Пишется «мигрень» или «мегрень»
Чтобы узнать как пишется то или иное слово, необходимо определить какой частью речи оно является. Далее найти правило русского языка, которое определяет правописание необходимого слова. С этим мы сейчас вам поможем.
Правильно писать:
«МИГРЕНЬ»
По какому правилу проверить слово «мигрень»
Непроверяемые безударные гласные в корне слова
Данное правило гласит:
Правописание непроверяемых безударных гласных в корне слова нужно запоминать.
Неправильно писать
«МЕГРЕНЬ»
Употребление слова в цитатах «мигрень»
Отделаться от навязанной ей компании юной баронессе удалось, лишь сославшись на внезапную мигрень.
Классическая мигрень – болевому спазму предшествует аура, которая характеризирует-ся непонятными слуховыми, вкусовыми или обонятельными ощущениями, помутнение зрения («блёстки» или «туман» перед глазами), нарушением чувствительности рук.
У меня предчувствие: то, что меня мучает этим утром, это не обычная мигрень, не банальный ревматизм.
Как правильно пишется «мигрень»?
правильно
мигрень
неправильно
ме
грень
Непроверяемые безударные гласные в корне слова
Правописание непроверяемых безударных гласных в корне слова нужно запоминать.
Пример
Октябрь, хризантема.
В случае затруднения обращайтесь к орфографическому словарю.
УМК под редакцией Т. А. Ладыженской, 5 класс.
Проверить правописание любого слова
Результаты поиска
Слово/Фраза
Правило
мигрень Непроверяемые безударные гласные в корне слова
Непроверяемые безударные гласные в корне слова
Записи 1-1 из 1
Смотри также слово «мигрень» в Викисловаре.
Русский[править]
Морфологические и синтаксические свойства[править]
| падеж | ед. ч. | мн. ч. |
|---|---|---|
| Им. | мигре́нь | мигре́ни |
| Р. | мигре́ни | мигре́ней |
| Д. | мигре́ни | мигре́ням |
| В. | мигре́нь | мигре́ни |
| Тв. | мигре́нью | мигре́нями |
| Пр. | мигре́ни | мигре́нях |
ми—гре́нь
Существительное, неодушевлённое, женский род, 3-е склонение (тип склонения 8a по классификации А. А. Зализняка).
Корень: -мигрень- [Тихонов, 1996].
Произношение[править]
- МФА: ед. ч. [mʲɪˈɡrʲenʲ], мн. ч. [mʲɪˈɡrʲenʲɪ]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- мед. неврологическое заболевание, наиболее частым и характерным симптомом которого являются эпизодические или регулярные сильные и мучительные приступы головной боли в одной (редко обеих) половине головы ◆ — Да, у ней ужасно голова болит, — промолвила Марья Дмитриевна, обращаясь к Варваре Павловне и закатывая глаза. — У меня самой такие бывают мигрени… Скажите! — возразила Варвара Павловна. И. С. Тургенев, «Дворянское гнездо», 1859 г. [НКРЯ] ◆ Он кашлял и страдал мигренью, вообще казался болезненным и слабеньким. А. П. Чехов, «Рассказ неизвестного человека», 1893 г. [НКРЯ] ◆ Рвущие мозг мигрени, доводившие почти до помешательства. Сколько она проглотила пирамидона, фенацетина, кофеина! И только незадолго до смерти выяснилось, что мигрени вызывались скрытою малярией, не разгаданною врачами. В. В. Вересаев, «Euthymia (Эйтемия)», 1943 г. [НКРЯ] ◆ Существуют исторические факты, свидетельствующие, что мигрень преследует человечество уже по крайней мере 7 тыс. лет, однако она всё ещё остается одним из самых загадочных и непризнанных недугов. Многие люди не обращаются за медицинской помощью, считая, что доктора не смогут облегчить их страдания или же проявят по отношению к ним недоверие и враждебность. Раньше мигрень считали сосудистым расстройством, однако новые исследования показали её нейробиологическую природу. Возможно, причина коренится в нарушении функционирования ствола мозга. «Умный журнал для умных людей », 2008 г. // «Наука и жизнь» [НКРЯ]
Синонимы[править]
- гемикрания
Антонимы[править]
- —
Гиперонимы[править]
- болезнь, заболевание
Гипонимы[править]
- —
Родственные слова[править]
| Ближайшее родство | |
|
Этимология[править]
Происходит от франц. migraine «гемикрания, мигрень», искаж. лат. hemicrania, далее из др.-греч. ἡμικρανία «гемикрания», далее из ἡμι «полу-», из праиндоевр. *semi-, + κρανίον «череп», далее из праиндоевр. *ker-.
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
- мигрень Хортона
Перевод[править]
| Список переводов | |
|
Библиография[править]
Башкирский[править]
Морфологические и синтаксические свойства[править]
мигрень
Существительное.
Корень: —.
Произношение[править]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- мед. мигрень (аналогично русскому слову) ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
Антонимы[править]
Гиперонимы[править]
Гипонимы[править]
Родственные слова[править]
| Ближайшее родство | |
Этимология[править]
От франц. migraine «гемикрания, мигрень», искаж. лат. hemicrania, далее из др.-греч. ἡμικρανία «гемикрания», далее из ἡμι «полу-», из праиндоевр. *semi-, + κρανίον «череп», далее из праиндоевр. *ker-.
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
Марийский[править]
Морфологические и синтаксические свойства[править]
мигрень
Существительное.
Корень: —.
Произношение[править]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- мед. мигрень (аналогично русскому слову) ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
Антонимы[править]
Гиперонимы[править]
Гипонимы[править]
Родственные слова[править]
| Ближайшее родство | |
Этимология[править]
От франц. migraine «гемикрания, мигрень», искаж. лат. hemicrania, далее из др.-греч. ἡμικρανία «гемикрания», далее из ἡμι «полу-», из праиндоевр. *semi-, + κρανίον «череп», далее из праиндоевр. *ker-.
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
Таджикский[править]
Морфологические и синтаксические свойства[править]
мигрень
Существительное.
Корень: —.
Произношение[править]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- мед. мигрень (аналогично русскому слову) ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
Антонимы[править]
Гиперонимы[править]
Гипонимы[править]
Родственные слова[править]
| Ближайшее родство | |
Этимология[править]
От франц. migraine «гемикрания, мигрень», искаж. лат. hemicrania, далее из др.-греч. ἡμικρανία «гемикрания», далее из ἡμι «полу-», из праиндоевр. *semi-, + κρανίον «череп», далее из праиндоевр. *ker-.
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
Татарский[править]
Морфологические и синтаксические свойства[править]
мигрень
Существительное.
Корень: —.
Произношение[править]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- мед. мигрень (аналогично русскому слову) ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
Антонимы[править]
Гиперонимы[править]
Гипонимы[править]
Родственные слова[править]
| Ближайшее родство | |
Этимология[править]
От франц. migraine «гемикрания, мигрень», искаж. лат. hemicrania, далее из др.-греч. ἡμικρανία «гемикрания», далее из ἡμι «полу-», из праиндоевр. *semi-, + κρανίον «череп», далее из праиндоевр. *ker-.
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
Якутский[править]
Морфологические и синтаксические свойства[править]
мигрень
Существительное.
Корень: —.
Произношение[править]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- мед. мигрень (аналогично русскому слову) ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
Антонимы[править]
Гиперонимы[править]
Гипонимы[править]
Родственные слова[править]
| Ближайшее родство | |
Этимология[править]
От франц. migraine «гемикрания, мигрень», искаж. лат. hemicrania, далее из др.-греч. ἡμικρανία «гемикрания», далее из ἡμι «полу-», из праиндоевр. *semi-, + κρανίον «череп», далее из праиндоевр. *ker-.
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
| Migraine | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Woman with migraine headache | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Headaches, nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, and smell[1][2] |
| Usual onset | Around puberty[1] |
| Duration | Recurrent, long term[1] |
| Causes | Environmental and genetic[3] |
| Risk factors | Family history, female[4][5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Subarachnoid hemorrhage, venous thrombosis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, brain tumor, tension headache, sinusitis,[6] cluster headache[7] |
| Prevention | Metoprolol, valproate, topiramate[8][9] |
| Medication | Ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), triptans, ergotamines[5][10] |
| Prevalence | ~15%[11] |
Migraine (, )[12][13] is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches.[1] Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hours to three days.[1] Non-headache symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell.[2] The pain is generally made worse by physical activity during an attack,[14] although regular physical exercise may prevent future attacks.[15] Up to one-third of people affected have aura: typically, it is a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur.[14] Occasionally, aura can occur with little or no headache following, but not everyone has this symptom.[16]
Migraine is believed to be due to a mixture of environmental and genetic factors.[3] About two-thirds of cases run in families.[5] Changing hormone levels may also play a role, as migraine affects slightly more boys than girls before puberty and two to three times more women than men.[4][17] The risk of migraine usually decreases during pregnancy and after menopause.[4][18] The underlying mechanisms are not fully known.[18] They are, however, believed to involve the nerves and blood vessels of the brain.[5]
Initial recommended treatment is with simple pain medication such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) for the headache, medication for the nausea, and the avoidance of triggers.[10] Specific medications such as triptans or ergotamines may be used in those for whom simple pain medications are not effective.[5] Caffeine in combination with other analgesics is safe and effective in treatment of acute migraine.[19][20][21] A number of medications are useful to prevent attacks including metoprolol, valproate, and topiramate.[8][9]
Globally, approximately 15% of people are affected by migraine.[11] In the Global Burden of Disease Study of 2010, it was ranked as the third most prevalent disorder in the world.[22] It most often starts at puberty and is worst during middle age.[1] As of 2016, it is one of the most common causes of disability.[23] An early description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BC in ancient Egypt.[24] The word migraine is from the Greek ἡμικρᾱνίᾱ (hēmikrāníā), ‘pain in half of the head’,[25] from ἡμι- (hēmi-), ‘half’ and κρᾱνίον (krāníon), ‘skull’.[26]
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Migraine typically presents with self-limited, recurrent severe headache associated with autonomic symptoms.[5][27] About 15–30% of people living with migraine experience episodes with aura,[10][28] and they also frequently experience episodes without aura.[29] The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks are variable.[5] A migraine attack lasting longer than 72 hours is termed status migrainosus.[30] There are four possible phases to a migraine attack, although not all the phases are necessarily experienced:[14]
- The prodrome, which occurs hours or days before the headache
- The aura, which immediately precedes the headache
- The pain phase, also known as headache phase
- The postdrome, the effects experienced following the end of a migraine attack
Migraine is associated with major depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. These psychiatric disorders are approximately 2–5 times more common in people without aura, and 3–10 times more common in people with aura.[31]
Prodrome phase[edit]
Prodromal or premonitory symptoms occur in about 60% of those with migraines,[2][32] with an onset that can range from two hours to two days before the start of pain or the aura.[33] These symptoms may include a wide variety of phenomena,[34] including altered mood, irritability, depression or euphoria, fatigue, craving for certain food(s), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), constipation or diarrhea, and sensitivity to smells or noise.[32] This may occur in those with either migraine with aura or migraine without aura.[35] Neuroimaging indicates the limbic system and hypothalamus as the origin of prodromal symptoms in migraine.[36]
Aura phase[edit]
Aura is a transient focal neurological phenomenon that occurs before or during the headache.[2] Aura appears gradually over a number of minutes (usually occurring over 5–60 minutes) and generally lasts less than 60 minutes.[37][38] Symptoms can be visual, sensory or motoric in nature, and many people experience more than one.[39] Visual effects occur most frequently: they occur in up to 99% of cases and in more than 50% of cases are not accompanied by sensory or motor effects.[39]
Visual disturbances often consist of a scintillating scotoma (an area of partial alteration in the field of vision which flickers and may interfere with a person’s ability to read or drive).[2] These typically start near the center of vision and then spread out to the sides with zigzagging lines which have been described as looking like fortifications or walls of a castle.[39] Usually the lines are in black and white but some people also see colored lines.[39] Some people lose part of their field of vision known as hemianopsia while others experience blurring.[39]
Sensory aura are the second most common type; they occur in 30–40% of people with auras.[39] Often a feeling of pins-and-needles begins on one side in the hand and arm and spreads to the nose–mouth area on the same side.[39] Numbness usually occurs after the tingling has passed with a loss of position sense.[39] Other symptoms of the aura phase can include speech or language disturbances, world spinning, and less commonly motor problems.[39] Motor symptoms indicate that this is a hemiplegic migraine, and weakness often lasts longer than one hour unlike other auras.[39] Auditory hallucinations or delusions have also been described.[40]
Pain phase[edit]
Classically the headache is unilateral, throbbing, and moderate to severe in intensity.[37] It usually comes on gradually[37] and is aggravated by physical activity during a migraine attack.[14] However, the effects of physical activity on migraine are complex, and some researchers have concluded that, while exercise can trigger migraine attacks, regular exercise may have a prophylactic effect and decrease frequency of attacks.[15] The feeling of pulsating pain is not in phase with the pulse.[41] In more than 40% of cases, however, the pain may be bilateral (both sides of the head), and neck pain is commonly associated with it.[42] Bilateral pain is particularly common in those who have migraine without aura.[2] Less commonly pain may occur primarily in the back or top of the head.[2] The pain usually lasts 4 to 72 hours in adults;[37] however, in young children frequently lasts less than 1 hour.[43] The frequency of attacks is variable, from a few in a lifetime to several a week, with the average being about one a month.[44][45]
The pain is frequently accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to smells, fatigue and irritability.[2] Many thus seek a dark and quiet room.[46] In a basilar migraine, a migraine with neurological symptoms related to the brain stem or with neurological symptoms on both sides of the body,[47] common effects include a sense of the world spinning, light-headedness, and confusion.[2] Nausea occurs in almost 90% of people, and vomiting occurs in about one-third.[46] Other symptoms may include blurred vision, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, frequent urination, pallor, or sweating.[48] Swelling or tenderness of the scalp may occur as can neck stiffness.[48] Associated symptoms are less common in the elderly.[49]
Silent migraine[edit]
Sometimes, aura occurs without a subsequent headache.[39] This is known in modern classification as a typical aura without headache, or acephalgic migraine in previous classification, or commonly as a silent migraine.[50][51] However, silent migraine can still produce debilitating symptoms, with visual disturbance, vision loss in half of both eyes, alterations in color perception, and other sensory problems, like sensitivity to light, sound, and odors, and aura sudden outbreak without headache can be scary.[52] It can last from 15 to 30 minutes, usually no longer than 60 minutes, and it can recur or appear as an isolated event.[51]
Postdrome[edit]
The migraine postdrome could be defined as that constellation of symptoms occurring once the acute headache has settled.[53] Many report a sore feeling in the area where the migraine was, and some report impaired thinking for a few days after the headache has passed. The person may feel tired or «hung over» and have head pain, cognitive difficulties, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood changes, and weakness.[54] According to one summary, «Some people feel unusually refreshed or euphoric after an attack, whereas others note depression and malaise.»[55] For some individuals this can vary each time.
Cause[edit]
The underlying causes of migraines are unknown.[56] However, they are believed to be related to a mix of environmental and genetic factors.[3] They run in families in about two-thirds of cases[5] and rarely occur due to a single gene defect.[57] While migraines were once believed to be more common in those of high intelligence, this does not appear to be true.[58] A number of psychological conditions are associated, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder,[59] as are many biological events or triggers.
Genetics[edit]
Studies of twins indicate a 34% to 51% genetic influence of likelihood to develop migraine.[3] This genetic relationship is stronger for migraine with aura than for migraines without aura.[29] A number of specific variants of genes increase the risk by a small to moderate amount.[57]
Single gene disorders that result in migraines are rare.[57] One of these is known as familial hemiplegic migraine, a type of migraine with aura, which is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.[60][61] Four genes have been shown to be involved in familial hemiplegic migraine.[62] Three of these genes are involved in ion transport.[62] The fourth is an axonal protein associated with the exocytosis complex.[62] Another genetic disorder associated with migraine is CADASIL syndrome or cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy.[2] One meta-analysis found a protective effect from angiotensin converting enzyme polymorphisms on migraine.[63] The TRPM8 gene, which codes for a cation channel, has been linked to migraines.[64]
Triggers[edit]
Migraine may be induced by triggers, with some reporting it as an influence in a minority of cases[5] and others the majority.[65] Many things such as fatigue, certain foods, alcohol, and weather have been labeled as triggers; however, the strength and significance of these relationships are uncertain.[65][66] Most people with migraines report experiencing triggers.[67] Symptoms may start up to 24 hours after a trigger.[5]
Physiological aspects[edit]
Common triggers quoted are stress, hunger, and fatigue (these equally contribute to tension headaches).[65] Psychological stress has been reported as a factor by 50 to 80% of people.[68] Migraine has also been associated with post-traumatic stress disorder and abuse.[69] Migraine episodes are more likely to occur around menstruation.[68] Other hormonal influences, such as menarche, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause, also play a role.[70] These hormonal influences seem to play a greater role in migraine without aura.[58] Migraine episodes typically do not occur during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, or following menopause.[2]
Dietary aspects[edit]
Between 12 and 60% of people report foods as triggers.[71][72]
There are many reports[73][74][75][76][77] that tyramine – which is naturally present in chocolate, alcoholic beverages, most cheeses, processed meats, and other foods – can trigger migraine symptoms in some individuals. Likewise, monosodium glutamate (MSG) is frequently reported as a trigger for migraine symptoms.[78]
Environmental aspects[edit]
A 2009 review on potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded that while there were insufficient studies to confirm environmental factors as causing migraine, «migraineurs worldwide consistently report similar environmental triggers».[79] The article suggests that people living with migraine take some preventive measures related to indoor air quality and lighting.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Migraine is believed to be primarily a neurological disorder,[80][81][82] while others believe it to be a neurovascular disorder with blood vessels playing the key role, although current evidence does not support this completely.[83][84][85][86] Others believe both are likely important.[87][88][89][90] One theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex and abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.[91]
Aura[edit]
Cortical spreading depression, or spreading depression according to Leão, is a burst of neuronal activity followed by a period of inactivity, which is seen in those with migraines with aura.[92] There are a number of explanations for its occurrence, including activation of NMDA receptors leading to calcium entering the cell.[92] After the burst of activity, the blood flow to the cerebral cortex in the area affected is decreased for two to six hours.[92] It is believed that when depolarization travels down the underside of the brain, nerves that sense pain in the head and neck are triggered.[92]
Pain[edit]
The exact mechanism of the head pain which occurs during a migraine episode is unknown.[93] Some evidence supports a primary role for central nervous system structures (such as the brainstem and diencephalon),[94] while other data support the role of peripheral activation (such as via the sensory nerves that surround blood vessels of the head and neck).[93] The potential candidate vessels include dural arteries, pial arteries and extracranial arteries such as those of the scalp.[93] The role of vasodilatation of the extracranial arteries, in particular, is believed to be significant.[95]
Neuromodulators[edit]
Adenosine, a neuromodulator, may be involved.[96] Released after the progressive cleavage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine acts on adenosine receptors to put the body and brain in a low activity state by dilating blood vessels and slowing the heart rate, such as before and during the early stages of sleep. Adenosine levels have been found to be high during migraine attacks.[96][97] Caffeine’s role as an inhibitor of adenosine may explain its effect in reducing migraine.[98] Low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), are also believed to be involved.[99]
Calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as levels of it become elevated during an attack.[10][41]
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of a migraine is based on signs and symptoms.[5] Neuroimaging tests are not necessary to diagnose migraine, but may be used to find other causes of headaches in those whose examination and history do not confirm a migraine diagnosis.[100] It is believed that a substantial number of people with the condition remain undiagnosed.[5]
The diagnosis of migraine without aura, according to the International Headache Society, can be made according to the following criteria, the «5, 4, 3, 2, 1 criteria»:[14]
- Five or more attacks—for migraine with aura, two attacks are sufficient for diagnosis.
- Four hours to three days in duration
- Two or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affecting one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- One or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia)
If someone experiences two of the following: photophobia, nausea, or inability to work or study for a day, the diagnosis is more likely.[101] In those with four out of five of the following: pulsating headache, duration of 4–72 hours, pain on one side of the head, nausea, or symptoms that interfere with the person’s life, the probability that this is a migraine attack is 92%.[10] In those with fewer than three of these symptoms, the probability is 17%.[10]
Classification[edit]
Migraine was first comprehensively classified in 1988.[29] The International Headache Society updated their classification of headaches in 2004.[14] A third version was published in 2018.[102] According to this classification, migraine is a primary headache disorder along with tension-type headaches and cluster headaches, among others.[103]
Migraine is divided into seven subclasses (some of which include further subdivisions):
- Migraine without aura, or «common migraine», involves migraine headaches that are not accompanied by aura.
- Migraine with aura, or «classic migraine», usually involves migraine headaches accompanied by aura. Less commonly, aura can occur without a headache, or with a nonmigraine headache. Two other varieties are familial hemiplegic migraine and sporadic hemiplegic migraine, in which a person has migraine with aura and with accompanying motor weakness. If a close relative has had the same condition, it is called «familial», otherwise it is called «sporadic». Another variety is basilar-type migraine, where a headache and aura are accompanied by difficulty speaking, world spinning, ringing in ears, or a number of other brainstem-related symptoms, but not motor weakness. This type was initially believed to be due to spasms of the basilar artery, the artery that supplies the brainstem. Now that this mechanism is not believed to be primary, the symptomatic term migraine with brainstem aura (MBA) is preferred.[47]
- Childhood periodic syndromes that are commonly precursors of migraine include cyclical vomiting (occasional intense periods of vomiting), abdominal migraine (abdominal pain, usually accompanied by nausea), and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (occasional attacks of vertigo).
- Retinal migraine involves migraine headaches accompanied by visual disturbances or even temporary blindness in one eye.
- Complications of migraine describe migraine headaches and/or auras that are unusually long or unusually frequent, or associated with a seizure or brain lesion.
- Probable migraine describes conditions that have some characteristics of migraines, but where there is not enough evidence to diagnose it as a migraine with certainty (in the presence of concurrent medication overuse).
- Chronic migraine is a complication of migraines, and is a headache that fulfills diagnostic criteria for migraine headache and occurs for a greater time interval. Specifically, greater or equal to 15 days/month for longer than 3 months.[104]
Abdominal migraine[edit]
The diagnosis of abdominal migraine is controversial.[105] Some evidence indicates that recurrent episodes of abdominal pain in the absence of a headache may be a type of migraine[105][106] or are at least a precursor to migraines.[29] These episodes of pain may or may not follow a migraine-like prodrome and typically last minutes to hours.[105] They often occur in those with either a personal or family history of typical migraine.[105] Other syndromes that are believed to be precursors include cyclical vomiting syndrome and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood.[29]
Differential diagnosis[edit]
Other conditions that can cause similar symptoms to a migraine headache include temporal arteritis, cluster headaches, acute glaucoma, meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage.[10] Temporal arteritis typically occurs in people over 50 years old and presents with tenderness over the temple, cluster headache presents with one-sided nose stuffiness, tears and severe pain around the orbits, acute glaucoma is associated with vision problems, meningitis with fevers, and subarachnoid hemorrhage with a very fast onset.[10] Tension headaches typically occur on both sides, are not pounding, and are less disabling.[10]
Those with stable headaches that meet criteria for migraines should not receive neuroimaging to look for other intracranial disease.[107][108][109] This requires that other concerning findings such as papilledema (swelling of the optic disc) are not present. People with migraines are not at an increased risk of having another cause for severe headaches.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive treatments of migraine include medications, nutritional supplements, lifestyle alterations, and surgery. Prevention is recommended in those who have headaches more than two days a week, cannot tolerate the medications used to treat acute attacks, or those with severe attacks that are not easily controlled.[10] Recommended lifestyle changes include stopping tobacco use and reducing behaviors that interfere with sleep.[110]
The goal is to reduce the frequency, painfulness, and duration of migraine episodes, and to increase the effectiveness of abortive therapy.[111] Another reason for prevention is to avoid medication overuse headache. This is a common problem and can result in chronic daily headache.[112][113]
Medication[edit]
Preventive migraine medications are considered effective if they reduce the frequency or severity of the migraine attacks by at least 50%.[114] Due to few medications being approved specifically for the preventative treatment of migraine headaches; many medications such as beta-blockers, anticonvulsive agents such as topiramate or sodium valproate, antidepressants such as amitriptyline and calcium channel blockers such as flunarizine are used off label for the preventative treatment of migraine headaches.[38] Guidelines are fairly consistent in rating the anticonvulsants topiramate and divalproex/sodium valproate, and the beta blockers propranolol and metoprolol as having the highest level of evidence for first-line use for migraine prophylaxis in adults.[115][116] Propranolol and topiramate have the best evidence in children; however, evidence only supports short-term benefit as of 2020.[110][117]
The beta blocker timolol is also effective for migraine prevention and in reducing migraine attack frequency and severity.[115] While beta blockers are often used for first-line treatment, other antihypertensives also have a proven efficiency in migraine prevention, namely the calcium channel blocker verapamil[118] and the angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan.[119][120]
Tentative evidence also supports the use of magnesium supplementation.[121] Increasing dietary intake may be better.[122] Recommendations regarding effectiveness varied for the anticonvulsants gabapentin and pregabalin. Frovatriptan is effective for prevention of menstrual migraine.[115]
The antidepressants amitriptyline and venlafaxine are probably also effective.[123] Angiotensin inhibition by either an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist may reduce attacks.[124]
Medications in the anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide, including eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab, appear to decrease the frequency of migraines by one to two per month.[125] They are, however, expensive: a year of erenumab costs $6,900 as of 2019.[126]
Alternative therapies[edit]
Acupuncture has a small effect in reducing migraine frequency, compared to sham acupuncture, a practice where needles are placed randomly or do not penetrate the skin.[127] Physiotherapy, massage and relaxation, and chiropractic manipulation might be as effective as propranolol or topiramate in the prevention of migraine headaches; however, the research had some problems with methodology.[128][129] Another review, however, found evidence to support spinal manipulation to be poor and insufficient to support its use.[130]
Tentative evidence supports the use of stress reduction techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques.[68] Regular physical exercise may decrease the frequency.[15] Numerous psychological approaches have been developed that are aimed at preventing or reducing the frequency of migraine in adults including educational approaches, relaxation techniques, assistance in developing coping strategies, strategies to change the way one thinks of a migraine attack, and strategies to reduce symptoms.[131] The medical evidence supporting the effectiveness of these types of psychological approaches is very limited.[131]
Among alternative medicines, butterbur has the best evidence for its use.[132][133] However, unprocessed butterbur contains chemicals called pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) which can cause liver damage, however there are versions that are PA free.[134] In addition, butterbur may cause allergic reactions in people who are sensitive to plants such as ragweed.[135] There is tentative evidence that coenzyme Q10 reduces migraine frequency.[136]
Feverfew has traditionally been used as a treatment for fever, headache and migraine, women’s conditions such as difficulties in labour and regulation of menstruation, relief of stomach ache, toothache and insect bites. During the last decades, it has mainly been used for headache and as a preventive treatment for migraine.[137] The plant parts used for medicinal use are the dried leaves or the dried aerial parts. Several historical data supports feverfew’s traditional medicinal uses.[138] In addition, several clinical studies have been performed assessing the efficacy and safety of feverfew monotherapy in the prevention of migraine.[139] The majority of the clinical trials favoured feverfew over placebo. The data also suggest that feverfew is associated with only mild and transient adverse effects. The frequency of migraine was positively affected after treatment with feverfew. Reduction of migraine severity was also reported after intake of feverfew and incidence of nausea and vomiting decreased significantly. No effect of feverfew was reported in one study.[139]
There is tentative evidence for melatonin as an add-on therapy for prevention and treatment of migraine.[140][141] The data on melatonin are mixed and certain studies have had negative results.[140] The reasons for the mixed findings are unclear but may stem from differences in study design and dosage.[140] Melatonin’s possible mechanisms of action in migraine are not completely clear, but may include improved sleep, direct action on melatonin receptors in the brain, and anti-inflammatory properties.[140][142]
Devices and surgery[edit]
Medical devices, such as biofeedback and neurostimulators, have some advantages in migraine prevention, mainly when common anti-migraine medications are contraindicated or in case of medication overuse. Biofeedback helps people be conscious of some physiological parameters so as to control them and try to relax and may be efficient for migraine treatment.[143][144] Neurostimulation uses noninvasive or implantable neurostimulators similar to pacemakers for the treatment of intractable chronic migraine with encouraging results for severe cases.[145][146] A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator and a transcranial magnetic stimulator are approved in the United States for the prevention of migraines.[147][148] There is also tentative evidence for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation decreases the frequency of migraines.[149] Migraine surgery, which involves decompression of certain nerves around the head and neck, may be an option in certain people who do not improve with medications.[150]
Management[edit]
There are three main aspects of treatment: trigger avoidance, acute symptomatic control, and medication for prevention.[5] Medications are more effective if used earlier in an attack.[5] The frequent use of medications may result in medication overuse headache, in which the headaches become more severe and more frequent.[14] This may occur with triptans, ergotamines, and analgesics, especially opioid analgesics.[14] Due to these concerns simple analgesics are recommended to be used less than three days per week at most.[151]
Analgesics[edit]
Recommended initial treatment for those with mild to moderate symptoms are simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or the combination of paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen), aspirin, and caffeine.[10] Several NSAIDs, including diclofenac and ibuprofen have evidence to support their use.[152][153] Aspirin (900 to 1000 mg) can relieve moderate to severe migraine pain, with an effectiveness similar to sumatriptan.[154] Ketorolac is available in intravenous and intramuscular formulations.[10]
Paracetamol, either alone or in combination with metoclopramide, is another effective treatment with a low risk of adverse effects.[155] Intravenous metoclopramide is also effective by itself.[156][157] In pregnancy, paracetamol and metoclopramide are deemed safe as are NSAIDs until the third trimester.[10]
Naproxen by itself may not be effective as a stand-alone medicine to stop a migraine headache as it is only weakly better than a placebo medication in clinical trials.[158]
Antiemetics[edit]
Triptans[edit]
Triptans such as sumatriptan are medications used to stop an active migraine headache (an abortive medication). Triptans are the initially recommended treatments for those with moderate to severe pain from an acute migraine headache or those with milder symptoms who do not respond to simple analgesics.[10] Triptans have been shown to be effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people.[159][160] There are different methods or routes of administration to take sumatriptan including oral (by mouth), injectable (subcutaneous), rectal, nasal spray, and oral dissolving tablets.[5][161][162][163] For people with migraine symptoms such as nausea or vomiting, taking the abortive medicine by mouth or through the nose may be difficult. All route of administration have been shown to be effective at reducing migraine symptoms, however, nasal and injectable subcutaneous administration may result in more side effects.[163][162] The adverse effects associated with rectal administration have not been well studied.[161] Some people may find that they respond to one type of sumatriptan better than another.[10]
Most side effects are mild, including flushing; however, rare cases of myocardial ischemia have occurred.[5] They are thus not recommended for people with cardiovascular disease,[10] who have had a stroke, or have migraines that are accompanied by neurological problems.[164] In addition, triptans should be prescribed with caution for those with risk factors for vascular disease.[164] While historically not recommended in those with basilar migraines there is no specific evidence of harm from their use in this population to support this caution.[47] Triptans are not addictive, but may cause medication-overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.[165]
Sumatriptan does not prevent other migraine headaches from starting in the future.[162] For increased effectiveness at stopping migraine symptoms, a combined therapy that includes sumatriptan and naproxen may be suggested.[166]
CGRP receptor antagonists[edit]
CGRP receptor antagonists target calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor to prevent migraine headaches or reduce their severity.[38] CGRP is a signaling molecule as well as a potent vasodilator that is involved in the development of a migraine headache.[38] There are four injectable monoclonal antibodies that target CGRP or its receptor (eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab and galcanezumab) and the medications have demonstrated efficacy in the preventative treatment of episodic and chronic migraine headaches in phase 3 randomized clinical trials.[38] Eptinezumab is available as an infusion every three months, Erenumab and galcanezumab are once monthly injections and fremanezumab is a monthly or quarterly injection.
Ergotamines[edit]
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms.[5][167] They appear equally effective to the triptans[168] and experience adverse effects that typically are benign.[169] In the most severe cases, such as those with status migrainosus, they appear to be the most effective treatment option.[169] They can cause vasospasm including coronary vasospasm and are contraindicated in people with coronary artery disease.[170]
Magnesium[edit]
Magnesium is recognized as an inexpensive, over-the-counter supplement which can be part of a multimodal approach to migraine reduction. Some studies have shown to be effective in both preventing and treating migraine in intravenous form.[171] The intravenous form reduces attacks as measured in approximately 15-45 minutes, 120 minutes, and 24 hour time periods, magnesium taken orally alleviates the frequency and intensity of migraines.[172][173]
Other[edit]
Intravenous metoclopramide, intravenous prochlorperazine, or intranasal lidocaine are other potential options.[10][157] Metoclopramide or prochlorperazine are the recommended treatment for those who present to the emergency department.[10][157] Haloperidol may also be useful in this group.[157][167] A single dose of intravenous dexamethasone, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours.[174] Spinal manipulation for treating an ongoing migraine headache is not supported by evidence.[130] It is recommended that opioids and barbiturates not be used due to questionable efficacy, addictive potential, and the risk of rebound headache.[10][38] There is tentative evidence that propofol may be useful if other measures are not effective.[175]
Occipital nerve stimulation, may be effective but has the downsides of being cost-expensive and has a significant amount of complications.[176]
There is modest evidence for the effectiveness of non-invasive neuromodulatory devices, behavioral therapies and acupuncture in the treatment of migraine headaches.[38] There is little to no evidence for the effectiveness of physical therapy, chiropractic manipulation and dietary approaches to the treatment of migraine headaches.[38] Behavioral treatment of migraine headaches may be helpful for those who may not be able to take medications (for example pregnant women).[38]
Feverfew is registered as a traditional herbal medicine in the Nordic countries under the brand name Glitinum, only powdered feverfew is approved in the Herbal community monograph issued by European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Sexual activity, particularly orgasm, may provide relief for some migraineurs.[177]
Children[edit]
Ibuprofen helps decrease pain in children with migraines and is the initially recommended treatment.[178][179] Paracetamol does not appear to be effective in providing pain relief.[178] Triptans are effective, though there is a risk of causing minor side effects like taste disturbance, nasal symptoms, dizziness, fatigue, low energy, nausea, or vomiting.[178][180] Ibuprofen should be used less than half the days in a month and triptans less than a third of the days in a month to decrease the risk of medication overuse headache.[179]
Chronic migraine[edit]
Topiramate and botulinum toxin (Botox) have evidence in treating chronic migraine.[123][181] Botulinum toxin has been found to be useful in those with chronic migraine but not those with episodic ones.[182][183] The anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody erenumab was found in one study to decrease chronic migraines by 2.4 days more than placebo.[184]
Prognosis[edit]
«Migraine exists on a continuum of different attack frequencies and associated levels of disability.»[185] For those with occasional, episodic migraine, a «proper combination of drugs for prevention and treatment of migraine attacks» can limit the disease’s impact on patients’ personal and professional lives.[186] But fewer than half of people with migraine seek medical care and more than half go undiagnosed and undertreated.[187] «Responsive prevention and treatment of migraine is incredibly important» because evidence shows «an increased sensitivity after each successive attack, eventually leading to chronic daily migraine in some individuals.»[186] Repeated migraine results in «reorganization of brain circuitry,» causing «profound functional as well as structural changes in the brain.»[188] «One of the most important problems in clinical migraine is the progression from an intermittent, self-limited inconvenience to a life-changing disorder of chronic pain, sensory amplification, and autonomic and affective disruption. This progression, sometimes termed chronification in the migraine literature, is common, affecting 3% of migraineurs in a given year, such that 8% of migraineurs have chronic migraine in any given year.» Brain imagery reveals that the electrophysiological changes seen during an attack become permanent in people with chronic migraine; «thus, from an electrophysiological point of view, chronic migraine indeed resembles a never-ending migraine attack.»[188] Severe migraine ranks in the highest category of disability, according to the World Health Organization, which uses objective metrics to determine disability burden for the authoritative annual Global Burden of Disease report. The report classifies severe migraine alongside severe depression, active psychosis, quadriplegia, and terminal-stage cancer.[189]
Migraine with aura appears to be a risk factor for ischemic stroke[190] doubling the risk.[191] Being a young adult, being female, using hormonal birth control, and smoking further increases this risk.[190] There also appears to be an association with cervical artery dissection.[192] Migraine without aura does not appear to be a factor.[193] The relationship with heart problems is inconclusive with a single study supporting an association.[190] Migraine does not appear to increase the risk of death from stroke or heart disease.[194] Preventative therapy of migraines in those with migraine with aura may prevent associated strokes.[195] People with migraine, particularly women, may develop higher than average numbers of white matter brain lesions of unclear significance.[196]
Epidemiology[edit]
Disability-adjusted life year for migraines per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004
no data
<45
45–65
65–85
85–105
105–125
125–145
145–165
165–185
185–205
205–225
225–245
>245
Worldwide, migraine affects nearly 15% or approximately one billion people.[11] It is more common in women at 19% than men at 11%.[11] In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women experience a migraine attack in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively.[5] In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives with about 6–15% of adult men and 14–35% of adult women getting at least one yearly.[17] Rates of migraine are slightly lower in Asia and Africa than in Western countries.[58][197] Chronic migraine occurs in approximately 1.4 to 2.2% of the population.[198]
These figures vary substantially with age: onset of migraine is most commonly between 15 and 24 years of age, and occur most frequently in those 35 to 45 years of age.[5] In children, about 1.7% of 7 year olds and 3.9% of those between 7 and 15 experience migraine, with the condition being slightly more common in boys before puberty.[199] Children as young as two years may be affected.[178] During adolescence, migraine becomes more common among women[199] and this persists for the rest of the lifespan, being twice as common among elderly females than males.[200] In women migraine without aura are more common than migraine with aura; however in men the two types occur with similar frequency.[58]
During perimenopause symptoms often get worse before decreasing in severity.[200] While symptoms resolve in about two thirds of the elderly, in 3 to 10% they persist.[49]
History[edit]
The Head Ache, George Cruikshank (1819)
An early description consistent with migraine is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BCE in ancient Egypt.[24] In 200 BCE, writings from the Hippocratic school of medicine described the visual aura that can precede the headache and a partial relief occurring through vomiting.[201]
A second-century description by Aretaeus of Cappadocia divided headaches into three types: cephalalgia, cephalea, and heterocrania.[202] Galen of Pergamon used the term hemicrania (half-head), from which the word migraine was eventually derived.[202] He also proposed that the pain arose from the meninges and blood vessels of the head.[201] Migraine was first divided into the two now used types – migraine with aura (migraine ophthalmique) and migraine without aura (migraine vulgaire) in 1887 by Louis Hyacinthe Thomas, a French Librarian.[201] The mystical visions of Hildegard von Bingen, which she described as “reflections of the living light», are consistent with the visual aura experienced during migraines.[203]
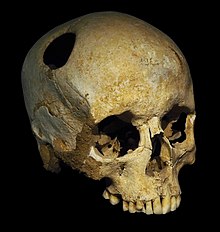
A trepanated skull, from the Neolithic. The perimeter of the hole in the skull is rounded off by ingrowth of new bony tissue, indicating that the person survived the operation.
Trepanation, the deliberate drilling of holes into a skull, was practiced as early as 7,000 BCE.[24] While sometimes people survived, many would have died from the procedure due to infection.[204] It was believed to work via «letting evil spirits escape».[205] William Harvey recommended trepanation as a treatment for migraines in the 17th century.[206] The association between trepanation and headaches in ancient history may simply be a myth or unfounded speculation that originated several centuries later. In 1913, the world-famous American physician William Osler misinterpreted the French anthropologist and physician Paul Broca ’s words about a set of children’s skulls from the Neolithic age that he found during the 1870s. These skulls presented no evident signs of fractures that could justify this complex surgery for mere medical reasons. Trepanation was probably born of superstitions, to remove “confined demons” inside the head, or to create healing or fortune talismans with the bone fragments removed from the skulls of the patients. However, Osler wanted to make Broca’s theory more palatable to his modern audiences, and explained that trepanation procedures were used for mild conditions such as “infantile convulsions headache and various cerebral diseases believed to be caused by confined demons.”[207]
While many treatments for migraine have been attempted, it was not until 1868 that use of a substance which eventually turned out to be effective began.[201] This substance was the fungus ergot from which ergotamine was isolated in 1918.[208] Methysergide was developed in 1959 and the first triptan, sumatriptan, was developed in 1988.[208] During the 20th century with better study-design, effective preventive measures were found and confirmed.[201]
Society and culture[edit]
Migraine is a significant source of both medical costs and lost productivity. It has been estimated that migraine is the most costly neurological disorder in the European Community, costing more than €27 billion per year.[209] In the United States, direct costs have been estimated at $17 billion, while indirect costs — such as missed or decreased ability to work — is estimated at $15 billion.[210] Nearly a tenth of the direct cost is due to the cost of triptans.[210] In those who do attend work during a migraine attack, effectiveness is decreased by around a third.[209] Negative impacts also frequently occur for a person’s family.[209]
Research[edit]
Potential prevention mechanisms[edit]
Transcranial magnetic stimulation shows promise[10][211] as does transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation.[212] There is preliminary evidence that a ketogenic diet may help prevent episodic and long-term migraine.[213][214]
Potential gender dependency[edit]
While no definitive proof has been found linking migraine to gender, statistical data indicates that women may be more prone to having migraine, showing migraine incidence three times higher among women than men.[215][216] The Society for Women’s Health Research has also mentioned hormonal influences, mainly estrogen, as having a considerable role in provoking migraine pain. Studies and research related to the gender dependencies of migraine are still ongoing, and conclusions have yet to be achieved.[217][218][219]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f «Headache disorders Fact sheet N°277». October 2012. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Simon RP, Aminoff MJ, Greenberg DA (2009). Clinical neurology (7 ed.). New York, N.Y: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. pp. 85–88. ISBN 9780071664332.
- ^ a b c d Piane M, Lulli P, Farinelli I, Simeoni S, De Filippis S, Patacchioli FR, Martelletti P (December 2007). «Genetics of migraine and pharmacogenomics: some considerations». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 8 (6): 334–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-007-0427-2. PMC 2779399. PMID 18058067.
- ^ a b c Lay CL, Broner SW (May 2009). «Migraine in women». Neurologic Clinics. 27 (2): 503–11. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2009.01.002. PMID 19289228.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Bartleson JD, Cutrer FM (May 2010). «Migraine update. Diagnosis and treatment». Minnesota Medicine. 93 (5): 36–41. PMID 20572569.
- ^ Olesen J (2006). The Headaches. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 424. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ «Cluster Headache». American Migraine Foundation. 15 February 2017. Archived from the original on 9 May 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ a b Armstrong C (April 2013). «AAN/AHS update recommendations for migraine prevention in adults». American Family Physician. 87 (8): 584–5. PMID 23668450.
- ^ a b Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). «Valproate (valproic acid or sodium valproate or a combination of the two) for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD010611. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010611. PMID 23797677.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Gilmore B, Michael M (February 2011). «Treatment of acute migraine headache». American Family Physician. 83 (3): 271–80. PMID 21302868.
- ^ a b c d Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. (December 2012). «Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010». Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMC 6350784. PMID 23245607.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (2011). Roach, Peter; Setter, Jane; Esling, John (eds.). Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-15255-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004). «The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition». Cephalalgia. 24 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1): 9–160. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00653.x. PMID 14979299. as PDF Archived 31 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, Czapinska-Ciepiela EK, Ariadni DD, Di Lenola D, et al. (September 2018). «The association between migraine and physical exercise». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y. PMC 6134860. PMID 30203180.
- ^ Pryse-Phillips W (2003). Companion to clinical neurology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford university press. p. 587. ISBN 9780195159387. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Stovner LJ, Zwart JA, Hagen K, Terwindt GM, Pascual J (April 2006). «Epidemiology of headache in Europe». European Journal of Neurology. 13 (4): 333–45. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01184.x. PMID 16643310. S2CID 7490176.
- ^ a b «NINDS Migraine Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 3 November 2015. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ Nowaczewska M, Wiciński M, Kaźmierczak W (July 2020). «The Ambiguous Role of Caffeine in Migraine Headache: From Trigger to Treatment». Nutrients. 12 (8): 2259. doi:10.3390/nu12082259. PMC 7468766. PMID 32731623.
- ^ Shapiro RE, Cowan R (2017-01-10). «Caffeine and Migraine». American Migraine Foundation. Retrieved 2021-06-08.
- ^ Diener HC, Charles A, Goadsby PJ, Holle D (October 2015). «New therapeutic approaches for the prevention and treatment of migraine». The Lancet. Neurology. 14 (10): 1010–22. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00198-2. PMID 26376968. S2CID 26523013.
- ^ Gobel H. «1. Migraine». ICHD-3 The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- ^ Vos, Theo; et al. (GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (September 2017). «Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016». Lancet. 390 (10100): 1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. PMC 5605509. PMID 28919117.
- ^ a b c Miller N (2005). Walsh and Hoyt’s clinical neuro-ophthalmology (6 ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1275. ISBN 9780781748117. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ Liddell HG, Scott R. «ἡμικρανία». A Greek-English Lexicon. Archived from the original on 8 November 2013. on Perseus
- ^ Anderson K, Anderson LE, Glanze WD (1994). Mosby’s Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary (4 ed.). Mosby. p. 998. ISBN 978-0-8151-6111-0.
- ^ Bigal ME, Lipton RB (June 2008). «The prognosis of migraine». Current Opinion in Neurology. 21 (3): 301–8. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328300c6f5. PMID 18451714. S2CID 34805084.
- ^ Gutman SA (2008). Quick reference neuroscience for rehabilitation professionals: the essential neurologic principles underlying rehabilitation practice (2 ed.). Thorofare, NJ: SLACK. p. 231. ISBN 9781556428005. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ a b c d e The Headaches, Pg 232–233
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 512. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Baskin SM, Lipchik GL, Smitherman TA (October 2006). «Mood and anxiety disorders in chronic headache». Headache. 46 Suppl 3: S76-87. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00559.x. PMID 17034402. S2CID 35451906.
- ^ a b Lynn DJ, Newton HB, Rae-Grant A (2004). The 5-minute neurology consult. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 26. ISBN 9780683307238. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Buzzi MG, Cologno D, Formisano R, Rossi P (October–December 2005). «Prodromes and the early phase of the migraine attack: therapeutic relevance». Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 179–83. PMID 16483458.
- ^ Rossi P, Ambrosini A, Buzzi MG (October–December 2005). «Prodromes and predictors of migraine attack». Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 185–91. PMID 16483459.
- ^ Ropper AH, Adams RD, Victor M, Samuels MA (2009). Adams and Victor’s principles of neurology (9 ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. Chapter 10. ISBN 9780071499927.
- ^ May A, Burstein R (November 2019). «Hypothalamic regulation of headache and migraine». Cephalalgia. 39 (13): 1710–1719. doi:10.1177/0333102419867280. PMC 7164212. PMID 31466456.
- ^ a b c d Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. pp. 1116–1117. ISBN 978-0-07-148480-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Ashina M (November 2020). «Migraine». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (19): 1866–1876. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1915327. PMID 33211930. S2CID 227078662.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k The Headaches, pp. 407–419
- ^ Slap, GB (2008). Adolescent medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 105. ISBN 9780323040730. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Qubty W, Patniyot I (June 2020). «Migraine Pathophysiology». Pediatric Neurology. 107: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2019.12.014. PMID 32192818. S2CID 213191464.
- ^ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (1 January 2011). The Cleveland Clinic manual of headache therapy. New York: Springer. p. 6. ISBN 9781461401780. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Bigal ME, Arruda MA (July 2010). «Migraine in the pediatric population—evolving concepts». Headache. 50 (7): 1130–43. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01717.x. PMID 20572878. S2CID 23256755.
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 238. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Dalessio (2001). Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Dalessio DJ (eds.). Wolff’s headache and other head pain (7 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 122. ISBN 9780195135183.
- ^ a b Lisak RP, Truong DD, Carroll W, Bhidayasiri R (2009). International neurology: a clinical approach. Chichester, UK: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 670. ISBN 9781405157384.
- ^ a b c Kaniecki RG (June 2009). «Basilar-type migraine». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (3): 217–20. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0036-7. PMID 19457282. S2CID 22242504.
- ^ a b Joel S. Glaser (1999). Neuro-ophthalmology (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 555. ISBN 9780781717298. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Sirven JI, Malamut BL (2008). Clinical neurology of the older adult (2 ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 197. ISBN 9780781769471. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ Dr. Jennifer Robblee (21 August 2019). «Silent Migraine: A Guide». American Migraine Foundation. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ a b He Y, Li Y, Nie Z (February 2015). «Typical aura without headache: a case report and review of the literature». Journal of Medical Case Reports. 9 (1): 40. doi:10.1186/s13256-014-0510-7. PMC 4344793. PMID 25884682.
- ^ Jayne Leonard (medically reviewed by Seunggu Han, M.D.) (7 September 2018). «Silent migraine: Symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention». www.medicalnewstoday.com. Medical News Today. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ Bose P, Goadsby PJ (June 2016). «The migraine postdrome». Current Opinion in Neurology. 29 (3): 299–301. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000310. PMID 26886356. S2CID 22445093.
- ^ Kelman L (February 2006). «The postdrome of the acute migraine attack». Cephalalgia. 26 (2): 214–20. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.01026.x. PMID 16426278. S2CID 21519111.
- ^ Halpern AL, Silberstein SD (2005). «Ch. 9: The Migraine Attack—A Clinical Description». In Kaplan PW, Fisher RS (eds.). Imitators of Epilepsy (2 ed.). New York: Demos Medical. ISBN 978-1-888799-83-5. NBK7326.
- ^ Robbins MS, Lipton RB (April 2010). «The epidemiology of primary headache disorders». Seminars in Neurology. 30 (2): 107–19. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1249220. PMID 20352581.
- ^ a b c Schürks M (January 2012). «Genetics of migraine in the age of genome-wide association studies». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 13 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0399-0. PMC 3253157. PMID 22072275.
- ^ a b c d The Headaches, pp. 238–40
- ^ The Headaches, pp. 246–247
- ^ de Vries B, Frants RR, Ferrari MD, van den Maagdenberg AM (July 2009). «Molecular genetics of migraine». Human Genetics. 126 (1): 115–32. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0684-z. PMID 19455354. S2CID 20119237.
- ^ Montagna P (September 2008). «Migraine genetics». Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 8 (9): 1321–30. doi:10.1586/14737175.8.9.1321. PMID 18759544. S2CID 207195127.
- ^ a b c Ducros A (May 2013). «[Genetics of migraine]». Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 360–71. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.010. PMID 23618705.
- ^ Wan D, Wang C, Zhang X, Tang W, Chen M, Dong Z, Yu S (1 January 2016). «Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and migraine: a meta-analysis». The International Journal of Neuroscience. 126 (5): 393–9. doi:10.3109/00207454.2015.1025395. PMID 26000817. S2CID 34902092.
- ^ Dussor G, Cao YQ (October 2016). «TRPM8 and Migraine». Headache. 56 (9): 1406–1417. doi:10.1111/head.12948. PMC 5335856. PMID 27634619.
- ^ a b c Levy D, Strassman AM, Burstein R (June 2009). «A critical view on the role of migraine triggers in the genesis of migraine pain». Headache. 49 (6): 953–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01444.x. PMID 19545256. S2CID 31707887.
- ^ Martin PR (June 2010). «Behavioral management of migraine headache triggers: learning to cope with triggers». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 14 (3): 221–7. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0112-z. PMID 20425190. S2CID 5511782.
- ^ Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB (2014). «Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies». Headache. 54 (10): 1670–9. doi:10.1111/head.12468. PMID 25399858. S2CID 25016889.
- ^ a b c Radat F (May 2013). «[Stress and migraine]». Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 406–12. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.008. PMID 23608071.
- ^ Peterlin BL, Katsnelson MJ, Calhoun AH (October 2009). «The associations between migraine, unipolar psychiatric comorbidities, and stress-related disorders and the role of estrogen». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (5): 404–12. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0066-1. PMC 3972495. PMID 19728969.
- ^ Chai NC, Peterlin BL, Calhoun AH (June 2014). «Migraine and estrogen». Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 315–24. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000091. PMC 4102139. PMID 24792340.
- ^ Finocchi C, Sivori G (May 2012). «Food as trigger and aggravating factor of migraine». Neurological Sciences. 33 Suppl 1 (1): S77-80. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1046-5. PMID 22644176. S2CID 19582697.
- ^ Rockett FC, de Oliveira VR, Castro K, Chaves ML, Perla A, Perry ID (June 2012). «Dietary aspects of migraine trigger factors». Nutrition Reviews. 70 (6): 337–56. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00468.x. PMID 22646127.
- ^ Ghose, K.; Carroll, J. D. (1984). «Mechanism of Tyramine-Induced Migraine: Similarity with Dopamine and Interactions with Disulfiram and Propranolol in Migraine Patients». Neuropsychobiology. 12 (2–3): 122–126. doi:10.1159/000118123. PMID 6527752.
- ^ Moffett, A.; Swash, M.; Scott, D. F. (1972). «Effect of tyramine in migraine : a double-blind study» (PDF). Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 35 (4): 496–499. doi:10.1136/jnnp.35.4.496. PMC 494110. PMID 4559027.
- ^ «Tyramine and Migraines: What You Need to Know». www.excedrin.com. Retrieved 2022-03-04.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second ed.). Academic Press. 2003. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0.
- ^ Özturan; et al. (2016). «The Relationship Between Migraine and Nutrition» (PDF). Turk J Neurol. 22 (2): 44–50. doi:10.4274/tnd.37132.
- ^ Sun-Edelstein C, Mauskop A (June 2009). «Foods and supplements in the management of migraine headaches» (PDF). The Clinical Journal of Pain. 25 (5): 446–52. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.530.1223. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31819a6f65. PMID 19454881. S2CID 3042635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 August 2017.
- ^ Friedman DI, De ver Dye T (June 2009). «Migraine and the environment». Headache. 49 (6): 941–52. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01443.x. PMID 19545255. S2CID 29764274.
- ^ Andreou AP, Edvinsson L (December 2019). «Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 20 (1): 117. doi:10.1186/s10194-019-1066-0. PMC 6929435. PMID 31870279.
- ^ «What is Migraine?». Migraine Research Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020.
- ^ «Migraine Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020.
- ^ Hoffmann J, Baca SM, Akerman S (April 2019). «Neurovascular mechanisms of migraine and cluster headache». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 39 (4): 573–594. doi:10.1177/0271678×17733655. PMC 6446418. PMID 28948863.
- ^ Brennan KC, Charles A (June 2010). «An update on the blood vessel in migraine». Current Opinion in Neurology. 23 (3): 266–74. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833821c1. PMC 5500293. PMID 20216215.
- ^ Spiri, Daniele; Titomanlio, Luigi; Pogliani, Laura; Zuccotti, Gianvincenzo (1 January 2012). «Pathophysiology of migraine: The neurovascular theory». Headaches: Causes, Treatment and Prevention: 51–64.
- ^ Goadsby PJ (January 2009). «The vascular theory of migraine—a great story wrecked by the facts». Brain. 132 (Pt 1): 6–7. doi:10.1093/brain/awn321. PMID 19098031.
- ^ Dodick DW (April 2008). «Examining the essence of migraine—is it the blood vessel or the brain? A debate». Headache. 48 (4): 661–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01079.x. PMID 18377395. S2CID 6272233.
- ^ Chen D, Willis-Parker M, Lundberg GP (October 2020). «Migraine headache: Is it only a neurological disorder? Links between migraine and cardiovascular disorders». Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 30 (7): 424–430. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.10.005. PMID 31679956.
- ^ Jacobs B, Dussor G (December 2016). «Neurovascular contributions to migraine: Moving beyond vasodilation». Neuroscience. 338: 130–144. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.012. PMC 5083225. PMID 27312704.
- ^ Mason BN, Russo AF (2018). «Vascular Contributions to Migraine: Time to Revisit?». Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 12: 233. doi:10.3389/fncel.2018.00233. PMC 6088188. PMID 30127722.
- ^ Dodick DW, Gargus JJ (August 2008). «Why migraines strike». Scientific American. 299 (2): 56–63. Bibcode:2008SciAm.299b..56D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0808-56. PMID 18666680.
- ^ a b c d The Headaches, Chp. 28, pp. 269–72
- ^ a b c Olesen J, Burstein R, Ashina M, Tfelt-Hansen P (July 2009). «Origin of pain in migraine: evidence for peripheral sensitisation». The Lancet. Neurology. 8 (7): 679–90. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70090-0. PMID 19539239. S2CID 20452008.
- ^ Akerman S, Holland PR, Goadsby PJ (September 2011). «Diencephalic and brainstem mechanisms in migraine». Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 12 (10): 570–84. doi:10.1038/nrn3057. PMID 21931334. S2CID 8472711.
- ^ Shevel E (March 2011). «The extracranial vascular theory of migraine—a great story confirmed by the facts». Headache. 51 (3): 409–417. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01844.x. PMID 21352215. S2CID 6939786.
- ^ a b Burnstock G (1 January 2016). «Purinergic Mechanisms and Pain». In Barrett JE (ed.). Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain. Advances in Pharmacology. Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain. Vol. 75. Academic Press. pp. 91–137. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2015.09.001. ISBN 9780128038833. PMID 26920010.
- ^ Davidoff R (14 February 2002). Migraine: Manifestations, Pathogenesis, and Management. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-803135-2.
- ^ Lipton RB, Diener HC, Robbins MS, Garas SY, Patel K (October 2017). «Caffeine in the management of patients with headache». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 18 (1): 107. doi:10.1186/s10194-017-0806-2. PMC 5655397. PMID 29067618.
- ^ Hamel E (November 2007). «Serotonin and migraine: biology and clinical implications». Cephalalgia. 27 (11): 1293–300. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01476.x. PMID 17970989. S2CID 26543041.
- ^
- American Headache Society (September 2013). «Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question». Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). «The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations». Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658. S2CID 14443890.
- Silberstein SD (September 2000). «Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). «Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis». Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ^ Cousins G, Hijazze S, Van de Laar FA, Fahey T (Jul–Aug 2011). «Diagnostic accuracy of the ID Migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Headache. 51 (7): 1140–8. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01916.x. PMID 21649653. S2CID 205684294.
- ^ «Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition». Cephalalgia. 38 (1): 1–211. January 2018. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202. PMID 29368949.
- ^ Nappi G (September 2005). «Introduction to the new International Classification of Headache Disorders». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 6 (4): 203–4. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0185-y. PMC 3452009. PMID 16362664.
- ^ Negro A, Rocchietti-March M, Fiorillo M, Martelletti P (December 2011). «Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments». European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 15 (12): 1401–20. PMID 22288302.
- ^ a b c d Davidoff RA (2002). Migraine : manifestations, pathogenesis, and management (2 ed.). Oxford [u.a.]: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 81. ISBN 9780195137057. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Russell G, Abu-Arafeh I, Symon DN (2002). «Abdominal migraine: evidence for existence and treatment options». Paediatric Drugs. 4 (1): 1–8. doi:10.2165/00128072-200204010-00001. PMID 11817981. S2CID 12289726.
- ^ Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). «The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations». Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658. S2CID 14443890.
- ^ Silberstein SD (September 2000). «Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- ^ Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). «Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis». Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ^ a b Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- ^ Modi S, Lowder DM (January 2006). «Medications for migraine prophylaxis». American Family Physician. 73 (1): 72–8. PMID 16417067.
- ^ Diener HC, Limmroth V (August 2004). «Medication-overuse headache: a worldwide problem». The Lancet. Neurology. 3 (8): 475–83. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00824-5. PMID 15261608. S2CID 43840120.
- ^ Fritsche G, Diener HC (November 2002). «Medication overuse headaches — what is new?». Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 1 (4): 331–8. doi:10.1517/14740338.1.4.331. PMID 12904133. S2CID 23422679.
- ^ Kaniecki R, Lucas S (2004). «Treatment of primary headache: preventive treatment of migraine». Standards of care for headache diagnosis and treatment. Chicago: National Headache Foundation. pp. 40–52.
- ^ a b c Loder E, Burch R, Rizzoli P (June 2012). «The 2012 AHS/AAN guidelines for prevention of episodic migraine: a summary and comparison with other recent clinical practice guidelines». Headache. 52 (6): 930–45. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02185.x. PMID 22671714. S2CID 540800.
- ^ Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). «Antiepileptics other than gabapentin, pregabalin, topiramate, and valproate for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (6): CD010608. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010608. PMC 8221229. PMID 23797674.
- ^ Locher C, Kossowsky J, Koechlin H, Lam TL, Barthel J, Berde CB, et al. (April 2020). «Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Pharmacologic Treatments for Pediatric Migraine Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis». JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (4): 341–349. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856. PMC 7042942. PMID 32040139.
- ^ Merison K, Jacobs H (November 2016). «Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood Migraine». Current Treatment Options in Neurology. 18 (11): 48. doi:10.1007/s11940-016-0431-4. PMID 27704257. S2CID 28302667.
- ^ Dorosch T, Ganzer CA, Lin M, Seifan A (September 2019). «Efficacy of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Preventative Treatment of Episodic Migraine in Adults». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 23 (11): 85. doi:10.1007/s11916-019-0823-8. PMID 31515634. S2CID 202557362.
- ^ Cernes R, Mashavi M, Zimlichman R (2011). «Differential clinical profile of candesartan compared to other angiotensin receptor blockers». Vascular Health and Risk Management. 7: 749–59. doi:10.2147/VHRM.S22591. PMC 3253768. PMID 22241949.
- ^ Rajapakse T, Pringsheim T (April 2016). «Nutraceuticals in Migraine: A Summary of Existing Guidelines for Use». Headache. 56 (4): 808–16. doi:10.1111/head.12789. PMID 26954394. S2CID 31097792.
- ^ Teigen L, Boes CJ (September 2015). «An evidence-based review of oral magnesium supplementation in the preventive treatment of migraine». Cephalalgia. 35 (10): 912–22. doi:10.1177/0333102414564891. PMID 25533715. S2CID 25398410.
- ^ a b Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). «Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 78 (17): 1337–45. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d20. PMC 3335452. PMID 22529202.
- ^ Shamliyan TA, Choi JY, Ramakrishnan R, Miller JB, Wang SY, Taylor FR, Kane RL (September 2013). «Preventive pharmacologic treatments for episodic migraine in adults». Journal of General Internal Medicine. 28 (9): 1225–37. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2433-1. PMC 3744311. PMID 23592242.
- ^ Ibekwe, A.; Perras, C.; Mierzwinski-Urban, M. (2016). «Monoclonal Antibodies to Prevent Migraine Headaches». PMID 30855775.
- ^ Loder E, Renthal W (March 2019). «Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Treatments for Migraine». JAMA Internal Medicine. 179 (3): 421–422. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536. PMID 30640381. S2CID 58601441.
- ^ Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, Fei Y, Mehring M, Vertosick EA, et al. (June 2016). «Acupuncture for the prevention of episodic migraine». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (6): CD001218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001218.pub3. PMC 4977344. PMID 27351677.
- ^ Chaibi A, Tuchin PJ, Russell MB (April 2011). «Manual therapies for migraine: a systematic review». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 12 (2): 127–33. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0296-6. PMC 3072494. PMID 21298314.
- ^ Millstine D, Chen CY, Bauer B (May 2017). «Complementary and integrative medicine in the management of headache». BMJ. 357: j1805. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1805. PMID 28512119. S2CID 19155758.
- ^ a b Posadzki P, Ernst E (June 2011). «Spinal manipulations for the treatment of migraine: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials». Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 964–70. doi:10.1177/0333102411405226. PMID 21511952. S2CID 31205541.
- ^ a b Sharpe L, Dudeney J, Williams AC, Nicholas M, McPhee I, Baillie A, et al. (July 2019). «Psychological therapies for the prevention of migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7: CD012295. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012295.pub2. PMC 6603250. PMID 31264211.
- ^ Holland S, Silberstein SD, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). «Evidence-based guideline update: NSAIDs and other complementary treatments for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 78 (17): 1346–53. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d0c. PMC 3335449. PMID 22529203.
- ^ Pringsheim T, Davenport W, Mackie G, Worthington I, Aubé M, Christie SN, et al. (March 2012). «Canadian Headache Society guideline for migraine prophylaxis». The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 39 (2 Suppl 2): S1-59. PMID 22683887.
- ^ «Butterbur: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning». www.webmd.com. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ «Butterbur». NCCIH. 8 February 2012. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ Littarru GP, Tiano L (November 2005). «Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q10: an update». Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 8 (6): 641–6. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000171123.60665.16. PMID 16205466. S2CID 25010508.
- ^ Groenewegen WA, Knight DW, Heptinstall S (1992). «Progress in the medicinal chemistry of the herb feverfew». Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. 29: 217–38. doi:10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70009-2. ISBN 9780444894724. PMID 1475370.
- ^ Barnes, J; Anderson, LA; Philipson, JD (2007). Herbal Medicines. 3rd ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press.
- ^ a b EMA. «Assessment report on Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Schultz Bip., herba» (PDF). www.ema.europa.eu. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- ^ a b c d Gelfand AA, Goadsby PJ (September 2016). «The Role of Melatonin in the Treatment of Primary Headache Disorders». Headache (Review). 56 (8): 1257–66. doi:10.1111/head.12862. PMC 5012937. PMID 27316772.
- ^ Long R, Zhu Y, Zhou S (January 2019). «Therapeutic role of melatonin in migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review». Medicine. 98 (3): e14099. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014099. PMC 6370052. PMID 30653130.
- ^ Nesbitt AD, Leschziner GD, Peatfield RC (September 2014). «Headache, drugs and sleep». Cephalalgia (Review). 34 (10): 756–66. doi:10.1177/0333102414542662. PMID 25053748. S2CID 33548757.
- ^ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A (March 2007). «Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis». Pain. 128 (1–2): 111–27. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007. PMID 17084028. S2CID 23351902.
- ^ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A, Rief W, Andrasik F (September 2008). «Biofeedback treatment for headache disorders: a comprehensive efficacy review». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 33 (3): 125–40. doi:10.1007/s10484-008-9060-3. PMID 18726688. S2CID 29122354.
- ^ Schoenen J, Allena M, Magis D (2010). «Neurostimulation therapy in intractable headaches». In Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds.). Headache. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. pp. 443–50. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97037-1. ISBN 9780444521392. PMID 20816443.
- ^ Reed KL, Black SB, Banta CJ, Will KR (March 2010). «Combined occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine headaches: initial experience». Cephalalgia. 30 (3): 260–71. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01996.x. PMID 19732075. S2CID 18639211.
- ^ «FDA allows marketing of first medical device to prevent migraine headaches». Food and Drug Administration. 11 March 2014. Archived from the original on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ^ «FDA approves transcranial magnetic stimulator» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 February 2014.
- ^ Tao H, Wang T, Dong X, Guo Q, Xu H, Wan Q (May 2018). «Effectiveness of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the treatment of migraine: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 42. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0868-9. PMC 5975046. PMID 29845369.
We found significant reduction of monthly headache days
- ^ Kung TA, Guyuron B, Cederna PS (January 2011). «Migraine surgery: a plastic surgery solution for refractory migraine headache». Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 127 (1): 181–189. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f95a01. PMID 20871488. S2CID 18817383.
- ^ «American Headache Society Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question». Choosing Wisely. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
- ^ Rabbie R, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Ibuprofen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008039. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008039.pub3. PMC 4161114. PMID 23633348.
- ^ Derry S, Rabbie R, Moore RA (April 2013). «Diclofenac with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008783. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008783.pub3. PMC 4164457. PMID 23633360.
- ^ Kirthi V, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Aspirin with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008041. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008041.pub3. PMC 4163048. PMID 23633350.
- ^ Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008040. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008040.pub3. PMC 4161111. PMID 23633349.
- ^ Eken C (March 2015). «Critical reappraisal of intravenous metoclopramide in migraine attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis». The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 33 (3): 331–7. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2014.11.013. PMID 25579820.
- ^ a b c d Orr SL, Friedman BW, Christie S, Minen MT, Bamford C, Kelley NE, Tepper D (June 2016). «Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies». Headache. 56 (6): 911–40. doi:10.1111/head.12835. PMID 27300483.
- ^ Law, Simon; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2013-10-20). «Naproxen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD009455. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009455.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6540401. PMID 24142263.
- ^ Singh, Rashmi B. Halker; VanderPluym, Juliana H.; Morrow, Allison S.; Urtecho, Meritxell; Nayfeh, Tarek; Roldan, Victor D. Torres; Farah, Magdoleen H.; Hasan, Bashar; Saadi, Samer (2020). Acute Treatments for Episodic Migraine. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 33411427.
- ^ Johnston MM, Rapoport AM (August 2010). «Triptans for the management of migraine». Drugs. 70 (12): 1505–18. doi:10.2165/11537990-000000000-00000. PMID 20687618. S2CID 41613179.
- ^ a b Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (rectal route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (2): CD009664. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009664. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4170908. PMID 22336868.
- ^ a b c Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (intranasal route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009663. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009663. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164476. PMID 22336867.
- ^ a b Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (subcutaneous route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009665. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009665. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164380. PMID 22336869.
- ^ a b «Generic migraine drug could relieve your pain and save you money». Best Buy Drugs. Consumer Reports. Archived from the original on 4 August 2013.
- ^ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (April 2010). «Breaking the cycle of medication overuse headache». Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 77 (4): 236–42. doi:10.3949/ccjm.77a.09147. PMID 20360117. S2CID 36333666.
- ^ Law S, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2016). «Sumatriptan plus naproxen for the treatment of acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD008541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008541.pub3. PMC 6485397. PMID 27096438.
- ^ a b Sumamo Schellenberg, E.; Dryden, D. M.; Pasichnyk, D.; Ha, C.; Vandermeer, B.; Friedman, B. W.; Colman, I.; Rowe, B. H. (2012). «Acute migraine treatment in emergency settings». PMID 23304741.
- ^ Kelley NE, Tepper DE (January 2012). «Rescue therapy for acute migraine, part 1: triptans, dihydroergotamine, and magnesium». Headache. 52 (1): 114–28. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.02062.x. PMID 22211870. S2CID 45767513.
- ^ a b Morren JA, Galvez-Jimenez N (December 2010). «Where is dihydroergotamine mesylate in the changing landscape of migraine therapy?». Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (18): 3085–93. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.533839. PMID 21080856. S2CID 44639896.
- ^ Tfelt-Hansen P, Saxena PR, Dahlöf C, Pascual J, Láinez M, Henry P, et al. (January 2000). «Ergotamine in the acute treatment of migraine: a review and European consensus». Brain. 123 ( Pt 1): 9–18. doi:10.1093/brain/123.1.9. PMID 10611116.
- ^ Yablon LA, Mauskop A (2011). «Magnesium in headache». In Vink R, Nechifor M (eds.). Magnesium in the Central Nervous System. Adelaide (AU): University of Adelaide Press. ISBN 978-0-9870730-5-1. PMID 29920023. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- ^ HY, Chiu; TH, Yeh; YC, Huang; PY, Chen (2015-02-24). «Effects of Intravenous and Oral Magnesium on Reducing Migraine: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials». Pain Physician. 19 (1). ISSN 2150-1149. PMID 26752497. Retrieved 2022-12-02.
- ^ Veronese, Nicola; Demurtas, Jacopo; Pesolillo, Gabriella; Celotto, Stefano; Barnini, Tommaso; Calusi, Giovanni; Caruso, Maria Gabriella; Notarnicola, Maria; Reddavide, Rosa; Stubbs, Brendon; Solmi, Marco; Maggi, Stefania; Vaona, Alberto; Firth, Joseph; Smith, Lee; Koyanagi, Ai; Dominguez, Ligia; Barbagallo, Mario (2019-01-25). «Magnesium and health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational and intervention studies». European Journal of Nutrition. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 59 (1): 263–272. doi:10.1007/s00394-019-01905-w. ISSN 1436-6207. PMID 30684032. S2CID 59275463.
- ^ Colman I, Friedman BW, Brown MD, Innes GD, Grafstein E, Roberts TE, Rowe BH (June 2008). «Parenteral dexamethasone for acute severe migraine headache: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials for preventing recurrence». BMJ. 336 (7657): 1359–61. doi:10.1136/bmj.39566.806725.BE. PMC 2427093. PMID 18541610.
- ^ Piatka C, Beckett RD (February 2020). «Propofol for Treatment of Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review». Academic Emergency Medicine. 27 (2): 148–160. doi:10.1111/acem.13870. PMID 31621134.
- ^ Vukovic Cvetkovic V, Jensen RH (January 2019). «Neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine and cluster headache». Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 139 (1): 4–17. doi:10.1111/ane.13034. PMID 30291633. S2CID 52923061.
- ^ Hambach, A.; Frese, A.; Evers, S. (2013). «Sexuelle Aktivität und Kopfschmerz». Nervenheilkunde (in German). Georg Thieme Verlag KG. 32 (3): 118–122. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1628490. ISSN 0722-1541.
- ^ a b c d Richer L, Billinghurst L, Linsdell MA, Russell K, Vandermeer B, Crumley ET, et al. (April 2016). «Drugs for the acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (10): CD005220. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005220.pub2. PMC 6516975. PMID 27091010.
- ^ a b Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171.
- ^ Wang, Guihua; Tan, Tianlin; Liu, Yao; Hong, Peiwei (2020). «Drugs for Acute Attack of Pediatric Migraine: A Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials». Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 195: 105853. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105853. ISSN 1872-6968. PMID 32464520. S2CID 215814011.
- ^ Herd CP, Tomlinson CL, Rick C, Scotton WJ, Edwards J, Ives N, et al. (June 2018). «Botulinum toxins for the prevention of migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (6): CD011616. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011616.pub2. PMC 6513576. PMID 29939406.
- ^ Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Hayashino Y (April 2012). «Botulinum toxin A for prophylactic treatment of migraine and tension headaches in adults: a meta-analysis». JAMA. 307 (16): 1736–45. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.505. PMID 22535858.
- ^ Simpson DM, Hallett M, Ashman EJ, Comella CL, Green MW, Gronseth GS, et al. (May 2016). «Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 86 (19): 1818–26. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560. PMC 4862245. PMID 27164716.
- ^ Markham A (July 2018). «Erenumab: First Global Approval». Drugs. 78 (11): 1157–1161. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0944-0. PMID 29968151. S2CID 49559342.
- ^ Silberstein, Stephen D.; Lee, Lulu; Gandhi, Kavita; Fitzgerald, Timothy; Bell, Jvawnna; Cohen, Joshua M. (2018). «Health care Resource Utilization and Migraine Disability Along the Migraine Continuum Among Patients Treated for Migraine». Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain. 58 (10): 1579–1592. doi:10.1111/head.13421. PMID 30375650. S2CID 53114546.
- ^ a b «Migraine Information Page: Prognosis Archived 2020-06-10 at the Wayback Machine,» National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), National Institutes of Health (US).
- ^ «Facts and Figures». The Migraine Trust.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Brennan, KC; Pietrobon, D (March 2018). «A systems neuroscience approach to migraine». Neuron. 97 (5): 1004–1021. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.029. PMC 6402597. PMID 29518355.
- ^ World Health Organization (2008). «Disability classes for the Global Burden of Disease study» (table 8), The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update, p 33.
- ^ a b c Schürks M, Rist PM, Bigal ME, Buring JE, Lipton RB, Kurth T (October 2009). «Migraine and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ. 339: b3914. doi:10.1136/bmj.b3914. PMC 2768778. PMID 19861375.
- ^ Kurth T, Chabriat H, Bousser MG (January 2012). «Migraine and stroke: a complex association with clinical implications». The Lancet. Neurology. 11 (1): 92–100. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70266-6. PMID 22172624. S2CID 31939284.
- ^ Rist PM, Diener HC, Kurth T, Schürks M (June 2011). «Migraine, migraine aura, and cervical artery dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 886–96. doi:10.1177/0333102411401634. PMC 3303220. PMID 21511950.
- ^ Kurth T (March 2010). «The association of migraine with ischemic stroke». Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 10 (2): 133–9. doi:10.1007/s11910-010-0098-2. PMID 20425238. S2CID 27227332.
- ^ Schürks M, Rist PM, Shapiro RE, Kurth T (September 2011). «Migraine and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Cephalalgia. 31 (12): 1301–14. doi:10.1177/0333102411415879. PMC 3175288. PMID 21803936.
- ^ Weinberger J (March 2007). «Stroke and migraine». Current Cardiology Reports. 9 (1): 13–9. doi:10.1007/s11886-007-0004-y. PMID 17362679. S2CID 46681674.
- ^ Hougaard A, Amin FM, Ashina M (June 2014). «Migraine and structural abnormalities in the brain». Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 309–14. doi:10.1097/wco.0000000000000086. PMID 24751961.
- ^ Wang SJ (March 2003). «Epidemiology of migraine and other types of headache in Asia». Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 3 (2): 104–8. doi:10.1007/s11910-003-0060-7. PMID 12583837. S2CID 24939546.
- ^ Natoli JL, Manack A, Dean B, Butler Q, Turkel CC, Stovner L, Lipton RB (May 2010). «Global prevalence of chronic migraine: a systematic review». Cephalalgia. 30 (5): 599–609. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01941.x. PMID 19614702. S2CID 5328642.
- ^ a b Hershey AD (February 2010). «Current approaches to the diagnosis and management of paediatric migraine». The Lancet. Neurology. 9 (2): 190–204. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70303-5. PMID 20129168. S2CID 12603488.
- ^ a b Nappi RE, Sances G, Detaddei S, Ornati A, Chiovato L, Polatti F (June 2009). «Hormonal management of migraine at menopause». Menopause International. 15 (2): 82–6. doi:10.1258/mi.2009.009022. PMID 19465675. S2CID 23204921.
- ^ a b c d e Borsook D (2012). The migraine brain : imaging, structure, and function. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–11. ISBN 9780199754564. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Steven D. Waldman (2011). Pain management (2 ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 2122–2124. ISBN 9781437736038.
- ^ «Sex(ism), Drugs, and Migraines». Distillations. Science History Institute. 15 January 2019. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ^ Margaret C, Simon M (2002). Human osteology : in archaeology and forensic science (Repr. ed.). Cambridge [etc.]: Cambridge University Press. p. 345. ISBN 9780521691468. Archived from the original on 17 June 2013.
- ^ Colen C (2008). Neurosurgery. Colen Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 9781935345039.
- ^ Daniel BT (2010). Migraine. Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse. p. 101. ISBN 9781449069629. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Butticè, Claudio (April 2022). What you need to know about headaches. Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood_Publishing_Group. pp. 29–30. ISBN 978-1-4408-7531-1. OCLC 1259297708.
- ^ a b Tfelt-Hansen PC, Koehler PJ (May 2011). «One hundred years of migraine research: major clinical and scientific observations from 1910 to 2010». Headache. 51 (5): 752–78. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01892.x. PMID 21521208. S2CID 31940152.
- ^ a b c Stovner LJ, Andrée C (June 2008). «Impact of headache in Europe: a review for the Eurolight project». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (3): 139–46. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0038-6. PMC 2386850. PMID 18418547.
- ^ a b Mennini FS, Gitto L, Martelletti P (August 2008). «Improving care through health economics analyses: cost of illness and headache». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (4): 199–206. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0051-9. PMC 3451939. PMID 18604472.
- ^ Magis D, Jensen R, Schoenen J (June 2012). «Neurostimulation therapies for primary headache disorders: present and future». Current Opinion in Neurology. 25 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283532023. PMID 22543428.
- ^ Jürgens TP, Leone M (June 2013). «Pearls and pitfalls: neurostimulation in headache». Cephalalgia. 33 (8): 512–25. doi:10.1177/0333102413483933. PMID 23671249. S2CID 42537455.
- ^ Barbanti P, Fofi L, Aurilia C, Egeo G, Caprio M (May 2017). «Ketogenic diet in migraine: rationale, findings and perspectives». Neurological Sciences (Review). 38 (Suppl 1): 111–115. doi:10.1007/s10072-017-2889-6. PMID 28527061. S2CID 3805337.
- ^ Gross EC, Klement RJ, Schoenen J, D’Agostino DP, Fischer D (April 2019). «Potential Protective Mechanisms of Ketone Bodies in Migraine Prevention». Nutrients. 11 (4): 811. doi:10.3390/nu11040811. PMC 6520671. PMID 30974836.
- ^ Artero-Morales M, González-Rodríguez S, Ferrer-Montiel A (2018). «TRP Channels as Potential Targets for Sex-Related Differences in Migraine Pain». Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 5: 73. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2018.00073. PMC 6102492. PMID 30155469.
- ^ Stewart, Walter F.; Lipton, Richard B.; Celentano, David D.; Reed, Michael L. (1992-01-01). «Prevalence of Migraine Headache in the United States: Relation to Age, Income, Race, and Other Sociodemographic Factors». JAMA. 267 (1): 64–69. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03480010072027. ISSN 0098-7484. PMID 1727198.
- ^ «Speeding Progress in Migraine Requires Unraveling Sex Differences». SWHR. 2018-08-28. Retrieved 2021-03-17.
- ^ «Migraine in Women Needs More Sex-Specific Research». Migraine Again. 2021-03-11. Retrieved 2021-03-17.
- ^ Schroeder RA, Brandes J, Buse DC, Calhoun A, Eikermann-Haerter K, Golden K, et al. (August 2018). «Sex and Gender Differences in Migraine-Evaluating Knowledge Gaps». Journal of Women’s Health. 27 (8): 965–973. doi:10.1089/jwh.2018.7274. PMID 30129895. S2CID 52048078.
Notes[edit]
- Olesen J (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9780781754002.
Further reading[edit]
- Ashina M (November 2020). Ropper AH (ed.). «Migraine». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (19): 1866–1876. doi:10.1056/nejmra1915327. PMID 33211930. S2CID 227078662.
- Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171. S2CID 199662718.
External links[edit]
| External audio |
|---|
- Migraine at Curlie
| Migraine | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Woman with migraine headache | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Headaches, nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, and smell[1][2] |
| Usual onset | Around puberty[1] |
| Duration | Recurrent, long term[1] |
| Causes | Environmental and genetic[3] |
| Risk factors | Family history, female[4][5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Subarachnoid hemorrhage, venous thrombosis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, brain tumor, tension headache, sinusitis,[6] cluster headache[7] |
| Prevention | Metoprolol, valproate, topiramate[8][9] |
| Medication | Ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), triptans, ergotamines[5][10] |
| Prevalence | ~15%[11] |
Migraine (, )[12][13] is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches.[1] Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hours to three days.[1] Non-headache symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell.[2] The pain is generally made worse by physical activity during an attack,[14] although regular physical exercise may prevent future attacks.[15] Up to one-third of people affected have aura: typically, it is a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur.[14] Occasionally, aura can occur with little or no headache following, but not everyone has this symptom.[16]
Migraine is believed to be due to a mixture of environmental and genetic factors.[3] About two-thirds of cases run in families.[5] Changing hormone levels may also play a role, as migraine affects slightly more boys than girls before puberty and two to three times more women than men.[4][17] The risk of migraine usually decreases during pregnancy and after menopause.[4][18] The underlying mechanisms are not fully known.[18] They are, however, believed to involve the nerves and blood vessels of the brain.[5]
Initial recommended treatment is with simple pain medication such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) for the headache, medication for the nausea, and the avoidance of triggers.[10] Specific medications such as triptans or ergotamines may be used in those for whom simple pain medications are not effective.[5] Caffeine in combination with other analgesics is safe and effective in treatment of acute migraine.[19][20][21] A number of medications are useful to prevent attacks including metoprolol, valproate, and topiramate.[8][9]
Globally, approximately 15% of people are affected by migraine.[11] In the Global Burden of Disease Study of 2010, it was ranked as the third most prevalent disorder in the world.[22] It most often starts at puberty and is worst during middle age.[1] As of 2016, it is one of the most common causes of disability.[23] An early description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BC in ancient Egypt.[24] The word migraine is from the Greek ἡμικρᾱνίᾱ (hēmikrāníā), ‘pain in half of the head’,[25] from ἡμι- (hēmi-), ‘half’ and κρᾱνίον (krāníon), ‘skull’.[26]
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Migraine typically presents with self-limited, recurrent severe headache associated with autonomic symptoms.[5][27] About 15–30% of people living with migraine experience episodes with aura,[10][28] and they also frequently experience episodes without aura.[29] The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks are variable.[5] A migraine attack lasting longer than 72 hours is termed status migrainosus.[30] There are four possible phases to a migraine attack, although not all the phases are necessarily experienced:[14]
- The prodrome, which occurs hours or days before the headache
- The aura, which immediately precedes the headache
- The pain phase, also known as headache phase
- The postdrome, the effects experienced following the end of a migraine attack
Migraine is associated with major depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. These psychiatric disorders are approximately 2–5 times more common in people without aura, and 3–10 times more common in people with aura.[31]
Prodrome phase[edit]
Prodromal or premonitory symptoms occur in about 60% of those with migraines,[2][32] with an onset that can range from two hours to two days before the start of pain or the aura.[33] These symptoms may include a wide variety of phenomena,[34] including altered mood, irritability, depression or euphoria, fatigue, craving for certain food(s), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), constipation or diarrhea, and sensitivity to smells or noise.[32] This may occur in those with either migraine with aura or migraine without aura.[35] Neuroimaging indicates the limbic system and hypothalamus as the origin of prodromal symptoms in migraine.[36]
Aura phase[edit]
Aura is a transient focal neurological phenomenon that occurs before or during the headache.[2] Aura appears gradually over a number of minutes (usually occurring over 5–60 minutes) and generally lasts less than 60 minutes.[37][38] Symptoms can be visual, sensory or motoric in nature, and many people experience more than one.[39] Visual effects occur most frequently: they occur in up to 99% of cases and in more than 50% of cases are not accompanied by sensory or motor effects.[39]
Visual disturbances often consist of a scintillating scotoma (an area of partial alteration in the field of vision which flickers and may interfere with a person’s ability to read or drive).[2] These typically start near the center of vision and then spread out to the sides with zigzagging lines which have been described as looking like fortifications or walls of a castle.[39] Usually the lines are in black and white but some people also see colored lines.[39] Some people lose part of their field of vision known as hemianopsia while others experience blurring.[39]
Sensory aura are the second most common type; they occur in 30–40% of people with auras.[39] Often a feeling of pins-and-needles begins on one side in the hand and arm and spreads to the nose–mouth area on the same side.[39] Numbness usually occurs after the tingling has passed with a loss of position sense.[39] Other symptoms of the aura phase can include speech or language disturbances, world spinning, and less commonly motor problems.[39] Motor symptoms indicate that this is a hemiplegic migraine, and weakness often lasts longer than one hour unlike other auras.[39] Auditory hallucinations or delusions have also been described.[40]
Pain phase[edit]
Classically the headache is unilateral, throbbing, and moderate to severe in intensity.[37] It usually comes on gradually[37] and is aggravated by physical activity during a migraine attack.[14] However, the effects of physical activity on migraine are complex, and some researchers have concluded that, while exercise can trigger migraine attacks, regular exercise may have a prophylactic effect and decrease frequency of attacks.[15] The feeling of pulsating pain is not in phase with the pulse.[41] In more than 40% of cases, however, the pain may be bilateral (both sides of the head), and neck pain is commonly associated with it.[42] Bilateral pain is particularly common in those who have migraine without aura.[2] Less commonly pain may occur primarily in the back or top of the head.[2] The pain usually lasts 4 to 72 hours in adults;[37] however, in young children frequently lasts less than 1 hour.[43] The frequency of attacks is variable, from a few in a lifetime to several a week, with the average being about one a month.[44][45]
The pain is frequently accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to smells, fatigue and irritability.[2] Many thus seek a dark and quiet room.[46] In a basilar migraine, a migraine with neurological symptoms related to the brain stem or with neurological symptoms on both sides of the body,[47] common effects include a sense of the world spinning, light-headedness, and confusion.[2] Nausea occurs in almost 90% of people, and vomiting occurs in about one-third.[46] Other symptoms may include blurred vision, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, frequent urination, pallor, or sweating.[48] Swelling or tenderness of the scalp may occur as can neck stiffness.[48] Associated symptoms are less common in the elderly.[49]
Silent migraine[edit]
Sometimes, aura occurs without a subsequent headache.[39] This is known in modern classification as a typical aura without headache, or acephalgic migraine in previous classification, or commonly as a silent migraine.[50][51] However, silent migraine can still produce debilitating symptoms, with visual disturbance, vision loss in half of both eyes, alterations in color perception, and other sensory problems, like sensitivity to light, sound, and odors, and aura sudden outbreak without headache can be scary.[52] It can last from 15 to 30 minutes, usually no longer than 60 minutes, and it can recur or appear as an isolated event.[51]
Postdrome[edit]
The migraine postdrome could be defined as that constellation of symptoms occurring once the acute headache has settled.[53] Many report a sore feeling in the area where the migraine was, and some report impaired thinking for a few days after the headache has passed. The person may feel tired or «hung over» and have head pain, cognitive difficulties, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood changes, and weakness.[54] According to one summary, «Some people feel unusually refreshed or euphoric after an attack, whereas others note depression and malaise.»[55] For some individuals this can vary each time.
Cause[edit]
The underlying causes of migraines are unknown.[56] However, they are believed to be related to a mix of environmental and genetic factors.[3] They run in families in about two-thirds of cases[5] and rarely occur due to a single gene defect.[57] While migraines were once believed to be more common in those of high intelligence, this does not appear to be true.[58] A number of psychological conditions are associated, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder,[59] as are many biological events or triggers.
Genetics[edit]
Studies of twins indicate a 34% to 51% genetic influence of likelihood to develop migraine.[3] This genetic relationship is stronger for migraine with aura than for migraines without aura.[29] A number of specific variants of genes increase the risk by a small to moderate amount.[57]
Single gene disorders that result in migraines are rare.[57] One of these is known as familial hemiplegic migraine, a type of migraine with aura, which is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.[60][61] Four genes have been shown to be involved in familial hemiplegic migraine.[62] Three of these genes are involved in ion transport.[62] The fourth is an axonal protein associated with the exocytosis complex.[62] Another genetic disorder associated with migraine is CADASIL syndrome or cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy.[2] One meta-analysis found a protective effect from angiotensin converting enzyme polymorphisms on migraine.[63] The TRPM8 gene, which codes for a cation channel, has been linked to migraines.[64]
Triggers[edit]
Migraine may be induced by triggers, with some reporting it as an influence in a minority of cases[5] and others the majority.[65] Many things such as fatigue, certain foods, alcohol, and weather have been labeled as triggers; however, the strength and significance of these relationships are uncertain.[65][66] Most people with migraines report experiencing triggers.[67] Symptoms may start up to 24 hours after a trigger.[5]
Physiological aspects[edit]
Common triggers quoted are stress, hunger, and fatigue (these equally contribute to tension headaches).[65] Psychological stress has been reported as a factor by 50 to 80% of people.[68] Migraine has also been associated with post-traumatic stress disorder and abuse.[69] Migraine episodes are more likely to occur around menstruation.[68] Other hormonal influences, such as menarche, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause, also play a role.[70] These hormonal influences seem to play a greater role in migraine without aura.[58] Migraine episodes typically do not occur during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, or following menopause.[2]
Dietary aspects[edit]
Between 12 and 60% of people report foods as triggers.[71][72]
There are many reports[73][74][75][76][77] that tyramine – which is naturally present in chocolate, alcoholic beverages, most cheeses, processed meats, and other foods – can trigger migraine symptoms in some individuals. Likewise, monosodium glutamate (MSG) is frequently reported as a trigger for migraine symptoms.[78]
Environmental aspects[edit]
A 2009 review on potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded that while there were insufficient studies to confirm environmental factors as causing migraine, «migraineurs worldwide consistently report similar environmental triggers».[79] The article suggests that people living with migraine take some preventive measures related to indoor air quality and lighting.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Migraine is believed to be primarily a neurological disorder,[80][81][82] while others believe it to be a neurovascular disorder with blood vessels playing the key role, although current evidence does not support this completely.[83][84][85][86] Others believe both are likely important.[87][88][89][90] One theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex and abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.[91]
Aura[edit]
Cortical spreading depression, or spreading depression according to Leão, is a burst of neuronal activity followed by a period of inactivity, which is seen in those with migraines with aura.[92] There are a number of explanations for its occurrence, including activation of NMDA receptors leading to calcium entering the cell.[92] After the burst of activity, the blood flow to the cerebral cortex in the area affected is decreased for two to six hours.[92] It is believed that when depolarization travels down the underside of the brain, nerves that sense pain in the head and neck are triggered.[92]
Pain[edit]
The exact mechanism of the head pain which occurs during a migraine episode is unknown.[93] Some evidence supports a primary role for central nervous system structures (such as the brainstem and diencephalon),[94] while other data support the role of peripheral activation (such as via the sensory nerves that surround blood vessels of the head and neck).[93] The potential candidate vessels include dural arteries, pial arteries and extracranial arteries such as those of the scalp.[93] The role of vasodilatation of the extracranial arteries, in particular, is believed to be significant.[95]
Neuromodulators[edit]
Adenosine, a neuromodulator, may be involved.[96] Released after the progressive cleavage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine acts on adenosine receptors to put the body and brain in a low activity state by dilating blood vessels and slowing the heart rate, such as before and during the early stages of sleep. Adenosine levels have been found to be high during migraine attacks.[96][97] Caffeine’s role as an inhibitor of adenosine may explain its effect in reducing migraine.[98] Low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), are also believed to be involved.[99]
Calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as levels of it become elevated during an attack.[10][41]
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of a migraine is based on signs and symptoms.[5] Neuroimaging tests are not necessary to diagnose migraine, but may be used to find other causes of headaches in those whose examination and history do not confirm a migraine diagnosis.[100] It is believed that a substantial number of people with the condition remain undiagnosed.[5]
The diagnosis of migraine without aura, according to the International Headache Society, can be made according to the following criteria, the «5, 4, 3, 2, 1 criteria»:[14]
- Five or more attacks—for migraine with aura, two attacks are sufficient for diagnosis.
- Four hours to three days in duration
- Two or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affecting one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- One or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia)
If someone experiences two of the following: photophobia, nausea, or inability to work or study for a day, the diagnosis is more likely.[101] In those with four out of five of the following: pulsating headache, duration of 4–72 hours, pain on one side of the head, nausea, or symptoms that interfere with the person’s life, the probability that this is a migraine attack is 92%.[10] In those with fewer than three of these symptoms, the probability is 17%.[10]
Classification[edit]
Migraine was first comprehensively classified in 1988.[29] The International Headache Society updated their classification of headaches in 2004.[14] A third version was published in 2018.[102] According to this classification, migraine is a primary headache disorder along with tension-type headaches and cluster headaches, among others.[103]
Migraine is divided into seven subclasses (some of which include further subdivisions):
- Migraine without aura, or «common migraine», involves migraine headaches that are not accompanied by aura.
- Migraine with aura, or «classic migraine», usually involves migraine headaches accompanied by aura. Less commonly, aura can occur without a headache, or with a nonmigraine headache. Two other varieties are familial hemiplegic migraine and sporadic hemiplegic migraine, in which a person has migraine with aura and with accompanying motor weakness. If a close relative has had the same condition, it is called «familial», otherwise it is called «sporadic». Another variety is basilar-type migraine, where a headache and aura are accompanied by difficulty speaking, world spinning, ringing in ears, or a number of other brainstem-related symptoms, but not motor weakness. This type was initially believed to be due to spasms of the basilar artery, the artery that supplies the brainstem. Now that this mechanism is not believed to be primary, the symptomatic term migraine with brainstem aura (MBA) is preferred.[47]
- Childhood periodic syndromes that are commonly precursors of migraine include cyclical vomiting (occasional intense periods of vomiting), abdominal migraine (abdominal pain, usually accompanied by nausea), and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (occasional attacks of vertigo).
- Retinal migraine involves migraine headaches accompanied by visual disturbances or even temporary blindness in one eye.
- Complications of migraine describe migraine headaches and/or auras that are unusually long or unusually frequent, or associated with a seizure or brain lesion.
- Probable migraine describes conditions that have some characteristics of migraines, but where there is not enough evidence to diagnose it as a migraine with certainty (in the presence of concurrent medication overuse).
- Chronic migraine is a complication of migraines, and is a headache that fulfills diagnostic criteria for migraine headache and occurs for a greater time interval. Specifically, greater or equal to 15 days/month for longer than 3 months.[104]
Abdominal migraine[edit]
The diagnosis of abdominal migraine is controversial.[105] Some evidence indicates that recurrent episodes of abdominal pain in the absence of a headache may be a type of migraine[105][106] or are at least a precursor to migraines.[29] These episodes of pain may or may not follow a migraine-like prodrome and typically last minutes to hours.[105] They often occur in those with either a personal or family history of typical migraine.[105] Other syndromes that are believed to be precursors include cyclical vomiting syndrome and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood.[29]
Differential diagnosis[edit]
Other conditions that can cause similar symptoms to a migraine headache include temporal arteritis, cluster headaches, acute glaucoma, meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage.[10] Temporal arteritis typically occurs in people over 50 years old and presents with tenderness over the temple, cluster headache presents with one-sided nose stuffiness, tears and severe pain around the orbits, acute glaucoma is associated with vision problems, meningitis with fevers, and subarachnoid hemorrhage with a very fast onset.[10] Tension headaches typically occur on both sides, are not pounding, and are less disabling.[10]
Those with stable headaches that meet criteria for migraines should not receive neuroimaging to look for other intracranial disease.[107][108][109] This requires that other concerning findings such as papilledema (swelling of the optic disc) are not present. People with migraines are not at an increased risk of having another cause for severe headaches.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive treatments of migraine include medications, nutritional supplements, lifestyle alterations, and surgery. Prevention is recommended in those who have headaches more than two days a week, cannot tolerate the medications used to treat acute attacks, or those with severe attacks that are not easily controlled.[10] Recommended lifestyle changes include stopping tobacco use and reducing behaviors that interfere with sleep.[110]
The goal is to reduce the frequency, painfulness, and duration of migraine episodes, and to increase the effectiveness of abortive therapy.[111] Another reason for prevention is to avoid medication overuse headache. This is a common problem and can result in chronic daily headache.[112][113]
Medication[edit]
Preventive migraine medications are considered effective if they reduce the frequency or severity of the migraine attacks by at least 50%.[114] Due to few medications being approved specifically for the preventative treatment of migraine headaches; many medications such as beta-blockers, anticonvulsive agents such as topiramate or sodium valproate, antidepressants such as amitriptyline and calcium channel blockers such as flunarizine are used off label for the preventative treatment of migraine headaches.[38] Guidelines are fairly consistent in rating the anticonvulsants topiramate and divalproex/sodium valproate, and the beta blockers propranolol and metoprolol as having the highest level of evidence for first-line use for migraine prophylaxis in adults.[115][116] Propranolol and topiramate have the best evidence in children; however, evidence only supports short-term benefit as of 2020.[110][117]
The beta blocker timolol is also effective for migraine prevention and in reducing migraine attack frequency and severity.[115] While beta blockers are often used for first-line treatment, other antihypertensives also have a proven efficiency in migraine prevention, namely the calcium channel blocker verapamil[118] and the angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan.[119][120]
Tentative evidence also supports the use of magnesium supplementation.[121] Increasing dietary intake may be better.[122] Recommendations regarding effectiveness varied for the anticonvulsants gabapentin and pregabalin. Frovatriptan is effective for prevention of menstrual migraine.[115]
The antidepressants amitriptyline and venlafaxine are probably also effective.[123] Angiotensin inhibition by either an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist may reduce attacks.[124]
Medications in the anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide, including eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab, appear to decrease the frequency of migraines by one to two per month.[125] They are, however, expensive: a year of erenumab costs $6,900 as of 2019.[126]
Alternative therapies[edit]
Acupuncture has a small effect in reducing migraine frequency, compared to sham acupuncture, a practice where needles are placed randomly or do not penetrate the skin.[127] Physiotherapy, massage and relaxation, and chiropractic manipulation might be as effective as propranolol or topiramate in the prevention of migraine headaches; however, the research had some problems with methodology.[128][129] Another review, however, found evidence to support spinal manipulation to be poor and insufficient to support its use.[130]
Tentative evidence supports the use of stress reduction techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques.[68] Regular physical exercise may decrease the frequency.[15] Numerous psychological approaches have been developed that are aimed at preventing or reducing the frequency of migraine in adults including educational approaches, relaxation techniques, assistance in developing coping strategies, strategies to change the way one thinks of a migraine attack, and strategies to reduce symptoms.[131] The medical evidence supporting the effectiveness of these types of psychological approaches is very limited.[131]
Among alternative medicines, butterbur has the best evidence for its use.[132][133] However, unprocessed butterbur contains chemicals called pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) which can cause liver damage, however there are versions that are PA free.[134] In addition, butterbur may cause allergic reactions in people who are sensitive to plants such as ragweed.[135] There is tentative evidence that coenzyme Q10 reduces migraine frequency.[136]
Feverfew has traditionally been used as a treatment for fever, headache and migraine, women’s conditions such as difficulties in labour and regulation of menstruation, relief of stomach ache, toothache and insect bites. During the last decades, it has mainly been used for headache and as a preventive treatment for migraine.[137] The plant parts used for medicinal use are the dried leaves or the dried aerial parts. Several historical data supports feverfew’s traditional medicinal uses.[138] In addition, several clinical studies have been performed assessing the efficacy and safety of feverfew monotherapy in the prevention of migraine.[139] The majority of the clinical trials favoured feverfew over placebo. The data also suggest that feverfew is associated with only mild and transient adverse effects. The frequency of migraine was positively affected after treatment with feverfew. Reduction of migraine severity was also reported after intake of feverfew and incidence of nausea and vomiting decreased significantly. No effect of feverfew was reported in one study.[139]
There is tentative evidence for melatonin as an add-on therapy for prevention and treatment of migraine.[140][141] The data on melatonin are mixed and certain studies have had negative results.[140] The reasons for the mixed findings are unclear but may stem from differences in study design and dosage.[140] Melatonin’s possible mechanisms of action in migraine are not completely clear, but may include improved sleep, direct action on melatonin receptors in the brain, and anti-inflammatory properties.[140][142]
Devices and surgery[edit]
Medical devices, such as biofeedback and neurostimulators, have some advantages in migraine prevention, mainly when common anti-migraine medications are contraindicated or in case of medication overuse. Biofeedback helps people be conscious of some physiological parameters so as to control them and try to relax and may be efficient for migraine treatment.[143][144] Neurostimulation uses noninvasive or implantable neurostimulators similar to pacemakers for the treatment of intractable chronic migraine with encouraging results for severe cases.[145][146] A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator and a transcranial magnetic stimulator are approved in the United States for the prevention of migraines.[147][148] There is also tentative evidence for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation decreases the frequency of migraines.[149] Migraine surgery, which involves decompression of certain nerves around the head and neck, may be an option in certain people who do not improve with medications.[150]
Management[edit]
There are three main aspects of treatment: trigger avoidance, acute symptomatic control, and medication for prevention.[5] Medications are more effective if used earlier in an attack.[5] The frequent use of medications may result in medication overuse headache, in which the headaches become more severe and more frequent.[14] This may occur with triptans, ergotamines, and analgesics, especially opioid analgesics.[14] Due to these concerns simple analgesics are recommended to be used less than three days per week at most.[151]
Analgesics[edit]
Recommended initial treatment for those with mild to moderate symptoms are simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or the combination of paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen), aspirin, and caffeine.[10] Several NSAIDs, including diclofenac and ibuprofen have evidence to support their use.[152][153] Aspirin (900 to 1000 mg) can relieve moderate to severe migraine pain, with an effectiveness similar to sumatriptan.[154] Ketorolac is available in intravenous and intramuscular formulations.[10]
Paracetamol, either alone or in combination with metoclopramide, is another effective treatment with a low risk of adverse effects.[155] Intravenous metoclopramide is also effective by itself.[156][157] In pregnancy, paracetamol and metoclopramide are deemed safe as are NSAIDs until the third trimester.[10]
Naproxen by itself may not be effective as a stand-alone medicine to stop a migraine headache as it is only weakly better than a placebo medication in clinical trials.[158]
Antiemetics[edit]
Triptans[edit]
Triptans such as sumatriptan are medications used to stop an active migraine headache (an abortive medication). Triptans are the initially recommended treatments for those with moderate to severe pain from an acute migraine headache or those with milder symptoms who do not respond to simple analgesics.[10] Triptans have been shown to be effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people.[159][160] There are different methods or routes of administration to take sumatriptan including oral (by mouth), injectable (subcutaneous), rectal, nasal spray, and oral dissolving tablets.[5][161][162][163] For people with migraine symptoms such as nausea or vomiting, taking the abortive medicine by mouth or through the nose may be difficult. All route of administration have been shown to be effective at reducing migraine symptoms, however, nasal and injectable subcutaneous administration may result in more side effects.[163][162] The adverse effects associated with rectal administration have not been well studied.[161] Some people may find that they respond to one type of sumatriptan better than another.[10]
Most side effects are mild, including flushing; however, rare cases of myocardial ischemia have occurred.[5] They are thus not recommended for people with cardiovascular disease,[10] who have had a stroke, or have migraines that are accompanied by neurological problems.[164] In addition, triptans should be prescribed with caution for those with risk factors for vascular disease.[164] While historically not recommended in those with basilar migraines there is no specific evidence of harm from their use in this population to support this caution.[47] Triptans are not addictive, but may cause medication-overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.[165]
Sumatriptan does not prevent other migraine headaches from starting in the future.[162] For increased effectiveness at stopping migraine symptoms, a combined therapy that includes sumatriptan and naproxen may be suggested.[166]
CGRP receptor antagonists[edit]
CGRP receptor antagonists target calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor to prevent migraine headaches or reduce their severity.[38] CGRP is a signaling molecule as well as a potent vasodilator that is involved in the development of a migraine headache.[38] There are four injectable monoclonal antibodies that target CGRP or its receptor (eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab and galcanezumab) and the medications have demonstrated efficacy in the preventative treatment of episodic and chronic migraine headaches in phase 3 randomized clinical trials.[38] Eptinezumab is available as an infusion every three months, Erenumab and galcanezumab are once monthly injections and fremanezumab is a monthly or quarterly injection.
Ergotamines[edit]
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms.[5][167] They appear equally effective to the triptans[168] and experience adverse effects that typically are benign.[169] In the most severe cases, such as those with status migrainosus, they appear to be the most effective treatment option.[169] They can cause vasospasm including coronary vasospasm and are contraindicated in people with coronary artery disease.[170]
Magnesium[edit]
Magnesium is recognized as an inexpensive, over-the-counter supplement which can be part of a multimodal approach to migraine reduction. Some studies have shown to be effective in both preventing and treating migraine in intravenous form.[171] The intravenous form reduces attacks as measured in approximately 15-45 minutes, 120 minutes, and 24 hour time periods, magnesium taken orally alleviates the frequency and intensity of migraines.[172][173]
Other[edit]
Intravenous metoclopramide, intravenous prochlorperazine, or intranasal lidocaine are other potential options.[10][157] Metoclopramide or prochlorperazine are the recommended treatment for those who present to the emergency department.[10][157] Haloperidol may also be useful in this group.[157][167] A single dose of intravenous dexamethasone, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours.[174] Spinal manipulation for treating an ongoing migraine headache is not supported by evidence.[130] It is recommended that opioids and barbiturates not be used due to questionable efficacy, addictive potential, and the risk of rebound headache.[10][38] There is tentative evidence that propofol may be useful if other measures are not effective.[175]
Occipital nerve stimulation, may be effective but has the downsides of being cost-expensive and has a significant amount of complications.[176]
There is modest evidence for the effectiveness of non-invasive neuromodulatory devices, behavioral therapies and acupuncture in the treatment of migraine headaches.[38] There is little to no evidence for the effectiveness of physical therapy, chiropractic manipulation and dietary approaches to the treatment of migraine headaches.[38] Behavioral treatment of migraine headaches may be helpful for those who may not be able to take medications (for example pregnant women).[38]
Feverfew is registered as a traditional herbal medicine in the Nordic countries under the brand name Glitinum, only powdered feverfew is approved in the Herbal community monograph issued by European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Sexual activity, particularly orgasm, may provide relief for some migraineurs.[177]
Children[edit]
Ibuprofen helps decrease pain in children with migraines and is the initially recommended treatment.[178][179] Paracetamol does not appear to be effective in providing pain relief.[178] Triptans are effective, though there is a risk of causing minor side effects like taste disturbance, nasal symptoms, dizziness, fatigue, low energy, nausea, or vomiting.[178][180] Ibuprofen should be used less than half the days in a month and triptans less than a third of the days in a month to decrease the risk of medication overuse headache.[179]
Chronic migraine[edit]
Topiramate and botulinum toxin (Botox) have evidence in treating chronic migraine.[123][181] Botulinum toxin has been found to be useful in those with chronic migraine but not those with episodic ones.[182][183] The anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody erenumab was found in one study to decrease chronic migraines by 2.4 days more than placebo.[184]
Prognosis[edit]
«Migraine exists on a continuum of different attack frequencies and associated levels of disability.»[185] For those with occasional, episodic migraine, a «proper combination of drugs for prevention and treatment of migraine attacks» can limit the disease’s impact on patients’ personal and professional lives.[186] But fewer than half of people with migraine seek medical care and more than half go undiagnosed and undertreated.[187] «Responsive prevention and treatment of migraine is incredibly important» because evidence shows «an increased sensitivity after each successive attack, eventually leading to chronic daily migraine in some individuals.»[186] Repeated migraine results in «reorganization of brain circuitry,» causing «profound functional as well as structural changes in the brain.»[188] «One of the most important problems in clinical migraine is the progression from an intermittent, self-limited inconvenience to a life-changing disorder of chronic pain, sensory amplification, and autonomic and affective disruption. This progression, sometimes termed chronification in the migraine literature, is common, affecting 3% of migraineurs in a given year, such that 8% of migraineurs have chronic migraine in any given year.» Brain imagery reveals that the electrophysiological changes seen during an attack become permanent in people with chronic migraine; «thus, from an electrophysiological point of view, chronic migraine indeed resembles a never-ending migraine attack.»[188] Severe migraine ranks in the highest category of disability, according to the World Health Organization, which uses objective metrics to determine disability burden for the authoritative annual Global Burden of Disease report. The report classifies severe migraine alongside severe depression, active psychosis, quadriplegia, and terminal-stage cancer.[189]
Migraine with aura appears to be a risk factor for ischemic stroke[190] doubling the risk.[191] Being a young adult, being female, using hormonal birth control, and smoking further increases this risk.[190] There also appears to be an association with cervical artery dissection.[192] Migraine without aura does not appear to be a factor.[193] The relationship with heart problems is inconclusive with a single study supporting an association.[190] Migraine does not appear to increase the risk of death from stroke or heart disease.[194] Preventative therapy of migraines in those with migraine with aura may prevent associated strokes.[195] People with migraine, particularly women, may develop higher than average numbers of white matter brain lesions of unclear significance.[196]
Epidemiology[edit]
Disability-adjusted life year for migraines per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004
no data
<45
45–65
65–85
85–105
105–125
125–145
145–165
165–185
185–205
205–225
225–245
>245
Worldwide, migraine affects nearly 15% or approximately one billion people.[11] It is more common in women at 19% than men at 11%.[11] In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women experience a migraine attack in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively.[5] In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives with about 6–15% of adult men and 14–35% of adult women getting at least one yearly.[17] Rates of migraine are slightly lower in Asia and Africa than in Western countries.[58][197] Chronic migraine occurs in approximately 1.4 to 2.2% of the population.[198]
These figures vary substantially with age: onset of migraine is most commonly between 15 and 24 years of age, and occur most frequently in those 35 to 45 years of age.[5] In children, about 1.7% of 7 year olds and 3.9% of those between 7 and 15 experience migraine, with the condition being slightly more common in boys before puberty.[199] Children as young as two years may be affected.[178] During adolescence, migraine becomes more common among women[199] and this persists for the rest of the lifespan, being twice as common among elderly females than males.[200] In women migraine without aura are more common than migraine with aura; however in men the two types occur with similar frequency.[58]
During perimenopause symptoms often get worse before decreasing in severity.[200] While symptoms resolve in about two thirds of the elderly, in 3 to 10% they persist.[49]
History[edit]
The Head Ache, George Cruikshank (1819)
An early description consistent with migraine is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BCE in ancient Egypt.[24] In 200 BCE, writings from the Hippocratic school of medicine described the visual aura that can precede the headache and a partial relief occurring through vomiting.[201]
A second-century description by Aretaeus of Cappadocia divided headaches into three types: cephalalgia, cephalea, and heterocrania.[202] Galen of Pergamon used the term hemicrania (half-head), from which the word migraine was eventually derived.[202] He also proposed that the pain arose from the meninges and blood vessels of the head.[201] Migraine was first divided into the two now used types – migraine with aura (migraine ophthalmique) and migraine without aura (migraine vulgaire) in 1887 by Louis Hyacinthe Thomas, a French Librarian.[201] The mystical visions of Hildegard von Bingen, which she described as “reflections of the living light», are consistent with the visual aura experienced during migraines.[203]
A trepanated skull, from the Neolithic. The perimeter of the hole in the skull is rounded off by ingrowth of new bony tissue, indicating that the person survived the operation.
Trepanation, the deliberate drilling of holes into a skull, was practiced as early as 7,000 BCE.[24] While sometimes people survived, many would have died from the procedure due to infection.[204] It was believed to work via «letting evil spirits escape».[205] William Harvey recommended trepanation as a treatment for migraines in the 17th century.[206] The association between trepanation and headaches in ancient history may simply be a myth or unfounded speculation that originated several centuries later. In 1913, the world-famous American physician William Osler misinterpreted the French anthropologist and physician Paul Broca ’s words about a set of children’s skulls from the Neolithic age that he found during the 1870s. These skulls presented no evident signs of fractures that could justify this complex surgery for mere medical reasons. Trepanation was probably born of superstitions, to remove “confined demons” inside the head, or to create healing or fortune talismans with the bone fragments removed from the skulls of the patients. However, Osler wanted to make Broca’s theory more palatable to his modern audiences, and explained that trepanation procedures were used for mild conditions such as “infantile convulsions headache and various cerebral diseases believed to be caused by confined demons.”[207]
While many treatments for migraine have been attempted, it was not until 1868 that use of a substance which eventually turned out to be effective began.[201] This substance was the fungus ergot from which ergotamine was isolated in 1918.[208] Methysergide was developed in 1959 and the first triptan, sumatriptan, was developed in 1988.[208] During the 20th century with better study-design, effective preventive measures were found and confirmed.[201]
Society and culture[edit]
Migraine is a significant source of both medical costs and lost productivity. It has been estimated that migraine is the most costly neurological disorder in the European Community, costing more than €27 billion per year.[209] In the United States, direct costs have been estimated at $17 billion, while indirect costs — such as missed or decreased ability to work — is estimated at $15 billion.[210] Nearly a tenth of the direct cost is due to the cost of triptans.[210] In those who do attend work during a migraine attack, effectiveness is decreased by around a third.[209] Negative impacts also frequently occur for a person’s family.[209]
Research[edit]
Potential prevention mechanisms[edit]
Transcranial magnetic stimulation shows promise[10][211] as does transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation.[212] There is preliminary evidence that a ketogenic diet may help prevent episodic and long-term migraine.[213][214]
Potential gender dependency[edit]
While no definitive proof has been found linking migraine to gender, statistical data indicates that women may be more prone to having migraine, showing migraine incidence three times higher among women than men.[215][216] The Society for Women’s Health Research has also mentioned hormonal influences, mainly estrogen, as having a considerable role in provoking migraine pain. Studies and research related to the gender dependencies of migraine are still ongoing, and conclusions have yet to be achieved.[217][218][219]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f «Headache disorders Fact sheet N°277». October 2012. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Simon RP, Aminoff MJ, Greenberg DA (2009). Clinical neurology (7 ed.). New York, N.Y: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. pp. 85–88. ISBN 9780071664332.
- ^ a b c d Piane M, Lulli P, Farinelli I, Simeoni S, De Filippis S, Patacchioli FR, Martelletti P (December 2007). «Genetics of migraine and pharmacogenomics: some considerations». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 8 (6): 334–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-007-0427-2. PMC 2779399. PMID 18058067.
- ^ a b c Lay CL, Broner SW (May 2009). «Migraine in women». Neurologic Clinics. 27 (2): 503–11. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2009.01.002. PMID 19289228.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Bartleson JD, Cutrer FM (May 2010). «Migraine update. Diagnosis and treatment». Minnesota Medicine. 93 (5): 36–41. PMID 20572569.
- ^ Olesen J (2006). The Headaches. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 424. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ «Cluster Headache». American Migraine Foundation. 15 February 2017. Archived from the original on 9 May 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ a b Armstrong C (April 2013). «AAN/AHS update recommendations for migraine prevention in adults». American Family Physician. 87 (8): 584–5. PMID 23668450.
- ^ a b Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). «Valproate (valproic acid or sodium valproate or a combination of the two) for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD010611. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010611. PMID 23797677.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Gilmore B, Michael M (February 2011). «Treatment of acute migraine headache». American Family Physician. 83 (3): 271–80. PMID 21302868.
- ^ a b c d Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. (December 2012). «Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010». Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMC 6350784. PMID 23245607.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (2011). Roach, Peter; Setter, Jane; Esling, John (eds.). Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-15255-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004). «The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition». Cephalalgia. 24 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1): 9–160. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00653.x. PMID 14979299. as PDF Archived 31 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, Czapinska-Ciepiela EK, Ariadni DD, Di Lenola D, et al. (September 2018). «The association between migraine and physical exercise». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y. PMC 6134860. PMID 30203180.
- ^ Pryse-Phillips W (2003). Companion to clinical neurology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford university press. p. 587. ISBN 9780195159387. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Stovner LJ, Zwart JA, Hagen K, Terwindt GM, Pascual J (April 2006). «Epidemiology of headache in Europe». European Journal of Neurology. 13 (4): 333–45. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01184.x. PMID 16643310. S2CID 7490176.
- ^ a b «NINDS Migraine Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 3 November 2015. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ Nowaczewska M, Wiciński M, Kaźmierczak W (July 2020). «The Ambiguous Role of Caffeine in Migraine Headache: From Trigger to Treatment». Nutrients. 12 (8): 2259. doi:10.3390/nu12082259. PMC 7468766. PMID 32731623.
- ^ Shapiro RE, Cowan R (2017-01-10). «Caffeine and Migraine». American Migraine Foundation. Retrieved 2021-06-08.
- ^ Diener HC, Charles A, Goadsby PJ, Holle D (October 2015). «New therapeutic approaches for the prevention and treatment of migraine». The Lancet. Neurology. 14 (10): 1010–22. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00198-2. PMID 26376968. S2CID 26523013.
- ^ Gobel H. «1. Migraine». ICHD-3 The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- ^ Vos, Theo; et al. (GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (September 2017). «Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016». Lancet. 390 (10100): 1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. PMC 5605509. PMID 28919117.
- ^ a b c Miller N (2005). Walsh and Hoyt’s clinical neuro-ophthalmology (6 ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1275. ISBN 9780781748117. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ Liddell HG, Scott R. «ἡμικρανία». A Greek-English Lexicon. Archived from the original on 8 November 2013. on Perseus
- ^ Anderson K, Anderson LE, Glanze WD (1994). Mosby’s Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary (4 ed.). Mosby. p. 998. ISBN 978-0-8151-6111-0.
- ^ Bigal ME, Lipton RB (June 2008). «The prognosis of migraine». Current Opinion in Neurology. 21 (3): 301–8. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328300c6f5. PMID 18451714. S2CID 34805084.
- ^ Gutman SA (2008). Quick reference neuroscience for rehabilitation professionals: the essential neurologic principles underlying rehabilitation practice (2 ed.). Thorofare, NJ: SLACK. p. 231. ISBN 9781556428005. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ a b c d e The Headaches, Pg 232–233
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 512. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Baskin SM, Lipchik GL, Smitherman TA (October 2006). «Mood and anxiety disorders in chronic headache». Headache. 46 Suppl 3: S76-87. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00559.x. PMID 17034402. S2CID 35451906.
- ^ a b Lynn DJ, Newton HB, Rae-Grant A (2004). The 5-minute neurology consult. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 26. ISBN 9780683307238. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Buzzi MG, Cologno D, Formisano R, Rossi P (October–December 2005). «Prodromes and the early phase of the migraine attack: therapeutic relevance». Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 179–83. PMID 16483458.
- ^ Rossi P, Ambrosini A, Buzzi MG (October–December 2005). «Prodromes and predictors of migraine attack». Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 185–91. PMID 16483459.
- ^ Ropper AH, Adams RD, Victor M, Samuels MA (2009). Adams and Victor’s principles of neurology (9 ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. Chapter 10. ISBN 9780071499927.
- ^ May A, Burstein R (November 2019). «Hypothalamic regulation of headache and migraine». Cephalalgia. 39 (13): 1710–1719. doi:10.1177/0333102419867280. PMC 7164212. PMID 31466456.
- ^ a b c d Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. pp. 1116–1117. ISBN 978-0-07-148480-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Ashina M (November 2020). «Migraine». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (19): 1866–1876. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1915327. PMID 33211930. S2CID 227078662.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k The Headaches, pp. 407–419
- ^ Slap, GB (2008). Adolescent medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 105. ISBN 9780323040730. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Qubty W, Patniyot I (June 2020). «Migraine Pathophysiology». Pediatric Neurology. 107: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2019.12.014. PMID 32192818. S2CID 213191464.
- ^ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (1 January 2011). The Cleveland Clinic manual of headache therapy. New York: Springer. p. 6. ISBN 9781461401780. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Bigal ME, Arruda MA (July 2010). «Migraine in the pediatric population—evolving concepts». Headache. 50 (7): 1130–43. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01717.x. PMID 20572878. S2CID 23256755.
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 238. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Dalessio (2001). Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Dalessio DJ (eds.). Wolff’s headache and other head pain (7 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 122. ISBN 9780195135183.
- ^ a b Lisak RP, Truong DD, Carroll W, Bhidayasiri R (2009). International neurology: a clinical approach. Chichester, UK: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 670. ISBN 9781405157384.
- ^ a b c Kaniecki RG (June 2009). «Basilar-type migraine». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (3): 217–20. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0036-7. PMID 19457282. S2CID 22242504.
- ^ a b Joel S. Glaser (1999). Neuro-ophthalmology (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 555. ISBN 9780781717298. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Sirven JI, Malamut BL (2008). Clinical neurology of the older adult (2 ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 197. ISBN 9780781769471. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ Dr. Jennifer Robblee (21 August 2019). «Silent Migraine: A Guide». American Migraine Foundation. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ a b He Y, Li Y, Nie Z (February 2015). «Typical aura without headache: a case report and review of the literature». Journal of Medical Case Reports. 9 (1): 40. doi:10.1186/s13256-014-0510-7. PMC 4344793. PMID 25884682.
- ^ Jayne Leonard (medically reviewed by Seunggu Han, M.D.) (7 September 2018). «Silent migraine: Symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention». www.medicalnewstoday.com. Medical News Today. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ Bose P, Goadsby PJ (June 2016). «The migraine postdrome». Current Opinion in Neurology. 29 (3): 299–301. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000310. PMID 26886356. S2CID 22445093.
- ^ Kelman L (February 2006). «The postdrome of the acute migraine attack». Cephalalgia. 26 (2): 214–20. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.01026.x. PMID 16426278. S2CID 21519111.
- ^ Halpern AL, Silberstein SD (2005). «Ch. 9: The Migraine Attack—A Clinical Description». In Kaplan PW, Fisher RS (eds.). Imitators of Epilepsy (2 ed.). New York: Demos Medical. ISBN 978-1-888799-83-5. NBK7326.
- ^ Robbins MS, Lipton RB (April 2010). «The epidemiology of primary headache disorders». Seminars in Neurology. 30 (2): 107–19. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1249220. PMID 20352581.
- ^ a b c Schürks M (January 2012). «Genetics of migraine in the age of genome-wide association studies». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 13 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0399-0. PMC 3253157. PMID 22072275.
- ^ a b c d The Headaches, pp. 238–40
- ^ The Headaches, pp. 246–247
- ^ de Vries B, Frants RR, Ferrari MD, van den Maagdenberg AM (July 2009). «Molecular genetics of migraine». Human Genetics. 126 (1): 115–32. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0684-z. PMID 19455354. S2CID 20119237.
- ^ Montagna P (September 2008). «Migraine genetics». Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 8 (9): 1321–30. doi:10.1586/14737175.8.9.1321. PMID 18759544. S2CID 207195127.
- ^ a b c Ducros A (May 2013). «[Genetics of migraine]». Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 360–71. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.010. PMID 23618705.
- ^ Wan D, Wang C, Zhang X, Tang W, Chen M, Dong Z, Yu S (1 January 2016). «Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and migraine: a meta-analysis». The International Journal of Neuroscience. 126 (5): 393–9. doi:10.3109/00207454.2015.1025395. PMID 26000817. S2CID 34902092.
- ^ Dussor G, Cao YQ (October 2016). «TRPM8 and Migraine». Headache. 56 (9): 1406–1417. doi:10.1111/head.12948. PMC 5335856. PMID 27634619.
- ^ a b c Levy D, Strassman AM, Burstein R (June 2009). «A critical view on the role of migraine triggers in the genesis of migraine pain». Headache. 49 (6): 953–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01444.x. PMID 19545256. S2CID 31707887.
- ^ Martin PR (June 2010). «Behavioral management of migraine headache triggers: learning to cope with triggers». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 14 (3): 221–7. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0112-z. PMID 20425190. S2CID 5511782.
- ^ Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB (2014). «Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies». Headache. 54 (10): 1670–9. doi:10.1111/head.12468. PMID 25399858. S2CID 25016889.
- ^ a b c Radat F (May 2013). «[Stress and migraine]». Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 406–12. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.008. PMID 23608071.
- ^ Peterlin BL, Katsnelson MJ, Calhoun AH (October 2009). «The associations between migraine, unipolar psychiatric comorbidities, and stress-related disorders and the role of estrogen». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (5): 404–12. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0066-1. PMC 3972495. PMID 19728969.
- ^ Chai NC, Peterlin BL, Calhoun AH (June 2014). «Migraine and estrogen». Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 315–24. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000091. PMC 4102139. PMID 24792340.
- ^ Finocchi C, Sivori G (May 2012). «Food as trigger and aggravating factor of migraine». Neurological Sciences. 33 Suppl 1 (1): S77-80. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1046-5. PMID 22644176. S2CID 19582697.
- ^ Rockett FC, de Oliveira VR, Castro K, Chaves ML, Perla A, Perry ID (June 2012). «Dietary aspects of migraine trigger factors». Nutrition Reviews. 70 (6): 337–56. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00468.x. PMID 22646127.
- ^ Ghose, K.; Carroll, J. D. (1984). «Mechanism of Tyramine-Induced Migraine: Similarity with Dopamine and Interactions with Disulfiram and Propranolol in Migraine Patients». Neuropsychobiology. 12 (2–3): 122–126. doi:10.1159/000118123. PMID 6527752.
- ^ Moffett, A.; Swash, M.; Scott, D. F. (1972). «Effect of tyramine in migraine : a double-blind study» (PDF). Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 35 (4): 496–499. doi:10.1136/jnnp.35.4.496. PMC 494110. PMID 4559027.
- ^ «Tyramine and Migraines: What You Need to Know». www.excedrin.com. Retrieved 2022-03-04.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second ed.). Academic Press. 2003. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0.
- ^ Özturan; et al. (2016). «The Relationship Between Migraine and Nutrition» (PDF). Turk J Neurol. 22 (2): 44–50. doi:10.4274/tnd.37132.
- ^ Sun-Edelstein C, Mauskop A (June 2009). «Foods and supplements in the management of migraine headaches» (PDF). The Clinical Journal of Pain. 25 (5): 446–52. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.530.1223. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31819a6f65. PMID 19454881. S2CID 3042635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 August 2017.
- ^ Friedman DI, De ver Dye T (June 2009). «Migraine and the environment». Headache. 49 (6): 941–52. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01443.x. PMID 19545255. S2CID 29764274.
- ^ Andreou AP, Edvinsson L (December 2019). «Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 20 (1): 117. doi:10.1186/s10194-019-1066-0. PMC 6929435. PMID 31870279.
- ^ «What is Migraine?». Migraine Research Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020.
- ^ «Migraine Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020.
- ^ Hoffmann J, Baca SM, Akerman S (April 2019). «Neurovascular mechanisms of migraine and cluster headache». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 39 (4): 573–594. doi:10.1177/0271678×17733655. PMC 6446418. PMID 28948863.
- ^ Brennan KC, Charles A (June 2010). «An update on the blood vessel in migraine». Current Opinion in Neurology. 23 (3): 266–74. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833821c1. PMC 5500293. PMID 20216215.
- ^ Spiri, Daniele; Titomanlio, Luigi; Pogliani, Laura; Zuccotti, Gianvincenzo (1 January 2012). «Pathophysiology of migraine: The neurovascular theory». Headaches: Causes, Treatment and Prevention: 51–64.
- ^ Goadsby PJ (January 2009). «The vascular theory of migraine—a great story wrecked by the facts». Brain. 132 (Pt 1): 6–7. doi:10.1093/brain/awn321. PMID 19098031.
- ^ Dodick DW (April 2008). «Examining the essence of migraine—is it the blood vessel or the brain? A debate». Headache. 48 (4): 661–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01079.x. PMID 18377395. S2CID 6272233.
- ^ Chen D, Willis-Parker M, Lundberg GP (October 2020). «Migraine headache: Is it only a neurological disorder? Links between migraine and cardiovascular disorders». Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 30 (7): 424–430. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.10.005. PMID 31679956.
- ^ Jacobs B, Dussor G (December 2016). «Neurovascular contributions to migraine: Moving beyond vasodilation». Neuroscience. 338: 130–144. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.012. PMC 5083225. PMID 27312704.
- ^ Mason BN, Russo AF (2018). «Vascular Contributions to Migraine: Time to Revisit?». Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 12: 233. doi:10.3389/fncel.2018.00233. PMC 6088188. PMID 30127722.
- ^ Dodick DW, Gargus JJ (August 2008). «Why migraines strike». Scientific American. 299 (2): 56–63. Bibcode:2008SciAm.299b..56D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0808-56. PMID 18666680.
- ^ a b c d The Headaches, Chp. 28, pp. 269–72
- ^ a b c Olesen J, Burstein R, Ashina M, Tfelt-Hansen P (July 2009). «Origin of pain in migraine: evidence for peripheral sensitisation». The Lancet. Neurology. 8 (7): 679–90. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70090-0. PMID 19539239. S2CID 20452008.
- ^ Akerman S, Holland PR, Goadsby PJ (September 2011). «Diencephalic and brainstem mechanisms in migraine». Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 12 (10): 570–84. doi:10.1038/nrn3057. PMID 21931334. S2CID 8472711.
- ^ Shevel E (March 2011). «The extracranial vascular theory of migraine—a great story confirmed by the facts». Headache. 51 (3): 409–417. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01844.x. PMID 21352215. S2CID 6939786.
- ^ a b Burnstock G (1 January 2016). «Purinergic Mechanisms and Pain». In Barrett JE (ed.). Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain. Advances in Pharmacology. Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain. Vol. 75. Academic Press. pp. 91–137. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2015.09.001. ISBN 9780128038833. PMID 26920010.
- ^ Davidoff R (14 February 2002). Migraine: Manifestations, Pathogenesis, and Management. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-803135-2.
- ^ Lipton RB, Diener HC, Robbins MS, Garas SY, Patel K (October 2017). «Caffeine in the management of patients with headache». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 18 (1): 107. doi:10.1186/s10194-017-0806-2. PMC 5655397. PMID 29067618.
- ^ Hamel E (November 2007). «Serotonin and migraine: biology and clinical implications». Cephalalgia. 27 (11): 1293–300. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01476.x. PMID 17970989. S2CID 26543041.
- ^
- American Headache Society (September 2013). «Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question». Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). «The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations». Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658. S2CID 14443890.
- Silberstein SD (September 2000). «Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). «Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis». Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ^ Cousins G, Hijazze S, Van de Laar FA, Fahey T (Jul–Aug 2011). «Diagnostic accuracy of the ID Migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Headache. 51 (7): 1140–8. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01916.x. PMID 21649653. S2CID 205684294.
- ^ «Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition». Cephalalgia. 38 (1): 1–211. January 2018. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202. PMID 29368949.
- ^ Nappi G (September 2005). «Introduction to the new International Classification of Headache Disorders». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 6 (4): 203–4. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0185-y. PMC 3452009. PMID 16362664.
- ^ Negro A, Rocchietti-March M, Fiorillo M, Martelletti P (December 2011). «Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments». European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 15 (12): 1401–20. PMID 22288302.
- ^ a b c d Davidoff RA (2002). Migraine : manifestations, pathogenesis, and management (2 ed.). Oxford [u.a.]: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 81. ISBN 9780195137057. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Russell G, Abu-Arafeh I, Symon DN (2002). «Abdominal migraine: evidence for existence and treatment options». Paediatric Drugs. 4 (1): 1–8. doi:10.2165/00128072-200204010-00001. PMID 11817981. S2CID 12289726.
- ^ Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). «The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations». Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658. S2CID 14443890.
- ^ Silberstein SD (September 2000). «Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- ^ Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). «Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis». Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ^ a b Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- ^ Modi S, Lowder DM (January 2006). «Medications for migraine prophylaxis». American Family Physician. 73 (1): 72–8. PMID 16417067.
- ^ Diener HC, Limmroth V (August 2004). «Medication-overuse headache: a worldwide problem». The Lancet. Neurology. 3 (8): 475–83. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00824-5. PMID 15261608. S2CID 43840120.
- ^ Fritsche G, Diener HC (November 2002). «Medication overuse headaches — what is new?». Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 1 (4): 331–8. doi:10.1517/14740338.1.4.331. PMID 12904133. S2CID 23422679.
- ^ Kaniecki R, Lucas S (2004). «Treatment of primary headache: preventive treatment of migraine». Standards of care for headache diagnosis and treatment. Chicago: National Headache Foundation. pp. 40–52.
- ^ a b c Loder E, Burch R, Rizzoli P (June 2012). «The 2012 AHS/AAN guidelines for prevention of episodic migraine: a summary and comparison with other recent clinical practice guidelines». Headache. 52 (6): 930–45. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02185.x. PMID 22671714. S2CID 540800.
- ^ Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). «Antiepileptics other than gabapentin, pregabalin, topiramate, and valproate for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (6): CD010608. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010608. PMC 8221229. PMID 23797674.
- ^ Locher C, Kossowsky J, Koechlin H, Lam TL, Barthel J, Berde CB, et al. (April 2020). «Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Pharmacologic Treatments for Pediatric Migraine Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis». JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (4): 341–349. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856. PMC 7042942. PMID 32040139.
- ^ Merison K, Jacobs H (November 2016). «Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood Migraine». Current Treatment Options in Neurology. 18 (11): 48. doi:10.1007/s11940-016-0431-4. PMID 27704257. S2CID 28302667.
- ^ Dorosch T, Ganzer CA, Lin M, Seifan A (September 2019). «Efficacy of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Preventative Treatment of Episodic Migraine in Adults». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 23 (11): 85. doi:10.1007/s11916-019-0823-8. PMID 31515634. S2CID 202557362.
- ^ Cernes R, Mashavi M, Zimlichman R (2011). «Differential clinical profile of candesartan compared to other angiotensin receptor blockers». Vascular Health and Risk Management. 7: 749–59. doi:10.2147/VHRM.S22591. PMC 3253768. PMID 22241949.
- ^ Rajapakse T, Pringsheim T (April 2016). «Nutraceuticals in Migraine: A Summary of Existing Guidelines for Use». Headache. 56 (4): 808–16. doi:10.1111/head.12789. PMID 26954394. S2CID 31097792.
- ^ Teigen L, Boes CJ (September 2015). «An evidence-based review of oral magnesium supplementation in the preventive treatment of migraine». Cephalalgia. 35 (10): 912–22. doi:10.1177/0333102414564891. PMID 25533715. S2CID 25398410.
- ^ a b Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). «Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 78 (17): 1337–45. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d20. PMC 3335452. PMID 22529202.
- ^ Shamliyan TA, Choi JY, Ramakrishnan R, Miller JB, Wang SY, Taylor FR, Kane RL (September 2013). «Preventive pharmacologic treatments for episodic migraine in adults». Journal of General Internal Medicine. 28 (9): 1225–37. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2433-1. PMC 3744311. PMID 23592242.
- ^ Ibekwe, A.; Perras, C.; Mierzwinski-Urban, M. (2016). «Monoclonal Antibodies to Prevent Migraine Headaches». PMID 30855775.
- ^ Loder E, Renthal W (March 2019). «Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Treatments for Migraine». JAMA Internal Medicine. 179 (3): 421–422. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536. PMID 30640381. S2CID 58601441.
- ^ Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, Fei Y, Mehring M, Vertosick EA, et al. (June 2016). «Acupuncture for the prevention of episodic migraine». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (6): CD001218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001218.pub3. PMC 4977344. PMID 27351677.
- ^ Chaibi A, Tuchin PJ, Russell MB (April 2011). «Manual therapies for migraine: a systematic review». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 12 (2): 127–33. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0296-6. PMC 3072494. PMID 21298314.
- ^ Millstine D, Chen CY, Bauer B (May 2017). «Complementary and integrative medicine in the management of headache». BMJ. 357: j1805. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1805. PMID 28512119. S2CID 19155758.
- ^ a b Posadzki P, Ernst E (June 2011). «Spinal manipulations for the treatment of migraine: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials». Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 964–70. doi:10.1177/0333102411405226. PMID 21511952. S2CID 31205541.
- ^ a b Sharpe L, Dudeney J, Williams AC, Nicholas M, McPhee I, Baillie A, et al. (July 2019). «Psychological therapies for the prevention of migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7: CD012295. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012295.pub2. PMC 6603250. PMID 31264211.
- ^ Holland S, Silberstein SD, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). «Evidence-based guideline update: NSAIDs and other complementary treatments for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 78 (17): 1346–53. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d0c. PMC 3335449. PMID 22529203.
- ^ Pringsheim T, Davenport W, Mackie G, Worthington I, Aubé M, Christie SN, et al. (March 2012). «Canadian Headache Society guideline for migraine prophylaxis». The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 39 (2 Suppl 2): S1-59. PMID 22683887.
- ^ «Butterbur: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning». www.webmd.com. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ «Butterbur». NCCIH. 8 February 2012. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ Littarru GP, Tiano L (November 2005). «Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q10: an update». Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 8 (6): 641–6. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000171123.60665.16. PMID 16205466. S2CID 25010508.
- ^ Groenewegen WA, Knight DW, Heptinstall S (1992). «Progress in the medicinal chemistry of the herb feverfew». Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. 29: 217–38. doi:10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70009-2. ISBN 9780444894724. PMID 1475370.
- ^ Barnes, J; Anderson, LA; Philipson, JD (2007). Herbal Medicines. 3rd ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press.
- ^ a b EMA. «Assessment report on Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Schultz Bip., herba» (PDF). www.ema.europa.eu. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- ^ a b c d Gelfand AA, Goadsby PJ (September 2016). «The Role of Melatonin in the Treatment of Primary Headache Disorders». Headache (Review). 56 (8): 1257–66. doi:10.1111/head.12862. PMC 5012937. PMID 27316772.
- ^ Long R, Zhu Y, Zhou S (January 2019). «Therapeutic role of melatonin in migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review». Medicine. 98 (3): e14099. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014099. PMC 6370052. PMID 30653130.
- ^ Nesbitt AD, Leschziner GD, Peatfield RC (September 2014). «Headache, drugs and sleep». Cephalalgia (Review). 34 (10): 756–66. doi:10.1177/0333102414542662. PMID 25053748. S2CID 33548757.
- ^ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A (March 2007). «Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis». Pain. 128 (1–2): 111–27. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007. PMID 17084028. S2CID 23351902.
- ^ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A, Rief W, Andrasik F (September 2008). «Biofeedback treatment for headache disorders: a comprehensive efficacy review». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 33 (3): 125–40. doi:10.1007/s10484-008-9060-3. PMID 18726688. S2CID 29122354.
- ^ Schoenen J, Allena M, Magis D (2010). «Neurostimulation therapy in intractable headaches». In Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds.). Headache. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. pp. 443–50. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97037-1. ISBN 9780444521392. PMID 20816443.
- ^ Reed KL, Black SB, Banta CJ, Will KR (March 2010). «Combined occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine headaches: initial experience». Cephalalgia. 30 (3): 260–71. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01996.x. PMID 19732075. S2CID 18639211.
- ^ «FDA allows marketing of first medical device to prevent migraine headaches». Food and Drug Administration. 11 March 2014. Archived from the original on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ^ «FDA approves transcranial magnetic stimulator» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 February 2014.
- ^ Tao H, Wang T, Dong X, Guo Q, Xu H, Wan Q (May 2018). «Effectiveness of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the treatment of migraine: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 42. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0868-9. PMC 5975046. PMID 29845369.
We found significant reduction of monthly headache days
- ^ Kung TA, Guyuron B, Cederna PS (January 2011). «Migraine surgery: a plastic surgery solution for refractory migraine headache». Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 127 (1): 181–189. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f95a01. PMID 20871488. S2CID 18817383.
- ^ «American Headache Society Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question». Choosing Wisely. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
- ^ Rabbie R, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Ibuprofen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008039. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008039.pub3. PMC 4161114. PMID 23633348.
- ^ Derry S, Rabbie R, Moore RA (April 2013). «Diclofenac with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008783. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008783.pub3. PMC 4164457. PMID 23633360.
- ^ Kirthi V, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Aspirin with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008041. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008041.pub3. PMC 4163048. PMID 23633350.
- ^ Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008040. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008040.pub3. PMC 4161111. PMID 23633349.
- ^ Eken C (March 2015). «Critical reappraisal of intravenous metoclopramide in migraine attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis». The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 33 (3): 331–7. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2014.11.013. PMID 25579820.
- ^ a b c d Orr SL, Friedman BW, Christie S, Minen MT, Bamford C, Kelley NE, Tepper D (June 2016). «Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies». Headache. 56 (6): 911–40. doi:10.1111/head.12835. PMID 27300483.
- ^ Law, Simon; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2013-10-20). «Naproxen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD009455. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009455.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6540401. PMID 24142263.
- ^ Singh, Rashmi B. Halker; VanderPluym, Juliana H.; Morrow, Allison S.; Urtecho, Meritxell; Nayfeh, Tarek; Roldan, Victor D. Torres; Farah, Magdoleen H.; Hasan, Bashar; Saadi, Samer (2020). Acute Treatments for Episodic Migraine. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 33411427.
- ^ Johnston MM, Rapoport AM (August 2010). «Triptans for the management of migraine». Drugs. 70 (12): 1505–18. doi:10.2165/11537990-000000000-00000. PMID 20687618. S2CID 41613179.
- ^ a b Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (rectal route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (2): CD009664. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009664. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4170908. PMID 22336868.
- ^ a b c Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (intranasal route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009663. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009663. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164476. PMID 22336867.
- ^ a b Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (subcutaneous route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009665. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009665. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164380. PMID 22336869.
- ^ a b «Generic migraine drug could relieve your pain and save you money». Best Buy Drugs. Consumer Reports. Archived from the original on 4 August 2013.
- ^ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (April 2010). «Breaking the cycle of medication overuse headache». Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 77 (4): 236–42. doi:10.3949/ccjm.77a.09147. PMID 20360117. S2CID 36333666.
- ^ Law S, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2016). «Sumatriptan plus naproxen for the treatment of acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD008541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008541.pub3. PMC 6485397. PMID 27096438.
- ^ a b Sumamo Schellenberg, E.; Dryden, D. M.; Pasichnyk, D.; Ha, C.; Vandermeer, B.; Friedman, B. W.; Colman, I.; Rowe, B. H. (2012). «Acute migraine treatment in emergency settings». PMID 23304741.
- ^ Kelley NE, Tepper DE (January 2012). «Rescue therapy for acute migraine, part 1: triptans, dihydroergotamine, and magnesium». Headache. 52 (1): 114–28. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.02062.x. PMID 22211870. S2CID 45767513.
- ^ a b Morren JA, Galvez-Jimenez N (December 2010). «Where is dihydroergotamine mesylate in the changing landscape of migraine therapy?». Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (18): 3085–93. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.533839. PMID 21080856. S2CID 44639896.
- ^ Tfelt-Hansen P, Saxena PR, Dahlöf C, Pascual J, Láinez M, Henry P, et al. (January 2000). «Ergotamine in the acute treatment of migraine: a review and European consensus». Brain. 123 ( Pt 1): 9–18. doi:10.1093/brain/123.1.9. PMID 10611116.
- ^ Yablon LA, Mauskop A (2011). «Magnesium in headache». In Vink R, Nechifor M (eds.). Magnesium in the Central Nervous System. Adelaide (AU): University of Adelaide Press. ISBN 978-0-9870730-5-1. PMID 29920023. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- ^ HY, Chiu; TH, Yeh; YC, Huang; PY, Chen (2015-02-24). «Effects of Intravenous and Oral Magnesium on Reducing Migraine: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials». Pain Physician. 19 (1). ISSN 2150-1149. PMID 26752497. Retrieved 2022-12-02.
- ^ Veronese, Nicola; Demurtas, Jacopo; Pesolillo, Gabriella; Celotto, Stefano; Barnini, Tommaso; Calusi, Giovanni; Caruso, Maria Gabriella; Notarnicola, Maria; Reddavide, Rosa; Stubbs, Brendon; Solmi, Marco; Maggi, Stefania; Vaona, Alberto; Firth, Joseph; Smith, Lee; Koyanagi, Ai; Dominguez, Ligia; Barbagallo, Mario (2019-01-25). «Magnesium and health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational and intervention studies». European Journal of Nutrition. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 59 (1): 263–272. doi:10.1007/s00394-019-01905-w. ISSN 1436-6207. PMID 30684032. S2CID 59275463.
- ^ Colman I, Friedman BW, Brown MD, Innes GD, Grafstein E, Roberts TE, Rowe BH (June 2008). «Parenteral dexamethasone for acute severe migraine headache: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials for preventing recurrence». BMJ. 336 (7657): 1359–61. doi:10.1136/bmj.39566.806725.BE. PMC 2427093. PMID 18541610.
- ^ Piatka C, Beckett RD (February 2020). «Propofol for Treatment of Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review». Academic Emergency Medicine. 27 (2): 148–160. doi:10.1111/acem.13870. PMID 31621134.
- ^ Vukovic Cvetkovic V, Jensen RH (January 2019). «Neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine and cluster headache». Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 139 (1): 4–17. doi:10.1111/ane.13034. PMID 30291633. S2CID 52923061.
- ^ Hambach, A.; Frese, A.; Evers, S. (2013). «Sexuelle Aktivität und Kopfschmerz». Nervenheilkunde (in German). Georg Thieme Verlag KG. 32 (3): 118–122. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1628490. ISSN 0722-1541.
- ^ a b c d Richer L, Billinghurst L, Linsdell MA, Russell K, Vandermeer B, Crumley ET, et al. (April 2016). «Drugs for the acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (10): CD005220. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005220.pub2. PMC 6516975. PMID 27091010.
- ^ a b Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171.
- ^ Wang, Guihua; Tan, Tianlin; Liu, Yao; Hong, Peiwei (2020). «Drugs for Acute Attack of Pediatric Migraine: A Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials». Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 195: 105853. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105853. ISSN 1872-6968. PMID 32464520. S2CID 215814011.
- ^ Herd CP, Tomlinson CL, Rick C, Scotton WJ, Edwards J, Ives N, et al. (June 2018). «Botulinum toxins for the prevention of migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (6): CD011616. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011616.pub2. PMC 6513576. PMID 29939406.
- ^ Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Hayashino Y (April 2012). «Botulinum toxin A for prophylactic treatment of migraine and tension headaches in adults: a meta-analysis». JAMA. 307 (16): 1736–45. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.505. PMID 22535858.
- ^ Simpson DM, Hallett M, Ashman EJ, Comella CL, Green MW, Gronseth GS, et al. (May 2016). «Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 86 (19): 1818–26. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560. PMC 4862245. PMID 27164716.
- ^ Markham A (July 2018). «Erenumab: First Global Approval». Drugs. 78 (11): 1157–1161. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0944-0. PMID 29968151. S2CID 49559342.
- ^ Silberstein, Stephen D.; Lee, Lulu; Gandhi, Kavita; Fitzgerald, Timothy; Bell, Jvawnna; Cohen, Joshua M. (2018). «Health care Resource Utilization and Migraine Disability Along the Migraine Continuum Among Patients Treated for Migraine». Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain. 58 (10): 1579–1592. doi:10.1111/head.13421. PMID 30375650. S2CID 53114546.
- ^ a b «Migraine Information Page: Prognosis Archived 2020-06-10 at the Wayback Machine,» National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), National Institutes of Health (US).
- ^ «Facts and Figures». The Migraine Trust.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Brennan, KC; Pietrobon, D (March 2018). «A systems neuroscience approach to migraine». Neuron. 97 (5): 1004–1021. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.029. PMC 6402597. PMID 29518355.
- ^ World Health Organization (2008). «Disability classes for the Global Burden of Disease study» (table 8), The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update, p 33.
- ^ a b c Schürks M, Rist PM, Bigal ME, Buring JE, Lipton RB, Kurth T (October 2009). «Migraine and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ. 339: b3914. doi:10.1136/bmj.b3914. PMC 2768778. PMID 19861375.
- ^ Kurth T, Chabriat H, Bousser MG (January 2012). «Migraine and stroke: a complex association with clinical implications». The Lancet. Neurology. 11 (1): 92–100. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70266-6. PMID 22172624. S2CID 31939284.
- ^ Rist PM, Diener HC, Kurth T, Schürks M (June 2011). «Migraine, migraine aura, and cervical artery dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 886–96. doi:10.1177/0333102411401634. PMC 3303220. PMID 21511950.
- ^ Kurth T (March 2010). «The association of migraine with ischemic stroke». Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 10 (2): 133–9. doi:10.1007/s11910-010-0098-2. PMID 20425238. S2CID 27227332.
- ^ Schürks M, Rist PM, Shapiro RE, Kurth T (September 2011). «Migraine and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Cephalalgia. 31 (12): 1301–14. doi:10.1177/0333102411415879. PMC 3175288. PMID 21803936.
- ^ Weinberger J (March 2007). «Stroke and migraine». Current Cardiology Reports. 9 (1): 13–9. doi:10.1007/s11886-007-0004-y. PMID 17362679. S2CID 46681674.
- ^ Hougaard A, Amin FM, Ashina M (June 2014). «Migraine and structural abnormalities in the brain». Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 309–14. doi:10.1097/wco.0000000000000086. PMID 24751961.
- ^ Wang SJ (March 2003). «Epidemiology of migraine and other types of headache in Asia». Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 3 (2): 104–8. doi:10.1007/s11910-003-0060-7. PMID 12583837. S2CID 24939546.
- ^ Natoli JL, Manack A, Dean B, Butler Q, Turkel CC, Stovner L, Lipton RB (May 2010). «Global prevalence of chronic migraine: a systematic review». Cephalalgia. 30 (5): 599–609. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01941.x. PMID 19614702. S2CID 5328642.
- ^ a b Hershey AD (February 2010). «Current approaches to the diagnosis and management of paediatric migraine». The Lancet. Neurology. 9 (2): 190–204. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70303-5. PMID 20129168. S2CID 12603488.
- ^ a b Nappi RE, Sances G, Detaddei S, Ornati A, Chiovato L, Polatti F (June 2009). «Hormonal management of migraine at menopause». Menopause International. 15 (2): 82–6. doi:10.1258/mi.2009.009022. PMID 19465675. S2CID 23204921.
- ^ a b c d e Borsook D (2012). The migraine brain : imaging, structure, and function. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–11. ISBN 9780199754564. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Steven D. Waldman (2011). Pain management (2 ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 2122–2124. ISBN 9781437736038.
- ^ «Sex(ism), Drugs, and Migraines». Distillations. Science History Institute. 15 January 2019. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ^ Margaret C, Simon M (2002). Human osteology : in archaeology and forensic science (Repr. ed.). Cambridge [etc.]: Cambridge University Press. p. 345. ISBN 9780521691468. Archived from the original on 17 June 2013.
- ^ Colen C (2008). Neurosurgery. Colen Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 9781935345039.
- ^ Daniel BT (2010). Migraine. Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse. p. 101. ISBN 9781449069629. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Butticè, Claudio (April 2022). What you need to know about headaches. Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood_Publishing_Group. pp. 29–30. ISBN 978-1-4408-7531-1. OCLC 1259297708.
- ^ a b Tfelt-Hansen PC, Koehler PJ (May 2011). «One hundred years of migraine research: major clinical and scientific observations from 1910 to 2010». Headache. 51 (5): 752–78. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01892.x. PMID 21521208. S2CID 31940152.
- ^ a b c Stovner LJ, Andrée C (June 2008). «Impact of headache in Europe: a review for the Eurolight project». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (3): 139–46. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0038-6. PMC 2386850. PMID 18418547.
- ^ a b Mennini FS, Gitto L, Martelletti P (August 2008). «Improving care through health economics analyses: cost of illness and headache». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (4): 199–206. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0051-9. PMC 3451939. PMID 18604472.
- ^ Magis D, Jensen R, Schoenen J (June 2012). «Neurostimulation therapies for primary headache disorders: present and future». Current Opinion in Neurology. 25 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283532023. PMID 22543428.
- ^ Jürgens TP, Leone M (June 2013). «Pearls and pitfalls: neurostimulation in headache». Cephalalgia. 33 (8): 512–25. doi:10.1177/0333102413483933. PMID 23671249. S2CID 42537455.
- ^ Barbanti P, Fofi L, Aurilia C, Egeo G, Caprio M (May 2017). «Ketogenic diet in migraine: rationale, findings and perspectives». Neurological Sciences (Review). 38 (Suppl 1): 111–115. doi:10.1007/s10072-017-2889-6. PMID 28527061. S2CID 3805337.
- ^ Gross EC, Klement RJ, Schoenen J, D’Agostino DP, Fischer D (April 2019). «Potential Protective Mechanisms of Ketone Bodies in Migraine Prevention». Nutrients. 11 (4): 811. doi:10.3390/nu11040811. PMC 6520671. PMID 30974836.
- ^ Artero-Morales M, González-Rodríguez S, Ferrer-Montiel A (2018). «TRP Channels as Potential Targets for Sex-Related Differences in Migraine Pain». Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 5: 73. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2018.00073. PMC 6102492. PMID 30155469.
- ^ Stewart, Walter F.; Lipton, Richard B.; Celentano, David D.; Reed, Michael L. (1992-01-01). «Prevalence of Migraine Headache in the United States: Relation to Age, Income, Race, and Other Sociodemographic Factors». JAMA. 267 (1): 64–69. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03480010072027. ISSN 0098-7484. PMID 1727198.
- ^ «Speeding Progress in Migraine Requires Unraveling Sex Differences». SWHR. 2018-08-28. Retrieved 2021-03-17.
- ^ «Migraine in Women Needs More Sex-Specific Research». Migraine Again. 2021-03-11. Retrieved 2021-03-17.
- ^ Schroeder RA, Brandes J, Buse DC, Calhoun A, Eikermann-Haerter K, Golden K, et al. (August 2018). «Sex and Gender Differences in Migraine-Evaluating Knowledge Gaps». Journal of Women’s Health. 27 (8): 965–973. doi:10.1089/jwh.2018.7274. PMID 30129895. S2CID 52048078.
Notes[edit]
- Olesen J (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9780781754002.
Further reading[edit]
- Ashina M (November 2020). Ropper AH (ed.). «Migraine». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (19): 1866–1876. doi:10.1056/nejmra1915327. PMID 33211930. S2CID 227078662.
- Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171. S2CID 199662718.
External links[edit]
| External audio |
|---|
- Migraine at Curlie
Мигрень
Версия: Клинические рекомендации РФ 2021 (Россия)
Категории МКБ:
Мигрень (G43)
Разделы медицины:
Неврология
Общая информация
Краткое описание
Разработчик клинических рекомендаций:
- Общественная организация «Всероссийское общество неврологов»
- Межрегиональная общественная организация «Российское общество по изучению головной боли»
Клинические рекомендации Мигрень
Кодирование по Международной статистической классификации болезней и проблем, связанных со здоровьем: G43
Год утверждения: 2021
Возрастная группа: взрослые
1. Краткая информация по заболеванию или состоянию (группе заболеваний или состояний)
1.1 Определение заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Мигрень – первичная форма головной боли (ГБ), проявляющаяся приступами пульсирующей односторонней ГБ, продолжительностью 4 — 72 часа, которая сопровождается повышенной чувствительностью к свету, звуку, тошнотой и/или рвотой.
М обычно возникает в молодом возрасте, до 20 лет. В детском возрасте заболевание чаще встречается у мальчиков; взрослые женщины болеют в 2,5 – 3 раза чаще, чем мужчины. В возрасте 35 — 45 лет частота и интенсивность мигренозных приступов достигает максимума, а после 55 — 60 лет течение болезни облегчается или приступы ГБ полностью прекращаются. В то же время у некоторых пациентов после 50 лет могут сохраняться типичные приступы мигрени и/или только мигренозная аура (мигренозное сопровождение пожилого возраста) [1 — 3].
1.4 Особенности кодирования заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний) по Международной статистической классификации болезней и проблем, связанных со здоровьем
G43 – Мигрень
G43.0 – Мигрень без ауры [простая мигрень]
G43.1 – Мигрень с аурой [классическая мигрень]
G43.2 – Мигренозный статус
G43.3 – Осложненная (в том числе, хроническая) мигрень
G43.8 – Другая мигрень (офтальмоплегическая, ретинальная)
G43.9 – Мигрень неуточненная
Комментарии: М может сочетаться с ГБН (G43.0/1, G44.2). Частая эпизодическая и особенно хроническая мигрень (ХМ) могут сочетаться с лекарственно- индуцированной головной болью (ЛИГБ, G44.4).
Облачная МИС «МедЭлемент»
Облачная МИС «МедЭлемент»

Автоматизация клиники: быстро и недорого!
- Подключено 300 клиник из 4 стран
- 1 место — 800 RUB / 5500 KZT / 27 BYN в месяц
Классификация
1.5 Классификация заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
В соответствии с последней версией Международной классификацией расстройств, сопровождающихся головной и лицевой болью (МКГБ-3, 2018), М относится к первичным (доброкачественным) цефалгиям (часть I, МКГБ-3), которые не связаны с органическим поражением головного мозга, мозговых сосудов, других структур, расположенных в области головы и шеи и системными заболеваниями (таб. 1) [8].
Таблица 1. Оглавление Международной классификации головной боли-3 (2018) [8]
В соответствии с МКГБ-3 выделяют две основные формы М: мигрень без ауры (МбА), наиболее частая – до 80% случаев и мигрень с аурой (МА) – до 20% случаев [1, 3]. Основным клиническим проявлением МбА является приступ ГБ; при МА болевой фазе приступа предшествует стадия ауры. Реже встречаются другие формы МА: мигрень со стволовой аурой (ранее «базилярная М»), ретинальная и гемиплегическая М.
Отдельно в МКГБ-3 выделяют хроническую мигрень (ХМ), осложнения мигрени и эпизодические синдромы, которые могут сочетаться с М (чаще встречаются в детском возрасте) [8]. При невыполнении одного из диагностических критериев может быть выставлен диагноз «Возможная М» (таб. 2) [8].
Таблица 2. Классификация мигрени (согласно МКГБ-3, 2018) [8]
Комментарии: эпизодические синдромы чаще встречаются в детском возрасте и могут предшествовать появлению типичных приступов мигрени без ауры или с аурой.
В «Приложении» к МКГБ-3 выделяют также истинную менструальную мигрень, при которой приступы М возникают только в перименструальный период (за 2 — 3 дня до и в первые 3 дня менструации), и мигрень, связанную с менструацией, при которой приступы ГБ могут возникать и в другие дни месяца (то есть провокаторами приступа М является не только менструация, но и другие триггеры) [8].
Этиология и патогенез
1.2 Этиология и патогенез заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Мигрень является хроническим нейроваскулярным заболеванием с наследственной предрасположенностью. Основное звено патогенеза – периодическое развитие периваскулярного нейрогенного воспаления мозговых сосудов, в первую очередь, сосудов твердой мозговой оболочки (ТМО). Показано, что для пациентов с М характерна повышенная возбудимость нейронов коры головного мозга и тригемино-васкулярной системы [3, 4]. При воздействии эндогенных и экзогенных мигренозных триггеров возбудимость тригеминальной системы, гипоталамуса, корковых и некоторых других структур головного мозга усиливается, возникает активация тригеминального ганглия, сенсорного спинномозгового ядра тройничного нерва и волокон тройничного нерва, иннервирующих сосуды ТМО — тригемино-васкулярных волокон. Активация тригемино- васкулярной системы (ТВС) сопровождается выбросом из тригемино-васкулярных окончаний болевых провоспалительных пептидов-вазодилататоров (в первую очередь, кальцитонин-ген-родственного пептида (КГРП или CGRP)), а также нейрокинина А и субстанции Р [3, 4]. Возникающие затем вазодилатация и нейрогенное воспаление приводят к активации болевых рецепторов в стенке сосудов ТМО. Болевые импульсы поступают в сенсорную кору головного мозга, и таким образом формируется ощущение пульсирующей ГБ. Сохраняющаяся гипервозбудимость ТВС, центральных ноцицептивных структур и истощение противоболевой системы постепенно приводят к формированию перманентной гиперчувствительности (сенситизации) болевых структур, что способствует учащению приступов ГБ и, в конечном счёте, к хронизации М [1 — 4].
Механизм мигренозной ауры связывают с возникновением и распространением в направлении от зрительной коры к соматосенсорной и лобно-височной областям головного мозга волны деполяризации (возбуждения) нейронов — распространяющаяся корковая депрессия (РКД). Скорость и топография РКД определяют темп, характер и последовательность симптомов мигренозной ауры [1, 3].
Эпидемиология
1.3 Эпидемиология заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Распространённость М в популяции стран Европы и США в среднем составляет 14% (17% среди женщин и 8% среди мужчин) [1, 3, 5]. По данным популяционного исследования, проведенного в 2009 – 2011 гг. с помощью подворного опроса в 35 городах и 9 сельских районах России, распространенность М за один год составила 20,8%, что несколько превышает показатели большинства стран мира [6]. По данным другого российского исследования, распространённость М в течение года составила 15,9% (М без ауры 13,5%, М с аурой 2,4%) [7].
Клиническая картина
Cимптомы, течение
1.6 Клиническая картина заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Мигрень без ауры (МбА) проявляется повторяющимися, в целом однотипными приступами интенсивной, чаще односторонней пульсирующей ГБ преимущественно в области виска, глаза и темени, но нередко может начинаться в области затылка. ГБ часто сопровождается тошнотой, рвотой, повышенной чувствительностью к свету, звукам и усиливается при физической нагрузке. Продолжительность приступа – от 4 часов до 3 суток; частота дней с ГБ при эпизодической М колеблется от 1 дня в год до 14 дней в месяц (в среднем 2 — 4 дня с ГБ в месяц), при ХМ – от 15 и более дней с ГБ в месяц [1, 9, 10].
При мигрени с аурой (МА) фазе ГБ предшествуют преходящие неврологические нарушения. Чаще встречается М с типичной аурой, когда отмечаются полностью обратимые зрительные, чувствительные и/или речевые симптомы, но при этом нет двигательных и стволовых нарушений [11, 12]. В редких случаях после ауры ГБ не развивается — типичная аура без ГБ. При М со стволовой аурой наряду со зрительными, чувствительными и/или речевыми нарушениями возникают два или более полностью обратимых стволовых симптома: дизартрия, головокружение, шум в ушах, снижение слуха, диплопия, атаксия, изменение уровня сознания. Для гемиплегической М, которая встречается чрезвычайно редко и почти всегда имеет наследственный характер, характерны полностью обратимые как зрительные, чувствительные и/или речевые симптомы, так и двигательные нарушения (гемипарез или гемиплегия). Продолжительность немоторных симптомов — 5 – 60 минут, двигательных расстройств — до 72 часов. При семейной гемиплегической М, по крайней мере, один из родственников первой или второй линии родства имеет или имел в прошлом приступы ГБ, соответствующие критериям гемиплегической М; для спорадической гемиплегической М такая наследственная предрасположенность не характерна. При ретинальной М аура представляет собой полностью обратимые односторонние позитивные и/или негативные зрительные феномены (вспышки, скотомы), наличие которых подтверждается исследованием полей зрения офтальмологом во время приступов М, и/или пациент может нарисовать или описать имеющийся в этот момент монокулярный дефект поля зрения [9, 10].
Приступ М может быть спровоцирован различными экзо- и эндогенными факторами. Наиболее частыми триггерами мигрени являются [2, 9, 10, 13]:
- психологические факторы: стресс или расслаблением после стресса, тревожные или депрессивные нарушения, переутомление;
- изменения погоды;
- гормональные факторы: менструация (перименструальное «окно»), овуляция, приём заместительной гормональной эстроген-содержащей терапии или оральных контрацептивов;
- диетические факторы: голод, употребление ряда пищевых продуктов (сыра, шоколада, орехов, копчёностей, куриной печени, авокадо, цитрусовых или кофеин- содержащих продуктов); приём алкоголя (особенно красного вина);
- другие факторы: недостаток или избыток ночного сна, духота, физическая аэробная нагрузка, зрительные стимулы (яркий или мерцающий свет), шум, пребывание на высоте.
Хроническая мигрень (ХМ) – тяжелая форма с высокой частотой дней с ГБ (15 и более в месяц), большой продолжительностью и интенсивностью приступов, что приводит к развитию дезадаптации и снижению качества жизни пациентов. Для ХМ характерны следующие проявления: развитие коморбидных, в первую очередь, психических расстройств (депрессия, тревожные расстройства), нарушений сна, снижение эффективности препаратов для купирования атак и высокий риск их избыточного применения (лекарственный абузус) Основными модифицируемыми факторами хронизации М являются: эмоциональный стресс, депрессия, избыточный прием лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, и кофеина [14 — 17].
ХМ и частая эпизодическая М нередко сочетаются с лекарственно- индуцированной головной болью (ЛИГБ). При этом ГБ имеет смешанный характер: мигренозные ГБ сочетаются с ГБН-подобными цефалгиями в виде диффузной монотонной чаще утренней или ночной ГБ давящего или сжимающего характера, которая нарастает по интенсивности по мере ослабления действия принятого ранее лекарственного препарата с обезболивающим действием. Типичными проявлениями длительно существующей ЛИГБ являются ночной прием лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием», их прием на стадии слабой ГБ, чтобы предотвратить ее усиление (прием «впрок»), а также жалобы на трудности концентрации внимания, снижение памяти и работоспособности. ЛИГБ, как правило, облегчается после отмены препарата(ов) злоупотребления.
Осложнения мигрени включают несколько состояний.
Мигренозный статус– типичный изнуряющий приступ М, длящийся более 72 часов, на протяжении которого допускаются ремиссии до 12 часов, связанные со сном или действием препаратов.
Персистирующая аура без инфаркта– один или несколько симптомов ауры, возникающие у пациентов более одной недели, без радиографических признаков инфаркта мозга.
Мигренозный инфаркт (инсульт)–сочетание одного или более симптомов мигренозной ауры с ишемическим повреждением мозга, подтвержденным нейровизуализационными методами. Истинный мигренозный инфаркт развивается на фоне типичного приступа М с аурой, причем один или несколько симптомов ауры имеют продолжительность более 60 минут. Мозговые инфаркты, не совпадающие по времени с приступом М с аурой, не могут быть отнесены к мигренозным инфарктам.
Мигренозная аура – триггер эпилептического припадка – эпилептический приступ, возникающий во время приступа МА или в течение 1 часа после него.
Эпизодические синдромы, которые могут сочетаться с мигренью. Эти расстройства встречаются преимущественно в детском возрасте, значительно реже могут отмечаться и у взрослых.
Синдром циклической рвоты– эпизодически повторяющиеся приступы сильной тошноты и рвоты, обычно стереотипные для каждого пациента и с предсказуемым временем начала; приступы сопровождаются бледностью кожных покровов и вялостью; между приступами симптомы полностью исчезают.
Абдоминальная мигрень – идиопатическое расстройство, встречающееся преимущественно у детей, в виде повторяющихся приступов боли в животе (по средней линии) умеренной или выраженной интенсивности, длительностью 2 – 72 часа; типичны тошнота и/или рвота; во время этих эпизодов ГБ не возникает. Между приступами состояние пациентов не нарушено. У подавляющего большинства детей с абдоминальной М позднее развиваются типичные мигренозные ГБ.
Доброкачественное пароксизмальное головокружение –
повторяющиеся кратковременные приступы головокружения у детей, которые как внезапно возникают, так и внезапно проходят.
Доброкачественный пароксизмальный тортиколлис/кривошея — повторяющиеся эпизоды наклона головы в одну сторону, возможно с небольшим поворотом головы, которые проходят спонтанно. Это состояние встречается у младенцев и маленьких детей и начинается на первом году жизни. У детей старшего возраста возможно присоединение атаксии.
Диагностика
2. Диагностика заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний), медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов диагностики
- Рекомендуется всем пациентам с жалобой на головную боль клиническая диагностика мигрени, основанная на специфических клинических проявлениях ее отдельных форм и соответствии диагностическим критериям последней версии Международной классификации головной и лицевой боли (МКГБ-3) [8, 9, 18, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: МКГБ-3, одобренная Международным обществом головной боли в 2018 году, является основным инструментом диагностики любых форм головной и лицевой боли, в том числе и форм мигрени. В таблицах 3а — 3в представлены диагностические критерии МбА, МА и ХМ согласно МКГБ-3.
Диагностика осложнений М и эпизодических синдромов, которые могут сочетаться с М, также проводится в соответствии диагностическими критериям МКГБ-3 [8, 12].
Таблица 3а. Диагностические критерии мигрени без ауры (согласно МКГБ-3, 2018) [8]
- Рекомендуется у всех пациентов с мигренью клиническая диагностика мигренозной ауры с целью выбора дальнейшей тактики лечения [9, 15].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: при выявлении мигренозной ауры рекомендуется выставить соответствующий диагноз, например, «М с типичной аурой» или «М со стволовой аурой» [8, 11, 12, 18 — 20]. Не следует путать ауру с продромальными симптомами, которые могут возникать за несколько часов до начала приступа М: повышенная чувствительность к свету, звукам и запахам, изменение аппетита, жажда, эмоциональное возбуждение или, напротив, разбитость и др.
Таблица 3б. Диагностические критерии мигрени с аурой (согласно МКГБ-3, 2018) [8]
Примечания:
1 — при возникновении 3 симптомов во время ауры допустимая максимальная продолжительность 180 минут. Моторные симптомы могут длиться до 72 часов;
2 — афазия всегда рассматривается как односторонний симптом; возможно развитие дизартрии;
3 — осцилляции и ощущение покалывания рассматриваются как позитивные симптомы ауры [8].
- Рекомендуется клиническая диагностика ХМ у пациентов с частыми приступами М (более 10 дней с ГБ в месяц) (таб. 3в) [8, 21, 22].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4).
Таблица 3в. Диагностические критерии хронической мигрени (согласно МКГБ-3, 2018) [8]
Комментарии: с помощью расспроса и анализа дневника ГБ (при его наличии) следует установить число дней с ГБ в месяц на протяжении последних 3 месяцев, в том числе, число дней с М в месяц, уточнить клинические характеристики боли и сопоставить эти данные с диагностическими критериями ХМ (таб. 3в). Важным диагностическим критерием ХМ также является наличие типичных приступов эпизодической М в начале заболевания [15, 21, 22].
Сочетание М и лекарственно-индуцированной головной боли (ЛИГБ). Частая эпизодическая М (более 10 дней с ГБ в месяц) и особенно ХМ (более 15 дней с ГБ в месяц) могут сочетаться с избыточным использованием лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, (лекарственный абузус) [8, 16]. При значительном злоупотреблении возможно развитие ЛИГБ, представленной в п. 8.2 МКГБ- 3 «Головная боль при избыточном применении лекарственных препаратов» (таб. 4а) [8]. Лекарственный абузус способствует увеличению количества эпизодов ГБ и рассматривается как один из ведущих факторов хронизации М [14 — 17].
- Рекомендуется у пациентов с частой ЭМ (более 10 дней с ГБ в месяц) и ХМ (15 и более дней с ГБ в месяц) клиническая диагностика ЛИГБ (таб. 4а и 4б), основанная на специфических клинических проявлениях и на соответствии клинической картины диагностическим критериям ЛИГБ (МКГБ-3) [8, 16].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Таблица 4а. Диагностические критерии лекарственно-индуцированной головной боли (согласно МКГБ-3, 2018) [8]
Комментарии: диагностика ЛИГБ основывается на клинической оценке ГБ, анализе данных о числе, кратности приема лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, и типе препаратов злоупотребления [8]. Для уточнения этих характеристик желательно ведение пациентом дневника ГБ (Приложение Г). ЛИГБ проявляется диффузной монотонной чаще утренней или ночной головной болью, которая нарастает по интенсивности с прекращением действия принятого ранее лекарственного препарата с обезболивающим действием. Сходство клинических характеристик ЛИГБ и ХМ нередко затрудняет дифференциальную диагностику этих цефалгий.
Важным является определение типа препаратов злоупотребления и установление «числа дней с приемом лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, в месяц» — главного диагностического критерия ЛИГБ (таб. 4б). Например, диагноз «ГБ, связанная с избыточным приемом препаратов, содержащих компоненты из разных классов, обладающих обезболивающим действием» выставляется при регулярном приеме одного или более таких препаратов ≥ 10 дней в месяц на протяжении более 3 месяцев, а «ГБ, связанная с избыточным приемом других НПВП» — при регулярном приеме одного или более НПВП ≥ 15 дней в месяц на протяжении более 3 месяцев [8]. Наибольший риск ЛИГБ отмечается при использовании лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, содержащих наркотические компоненты (кодеин и др.), барбитураты и кофеин** [8, 17, 23]. Инструментальные методы исследования для диагностики ЛИГБ не применяются вследствие их неинформативности [14].
При выявлении у пациента с ХМ клинических признаков ЛИГБ следует выставить два диагноза. Например, «Хроническая мигрень. ЛИГБ, связанная с избыточным применением триптанов» [9, 15, 17].
Таблица 4б. Классификация форм ЛИГБ (согласно МКГБ-3, 2018) [8]
2.1 Жалобы и анамнез
Пациенты с М предъявляют типичные жалобы на повторяющиеся приступы односторонней пульсирующей ГБ в лобно-височной или теменной области, средней или выраженной интенсивности (более 7 баллов по визуальной аналоговой шкале боли (ВАШ, Приложение Г2), продолжительностью 4 – 72 часа, которая ухудшается от обычной физической активности, сопровождается тошнотой и/или рвотой, а также повышенной чувствительностью к свету и звукам [1, 2, 3, 8]. Возможны жалобы на зрительные, чувствительные, речевые, реже двигательные нарушения, которые постепенно нарастают в течение 5 — 20 минут до начала или во время приступа ГБ, длятся обычно не более 60 минут (двигательные нарушения до 72 часов) и далее полностью исчезают; что характерно для мигренозной ауры [8, 11, 12, 18 — 20]. Приступы ГБ чаще всего провоцируются стрессом или расслаблением после стресса, недостатком или избытком ночного сна, изменением погоды, менструацией, голодом, духотой, ярким или мерцающим светом, шумом, физической нагрузкой, приемом алкоголя или кофеин- содержащих напитков [1, 3]. Частота приступов М и регулярность приема лекарств с целью купирования боли в приступе М может значительно варьировать, что также уточняется при сборе жалоб.
Анамнез пациентов с М имеет характерные черты [1, 2, 3, 9]. Типично возникновение первых приступов в молодом возрасте, до 20 лет и наличие аналогичных ГБ у родственников (наследственный анамнез). Пациенты рассказывают об особых периодах своей жизни, во время которых менялось течение М: урежение или полное прекращение приступов ГБ во время беременности или с наступлением менопаузы; ухудшение/прогрессирование/хронизация М под воздействием эмоционального стресса, депрессии и/или тревоги, избыточного приёма лекарственных препаратов с обезболивающим действием, применения гормональных пероральных контрацептивов и в период преклимакса у женщин [14 — 17]. В анамнезе пациентов с М часто имеется указание на различные сопутствующие соматические и психические расстройства, среди которых наиболее распространены эмоционально-аффективные нарушения (депрессия, тревожные расстройства), расстройства сна (инсомния, бруксизм, синдром беспокойных ног, апноэ во сне), другие хронические болевые синдромы, в т.ч. боль в спине и болевая дисфункция височно-нижнечелюстного сустава, а также синдром раздраженного кишечника, аллергия, ожирение, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания [14, 15].
- Рекомендуется у пациентов с любой формой М с помощью расспроса выявлять сопутствующие коморбидные нарушения (КН), в первую очередь, депрессию, тревожные расстройства, нарушение сна и другие болевые синдромы [2, 14, 15, 18, 19].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: КН способствуют более тяжелому течению и учащению приступов М (хронизации М), ухудшают состояние пациентов между приступами ГБ, приводят к более выраженной дезадаптации, худшему прогнозу. В связи с чем выявление и лечение коморбидных расстройств является важной задачей ведения пациентов с М.
2.2 Физикальное обследование
Клиническая диагностика М наряду с анализом жалоб и анамнеза включает неврологический осмотр пациента.
- Рекомендуется исследование неврологического статуса с целью исключения органической неврологической симптоматики и возможной симптоматической природы ГБ [9, 15, 19, 21, 24, 25].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: при типичном течении М не обнаруживается патологических изменений в неврологическом статусе. Может отмечаться снижение настроения, признаки повышенной тревожности, вегетативные нарушения (гипервентиляция, ладонный гипергидроз, признаки повышенной нервно-мышечной возбудимости в виде симптома Хвостека I — III степени), напряжение и болезненность перикраниальных мышц при пальпации.
При выявлении в неврологическом статусе органической симптоматики (менингеальных, общемозговых и/или очаговых неврологических знаков) проводятся дополнительные инструментальные и лабораторные исследования, выбор которых определяется характером патологических изменений и предполагаемым заболеванием – причиной выявленных нарушений [8, 15, 18 — 20].
2.3 Лабораторные диагностические исследования
Поскольку диагностика М является клинической, лабораторные методы не являются обязательными.
- Не рекомендуются для диагностики М лабораторные методы исследования в связи с их неинформативностью [1, 2, 3, 9, 15, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: Лабораторные методы исследования не информативны в диагностике М, поскольку не выявляют специфических для этого заболевания изменений.
2.4 Инструментальные диагностические исследования
Инструментальные исследования у пациентов с М не информативны, поскольку не выявляют специфических для М изменений.
- Не рекомендуются для диагностики М инструментальные исследования при типичной клинической картине и нормальных данных неврологического осмотра пациента [15, 18, 20, 24 — 26].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: у большинства пациентов с М инструментальные методы исследования не выявляют никаких специфических изменений. У ряда пациентов при проведении стандартной МРТ головного мозга в Т2 режиме могут обнаруживаться единичные субклинические гиперинтенсивные очаги в субкортикальном белом веществе полушарий мозга, реже в стволовых структурах [26]. Предполагают, что эти очаговые изменения являются следствием преходящих нарушений церебральной перфузии, которые по данным магнитно-резонансной томографии регистрируются во время повторных приступов М. Показано, что М может являться независимым фактором риска развития субклинического очагового ишемического поражения головного мозга [11]. Поскольку эти очаги не имеют специфических морфологических признаков, они не могут считаться нейровизуализационными маркерами М.
- Рекомендуются инструментальные исследования при редких формах МА и осложнениях М: МРТ головного мозга и магнитно-резонансная ангиография головного мозга с целью исключения органической патологии головного мозга [9, 12, 18, 20, 24, 25].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: В случае обнаружения патологии, лечащий врач должен принять решение о необходимости дополнительного обследования для исключения патологии церебральных сосудов (артериовенозных мальформаций, диссекции сонных артерий) или сердца (открытого овального окна).
- Рекомендуются для диагностики М инструментальные исследования и консультации специалистов пациентам с нетипичным течением М или имеющим хотя бы один настораживающий симптом, указывающий на наличие другого заболевания, которое может быть причиной ГБ (таб. 5) [10, 20, 24 — 26].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Таблица 5. Перечень настораживающих симптомов — «сигналов опасности» у пациентов с головной болью
2.5 Иные диагностические исследования
Для установления клинических характеристик приступа, числа дней с ГБ в месяц (определение формы М) и числа дней с приемом лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, целесообразно ведение пациентом дневника ГБ (Приложение Г1) Ведение дневника ГБ в течение 1 — 3 месяцев до осмотра помогает пациенту и врачу отличить один вариант ГБ от другого (например, приступ мигрени от эпизода ГБН), установить число дней с ГБ в месяц и число дней с приемом лекарственных препаратов с обезболивающим действием в месяц.
- Рекомендуются в специализированных центрах боли и головной боли у всех пациентов с подозрением на мигрень использование дневника ГБ для облегчения дифференциальной диагностики с ГБН и для выявления лекарственного абузуса [2, 5, 10].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
2.5.1 Дифференциальная диагностика
Дифференциальная диагностика у пациентов с М чаще всего проводится с ГБН, кластерной (пучковой) ГБ, хронической пароксизмальной гемикранией и цервикогенной ГБ. Для проведения дифференциального диагноза необходим тщательный расспрос и осмотр пациента, анализа анамнестических сведений и провоцирующих факторов; целесообразно ведение дневника ГБ. Реже приходится дифференцировать М и редкие вторичные цефалгии, связанные с неврологическими и соматическими заболеваниями [2, 9, 20, 21]. ГБ, напоминающие М, могут отмечаться при следующих заболеваниях:
- транзиторная ишемическая атака (ТИА) и инсульт;
- гигантоклеточный артериит;
- диссекция (расслоение) артерий, аневризмы и артериовенозные мальформации;
- церебральный венозный тромбоз;
- опухоль головного мозга;
- субарахноидальное кровоизлияние;
- антифосфолипидный синдром и тромбофилии;
- эпилепсия (при сочетании мигренозной ГБ с эпилептическим приступом);
- синдромы MELAS (англ. Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like episodes — митохондриальная энцефаломиопатия с лактатацидозом и инсультоподобными эпизодами) и CADASIL (англ. Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy — церебральная аутосомно- доминантная артериопатия с субкортикальными инфарктами и лейкоэнцефалопатией).
В отличие от типичной М как первичной формы ГБ, вышеупомянутые заболевания и синдромы всегда проявляются соответствующими симптомами неврологического дефицита или другими «сигналами опасности», не характерными для М (см. Раздел 2.4).
У одного пациента М может сочетаться с другими цефалгиями, как первичными (ГБН; первичные ГБ, связанные с физической, сексуальной активностью, холодовыми стимулами и др.), так и вторичными (ЛИГБ, цервикогенная ГБ, ГБ, связанная с дисфункцией височно-нижнечелюстного сустава). В этом случае в диагноз следует внести все выявленные формы ГБ; например, «М без ауры. ЭГБН с дисфункцией перикраниальных мышц» или «ХМ. ЛИГБ, связанная с применением селективных агонистов серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов (триптанов). ГБ, связанная с дисфункцией височно-нижнечелюстного сустава» [9, 16, 21].
- Рекомендуется дифференциальная диагностика М без ауры (МбА) с ГБН, кластерной (пучковой) ГБ, хронической пароксизмальной гемикранией и цервикогенной ГБ [1, 2, 9, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
- Рекомендуется дифференциальная диагностика мигрени с аурой (МА) с ТИА в связи со схожестью клинической картины [11, 12].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: для мигренозной ауры типично постепенное нарастание клинических проявлений в определенной последовательности на протяжении 10 — 30 (до 60) минут на одной стороне тела в виде так называемого «марша» и смены «позитивных» и «негативных» симптомов: зрительные симптомы (сцинтилляции, блестящие зигзагообразные линии или мушки, тёмные пятна, скотомы, выпадение полей зрения), затем парестезии, онемение, распространяющиеся от кисти руки вверх на плечо, область лица; далее возможно присоединение речевых расстройств; в конце мигренозной ауры развивается мигренозная ГБ. В отличие от приступа М с аурой при ТИА неврологические нарушения имеют «негативный» характер (выпадение полей зрения, скотомы, онемение одной конечности), появляются остро (в течение нескольких минут) и одновременно; развитие ГБ не характерно, у пациентов в анамнезе, как правило, нет данных о наличии М.
- Рекомендуется у пациентов с ХМ проведение дифференциальной диагностики с хронической ГБН (ХГБН), а также с новой ежедневной персистирующей ГБ и гемикранией континуа [10, 14, 21].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: трудности дифференциальной диагностики ХМ и ХГБН связаны с тем, что ведущими клиническими проявлениями ХМ являются как сохраняющиеся частые приступы М, так и ГБН-подобная «фоновая» боль. В этом случае следует опираться на данные раннего анамнеза: у пациентов с ХМ, в отличие от ХГБН, в начале заболевания отмечаются типичные приступы эпизодической М и другие, характерные для М признаки (наследственный анамнез, типичные мигренозные триггеры, облегчение ГБ во время беременности) [15, 22, 27]. При наличии лекарственного абузуса следует дифференцировать ХМ, сочетающуюся с ЛИГБ, и ХГБН, сочетающуюся с ЛИГБ.
Лечение
3. Лечение, включая медикаментозную и немедикаментозную терапию, диетотерапию, обезболивание, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов лечения
- Рекомендуются три подхода к лечению М: поведенческая терапия, купирование приступов ГБ и профилактическое лечение [15, 18, 20, 28].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: основные цели лечения М: уменьшение частоты и тяжести приступов ГБ, снижение количества принимаемых лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, коррекция коморбидных нарушений (КН), профилактика хронизации заболевания и улучшение качества жизни пациентов.
3.1 Поведенческая терапия
- Рекомендуется поведенческая терапия, направленная на модификацию образа жизни пациента с М [96, 140].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
Комментарии: информирование и обучение пациента с М может проводиться врачом или средним медицинским персоналом как при очной беседе, так и заочно с помощью популярной литературы и интернет-ресурсов. Основные положения поведенческой терапии включают: разъяснение доброкачественной природы и механизмов М (разубеждение в наличии органической причины ГБ); обоснование нецелесообразности проведения дополнительных исследований (за исключением случаев подозрения на симптоматический характер М); обсуждение роли провокаторов приступов ГБ и необходимости их избегать; обсуждение факторов риска хронизации заболевания (стресса, лекарственного абузуса, психических и других КН) и необходимости их профилактики; разъяснение целей лечения М, механизмов действия профилактических препаратов и пользы от использования немедикаментозных методов. Пациентам, злоупотребляющим лекарственными препаратами с обезболивающим действием, следует разъяснить роль лекарственного абузуса в хронизации М, необходимость временного отказа от приема и строгого постоянного контроля числа принимаемых лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием [15, 18, 20].
3.2 Купирование приступа мигрени
- Рекомендуется лечение приступа М для уменьшения интенсивности, длительности ГБ, сопутствующих симптомов и восстановления общего состояния пациента [15].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
- Рекомендуется назначать медикаментозную терапию в зависимости от тяжести приступа и степени дезадаптации пациента [18].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: лёгкий приступ М – это приступ, во время которого пациент в состоянии выполнять привычную домашнюю и профессиональную работу; приступ средней тяжести – выполнение этих видов деятельности существенно ограничено; тяжёлый приступ М — необходим постельный режим [20, 28].
3.2.1. Купирование приступов мигрени легкой и средней тяжести
Для купирования приступов М следует применять анальгетики и антипиретики, нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты (НПВП) (таб. 6а).
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов М как препарат выбора ацетилсалициловая кислота** 1000 мг [30, 31].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов М как препарат выбора ибупрофен** 400 мг [32, 33].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов М как препарат выбора напроксен 500 мг [34 — 35].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов М как препарат выбора парацетамол** 1000 мг [37].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов М как препарат выбора диклофенак** 50 мг в саше [36, 38].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов М кетопрофен** 75 или 150 мг [42].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Таблица 6а. Анальгетики и антипиретики, нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты, рекомендованные для купирования приступа мигрени
Комментарии: принципы использования других анальгетиков и антипиретиков и НПВП предполагают, что выбор лекарственного средства должен быть сделан на основании их эффективности и побочных эффектов [28, 30 — 39]:
- НПВП и ацетилсалициловая кислота** более эффективны, чем парацетамол**;
- препаратом первого выбора считается ибупрофен** в дозе 400 мг, который обладает наименьшим потенциалом вызывать желудочно-кишечные осложнения;
- для контроля правильного использования лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, целесообразно ведение дневника ГБ;
- при использовании НПВП необходимо учитывать побочные эффекты, в первую очередь воздействие на желудочно-кишечный тракт и риск кровотечений;
- не рекомендуются для купирования приступов М любые препараты, содержащие метамизол натрия в связи с риском развития агранулоцитоза; опиоидные анальгетики и лекарственные препараты с обезболивающим действием, содержащие кофеин**, кодеин или барбитураты (в связи с высоким риском лекарственного абузуса и ЛИГБ);
- быстрорастворимые формы НПВП (ацетилсалициловая кислота** экспресс форма, диклофенак** в порошке для приготовления раствора для приема внутрь, кетопрофен** в гранулах для приготовления раствора для приема внутрь, ибупрофен** капсулы-форте) действуют более эффективно, чем соответствующие лекарственные средства в таблетированной форме.
- Рекомендуется для лечения приступа мигрени у пациентов с тошнотой и/или рвотой противорвотный препарат (антиэметик) метоклопрамид** внутримышечно совместно с приемом анальгетика с целью облегчения этих симптомов и улучшения всасывания лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием (таб. 6б) [39].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется для лечения приступа мигрени у пациентов с тошнотой применение метоклопрамида** в дозе 10 — 20 мг внутрь или домперидона 20 — 30 мг внутрь для облегчения тошноты и улучшения всасывания лекарственных препаратов [39].
- Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: противорвотные препараты уменьшают гастростаз, обычно сопровождающий приступ М, и улучшают всасывание лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием. [1 — 3, 20].
Таблица 6б. Противорвотные лекарственные средства, рекомендованные для лечения приступа мигрени
3.2.2. Купирование тяжелых приступов мигрени
- Рекомендуются при тяжелых приступах М и при неэффективности других анальгетиков и антипиретиков и НПВП селективные агонисты серотониновых 5HT1- рецепторов (триптаны): суматриптан, элетриптан и золмитриптан (таб. 6в) [46 — 47, 51 — 52].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
Таблица 6в. Селективные агонисты серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов (триптаны), рекомендованные для купирования приступов мигрени
Комментарии: наибольшей эффективностью обладают селективные агонисты серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов (триптаны), которые могут также применяться при приступах М средней тяжести [28, 48 — 50, 53 — 55]. В Таблице 6в приведены селективные агонисты 5HT1-рецепторов, зарегистрированные в РФ. Для более эффективного купирования приступов МбА селективные агонисты 5HT1-рецепторов (триптаны) следует принимать в самом начале приступа ГБ — в первые 30 минут от начала ГБ [53]; также рекомендуется принимать суматриптан в дозе не менее 50 мг, элетриптан – не менее 40 мг, золмитриптан – не менее 2,5 мг [172]. При МА селективные агонисты 5HT1- серотониновых рецепторов не должны назначаться во время ауры: если ГБ возникает одновременно или в конце ауры, то селективные агонисты серотониновых 5HT1- рецепторов можно принимать в конце фазы ауры или в начале фазы ГБ [54]. Не следует использовать селективные агонисты серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов более 10 дней в месяц, чтобы избежать злоупотребления и развития ЛИГБ. Повторное использование селективных агонистов серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов возможно через 2 часа после приема первой дозы; не следует применять более 2 доз селективных агонистов серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов в сутки; при неэффективности одного селективного агониста серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов следует пробовать другие препараты из этой группы. Основные противопоказания для назначения селективных агонистов серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов включают ишемическую болезнь сердца, окклюзионные заболевания периферических сосудов, неконтролируемую артериальную гипертензию, М со стволовой аурой.
В связи с наименьшим констрикторным эффектом на коронарные артерии наиболее безопасным селективным агонистом серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов у пациентов с возможным риском сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний является элетриптан [54, 55].
- Рекомендуется для лечения тяжёлого приступа мигрени, особенно при невозможности принимать препараты внутрь из-за выраженной тошноты и рвоты кеторолак** 60 мг внутримышечно или 30 мг внутривенно [41].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
3.2.3. Купирование мигренозного статуса
Лечение мигренозного статуса (МС) направлено на уменьшение интенсивности, длительности ГБ, сопутствующих симптомов и восстановление общего состояния пациента.
- Рекомендуется у пациентов с мигренозным статусом использовать селективные агонисты серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов (триптаны), если пациент ранее не принимал их для купирования приступа М [28, 29, 46, 47].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется у пациентов с МС купировать его в условиях стационара парентеральным введением следующих лекарственных средств: метоклопрамида** [29, 39, 43], хлорпромазина [56, 57], #декскетопрофена** [40, 58], #кеторолака** [41], #магния сульфата** [59 — 61], #вальпроевой кислоты** [44, 62, 63], #дексаметазона** [64 — 68] (таб. 7).
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 2).
Комментарии: выбор (сочетание) средств определяется клинической картиной, тяжестью МС и индивидуальными особенностями пациента.
Таблица 7. Лекарственные средства, рекомендованные для купирования мигренозного статуса
- Не рекомендовано внутривенное введение дроперидола** при МС из-за риска развития побочных реакций [69, 70].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
- Не рекомендовано внутривенное капельное введение галоперидола** из-за высокого риска побочных реакций [71, 72].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: Меньшее количество нежелательных явлений наблюдается при применении метоклопрамида** по сравнению с дроперидолом** и галоперидолом**[72]. Побочными эффектами антипсихотических средств могут быть экстрапирамидные нарушения (акатизия, поздняя дискинезия и др.), снижение артериального давления, сонливость. Одним из противопоказаний к назначению антипсихотических средств является удлиненный интервал QT, поэтому перед их назначением рекомендована электрокардиография.
При МС #дексаметазон** применяют не для устранения ГБ, а для предотвращения возврата ГБ во время приступа М; #дексаметазон** применяется внутривенно в средней дозе 10 мг (диапазон доз от 10 до 24 мг) [64 — 68]. Парентеральное введение жидкостей для устранения ГБ при МС не показано, однако при повторной рвоте и дегидратации возможно парентеральное введение жидкостей с целью регидратации [73]. Пациенты с МС также испытывают значительный дискомфорт при воздействии света и звуков, поэтому следует проводить лечебные мероприятия в тихом и затемненном помещении.
3.3 Профилактическая терапия
- Рекомендуется профилактическое лечение пациентам с М, у которых наблюдается 3 и более тяжёлых дезадаптирующих приступа ГБ в месяц при адекватном купировании приступов М или ≥ 8 дней с ГБ в месяц, а также пациентам с пролонгированной аурой, даже при небольшой частоте приступов [2, 9, 20, 74].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: другие показания к профилактическому лечению М включают [9, 15, 20, 74 — 78]:
- неэффективность или плохая переносимость препаратов для купирования приступов М;
- хроническая мигрень;
- лекарственный абузус, ЛИГБ;
- подтипы М, представляющие риск в отношении повреждения мозга (инсульта): мигренозный инфаркт или мигренозный статус в анамнезе, М со стволовой аурой, гемиплегическая М;
- тяжелые коморбидные нарушения (в первую очередь, психические – депрессия, тревога, фобии, диссомния);
- пациент сам предпочитает профилактическую терапию для облегчения течения М и улучшения качества жизни.
- Рекомендуется считать профилактическое лечение эффективным, если частота дней с ГБ сокращается через 3 месяца терапии на 50% и более от исходной [2, 9, 75, 76].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: профилактическое лечение у пациентов с М проводится с соблюдением следующих принципов:
- разъяснение пациенту целесообразности, механизмов действия и возможных побочных эффектов профилактических средств;
- следует применять препараты с доказанной эффективностью, начиная лечение с монотерапии;
- необходимо назначать препараты в адекватных терапевтических дозах в течение достаточного для развития клинического эффекта времени (от 3 месяцев и более);
- при отсутствии эффекта в течение 3 месяцев следует заменить выбранное профилактическое средство на другой препарат; эффективность БТА – минимум через 6 месяцев терапии.
- при достижении эффекта необходимо продолжительное (6-12 месяцев) использование выбранного профилактического средства в адекватно переносимой дозе;
- затем возможно предпринять попытку постепенной отмены препарата(ов);
- для минимизации побочных эффектов целесообразно медленное увеличение дозы;
- необходимо избегать ситуаций, когда недостаточно эффективная профилактика (в силу неправильно подобранного препарата или его недостаточной дозы) приводит к избыточному применению средств для купирования приступов М (чаще, чем 2 дня в неделю);
- при выборе профилактического средства следует принимать во внимание сопутствующие/коморбидные заболевания. В частности, следует выбирать препарат, который также эффективен при лечении сопутствующей патологии (например, антидепрессант у пациента с М и коморбидной депрессией);
- не следует назначать психостимуляторы и ноотропные препараты, не обладающие доказанным специфическим действием в профилактике М;
- необходимо избегать терапии сопутствующего заболевания, которая может способствовать обострению М или увеличению лекарственного абузуса.
Профилактические средства первого выбора (таб. 
- Рекомендуются для профилактики М в качестве средств первого выбора бета-адреноблокаторы метопролол** 100 — 200 мг/сут [76, 80, 167].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 2).
- Рекомендуются для профилактики М в качестве средств первого выбора бета-адреноблокаторы пропранолол** 80 — 160 мг/сут) [76, 79, 80].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств — 1).
Комментарии: у пациентов с артериальной гитотензией возможно применение меньших доз бета-адреноблокаторов [2, 3, 9].
- Рекомендуется для профилактики М в качестве средства первого выбора топирамат** 100 — 200 мг/сут [81, 83, 84, 168].
- Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 1).
Комментарии: топирамат** назначается длительным курсом (до 12 месяцев) с титрованием дозы от 25 мг до рекомендованной дозы 100 мг; возможно увеличение дозы до 200 мг в сутки; прием основной дозы препарата предпочтителен в вечернее время.
- Рекомендуется для профилактики хронической М в качестве средства первого выбора ботулинический токсин типа А — гемагглютинин комплекс** 155 — 195 ЕД по протоколу PREEMPT [85].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств — 1).
Комментарии: ботулинический токсин типа А — гемагглютинин комплекс** применяется при М только у пациентов с хронической формой. После разведения 100 ЕД препарата на 2 мл или 200 ЕД — на 4 мл раствора хлорида натрия** вводят по протоколу PREEMPT в проекции 7 групп мышц головы и шеи (билатерально в mm. frontalis; mm. corrugator supercilii; mm. temporalis; mm. occipitalis; mm. trapezius; mm. paraspinalis cervicis и m. Procerus) [85, 99, 108]. Суммарная доза препарата на одну процедуру составляет 155 — 195 ЕД. Эффективность одной процедуры (снижение числа дней с ГБ на 50% и более) обычно сохраняется в течение 3 месяцев, поэтому инъекции препарата рекомендуется повторять каждые 12 недель. Одновременно пациенты могут получать другие лекарственные средства с целью профилактики М. Ботулинический токсин типа А—гемагглютинин комплекс** эффективен также у пациентов с ХМ, сочетающейся с лекарственно-индуцированной ГБ [100].
- Рекомендуются для профилактики М у пациентов с числом дней с ГБ 4 и более в месяц в качестве средств первого выбора антагонисты пептидов, связанных с геном кальцитонина (CGRP или КГРП) фреманезумаб 225 мг подкожно ежемесячно или 625 мг подкожно один раз в три месяца и эренумаб 70 или 140 мг подкожно ежемесячно [86 — 89].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств — 2).
Комментарии: антагонисты пептидов, связанных с геном кальцитонина (моноклональные антитела к основному болевому медиатору мигрени кальцитонин-ген- родственному пептиду или его рецептору (или анти-CGRP моноклональные антитела)), представляют собой первый класс препаратов, специально разработанных для таргетной (патогенетически обоснованной) профилактической терапии эпизодической и хронической мигрени у взрослых. Терапия мАТ может применяться при частоте от 4 дней с М в месяц.
Фреманезумаб, эренумаб могут быть назначены длительностью от 6 до 12 месяцев и более в зависимости от эффективности и переносимости терапии. Эффективность терапии следует оценивать через 3 мес. после ее начала. По данным исследований в реальной клинической практике на фоне лечения антагонистами пептида, связанного с геном кальцинонина, возможно снижение числа дней с ГБ в месяц на 50%, 75%, а также на 100% (временная ремиссия). В реальной клинической практике в США и Европе антагонисты пептидов, связанных с геном кальцитонина, применяются на протяжении нескольких лет (период непрерывного применения до 5 лет). Решение о продолжительности лечения принимается лечащим врачом и зависит от эффективности и переносимости терапии [86 — 89].
Профилактические средства второго выбора (таб. 
- Рекомендуется для профилактики М #атенолол** 100 мг/сут [97].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 2).
- Рекомендуются для профилактики М антидепрессанты: #амитриптилин** 50 — 150 мг/сут и #венлафаксин 75 — 150 мг/сут [90 — 93].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 1).
Комментарии: перечисленные антидепрессанты обладают собственным противоболевым действием [1, 2, 9, 15]. Применение антидепрессантов особенно полезно у пациентов с коморбидными нарушениями (депрессия, тревожные расстройства, диссомния) [1, 2, 9, 15].
- Рекомендуется для профилактики М #кандесартан 16 мг/сут [94 — 95].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 2).
- Рекомендуется для профилактики М #вальпроевая кислота** 400 — 1500 мг внутрь [81,82].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств — 2).
Комментарии: назначение #вальпроевой кислоты** нежелательно женщинам с детородным потенциалом в силу высокого риска тератогенного действия [81, 82].
Таблица 8. Лекарственные средства, рекомендованные для профилактики мигрени
1 — PREEMPT — англ. Phase III Research Evaluating Migraine Prophylaxis Therapy — клиническая программа исследования по оценке профилактической терапии М 3-й фазы.
3.4 Особенности лечения мигрени, сочетающейся с лекарственно- индуцированной головной болью (ЛИГБ)
- Рекомендуется у пациентов с частой эпизодической М поведенческая терапия (информирование пациентов) для предотвращения развития ЛИГБ [101].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: пациенты с частой эпизодической М (число дней с мигренозной ГБ 8 и более в месяц и около 8 — 10 дней с приемом лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием в месяц) представляют группу риска по развитию ЛИГБ.У пациентов группы риска предотвращение лекарственного абузуса с помощью поведенческой терапии более эффективно, чем лечение уже развившейся ЛИГБ[102].
Основные стратегии профилактики развития ЛИГБ в группе риска включают: информирование пациентов о безопасном режиме приема средств для купирования приступов М (не чаще 2 дней в неделю – не более 8 дней в месяц) и контроль других факторов риска хронизации М (эмоционального статуса, стрессовых жизненных событий, качества сна, приема кофеина, массы тела). Необходимо объяснить пациенту, что злоупотребление препаратами для купирования приступов М способствует учащению дней с ГБ (хронизации М и развитию ЛИГБ), и что единственный путь к облегчению ГБ — это отмена препарата(ов) злоупотребления.
- Рекомендуются у пациентов, злоупотребляющих другими анальгетиками и антипиретиками и/или селективными агонистами серотониновых 5HT1-рецепторов (триптанами) консультирование и советы по временной отмене или значительному сокращению приема препаратов, вызвавших ЛИГБ [103, 104].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: эти методы недостаточно эффективны у пациентов с коморбидными психическими нарушениями (депрессия, тревога), злоупотребляющих опиоидами, анксиолитиками, барбитуратами или несколькими классами лекарственных препаратов с обезболивающим действием одновременно и имеющих неудачные попытки отмены препаратов злоупотребления в анамнезе.
- Рекомендуется для обратной трансформации ХМ в эпизодическую форму отмена лекарственного препарата(ов) с обезболивающим действием, вызвавшего(их) ЛИГБ [105 — 119, 169 — 171].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3).
Комментарии: может применяться как полная, так и частичная отмена «виновных» препарата(ов). Число дней с приемом любых лекарственных препаратов с обезболивающим действием не должно превышать 2 в неделю (8 в месяц). Отмену других анальгетиков и антипиретиков, селективных агонистов серотониновых 5HT1- рецепторов (триптанов) можно проводить в амбулаторных условиях; отмену опиоидов, спазмолитиков, психотропных препаратов и анальгетиков в комбинации, в том числе при сочетании со злоупотреблением производными бензодиазепина — в условиях стационара/дневного стационара [105].
- Рекомендуется в период отмены препарата(ов) злоупотребления пациентам с ЛИГБ лечение «рикошетной ГБ» и других симптомов отмены (детоксикационная терапия внутрь или парентерально) [63, 105].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
- Рекомендуются для лечения ГБ отмены, других симптомов отмены и для купирования возможных приступов М в качестве препаратов первого выбора кортикостероиды системного действия, НПВП, противорвотные препараты и анксиолитики (таб. 9).
Таблица 9. Лекарственные средства, рекомендованные для лечения ГБ отмены у пациентов с ЛИГБ
Комментарии: лечение ГБ и других симптомов отмены (детоксикацию) следует проводить в первые две недели периода отмены. Выбор препаратов определяется клиническими проявлениями (например, при наличии рвоты целесообразно применение противорвотных препаратов) [128].
В период отмены обезболивающих препаратов в качестве альтернативных лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, могут применяться препараты тех классов, которыми пациент ранее не злоупотреблял (например, при наличии у пациента с частой эпизодической или хронической мигрени и ЛИГБ, связанной со злоупотреблением лекарственными препаратами, содержащими компоненты из разных классов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, для купирования приступов М в период отмены могут быть рекомендованы селективные агонисты серотониновых 5TH1-рецепторов (триптаны). Целекоксиб и напроксен (см. ниже) могут также применяться в период отмены как альтернативные лекарственные препараты с обезболивающим действием при условии, что пациент ими ранее не злоупотреблял.
При назначении кортикостероидов системного действия или НПВП необходимо добавлять ингибиторы протонного насоса для снижения риска нежелательных явлений со стороны ЖКТ. Пациентам, злоупотребляющим опиоидами, производными бензодиазепина, барбитуратами необходим мониторинг метаболических показателей крови, артериального давления и регидратация, в т.ч. обильное питье).
- Рекомендуются для профилактической терапии частой эпизодической и хронической М, сочетающейся с ЛИГБ топирамат**, ботулинический токсин типа А — гемагглютинин комплекс**и антагонисты пептидов, связанных с геном кальцитонина (таб. 10).
Таблица 10. Препараты, рекомендованные для профилактической терапии частой эпизодической и хронической мигрени, сочетающейся с ЛИГБ
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: профилактическую терапию М, сочетающейся с ЛИГБ, предпочтительно начинать вместе с отменой препарата(ов), вызвавшего(их) ЛИГБ, и лечением ГБ отмены [119], однако терапию можно начинать и до отмены «виновных» анальгетиков и антипиретиков [107, 110, 112, 113].
- Не рекомендуются для профилактики М психостимуляторы и ноотропные препараты [2, 9, 15, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – C (уровень достоверности доказательств — 5).
Комментарий: психостимуляторы и ноотропные препараты не обладают доказанным специфическим действием в профилактическом лечении М, однако могут применяться у пациентов с М в качестве дополнительных средств с целью коррекции легких когнитивных нарушений [2, 9, 15, 20].
3.5 Немедикаментозное лечение
- Рекомендуется комбинировать фармакологическое лечение М с немедикаментозными методами с целью повышения эффективности терапии [20, 33].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: комбинированное лечение может рассматриваться как возможный вариант лечения первичной ГБ, в том числе у резистентных к фармакологическому лечению пациентов [134, 135].
- Рекомендуются пациентам с сопутствующими психическими (тревожно- депрессивными и соматоформными) расстройствами индивидуальная когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ), психотерапия и методы психологической релаксации [136].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств — 1).
Комментарии: классическая КПТ включает два метода: поведенческий (направлен на активизацию пациента, индивидуальную профилактику приступов М и умение справляться с ними) и когнитивный (включает работу с негативными мыслями и ложными представлениями о болезни, а также по уменьшению катастрофизации боли) [137 — 141].
- Рекомендуется нейропсихологическая реабилитация с помощью биологической обратной связи (БОС) по показателю частоты пульса и электромиографии мышц скальпа и шеи с целью обучения психологическому и мышечному расслаблению [142].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: БОС можно рекомендовать в качестве альтернативного эффективного немедикаментозного лечения пациентов с ХМ для долгосрочной профилактики приступов М. БОС в сочетании с домашними релаксационными тренировками более эффективны, чем без них [143].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с М рефлексотерапия при заболеваниях центральной нервной системы (акупунктура) как дополнительный метод профилактического лечения [144 — 146].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
Комментарии: рефлексотерапию можно рассматривать как эффективный и безопасный вариант лечения, так как при его применении не отмечается побочных эффектов [144 — 146].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с выраженной дисфункцией перикраниальных мышц (мышечно-тоническим синдромом) постизометрическая релаксация с целью достижения мышечного расслабления [147].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – A (уровень достоверности доказательств – 1).
- Рекомендуется пациентам с М лечебная физкультура для повышения эффективности профилактической терапии [148].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: пациентам с М показаны упражнения с легкой интенсивностью; тренировки на выносливость, например, на беговой дорожке, велоэргометре; скандинавская ходьба; общефизические упражнения; релаксационные и функциональные тренировки. Количество тренировок: максимум 3 — 4 раза в неделю; продолжительность сеанса: от 20 до 60 минут [149].
- Рекомендуется пациентам с М в качестве дополнительного метода лечения (в комбинации с другими нелекарственными методами и фармакотерапией) блокады большого затылочного нерва с использованием кортикостероидов системного действия и местных анестетиков [151].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: блокада большого затылочного нерва может являться эффективным методом неотложного лечения приступа М и может быть эффективна в краткосрочной перспективе при ХM [150].
- Рекомендуется в качестве дополнительного метода профилактического лечения М, в том числе ХМ, неинвазивная высокочастотная ритмическая транскраниальная магнитная стимуляция (ТМС) [152 — 155].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: эффект
высокочастотной ритмической ТМС при М связывают с нейромодулирующим влиянием на кортикальную гипервозбудимость – один из базовых патофизиологических механизмов мигрени [154 — 155].
- Рекомендуется для купирования приступов ГБ и профилактики М внешняя стимуляция первой ветви тройничного нерва аппаратом Цефали [157].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – A (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии: аппарат Цефали удобен для самостоятельного применения пациентами [156].
- Рекомендуется для лечения рефрактерной ХМ (устойчивой к адекватной профилактической терапии) применение инвазивной нейростимуляции (НС) большого затылочного нерва [161 — 163].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций- А (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2).
Комментарии
: эффективность НС при ХМ/рефрактерной ХМ связана с действием на тригемино-цервикальный комплекс и опосредованным ингибированием патологической активности болевых структур мозга [157]. Показано, что благодаря НС уменьшается частота и тяжесть приступов мигрени, снижается число потребляемых медикаментов, улучшается качество жизни пациентов [159, 160.]. Направление пациентов на инвазивную НС должно осуществляться совместно специалистом по диагностике и лечению головной боли и нейрохирургом.
- Не рекомендуется для профилактической терапии М диетотерапия [5, 6, 8, 10].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: хотя диетотерапия для лечения М не применяется, целесообразно давать пациентам совет по исключению из рациона некоторых продуктов, которые потенциально могут провоцировать приступ М. К таким продуктам относятся: шоколад, бананы, орехи, цитрусовые, жирные сорта сыров, алкоголь. [1, 2, 3 ,9].
7. Дополнительная информация (в том числе факторы, влияющие на исход заболевания или состояния)
В повседневной клинической практике мигрень плохо диагностируется [9, 15]; в РФ пациентам с жалобой на ГБ нередко устанавливаются ошибочные диагнозы, что определяет выбор неправильной тактики лечения и может способствовать прогрессированию (хронизации) заболевания. Примеры ошибочных диагнозов:
- дисциркуляторная энцефалопатия (ДЭП) с цефалгическим синдромом;
- остеохондроз шейного отдела позвоночника с мигренозными пароксизмами;
- вегетососудистая дистония с цефалгическим синдромом;
- цервикогенная ГБ;
- ГБ, связанная с артериальной гипертензией.
К ошибочным диагнозам, как правило, приводит ошибочная трактовка неспецифических изменений, выявленных при инструментальных исследованиях, как признаков органического поражения головного мозга или мозговых сосудов [2,9,15]. Например, незначительное снижение линейной скорости кровотока в краниовертебральных артериях на ультразвуковой допплерографии (УЗДГ) является основанием для неверного диагноза «ДЭП» или «хроническая ишемия мозга», а дегенеративные изменения шейного отдела позвоночника (ШОП) – для диагноза «Остеохондроз ШОП с цефалгическим синдромом» или «Цервикогенная ГБ». Установление неверного диагноза приводит к выбору неадекватного лечения (например, психостимуляторов и ноотропных препаратов), которое не улучшает течение М, а, напротив, способствует ее хронизации.
7.1 Оценка эффекта проводимой терапии
- Рекомендуется считать профилактическое лечение М эффективным, если число дней с ГБ сокращается через 3 месяца терапии на 50% и более от исходного [9, 15, 20, 76].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: к дополнительным критериям эффективности относятся уменьшение использования лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием и выраженности КН (улучшение настроения, снижение тревоги, нормализация сна), повышение работоспособности, уровня социальной адаптации и качества жизни пациента с М в целом.
- Рекомендуется пациентов, у которых не было достигнуто улучшение состояния, а также пациентов с тяжелым течением М (ХМ, множественные коморбидные нарушения, сопутствующая ЛИГБ) перенаправить в специализированное болевое отделение / центр лечения ГБ для дальнейшего лечения и наблюдения [2, 6, 8, 10, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Медицинская реабилитация
4. Медицинская реабилитация и санаторно-курортное лечение, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов медицинской реабилитации, в том числе основанных на использовании природных лечебных факторов
- Рекомендуются реабилитационные мероприятия, направленные на улучшение функционирования и качества жизни пациента, страдающего М [2, 9, 15, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: реабилитационные мероприятия могут включать постизометрическую релаксацию, лечебную физкультуру (в том числе упражнения на укрепление мышц шеи, координацию, растяжку), дыхательные упражнения, коррекцию осанки, обучение эргономике рабочего места. В дополнение к перечисленным нелекарственным методам могут быть рекомендованы общеукрепляющие и водные процедуры, массаж воротниковой зоны, санаторно-курортное лечение.
Госпитализация
6. Организация оказания медицинской помощи
Показания для экстренной госпитализации пациента в неврологическое отделение:
- Головная боль, сопровождающаяся изменением сознания;
- Головная боль, сопровождающаяся лихорадкой и менингеальными симптомами;
- Головная боль с нарастающей очаговой неврологической симптоматикой;
- Головная боль с нарастающей общемозговой симптоматикой;
- «Громоподобная» головная боль;
- Мигренозный статус.
Показания для плановой госпитализации пациента в неврологическое отделение:
- Прогрессирующая головная боль;
- Некупируемая головная боль;
- Тяжелая ЛИГБ, связанная с избыточным употреблением опиоидов, спазмолитиков, психотропных препаратов и анальгетиков в комбинации;
- Атипичная аура, длящаяся более 1 часа;
Показания к выписке пациентов из неврологического отделения:
- Купирование головной боли;
- Уменьшение головной боли до 3 — 4 баллов по визуальной аналоговой шкале;
- Успешная замена препарата злоупотребления на адекватную обезболивающую лекарственную терапию.
Профилактика
5. Профилактика и диспансерное наблюдение, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов профилактики
- Рекомендуется для всех пациентов с М динамическое наблюдение [2, 9, 15, 20].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций – С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5).
Комментарии: для профилактики учащения приступов М следует разъяснить пациентам роль мигренозных триггеров М и необходимости их избегания. Для предотвращения хронизации заболевания необходимо разъяснение роли факторов хронизации М (стресса, депрессии, лекарственного абузуса, избыточного употребления кофеина, ожирения, синдрома апноэ во сне) и необходимости модификации образа жизни. Необходимы контроль эффективности и переносимости профилактической терапии, соблюдение режима и правил приёма препаратов. Для обеспечения такого контроля необходима связь с пациентом на протяжении всего периода лечения, в том числе, с помощью телефонных визитов. Разъяснительная работа может проводиться врачами общей практики и врачами-неврологами, к которым обращаются пациенты с М.
Информация
Источники и литература
-
Клинические рекомендации Всероссийского общества неврологов
- Клинические рекомендации Всероссийского общества неврологов — 1 Амелин А.В., Игнатов Ю.Д., Скоромец А.А., Соколов А.Ю. Мигрень (патогенез, клиника, лечение). М.: МЕДпресс, 2011; 265с.
2 Осипова В.В, Табеева Г.Р. Первичные головные боли: диагностика, клиника, терапия: Практическое руководство. М.:ООО «Издательство «Медицинское информационное агентство», 2014; 336 с.
3 Табеева Г.Р., Яхно Н.Н. Мигрень. М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2011; 622 с.
4 Сергеев А.В., Табеева Г.Р., Азимова Ю.Э. Центральная нейрональная гипервозбудимость — предиспозиция к мигрени. Российский журнал боли. 2010; 2(27): 3- 11.
5 Rasmussen B.K., Jensen R., Schroll M., Olesen J. Epidemiology of headache in a general population — a prevalence study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991;44:1147–1157.
6 Ayzenberg I., Katsarava Z., Sborowski A. et al. The prevalence of primary headache disorders in Russia: A countrywide survey. Cephalalgia. 2012;32(5):373–381.
7 Лебедева Е.Р., Кобзева Н.Р., Гилев Д.В., Олесен Ес. Анализ качества диагностики и лечения первичных головных болей в различных социальных группах Уральского региона. Неврология, нейропсихиатрия, психосоматика. 2015;1:19-26.
8 The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (ICHD-3). Cephalalgia. 2018;38(1):1-211.
9 Осипова В.В. Мигрень и головная боль напряжения. В: Клинические рекомендации. Неврология и нейрохирургия. Под ред. Е.И. Гусева, А.Н. Коновалова. 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2015; 424 с.
10 Li D., Christensen A.F., Olesen J. Field-testing of the ICHD-3 beta/proposed ICD- 11 diagnostic criteria for migraine with aura. Cephalalgia. 2015;35(9):748-756.
11 Lebedeva E.R., Gurary N.M., Gilev D.V., Olesen J. Prospective testing of ICHD- 3 beta diagnostic criteria for migraine with aura and migraine with typical aura in patients with transient ischemic attacks. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(3):561-567.
12 Lebedeva E.R., Gurary N.M., Gilev D.V.et al. Explicit diagnostic criteria for transient ischemic attacks to differentiate it from migraine with aura. Cephalalgia. 2018;38(8):1463-1470.
13 Екушева Е.В., Карпова М.И., Осипова В.В. Гормональные контрацептивы и риск ишемического инсульта у женщин с мигренью: новый международный консенсус. Неврология, нейропсихиатрия и психосоматика. 2019; 11(3): 11-15.14 Артеменко А.Р., Куренков А.Л., Беломестова К.В. Классификация, диагностика и лечение хронической мигрени: обзор новых данных. Журн. неврологии и психиатрии им. Корсакова. 2013;11:91-96.
15 Осипова В.В., Филатова Е.Г., Артеменко А.Р. с соавт. Диагностика и лечение мигрени: рекомендации российских экспертов. Журнал неврологии и психиатрии им. Корсакова 2017;2:28-42.
16 Westergaard M.L., Hansen E.H., Glümer C. et al. Definitions of medication- overuse headache in population-based studies and their implications on prevalence estimates: a systematic review. Cephalalgia. 2014;34(6):409-425.
17 Zeeberg P., Olesen J., Jensen R. Medication overuse headache and chronic migraine in a specialized headache centre: field-testing proposed new appendix criteria. Cephalalgia. 2009;29(2):214-220.
18 Steiner T.J., MacGregor E.A., Davies P.T.G. Guidelines for all healthcare professionals in the diagnosis and management of migraine, tension-type, cluster and medication overuse headache. British Association for the Study of Headache, 3rdedn. 2007.
19 Tepper S.J., Dahlöf C.G., Dowson A. et al. Prevalence and diagnosis of migraine in patients consulting their physician with a complaint of headache: data from the Landmark Study. Headache. 2004;44(9):856-864.
20 Reference programme: Diagnosis and treatment of headache disorders and facial pain. Danish Headache Society, 2nd Edition, 2012. J. Headache Pain. 2012; 13:S1–S29.
21 Lipton R.B., Serrano D., Buse D.C. et al. Improving the detection of chronic migraine: Development and validation of Identify Chronic Migraine (ID-CM). Cephalalgia. 2016;36(3):203-215.
22 Jiang H., Deng Y., Zhang Y. et al. Field testing of the ICHD-3β and expert opinion criteria for chronic migraine. J. Headache Pain. 2016;17(1):85.
23 Lampl C., Buzath A., Yazdi K., Sandor P.S. Ergot and triptan overuse in Austria
—an evaluation of clinical data and cost. Cephalalgia. 2002;22:807–811.
24 Mitsikostas D., Ashina M., Craven A. et al. EHF committee. European headache federation consensus on technical investigation for primary headache disorders. J. Headache Pain. 2015;17:5.
25 Kamtchum-Tatuene J. et al. Neuroimaging findings in headache with normal neurologic examination: Systematic review and meta-analysis //Journal of the Neurological Sciences. – 2020. – Т. 416. – С. 116997.26 Kruit M.C., van Buchem M.A., Launer L.J. et al. Migraine is associated with an increased risk of deep white matter lesions, subclinical posterior circulation infarcts and brain iron accumulation: the population-based MRI CAMERA study. Cephalalgia. 2010;30(2):129-36.
27 Екушева Е.В. Многоликая женская мигрень. М.: МЕДпресс-информ, 2019;96
с.
28 Mett A., Tfelt-Hansen P. Acute migraine therapy: recent evidence from
randomized comparative trials. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2008; 21(3): 331-337.
29 Orr S.L., Aube´ M., Becker W.J. et al. Canadian Headache Society systematic review and recommendations on the treatment of migraine pain in emergency settings. Cephalalgia. 2015; 35: 271.
30 Kirthi V., Derry S., Moore R. Aspirin with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013; 4: CD008041.
31 Lampl C., Voelker M., Diener H.C. Efficacy and safety of 1,000 mg effervescent aspirin: individual patient data meta-analysis of three trials in migraine headache and migraine accompanying symptoms. J. Neurol. 2007;254(6):705-712.
32 Rabbie R, Derry S, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. Ibuprofen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Oct 6; (10):CD008039. .
33 Rabbie R., Derry S., Moore R.A. Ibuprofen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013;4:CD008039.
34 Suthisisang C.C., Poolsup N., Suksomboon N. et al. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of naproxen sodium in the acute treatment of migraine. Headache. 2010;50(5):808- 818.
35 Law S., Derry S., Moore R.A. Naproxen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013;10: CD009455.
36 Derry S., Rabbie R., Moore R.A. Diclofenac with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013; 4: CD008783.
37 Derry S., Moore R.A. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013; 4: CD008040.
38 Diener H.C., Montagna P., Gacs G. et al. Efficacy and tolerability of diclofenac potassium sachets in migraine: A randomized, double-blind, cross-over study in comparison with diclofenac potassium tablets and placebo. Cephalalgia. 2006;26:537-547.
39 Colman I., Brown M.D., Innes G.D. et al. Parenteral metoclopramide for acute migraine: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2004; 329(7479): 1369-1373.40 Turkcuer I., Serinken M., Eken C. et al. Intravenous paracetamol versus dexketoprofen in acute migraine attack in the emergency department: A randomised clinical trial. Emerg. Med. J. 2014;31: 182-185.
41 Taggart E, Doran S, Kokotillo A, Campbell S, Villa-Roel C, Rowe BH. Ketorolac in the treatment of acute migraine: a systematic review. Headache. 2013;53(2):277-87.
42 Dib M, Massiou H, Weber M, Henry P, Garcia-Acosta S, Bousser MG; Bi- Profenid Migraine Study Group. Efficacy of oral ketoprofen in acute migraine: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Neurology. 2002 ;58(11):1660-5.
43 Friedman B.W., Mulvey L., Esses D. et al. Metoclopramide for acute migraine: a dose finding randomized clinical trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57(5):475-482.
44 Friedman B.W., Garber L., Yoon A. et al. Randomized trial of IV valproate vs metoclopramide vs ketorolac for acute migraine. Neurology. 2014;82:976-983.
45 Kellstein D.E., Lipton R.B., Geetha R. et al. Evaluation of a novel solubilized formulation of ibuprofen in the treatment of migraine headache: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:233-243.
46 Cameron C., Kelly S., Hsieh S.C. et al. Triptans in the Acute Treatment of Migraine: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Headache. 2015;55(Suppl 4):221- 235.
47 Ferrari M.D., Goadsby P.J., Roon K.I., Lipton R.B. Triptans (serotonin, 5-HT1B/1D agonists) in migraine: detailed results and methods of a meta-analysis of 53 trials. Cephalalgia. 2002; 22: 633-658.
48 Lipton R.B., Bigal M.E., Goadsby P.J. Double-blind clinical trials of oral triptans vs other classes of acute migraine medication. A review. Cephalalgia. 2004; 24: 321-332.
49 Pascual J., Mateos V., Roig C. et al. Marketed oral triptans in the acute treatment of migraine: A systematic review on efficacy and tolerability. Headache. 2007;47:1152-1168.
50 Thorlund K., Mills E.J., Wu P. et al. Comparative efficacy of triptans for the abortive treatment of migraine: A multiple treatment comparison meta-analysis. Cephalalgia. 2014;34:258-267.
51 Derry C.J., Derry S., Moore R.A. Sumatriptan (oral route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012:CD008615.
52 Smith LA., Oldman A.D., McQuay H.J., Moore R.A. Eletriptan for acute migraine. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001: CD003224.
53 Cady R.K., Sheftell F., Lipton R.B. et al. Effect of early intervention with sumatriptan on migraine pain: retrospective analyses of data from three clinical trials. Clin. Ther. 2000; 22(9): 1035-1048.54 Olesen J., Diener H.C., Schoenen J., Hettiarachchi J. No effect of eletriptan administration during the aura phase of migraine. 2004; 11: 671-677.
55 Филатова Е.Г., Амелин А.В., Табеева Г.Р. с соавт. Ready — первое российское мультицентровое исследование эффективности препарата релпакс (элетриптан) при лечении мигрени. Лечение нервных болезней. 2006; 2: 19-22.
56 Bigal M.E., Bordini C.A., Speciali J.G. Intravenous chlorpromazine in the emergency department treatment of migraines: a randomized controlled trial. J. Emerg. Med. 2002;23(2):141-148.
57 Cameron J.D., Lane P.L., Speechley M. Intravenous chlorpromazine vs intravenous metoclopramide in acute migraine headache. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1995; 2(7): 597- 602.
58 Gungor F., Akyol K.C., Kesapli M. et al. Intravenous dexketoprofen vs placebo for migraine attack in the emergency department: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Cephalalgia. 2016;36:179-184.
59 Bigal M.E., Bordini C.A., Tepper S.J. et al. Intravenous magnesium sulphate in the acute treatment of migraine without aura and migraine with aura: A randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2002;22:345-353.
60 Corbo J., Esses D., Bijur P.E. et al. Randomized clinical trial of intravenous magnesium sulfate as an adjunctive medication for emergency department treatment of migraine headache. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001;38:621-627.
61 Cete Y., Dora B., Ertan C. et al. A randomized prospective placebo-controlled study of intravenous magnesium sulphate vs. metoclopramide in the management of acute migraine attacks in the emergency department. Cephalalgia. 2005;25:199-204.
62 Leniger T., Pageler L., Stude P., Diener H.C., Limmroth V. Comparison of intravenous valproate with intravenous lysine-acetylsalicylic acid in acute migraine attacks. Headache. 2005; 45: 42-46.
63 Diener HC, Antonaci F, Braschinsky M, Evers S, Jensen R, Lainez M, Kristoffersen ES, Tassorelli C, Ryliskiene K, Petersen JA. European Academy of Neurology guideline on the management of medication-overuse headache. Eur J Neurol. 2020;27(7):1102- 1116.
64 Woldeamanuel Y.W., Rapoport A.M., Cowan R.P. The place of corticosteroids in migraine attack management: a 65-year systematic review with pooled analysis and critical appraisal. Cephalalgia. 2015; 35(11): 996–1024.
- Клинические рекомендации Всероссийского общества неврологов — 1 Амелин А.В., Игнатов Ю.Д., Скоромец А.А., Соколов А.Ю. Мигрень (патогенез, клиника, лечение). М.: МЕДпресс, 2011; 265с.
Информация
Список сокращений
БОС – биологическая обратная связь
ВАШ – визуальная аналоговая шкала
ВОП – врач общей практики
В/В –внутривенно
ГБ – головная боль
ГБН – головная боль напряжения
ДПМ – дисфункция перикраниальных мышц
ДЭП – дисциркуляторная энцефалопатия
ЖНВЛП – жизненно необходимые и важнейшие лекарственные препараты
КГРП – кальцитонин-ген-родственный пептид
КН – коморбидные нарушения
ЛИГБ – лекарственно-индуцированная (абузусная) головная боль
М – мигрень
МА – мигрень с аурой
МбА – мигрень без ауры
мАТ – моноклональное антитело
МКБ-10 – международная классификация болезней 10-го пересмотра
МКГБ-3 – Международная классификация головных болей 3-го пересмотра
МРТ – магнитно-резонансная томография
МС – мигренозный статус
МТС – мышечно-тонический синдром
МФС – миофасциальный синдром
НПВП – нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты
НС – нейростимуляция
ПС – периферическая сенситизация
РКД – распространяющаяся корковая депрессия
ТВС –тригемино-васкулярная система
ТМО – твердая мозговая оболочка
ТЦА – трициклические антидепрессанты
УЗДГ – ультразвуковая допплерография
ХГБН – хроническая головная боль напряжения
ХМ – хроническая мигрень
ЦНС – центральная нервная система
ЦС – центральная сенситизация
ЭГБН – эпизодическая головная боль напряжения
CGRP – (англ. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide — кальцитонин-ген-родственный пептид (КГРП)
PREEMPT – Phase III REsearch Evaluating Migraine Prophylaxis Therapy (англ. исследование III фазы по оценке профилактической терапии мигрени).
Термины и определения
Виновные препараты (препараты, которыми злоупотребляют) – препараты, которые при избыточном приеме могут приводить к развитию ЛИГБ (все классы анальгетиков).
Вторичные ГБ – головные боли, являющиеся симптомом другого заболевания (симптоматические), возникающие de novo в тесной временной связи с другим (причинным) заболеванием, которое согласно научным данным может быть причиной ГБ.
Головная боль напряжения (ГБН) — одна из наиболее распространенных форм первичной ГБ, проявляющаяся болевыми эпизодами продолжительностью от 30 минут до нескольких суток.
Дисфункция перикраниальных мышц (ДПМ) – болезненное напряжение мышц головы, лица и шеи.
Ингибиторные антиноцицептивные механизмы – система нисходящего противоболевого или антиноцицептивного контроля.
Кальцитонин-ген-родственный пептид (КГРП или CGRP) – основной медиатор, реализующий передачу болевых импульсов и непосредственно участвующий в патогенезе мигрени.
Коморбидные нарушения (КН)–одно или несколько патологических состояний, наблюдающихся у одного больного, этиопатогенетически связанных между собой или совпадающих по времени появления вне зависимости от активности каждого их них.
Лекарственно-индуцированная головная боль (ЛИГБ) – клиническая разновидность вторичной хронической ГБ, развивающаяся у пациентов с первичными цефалгиями при избыточном применении препаратов для купирования ГБ.
Лекарственный абузус – избыточное применение любых препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, для купирования ГБ.
Моноклональные антитела (мАТ) к КГРП или его рецептору – первый класс препаратов, специально разработанных для таргетной (патогенетически обоснованной) профилактической терапии мигрени.
Первичные ГБ – идиопатические (доброкачественные) цефалгии, которые не связаны с органической патологией головного мозга, церебральных сосудов, любых структур головы и шеи и системными заболеваниями.
Периферическая сенситизация (ПС) – повышенный ответ возбужденных ноцицептивных нейронов периферической нервной системы на обычную и/или подпороговую стимуляцию.
Таргетная (целевая) профилактическая терапия мигрени – терапия моноклональными антителами (мАТ) к основному медиатору мигрени КГРП или его рецептору, воздействующая на основной патогенетический механизм мигрени.
Триггеры приступа мигрени – эндогенные и экзогенные факторы, способные спровоцировать приступ мигрени.
Факторы хронизации – генетические, метаболические, средовые, поведенческие и/или психические факторы, способствующие учащению имеющейся ГБ.
Хронизация мигрени – постепенное увеличение числа дней с головной болью в месяц.
Хроническая мигрень (ХМ) – ГБ, которая возникает
>
15 и более дней в месяц в течение
>
3 месяцев, при этом приступы ГБ имеют признаки М и наблюдаются не менее 8 дней в месяц.
Центральная сенситизация (ЦС) – усиление нервных импульсов в ЦНС, что приводит к гиперчувствительности организма к боли. ЦС отражает повышенную активность систем восприятия боли, сниженную активность нисходящих ингибирующих боль путей и в результате нарушение эндогенного контроля боли.
Цефалгия – головная боль (синоним).
Цефалголог — невролог, специализирующийся на диагностике и лечении ГБ.
Критерии оценки качества медицинской помощи
Критерии качества специализированной медицинской помощи взрослым с мигренью [2, 18, 20, 76].
Приложение А1. Состав рабочей группы по разработке и пересмотру клинических рекомендаций.
Азимова Юлия Эдвардовна, д.м.н., врач-невролог Университетской клиники головной боли. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли».
Амелин Александр Витальевич, д.м.н., профессор кафедры неврологии, Руководитель отдела общей неврологии НИИ Неврологии НКИЦ ГБОУ ВПО «Первый Санкт-Петербургский государственный медицинский университет им акад. И.П. Павлова МЗ РФ». Руководитель комитета по головной боли Российского Межрегионального Общества по изучению боли, Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли».
Алферова Вера Вадимовна, д.м.н., ведущий научный сотрудник кафедры неврологии, нейрохирургии и медицинской генетики ФГАОУ ВО «Российский национальный исследовательский медицинский университет имени Н.И. Пирогова» Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации, член президиума Всероссийского общества неврологов
Артеменко Ада Равильевна, д.м.н., профессор кафедры нервных болезней Института профессионального образования ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. И.М. Сеченова Минздрава России (Сеченовский Университет) и Центр Междисциплинарной Стоматологии и Неврологии, г. Москва. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли».
Ахмадеева Лейла Ринатовна, д.м.н., профессор кафедры неврологии с курсами нейрохирургии и медицинской генетики ФГБОУ ВО «Башкирский государственный медицинский университет МЗ РФ». Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли», председатель Башкирского отделения межрегионального общества специалистов доказательной медицины, член Межрегиональной общественной организации специалистов ботулинотерапии.
Головачева Вероника Александровна–к.м.н., ассистент кафедры нервных болезней и нейрохирургии лечебного факультета, ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет). Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли»,
Данилов Алексей Борисович – д.м.н., профессор, зав. кафедрой нервных болезней Института профессионального образования ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет). Директор Института Междисциплинарной Медицины. Исполнительный директор российской Ассоциации пациентов с головной болью. Член правления Международной Ассоциации мигрени и головной боли (EMHA).
Екушева Евгения Викторовна — д.м.н., заведующая кафедрой нервных болезней и нейрореабилитации Академии последипломного образования ФГБУ ФНКЦ ФМБА России и Клиника головной боли и вегетативных расстройств им. академика Александра Вейна, г. Москва. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению боли». Член комитетов по головной и лицевой боли Российского Межрегионального Общества по изучению боли. Член межрегиональной общественной организации специалистов ботулинотерапии. Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли» и международной общественной организации «Международное общество головной боли».
Исагулян Эмиль Давидович – к.м.н, научный сотрудник группы функциональной нейрохирургии НИИ Нейрохирургии им. акад. Н. Н. Бурденко РАМН. Президент Российской Ассоциации Нейромодуляции (NNSR). Вице-президент Российской Ассоциации Интервенционного Лечения Боли (АИЛБ). Вице-президент Российской Ассоциации Стереотаксических и Функциональных Нейрохирургов (RSSFN). Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли».
Корешкина Марина Игоревна, д.м.н., руководитель Центра лечения головной боли клиники «Скандинавия» (г. Санкт-Петербург). Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член международной общественной организации «Международное общество головной боли».
Курушина Ольга Викторовна, д.м.н., заведующий кафедрой неврологии, нейрохирургии, медицинской генетики с курсом мануальной терапии и рефлексотерапии ФУВ ГБОУ ВПО «Волгоградский государственный медицинский университет МЗ РФ». Главный внештатный специалист-невролог МЗ РФ по Южному федеральному округу. Член Правления Всероссийского общества неврологов. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли».
Латышева Нина Владимировна, д.м.н., доцент кафедры нервных болезней Института профессионального образования ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет) и Клиника головной боли и вегетативных расстройств им. академика Александра Вейна, г. Москва. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли». Член международной общественной организации «Международное общество головной боли».
Лебедева Елена Разумовна, д.м.н., доцент кафедры СМП ФГБОУ ВО «Уральский государственный медицинский университет МЗ РФ», руководитель Международного центра лечения головных болей «Европа-Азия», г. Екатеринбург. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член международной общественной организации «Международное общество головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли». Член секции головной боли в европейской общественной организации «Европейская Академия неврологии». Представитель России в образовательном комитете европейской общественной организации «Европейская Академия неврологии».
Наприенко Маргарита Валентиновна, д.м.н., профессор кафедры интегративной медицины Института профессионального образования ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. И.М. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет). Главный врач Клиники головной боли имени академика Александра Вейна. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член Межрегиональной общественной организации специалистов ботулинотерапии.
Осипова Вера Валентиновна, д.м.н., ведущий научный сотрудник ГБУЗ «Научно- практический психоневрологический центр им. Соловьева» ДЗ г. Москвы и врач-невролог Университетской клиники головной боли (Москва). Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли» (РОИГБ). Член панели «Головная боль» в Европейской общественной организации «Европейская Академия неврологии» (Headache Panel, EAN). Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли» (EHF).
Павлов Николай Александрович, к.м.н., ведущий научный сотрудник кафедры неврологии, нейрохирургии и медицинской генетики ФГАОУ ВО «Российский национальный исследовательский медицинский университет имени Н.И. Пирогова» Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации, член президиума Всероссийского общества неврологов
Парфенов Владимир Анатольевич, д.м.н., профессор, заведующий кафедрой нервных болезней и нейрохирургии лечебного факультета ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский университет). Член правления общественной организации «Всероссийское общество неврологов», член правления Национальной ассоциации по борьбе с инсультом, член панели «Общая неврология» Европейской академии неврологии.
Рачин Андрей Петрович, д.м.н., профессор, зав. отделом эволюционной неврологии и нейрофизиологии ФГБУ «Национальный медицинский исследовательский центр реабилитации и курортологии» МЗ РФ. Член Правления Всероссийского общества неврологов. Член Президиума и Ревизор Российского общества по изучению головной боли. Ответственный секретарь медицинского общества специалистов по дисфункциональным неврологическим расстройствам и нейростоматологии.
Сергеев Алексей Владимирович, к.м.н. доцент кафедры нервных болезней и нейрохирургии лечебного факультета ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет) и руководитель Центра неврологии Клиник Чайка, г. Москва. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли». Представитель России в международной общественной организации «Международное общество головной боли».
Скоробогатых Кирилл Владимирович, к.м.н., врач-невролог, директор Университетской клиники головной боли (г. Москва). Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Представитель РФ в европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли». Член международной общественной организации «Международное общество головной боли».
Табеева Гюзяль Рафкатовна, д.м.н., профессор кафедры нервных болезней и нейрохирургии лечебного факультета ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет). Президент общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли».
Филатова Елена Глебовна, д.м.н., профессор кафедры нервных болезней Института профессионального образования ФГАОУ ВО Первый МГМУ им. Сеченова МЗ РФ (Сеченовский Университет) и Клиника головной боли и вегетативных расстройств им. академика Александра Вейна, г. Москва. Член общероссийской общественной организации «Российское общество по изучению головной боли». Член европейской общественной организации «Европейская федерация головной боли».
Конфликт интересов отсутствует.
Приложение А2. Методология разработки клинических рекомендаций
Целевая аудитория данных клинических рекомендаций:
- врачи-неврологи, врачи-терапевты, врачи общей практики;
- студенты медицинских ВУЗов, ординаторы, аспиранты;
- преподаватели, научные сотрудники;
В данных клинических рекомендациях все сведения ранжированы по уровню достоверности (доказательности) в зависимости от количества и качества исследований по данной проблеме (Таблица 1, Таблица 2, Таблица 3).
Таблица П1. Шкала оценки уровней достоверности доказательств (УДД) для методов диагностики (диагностических вмешательств).
Таблица П2. Шкала оценки уровней достоверности доказательств (УДД) для методов профилактики, лечения и реабилитации (профилактических, лечебных, реабилитационных вмешательств)
Таблица П3. Шкала оценки уровней убедительности рекомендаций (УУР) для методов профилактики, диагностики, лечения и медицинской реабилитации, в том числе основанных на использовании природных лечебных факторов (профилактических, диагностических, лечебных, реабилитационных вмешательств).
Порядок обновления клинических рекомендаций
Механизм обновления клинических рекомендаций предусматривает их систематическую актуализацию – не реже чем один раз в три года, а также при появлении новых данных с позиции доказательной медицины по вопросам диагностики, лечения, профилактики и реабилитации конкретных заболеваний, наличии обоснованных дополнений/замечаний к ранее утверждённым КР, но не чаще 1 раза в 6 месяцев.
Порядок обновления клинических рекомендаций по мигрени предусматривает их систематическую актуализацию – не реже чем один раз в три года, а также при появлении новых данных с позиции доказательной медицины по вопросам диагностики, лечения, профилактики и реабилитации мигрени, наличии обоснованных дополнений/замечаний к ранее утверждённым КР,
но не чаще 1 раза в 6 месяцев
.
Приложение А3. Справочные материалы, включая соответствие показаний к применению и противопоказаний, способов применения и доз лекарственных препаратов, инструкции по применению лекарственного препарата
Данные клинические рекомендации разработаны с учётом следующих нормативно-правовых документов:
- Федеральный закон “Об основах охраны здоровья граждан в Российской Федерации” от 21.11.2011 N 323-ФЗ
- Порядок оказания медицинской помощи взрослому населению при заболеваниях нервной системы (приказ Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации от 15 ноября 2012 г. N 926н).
- Приказ Министерства Здравоохранения РФ от 28 февраля 2019 г. N 103н «Об утверждении порядка и сроков разработки клинических рекомендаций, их пересмотра, типовой формы клинических рекомендаций и требований к их структуре, составу и научной обоснованности включаемой в клинические рекомендации информации».
- Регистр лекарственных средств России (РЛС). Москва -2019
Приложение Б. Алгоритмы действий врача
Примечание: ГБ – головная боль; М — мигрень; МКГБ-3 – Международная классификация головной боли; КН – коморбидные нарушения
Приложение В. Информация для пациентов
Что такое мигрень?
“Во время приступа мигрени, я совершенно разбита и абсолютно вырвана из повседневной жизни на сутки или даже больше. Боль начинается постепенно в области виска, затем нарастает, становится все сильнее и сильнее, появляется тошнота, иногда меня может вырвать; раздражают даже обычные звуки и свет. Я чувствую себя настолько ужасно, что вынуждена лечь в постель. После приема лекарственного препарата, обладающего обезболивающим действием, боль может через пару часов стихнуть, но не всегда. На следующий день я чувствую тяжесть в голове и разбитость, но все-таки значительно лучше, чем накануне”.
Описание мигрени
Мигрень – доброкачественное неврологическое заболевание, проявляющееся приступами головной боли, которые могут возникать с различной частотой: от 1-2 раз в год до нескольких раз в месяц. Основные проявления мигренозного приступа: сильная пульсирующая головная боль лобно-височной локализации чаще в одной половине головы, тошнота, реже рвота, непереносимость света, звуков, запахов и усиление боли от обычной физичкой нагрузки. Во время приступа мигрени работоспособность и привычная активность в значительной степени нарушены.
Почему возникает мигрень?
Приступ мигрени является следствием возбуждения некоторых структур головного мозга, а также — выброса в кровь болевых веществ — медиаторов и расширения сосудов твердой мозговой оболочки, которая покрывает головной мозг. Мигрень — наследственное заболевание: «мигренозные» гены страдающие этим заболеванием люди получают от одного из родителей и могут «передать» ее детям.
У кого бывает мигрень?
Мигрень является самой распространенной формой цефалгии после головной боли напряжения; она встречается у 14% людей. Мигренью страдает каждый седьмой взрослый; у женщин мигрень возникает в три раза чаще, чем у мужчин. Обычно заболевание начинается в детстве или подростковом возрасте. У девочек мигрень нередко начинается в период полового созревания.
Какие бывают виды мигрени?
Самый частый вид мигрени – мигрень без ауры — встречается у 75% пациентов. Реже бывает мигрень с аурой, когда болевому приступу предшествуют преходящие и полностью обратимые неврологические нарушения. Чаще всего отмечаются нарушения зрения (светящиеся зигзаги, мерцание, выпадение полей зрения), реже чувствительные (распространяющееся снизу верх онемение одной руки, половины лица, языка) и речевые нарушения. Возможно сочетание обеих форм мигрени у одного пациента, а также развитие мигренозной ауры без головной боли.
Самая тяжеля форма – хроническая мигрень, при которой головная боль может возникать 15 и более дней в месяц или даже ежедневно. Основными факторами, которые приводят к учащению мигренозных приступов являются эмоциональный стресс, депрессия, злоупотребления лекарственными препаратами, обладающими обезболивающим действием, и кофеином (крепкий чай, кофе, энергетические напитки).
Как проявляется мигрень?
Приступ мигрени имеет четыре стадии, хотя не все могут быть полностью представлены у всех пациентов.
Фаза предвестников мигрени
(продром) возникает раньше других симптомов приступа и может проявляться за несколько часов или даже за сутки до развития головной боли следующими симптомами: боль в шее, раздражительность, подавленность, усталость или, напротив, повышение активности, аппетита, чувствительности к свету и запахам.
Аура
, если она есть, является следующей фазой. Лишь треть пациентов с мигренью когда-либо отмечали ауру, и она может развиваться не в каждом приступе. Аура не опасна для здоровья; она длится 10 — 30 минут, реже может быть и более продолжительной и полностью проходит. Чаще всего бывает зрительная аура. Вы можете «видеть» слепые пятна, вспышки света или разноцветную зигзагообразную линию, распространяющуюся из центра поля зрения на периферию. Реже возникают чувствительные симптомы – ощущение покалывания или онемение, которое возникает в кончиках пальцев с одной стороны, распространяется вверх к плечу, иногда переходит на щеку или язык на той же стороне. Чувствительные симптомы практически всегда сопровождаются зрительными нарушениями. Кроме этого, во время ауры могут быть затруднения речи или трудности в подборе слов.
Фаза головной боли
– самая тяжелая для большинства людей, длится от нескольких часов до 2 — 3 суток. Мигренозная головная боль может быть очень сильной, чаще возникает в лобной или височной области одной половины головы, но может начинаться в затылочной области, захватывать другие зоны и всю голову. Обычно это пульсирующая или распирающая боль, которая усиливается при движении и физических нагрузках.
Нередко возникает тошнота, и даже рвота, которая облегчает головную боль. Во время приступа очень часто неприятны свет и звуки даже обычной интенсивности, поэтому пациенты предпочитают оставаться в одиночестве в тихом и затемненном помещении.
За фазой головной боли следует
фаза разрешения
. В этот период вы вновь можете чувствовать усталость, раздражительность или подавленность, вам трудно концентрировать внимание. Эти симптомы могут сохраняться в течение суток до того, как вы почувствуете себя полностью здоровым.
Что такое триггеры мигрени?
Каждый пациент с мигренью хотел бы знать, что может вызвать приступ. Как правило, это трудно или невозможно, поскольку каждый пациент имеет «свои» триггеры; даже у одного и того же пациента разные приступы могут вызываться различными триггерами. К наиболее распространенным провокаторам приступа мигрени относят:
Психологические: эмоциональное напряжение, а также расслабление после стресса.
Факторы внешней среды: яркий или мерцающий свет, резкие запахи, перемена погоды, пребывание в духоте, на жаре.
Диетические факторы: некоторые продукты (цитрусовые, орехи, шоколад, бананы, копчености, жирные сыры) и алкоголь (красное вино, пиво, шампанское), пропуск приема пищи (голод), неадекватное питание, отмена кофеина и недостаточное потребление воды.
Сон: изменение режима сна, как недосыпание, так и избыточный сон (например, в выходные дни).
Гормональные факторы у женщин: менструация, гормональные контрацептивы и гормональная заместительная терапия.
Другие жизненные факторы: интенсивная физическая нагрузка, длительные переезды, особенно со сменой часовых поясов, воздушные перелеты.
Определить свои индивидуальные триггеры и научиться их избегать (если это возможно) является важной задачей каждого пациента и может в значительной степени сократить число приступов.
Что Вы можете ощущать между приступами мигрени?
Между приступами мигрени большинство людей чувствуют себя хорошо. Однако некоторые люди вне болевых приступов могут жаловаться на повышенную тревожность и даже панические атаки, снижение настроения вплоть до выраженной депрессии, плохой сон, другие боли (например, сжимающие по типу «каски» головные боли напряжения (ГБН), боли в спине и др.), болезненность и напряжение мышц шеи и затылка, желудочно-кишечные нарушения. Эти нарушения, часто сопутствующие мигрени, могут нарушать общее самочувствие и требуют лечения. Обязательно расскажите доктору об этих жалобах, чтобы он мог назначить вам необходимое лечение.
Как лечить мигрень?
Лекарственные средства, которые используют для снятия приступа, называют
средствами для купирования мигрени
. Правильно подобранные лекарства могут быть весьма эффективными, если принимаются правильно и в небольших количествах. К таким средствам относятся безрецептурные препараты, обладающие обезболивающим действием, большинство из которых содержит ацетилсалициловую кислоту, ибупрофен**или парацетамол**. Растворимые формы этих препаратов, например, в виде шипучих таблеток действуют быстрее и лучше.
Если вас очень беспокоит тошнота или рвота, можно использовать
противорвотные препараты
. Некоторые из них фактически усиливают действие лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, так как увеличивают их всасывание в желудочно-кишечном тракте. Если вы испытываете сильную тошноту или рвоту, то можно использовать эти препараты в форме ректальных свечей.
Врач может прописать вам один из
специфических антимигренозных препаратов
. К этим препаратам необходимо прибегнуть, если анальгетики и антипиретики и противорвотные препараты оказываются недостаточно эффективными. Антимигренозные средства отличаются от обычных лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием. Они воздействуют не на боль, а на патологические процессы, происходящие в головном мозге во время мигренозной атаки. К таким средствам относят селективные агонисты серотониновых 5НТ1-рецепторов (триптаны) – наиболее эффективные в купировании приступа мигрени — и препараты, содержащие эрготамин. При необходимости вы можете сочетать эти средства с НПВС и противорвотными препаратами.
Существует несколько приемов, позволяющих повысить эффективность медикаментозного лечения приступа мигрени.
1 Принимать препарат в самом начале приступа…
Всегда имейте при себе хотя бы одну дозу препарата, рекомендованного врачом. Принимайте препарат, в самом начале головной боли. Лекарств, способных купировать ауру мигрени, не существует. Во время приступа мигрени работа желудочно-кишечного тракта замедляется, поэтому лекарства, принимаемые в виде таблеток, всасываются в кровь медленнее, чем обычно. Если позволяет состояние, выпейте что-нибудь сладкое (крепкий сладкий чай).
2.… но не очень часто
Всегда строго придерживайтесь инструкций по применению препарата. В частности, не используйте средства для снятия головной боли слишком часто, так как это может привести к развитию лекарственно-индуцированной (абузусной) головной боли (ЛИГБ), связанной с избыточным применением обезболивающих препаратов. Чтобы у вас не развилась ЛИГБ, ни в коем случае не используйте средства для купирования мигрени и другой боли чаще, чем 8 дней в месяц. Избыточный прием лекарственных препаратов любых классов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, способствует учащению головной боли (не только мигрени, но и ГБН).
Что делать, если это лечение не помогает?
Если приступы мигрени очень частые или тяжелые, и плохо поддаются лечению препаратами, обладающими обезболивающим действием, то вам показано курсовое
профилактическое лечение
, которое назначает врач. В отличие от средств для купирования приступа при профилактической терапии необходимо принимать препараты
каждый день
, поскольку это лечение направлено на предотвращение развития приступов мигрени.
Большинство профилактических средств первоначально были разработаны для лечения других заболеваний, поэтому не следует удивляться, если Вам назначат препарат из группы антидепрессантов, противоэпилептических препаратов или применяющийся для снижения артериального давления. Вам назначили лечение не в связи с этими показаниями, просто эти препараты также обладают и противомигренозным действием.
При назначении вам одного или более препаратов, аккуратно следуйте инструкциям по их применению. Исследования показали, что наиболее частая причина недостаточной эффективности профилактического лечения — несоблюдение режима терапии. Профилактическое лечение мигрени должно продолжаться от 3 до 12 месяцев в зависимости от тяжести заболевания (в среднем 6 месяцев).
Для лечения очень частой (хронической) мигрени (когда число дней с головной болью превышает 15 в месяц) вам могут порекомендовать введение препарата ботулинического токсина типа А в мышцы головы и шеи. В клинических исследованиях этот метод показал высокую эффективность и широко используется в мире для лечения тяжелой мигрени.
Что еще вы можете сделать, чтобы помочь себе?
Регулярные занятия спортом, водные процедуры, приемы психологической релаксации, прогулки, хобби улучшат ваше самочувствие. При наличии болезненности и напряжения мышц шеи затылка полезны массаж воротниковой зоны и гимнастика на шейный отдел позвоночника. Важно избегать триггеров приступов, в первую очередь, эмоционального стресса, избыточных нагрузок, недосыпания, длительных перерывов между приёмами пищи.
Ведение дневника головной боли
Ведение дневника поможет собрать важную информацию о вашей головной боли: как часто болит голова, как долго длится головная боль, что ее вызывает, какие симптомы ее сопровождают, сколько лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, и как часто вы принимаете. Эта информация является очень ценной для постановки правильного диагноза, выявления лекарственного абузуса и факторов? провоцирующих головную боль, а также для оценки эффективности лечения.
Что делать, если Вы подозреваете, что забеременели?
Вам необходимо проконсультироваться с врачом, поскольку некоторые из антимигренозных препаратов во время беременности противопоказаны.
Нужны ли Вам дополнительные обследования?
В большинстве случаев после тщательного опроса диагностика мигрени не вызывает у врача затруднений. Диагностика основывается на вашем описании характеристик головной боли, сопутствующих симптомов, провоцирующих и облегчающих факторах; при этом обязательным является отсутствие каких-либо отклонений при неврологическом осмотре. Постарайтесь, как можно подробнее описать врачу свою головную боль. Очень важно сообщить о том, как часто и в каких количествах вы принимаете лекарственные препараты, обладающие обезболивающим действием, или другие лекарственные препараты.
Не существует методов обследования, подтверждающих диагноз мигрени. Сканирование головного мозга (КТ, МРТ), электроэнцефалография, РЭГ, ультразвуковое исследование сосудов головы, консультация окулиста, как правило, являются неинформативными, поскольку никаких специфических для мигрени нарушений при проведении этих исследований не обнаруживается. Выявленные незначительные отклонения могут часто обнаруживаются и у лиц без жалоб на головную боль.
Если ваш доктор не уверен в правильности диагноза, он может назначить Вам дополнительные обследования для исключения других причин головной боли. Как правило, в этом нет необходимости. Если доктор не назначил дополнительные исследования, это означает, что он уверен в диагнозе «Мигрень» и проведение обследований никаким образом не облегчит назначение лечения.
Можно ли вылечить мигрень?
Не существует методов полного излечения от мигрени. Тем не менее, современные лекарственные подходы позволяют существенно уменьшить частоту, продолжительность, тяжесть приступов мигрени и облегчить сопутствующие нарушения в межприступном периоде. У большинства людей с возрастом приступы мигрени становятся реже и, как правило, после 50 лет прекращаются. Чтобы не допустить учащение мигрени необходимо избегать факторов хронизации, в первую очередь, стресса, снижения настроения (депрессии), избыточного приема лекарственных препаратов, обладающих обезболивающим действием, и кофеина.
Приложение Г1 – Г2. Шкалы оценки, вопросники и другие оценочные инструменты состояния пациента, приведенные в клинических рекомендациях
Приложение Г1. ДНЕВНИК ГОЛОВНОЙ БОЛИ
ИНСТРУКЦИЯ ПО ЗАПОЛНЕНИЮ ДНЕВНИКА
Перед консультацией в Центре головной боли очень важно, чтобы Вы ежедневно заполняли этот дневник. Сведения, которые Вы внесете в дневник, помогут врачу правильно определить диагноз и степень тяжести Вашей головной боли (ГБ), а также оперативно назначить оптимальное для Вас лечение.
Вверху напишите свое имя (ФИО), дату рождения, а также дату, когда Вы начали заполнять дневник. Затем напротив Вопроса 1 в 1-й колонке напишите дату (число месяца) заполнения дневника. Вы можете сразу проставить даты во всех колонках, поскольку Вам предстоит заполнять дневник ежедневно.
Пожалуйста, заполняйте дневник каждый вечер перед отходом ко сну, отмечая галочкой [Ö] клетки (1) в вертикальной колонке. Эти данные представляют собой сжатую информацию о любой(ых) ГБ, если она(и) возникла(и) в этот день. Если ГБ в этот день у Вас не было, ответьте только на Вопросы 2 и 15. Если Вы завершили заполнение одной страницы дневника, пожалуйста, продолжайте на следующей странице (прилагаются несколько копий).
Ниже приведены инструкции по ответам на вопросы.
- Укажите только число (например, 12); месяц и год указывать не нужно.
- Отмечайте «Да» или «Нет» в клетках напротив всех вопросов, или сразу переходите к Вопросу 15 (если ГБ в этот день не было).
- Укажите время (час в 24-часовом формате), когда Вы впервые заметили появление ГБ. Если Вы проснулись уже с головной болью, укажите время пробуждения. (Если утренняя ГБ является продолжением вечерней, поставьте в колонке знак Х).
- Укажите время (час и минуты в 24-часовом формате), когда головная боль полностью прекратилась. Если в этот день перед отходом ко сну ГБ еще сохранялась, оставьте клетку не заполненной. Если ГБ утром отсутствовала, укажите время отхода ко сну. Если ГБ утром сохранялась, поставьте Х в графе этого дня, а также Х в графе Вопроса 3 в следующей колонке. Продолжайте Ваши записи на следующий день обычным образом.
- У некоторых людей в пределах 1 часа до начала ГБ отмечаются определенные зрительные нарушения. Это могут быть вспышки света, светящиеся зигзагообразные линии, «слепые» пятна или «черные дыры», присутствующие даже при закрывании глаз. Отметьте «Да», если у Вас отмечалось нечто подобное, или «Нет», если такие явления не возникали. Если Вас просто раздражал свет (см. Вопрос 12) и ничего более, отметьте «Нет».
- Отметьте клетку, соответствующую локализации ГБ (преимущественно с одной стороны головы или с обеих сторон.
- Хотя существует множество описаний характера ГБ, большинство ГБ являются либо «пульсирующими» (боль усиливается в такт с биением сердца) или «сжимающими» (по типу «обруча» или «каски»). Отметьте ту характеристику, которая в большей степени отражает тип Вашей ГБ.
- Некоторые виды ГБ усиливаются даже от незначительной физической нагрузки (например, при подъеме по лестнице) или вынуждают человека избегать такой активности. Отметьте «Да», если это относится к Вашей ГБ, и «Нет», если это для Вас не характерно.
- Интенсивность (сила) ГБ – важная составляющая диагноза. Оцените силу Вашей ГБ, отметив соответствующую клетку, если: «незначительная» ГБ –это ГБ, которая не нарушает выполнение обычных видов деятельности (т.е. Вашу работоспособность и обычную активность), «сильная» — затрудняет, но полностью не препятствует обычным видам деятельности, наконец, «очень сильная» боль – ГБ, которая полностью нарушает Вашу обычную активность. Постарайтесь оценить интенсивность ГБ в течение дня в целом. Например, если боль была незначительной в первой половине дня, а затем стала очень сильной, отметьте клетку «сильная». Если же боль на протяжении почти всего дня была очень интенсивной, отметьте «очень сильная».
- Отметьте «Нет», если в течение дня у Вас совсем не было тошноты. Если отмечалась легкая тошнота, которая Вас почти не беспокоила, не вызывала отрыжки и позывов на рвоту, отметьте «незначительная», в случае более выраженной тошноты – «заметная».
- Отметьте «Да» или «Нет». Отрыжка и позыв на рвоту не считается рвотой.
- Вопрос касается обычного дневного или комнатного света, а не очень яркого света. Отметьте «Да», если обычный свет раздражал Вас или Вы пытались избежать его, путем затемнения комнаты или ношения темных очков. В противном случае отметьте «Нет».
- Вопрос касается обычного шума, а не очень громких звуков. Отметьте «Да», если шум раздражал Вас или Вы пытались избежать его, путем уединения в тихой комнате. В противном случае отметьте «Нет».
- Перечислите, пожалуйста, любые причины (факторы) которые, по Вашему мнению, могли вызвать ГБ. Возможно, Вы что-то съели, выпили, сделали (например, пропустили обед, провели бессонную ночь, работали физически) или были др. причины (перемена погоды, стресс, менструация).
- Перечислите названия любых препаратов (таблетки, свечи, инъекции, назальные спреи), которые Вы принимали от головной или любой другой боли. Для каждого препарата укажите количество принятых доз, а также время приема (часы в 24- часовом формате) каждого из препаратов. Не указывайте препараты, принятые Вами по другим показаниям.
Пожалуйста, удостоверьтесь, что Вы заполнили все колонки!
Приложение Г2. Визуальная аналоговая шкала боли
Название на русском языке:
Визуальная аналоговая шкала боли (ВАШ)
Оригинальное название: Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) [164 — 166]
Тип: шкала оценки
Назначение: предназначена для измерения интенсивности боли (в случае ГБН – головной боли)
Содержание: ВАШ представляет собой непрерывную шкалу в виде горизонтальной или вертикальной линии длиной 10 см и расположенными на ней делениями через 1 см от 0 до 10, где 0 баллов — «отсутствие боли», а 10 баллов — «сильнейшая боль, какую можно только представить.
Ключ (интерпретация): более высокий балл указывает на большую интенсивность боли.
Пояснения: например, показатель от 2 до 4 баллов указывает на незначительную интенсивность боли, от 5 до 7 на умеренную (среднюю) интенсивность, 8 — 9 – на очень сильную, 10 – на невыносимую, крайне интенсивную боль
Прикреплённые файлы
Мобильное приложение «MedElement»

- Профессиональные медицинские справочники. Стандарты лечения
- Коммуникация с пациентами: онлайн-консультация, отзывы, запись на приём
Скачать приложение для ANDROID / для iOS
Мобильное приложение «MedElement»

- Профессиональные медицинские справочники
- Коммуникация с пациентами: онлайн-консультация, отзывы, запись на приём
Скачать приложение для ANDROID / для iOS
Внимание!
Если вы не являетесь медицинским специалистом:
-
Занимаясь самолечением, вы можете нанести непоправимый вред своему здоровью.
-
Информация, размещенная на сайте MedElement и в мобильных приложениях «MedElement (МедЭлемент)», «Lekar Pro»,
«Dariger Pro», «Заболевания: справочник терапевта», не может и не должна заменять очную консультацию врача.
Обязательно
обращайтесь в медицинские учреждения при наличии каких-либо заболеваний или беспокоящих вас симптомов.
-
Выбор лекарственных средств и их дозировки, должен быть оговорен со специалистом. Только врач может
назначить
нужное лекарство и его дозировку с учетом заболевания и состояния организма больного.
-
Сайт MedElement и мобильные приложения «MedElement (МедЭлемент)», «Lekar Pro»,
«Dariger Pro», «Заболевания: справочник терапевта» являются исключительно информационно-справочными ресурсами.
Информация, размещенная на данном
сайте, не должна использоваться для самовольного изменения предписаний врача.
-
Редакция MedElement не несет ответственности за какой-либо ущерб здоровью или материальный ущерб, возникший
в
результате использования данного сайта.
| Migraine | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Woman with migraine headache | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Headaches, nausea, sensitivity to light, sound, and smell[1][2] |
| Usual onset | Around puberty[1] |
| Duration | Recurrent, long term[1] |
| Causes | Environmental and genetic[3] |
| Risk factors | Family history, female[4][5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Subarachnoid hemorrhage, venous thrombosis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, brain tumor, tension headache, sinusitis,[6] cluster headache[7] |
| Prevention | Metoprolol, valproate, topiramate[8][9] |
| Medication | Ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), triptans, ergotamines[5][10] |
| Prevalence | ~15%[11] |
Migraine (, )[12][13] is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches.[1] Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hours to three days.[1] Non-headache symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell.[2] The pain is generally made worse by physical activity during an attack,[14] although regular physical exercise may prevent future attacks.[15] Up to one-third of people affected have aura: typically, it is a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur.[14] Occasionally, aura can occur with little or no headache following, but not everyone has this symptom.[16]
Migraine is believed to be due to a mixture of environmental and genetic factors.[3] About two-thirds of cases run in families.[5] Changing hormone levels may also play a role, as migraine affects slightly more boys than girls before puberty and two to three times more women than men.[4][17] The risk of migraine usually decreases during pregnancy and after menopause.[4][18] The underlying mechanisms are not fully known.[18] They are, however, believed to involve the nerves and blood vessels of the brain.[5]
Initial recommended treatment is with simple pain medication such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) for the headache, medication for the nausea, and the avoidance of triggers.[10] Specific medications such as triptans or ergotamines may be used in those for whom simple pain medications are not effective.[5] Caffeine in combination with other analgesics is safe and effective in treatment of acute migraine.[19][20][21] A number of medications are useful to prevent attacks including metoprolol, valproate, and topiramate.[8][9]
Globally, approximately 15% of people are affected by migraine.[11] In the Global Burden of Disease Study of 2010, it was ranked as the third most prevalent disorder in the world.[22] It most often starts at puberty and is worst during middle age.[1] As of 2016, it is one of the most common causes of disability.[23] An early description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BC in ancient Egypt.[24] The word migraine is from the Greek ἡμικρᾱνίᾱ (hēmikrāníā), ‘pain in half of the head’,[25] from ἡμι- (hēmi-), ‘half’ and κρᾱνίον (krāníon), ‘skull’.[26]
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Migraine typically presents with self-limited, recurrent severe headache associated with autonomic symptoms.[5][27] About 15–30% of people living with migraine experience episodes with aura,[10][28] and they also frequently experience episodes without aura.[29] The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks are variable.[5] A migraine attack lasting longer than 72 hours is termed status migrainosus.[30] There are four possible phases to a migraine attack, although not all the phases are necessarily experienced:[14]
- The prodrome, which occurs hours or days before the headache
- The aura, which immediately precedes the headache
- The pain phase, also known as headache phase
- The postdrome, the effects experienced following the end of a migraine attack
Migraine is associated with major depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. These psychiatric disorders are approximately 2–5 times more common in people without aura, and 3–10 times more common in people with aura.[31]
Prodrome phase[edit]
Prodromal or premonitory symptoms occur in about 60% of those with migraines,[2][32] with an onset that can range from two hours to two days before the start of pain or the aura.[33] These symptoms may include a wide variety of phenomena,[34] including altered mood, irritability, depression or euphoria, fatigue, craving for certain food(s), stiff muscles (especially in the neck), constipation or diarrhea, and sensitivity to smells or noise.[32] This may occur in those with either migraine with aura or migraine without aura.[35] Neuroimaging indicates the limbic system and hypothalamus as the origin of prodromal symptoms in migraine.[36]
Aura phase[edit]
Aura is a transient focal neurological phenomenon that occurs before or during the headache.[2] Aura appears gradually over a number of minutes (usually occurring over 5–60 minutes) and generally lasts less than 60 minutes.[37][38] Symptoms can be visual, sensory or motoric in nature, and many people experience more than one.[39] Visual effects occur most frequently: they occur in up to 99% of cases and in more than 50% of cases are not accompanied by sensory or motor effects.[39]
Visual disturbances often consist of a scintillating scotoma (an area of partial alteration in the field of vision which flickers and may interfere with a person’s ability to read or drive).[2] These typically start near the center of vision and then spread out to the sides with zigzagging lines which have been described as looking like fortifications or walls of a castle.[39] Usually the lines are in black and white but some people also see colored lines.[39] Some people lose part of their field of vision known as hemianopsia while others experience blurring.[39]
Sensory aura are the second most common type; they occur in 30–40% of people with auras.[39] Often a feeling of pins-and-needles begins on one side in the hand and arm and spreads to the nose–mouth area on the same side.[39] Numbness usually occurs after the tingling has passed with a loss of position sense.[39] Other symptoms of the aura phase can include speech or language disturbances, world spinning, and less commonly motor problems.[39] Motor symptoms indicate that this is a hemiplegic migraine, and weakness often lasts longer than one hour unlike other auras.[39] Auditory hallucinations or delusions have also been described.[40]
Pain phase[edit]
Classically the headache is unilateral, throbbing, and moderate to severe in intensity.[37] It usually comes on gradually[37] and is aggravated by physical activity during a migraine attack.[14] However, the effects of physical activity on migraine are complex, and some researchers have concluded that, while exercise can trigger migraine attacks, regular exercise may have a prophylactic effect and decrease frequency of attacks.[15] The feeling of pulsating pain is not in phase with the pulse.[41] In more than 40% of cases, however, the pain may be bilateral (both sides of the head), and neck pain is commonly associated with it.[42] Bilateral pain is particularly common in those who have migraine without aura.[2] Less commonly pain may occur primarily in the back or top of the head.[2] The pain usually lasts 4 to 72 hours in adults;[37] however, in young children frequently lasts less than 1 hour.[43] The frequency of attacks is variable, from a few in a lifetime to several a week, with the average being about one a month.[44][45]
The pain is frequently accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to smells, fatigue and irritability.[2] Many thus seek a dark and quiet room.[46] In a basilar migraine, a migraine with neurological symptoms related to the brain stem or with neurological symptoms on both sides of the body,[47] common effects include a sense of the world spinning, light-headedness, and confusion.[2] Nausea occurs in almost 90% of people, and vomiting occurs in about one-third.[46] Other symptoms may include blurred vision, nasal stuffiness, diarrhea, frequent urination, pallor, or sweating.[48] Swelling or tenderness of the scalp may occur as can neck stiffness.[48] Associated symptoms are less common in the elderly.[49]
Silent migraine[edit]
Sometimes, aura occurs without a subsequent headache.[39] This is known in modern classification as a typical aura without headache, or acephalgic migraine in previous classification, or commonly as a silent migraine.[50][51] However, silent migraine can still produce debilitating symptoms, with visual disturbance, vision loss in half of both eyes, alterations in color perception, and other sensory problems, like sensitivity to light, sound, and odors, and aura sudden outbreak without headache can be scary.[52] It can last from 15 to 30 minutes, usually no longer than 60 minutes, and it can recur or appear as an isolated event.[51]
Postdrome[edit]
The migraine postdrome could be defined as that constellation of symptoms occurring once the acute headache has settled.[53] Many report a sore feeling in the area where the migraine was, and some report impaired thinking for a few days after the headache has passed. The person may feel tired or «hung over» and have head pain, cognitive difficulties, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood changes, and weakness.[54] According to one summary, «Some people feel unusually refreshed or euphoric after an attack, whereas others note depression and malaise.»[55] For some individuals this can vary each time.
Cause[edit]
The underlying causes of migraines are unknown.[56] However, they are believed to be related to a mix of environmental and genetic factors.[3] They run in families in about two-thirds of cases[5] and rarely occur due to a single gene defect.[57] While migraines were once believed to be more common in those of high intelligence, this does not appear to be true.[58] A number of psychological conditions are associated, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder,[59] as are many biological events or triggers.
Genetics[edit]
Studies of twins indicate a 34% to 51% genetic influence of likelihood to develop migraine.[3] This genetic relationship is stronger for migraine with aura than for migraines without aura.[29] A number of specific variants of genes increase the risk by a small to moderate amount.[57]
Single gene disorders that result in migraines are rare.[57] One of these is known as familial hemiplegic migraine, a type of migraine with aura, which is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.[60][61] Four genes have been shown to be involved in familial hemiplegic migraine.[62] Three of these genes are involved in ion transport.[62] The fourth is an axonal protein associated with the exocytosis complex.[62] Another genetic disorder associated with migraine is CADASIL syndrome or cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy.[2] One meta-analysis found a protective effect from angiotensin converting enzyme polymorphisms on migraine.[63] The TRPM8 gene, which codes for a cation channel, has been linked to migraines.[64]
Triggers[edit]
Migraine may be induced by triggers, with some reporting it as an influence in a minority of cases[5] and others the majority.[65] Many things such as fatigue, certain foods, alcohol, and weather have been labeled as triggers; however, the strength and significance of these relationships are uncertain.[65][66] Most people with migraines report experiencing triggers.[67] Symptoms may start up to 24 hours after a trigger.[5]
Physiological aspects[edit]
Common triggers quoted are stress, hunger, and fatigue (these equally contribute to tension headaches).[65] Psychological stress has been reported as a factor by 50 to 80% of people.[68] Migraine has also been associated with post-traumatic stress disorder and abuse.[69] Migraine episodes are more likely to occur around menstruation.[68] Other hormonal influences, such as menarche, oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause, also play a role.[70] These hormonal influences seem to play a greater role in migraine without aura.[58] Migraine episodes typically do not occur during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, or following menopause.[2]
Dietary aspects[edit]
Between 12 and 60% of people report foods as triggers.[71][72]
There are many reports[73][74][75][76][77] that tyramine – which is naturally present in chocolate, alcoholic beverages, most cheeses, processed meats, and other foods – can trigger migraine symptoms in some individuals. Likewise, monosodium glutamate (MSG) is frequently reported as a trigger for migraine symptoms.[78]
Environmental aspects[edit]
A 2009 review on potential triggers in the indoor and outdoor environment concluded that while there were insufficient studies to confirm environmental factors as causing migraine, «migraineurs worldwide consistently report similar environmental triggers».[79] The article suggests that people living with migraine take some preventive measures related to indoor air quality and lighting.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Migraine is believed to be primarily a neurological disorder,[80][81][82] while others believe it to be a neurovascular disorder with blood vessels playing the key role, although current evidence does not support this completely.[83][84][85][86] Others believe both are likely important.[87][88][89][90] One theory is related to increased excitability of the cerebral cortex and abnormal control of pain neurons in the trigeminal nucleus of the brainstem.[91]
Aura[edit]
Cortical spreading depression, or spreading depression according to Leão, is a burst of neuronal activity followed by a period of inactivity, which is seen in those with migraines with aura.[92] There are a number of explanations for its occurrence, including activation of NMDA receptors leading to calcium entering the cell.[92] After the burst of activity, the blood flow to the cerebral cortex in the area affected is decreased for two to six hours.[92] It is believed that when depolarization travels down the underside of the brain, nerves that sense pain in the head and neck are triggered.[92]
Pain[edit]
The exact mechanism of the head pain which occurs during a migraine episode is unknown.[93] Some evidence supports a primary role for central nervous system structures (such as the brainstem and diencephalon),[94] while other data support the role of peripheral activation (such as via the sensory nerves that surround blood vessels of the head and neck).[93] The potential candidate vessels include dural arteries, pial arteries and extracranial arteries such as those of the scalp.[93] The role of vasodilatation of the extracranial arteries, in particular, is believed to be significant.[95]
Neuromodulators[edit]
Adenosine, a neuromodulator, may be involved.[96] Released after the progressive cleavage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine acts on adenosine receptors to put the body and brain in a low activity state by dilating blood vessels and slowing the heart rate, such as before and during the early stages of sleep. Adenosine levels have been found to be high during migraine attacks.[96][97] Caffeine’s role as an inhibitor of adenosine may explain its effect in reducing migraine.[98] Low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), are also believed to be involved.[99]
Calcitonin gene-related peptides (CGRPs) have been found to play a role in the pathogenesis of the pain associated with migraine, as levels of it become elevated during an attack.[10][41]
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of a migraine is based on signs and symptoms.[5] Neuroimaging tests are not necessary to diagnose migraine, but may be used to find other causes of headaches in those whose examination and history do not confirm a migraine diagnosis.[100] It is believed that a substantial number of people with the condition remain undiagnosed.[5]
The diagnosis of migraine without aura, according to the International Headache Society, can be made according to the following criteria, the «5, 4, 3, 2, 1 criteria»:[14]
- Five or more attacks—for migraine with aura, two attacks are sufficient for diagnosis.
- Four hours to three days in duration
- Two or more of the following:
- Unilateral (affecting one side of the head)
- Pulsating
- Moderate or severe pain intensity
- Worsened by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity
- One or more of the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to both light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia)
If someone experiences two of the following: photophobia, nausea, or inability to work or study for a day, the diagnosis is more likely.[101] In those with four out of five of the following: pulsating headache, duration of 4–72 hours, pain on one side of the head, nausea, or symptoms that interfere with the person’s life, the probability that this is a migraine attack is 92%.[10] In those with fewer than three of these symptoms, the probability is 17%.[10]
Classification[edit]
Migraine was first comprehensively classified in 1988.[29] The International Headache Society updated their classification of headaches in 2004.[14] A third version was published in 2018.[102] According to this classification, migraine is a primary headache disorder along with tension-type headaches and cluster headaches, among others.[103]
Migraine is divided into seven subclasses (some of which include further subdivisions):
- Migraine without aura, or «common migraine», involves migraine headaches that are not accompanied by aura.
- Migraine with aura, or «classic migraine», usually involves migraine headaches accompanied by aura. Less commonly, aura can occur without a headache, or with a nonmigraine headache. Two other varieties are familial hemiplegic migraine and sporadic hemiplegic migraine, in which a person has migraine with aura and with accompanying motor weakness. If a close relative has had the same condition, it is called «familial», otherwise it is called «sporadic». Another variety is basilar-type migraine, where a headache and aura are accompanied by difficulty speaking, world spinning, ringing in ears, or a number of other brainstem-related symptoms, but not motor weakness. This type was initially believed to be due to spasms of the basilar artery, the artery that supplies the brainstem. Now that this mechanism is not believed to be primary, the symptomatic term migraine with brainstem aura (MBA) is preferred.[47]
- Childhood periodic syndromes that are commonly precursors of migraine include cyclical vomiting (occasional intense periods of vomiting), abdominal migraine (abdominal pain, usually accompanied by nausea), and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (occasional attacks of vertigo).
- Retinal migraine involves migraine headaches accompanied by visual disturbances or even temporary blindness in one eye.
- Complications of migraine describe migraine headaches and/or auras that are unusually long or unusually frequent, or associated with a seizure or brain lesion.
- Probable migraine describes conditions that have some characteristics of migraines, but where there is not enough evidence to diagnose it as a migraine with certainty (in the presence of concurrent medication overuse).
- Chronic migraine is a complication of migraines, and is a headache that fulfills diagnostic criteria for migraine headache and occurs for a greater time interval. Specifically, greater or equal to 15 days/month for longer than 3 months.[104]
Abdominal migraine[edit]
The diagnosis of abdominal migraine is controversial.[105] Some evidence indicates that recurrent episodes of abdominal pain in the absence of a headache may be a type of migraine[105][106] or are at least a precursor to migraines.[29] These episodes of pain may or may not follow a migraine-like prodrome and typically last minutes to hours.[105] They often occur in those with either a personal or family history of typical migraine.[105] Other syndromes that are believed to be precursors include cyclical vomiting syndrome and benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood.[29]
Differential diagnosis[edit]
Other conditions that can cause similar symptoms to a migraine headache include temporal arteritis, cluster headaches, acute glaucoma, meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage.[10] Temporal arteritis typically occurs in people over 50 years old and presents with tenderness over the temple, cluster headache presents with one-sided nose stuffiness, tears and severe pain around the orbits, acute glaucoma is associated with vision problems, meningitis with fevers, and subarachnoid hemorrhage with a very fast onset.[10] Tension headaches typically occur on both sides, are not pounding, and are less disabling.[10]
Those with stable headaches that meet criteria for migraines should not receive neuroimaging to look for other intracranial disease.[107][108][109] This requires that other concerning findings such as papilledema (swelling of the optic disc) are not present. People with migraines are not at an increased risk of having another cause for severe headaches.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive treatments of migraine include medications, nutritional supplements, lifestyle alterations, and surgery. Prevention is recommended in those who have headaches more than two days a week, cannot tolerate the medications used to treat acute attacks, or those with severe attacks that are not easily controlled.[10] Recommended lifestyle changes include stopping tobacco use and reducing behaviors that interfere with sleep.[110]
The goal is to reduce the frequency, painfulness, and duration of migraine episodes, and to increase the effectiveness of abortive therapy.[111] Another reason for prevention is to avoid medication overuse headache. This is a common problem and can result in chronic daily headache.[112][113]
Medication[edit]
Preventive migraine medications are considered effective if they reduce the frequency or severity of the migraine attacks by at least 50%.[114] Due to few medications being approved specifically for the preventative treatment of migraine headaches; many medications such as beta-blockers, anticonvulsive agents such as topiramate or sodium valproate, antidepressants such as amitriptyline and calcium channel blockers such as flunarizine are used off label for the preventative treatment of migraine headaches.[38] Guidelines are fairly consistent in rating the anticonvulsants topiramate and divalproex/sodium valproate, and the beta blockers propranolol and metoprolol as having the highest level of evidence for first-line use for migraine prophylaxis in adults.[115][116] Propranolol and topiramate have the best evidence in children; however, evidence only supports short-term benefit as of 2020.[110][117]
The beta blocker timolol is also effective for migraine prevention and in reducing migraine attack frequency and severity.[115] While beta blockers are often used for first-line treatment, other antihypertensives also have a proven efficiency in migraine prevention, namely the calcium channel blocker verapamil[118] and the angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan.[119][120]
Tentative evidence also supports the use of magnesium supplementation.[121] Increasing dietary intake may be better.[122] Recommendations regarding effectiveness varied for the anticonvulsants gabapentin and pregabalin. Frovatriptan is effective for prevention of menstrual migraine.[115]
The antidepressants amitriptyline and venlafaxine are probably also effective.[123] Angiotensin inhibition by either an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor antagonist may reduce attacks.[124]
Medications in the anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide, including eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab, appear to decrease the frequency of migraines by one to two per month.[125] They are, however, expensive: a year of erenumab costs $6,900 as of 2019.[126]
Alternative therapies[edit]
Acupuncture has a small effect in reducing migraine frequency, compared to sham acupuncture, a practice where needles are placed randomly or do not penetrate the skin.[127] Physiotherapy, massage and relaxation, and chiropractic manipulation might be as effective as propranolol or topiramate in the prevention of migraine headaches; however, the research had some problems with methodology.[128][129] Another review, however, found evidence to support spinal manipulation to be poor and insufficient to support its use.[130]
Tentative evidence supports the use of stress reduction techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, biofeedback, and relaxation techniques.[68] Regular physical exercise may decrease the frequency.[15] Numerous psychological approaches have been developed that are aimed at preventing or reducing the frequency of migraine in adults including educational approaches, relaxation techniques, assistance in developing coping strategies, strategies to change the way one thinks of a migraine attack, and strategies to reduce symptoms.[131] The medical evidence supporting the effectiveness of these types of psychological approaches is very limited.[131]
Among alternative medicines, butterbur has the best evidence for its use.[132][133] However, unprocessed butterbur contains chemicals called pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) which can cause liver damage, however there are versions that are PA free.[134] In addition, butterbur may cause allergic reactions in people who are sensitive to plants such as ragweed.[135] There is tentative evidence that coenzyme Q10 reduces migraine frequency.[136]
Feverfew has traditionally been used as a treatment for fever, headache and migraine, women’s conditions such as difficulties in labour and regulation of menstruation, relief of stomach ache, toothache and insect bites. During the last decades, it has mainly been used for headache and as a preventive treatment for migraine.[137] The plant parts used for medicinal use are the dried leaves or the dried aerial parts. Several historical data supports feverfew’s traditional medicinal uses.[138] In addition, several clinical studies have been performed assessing the efficacy and safety of feverfew monotherapy in the prevention of migraine.[139] The majority of the clinical trials favoured feverfew over placebo. The data also suggest that feverfew is associated with only mild and transient adverse effects. The frequency of migraine was positively affected after treatment with feverfew. Reduction of migraine severity was also reported after intake of feverfew and incidence of nausea and vomiting decreased significantly. No effect of feverfew was reported in one study.[139]
There is tentative evidence for melatonin as an add-on therapy for prevention and treatment of migraine.[140][141] The data on melatonin are mixed and certain studies have had negative results.[140] The reasons for the mixed findings are unclear but may stem from differences in study design and dosage.[140] Melatonin’s possible mechanisms of action in migraine are not completely clear, but may include improved sleep, direct action on melatonin receptors in the brain, and anti-inflammatory properties.[140][142]
Devices and surgery[edit]
Medical devices, such as biofeedback and neurostimulators, have some advantages in migraine prevention, mainly when common anti-migraine medications are contraindicated or in case of medication overuse. Biofeedback helps people be conscious of some physiological parameters so as to control them and try to relax and may be efficient for migraine treatment.[143][144] Neurostimulation uses noninvasive or implantable neurostimulators similar to pacemakers for the treatment of intractable chronic migraine with encouraging results for severe cases.[145][146] A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator and a transcranial magnetic stimulator are approved in the United States for the prevention of migraines.[147][148] There is also tentative evidence for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation decreases the frequency of migraines.[149] Migraine surgery, which involves decompression of certain nerves around the head and neck, may be an option in certain people who do not improve with medications.[150]
Management[edit]
There are three main aspects of treatment: trigger avoidance, acute symptomatic control, and medication for prevention.[5] Medications are more effective if used earlier in an attack.[5] The frequent use of medications may result in medication overuse headache, in which the headaches become more severe and more frequent.[14] This may occur with triptans, ergotamines, and analgesics, especially opioid analgesics.[14] Due to these concerns simple analgesics are recommended to be used less than three days per week at most.[151]
Analgesics[edit]
Recommended initial treatment for those with mild to moderate symptoms are simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or the combination of paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen), aspirin, and caffeine.[10] Several NSAIDs, including diclofenac and ibuprofen have evidence to support their use.[152][153] Aspirin (900 to 1000 mg) can relieve moderate to severe migraine pain, with an effectiveness similar to sumatriptan.[154] Ketorolac is available in intravenous and intramuscular formulations.[10]
Paracetamol, either alone or in combination with metoclopramide, is another effective treatment with a low risk of adverse effects.[155] Intravenous metoclopramide is also effective by itself.[156][157] In pregnancy, paracetamol and metoclopramide are deemed safe as are NSAIDs until the third trimester.[10]
Naproxen by itself may not be effective as a stand-alone medicine to stop a migraine headache as it is only weakly better than a placebo medication in clinical trials.[158]
Antiemetics[edit]
Triptans[edit]
Triptans such as sumatriptan are medications used to stop an active migraine headache (an abortive medication). Triptans are the initially recommended treatments for those with moderate to severe pain from an acute migraine headache or those with milder symptoms who do not respond to simple analgesics.[10] Triptans have been shown to be effective for both pain and nausea in up to 75% of people.[159][160] There are different methods or routes of administration to take sumatriptan including oral (by mouth), injectable (subcutaneous), rectal, nasal spray, and oral dissolving tablets.[5][161][162][163] For people with migraine symptoms such as nausea or vomiting, taking the abortive medicine by mouth or through the nose may be difficult. All route of administration have been shown to be effective at reducing migraine symptoms, however, nasal and injectable subcutaneous administration may result in more side effects.[163][162] The adverse effects associated with rectal administration have not been well studied.[161] Some people may find that they respond to one type of sumatriptan better than another.[10]
Most side effects are mild, including flushing; however, rare cases of myocardial ischemia have occurred.[5] They are thus not recommended for people with cardiovascular disease,[10] who have had a stroke, or have migraines that are accompanied by neurological problems.[164] In addition, triptans should be prescribed with caution for those with risk factors for vascular disease.[164] While historically not recommended in those with basilar migraines there is no specific evidence of harm from their use in this population to support this caution.[47] Triptans are not addictive, but may cause medication-overuse headaches if used more than 10 days per month.[165]
Sumatriptan does not prevent other migraine headaches from starting in the future.[162] For increased effectiveness at stopping migraine symptoms, a combined therapy that includes sumatriptan and naproxen may be suggested.[166]
CGRP receptor antagonists[edit]
CGRP receptor antagonists target calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor to prevent migraine headaches or reduce their severity.[38] CGRP is a signaling molecule as well as a potent vasodilator that is involved in the development of a migraine headache.[38] There are four injectable monoclonal antibodies that target CGRP or its receptor (eptinezumab, erenumab, fremanezumab and galcanezumab) and the medications have demonstrated efficacy in the preventative treatment of episodic and chronic migraine headaches in phase 3 randomized clinical trials.[38] Eptinezumab is available as an infusion every three months, Erenumab and galcanezumab are once monthly injections and fremanezumab is a monthly or quarterly injection.
Ergotamines[edit]
Ergotamine and dihydroergotamine are older medications still prescribed for migraines, the latter in nasal spray and injectable forms.[5][167] They appear equally effective to the triptans[168] and experience adverse effects that typically are benign.[169] In the most severe cases, such as those with status migrainosus, they appear to be the most effective treatment option.[169] They can cause vasospasm including coronary vasospasm and are contraindicated in people with coronary artery disease.[170]
Magnesium[edit]
Magnesium is recognized as an inexpensive, over-the-counter supplement which can be part of a multimodal approach to migraine reduction. Some studies have shown to be effective in both preventing and treating migraine in intravenous form.[171] The intravenous form reduces attacks as measured in approximately 15-45 minutes, 120 minutes, and 24 hour time periods, magnesium taken orally alleviates the frequency and intensity of migraines.[172][173]
Other[edit]
Intravenous metoclopramide, intravenous prochlorperazine, or intranasal lidocaine are other potential options.[10][157] Metoclopramide or prochlorperazine are the recommended treatment for those who present to the emergency department.[10][157] Haloperidol may also be useful in this group.[157][167] A single dose of intravenous dexamethasone, when added to standard treatment of a migraine attack, is associated with a 26% decrease in headache recurrence in the following 72 hours.[174] Spinal manipulation for treating an ongoing migraine headache is not supported by evidence.[130] It is recommended that opioids and barbiturates not be used due to questionable efficacy, addictive potential, and the risk of rebound headache.[10][38] There is tentative evidence that propofol may be useful if other measures are not effective.[175]
Occipital nerve stimulation, may be effective but has the downsides of being cost-expensive and has a significant amount of complications.[176]
There is modest evidence for the effectiveness of non-invasive neuromodulatory devices, behavioral therapies and acupuncture in the treatment of migraine headaches.[38] There is little to no evidence for the effectiveness of physical therapy, chiropractic manipulation and dietary approaches to the treatment of migraine headaches.[38] Behavioral treatment of migraine headaches may be helpful for those who may not be able to take medications (for example pregnant women).[38]
Feverfew is registered as a traditional herbal medicine in the Nordic countries under the brand name Glitinum, only powdered feverfew is approved in the Herbal community monograph issued by European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Sexual activity, particularly orgasm, may provide relief for some migraineurs.[177]
Children[edit]
Ibuprofen helps decrease pain in children with migraines and is the initially recommended treatment.[178][179] Paracetamol does not appear to be effective in providing pain relief.[178] Triptans are effective, though there is a risk of causing minor side effects like taste disturbance, nasal symptoms, dizziness, fatigue, low energy, nausea, or vomiting.[178][180] Ibuprofen should be used less than half the days in a month and triptans less than a third of the days in a month to decrease the risk of medication overuse headache.[179]
Chronic migraine[edit]
Topiramate and botulinum toxin (Botox) have evidence in treating chronic migraine.[123][181] Botulinum toxin has been found to be useful in those with chronic migraine but not those with episodic ones.[182][183] The anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody erenumab was found in one study to decrease chronic migraines by 2.4 days more than placebo.[184]
Prognosis[edit]
«Migraine exists on a continuum of different attack frequencies and associated levels of disability.»[185] For those with occasional, episodic migraine, a «proper combination of drugs for prevention and treatment of migraine attacks» can limit the disease’s impact on patients’ personal and professional lives.[186] But fewer than half of people with migraine seek medical care and more than half go undiagnosed and undertreated.[187] «Responsive prevention and treatment of migraine is incredibly important» because evidence shows «an increased sensitivity after each successive attack, eventually leading to chronic daily migraine in some individuals.»[186] Repeated migraine results in «reorganization of brain circuitry,» causing «profound functional as well as structural changes in the brain.»[188] «One of the most important problems in clinical migraine is the progression from an intermittent, self-limited inconvenience to a life-changing disorder of chronic pain, sensory amplification, and autonomic and affective disruption. This progression, sometimes termed chronification in the migraine literature, is common, affecting 3% of migraineurs in a given year, such that 8% of migraineurs have chronic migraine in any given year.» Brain imagery reveals that the electrophysiological changes seen during an attack become permanent in people with chronic migraine; «thus, from an electrophysiological point of view, chronic migraine indeed resembles a never-ending migraine attack.»[188] Severe migraine ranks in the highest category of disability, according to the World Health Organization, which uses objective metrics to determine disability burden for the authoritative annual Global Burden of Disease report. The report classifies severe migraine alongside severe depression, active psychosis, quadriplegia, and terminal-stage cancer.[189]
Migraine with aura appears to be a risk factor for ischemic stroke[190] doubling the risk.[191] Being a young adult, being female, using hormonal birth control, and smoking further increases this risk.[190] There also appears to be an association with cervical artery dissection.[192] Migraine without aura does not appear to be a factor.[193] The relationship with heart problems is inconclusive with a single study supporting an association.[190] Migraine does not appear to increase the risk of death from stroke or heart disease.[194] Preventative therapy of migraines in those with migraine with aura may prevent associated strokes.[195] People with migraine, particularly women, may develop higher than average numbers of white matter brain lesions of unclear significance.[196]
Epidemiology[edit]
Disability-adjusted life year for migraines per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004
no data
<45
45–65
65–85
85–105
105–125
125–145
145–165
165–185
185–205
205–225
225–245
>245
Worldwide, migraine affects nearly 15% or approximately one billion people.[11] It is more common in women at 19% than men at 11%.[11] In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women experience a migraine attack in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively.[5] In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives with about 6–15% of adult men and 14–35% of adult women getting at least one yearly.[17] Rates of migraine are slightly lower in Asia and Africa than in Western countries.[58][197] Chronic migraine occurs in approximately 1.4 to 2.2% of the population.[198]
These figures vary substantially with age: onset of migraine is most commonly between 15 and 24 years of age, and occur most frequently in those 35 to 45 years of age.[5] In children, about 1.7% of 7 year olds and 3.9% of those between 7 and 15 experience migraine, with the condition being slightly more common in boys before puberty.[199] Children as young as two years may be affected.[178] During adolescence, migraine becomes more common among women[199] and this persists for the rest of the lifespan, being twice as common among elderly females than males.[200] In women migraine without aura are more common than migraine with aura; however in men the two types occur with similar frequency.[58]
During perimenopause symptoms often get worse before decreasing in severity.[200] While symptoms resolve in about two thirds of the elderly, in 3 to 10% they persist.[49]
History[edit]
The Head Ache, George Cruikshank (1819)
An early description consistent with migraine is contained in the Ebers papyrus, written around 1500 BCE in ancient Egypt.[24] In 200 BCE, writings from the Hippocratic school of medicine described the visual aura that can precede the headache and a partial relief occurring through vomiting.[201]
A second-century description by Aretaeus of Cappadocia divided headaches into three types: cephalalgia, cephalea, and heterocrania.[202] Galen of Pergamon used the term hemicrania (half-head), from which the word migraine was eventually derived.[202] He also proposed that the pain arose from the meninges and blood vessels of the head.[201] Migraine was first divided into the two now used types – migraine with aura (migraine ophthalmique) and migraine without aura (migraine vulgaire) in 1887 by Louis Hyacinthe Thomas, a French Librarian.[201] The mystical visions of Hildegard von Bingen, which she described as “reflections of the living light», are consistent with the visual aura experienced during migraines.[203]
A trepanated skull, from the Neolithic. The perimeter of the hole in the skull is rounded off by ingrowth of new bony tissue, indicating that the person survived the operation.
Trepanation, the deliberate drilling of holes into a skull, was practiced as early as 7,000 BCE.[24] While sometimes people survived, many would have died from the procedure due to infection.[204] It was believed to work via «letting evil spirits escape».[205] William Harvey recommended trepanation as a treatment for migraines in the 17th century.[206] The association between trepanation and headaches in ancient history may simply be a myth or unfounded speculation that originated several centuries later. In 1913, the world-famous American physician William Osler misinterpreted the French anthropologist and physician Paul Broca ’s words about a set of children’s skulls from the Neolithic age that he found during the 1870s. These skulls presented no evident signs of fractures that could justify this complex surgery for mere medical reasons. Trepanation was probably born of superstitions, to remove “confined demons” inside the head, or to create healing or fortune talismans with the bone fragments removed from the skulls of the patients. However, Osler wanted to make Broca’s theory more palatable to his modern audiences, and explained that trepanation procedures were used for mild conditions such as “infantile convulsions headache and various cerebral diseases believed to be caused by confined demons.”[207]
While many treatments for migraine have been attempted, it was not until 1868 that use of a substance which eventually turned out to be effective began.[201] This substance was the fungus ergot from which ergotamine was isolated in 1918.[208] Methysergide was developed in 1959 and the first triptan, sumatriptan, was developed in 1988.[208] During the 20th century with better study-design, effective preventive measures were found and confirmed.[201]
Society and culture[edit]
Migraine is a significant source of both medical costs and lost productivity. It has been estimated that migraine is the most costly neurological disorder in the European Community, costing more than €27 billion per year.[209] In the United States, direct costs have been estimated at $17 billion, while indirect costs — such as missed or decreased ability to work — is estimated at $15 billion.[210] Nearly a tenth of the direct cost is due to the cost of triptans.[210] In those who do attend work during a migraine attack, effectiveness is decreased by around a third.[209] Negative impacts also frequently occur for a person’s family.[209]
Research[edit]
Potential prevention mechanisms[edit]
Transcranial magnetic stimulation shows promise[10][211] as does transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation.[212] There is preliminary evidence that a ketogenic diet may help prevent episodic and long-term migraine.[213][214]
Potential gender dependency[edit]
While no definitive proof has been found linking migraine to gender, statistical data indicates that women may be more prone to having migraine, showing migraine incidence three times higher among women than men.[215][216] The Society for Women’s Health Research has also mentioned hormonal influences, mainly estrogen, as having a considerable role in provoking migraine pain. Studies and research related to the gender dependencies of migraine are still ongoing, and conclusions have yet to be achieved.[217][218][219]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f «Headache disorders Fact sheet N°277». October 2012. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Simon RP, Aminoff MJ, Greenberg DA (2009). Clinical neurology (7 ed.). New York, N.Y: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. pp. 85–88. ISBN 9780071664332.
- ^ a b c d Piane M, Lulli P, Farinelli I, Simeoni S, De Filippis S, Patacchioli FR, Martelletti P (December 2007). «Genetics of migraine and pharmacogenomics: some considerations». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 8 (6): 334–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-007-0427-2. PMC 2779399. PMID 18058067.
- ^ a b c Lay CL, Broner SW (May 2009). «Migraine in women». Neurologic Clinics. 27 (2): 503–11. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2009.01.002. PMID 19289228.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Bartleson JD, Cutrer FM (May 2010). «Migraine update. Diagnosis and treatment». Minnesota Medicine. 93 (5): 36–41. PMID 20572569.
- ^ Olesen J (2006). The Headaches. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 424. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ^ «Cluster Headache». American Migraine Foundation. 15 February 2017. Archived from the original on 9 May 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ a b Armstrong C (April 2013). «AAN/AHS update recommendations for migraine prevention in adults». American Family Physician. 87 (8): 584–5. PMID 23668450.
- ^ a b Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). «Valproate (valproic acid or sodium valproate or a combination of the two) for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD010611. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010611. PMID 23797677.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Gilmore B, Michael M (February 2011). «Treatment of acute migraine headache». American Family Physician. 83 (3): 271–80. PMID 21302868.
- ^ a b c d Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. (December 2012). «Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010». Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMC 6350784. PMID 23245607.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008). Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-1-4058-8118-0.
- ^ Jones, Daniel (2011). Roach, Peter; Setter, Jane; Esling, John (eds.). Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-15255-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004). «The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition». Cephalalgia. 24 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1): 9–160. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00653.x. PMID 14979299. as PDF Archived 31 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, Czapinska-Ciepiela EK, Ariadni DD, Di Lenola D, et al. (September 2018). «The association between migraine and physical exercise». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y. PMC 6134860. PMID 30203180.
- ^ Pryse-Phillips W (2003). Companion to clinical neurology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford university press. p. 587. ISBN 9780195159387. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Stovner LJ, Zwart JA, Hagen K, Terwindt GM, Pascual J (April 2006). «Epidemiology of headache in Europe». European Journal of Neurology. 13 (4): 333–45. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01184.x. PMID 16643310. S2CID 7490176.
- ^ a b «NINDS Migraine Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 3 November 2015. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ Nowaczewska M, Wiciński M, Kaźmierczak W (July 2020). «The Ambiguous Role of Caffeine in Migraine Headache: From Trigger to Treatment». Nutrients. 12 (8): 2259. doi:10.3390/nu12082259. PMC 7468766. PMID 32731623.
- ^ Shapiro RE, Cowan R (2017-01-10). «Caffeine and Migraine». American Migraine Foundation. Retrieved 2021-06-08.
- ^ Diener HC, Charles A, Goadsby PJ, Holle D (October 2015). «New therapeutic approaches for the prevention and treatment of migraine». The Lancet. Neurology. 14 (10): 1010–22. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00198-2. PMID 26376968. S2CID 26523013.
- ^ Gobel H. «1. Migraine». ICHD-3 The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd edition. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- ^ Vos, Theo; et al. (GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (September 2017). «Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016». Lancet. 390 (10100): 1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. PMC 5605509. PMID 28919117.
- ^ a b c Miller N (2005). Walsh and Hoyt’s clinical neuro-ophthalmology (6 ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1275. ISBN 9780781748117. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ Liddell HG, Scott R. «ἡμικρανία». A Greek-English Lexicon. Archived from the original on 8 November 2013. on Perseus
- ^ Anderson K, Anderson LE, Glanze WD (1994). Mosby’s Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary (4 ed.). Mosby. p. 998. ISBN 978-0-8151-6111-0.
- ^ Bigal ME, Lipton RB (June 2008). «The prognosis of migraine». Current Opinion in Neurology. 21 (3): 301–8. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328300c6f5. PMID 18451714. S2CID 34805084.
- ^ Gutman SA (2008). Quick reference neuroscience for rehabilitation professionals: the essential neurologic principles underlying rehabilitation practice (2 ed.). Thorofare, NJ: SLACK. p. 231. ISBN 9781556428005. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ a b c d e The Headaches, Pg 232–233
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 512. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Baskin SM, Lipchik GL, Smitherman TA (October 2006). «Mood and anxiety disorders in chronic headache». Headache. 46 Suppl 3: S76-87. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00559.x. PMID 17034402. S2CID 35451906.
- ^ a b Lynn DJ, Newton HB, Rae-Grant A (2004). The 5-minute neurology consult. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 26. ISBN 9780683307238. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Buzzi MG, Cologno D, Formisano R, Rossi P (October–December 2005). «Prodromes and the early phase of the migraine attack: therapeutic relevance». Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 179–83. PMID 16483458.
- ^ Rossi P, Ambrosini A, Buzzi MG (October–December 2005). «Prodromes and predictors of migraine attack». Functional Neurology. 20 (4): 185–91. PMID 16483459.
- ^ Ropper AH, Adams RD, Victor M, Samuels MA (2009). Adams and Victor’s principles of neurology (9 ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. Chapter 10. ISBN 9780071499927.
- ^ May A, Burstein R (November 2019). «Hypothalamic regulation of headache and migraine». Cephalalgia. 39 (13): 1710–1719. doi:10.1177/0333102419867280. PMC 7164212. PMID 31466456.
- ^ a b c d Tintinalli, Judith E. (2010). Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide (Emergency Medicine (Tintinalli)). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies. pp. 1116–1117. ISBN 978-0-07-148480-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Ashina M (November 2020). «Migraine». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (19): 1866–1876. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1915327. PMID 33211930. S2CID 227078662.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k The Headaches, pp. 407–419
- ^ Slap, GB (2008). Adolescent medicine. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 105. ISBN 9780323040730. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Qubty W, Patniyot I (June 2020). «Migraine Pathophysiology». Pediatric Neurology. 107: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2019.12.014. PMID 32192818. S2CID 213191464.
- ^ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (1 January 2011). The Cleveland Clinic manual of headache therapy. New York: Springer. p. 6. ISBN 9781461401780. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Bigal ME, Arruda MA (July 2010). «Migraine in the pediatric population—evolving concepts». Headache. 50 (7): 1130–43. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01717.x. PMID 20572878. S2CID 23256755.
- ^ Jes Olesen (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 238. ISBN 9780781754002. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Dalessio (2001). Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Dalessio DJ (eds.). Wolff’s headache and other head pain (7 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 122. ISBN 9780195135183.
- ^ a b Lisak RP, Truong DD, Carroll W, Bhidayasiri R (2009). International neurology: a clinical approach. Chichester, UK: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 670. ISBN 9781405157384.
- ^ a b c Kaniecki RG (June 2009). «Basilar-type migraine». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (3): 217–20. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0036-7. PMID 19457282. S2CID 22242504.
- ^ a b Joel S. Glaser (1999). Neuro-ophthalmology (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 555. ISBN 9780781717298. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Sirven JI, Malamut BL (2008). Clinical neurology of the older adult (2 ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 197. ISBN 9780781769471. Archived from the original on 12 March 2017.
- ^ Dr. Jennifer Robblee (21 August 2019). «Silent Migraine: A Guide». American Migraine Foundation. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ a b He Y, Li Y, Nie Z (February 2015). «Typical aura without headache: a case report and review of the literature». Journal of Medical Case Reports. 9 (1): 40. doi:10.1186/s13256-014-0510-7. PMC 4344793. PMID 25884682.
- ^ Jayne Leonard (medically reviewed by Seunggu Han, M.D.) (7 September 2018). «Silent migraine: Symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention». www.medicalnewstoday.com. Medical News Today. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ Bose P, Goadsby PJ (June 2016). «The migraine postdrome». Current Opinion in Neurology. 29 (3): 299–301. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000310. PMID 26886356. S2CID 22445093.
- ^ Kelman L (February 2006). «The postdrome of the acute migraine attack». Cephalalgia. 26 (2): 214–20. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.01026.x. PMID 16426278. S2CID 21519111.
- ^ Halpern AL, Silberstein SD (2005). «Ch. 9: The Migraine Attack—A Clinical Description». In Kaplan PW, Fisher RS (eds.). Imitators of Epilepsy (2 ed.). New York: Demos Medical. ISBN 978-1-888799-83-5. NBK7326.
- ^ Robbins MS, Lipton RB (April 2010). «The epidemiology of primary headache disorders». Seminars in Neurology. 30 (2): 107–19. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1249220. PMID 20352581.
- ^ a b c Schürks M (January 2012). «Genetics of migraine in the age of genome-wide association studies». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 13 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0399-0. PMC 3253157. PMID 22072275.
- ^ a b c d The Headaches, pp. 238–40
- ^ The Headaches, pp. 246–247
- ^ de Vries B, Frants RR, Ferrari MD, van den Maagdenberg AM (July 2009). «Molecular genetics of migraine». Human Genetics. 126 (1): 115–32. doi:10.1007/s00439-009-0684-z. PMID 19455354. S2CID 20119237.
- ^ Montagna P (September 2008). «Migraine genetics». Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 8 (9): 1321–30. doi:10.1586/14737175.8.9.1321. PMID 18759544. S2CID 207195127.
- ^ a b c Ducros A (May 2013). «[Genetics of migraine]». Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 360–71. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.010. PMID 23618705.
- ^ Wan D, Wang C, Zhang X, Tang W, Chen M, Dong Z, Yu S (1 January 2016). «Association between angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and migraine: a meta-analysis». The International Journal of Neuroscience. 126 (5): 393–9. doi:10.3109/00207454.2015.1025395. PMID 26000817. S2CID 34902092.
- ^ Dussor G, Cao YQ (October 2016). «TRPM8 and Migraine». Headache. 56 (9): 1406–1417. doi:10.1111/head.12948. PMC 5335856. PMID 27634619.
- ^ a b c Levy D, Strassman AM, Burstein R (June 2009). «A critical view on the role of migraine triggers in the genesis of migraine pain». Headache. 49 (6): 953–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01444.x. PMID 19545256. S2CID 31707887.
- ^ Martin PR (June 2010). «Behavioral management of migraine headache triggers: learning to cope with triggers». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 14 (3): 221–7. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0112-z. PMID 20425190. S2CID 5511782.
- ^ Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB (2014). «Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies». Headache. 54 (10): 1670–9. doi:10.1111/head.12468. PMID 25399858. S2CID 25016889.
- ^ a b c Radat F (May 2013). «[Stress and migraine]». Revue Neurologique. 169 (5): 406–12. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2012.11.008. PMID 23608071.
- ^ Peterlin BL, Katsnelson MJ, Calhoun AH (October 2009). «The associations between migraine, unipolar psychiatric comorbidities, and stress-related disorders and the role of estrogen». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (5): 404–12. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0066-1. PMC 3972495. PMID 19728969.
- ^ Chai NC, Peterlin BL, Calhoun AH (June 2014). «Migraine and estrogen». Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 315–24. doi:10.1097/WCO.0000000000000091. PMC 4102139. PMID 24792340.
- ^ Finocchi C, Sivori G (May 2012). «Food as trigger and aggravating factor of migraine». Neurological Sciences. 33 Suppl 1 (1): S77-80. doi:10.1007/s10072-012-1046-5. PMID 22644176. S2CID 19582697.
- ^ Rockett FC, de Oliveira VR, Castro K, Chaves ML, Perla A, Perry ID (June 2012). «Dietary aspects of migraine trigger factors». Nutrition Reviews. 70 (6): 337–56. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00468.x. PMID 22646127.
- ^ Ghose, K.; Carroll, J. D. (1984). «Mechanism of Tyramine-Induced Migraine: Similarity with Dopamine and Interactions with Disulfiram and Propranolol in Migraine Patients». Neuropsychobiology. 12 (2–3): 122–126. doi:10.1159/000118123. PMID 6527752.
- ^ Moffett, A.; Swash, M.; Scott, D. F. (1972). «Effect of tyramine in migraine : a double-blind study» (PDF). Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 35 (4): 496–499. doi:10.1136/jnnp.35.4.496. PMC 494110. PMID 4559027.
- ^ «Tyramine and Migraines: What You Need to Know». www.excedrin.com. Retrieved 2022-03-04.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second ed.). Academic Press. 2003. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0.
- ^ Özturan; et al. (2016). «The Relationship Between Migraine and Nutrition» (PDF). Turk J Neurol. 22 (2): 44–50. doi:10.4274/tnd.37132.
- ^ Sun-Edelstein C, Mauskop A (June 2009). «Foods and supplements in the management of migraine headaches» (PDF). The Clinical Journal of Pain. 25 (5): 446–52. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.530.1223. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e31819a6f65. PMID 19454881. S2CID 3042635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 August 2017.
- ^ Friedman DI, De ver Dye T (June 2009). «Migraine and the environment». Headache. 49 (6): 941–52. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01443.x. PMID 19545255. S2CID 29764274.
- ^ Andreou AP, Edvinsson L (December 2019). «Mechanisms of migraine as a chronic evolutive condition». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 20 (1): 117. doi:10.1186/s10194-019-1066-0. PMC 6929435. PMID 31870279.
- ^ «What is Migraine?». Migraine Research Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2020.
- ^ «Migraine Information Page». National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020.
- ^ Hoffmann J, Baca SM, Akerman S (April 2019). «Neurovascular mechanisms of migraine and cluster headache». Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 39 (4): 573–594. doi:10.1177/0271678×17733655. PMC 6446418. PMID 28948863.
- ^ Brennan KC, Charles A (June 2010). «An update on the blood vessel in migraine». Current Opinion in Neurology. 23 (3): 266–74. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833821c1. PMC 5500293. PMID 20216215.
- ^ Spiri, Daniele; Titomanlio, Luigi; Pogliani, Laura; Zuccotti, Gianvincenzo (1 January 2012). «Pathophysiology of migraine: The neurovascular theory». Headaches: Causes, Treatment and Prevention: 51–64.
- ^ Goadsby PJ (January 2009). «The vascular theory of migraine—a great story wrecked by the facts». Brain. 132 (Pt 1): 6–7. doi:10.1093/brain/awn321. PMID 19098031.
- ^ Dodick DW (April 2008). «Examining the essence of migraine—is it the blood vessel or the brain? A debate». Headache. 48 (4): 661–7. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01079.x. PMID 18377395. S2CID 6272233.
- ^ Chen D, Willis-Parker M, Lundberg GP (October 2020). «Migraine headache: Is it only a neurological disorder? Links between migraine and cardiovascular disorders». Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 30 (7): 424–430. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2019.10.005. PMID 31679956.
- ^ Jacobs B, Dussor G (December 2016). «Neurovascular contributions to migraine: Moving beyond vasodilation». Neuroscience. 338: 130–144. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.012. PMC 5083225. PMID 27312704.
- ^ Mason BN, Russo AF (2018). «Vascular Contributions to Migraine: Time to Revisit?». Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 12: 233. doi:10.3389/fncel.2018.00233. PMC 6088188. PMID 30127722.
- ^ Dodick DW, Gargus JJ (August 2008). «Why migraines strike». Scientific American. 299 (2): 56–63. Bibcode:2008SciAm.299b..56D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0808-56. PMID 18666680.
- ^ a b c d The Headaches, Chp. 28, pp. 269–72
- ^ a b c Olesen J, Burstein R, Ashina M, Tfelt-Hansen P (July 2009). «Origin of pain in migraine: evidence for peripheral sensitisation». The Lancet. Neurology. 8 (7): 679–90. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70090-0. PMID 19539239. S2CID 20452008.
- ^ Akerman S, Holland PR, Goadsby PJ (September 2011). «Diencephalic and brainstem mechanisms in migraine». Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 12 (10): 570–84. doi:10.1038/nrn3057. PMID 21931334. S2CID 8472711.
- ^ Shevel E (March 2011). «The extracranial vascular theory of migraine—a great story confirmed by the facts». Headache. 51 (3): 409–417. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01844.x. PMID 21352215. S2CID 6939786.
- ^ a b Burnstock G (1 January 2016). «Purinergic Mechanisms and Pain». In Barrett JE (ed.). Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain. Advances in Pharmacology. Pharmacological Mechanisms and the Modulation of Pain. Vol. 75. Academic Press. pp. 91–137. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2015.09.001. ISBN 9780128038833. PMID 26920010.
- ^ Davidoff R (14 February 2002). Migraine: Manifestations, Pathogenesis, and Management. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-803135-2.
- ^ Lipton RB, Diener HC, Robbins MS, Garas SY, Patel K (October 2017). «Caffeine in the management of patients with headache». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 18 (1): 107. doi:10.1186/s10194-017-0806-2. PMC 5655397. PMID 29067618.
- ^ Hamel E (November 2007). «Serotonin and migraine: biology and clinical implications». Cephalalgia. 27 (11): 1293–300. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01476.x. PMID 17970989. S2CID 26543041.
- ^
- American Headache Society (September 2013). «Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question». Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). «The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations». Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658. S2CID 14443890.
- Silberstein SD (September 2000). «Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). «Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis». Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ^ Cousins G, Hijazze S, Van de Laar FA, Fahey T (Jul–Aug 2011). «Diagnostic accuracy of the ID Migraine: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Headache. 51 (7): 1140–8. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01916.x. PMID 21649653. S2CID 205684294.
- ^ «Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition». Cephalalgia. 38 (1): 1–211. January 2018. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202. PMID 29368949.
- ^ Nappi G (September 2005). «Introduction to the new International Classification of Headache Disorders». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 6 (4): 203–4. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0185-y. PMC 3452009. PMID 16362664.
- ^ Negro A, Rocchietti-March M, Fiorillo M, Martelletti P (December 2011). «Chronic migraine: current concepts and ongoing treatments». European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 15 (12): 1401–20. PMID 22288302.
- ^ a b c d Davidoff RA (2002). Migraine : manifestations, pathogenesis, and management (2 ed.). Oxford [u.a.]: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 81. ISBN 9780195137057. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016.
- ^ Russell G, Abu-Arafeh I, Symon DN (2002). «Abdominal migraine: evidence for existence and treatment options». Paediatric Drugs. 4 (1): 1–8. doi:10.2165/00128072-200204010-00001. PMID 11817981. S2CID 12289726.
- ^ Lewis DW, Dorbad D (September 2000). «The utility of neuroimaging in the evaluation of children with migraine or chronic daily headache who have normal neurological examinations». Headache. 40 (8): 629–32. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.040008629.x. PMID 10971658. S2CID 14443890.
- ^ Silberstein SD (September 2000). «Practice parameter: evidence-based guidelines for migraine headache (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 55 (6): 754–62. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.6.754. PMID 10993991.
- ^ Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010). «Neuroimaging for the evaluation of chronic headaches: an evidence-based analysis». Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series. 10 (26): 1–57. PMC 3377587. PMID 23074404.
- ^ a b Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- ^ Modi S, Lowder DM (January 2006). «Medications for migraine prophylaxis». American Family Physician. 73 (1): 72–8. PMID 16417067.
- ^ Diener HC, Limmroth V (August 2004). «Medication-overuse headache: a worldwide problem». The Lancet. Neurology. 3 (8): 475–83. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00824-5. PMID 15261608. S2CID 43840120.
- ^ Fritsche G, Diener HC (November 2002). «Medication overuse headaches — what is new?». Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 1 (4): 331–8. doi:10.1517/14740338.1.4.331. PMID 12904133. S2CID 23422679.
- ^ Kaniecki R, Lucas S (2004). «Treatment of primary headache: preventive treatment of migraine». Standards of care for headache diagnosis and treatment. Chicago: National Headache Foundation. pp. 40–52.
- ^ a b c Loder E, Burch R, Rizzoli P (June 2012). «The 2012 AHS/AAN guidelines for prevention of episodic migraine: a summary and comparison with other recent clinical practice guidelines». Headache. 52 (6): 930–45. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02185.x. PMID 22671714. S2CID 540800.
- ^ Linde M, Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, McCrory DC (June 2013). «Antiepileptics other than gabapentin, pregabalin, topiramate, and valproate for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2021 (6): CD010608. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010608. PMC 8221229. PMID 23797674.
- ^ Locher C, Kossowsky J, Koechlin H, Lam TL, Barthel J, Berde CB, et al. (April 2020). «Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Pharmacologic Treatments for Pediatric Migraine Prophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis». JAMA Pediatrics. 174 (4): 341–349. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.5856. PMC 7042942. PMID 32040139.
- ^ Merison K, Jacobs H (November 2016). «Diagnosis and Treatment of Childhood Migraine». Current Treatment Options in Neurology. 18 (11): 48. doi:10.1007/s11940-016-0431-4. PMID 27704257. S2CID 28302667.
- ^ Dorosch T, Ganzer CA, Lin M, Seifan A (September 2019). «Efficacy of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Preventative Treatment of Episodic Migraine in Adults». Current Pain and Headache Reports. 23 (11): 85. doi:10.1007/s11916-019-0823-8. PMID 31515634. S2CID 202557362.
- ^ Cernes R, Mashavi M, Zimlichman R (2011). «Differential clinical profile of candesartan compared to other angiotensin receptor blockers». Vascular Health and Risk Management. 7: 749–59. doi:10.2147/VHRM.S22591. PMC 3253768. PMID 22241949.
- ^ Rajapakse T, Pringsheim T (April 2016). «Nutraceuticals in Migraine: A Summary of Existing Guidelines for Use». Headache. 56 (4): 808–16. doi:10.1111/head.12789. PMID 26954394. S2CID 31097792.
- ^ Teigen L, Boes CJ (September 2015). «An evidence-based review of oral magnesium supplementation in the preventive treatment of migraine». Cephalalgia. 35 (10): 912–22. doi:10.1177/0333102414564891. PMID 25533715. S2CID 25398410.
- ^ a b Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). «Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 78 (17): 1337–45. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d20. PMC 3335452. PMID 22529202.
- ^ Shamliyan TA, Choi JY, Ramakrishnan R, Miller JB, Wang SY, Taylor FR, Kane RL (September 2013). «Preventive pharmacologic treatments for episodic migraine in adults». Journal of General Internal Medicine. 28 (9): 1225–37. doi:10.1007/s11606-013-2433-1. PMC 3744311. PMID 23592242.
- ^ Ibekwe, A.; Perras, C.; Mierzwinski-Urban, M. (2016). «Monoclonal Antibodies to Prevent Migraine Headaches». PMID 30855775.
- ^ Loder E, Renthal W (March 2019). «Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Treatments for Migraine». JAMA Internal Medicine. 179 (3): 421–422. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.7536. PMID 30640381. S2CID 58601441.
- ^ Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, Fei Y, Mehring M, Vertosick EA, et al. (June 2016). «Acupuncture for the prevention of episodic migraine». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (6): CD001218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001218.pub3. PMC 4977344. PMID 27351677.
- ^ Chaibi A, Tuchin PJ, Russell MB (April 2011). «Manual therapies for migraine: a systematic review». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 12 (2): 127–33. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0296-6. PMC 3072494. PMID 21298314.
- ^ Millstine D, Chen CY, Bauer B (May 2017). «Complementary and integrative medicine in the management of headache». BMJ. 357: j1805. doi:10.1136/bmj.j1805. PMID 28512119. S2CID 19155758.
- ^ a b Posadzki P, Ernst E (June 2011). «Spinal manipulations for the treatment of migraine: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials». Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 964–70. doi:10.1177/0333102411405226. PMID 21511952. S2CID 31205541.
- ^ a b Sharpe L, Dudeney J, Williams AC, Nicholas M, McPhee I, Baillie A, et al. (July 2019). «Psychological therapies for the prevention of migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 7: CD012295. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012295.pub2. PMC 6603250. PMID 31264211.
- ^ Holland S, Silberstein SD, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E (April 2012). «Evidence-based guideline update: NSAIDs and other complementary treatments for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 78 (17): 1346–53. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182535d0c. PMC 3335449. PMID 22529203.
- ^ Pringsheim T, Davenport W, Mackie G, Worthington I, Aubé M, Christie SN, et al. (March 2012). «Canadian Headache Society guideline for migraine prophylaxis». The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 39 (2 Suppl 2): S1-59. PMID 22683887.
- ^ «Butterbur: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning». www.webmd.com. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ «Butterbur». NCCIH. 8 February 2012. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ Littarru GP, Tiano L (November 2005). «Clinical aspects of coenzyme Q10: an update». Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 8 (6): 641–6. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000171123.60665.16. PMID 16205466. S2CID 25010508.
- ^ Groenewegen WA, Knight DW, Heptinstall S (1992). «Progress in the medicinal chemistry of the herb feverfew». Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. 29: 217–38. doi:10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70009-2. ISBN 9780444894724. PMID 1475370.
- ^ Barnes, J; Anderson, LA; Philipson, JD (2007). Herbal Medicines. 3rd ed. London: Pharmaceutical Press.
- ^ a b EMA. «Assessment report on Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Schultz Bip., herba» (PDF). www.ema.europa.eu. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- ^ a b c d Gelfand AA, Goadsby PJ (September 2016). «The Role of Melatonin in the Treatment of Primary Headache Disorders». Headache (Review). 56 (8): 1257–66. doi:10.1111/head.12862. PMC 5012937. PMID 27316772.
- ^ Long R, Zhu Y, Zhou S (January 2019). «Therapeutic role of melatonin in migraine prophylaxis: A systematic review». Medicine. 98 (3): e14099. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014099. PMC 6370052. PMID 30653130.
- ^ Nesbitt AD, Leschziner GD, Peatfield RC (September 2014). «Headache, drugs and sleep». Cephalalgia (Review). 34 (10): 756–66. doi:10.1177/0333102414542662. PMID 25053748. S2CID 33548757.
- ^ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A (March 2007). «Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis». Pain. 128 (1–2): 111–27. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007. PMID 17084028. S2CID 23351902.
- ^ Nestoriuc Y, Martin A, Rief W, Andrasik F (September 2008). «Biofeedback treatment for headache disorders: a comprehensive efficacy review». Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback. 33 (3): 125–40. doi:10.1007/s10484-008-9060-3. PMID 18726688. S2CID 29122354.
- ^ Schoenen J, Allena M, Magis D (2010). «Neurostimulation therapy in intractable headaches». In Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds.). Headache. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. pp. 443–50. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97037-1. ISBN 9780444521392. PMID 20816443.
- ^ Reed KL, Black SB, Banta CJ, Will KR (March 2010). «Combined occipital and supraorbital neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine headaches: initial experience». Cephalalgia. 30 (3): 260–71. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01996.x. PMID 19732075. S2CID 18639211.
- ^ «FDA allows marketing of first medical device to prevent migraine headaches». Food and Drug Administration. 11 March 2014. Archived from the original on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ^ «FDA approves transcranial magnetic stimulator» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 February 2014.
- ^ Tao H, Wang T, Dong X, Guo Q, Xu H, Wan Q (May 2018). «Effectiveness of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for the treatment of migraine: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 19 (1): 42. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0868-9. PMC 5975046. PMID 29845369.
We found significant reduction of monthly headache days
- ^ Kung TA, Guyuron B, Cederna PS (January 2011). «Migraine surgery: a plastic surgery solution for refractory migraine headache». Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 127 (1): 181–189. doi:10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f95a01. PMID 20871488. S2CID 18817383.
- ^ «American Headache Society Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question». Choosing Wisely. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
- ^ Rabbie R, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Ibuprofen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008039. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008039.pub3. PMC 4161114. PMID 23633348.
- ^ Derry S, Rabbie R, Moore RA (April 2013). «Diclofenac with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008783. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008783.pub3. PMC 4164457. PMID 23633360.
- ^ Kirthi V, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Aspirin with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008041. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008041.pub3. PMC 4163048. PMID 23633350.
- ^ Derry S, Moore RA (April 2013). «Paracetamol (acetaminophen) with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (4): CD008040. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008040.pub3. PMC 4161111. PMID 23633349.
- ^ Eken C (March 2015). «Critical reappraisal of intravenous metoclopramide in migraine attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis». The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 33 (3): 331–7. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2014.11.013. PMID 25579820.
- ^ a b c d Orr SL, Friedman BW, Christie S, Minen MT, Bamford C, Kelley NE, Tepper D (June 2016). «Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies». Headache. 56 (6): 911–40. doi:10.1111/head.12835. PMID 27300483.
- ^ Law, Simon; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2013-10-20). «Naproxen with or without an antiemetic for acute migraine headaches in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD009455. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009455.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6540401. PMID 24142263.
- ^ Singh, Rashmi B. Halker; VanderPluym, Juliana H.; Morrow, Allison S.; Urtecho, Meritxell; Nayfeh, Tarek; Roldan, Victor D. Torres; Farah, Magdoleen H.; Hasan, Bashar; Saadi, Samer (2020). Acute Treatments for Episodic Migraine. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 33411427.
- ^ Johnston MM, Rapoport AM (August 2010). «Triptans for the management of migraine». Drugs. 70 (12): 1505–18. doi:10.2165/11537990-000000000-00000. PMID 20687618. S2CID 41613179.
- ^ a b Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (rectal route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (2): CD009664. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009664. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4170908. PMID 22336868.
- ^ a b c Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (intranasal route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009663. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009663. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164476. PMID 22336867.
- ^ a b Derry, Christopher J.; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R. Andrew (2012-02-15). «Sumatriptan (subcutaneous route of administration) for acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD009665. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009665. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4164380. PMID 22336869.
- ^ a b «Generic migraine drug could relieve your pain and save you money». Best Buy Drugs. Consumer Reports. Archived from the original on 4 August 2013.
- ^ Tepper SJ, Tepper DE (April 2010). «Breaking the cycle of medication overuse headache». Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 77 (4): 236–42. doi:10.3949/ccjm.77a.09147. PMID 20360117. S2CID 36333666.
- ^ Law S, Derry S, Moore RA (April 2016). «Sumatriptan plus naproxen for the treatment of acute migraine attacks in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD008541. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008541.pub3. PMC 6485397. PMID 27096438.
- ^ a b Sumamo Schellenberg, E.; Dryden, D. M.; Pasichnyk, D.; Ha, C.; Vandermeer, B.; Friedman, B. W.; Colman, I.; Rowe, B. H. (2012). «Acute migraine treatment in emergency settings». PMID 23304741.
- ^ Kelley NE, Tepper DE (January 2012). «Rescue therapy for acute migraine, part 1: triptans, dihydroergotamine, and magnesium». Headache. 52 (1): 114–28. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.02062.x. PMID 22211870. S2CID 45767513.
- ^ a b Morren JA, Galvez-Jimenez N (December 2010). «Where is dihydroergotamine mesylate in the changing landscape of migraine therapy?». Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (18): 3085–93. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.533839. PMID 21080856. S2CID 44639896.
- ^ Tfelt-Hansen P, Saxena PR, Dahlöf C, Pascual J, Láinez M, Henry P, et al. (January 2000). «Ergotamine in the acute treatment of migraine: a review and European consensus». Brain. 123 ( Pt 1): 9–18. doi:10.1093/brain/123.1.9. PMID 10611116.
- ^ Yablon LA, Mauskop A (2011). «Magnesium in headache». In Vink R, Nechifor M (eds.). Magnesium in the Central Nervous System. Adelaide (AU): University of Adelaide Press. ISBN 978-0-9870730-5-1. PMID 29920023. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- ^ HY, Chiu; TH, Yeh; YC, Huang; PY, Chen (2015-02-24). «Effects of Intravenous and Oral Magnesium on Reducing Migraine: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials». Pain Physician. 19 (1). ISSN 2150-1149. PMID 26752497. Retrieved 2022-12-02.
- ^ Veronese, Nicola; Demurtas, Jacopo; Pesolillo, Gabriella; Celotto, Stefano; Barnini, Tommaso; Calusi, Giovanni; Caruso, Maria Gabriella; Notarnicola, Maria; Reddavide, Rosa; Stubbs, Brendon; Solmi, Marco; Maggi, Stefania; Vaona, Alberto; Firth, Joseph; Smith, Lee; Koyanagi, Ai; Dominguez, Ligia; Barbagallo, Mario (2019-01-25). «Magnesium and health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational and intervention studies». European Journal of Nutrition. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 59 (1): 263–272. doi:10.1007/s00394-019-01905-w. ISSN 1436-6207. PMID 30684032. S2CID 59275463.
- ^ Colman I, Friedman BW, Brown MD, Innes GD, Grafstein E, Roberts TE, Rowe BH (June 2008). «Parenteral dexamethasone for acute severe migraine headache: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials for preventing recurrence». BMJ. 336 (7657): 1359–61. doi:10.1136/bmj.39566.806725.BE. PMC 2427093. PMID 18541610.
- ^ Piatka C, Beckett RD (February 2020). «Propofol for Treatment of Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review». Academic Emergency Medicine. 27 (2): 148–160. doi:10.1111/acem.13870. PMID 31621134.
- ^ Vukovic Cvetkovic V, Jensen RH (January 2019). «Neurostimulation for the treatment of chronic migraine and cluster headache». Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 139 (1): 4–17. doi:10.1111/ane.13034. PMID 30291633. S2CID 52923061.
- ^ Hambach, A.; Frese, A.; Evers, S. (2013). «Sexuelle Aktivität und Kopfschmerz». Nervenheilkunde (in German). Georg Thieme Verlag KG. 32 (3): 118–122. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1628490. ISSN 0722-1541.
- ^ a b c d Richer L, Billinghurst L, Linsdell MA, Russell K, Vandermeer B, Crumley ET, et al. (April 2016). «Drugs for the acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4 (10): CD005220. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005220.pub2. PMC 6516975. PMID 27091010.
- ^ a b Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171.
- ^ Wang, Guihua; Tan, Tianlin; Liu, Yao; Hong, Peiwei (2020). «Drugs for Acute Attack of Pediatric Migraine: A Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials». Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 195: 105853. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105853. ISSN 1872-6968. PMID 32464520. S2CID 215814011.
- ^ Herd CP, Tomlinson CL, Rick C, Scotton WJ, Edwards J, Ives N, et al. (June 2018). «Botulinum toxins for the prevention of migraine in adults». The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (6): CD011616. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011616.pub2. PMC 6513576. PMID 29939406.
- ^ Jackson JL, Kuriyama A, Hayashino Y (April 2012). «Botulinum toxin A for prophylactic treatment of migraine and tension headaches in adults: a meta-analysis». JAMA. 307 (16): 1736–45. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.505. PMID 22535858.
- ^ Simpson DM, Hallett M, Ashman EJ, Comella CL, Green MW, Gronseth GS, et al. (May 2016). «Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology». Neurology. 86 (19): 1818–26. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000002560. PMC 4862245. PMID 27164716.
- ^ Markham A (July 2018). «Erenumab: First Global Approval». Drugs. 78 (11): 1157–1161. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0944-0. PMID 29968151. S2CID 49559342.
- ^ Silberstein, Stephen D.; Lee, Lulu; Gandhi, Kavita; Fitzgerald, Timothy; Bell, Jvawnna; Cohen, Joshua M. (2018). «Health care Resource Utilization and Migraine Disability Along the Migraine Continuum Among Patients Treated for Migraine». Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain. 58 (10): 1579–1592. doi:10.1111/head.13421. PMID 30375650. S2CID 53114546.
- ^ a b «Migraine Information Page: Prognosis Archived 2020-06-10 at the Wayback Machine,» National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), National Institutes of Health (US).
- ^ «Facts and Figures». The Migraine Trust.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Brennan, KC; Pietrobon, D (March 2018). «A systems neuroscience approach to migraine». Neuron. 97 (5): 1004–1021. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.029. PMC 6402597. PMID 29518355.
- ^ World Health Organization (2008). «Disability classes for the Global Burden of Disease study» (table 8), The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update, p 33.
- ^ a b c Schürks M, Rist PM, Bigal ME, Buring JE, Lipton RB, Kurth T (October 2009). «Migraine and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis». BMJ. 339: b3914. doi:10.1136/bmj.b3914. PMC 2768778. PMID 19861375.
- ^ Kurth T, Chabriat H, Bousser MG (January 2012). «Migraine and stroke: a complex association with clinical implications». The Lancet. Neurology. 11 (1): 92–100. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70266-6. PMID 22172624. S2CID 31939284.
- ^ Rist PM, Diener HC, Kurth T, Schürks M (June 2011). «Migraine, migraine aura, and cervical artery dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Cephalalgia. 31 (8): 886–96. doi:10.1177/0333102411401634. PMC 3303220. PMID 21511950.
- ^ Kurth T (March 2010). «The association of migraine with ischemic stroke». Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 10 (2): 133–9. doi:10.1007/s11910-010-0098-2. PMID 20425238. S2CID 27227332.
- ^ Schürks M, Rist PM, Shapiro RE, Kurth T (September 2011). «Migraine and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Cephalalgia. 31 (12): 1301–14. doi:10.1177/0333102411415879. PMC 3175288. PMID 21803936.
- ^ Weinberger J (March 2007). «Stroke and migraine». Current Cardiology Reports. 9 (1): 13–9. doi:10.1007/s11886-007-0004-y. PMID 17362679. S2CID 46681674.
- ^ Hougaard A, Amin FM, Ashina M (June 2014). «Migraine and structural abnormalities in the brain». Current Opinion in Neurology. 27 (3): 309–14. doi:10.1097/wco.0000000000000086. PMID 24751961.
- ^ Wang SJ (March 2003). «Epidemiology of migraine and other types of headache in Asia». Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 3 (2): 104–8. doi:10.1007/s11910-003-0060-7. PMID 12583837. S2CID 24939546.
- ^ Natoli JL, Manack A, Dean B, Butler Q, Turkel CC, Stovner L, Lipton RB (May 2010). «Global prevalence of chronic migraine: a systematic review». Cephalalgia. 30 (5): 599–609. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01941.x. PMID 19614702. S2CID 5328642.
- ^ a b Hershey AD (February 2010). «Current approaches to the diagnosis and management of paediatric migraine». The Lancet. Neurology. 9 (2): 190–204. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70303-5. PMID 20129168. S2CID 12603488.
- ^ a b Nappi RE, Sances G, Detaddei S, Ornati A, Chiovato L, Polatti F (June 2009). «Hormonal management of migraine at menopause». Menopause International. 15 (2): 82–6. doi:10.1258/mi.2009.009022. PMID 19465675. S2CID 23204921.
- ^ a b c d e Borsook D (2012). The migraine brain : imaging, structure, and function. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–11. ISBN 9780199754564. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ a b Steven D. Waldman (2011). Pain management (2 ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 2122–2124. ISBN 9781437736038.
- ^ «Sex(ism), Drugs, and Migraines». Distillations. Science History Institute. 15 January 2019. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ^ Margaret C, Simon M (2002). Human osteology : in archaeology and forensic science (Repr. ed.). Cambridge [etc.]: Cambridge University Press. p. 345. ISBN 9780521691468. Archived from the original on 17 June 2013.
- ^ Colen C (2008). Neurosurgery. Colen Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 9781935345039.
- ^ Daniel BT (2010). Migraine. Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse. p. 101. ISBN 9781449069629. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017.
- ^ Butticè, Claudio (April 2022). What you need to know about headaches. Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood_Publishing_Group. pp. 29–30. ISBN 978-1-4408-7531-1. OCLC 1259297708.
- ^ a b Tfelt-Hansen PC, Koehler PJ (May 2011). «One hundred years of migraine research: major clinical and scientific observations from 1910 to 2010». Headache. 51 (5): 752–78. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01892.x. PMID 21521208. S2CID 31940152.
- ^ a b c Stovner LJ, Andrée C (June 2008). «Impact of headache in Europe: a review for the Eurolight project». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (3): 139–46. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0038-6. PMC 2386850. PMID 18418547.
- ^ a b Mennini FS, Gitto L, Martelletti P (August 2008). «Improving care through health economics analyses: cost of illness and headache». The Journal of Headache and Pain. 9 (4): 199–206. doi:10.1007/s10194-008-0051-9. PMC 3451939. PMID 18604472.
- ^ Magis D, Jensen R, Schoenen J (June 2012). «Neurostimulation therapies for primary headache disorders: present and future». Current Opinion in Neurology. 25 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283532023. PMID 22543428.
- ^ Jürgens TP, Leone M (June 2013). «Pearls and pitfalls: neurostimulation in headache». Cephalalgia. 33 (8): 512–25. doi:10.1177/0333102413483933. PMID 23671249. S2CID 42537455.
- ^ Barbanti P, Fofi L, Aurilia C, Egeo G, Caprio M (May 2017). «Ketogenic diet in migraine: rationale, findings and perspectives». Neurological Sciences (Review). 38 (Suppl 1): 111–115. doi:10.1007/s10072-017-2889-6. PMID 28527061. S2CID 3805337.
- ^ Gross EC, Klement RJ, Schoenen J, D’Agostino DP, Fischer D (April 2019). «Potential Protective Mechanisms of Ketone Bodies in Migraine Prevention». Nutrients. 11 (4): 811. doi:10.3390/nu11040811. PMC 6520671. PMID 30974836.
- ^ Artero-Morales M, González-Rodríguez S, Ferrer-Montiel A (2018). «TRP Channels as Potential Targets for Sex-Related Differences in Migraine Pain». Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 5: 73. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2018.00073. PMC 6102492. PMID 30155469.
- ^ Stewart, Walter F.; Lipton, Richard B.; Celentano, David D.; Reed, Michael L. (1992-01-01). «Prevalence of Migraine Headache in the United States: Relation to Age, Income, Race, and Other Sociodemographic Factors». JAMA. 267 (1): 64–69. doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03480010072027. ISSN 0098-7484. PMID 1727198.
- ^ «Speeding Progress in Migraine Requires Unraveling Sex Differences». SWHR. 2018-08-28. Retrieved 2021-03-17.
- ^ «Migraine in Women Needs More Sex-Specific Research». Migraine Again. 2021-03-11. Retrieved 2021-03-17.
- ^ Schroeder RA, Brandes J, Buse DC, Calhoun A, Eikermann-Haerter K, Golden K, et al. (August 2018). «Sex and Gender Differences in Migraine-Evaluating Knowledge Gaps». Journal of Women’s Health. 27 (8): 965–973. doi:10.1089/jwh.2018.7274. PMID 30129895. S2CID 52048078.
Notes[edit]
- Olesen J (2006). The headaches (3 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9780781754002.
Further reading[edit]
- Ashina M (November 2020). Ropper AH (ed.). «Migraine». The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (19): 1866–1876. doi:10.1056/nejmra1915327. PMID 33211930. S2CID 227078662.
- Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Billinghurst L, Potrebic S, Gersz EM, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Pharmacologic treatment for pediatric migraine prevention: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 500–509. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008105. PMC 6746206. PMID 31413170.
- Oskoui M, Pringsheim T, Holler-Managan Y, Potrebic S, Billinghurst L, Gloss D, et al. (September 2019). «Practice guideline update summary: Acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society». Neurology. 93 (11): 487–499. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000008095. PMID 31413171. S2CID 199662718.
External links[edit]
| External audio |
|---|
- Migraine at Curlie