This article is about the capital city of Kanagawa Prefecture. For other uses, see Yokohama (disambiguation).
|
Yokohama 横浜市 |
|
|---|---|
|
Designated city |
|
| City of Yokohama | |
|
From top, left to right: Minato Mirai 21 at dusk, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Sankei-en, Harbor View Park, Yokohama Marine Tower viewed from Yamashita Park and Ōsanbashi Pier |
|
|
Flag Seal |
|
 |
|
Map of Kanagawa Prefecture with Yokohama highlighted in purple |
|
|
Yokohama Yokohama Yokohama (Asia) |
|
| Coordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°ECoordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Kanagawa Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Takeharu Yamanaka |
| Area | |
| • Total | 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) |
| Population
(January 1, 2023) |
|
| • Total | 3,769,595 |
| • Density | 8,606/km2 (22,290/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| – Tree | Camellia, Chinquapin, Sangoju Sasanqua, Ginkgo, Zelkova |
| – Flower | Dahlia Rose |
| Address | 1-1 Minato-chō, Naka-ku, Yokohama-shi, Kanagawa-ken 231-0017 |
| Website | www.city.yokohama.lg.jp |
| Yokohama | |||
|---|---|---|---|
«Yokohama» in new-style (shinjitai) kanji |
|||
| Japanese name | |||
| Hiragana | よこはま | ||
| Katakana | ヨコハマ | ||
| Kyūjitai | 橫濱 | ||
| Shinjitai | 横浜 | ||
|
Yokohama (Japanese: 横浜, pronounced [jokohama] (listen)) is the second-largest city in Japan by population[1] and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu. Yokohama is also the major economic, cultural, and commercial hub of the Greater Tokyo Area along the Keihin Industrial Zone.
Yokohama was one of the cities to open for trade with the West following the 1859 end of the policy of seclusion and has since been known as a cosmopolitan port city, after Kobe opened in 1853. Yokohama is the home of many Japan’s firsts in the Meiji period, including the first foreign trading port and Chinatown (1859), European-style sport venues (1860s), English-language newspaper (1861), confectionery and beer manufacturing (1865), daily newspaper (1870), gas-powered street lamps (1870s), railway station (1872), and power plant (1882). Yokohama developed rapidly as Japan’s prominent port city following the end of Japan’s relative isolation in the mid-19th century and is today one of its major ports along with Kobe, Osaka, Nagoya, Fukuoka, Tokyo and Chiba.
Yokohama is the largest port city and high tech industrial hub in the Greater Tokyo Area and the Kantō region. The city proper is headquarters to companies such as Isuzu, Nissan, JVCKenwood, Keikyu, Koei Tecmo, Sotetsu, Salesforce Japan and Bank of Yokohama. Famous landmarks in Yokohama include Minato Mirai 21, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Yokohama Marine Tower, Yamashita Park, and Ōsanbashi Pier.
Etymology[edit]
Yokohama (横浜) means «horizontal beach».[2] The current area surrounded by Maita Park, the Ōoka River and the Nakamura River have been a gulf divided by a sandbar from the open sea. This sandbar was the original Yokohama fishing village. Since the sandbar protruded perpendicularly from the land, or horizontally when viewed from the sea, it was called a «horizontal beach».[3]
History[edit]
Opening of the Treaty Port (1859–1868)[edit]
Before the Western foreigners arrived, Yokohama was a small fishing village up to the end of the feudal Edo period, when Japan held a policy of national seclusion, having little contact with foreigners.[4] A major turning point in Japanese history happened in 1853–54, when Commodore Matthew Perry arrived just south of Yokohama with a fleet of American warships, demanding that Japan open several ports for commerce, and the Tokugawa shogunate agreed by signing the Treaty of Peace and Amity.[5]
It was initially agreed that one of the ports to be opened to foreign ships would be the bustling town of Kanagawa-juku (in what is now Kanagawa Ward) on the Tōkaidō, a strategic highway that linked Edo to Kyoto and Osaka. However, the Tokugawa shogunate decided that Kanagawa-juku was too close to the Tōkaidō for comfort, and port facilities were instead built across the inlet in the sleepy fishing village of Yokohama. The Port of Yokohama was officially opened on June 2, 1859.[6]
Yokohama quickly became the base of foreign trade in Japan. Foreigners initially occupied the low-lying district of the city called Kannai, residential districts later expanding as the settlement grew to incorporate much of the elevated Yamate district overlooking the city, commonly referred to by English speaking residents as The Bluff.
Kannai, the foreign trade and commercial district (literally, inside the barrier), was surrounded by a moat, foreign residents enjoying extraterritorial status both within and outside the compound. Interactions with the local population, particularly young samurai, outside the settlement inevitably caused problems; the Namamugi Incident, one of the events that preceded the downfall of the shogunate, took place in what is now Tsurumi Ward in 1862, and prompted the Bombardment of Kagoshima in 1863.
To protect British commercial and diplomatic interests in Yokohama a military garrison was established in 1862. With the growth in trade increasing numbers of Chinese also came to settle in the city.[7] Yokohama was the scene of many notable firsts for Japan including the growing acceptance of western fashion, photography by pioneers such as Felice Beato, Japan’s first English language newspaper, the Japan Herald published in 1861 and in 1865 the first ice cream confectionery and beer to be produced in Japan.[8] Recreational sports introduced to Japan by foreign residents in Yokohama included European style horse racing in 1862, cricket in 1863[9] and rugby union in 1866. A great fire destroyed much of the foreign settlement on November 26, 1866, and smallpox was a recurrent public health hazard, but the city continued to grow rapidly – attracting foreigners and Japanese alike.
- Gallery
-
Landing of Commodore Perry and men to meet the Imperial commissioners at Yokohama, 14 July 1853
-
Foreign ships in Yokohama harbor in 1861
-
A foreign trading house in Yokohama in 1861
Meiji and Taisho Periods (1868–1923)[edit]
After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the port was developed for trading silk, the main trading partner being Great Britain. Western influence and technological transfer contributed to the establishment of Japan’s first daily newspaper (1870), first gas-powered street lamps (1872) and Japan’s first railway constructed in the same year to connect Yokohama to Shinagawa and Shinbashi in Tokyo. In 1872 Jules Verne portrayed Yokohama, which he had never visited, in an episode of his widely read novel Around the World in Eighty Days, capturing the atmosphere of the fast-developing, internationally oriented Japanese city.
In 1887, a British merchant, Samuel Cocking, built the city’s first power plant. At first for his own use, this coal power plant became the basis for the Yokohama Cooperative Electric Light Company. The city was officially incorporated on April 1, 1889.[10] By the time the extraterritoriality of foreigner areas was abolished in 1899, Yokohama was the most international city in Japan, with foreigner areas stretching from Kannai to the Bluff area and the large Yokohama Chinatown.
The early 20th century was marked by rapid growth of industry. Entrepreneurs built factories along reclaimed land to the north of the city toward Kawasaki, which eventually grew to be the Keihin Industrial Area. The growth of Japanese industry brought affluence, and many wealthy trading families constructed sprawling residences there, while the rapid influx of population from Japan and Korea also led to the formation of Kojiki-Yato, then the largest slum in Japan.
- Gallery
-
Street scene c. 1880
-
Yokohama c. 1880
-
Great Kantō earthquake and the Second World War (1923–1945)[edit]
- Gallery
-
View of Yokohama after the bombing in 1945
Much of Yokohama was destroyed on September 1, 1923, by the Great Kantō earthquake. The Yokohama police reported casualties at 30,771 dead and 47,908 injured, out of a pre-earthquake population of 434,170.[11] Fuelled by rumors of rebellion and sabotage, vigilante mobs thereupon murdered many Koreans in the Kojiki-yato slum.[12] Many people believed that Koreans used black magic to cause the earthquake. Martial law was in place until November 19. Rubble from the quake was used to reclaim land for parks, the most famous being the Yamashita Park on the waterfront which opened in 1930.
Yokohama was rebuilt, only to be destroyed again by U.S. air raids during World War II. The first bombing was in the April 18, 1942 Doolittle Raid. An estimated 7,000–8,000 people were killed in a single morning on May 29, 1945, in what is now known as the Great Yokohama Air Raid, when B-29s firebombed the city and in just one hour and nine minutes, reducing 42% of it to rubble.[10]
Postwar growth and development[edit]
During the American occupation, Yokohama was a major transshipment base for American supplies and personnel, especially during the Korean War. After the occupation, most local U.S. naval activity moved from Yokohama to an American base in nearby Yokosuka.
Four years after the Treaty of San Francisco signed, the city was designated by government ordinance on September 1, 1956.[citation needed] The city’s tram and trolleybus system was abolished in 1972, the same year as the opening of the first line of Yokohama Municipal Subway. Construction of Minato Mirai 21 («Port Future 21»), a major urban development project on reclaimed land started in 1983, nicknamed the «Philadelphia and Boston of the Orient» was compared to Center City, Philadelphia and Downtown Boston located in the East Coast of the United States. Minato Mirai 21 hosted the Yokohama Exotic Showcase in 1989, which saw the first public operation of maglev trains in Japan and the opening of Cosmo Clock 21, then the tallest Ferris wheel in the world. The 860-metre-long (2,820 ft) Yokohama Bay Bridge opened in the same year. In 1993, Minato Mirai 21 saw the opening of the Yokohama Landmark Tower, the second-tallest building in Japan.
The 2002 FIFA World Cup final was held in June at the International Stadium Yokohama. In 2009, the city marked the 150th anniversary of the opening of the port and the 120th anniversary of the commencement of the City Administration. An early part in the commemoration project incorporated the Fourth Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD IV), which was held in Yokohama in May 2008. In November 2010, Yokohama hosted the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) meeting.
- Gallery
-
Geography[edit]
Sentinel-2 image of Yokohama (2020)
Topography[edit]
Yokohama has a total area of 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) at an elevation of 5 metres (16 ft) above sea level. It is the capital of Kanagawa Prefecture, bordered to the east by Tokyo Bay and located in the middle of the Kantō plain. The city is surrounded by hills and the characteristic mountain system of the island of Honshū, so its growth has been limited and it has had to gain ground from the sea. This also affects the population density, one of the highest in Japan with 8,500 inhabitants per km2.
The highest points within the urban boundary are Omaruyama (156 m [512 ft]) and Mount Enkaizan (153 m [502 ft]). The main river is the Tsurumi River, which begins in the Tama Hills and empties into the Pacific Ocean.[13]
These municipalities surround Yokohama: Kawasaki, Yokosuka, Zushi, Kamakura, Fujisawa, Yamato, Machida.
Geology[edit]
The city is very prone to natural phenomena such as earthquakes and tropical cyclones because the island of Honshū has a high level of seismic activity, being in the middle of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Most seismic movements are of low intensity and are generally not perceived by people. However, Yokohama has experienced two major tremors that reflect the evolution of Earthquake engineering: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake devastated the city and caused more than 100,000 fatalities throughout the region,[14] while the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, with its epicenter on the east coast, was felt in the locality but only material damage was lamented because most buildings were already prepared to withstand them.[15]
Climate[edit]
Yokohama features a humid subtropical climate (Köppen: Cfa) with hot, humid summers and chilly winters.[16] Weatherwise, Yokohama has a pattern of rain, clouds and sun, although in winter, it is surprisingly sunny, more so than Southern Spain. Winter temperatures rarely drop below freezing, while summer can seem quite warm, because of the effects of humidity.[17] The coldest temperature was on 24 January 1927 when −8.2 °C (17.2 °F) was reached, whilst the hottest day was 11 August 2013 at 37.4 °C (99.3 °F). The highest monthly rainfall was in October 2004 with 761.5 millimetres (30.0 in), closely followed by July 1941 with 753.4 millimetres (29.66 in), whilst December and January have recorded no measurable precipitation three times each.
| Climate data for Yokohama (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1896−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.7 (83.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
37.2 (99.0) |
37.4 (99.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
8.7 (47.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.1 (37.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.2 (17.2) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.7 (2.55) |
64.7 (2.55) |
139.5 (5.49) |
143.1 (5.63) |
152.6 (6.01) |
188.8 (7.43) |
182.5 (7.19) |
139.0 (5.47) |
241.5 (9.51) |
240.4 (9.46) |
107.6 (4.24) |
66.4 (2.61) |
1,730.8 (68.14) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
9 (3.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.7 | 6.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 11.1 | 13.5 | 12.0 | 8.8 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 6.2 | 118.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 53 | 54 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 76 | 71 | 65 | 57 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.7 | 167.2 | 168.8 | 181.2 | 187.4 | 135.9 | 170.9 | 206.4 | 141.2 | 137.3 | 151.1 | 178.1 | 2,018.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[18] |
Cityscape[edit]
-
Yokohama night view (2014)
-
View from Mosaic Mall Kohoku (2015)
Yokohama skyline from Grand Oriental Hotel rooftop (2015)
Demographics[edit]
Population[edit]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 64,602[19] | — |
| 1880 | 72,630 | +12.4% |
| 1890 | 132,627 | +82.6% |
| 1900 | 196,653 | +48.3% |
| 1910 | 403,303 | +105.1% |
| 1920 | 422,942 | +4.9% |
| 1925 | 405,888 | −4.0% |
| 1930 | 620,306 | +52.8% |
| 1935 | 704,290 | +13.5% |
| 1940 | 968,091 | +37.5% |
| 1945 | 814,379 | −15.9% |
| 1950 | 951,188 | +16.8% |
| 1955 | 1,143,687 | +20.2% |
| 1960 | 1,375,710 | +20.3% |
| 1965 | 1,788,915 | +30.0% |
| 1970 | 2,238,264 | +25.1% |
| 1975 | 2,621,771 | +17.1% |
| 1980 | 2,773,674 | +5.8% |
| 1985 | 2,992,926 | +7.9% |
| 1990 | 3,220,331 | +7.6% |
| 1995 | 3,307,136 | +2.7% |
| 2000 | 3,426,651 | +3.6% |
| 2005 | 3,579,133 | +4.4% |
| 2010 | 3,670,669 | +2.6% |
| 2015 | 3,710,824 | +1.1% |
| 2020 | 3,760,157 | +1.3% |
Yokohama’s foreign population of 92,139 includes Chinese, Koreans, Filipinos, and Vietnamese.[20]
Wards[edit]
Yokohama has 18 wards (ku):
| Wards of Yokohama | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place Name | Map of Yokohama | |||||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | Population | Land area in km2 | Pop. density
per km2 |
||
| 1 | Aoba-ku | 青葉区 | 302,643 | 35.14 | 8,610 |
|
| 2 | Asahi-ku | 旭区 | 249,045 | 32.77 | 7,600 | |
| 3 | Hodogaya-ku | 保土ヶ谷区 | 205,887 | 21.81 | 9,400 | |
| 4 | Isogo-ku | 磯子区 | 163,406 | 19.17 | 8,520 | |
| 5 | Izumi-ku | 泉区 | 155,674 | 23.51 | 6,620 | |
| 6 | Kanagawa-ku | 神奈川区 | 230,401 | 23.88 | 9,650 | |
| 7 | Kanazawa-ku | 金沢区 | 209,565 | 31.01 | 6,760 | |
| 8 | Kōhoku-ku | 港北区 | 332,488 | 31.40 | 10,588 | |
| 9 | Kōnan-ku | 港南区 | 221,536 | 19.87 | 11,500 | |
| 10 | Midori-ku | 緑区 | 176,038 | 25.42 | 6,900 | |
| 11 | Minami-ku | 南区 | 197,019 | 12.67 | 15,500 | |
| 12 | Naka-ku (administrative center) | 中区 | 146,563 | 20.86 | 7,030 | |
| 13 | Nishi-ku | 西区 | 93,210 | 7.04 | 13,210 | |
| 14 | Sakae-ku | 栄区 | 124,845 | 18.55 | 6,750 | |
| 15 | Seya-ku | 瀬谷区 | 126,839 | 17.11 | 7,390 | |
| 16 | Totsuka-ku | 戸塚区 | 274,783 | 35.70 | 7,697 | |
| 17 | Tsurumi-ku | 鶴見区 | 270,433 | 33.23 | 8,140 | |
| 18 | Tsuzuki-ku | 都筑区 | 211,455 | 27.93 | 7,535 |
Government and politics[edit]
The Yokohama City Council consists of 86 members elected from a total of 18 Wards. The LDP has minority control with 36 seats. The incumbent mayor is Takeharu Yamanaka, who defeated Fumiko Hayashi in the 2021 Yokohama mayoral election.
List of mayors (from 1889)[edit]
|
|
Culture and sights[edit]
Cherry blossoms on the Kisha-michi Promenade
Yokohama’s cultural and tourist sights include:
- Yokohama Chinatown
- Yokohama Three Towers
- Yamashita Park (at the harbor)
- Harbor View Park
- The Hikawa Maru, historic passenger and cargo ship
- Yokohama Marine Tower
- Yokohama Triennale
- Minato Mirai 21
- Landmark Tower, 296 m high, second tallest skyscraper in Japan
- Nippon Maru, museum ship
- Yokohama Stadium (the Yokohama DeNA BayStars Pro baseball teams’s home field)
- Yokohama Foreign Cemetery
- Sankei-en Garden
- Kishine-Park
- Kanazawa Bunko, preserves the cultural heritage of the Hōjō clan
- Zō-no-Hana Terrace (象の鼻テラス)[21]
- Gumyōji, oldest temple in the city
Museums[edit]
Yokohama Triennale at Yamashita Pier venue
There are 42 museums in the city area, including.[22]
- CupNoodles Museum (Momofuku Andō Instant Ramen Museum): Several-floors of interactive exhibits related to the invention of the Japanese instant noodle soup, including soup kitchens where you can try the culture-specific noodle soups.
- Kanagawa Prefectural Museum of Cultural History: Located in the historic Yokohama Specie Bank building.
- Kanazawa Bunko: Traditional Japanese and Chinese art objects, many dating from the Kamakura period.
- Matsuri Museum: Dedicated to the shrine festivals (Japanese Matsuri) taking place in Yokohama.
- Silk Museum: Exhibits focusing on the production and processing of silk; including many clothes.
- Yokohama Archives of History: Located in the former British Consulate building with exhibits related to port development and the arrival of Matthew Perry.
- Yokohama Museum of Art: Founded in 1989, featuring modern works by well-known international and Japanese artists.
Gallery[edit]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Yokohama World Porters
-
Mitsui Outlet Park Yokohama Bayside
-
Yokohama Municipal Kanazawa Zoo
-
-
-
-
Yokohama Foreign General Cemetery
-
-
-
-
Iseyama Kotai Shrine
-
Excursion destinations[edit]
In 2016, 46,017,157 tourists visited the city, 13.1% of whom were overnight guests.[22]
- Kodomo no kuni: Means «Children’s country». A nice destination to spend an eventful day with the family. Lots of space for walking and playing. There is also a petting zoo.
- Nogeyama Zoo: One of the few zoos that do not charge admission. It has a large number of animals and a petting zoo where children can play with small animals.
- Zoorasia: Nice zoo with lots of play options for children. However, in this zoo admission costs.
- Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise: A large park with an aquarium. Otherwise rides, shops, restaurants, etc.
- Since 2020, after six years of development, a giant robot named Gundam, which is 18 meters high and weighs 25 tons, has been watching over the port area as a tourist attraction. The giant robot, in which there is a cockpit and whose hands are each two meters long, is based as a figure on a science fiction television series, can move and sink to its knees.[23] The giant robot was manufactured by the company «Gundam Factory Yokohama» under Managing Director Shin Sasaki.
- Kamonyama Park
In popular media[edit]
- Yukio Mishima’s novel The Sailor Who Fell from Grace with the Sea is set mainly in Yokohama. Mishima describes the city’s port and its houses, and the Western influences that shaped them.
- From Up on Poppy Hill is a 2011 Studio Ghibli animated drama film directed by Gorō Miyazaki set in the Yamate district of Yokohama. The film is based on the serialized Japanese comic book of the same name.
- The main setting of James Clavell’s book Gai-Jin is in historical Yokohama.
- Vermillion City in the Kanto region from the Pokémon franchise is based on Yokohama.
- One of the Pretty Cure crossover movies takes place in Yokohama. In the fourth movie of the series, Pretty Cure All Stars New Stage: Friends of the Future, the Pretty Cure appear standing on top of the Cosmo Clock 21 in Minato Mirai.
- The main setting of the Japanese visual novel series Muv-Luv, first a school and then, in an alternate history, a military base is built in Yokohama with the objective of carrying out the Alternative IV Plan meant to save humanity.
- In Command & Conquer: Red Alert 3, Yokohama is under siege by the Soviet Union and Allied Nations to stop the Empire of The Rising Sun. The player must defend Yokohama and then lead a counterattack as the Empire.
- The manga Bungo Stray Dogs is set in Yokohama.
- The Japanese mixed-media project, Hamatora takes place in Yokohama.
- The final battle in Godzilla, Mothra and King Ghidorah: Giant Monsters All-Out Attack takes place in Yokohama.
- In My Hero Academia, it is the location of the Nomu Warehouse where they created artificial Humans (a.k.a. Nomus).
- Sumaru City in Persona 2: Innocent Sin and Eternal Punishment is based on Yokohama.
- Miyabi City in The Caligula Effect is based on Yokohama, including depictions of landmarks such as an unfinished Landmark Tower and Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise (referred to in game as Sea Paraiso).
- The video game Yakuza: Like a Dragon is set in Isezaki Ijincho, a fictional district in Yokohama based on Isezakichō.
- Yokohama is also represented in the multimedia project by King Records, Hypnosis Mic: Division Rap Battle
- Yokohama is the main setting of Japanese manga and anime series Komi Can’t Communicate. Multiple of the cities’ landmarks are featured on the manga, most notably in the more recently released chapters.
- Yokohama is the setting of the anime After the Rain as well as manga series with the same title by Jun Mayuzuki.
- In April 2022, The Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau announced the launch of a new interactive website to aid in the tourism and MICE elements of the city.[24]
Sports[edit]
- Baseball: Yokohama DeNA BayStars
- Soccer: Yokohama F. Marinos (J.League Division 1), Yokohama FC (J.League Division 1), YSCC Yokohama (J.League Division 3), NHK Yokohama FC Seagulls (Nadeshiko League Div.2)
- Velodrome: Kagetsu-en Velodrome
- Basketball: Yokohama B-Corsairs
- Rugby Union: Yokohama Eagles
- Tennis: Ai Sugiyama
- American football: Yokohama Harbors
Economy and infrastructure[edit]
The city has a strong economic base, especially in the shipping, biotechnology, and semiconductor industries. Nissan moved its headquarters to Yokohama from Chūō, Tokyo, in 2010.[25]
Yokohama’s GDP per capita (Nominal) was $30,625 ($1=¥120.13).[26][27]
As of 2016, the total production in Yokohama city reached ¥13.56 billion. It is located between Shizuoka and Hiroshima Prefectures compared to domestic prefectures.[28] It is located between Hungary, which ranks 26th, and New Zealand, which ranks 27th compared to OECD countries. Generally, the primary industry is 0.1%, the secondary industry is 21.7%, and the tertiary industry is 82.3%. The ratio of the primary industry is low, and the ratio of the secondary industry and the tertiary industry is high. Compared to other ordinance-designated cities, it is about 60% of the size of Osaka, which is almost the same as Nagoya. As shown in the attached table, there are not a few head office companies, but the major inferiority to Osaka is the traditional difference, the strong bed.[clarification needed] In connection with this, the absence of large block-type companies (JR, NTT, electric power, gas, major commercial broadcasters, etc.) has had an impact.
The breakdown is ¥11.9 million yen (0.1%) for the primary industry, ¥2.75 billion (21.7%) for the secondary industry, and ¥10.44 billion yen (82.3%) for the tertiary industry. Compared to other government-designated cities, the amount of the primary industry, the ratio of the construction industry of the secondary industry, and the ratio of the real estate industry of the tertiary industry are large, and the finance, insurance, wholesale, and retail of the tertiary industry The ratio of industry and service industry is small, but the tertiary industry is almost the same as Nagoya.
Major companies headquartered[edit]
-
-
-
Isuzu headquarters in Nishi-ku
Transport[edit]
A route map in Yokohama and Tokyo (JR East)
Yokohama is serviced by the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, a high-speed rail line with a stop at Shin-Yokohama Station. Yokohama Station is also a major station, with two million passengers daily. The Yokohama Municipal Subway, Minatomirai Line and Kanazawa Seaside Line provide metro services.
Maritime transport[edit]
Yokohama is the world’s 31st largest seaport in terms of total cargo volume, at 121,326 freight tons as of 2011, and is ranked 37th in terms of TEUs (Twenty-foot equivalent units).[29]
In 2013, APM Terminals Yokohama facility was recognized as the most productive container terminal in the world averaging 163 crane moves per hour, per ship between the vessel’s arrival and departure at the berth.[30]
Rail transport[edit]
Railway stations[edit]
- ■ East Japan Railway Company (JR East)
- ■ Tōkaidō Main Line
- – Yokohama – Totsuka –
- ■ Yokosuka Line
- – Yokohama – Hodogaya – Higashi-Totsuka – Totsuka –
- ■ Keihin-Tōhoku Line
- – Tsurumi – Shin-Koyasu – Higashi-Kanagawa – Yokohama
- ■ Negishi Line
- Yokohama – Sakuragichō – Kannai – Ishikawachō – Yamate – Negishi – Isogo – Shin-Sugita – Yōkōdai – Kōnandai – Hongōdai –
- ■ Yokohama Line
- Higashi-Kanagawa – Ōguchi – Kikuna – Shin-Yokohama – Kozukue – Kamoi – Nakayama – Tōkaichiba – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Nambu Line
- – Yakō –
- ■ Tsurumi Line
- Main Line : Tsurumi – Kokudō – Tsurumi-Ono – Bentembashi – Asano – Anzen –
- Umi-Shibaura Branch : Asano – Shin-Shibaura – Umi-Shibaura
- ■ Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central)
- ■ Tōkaidō Shinkansen
- – Shin-Yokohama –
- ■ Keikyu
- ■ Keikyu Main Line
- – Tsurumi-Ichiba – Keikyū Tsurumi – Kagetsuen-mae – Namamugi – Keikyū Shin-Koyasu – Koyasu – Kanagawa-Shinmachi – Naka-Kido – Kanagawa – Yokohama – Tobe – Hinodechō – Koganechō – Minami-Ōta – Idogaya – Gumyōji – Kami-Ōoka – Byōbugaura – Sugita – Keikyū Tomioka – Nōkendai – Kanazawa-Bunko – Kanazawa-Hakkei –
- ■ Keikyu Zushi Line
- Kanazawa-Hakkei – Mutsuura –
- ■ Tokyu Railways
- ■ Tōyoko Line
- – Hiyoshi – Tsunashima – Ōkurayama – Kikuna – Myōrenji – Hakuraku – Higashi-Hakuraku – Tammachi – Yokohama
- ■ Meguro Line
- – Hiyoshi
- ■ Den-en-toshi Line
- – Tama-Plaza – Azamino – Eda – Ichigao – Fujigaoka – Aobadai – Tana – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Kodomonokuni Line
- Nagatsuta – Onda – Kodomonokuni
- ■ Sagami Railway
- ■ Sagami Railway Main Line
- Yokohama – Hiranumabashi – Nishi-Yokohama – Tennōchō – Hoshikawa – Wadamachi – Kamihoshikawa – Nishiya – Tsurugamine – Futamatagawa – Kibōgaoka – Mitsukyō – Seya –
- ■ Izumino Line
- Futamatagawa – Minami-Makigahara – Ryokuentoshi – Yayoidai – Izumino – Izumi-chūō – Yumegaoka
- ■ Yokohama Minatomirai Railway
- ■ Minatomirai Line
- Yokohama – Shin-Takashima – Minato Mirai – Bashamichi – Nihon-ōdōri – Motomachi-Chūkagai
- ■ Yokohama City Transportation Bureau (Yokohama Municipal Subway)
- ■ Blue Line
- – Shimoiida – Tateba – Nakada – Odoriba – Totsuka – Maioka – Shimonagaya – Kaminagaya – Kōnan-Chūō – Kami-Ōoka – Gumyōji – Maita – Yoshinochō – Bandōbashi – Isezakichōjamachi – Kannai – Sakuragichō – Takashimachō – Yokohama – Mitsuzawa-shimochō – Mitsuzawa-kamichō – Katakurachō – Kishine-kōen – Shin-Yokohama – Kita Shin-Yokohama – Nippa – Nakamachidai – Center Minami – Center Kita – Nakagawa – Azamino
- ■ Green Line
- Nakayama – Kawawachō – Tsuzuki-Fureai-no-Oka – Center Minami – Center Kita – Kita-Yamata – Higashi-Yamata – Takata – Hiyoshi-Honchō – Hiyoshi
- ■ Yokohama New Transit
- ■ Kanazawa Seaside Line
- Shin-Sugita – Nambu-Shijō – Torihama – Namiki-Kita – Namiki-Chūō – Sachiura – Sangyō-Shinkō-Center – Fukuura – Shidai-Igakubu – Hakkeijima – Uminokōen-Shibaguchi – Uminokōen-Minamiguchi – Nojimakōen – Kanazawa-Hakkei
Education[edit]
Public elementary and middle schools are operated by the city of Yokohama. There are nine public high schools which are operated by the Yokohama City Board of Education,[31] and a number of public high schools which are operated by the Kanagawa Prefectural Board of Education. Yokohama National University is a leading university in Yokohama which is also one of the highest ranking national universities in Japan.
- 46,388 children attend the 260 kindergartens.
- Almost 386,000 students are taught in 351 primary schools.
- There are 16 universities including Yokohama National University. The number of students is around 83,000.
- 19 public libraries had 9.5 million loans in 2016.[22]
International relations[edit]
Twin towns – sister cities[edit]
Yokohama is twinned with:[32]
Constanța, Constanța County, Romania (since October 1977)
Lyon, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France (since April 1959)
Manila, Philippines (since July 1965)
Mumbai, Maharashtra, India (since June 1965)
Odesa, Odesa Oblast, Ukraine (since July 1965)
San Diego, CA, United States (former partnership, October 1957–October 2021)
San Francisco, CA, United States (since October 2021)
Shanghai, China (since November 1973)
Vancouver, BC, Canada (since July 1965)
Partner cities[edit]
Abidjan, Ivory Coast
Beijing, China (since May 2006)
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (since June 2008)
Busan, South Korea (since June 2006)
Frankfurt, Hesse, Germany (since September 2011)
Hanoi, Vietnam (since November 2007)
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam (since October 2007)
Incheon, South Korea (since December 2009)
Seberang Perai, Penang, Malaysia (since August 2016)[33]
Taipei, Taiwan (since May 2006)
Tel Aviv, Israel (since July 2012)
Tianjin, China (since May 2008)
Sister ports[edit]
Notable people[edit]
- Toru Furuya, singer and seiyū
- Yuma Kagiyama, figure skater
- Miki Koyama, racing driver
- Takehito Koyasu, singer and seiyū
- Ryuji Kumita, racing driver and CEO of B-Max Racing
- Keisuke Kunimoto, racing driver
- Yuji Kunimoto, racing driver
- Minoru Suzuki, professional wrestler
- Yuta Watanabe, NBA player for the Toronto Raptors.
- Radwimps
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ «YOKOHAMA | Meaning & Definition for UK English | Lexico.com». En.oxforddictionaries.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- ^ «Memories of old Honmoku». The Japan Times. May 19, 1999. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved March 3, 2021.
- ^ «Yokohama City History, pg. 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on July 9, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- ^ Der Große Brockhaus. 16. edition. Vol. 6. F. A. Brockhaus, Wiesbaden 1955, p. 82
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website it is fresh». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 12, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ Arita, Erika, «Happy Birthday Yokohama! Archived August 31, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», The Japan Times, May 24, 2009, p. 7.
- ^ Fukue, Natsuko, «Chinese immigrants played vital role Archived August 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 28, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Matsutani, Minoru, «Yokohama – city on the cutting edge Archived August 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 29, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Galbraith, Michael (June 16, 2013). «Death threats sparked Japan’s first cricket game». Japan Times. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ a b «Interesting Tidbits of Yokohama». Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau. Archived from the original on May 5, 2009. Retrieved February 7, 2009.
- ^ Hammer, Joshua. (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II, p. 143. Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Hammer, pp. 149 Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine-170.
- ^ «Tsurumi River Multipurpose Retarding Basin». www.japanriver.or.jp. Archived from the original on September 26, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Collection of 1923 Japan earthquake massacre testimonies released». www.hani.co.kr. September 3, 2013. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- ^ «FNN Remembering 3/11: Yokohama station and surrounding areas at time of earthquake occurrence». www.fnn-news.com. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved January 10, 2016.
- ^ «Yokohama, Japan Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)». Weatherbase. Archived from the original on December 21, 2019. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information». world-guides.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved January 11, 2010.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 17, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ Japanese Imperial Commission (1878). Le Japon à l’exposition universelle de 1878. Géographie et histoire du Japon (in French).
- ^ 横浜市区別外国人登録人口(平成30年3月末現在). Archived from the original on March 11, 2017. Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ^ «Webseite des Kulturzentrums». Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c «Statistical Booklet Book of Yokohama 2018» (PDF). www.city.yokohama.lg.jp. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2018. Retrieved November 2, 2020.
- ^ Tagesthemen. Beitrag in der Nachrichtensendung der ARD, Moderation: Ingo Zamperoni, 30. November 2020, 35 Min. Eine Produktion von Das Erste
- ^ «Virtual Yokohama: Interactive Website Launched». Business wire. April 28, 2022. Retrieved April 29, 2022.
- ^ «Nissan To Create New Global and Domestic Headquarters in Yokohama City by 2010». Japancorp.net. Archived from the original on September 14, 2007. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ «Yokohama GDP 2015». Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «Yokohama 2015 population» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 3, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «「平成28年度 横浜市の市民経済計算」がまとまりました。» (PDF). 横浜市. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 4, 2021. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ «Ports & World Trade». www.aapa-ports.org. Archived from the original on May 4, 2011. Retrieved July 3, 2014.
- ^ «Chinese Ports Lead the World in Berth Productivity, JOC Group Inc. Data Shows». Press Release. AXIO Data Group. JOC Inc. June 24, 2014. Archived from the original on April 6, 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2015.
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 19, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ «Yokohama’s Sister/Friendship Cities». city.yokohama.lg.jp. Yokohama. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ «MPSP sets sights on city status». The Star. August 1, 2016. Archived from the original on July 5, 2018. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
Sources[edit]
- Hammer, Joshua (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II Archived June 23, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-6465-5 (cloth).
- Heilbrun, Jacob. «Aftershocks» Archived January 15, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times, September 17, 2006.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yokohama.
- Official Website (in Japanese)
- Yokohama Tourism Website (in English)
Geographic data related to Yokohama at OpenStreetMap
This article is about the capital city of Kanagawa Prefecture. For other uses, see Yokohama (disambiguation).
|
Yokohama 横浜市 |
|
|---|---|
|
Designated city |
|
| City of Yokohama | |
|
From top, left to right: Minato Mirai 21 at dusk, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Sankei-en, Harbor View Park, Yokohama Marine Tower viewed from Yamashita Park and Ōsanbashi Pier |
|
|
Flag Seal |
|
 |
|

Map of Kanagawa Prefecture with Yokohama highlighted in purple |
|
|
Yokohama Yokohama Yokohama (Asia) |
|
| Coordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°ECoordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Kanagawa Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Takeharu Yamanaka |
| Area | |
| • Total | 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) |
| Population
(January 1, 2023) |
|
| • Total | 3,769,595 |
| • Density | 8,606/km2 (22,290/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| – Tree | Camellia, Chinquapin, Sangoju Sasanqua, Ginkgo, Zelkova |
| – Flower | Dahlia Rose |
| Address | 1-1 Minato-chō, Naka-ku, Yokohama-shi, Kanagawa-ken 231-0017 |
| Website | www.city.yokohama.lg.jp |
| Yokohama | |||
|---|---|---|---|
«Yokohama» in new-style (shinjitai) kanji |
|||
| Japanese name | |||
| Hiragana | よこはま | ||
| Katakana | ヨコハマ | ||
| Kyūjitai | 橫濱 | ||
| Shinjitai | 横浜 | ||
|
Yokohama (Japanese: 横浜, pronounced [jokohama] (listen)) is the second-largest city in Japan by population[1] and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu. Yokohama is also the major economic, cultural, and commercial hub of the Greater Tokyo Area along the Keihin Industrial Zone.
Yokohama was one of the cities to open for trade with the West following the 1859 end of the policy of seclusion and has since been known as a cosmopolitan port city, after Kobe opened in 1853. Yokohama is the home of many Japan’s firsts in the Meiji period, including the first foreign trading port and Chinatown (1859), European-style sport venues (1860s), English-language newspaper (1861), confectionery and beer manufacturing (1865), daily newspaper (1870), gas-powered street lamps (1870s), railway station (1872), and power plant (1882). Yokohama developed rapidly as Japan’s prominent port city following the end of Japan’s relative isolation in the mid-19th century and is today one of its major ports along with Kobe, Osaka, Nagoya, Fukuoka, Tokyo and Chiba.
Yokohama is the largest port city and high tech industrial hub in the Greater Tokyo Area and the Kantō region. The city proper is headquarters to companies such as Isuzu, Nissan, JVCKenwood, Keikyu, Koei Tecmo, Sotetsu, Salesforce Japan and Bank of Yokohama. Famous landmarks in Yokohama include Minato Mirai 21, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Yokohama Marine Tower, Yamashita Park, and Ōsanbashi Pier.
Etymology[edit]
Yokohama (横浜) means «horizontal beach».[2] The current area surrounded by Maita Park, the Ōoka River and the Nakamura River have been a gulf divided by a sandbar from the open sea. This sandbar was the original Yokohama fishing village. Since the sandbar protruded perpendicularly from the land, or horizontally when viewed from the sea, it was called a «horizontal beach».[3]
History[edit]
Opening of the Treaty Port (1859–1868)[edit]
Before the Western foreigners arrived, Yokohama was a small fishing village up to the end of the feudal Edo period, when Japan held a policy of national seclusion, having little contact with foreigners.[4] A major turning point in Japanese history happened in 1853–54, when Commodore Matthew Perry arrived just south of Yokohama with a fleet of American warships, demanding that Japan open several ports for commerce, and the Tokugawa shogunate agreed by signing the Treaty of Peace and Amity.[5]
It was initially agreed that one of the ports to be opened to foreign ships would be the bustling town of Kanagawa-juku (in what is now Kanagawa Ward) on the Tōkaidō, a strategic highway that linked Edo to Kyoto and Osaka. However, the Tokugawa shogunate decided that Kanagawa-juku was too close to the Tōkaidō for comfort, and port facilities were instead built across the inlet in the sleepy fishing village of Yokohama. The Port of Yokohama was officially opened on June 2, 1859.[6]
Yokohama quickly became the base of foreign trade in Japan. Foreigners initially occupied the low-lying district of the city called Kannai, residential districts later expanding as the settlement grew to incorporate much of the elevated Yamate district overlooking the city, commonly referred to by English speaking residents as The Bluff.
Kannai, the foreign trade and commercial district (literally, inside the barrier), was surrounded by a moat, foreign residents enjoying extraterritorial status both within and outside the compound. Interactions with the local population, particularly young samurai, outside the settlement inevitably caused problems; the Namamugi Incident, one of the events that preceded the downfall of the shogunate, took place in what is now Tsurumi Ward in 1862, and prompted the Bombardment of Kagoshima in 1863.
To protect British commercial and diplomatic interests in Yokohama a military garrison was established in 1862. With the growth in trade increasing numbers of Chinese also came to settle in the city.[7] Yokohama was the scene of many notable firsts for Japan including the growing acceptance of western fashion, photography by pioneers such as Felice Beato, Japan’s first English language newspaper, the Japan Herald published in 1861 and in 1865 the first ice cream confectionery and beer to be produced in Japan.[8] Recreational sports introduced to Japan by foreign residents in Yokohama included European style horse racing in 1862, cricket in 1863[9] and rugby union in 1866. A great fire destroyed much of the foreign settlement on November 26, 1866, and smallpox was a recurrent public health hazard, but the city continued to grow rapidly – attracting foreigners and Japanese alike.
- Gallery
-
Landing of Commodore Perry and men to meet the Imperial commissioners at Yokohama, 14 July 1853
-
Foreign ships in Yokohama harbor in 1861
-
A foreign trading house in Yokohama in 1861
Meiji and Taisho Periods (1868–1923)[edit]
After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the port was developed for trading silk, the main trading partner being Great Britain. Western influence and technological transfer contributed to the establishment of Japan’s first daily newspaper (1870), first gas-powered street lamps (1872) and Japan’s first railway constructed in the same year to connect Yokohama to Shinagawa and Shinbashi in Tokyo. In 1872 Jules Verne portrayed Yokohama, which he had never visited, in an episode of his widely read novel Around the World in Eighty Days, capturing the atmosphere of the fast-developing, internationally oriented Japanese city.
In 1887, a British merchant, Samuel Cocking, built the city’s first power plant. At first for his own use, this coal power plant became the basis for the Yokohama Cooperative Electric Light Company. The city was officially incorporated on April 1, 1889.[10] By the time the extraterritoriality of foreigner areas was abolished in 1899, Yokohama was the most international city in Japan, with foreigner areas stretching from Kannai to the Bluff area and the large Yokohama Chinatown.
The early 20th century was marked by rapid growth of industry. Entrepreneurs built factories along reclaimed land to the north of the city toward Kawasaki, which eventually grew to be the Keihin Industrial Area. The growth of Japanese industry brought affluence, and many wealthy trading families constructed sprawling residences there, while the rapid influx of population from Japan and Korea also led to the formation of Kojiki-Yato, then the largest slum in Japan.
- Gallery
-
Street scene c. 1880
-
Yokohama c. 1880
-
Great Kantō earthquake and the Second World War (1923–1945)[edit]
- Gallery
-
View of Yokohama after the bombing in 1945
Much of Yokohama was destroyed on September 1, 1923, by the Great Kantō earthquake. The Yokohama police reported casualties at 30,771 dead and 47,908 injured, out of a pre-earthquake population of 434,170.[11] Fuelled by rumors of rebellion and sabotage, vigilante mobs thereupon murdered many Koreans in the Kojiki-yato slum.[12] Many people believed that Koreans used black magic to cause the earthquake. Martial law was in place until November 19. Rubble from the quake was used to reclaim land for parks, the most famous being the Yamashita Park on the waterfront which opened in 1930.
Yokohama was rebuilt, only to be destroyed again by U.S. air raids during World War II. The first bombing was in the April 18, 1942 Doolittle Raid. An estimated 7,000–8,000 people were killed in a single morning on May 29, 1945, in what is now known as the Great Yokohama Air Raid, when B-29s firebombed the city and in just one hour and nine minutes, reducing 42% of it to rubble.[10]
Postwar growth and development[edit]
During the American occupation, Yokohama was a major transshipment base for American supplies and personnel, especially during the Korean War. After the occupation, most local U.S. naval activity moved from Yokohama to an American base in nearby Yokosuka.
Four years after the Treaty of San Francisco signed, the city was designated by government ordinance on September 1, 1956.[citation needed] The city’s tram and trolleybus system was abolished in 1972, the same year as the opening of the first line of Yokohama Municipal Subway. Construction of Minato Mirai 21 («Port Future 21»), a major urban development project on reclaimed land started in 1983, nicknamed the «Philadelphia and Boston of the Orient» was compared to Center City, Philadelphia and Downtown Boston located in the East Coast of the United States. Minato Mirai 21 hosted the Yokohama Exotic Showcase in 1989, which saw the first public operation of maglev trains in Japan and the opening of Cosmo Clock 21, then the tallest Ferris wheel in the world. The 860-metre-long (2,820 ft) Yokohama Bay Bridge opened in the same year. In 1993, Minato Mirai 21 saw the opening of the Yokohama Landmark Tower, the second-tallest building in Japan.
The 2002 FIFA World Cup final was held in June at the International Stadium Yokohama. In 2009, the city marked the 150th anniversary of the opening of the port and the 120th anniversary of the commencement of the City Administration. An early part in the commemoration project incorporated the Fourth Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD IV), which was held in Yokohama in May 2008. In November 2010, Yokohama hosted the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) meeting.
- Gallery
-
Geography[edit]
Sentinel-2 image of Yokohama (2020)
Topography[edit]
Yokohama has a total area of 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) at an elevation of 5 metres (16 ft) above sea level. It is the capital of Kanagawa Prefecture, bordered to the east by Tokyo Bay and located in the middle of the Kantō plain. The city is surrounded by hills and the characteristic mountain system of the island of Honshū, so its growth has been limited and it has had to gain ground from the sea. This also affects the population density, one of the highest in Japan with 8,500 inhabitants per km2.
The highest points within the urban boundary are Omaruyama (156 m [512 ft]) and Mount Enkaizan (153 m [502 ft]). The main river is the Tsurumi River, which begins in the Tama Hills and empties into the Pacific Ocean.[13]
These municipalities surround Yokohama: Kawasaki, Yokosuka, Zushi, Kamakura, Fujisawa, Yamato, Machida.
Geology[edit]
The city is very prone to natural phenomena such as earthquakes and tropical cyclones because the island of Honshū has a high level of seismic activity, being in the middle of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Most seismic movements are of low intensity and are generally not perceived by people. However, Yokohama has experienced two major tremors that reflect the evolution of Earthquake engineering: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake devastated the city and caused more than 100,000 fatalities throughout the region,[14] while the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, with its epicenter on the east coast, was felt in the locality but only material damage was lamented because most buildings were already prepared to withstand them.[15]
Climate[edit]
Yokohama features a humid subtropical climate (Köppen: Cfa) with hot, humid summers and chilly winters.[16] Weatherwise, Yokohama has a pattern of rain, clouds and sun, although in winter, it is surprisingly sunny, more so than Southern Spain. Winter temperatures rarely drop below freezing, while summer can seem quite warm, because of the effects of humidity.[17] The coldest temperature was on 24 January 1927 when −8.2 °C (17.2 °F) was reached, whilst the hottest day was 11 August 2013 at 37.4 °C (99.3 °F). The highest monthly rainfall was in October 2004 with 761.5 millimetres (30.0 in), closely followed by July 1941 with 753.4 millimetres (29.66 in), whilst December and January have recorded no measurable precipitation three times each.
| Climate data for Yokohama (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1896−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.7 (83.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
37.2 (99.0) |
37.4 (99.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
8.7 (47.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.1 (37.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.2 (17.2) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.7 (2.55) |
64.7 (2.55) |
139.5 (5.49) |
143.1 (5.63) |
152.6 (6.01) |
188.8 (7.43) |
182.5 (7.19) |
139.0 (5.47) |
241.5 (9.51) |
240.4 (9.46) |
107.6 (4.24) |
66.4 (2.61) |
1,730.8 (68.14) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
9 (3.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.7 | 6.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 11.1 | 13.5 | 12.0 | 8.8 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 6.2 | 118.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 53 | 54 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 76 | 71 | 65 | 57 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.7 | 167.2 | 168.8 | 181.2 | 187.4 | 135.9 | 170.9 | 206.4 | 141.2 | 137.3 | 151.1 | 178.1 | 2,018.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[18] |
Cityscape[edit]
-
Yokohama night view (2014)
-
View from Mosaic Mall Kohoku (2015)
Yokohama skyline from Grand Oriental Hotel rooftop (2015)
Demographics[edit]
Population[edit]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 64,602[19] | — |
| 1880 | 72,630 | +12.4% |
| 1890 | 132,627 | +82.6% |
| 1900 | 196,653 | +48.3% |
| 1910 | 403,303 | +105.1% |
| 1920 | 422,942 | +4.9% |
| 1925 | 405,888 | −4.0% |
| 1930 | 620,306 | +52.8% |
| 1935 | 704,290 | +13.5% |
| 1940 | 968,091 | +37.5% |
| 1945 | 814,379 | −15.9% |
| 1950 | 951,188 | +16.8% |
| 1955 | 1,143,687 | +20.2% |
| 1960 | 1,375,710 | +20.3% |
| 1965 | 1,788,915 | +30.0% |
| 1970 | 2,238,264 | +25.1% |
| 1975 | 2,621,771 | +17.1% |
| 1980 | 2,773,674 | +5.8% |
| 1985 | 2,992,926 | +7.9% |
| 1990 | 3,220,331 | +7.6% |
| 1995 | 3,307,136 | +2.7% |
| 2000 | 3,426,651 | +3.6% |
| 2005 | 3,579,133 | +4.4% |
| 2010 | 3,670,669 | +2.6% |
| 2015 | 3,710,824 | +1.1% |
| 2020 | 3,760,157 | +1.3% |
Yokohama’s foreign population of 92,139 includes Chinese, Koreans, Filipinos, and Vietnamese.[20]
Wards[edit]
Yokohama has 18 wards (ku):
| Wards of Yokohama | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place Name | Map of Yokohama | |||||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | Population | Land area in km2 | Pop. density
per km2 |
||
| 1 | Aoba-ku | 青葉区 | 302,643 | 35.14 | 8,610 |
|
| 2 | Asahi-ku | 旭区 | 249,045 | 32.77 | 7,600 | |
| 3 | Hodogaya-ku | 保土ヶ谷区 | 205,887 | 21.81 | 9,400 | |
| 4 | Isogo-ku | 磯子区 | 163,406 | 19.17 | 8,520 | |
| 5 | Izumi-ku | 泉区 | 155,674 | 23.51 | 6,620 | |
| 6 | Kanagawa-ku | 神奈川区 | 230,401 | 23.88 | 9,650 | |
| 7 | Kanazawa-ku | 金沢区 | 209,565 | 31.01 | 6,760 | |
| 8 | Kōhoku-ku | 港北区 | 332,488 | 31.40 | 10,588 | |
| 9 | Kōnan-ku | 港南区 | 221,536 | 19.87 | 11,500 | |
| 10 | Midori-ku | 緑区 | 176,038 | 25.42 | 6,900 | |
| 11 | Minami-ku | 南区 | 197,019 | 12.67 | 15,500 | |
| 12 | Naka-ku (administrative center) | 中区 | 146,563 | 20.86 | 7,030 | |
| 13 | Nishi-ku | 西区 | 93,210 | 7.04 | 13,210 | |
| 14 | Sakae-ku | 栄区 | 124,845 | 18.55 | 6,750 | |
| 15 | Seya-ku | 瀬谷区 | 126,839 | 17.11 | 7,390 | |
| 16 | Totsuka-ku | 戸塚区 | 274,783 | 35.70 | 7,697 | |
| 17 | Tsurumi-ku | 鶴見区 | 270,433 | 33.23 | 8,140 | |
| 18 | Tsuzuki-ku | 都筑区 | 211,455 | 27.93 | 7,535 |
Government and politics[edit]
The Yokohama City Council consists of 86 members elected from a total of 18 Wards. The LDP has minority control with 36 seats. The incumbent mayor is Takeharu Yamanaka, who defeated Fumiko Hayashi in the 2021 Yokohama mayoral election.
List of mayors (from 1889)[edit]
|
|
Culture and sights[edit]
Cherry blossoms on the Kisha-michi Promenade
Yokohama’s cultural and tourist sights include:
- Yokohama Chinatown
- Yokohama Three Towers
- Yamashita Park (at the harbor)
- Harbor View Park
- The Hikawa Maru, historic passenger and cargo ship
- Yokohama Marine Tower
- Yokohama Triennale
- Minato Mirai 21
- Landmark Tower, 296 m high, second tallest skyscraper in Japan
- Nippon Maru, museum ship
- Yokohama Stadium (the Yokohama DeNA BayStars Pro baseball teams’s home field)
- Yokohama Foreign Cemetery
- Sankei-en Garden
- Kishine-Park
- Kanazawa Bunko, preserves the cultural heritage of the Hōjō clan
- Zō-no-Hana Terrace (象の鼻テラス)[21]
- Gumyōji, oldest temple in the city
Museums[edit]
Yokohama Triennale at Yamashita Pier venue
There are 42 museums in the city area, including.[22]
- CupNoodles Museum (Momofuku Andō Instant Ramen Museum): Several-floors of interactive exhibits related to the invention of the Japanese instant noodle soup, including soup kitchens where you can try the culture-specific noodle soups.
- Kanagawa Prefectural Museum of Cultural History: Located in the historic Yokohama Specie Bank building.
- Kanazawa Bunko: Traditional Japanese and Chinese art objects, many dating from the Kamakura period.
- Matsuri Museum: Dedicated to the shrine festivals (Japanese Matsuri) taking place in Yokohama.
- Silk Museum: Exhibits focusing on the production and processing of silk; including many clothes.
- Yokohama Archives of History: Located in the former British Consulate building with exhibits related to port development and the arrival of Matthew Perry.
- Yokohama Museum of Art: Founded in 1989, featuring modern works by well-known international and Japanese artists.
Gallery[edit]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Yokohama World Porters
-
Mitsui Outlet Park Yokohama Bayside
-
Yokohama Municipal Kanazawa Zoo
-
-
-
-
Yokohama Foreign General Cemetery
-
-
-
-
Iseyama Kotai Shrine
-
Excursion destinations[edit]
In 2016, 46,017,157 tourists visited the city, 13.1% of whom were overnight guests.[22]
- Kodomo no kuni: Means «Children’s country». A nice destination to spend an eventful day with the family. Lots of space for walking and playing. There is also a petting zoo.
- Nogeyama Zoo: One of the few zoos that do not charge admission. It has a large number of animals and a petting zoo where children can play with small animals.
- Zoorasia: Nice zoo with lots of play options for children. However, in this zoo admission costs.
- Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise: A large park with an aquarium. Otherwise rides, shops, restaurants, etc.
- Since 2020, after six years of development, a giant robot named Gundam, which is 18 meters high and weighs 25 tons, has been watching over the port area as a tourist attraction. The giant robot, in which there is a cockpit and whose hands are each two meters long, is based as a figure on a science fiction television series, can move and sink to its knees.[23] The giant robot was manufactured by the company «Gundam Factory Yokohama» under Managing Director Shin Sasaki.
- Kamonyama Park
In popular media[edit]
- Yukio Mishima’s novel The Sailor Who Fell from Grace with the Sea is set mainly in Yokohama. Mishima describes the city’s port and its houses, and the Western influences that shaped them.
- From Up on Poppy Hill is a 2011 Studio Ghibli animated drama film directed by Gorō Miyazaki set in the Yamate district of Yokohama. The film is based on the serialized Japanese comic book of the same name.
- The main setting of James Clavell’s book Gai-Jin is in historical Yokohama.
- Vermillion City in the Kanto region from the Pokémon franchise is based on Yokohama.
- One of the Pretty Cure crossover movies takes place in Yokohama. In the fourth movie of the series, Pretty Cure All Stars New Stage: Friends of the Future, the Pretty Cure appear standing on top of the Cosmo Clock 21 in Minato Mirai.
- The main setting of the Japanese visual novel series Muv-Luv, first a school and then, in an alternate history, a military base is built in Yokohama with the objective of carrying out the Alternative IV Plan meant to save humanity.
- In Command & Conquer: Red Alert 3, Yokohama is under siege by the Soviet Union and Allied Nations to stop the Empire of The Rising Sun. The player must defend Yokohama and then lead a counterattack as the Empire.
- The manga Bungo Stray Dogs is set in Yokohama.
- The Japanese mixed-media project, Hamatora takes place in Yokohama.
- The final battle in Godzilla, Mothra and King Ghidorah: Giant Monsters All-Out Attack takes place in Yokohama.
- In My Hero Academia, it is the location of the Nomu Warehouse where they created artificial Humans (a.k.a. Nomus).
- Sumaru City in Persona 2: Innocent Sin and Eternal Punishment is based on Yokohama.
- Miyabi City in The Caligula Effect is based on Yokohama, including depictions of landmarks such as an unfinished Landmark Tower and Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise (referred to in game as Sea Paraiso).
- The video game Yakuza: Like a Dragon is set in Isezaki Ijincho, a fictional district in Yokohama based on Isezakichō.
- Yokohama is also represented in the multimedia project by King Records, Hypnosis Mic: Division Rap Battle
- Yokohama is the main setting of Japanese manga and anime series Komi Can’t Communicate. Multiple of the cities’ landmarks are featured on the manga, most notably in the more recently released chapters.
- Yokohama is the setting of the anime After the Rain as well as manga series with the same title by Jun Mayuzuki.
- In April 2022, The Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau announced the launch of a new interactive website to aid in the tourism and MICE elements of the city.[24]
Sports[edit]
- Baseball: Yokohama DeNA BayStars
- Soccer: Yokohama F. Marinos (J.League Division 1), Yokohama FC (J.League Division 1), YSCC Yokohama (J.League Division 3), NHK Yokohama FC Seagulls (Nadeshiko League Div.2)
- Velodrome: Kagetsu-en Velodrome
- Basketball: Yokohama B-Corsairs
- Rugby Union: Yokohama Eagles
- Tennis: Ai Sugiyama
- American football: Yokohama Harbors
Economy and infrastructure[edit]
The city has a strong economic base, especially in the shipping, biotechnology, and semiconductor industries. Nissan moved its headquarters to Yokohama from Chūō, Tokyo, in 2010.[25]
Yokohama’s GDP per capita (Nominal) was $30,625 ($1=¥120.13).[26][27]
As of 2016, the total production in Yokohama city reached ¥13.56 billion. It is located between Shizuoka and Hiroshima Prefectures compared to domestic prefectures.[28] It is located between Hungary, which ranks 26th, and New Zealand, which ranks 27th compared to OECD countries. Generally, the primary industry is 0.1%, the secondary industry is 21.7%, and the tertiary industry is 82.3%. The ratio of the primary industry is low, and the ratio of the secondary industry and the tertiary industry is high. Compared to other ordinance-designated cities, it is about 60% of the size of Osaka, which is almost the same as Nagoya. As shown in the attached table, there are not a few head office companies, but the major inferiority to Osaka is the traditional difference, the strong bed.[clarification needed] In connection with this, the absence of large block-type companies (JR, NTT, electric power, gas, major commercial broadcasters, etc.) has had an impact.
The breakdown is ¥11.9 million yen (0.1%) for the primary industry, ¥2.75 billion (21.7%) for the secondary industry, and ¥10.44 billion yen (82.3%) for the tertiary industry. Compared to other government-designated cities, the amount of the primary industry, the ratio of the construction industry of the secondary industry, and the ratio of the real estate industry of the tertiary industry are large, and the finance, insurance, wholesale, and retail of the tertiary industry The ratio of industry and service industry is small, but the tertiary industry is almost the same as Nagoya.
Major companies headquartered[edit]
-
-
-
Isuzu headquarters in Nishi-ku
Transport[edit]
A route map in Yokohama and Tokyo (JR East)
Yokohama is serviced by the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, a high-speed rail line with a stop at Shin-Yokohama Station. Yokohama Station is also a major station, with two million passengers daily. The Yokohama Municipal Subway, Minatomirai Line and Kanazawa Seaside Line provide metro services.
Maritime transport[edit]
Yokohama is the world’s 31st largest seaport in terms of total cargo volume, at 121,326 freight tons as of 2011, and is ranked 37th in terms of TEUs (Twenty-foot equivalent units).[29]
In 2013, APM Terminals Yokohama facility was recognized as the most productive container terminal in the world averaging 163 crane moves per hour, per ship between the vessel’s arrival and departure at the berth.[30]
Rail transport[edit]
Railway stations[edit]
- ■ East Japan Railway Company (JR East)
- ■ Tōkaidō Main Line
- – Yokohama – Totsuka –
- ■ Yokosuka Line
- – Yokohama – Hodogaya – Higashi-Totsuka – Totsuka –
- ■ Keihin-Tōhoku Line
- – Tsurumi – Shin-Koyasu – Higashi-Kanagawa – Yokohama
- ■ Negishi Line
- Yokohama – Sakuragichō – Kannai – Ishikawachō – Yamate – Negishi – Isogo – Shin-Sugita – Yōkōdai – Kōnandai – Hongōdai –
- ■ Yokohama Line
- Higashi-Kanagawa – Ōguchi – Kikuna – Shin-Yokohama – Kozukue – Kamoi – Nakayama – Tōkaichiba – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Nambu Line
- – Yakō –
- ■ Tsurumi Line
- Main Line : Tsurumi – Kokudō – Tsurumi-Ono – Bentembashi – Asano – Anzen –
- Umi-Shibaura Branch : Asano – Shin-Shibaura – Umi-Shibaura
- ■ Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central)
- ■ Tōkaidō Shinkansen
- – Shin-Yokohama –
- ■ Keikyu
- ■ Keikyu Main Line
- – Tsurumi-Ichiba – Keikyū Tsurumi – Kagetsuen-mae – Namamugi – Keikyū Shin-Koyasu – Koyasu – Kanagawa-Shinmachi – Naka-Kido – Kanagawa – Yokohama – Tobe – Hinodechō – Koganechō – Minami-Ōta – Idogaya – Gumyōji – Kami-Ōoka – Byōbugaura – Sugita – Keikyū Tomioka – Nōkendai – Kanazawa-Bunko – Kanazawa-Hakkei –
- ■ Keikyu Zushi Line
- Kanazawa-Hakkei – Mutsuura –
- ■ Tokyu Railways
- ■ Tōyoko Line
- – Hiyoshi – Tsunashima – Ōkurayama – Kikuna – Myōrenji – Hakuraku – Higashi-Hakuraku – Tammachi – Yokohama
- ■ Meguro Line
- – Hiyoshi
- ■ Den-en-toshi Line
- – Tama-Plaza – Azamino – Eda – Ichigao – Fujigaoka – Aobadai – Tana – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Kodomonokuni Line
- Nagatsuta – Onda – Kodomonokuni
- ■ Sagami Railway
- ■ Sagami Railway Main Line
- Yokohama – Hiranumabashi – Nishi-Yokohama – Tennōchō – Hoshikawa – Wadamachi – Kamihoshikawa – Nishiya – Tsurugamine – Futamatagawa – Kibōgaoka – Mitsukyō – Seya –
- ■ Izumino Line
- Futamatagawa – Minami-Makigahara – Ryokuentoshi – Yayoidai – Izumino – Izumi-chūō – Yumegaoka
- ■ Yokohama Minatomirai Railway
- ■ Minatomirai Line
- Yokohama – Shin-Takashima – Minato Mirai – Bashamichi – Nihon-ōdōri – Motomachi-Chūkagai
- ■ Yokohama City Transportation Bureau (Yokohama Municipal Subway)
- ■ Blue Line
- – Shimoiida – Tateba – Nakada – Odoriba – Totsuka – Maioka – Shimonagaya – Kaminagaya – Kōnan-Chūō – Kami-Ōoka – Gumyōji – Maita – Yoshinochō – Bandōbashi – Isezakichōjamachi – Kannai – Sakuragichō – Takashimachō – Yokohama – Mitsuzawa-shimochō – Mitsuzawa-kamichō – Katakurachō – Kishine-kōen – Shin-Yokohama – Kita Shin-Yokohama – Nippa – Nakamachidai – Center Minami – Center Kita – Nakagawa – Azamino
- ■ Green Line
- Nakayama – Kawawachō – Tsuzuki-Fureai-no-Oka – Center Minami – Center Kita – Kita-Yamata – Higashi-Yamata – Takata – Hiyoshi-Honchō – Hiyoshi
- ■ Yokohama New Transit
- ■ Kanazawa Seaside Line
- Shin-Sugita – Nambu-Shijō – Torihama – Namiki-Kita – Namiki-Chūō – Sachiura – Sangyō-Shinkō-Center – Fukuura – Shidai-Igakubu – Hakkeijima – Uminokōen-Shibaguchi – Uminokōen-Minamiguchi – Nojimakōen – Kanazawa-Hakkei
Education[edit]
Public elementary and middle schools are operated by the city of Yokohama. There are nine public high schools which are operated by the Yokohama City Board of Education,[31] and a number of public high schools which are operated by the Kanagawa Prefectural Board of Education. Yokohama National University is a leading university in Yokohama which is also one of the highest ranking national universities in Japan.
- 46,388 children attend the 260 kindergartens.
- Almost 386,000 students are taught in 351 primary schools.
- There are 16 universities including Yokohama National University. The number of students is around 83,000.
- 19 public libraries had 9.5 million loans in 2016.[22]
International relations[edit]
Twin towns – sister cities[edit]
Yokohama is twinned with:[32]
Constanța, Constanța County, Romania (since October 1977)
Lyon, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France (since April 1959)
Manila, Philippines (since July 1965)
Mumbai, Maharashtra, India (since June 1965)
Odesa, Odesa Oblast, Ukraine (since July 1965)
San Diego, CA, United States (former partnership, October 1957–October 2021)
San Francisco, CA, United States (since October 2021)
Shanghai, China (since November 1973)
Vancouver, BC, Canada (since July 1965)
Partner cities[edit]
Abidjan, Ivory Coast
Beijing, China (since May 2006)
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (since June 2008)
Busan, South Korea (since June 2006)
Frankfurt, Hesse, Germany (since September 2011)
Hanoi, Vietnam (since November 2007)
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam (since October 2007)
Incheon, South Korea (since December 2009)
Seberang Perai, Penang, Malaysia (since August 2016)[33]
Taipei, Taiwan (since May 2006)
Tel Aviv, Israel (since July 2012)
Tianjin, China (since May 2008)
Sister ports[edit]
Notable people[edit]
- Toru Furuya, singer and seiyū
- Yuma Kagiyama, figure skater
- Miki Koyama, racing driver
- Takehito Koyasu, singer and seiyū
- Ryuji Kumita, racing driver and CEO of B-Max Racing
- Keisuke Kunimoto, racing driver
- Yuji Kunimoto, racing driver
- Minoru Suzuki, professional wrestler
- Yuta Watanabe, NBA player for the Toronto Raptors.
- Radwimps
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ «YOKOHAMA | Meaning & Definition for UK English | Lexico.com». En.oxforddictionaries.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- ^ «Memories of old Honmoku». The Japan Times. May 19, 1999. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved March 3, 2021.
- ^ «Yokohama City History, pg. 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on July 9, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- ^ Der Große Brockhaus. 16. edition. Vol. 6. F. A. Brockhaus, Wiesbaden 1955, p. 82
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website it is fresh». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 12, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ Arita, Erika, «Happy Birthday Yokohama! Archived August 31, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», The Japan Times, May 24, 2009, p. 7.
- ^ Fukue, Natsuko, «Chinese immigrants played vital role Archived August 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 28, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Matsutani, Minoru, «Yokohama – city on the cutting edge Archived August 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 29, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Galbraith, Michael (June 16, 2013). «Death threats sparked Japan’s first cricket game». Japan Times. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ a b «Interesting Tidbits of Yokohama». Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau. Archived from the original on May 5, 2009. Retrieved February 7, 2009.
- ^ Hammer, Joshua. (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II, p. 143. Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Hammer, pp. 149 Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine-170.
- ^ «Tsurumi River Multipurpose Retarding Basin». www.japanriver.or.jp. Archived from the original on September 26, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Collection of 1923 Japan earthquake massacre testimonies released». www.hani.co.kr. September 3, 2013. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- ^ «FNN Remembering 3/11: Yokohama station and surrounding areas at time of earthquake occurrence». www.fnn-news.com. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved January 10, 2016.
- ^ «Yokohama, Japan Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)». Weatherbase. Archived from the original on December 21, 2019. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information». world-guides.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved January 11, 2010.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 17, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ Japanese Imperial Commission (1878). Le Japon à l’exposition universelle de 1878. Géographie et histoire du Japon (in French).
- ^ 横浜市区別外国人登録人口(平成30年3月末現在). Archived from the original on March 11, 2017. Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ^ «Webseite des Kulturzentrums». Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c «Statistical Booklet Book of Yokohama 2018» (PDF). www.city.yokohama.lg.jp. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2018. Retrieved November 2, 2020.
- ^ Tagesthemen. Beitrag in der Nachrichtensendung der ARD, Moderation: Ingo Zamperoni, 30. November 2020, 35 Min. Eine Produktion von Das Erste
- ^ «Virtual Yokohama: Interactive Website Launched». Business wire. April 28, 2022. Retrieved April 29, 2022.
- ^ «Nissan To Create New Global and Domestic Headquarters in Yokohama City by 2010». Japancorp.net. Archived from the original on September 14, 2007. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ «Yokohama GDP 2015». Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «Yokohama 2015 population» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 3, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «「平成28年度 横浜市の市民経済計算」がまとまりました。» (PDF). 横浜市. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 4, 2021. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ «Ports & World Trade». www.aapa-ports.org. Archived from the original on May 4, 2011. Retrieved July 3, 2014.
- ^ «Chinese Ports Lead the World in Berth Productivity, JOC Group Inc. Data Shows». Press Release. AXIO Data Group. JOC Inc. June 24, 2014. Archived from the original on April 6, 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2015.
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 19, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ «Yokohama’s Sister/Friendship Cities». city.yokohama.lg.jp. Yokohama. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ «MPSP sets sights on city status». The Star. August 1, 2016. Archived from the original on July 5, 2018. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
Sources[edit]
- Hammer, Joshua (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II Archived June 23, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-6465-5 (cloth).
- Heilbrun, Jacob. «Aftershocks» Archived January 15, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times, September 17, 2006.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yokohama.
- Official Website (in Japanese)
- Yokohama Tourism Website (in English)
Geographic data related to Yokohama at OpenStreetMap
-
-
January 31 2011, 21:58
Иокогама?
В прошлый раз я неправильно написала слово «Иокогама»… Вот так : «Ёкогама»
А мне интересно, почему так пишут по-русски? У нас читается как «Ёкохама/よこはま/Yokohama».
Кстати, на западе находится город «長浜/ながはま/Nagahama», как его пишут по-русски? «Нагагама»???
Я вообще не понимаю этот «закон»!
前回(ぜんかい)、私(わたし)は「Иокогама」を間違(まちが)ってこう書(か)いてしまいました — 「Ёкогама」
ところで、なぜロシア語(ご)ではこのように書(か)くのですか?日本(にほん)では横浜(よこはま)を「Ёкохама/ヨコハマ」と言(い)いますが・・・。おもしろいです。
ちなみに、西(にし)の方(ほう)に「長浜(ながはま)」という街(まち)がありますが、これはロシア語(ご)でどのように書(か)きますか?「Нагагама/ナガガマ」ですか???
この「法則(ほうそく)」がよくわかりませんっ!
This article is about the capital city of Kanagawa Prefecture. For other uses, see Yokohama (disambiguation).
|
Yokohama 横浜市 |
|
|---|---|
|
Designated city |
|
| City of Yokohama | |
|
From top, left to right: Minato Mirai 21 at dusk, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Sankei-en, Harbor View Park, Yokohama Marine Tower viewed from Yamashita Park and Ōsanbashi Pier |
|
|
Flag Emblem |
|

Interactive map outlining Yokohama |
|

Location of Yokohama in Kanagawa Prefecture |
|
|
Yokohama |
|
| Coordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°ECoordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Kanagawa Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Takeharu Yamanaka |
| Area | |
| • Total | 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) |
| Population
(October 1, 2022) |
|
| • Total | 3,771,961 |
| • Density | 8,600/km2 (22,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| – Tree | Camellia, Chinquapin, Sangoju Sasanqua, Ginkgo, Zelkova |
| – Flower | Dahlia Rose |
| Address | 1-1 Minato-chō, Naka-ku, Yokohama-shi, Kanagawa-ken 231-0017 |
| Website | www.city.yokohama.lg.jp |
| Yokohama | |||
|---|---|---|---|
«Yokohama» in new-style (shinjitai) kanji |
|||
| Japanese name | |||
| Hiragana | よこはま | ||
| Katakana | ヨコハマ | ||
| Kyūjitai | 橫濱 | ||
| Shinjitai | 横浜 | ||
|
Yokohama (Japanese: 横浜, pronounced [jokohama] (listen)) is the second-largest city in Japan by population[1] and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu. Yokohama is also the major economic, cultural, and commercial hub of the Greater Tokyo Area along the Keihin Industrial Zone.
Yokohama was one of the cities to open for trade with the West following the 1859 end of the policy of seclusion and has since been known as a cosmopolitan port city, after Kobe opened in 1853. Yokohama is the home of many Japan’s firsts in the Meiji period, including the first foreign trading port and Chinatown (1859), European-style sport venues (1860s), English-language newspaper (1861), confectionery and beer manufacturing (1865), daily newspaper (1870), gas-powered street lamps (1870s), railway station (1872), and power plant (1882). Yokohama developed rapidly as Japan’s prominent port city following the end of Japan’s relative isolation in the mid-19th century and is today one of its major ports along with Kobe, Osaka, Nagoya, Fukuoka, Tokyo and Chiba. Yokohama is classified as a Large-Port Metropolis.[2]
Yokohama is the largest port city and high tech industrial hub in the Greater Tokyo Area and the Kantō region. The city proper is headquarters to companies such as Isuzu, Nissan, JVCKenwood, Keikyu, Koei Tecmo, Sotetsu, Salesforce Japan and Bank of Yokohama. Famous landmarks in Yokohama include Minato Mirai 21, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Yokohama Marine Tower, Yamashita Park, and Ōsanbashi Pier.
Etymology[edit]
Yokohama (横浜) means «horizontal beach».[3] The current area surrounded by Maita Park, the Ōoka River and the Nakamura River have been a gulf divided by a sandbar from the open sea. This sandbar was the original Yokohama fishing village. Since the sandbar protruded perpendicularly from the land, or horizontally when viewed from the sea, it was called a «horizontal beach».[4]
History[edit]
Opening of the Treaty Port (1859–1868)[edit]
Before the Western foreigners arrived, Yokohama was a small fishing village up to the end of the feudal Edo period, when Japan held a policy of national seclusion, having little contact with foreigners.[5] A major turning point in Japanese history happened in 1853–54, when Commodore Matthew Perry arrived just south of Yokohama with a fleet of American warships, demanding that Japan open several ports for commerce, and the Tokugawa shogunate agreed by signing the Treaty of Peace and Amity.[6]
It was initially agreed that one of the ports to be opened to foreign ships would be the bustling town of Kanagawa-juku (in what is now Kanagawa Ward) on the Tōkaidō, a strategic highway that linked Edo to Kyoto and Osaka. However, the Tokugawa shogunate decided that Kanagawa-juku was too close to the Tōkaidō for comfort, and port facilities were instead built across the inlet in the sleepy fishing village of Yokohama. The Port of Yokohama was officially opened on June 2, 1859.[7]
Yokohama quickly became the base of foreign trade in Japan. Foreigners initially occupied the low-lying district of the city called Kannai, residential districts later expanding as the settlement grew to incorporate much of the elevated Yamate district overlooking the city, commonly referred to by English speaking residents as The Bluff.
Kannai, the foreign trade and commercial district (literally, inside the barrier), was surrounded by a moat, foreign residents enjoying extraterritorial status both within and outside the compound. Interactions with the local population, particularly young samurai, outside the settlement inevitably caused problems; the Namamugi Incident, one of the events that preceded the downfall of the shogunate, took place in what is now Tsurumi Ward in 1862, and prompted the Bombardment of Kagoshima in 1863.
To protect British commercial and diplomatic interests in Yokohama a military garrison was established in 1862. With the growth in trade increasing numbers of Chinese also came to settle in the city.[8] Yokohama was the scene of many notable firsts for Japan including the growing acceptance of western fashion, photography by pioneers such as Felice Beato, Japan’s first English language newspaper, the Japan Herald published in 1861 and in 1865 the first ice cream confectionery and beer to be produced in Japan.[9] Recreational sports introduced to Japan by foreign residents in Yokohama included European style horse racing in 1862, cricket in 1863[10] and rugby union in 1866. A great fire destroyed much of the foreign settlement on November 26, 1866, and smallpox was a recurrent public health hazard, but the city continued to grow rapidly – attracting foreigners and Japanese alike.
- Gallery
-
Landing of Commodore Perry and men to meet the Imperial commissioners at Yokohama, 14 July 1853
-
Foreign ships in Yokohama harbor in 1861
-
A foreign trading house in Yokohama in 1861
Meiji and Taisho Periods (1868–1923)[edit]
After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the port was developed for trading silk, the main trading partner being Great Britain. Western influence and technological transfer contributed to the establishment of Japan’s first daily newspaper (1870), first gas-powered street lamps (1872) and Japan’s first railway constructed in the same year to connect Yokohama to Shinagawa and Shinbashi in Tokyo. In 1872 Jules Verne portrayed Yokohama, which he had never visited, in an episode of his widely read novel Around the World in Eighty Days, capturing the atmosphere of the fast-developing, internationally oriented Japanese city.
In 1887, a British merchant, Samuel Cocking, built the city’s first power plant. At first for his own use, this coal power plant became the basis for the Yokohama Cooperative Electric Light Company. The city was officially incorporated on April 1, 1889.[11] By the time the extraterritoriality of foreigner areas was abolished in 1899, Yokohama was the most international city in Japan, with foreigner areas stretching from Kannai to the Bluff area and the large Yokohama Chinatown.
The early 20th century was marked by rapid growth of industry. Entrepreneurs built factories along reclaimed land to the north of the city toward Kawasaki, which eventually grew to be the Keihin Industrial Area. The growth of Japanese industry brought affluence, and many wealthy trading families constructed sprawling residences there, while the rapid influx of population from Japan and Korea also led to the formation of Kojiki-Yato, then the largest slum in Japan.
- Gallery
-
Street scene c. 1880
-
Yokohama c. 1880
-
Great Kantō earthquake and the Second World War (1923–1945)[edit]
- Gallery
-
View of Yokohama after the bombing in 1945
Much of Yokohama was destroyed on September 1, 1923, by the Great Kantō earthquake. The Yokohama police reported casualties at 30,771 dead and 47,908 injured, out of a pre-earthquake population of 434,170.[12] Fuelled by rumors of rebellion and sabotage, vigilante mobs thereupon murdered many Koreans in the Kojiki-yato slum.[13] Many people believed that Koreans used black magic to cause the earthquake. Martial law was in place until November 19. Rubble from the quake was used to reclaim land for parks, the most famous being the Yamashita Park on the waterfront which opened in 1930.
Yokohama was rebuilt, only to be destroyed again by U.S. air raids during World War II. The first bombing was in the April 18, 1942 Doolittle Raid. An estimated 7,000–8,000 people were killed in a single morning on May 29, 1945, in what is now known as the Great Yokohama Air Raid, when B-29s firebombed the city and in just one hour and nine minutes, reducing 42% of it to rubble.[11]
Postwar growth and development[edit]
During the American occupation, Yokohama was a major transshipment base for American supplies and personnel, especially during the Korean War. After the occupation, most local U.S. naval activity moved from Yokohama to an American base in nearby Yokosuka.
Four years after the Treaty of San Francisco signed, the city was designated by government ordinance on September 1, 1956.[citation needed] The city’s tram and trolleybus system was abolished in 1972, the same year as the opening of the first line of Yokohama Municipal Subway. Construction of Minato Mirai 21 («Port Future 21»), a major urban development project on reclaimed land started in 1983, nicknamed the «Philadelphia and Boston of the Orient» was compared to Center City, Philadelphia and Downtown Boston located in the East Coast of the United States. Minato Mirai 21 hosted the Yokohama Exotic Showcase in 1989, which saw the first public operation of maglev trains in Japan and the opening of Cosmo Clock 21, then the tallest Ferris wheel in the world. The 860-metre-long (2,820 ft) Yokohama Bay Bridge opened in the same year. In 1993, Minato Mirai 21 saw the opening of the Yokohama Landmark Tower, the third-tallest building in Japan.
The 2002 FIFA World Cup final was held in June at the International Stadium Yokohama. In 2009, the city marked the 150th anniversary of the opening of the port and the 120th anniversary of the commencement of the City Administration. An early part in the commemoration project incorporated the Fourth Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD IV), which was held in Yokohama in May 2008. In November 2010, Yokohama hosted the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) meeting.
- Gallery
-
Geography[edit]
Sentinel-2 image of Yokohama (2020)
Topography[edit]
Yokohama has a total area of 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) at an elevation of 5 metres (16 ft) above sea level. It is the capital of Kanagawa Prefecture, bordered to the east by Tokyo Bay and located in the middle of the Kantō plain. The city is surrounded by hills and the characteristic mountain system of the island of Honshū, so its growth has been limited and it has had to gain ground from the sea. This also affects the population density, one of the highest in Japan with 8,500 inhabitants per km2.
The highest points within the urban boundary are Omaruyama (156 m [512 ft]) and Mount Enkaizan (153 m [502 ft]). The main river is the Tsurumi River, which begins in the Tama Hills and empties into the Pacific Ocean.[14]
These municipalities surround Yokohama: Kawasaki, Yokosuka, Zushi, Kamakura, Fujisawa, Yamato, Machida.
Geology[edit]
The city is very prone to natural phenomena such as earthquakes and tropical cyclones because the island of Honshū has a high level of seismic activity, being in the middle of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Most seismic movements are of low intensity and are generally not perceived by people. However, Yokohama has experienced two major tremors that reflect the evolution of Earthquake engineering: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake devastated the city and caused more than 100,000 fatalities throughout the region,[15] while the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, with its epicenter on the east coast, was felt in the locality but only material damage was lamented because most buildings were already prepared to withstand them.[16]
Climate[edit]
Yokohama features a humid subtropical climate (Köppen: Cfa) with hot, humid summers and chilly winters.[17] Weatherwise, Yokohama has a pattern of rain, clouds and sun, although in winter, it is surprisingly sunny, more so than Southern Spain. Winter temperatures rarely drop below freezing, while summer can seem quite warm, because of the effects of humidity.[18] The coldest temperature was on 24 January 1927 when −8.2 °C (17.2 °F) was reached, whilst the hottest day was 11 August 2013 at 37.4 °C (99.3 °F). The highest monthly rainfall was in October 2004 with 761.5 millimetres (30.0 in), closely followed by July 1941 with 753.4 millimetres (29.66 in), whilst December and January have recorded no measurable precipitation three times each.
| Climate data for Yokohama (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1896−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.7 (83.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
37.2 (99.0) |
37.4 (99.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
8.7 (47.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.1 (37.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.2 (17.2) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.7 (2.55) |
64.7 (2.55) |
139.5 (5.49) |
143.1 (5.63) |
152.6 (6.01) |
188.8 (7.43) |
182.5 (7.19) |
139.0 (5.47) |
241.5 (9.51) |
240.4 (9.46) |
107.6 (4.24) |
66.4 (2.61) |
1,730.8 (68.14) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
9 (3.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.7 | 6.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 11.1 | 13.5 | 12.0 | 8.8 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 6.2 | 118.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 53 | 54 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 76 | 71 | 65 | 57 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.7 | 167.2 | 168.8 | 181.2 | 187.4 | 135.9 | 170.9 | 206.4 | 141.2 | 137.3 | 151.1 | 178.1 | 2,018.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[19] |
Cityscape[edit]
-
Yokohama night view (2014)
-
View from Mosaic Mall Kohoku (2015)
Yokohama skyline from Grand Oriental Hotel rooftop (2015)
Demographics[edit]
Population[edit]
Historical population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 64,602[20] | — |
| 1880 | 72,630 | +12.4% |
| 1890 | 132,627 | +82.6% |
| 1900 | 196,653 | +48.3% |
| 1910 | 403,303 | +105.1% |
| 1920 | 422,942 | +4.9% |
| 1925 | 405,888 | −4.0% |
| 1930 | 620,306 | +52.8% |
| 1935 | 704,290 | +13.5% |
| 1940 | 968,091 | +37.5% |
| 1945 | 814,379 | −15.9% |
| 1950 | 951,188 | +16.8% |
| 1955 | 1,143,687 | +20.2% |
| 1960 | 1,375,710 | +20.3% |
| 1965 | 1,788,915 | +30.0% |
| 1970 | 2,238,264 | +25.1% |
| 1975 | 2,621,771 | +17.1% |
| 1980 | 2,773,674 | +5.8% |
| 1985 | 2,992,926 | +7.9% |
| 1990 | 3,220,331 | +7.6% |
| 1995 | 3,307,136 | +2.7% |
| 2000 | 3,426,651 | +3.6% |
| 2005 | 3,579,133 | +4.4% |
| 2010 | 3,670,669 | +2.6% |
| 2015 | 3,710,824 | +1.1% |
| 2020 | 3,760,157 | +1.3% |
Yokohama’s foreign population of 92,139 includes Chinese, Koreans, Filipinos, and Vietnamese.[21]
Wards[edit]
Yokohama has 18 wards (ku):
| Wards of Yokohama | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place Name | Map of Yokohama | |||||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | Population | Land area in km2 | Pop. density
per km2 |
||
| 1 | Aoba-ku | 青葉区 | 302,643 | 35.14 | 8,610 |
|
| 2 | Asahi-ku | 旭区 | 249,045 | 32.77 | 7,600 | |
| 3 | Hodogaya-ku | 保土ヶ谷区 | 205,887 | 21.81 | 9,400 | |
| 4 | Isogo-ku | 磯子区 | 163,406 | 19.17 | 8,520 | |
| 5 | Izumi-ku | 泉区 | 155,674 | 23.51 | 6,620 | |
| 6 | Kanagawa-ku | 神奈川区 | 230,401 | 23.88 | 9,650 | |
| 7 | Kanazawa-ku | 金沢区 | 209,565 | 31.01 | 6,760 | |
| 8 | Kōhoku-ku | 港北区 | 332,488 | 31.40 | 10,588 | |
| 9 | Kōnan-ku | 港南区 | 221,536 | 19.87 | 11,500 | |
| 10 | Midori-ku | 緑区 | 176,038 | 25.42 | 6,900 | |
| 11 | Minami-ku | 南区 | 197,019 | 12.67 | 15,500 | |
| 12 | Naka-ku (administrative center) | 中区 | 146,563 | 20.86 | 7,030 | |
| 13 | Nishi-ku | 西区 | 93,210 | 7.04 | 13,210 | |
| 14 | Sakae-ku | 栄区 | 124,845 | 18.55 | 6,750 | |
| 15 | Seya-ku | 瀬谷区 | 126,839 | 17.11 | 7,390 | |
| 16 | Totsuka-ku | 戸塚区 | 274,783 | 35.70 | 7,697 | |
| 17 | Tsurumi-ku | 鶴見区 | 270,433 | 33.23 | 8,140 | |
| 18 | Tsuzuki-ku | 都筑区 | 211,455 | 27.93 | 7,535 |
Government and politics[edit]
The Yokohama City Council consists of 86 members elected from a total of 18 Wards. The LDP has minority control with 36 seats. The incumbent mayor is Takeharu Yamanaka, who defeated Fumiko Hayashi in the 2021 Yokohama mayoral election.
List of mayors (from 1889)[edit]
|
|
|
Culture and sights[edit]
Cherry blossoms on the Kisha-michi Promenade
Yokohama’s cultural and tourist sights include:
- Yokohama Chinatown
- Yokohama Three Towers
- Yamashita Park (at the harbor)
- Harbor View Park
- The Hikawa Maru, historic passenger and cargo ship
- Yokohama Marine Tower
- Yokohama Triennale
- Minato Mirai 21
- Landmark Tower, 296 m high, second tallest skyscraper in Japan
- Nippon Maru, museum ship
- Yokohama Stadium (the Yokohama DeNA BayStars Pro baseball team’s home field)
- Yokohama Foreign Cemetery
- Sankei-en Garden
- Kishine-Park
- Kanazawa Bunko, preserves the cultural heritage of the Hōjō clan
- Zō-no-Hana Terrace (象の鼻テラス)[22]
- Gumyōji, oldest temple in the city
Museums[edit]
Yokohama Triennale at Yamashita Pier venue
There are 42 museums in the city area, including.[23]
- CupNoodles Museum (Momofuku Andō Instant Ramen Museum): Several-floors of interactive exhibits related to the invention of the Japanese instant noodle soup, including soup kitchens where you can try the culture-specific noodle soups.
- Kanagawa Prefectural Museum of Cultural History: Located in the historic Yokohama Specie Bank building.
- Kanazawa Bunko: Traditional Japanese and Chinese art objects, many dating from the Kamakura period.
- Matsuri Museum: Dedicated to the shrine festivals (Japanese Matsuri) taking place in Yokohama.
- Silk Museum: Exhibits focusing on the production and processing of silk; including many clothes.
- Yokohama Archives of History: Located in the former British Consulate building with exhibits related to port development and the arrival of Matthew Perry.
- Yokohama Museum of Art: Founded in 1989, featuring modern works by well-known international and Japanese artists.
Gallery[edit]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Yokohama World Porters
-
Mitsui Outlet Park Yokohama Bayside
-
Yokohama Municipal Kanazawa Zoo
-
-
-
-
Yokohama Foreign General Cemetery
-
-
-
-
Iseyama Kotai Shrine
-
Excursion destinations[edit]
In 2016, 46,017,157 tourists visited the city, 13.1% of whom were overnight guests.[23]
- Kodomo no kuni: Means «Children’s country». A nice destination to spend an eventful day with the family. Lots of space for walking and playing. There is also a petting zoo.
- Nogeyama Zoo: One of the few zoos that do not charge admission. It has a large number of animals and a petting zoo where children can play with small animals.
- Zoorasia: Nice zoo with lots of play options for children. However, in this zoo admission costs.
- Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise: A large park with an aquarium. Otherwise rides, shops, restaurants, etc.
- Since 2020, after six years of development, a giant robot named Gundam, which is 18 meters high and weighs 25 tons, has been watching over the port area as a tourist attraction. The giant robot, in which there is a cockpit and whose hands are each two meters long, is based as a figure on a science fiction television series, can move and sink to its knees.[24] The giant robot was manufactured by the company «Gundam Factory Yokohama» under Managing Director Shin Sasaki.
- Kamonyama Park
In popular media[edit]
- Yukio Mishima’s novel The Sailor Who Fell from Grace with the Sea is set mainly in Yokohama. Mishima describes the city’s port and its houses, and the Western influences that shaped them.
- From Up on Poppy Hill is a 2011 Studio Ghibli animated drama film directed by Gorō Miyazaki set in the Yamate district of Yokohama. The film is based on the serialized Japanese comic book of the same name.
- The main setting of James Clavell’s book Gai-Jin is in historical Yokohama.
- Vermillion City in the Kanto region from the Pokémon franchise is based on Yokohama.
- One of the Pretty Cure crossover movies takes place in Yokohama. In the fourth movie of the series, Pretty Cure All Stars New Stage: Friends of the Future, the Pretty Cure appear standing on top of the Cosmo Clock 21 in Minato Mirai.
- The main setting of the Japanese visual novel series Muv-Luv, first a school and then, in an alternate history, a military base is built in Yokohama with the objective of carrying out the Alternative IV Plan meant to save humanity.
- In Command & Conquer: Red Alert 3, Yokohama is under siege by the Soviet Union and Allied Nations to stop the Empire of The Rising Sun. The player must defend Yokohama and then lead a counterattack as the Empire.
- The manga Bungo Stray Dogs is set in Yokohama.
- The Japanese mixed-media project, Hamatora takes place in Yokohama.
- The final battle in Godzilla, Mothra and King Ghidorah: Giant Monsters All-Out Attack takes place in Yokohama.
- In My Hero Academia, it is the location of the Nomu Warehouse where they created artificial Humans (a.k.a. Nomus).
- Sumaru City in Persona 2: Innocent Sin and Eternal Punishment is based on Yokohama.
- Miyabi City in The Caligula Effect is based on Yokohama, including depictions of landmarks such as an unfinished Landmark Tower and Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise (referred to in game as Sea Paraiso).
- The video game Yakuza: Like a Dragon is set in Isezaki Ijincho, a fictional district in Yokohama based on Isezakichō.
- Yokohama is also represented in the multimedia project by King Records, Hypnosis Mic: Division Rap Battle
- Yokohama is the main setting of Japanese manga and anime series Komi Can’t Communicate. Multiple of the cities’ landmarks are featured on the manga, most notably in the more recently released chapters.
- Yokohama is the setting of the anime After the Rain as well as manga series with the same title by Jun Mayuzuki.
- In April 2022, The Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau announced the launch of a new interactive website to aid in the tourism and MICE elements of the city.[25]
Sports[edit]
- Baseball: Yokohama DeNA BayStars
- Football: Yokohama F. Marinos (J.League Division 1), Yokohama FC (J.League Division 1), YSCC Yokohama (J.League Division 3), NHK Yokohama FC Seagulls (Nadeshiko League Div.2)
- Velodrome: Kagetsu-en Velodrome
- Basketball: Yokohama B-Corsairs
- Rugby Union: Yokohama Eagles
- Tennis: Ai Sugiyama
- American football: Yokohama Harbors
- Ice Hockey: Yokohama Grits
Economy and infrastructure[edit]
The city has a strong economic base, especially in the shipping, biotechnology, and semiconductor industries. Nissan moved its headquarters to Yokohama from Chūō, Tokyo in 2010.[26]
Yokohama’s GDP per capita (Nominal) was $30,625 ($1=¥120.13).[27][28]
As of 2016, the total production in Yokohama city reached ¥13.56 billion. It is located between Shizuoka and Hiroshima Prefectures compared to domestic prefectures.[29] It is located between Hungary, which ranks 26th, and New Zealand, which ranks 27th compared to OECD countries. Generally, the primary industry is 0.1%, the secondary industry is 21.7%, and the tertiary industry is 82.3%. The ratio of the primary industry is low, and the ratio of the secondary industry and the tertiary industry is high. Compared to other ordinance-designated cities, it is about 60% of the size of Osaka, which is almost the same as Nagoya. As shown in the attached table, there are not a few head office companies, but the major inferiority to Osaka is the traditional difference, the strong bed.[clarification needed] In connection with this, the absence of large block-type companies (JR, NTT, electric power, gas, major commercial broadcasters, etc.) has had an impact.
The breakdown is ¥11.9 million yen (0.1%) for the primary industry, ¥2.75 billion (21.7%) for the secondary industry, and ¥10.44 billion yen (82.3%) for the tertiary industry. Compared to other government-designated cities, the amount of the primary industry, the ratio of the construction industry of the secondary industry, and the ratio of the real estate industry of the tertiary industry are large, and the finance, insurance, wholesale, and retail of the tertiary industry The ratio of industry and service industry is small, but the tertiary industry is almost the same as Nagoya.
Major companies headquartered[edit]
-
-
-
Isuzu headquarters in Nishi-ku
Transport[edit]
A route map in Yokohama and Tokyo (JR East)
Yokohama is serviced by the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, a high-speed rail line with a stop at Shin-Yokohama Station. Yokohama Station is also a major station, with two million passengers daily. The Yokohama Municipal Subway, Minatomirai Line and Kanazawa Seaside Line provide metro services.
Maritime transport[edit]
Yokohama is the world’s 31st largest seaport in terms of total cargo volume, at 121,326 freight tons as of 2011, and is ranked 37th in terms of TEUs (Twenty-foot equivalent units).[30]
In 2013, APM Terminals Yokohama facility was recognized as the most productive container terminal in the world averaging 163 crane moves per hour, per ship between the vessel’s arrival and departure at the berth.[31]
Rail transport[edit]
Railway stations[edit]
- ■ East Japan Railway Company (JR East)
- ■ Tōkaidō Main Line
- – Yokohama – Totsuka –
- ■ Yokosuka Line
- – Yokohama – Hodogaya – Higashi-Totsuka – Totsuka –
- ■ Keihin-Tōhoku Line
- – Tsurumi – Shin-Koyasu – Higashi-Kanagawa – Yokohama
- ■ Negishi Line
- Yokohama – Sakuragichō – Kannai – Ishikawachō – Yamate – Negishi – Isogo – Shin-Sugita – Yōkōdai – Kōnandai – Hongōdai –
- ■ Yokohama Line
- Higashi-Kanagawa – Ōguchi – Kikuna – Shin-Yokohama – Kozukue – Kamoi – Nakayama – Tōkaichiba – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Nambu Line
- – Yakō –
- ■ Tsurumi Line
- Main Line : Tsurumi – Kokudō – Tsurumi-Ono – Bentembashi – Asano – Anzen –
- Umi-Shibaura Branch : Asano – Shin-Shibaura – Umi-Shibaura
- ■ Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central)
- ■ Tōkaidō Shinkansen
- – Shin-Yokohama –
- ■ Keikyu
- ■ Keikyu Main Line
- – Tsurumi-Ichiba – Keikyū Tsurumi – Kagetsuen-mae – Namamugi – Keikyū Shin-Koyasu – Koyasu – Kanagawa-Shinmachi – Naka-Kido – Kanagawa – Yokohama – Tobe – Hinodechō – Koganechō – Minami-Ōta – Idogaya – Gumyōji – Kami-Ōoka – Byōbugaura – Sugita – Keikyū Tomioka – Nōkendai – Kanazawa-Bunko – Kanazawa-Hakkei –
- ■ Keikyu Zushi Line
- Kanazawa-Hakkei – Mutsuura –
- ■ Tokyu Railways
- ■ Tōyoko Line
- – Hiyoshi – Tsunashima – Ōkurayama – Kikuna – Myōrenji – Hakuraku – Higashi-Hakuraku – Tammachi – Yokohama
- ■ Meguro Line
- – Hiyoshi
- ■ Den-en-toshi Line
- – Tama-Plaza – Azamino – Eda – Ichigao – Fujigaoka – Aobadai – Tana – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Kodomonokuni Line
- Nagatsuta – Onda – Kodomonokuni
- ■ Sagami Railway
- ■ Sagami Railway Main Line
- Yokohama – Hiranumabashi – Nishi-Yokohama – Tennōchō – Hoshikawa – Wadamachi – Kamihoshikawa – Nishiya – Tsurugamine – Futamatagawa – Kibōgaoka – Mitsukyō – Seya –
- ■ Izumino Line
- Futamatagawa – Minami-Makigahara – Ryokuentoshi – Yayoidai – Izumino – Izumi-chūō – Yumegaoka
- ■ Yokohama Minatomirai Railway
- ■ Minatomirai Line
- Yokohama – Shin-Takashima – Minato Mirai – Bashamichi – Nihon-ōdōri – Motomachi-Chūkagai
- ■ Yokohama City Transportation Bureau (Yokohama Municipal Subway)
- ■ Blue Line
- – Shimoiida – Tateba – Nakada – Odoriba – Totsuka – Maioka – Shimonagaya – Kaminagaya – Kōnan-Chūō – Kami-Ōoka – Gumyōji – Maita – Yoshinochō – Bandōbashi – Isezakichōjamachi – Kannai – Sakuragichō – Takashimachō – Yokohama – Mitsuzawa-shimochō – Mitsuzawa-kamichō – Katakurachō – Kishine-kōen – Shin-Yokohama – Kita Shin-Yokohama – Nippa – Nakamachidai – Center Minami – Center Kita – Nakagawa – Azamino
- ■ Green Line
- Nakayama – Kawawachō – Tsuzuki-Fureai-no-Oka – Center Minami – Center Kita – Kita-Yamata – Higashi-Yamata – Takata – Hiyoshi-Honchō – Hiyoshi
- ■ Yokohama New Transit
- ■ Kanazawa Seaside Line
- Shin-Sugita – Nambu-Shijō – Torihama – Namiki-Kita – Namiki-Chūō – Sachiura – Sangyō-Shinkō-Center – Fukuura – Shidai-Igakubu – Hakkeijima – Uminokōen-Shibaguchi – Uminokōen-Minamiguchi – Nojimakōen – Kanazawa-Hakkei
Education[edit]
Public elementary and middle schools are operated by the Yokohama Municipal Board of Education [ja]. There are nine public high schools which are operated by the Yokohama City Board of Education,[32] and a number of public high schools which are operated by the Kanagawa Prefectural Board of Education. Yokohama National University is a leading university in Yokohama which is also one of the highest ranking national universities in Japan.
- 46,388 children attend the 260 kindergartens.
- Almost 386,000 students are taught in 351 primary schools.
- There are 16 universities including Yokohama National University. The number of students is around 83,000.
- 19 public libraries had 9.5 million loans in 2016.[23]
International relations[edit]
Twin towns – sister cities[edit]
Yokohama is twinned with:[33]
Constanța, Constanța County, Romania (since October 1977)
Lyon, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France (since April 1959)
Manila, Philippines (since July 1965)
Mumbai, Maharashtra, India (since June 1965)
Odesa, Odesa Oblast, Ukraine (since July 1965)
San Diego, CA, United States (former partnership, October 1957–October 2021)
San Francisco, CA, United States (since October 2021)
Shanghai, China (since November 1973)
Vancouver, BC, Canada (since July 1965)
Partner cities[edit]
Abidjan, Ivory Coast
Beijing, China (since May 2006)
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (since June 2008)
Busan, South Korea (since June 2006)
Frankfurt, Hesse, Germany (since September 2011)
Hanoi, Vietnam (since November 2007)
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam (since October 2007)
Incheon, South Korea (since December 2009)
Seberang Perai, Penang, Malaysia (since August 2016)[34]
Taipei, Taiwan (since May 2006)
Tel Aviv, Israel (since July 2012)
Tianjin, China (since May 2008)
Sister ports[edit]
Notable people[edit]
- Toru Furuya, singer and seiyū
- Yuma Kagiyama, figure skater
- Teiko Kiwa, Japanese-Dutch opera singer in the 1920s and 1930s
- Miki Koyama, racing driver
- Takehito Koyasu, singer and seiyū
- Ryuji Kumita, racing driver and CEO of B-Max Racing
- Keisuke Kunimoto, racing driver
- Yuji Kunimoto, racing driver
- Minoru Suzuki, professional wrestler
- Yuta Watanabe, NBA player for the Toronto Raptors.
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ «YOKOHAMA | Meaning & Definition for UK English | Lexico.com». En.oxforddictionaries.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- ^ Roberts, Toby; Williams, Ian; Preston, John (2021). «The Southampton system: A new universal standard approach for port-city classification». Maritime Policy & Management. 48 (4): 530–542. doi:10.1080/03088839.2020.1802785. S2CID 225502755.
- ^ «Memories of old Honmoku». The Japan Times. May 19, 1999. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved March 3, 2021.
- ^ «Yokohama City History, pg. 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on July 9, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- ^ Der Große Brockhaus. 16. edition. Vol. 6. F. A. Brockhaus, Wiesbaden 1955, p. 82
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website it is fresh». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 12, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ Arita, Erika, «Happy Birthday Yokohama! Archived August 31, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», The Japan Times, May 24, 2009, p. 7.
- ^ Fukue, Natsuko, «Chinese immigrants played vital role Archived August 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 28, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Matsutani, Minoru, «Yokohama – city on the cutting edge Archived August 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 29, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Galbraith, Michael (June 16, 2013). «Death threats sparked Japan’s first cricket game». Japan Times. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ a b «Interesting Tidbits of Yokohama». Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau. Archived from the original on May 5, 2009. Retrieved February 7, 2009.
- ^ Hammer, Joshua. (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II, p. 143. Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Hammer, pp. 149 Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine-170.
- ^ «Tsurumi River Multipurpose Retarding Basin». www.japanriver.or.jp. Archived from the original on September 26, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Collection of 1923 Japan earthquake massacre testimonies released». www.hani.co.kr. September 3, 2013. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- ^ «FNN Remembering 3/11: Yokohama station and surrounding areas at time of earthquake occurrence». www.fnn-news.com. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved January 10, 2016.
- ^ «Yokohama, Japan Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)». Weatherbase. Archived from the original on December 21, 2019. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information». world-guides.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved January 11, 2010.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 17, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ Japanese Imperial Commission (1878). Le Japon à l’exposition universelle de 1878. Géographie et histoire du Japon (in French).
- ^ 横浜市区別外国人登録人口(平成30年3月末現在). Archived from the original on March 11, 2017. Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ^ «Webseite des Kulturzentrums». Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c «Statistical Booklet Book of Yokohama 2018» (PDF). www.city.yokohama.lg.jp. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2018. Retrieved November 2, 2020.
- ^ Tagesthemen. Beitrag in der Nachrichtensendung der ARD, Moderation: Ingo Zamperoni, 30. November 2020, 35 Min. Eine Produktion von Das Erste
- ^ «Virtual Yokohama: Interactive Website Launched». Business Wire. April 28, 2022. Retrieved April 29, 2022.
- ^ «Nissan To Create New Global and Domestic Headquarters in Yokohama City by 2010». Japancorp.net. Archived from the original on September 14, 2007. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ «Yokohama GDP 2015». Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «Yokohama 2015 population» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 3, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «「平成28年度 横浜市の市民経済計算」がまとまりました。» (PDF). 横浜市. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 4, 2021. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ «Ports & World Trade». www.aapa-ports.org. Archived from the original on May 4, 2011. Retrieved July 3, 2014.
- ^ «Chinese Ports Lead the World in Berth Productivity, JOC Group Inc. Data Shows». Press Release. AXIO Data Group. JOC Inc. June 24, 2014. Archived from the original on April 6, 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2015.
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 19, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ «Yokohama’s Sister/Friendship Cities». city.yokohama.lg.jp. Yokohama. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ «MPSP sets sights on city status». The Star. August 1, 2016. Archived from the original on July 5, 2018. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
Sources[edit]
- Hammer, Joshua (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II Archived June 23, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-6465-5 (cloth).
- Heilbrun, Jacob. «Aftershocks» Archived January 15, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times, September 17, 2006.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yokohama.
- Official Website (in Japanese)
- Yokohama Tourism Website (in English)
Geographic data related to Yokohama at OpenStreetMap
This article is about the capital city of Kanagawa Prefecture. For other uses, see Yokohama (disambiguation).
|
Yokohama 横浜市 |
|
|---|---|
|
Designated city |
|
| City of Yokohama | |
|
From top, left to right: Minato Mirai 21 at dusk, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Sankei-en, Harbor View Park, Yokohama Marine Tower viewed from Yamashita Park and Ōsanbashi Pier |
|
|
Flag Emblem |
|

Interactive map outlining Yokohama |
|

Location of Yokohama in Kanagawa Prefecture |
|
|
Yokohama |
|
| Coordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°ECoordinates: 35°26′39″N 139°38′17″E / 35.44417°N 139.63806°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kantō |
| Prefecture | Kanagawa Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Takeharu Yamanaka |
| Area | |
| • Total | 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) |
| Population
(October 1, 2022) |
|
| • Total | 3,771,961 |
| • Density | 8,600/km2 (22,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| – Tree | Camellia, Chinquapin, Sangoju Sasanqua, Ginkgo, Zelkova |
| – Flower | Dahlia Rose |
| Address | 1-1 Minato-chō, Naka-ku, Yokohama-shi, Kanagawa-ken 231-0017 |
| Website | www.city.yokohama.lg.jp |
| Yokohama | |||
|---|---|---|---|
«Yokohama» in new-style (shinjitai) kanji |
|||
| Japanese name | |||
| Hiragana | よこはま | ||
| Katakana | ヨコハマ | ||
| Kyūjitai | 橫濱 | ||
| Shinjitai | 横浜 | ||
|
Yokohama (Japanese: 横浜, pronounced [jokohama] (listen)) is the second-largest city in Japan by population[1] and the most populous municipality of Japan. It is the capital city and the most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a 2020 population of 3.8 million. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu. Yokohama is also the major economic, cultural, and commercial hub of the Greater Tokyo Area along the Keihin Industrial Zone.
Yokohama was one of the cities to open for trade with the West following the 1859 end of the policy of seclusion and has since been known as a cosmopolitan port city, after Kobe opened in 1853. Yokohama is the home of many Japan’s firsts in the Meiji period, including the first foreign trading port and Chinatown (1859), European-style sport venues (1860s), English-language newspaper (1861), confectionery and beer manufacturing (1865), daily newspaper (1870), gas-powered street lamps (1870s), railway station (1872), and power plant (1882). Yokohama developed rapidly as Japan’s prominent port city following the end of Japan’s relative isolation in the mid-19th century and is today one of its major ports along with Kobe, Osaka, Nagoya, Fukuoka, Tokyo and Chiba. Yokohama is classified as a Large-Port Metropolis.[2]
Yokohama is the largest port city and high tech industrial hub in the Greater Tokyo Area and the Kantō region. The city proper is headquarters to companies such as Isuzu, Nissan, JVCKenwood, Keikyu, Koei Tecmo, Sotetsu, Salesforce Japan and Bank of Yokohama. Famous landmarks in Yokohama include Minato Mirai 21, Nippon Maru Memorial Park, Yokohama Chinatown, Motomachi Shopping Street, Yokohama Marine Tower, Yamashita Park, and Ōsanbashi Pier.
Etymology[edit]
Yokohama (横浜) means «horizontal beach».[3] The current area surrounded by Maita Park, the Ōoka River and the Nakamura River have been a gulf divided by a sandbar from the open sea. This sandbar was the original Yokohama fishing village. Since the sandbar protruded perpendicularly from the land, or horizontally when viewed from the sea, it was called a «horizontal beach».[4]
History[edit]
Opening of the Treaty Port (1859–1868)[edit]
Before the Western foreigners arrived, Yokohama was a small fishing village up to the end of the feudal Edo period, when Japan held a policy of national seclusion, having little contact with foreigners.[5] A major turning point in Japanese history happened in 1853–54, when Commodore Matthew Perry arrived just south of Yokohama with a fleet of American warships, demanding that Japan open several ports for commerce, and the Tokugawa shogunate agreed by signing the Treaty of Peace and Amity.[6]
It was initially agreed that one of the ports to be opened to foreign ships would be the bustling town of Kanagawa-juku (in what is now Kanagawa Ward) on the Tōkaidō, a strategic highway that linked Edo to Kyoto and Osaka. However, the Tokugawa shogunate decided that Kanagawa-juku was too close to the Tōkaidō for comfort, and port facilities were instead built across the inlet in the sleepy fishing village of Yokohama. The Port of Yokohama was officially opened on June 2, 1859.[7]
Yokohama quickly became the base of foreign trade in Japan. Foreigners initially occupied the low-lying district of the city called Kannai, residential districts later expanding as the settlement grew to incorporate much of the elevated Yamate district overlooking the city, commonly referred to by English speaking residents as The Bluff.
Kannai, the foreign trade and commercial district (literally, inside the barrier), was surrounded by a moat, foreign residents enjoying extraterritorial status both within and outside the compound. Interactions with the local population, particularly young samurai, outside the settlement inevitably caused problems; the Namamugi Incident, one of the events that preceded the downfall of the shogunate, took place in what is now Tsurumi Ward in 1862, and prompted the Bombardment of Kagoshima in 1863.
To protect British commercial and diplomatic interests in Yokohama a military garrison was established in 1862. With the growth in trade increasing numbers of Chinese also came to settle in the city.[8] Yokohama was the scene of many notable firsts for Japan including the growing acceptance of western fashion, photography by pioneers such as Felice Beato, Japan’s first English language newspaper, the Japan Herald published in 1861 and in 1865 the first ice cream confectionery and beer to be produced in Japan.[9] Recreational sports introduced to Japan by foreign residents in Yokohama included European style horse racing in 1862, cricket in 1863[10] and rugby union in 1866. A great fire destroyed much of the foreign settlement on November 26, 1866, and smallpox was a recurrent public health hazard, but the city continued to grow rapidly – attracting foreigners and Japanese alike.
- Gallery
-
Landing of Commodore Perry and men to meet the Imperial commissioners at Yokohama, 14 July 1853
-
Foreign ships in Yokohama harbor in 1861
-
A foreign trading house in Yokohama in 1861
Meiji and Taisho Periods (1868–1923)[edit]
After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the port was developed for trading silk, the main trading partner being Great Britain. Western influence and technological transfer contributed to the establishment of Japan’s first daily newspaper (1870), first gas-powered street lamps (1872) and Japan’s first railway constructed in the same year to connect Yokohama to Shinagawa and Shinbashi in Tokyo. In 1872 Jules Verne portrayed Yokohama, which he had never visited, in an episode of his widely read novel Around the World in Eighty Days, capturing the atmosphere of the fast-developing, internationally oriented Japanese city.
In 1887, a British merchant, Samuel Cocking, built the city’s first power plant. At first for his own use, this coal power plant became the basis for the Yokohama Cooperative Electric Light Company. The city was officially incorporated on April 1, 1889.[11] By the time the extraterritoriality of foreigner areas was abolished in 1899, Yokohama was the most international city in Japan, with foreigner areas stretching from Kannai to the Bluff area and the large Yokohama Chinatown.
The early 20th century was marked by rapid growth of industry. Entrepreneurs built factories along reclaimed land to the north of the city toward Kawasaki, which eventually grew to be the Keihin Industrial Area. The growth of Japanese industry brought affluence, and many wealthy trading families constructed sprawling residences there, while the rapid influx of population from Japan and Korea also led to the formation of Kojiki-Yato, then the largest slum in Japan.
- Gallery
-
Street scene c. 1880
-
Yokohama c. 1880
-
Great Kantō earthquake and the Second World War (1923–1945)[edit]
- Gallery
-
View of Yokohama after the bombing in 1945
Much of Yokohama was destroyed on September 1, 1923, by the Great Kantō earthquake. The Yokohama police reported casualties at 30,771 dead and 47,908 injured, out of a pre-earthquake population of 434,170.[12] Fuelled by rumors of rebellion and sabotage, vigilante mobs thereupon murdered many Koreans in the Kojiki-yato slum.[13] Many people believed that Koreans used black magic to cause the earthquake. Martial law was in place until November 19. Rubble from the quake was used to reclaim land for parks, the most famous being the Yamashita Park on the waterfront which opened in 1930.
Yokohama was rebuilt, only to be destroyed again by U.S. air raids during World War II. The first bombing was in the April 18, 1942 Doolittle Raid. An estimated 7,000–8,000 people were killed in a single morning on May 29, 1945, in what is now known as the Great Yokohama Air Raid, when B-29s firebombed the city and in just one hour and nine minutes, reducing 42% of it to rubble.[11]
Postwar growth and development[edit]
During the American occupation, Yokohama was a major transshipment base for American supplies and personnel, especially during the Korean War. After the occupation, most local U.S. naval activity moved from Yokohama to an American base in nearby Yokosuka.
Four years after the Treaty of San Francisco signed, the city was designated by government ordinance on September 1, 1956.[citation needed] The city’s tram and trolleybus system was abolished in 1972, the same year as the opening of the first line of Yokohama Municipal Subway. Construction of Minato Mirai 21 («Port Future 21»), a major urban development project on reclaimed land started in 1983, nicknamed the «Philadelphia and Boston of the Orient» was compared to Center City, Philadelphia and Downtown Boston located in the East Coast of the United States. Minato Mirai 21 hosted the Yokohama Exotic Showcase in 1989, which saw the first public operation of maglev trains in Japan and the opening of Cosmo Clock 21, then the tallest Ferris wheel in the world. The 860-metre-long (2,820 ft) Yokohama Bay Bridge opened in the same year. In 1993, Minato Mirai 21 saw the opening of the Yokohama Landmark Tower, the third-tallest building in Japan.
The 2002 FIFA World Cup final was held in June at the International Stadium Yokohama. In 2009, the city marked the 150th anniversary of the opening of the port and the 120th anniversary of the commencement of the City Administration. An early part in the commemoration project incorporated the Fourth Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD IV), which was held in Yokohama in May 2008. In November 2010, Yokohama hosted the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) meeting.
- Gallery
-
Geography[edit]
Sentinel-2 image of Yokohama (2020)
Topography[edit]
Yokohama has a total area of 437.38 km2 (168.87 sq mi) at an elevation of 5 metres (16 ft) above sea level. It is the capital of Kanagawa Prefecture, bordered to the east by Tokyo Bay and located in the middle of the Kantō plain. The city is surrounded by hills and the characteristic mountain system of the island of Honshū, so its growth has been limited and it has had to gain ground from the sea. This also affects the population density, one of the highest in Japan with 8,500 inhabitants per km2.
The highest points within the urban boundary are Omaruyama (156 m [512 ft]) and Mount Enkaizan (153 m [502 ft]). The main river is the Tsurumi River, which begins in the Tama Hills and empties into the Pacific Ocean.[14]
These municipalities surround Yokohama: Kawasaki, Yokosuka, Zushi, Kamakura, Fujisawa, Yamato, Machida.
Geology[edit]
The city is very prone to natural phenomena such as earthquakes and tropical cyclones because the island of Honshū has a high level of seismic activity, being in the middle of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Most seismic movements are of low intensity and are generally not perceived by people. However, Yokohama has experienced two major tremors that reflect the evolution of Earthquake engineering: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake devastated the city and caused more than 100,000 fatalities throughout the region,[15] while the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, with its epicenter on the east coast, was felt in the locality but only material damage was lamented because most buildings were already prepared to withstand them.[16]
Climate[edit]
Yokohama features a humid subtropical climate (Köppen: Cfa) with hot, humid summers and chilly winters.[17] Weatherwise, Yokohama has a pattern of rain, clouds and sun, although in winter, it is surprisingly sunny, more so than Southern Spain. Winter temperatures rarely drop below freezing, while summer can seem quite warm, because of the effects of humidity.[18] The coldest temperature was on 24 January 1927 when −8.2 °C (17.2 °F) was reached, whilst the hottest day was 11 August 2013 at 37.4 °C (99.3 °F). The highest monthly rainfall was in October 2004 with 761.5 millimetres (30.0 in), closely followed by July 1941 with 753.4 millimetres (29.66 in), whilst December and January have recorded no measurable precipitation three times each.
| Climate data for Yokohama (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1896−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.7 (83.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
37.2 (99.0) |
37.4 (99.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
37.4 (99.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
27.0 (80.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
8.7 (47.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.1 (37.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.2 (17.2) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.7 (2.55) |
64.7 (2.55) |
139.5 (5.49) |
143.1 (5.63) |
152.6 (6.01) |
188.8 (7.43) |
182.5 (7.19) |
139.0 (5.47) |
241.5 (9.51) |
240.4 (9.46) |
107.6 (4.24) |
66.4 (2.61) |
1,730.8 (68.14) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
9 (3.5) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.7 | 6.3 | 11.0 | 10.7 | 11.1 | 13.5 | 12.0 | 8.8 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 6.2 | 118.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 53 | 54 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 76 | 71 | 65 | 57 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.7 | 167.2 | 168.8 | 181.2 | 187.4 | 135.9 | 170.9 | 206.4 | 141.2 | 137.3 | 151.1 | 178.1 | 2,018.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[19] |
Cityscape[edit]
-
Yokohama night view (2014)
-
View from Mosaic Mall Kohoku (2015)
Yokohama skyline from Grand Oriental Hotel rooftop (2015)
Demographics[edit]
Population[edit]
Historical population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 64,602[20] | — |
| 1880 | 72,630 | +12.4% |
| 1890 | 132,627 | +82.6% |
| 1900 | 196,653 | +48.3% |
| 1910 | 403,303 | +105.1% |
| 1920 | 422,942 | +4.9% |
| 1925 | 405,888 | −4.0% |
| 1930 | 620,306 | +52.8% |
| 1935 | 704,290 | +13.5% |
| 1940 | 968,091 | +37.5% |
| 1945 | 814,379 | −15.9% |
| 1950 | 951,188 | +16.8% |
| 1955 | 1,143,687 | +20.2% |
| 1960 | 1,375,710 | +20.3% |
| 1965 | 1,788,915 | +30.0% |
| 1970 | 2,238,264 | +25.1% |
| 1975 | 2,621,771 | +17.1% |
| 1980 | 2,773,674 | +5.8% |
| 1985 | 2,992,926 | +7.9% |
| 1990 | 3,220,331 | +7.6% |
| 1995 | 3,307,136 | +2.7% |
| 2000 | 3,426,651 | +3.6% |
| 2005 | 3,579,133 | +4.4% |
| 2010 | 3,670,669 | +2.6% |
| 2015 | 3,710,824 | +1.1% |
| 2020 | 3,760,157 | +1.3% |
Yokohama’s foreign population of 92,139 includes Chinese, Koreans, Filipinos, and Vietnamese.[21]
Wards[edit]
Yokohama has 18 wards (ku):
| Wards of Yokohama | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place Name | Map of Yokohama | |||||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | Population | Land area in km2 | Pop. density
per km2 |
||
| 1 | Aoba-ku | 青葉区 | 302,643 | 35.14 | 8,610 |
|
| 2 | Asahi-ku | 旭区 | 249,045 | 32.77 | 7,600 | |
| 3 | Hodogaya-ku | 保土ヶ谷区 | 205,887 | 21.81 | 9,400 | |
| 4 | Isogo-ku | 磯子区 | 163,406 | 19.17 | 8,520 | |
| 5 | Izumi-ku | 泉区 | 155,674 | 23.51 | 6,620 | |
| 6 | Kanagawa-ku | 神奈川区 | 230,401 | 23.88 | 9,650 | |
| 7 | Kanazawa-ku | 金沢区 | 209,565 | 31.01 | 6,760 | |
| 8 | Kōhoku-ku | 港北区 | 332,488 | 31.40 | 10,588 | |
| 9 | Kōnan-ku | 港南区 | 221,536 | 19.87 | 11,500 | |
| 10 | Midori-ku | 緑区 | 176,038 | 25.42 | 6,900 | |
| 11 | Minami-ku | 南区 | 197,019 | 12.67 | 15,500 | |
| 12 | Naka-ku (administrative center) | 中区 | 146,563 | 20.86 | 7,030 | |
| 13 | Nishi-ku | 西区 | 93,210 | 7.04 | 13,210 | |
| 14 | Sakae-ku | 栄区 | 124,845 | 18.55 | 6,750 | |
| 15 | Seya-ku | 瀬谷区 | 126,839 | 17.11 | 7,390 | |
| 16 | Totsuka-ku | 戸塚区 | 274,783 | 35.70 | 7,697 | |
| 17 | Tsurumi-ku | 鶴見区 | 270,433 | 33.23 | 8,140 | |
| 18 | Tsuzuki-ku | 都筑区 | 211,455 | 27.93 | 7,535 |
Government and politics[edit]
The Yokohama City Council consists of 86 members elected from a total of 18 Wards. The LDP has minority control with 36 seats. The incumbent mayor is Takeharu Yamanaka, who defeated Fumiko Hayashi in the 2021 Yokohama mayoral election.
List of mayors (from 1889)[edit]
|
|
|
Culture and sights[edit]
Cherry blossoms on the Kisha-michi Promenade
Yokohama’s cultural and tourist sights include:
- Yokohama Chinatown
- Yokohama Three Towers
- Yamashita Park (at the harbor)
- Harbor View Park
- The Hikawa Maru, historic passenger and cargo ship
- Yokohama Marine Tower
- Yokohama Triennale
- Minato Mirai 21
- Landmark Tower, 296 m high, second tallest skyscraper in Japan
- Nippon Maru, museum ship
- Yokohama Stadium (the Yokohama DeNA BayStars Pro baseball team’s home field)
- Yokohama Foreign Cemetery
- Sankei-en Garden
- Kishine-Park
- Kanazawa Bunko, preserves the cultural heritage of the Hōjō clan
- Zō-no-Hana Terrace (象の鼻テラス)[22]
- Gumyōji, oldest temple in the city
Museums[edit]
Yokohama Triennale at Yamashita Pier venue
There are 42 museums in the city area, including.[23]
- CupNoodles Museum (Momofuku Andō Instant Ramen Museum): Several-floors of interactive exhibits related to the invention of the Japanese instant noodle soup, including soup kitchens where you can try the culture-specific noodle soups.
- Kanagawa Prefectural Museum of Cultural History: Located in the historic Yokohama Specie Bank building.
- Kanazawa Bunko: Traditional Japanese and Chinese art objects, many dating from the Kamakura period.
- Matsuri Museum: Dedicated to the shrine festivals (Japanese Matsuri) taking place in Yokohama.
- Silk Museum: Exhibits focusing on the production and processing of silk; including many clothes.
- Yokohama Archives of History: Located in the former British Consulate building with exhibits related to port development and the arrival of Matthew Perry.
- Yokohama Museum of Art: Founded in 1989, featuring modern works by well-known international and Japanese artists.
Gallery[edit]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Yokohama World Porters
-
Mitsui Outlet Park Yokohama Bayside
-
Yokohama Municipal Kanazawa Zoo
-
-
-
-
Yokohama Foreign General Cemetery
-
-
-
-
Iseyama Kotai Shrine
-
Excursion destinations[edit]
In 2016, 46,017,157 tourists visited the city, 13.1% of whom were overnight guests.[23]
- Kodomo no kuni: Means «Children’s country». A nice destination to spend an eventful day with the family. Lots of space for walking and playing. There is also a petting zoo.
- Nogeyama Zoo: One of the few zoos that do not charge admission. It has a large number of animals and a petting zoo where children can play with small animals.
- Zoorasia: Nice zoo with lots of play options for children. However, in this zoo admission costs.
- Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise: A large park with an aquarium. Otherwise rides, shops, restaurants, etc.
- Since 2020, after six years of development, a giant robot named Gundam, which is 18 meters high and weighs 25 tons, has been watching over the port area as a tourist attraction. The giant robot, in which there is a cockpit and whose hands are each two meters long, is based as a figure on a science fiction television series, can move and sink to its knees.[24] The giant robot was manufactured by the company «Gundam Factory Yokohama» under Managing Director Shin Sasaki.
- Kamonyama Park
In popular media[edit]
- Yukio Mishima’s novel The Sailor Who Fell from Grace with the Sea is set mainly in Yokohama. Mishima describes the city’s port and its houses, and the Western influences that shaped them.
- From Up on Poppy Hill is a 2011 Studio Ghibli animated drama film directed by Gorō Miyazaki set in the Yamate district of Yokohama. The film is based on the serialized Japanese comic book of the same name.
- The main setting of James Clavell’s book Gai-Jin is in historical Yokohama.
- Vermillion City in the Kanto region from the Pokémon franchise is based on Yokohama.
- One of the Pretty Cure crossover movies takes place in Yokohama. In the fourth movie of the series, Pretty Cure All Stars New Stage: Friends of the Future, the Pretty Cure appear standing on top of the Cosmo Clock 21 in Minato Mirai.
- The main setting of the Japanese visual novel series Muv-Luv, first a school and then, in an alternate history, a military base is built in Yokohama with the objective of carrying out the Alternative IV Plan meant to save humanity.
- In Command & Conquer: Red Alert 3, Yokohama is under siege by the Soviet Union and Allied Nations to stop the Empire of The Rising Sun. The player must defend Yokohama and then lead a counterattack as the Empire.
- The manga Bungo Stray Dogs is set in Yokohama.
- The Japanese mixed-media project, Hamatora takes place in Yokohama.
- The final battle in Godzilla, Mothra and King Ghidorah: Giant Monsters All-Out Attack takes place in Yokohama.
- In My Hero Academia, it is the location of the Nomu Warehouse where they created artificial Humans (a.k.a. Nomus).
- Sumaru City in Persona 2: Innocent Sin and Eternal Punishment is based on Yokohama.
- Miyabi City in The Caligula Effect is based on Yokohama, including depictions of landmarks such as an unfinished Landmark Tower and Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise (referred to in game as Sea Paraiso).
- The video game Yakuza: Like a Dragon is set in Isezaki Ijincho, a fictional district in Yokohama based on Isezakichō.
- Yokohama is also represented in the multimedia project by King Records, Hypnosis Mic: Division Rap Battle
- Yokohama is the main setting of Japanese manga and anime series Komi Can’t Communicate. Multiple of the cities’ landmarks are featured on the manga, most notably in the more recently released chapters.
- Yokohama is the setting of the anime After the Rain as well as manga series with the same title by Jun Mayuzuki.
- In April 2022, The Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau announced the launch of a new interactive website to aid in the tourism and MICE elements of the city.[25]
Sports[edit]
- Baseball: Yokohama DeNA BayStars
- Football: Yokohama F. Marinos (J.League Division 1), Yokohama FC (J.League Division 1), YSCC Yokohama (J.League Division 3), NHK Yokohama FC Seagulls (Nadeshiko League Div.2)
- Velodrome: Kagetsu-en Velodrome
- Basketball: Yokohama B-Corsairs
- Rugby Union: Yokohama Eagles
- Tennis: Ai Sugiyama
- American football: Yokohama Harbors
- Ice Hockey: Yokohama Grits
Economy and infrastructure[edit]
The city has a strong economic base, especially in the shipping, biotechnology, and semiconductor industries. Nissan moved its headquarters to Yokohama from Chūō, Tokyo in 2010.[26]
Yokohama’s GDP per capita (Nominal) was $30,625 ($1=¥120.13).[27][28]
As of 2016, the total production in Yokohama city reached ¥13.56 billion. It is located between Shizuoka and Hiroshima Prefectures compared to domestic prefectures.[29] It is located between Hungary, which ranks 26th, and New Zealand, which ranks 27th compared to OECD countries. Generally, the primary industry is 0.1%, the secondary industry is 21.7%, and the tertiary industry is 82.3%. The ratio of the primary industry is low, and the ratio of the secondary industry and the tertiary industry is high. Compared to other ordinance-designated cities, it is about 60% of the size of Osaka, which is almost the same as Nagoya. As shown in the attached table, there are not a few head office companies, but the major inferiority to Osaka is the traditional difference, the strong bed.[clarification needed] In connection with this, the absence of large block-type companies (JR, NTT, electric power, gas, major commercial broadcasters, etc.) has had an impact.
The breakdown is ¥11.9 million yen (0.1%) for the primary industry, ¥2.75 billion (21.7%) for the secondary industry, and ¥10.44 billion yen (82.3%) for the tertiary industry. Compared to other government-designated cities, the amount of the primary industry, the ratio of the construction industry of the secondary industry, and the ratio of the real estate industry of the tertiary industry are large, and the finance, insurance, wholesale, and retail of the tertiary industry The ratio of industry and service industry is small, but the tertiary industry is almost the same as Nagoya.
Major companies headquartered[edit]
-
-
-
Isuzu headquarters in Nishi-ku
Transport[edit]
A route map in Yokohama and Tokyo (JR East)
Yokohama is serviced by the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, a high-speed rail line with a stop at Shin-Yokohama Station. Yokohama Station is also a major station, with two million passengers daily. The Yokohama Municipal Subway, Minatomirai Line and Kanazawa Seaside Line provide metro services.
Maritime transport[edit]
Yokohama is the world’s 31st largest seaport in terms of total cargo volume, at 121,326 freight tons as of 2011, and is ranked 37th in terms of TEUs (Twenty-foot equivalent units).[30]
In 2013, APM Terminals Yokohama facility was recognized as the most productive container terminal in the world averaging 163 crane moves per hour, per ship between the vessel’s arrival and departure at the berth.[31]
Rail transport[edit]
Railway stations[edit]
- ■ East Japan Railway Company (JR East)
- ■ Tōkaidō Main Line
- – Yokohama – Totsuka –
- ■ Yokosuka Line
- – Yokohama – Hodogaya – Higashi-Totsuka – Totsuka –
- ■ Keihin-Tōhoku Line
- – Tsurumi – Shin-Koyasu – Higashi-Kanagawa – Yokohama
- ■ Negishi Line
- Yokohama – Sakuragichō – Kannai – Ishikawachō – Yamate – Negishi – Isogo – Shin-Sugita – Yōkōdai – Kōnandai – Hongōdai –
- ■ Yokohama Line
- Higashi-Kanagawa – Ōguchi – Kikuna – Shin-Yokohama – Kozukue – Kamoi – Nakayama – Tōkaichiba – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Nambu Line
- – Yakō –
- ■ Tsurumi Line
- Main Line : Tsurumi – Kokudō – Tsurumi-Ono – Bentembashi – Asano – Anzen –
- Umi-Shibaura Branch : Asano – Shin-Shibaura – Umi-Shibaura
- ■ Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central)
- ■ Tōkaidō Shinkansen
- – Shin-Yokohama –
- ■ Keikyu
- ■ Keikyu Main Line
- – Tsurumi-Ichiba – Keikyū Tsurumi – Kagetsuen-mae – Namamugi – Keikyū Shin-Koyasu – Koyasu – Kanagawa-Shinmachi – Naka-Kido – Kanagawa – Yokohama – Tobe – Hinodechō – Koganechō – Minami-Ōta – Idogaya – Gumyōji – Kami-Ōoka – Byōbugaura – Sugita – Keikyū Tomioka – Nōkendai – Kanazawa-Bunko – Kanazawa-Hakkei –
- ■ Keikyu Zushi Line
- Kanazawa-Hakkei – Mutsuura –
- ■ Tokyu Railways
- ■ Tōyoko Line
- – Hiyoshi – Tsunashima – Ōkurayama – Kikuna – Myōrenji – Hakuraku – Higashi-Hakuraku – Tammachi – Yokohama
- ■ Meguro Line
- – Hiyoshi
- ■ Den-en-toshi Line
- – Tama-Plaza – Azamino – Eda – Ichigao – Fujigaoka – Aobadai – Tana – Nagatsuta –
- ■ Kodomonokuni Line
- Nagatsuta – Onda – Kodomonokuni
- ■ Sagami Railway
- ■ Sagami Railway Main Line
- Yokohama – Hiranumabashi – Nishi-Yokohama – Tennōchō – Hoshikawa – Wadamachi – Kamihoshikawa – Nishiya – Tsurugamine – Futamatagawa – Kibōgaoka – Mitsukyō – Seya –
- ■ Izumino Line
- Futamatagawa – Minami-Makigahara – Ryokuentoshi – Yayoidai – Izumino – Izumi-chūō – Yumegaoka
- ■ Yokohama Minatomirai Railway
- ■ Minatomirai Line
- Yokohama – Shin-Takashima – Minato Mirai – Bashamichi – Nihon-ōdōri – Motomachi-Chūkagai
- ■ Yokohama City Transportation Bureau (Yokohama Municipal Subway)
- ■ Blue Line
- – Shimoiida – Tateba – Nakada – Odoriba – Totsuka – Maioka – Shimonagaya – Kaminagaya – Kōnan-Chūō – Kami-Ōoka – Gumyōji – Maita – Yoshinochō – Bandōbashi – Isezakichōjamachi – Kannai – Sakuragichō – Takashimachō – Yokohama – Mitsuzawa-shimochō – Mitsuzawa-kamichō – Katakurachō – Kishine-kōen – Shin-Yokohama – Kita Shin-Yokohama – Nippa – Nakamachidai – Center Minami – Center Kita – Nakagawa – Azamino
- ■ Green Line
- Nakayama – Kawawachō – Tsuzuki-Fureai-no-Oka – Center Minami – Center Kita – Kita-Yamata – Higashi-Yamata – Takata – Hiyoshi-Honchō – Hiyoshi
- ■ Yokohama New Transit
- ■ Kanazawa Seaside Line
- Shin-Sugita – Nambu-Shijō – Torihama – Namiki-Kita – Namiki-Chūō – Sachiura – Sangyō-Shinkō-Center – Fukuura – Shidai-Igakubu – Hakkeijima – Uminokōen-Shibaguchi – Uminokōen-Minamiguchi – Nojimakōen – Kanazawa-Hakkei
Education[edit]
Public elementary and middle schools are operated by the Yokohama Municipal Board of Education [ja]. There are nine public high schools which are operated by the Yokohama City Board of Education,[32] and a number of public high schools which are operated by the Kanagawa Prefectural Board of Education. Yokohama National University is a leading university in Yokohama which is also one of the highest ranking national universities in Japan.
- 46,388 children attend the 260 kindergartens.
- Almost 386,000 students are taught in 351 primary schools.
- There are 16 universities including Yokohama National University. The number of students is around 83,000.
- 19 public libraries had 9.5 million loans in 2016.[23]
International relations[edit]
Twin towns – sister cities[edit]
Yokohama is twinned with:[33]
Constanța, Constanța County, Romania (since October 1977)
Lyon, Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, France (since April 1959)
Manila, Philippines (since July 1965)
Mumbai, Maharashtra, India (since June 1965)
Odesa, Odesa Oblast, Ukraine (since July 1965)
San Diego, CA, United States (former partnership, October 1957–October 2021)
San Francisco, CA, United States (since October 2021)
Shanghai, China (since November 1973)
Vancouver, BC, Canada (since July 1965)
Partner cities[edit]
Abidjan, Ivory Coast
Beijing, China (since May 2006)
Brisbane, Queensland, Australia (since June 2008)
Busan, South Korea (since June 2006)
Frankfurt, Hesse, Germany (since September 2011)
Hanoi, Vietnam (since November 2007)
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam (since October 2007)
Incheon, South Korea (since December 2009)
Seberang Perai, Penang, Malaysia (since August 2016)[34]
Taipei, Taiwan (since May 2006)
Tel Aviv, Israel (since July 2012)
Tianjin, China (since May 2008)
Sister ports[edit]
Notable people[edit]
- Toru Furuya, singer and seiyū
- Yuma Kagiyama, figure skater
- Teiko Kiwa, Japanese-Dutch opera singer in the 1920s and 1930s
- Miki Koyama, racing driver
- Takehito Koyasu, singer and seiyū
- Ryuji Kumita, racing driver and CEO of B-Max Racing
- Keisuke Kunimoto, racing driver
- Yuji Kunimoto, racing driver
- Minoru Suzuki, professional wrestler
- Yuta Watanabe, NBA player for the Toronto Raptors.
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ «YOKOHAMA | Meaning & Definition for UK English | Lexico.com». En.oxforddictionaries.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- ^ Roberts, Toby; Williams, Ian; Preston, John (2021). «The Southampton system: A new universal standard approach for port-city classification». Maritime Policy & Management. 48 (4): 530–542. doi:10.1080/03088839.2020.1802785. S2CID 225502755.
- ^ «Memories of old Honmoku». The Japan Times. May 19, 1999. Archived from the original on April 15, 2021. Retrieved March 3, 2021.
- ^ «Yokohama City History, pg. 3» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on July 9, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- ^ Der Große Brockhaus. 16. edition. Vol. 6. F. A. Brockhaus, Wiesbaden 1955, p. 82
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website it is fresh». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 12, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ Arita, Erika, «Happy Birthday Yokohama! Archived August 31, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», The Japan Times, May 24, 2009, p. 7.
- ^ Fukue, Natsuko, «Chinese immigrants played vital role Archived August 24, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 28, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Matsutani, Minoru, «Yokohama – city on the cutting edge Archived August 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine», Japan Times, May 29, 2009, p. 3.
- ^ Galbraith, Michael (June 16, 2013). «Death threats sparked Japan’s first cricket game». Japan Times. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ a b «Interesting Tidbits of Yokohama». Yokohama Convention & Visitors Bureau. Archived from the original on May 5, 2009. Retrieved February 7, 2009.
- ^ Hammer, Joshua. (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II, p. 143. Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Hammer, pp. 149 Archived February 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine-170.
- ^ «Tsurumi River Multipurpose Retarding Basin». www.japanriver.or.jp. Archived from the original on September 26, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Collection of 1923 Japan earthquake massacre testimonies released». www.hani.co.kr. September 3, 2013. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 8, 2016.
- ^ «FNN Remembering 3/11: Yokohama station and surrounding areas at time of earthquake occurrence». www.fnn-news.com. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved January 10, 2016.
- ^ «Yokohama, Japan Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)». Weatherbase. Archived from the original on December 21, 2019. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information». world-guides.com. Archived from the original on April 30, 2012. Retrieved January 11, 2010.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 17, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ Japanese Imperial Commission (1878). Le Japon à l’exposition universelle de 1878. Géographie et histoire du Japon (in French).
- ^ 横浜市区別外国人登録人口(平成30年3月末現在). Archived from the original on March 11, 2017. Retrieved April 13, 2018.
- ^ «Webseite des Kulturzentrums». Archived from the original on April 17, 2021. Retrieved April 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c «Statistical Booklet Book of Yokohama 2018» (PDF). www.city.yokohama.lg.jp. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2018. Retrieved November 2, 2020.
- ^ Tagesthemen. Beitrag in der Nachrichtensendung der ARD, Moderation: Ingo Zamperoni, 30. November 2020, 35 Min. Eine Produktion von Das Erste
- ^ «Virtual Yokohama: Interactive Website Launched». Business Wire. April 28, 2022. Retrieved April 29, 2022.
- ^ «Nissan To Create New Global and Domestic Headquarters in Yokohama City by 2010». Japancorp.net. Archived from the original on September 14, 2007. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ «Yokohama GDP 2015». Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «Yokohama 2015 population» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on February 3, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2018.
- ^ «「平成28年度 横浜市の市民経済計算」がまとまりました。» (PDF). 横浜市. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 4, 2021. Retrieved March 24, 2021.
- ^ «Ports & World Trade». www.aapa-ports.org. Archived from the original on May 4, 2011. Retrieved July 3, 2014.
- ^ «Chinese Ports Lead the World in Berth Productivity, JOC Group Inc. Data Shows». Press Release. AXIO Data Group. JOC Inc. June 24, 2014. Archived from the original on April 6, 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2015.
- ^ «Official Yokohama city website». City.yokohama.jp. Archived from the original on June 19, 2010. Retrieved May 5, 2010.
- ^ «Yokohama’s Sister/Friendship Cities». city.yokohama.lg.jp. Yokohama. Archived from the original on February 3, 2021. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ «MPSP sets sights on city status». The Star. August 1, 2016. Archived from the original on July 5, 2018. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
Sources[edit]
- Hammer, Joshua (2006). Yokohama Burning: The Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II Archived June 23, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-7432-6465-5 (cloth).
- Heilbrun, Jacob. «Aftershocks» Archived January 15, 2018, at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times, September 17, 2006.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yokohama.
- Official Website (in Japanese)
- Yokohama Tourism Website (in English)
Geographic data related to Yokohama at OpenStreetMap
0
2 ответа:
1
0
Правильно по-русски говорить «Йокогама», у этого слова несколько значений. Это и город (название) в Японии, и компания, которая является одним из лидеров, по производству шин для автомобилей (выпускает и летние и зимние шины).
Сами японцы, между тем произносят как «Йокохама», через согласную «х».
Более подробно, можно и самим прослушать произношение Yokohama, тут.
1
0
Русский вариант названия этого города — Йокогама. В Британии и США, произносят Йокохама. Существуют также версии — Иокогама и Иокохама. Всё дело в произношении буквы Х (H), которая в разных транскрипциях и в разных традициях, пишется и произносится несколько по разному.
Йокогама, это крупнейший портовый город и административный центр префектуры Канагава в Японии.
Читайте также
На самом деле, право на существование имеют оба эти слова известного в России внедорожника, ведь есть даже свидетельства о регистрации транспортных средств, где в позиции «транспортные средства» обозначено как Рено Дустер, хотя по моему мнению, да и более созвучнее, будет все таки Дастер, ввиду того, что слово «duster» или пыльник, берет свое начало из английского языка, и, соответственно, буква «u» на языке страны туманного Альбиона звучит как «а».
Русский язык многогранен и стерпит оба оборота.
Однако, если разобраться с помощью логики, то «за» относится к местоположению, а «после» к моменту времени. Т.е. правильнее было бы сказать «после того, как проедете поворот», но мы же всегда торопимся и сокращаем, сокращаем. Однако, мы стараемся не говорить — «после двери», «после шкафа», а говорим «за дверью», подразумевая «в коридоре за дверью», «за шкафом», подразумевая — «между шкафом и стеной». Зато мы можем сказать «после поворота ключа», но правильнее было бы сказать «после того, как мы повернули ключ».
Так что правильно было бы сказать «за поворотом» и «после прохождения поворота».
Я родилась на дальнем востоке и не по наслышке знаю кету. Это рыба лососевых пород, но по мне она совсем не похожа на лосось и семгу — слишком сухая. Зато икра у нее хорошая. Правильно говорит кетА. По крайнем мере на дальнем востоке все говорят именно так. Столкнулась с другим произношением в Санкт-Петербурге.
Правильно следует говорить «Я покрасила волосы». Это слово в значении «весь обьем волос на голове, все волосы» употребляется во множественном числе в литературном русском языке. Слово «волос» в единственном числе может обозначать отдельно взятый волосок. Или это просторечие.
Существует правило, которое применимо в данном случае: в существительных, которые образованы от глагола, ударение ставится на то же слог, что и в глаголе.
В нашем случае слово образовано от глагола «обеспечить» с ударением на втором слоге. Соответственно, правильно поставить ударение в слове так — обеспЕчение (на второй слог).
Иокога́ма или Йокогама (яп. 横浜市 Ёкохама-си?) — крупнейший портовый город Японии, административный центр префектуры Канагава. Площадь города составляет 437,38 км²[1], население — 3 681 279 человек (1 июня 2010)[2], плотность населения — 8416,66 чел./км².
Город расположен в 30 километрах к юго-западу от Токио. Имеет сильную экономическую базу, представленную в основном морским транспортом, а также биотехнологической и полупроводниковой индустриями.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Население
- 3 География
- 4 Климат
- 5 Образование и наука
- 6 Города побратимы
- 7 Администрация
- 8 Примечания
- 9 См. также
- 10 Ссылки
История
Иностранные суда в бухте Йокогамы
Иностранный торговый дом в городе, 1861 г.
Город был основан в 1858 г., путем объединения двух небольших деревень — Иокогама и Канагава, жители которой занимались сельским хозяйством и рыболовством. Затем началось строительство порта, способного принять иностранные коммерческие суда.
В течение следующих двух десятилетий Иокогама стала одним из крупнейших портов японских островов, и в 1889 ее численность достигла 122 тысяч жителей. Значительным успехом в развитии городской инфраструктуры стало строительство водопровода (1887) и электрификация города (1890). Одним из самых драматических событий за всю историю города было мощное землетрясение в 1923 году, во время которого погибли около 20 тысяч. человек, лежало в руинах или сожжено 60 тысяч. зданий. Благодаря большим усилиям властей и жителей город был восстановлен к концу 1929 г.
В 1931 г., проводились работы по привозу сухой земли в устье реки Цуруми, на которой были построены впоследствии многие промышленные объекты. Город пережил драматический период во время американской бомбардировки в 1945, когда погибло более 14 тысяч человек и было разрушено около 80 тысяч. зданий.
3 апреля 1934 года в Иокогаме был подписан Протокол № 1 между лидером Российской фашистской партии К. В. Родзаевским и лидером Всероссийской фашистской организации А. А. Вонсяцким в котором провозглашалось слияние Р.Ф.П. и В.Ф.О. и создание Всероссийской фашистской партии (В.Ф.П.).
Население
Станция Иокогама
Вид ночью
Население
| Год переписи |
Население | Место среди городов Японии |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 422 942 | 6 |
| 1925 | 405 888 | 6 |
| 1930 | 620 306 | 6 |
| 1935 | 704 290 | 6 |
| 1940 | 968 091 | 5 |
| 1945 | 814 379 | 4 |
| 1950 | 951 189 | 4 |
| 1955 | 1 143 687 | 4 |
| 1960 | 1 375 710 | 3 |
| 1965 | 1 788 915 | 3 |
| 1970 | 2 238 264 | 3 |
| 1975 | 2 621 771 | 2 |
| 1980 | 2 773 674 | 2 |
| 1985 | 2 992 926 | 2 |
| 1990 | 3 220 331 | 2 |
| 1995 | 3 307 136 | 2 |
| 2000 | 3 426 651 | 2 |
| 2005 | 3 579 133 | 2 |
| 2009 | 3 670 669 | 2 |
География
Иокогама расположена на западном берегу Токийского залива, в 30-ти километрах от Токио, с которым она связана железными и шоссейными дорогами, а также улицами города Кавасаки.
Памятник в Парке Ямашита
Климат
Климат субтропический океанический, мягкий благодаря прибрежному расположению города. Средняя температура года 16-17 ° C; средняя температура в январе и августе, соответственно, 5,6 ° С и 26,4 ° С. Годовое количество осадков достигает 1 630 мм, а максимум приходится на июнь и сентябрь (соответственно 190 и 230 мм)[3].
Образование и наука
Национальный университет Иокогамы учреждён в 1949.
Города побратимы
Администрация
- Адрес: г. Иокогама, район Нака, Минато-тё 1-1
- Телефон: 045—671-2121
Примечания
- ↑ Площадь указывается по данным сайта Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (яп.) с учётом изменений, опубликованных 1 октября 2011 года.
- ↑ 神奈川県の人口と世帯 : 神奈川県 (яп.). Администрация префектуры Канагава (1 июня 2010). — Численность населения префектуры Канагава. Проверено 16 июля 2010.
- ↑ Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information. world-guides.com. Архивировано из первоисточника 26 июля 2012. Проверено 11 января 2010.
См. также
- Йокогамский женский марафон
Ссылки
На Викискладе есть медиафайлы по теме Иокогама
- Официальный сайт (яп.)
- ИОКОГАМА // Япония от А до Я. Популярная иллюстрированная энциклопедия. (CD-ROM). — М.: Directmedia Publishing, «Япония сегодня», 2008. — ISBN 978-5-94865-190-3
Содержание
- Йокогама
- См. также в других словарях:
- Йокогама
- См. также в других словарях:
Йокогама
1 Йокогама
2 Йокогама
3 Йокогама
4 Йокогама
См. также в других словарях:
йокогама — сущ., кол во синонимов: 2 • город (2765) • порт (361) Словарь синонимов ASIS. В.Н. Тришин. 2013 … Словарь синонимов
Йокогама — Город Иокогама яп. 横浜市 Флаг … Википедия
Йокогама — іменник жіночого роду місто в Японії … Орфографічний словник української мови
Йокогама — Йокохама, Иокогама (Yokohama), город и порт в Японии, на острове Хонсю, на побережье Токийского залива, в 30 км к юго западу от… … Города мира
Йокогама Ф. Маринос — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость 72 327 … Википедия
Йокогама Ф. Маринос (футбольный клуб) — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Йокогама Ф.Маринос — Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Йокогама Флюгелс — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Международный стадион (Йокогама) — Координаты: 35°30′36.16″ с. ш. 139°36′22.49″ в. д. / 35.510044° с. ш. 139.606247° в. д. … Википедия
Международный стадион Йокогама — Координаты: 35°30′36.16″ с. ш. 139°36′22.49″ в. д. / 35.510044° с. ш. 139.606247° в. д. … Википедия
Ниссан Йокогама (футбольный клуб) — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Источник
Йокогама
1 Yokohama
См. также в других словарях:
йокогама — сущ., кол во синонимов: 2 • город (2765) • порт (361) Словарь синонимов ASIS. В.Н. Тришин. 2013 … Словарь синонимов
Йокогама — Город Иокогама яп. 横浜市 Флаг … Википедия
Йокогама — іменник жіночого роду місто в Японії … Орфографічний словник української мови
Йокогама — Йокохама, Иокогама (Yokohama), город и порт в Японии, на острове Хонсю, на побережье Токийского залива, в 30 км к юго западу от… … Города мира
Йокогама Ф. Маринос — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость 72 327 … Википедия
Йокогама Ф. Маринос (футбольный клуб) — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Йокогама Ф.Маринос — Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Йокогама Флюгелс — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Международный стадион (Йокогама) — Координаты: 35°30′36.16″ с. ш. 139°36′22.49″ в. д. / 35.510044° с. ш. 139.606247° в. д. … Википедия
Международный стадион Йокогама — Координаты: 35°30′36.16″ с. ш. 139°36′22.49″ в. д. / 35.510044° с. ш. 139.606247° в. д. … Википедия
Ниссан Йокогама (футбольный клуб) — Йокогама Ф.Маринос Основан 1972 Стадион Ниссан Вместимость … Википедия
Источник
Иокога́ма, Йокоха́ма[4] (яп. 横浜市 Ёкохама-си) — крупнейший портовый город Японии, административный центр префектуры Канагава. Площадь города составляет 437,38 км²[5], население — 3 709 686 человек (1 августа 2014)[6], плотность населения — 8481,61 чел./км².
Название
Иокогама (横 浜) буквально означает «горизонтальный пляж»[7]. Нынешняя территория, окруженная парком Майта, рекой Зока и рекой Накамура, была заливом, отделённым песчаной отмелью от открытого моря. Эта песчаная отмель была рыбацкой деревней Иокогама. Так как песчаная полоса выступала перпендикулярно от земли, или горизонтально, если смотреть с моря, она называлась «горизонтальный пляж»[8].
Географическое положение
Иокогама расположена на западном берегу Токийского залива, в 30 километрах к юго-западу от Токио, с которым она связана железными и шоссейными дорогами, а также улицами города Кавасаки.
Климат
Климат субтропический океанический, мягкий благодаря прибрежному расположению города. Средняя температура года 16-17 °C; средняя температура в январе и августе соответственно 5,6 °С и 26,4 °С. Годовое количество осадков достигает 1630 мм, а максимум приходится на июнь и сентябрь (соответственно 190 и 230 мм)[9].
Для погодных условий Иокогамы характерны дожди, облака и солнце, хотя зимой на удивление солнечно. Зимние температуры редко опускаются ниже нуля, а лето может показаться довольно теплым из-за воздействия влажности[10]. Самая холодная температура была зафиксирована 24 января 1927 года, когда была достигнута температура −8,2 °C, тогда как в самый жаркий день (11 августа 2013 года) температура достигла 37,4 °C. Наибольшее месячное количество осадков было зафиксировано в октябре 2004 года — 761,5 мм.
История

Иностранные суда в бухте Иокогамы

Иностранный торговый дом в городе, 1861 г.
Город был основан в 1858 году путём объединения двух небольших деревень — Иокогама и Канагава, жители которой занимались сельским хозяйством и рыболовством. Затем началось строительство порта, способного принять иностранные коммерческие суда. Здесь возникло «международное поселение», где на правах экстерриториальности жили иностранцы. Оно располагалось в районах Каннай и Яматэ. Здесь даже сформировался своего рода контактный язык — иокогамско-японский пиджин (также известный, как «иокогамский диалект»), служивший для общения между иностранцами и японцами (исчез к 1910-м годам).
Благодаря тому, что Иокогама стала важнейшей точкой контактов между Японией и внешним миром, здесь впервые в Японии появились многие нововведения. В частности, в Иокогаме впервые в Японии стали выпекать хлеб (первоначально — для жителей «иностранного поселения»), в 1865 году здесь открылось первое в Японии кафе-мороженое, а в 1872 году Иокогама стала первым городом Японии, получившим газовое уличное освещение[11]. Также в 1872 году начала действовать первая в Японии железная дорога Токио-Иокогама.
В 1880 году здесь был создан банк «Yokohama Specie Bank» (в дальнейшем ставший одним из крупнейших банков Японской империи).
В течение следующих двух десятилетий Иокогама стала одним из крупнейших портов японских островов, и в 1889 году её численность достигла 122 тысяч жителей. Значительным успехом в развитии городской инфраструктуры стало строительство водопровода (1887) и электрификация города (1890). Одним из самых драматических событий за всю историю города было мощное землетрясение в 1923 году, во время которого погибли около 20 тысяч человек, лежало в руинах или сожжено 60 тысяч зданий. Три башни Иокогамы чудом уцелели. Благодаря большим усилиям властей и жителей город был восстановлен к концу 1929 года.
В 1931 году проводились работы по привозу сухой земли в устье реки Цуруми, на которой были построены впоследствии многие промышленные объекты.
3 апреля 1934 года в Иокогаме был подписан Протокол № 1 между лидером Российской фашистской партии К. В. Родзаевским и лидером Всероссийской фашистской организации А. А. Вонсяцким, в котором провозглашалось слияние Р. Ф. П. и В. Ф. О. и создание Всероссийской фашистской партии (В. Ф. П.).
Во время Второй мировой войны 18 апреля 1942 года в ходе «рейда Дулиттла» два бомбардировщика Б-25 ВВС США сбросили на Иокогаму первые бомбы, в 1945 году США осуществили несколько массированных бомбардировок Иокогамы, в результате которых город серьёзно пострадал[12], тогда погибло более 14 тысяч человек и было разрушено около 80 тысяч зданий.
В 1998 году здесь был открыт международный стадион, принявший в 2002 году финал чемпионата мира по футболу.
С 2009 года здесь проходит Иокогамский женский марафон.
Экономика
Иокогама является крупным торговым центром района Большого Токио. Город имеет сильную экономическую базу, представленную в основном морским транспортом, а также биотехнологической и полупроводниковой индустриями.
Является крупным центром судостроения, здесь находятся два крупных судостроительных предприятия, выполняющих военные заказы и принадлежащих компании Japan Marine United (JMU, «Джапан Марин Юнайтед»): «Цуруми кодзё» и «Исого кодзё»[13].
Образование и наука
Иокогамский государственный университет учреждён в 1949 году.
Государственные начальные и средние школы находятся в ведении города Иокогама. Существует девять государственных средних школ, которые находятся в ведении Совета по образованию города Иокогама[14], и ряд государственных средних школ, которые находятся в ведении Совета по образованию префектуры Канагава.
Культура и достопримечательности

Сад Санкей-эн
В Иокогаме сохранилось довольно много памятников архитектуры «европейского типа» начала XX века, являющихся свидетельством эпохи модернизации Японии и ее контактов с внешним миром. В бывшем «иностранным поселении» Яматэ сохранилось несколько особняков европейского типа (открыты для посещения), иностранное кладбище и две церкви, римско-католический Собор Святейшего Сердца Иисуса и англиканская Церковь Христа.
В центре города расположен Мемориальный зал открытия порта Иокогамы, построенный в европейском стиле в память о пятидесятилетии открытия порта Иокогамы. В районе старого порта, преобразованного в общественное пространство, сохранились так называемые «краснокирпичный склады» — портовые пакгаузы начала XX века.
Популярной достопримечательностью также является чайнатаун, который считается одним из самых больших чайнатаунов в мире. Несмотря на молодость города, в Иокогаме есть и традиционный японский сад Санкей-эн (основан в 1906 году).
В конце XX века в Иокогаме был создан деловой и туристический район Минато-Мирай 21, главной достопримечательностью которого является башня Yokohama Landmark Tower.
Важнейшие музеи города — Музей искусств Иокогамы и Префектурный музей культурной истории Канагавы. Помимо них в городе есть большое количество специализированных музеев, включая музей трамваев, музей шёлка, музей рамэна и другие. Исторический архив Иокогамы также имеет музейную экспозицию. В Иокогаме на вечную стоянку установлено два корабля-музея, учебный парусник Ниппон Мару и лайне Хикава-мару.
Население
Иокогама является вторым по величине городом в Японии по численности населения[15] и самым густонаселенным муниципалитетом Японии. Население города составляет 3 709 686 человек (1 августа 2014), а плотность — 8481,61 чел./км². Изменение численности населения с 1980 по 2005 годы[16]:

Станция Иокогама

Население
| Год переписи |
Население | Место среди городов Японии |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 422 942 | 6 |
| 1925 | 405 888 | 6 |
| 1930 | 620 306 | 6 |
| 1935 | 704 290 | 6 |
| 1940 | 968 091 | 5 |
| 1945 | 814 379 | 4 |
| 1950 | 951 189 | 4 |
| 1955 | 1 143 687 | 4 |
| 1960 | 1 375 710 | 3 |
| 1965 | 1 788 915 | 3 |
| 1970 | 2 238 264 | 3 |
| 1975 | 2 621 771 | 2 |
| 1980 | 2 773 674 | 2 |
| 1985 | 2 992 926 | 2 |
| 1990 | 3 220 331 | 2 |
| 1995 | 3 307 136 | 2 |
| 2000 | 3 426 651 | 2 |
| 2005 | 3 579 133 | 2 |
| 2009 | 3 670 669 | 2 |
| 2013 | 3 702 551[17] | 2 |
Иностранное население Иокогамы, насчитывающее 92 139 человек, включает китайцев, корейцев, филиппинцев и вьетнамцев[18].
Города-побратимы
Примечания
- ↑ 市長名|全国市長会 Japan Association of City Mayors|都市情報|市長名の検索結果. Дата обращения: 6 мая 2022. Архивировано 23 марта 2016 года. (яп.)
- ↑ 横浜市史資料室:「横浜市のあゆみ」略年表(chronological-table)
- ↑ http://www.geopostcodes.com/Kanagawa_ku
- ↑ Географический энциклопедический словарь: географические названия / Гл. ред. В. М. Котляков. — 3-е изд., доп. — М.: Большая российская энциклопедия, 2003. — С. 300. — 903 с. — 5000 экз. — ISBN 5-85270-216-1.
- ↑ Площадь указывается по данным сайта Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (яп.) с учётом изменений, опубликованных 1 октября 2011 года.
- ↑ 神奈川県人口統計調査結果平成26年8月1日現在 (яп.). Администрация префектуры Канагава (29 августа 2014). — Численность населения префектуры Канагава. Дата обращения: 29 августа 2014.
- ↑ Japan Times, meaning of «Yokohama» is mentioned Архивная копия от 15 апреля 2021 на Wayback Machine // japantimes.co.jp
- ↑ Yokohama City History Архивная копия от 9 июля 2018 на Wayback Machine, pg. 3 // rekihaku.city.yokohama.jp
- ↑ Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information. world-guides.com. Дата обращения: 11 января 2010. Архивировано 26 июля 2012 года.
- ↑ Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information. world-guides.com. Дата обращения: 11 января 2010. Архивировано 30 апреля 2012 года.
- ↑ Gvidlibro pri Jokohamo, havenurbo nova kaj malnova kaj Kamakura, ĉefurbo antikva. — Jokohamo: Mevo-libroj, 2005. — С. 78—79. — ISBN 4-88887-037-3.
- ↑ Иокогама // Большая Советская Энциклопедия. / редколл., гл. ред. Б. А. Введенский. 2-е изд. том 18. М., Государственное научное издательство «Большая Советская энциклопедия», 1953. стр.349
- ↑ Кошкин, Д. Судостроительная промышленность Японии (2017) // Зарубежное военное обозрение. — 2017. — № 12. — С. 60—67.
- ↑ Official Yokohama city website. City.yokohama.jp. Дата обращения: 5 мая 2010. Архивировано из оригинала 19 июня 2010 года.
- ↑ Yokohama Архивная копия от 1 апреля 2019 на Wayback Machine // oxforddictionaries.com
- ↑ Численность указывается по данным переписей населения Японии 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 и 2005 годов.
- ↑ Population News No.1046(Oct 1, 2013). Дата обращения: 14 октября 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 5 мая 2014 года.
- ↑ 横浜市区別外国人登録人口(平成30年3月末現在). Дата обращения: 13 апреля 2018. Архивировано 11 марта 2017 года.
Ссылки
На Викискладе есть медиафайлы по теме Иокогама
- Официальный сайт (яп.)
- Иокогама // Япония от А до Я. Популярная иллюстрированная энциклопедия. (CD-ROM). — М.: Directmedia Publishing, «Япония сегодня», 2008. — ISBN 978-5-94865-190-3.
Эта страница в последний раз была отредактирована 10 сентября 2022 в 19:35.
Как только страница обновилась в Википедии она обновляется в Вики 2.
Обычно почти сразу, изредка в течении часа.
Иокога́ма или Йокогама (яп. 横浜市 Ёкохама-си?) — крупнейший портовый город Японии, административный центр префектуры Канагава. Площадь города составляет 437,38 км²[1], население — 3 681 279 человек (1 июня 2010)[2], плотность населения — 8416,66 чел./км².
Город расположен в 30 километрах к юго-западу от Токио. Имеет сильную экономическую базу, представленную в основном морским транспортом, а также биотехнологической и полупроводниковой индустриями.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Население
- 3 География
- 4 Климат
- 5 Образование и наука
- 6 Города побратимы
- 7 Администрация
- 8 Примечания
- 9 См. также
- 10 Ссылки
История
Иностранные суда в бухте Йокогамы
Иностранный торговый дом в городе, 1861 г.
Город был основан в 1858 г., путем объединения двух небольших деревень — Иокогама и Канагава, жители которой занимались сельским хозяйством и рыболовством. Затем началось строительство порта, способного принять иностранные коммерческие суда.
В течение следующих двух десятилетий Иокогама стала одним из крупнейших портов японских островов, и в 1889 ее численность достигла 122 тысяч жителей. Значительным успехом в развитии городской инфраструктуры стало строительство водопровода (1887) и электрификация города (1890). Одним из самых драматических событий за всю историю города было мощное землетрясение в 1923 году, во время которого погибли около 20 тысяч. человек, лежало в руинах или сожжено 60 тысяч. зданий. Благодаря большим усилиям властей и жителей город был восстановлен к концу 1929 г.
В 1931 г., проводились работы по привозу сухой земли в устье реки Цуруми, на которой были построены впоследствии многие промышленные объекты. Город пережил драматический период во время американской бомбардировки в 1945, когда погибло более 14 тысяч человек и было разрушено около 80 тысяч. зданий.
3 апреля 1934 года в Иокогаме был подписан Протокол № 1 между лидером Российской фашистской партии К. В. Родзаевским и лидером Всероссийской фашистской организации А. А. Вонсяцким в котором провозглашалось слияние Р.Ф.П. и В.Ф.О. и создание Всероссийской фашистской партии (В.Ф.П.).
Население
Станция Иокогама
Вид ночью
| Год переписи |
Население | Место среди городов Японии |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 422 942 | 6 |
| 1925 | 405 888 | 6 |
| 1930 | 620 306 | 6 |
| 1935 | 704 290 | 6 |
| 1940 | 968 091 | 5 |
| 1945 | 814 379 | 4 |
| 1950 | 951 189 | 4 |
| 1955 | 1 143 687 | 4 |
| 1960 | 1 375 710 | 3 |
| 1965 | 1 788 915 | 3 |
| 1970 | 2 238 264 | 3 |
| 1975 | 2 621 771 | 2 |
| 1980 | 2 773 674 | 2 |
| 1985 | 2 992 926 | 2 |
| 1990 | 3 220 331 | 2 |
| 1995 | 3 307 136 | 2 |
| 2000 | 3 426 651 | 2 |
| 2005 | 3 579 133 | 2 |
| 2009 | 3 670 669 | 2 |
География
Иокогама расположена на западном берегу Токийского залива, в 30-ти километрах от Токио, с которым она связана железными и шоссейными дорогами, а также улицами города Кавасаки.
Памятник в Парке Ямашита
Климат
Климат субтропический океанический, мягкий благодаря прибрежному расположению города. Средняя температура года 16-17 ° C; средняя температура в январе и августе, соответственно, 5,6 ° С и 26,4 ° С. Годовое количество осадков достигает 1 630 мм, а максимум приходится на июнь и сентябрь (соответственно 190 и 230 мм)[3].
Образование и наука
Национальный университет Иокогамы учреждён в 1949.
Города побратимы
Администрация
- Адрес: г. Иокогама, район Нака, Минато-тё 1-1
- Телефон: 045—671-2121
Примечания
- ↑ Площадь указывается по данным сайта Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (яп.) с учётом изменений, опубликованных 1 октября 2011 года.
- ↑ 神奈川県の人口と世帯 : 神奈川県 (яп.). Администрация префектуры Канагава (1 июня 2010). — Численность населения префектуры Канагава. Проверено 16 июля 2010.
- ↑ Yokohama Weather, When to Go and Yokohama Climate Information. world-guides.com. Архивировано из первоисточника 26 июля 2012. Проверено 11 января 2010.
См. также
- Йокогамский женский марафон
Ссылки
На Викискладе есть медиафайлы по теме Иокогама
- Официальный сайт (яп.)
- ИОКОГАМА // Япония от А до Я. Популярная иллюстрированная энциклопедия. (CD-ROM). — М.: Directmedia Publishing, «Япония сегодня», 2008. — ISBN 978-5-94865-190-3
Указанный город в Канто, Япония
Указанный город в Канто, Япония
| Иокогама. 横 浜 市 | |
|---|---|
| Указанный город | |
| Город Иокогама | |
 Слева вверху: Минато Мираи 21, Чайнатаун Йокогама, Ниппон Мару, Станция Йокогама, Морская башня Йокогамы Слева вверху: Минато Мираи 21, Чайнатаун Йокогама, Ниппон Мару, Станция Йокогама, Морская башня Йокогамы |
|
 Флаг Флаг  Печать Печать |
|
 |
|
 Карта префектуры Канагава с Иокогамой, выделенной фиолетовым цветом Карта префектуры Канагава с Иокогамой, выделенной фиолетовым цветом |
|
 |
|
| Координаты: 35 ° 26 ′ 39 ″ с.ш., 139 ° 38’17 ″ в.д. / 35,44417 ° с.ш., 139,63806 ° в.д. / 35,44417; 139,63806 Координаты : 35 ° 26’39 ″ N 139 ° 38’17 ″ E / 35,44417 ° N 139,63806 ° E / 35,44417; 139.63806 | |
| Страна | |
| Регион | Канто |
| Префектура | Префектура Канагава |
| Правительство | |
| • Мэр | Фумико Хаяси |
| Площадь | |
| • Всего | 437,38 км (168,87 квадратных миль) |
| Население (1 октября 2016 г.) | |
| • Всего | 3,732,616 |
| • Плотность | 8,534,03 / км (22 103,0 / кв. Миль) |
| Часовой пояс | UTC + 9 (Стандартное время Японии ) |
| — Дерево | Камелия, Чинквапин, Сангоджу. Сасанква, Гинкго, Зелькова |
| — Цветок | Роза |
| Адрес | 1-1 Минато-чо, Нака-ку, Йокогама-ши, Канагава-кен. 231-0017 |
| Веб-сайт | www.city.yokohama.lg.jp |
| Йокогама | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| японское имя | |||
| Хирагана | よ こ は ま | ||
| Катакана | ヨ コ ハ マ | ||
| Кюдзитай | 橫濱 | ||
| Синдзитай | 横浜 | ||
|
|||
Иокогама (японский : 横浜, произносится (слушайте )) является второй по величине город в Японии по населению, и самый густонаселенный муниципалитет Японии. Это столица город префектуры Канагава. Он расположен в Токийском заливе, к югу от Токио, в Канто региона главного острова Хонсю. Это крупный торговый центр Большого Токио.
Иокогама быстро развивалась как выдающий портовый город после окончания относительной изоляции Японии в середине 19 века, и сегодня это один из его основных портов, а также Кобе, Осака, Нагоя, Фукуока, Токио и Тиба.
Содержание
- 1 Этимология
- 2 История
- 2.1 Открытие порта Договора (1859–1868)
- 2.2 Периоды Мэйдзи и Тайсё (1868–1923)
- 2.3 Великое землетрясение Канто и Вторая мировая война (1923–1923 гг.) 1945)
- 2.4 Рост после Второй мировой войны
- 3 География
- 3.1 Окружающие муниципалитеты
- 3.2 Климат
- 4 Демография
- 4.1 Историческое население
- 4.2 Районы
- 5 Правительство и политика
- 5.1 Список мэров Йокогамы ( с 1889 г.)
- 5.2 Международные отношения
- 6 Культура
- 6.1 Изображения города в популярных СМИ
- 6.2 Спорт
- 7 Экономика и инфраструктура
- 7.1 Транспорт
- 7.1.1 Морской транспорт
- 7.1.2 Железнодорожный транспорт
- 7.1.2.1 Железнодорожные вокзалы
- 7.1 Транспорт
- 8 Образование
- 9 Ссылки
- 9.1 Цитаты
- 9.2 Источники
- 10 Внешние ссылки
Этимология
Иокогама (横 浜) буквально означает «горизонтальный» пляж ». Нынешняя территория, окруженная парком Майта, рекой Чока и рекой Накамура, была заливом, отделенным от открытого моря песчаной косой. Эта отмель была оригинальной рыбацкой деревней Иокогамы. Песчаная отмель выступала перпендикулярно суше или горизонтально, если смотреть со стороны моря, ее называли «горизонтальным пляжем».
История
Открытие порта Договора (1859–1868)
Иокогама была небольшая рыбацкой деревушкой до конца феодального периода Эдо, когда Япония проводила политику национального уединения, почти не контактируя с иностранцами. Важный поворотный момент в истории Японии произошел в 1853–1854 годах, когда коммодор Мэтью Перри прибыл к югу от Иокогамы с флотом военных американских кораблей, потребовав, чтобы Япония открыла несколько портов для торговли, и Токугава. сёгунат согласился подписанием Договора о мире и дружбе.
Первоначально было решено, что одним из портов, которые будут открыты для иностранных судов, будет шумный город Канагава-дзюку (на территории округа Канагава ) на Токайдо, стратегическом шоссе, соединяющем Эдо с Киото и Осакой. Однако сёгунат Токугава решил, что Канагава-дзюку находится слишком близко к Токайдо, и вместо этого были построены портовые сооружения через залив в сонной рыбацкой деревне Иокогама. Порт Йокогама был официально открыт 2 июня 1859 года.
Иокогама быстро стала базой внешней торговли Японии. Первоначально иностранцы занимали низменный район города под названием Каннай, жилые районы позже расширялись по мере роста поселения и включали большую часть возвышенного района Ямате с видом на город, обычно называемого Англоговорящие жители как Утес.
Каннай, внешнеторговый и коммерческий район (буквально внутри заграждения), был окружен рвом, иностранные жители пользовались экстерриториальным статусом как внутри, так и за пределами комплекса. Взаимодействие с местным населением, особенно с молодыми самураями, за пределами поселения неизбежно создавало проблемы; Инцидент Намамуги, одно из событий, предшествовавших падению сёгуната, произошло в 1862 году на территории, что сейчас называется Цуруми, и послужило поводом для бомбардировки Кагосимы в 1863 году.
Для защиты британских коммерческих и дипломатических интересов в Иокогаме в 1862 году был основан военный гарнизон. С ростом торговли в город приезжало все больше китайцев. Иокогама была ареной многих заметных новшеств в Японии, включая растущее признание западной моды, фотографии пионеров, таких как Феличе Беато, первая русскоязычная газета Японии, вышедшая в 1865 году и в 1865 году первое мороженое и пиво будут производиться в Японии. Развлекательные виды спорта, привезенные в Японию иностранными жителями Иокогамы, включают европейский стиль скачки в 1862 году, крикет в 1863 году и союз регби в 1866 году. Большой пожар уничтожил многое. поселения за границей 26 ноября 1866 г. и оспа была периодической угрозой для здоровья населения, но город продолжал быстро расти, привлекая иностранцев и японцев.
- Галерея
Высадка коммодора Перри и людей для встречи с имперскими комиссарами в Иокогаме, 14 июля 1853 года.
Иностранные корабли в гавани Иокогамы
Иностранный торговый дом в Иокогаме в 1861 году
Периоды Мэйдзи и Тайсё (1868–1923 гг.)
После Реставрации Мэйдзи 1868 г. порт был разработан для торговли шелком, основным торговым партнером которого был Великобритания. Западное влияние и передача технологий способствовали первой в Японии ежедневной газеты (1870 г.), газовых уличных фонарей (1872 г.) и первой в Японии железной дороги, построенной в том же году, чтобы соединить Иокогаму с Синагавой. и Синбаши в Токио. В 1872 году Жюль Верн изобразил Иокогаму, который никогда не посещал, в эпизоде своего широко читаемого романа Вокруг света за восемьдесят дней, запечатлевая атмосферу быстро развивающейся международной жизни. ориентированный японский город.
В 1887 году британский купец Сэмюэл Кокинг построил первую в городе электростанцию . Сначала для его собственного использования эта угольная установка для сжигания угля стала использованием для Yokohama Cooperative Electric Light Company. Город был официально включен 1 апреля 1889 года. К тому времени, когда в 1899 году была отменена экстерриториальность иностранных территорий, Иокогама была самым интернациональным городом Японии, с иностранными территориями, простирающимися от Каннаи до Район Блафф и большой Чайнатаун Йокогамы.
Начало 20 века ознаменовалось бурным ростом промышленности. Предприниматели построили фабрики на мелиорированных землях к северу от города в сторону Кавасаки, которая в итоге превратилась в промышленную зону Кейхин. Японская промышленность обладает обширными услугами, в том числе специальными услугами для населения из Японии и Кореи также привел к образованию Кодзики-Ято, тогдашние трущобы в Японии.
- Галерея
Уличная сцена ок. 1880 г.
Отамати в эпоху Мэйдзи
Склад из красного кирпича в Йокогаме был построен в 1913 году
Великое землетрясение Канто и Вторая мировая война (1923–1945)
Большая часть Иокогамы была разрушена на 1 сентября 1923 года в результате Великого землетрясения Канто. Полиция Иокогамы сообщила о потерях в 30 771 человеке погибших и 47 908 раненых из 434 170 человек, проживавших до землетрясения. Подпитываемые слухами о восстании и саботаже, дружинники убили много корейцев в трущобах Кодзики-ято. Многие считали, что корейцы использовали черную магию, чтобы вызвать землетрясение. Военное положение действовало до 19 ноября. Обломки землетрясения использовались для восстановления земель под парки, самым известным из которых был парк Ямасита на набережной, который открылся в 1930 году.

Иокогама была восстановлена, но снова разрушена авианалётами США во время Второй мировой войны. Примерно семь или восемь тысяч человек были убиты за одно утро 29 мая 1945 года в результате того, что сейчас известно как Великий воздушный налет на Иокогаму, когда B-29 бомбили город и всего за один час девять минут превратили 42 % его в руины.
Рост после Второй мировой войны
Во время оккупации Йокогама была главной перевалочной базой для американских грузов и персонала, особенно во время Корейской войны. После оккупации большая часть местных военно-морских сил США переместилась из Иокогамы на американскую базу в соседнем Йокосука.
Город был обозначен постановлением правительства от 1 сентября 1956 года.
Городской трамвай и троллейбус были упразднены в 1972 году, в том же году, когда открылась первая линия муниципального метро Йокогамы.
Строительство Минато Мираи 21 («Port Future 21»), крупный городской проект развития на мелиорированных землях, стартовал в 1983 году. В 1989 году Minato Mirai 21 провела выставку Yokohama Exotic Showcase, на которой была впервые открыта общественная эксплуатация поездов на магнитной подвеске в Японии и открытие из Cosmo Clock 21, самого высокого колеса обозрения в мире. В том же году открылся мост через залив Йокогама длиной 860 м .
В 1993 году Минато Мираи увидел открытие Башни Йокогамы, второго по высоте здания в Японии.
Финал Чемпионата мира по футболу 2002 года проходил в июне на Международном стадионе Йокогамы.
В 2009 году город отметили 150-летие открытия и 120-летие начала деятельности городской администрации. Первой частью этого памятного проекта стала Четвертая Токийская международная конференция по развитию Африки (TICAD IV), которая прошла в Йокогаме в мае 2008 года.
В ноябре 2010 года в Иокогаме прошла конференция Встреча (АТЭС) Азиатско-Тихоокеанского экономического сотрудничества.
- Галерея
В 1951 году, во время Корейской войны, этот корабль ВМС США покинул Иокогаму, доставив погибших на войне в США.
Башня Йокогамы Лендмарк является самой высокой. небоскреб в Иокогаме (1993)
География

Окружающие муниципалитеты
Эти муниципалитеты окружают Иокогаму.
Префектура Канагава
- Кавасаки
- Йокосука
- Дзуси
- Камакура
- Фудзисава
- Ямато
Токио
- Мачида
Климат
Особенности Йокогамы: влажный субтропический климат (Кеппен : Cfa) с жарким и влажным летом и холодной зимой. С точки зрения погоды в Иокогаме есть картина дождя, облаков и солнца, хотя зимой здесь на удивление солнечно, больше, чем в Южной Испании. Зимние температуры редко опускаются ниже нуля, в то время как лето может довольно теплым из-за воздействия показ. Самая холодная температура была 24 января 1927 года, когда была достигнута температура -8,2 ° C (17,2 ° F), самым жарким днем было 11 августа 2013 года при 37,4 ° C (99,3 ° F)). Выпало 761,5 миллиметра (30,0 дюйма), за последовал июль 1941 года, когда выпало 753,4 миллиметра (29,66 дюйма), за последний месяц 1941 года. по три раза не было измеряемых осадков.
| Климатические данные для Иокогамы, Канагава (1981–2010 гг., За исключением записей) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Месяц | Янв | Фев | Мар | Апр | май | июн | июл | авг | сен | октябрь | ноя | Дек | Год |
| Рекордно высокий ° C (° F) | 20,8. (69,4) | 24, 8. (76,6) | 24,5. (76,1) | 28,7. (83,7) | 31,1. (88,0) | 35,5. (95,9) | 36,9. (98,4) | 37,4. (99,3) | 36,2. (97,2) | 30,9. (87,6) | 26,2. (79,2) | 23,5. (74,3) | 37,4. (99,3) |
| Средняя высокая ° C (° F) | 9,9. (49,8) | 10,3. (50,5) | 13, 2. (55,8) | 18,5. (65,3) | 22,4. (72,3) | 24, 9. (76,8) | 28,7. (83,7) | 30,6. (87,1) | 26,7. (80,1) | 21,5. (70,7) | 16,7. (62,1) | 12,4. (5 4,3) | 19,7. (67,5) |
| Среднесуточное значение ° C (° F) | 5.9. (42,6) | 6,2. (43,2) | 9,1. (48,4) | 14,2. (57,6) | 18,3. (64,9) | 21,3. (70,3) | 25,0. (77,0) | 26,7. (80,1) | 23,3. (73,9) | 18,0. (64, 4) | 13,0. (55,4) | 8,5. (47,3) | 15,8. (60, 4) |
| Средняя низкая ° C (° F) | 2,3. (36,1) | 2,6. (36,7) | 5,3. (41,5) | 10,4. (50,7) | 15,0. (59,0) | 18,6. (65,5) | 22,4. (72,3) | 24,0. (75,2) | 20,6. (69,1) | 15,0. (59,0) | 9,6. (49,3) | 4,9. (40,8) | 12,5. (54,5) |
| Запись низкого ° C (° F) | -8,2. (17,2) | -6,8. (19,8) | -4,6. (23,7) | -0,5. (31,1) | 3,6. (38,5) | 9,2. (48, 6) | 13,3. (55,9) | 15,5. (59,9) | 11,2. (52,2) | 2,2. (36,0) | −2,4. (27,7) | -5,6. (21,9) | -8,2. (17,2) |
| Среднее осаждение мм (дюймов) | 58,9. (2,32) | 67,5. (2,66) | 140, 7. (5,54) | 144,1. (5,67) | 152,2. (5,99) | 190,4. (7,50) | 168,9. (6,65) | 165,0. (6,50) | 233,8. (9,20) | 205,5. (8,09) | 107,0. (4,21) | 54,8. (2,16) | 1,688,8. (66,49) |
| Средний снегопад, см (дюйммы) | 5. (2,0) | 6. (2,4) | 1. (0,4) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 0. (0) | 12. (4.8) |
| Среднее количество дней с осадками (≥ 0,5 мм) | 6,0 | 6,7 | 11,8 | 11,1 | 11,5 | 13,6 | 11, 7 | 8,7 | 12,7 | 11,5 | 8,3 | 5,5 | 119,1 |
| Среднее количество снежных дней | 1,6 | 2,3 | 0, 7 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 4,9 |
| Средняя относительная влажность (%) | 53 | 54 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 78 | 78 | 76 | 76 | 71 | 64 | 56 | 67 |
| Среднемесячное значение количество солнечных часов | 186,4 | 164,0 | 159,5 | 175,2 | 177,1 | 131,7 | 162,9 | 206,3 | 130,7 | 141,0 | 149,3 | 180,4 | 1,964,4 |
| Источник 1: | |||||||||||||
| Источник 2: (записи) |
Демография
Историческое население



| Год. census | Население | Место среди городов Японии |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 422,942 | 6-е место после Кобе, Киото,. Нагоя, Осака и Токио |
| 1925 | 405,888 | 6-е место |
| 1930 | 620,306 | 6-й |
| 1935 | 704,290 | 6-й |
| 1940 | 968,091 | 5-й, превосходя Кобе |
| 1945 | 814,379 | 4-й, город правительство Токио., распущенное в 1943 г. |
| 1950 | 951,189 | 4-е место |
| 1955 | 1,143,687 | 4-е место |
| 1960 | 1,375,710 | 3-е место, превосходящее Киото |
| 1965 | 1788,915 | 3-е место |
| 1970 | 2,238,264 | 2-е место, превосходя Нагоя |
| 1975 | 2,621,771 | 2-е место |
| 1980 | 2,773,674 | 1-й, опередив Осака |
| 1985 | 2,992,926 | 1-й |
| 1990 | 3,220,331 | 1-й |
| 1995 | 3,307,136 | 1-й |
| 2000 | 3,426,651 | 1-й |
| 2005 г. | 3,579,133 | 1-й |
| 2010 | 3,670,669 | 1-й |
| 2015 | 3,710,824 | 1-й |
Иностранное население Иокогамы, насчитывающее 92,139 человек, включает китайцев, корейцы, филиппинцы и вьетнамцы.
палаты
В Йокогаме 18 палаты (ку):
| Районы Иокогамы | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Название места | Карта Иокогамы | |||||
| Рамадзи | Кандзи | Население | Площад ь суши в км | Поп. плотность
на км |
||
| 1 | Аоба-ку | 青葉 区 | 302,643 | 35,14 | 8,610 | 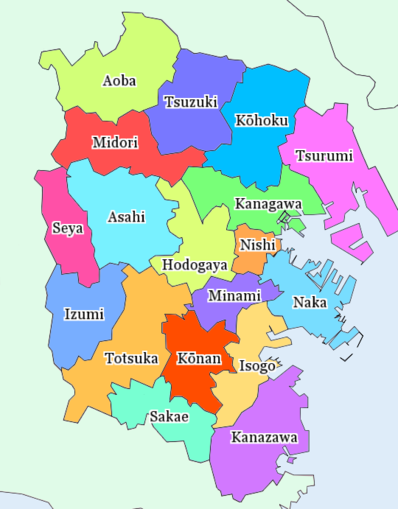 |
| 2 | Асахи-ку | 旭区 | 249,045 | 32,77 | 7,600 | |
| 3 | . Ходогая-ку | 保 土 ヶ 谷 区 | 205,887 | 21,81 | 9 400 | |
| 4 | Исого-ку | 磯 子 区 | 163,406 | 19,17 | 8,520 | |
| 5 | Идзуми-ку | 泉 区 | 155 674 | 23,51 | 6 620 | |
| 6 | Канагава-ку | 神奈川 区 | 230 401 | 23,88 | 9650 | |
| 7 | Канадзава-ку | 金 沢 区 | 209,565 | 31,01 | 6,760 | |
| 8 | Кохоку-ку | 港 北区 | 332,488 | 31,40 | 10,588 | |
| 9 | Конан-ку | 港 南 区 | 221,536 | 19,87 | 11,500 | |
| 10 | Мидори-ку | 緑 区 | 176,038 | 25,42 | 6,900 | |
| 11 | Минами-ку | 南 区 | 197 019 | 12,67 | 15 500 | |
| 12 | Нака-ку — (административный центр) | 中 区 | 146 563 | 20,86 | 7,030 | |
| 13 | Ниси-ку | 西区 | 93210 | 7,04 | 13,210 | |
| 14 | Сакаэ-ку | 栄 区 | 124,845 | 18,55 | 6,750 | |
| 15 | Сея-ку | 瀬 谷 区 | 126,839 | 17,11 | 7,390 | |
| 16 | Тоцука-ку | 戸 塚 区 | 274,783 | 35,70 | 7,697 | |
| 17 | Цуруми-ку | 鶴 見 区 | 270,433 | 33,23 | 8,140 | |
| 18 | Цузуки-ку | 都 筑 区 | 211,455 | 27,93 | 7,535 |
Правительство и политика
Муниципальная ассамблея Иокогамы из 92 членов, избранных из общего числа 18 подопечных. ЛДП контролирует меньшинство с 30 местами с Демократической партией Японии с почти 29. Мэр — Фумико Хаяси, сменивший Хироши Накада в сентябре 2009 г.
Список мэров Иокогамы (с 1889 г.)
|
|
|
Международные отношения

У Йокогамы есть побратим отношения с 13 городами по всему миру.
Бандунг, Индонезия
Себу, Филиппины
Констанца, Румыния
Чимботе, Перу
Лион, Франция
Манила, Филиппины
Мумбаи, Индия
Одесса, Украина
Сан-Диего, США
Себеранг Пераи, Малайзия
Шанхай, Китайская Народная Республика
Франкфурт, Германия
Абиджан, Кот-д’Ивуар
Ванкувер, Канада
Культура
Изображения города в популярных СМИ
- Роман Юкио Мисимы Моряк, упавший с моря с моря, действие происходит в основном в Иокогаме. Мисима порт города и его дома, а также влияние Запада, которое их сформировало.
- Сверху на Поппи-Хилл — это анимационный драматический фильм студии Ghibli, снятый Горо Миядзаки, 2011 года 125>расположен в районе Ямате Иокогамы. Фильм основан на сериализованном японском комиксе с одноименным названием.
- Основное действие книги Джеймса Клавелла Гай-Джин находится в исторической Иокогаме.
- Некоторые из событий манги Хитоши Ашинано Йокогама Кайдаси Кико разворачиваются в Иокогаме и его окрестности.
- Город Вермиллион в Канто регионе из франшизы Покемон основан на Йокогаме.
- Один из фильмов-кроссоверов Pretty Cure происходит в Иокогаме. В четвертом фильме серии, Pretty Cure All Stars New Stage: Friends of the Future, Pretty Cure появляется наверху Cosmo Clock 21 в Минато Мираи.
- . из японского визуального романа серия Мув-Лув, сначала школа, а затем в альтернативной истории, военная база строится в Иокогаме с целью выполнения Альтернативного плана IV предназначено для спасения человечества.
- В Command and Conquer: Red Alert 3 Иокогама находится в осаде Советского Союза и союзных наций, чтобы остановить Империю восходящего солнца. Игрок должен защищать Иокогаму, а затем возглавить контратаку, играя за Империю.
- Манга Бродячие псы Банго происходит в Иокогаме.
- Японский смешанный медиа-проект Хаматора происходит в Иокогаме.
- Финальная битва в Годзилла, Мотра и Король Гидора: Тотальная атака гигантских монстров происходит в Иокогаме.
- В Моя геройская академия, это место складов Ному, где они создали искусственных людей (также известные как Номус).
- Город Сумару в Персона 2: Невинный грех и Персона 2: Вечное наказание основан на Иокогаме.
- Город Мияби в Эффект Калигулы основан на Иокогаме, включая таких изображений, как недостроенная башня Landmark и Yokohama Hakkeijima Sea Paradise (в игре упоминается как Sea Paraiso).
- Видеоигра Якудза: Как дракон происходит в Исезаки Иджинчо, вымышленном районе в Иокогама на основе Исезакичо.
- Иокогама — это все так представлено в мультимедийном проекте King Records Hypnosis Mic: Division Rap Battle
Sports

- Soccer: Yokohama F. Marinos (J.League Division 1), Yokohama FC (J.League Division 1), YSCC Yokohama (J.League Division 3), (Nadeshiko League Div.2)
- Бейсбол: Йокогама Дена БэйСтарс
- Велодром: Велодром Кагецу-эн
- Баскетбол: Йокогама Би-Корсарс
- Теннис : Ай Сугияма
- американец футбол : Гавань Йокогамы
Экономика и инфраструктура
У города сильная экономическая база, особенно в судоходстве, биотехнологиях и полупроводниковая промышленность. Nissan переместил штаб-квартиру в Иокогаму из Тюо, Токио в 2010 году. ВВП на душу населения в Иокогаме (номинальный) составлял 30 625 долларов (1 доллар = 120,13).
Транспорт

Иокогама обслуживается высокоскоростной железнодорожной линией Токайдо Синкансэн с остановкой Станция Син-Йокогама. Станция Муниципальное метро Иокогама, Линия Минатомираи и Приморская линия Канадзава оказывает услуги метро.
. Йокогама также является крупной станцией, ежедневно обслуживающей два миллиона пассажиров.
Морской транспорт
Иокогама является 31-м крупнейшим морским портом в мире по общему объему грузов (121 326 тонн грузов по состоянию на 2011 г.) и 37-м местом по объему TEU (Двадцать — в футовом эквиваленте ).
в 2013 году APM Terminals в Йокогаме был признан самым производительным контейнерным терминалом в мире, в котором в среднем было 163 крана в час на судно между прибытием и отправлением судна у причала. 606>
Железнодорожный транспорт
Железнодорожные станции
- ■ Восточно-Японская жел езнодорожная компания
- ■ Основная линия Токайдо
- – Йокогама — Тоцука –
- ■ Линия Йокосука
- — Йокогама — Ходогая — Хигаси-Тоцука — Тоцука —
- ■ Линия Кейхин-Тохоку
- – Цуруми — Син-Коясу — Хигаси-Канагава — Йокогама
- ■ Линия Негиси
- Йокогама — Сакурагичо — Каннаи — Исикавачо — Ямате — Негиси — Исого — Син- Сугита — Ёкодай — Конандай — Хонгодай –
- ■ Линия Йокогама
- Хигаси-Канагава — Огучи — Кикуна — Син-Йокогама — Кодзукуэ — Камои — Накаяма — Токаичиба — Нагацута –
- ■ Линия Намбу
- – Яко –
- ■ Линия Цуруми
- Основная линия : Цуруми — Кокудо — Цуруми-Оно — Бентембаши — Асано — Анзен –
- Ветвь Уми-Шибаура : Асано — Шин-Шибаура — Уми-Шибаура
- ■ Центральный Дж. Железнодорожная компания апан
- ■ Токайдо Синкансэн
- — Син-Йокогама —
- ■ Кейкю
- ■ Основная линия Кейкю
- – Цуруми-Ичиба — Кейкю Цуруми — Кагецуен- маэ — Намамуги — Кейкю Син-Коясу — Коясу — Канагава-Синмачи — Нака-Кидо — Канагава — Йокогама — Тобе — Хинодечо — Коганечо — Минами-Ōta — Идогая — Гумиёдзи — Ками-Оока — Бёбугаура — Сугита — Кейкю Томиока — Нокендай — Канадзава-Бунко — Линия Канадзава-Хаккей –
- ■ Линия Кейкю Дзуси
- Канадзава-Хаккей — –
- ■ Корпорация Токю
- ■ Линия Тёёко
- – Хиёси — Цунашима — Окураяма — Кикуна — Мёрэндзи — Хакураку — Хигаси-Хакку — Таммачи — Йокогама
- ■ Линия Мэгуро
- — Хиёси
- ■ Линия Дэн-эн-тоши
- – Тама-Плаза — Азамино — Эда — Ичигао — Фудзигаока — Аобадай — Тана — Нагацута —
- ■ Линия Кодомонокуни
- Нагацута — Онда — Кодомонокуни
- ■ Железная дорога Сагами
- ■ Железнодорожная магистраль Сагами
- Иокогама — Хиранумабаси — Ниси-Йокогама — Теннучо — Хосикава — Вадамачи — Камихосикава — Нишия — Цуругамине — Футаматагава — Кибогаока — Мицукё — Сэя –
- ■ Линия Идзумино
- Футаматагава — Минами-Макигахара — Рёкуэнтоши — Яёдай — Идзумино — Изуми-тюо — Юмегаока
- ■ Йокогама, Минатомирайская железная дорога
- ■ Линия Минатомираи
- Иокогама — Син -Такашима — Минато Мираи — Башамичи — Нихон-Одори — Мотомачи-Чукагай
- ■ Городское транспортное бюро Йокогамы
- ■ Синяя линия
- – Симойида — Татеба — Накада — О дориба — Тоцука — Майока — Шимонагая — Каминагая — Кона н-Тюо — Ками-Оока — Гумиёдзи — Майта — Йошиночо — Бандобаши — Исезакичёджамачи — Каннай — Сакурагичо — Такашимачо — Йогама — Мицзава-симочо — Мицзава-камичо — Катакурачо — Кишин-Коэн — Син-Йокогама — Кита Син-Йокогама — Ниппа — Накаматидай — Центр Минами — Центр Кита — Накагава — Азамино
- ■ Зеленая линия
- Накаяма — Кававачо — Цузуки-Фуреай-но-Ока — Центр Минами — Центр Кита — Кита-Ямата — Хигаси-Ямата — Таката — Хиёси-Хенчо — Хиёси
- ■ Йокогама Новый Транзит
- ■ Приморская линия Канадзавы
- Син-Сугита — Намбу -Шидзё — Торихама — Намики-Кита — Намики-Тюо — Сачиура — Сангё-Синко-Центр — Фуку ур а — Сидай-Игакубу — Хаккейдзима — Уминокоэн-Сибагути — Уминокен -Минамигучи — Ноджимакэн — Канадзава-Хаккей
Образование
Государственные начальные и средние школы находятся в ведении города Иокогама. Есть девять государственных средних школ, которыми управляет Городской совет по образованию Иокогамы, и ряд государственных средних школ, которые находятся в ведении Совета по образованию префектуры Канагава. Йокогамский национальный университет — ведущий университет в Иокогаме, который также является одним из самых популярных национальных университетов Японии.
Ссылки
Цитаты
Источники
Внешние ссылки
| На Викискладе есть средства массовой информации, связанные с Yokohama. |
- Официальный сайт (на японском языке)
- Туристический веб-сайт Йокогамы (на английском языке)
Географические данные, относящиеся к Иокогаме в OpenStreetMap