Как правильно пишется слово «димедрол»
димедро́л
димедро́л, -а
Источник: Орфографический
академический ресурс «Академос» Института русского языка им. В.В. Виноградова РАН (словарная база
2020)
Делаем Карту слов лучше вместе
Привет! Меня зовут Лампобот, я компьютерная программа, которая помогает делать
Карту слов. Я отлично
умею считать, но пока плохо понимаю, как устроен ваш мир. Помоги мне разобраться!
Спасибо! Я стал чуточку лучше понимать мир эмоций.
Вопрос: априоризм — это что-то нейтральное, положительное или отрицательное?
Ассоциации к слову «димедрол»
Синонимы к слову «димедрол»
Предложения со словом «димедрол»
- Я даже встала и выпила таблетку димедрола, хотя со мной такое случается крайне редко.
- Не нарваться бы на дурочку вроде той, что живёт через один подъезд, – на почве несчастной любви выпила пригоршню димедрола, еле откачали.
- Вытягивая иглу, вводят 2 мл 2% раствора новокаина и 1 мл 1% раствора димедрола.
- (все предложения)
Отправить комментарий
Дополнительно
РусскийПравить
Морфологические и синтаксические свойстваПравить
| падеж | ед. ч. | мн. ч. |
|---|---|---|
| Им. | димедро́л | димедро́лы |
| Р. | димедро́ла | димедро́лов |
| Д. | димедро́лу | димедро́лам |
| В. | димедро́л | димедро́лы |
| Тв. | димедро́лом | димедро́лами |
| Пр. | димедро́ле | димедро́лах |
ди—мед—ро́л
Существительное, неодушевлённое, мужской род, 2-е склонение (тип склонения 1a по классификации А. А. Зализняка).
Корень: -димедрол- [Тихонов, 1996].
ПроизношениеПравить
- МФА: [dʲɪmʲɪˈdroɫ]
Семантические свойстваПравить
ЗначениеПравить
- антигистаминный препарат ◆ То ли Док переборщил с дозой снотворного, то ли организм Томаса оказался слишком восприимчив к димедролу, но после капельницы и уколов он продрых не сутки, а почти двое. В. В. Левашов, «Заговор патриота», 2000 г. [НКРЯ]
СинонимыПравить
- дифенгидрамин
АнтонимыПравить
ГиперонимыПравить
ГипонимыПравить
Родственные словаПравить
| Ближайшее родство | |
ЭтимологияПравить
Происходит от ??
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетанияПравить
ПереводПравить
| Список переводов | |
БиблиографияПравить
- Словарь новых слов русского языка (середина 50-х — середина 80-х годов) / Под ред. Н. З. Котеловой. — СПб. : Дмитрий Буланин, 1995. — ISBN 5-86007-016-0.
- Добавить гиперонимы в секцию «Семантические свойства»
- Добавить сведения об этимологии в секцию «Этимология»
- Добавить хотя бы один перевод в секцию «Перевод»
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | |
| Trade names | Benadryl, Unisom, Nytol, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682539 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability |
Low–moderate[1][2] |
| Addiction liability |
Moderate[3][2] |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth, intramuscular, intravenous, topical, rectal |
| Drug class | first-generation antihistamine (ethanolamine), anticholinergic, hallucinogen (deliriant) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 40–60%[5] |
| Protein binding | 98–99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6, others)[9][10] |
| Elimination half-life | Range: 2.4–13.5 h[6][5][7] |
| Excretion | Urine: 94%[8] Feces: 6%[8] |
| Identifiers | |
|
IUPAC name
|
|
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| IUPHAR/BPS |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.360 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
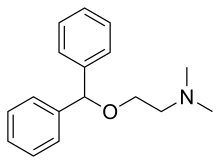
| Formula | C17H21NO |
| Molar mass | 255.361 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
|
SMILES
|
|
|
InChI
|
|
| |
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremor in parkinsonism, and nausea.[11] It is taken by mouth, injected into a vein, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin.[11] Maximal effect is typically around two hours after a dose, and effects can last for up to seven hours.[11]
Common side effects include sleepiness, poor coordination and an upset stomach.[11] Its use is not recommended in young children or the elderly.[11][12] There is no clear risk of harm when used during pregnancy; however, use during breastfeeding is not recommended.[13] It is a first generation H1-antihistamine and ethanolamine and works by blocking certain effects of histamine, which produces its antihistamine and sedative effects.[11][2] Diphenhydramine is also a potent anticholinergic, which means it also works as a deliriant at higher than recommended doses as a result.[14] Its sedative and deliriant effects have led to some cases of recreational use and addiction.[3][2]
Diphenhydramine was first made by George Rieveschl and came into commercial use in 1946.[15][16] It is available as a generic medication.[11] It is sold under the brand name Benadryl, among others.[11] In 2020, it was the 192nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[17][18]
Medical uses[edit]
Diphenhydramine is a first-generation antihistamine used to treat a number of conditions including allergic symptoms and itchiness, the common cold, insomnia, motion sickness, and extrapyramidal symptoms.[19][20] Diphenhydramine also has local anesthetic properties, and has been used as such in people allergic to common local anesthetics such as lidocaine.[21]
Allergies[edit]
Diphenhydramine is effective in treatment of allergies.[22] As of 2007, it was the most commonly used antihistamine for acute allergic reactions in the emergency department.[23]
By injection it is often used in addition to epinephrine for anaphylaxis,[24] although as of 2007 its use for this purpose had not been properly studied.[25] Its use is only recommended once acute symptoms have improved.[22]
A bottle of topical «Itch-Stopping Gel» diphenhydramine
Topical formulations of diphenhydramine are available, including creams, lotions, gels, and sprays. These are used to relieve itching and have the advantage of causing fewer systemic effects (e.g., drowsiness) than oral forms.[26]
Movement disorders[edit]
Diphenhydramine is used to treat akathisia and Parkinson’s disease–like extrapyramidal symptoms caused by antipsychotics.[27] It is also used to treat acute dystonia including torticollis and oculogyric crisis caused by first generation antipsychotics.
Sleep[edit]
Because of its sedative properties, diphenhydramine is widely used in nonprescription sleep aids for insomnia. The drug is an ingredient in several products sold as sleep aids, either alone or in combination with other ingredients such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) in Tylenol PM or ibuprofen in Advil PM. Diphenhydramine can cause minor psychological dependence.[28] Diphenhydramine has also been used as an anxiolytic.[29]
Diphenhydramine has also been used off prescription by parents in an attempt to make their children sleep or remain sedated on long-distance flights.[30] This has been met with criticism, both by doctors and members of the airline industry, as sedating young passengers may put them at risk if the flight encounters an emergency and they are unable to react to the situation efficiently,[31] and the drug’s side effects, especially the chance of a paradoxical reaction, may result in some individuals becoming hyperactive rather than sedated. The ethics of this use have also been challenged, with the Seattle Children’s hospital arguing in a 2009 article that «Using a medication for your convenience is never an indication for medication in a child.»[32]
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine’s 2017 clinical practice guidelines recommended against the use of diphenhydramine in the treatment of insomnia due to poor effectiveness and low quality of evidence.[33] A major systematic review and network meta-analysis of medications for the treatment of insomnia published in 2022 found little evidence to inform the use of diphenhydramine for insomnia.[34]
Nausea[edit]
Diphenhydramine also has antiemetic properties, which make it useful in treating the nausea that occurs in vertigo and motion sickness. However, when taken above recommended doses, it can cause nausea (especially above 200 mg).[35]
Special populations[edit]
Diphenhydramine is not recommended for people older than 60 or children under the age of six, unless a physician is consulted.[11][12][36] These populations should be treated with second-generation antihistamines such as loratadine, desloratadine, fexofenadine, cetirizine, levocetirizine, and azelastine.[37] Due to its strong anticholinergic effects, diphenhydramine is on the Beers list of drugs to avoid in the elderly.[38][39]
Diphenhydramine is category B in the FDA Classification of Drug Safety During Pregnancy.[40] It is also excreted in breast milk.[41] It is expected that low doses of diphenhydramine taken occasionally will not cause any adverse effects on breastfed infants. Large doses or long-term use may affect the baby or reduce breast milk supply, especially when combined with sympathomimetic drugs such as pseudoephedrine or before the establishment of lactation. A single bedtime dose after the last feeding of the day may minimize any harmful effects of the medication on the baby and on the milk supply. Still, non-sedating antihistamines are the preferred alternative.[42]
Paradoxical reactions to diphenhydramine have been documented, in particular among children, and it may cause excitation instead of sedation.[43]
Topical diphenhydramine is sometimes used especially for people in hospice. This use is without indication and topical diphenhydramine should not be used as treatment for nausea because research does not indicate this therapy is more effective than alternatives.[44]
There were no documented cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury caused by normal doses of diphenhydramine.[45]
Adverse effects[edit]
The most prominent side effect is sedation. A typical dose creates driving impairment equivalent to a blood-alcohol level of 0.10, which is higher than the 0.08 limit of most drunk-driving laws.[23]
Diphenhydramine is a potent anticholinergic agent and potential deliriant in higher doses. This activity is responsible for the side effects of dry mouth and throat, increased heart rate, pupil dilation, urinary retention, constipation, and, at high doses, hallucinations or delirium. Other side effects include motor impairment (ataxia), flushed skin, blurred vision at nearpoint owing to lack of accommodation (cycloplegia), abnormal sensitivity to bright light (photophobia), sedation, difficulty concentrating, short-term memory loss, visual disturbances, irregular breathing, dizziness, irritability, itchy skin, confusion, increased body temperature (in general, in the hands and/or feet), temporary erectile dysfunction, and excitability, and although it can be used to treat nausea, higher doses may cause vomiting.[46] Diphenhydramine in overdose may occasionally result in QT prolongation.[47]
Some individuals experience an allergic reaction to diphenhydramine in the form of hives.[48][49]
Conditions such as restlessness or akathisia can worsen from increased levels of diphenhydramine, especially with recreational dosages.[43] Normal doses of diphenhydramine, like other first generation antihistamines, can also make symptoms of restless legs syndrome worse.[50]
As diphenhydramine is extensively metabolized by the liver, caution should be exercised when giving the drug to individuals with hepatic impairment.
Anticholinergic use later in life is associated with an increased risk for cognitive decline and dementia among older people.[51]
Contraindications[edit]
Diphenhydramine is contraindicated in premature infants and neonates as well as people who are breastfeeding. It is a pregnancy Category B drug. Diphenhydramine has additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants. Monoamine Oxidase inhibitors prolong and intensify the anticholinergic effect of antihistamines.[52]
Overdose[edit]
Diphenhydramine is one of the most commonly misused over-the-counter drugs in the United States.[53] In cases of extreme overdose, if not treated in time, acute diphenhydramine poisoning may have serious and potentially fatal consequences. Overdose symptoms may include:[54]
- Euphoria or dysphoria
- Hallucinations (auditory, visual, tactile, etc.)
- Heart palpitations
- Extreme drowsiness
- Severe dizziness
- Abnormal speech (inaudibility, forced speech, etc.)
- Flushed skin
- Severe mouth and throat dryness
- Tremors
- Seizures
- Muscle spasms
- Inability to urinate
- Vomiting
- Acute megacolon
- Motor disturbances
- Anxiety/nervousness
- Disorientation
- Disassociation
- Abdominal pain
- Delirium
- Coma
- Death
Acute poisoning can be fatal, leading to cardiovascular collapse and death in 2–18 hours, and in general is treated using a symptomatic and supportive approach.[37] Diagnosis of toxicity is based on history and clinical presentation, and in general specific levels are not useful.[55] Several levels of evidence strongly indicate diphenhydramine (similar to chlorpheniramine) can block the delayed rectifier potassium channel and, as a consequence, prolong the QT interval, leading to cardiac arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes.[56]
No specific antidote for diphenhydramine toxicity is known, but the anticholinergic syndrome has been treated with physostigmine for severe delirium or tachycardia.[55] Benzodiazepines may be administered to decrease the likelihood of psychosis, agitation, and seizures in people who are prone to these symptoms.[57]
Interactions[edit]
Alcohol may increase the drowsiness caused by diphenhydramine.[58][59]
Pharmacology[edit]
Pharmacodynamics[edit]
| Site | Ki (nM) | Species | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| SERT | ≥3,800 | Human | [61][62] |
| NET | 960–2,400 | Human | [61][62] |
| DAT | 1,100–2,200 | Human | [61][62] |
| 5-HT2A | 260 | Human | [62] |
| 5-HT2C | 780 | Human | [62] |
| α1B | 1,300 | Human | [62] |
| α2A | 2,900 | Human | [62] |
| α2B | 1,600 | Human | [62] |
| α2C | 2,100 | Human | [62] |
| D2 | 20,000 | Rat | [63] |
| H1 | 9.6–16 | Human | [64][62] |
| H2 | >100,000 | Canine | [65] |
| H3 | >10,000 | Human | [62][66][67] |
| H4 | >10,000 | Human | [67] |
| M1 | 80–100 | Human | [68][62] |
| M2 | 120–490 | Human | [68][62] |
| M3 | 84–229 | Human | [68][62] |
| M4 | 53–112 | Human | [68][62] |
| M5 | 30–260 | Human | [68][62] |
| VGSC | 48,000–86,000 | Rat | [69] |
| hERG | 27,100 (IC50) | Human | [70] |
| Values are Ki (nM), unless otherwise noted. The smaller the value, the more strongly the drug binds to the site. |
Diphenhydramine, while traditionally known as an antagonist, acts primarily as an inverse agonist of the histamine H1 receptor.[71] It is a member of the ethanolamine class of antihistaminergic agents.[37] By reversing the effects of histamine on the capillaries, it can reduce the intensity of allergic symptoms. It also crosses the blood–brain barrier and inversely agonizes the H1 receptors centrally.[71] Its effects on central H1 receptors cause drowsiness.
Like many other first-generation antihistamines, diphenhydramine is also a potent antimuscarinic (a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors) and, as such, at high doses can cause anticholinergic syndrome.[72] The utility of diphenhydramine as an antiparkinson agent is the result of its blocking properties on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain.
Diphenhydramine also acts as an intracellular sodium channel blocker, which is responsible for its actions as a local anesthetic.[69] Diphenhydramine has also been shown to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin.[73] It has been shown to be a potentiator of analgesia induced by morphine, but not by endogenous opioids, in rats.[74] The drug has also been found to act as an inhibitor of histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT).[75][76]
| Biological target | Mode of action | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| H1 receptor | Inverse agonist | Allergy reduction; Sedation |
| mACh receptors | Antagonist | Anticholinergic; Antiparkinson |
| Sodium channels | Blocker | Local anesthetic |
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Oral bioavailability of diphenhydramine is in the range of 40% to 60%, and peak plasma concentration occurs about 2 to 3 hours after administration.[5]
The primary route of metabolism is two successive demethylations of the tertiary amine. The resulting primary amine is further oxidized to the carboxylic acid.[5] Diphenhydramine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19.[9]
The elimination half-life of diphenhydramine has not been fully elucidated, but appears to range between 2.4 and 9.3 hours in healthy adults.[6] A 1985 review of antihistamine pharmacokinetics found that the elimination half-life of diphenhydramine ranged between 3.4 and 9.3 hours across five studies, with a median elimination half-life of 4.3 hours.[5] A subsequent 1990 study found that the elimination half-life of diphenhydramine was 5.4 hours in children, 9.2 hours in young adults, and 13.5 hours in the elderly.[7] A 1998 study found a half-life of 4.1 ± 0.3 hours in young men, 7.4 ± 3.0 hours in elderly men, 4.4 ± 0.3 hours in young women, and 4.9 ± 0.6 hours in elderly women.[77] In a 2018 study in children and adolescents, the half-life of diphenhydramine was 8 to 9 hours.[78]
Chemistry[edit]
Diphenhydramine is a diphenylmethane derivative. Analogues of diphenhydramine include orphenadrine, an anticholinergic, nefopam, an analgesic, and tofenacin, an antidepressant.
Detection in body fluids[edit]
Diphenhydramine can be quantified in blood, plasma, or serum.[79] Gas chromatography with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) can be used with electron ionization on full scan mode as a screening test. GC-MS or GC-NDP can be used for quantification.[79] Rapid urine drug screens using immunoassays based on the principle of competitive binding may show false-positive methadone results for people having ingested diphenhydramine.[80] Quantification can be used to monitor therapy, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in people who are hospitalized, provide evidence in an impaired driving arrest, or assist in a death investigation.[79]
History[edit]
Diphenhydramine was discovered in 1943 by George Rieveschl, a former professor at the University of Cincinnati.[81][82] In 1946, it became the first prescription antihistamine approved by the U.S. FDA.[83]
In the 1960s, diphenhydramine was found to weakly inhibit reuptake of the neurotransmitter serotonin.[73] This discovery led to a search for viable antidepressants with similar structures and fewer side effects, culminating in the invention of fluoxetine (Prozac), a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).[73][84] A similar search had previously led to the synthesis of the first SSRI, zimelidine, from brompheniramine, also an antihistamine.[85]
Society and culture[edit]
Diphenhydramine is deemed to have limited abuse potential in the United States owing to its potentially serious side-effect profile and limited euphoric effects, and is not a controlled substance. Since 2002, the U.S. FDA has required special labeling warning against use of multiple products that contain diphenhydramine.[86] In some jurisdictions, diphenhydramine is often present in postmortem specimens collected during investigation of sudden infant deaths; the drug may play a role in these events.[87][88]
Diphenhydramine is among prohibited and controlled substances in the Republic of Zambia,[89] and travelers are advised not to bring the drug into the country. Several Americans have been detained by the Zambian Drug Enforcement Commission for possession of Benadryl and other over-the-counter medications containing diphenhydramine.[90]
Recreational use[edit]
Although diphenhydramine is widely used and generally considered to be safe for occasional usage, multiple cases of abuse and addiction have been documented.[3] Because the drug is cheap and sold over the counter in most countries, adolescents without access to more sought-after, illicit drugs are particularly at risk.[91] People with mental health problems—especially those with schizophrenia—are also prone to abuse the drug, which is self-administered in large doses to treat extrapyramidal symptoms caused by the use of antipsychotics.[92]
Recreational users report calming effects, mild euphoria, and hallucinations as the desired effects of the drug.[92][93] Research has shown that antimuscarinic agents, including diphenhydramine, «may have antidepressant and mood-elevating properties».[94] A study conducted on adult males with a history of sedative abuse found that subjects who were administered a high dose (400 mg) of diphenhydramine reported a desire to take the drug again, despite also reporting negative effects, such as difficulty concentrating, confusion, tremors, and blurred vision.[95]
In 2020, an Internet challenge emerged on social media platform TikTok involving deliberately overdosing on diphenhydramine; dubbed the Benadryl challenge, the challenge encourages participants to consume dangerous amounts of Benadryl for the purpose of filming the resultant psychoactive effects, and has been implicated in several hospitalisations[96] and at least one death.[97][98]
Names[edit]
Diphenhydramine is marketed under the trade name Benadryl by McNeil Consumer Healthcare in the U.S., Canada, and South Africa.[99] Trade names in other countries include Dimedrol, Daedalon, and Nytol. It is also available as a generic medication.
Procter & Gamble markets an over-the-counter formulation of diphenhydramine as a sleep aid under the brand ZzzQuil. In 2014 this product had annual sales of over $120 million and had a 29.3% share of the $411 million sleep-aid market category.[100]
Other organisms[edit]
Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum) have a high uptake of diphenhydramine.[101]
See also[edit]
- Tripelennamine
References[edit]
- ^ Hubbard JR, Martin PR (2001). Substance Abuse in the Mentally and Physically Disabled. CRC Press. p. 26. ISBN 9780824744977.
- ^ a b c d Saran JS, Barbano RL, Schult R, Wiegand TJ, Selioutski O (October 2017). «Chronic diphenhydramine abuse and withdrawal: A diagnostic challenge». Neurology. Clinical Practice. 7 (5): 439–441. doi:10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000304. PMC 5874453. PMID 29620065.
- ^ a b c Thomas A, Nallur DG, Jones N, Deslandes PN (January 2009). «Diphenhydramine abuse and detoxification: a brief review and case report». Journal of Psychopharmacology. 23 (1): 101–5. doi:10.1177/0269881107083809. PMID 18308811. S2CID 45490366.
- ^ «Benylin Chesty Coughs (Original) — Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)». (emc). 24 February 2022. Archived from the original on 30 December 2022. Retrieved 29 December 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Paton DM, Webster DR (1985). «Clinical pharmacokinetics of H1-receptor antagonists (the antihistamines)». Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 10 (6): 477–97. doi:10.2165/00003088-198510060-00002. PMID 2866055. S2CID 33541001.
- ^ a b AHFS Drug Information. Published by authority of the Board of Directors of the American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. 1990. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 9 October 2017.
- ^ a b Simons KJ, Watson WT, Martin TJ, Chen XY, Simons FE (July 1990). «Diphenhydramine: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in elderly adults, young adults, and children». Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 30 (7): 665–71. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1990.tb01871.x. PMID 2391399. S2CID 25452263.
- ^ a b Garnett WR (February 1986). «Diphenhydramine». American Pharmacy. NS26 (2): 35–40. doi:10.1016/s0095-9561(16)38634-0. PMID 3962845.
- ^ a b Krystal AD (August 2009). «A compendium of placebo-controlled trials of the risks/benefits of pharmacological treatments for insomnia: the empirical basis for U.S. clinical practice». Sleep Med Rev. 13 (4): 265–74. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2008.08.001. PMID 19153052.
- ^ «Showing Diphenhydramine (DB01075)». DrugBank. Archived from the original on 31 August 2009. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i «Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride». Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 6 September 2016. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- ^ a b Schroeck JL, Ford J, Conway EL, Kurtzhalts KE, Gee ME, Vollmer KA, Mergenhagen KA (November 2016). «Review of Safety and Efficacy of Sleep Medicines in Older Adults». Clinical Therapeutics. 38 (11): 2340–2372. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.09.010. PMID 27751669.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- ^ Ayd FJ (2000). Lexicon of Psychiatry, Neurology, and the Neurosciences. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-7817-2468-5. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ Dörwald FZ (2013). Lead Optimization for Medicinal Chemists: Pharmacokinetic Properties of Functional Groups and Organic Compounds. John Wiley & Sons. p. 225. ISBN 978-3-527-64565-7. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016.
- ^ «Benadryl». Ohio History Central. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- ^ «The Top 300 of 2020». ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine — Drug Usage Statistics». ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride Monograph». Drugs.com. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 15 June 2011.
- ^ Brown HE, Stoklosa J, Freudenreich O (December 2012). «How to stabilize an acutely psychotic patient» (PDF). Current Psychiatary. 11 (12): 10–16. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2013.
- ^ Smith DW, Peterson MR, DeBerard SC (August 1999). «Local anesthesia. Topical application, local infiltration, and field block». Postgraduate Medicine. 106 (2): 57–60, 64–6. doi:10.3810/pgm.1999.08.650. PMID 10456039.
- ^ a b American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. «Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 2 August 2016.
- ^ a b Banerji A, Long AA, Camargo CA (2007). «Diphenhydramine versus nonsedating antihistamines for acute allergic reactions: a literature review». Allergy and Asthma Proceedings. 28 (4): 418–26. doi:10.2500/aap.2007.28.3015. PMID 17883909. S2CID 7596980.
- ^ Young WF (2011). «Chapter 11: Shock». In Humphries RL, Stone CK (eds.). CURRENT Diagnosis and Treatment Emergency Medicine. LANGE CURRENT Series (Seventh ed.). McGraw–Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-170107-5.
- ^ Sheikh A, ten Broek VM, Brown SG, Simons FE (January 2007). «H1-antihistamines for the treatment of anaphylaxis with and without shock». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2007 (1): CD006160. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006160.pub2. PMC 6517288. PMID 17253584.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Topical». MedlinePlus. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ Aminoff MJ (2012). «Chapter 28. Pharmacologic Management of Parkinsonism & Other Movement Disorders». In Katzung B, Masters S, Trevor A (eds.). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (12th ed.). The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. pp. 483–500. ISBN 978-0-07-176401-8.
- ^ Monson K, Schoenstadt A (8 September 2013). «Benadryl Addiction». eMedTV. Archived from the original on 4 January 2014.
- ^ Dinndorf PA, McCabe MA, Friedrich S (August 1998). «Risk of abuse of diphenhydramine in children and adolescents with chronic illnesses». The Journal of Pediatrics. 133 (2): 293–5. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(98)70240-9. PMID 9709726.
- ^ Crier F (2 August 2017). «Is it wrong to drug your children so they sleep on a flight?». The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ Morris R (3 April 2013). «Should parents drug babies on long flights?». BBC News. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ Swanson WS (25 November 2009). «If It Were My Child: No Benadryl for the Plane». Seattle Children’s. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ Sateia MJ, Buysse DJ, Krystal AD, Neubauer DN, Heald JL (February 2017). «Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Insomnia in Adults: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline». J Clin Sleep Med. 13 (2): 307–349. doi:10.5664/jcsm.6470. PMC 5263087. PMID 27998379.
- ^ De Crescenzo F, D’Alò GL, Ostinelli EG, Ciabattini M, Di Franco V, Watanabe N, Kurtulmus A, Tomlinson A, Mitrova Z, Foti F, Del Giovane C, Quested DJ, Cowen PJ, Barbui C, Amato L, Efthimiou O, Cipriani A (July 2022). «Comparative effects of pharmacological interventions for the acute and long-term management of insomnia disorder in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis». Lancet. 400 (10347): 170–184. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00878-9. PMID 35843245. S2CID 250536370.
- ^ Flake ZA, Scalley RD, Bailey AG (March 2004). «Practical selection of antiemetics». American Family Physician. 69 (5): 1169–74. PMID 15023018. Archived from the original on 24 March 2016. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ Medical Economics (2000). Physicians’ Desk Reference for Nonprescription Drugs and Dietary Supplements, 2000 (21st ed.). Montvale, NJ: Medical Economics Company. ISBN 978-1-56363-341-6.
- ^ a b c Brunton L, Chabner B, Knollmann B (2011). «Chapter 32. Histamine, Bradykinin, and Their Antagonists». In Brunton L (ed.). Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (12e ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 242–245. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- ^ «High risk medications as specified by NCQA’s HEDIS Measure: Use of High Risk Medications in the Elderly» (PDF). National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA). Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 February 2010.
- ^ «2012 AGS Beers List» (PDF). The American Geriatrics Society. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2012. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- ^ Black RA, Hill DA (June 2003). «Over-the-counter medications in pregnancy». American Family Physician. 67 (12): 2517–24. PMID 12825840.
- ^ Spencer JP, Gonzalez LS, Barnhart DJ (July 2001). «Medications in the breast-feeding mother». American Family Physician. 64 (1): 119–26. PMID 11456429.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine». Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). October 2020. PMID 30000938.
- ^ a b de Leon J, Nikoloff DM (February 2008). «Paradoxical excitation on diphenhydramine may be associated with being a CYP2D6 ultrarapid metabolizer: three case reports». CNS Spectrums. 13 (2): 133–5. doi:10.1017/s109285290001628x. PMID 18227744. S2CID 10856872.
- ^ American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine, «Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question», Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine, archived from the original on 1 September 2013, retrieved 1 August 2013, which cites
- Smith TJ, Ritter JK, Poklis JL, Fletcher D, Coyne PJ, Dodson P, Parker G (May 2012). «ABH gel is not absorbed from the skin of normal volunteers». Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 43 (5): 961–6. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2011.05.017. PMID 22560361.
- Weschules DJ (December 2005). «Tolerability of the compound ABHR in hospice patients». Journal of Palliative Medicine. 8 (6): 1135–43. doi:10.1089/jpm.2005.8.1135. PMID 16351526.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine». LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. PMID 31643789. Archived from the original on 29 July 2021. Retrieved 21 June 2021.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Side Effects». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2009.
- ^ Aronson JK (2009). Meyler’s Side Effects of Cardiovascular Drugs. Elsevier. p. 623. ISBN 978-0-08-093289-7. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ^ Heine A (November 1996). «Diphenhydramine: a forgotten allergen?». Contact Dermatitis. 35 (5): 311–2. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02402.x. PMID 9007386. S2CID 32839996.
- ^ Coskey RJ (February 1983). «Contact dermatitis caused by diphenhydramine hydrochloride». Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 8 (2): 204–6. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(83)70024-1. PMID 6219138.
- ^ «Restless Legs Syndrome Fact Sheet | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke». www.ninds.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ^ Salahudeen MS, Duffull SB, Nishtala PS (March 2015). «Anticholinergic burden quantified by anticholinergic risk scales and adverse outcomes in older people: a systematic review». BMC Geriatrics. 15 (31): 31. doi:10.1186/s12877-015-0029-9. PMC 4377853. PMID 25879993.
- ^ Sicari V, Zabbo CP (2021). «Diphenhydramine». StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30252266. Archived from the original on 28 May 2022. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ Huynh DA, Abbas M, Dabaja A (2021). Diphenhydramine Toxicity. PMID 32491510.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine overdose». MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 30 May 2013.
- ^ a b Manning B (2012). «Chapter 18. Antihistamines». In Olson K (ed.). Poisoning & Drug Overdose (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-166833-0. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ^ Khalifa M, Drolet B, Daleau P, Lefez C, Gilbert M, Plante S, O’Hara GE, Gleeton O, Hamelin BA, Turgeon J (February 1999). «Block of potassium currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes and lengthening of cardiac repolarization in man by the histamine H1 receptor antagonist diphenhydramine». The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 288 (2): 858–65. PMID 9918600.
- ^ Cole JB, Stellpflug SJ, Gross EA, Smith SW (December 2011). «Wide complex tachycardia in a pediatric diphenhydramine overdose treated with sodium bicarbonate». Pediatric Emergency Care. 27 (12): 1175–7. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e31823b0e47. PMID 22158278. S2CID 5602304.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine and Alcohol / Food Interactions». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 February 2013.
- ^ Zimatkin SM, Anichtchik OV (1999). «Alcohol-histamine interactions». Alcohol and Alcoholism. 34 (2): 141–7. doi:10.1093/alcalc/34.2.141. PMID 10344773.
- ^ Roth BL, Driscol J. «PDSP Ki Database». Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP). University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- ^ a b c Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson E (December 1997). «Pharmacological profile of antidepressants and related compounds at human monoamine transporters». European Journal of Pharmacology. 340 (2–3): 249–58. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01393-9. PMID 9537821.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Krystal AD, Richelson E, Roth T (August 2013). «Review of the histamine system and the clinical effects of H1 antagonists: basis for a new model for understanding the effects of insomnia medications». Sleep Medicine Reviews. 17 (4): 263–72. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2012.08.001. PMID 23357028.
- ^ Tsuchihashi H, Sasaki T, Kojima S, Nagatomo T (1992). «Binding of [3H]haloperidol to dopamine D2 receptors in the rat striatum». J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 44 (11): 911–4. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1992.tb03235.x. PMID 1361536. S2CID 19420332.
- ^ Ghoneim OM, Legere JA, Golbraikh A, Tropsha A, Booth RG (October 2006). «Novel ligands for the human histamine H1 receptor: synthesis, pharmacology, and comparative molecular field analysis studies of 2-dimethylamino-5-(6)-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalenes». Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 14 (19): 6640–58. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.05.077. PMID 16782354.
- ^ Gantz I, Schäffer M, DelValle J, Logsdon C, Campbell V, Uhler M, Yamada T (1991). «Molecular cloning of a gene encoding the histamine H2 receptor». Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (2): 429–33. Bibcode:1991PNAS…88..429G. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.2.429. PMC 50824. PMID 1703298.
- ^ Lovenberg TW, Roland BL, Wilson SJ, Jiang X, Pyati J, Huvar A, Jackson MR, Erlander MG (June 1999). «Cloning and functional expression of the human histamine H3 receptor». Molecular Pharmacology. 55 (6): 1101–7. doi:10.1124/mol.55.6.1101. PMID 10347254. S2CID 25542667.
- ^ a b Liu C, Ma X, Jiang X, Wilson SJ, Hofstra CL, Blevitt J, Pyati J, Li X, Chai W, Carruthers N, Lovenberg TW (March 2001). «Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H(4)) expressed in bone marrow». Molecular Pharmacology. 59 (3): 420–6. doi:10.1124/mol.59.3.420. PMID 11179434. S2CID 123619.
- ^ a b c d e Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E (February 1992). «Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells». The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 260 (2): 576–80. PMID 1346637.
- ^ a b Kim YS, Shin YK, Lee C, Song J (October 2000). «Block of sodium currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons by diphenhydramine». Brain Research. 881 (2): 190–8. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02860-2. PMID 11036158. S2CID 18560451.
- ^ Suessbrich H, Waldegger S, Lang F, Busch AE (April 1996). «Blockade of HERG channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the histamine receptor antagonists terfenadine and astemizole». FEBS Letters. 385 (1–2): 77–80. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00355-9. PMID 8641472. S2CID 40355762.
- ^ a b Khilnani G, Khilnani AK (September 2011). «Inverse agonism and its therapeutic significance». Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 43 (5): 492–501. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.84947. PMC 3195115. PMID 22021988.
- ^ Lopez AM (10 May 2010). «Antihistamine Toxicity». Medscape Reference. WebMD LLC. Archived from the original on 13 October 2010.
- ^ a b c Domino EF (1999). «History of modern psychopharmacology: a personal view with an emphasis on antidepressants». Psychosomatic Medicine. 61 (5): 591–8. doi:10.1097/00006842-199909000-00002. PMID 10511010.
- ^ Carr KD, Hiller JM, Simon EJ (February 1985). «Diphenhydramine potentiates narcotic but not endogenous opioid analgesia». Neuropeptides. 5 (4–6): 411–4. doi:10.1016/0143-4179(85)90041-1. PMID 2860599. S2CID 45054719.
- ^ Horton JR, Sawada K, Nishibori M, Cheng X (October 2005). «Structural basis for inhibition of histamine N-methyltransferase by diverse drugs». Journal of Molecular Biology. 353 (2): 334–344. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.08.040. PMC 4021489. PMID 16168438.
- ^ Taylor KM, Snyder SH (May 1972). «Histamine methyltransferase: inhibition and potentiation by antihistamines». Molecular Pharmacology. 8 (3): 300–10. PMID 4402747.
- ^ Scavone JM, Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Engelhardt N, Shader RI (July 1998). «Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of diphenhydramine 25 mg in young and elderly volunteers». J Clin Pharmacol. 38 (7): 603–9. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1998.tb04466.x. PMID 9702844. S2CID 24989721.
- ^ Gelotte CK, Zimmerman BA, Thompson GA (May 2018). «Single-Dose Pharmacokinetic Study of Diphenhydramine HCl in Children and Adolescents». Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 7 (4): 400–407. doi:10.1002/cpdd.391. PMC 5947143. PMID 28967696.
- ^ a b c Pragst F (2007). «Chapter 13: High performance liquid chromatography in forensic toxicological analysis». In Smith RK, Bogusz MJ (eds.). Forensic Science (Handbook of Analytical Separations). Vol. 6 (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science. p. 471. ISBN 978-0-444-52214-6.
- ^ Rogers SC, Pruitt CW, Crouch DJ, Caravati EM (September 2010). «Rapid urine drug screens: diphenhydramine and methadone cross-reactivity». Pediatric Emergency Care. 26 (9): 665–6. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e3181f05443. PMID 20838187. S2CID 31581678.
- ^ Hevesi D (29 September 2007). «George Rieveschl, 91, Allergy Reliever, Dies». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 13 December 2011. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
- ^ «Benadryl». Ohio History Central. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ^ Ritchie J (24 September 2007). «UC prof, Benadryl inventor dies». Business Courier of Cincinnati. Archived from the original on 24 December 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
- ^ Awdishn RA, Whitmill M, Coba V, Killu K (October 2008). «Serotonin reuptake inhibition by diphenhydramine and concomitant linezolid use can result in serotonin syndrome». Chest. 134 (4 Meeting abstracts): 4C. doi:10.1378/chest.134.4_MeetingAbstracts.c4002. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ^ Barondes SH (2003). Better Than Prozac. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 39–40. ISBN 978-0-19-515130-5.
- ^ Food and Drug Administration, HHS (December 2002). «Labeling of diphenhydramine-containing drug products for over-the-counter human use. Final rule». Federal Register. 67 (235): 72555–9. PMID 12474879. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008.
- ^ Marinetti L, Lehman L, Casto B, Harshbarger K, Kubiczek P, Davis J (October 2005). «Over-the-counter cold medications-postmortem findings in infants and the relationship to cause of death». Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 29 (7): 738–43. doi:10.1093/jat/29.7.738. PMID 16419411.
- ^ Baselt RC (2008). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man. Biomedical Publications. pp. 489–492. ISBN 978-0-9626523-7-0.
- ^ «List of prohibited and controlled drugs according to chapter 96 of the laws of Zambia». The Drug Enforcement Commission ZAMBIA. Archived from the original (DOC) on 16 November 2013. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
- ^ «Zambia». Country Information > Zambia. Bureau of Consular Affairs, U.S. Department of State. Archived from the original on 21 July 2015. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- ^ Forest E (27 July 2008). «Atypical Drugs of Abuse». Articles & Interviews. Student Doctor Network. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013.
- ^ a b Halpert AG, Olmstead MC, Beninger RJ (January 2002). «Mechanisms and abuse liability of the anti-histamine dimenhydrinate» (PDF). Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 26 (1): 61–7. doi:10.1016/s0149-7634(01)00038-0. PMID 11835984. S2CID 46619422. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ Gracious B, Abe N, Sundberg J (December 2010). «The importance of taking a history of over-the-counter medication use: a brief review and case illustration of «PRN» antihistamine dependence in a hospitalized adolescent». Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 20 (6): 521–4. doi:10.1089/cap.2010.0031. PMC 3025184. PMID 21186972.
- ^ Dilsaver SC (February 1988). «Antimuscarinic agents as substances of abuse: a review». Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 8 (1): 14–22. doi:10.1097/00004714-198802000-00003. PMID 3280616. S2CID 31355546.
- ^ Mumford GK, Silverman K, Griffiths RR (1996). «Reinforcing, subjective, and performance effects of lorazepam and diphenhydramine in humans». Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 4 (4): 421–430. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.4.4.421.
- ^ «TikTok Videos Encourage Viewers to Overdose on Benadryl». TikTok Videos Encourage Viewers to Overdose on Benadryl. Archived from the original on 8 October 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ «Dangerous ‘Benadryl Challenge’ on Tik Tok may be to blame for the death of Oklahoma teen». KFOR.com Oklahoma City. 28 August 2020. Archived from the original on 2 August 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ «Teen’s Death Prompts Warning on ‘Benadryl Challenge’«. www.medpagetoday.com. 25 September 2020. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ «Childrens Benadryl ALLERGY (solution) Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc., McNeil Consumer Healthcare Division». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ^ «Is P&G Preparing to Expand ZzzQuil?». Archived from the original on 11 February 2017. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ Christou A, Papadavid G, Dalias P, Fotopoulos V, Michael C, Bayona JM, et al. (March 2019). «Ranking of crop plants according to their potential to uptake and accumulate contaminants of emerging concern». Environmental Research. Elsevier BV. 170: 422–432. Bibcode:2019ER….170..422C. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.048. hdl:10261/202657. PMID 30623890. S2CID 58564142.
Further reading[edit]
- Björnsdóttir I, Einarson TR, Gudmundsson LS, Einarsdóttir RA (December 2007). «Efficacy of diphenhydramine against cough in humans: a review». Pharmacy World & Science. 29 (6): 577–83. doi:10.1007/s11096-007-9122-2. PMID 17486423. S2CID 8168920.
- Cox D, Ahmed Z, McBride AJ (March 2001). «Diphenhydramine dependence». Addiction. 96 (3): 516–7. PMID 11310441.
- Lieberman JA (2003). «History of the use of antidepressants in primary care» (PDF). Primary Care Companion J. Clinical Psychiatry. 5 (supplement 7): 6–10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2014. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
External links[edit]
- «Diphenhydramine». Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | |
| Trade names | Benadryl, Unisom, Nytol, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682539 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability |
Low–moderate[1][2] |
| Addiction liability |
Moderate[3][2] |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth, intramuscular, intravenous, topical, rectal |
| Drug class | first-generation antihistamine (ethanolamine), anticholinergic, hallucinogen (deliriant) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 40–60%[5] |
| Protein binding | 98–99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6, others)[9][10] |
| Elimination half-life | Range: 2.4–13.5 h[6][5][7] |
| Excretion | Urine: 94%[8] Feces: 6%[8] |
| Identifiers | |
|
IUPAC name
|
|
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| IUPHAR/BPS |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.360 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO |
| Molar mass | 255.361 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
|
SMILES
|
|
|
InChI
|
|
| |
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremor in parkinsonism, and nausea.[11] It is taken by mouth, injected into a vein, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin.[11] Maximal effect is typically around two hours after a dose, and effects can last for up to seven hours.[11]
Common side effects include sleepiness, poor coordination and an upset stomach.[11] Its use is not recommended in young children or the elderly.[11][12] There is no clear risk of harm when used during pregnancy; however, use during breastfeeding is not recommended.[13] It is a first generation H1-antihistamine and ethanolamine and works by blocking certain effects of histamine, which produces its antihistamine and sedative effects.[11][2] Diphenhydramine is also a potent anticholinergic, which means it also works as a deliriant at higher than recommended doses as a result.[14] Its sedative and deliriant effects have led to some cases of recreational use and addiction.[3][2]
Diphenhydramine was first made by George Rieveschl and came into commercial use in 1946.[15][16] It is available as a generic medication.[11] It is sold under the brand name Benadryl, among others.[11] In 2020, it was the 192nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[17][18]
Medical uses[edit]
Diphenhydramine is a first-generation antihistamine used to treat a number of conditions including allergic symptoms and itchiness, the common cold, insomnia, motion sickness, and extrapyramidal symptoms.[19][20] Diphenhydramine also has local anesthetic properties, and has been used as such in people allergic to common local anesthetics such as lidocaine.[21]
Allergies[edit]
Diphenhydramine is effective in treatment of allergies.[22] As of 2007, it was the most commonly used antihistamine for acute allergic reactions in the emergency department.[23]
By injection it is often used in addition to epinephrine for anaphylaxis,[24] although as of 2007 its use for this purpose had not been properly studied.[25] Its use is only recommended once acute symptoms have improved.[22]
A bottle of topical «Itch-Stopping Gel» diphenhydramine
Topical formulations of diphenhydramine are available, including creams, lotions, gels, and sprays. These are used to relieve itching and have the advantage of causing fewer systemic effects (e.g., drowsiness) than oral forms.[26]
Movement disorders[edit]
Diphenhydramine is used to treat akathisia and Parkinson’s disease–like extrapyramidal symptoms caused by antipsychotics.[27] It is also used to treat acute dystonia including torticollis and oculogyric crisis caused by first generation antipsychotics.
Sleep[edit]
Because of its sedative properties, diphenhydramine is widely used in nonprescription sleep aids for insomnia. The drug is an ingredient in several products sold as sleep aids, either alone or in combination with other ingredients such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) in Tylenol PM or ibuprofen in Advil PM. Diphenhydramine can cause minor psychological dependence.[28] Diphenhydramine has also been used as an anxiolytic.[29]
Diphenhydramine has also been used off prescription by parents in an attempt to make their children sleep or remain sedated on long-distance flights.[30] This has been met with criticism, both by doctors and members of the airline industry, as sedating young passengers may put them at risk if the flight encounters an emergency and they are unable to react to the situation efficiently,[31] and the drug’s side effects, especially the chance of a paradoxical reaction, may result in some individuals becoming hyperactive rather than sedated. The ethics of this use have also been challenged, with the Seattle Children’s hospital arguing in a 2009 article that «Using a medication for your convenience is never an indication for medication in a child.»[32]
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine’s 2017 clinical practice guidelines recommended against the use of diphenhydramine in the treatment of insomnia due to poor effectiveness and low quality of evidence.[33] A major systematic review and network meta-analysis of medications for the treatment of insomnia published in 2022 found little evidence to inform the use of diphenhydramine for insomnia.[34]
Nausea[edit]
Diphenhydramine also has antiemetic properties, which make it useful in treating the nausea that occurs in vertigo and motion sickness. However, when taken above recommended doses, it can cause nausea (especially above 200 mg).[35]
Special populations[edit]
Diphenhydramine is not recommended for people older than 60 or children under the age of six, unless a physician is consulted.[11][12][36] These populations should be treated with second-generation antihistamines such as loratadine, desloratadine, fexofenadine, cetirizine, levocetirizine, and azelastine.[37] Due to its strong anticholinergic effects, diphenhydramine is on the Beers list of drugs to avoid in the elderly.[38][39]
Diphenhydramine is category B in the FDA Classification of Drug Safety During Pregnancy.[40] It is also excreted in breast milk.[41] It is expected that low doses of diphenhydramine taken occasionally will not cause any adverse effects on breastfed infants. Large doses or long-term use may affect the baby or reduce breast milk supply, especially when combined with sympathomimetic drugs such as pseudoephedrine or before the establishment of lactation. A single bedtime dose after the last feeding of the day may minimize any harmful effects of the medication on the baby and on the milk supply. Still, non-sedating antihistamines are the preferred alternative.[42]
Paradoxical reactions to diphenhydramine have been documented, in particular among children, and it may cause excitation instead of sedation.[43]
Topical diphenhydramine is sometimes used especially for people in hospice. This use is without indication and topical diphenhydramine should not be used as treatment for nausea because research does not indicate this therapy is more effective than alternatives.[44]
There were no documented cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury caused by normal doses of diphenhydramine.[45]
Adverse effects[edit]
The most prominent side effect is sedation. A typical dose creates driving impairment equivalent to a blood-alcohol level of 0.10, which is higher than the 0.08 limit of most drunk-driving laws.[23]
Diphenhydramine is a potent anticholinergic agent and potential deliriant in higher doses. This activity is responsible for the side effects of dry mouth and throat, increased heart rate, pupil dilation, urinary retention, constipation, and, at high doses, hallucinations or delirium. Other side effects include motor impairment (ataxia), flushed skin, blurred vision at nearpoint owing to lack of accommodation (cycloplegia), abnormal sensitivity to bright light (photophobia), sedation, difficulty concentrating, short-term memory loss, visual disturbances, irregular breathing, dizziness, irritability, itchy skin, confusion, increased body temperature (in general, in the hands and/or feet), temporary erectile dysfunction, and excitability, and although it can be used to treat nausea, higher doses may cause vomiting.[46] Diphenhydramine in overdose may occasionally result in QT prolongation.[47]
Some individuals experience an allergic reaction to diphenhydramine in the form of hives.[48][49]
Conditions such as restlessness or akathisia can worsen from increased levels of diphenhydramine, especially with recreational dosages.[43] Normal doses of diphenhydramine, like other first generation antihistamines, can also make symptoms of restless legs syndrome worse.[50]
As diphenhydramine is extensively metabolized by the liver, caution should be exercised when giving the drug to individuals with hepatic impairment.
Anticholinergic use later in life is associated with an increased risk for cognitive decline and dementia among older people.[51]
Contraindications[edit]
Diphenhydramine is contraindicated in premature infants and neonates as well as people who are breastfeeding. It is a pregnancy Category B drug. Diphenhydramine has additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants. Monoamine Oxidase inhibitors prolong and intensify the anticholinergic effect of antihistamines.[52]
Overdose[edit]
Diphenhydramine is one of the most commonly misused over-the-counter drugs in the United States.[53] In cases of extreme overdose, if not treated in time, acute diphenhydramine poisoning may have serious and potentially fatal consequences. Overdose symptoms may include:[54]
- Euphoria or dysphoria
- Hallucinations (auditory, visual, tactile, etc.)
- Heart palpitations
- Extreme drowsiness
- Severe dizziness
- Abnormal speech (inaudibility, forced speech, etc.)
- Flushed skin
- Severe mouth and throat dryness
- Tremors
- Seizures
- Muscle spasms
- Inability to urinate
- Vomiting
- Acute megacolon
- Motor disturbances
- Anxiety/nervousness
- Disorientation
- Disassociation
- Abdominal pain
- Delirium
- Coma
- Death
Acute poisoning can be fatal, leading to cardiovascular collapse and death in 2–18 hours, and in general is treated using a symptomatic and supportive approach.[37] Diagnosis of toxicity is based on history and clinical presentation, and in general specific levels are not useful.[55] Several levels of evidence strongly indicate diphenhydramine (similar to chlorpheniramine) can block the delayed rectifier potassium channel and, as a consequence, prolong the QT interval, leading to cardiac arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes.[56]
No specific antidote for diphenhydramine toxicity is known, but the anticholinergic syndrome has been treated with physostigmine for severe delirium or tachycardia.[55] Benzodiazepines may be administered to decrease the likelihood of psychosis, agitation, and seizures in people who are prone to these symptoms.[57]
Interactions[edit]
Alcohol may increase the drowsiness caused by diphenhydramine.[58][59]
Pharmacology[edit]
Pharmacodynamics[edit]
| Site | Ki (nM) | Species | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| SERT | ≥3,800 | Human | [61][62] |
| NET | 960–2,400 | Human | [61][62] |
| DAT | 1,100–2,200 | Human | [61][62] |
| 5-HT2A | 260 | Human | [62] |
| 5-HT2C | 780 | Human | [62] |
| α1B | 1,300 | Human | [62] |
| α2A | 2,900 | Human | [62] |
| α2B | 1,600 | Human | [62] |
| α2C | 2,100 | Human | [62] |
| D2 | 20,000 | Rat | [63] |
| H1 | 9.6–16 | Human | [64][62] |
| H2 | >100,000 | Canine | [65] |
| H3 | >10,000 | Human | [62][66][67] |
| H4 | >10,000 | Human | [67] |
| M1 | 80–100 | Human | [68][62] |
| M2 | 120–490 | Human | [68][62] |
| M3 | 84–229 | Human | [68][62] |
| M4 | 53–112 | Human | [68][62] |
| M5 | 30–260 | Human | [68][62] |
| VGSC | 48,000–86,000 | Rat | [69] |
| hERG | 27,100 (IC50) | Human | [70] |
| Values are Ki (nM), unless otherwise noted. The smaller the value, the more strongly the drug binds to the site. |
Diphenhydramine, while traditionally known as an antagonist, acts primarily as an inverse agonist of the histamine H1 receptor.[71] It is a member of the ethanolamine class of antihistaminergic agents.[37] By reversing the effects of histamine on the capillaries, it can reduce the intensity of allergic symptoms. It also crosses the blood–brain barrier and inversely agonizes the H1 receptors centrally.[71] Its effects on central H1 receptors cause drowsiness.
Like many other first-generation antihistamines, diphenhydramine is also a potent antimuscarinic (a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors) and, as such, at high doses can cause anticholinergic syndrome.[72] The utility of diphenhydramine as an antiparkinson agent is the result of its blocking properties on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain.
Diphenhydramine also acts as an intracellular sodium channel blocker, which is responsible for its actions as a local anesthetic.[69] Diphenhydramine has also been shown to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin.[73] It has been shown to be a potentiator of analgesia induced by morphine, but not by endogenous opioids, in rats.[74] The drug has also been found to act as an inhibitor of histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT).[75][76]
| Biological target | Mode of action | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| H1 receptor | Inverse agonist | Allergy reduction; Sedation |
| mACh receptors | Antagonist | Anticholinergic; Antiparkinson |
| Sodium channels | Blocker | Local anesthetic |
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Oral bioavailability of diphenhydramine is in the range of 40% to 60%, and peak plasma concentration occurs about 2 to 3 hours after administration.[5]
The primary route of metabolism is two successive demethylations of the tertiary amine. The resulting primary amine is further oxidized to the carboxylic acid.[5] Diphenhydramine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19.[9]
The elimination half-life of diphenhydramine has not been fully elucidated, but appears to range between 2.4 and 9.3 hours in healthy adults.[6] A 1985 review of antihistamine pharmacokinetics found that the elimination half-life of diphenhydramine ranged between 3.4 and 9.3 hours across five studies, with a median elimination half-life of 4.3 hours.[5] A subsequent 1990 study found that the elimination half-life of diphenhydramine was 5.4 hours in children, 9.2 hours in young adults, and 13.5 hours in the elderly.[7] A 1998 study found a half-life of 4.1 ± 0.3 hours in young men, 7.4 ± 3.0 hours in elderly men, 4.4 ± 0.3 hours in young women, and 4.9 ± 0.6 hours in elderly women.[77] In a 2018 study in children and adolescents, the half-life of diphenhydramine was 8 to 9 hours.[78]
Chemistry[edit]
Diphenhydramine is a diphenylmethane derivative. Analogues of diphenhydramine include orphenadrine, an anticholinergic, nefopam, an analgesic, and tofenacin, an antidepressant.
Detection in body fluids[edit]
Diphenhydramine can be quantified in blood, plasma, or serum.[79] Gas chromatography with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) can be used with electron ionization on full scan mode as a screening test. GC-MS or GC-NDP can be used for quantification.[79] Rapid urine drug screens using immunoassays based on the principle of competitive binding may show false-positive methadone results for people having ingested diphenhydramine.[80] Quantification can be used to monitor therapy, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in people who are hospitalized, provide evidence in an impaired driving arrest, or assist in a death investigation.[79]
History[edit]
Diphenhydramine was discovered in 1943 by George Rieveschl, a former professor at the University of Cincinnati.[81][82] In 1946, it became the first prescription antihistamine approved by the U.S. FDA.[83]
In the 1960s, diphenhydramine was found to weakly inhibit reuptake of the neurotransmitter serotonin.[73] This discovery led to a search for viable antidepressants with similar structures and fewer side effects, culminating in the invention of fluoxetine (Prozac), a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).[73][84] A similar search had previously led to the synthesis of the first SSRI, zimelidine, from brompheniramine, also an antihistamine.[85]
Society and culture[edit]
Diphenhydramine is deemed to have limited abuse potential in the United States owing to its potentially serious side-effect profile and limited euphoric effects, and is not a controlled substance. Since 2002, the U.S. FDA has required special labeling warning against use of multiple products that contain diphenhydramine.[86] In some jurisdictions, diphenhydramine is often present in postmortem specimens collected during investigation of sudden infant deaths; the drug may play a role in these events.[87][88]
Diphenhydramine is among prohibited and controlled substances in the Republic of Zambia,[89] and travelers are advised not to bring the drug into the country. Several Americans have been detained by the Zambian Drug Enforcement Commission for possession of Benadryl and other over-the-counter medications containing diphenhydramine.[90]
Recreational use[edit]
Although diphenhydramine is widely used and generally considered to be safe for occasional usage, multiple cases of abuse and addiction have been documented.[3] Because the drug is cheap and sold over the counter in most countries, adolescents without access to more sought-after, illicit drugs are particularly at risk.[91] People with mental health problems—especially those with schizophrenia—are also prone to abuse the drug, which is self-administered in large doses to treat extrapyramidal symptoms caused by the use of antipsychotics.[92]
Recreational users report calming effects, mild euphoria, and hallucinations as the desired effects of the drug.[92][93] Research has shown that antimuscarinic agents, including diphenhydramine, «may have antidepressant and mood-elevating properties».[94] A study conducted on adult males with a history of sedative abuse found that subjects who were administered a high dose (400 mg) of diphenhydramine reported a desire to take the drug again, despite also reporting negative effects, such as difficulty concentrating, confusion, tremors, and blurred vision.[95]
In 2020, an Internet challenge emerged on social media platform TikTok involving deliberately overdosing on diphenhydramine; dubbed the Benadryl challenge, the challenge encourages participants to consume dangerous amounts of Benadryl for the purpose of filming the resultant psychoactive effects, and has been implicated in several hospitalisations[96] and at least one death.[97][98]
Names[edit]
Diphenhydramine is marketed under the trade name Benadryl by McNeil Consumer Healthcare in the U.S., Canada, and South Africa.[99] Trade names in other countries include Dimedrol, Daedalon, and Nytol. It is also available as a generic medication.
Procter & Gamble markets an over-the-counter formulation of diphenhydramine as a sleep aid under the brand ZzzQuil. In 2014 this product had annual sales of over $120 million and had a 29.3% share of the $411 million sleep-aid market category.[100]
Other organisms[edit]
Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum) have a high uptake of diphenhydramine.[101]
See also[edit]
- Tripelennamine
References[edit]
- ^ Hubbard JR, Martin PR (2001). Substance Abuse in the Mentally and Physically Disabled. CRC Press. p. 26. ISBN 9780824744977.
- ^ a b c d Saran JS, Barbano RL, Schult R, Wiegand TJ, Selioutski O (October 2017). «Chronic diphenhydramine abuse and withdrawal: A diagnostic challenge». Neurology. Clinical Practice. 7 (5): 439–441. doi:10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000304. PMC 5874453. PMID 29620065.
- ^ a b c Thomas A, Nallur DG, Jones N, Deslandes PN (January 2009). «Diphenhydramine abuse and detoxification: a brief review and case report». Journal of Psychopharmacology. 23 (1): 101–5. doi:10.1177/0269881107083809. PMID 18308811. S2CID 45490366.
- ^ «Benylin Chesty Coughs (Original) — Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)». (emc). 24 February 2022. Archived from the original on 30 December 2022. Retrieved 29 December 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Paton DM, Webster DR (1985). «Clinical pharmacokinetics of H1-receptor antagonists (the antihistamines)». Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 10 (6): 477–97. doi:10.2165/00003088-198510060-00002. PMID 2866055. S2CID 33541001.
- ^ a b AHFS Drug Information. Published by authority of the Board of Directors of the American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. 1990. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 9 October 2017.
- ^ a b Simons KJ, Watson WT, Martin TJ, Chen XY, Simons FE (July 1990). «Diphenhydramine: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in elderly adults, young adults, and children». Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 30 (7): 665–71. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1990.tb01871.x. PMID 2391399. S2CID 25452263.
- ^ a b Garnett WR (February 1986). «Diphenhydramine». American Pharmacy. NS26 (2): 35–40. doi:10.1016/s0095-9561(16)38634-0. PMID 3962845.
- ^ a b Krystal AD (August 2009). «A compendium of placebo-controlled trials of the risks/benefits of pharmacological treatments for insomnia: the empirical basis for U.S. clinical practice». Sleep Med Rev. 13 (4): 265–74. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2008.08.001. PMID 19153052.
- ^ «Showing Diphenhydramine (DB01075)». DrugBank. Archived from the original on 31 August 2009. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i «Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride». Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 6 September 2016. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- ^ a b Schroeck JL, Ford J, Conway EL, Kurtzhalts KE, Gee ME, Vollmer KA, Mergenhagen KA (November 2016). «Review of Safety and Efficacy of Sleep Medicines in Older Adults». Clinical Therapeutics. 38 (11): 2340–2372. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.09.010. PMID 27751669.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- ^ Ayd FJ (2000). Lexicon of Psychiatry, Neurology, and the Neurosciences. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 332. ISBN 978-0-7817-2468-5. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ Dörwald FZ (2013). Lead Optimization for Medicinal Chemists: Pharmacokinetic Properties of Functional Groups and Organic Compounds. John Wiley & Sons. p. 225. ISBN 978-3-527-64565-7. Archived from the original on 2 October 2016.
- ^ «Benadryl». Ohio History Central. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- ^ «The Top 300 of 2020». ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine — Drug Usage Statistics». ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride Monograph». Drugs.com. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 15 June 2011.
- ^ Brown HE, Stoklosa J, Freudenreich O (December 2012). «How to stabilize an acutely psychotic patient» (PDF). Current Psychiatary. 11 (12): 10–16. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2013.
- ^ Smith DW, Peterson MR, DeBerard SC (August 1999). «Local anesthesia. Topical application, local infiltration, and field block». Postgraduate Medicine. 106 (2): 57–60, 64–6. doi:10.3810/pgm.1999.08.650. PMID 10456039.
- ^ a b American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. «Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016. Retrieved 2 August 2016.
- ^ a b Banerji A, Long AA, Camargo CA (2007). «Diphenhydramine versus nonsedating antihistamines for acute allergic reactions: a literature review». Allergy and Asthma Proceedings. 28 (4): 418–26. doi:10.2500/aap.2007.28.3015. PMID 17883909. S2CID 7596980.
- ^ Young WF (2011). «Chapter 11: Shock». In Humphries RL, Stone CK (eds.). CURRENT Diagnosis and Treatment Emergency Medicine. LANGE CURRENT Series (Seventh ed.). McGraw–Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-170107-5.
- ^ Sheikh A, ten Broek VM, Brown SG, Simons FE (January 2007). «H1-antihistamines for the treatment of anaphylaxis with and without shock». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2007 (1): CD006160. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006160.pub2. PMC 6517288. PMID 17253584.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Topical». MedlinePlus. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ Aminoff MJ (2012). «Chapter 28. Pharmacologic Management of Parkinsonism & Other Movement Disorders». In Katzung B, Masters S, Trevor A (eds.). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (12th ed.). The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. pp. 483–500. ISBN 978-0-07-176401-8.
- ^ Monson K, Schoenstadt A (8 September 2013). «Benadryl Addiction». eMedTV. Archived from the original on 4 January 2014.
- ^ Dinndorf PA, McCabe MA, Friedrich S (August 1998). «Risk of abuse of diphenhydramine in children and adolescents with chronic illnesses». The Journal of Pediatrics. 133 (2): 293–5. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(98)70240-9. PMID 9709726.
- ^ Crier F (2 August 2017). «Is it wrong to drug your children so they sleep on a flight?». The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ Morris R (3 April 2013). «Should parents drug babies on long flights?». BBC News. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ Swanson WS (25 November 2009). «If It Were My Child: No Benadryl for the Plane». Seattle Children’s. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ Sateia MJ, Buysse DJ, Krystal AD, Neubauer DN, Heald JL (February 2017). «Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Insomnia in Adults: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline». J Clin Sleep Med. 13 (2): 307–349. doi:10.5664/jcsm.6470. PMC 5263087. PMID 27998379.
- ^ De Crescenzo F, D’Alò GL, Ostinelli EG, Ciabattini M, Di Franco V, Watanabe N, Kurtulmus A, Tomlinson A, Mitrova Z, Foti F, Del Giovane C, Quested DJ, Cowen PJ, Barbui C, Amato L, Efthimiou O, Cipriani A (July 2022). «Comparative effects of pharmacological interventions for the acute and long-term management of insomnia disorder in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis». Lancet. 400 (10347): 170–184. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00878-9. PMID 35843245. S2CID 250536370.
- ^ Flake ZA, Scalley RD, Bailey AG (March 2004). «Practical selection of antiemetics». American Family Physician. 69 (5): 1169–74. PMID 15023018. Archived from the original on 24 March 2016. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ Medical Economics (2000). Physicians’ Desk Reference for Nonprescription Drugs and Dietary Supplements, 2000 (21st ed.). Montvale, NJ: Medical Economics Company. ISBN 978-1-56363-341-6.
- ^ a b c Brunton L, Chabner B, Knollmann B (2011). «Chapter 32. Histamine, Bradykinin, and Their Antagonists». In Brunton L (ed.). Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (12e ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 242–245. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- ^ «High risk medications as specified by NCQA’s HEDIS Measure: Use of High Risk Medications in the Elderly» (PDF). National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA). Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 February 2010.
- ^ «2012 AGS Beers List» (PDF). The American Geriatrics Society. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2012. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- ^ Black RA, Hill DA (June 2003). «Over-the-counter medications in pregnancy». American Family Physician. 67 (12): 2517–24. PMID 12825840.
- ^ Spencer JP, Gonzalez LS, Barnhart DJ (July 2001). «Medications in the breast-feeding mother». American Family Physician. 64 (1): 119–26. PMID 11456429.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine». Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). October 2020. PMID 30000938.
- ^ a b de Leon J, Nikoloff DM (February 2008). «Paradoxical excitation on diphenhydramine may be associated with being a CYP2D6 ultrarapid metabolizer: three case reports». CNS Spectrums. 13 (2): 133–5. doi:10.1017/s109285290001628x. PMID 18227744. S2CID 10856872.
- ^ American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine, «Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question», Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine, archived from the original on 1 September 2013, retrieved 1 August 2013, which cites
- Smith TJ, Ritter JK, Poklis JL, Fletcher D, Coyne PJ, Dodson P, Parker G (May 2012). «ABH gel is not absorbed from the skin of normal volunteers». Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 43 (5): 961–6. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2011.05.017. PMID 22560361.
- Weschules DJ (December 2005). «Tolerability of the compound ABHR in hospice patients». Journal of Palliative Medicine. 8 (6): 1135–43. doi:10.1089/jpm.2005.8.1135. PMID 16351526.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine». LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. PMID 31643789. Archived from the original on 29 July 2021. Retrieved 21 June 2021.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine Side Effects». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2009.
- ^ Aronson JK (2009). Meyler’s Side Effects of Cardiovascular Drugs. Elsevier. p. 623. ISBN 978-0-08-093289-7. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ^ Heine A (November 1996). «Diphenhydramine: a forgotten allergen?». Contact Dermatitis. 35 (5): 311–2. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1996.tb02402.x. PMID 9007386. S2CID 32839996.
- ^ Coskey RJ (February 1983). «Contact dermatitis caused by diphenhydramine hydrochloride». Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 8 (2): 204–6. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(83)70024-1. PMID 6219138.
- ^ «Restless Legs Syndrome Fact Sheet | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke». www.ninds.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ^ Salahudeen MS, Duffull SB, Nishtala PS (March 2015). «Anticholinergic burden quantified by anticholinergic risk scales and adverse outcomes in older people: a systematic review». BMC Geriatrics. 15 (31): 31. doi:10.1186/s12877-015-0029-9. PMC 4377853. PMID 25879993.
- ^ Sicari V, Zabbo CP (2021). «Diphenhydramine». StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30252266. Archived from the original on 28 May 2022. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ Huynh DA, Abbas M, Dabaja A (2021). Diphenhydramine Toxicity. PMID 32491510.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine overdose». MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 30 May 2013.
- ^ a b Manning B (2012). «Chapter 18. Antihistamines». In Olson K (ed.). Poisoning & Drug Overdose (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-166833-0. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ^ Khalifa M, Drolet B, Daleau P, Lefez C, Gilbert M, Plante S, O’Hara GE, Gleeton O, Hamelin BA, Turgeon J (February 1999). «Block of potassium currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes and lengthening of cardiac repolarization in man by the histamine H1 receptor antagonist diphenhydramine». The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 288 (2): 858–65. PMID 9918600.
- ^ Cole JB, Stellpflug SJ, Gross EA, Smith SW (December 2011). «Wide complex tachycardia in a pediatric diphenhydramine overdose treated with sodium bicarbonate». Pediatric Emergency Care. 27 (12): 1175–7. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e31823b0e47. PMID 22158278. S2CID 5602304.
- ^ «Diphenhydramine and Alcohol / Food Interactions». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 February 2013.
- ^ Zimatkin SM, Anichtchik OV (1999). «Alcohol-histamine interactions». Alcohol and Alcoholism. 34 (2): 141–7. doi:10.1093/alcalc/34.2.141. PMID 10344773.
- ^ Roth BL, Driscol J. «PDSP Ki Database». Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP). University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health. Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- ^ a b c Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson E (December 1997). «Pharmacological profile of antidepressants and related compounds at human monoamine transporters». European Journal of Pharmacology. 340 (2–3): 249–58. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01393-9. PMID 9537821.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Krystal AD, Richelson E, Roth T (August 2013). «Review of the histamine system and the clinical effects of H1 antagonists: basis for a new model for understanding the effects of insomnia medications». Sleep Medicine Reviews. 17 (4): 263–72. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2012.08.001. PMID 23357028.
- ^ Tsuchihashi H, Sasaki T, Kojima S, Nagatomo T (1992). «Binding of [3H]haloperidol to dopamine D2 receptors in the rat striatum». J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 44 (11): 911–4. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1992.tb03235.x. PMID 1361536. S2CID 19420332.
- ^ Ghoneim OM, Legere JA, Golbraikh A, Tropsha A, Booth RG (October 2006). «Novel ligands for the human histamine H1 receptor: synthesis, pharmacology, and comparative molecular field analysis studies of 2-dimethylamino-5-(6)-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalenes». Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 14 (19): 6640–58. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.05.077. PMID 16782354.
- ^ Gantz I, Schäffer M, DelValle J, Logsdon C, Campbell V, Uhler M, Yamada T (1991). «Molecular cloning of a gene encoding the histamine H2 receptor». Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (2): 429–33. Bibcode:1991PNAS…88..429G. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.2.429. PMC 50824. PMID 1703298.
- ^ Lovenberg TW, Roland BL, Wilson SJ, Jiang X, Pyati J, Huvar A, Jackson MR, Erlander MG (June 1999). «Cloning and functional expression of the human histamine H3 receptor». Molecular Pharmacology. 55 (6): 1101–7. doi:10.1124/mol.55.6.1101. PMID 10347254. S2CID 25542667.
- ^ a b Liu C, Ma X, Jiang X, Wilson SJ, Hofstra CL, Blevitt J, Pyati J, Li X, Chai W, Carruthers N, Lovenberg TW (March 2001). «Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a fourth histamine receptor (H(4)) expressed in bone marrow». Molecular Pharmacology. 59 (3): 420–6. doi:10.1124/mol.59.3.420. PMID 11179434. S2CID 123619.
- ^ a b c d e Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E (February 1992). «Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells». The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 260 (2): 576–80. PMID 1346637.
- ^ a b Kim YS, Shin YK, Lee C, Song J (October 2000). «Block of sodium currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons by diphenhydramine». Brain Research. 881 (2): 190–8. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02860-2. PMID 11036158. S2CID 18560451.
- ^ Suessbrich H, Waldegger S, Lang F, Busch AE (April 1996). «Blockade of HERG channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the histamine receptor antagonists terfenadine and astemizole». FEBS Letters. 385 (1–2): 77–80. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(96)00355-9. PMID 8641472. S2CID 40355762.
- ^ a b Khilnani G, Khilnani AK (September 2011). «Inverse agonism and its therapeutic significance». Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 43 (5): 492–501. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.84947. PMC 3195115. PMID 22021988.
- ^ Lopez AM (10 May 2010). «Antihistamine Toxicity». Medscape Reference. WebMD LLC. Archived from the original on 13 October 2010.
- ^ a b c Domino EF (1999). «History of modern psychopharmacology: a personal view with an emphasis on antidepressants». Psychosomatic Medicine. 61 (5): 591–8. doi:10.1097/00006842-199909000-00002. PMID 10511010.
- ^ Carr KD, Hiller JM, Simon EJ (February 1985). «Diphenhydramine potentiates narcotic but not endogenous opioid analgesia». Neuropeptides. 5 (4–6): 411–4. doi:10.1016/0143-4179(85)90041-1. PMID 2860599. S2CID 45054719.
- ^ Horton JR, Sawada K, Nishibori M, Cheng X (October 2005). «Structural basis for inhibition of histamine N-methyltransferase by diverse drugs». Journal of Molecular Biology. 353 (2): 334–344. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.08.040. PMC 4021489. PMID 16168438.
- ^ Taylor KM, Snyder SH (May 1972). «Histamine methyltransferase: inhibition and potentiation by antihistamines». Molecular Pharmacology. 8 (3): 300–10. PMID 4402747.
- ^ Scavone JM, Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Engelhardt N, Shader RI (July 1998). «Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of diphenhydramine 25 mg in young and elderly volunteers». J Clin Pharmacol. 38 (7): 603–9. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1998.tb04466.x. PMID 9702844. S2CID 24989721.
- ^ Gelotte CK, Zimmerman BA, Thompson GA (May 2018). «Single-Dose Pharmacokinetic Study of Diphenhydramine HCl in Children and Adolescents». Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 7 (4): 400–407. doi:10.1002/cpdd.391. PMC 5947143. PMID 28967696.
- ^ a b c Pragst F (2007). «Chapter 13: High performance liquid chromatography in forensic toxicological analysis». In Smith RK, Bogusz MJ (eds.). Forensic Science (Handbook of Analytical Separations). Vol. 6 (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science. p. 471. ISBN 978-0-444-52214-6.
- ^ Rogers SC, Pruitt CW, Crouch DJ, Caravati EM (September 2010). «Rapid urine drug screens: diphenhydramine and methadone cross-reactivity». Pediatric Emergency Care. 26 (9): 665–6. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e3181f05443. PMID 20838187. S2CID 31581678.
- ^ Hevesi D (29 September 2007). «George Rieveschl, 91, Allergy Reliever, Dies». The New York Times. Archived from the original on 13 December 2011. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
- ^ «Benadryl». Ohio History Central. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- ^ Ritchie J (24 September 2007). «UC prof, Benadryl inventor dies». Business Courier of Cincinnati. Archived from the original on 24 December 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
- ^ Awdishn RA, Whitmill M, Coba V, Killu K (October 2008). «Serotonin reuptake inhibition by diphenhydramine and concomitant linezolid use can result in serotonin syndrome». Chest. 134 (4 Meeting abstracts): 4C. doi:10.1378/chest.134.4_MeetingAbstracts.c4002. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ^ Barondes SH (2003). Better Than Prozac. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 39–40. ISBN 978-0-19-515130-5.
- ^ Food and Drug Administration, HHS (December 2002). «Labeling of diphenhydramine-containing drug products for over-the-counter human use. Final rule». Federal Register. 67 (235): 72555–9. PMID 12474879. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008.
- ^ Marinetti L, Lehman L, Casto B, Harshbarger K, Kubiczek P, Davis J (October 2005). «Over-the-counter cold medications-postmortem findings in infants and the relationship to cause of death». Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 29 (7): 738–43. doi:10.1093/jat/29.7.738. PMID 16419411.
- ^ Baselt RC (2008). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man. Biomedical Publications. pp. 489–492. ISBN 978-0-9626523-7-0.
- ^ «List of prohibited and controlled drugs according to chapter 96 of the laws of Zambia». The Drug Enforcement Commission ZAMBIA. Archived from the original (DOC) on 16 November 2013. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
- ^ «Zambia». Country Information > Zambia. Bureau of Consular Affairs, U.S. Department of State. Archived from the original on 21 July 2015. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- ^ Forest E (27 July 2008). «Atypical Drugs of Abuse». Articles & Interviews. Student Doctor Network. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013.
- ^ a b Halpert AG, Olmstead MC, Beninger RJ (January 2002). «Mechanisms and abuse liability of the anti-histamine dimenhydrinate» (PDF). Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 26 (1): 61–7. doi:10.1016/s0149-7634(01)00038-0. PMID 11835984. S2CID 46619422. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ Gracious B, Abe N, Sundberg J (December 2010). «The importance of taking a history of over-the-counter medication use: a brief review and case illustration of «PRN» antihistamine dependence in a hospitalized adolescent». Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology. 20 (6): 521–4. doi:10.1089/cap.2010.0031. PMC 3025184. PMID 21186972.
- ^ Dilsaver SC (February 1988). «Antimuscarinic agents as substances of abuse: a review». Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 8 (1): 14–22. doi:10.1097/00004714-198802000-00003. PMID 3280616. S2CID 31355546.
- ^ Mumford GK, Silverman K, Griffiths RR (1996). «Reinforcing, subjective, and performance effects of lorazepam and diphenhydramine in humans». Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 4 (4): 421–430. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.4.4.421.
- ^ «TikTok Videos Encourage Viewers to Overdose on Benadryl». TikTok Videos Encourage Viewers to Overdose on Benadryl. Archived from the original on 8 October 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ «Dangerous ‘Benadryl Challenge’ on Tik Tok may be to blame for the death of Oklahoma teen». KFOR.com Oklahoma City. 28 August 2020. Archived from the original on 2 August 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ «Teen’s Death Prompts Warning on ‘Benadryl Challenge’«. www.medpagetoday.com. 25 September 2020. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ^ «Childrens Benadryl ALLERGY (solution) Johnson & Johnson Consumer Inc., McNeil Consumer Healthcare Division». Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ^ «Is P&G Preparing to Expand ZzzQuil?». Archived from the original on 11 February 2017. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ Christou A, Papadavid G, Dalias P, Fotopoulos V, Michael C, Bayona JM, et al. (March 2019). «Ranking of crop plants according to their potential to uptake and accumulate contaminants of emerging concern». Environmental Research. Elsevier BV. 170: 422–432. Bibcode:2019ER….170..422C. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2018.12.048. hdl:10261/202657. PMID 30623890. S2CID 58564142.
Further reading[edit]
- Björnsdóttir I, Einarson TR, Gudmundsson LS, Einarsdóttir RA (December 2007). «Efficacy of diphenhydramine against cough in humans: a review». Pharmacy World & Science. 29 (6): 577–83. doi:10.1007/s11096-007-9122-2. PMID 17486423. S2CID 8168920.
- Cox D, Ahmed Z, McBride AJ (March 2001). «Diphenhydramine dependence». Addiction. 96 (3): 516–7. PMID 11310441.
- Lieberman JA (2003). «History of the use of antidepressants in primary care» (PDF). Primary Care Companion J. Clinical Psychiatry. 5 (supplement 7): 6–10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2014. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
External links[edit]
- «Diphenhydramine». Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Dimedrol
Регистрационный номер
Торговое наименование
Димедрол
Международное непатентованное наименование
Лекарственная форма
раствор для внутривенного и внутримышечного введения
Состав
Описание
Прозрачный бесцветный раствор.
Фармакотерапевтическая группа
Код АТХ
Фармакологические свойства
Фармакодинамика
Блокатор Н1-гистаминовых рецепторов первого поколения. Действие на центральную нервную систему обусловлено блокадой H3-гистаминовых рецепторов и м-холинорецепторов головного мозга. Снимает спазм гладкой мускулатуры (непосредственное действие), уменьшает проницаемость капилляров, предупреждает и ослабляет аллергические реакции, обладает местноанестезирующим, противорвотным, седативным эффектами, оказывает снотворное действие. Антагонизм с гистамином проявляется в большей степени по отношению к местным сосудистым реакциям при воспалении и аллергии, чем к системным, то есть снижению артериального давления. Однако, при парентеральном введении пациентам с дефицитом объёма циркулирующей крови возможно снижение артериального давления и усиление имеющейся артериальной гипотензии. У людей с локальными повреждениями мозга и эпилепсией активирует (даже в низких дозах) эпилептические разряды на электроэнцефалограмме и может провоцировать эпилептический приступ.
Действие развивается в течение нескольких минут, длительность — до 12 ч.
Фармакокинетика
Связь с — белками плазмы — 98–99 %. Проникает через -гематоэнцефалический барьер. Метаболизируется главным образом в печени, частично — в лёгких и почках. Выводится из тканей через 6 ч. Период полувыведения — 4–10 ч. В течение суток полностью выводится почками в виде метаболитов, конъюгированных с глюкуроновой кислотой. Существенные количества выводятся с грудным молоком и могут вызывать седативный эффект у детей грудного возраста (может наблюдаться парадоксальная реакция, характеризующаяся чрезмерной возбудимостью).
Показания
В составе комплексной терапии — анафилактические и анафилактоидные реакции, отёк Квинке, морская и воздушная болезнь.
Противопоказания
Гиперчувствительность, период лактации, закрытоугольная глаукома, гиперплазия предстательной железы, стенозирующая язвенная — болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки, стеноз шейки мочевого пузыря, бронхиальная астма, эпилепсия, детский возраст до 7 месяцев.
Применение при беременности и в период грудного вскармливания
Применение дифенгидрамина при беременности возможно только под строгим контролем врача в том случае, когда предполагаемая польза для матери превышает потенциальный риск для плода. На время лечения следует прекратить грудное вскармливание.
Способ применения и дозы
Внутривенно или внутримышечно.
Для взрослых и детей старше 14 лет внутривенно или внутримышечно 1–5 мл 1 % раствора (10–50 мг) 1–3 раза в день; максимальная суточная доза — 200 мг.
Для детей в возрасте от 7 месяцев до 12 месяцев по 0,3–0,5 мл (3–5 мг), от 1 года до 3 лет по 0,5–1 мл (5–10 мг), от 4 до 6 лет по 1–1,5 мл (10–15 мг), от 7 до 14 лет по 1,5–3 мл (15–30 мг) при необходимости каждые 6-8 ч.
Максимальная суточная доза для детей в возрасте от 7 месяцев до 12 месяцев — 2,0 мл (20 мг), от 1 года до 3 лет — 4,0 мл (40 мг), от 4 до 6 лет — 6,0 мл (60 мг), от 7 до 14 лет — 12 мл (120 мг).
Побочное действие
Аллергические реакции:
анафилактический шок, крапивница, фоточувствительность, кожная сыпь, зуд.
Со стороны нервной системы:
головная боль, седативный эффект, головокружение, спутанность сознания, беспокойство, нервозность, тремор, парестезии, неврит, судороги, сонливость, общая слабость, снижение скорости психомоторных реакций, нарушения координации движения, чувство усталости. В некоторых случаях возбуждение (особенно у детей), бессонница, раздражительность, эйфория.
Со стороны пищеварительной системы:
сухость слизистой оболочки полости рта, тошнота, рвота, дискомфорт в эпигастральной области, анорексия, диарея, запор.
Со стороны дыхательной системы: сухость слизистой оболочки носа и горла, бронхов, чувство сдавления в груди или горле, чихание, заложенность носа.
Со стороны органов кроветворения:
гемолитическая анемия, тромбоцитопения, агранулоцитоз.
Со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы:
снижение артериального давления, тахикардия, экстрасистолия, ощущение сердцебиения, тахикардия.
Со стороны мочеполовой системы:
учащение или затруднение мочеиспускания, задержка мочи, ранние менструации.
Со стороны органов чувств:
нарушение зрительного восприятия, диплопия, вертиго, шум в ушах, острый лабиринтит.
Прочие:
повышенное потоотделение, озноб.
Передозировка
Симптомы: угнетение или возбуждение (особенно у детей) функций центральной нервной системы, в том числе депрессия, расширение зрачков, сухость слизистой оболочки полости рта, расстройство функций желудочно-кишечного тракта.
Лечение: специального антидота не существует. Поддерживающие меры включают контроль артериального давления, препараты, повышающие артериальное давление, кислород, введение плазмозамещающих жидкостей внутривенно.
Нельзя применять эпинефрин и аналептики.
Взаимодействие с другими лекарственными средствами
Усиливает действие алкоголя и препаратов, угнетающих центральную нервную систему. Ингибиторы моноаминоксидазы (МАО) усиливают антихолинергическую активность дифенгидрамина. Антагонистическое взаимодействие отмечается при совместном назначении с психостимуляторами. Снижает эффективность апоморфина как рвотного лекарственного средства при лечении отравления. Усиливает антихолинергические эффекты лекарственных средств с м-холиноблокирующей активностью.
Особые указания
Нельзя вводить подкожно из-за раздражающего действия.
Во время лечения дифенгидрамином следует избегать ультрафиолетового излучения и употребления алкогольных напитков.
Из-за риска развития локального некроза нельзя использовать Димедрол в качестве местного анестетика.
Необходимо проинформировать врача о применении этого препарата: противорвотное действие может затруднять диагностику аппендицита и распознавание симптомов передозировки других лекарственных средств.
Влияние на способность управлять транспортными средствами, механизмами
В период лечения необходимо соблюдать осторожность при вождении автотранспорта и занятии другими потенциально опасными видами деятельности, требующими повышенной концентрации внимания и быстроты психомоторных реакций.
Форма выпуска
Раствор для внутривенного и внутримышечного введения 10 мг/мл.
По 1 мл в ампулы.
По 10 ампул вместе с инструкцией по применению и скарификатором ампульным помещают в коробку из картона.
По 5 ампул помещают в контурную ячейковую упаковку.
По 1 или 2 контурные ячейковые упаковки вместе с инструкцией по применению и скарификатором ампульным помещают в пачку из картона.
При использовании ампул, имеющих кольцо излома, допускается упаковка ампул без скарификатора ампульного.
Хранение
В защищённом от света месте при температуре не выше 25 °C.
Хранить в недоступном для детей месте.
Срок годности
4 года. Не применять после истечения срока годности, указанного на упаковке.
Условия отпуска из аптек
Отпускают по рецепту.
Производитель
Димедрол (Dimedrol)
💊 Состав препарата Димедрол
✅ Применение препарата Димедрол
Описание активных компонентов препарата
Димедрол
(Dimedrol)
Приведенная научная информация является обобщающей и не может быть использована для принятия
решения о возможности применения конкретного лекарственного препарата.
Дата обновления: 2020.11.09
Владелец регистрационного удостоверения:
Код ATX:
R06AA02
(Дифенгидрамин)
Лекарственная форма
| Димедрол |
Р-р д/в/в и в/м введения 10 мг/мл: амп. 10 шт. рег. №: Р N003089/01 |
Форма выпуска, упаковка и состав
препарата Димедрол
Раствор для в/в и в/м введения прозрачный, бесцветный.
1 мл — ампулы (10) — пачки картонные.
Фармакологическое действие
Блокатор гистаминовых Н1-рецепторов. Обладает противоаллергической активностью, оказывает местноанестезирующее, спазмолитическое и умеренное ганглиоблокирующее действие. При приеме внутрь вызывает седативный и снотворный эффект, оказывает умеренное противорвотное действие, а также обладает центральной холинолитической активностью.
При парентеральном введении пациентам с дефицитом объема циркулирующей крови возможно снижение АД и усиление имеющейся гипотензии.
При наружном применении оказывает противоаллергическое действие.
Фармакокинетика
Быстро абсорбируется из ЖКТ. Биодоступность составляет 50%. Cmax достигается через 20-40 мин (в наибольшей концентрации определяется в легких, селезенке, почках, печени, головном мозге и мышцах). Связывание с белками плазмы – 98-99%. Проникает через ГЭБ. Метаболизируется главным образом в печени, частично — в легких и почках. T1/2 — 4-10 ч. В течение суток полностью выводится почками в виде метаболитов, конъюгированных с глюкуроновой кислотой. Существенные количества выводятся с молоком и могут вызывать седативный эффект у детей грудного возраста (может наблюдаться парадоксальная реакция, характеризующаяся чрезмерной возбудимостью).
При наружном применении абсорбция незначительная, нарушение целостности кожных покровов повышает всасывание дифенгидрамина.
Показания активных веществ препарата
Димедрол
Аллергический конъюнктивит, аллергический ринит, хроническая крапивница, зудящие дерматозы, дерматографизм, сывороточная болезнь; в комплексной терапии анафилактических и анафилактоидных реакций, отека Квинке и других аллергических состояний. Бессонница, хорея, синдром Меньера, морская и воздушная болезнь, в качестве противорвотного средства. Солнечные ожоги и ожоги I степени; укусы насекомых; кожный зуд различного происхождения (за исключением зуда при холестазе): экзема, ветряная оспа, аллергические раздражения кожи, контактные дерматиты, вызванные соприкосновением с растениями.
Режим дозирования
Способ применения и режим дозирования конкретного препарата зависят от его формы выпуска и других факторов. Оптимальный режим дозирования определяет врач. Следует строго соблюдать соответствие используемой лекарственной формы конкретного препарата показаниям к применению и режиму дозирования.
Применяют внутрь, парентерально и наружно.
Внутрь назначают взрослым и детям старше 14 лет в разовой дозе 50 мг. Схему и продолжительность применения определяют индивидуально, в зависимости от показаний.
В/в или глубоко в/м назначают взрослым и детям старше 14 лет в разовой дозе 10-50 мг, максимальная суточная доза — 200 мг. Для детей в возрасте от 7 мес до 14 лет дозу устанавливают в зависимости от возраста.
Наружно. Наносят на пораженные участки кожи 3-4 раза/сут.
Побочное действие
Со стороны нервной системы: головная боль, седативный эффект, сонливость, головокружение, нарушение координации, слабость, спутанность сознания, беспокойство, возбуждение, нервозность, тремор, раздражительность, бессонница, эйфория, парестезии, неврит, судороги.
Со стороны пищеварительной системы: сухость слизистой оболочки полости рта, тошнота, рвота, боль в эпигастральной области, анорексия, диарея, запор.
Со стороны дыхательной системы: сухость слизистой оболочки полости носа и горла, повышение вязкости мокроты, чувство сдавления в груди, чихание, заложенность носа.
Со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы: ощущение сердцебиения, снижение АД, тахикардия, экстрасистолия.
Со стороны системы кроветворения: гемолитическая анемия, тромбоцитопения, агранулоцитоз.
Со стороны мочеполовой системы: учащенное или затрудненное мочеиспускание, задержка мочи, ранние менструации.
Со стороны органов чувств: нарушение зрительного восприятия, диплопия, вертиго, шум в ушах, острый лабиринтит.
Аллергические реакции: крапивница, кожная сыпь, зуд, анафилактичекий шок, фотосенсибилизация.
Прочие: повышенное потоотделение, озноб.
Противопоказания к применению
Повышенная чувствительность к дифенгидрамину.
Для системного применения: закрытоугольная глаукома, гипертрофия предстательной железы, стенозирующая язва желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки, стеноз шейки мочевого пузыря, бронхиальная астма, эпилепсия; детский возраст до 14 лет (для приема внутрь); детский возраст до 7 месяцев (для парентерального применения).
С осторожностью: повышение внутриглазного давления, гипертиреоз, артериальная гипертензия заболевания сердечно-сосудистой системы, бронхо-легочные заболевания.
Для наружного применения: одновременное применение любых препаратов, содержащих дифенгидрамин; применение на обширных поверхностях кожи; детский возраст до 2 лет.
С осторожностью: повреждение кожных покровов в месте нанесения, нанесение на слизистые оболочки.
Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
При беременности и в период лактации (грудного вскармливания) дифенгидрамин применяют с осторожностью, по строгим показаниям, в случаях, когда ожидаемый терапевтический эффект для матери превышает потенциальный риск для плода или грудного ребенка.
Существенные количества дифенгидрамина выводятся с грудным молоком и могут вызывать седативный эффект у детей грудного возраста (может наблюдаться парадоксальная реакция, характеризующаяся чрезмерной возбудимостью).
Применение при нарушениях функции почек
С осторожностью следует применять у пациентов с нарушениями функции почек.
Применение у детей
Возможно применение у детей по показаниям в рекомендуемых соответственно возрасту дозах и лекарственных формах.
Применение у пожилых пациентов
С осторожностью следует назначать пожилым пациентам во избежание ухудшения течения сопутствующих заболеваний.
Особые указания
В период лечения не следует подвергаться воздействию солнечного излучения; необходимо избегать употребления алкоголя.
Влияние на способность к управлению транспортными средствами и механизмами
С осторожностью применяют у пациентов, занимающихся потенциально опасными видами деятельности, требующими повышенного внимания и быстрых психомоторных реакций.
Лекарственное взаимодействие
При одновременном применении усиливает действие этанола и препаратов, угнетающих ЦНС.
При одновременном применении ингибиторы МАО усиливают антихолинергическую активность дифенгидрамина.
Антагонистическое взаимодействие отмечается при совместном назначении с психостимуляторами.
Снижает эффективность апоморфина как рвотного средства при лечении отравления.
Усиливает антихолинергические эффекты препаратов с холиноблокирующей активностью.
Если вы хотите разместить ссылку на описание этого препарата — используйте данный код
Аналоги препарата
Димедрол
(БЕЛМЕДПРЕПАРАТЫ, Республика Беларусь)
Димедрол
(БОРИСОВСКИЙ ЗАВОД МЕДИЦИНСКИХ ПРЕПАРАТОВ, Республика Беларусь)
Димедрол
(САМСОН-МЕД, Россия)
Димедрол
(ДАЛЬХИМФАРМ, Россия)
Димедрол
(НОВОСИБХИМФАРМ, Россия)
Димедрол
(МОСХИМФАРМПРЕПАРАТЫ им. Н.А.Семашко, Россия)
Димедрол
(Фирма ФЕРМЕНТ, Россия)
Димедрол
(БИОСИНТЕЗ ПАО, Россия)
Димедрол
(ВЕЛФАРМ, Россия)
Димедрол-Виал
(ВИАЛ, Россия)
Все аналоги
Одна ампула (1 мл) содержит: действующее вещество – дифенгидрамина гидрохлорид 10 мг; вспомогательное вещество — вода для инъекций – до 1 мл.
Прозрачная бесцветная жидкость.
Аллергические реакции (крапивница, сенная лихорадка, ангионевротический отек, капилляротоксикоз), аллергический конъюнктивит, острый иридоциклит, вазомоторный ринит, риносинусопатия, аллергический дерматит, зудящий дерматоз.
В составе комбинированной терапии для лечения язвенной болезни желудка и 12-перстной кишки, гиперацидного гастрита.
Паркинсонизм, хорея, бессонница.
Рвота беременных, синдром Меньера, морская и воздушная болезнь, лучевая болезнь.
Обширные травматические повреждения кожи и мягких тканей (ожоги, размозжения), геморрагический васкулит, сывороточная болезнь.
Премедикация.
С осторожностью используют у пациентов с гипертиреозом, повышенным внутриглазным давлением, заболеваниями сердечно-сосудистой системы, в пожилом возрасте. В период лечения следует избегать употребления алкогольных напитков и УФ-облучения.
Гиперчувствительность, кормление грудью, детский возраст (период новорожденности и состояние недоношенности), закрытоугольная глаукома, гипертрофия предстательной железы, стенозирующая язва желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки, пилородуоденальная обструкция, стеноз шейки мочевого пузыря, беременность, бронхиальная астма.
Внутримышечно. Взрослым и детям старше 12 лет по 10-50 мг. Высшая разовая доза — 50 мг, суточная — 150 мг. Детям до 1 года в дозе 2-5 мг (0,2-0,5 мл), 2-5 лет – 5-15 мг (0,5-1,5 мл), 6-12 лет – 15-30 мг (1,5-3,0 мл) на введение. Коррекции режима дозирования у пациентов с нарушением функции печени и почек, а также у лиц в возрасте старше 60 лет не требуется.
При появлении любого из нижеперечисленных симптомов или симптомов не описанных в данном разделе следует незамедлительно прекратить применение лекарственного средства и обратиться к врачу.
Со стороны пищеварительной системы: сухость во рту, онемение слизистой оболочки полости рта, тошнота, рвота, диарея, запор.
Со стороны нервной системы: головная боль, сонливость, седативный эффект, головокружение, нарушение координации, слабость, спутанность сознания, беспокойство, возбуждение, нервозность, тремор, раздражительность, бессонница, эйфория, парестезии, неврит, судороги.
Со стороны органов чувств: нарушение зрительного восприятия, диплопия, вертиго, шум в ушах, острый лабиринтит.
Со стороны мочеполовой системы: учащенное или затрудненное мочеиспускание, задержка мочи, ранние менструации.
Со стороны органов кроветворения: гемолитическая анемия, тромбоцитопения, агранулоцитоз.
Аллергические реакции: крапивница, лекарственная сыпь, анафилактический шок, фотосенсибилизация.
Симптомы: угнетение центральной нервной системы, развитие возбуждения (особенно у детей) или депрессии, расширение зрачков, сухость во рту, парез органов желудочно-кишечного тракта.
Лечение: специфического антидота нет, промывание желудка, при необходимости – лекарственные средства, повышающие артериальное давление, кислород, внутривенное введение плазмозамещающих жидкостей. Нельзя использовать эпинефрин и аналептики.
Усиливает действие этанола и лекарственных средств, угнетающих центральную нервную систему.
Ингибиторы моноаминоксидазы усиливают антихолинергическую активность дифенгидрамина.
Антагонистическое взаимодействие отмечается при совместном назначении с психостимуляторами.
Снижает эффективность апоморфина как рвотного лекарственного средства при лечении отравления.
Усиливает антихолинергические эффекты лекарственного средства с М-холиноблокирующей активностью.
Фармацевтически несовместим с амфотерицином В, цефметазолом натрия, цефалотином натрия, гидрокортизона сукцинатом, барбитуратами, некоторыми рентгенконтрастными средствами, растворами щелочей и сильных кислот.
Беременность. С осторожностью, под строгим контролем врача, во время беременности (адекватных и строго контролируемых исследований у беременных женщин не проведено). Имеются сообщения о развитии у новорожденных диареи и тремора в первые 5 дней после рождения при назначении матери в период беременности димедрола. На время лечения следует прекратить грудное вскармливание.
Использование в педиатрии: димедрол не должен использоваться у новорожденных и недоношенных детей. У педиатрических пациентов антигистаминные препараты, особенно при передозировке, могут вызвать галлюцинации, конвульсии или смерть. Как и у взрослых, антигистаминные препараты могут уменьшить психическую активность у детей. У маленьких детей димедрол может приводить к возбуждению.
Использование в пожилом возрасте (около 60 лет и старше): антигистаминные препараты чаще вызывают головокружение, седативный эффект и гипотонию у пожилых пациентов.
Димедрол обладает атропинподобным действием и, следовательно, должен использоваться с предостережением у пациентов в анамнезе с бронхиальной астмой, повышенным внутриглазным давлением, гипертиреозом, сердечнососудистыми заболеваниями или гипертонией. Использовать с осторожностью у пациентов с заболеваниями нижних дыхательных путей, включая астму.
Информация для пациентов. Димедрол может вызвать сонливость и имеет аддитивный эффект с алкоголем.
Канцерогенез, мутагенез, влияние на фертильность: Длительных исследований на животных, чтобы определить мутагенный и канцерогенный потенциал, не проводилось.
Влияние на способность управлять автомобилем и потенциально опасными механизмами: больные должны воздерживаться от всех видов деятельности, требующих повышенного внимания, быстрой психической и двигательной реакции.
В ампулах по 1 мл в упаковке №10, №10х1.
В защищенном от света месте, при температуре не выше 25 °С. Хранить в недоступном для детей месте.
4 года. Не использовать после истечения срока годности.



