] |
| Chile | $12.000 CLP | |
| China | CN¥1000[60] | UnionPay QuickPass. PIN required unless disabled with bank. |
| Colombia | No limit | For transactions over COP 100.000 PIN is required. |
| Costa Rica | No limit | For transactions over ₡30000 signature is required.[61] Beginning July 1, 2022, PIN will be required instead.[62] |
| Croatia[63] | No limit | For transactions over 250HRK PIN or signature are needed. |
| Curaçao | ANG 45 | For transactions over ANG 45 a PIN is required. When several contactless payments in a row reach the amount of ANG 100, the PIN is required. |
| Czech Republic | No limit | For transactions over 500 CZK PIN is needed. After 3 consecutive contactless transactions, PIN is required. |
| Denmark[64] | 350 DKK | For transactions over 350 DKK PIN is needed. Sometimes PIN is needed anyway to ensure the card is used by its owner. |
| Dominican Republic | No limit | |
| Estonia[65] | €50 | |
| Finland | €50 | €25 up until April 12, 2019. After that it will be €50. |
| France | €50 | Can be used up to three times a day. |
| Germany | No limit | For each transaction over €25 or €50 (some Visa cards) a PIN or CDCVM verification is required. |
| Greece | €50 | For transactions over €50 a PIN is required |
| Hong Kong | No limit | Initially banks, not government, set it for $500 or under, then (for some banks) under $1000 (HKD), until the limits were removed. |
| Hungary | No limit | For transactions over 5000 HUF PIN is needed. For every 10 consecutive contactless transactions or if you reach 10.000 HUF PIN is needed. Due the COVID-19 pandemic, the 5000 HUF limit is increased to 15 000 HUF. No limit for Apple Pay or similar contactless purchases. |
| Iceland | ISK 5.000 | Íslandsbanki has a lower limit of ISK 4.200. For each transaction over the limit, Chip and PIN are required. Also, a cumulative limit of ISK 10.000 between Chip and PIN uses. |
| India | ₹5000 | For transactions above ₹5000, a PIN is required. |
| Indonesia | Rp1.000.000 | Transactions above Rp1.000.000, must require 6-digits PIN authorization. |
| Ireland | €50 | Increased from €30 to €50 on 1 April 2020.[66] There is no transaction limit when using contactless with two-factor authentication (e.g. Apple Pay), although some merchants still apply a €50 transaction limit[67] |
| Israel | 300 ILS | For transactions over 300 ILS PIN is needed |
| Italy | No limit | For transactions over €50 PIN is needed |
| Japan | JP¥20000 | JCB QUICPay and QUICPay+[68] |
| Latvia[69] | €50 | |
| Lithuania[70] | €50 | |
| North Macedonia | 750 MKD | |
| Malaysia | RM250 | Cumulative limits (total amount and/or consecutive transactions) differ between card issuers.[71]
By default, for each transaction above RM250 PIN is required. But the limit is customizable.[72] |
| Netherlands[73] | No limit | For card payments of more than €25 at once or €50 in a row a PIN is required. Some older cards only allow five transactions in a row without a PIN. Most if not all retailers have, by now, terminals that support CDCVM as verification (i.e. Apple Pay). Most banks have had Android NFC/Tap&Pay through their mobile banking apps for a few years now. While Apple Pay was launched (unofficially) by bunq on March 20, 2018, through a workaround,[74] and to be joined officially by ING on June 11, 2019,[75] followed by the official launch for bunq on Sept. 3rd and the announcement that banks ABN AMRO and Rabobank will also start to offer Apple Pay in The Netherlands sometime in 2019.[76] Also note that broad acceptance of credit cards isn’t commonplace yet, so that’s up to the individual merchant. Maestro by Mastercard is the dominant card type and accepted everywhere. |
| New Zealand | $200 | For each transaction over NZ$200 a PIN is required. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, this amount was temporarily raised to NZ$200, in an effort to further reduce unnecessary contact.[77] |
| Norway[78] | No limit | For each transactions over 500 NOK a PIN is required.[79] Sometimes PIN is needed anyway to ensure the card is used by its owner. |
| Pakistan | Rs 3500 | Transactions above Rs 3500 require pin verification. |
| Philippines | ₱5000 | Increased from ₱2000 to ₱5000 in 2020.[80] |
| Poland | No limit | For transactions over or equal to 100 PLN PIN is required. |
| Portugal | No limit | For more than €50 PIN verification is mandatory[81] |
| Romania | No limit | For transactions over or equal to 100 lei PIN is required. |
| Russia | No limit | For transactions over ₽1000 PIN or signature is required. |
| Saudi Arabia | 300 SAR | For transactions over 300 SAR, PIN is required. |
| Serbia | 4000 RSD | For transactions over 4000 RSD, PIN verification is required. |
| Singapore | S$100 | The current transaction limit for contactless payments in Singapore is S$100, although some banks offer higher.[82] |
| Slovakia | No limit | For transactions over €20 PIN is needed. After 3 consecutive contactless transactions, PIN is required. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, this amount was temporarily raised to €50, in an effort to further reduce unnecessary contact.[83] |
| Slovenia | No limit | For transactions over €25 PIN is needed. |
| South Africa | 500 ZAR | Increased to R500 in May 2017 (except for ABSA Bank which remained at R200)[84] |
| Spain | No limit | For more than €50 PIN verification is mandatory except using mobile payments sometimes. It was increased from €20 to €50 to avoid contact because of the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Sri Lanka | No limit | For more than LKR 5000 PIN/signature verification is required |
| Sweden | 200 SEK | For each transaction over 200 SEK a PIN is required. |
| Switzerland | 80 CHF | For transactions over 80 CHF a PIN is required. |
| Taiwan | No limit | Signatures may be required for large purchases. |
| Thailand | ฿1500 | |
| Turkey | ₺500 | For transactions over ₺500 PIN is required. |
| Ukraine | 1500 UAH | For transactions over 1500 UAH a PIN is required |
| United Kingdom | £100 | Previous limits:
Chancellor of the Exchequer Rishi Sunak confirmed in the 2021 budget that this limit would increase to £100 on 15 October 2021. This floor limit increase was later confirmed by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) |
| United States of America | No limit | A signature may be required for large purchases. Banks may set their own limits or require a PIN. |
See also[edit]
- Apple Pay
- Digital currency
- Contactless smart card
- Cashless society and reducing disease transmittal
- Dashtop mobile
- Google Pay
- Microsoft Pay
- Mobile payment
- Near field communication
- Proximity card
- Octopus card
- OPUS card
- Oyster card
- Opal card
- Presto card
- Rav-Kav
- Ventra
- Samsung Pay
- Softcard (formerly Isis mobile wallet)
- Vicinity cards
References[edit]
- ^ Reserve Bank of Australia (19 April 2022). «How Australians pay Snapshot (2019 Consumer Payments Survey)». Reserve Bank of Australia. Archived from the original on 2020-03-01. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ «FreedomPay makes waves in contactless payment — SecureIDNews».
- ^ «McDonald’s testing e-payment system». USA Today. 2001-05-29.
- ^ «Sony et Philips contrent Bluetooth» (in French). 01net.com. 18 September 2002. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ a b c d «Les transports en commun niçois se mettent au paiement sans contact» (in French). 01net.com. 24 May 2009. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «Philippe Maugars : le père français du NFC sacré inventeur européen de l’année» (in French). 01net.com. 12 June 2015. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ a b «Caen, la ville où l’on paye et s’informe en sortant son portable» (in French). 01net.com. 20 October 2005. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «A Hanau, le portable-ticket de bus joue au juste prix» (in French). 01net.com. 2 May 2005. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Les transports rennais payés par mobile ‘sans contact’» (in French). 01net.com. 7 November 2007. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Barclaycard rolls out Oyster payments card». Finextra. Finextra. September 2007.
- ^ «Nokia 6131 NFC – touch to pay credit card mobile phones start trickling onto the market». 22 November 2007.
- ^ «First Fully Integrated Contactless Payment System in UK». www.paymentnews.com. 2008-03-26. Archived from the original on 2014-03-02. Retrieved 2012-08-26.
- ^ «Mobile and transit operators launch NFC payments system in Chongqing». nfcw.com. 19 January 2019. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Orange and Barclaycard deliver next step in their partnership with contactless co-branded credit card». Barclaycard. Barclaycard. January 2010.
- ^ «Barclaycard and Orange unveil pay-by-mobile service by Garry White». Daily Telegraph. London. 2009-03-08. Retrieved 2010-08-06.
- ^ a b «Télécoms — La révolution mobile sans contact arrive en 2008» (in French). banquedesterritoires.fr. 21 December 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «Nice, première ville à passer au paiement sans contact» (in French). 01net.com. 21 May 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ «A Caen, avec un mobile sans contact, on valide dans les bus et trams». 01net.com (in French). 18 June 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «NFC transit ticketing service goes live in French city of Caen». nfcw.com. 18 June 2013. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ «A Strasbourg, on voyage en bus et en tram grâce à un mobile sans contact» (in French). 01net.com. 27 June 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «Strasbourg NFC ticketing moves to commercial launch». nfcw.com. 5 July 2013. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ «Ça y est, certains smartphones Samsung peuvent servir de titres de transport en Île-de-France !» (in French). Twitter. 8 April 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ «Le dernier (ticket de) métro, at 2:10 and 2:38» (in French). YouTube. 24 September 2018. Archived from the original on 2021-12-17. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «Et si vous achetiez vos titres de transport depuis votre appli RATP ?» (in French). RATP. 12 November 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «KDDI, Softbank Mobile and SK Telecom to introduce NFC standard services in Japan and Korea». nfcw.com. 15 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «SK Telecom and Hana launch SIM-based mobile contactless payments and promotions service». nfcw.com. 25 March 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Gemalto provides KDDI with end-to-end NFC security solution». nfcw.com. 14 June 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «NTT Docomo partners with Korea’s KT to switch to NFC at end of 2012». nfcw.com. 9 February 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «China Unicom launches commercial NFC service in Beijing». nfcw.com. 5 January 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «3 Hong Kong and Citibank Jointly Launch ‘3 Citi Wallet’ New Mobile Payment Technology Turns Mobile Phones into Digital Wallets New Milestone in Mobile Payment». www.citigroup.com. Retrieved 2021-05-11.
- ^ Villarreal, Alexandra. «MasterCard, Weve partner to accelerate contactless payments shift in U.K.» Archived 2016-01-17 at the Wayback Machine Bank Credit News. 2/10/2014. Retrieved 2/10/2014.
- ^ Jeffries, Adrianne (September 9, 2014). «Apple Pay allows you to pay at the counter with your iPhone 6». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 10, 2014. Retrieved September 13, 2014.
- ^ «Contactless has caught on underground». Barclaycard. Barclaycard. February 2016.
- ^ «BankCard Sticker». Erste Bank und Sparkassen. Erste Bank Group. January 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-08-22.
- ^ WHO encourages use of contactless payments due to COVID-19
- ^ Increase in contactless payments limit may not be ready until April
- ^ Contactless card payment limit to change in emergency move amid coronavirus pandemic
- ^ «Contactless limit in UK to be increased to £45». UK Finance. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Clark, Derin (24 March 2020). «Contactless limit is set to rise to £45 to help fight Covid-19». Moneyfacts.co.uk. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ «Contactless limit to increase to £100 from 15 October».
- ^ «Certified phones». nfc-phones.org. Archived from the original on 2015-10-11. Retrieved 2015-02-07.
- ^ «New MasterCard Advisors Study on Contactless Payments Shows Almost 30% Lift in Total Spend Within First Year of Adoption». newsroom.mastercard.com. 2012-05-03. Retrieved 2013-03-13.
- ^ Dubinsky, Zach. «New credit cards pose security problem». CBCNews.ca. 2010-06-02. Retrieved 2010-06-03.
- ^ Campbell, Francis. «Contactless payments taking off in the UK in 2015». mobiletransaction.org. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ «Key Facts and Stats». Archived from the original on July 21, 2010. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- ^ Jones, Rupert (2017-07-12). «Cash no longer king as contactless payments soar in UK stores». The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2019-05-03.
- ^ https://www.ukfinance.org.uk/sites/default/files/uploads/pdf/UK-Finance-UK-Payment-Markets-Report-2019-SUMMARY.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ «Contactless Payments Statistics Australia 2017 | Westpac». www.westpac.com.au. Retrieved 2018-07-09.
- ^ Sacchi, Guido. «Payment Security: Can It Be Frictionless and Secure?». Global Payments.
- ^ https://www.iso.org/standard/73599.html
- ^ Schwartz, John (2006-10-23). «Researchers See Privacy Pitfalls in No-Swipe Credit Cards». The New York Times. Retrieved 2019-09-22.
- ^ «Lloyds Bank — UK Bank Accounts — Contactless Debit Cards».
- ^ «Why doesn’t my contactless card work?».
- ^ «MasterCard® contactless». MasterCard. MasterCard Australia. Archived from the original on 18 February 2016. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ «Visa payWave: FAQs». Visa Australia. Visa. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ «Maestro® kontraktlos». Maestro. Maestro Austria. Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- ^ «Empresas aumentam limite de pagamentos por aproximação; veja valores». OlharDigital. Olhar Digital. 24 December 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ Jon Rumley (2020-04-07). «Mastercard, Visa Raise Tap Limits, And Stores Want Interac To Follow». huffingtonpost.ca. Huffington Post. Retrieved 2020-04-13.
- ^ Gary Ng (2020-04-07). «American Express Canada Increases Tap Payment Limit to $250 Due to COVID-19». iphoneincanada.ca. iPhone In Canada. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «UnionPay «Quickpass» sets foot on first foreign market». Archived from the original on 2017-01-04. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ Sequeira, Rebeca. «Pagos con tarjeta por menos de ₡30 mil no requerirán firma» [Card payments of less than ₡30,000 will not require a signature]. La República (in Spanish). Retrieved 27 August 2021.
- ^ Gudiño, Ronny. «Le solicitarán PIN en compras superiores a los ₡30 mil a partir de julio del 2022» [You will be asked your PIN on purchases over ₡30,000 beginning July 2022]. La República (in Spanish). Retrieved 27 August 2021.
- ^ «Beskontaktno plaćanje — Prihvat kartica — PBZCard.hr».
- ^ «Dankortet bliver nu kontaktløst»
- ^ «Swedbank». Swedbank. Retrieved 2017-01-02.
- ^ «Rollout of contactless limit increase well underway as all parties work towards national completion by 1 April — Banking and Payments Federation Ireland». www.bpfi.ie. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 2020-04-18.
- ^ «Apple Pay contactless service launches in Ireland». 7 March 2017. Retrieved 2019-12-05 – via www.irishtimes.com.
- ^ «JCB QUICPay». Retrieved 5 September 2017.
- ^ «Banks Increase Contactless Card Limits to 50 Euro». Finance Latvia Association. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 2021-01-07.
- ^ «Contactless cards». Swedbank. Retrieved 2016-09-01.
- ^ «FAQs on migration to PIN-based payment cards» (PDF). Bank Negara Malaysia. 28 October 2016. p. 2. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ^ John Lim (3 January 2017). «How to disable contactless payment?». says.com.
- ^ «Mijlpaal: 100 miljoen contactloze betalingen | CCV Holland». www.ccv.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2015-11-20.
- ^ «Apple Pay via omweg voor bunq-klanten alweer teruggedraaid». Bright.nl (in Dutch). 21 March 2018. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ^ «Apple Pay nu gratis beschikbaar voor ING-klanten met iPhone». AD.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2019-10-10.
- ^ «Ook ABN AMRO, Rabobank en bunq kondigen Apple Pay ondersteuning aan». AD.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2019-09-24.
- ^ «Covid 19 coronavirus: Paywave eftpos limit raised to $200 — but two banks lag». NZ Herald. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ «200.000 tæpper hver dag | BankAxept». www.ntbinfo.no (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2019-04-01.
- ^ «Grensen for kontaktløs betaling med BankAxept uten PIN-kode økes». Finans Norge (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ «MasterCard raises payments limits for PH». The Manila Times. 26 July 2020. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ^ «Os pagamentos «sem contacto» até 50 euros vieram para ficar». www.bportugal.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2020-07-13.
- ^ Boon, Rachel (8 February 2017). «Nets payments to go digital and contactless». The Straits Times. Retrieved 25 August 2017.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ «‘Tap ‘n go’ not as risky as many fear». Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- ^ Barclays. «Ten years of contactless | Barclays». Barclays. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ Gough, Owen (2 March 2017). «Supermarket contactless spending jumps as ‘touch and go’ overtakes Chip and PIN». Small Business. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ BBC News (1 June 2012). «Contactless pay limit up to £20». BBC News. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ «Contactless card limit rises to £30 as card use surges». BBC News. 1 September 2015.
- ^ «Apple Pay 100% Backed By UK’s Major Banks — Including Barclays». Know Your Mobile. Retrieved 2016-05-04.
External links[edit]
- A Comprehensive Technical Overview of Contactless
- Contactless.info, archived from the original on April 24, 2014 is designed to provide information for UK retailers that have an interest in Contactless card acceptance]
- New credit cards pose security problem, CBC News
- Chase’s «blink» uses RFID
EMV contactless symbol used on compatible payment terminals
Contactless payment systems are credit cards and debit cards, key fobs, smart cards, or other devices, including smartphones and other mobile devices, that use radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near-field communication (NFC, e.g. Samsung Pay, Apple Pay, Google Pay, Fitbit Pay, or any bank mobile application that supports contactless) for making secure payments. The embedded integrated circuit chip and antenna enable consumers to wave their card, fob, or handheld device over a reader at the point of sale terminal. Contactless payments are made in close physical proximity, unlike other types of mobile payments which use broad-area cellular or WiFi networks and do not involve close physical proximity.
EMV is a common standard used by major credit card and smartphone companies for use in general commerce. Contactless smart cards that function as stored-value cards are becoming popular for use as transit system farecards, such as the Oyster card or RioCard. These can often store non-currency value (such as monthly passes), in additional to fare value purchased with cash or electronic payment.
Tokenisation is a newer concept of encapsulating a card issuers details within a hardware device application such as via Apple Pay app on iPhones.
Some suppliers claim that transactions can be almost twice as fast as a conventional cash, credit, or debit card purchase. Because no signature or PIN verification is typically required, contactless purchases are usually limited to small value sales. Lack of authentication provides a window during which fraudulent purchases can be made while the card owner is unaware of the card’s loss.
Major financial institutions and multinational corporations now offer contactless payment systems to customers as contactless credit cards have become widespread in the U.S., U.K., Japan, Germany, Canada, Australia, France, the Netherlands, etc., as consumers are likely to spend more money using their cards due to the ease of small transactions. With contactless cards growing in numbers and percentages of adoption, the number of payments by this method had increased significantly since the spending limit was raised.[when?] Purchases made by card now surpass those made by cash and account for approximately one-third of all card transactions in countries like the UK.[citation needed] Contactless payments specifically have become increasingly popular, accounting for 4 out of 5 point-of-sale purchases in Australia as of 2019.[1] Card issuers indicate that they will increase the availability of contactless cards to consumers. There are over 58 million contactless-enabled cards and over 147,000 terminals in use in the UK alone,[citation needed] VISA estimated that there would be 300 million contactless cards issued in the US by the end of 2020, up from the predicted 100 million at the end of 2019.[citation needed]
Image of Contactless Card, opened up
History[edit]
1990s—2000s[edit]
Mobil was one of the most notable early adopters of a similar technology, and offered their «Speedpass» contactless payment system for participating Mobil gas stations as early as 1997. Although Mobil has since merged with Exxon, the service is still offered at many of ExxonMobil’s stations. Freedompay also had early wins in the contactless space with Bank of America[2] and McDonald’s.[3]
In 2002, Philips teamed up with Sony to elaborate the NFC standard.[4][5] Then Philips Semiconductors applied for the six fundamental patents of NFC, invented by the Austrian and French engineers Franz Amtmann and Philippe Maugars who received the European Inventor Award in 2015.[6]
In July 2004, Sony, who had implemented the contactless RFID smart card FeliCa in Japan, introduced the Osaifu-Keitai (おサイフケータイ) system (literal translation: «wallet-phone») developed with the mobile phone operator NTT DoCoMo on multiple FeliCa systems such as Edy and, on 28 January 2006, on Mobile Suica used primarily on the railway networks owned by JR East.[7]
In May 2005, after some experimentation in the Netherlands, the contactless deferred payment at the end of each month, after the registration of the trips aboard with a contactless mobile phone on the client’s account, was first experimented in Germany during 6 months on the tramways and bus of Hanau with the Nokia 3220 using the NFC standard of Philips and Sony.[8]
In October 2005, the immediate contactless payment was first experimented in France in Caen during 6 months with a Samsung NFC smartphone by Orange in collaboration with Philips Semiconductors in the Cofinoga shops (Galeries Lafayette, Monoprix) and Vinci parkings. For the first time, thanks to «Fly Tag», the system allowed to receive as well audiovisual informations, like bus timetables or cinema trailers from the concerned services.[7][5] In June 2007, the payment with a contactless bank card was tested at the FNAC of La Défense in Paris and from 19 November 2007 to 2009 in some shops of Caen and Strasbourg, this time with smartphones NFC, provided by four operators (Orange, Bouygues Telecom, SFR and NRJ Mobile).[5] On 5 November 2007, Orange and the transport societies SNCF and Keolis associated themselves for a 2 months experimentation with smartphones in Rennes in the metro, bus and TER trains.[9][5]
The first contactless cards in the UK were issued by Barclaycard in September 2007.[10] PayPass trialed the world’s first NFC-enabled phone, the Nokia 6131 NFC, in New York in 2007.[11]
In March 2008, Eat became the first restaurant chain to adopt contactless.[12]
On 19 January 2009, NFC is used in transports for the first time in the world by China Unicom and Yucheng Transportation Card with Changhong DG28 and F4 mobile phones in the tramways and bus of Chongqing in China.[13]
2010s[edit]
In January 2010, Barclaycard partnered with mobile phone firm Orange, to launch a contactless credit card in the UK.[14] Orange and Barclaycard also announced in 2009 that they would be launching a mobile phone with contactless technology.[15]
After a test conducted from October 2005 to November 2006 with 27 users,[16] on 21 May 2010, the transport authority of Nice Régie Lignes d’Azur was the first public transport provider in Europe to add definitely to its own offer a contactless payment on its tramways and bus network either with a NFC bank card or smartphone application notably on Samsung Player One (with the same mobile phone operators than in Caen and Strasbourg in 2007), as well as the validation aboard with them of the transport titles and the loading of these titles onto the smartphone, in addition to the season tickets contactless card.[17] This service was as well experimented then respectively implemented for NFC smartphones on 18 and 25 June 2013 in the tramways and bus of Caen[18][19] and Strasbourg.,[20][21] after the contactless payment on the 765 pay and display parking machines of Strasbourg was made available in October 2011. In the Paris transport network, after a 4 months testing from November 2006 with Bouygues Telecom and 43 persons[16] and finally with 8,000 users from July 2018, the contactless mobile payment and direct validation on the turnstile readers with a smartphone was adopted on 25 September 2019[22][23][24] in collaboration with the societies Orange, Samsung, Wizway Solutions, Worldline and Conduent.
NFC is used in Seoul[25] after its introduction in Korea by the discount retailer Homeplus in March 2010[26] and in Tokyo it is tested then adopted or added to the existing systems, like the mobile wallet Osaifu-Keitai, from May 2010 to end of 2012.[27][28] The NFC standard is implemented for the first time in a metro network, by China Unicom in Beijing on 31 December 2010.[29]
In October 2011, the first mobile phones with Mastercard PayPass and/or Visa payWave certification appeared. A PayPass or payWave account can be assigned to the embedded secure element and/or SIM card within the phones.
In October 2013, Citi Enterprise Payments and 3 Hong Kong, the mobile operation of Hutchison Telecommunications Hong Kong Holdings Limited (SEHK: 215), jointly announced the launch of ‘3 Citi Wallet.’ Using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology, the ‘3 Citi Wallet’ was a multi-purpose mobile wallet service that included mobile payment, transaction history, a location-based special offer service and a search function that directed customers to the best deals within their vicinity. The 3Citi wallet was compatible with a wide range of designated smartphones, from Samsung, Sony, HTC, LG and iPhone. Over 9,000 Visa payWave readers across Hong Kong were able to accept contactless payments on Day 1.[30]
In February 2014, Mastercard announced that it would partner with Weve, which is a joint venture between EE, Telefónica UK, and Vodafone UK, to focus on mobile payments. The partnership will promote the development of «contactless mobile payment systems» by creating a universal platform in Europe for it.[31]
On 9 September 2014, Apple Inc. announced Apple Pay, a proprietary form of contactless payment integrated with its smartphones, with the release of the iPhone 6.[32]
In September 2014, Transport for London’s Tube began accepting contactless payment. TFL are claiming that they pushed the banking industry to develop the contactless system. See the tv programme Secrets of the London Underground Series 2 Episode 9 (around minute 58).The number of completed contactless journeys has now exceeded 300m. On Friday 18 December, the busiest single day in 2015, a record 1.24m journeys were completed by over 500k unique contactless cards.[33]
In 2016 Erste Group launched an NFC-only debit card implemented as a sticker in Austria. It can be used at any NFC supporting terminal for transactions of unlimited amount however for transactions over the floor limit of €25 a PIN is required to confirm the transaction.[34]
In 2016, contactless payments start to become even broader with wearable technology devices also offering this payment feature.
2020s[edit]
A Transport for London bus stop advertisement recommending contactless payment as safe during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During the COVID-19 pandemic,[35] several banks raised their contactless payment limits.[36][37] In the United Kingdom, the limit was increased from £30 to £45 in March 2020.[38] Contactless payments were recommended as a safer payment method compared to Chip and PIN card payments and cash transactions.[39] It was later raised to £100. [40]
Adoption and usage[edit]
Google Pay is an application for devices running Google’s Android OS, which allows users to make purchases using NFC, which initially required a physical secure element but this was replaced by host card emulation which was introduced in Android 4.4 (KitKat). Softcard (formerly known as Isis mobile wallet), Cityzi and Quick Tap wallets for example, use a secure SIM card to store encrypted personal information. Contactless payments with enabled mobile phones still occur on a small scale, but every month an increasing number of mobile phones are certified.[41]
In 2012, Mastercard Advisors wrote that consumers are likely to spend more money using their cards due to the ease of small transactions.[42] Mastercard Canada says it has seen «about 25 percent» higher spending by users of its Mastercard Contactless-brand RFID credit cards.[43]
As of December 2014, there were approximately 58 million contactless-enabled cards in use in the UK, and over 147,000 terminals in use.[44][45] By June 2017 purchases made by card surpassed those made by cash. This was reported to have been driven by the rise in contactless payments, which accounted for approximately one third of all card transactions in the UK. The number of payments by this method had increased significantly since the spending limit was raised from £20 to £30.[46] In 2018, contactless payments made up around 19% of transactions in the UK.[47]
In 2018, the Westpac Banking Corporation in Australia revealed contactless payment statistics from 2017 and claimed in the report that contactless payments approached saturation point by being used in over 90% of purchases. The Australian St.George Bank reported 94.6% usage for the same period.[48]
Recent statements by Visa and other US card issuers indicate that they will increase the availability of contactless cards to US consumers in the near future. Visa estimates there will be 300 million contactless cards issued in the US by the end of 2020, up from the predicted 100 million at the end of 2019 as announced on its 2018 Q4 earnings call.[49]
Telecom operators are starting to get involved in contactless payments via the use of NFC-enabled phones. Belgacom’s Pingping, for example, has a stored value account and via a partnership with Alcatel-Lucent’s Touchatag provides contactless payment functionalities.
Major financial entities now offering contactless payment systems include Mastercard, China UnionPay, Citibank, JPMorgan Chase, American Express, KeyBank, Barclays, Barclaycard, HSBC, Lloyds Banking Group, FreedomPay, RuPay, The Co-operative Bank, Nationwide Building Society and NatWest Group. Visa payWave, American Express Expresspay, and Mastercard Contactless are examples of contactless credit cards which have become widespread in the U.S. and U.K.
Technology[edit]
There are two main standard usages for contactless payments adopted throughout payment terminals with the EMV standard.
EMV Chip
On issued bank cards a smart chip or cryptographic chip is placed on the card known as a smart card which allows wireless payments to be made from the EMV chip in range of a payment terminal using RFID technology following the EMVCo standard. When the smart card is tapped against a payment terminal that authenticates the card issuer’s details through a series of PIN interactions the payment for the interaction will succeed.
Tokenisation
A newer approach to smart card technology is achieved by linking a smart card to a hardware device, such as through the Apple Pay application on an iPhone mobile phone, thereby allowing mobile devices the ability to make payments using RFID technology against a payment terminal on behalf of a smart card using a token generated by the card issuer, a process known as tokenisation. A Device Account Number (DAN) similar to a Private Account Number (PAN) in traditional payment stripe and chip cards, is generated along with a private key and sent to the card issuer during initial setup of the smart card on the hardware device. When payments are made via the respective approved application on the hardware device the DAN and relevant details such as expiry date and CVV are sent to the card issuer via a payment terminal for cryptography where the associated private key is then used to authorise the transaction.
NFC
The near field communication (NFC, compliant with ISO/IEC 14443[50] standard) technology in contactless cards uses a 13.56Mhz radio frequency technology that only transmits digital data within a concise range.
Typically the optimum distance is 4 centimetres or less — beyond, the signal is rapidly decreasing and can never exceed 10 centimetres.
Security[edit]
In 2006 security researchers found that the cardholder’s name, credit card number, and expiration date may be transmitted by contactless payment cards without encryption. They were able to use information leaked from a contactless credit card to make a purchase online, without opening the envelope in which the card was sent.[51]
Depending on the economic space, there may be a payment limit on single transactions without the need to input the PIN, and some contactless cards can only be used a certain number of times before customers are asked for their PIN.[52] Contactless debit and credit transactions use the same chip and PIN network as older cards and are protected by the same fraud guarantees. Where PIN is supported, the contactless part of the card may remain non-functional until a standard chip and PIN transaction has been executed.[53] This provides some verification that the card was delivered to the actual cardholder.
Under fraud guarantee standards, U.S. banks are liable for any fraudulent transactions charged to the contactless cards.
CVM limit[edit]
Because no signature or PIN verification is typically required, contactless purchases are often limited to a maximum amount per transaction, known as a Cardholder Verification Limit (CVM limit). Limits vary between banks. For transactions over the defined CVM limit a verification is usually required (e.g. PIN, signature, or biometric authentication).
Transactions under the floor limit, in addition to not requiring consumer authentication, are also accepted without sending the transaction online for verification by the acquiring host.
Note that these limits typically do not apply when CDCVM verification (such as in Apple Pay) is used.
| Economic space | CVM limit | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | $200 | For transactions over A$200 a PIN or biometric authentication is required.[54][55] |
| Austria | €25 | For transactions exceeding €25 a PIN is required. Additionally for cards produced before 2017 only five transactions can be made without a PIN.[56] Cards issued after December 2016 need a PIN code for transactions over €25 or a contactless total of €125. |
| Azerbaijan | ₼100 | For transactions of ₼100 and above using a physical card a PIN is required. There’s no mandatory PIN requirement when CDCVM (Apply Pay, Garmin Pay, or Google Pay) is used. |
| Bahrain | 20 BHD | |
| Bangladesh | BDT3000.00 | For transactions over BDT3000.00 a PIN is required. |
| Belgium | €50 | Since the COVID crisis, transaction limits in Belgium were increased. For transactions over €50 a PIN is required. When several contactless payments in a row reach the amount of €125, the PIN is required. |
| Brazil | R$200 | For transactions over R$200,00 a PIN is required.[57] |
| Bulgaria | 50 BGN | For transactions over 50 BGN (~€25) a PIN is required. 25 BGN (~€12) until April 12, 2019. |
| Canada | No limit | Limits are completely at the discretion of the merchant’s acquiring bank and the consumer’s bank. There is no law limiting the amounts. However, in practice, financial institutions limit contactless payments to $CA100. Some merchants may accept higher amounts subject to signature verification. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, MasterCard, Visa, and American Express increased their limits to $250.[58][59] |
| Chile | $12.000 CLP | |
| China | CN¥1000[60] | UnionPay QuickPass. PIN required unless disabled with bank. |
| Colombia | No limit | For transactions over COP 100.000 PIN is required. |
| Costa Rica | No limit | For transactions over ₡30000 signature is required.[61] Beginning July 1, 2022, PIN will be required instead.[62] |
| Croatia[63] | No limit | For transactions over 250HRK PIN or signature are needed. |
| Curaçao | ANG 45 | For transactions over ANG 45 a PIN is required. When several contactless payments in a row reach the amount of ANG 100, the PIN is required. |
| Czech Republic | No limit | For transactions over 500 CZK PIN is needed. After 3 consecutive contactless transactions, PIN is required. |
| Denmark[64] | 350 DKK | For transactions over 350 DKK PIN is needed. Sometimes PIN is needed anyway to ensure the card is used by its owner. |
| Dominican Republic | No limit | |
| Estonia[65] | €50 | |
| Finland | €50 | €25 up until April 12, 2019. After that it will be €50. |
| France | €50 | Can be used up to three times a day. |
| Germany | No limit | For each transaction over €25 or €50 (some Visa cards) a PIN or CDCVM verification is required. |
| Greece | €50 | For transactions over €50 a PIN is required |
| Hong Kong | No limit | Initially banks, not government, set it for $500 or under, then (for some banks) under $1000 (HKD), until the limits were removed. |
| Hungary | No limit | For transactions over 5000 HUF PIN is needed. For every 10 consecutive contactless transactions or if you reach 10.000 HUF PIN is needed. Due the COVID-19 pandemic, the 5000 HUF limit is increased to 15 000 HUF. No limit for Apple Pay or similar contactless purchases. |
| Iceland | ISK 5.000 | Íslandsbanki has a lower limit of ISK 4.200. For each transaction over the limit, Chip and PIN are required. Also, a cumulative limit of ISK 10.000 between Chip and PIN uses. |
| India | ₹5000 | For transactions above ₹5000, a PIN is required. |
| Indonesia | Rp1.000.000 | Transactions above Rp1.000.000, must require 6-digits PIN authorization. |
| Ireland | €50 | Increased from €30 to €50 on 1 April 2020.[66] There is no transaction limit when using contactless with two-factor authentication (e.g. Apple Pay), although some merchants still apply a €50 transaction limit[67] |
| Israel | 300 ILS | For transactions over 300 ILS PIN is needed |
| Italy | No limit | For transactions over €50 PIN is needed |
| Japan | JP¥20000 | JCB QUICPay and QUICPay+[68] |
| Latvia[69] | €50 | |
| Lithuania[70] | €50 | |
| North Macedonia | 750 MKD | |
| Malaysia | RM250 | Cumulative limits (total amount and/or consecutive transactions) differ between card issuers.[71]
By default, for each transaction above RM250 PIN is required. But the limit is customizable.[72] |
| Netherlands[73] | No limit | For card payments of more than €25 at once or €50 in a row a PIN is required. Some older cards only allow five transactions in a row without a PIN. Most if not all retailers have, by now, terminals that support CDCVM as verification (i.e. Apple Pay). Most banks have had Android NFC/Tap&Pay through their mobile banking apps for a few years now. While Apple Pay was launched (unofficially) by bunq on March 20, 2018, through a workaround,[74] and to be joined officially by ING on June 11, 2019,[75] followed by the official launch for bunq on Sept. 3rd and the announcement that banks ABN AMRO and Rabobank will also start to offer Apple Pay in The Netherlands sometime in 2019.[76] Also note that broad acceptance of credit cards isn’t commonplace yet, so that’s up to the individual merchant. Maestro by Mastercard is the dominant card type and accepted everywhere. |
| New Zealand | $200 | For each transaction over NZ$200 a PIN is required. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, this amount was temporarily raised to NZ$200, in an effort to further reduce unnecessary contact.[77] |
| Norway[78] | No limit | For each transactions over 500 NOK a PIN is required.[79] Sometimes PIN is needed anyway to ensure the card is used by its owner. |
| Pakistan | Rs 3500 | Transactions above Rs 3500 require pin verification. |
| Philippines | ₱5000 | Increased from ₱2000 to ₱5000 in 2020.[80] |
| Poland | No limit | For transactions over or equal to 100 PLN PIN is required. |
| Portugal | No limit | For more than €50 PIN verification is mandatory[81] |
| Romania | No limit | For transactions over or equal to 100 lei PIN is required. |
| Russia | No limit | For transactions over ₽1000 PIN or signature is required. |
| Saudi Arabia | 300 SAR | For transactions over 300 SAR, PIN is required. |
| Serbia | 4000 RSD | For transactions over 4000 RSD, PIN verification is required. |
| Singapore | S$100 | The current transaction limit for contactless payments in Singapore is S$100, although some banks offer higher.[82] |
| Slovakia | No limit | For transactions over €20 PIN is needed. After 3 consecutive contactless transactions, PIN is required. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, this amount was temporarily raised to €50, in an effort to further reduce unnecessary contact.[83] |
| Slovenia | No limit | For transactions over €25 PIN is needed. |
| South Africa | 500 ZAR | Increased to R500 in May 2017 (except for ABSA Bank which remained at R200)[84] |
| Spain | No limit | For more than €50 PIN verification is mandatory except using mobile payments sometimes. It was increased from €20 to €50 to avoid contact because of the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Sri Lanka | No limit | For more than LKR 5000 PIN/signature verification is required |
| Sweden | 200 SEK | For each transaction over 200 SEK a PIN is required. |
| Switzerland | 80 CHF | For transactions over 80 CHF a PIN is required. |
| Taiwan | No limit | Signatures may be required for large purchases. |
| Thailand | ฿1500 | |
| Turkey | ₺500 | For transactions over ₺500 PIN is required. |
| Ukraine | 1500 UAH | For transactions over 1500 UAH a PIN is required |
| United Kingdom | £100 | Previous limits:
Chancellor of the Exchequer Rishi Sunak confirmed in the 2021 budget that this limit would increase to £100 on 15 October 2021. This floor limit increase was later confirmed by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) |
| United States of America | No limit | A signature may be required for large purchases. Banks may set their own limits or require a PIN. |
See also[edit]
- Apple Pay
- Digital currency
- Contactless smart card
- Cashless society and reducing disease transmittal
- Dashtop mobile
- Google Pay
- Microsoft Pay
- Mobile payment
- Near field communication
- Proximity card
- Octopus card
- OPUS card
- Oyster card
- Opal card
- Presto card
- Rav-Kav
- Ventra
- Samsung Pay
- Softcard (formerly Isis mobile wallet)
- Vicinity cards
References[edit]
- ^ Reserve Bank of Australia (19 April 2022). «How Australians pay Snapshot (2019 Consumer Payments Survey)». Reserve Bank of Australia. Archived from the original on 2020-03-01. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ «FreedomPay makes waves in contactless payment — SecureIDNews».
- ^ «McDonald’s testing e-payment system». USA Today. 2001-05-29.
- ^ «Sony et Philips contrent Bluetooth» (in French). 01net.com. 18 September 2002. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ a b c d «Les transports en commun niçois se mettent au paiement sans contact» (in French). 01net.com. 24 May 2009. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «Philippe Maugars : le père français du NFC sacré inventeur européen de l’année» (in French). 01net.com. 12 June 2015. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ a b «Caen, la ville où l’on paye et s’informe en sortant son portable» (in French). 01net.com. 20 October 2005. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «A Hanau, le portable-ticket de bus joue au juste prix» (in French). 01net.com. 2 May 2005. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Les transports rennais payés par mobile ‘sans contact’» (in French). 01net.com. 7 November 2007. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «Barclaycard rolls out Oyster payments card». Finextra. Finextra. September 2007.
- ^ «Nokia 6131 NFC – touch to pay credit card mobile phones start trickling onto the market». 22 November 2007.
- ^ «First Fully Integrated Contactless Payment System in UK». www.paymentnews.com. 2008-03-26. Archived from the original on 2014-03-02. Retrieved 2012-08-26.
- ^ «Mobile and transit operators launch NFC payments system in Chongqing». nfcw.com. 19 January 2019. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Orange and Barclaycard deliver next step in their partnership with contactless co-branded credit card». Barclaycard. Barclaycard. January 2010.
- ^ «Barclaycard and Orange unveil pay-by-mobile service by Garry White». Daily Telegraph. London. 2009-03-08. Retrieved 2010-08-06.
- ^ a b «Télécoms — La révolution mobile sans contact arrive en 2008» (in French). banquedesterritoires.fr. 21 December 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «Nice, première ville à passer au paiement sans contact» (in French). 01net.com. 21 May 2010. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ «A Caen, avec un mobile sans contact, on valide dans les bus et trams». 01net.com (in French). 18 June 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «NFC transit ticketing service goes live in French city of Caen». nfcw.com. 18 June 2013. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ «A Strasbourg, on voyage en bus et en tram grâce à un mobile sans contact» (in French). 01net.com. 27 June 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ «Strasbourg NFC ticketing moves to commercial launch». nfcw.com. 5 July 2013. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ «Ça y est, certains smartphones Samsung peuvent servir de titres de transport en Île-de-France !» (in French). Twitter. 8 April 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ «Le dernier (ticket de) métro, at 2:10 and 2:38» (in French). YouTube. 24 September 2018. Archived from the original on 2021-12-17. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- ^ «Et si vous achetiez vos titres de transport depuis votre appli RATP ?» (in French). RATP. 12 November 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2020.
- ^ «KDDI, Softbank Mobile and SK Telecom to introduce NFC standard services in Japan and Korea». nfcw.com. 15 July 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «SK Telecom and Hana launch SIM-based mobile contactless payments and promotions service». nfcw.com. 25 March 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «Gemalto provides KDDI with end-to-end NFC security solution». nfcw.com. 14 June 2010. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «NTT Docomo partners with Korea’s KT to switch to NFC at end of 2012». nfcw.com. 9 February 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «China Unicom launches commercial NFC service in Beijing». nfcw.com. 5 January 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ «3 Hong Kong and Citibank Jointly Launch ‘3 Citi Wallet’ New Mobile Payment Technology Turns Mobile Phones into Digital Wallets New Milestone in Mobile Payment». www.citigroup.com. Retrieved 2021-05-11.
- ^ Villarreal, Alexandra. «MasterCard, Weve partner to accelerate contactless payments shift in U.K.» Archived 2016-01-17 at the Wayback Machine Bank Credit News. 2/10/2014. Retrieved 2/10/2014.
- ^ Jeffries, Adrianne (September 9, 2014). «Apple Pay allows you to pay at the counter with your iPhone 6». The Verge. Archived from the original on September 10, 2014. Retrieved September 13, 2014.
- ^ «Contactless has caught on underground». Barclaycard. Barclaycard. February 2016.
- ^ «BankCard Sticker». Erste Bank und Sparkassen. Erste Bank Group. January 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-08-22.
- ^ WHO encourages use of contactless payments due to COVID-19
- ^ Increase in contactless payments limit may not be ready until April
- ^ Contactless card payment limit to change in emergency move amid coronavirus pandemic
- ^ «Contactless limit in UK to be increased to £45». UK Finance. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ Clark, Derin (24 March 2020). «Contactless limit is set to rise to £45 to help fight Covid-19». Moneyfacts.co.uk. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ^ «Contactless limit to increase to £100 from 15 October».
- ^ «Certified phones». nfc-phones.org. Archived from the original on 2015-10-11. Retrieved 2015-02-07.
- ^ «New MasterCard Advisors Study on Contactless Payments Shows Almost 30% Lift in Total Spend Within First Year of Adoption». newsroom.mastercard.com. 2012-05-03. Retrieved 2013-03-13.
- ^ Dubinsky, Zach. «New credit cards pose security problem». CBCNews.ca. 2010-06-02. Retrieved 2010-06-03.
- ^ Campbell, Francis. «Contactless payments taking off in the UK in 2015». mobiletransaction.org. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^ «Key Facts and Stats». Archived from the original on July 21, 2010. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- ^ Jones, Rupert (2017-07-12). «Cash no longer king as contactless payments soar in UK stores». The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2019-05-03.
- ^ https://www.ukfinance.org.uk/sites/default/files/uploads/pdf/UK-Finance-UK-Payment-Markets-Report-2019-SUMMARY.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ «Contactless Payments Statistics Australia 2017 | Westpac». www.westpac.com.au. Retrieved 2018-07-09.
- ^ Sacchi, Guido. «Payment Security: Can It Be Frictionless and Secure?». Global Payments.
- ^ https://www.iso.org/standard/73599.html
- ^ Schwartz, John (2006-10-23). «Researchers See Privacy Pitfalls in No-Swipe Credit Cards». The New York Times. Retrieved 2019-09-22.
- ^ «Lloyds Bank — UK Bank Accounts — Contactless Debit Cards».
- ^ «Why doesn’t my contactless card work?».
- ^ «MasterCard® contactless». MasterCard. MasterCard Australia. Archived from the original on 18 February 2016. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ «Visa payWave: FAQs». Visa Australia. Visa. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- ^ «Maestro® kontraktlos». Maestro. Maestro Austria. Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- ^ «Empresas aumentam limite de pagamentos por aproximação; veja valores». OlharDigital. Olhar Digital. 24 December 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ^ Jon Rumley (2020-04-07). «Mastercard, Visa Raise Tap Limits, And Stores Want Interac To Follow». huffingtonpost.ca. Huffington Post. Retrieved 2020-04-13.
- ^ Gary Ng (2020-04-07). «American Express Canada Increases Tap Payment Limit to $250 Due to COVID-19». iphoneincanada.ca. iPhone In Canada. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «UnionPay «Quickpass» sets foot on first foreign market». Archived from the original on 2017-01-04. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ Sequeira, Rebeca. «Pagos con tarjeta por menos de ₡30 mil no requerirán firma» [Card payments of less than ₡30,000 will not require a signature]. La República (in Spanish). Retrieved 27 August 2021.
- ^ Gudiño, Ronny. «Le solicitarán PIN en compras superiores a los ₡30 mil a partir de julio del 2022» [You will be asked your PIN on purchases over ₡30,000 beginning July 2022]. La República (in Spanish). Retrieved 27 August 2021.
- ^ «Beskontaktno plaćanje — Prihvat kartica — PBZCard.hr».
- ^ «Dankortet bliver nu kontaktløst»
- ^ «Swedbank». Swedbank. Retrieved 2017-01-02.
- ^ «Rollout of contactless limit increase well underway as all parties work towards national completion by 1 April — Banking and Payments Federation Ireland». www.bpfi.ie. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 2020-04-18.
- ^ «Apple Pay contactless service launches in Ireland». 7 March 2017. Retrieved 2019-12-05 – via www.irishtimes.com.
- ^ «JCB QUICPay». Retrieved 5 September 2017.
- ^ «Banks Increase Contactless Card Limits to 50 Euro». Finance Latvia Association. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 2021-01-07.
- ^ «Contactless cards». Swedbank. Retrieved 2016-09-01.
- ^ «FAQs on migration to PIN-based payment cards» (PDF). Bank Negara Malaysia. 28 October 2016. p. 2. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ^ John Lim (3 January 2017). «How to disable contactless payment?». says.com.
- ^ «Mijlpaal: 100 miljoen contactloze betalingen | CCV Holland». www.ccv.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2015-11-20.
- ^ «Apple Pay via omweg voor bunq-klanten alweer teruggedraaid». Bright.nl (in Dutch). 21 March 2018. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ^ «Apple Pay nu gratis beschikbaar voor ING-klanten met iPhone». AD.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2019-10-10.
- ^ «Ook ABN AMRO, Rabobank en bunq kondigen Apple Pay ondersteuning aan». AD.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 2019-09-24.
- ^ «Covid 19 coronavirus: Paywave eftpos limit raised to $200 — but two banks lag». NZ Herald. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ «200.000 tæpper hver dag | BankAxept». www.ntbinfo.no (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2019-04-01.
- ^ «Grensen for kontaktløs betaling med BankAxept uten PIN-kode økes». Finans Norge (in Norwegian). Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ «MasterCard raises payments limits for PH». The Manila Times. 26 July 2020. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ^ «Os pagamentos «sem contacto» até 50 euros vieram para ficar». www.bportugal.pt (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2020-07-13.
- ^ Boon, Rachel (8 February 2017). «Nets payments to go digital and contactless». The Straits Times. Retrieved 25 August 2017.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ «‘Tap ‘n go’ not as risky as many fear». Retrieved 2018-03-28.
- ^ Barclays. «Ten years of contactless | Barclays». Barclays. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ Gough, Owen (2 March 2017). «Supermarket contactless spending jumps as ‘touch and go’ overtakes Chip and PIN». Small Business. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ BBC News (1 June 2012). «Contactless pay limit up to £20». BBC News. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ «Contactless card limit rises to £30 as card use surges». BBC News. 1 September 2015.
- ^ «Apple Pay 100% Backed By UK’s Major Banks — Including Barclays». Know Your Mobile. Retrieved 2016-05-04.
External links[edit]
- A Comprehensive Technical Overview of Contactless
- Contactless.info, archived from the original on April 24, 2014 is designed to provide information for UK retailers that have an interest in Contactless card acceptance]
- New credit cards pose security problem, CBC News
- Chase’s «blink» uses RFID
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать грубую лексику.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать разговорную лексику.
Перевод «бесконтактной оплаты» на английский
contactless payment
contactless payments
Это указывает на большой потенциал сервисов бесконтактной оплаты как способа пополнить баланс телефона.
This indicates the great potential of contactless payment services as a way to replenish the balance of the phone.
На 11 основных станциях киевской городской электрички установили турникеты для бесконтактной оплаты.
At the 11 key stations of the Kyiv city train set turnstiles for contactless payment.
Apple Pay работает в качестве бесконтактной оплаты.
Это традиционная дебетовая карта с функцией бесконтактной оплаты PayPass.
This is a traditional debit card with the function of contactless payment PayPass.
Теперь уникальная технология бесконтактной оплаты покупок, выполненная в видеукрашения, стала доступна всем клиентам Россельхозбанка.
Now the unique technology of contactless payment purchases, made in the form of jewelry, was made available to all clients of Rosselkhozbank.
Сегодня телефон можно использовать для бесконтактной оплаты покупок
Расплачиваясь, ищите символ бесконтактной оплаты.
Сегодня достаточно нажать на кнопку, провести пластиковой картой в магазине или просто использовать устройство бесконтактной оплаты, чтобы необходимая сумма денег была снята со счета.
Today it is enough to click on the button, swipe the plastic card at the store or simply use device for contactless payment and the necessary amount of money will be written off from the account.
Speedpass стала первым опытом бесконтактной оплаты, которая в настоящее время распространилась по всему миру.
Speedpass was the first example of contactless payment, a concept which has now spread across the world.
Пользователи могут пользоваться услугой бесконтактной оплаты, продолжая получать все преимущества от использования своих кредитных и дебетовых карт.
Users can enjoy contactless payment service while continuing to receive all the benefits from using their credit and debit cards.
Создание автоматизированных систем учета пассажиропотока, а также систем бесконтактной оплаты проезда.
Designing automatic passenger flow system and contactless payment of travel fare.
Технологии бесконтактной оплаты становятся все более популярны.
Сейчас мы запускаем еще два удобных сервиса, и теперь нашим клиентам доступны все популярные инструменты бесконтактной оплаты.
Now we are launching two more convenient services, and now all popular contactless payment tools are available to our customers.
Банковские карты платежной системы UnionPay начали принимать на турникетах бесконтактной оплаты в столичном метрополитене.
Bank cards of the payment system UnionPay began to be accepted on contactless payment turnstiles in the Metropolitan metro.
Терминалы бесконтактной оплаты MasterCard расположены по всему миру.
The terminals of the MasterCard contactless payment are located all over the world.
Все турникеты казанского метро оборудованы устройствами бесконтактной оплаты проезда
Она обеспечила ее совместимость со старыми терминалами без поддержки бесконтактной оплаты PayPass/PayWire.
She ensured that it was compatible with old terminals that do not support contactless payment PayPass/PayWire.
NFC для бесконтактной оплаты, что в этом ценовом сегменте редкость.
Мы нашли самый дешевый смартфон с поддержкой бесконтактной оплаты
Previous Article We found the cheapest smartphone with support for contactless payment
Сторонние разработчики лишены возможности создавать собственные приложения для iPhone с использованием бесконтактной оплаты.
Third-party developers are unable to create their own applications for the iPhone using contactless payment.
Результатов: 137. Точных совпадений: 137. Затраченное время: 77 мс
Documents
Корпоративные решения
Спряжение
Синонимы
Корректор
Справка и о нас
Индекс слова: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Индекс выражения: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Индекс фразы: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Оплачивать товары и услуги с помощью гаджетов стало возможным, благодаря бесконтактным технологиям оплаты с банковской карты. Как же называется эта функция оплаты картой в одно касание, в чем ее преимущества? Как настроить функцию бесконтактной оплаты через терминал, и какие карты ее поддерживают? Безопасно ли такое новшество?
Как называется, когда прикладываешь карту к терминалу
Функция бесконтактной оплаты картой называется – PayPass (Пэйпасс). В переводе с английского означает — передать платеж.
Появилась эта система платежей в 2005 году, но популярной бесконтактная оплата картой стала спустя 7 лет, примерно в 2012 году.
В этот период количество пользователей возросло с 20 миллионов до 95 миллионов владельцев карт с PayPass. Такой эпический прирост пользователей возник в результате обширных, а главное, доступных для понимания, рекламных кампаний со стороны банков.
В своих рекламах они показывали насколько просто расплачиваться за покупки в магазинах, всего лишь приложив карту.
Отметим, что ранее большинство пользователей не понимало, как работает функция. Для сохранности личных средств — лишний раз не прибегали к пользованию новой технологией. Вдруг обман?
Отличительные особенности PayPass — бесконтактного платежа
Преимущество такого типа оплаты в скорости проведения платежа. Для того, чтобы оплатить покупку достаточно прикоснуться картой или гаджетом к считывающему устройству терминала. Разумеется, предварительно проверить сумму платежа.
Напомним, что ранее для возможности оплаты было необходимо вставить карту в терминал (при наличии чипа) или провести ее магнитной лентой (без чипа).
Основным недостатком PayPass является достаточно низкий лимит на оплату. К слову, это один из способов защитить денежные средства на карте. При необходимости сумму расходов можно увеличить в отделении банка или в его онлайн поддержке.
Если сумма покупки превысит лимит PayPass, терминал запросит введение пароля карты или же откажет в проведении операции.
Как настроить функцию и какие карты ее поддерживают
Настраивать карту нет необходимости, функция предусмотрена банком эмитентом, который выдал карту. Логотип PayPass на банковской карте означает возможность бесконтактного и быстрого расчета. Оснащены этой функцией карты MasterCard, Visa.
Информация для оплаты может считываться с брелка с меткой RFID или мобильного устройства с NFC.
Безопасность PayPass
Бесконтактная система оплат достаточна безопасна. Завладение данными карты маловозможно, так как для того, чтобы считать информацию с карты или чипа необходимо расстояние, не превышающее 2 см.
Даже, если считать данные удастся, они не содержат кода CVC2 (код с обратной стороны пластика) и персональных данных держателя карты, а полученной информация для взлома карты недостаточно.
К тому же система, PayPass предусматривает уникальный код для каждой новой платежной операции. В случае копирования этого шифра, по карте-клону удастся провести лишь одну операцию.
Но из-за того, что для бесконтактных оплат установлен низкий лимит расходов, мошенники редко пытаются завладеть данными карт с помощью PayPass — абсолютно не выгодно.

Как называется и как работает данная система?

Чип, внедренный в карту, имеет специальную антенну, называемую RFID-меткой. При сближении со считывающим устройством (ридером), чип активируется, запускается программа, записанная на нем, и производится оплата.
Как узнать, есть на карточке функция бесконтактной оплаты или нет? Это очень просто – о ее наличии свидетельствует специально нанесенный значок в форме радиоволн (похоже на знак вайфай). Такой значок – обычная картинка и наносится на все предметы с функцией NFC. В том числе и на банкоматах, стационарных терминалах для оплаты и на магазинных переносных терминалах.
Сам чип находится в середине, в пластике и его не видно. Он не нуждается в какой-либо активации и срабатывает автоматически. При этом, каждая операция по оплате индивидуальна и персонально закодирована. Поэтому повторное списание средств за одну и ту же торговую операцию исключается.
Диапазон действия радиоволн при взаимодействии с ридером сравнительно невысок – до 10 см. Соединение происходит очень быстро, за доли секунды (в отличие от функции блютуз, например).
Чип программируется производителем. В него закладывается функция бесконтактной оплаты за товары, но могут быть включены и дополнительные сервисы, например, оплата за проезд в конкретном населенном пункте (так как везде различные цены и виды транспорта).

Для сервиса дистанционной оплаты не имеет большого значения носитель чипа. Поэтому платеж используется как на дебетовых картах, так и на кредитках. Для NFC – функции не имеет значения сколько денег лежит на карте вообще, главное, чтобы их хватило на оплату товаров. Действие карт осуществляется даже через неметаллические преграды, поэтому их можно не доставать из портмоне (некоторые носят в перчатках).
Как платить? Достаточно поднести платежную карту к считывателю и оплата будет произведена. Нет необходимости вводить ПИН-код или вводить карту в устройство терминала.
Предлагаем посмотреть видео о бесконтактных банковских картах:
Преимущества и недостатки
Банковские карточки с функцией оплаты без контакта имеют ряд плюсов:
- Быстрота оплаты. При использовании таких карт очередь в транспорте и торговых точках движется очень быстро. Не расходуется время на вставку карты в терминал, введение ПИН-кода, распечатку чека и подпись пользователя. Поток покупателей проходит очень быстро, оплата занимает секунды.
- Гигиеничность. Карта не передается в посторонние руки, не соприкасается с посторонними предметами и не может служить источником вирусов и инфекций.
- Удобство. Так как оплата безналична, то отпадает необходимость носить деньги в кошельке, не требуется запоминать ПИН-код, можно по согласию, пользоваться картой другого лица (например, родственника или сотрудника).
Карта может находиться в кошельке или портмоне – не обязательно ее доставать, оплата производится в любом случае.
- Сумма для оплаты без введения ПИН-кода до 1 тыс. руб. в России, сравнительно невелика. При этом снять наличные деньги таким образом невозможно. Эти условия являются дополнительной гарантией безопасности платежей.
- Если сумма покупки превышает 1 тыс.руб. и бесконтактный платеж совершить невозможно, то карточка работает как обычный банковский пластик – вставляется в терминал оплаты и вводится ПИН-код.
- За одну покупку производится только одна оплата. Для каждой торговой операции предусмотрен алгоритм действий и повторное списание без нового введения суммы для оплаты невозможно.
- Посторонние лица не видят ПИН-код и не смогут его украсть, так же как и данные карты.
- Чип с бесконтактной платой не содержит информации о банковском счете и даже при считывании информации на ридер мошенника, получить доступ к банковскому счету с деньгами невозможно.
К недостаткам пользования бесконтактными карточками можно отнести:
- Ограниченное количество терминалов с NFC – функцией в торговых точках. Особенно это актуально в небольших и периферийных заведениях, где менять терминал оплаты для собственника дорого.
При утере или воровстве пластика, постороннее лицо сможет совершить оплату покупок без проблем, если на счету есть финансы. Даже несколько списаний по 1 тыс. руб. могут нанести существенный урон бюджету клиента.
- Лимит оплаты ограничен суммой в 1 тыс рублей и увеличить его ни при каких обстоятельствах невозможно. Для жителей больших городов такая сумма зачастую недостаточна для оплаты разовой покупки в супермаркетах.
В случае, если деньги со счета были списаны не по вине держателя пластика и он добросовестно исполнял правила пользования карточкой (не передавал другим лицам и не сообщал им информацию), то банк обязан вернуть украденные средства. Для этого обратиться в банк нужно оперативно, в течение одного дня с момента пропажи.
Как настроить nfc для этой технологии?
Ведущие банки страны все новые банковские карты автоматически выпускают с функцией nfc для бесконтактной оплаты. Как понять, что она присутствует на вашей карточке? Ее наличие легко определить по нанесенному на поверхность пластика характерному рисунку с волнами. Поскольку чип встроен в пластик карты и уже содержит все необходимые функции, то дополнительная настройка не требуется. При активации банковской карточки, функция nfc активируется автоматически (как настроить приложение NFC для карты Сбербанка?).
Насколько безопасна данная функция, как ее отключить?
Карточку (пластик) следует беречь от механических повреждений, сгибания, воздействий повышенных температур и возможности намокания.
Для предупреждения краж с банковской карточки с nfc следует соблюдать несколько правил:
Хранить карту в местах, недоступных для посторонних лиц (также как наличные или документы).
- При утере карточки (ее похищении) сразу же ее заблокировать, позвонив в банк или через интернет в личном кабинете самостоятельно. Можно также лично обратиться в офис банковского учреждения.
- Носить карту в специальном металлизированном чехле, не пропускающем волны (на Алиэкспресс стоит около 200 руб.). Это убережет от автоматических списываний мошенниками с переносным ридером в местах большого скопления людей (транспорт, супермаркеты).
- Отдельные банки позволяют установить ежедневный максимальный лимит снятия денег с карточки. Это можно сделать либо онлайн, в своем личном кабинете, либо обратившись в офис банка. При утере или кражи пластика, посторонний субъект не сможет снять лишнюю сумму денег сверх лимита до блокировки карты.
- Желательно подключить функцию смс-информирования. Она платная, но при этом о каждой покупке пользователь узнает, получив сообщение на мобильный телефон.
- Можно воспользоваться функцией страхования карточки. Договор заключается на 12 календарных месяцев. Если карточка выбывает из владения держателя, а деньги списываются, то страховая компания покроет все убытки.
- При подключении интернет-банкинга, пользователь может увидеть все покупки, оплаченные с его карточки.
- Карточку можно вообще не носить с собой, если подключить счет к мобильному телефону с функцией бесконтактной оплаты, если сам гаджет имеет такой чип. Оплачивать телефонами разных марок, например Хуавей, можно вместо карт Сбербанка, ВТБ и других банков.

Отключить функцию nfc можно в личном кабинете, через интернет. Для этого (общая процедура может иметь различия в разных банковских учреждениях):
- нужно зайти онлайн на сайт банковского учреждения;
- ввести свои логин и пароль;
- получить смс с кодом подтверждения и внеси его;
- нужно зайти в личный пользовательский кабинет;
- выбрать из всех карточек субъекта нужную;
- установить запрет на функцию paypass (бесконтактный платеж).
После этого банковской карточкой можно пользоваться как обычной, дебетовой или кредитной, с введением ПИН-кода. Подробнее о том, как можно защитить банковскую карту с бесконтактной оплатой, написано тут.
Предлагаем посмотреть видео о том, насколько безопасны бесконтактные платежи картой:
Особенности MasterCard PayPass, Visa payWave и визуальных электронных карточек
Возможность произвести оплату на расстоянии называют еще оплатой в одно движение (прикосновение). Принцип действия идентичен для всех карт и фирм, их выпускающих, выдающих и обслуживающих. Названия отличны.
- Фирма Мастеркард называет функцию PayPass.
Фирма Виза называет – payWave.
- Соцкарта «Мир» назвала это – «Бесконтакт». У карты Мир есть также сервис бесконтактной оплаты под названием MirPay, о котором вы можете узнать здесь.
- У China UnionPay функция называется QuickPass.
Пластик карточки имеет обычный вид: логотип, информация о держателе (на именных), срок окончания действия, код. На обратной стороне трехзначный код, магнитная лента и (или) чип, подпись держателя. Чип бесконтактной оплаты не виден, однако на поверхность пластика нанесен знак волн.
Виртуальные карты (электронные) – это карты без физического носителя. Они имеют реквизиты и привязаны к банковскому счету. Их удобство в том, что выпуск и обслуживание бесплатно. Их невозможно потерять. Они предназначены для оплаты в интернете.
Где и как оформить?
Крупные банки в России, например Сбербанк и Тинькофф, выпускают все новые карточки с возможностью бесконтактной оплаты. При этом согласие клиента не требуется, продукт выдается стандартный. Получить функцию бесконтактной оплаты со старой карточкой невозможно, так как в ней нет встроенного чипа.
Субъект, желающий получить сервис бесконтактной платы, должен обратиться в банковское учреждение, клиентом которого он является и подать заявление на перевыпуск карты. Услуга платная, стоимость в пределах 150-250 рублей. Процедура получения и активации, как у обычной карточки.
По желанию, гражданин может оформить дополнительную карточку с функцией бесконтактной оплаты и привязать ее к текущему счету, если банк предоставляет такую услугу.
Как расплачиваться, какой стороной прикладывать к терминалу – пошаговая инструкция
Для того, чтобы произвести оплату за товар бесконтактной картой, существует порядок:
Кассир считывает коды с товаров клиента в кассовое устройство. На терминале высвечивается общая сумма для оплаты.
- Покупатель убеждается в правильности суммы и подносит карточку к терминалу на расстояние 2-4 см на несколько секунд.
- Сумма списывается и на экране высвечивается информация о проведении оплаты.
- Дополнительно раздается звуковой сигнал.
Не имеет значения, какой стороной подносить пластик к терминалу. Чип внутри и действует равномерно во все стороны. Даже если пластик подносить несколько раз, оплата будет только одна. Чтобы еще снять деньги, нужно ввести новую сумму для оплаты товаров.
Банковские стикеры – что это такое, как выглядят и как ими пользоваться?
Стикеры – это наклейки с чипом nfc, выполняющие функцию PayPass. Их можно клеить на любые предметы, за исключением металлических. Стикер привязывается к банковскому счету, и при приближении к терминалу производит бесконтактную оплату, как будто самой картой.
По стикерам нельзя проводить платежи в интернет-магазинах. Как оплачивать покупки при помощи подобной наклейки? Стикеры следует подносить к считывающему устройству лицевой стороной. Остальные функции идентичны сервису бесконтактной оплаты на банковских карточках.
Лимиты по операциям

Какие трудности могут возникнуть при платежах?
Оплата банковской карточкой с сервисом PayPass не работает в следующих случаях:
- Физического повреждения карты и чипа. Например, изгиба, намокания, нагрева высокими температурами.
- Наличия нескольких пластиков с PayPass услугой. Оплата не будет автоматической, пользователь должен будет выбрать конкретную карточку для списания денег.
- Блокировки карты. Карта может быть заблокирована банковским учреждением в случаях, предусмотренных законодательством. Например, при проведении нетипичной для клиента оплаты, больших сумм, нескольких платежей подряд и др.
- Отсутствия денежных средств на счету субъекта. Необходимо проверить счет и пополнить его.
Если очевидные причины отказа действия функции бесконтактной оплаты отсутствуют или карточка явно повреждена, следует обратиться с заявлением в банковское учреждение. Детали согласовывают через интернет или позвонив в службу поддержки банка. Таким образом, за бесконтактными платежами будущее. При умении правильно пользоваться этим сервисом, его преимущества очевидны.
Чтобы заполучить клиента банки постоянно совершенствуют свой сервис и внедряют новые технологии. Так, обыкновенные карты с магнитной полосой уже успели устареть. Теперь их место заняли карты с бесконтактной технологией оплаты.
Что такое бесконтактная платежная карта
Уже во многих городах действуют электронные проездные билеты в метро и наземном транспорте. В магазинах для оплаты просто подносят карту к терминалу, а молодые люди оплачивают покупки смартфоном. Все это стало возможным благодаря бесконтактной платежной карте.
Если сравнить платежное средство старого образца с новым, можно заметить, что на лицевой стороне выглядывает миниатюрный чип – NFC. Благодаря нему данные, зашифрованные в карте, передаются бесконтактному терминалу оплаты. Без него, придется считывать магнитную полосу традиционным способом.
Сейчас такие карты есть у всех популярных банков – ВТБ, Сбербанк, Тинькофф и пр. Также их выпускают другие организации, вроде Яндекс, МТС, Билайн, Пятерочка, Магнит и многие другие.
Помимо этого, бесконтактный способ оплаты работает на большинстве новых телефонов под управлением Android и IOS с помощью приложений Apple и Google Pay. Но, чтобы подключить такую функцию, нужно иметь карту с поддержкой NFC.
Обратите внимание! Бесконтактные платежи работают отнюдь не по воздуху. Для применения NFC, необходимо поднести чип к принимающему устройству на расстояние до 10 см. Это радиус действия магнитных волн, с помощью которых информация передается от устройства к устройству. На большем расстоянии передать данные невозможно.
Функции технологии NFC в повседневной жизни
NFC, что в расшифровке переводится, как «коммуникация ближнего поля» далеко не новая технология. Впервые чип установили в телефон Нокиа 6131 в 2006 году, но торговая и банковская инфраструктура была еще не готова к его использованию.
Сейчас ее применяют:
- в электронной оплате проезда;
- для передачи данных и средств от смартфона к смартфону (как когда-то ИК-порт);
- в электронных ключах с личной информацией сотрудника;
- в специальных метках, для хранения важных данных в деловой сфере.
Даже привычное подключение смартфона к любой технике с помощью USB-кабеля теперь может заменить NFC-чип. Достаточно просто поднести телефон к принтеру, чтобы напечатать нужную фотографию или воспроизвести видео на телевизоре подключившись к ДУ устройства.
Безопасно ли пользоваться бесконтактной картой
Как это бывает со всем новым, бесконтактная оплата картой успела обрасти мифами. Самые популярные:
- В магазине два раза спишут деньги. Нет. Терминал не может дважды списать деньги пока продавец вручную не введет сумму покупки. Также одновременное списание двух платежей не предусмотрено системой.
- В толпе кто-то незаметно снимет деньги с карты. Риск того, что кому-то это удастся – есть. Но на практике это мало реализуемо. Списать больше 1000 рублей за один раз не выйдет из-за ограничения банка. Оптимальное расстояние для оплаты 2-4 см, незаметно поднести терминал и подождать несколько секунд пока тот словит сигнал крайне трудно. Плюс приобрести терминал стоит от 200 тыс. рублей.
- Кто-то украдет информацию карты. Такие приборы есть. Но использовать их незаметно без отвлечения внимания покупателя и продавца не получится. Суть в том, что завладеть данными можно только разместив прибор между платежным средством и терминалом во время проведения операции. Оплачивая покупки в проверенных местах такой вариант маловероятен.
Самым безопасным решением является бесконтактная система оплаты через телефон. Гаджеты также имеют свои способы защиты от злоумышленников и данные карты в платежном приложении надежно защищены.
Виды платёжных сервисов
Бесконтактной оплатой может пользоваться любой клиент банка, который подключен к мировым платежным системам Visa, Mastercard и Union.
Владельцы смартфонов, помимо наличия такой карты, должны иметь доступ к приложениям. Они могут называться Apple, Google, Union, Huawei или Samsung Pay, в зависимости от установленной ОС.
Лимиты по операциям
Лимит операции в виде бесконтактной оплаты ограничен лишь балансом карты. Дополнительно, для оплаты чека на сумму более 1000 рублей, придется ввести ПИН-код карты, а при оплате через телефон, пароль, установленный системой. Отключить такое ограничение можно, но не рекомендуется.
Как пользоваться бесконтактными кредитными карточками
Расплатиться бесконтактной картой можно не везде. Хотя большинство терминалов в магазинах уже давно перешли на модели с NFC-чипом, все еще остаются торговые точки, где это невозможно. Оплатить покупки можно в местах, где присутствует соответствующий логотип.
Дополнительная информация. Для тех, кто внес платежное средство в память смартфона, на кассе нужно искать логотипы своей платежной системы (IOS ил Android).
Куда прикладывать
После того, как кассир просканирует товары и озвучит сумму покупки, нужно:
- Проверить сумму на экране.
- Поднести платежное средство устройству приема оплаты (достаточно сохранять дистанцию в 1-2 см).
- Дождаться пока загорится экран термина, сообщая, что средства перечислены и убрать карту.
Если сумма больше 1000 рублей дополнительно ввести ПИН-код.
Как настроить и платить телефоном
Настроить бесконтактную оплату на телефоне не трудно. Единственное, нужно удостовериться, что NFC-чип присутствует в имеющейся модели телефона. Тут стоит отметить, что даже в хороших телефонах он не всегда есть.
Так, у Xiaomi даже мощные смартфоны не всегда его получают, потому что для NFC-чипа нужен пластиковый или керамический корпус. Через металл сигнал передается слабо.
Чтобы настроить оплату через телефон на Андроиде, нужно:
- Активировать NFC, перейдя в настройки телефона в раздел «Еще».
- Скачать Гугл Пей.
- Авторизоваться в Гугл-аккаунте.
- Нажать на значок + в правом верхнем углу.
- Далее «Добавить кредитную карту или дебетовую карту».
- Ввести реквизиты вручную или отсканировать карту.
- Подтвердить привязку через СМС от банка.
Чтобы расплатиться телефоном на примере Xiaomi, нужно:
- Разблокировать смартфон.
- Поднести к терминалу после проверки суммы платежа.
- Если нужно, выбрать другую карту для оплаты.
- Дождаться характерного звукового сигнала, либо вибрации.
- После отключать ничего не нужно, просто убрать телефон от терминала.
Важно! Даже, если карта поддерживает бесконтактные платежи, нужно удостовериться, что банк является партнером мобильного сервиса.
Что делать, если не работает
Приведенная инструкция работает на всех гаджетах под управлением Андроид. Если настроить бесконтактную оплату не получилось, значит проблема может заключаться в:
- нулевом балансе на карте;
- банк не работает с приложением;
- в устройстве нет NFC;
- чип есть, но он неисправен.
Также часто приходится дополнительно идти в настройки безопасности и устанавливать автозапуск чипа. Для этого:
- Перейти в настройки телефона.
- Раздел «Безопасность».
- «Разрешения».
- Следом «Другие разрешения».
- Найти «Google Pay» и поставить галочку возле «Разрешить».
- Далее снова в «Безопасность», пункт «Автозапуск».
- Поставить галочку напротив платежного приложения.
Если этого недостаточно, еще:
- Перейти в настройки в раздел «Батарея и производительность».
- Выбрать «Расход заряда батареи приложениями».
- Кликнуть на Google Pay.
- «Нет ограничений», выбрать «Разрешить».
Если это не помогло, стоит еще попробовать переустановить приложение и перепривязать карту.
Насколько популярны дистанционные платежи
Сейчас бесконтактная оплата работает в каждом супермаркете и торговом центре. Во многих городах действуют электронные проездные на автобусы и метро. Но в малонаселенных пунктах по-прежнему не всегда можно встретить торговую точку с терминалом. А если он есть, он может не поддерживать дистанционные платежи. У жителей крупных городов с оплатой через карту или телефон проблем обычно не возникает.
Преимущества и недостатки бесконтактных платежей
Учитывая, что сейчас все банки и организации переходят на выпуск именно бесконтактных карт и стараются стать партнерами мобильных сервисов, стоит отметить в чем преимущества такого рода платежей:
- Быстрота. Нет нужды вводить ПИН-код, передача данных быстрее, чем у карт старого образца.
- Долговечность. По сравнению с классическими картами, бесконтактные не так быстро изнашиваются, поэтому их выпускают с увеличенным сроком годности.
- Нет опасности выхода из строя. Магнитные карты часто переставали работать из-за размагничивания ленты. В новых платежных средствах такой проблемы нет.
- Безопасность. Карта всегда у владельца. Больше не нужно ее передавать в руки третьим лицам.
Из недостатков можно отметить только необходимость ввода ПИН-кода при оплате свыше 1000 рублей и отсутствие нужного терминала в некоторых магазинах. Последняя проблема решится в ближайшие пару лет.
Заключение
Бесконтактная оплата плотно внедряется по всем направлениям. Получить карту не проблема, их выпускает каждый крупный банк. Дистанционные платежи безопасны. Методы кражи данных тяжелы и дорогостоящи в реализации, поэтому многим мошенникам они не интересны. При желании платежные средства можно оставить дома, оцифровав их в мобильное приложение, оплачивая покупки прямо через телефон.















 Карта может находиться в кошельке или портмоне – не обязательно ее доставать, оплата производится в любом случае.
Карта может находиться в кошельке или портмоне – не обязательно ее доставать, оплата производится в любом случае. При утере или воровстве пластика, постороннее лицо сможет совершить оплату покупок без проблем, если на счету есть финансы. Даже несколько списаний по 1 тыс. руб. могут нанести существенный урон бюджету клиента.
При утере или воровстве пластика, постороннее лицо сможет совершить оплату покупок без проблем, если на счету есть финансы. Даже несколько списаний по 1 тыс. руб. могут нанести существенный урон бюджету клиента. Хранить карту в местах, недоступных для посторонних лиц (также как наличные или документы).
Хранить карту в местах, недоступных для посторонних лиц (также как наличные или документы). Фирма Виза называет – payWave.
Фирма Виза называет – payWave. Кассир считывает коды с товаров клиента в кассовое устройство. На терминале высвечивается общая сумма для оплаты.
Кассир считывает коды с товаров клиента в кассовое устройство. На терминале высвечивается общая сумма для оплаты.