|
Hakim Omar Khayyam |
|
|---|---|

Statue of Omar Khayyam by Abolhassan Sadighi |
|
| Born | 18 May[1] 1048[2]
Nishapur, Khorasan, Seljuk Empire |
| Died | 4 December[1] 1131 (aged 83)[2]
Nishapur, Khorasan, Seljuk Empire |
| Academic background | |
| Influences | Avicenna, al-Khwārizmī, Euclid, Apollonius of Perge |
| Academic work | |
| Main interests | Mathematics (medieval Islamic), astronomy, Persian philosophy, Persian poetry |
| Influenced | Tusi, Al-Khazini, Nizami Aruzi of Samarcand, Hafez, Sadegh Hedayat, André Gide, John Wallis, Saccheri, Edward FitzGerald, Maurice Bouchor, Henri Cazalis, Jean Chapelain, Amin Maalouf |
Ghiyāth al-Dīn Abū al-Fatḥ ʿUmar ibn Ibrāhīm Nīsābūrī[3][4] (18 May 1048 – 4 December 1131), commonly known as Omar Khayyam (Persian: عمر خیّام),[a] was a polymath, known for his contributions to mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, and Persian poetry.[5] He was born in Nishapur, the initial capital of the Seljuk Empire. As a scholar, he was contemporary with the rule of the Seljuk dynasty around the time of the First Crusade.
As a mathematician, he is most notable for his work on the classification and solution of cubic equations, where he provided geometric solutions by the intersection of conics.[6] Khayyam also contributed to the understanding of the parallel axiom.[7]: 284 As an astronomer, he calculated the duration of the solar year with remarkable precision and accuracy, and designed the Jalali calendar, a solar calendar with a very precise 33-year intercalation cycle[8][9]: 659 that provided the basis for the Persian calendar that is still in use after nearly a millennium.
There is a tradition of attributing poetry to Omar Khayyam, written in the form of quatrains (rubāʿiyāt رباعیات). This poetry became widely known to the English-reading world in a translation by Edward FitzGerald (Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, 1859), which enjoyed great success in the Orientalism of the fin de siècle.
Life[edit]
Omar Khayyam was born, of Khorasani Persian ancestry, in Nishapur in 1048.[10][11][12][13][14] In medieval Persian texts he is usually simply called Omar Khayyam.[15] Although open to doubt, it has often been assumed that his forebears followed the trade of tent-making, since Khayyam means tent-maker in Arabic.[16]: 30 The historian Bayhaqi, who was personally acquainted with Omar, provides the full details of his horoscope: «he was Gemini, the sun and Mercury being in the ascendant[…]».[17]: 471 This was used by modern scholars to establish his date of birth as 18 May 1048.[9]: 658
Khayyam’s boyhood was spent in Nishapur,[9]: 659 a leading metropolis under the Great Seljuq Empire,[18]: 15 [19] and it had been a major center of the Zoroastrian religion.[10]: 68 His full name, as it appears in the Arabic sources, was Abu’l Fath Omar ibn Ibrahim al-Khayyam.[20] His gifts were recognized by his early tutors who sent him to study under Imam Muwaffaq Nishaburi, the greatest teacher of the Khorasan region who tutored the children of the highest nobility. Omar made a great friendship with him through the years.[10]: 20 Khayyam was also taught by the Zoroastrian mathematician, Abu Hassan Bahmanyar bin Marzban.[21] After studying science, philosophy, mathematics and astronomy at Nishapur, about the year 1068 he traveled to the province of Bukhara, where he frequented the renowned library of the Ark. In about 1070 he moved to Samarkand, where he started to compose his famous treatise on algebra under the patronage of Abu Tahir Abd al-Rahman ibn ʿAlaq, the governor and chief judge of the city.[22] Omar Khayyam was kindly received by the Karakhanid ruler Shams al-Mulk Nasr, who according to Bayhaqi, would «show him the greatest honour, so much so that he would seat [Omar] beside him on his throne».[16]: 34 [10]: 47
In 1073–4 peace was concluded with Sultan Malik-Shah I who had made incursions into Karakhanid dominions. Khayyam entered the service of Malik-Shah in 1074–5 when he was invited by the Grand Vizier Nizam al-Mulk to meet Malik-Shah in the city of Marv. Khayyam was subsequently commissioned to set up an observatory in Isfahan and lead a group of scientists in carrying out precise astronomical observations aimed at the revision of the Persian calendar. The undertaking began probably in 1076 and ended in 1079[10]: 28 when Omar Khayyam and his colleagues concluded their measurements of the length of the year, reporting it as 365.24219858156 days.[23] Given that the length of the year is changing in the sixth decimal place over a person’s lifetime, this is outstandingly accurate. For comparison the length of the year at the end of the 19th century was 365.242196 days, while today it is 365.242190 days.
After the death of Malik-Shah and his vizier (murdered, it is thought, by the Ismaili order of Assassins), Omar fell from favor at court, and as a result, he soon set out on his pilgrimage to Mecca. A possible ulterior motive for his pilgrimage reported by Al-Qifti, was a public demonstration of his faith with a view to allaying suspicions of skepticism and confuting the allegations of unorthodoxy (including possible sympathy or adherence to Zoroastrianism) levelled at him by a hostile clergy.[24][10]: 29 He was then invited by the new Sultan Sanjar to Marv, possibly to work as a court astrologer.[1] He was later allowed to return to Nishapur owing to his declining health. Upon his return, he seems to have lived the life of a recluse.[25]: 99
Omar Khayyam died at the age of 83 in his hometown of Nishapur on 4 December 1131, and he is buried in what is now the Mausoleum of Omar Khayyam. One of his disciples Nizami Aruzi relates the story that sometime during 1112–3 Khayyam was in Balkh in the company of Al-Isfizari (one of the scientists who had collaborated with him on the Jalali calendar) when he made a prophecy that «my tomb shall be in a spot where the north wind may scatter roses over it».[16]: 36 [19] Four years after his death, Aruzi located his tomb in a cemetery in a then large and well-known quarter of Nishapur on the road to Marv. As it had been foreseen by Khayyam, Aruzi found the tomb situated at the foot of a garden-wall over which pear trees and peach trees had thrust their heads and dropped their flowers so that his tombstone was hidden beneath them.[16]
Mathematics[edit]
Khayyam was famous during his life as a mathematician. His surviving mathematical works include: A commentary on the difficulties concerning the postulates of Euclid’s Elements (Risāla fī šarḥ mā aškala min muṣādarāt kitāb Uqlīdis, completed in December 1077),[citation needed] On the division of a quadrant of a circle (Risālah fī qismah rub‘ al-dā’irah, undated but completed prior to the treatise on algebra),[citation needed] and On proofs for problems concerning Algebra (Maqāla fi l-jabr wa l-muqābala, most likely completed in 1079[7]: 281 ). He furthermore wrote a treatise on the binomial theorem and extracting the nth root of natural numbers, which has been lost.[10]: 197
Theory of parallels[edit]
A part of Khayyam’s commentary on Euclid’s Elements deals with the parallel axiom.[7]: 282 The treatise of Khayyam can be considered the first treatment of the axiom not based on petitio principii, but on a more intuitive postulate. Khayyam refutes the previous attempts by other mathematicians to prove the proposition, mainly on grounds that each of them had postulated something that was by no means easier to admit than the Fifth Postulate itself.[citation needed] Drawing upon Aristotle’s views, he rejects the usage of movement in geometry and therefore dismisses the different attempt by Al-Haytham.[26][27] Unsatisfied with the failure of mathematicians to prove Euclid’s statement from his other postulates, Omar tried to connect the axiom with the Fourth Postulate, which states that all right angles are equal to one another.[7]: 282
Khayyam was the first to consider the three distinct cases of acute, obtuse, and right angle for the summit angles of a Khayyam-Saccheri quadrilateral.[7]: 283 After proving a number of theorems about them, he showed that Postulate V follows from the right angle hypothesis, and refuted the obtuse and acute cases as self-contradictory.[citation needed] His elaborate attempt to prove the parallel postulate was significant for the further development of geometry, as it clearly shows the possibility of non-Euclidean geometries. The hypotheses of acute, obtuse, and right angles are now known to lead respectively to the non-Euclidean hyperbolic geometry of Gauss-Bolyai-Lobachevsky, to that of Riemannian geometry, and to Euclidean geometry.[28]
«Cubic equation and intersection of conic sections» the first page of a two-chaptered manuscript kept in Tehran University.
Tusi’s commentaries on Khayyam’s treatment of parallels made its way to Europe. John Wallis, professor of geometry at Oxford, translated Tusi’s commentary into Latin. Jesuit geometer Girolamo Saccheri, whose work (euclides ab omni naevo vindicatus, 1733) is generally considered the first step in the eventual development of non-Euclidean geometry, was familiar with the work of Wallis. The American historian of mathematics David Eugene Smith mentions that Saccheri «used the same lemma as the one of Tusi, even lettering the figure in precisely the same way and using the lemma for the same purpose». He further says that «Tusi distinctly states that it is due to Omar Khayyam, and from the text, it seems clear that the latter was his inspirer.»[25]: 104 [29][10]: 195
The real number concept[edit]
This treatise on Euclid contains another contribution dealing with the theory of proportions and with the compounding of ratios. Khayyam discusses the relationship between the concept of ratio and the concept of number and explicitly raises various theoretical difficulties. In particular, he contributes to the theoretical study of the concept of irrational number.[citation needed] Displeased with Euclid’s definition of equal ratios, he redefined the concept of a number by the use of a continuous fraction as the means of expressing a ratio. Rosenfeld and Youschkevitch (1973) argue that «by placing irrational quantities and numbers on the same operational scale, [Khayyam] began a true revolution in the doctrine of number.» Likewise, it was noted by D. J. Struik that Omar was «on the road to that extension of the number concept which leads to the notion of the real number.»[7]: 284
Geometric algebra[edit]
Omar Khayyam’s construction of a solution to the cubic x3 + 2x = 2x2 + 2. The intersection point produced by the circle and the hyperbola determine the desired segment.
Rashed and Vahabzadeh (2000) have argued that because of his thoroughgoing geometrical approach to algebraic equations, Khayyam can be considered the precursor of Descartes in the invention of analytic geometry.[30]: 248 In The Treatise on the Division of a Quadrant of a Circle Khayyam applied algebra to geometry. In this work, he devoted himself mainly to investigating whether it is possible to divide a circular quadrant into two parts such that the line segments projected from the dividing point to the perpendicular diameters of the circle form a specific ratio. His solution, in turn, employed several curve constructions that led to equations containing cubic and quadratic terms.[30]: 248
The solution of cubic equations[edit]
Khayyam seems to have been the first to conceive a general theory of cubic equations[31] and the first to geometrically solve every type of cubic equation, so far as positive roots are concerned.[32] The treatise on algebra contains his work on cubic equations.[33] It is divided into three parts: (i) equations which can be solved with compass and straight edge, (ii) equations which can be solved by means of conic sections, and (iii) equations which involve the inverse of the unknown.[34]
Khayyam produced an exhaustive list of all possible equations involving lines, squares, and cubes.[35]: 43 He considered three binomial equations, nine trinomial equations, and seven tetranomial equations.[7]: 281 For the first and second degree polynomials, he provided numerical solutions by geometric construction. He concluded that there are fourteen different types of cubics that cannot be reduced to an equation of a lesser degree.[citation needed] For these he could not accomplish the construction of his unknown segment with compass and straight edge. He proceeded to present geometric solutions to all types of cubic equations using the properties of conic sections.[36]: 157 [7]: 281 The prerequisite lemmas for Khayyam’s geometrical proof include Euclid VI, Prop 13, and Apollonius II, Prop 12.[36]: 155 The positive root of a cubic equation was determined as the abscissa of a point of intersection of two conics, for instance, the intersection of two parabolas, or the intersection of a parabola and a circle, etc.[37]: 141 However, he acknowledged that the arithmetic problem of these cubics was still unsolved, adding that «possibly someone else will come to know it after us».[36]: 158 This task remained open until the sixteenth century, where algebraic solution of the cubic equation was found in its generality by Cardano, Del Ferro, and Tartaglia in Renaissance Italy.[7]: 282
Whoever thinks algebra is a trick in obtaining unknowns has thought it in vain. No attention should be paid to the fact that algebra and geometry are different in appearance. Algebras are geometric facts which are proved by propositions five and six of Book two of Elements.
Omar Khayyam[38]
In effect, Khayyam’s work is an effort to unify algebra and geometry.[39]: 241 This particular geometric solution of cubic equations has been further investigated by M. Hachtroudi and extended to solving fourth-degree equations.[40] Although similar methods had appeared sporadically since Menaechmus, and further developed by the 10th-century mathematician Abu al-Jud,[41][42] Khayyam’s work can be considered the first systematic study and the first exact method of solving cubic equations.[43] The mathematician Woepcke (1851) who offered translations of Khayyam’s algebra into French praised him for his «power of generalization and his rigorously systematic procedure.»[44]: 10
Binomial theorem and extraction of roots[edit]
From the Indians one has methods for obtaining square and cube roots, methods based on knowledge of individual cases – namely the knowledge of the squares of the nine digits 12, 22, 32 (etc.) and their respective products, i.e. 2 × 3 etc. We have written a treatise on the proof of the validity of those methods and that they satisfy the conditions. In addition we have increased their types, namely in the form of the determination of the fourth, fifth, sixth roots up to any desired degree. No one preceded us in this and those proofs are purely arithmetic, founded on the arithmetic of The Elements.
Omar Khayyam, Treatise on Demonstration of Problems of Algebra[45]
In his algebraic treatise, Khayyam alludes to a book he had written on the extraction of the 

Astronomy[edit]
Representation of the intercalation scheme of the Jalali calendar
In 1074–5, Omar Khayyam was commissioned by Sultan Malik-Shah to build an observatory at Isfahan and reform the Persian calendar. There was a panel of eight scholars working under the direction of Khayyam to make large-scale astronomical observations and revise the astronomical tables.[37]: 141 Recalibrating the calendar fixed the first day of the year at the exact moment of the passing of the Sun’s center across vernal equinox. This marks the beginning of spring or Nowrūz, a day in which the Sun enters the first degree of Aries before noon.[48]
[49] The resultant calendar was named in Malik-Shah’s honor as the Jalālī calendar, and was inaugurated on 15 March 1079.[50] The observatory itself was disused after the death of Malik-Shah in 1092.[9]: 659
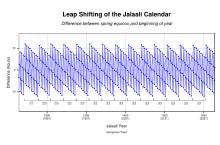
The Jalālī calendar was a true solar calendar where the duration of each month is equal to the time of the passage of the Sun across the corresponding sign of the Zodiac. The calendar reform introduced a unique 33-year intercalation cycle. As indicated by the works of Khazini, Khayyam’s group implemented an intercalation system based on quadrennial and quinquennial leap years. Therefore, the calendar consisted of 25 ordinary years that included 365 days, and 8 leap years that included 366 days.[51] The calendar remained in use across Greater Iran from the 11th to the 20th centuries. In 1911 the Jalali calendar became the official national calendar of Qajar Iran. In 1925 this calendar was simplified and the names of the months were modernized, resulting in the modern Iranian calendar. The Jalali calendar is more accurate than the Gregorian calendar of 1582,[9]: 659 with an error of one day accumulating over 5,000 years, compared to one day every 3,330 years in the Gregorian calendar.[10]: 200
Moritz Cantor considered it the most perfect calendar ever devised.[25]: 101
One of his pupils Nizami Aruzi of Samarcand relates that Khayyam apparently did not have a belief in astrology and divination: «I did not observe that he (scil. Omar Khayyam) had any great belief in astrological predictions, nor have I seen or heard of any of the great [scientists] who had such belief.»[44]: 11 While working for Sultan Sanjar as an astrologer he was asked to predict the weather – a job that he apparently did not do well.[10]: 30 George Saliba (2002) explains that the term ‘ilm al-nujūm, used in various sources in which references to Omar’s life and work could be found, has sometimes been incorrectly translated to mean astrology. He adds: «from at least the middle of the tenth century, according to Farabi’s enumeration of the sciences, that this science, ‘ilm al-nujūm, was already split into two parts, one dealing with astrology and the other with theoretical mathematical astronomy.»[52]: 224
Other works[edit]
He has a short treatise devoted to Archimedes’ principle (in full title, On the Deception of Knowing the Two Quantities of Gold and Silver in a Compound Made of the Two). For a compound of gold adulterated with silver, he describes a method to measure more exactly the weight per capacity of each element. It involves weighing the compound both in air and in water, since weights are easier to measure exactly than volumes. By repeating the same with both gold and silver one finds exactly how much heavier than water gold, silver and the compound were. This treatise was extensively examined by Eilhard Wiedemann who believed that Khayyam’s solution was more accurate and sophisticated than that of Khazini and Al-Nayrizi who also dealt with the subject elsewhere.[10]: 198
Another short treatise is concerned with music theory in which he discusses the connection between music and arithmetic. Khayyam’s contribution was in providing a systematic classification of musical scales, and discussing the mathematical relationship among notes, minor, major and tetrachords.[10]: 198
Poetry[edit]
Rendition of a ruba’i from the Bodleian manuscript, rendered in Shekasteh calligraphy.
The earliest allusion to Omar Khayyam’s poetry is from the historian Imad ad-Din al-Isfahani, a younger contemporary of Khayyam, who explicitly identifies him as both a poet and a scientist (Kharidat al-qasr, 1174).[10]: 49 [53]: 35 One of the earliest specimens of Omar Khayyam’s Rubiyat is from Fakhr al-Din Razi. In his work Al-tanbih ‘ala ba‘d asrar al-maw‘dat fi’l-Qur’an (ca. 1160), he quotes one of his poems (corresponding to quatrain LXII of FitzGerald’s first edition). Daya in his writings (Mirsad al-‘Ibad, ca. 1230) quotes two quatrains, one of which is the same as the one already reported by Razi. An additional quatrain is quoted by the historian Juvayni (Tarikh-i Jahangushay, ca. 1226–1283).[53]: 36–37 [10]: 92 In 1340 Jajarmi includes thirteen quatrains of Khayyam in his work containing an anthology of the works of famous Persian poets (Munis al-ahrār), two of which have hitherto been known from the older sources.[54] A comparatively late manuscript is the Bodleian MS. Ouseley 140, written in Shiraz in 1460, which contains 158 quatrains on 47 folia. The manuscript belonged to William Ouseley (1767–1842) and was purchased by the Bodleian Library in 1844.
There are occasional quotes of verses attributed to Omar in texts attributed to authors of the 13th and 14th centuries, but these are of doubtful authenticity, so that skeptical scholars point out that the entire tradition may be pseudepigraphic.[53]: 11
Hans Heinrich Schaeder in 1934 commented that the name of Omar Khayyam «is to be struck out from the history of Persian literature» due to the lack of any material that could confidently be attributed to him.
De Blois (2004) presents a bibliography of the manuscript tradition, concluding pessimistically that the situation has not changed significantly since Schaeder’s time.[55]
Five of the quatrains later attributed to Omar are found as early as 30 years after his death, quoted in Sindbad-Nameh. While this establishes that these specific verses were in circulation in Omar’s time or shortly later, it doesn’t imply that the verses must be his. De Blois concludes that at the least the process of attributing poetry to Omar Khayyam appears to have begun already in the 13th century.[56] Edward Granville Browne (1906) notes the difficulty of disentangling authentic from spurious quatrains: «while it is certain that Khayyam wrote many quatrains, it is hardly possible, save in a few exceptional cases, to assert positively that he wrote any of those ascribed to him».[9]: 663
In addition to the Persian quatrains, there are twenty-five Arabic poems attributed to Khayyam which are attested by historians such as al-Isfahani, Shahrazuri (Nuzhat al-Arwah, ca. 1201–1211), Qifti (Tārikh al-hukamā, 1255), and Hamdallah Mustawfi (Tarikh-i guzida, 1339).[10]: 39
Boyle and Frye (1975) emphasize that there are a number of other Persian scholars who occasionally wrote quatrains, including Avicenna, Ghazzali, and Tusi. They conclude that it is also possible that for Khayyam poetry was an amusement of his leisure hours: «these brief poems seem often to have been the work of scholars and scientists who composed them, perhaps, in moments of relaxation to edify or amuse the inner circle of their disciples».[9]: 662
The poetry attributed to Omar Khayyam has contributed greatly to his popular fame in the modern period as a direct result of the extreme popularity of the translation of such verses into English by Edward FitzGerald (1859). FitzGerald’s Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam contains loose translations of quatrains from the Bodleian manuscript. It enjoyed such success in the fin de siècle period that a bibliography compiled in 1929 listed more than 300 separate editions,[57] and many more have been published since.[58]
Philosophy[edit]
Khayyam considered himself intellectually to be a student of Avicenna.[59] According to Al-Bayhaqi, he was reading the metaphysics in Avicenna’s the Book of Healing before he died.[9]: 661 There are six philosophical papers believed to have been written by Khayyam. One of them, On existence (Fi’l-wujūd), was written originally in Persian and deals with the subject of existence and its relationship to universals. Another paper, titled The necessity of contradiction in the world, determinism and subsistence (Darurat al-tadād fi’l-‘ālam wa’l-jabr wa’l-baqā’), is written in Arabic and deals with free will and determinism.[59]: 475 The titles of his other works are On being and necessity (Risālah fī’l-kawn wa’l-taklīf), The Treatise on Transcendence in Existence (Al-Risālah al-ulā fi’l-wujūd), On the knowledge of the universal principles of existence (Risālah dar ‘ilm kulliyāt-i wujūd), and Abridgement concerning natural phenomena (Mukhtasar fi’l-Tabi‘iyyāt).
Religious views[edit]
A literal reading of Khayyam’s quatrains leads to the interpretation of his philosophic attitude toward life as a combination of pessimism, nihilism, Epicureanism, fatalism, and agnosticism.[10]: 6 [60] This view is taken by Iranologists such as Arthur Christensen, H. Schaeder, Richard N. Frye, E. D. Ross,[61]: 365 E. H. Whinfield[44]: 40 and George Sarton.[18]: 18 Conversely, the Khayyamic quatrains have also been described as mystical Sufi poetry.[62] In addition to his Persian quatrains, J. C. E. Bowen (1973) mentions that Khayyam’s Arabic poems also «express a pessimistic viewpoint which is entirely consonant with the outlook of the deeply thoughtful rationalist philosopher that Khayyam is known historically to have been.»[63]: 69 Edward FitzGerald emphasized the religious skepticism he found in Khayyam.[64] In his preface to the Rubáiyát he claimed that he «was hated and dreaded by the Sufis»,[65] and denied any pretense at divine allegory: «his Wine is the veritable Juice of the Grape: his Tavern, where it was to be had: his Saki, the Flesh and Blood that poured it out for him.»[66]: 62 Sadegh Hedayat is one of the most notable proponents of Khayyam’s philosophy as agnostic skepticism, and according to Jan Rypka (1934), he even considered Khayyam an atheist.[67] Hedayat (1923) states that «while Khayyam believes in the transmutation and transformation of the human body, he does not believe in a separate soul; if we are lucky, our bodily particles would be used in the making of a jug of wine.»[68] Omar Khayyam’s poetry has been cited in the context of New Atheism, such as in The Portable Atheist by Christopher Hitchens.[69]
Al-Qifti (ca. 1172–1248) appears to confirm this view of Omar’s philosophy.[9]: 663 In his work The History of Learned Men he reports that Omar’s poems were only outwardly in the Sufi style, but were written with an anti-religious agenda.[61]: 365 He also mentions that he was at one point indicted for impiety, but went on a pilgrimage to prove he was pious.[10]: 29 The report has it that upon returning to his native city he concealed his deepest convictions and practised a strictly religious life, going morning and evening to the place of worship.[61]: 355
In the context of a piece entitled On the Knowledge of the Principles of Existence, Khayyam endorses the Sufi path.[10]: 8 Csillik (1960) suggests the possibility that Omar Khayyam could see in Sufism an ally against orthodox religiosity.[70]: 75 Other commentators do not accept that Omar’s poetry has an anti-religious agenda and interpret his references to wine and drunkenness in the conventional metaphorical sense common in Sufism. The French translator J. B. Nicolas held that Omar’s constant exhortations to drink wine should not be taken literally, but should be regarded rather in the light of Sufi thought where rapturous intoxication by «wine» is to be understood as a metaphor for the enlightened state or divine rapture of baqaa.[71] The view of Omar Khayyam as a Sufi was defended by Bjerregaard (1915),[72] Idries Shah (1999),[73] and Dougan (1991) who attributes the reputation of hedonism to the failings of FitzGerald’s translation, arguing that Omar’s poetry is to be understood as «deeply esoteric».[74] On the other hand, Iranian experts such as Mohammad Ali Foroughi and Mojtaba Minovi rejected the hypothesis that Omar Khayyam was a Sufi.[63]: 72 Foroughi stated that Khayyam’s ideas may have been consistent with that of Sufis at times but there is no evidence that he was formally a Sufi. Aminrazavi (2007) states that «Sufi interpretation of Khayyam is possible only by reading into his Rubāʿīyyāt extensively and by stretching the content to fit the classical Sufi doctrine.»[10]: 128 Furthermore, Frye (1975) emphasizes that Khayyam was intensely disliked by a number of celebrated Sufi mystics who belonged to the same century. This includes Shams Tabrizi (spiritual guide of Rumi),[10]: 58 Najm al-Din Daya who described Omar Khayyam as «an unhappy philosopher, atheist, and materialist»,[63]: 71 and Attar who regarded him not as a fellow-mystic but a free-thinking scientist who awaited punishments hereafter.[9]: 663
Seyyed Hossein Nasr argues that it is «reductive» to use a literal interpretation of his verses (many of which are of uncertain authenticity to begin with) to establish Omar Khayyam’s philosophy. Instead, he adduces Khayyam’s interpretive translation of Avicenna’s treatise Discourse on Unity (Al-Khutbat al-Tawhīd), where he expresses orthodox views on Divine Unity in agreement with the author.[75] The prose works believed to be Omar’s are written in the Peripatetic style and are explicitly theistic, dealing with subjects such as the existence of God and theodicy.[10]: 160 As noted by Bowen these works indicate his involvement in the problems of metaphysics rather than in the subtleties of Sufism.[63]: 71 As evidence of Khayyam’s faith and/or conformity to Islamic customs, Aminrazavi mentions that in his treatises he offers salutations and prayers, praising God and Muhammad. In most biographical extracts, he is referred to with religious honorifics such as Imām, The Patron of Faith (Ghīyāth al-Dīn), and The Evidence of Truth (Hujjat al-Haqq).[10] He also notes that biographers who praise his religiosity generally avoid making reference to his poetry, while the ones who mention his poetry often do not praise his religious character.[10]: 48 For instance, Al-Bayhaqi’s account, which antedates by some years other biographical notices, speaks of Omar as a very pious man who professed orthodox views down to his last hour.[76]: 174
On the basis of all the existing textual and biographical evidence, the question remains somewhat open,[10]: 11 and as a result Khayyam has received sharply conflicting appreciations and criticisms.[61]: 350
Reception[edit]
The various biographical extracts referring to Omar Khayyam describe him as unequalled in scientific knowledge and achievement during his time.[77] Many called him by the epithet King of the Wise (Arabic: ملك الحکماء).[54]: 436 [37]: 141 Shahrazuri (d. 1300) esteems him highly as a mathematician, and claims that he may be regarded as «the successor of Avicenna in the various branches of philosophic learning».[61]: 352 Al-Qifti (d. 1248), even though disagreeing with his views, concedes he was «unrivalled in his knowledge of natural philosophy and astronomy».[61]: 355 Despite being hailed as a poet by a number of biographers, according to Richard N. Frye «it is still possible to argue that Khayyam’s status as a poet of the first rank is a comparatively late development.»[9]: 663
Thomas Hyde was the first European to call attention to Omar and to translate one of his quatrains into Latin (Historia religionis veterum Persarum eorumque magorum, 1700).[78]: 525 Western interest in Persia grew with the Orientalism movement in the 19th century. Joseph von Hammer-Purgstall (1774–1856) translated some of Khayyam’s poems into German in 1818, and Gore Ouseley (1770–1844) into English in 1846, but Khayyam remained relatively unknown in the West until after the publication of Edward FitzGerald’s Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam in 1859. FitzGerald’s work at first was unsuccessful but was popularised by Whitley Stokes from 1861 onward, and the work came to be greatly admired by the Pre-Raphaelites. In 1872 FitzGerald had a third edition printed which increased interest in the work in America. By the 1880s, the book was extremely well known throughout the English-speaking world, to the extent of the formation of numerous «Omar Khayyam Clubs» and a «fin de siècle cult of the Rubaiyat».[79] Khayyam’s poems have been translated into many languages; many of the more recent ones are more literal than that of FitzGerald.[80]
FitzGerald’s translation was a factor in rekindling interest in Khayyam as a poet even in his native Iran.[81] Sadegh Hedayat in his Songs of Khayyam (Taranehha-ye Khayyam, 1934) reintroduced Omar’s poetic legacy to modern Iran. Under the Pahlavi dynasty, a new monument of white marble, designed by the architect Houshang Seyhoun, was erected over his tomb. A statue by Abolhassan Sadighi was erected in Laleh Park, Tehran in the 1960s, and a bust by the same sculptor was placed near Khayyam’s mausoleum in Nishapur. In 2009, the state of Iran donated a pavilion to the United Nations Office in Vienna, inaugurated at Vienna International Center.[82] In 2016, three statues of Khayyam were unveiled: one at the University of Oklahoma, one in Nishapur and one in Florence, Italy.[83] Over 150 composers have used the Rubaiyat as their source of inspiration. The earliest such composer was Liza Lehmann.[citation needed]
FitzGerald rendered Omar’s name as «Tentmaker», and the anglicized name of «Omar the Tentmaker» resonated in English-speaking popular culture for a while. Thus, Nathan Haskell Dole published a novel called Omar, the Tentmaker: A Romance of Old Persia in 1898. Omar the Tentmaker of Naishapur is a historical novel by John Smith Clarke, published in 1910. «Omar the Tentmaker» is also the title of a 1914 play by Richard Walton Tully in an oriental setting, adapted as a silent film in 1922. US General Omar Bradley was given the nickname «Omar the Tent-Maker» in World War II.[84]
The Moving Finger quatrain[edit]
The quatrain by Omar Khayyam known as «The Moving Finger», in the form of its translation by the English poet Edward Fitzgerald is one of the most popular quatrains in the Anglosphere.[85] It reads:
The Moving Finger writes; and having writ,
Moves on: nor all your Piety nor Wit
Shall lure it back to cancel half a Line,
Nor all your Tears wash out a Word of it.[86][b]
The title of the novel «The Moving Finger» written by Agatha Christie and published in 1942 was inspired by this quatrain of the translation of Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam by Edward Fitzgerald.[85] Martin Luther King also cites this quatrain of Omar Khayyam in one of his speeches «Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence»:[85][87]
“We may cry out desperately for time to pause in her passage, but time is adamant to every plea and rushes on. Over the bleached bones and jumbled residues of numerous civilizations are written the pathetic words, ‘Too late.’ There is an invisible book of life that faithfully records our vigilance or our neglect. Omar Khayyam is right: ‘The moving finger writes, and having writ moves on.’”
In one of his apologetic speeches about the Clinton–Lewinsky scandal, Bill Clinton, the 42nd president of the US, also cites this quatrain.[85][88]
Other popular culture references[edit]
The French-Lebanese writer Amin Maalouf based the first half of his historical fiction novel Samarkand on Khayyam’s life and the creation of his Rubaiyat. The sculptor Eduardo Chillida produced four massive iron pieces titled Mesa de Omar Khayyam (Omar Khayyam’s Table) in the 1980s.[89][90]
The lunar crater Omar Khayyam was named in his honour in 1970, as was the minor planet 3095 Omarkhayyam discovered by Soviet astronomer Lyudmila Zhuravlyova in 1980.[91]
Google has released two Google Doodles commemorating him. The first was on his 964th birthday on 18 May 2012. The second was on his 971st birthday on 18 May 2019.[92]
Gallery[edit]
-
-
Monument to Omar Khayyam in Ciudad Universitaria of Madrid
See also[edit]
- The Keeper: The Legend of Omar Khayyam
- Nozhat al-Majales
- Omar Khayyam (film)
- Noted Khayyamologists:
- Badiozzaman Forouzanfar
- Abdolhossein Zarrinkoob
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ [oˈmæɾ xæjˈjɒːm];
- ^ … بر لوح نشان بودنیها بودهاست
… پیوسته قلم ز نیک و بد فرسودهاست
… در روز ازل هر آنچه بایست بداد
غم خوردن و کوشیدن ما بیهودهاست
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b c «Omar Khayyam (Persian poet and astronomer)». Britannica.com. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ^ a b Seyyed Hossein Nasr and Mehdi Aminrazavi. An Anthology of Philosophy in Iran, Vol. 1: From Zoroaster to ‘Umar Khayyam, I.B. Tauris in association with The Institute of Ismaili Studies, 2007.
- ^ Dehkhoda, Ali-Akbar. Dehkhoda Dictionary (in Persian). Tehran.
- ^ «Omar Khayyam | Persian poet and astronomer | Britannica». www.britannica.com. Retrieved 15 April 2022.
- ^ Levy, Reuben (2011). The Persian Language (RLE Iran B). Taylor & Francis Group. p. 94. ISBN 9780415608558.
- ^ O’Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., «Omar Khayyam», MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Struik, D. (1958). «Omar Khayyam, mathematician». The Mathematics Teacher, 51(4), 280–285.
- ^ With an error of one day accumulating over 5,000 years, it was more precise than the Gregorian calendar of 1582, which has an error of one day in 3,330 years in the Gregorian calendar (Aminrazavi 2007:200).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4. Cambridge University Press (1975): Richard Nelson Frye
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Mehdi Aminrazavi, The Wine of Wisdom: The Life, Poetry and Philosophy of Omar Khayyam, Oneworld Publications (2007)
- ^ Arberry 2008, p. 16. «Omar composed his shafts of wit and shapes of beauty in his native Persian, which by the tenth century had recovered from the stunning blow dealt it by Arabic.»
- ^ Al-Khalili, Jim (30 September 2010). Pathfinders: The Golden Age of Arabic Science. Penguin UK. ISBN 978-0-14-196501-7.
Later, al-Karkhi, Ibn-Tahir and the great Ibn al-Haytham in the tenth/eleventh century took it further by considering cubic and quartic equations, followed by the Persian mathematician and poet Omar Khayyam in the eleventh century
- ^ Rosenfeld, B. A.; Fouchécour, Ch-H. De (24 April 2012). «ʿUmar K̲h̲ayyam». Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition.
- ^ Peter Avery and John Heath-Stubbs, The Ruba’iyat of Omar Khayyam, (Penguin Group, 1981), 14; «These dates, 1048–1031, tell us that Khayyam lived when the Seljuq Turkish Sultans were extending and consolidating their power over Persia and when the effects of this power were particularly felt in Nishapur, Khayyam’s birthplace.»
- ^ Frye (1975:658); e.g. in Rashid-al-Din Hamadani (Browne 1899:409f) or in Munis al-ahrar (Ross 1927:436).
- ^ a b c d Boyle, J. A., Omar Khayyam: astronomer, mathematician, and poet, Bulletin of the John Rylands Library. 1969; 52(1):30–45.
- ^ E. D. R., & H. A. R. G. (1929). The Earliest Account of ‘Umar Khayyam. Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies, University of London, 5(3), 467–473.
- ^ a b «The Tomb of Omar Khayyâm», George Sarton, Isis, Vol. 29, No. 1 (Jul. 1938), 15.
- ^ a b Edward FitzGerald, Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, Ed. Christopher Decker, (University of Virginia Press, 1997), xv; «The Seljuq Turks had invaded the province of Khorasan in the 1030s, and the city of Nishapur surrendered to them voluntarily in 1038. Thus Omar Khayyam grew to maturity during the first of the several alien dynasties that would rule Iran until the twentieth century.».
- ^ in e.g. Al-Qifti (Aminrazavi 2007:55) or Abu’l-Hasan Bayhaqi. (E. D. R., & H. A. R. G. (1929:436).
- ^ «His own man». The Spectator. 21 November 2007. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- ^ Boris A. Rosenfeld «Umar al-Khayyam» in Helaine Selin, Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures, Springer-Verlag, 2008, p. 2175-2176
- ^ «Omar Khayyam — Biography». Maths History. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ Aminrazavi, Mehdi (2010). «Review of Omar Khayyam: Poet, Rebel, Astronomer». Iranian Studies. 43 (4): 569–571. doi:10.1080/00210862.2010.495592. ISSN 0021-0862. JSTOR 23033230. S2CID 162241136.
- ^ a b c Great Muslim Mathematicians. Penerbit UTM (July 2000): Mohini Mohamed
- ^ (Rozenfeld 1988, pp. 64–65)
- ^ (Katz 1998, p. 270). Excerpt: In some sense, his treatment was better than ibn al-Haytham’s because he explicitly formulated a new postulate to replace Euclid’s rather than have the latter hidden in a new definition.
- ^ Rolwing, R. & Levine, M. (1969). «The Parallel Postulate». The Mathematics Teacher, 62(8), 665–669.
- ^ Smith, David (1935). «Euclid, Omar Khayyam and Saccheri,» Scripta Mathematica.
- ^ a b Cooper, G. (2003). Journal of the American Oriental Society, 123(1), 248–249.
- ^ «Khayyam biography». www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk. Retrieved 13 July 2018.
However, Khayyam himself seems to have been the first to conceive a general theory of cubic equations.
- ^ Howard Eves (1958). «Omar Khayyam’s Solution of Cubic Equations», The Mathematics Teacher (1958), pp. 302–303.
- ^ «Omar Al Hay of Chorassan, about 1079 AD did most to elevate to a method the solution of the algebraic equations by intersecting conics.»
Guilbeau, Lucye (1930), «The History of the Solution of the Cubic Equation», Mathematics News Letter, 5 (4): 8–12, doi:10.2307/3027812, JSTOR 3027812, S2CID 125245433 - ^ Bijan Vahabzadeh,
«Khayyam, Omar xv. As Mathematician», Encyclopædia Iranica. - ^ Netz, R. (1999). «Archimedes Transformed: The Case of a Result Stating a Maximum for a Cubic Equation». Archive for History of Exact Sciences, 54(1), 1–47.
- ^ a b c Deborah A. Kent, & David J. Muraki (2016). «A Geometric Solution of a Cubic by Omar Khayyam … in Which Colored Diagrams Are Used Instead of Letters for the Greater Ease of Learners». The American Mathematical Monthly, 123(2), 149–160.
- ^ a b c d e Kennedy, E. (1958). «Omar Khayyam». The Mathematics Teacher, Vol. 59, No. 2 (1966), pp. 140–142.
- ^ A. R. Amir-Moez, «A Paper of Omar Khayyám», Scripta Mathematica 26 (1963), pp. 323–437
- ^ The Mathematics Teacher, 25(4), 238–241. (1932).
- ^ A. R. Amir-Moez, Khayyam’s Solution of Cubic Equations, Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 35, No. 5 (November 1962), pp. 269–271. This paper contains an extension by the late Mohsen Hashtroodi of Khayyam’s method to degree four equations.
- ^ Waerden, Bartel L. van der (2013). A History of Algebra: From al-Khwārizmī to Emmy Noether. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 29. ISBN 978-3-642-51599-6.
- ^ Sidoli, Nathan; Brummelen, Glen Van (30 October 2013). From Alexandria, Through Baghdad: Surveys and Studies in the Ancient Greek and Medieval Islamic Mathematical Sciences in Honor of J.L. Berggren. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 110. ISBN 978-3-642-36736-6.
- ^ Mathematical Masterpieces: Further Chronicles by the Explorers, p. 92
- ^ a b c E. H. Whinfield, The Quatrains of Omar Khayyam, Psychology Press (2000)
- ^ «Muslim extraction of roots». Mactutor History of Mathematics.
- ^ J. L. Coolidge, The Story of the Binomial Theorem, Amer. Math. Monthly, Vol. 56, No. 3 (Mar. 1949), pp. 147–157
- ^ Susan Nichols, Al-Karaji: Tenth-Century Mathematician and Engineer, 2017. Rosen Publishing. p. 60
- ^ Akrami, Musa (2011). «The development of Iranian calendar: historical and astronomical foundations». arXiv:1111.4926 [physics.hist-ph].
- ^ Panaino, A; Abdollahy, R; Balland, D. «Calendars (In the Islamic period)». Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^ Farrell, Charlotte (1996), «The ninth-century renaissance in astronomy», The Physics Teacher, 34 (5): 268–272, Bibcode:1996PhTea..34..268F, doi:10.1119/1.2344432.
- ^ Heydari-Malayeri, M (2004). «concise review of the Iranian calendar». arXiv:astro-ph/0409620.
- ^ Saliba, G. (2002). Iranian Studies, 35(1/3), 220–225.
- ^ a b c Ali Dashti (translated by L. P. Elwell-Sutton), In Search of Omar Khayyam, Routledge Library Editions: Iran (2012)
- ^ a b Edward Denison Ross, Omar Khayyam, Bulletin of the School Of Oriental Studies London Institution (1927)
- ^ Francois De Blois, Persian Literature – A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (2004), p. 307.
- ^ François De Blois, Persian Literature – A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (2004), p. 305.
- ^ Ambrose George Potter, A Bibliography of the Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam (1929).
- ^ François De Blois, Persian Literature – A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (2004), p. 312.
- ^ a b Nasr, S. H., & Aminrazavi, M. (2007). Anthology of philosophy in Persia: from Zoroaster to Omar Khayyam.[ISBN missing]
- ^ Boscaglia, F. (2015). Pessoa, Borges and Khayyam. Variaciones Borges
- ^ a b c d e f Ross, E. (1898). Al-Musaffariyé: Containing a Recent Contribution to the Study of ‘Omar Khayyām. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 349–366.
- ^ Aminrazavi, Mehdi. «Umar Khayyam». Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ^ a b c d J. C. E. Bowen. (1973). The Rubāՙiyyāt of Omar Khayyam: A Critical Assessment of Robert Graves’ and Omar Ali Shah’s Translation. Iran, 11, 63–73.
- ^ Davis, Dick. «FitzGerald, Edward». Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
- ^ FitzGerald, E. (2010). Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam (p. 12). Champaign, Ill.: Project Gutenberg
- ^ Schenker, D. (1981). Fugitive Articulation: An Introduction to «The Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyam». Victorian Poetry, 19(1), 49–64.
- ^ Hedayat’s «Blind Owl» as a Western Novel. Princeton Legacy Library: Michael Beard
- ^ Katouzian, H. (1991). Sadeq Hedayat: The life and literature of an Iranian writer (p. 138). London: I.B. Tauris
- ^ Hitchens, C. (2007). The portable atheist: Essential readings for the nonbeliever (p. 7). Philadelphia, PA: Da Capo.
- ^ Csillik, B. (1960). «The Real ‘Omar Khayyām'». Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 10(1), 59–77. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/23682646
- ^ Albano, G. (2008). The Benefits of Reading the «Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám» as Pastoral. Victorian Poetry, 46(1), 55–67.
- ^ C. H. A. Bjerregaard, Sufism: Omar Khayyam and E. Fitzgerald, The Sufi Publishing Society (1915), p. 3
- ^ Idries Shah, The Sufis, Octagon Press (1999), pp. 165–166
- ^ «Every line of the Rubaiyat has more meaning than almost anything you could read in Sufi literature» Abdullah Dougan Who is the Potter? Gnostic Press 1991 ISBN 0-473-01064-X
- ^ S. H. Nasr, 2006, Islamic Philosophy from Its Origin to the Present, Chapter 9., pp. 165–183
- ^ Meyerhof, M. (1948). ‘Alī al-Bayhaqī’s Tatimmat Siwān al-Hikma: A Biographical Work on Learned Men of the Islam. Osiris, 8, 122–217.
- ^ e.g. by the author of Firdaws al-tawārikh (Ross 1898:356), author of Tārikh alfī (Ross 1898:358), and al-Isfahani (Aminrazavi 2007:49).
- ^ Beveridge, H. (1905). XVIII. Omar Khayyam. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, 37(3), 521–526.
- ^ J. D. Yohannan, Persian Poetry in England and America, 1977. p. 202.
- ^ The Great Umar Khayyam: A Global Reception of the Rubaiyat (AUP – Leiden University Press) by A. A. Seyed-Gohrab, 2012.
- ^ Simidchieva, M. (2011). FitzGerald’s Rubáiyát and Agnosticism. In A. Poole, C. Van Ruymbeke, & W. Martin (Eds.), FitzGerald’s Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám: Popularity and Neglect (pp. 55–72). Anthem Press.
- ^ UNIS. «Monument to Be Inaugurated at the Vienna International Centre, ‘Scholars Pavilion’ donated to International Organizations in Vienna by Iran».
- ^ «Khayyam statue finally set up at University of Oklahoma». Tehran Times. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- ^ Jeffrey D. Lavoie, The Private Life of General Omar N. Bradley (2015), p. 13.
- ^ a b c d «The Moving Finger: Glimpses into the Life of a Persian Quatrain». www.leidenmedievalistsblog.nl. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ FitzGerald, Stanza LXXI, 4th ed.
- ^ «17. MLK Beyond Vietnam.pdf (hawaii.edu)» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2022.
- ^ «Quatrain 36». exploring khayyaam. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ Omar Khayyam’s Table II Retrieved 8 August 2021.
- ^ Omar Khayyam’s Table III Retrieved 8 August 2021.
- ^ Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. 1979. p. 255. Retrieved 8 September 2012 – via Google Books.
- ^ «How Omar Khayyam changed the way people measure time». The Independent. 17 May 2019. Archived from the original on 24 May 2022. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
Further reading[edit]
- Arberry, Arthur John (2008). Aspects of Islamic Civilization: As Depicted in the Original Texts. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-42600-8.
- Biegstraaten, Jos (2008). «Omar Khayyam (Impact On Literature And Society In The West)». Encyclopaedia Iranica. Vol. 15. Encyclopaedia Iranica Foundation.
- Boyle, J. A., ed. (1968). The Cambridge History of Iran (5): The Saljug and Mongol Periods. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-06936-X.
- Browne, E. (1899). «Yet More Light on ‘Umar-i-Khayyām». Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 409–420. JSTOR 25208104.
- Katz, Victor (1998). A History of Mathematics: An Introduction (2nd ed.). Addison-Wesley. p. 879. ISBN 0-321-01618-1.
- Knoebel, Art; Laubenbacher, Reinhard; Lodder, Jerry (2007). Mathematical Masterpieces: Further Chronicles by the Explorers. Springer. ISBN 978-0387330617.
- Nasr, S. H. (2006). Islamic Philosophy from Its Origin to the Present: Philosophy in the Land of Prophecy. SUNY Press. ISBN 0-7914-6799-6.
- Ross, E. (1927). «Omar Khayyam». Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies, University of London, 4(3), 433–439. JSTOR 606948.
- Rozenfeld, Boris A. (1988). A History of Non-Euclidean Geometry: Evolution of the Concept of a Geometric Space. Springer Verlag. pp. 65, 471. ISBN 0-387-96458-4.
- Rypka, Jan (1968). History of Iranian Literature. Reidel Publishing Company. OCLC 460598. ISBN 90-277-0143-1
- Smith, David Eugene (1935). «Euclid, Omar Khayyâm, and Saccheri». Scripta Mathematica. III (1): 5–10. OCLC 14156259.
- Turner, Howard R. (1997). Science in Medieval Islam: An Illustrated Introduction. University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-78149-0.
External links[edit]
- Works by or about Omar Khayyam at Internet Archive
- Works by Omar Khayyam at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
- Hashemipour, Behnaz (2007). «Khayyām: Ghiyāth al‐Dīn Abū al‐Fatḥ ʿUmar ibn Ibrāhīm al‐Khayyāmī al‐Nīshāpūrī». In Thomas Hockey; et al. (eds.). The Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers. New York: Springer. pp. 627–8. ISBN 978-0-387-31022-0. (PDF version)
- Umar Khayyam, in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- The illustrated Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám at Internet Archive.
|
Hakim Omar Khayyam |
|
|---|---|

Statue of Omar Khayyam by Abolhassan Sadighi |
|
| Born | 18 May[1] 1048[2]
Nishapur, Khorasan, Seljuk Empire |
| Died | 4 December[1] 1131 (aged 83)[2]
Nishapur, Khorasan, Seljuk Empire |
| Academic background | |
| Influences | Avicenna, al-Khwārizmī, Euclid, Apollonius of Perge |
| Academic work | |
| Main interests | Mathematics (medieval Islamic), astronomy, Persian philosophy, Persian poetry |
| Influenced | Tusi, Al-Khazini, Nizami Aruzi of Samarcand, Hafez, Sadegh Hedayat, André Gide, John Wallis, Saccheri, Edward FitzGerald, Maurice Bouchor, Henri Cazalis, Jean Chapelain, Amin Maalouf |
Ghiyāth al-Dīn Abū al-Fatḥ ʿUmar ibn Ibrāhīm Nīsābūrī[3][4] (18 May 1048 – 4 December 1131), commonly known as Omar Khayyam (Persian: عمر خیّام),[a] was a polymath, known for his contributions to mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, and Persian poetry.[5] He was born in Nishapur, the initial capital of the Seljuk Empire. As a scholar, he was contemporary with the rule of the Seljuk dynasty around the time of the First Crusade.
As a mathematician, he is most notable for his work on the classification and solution of cubic equations, where he provided geometric solutions by the intersection of conics.[6] Khayyam also contributed to the understanding of the parallel axiom.[7]: 284 As an astronomer, he calculated the duration of the solar year with remarkable precision and accuracy, and designed the Jalali calendar, a solar calendar with a very precise 33-year intercalation cycle[8][9]: 659 that provided the basis for the Persian calendar that is still in use after nearly a millennium.
There is a tradition of attributing poetry to Omar Khayyam, written in the form of quatrains (rubāʿiyāt رباعیات). This poetry became widely known to the English-reading world in a translation by Edward FitzGerald (Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, 1859), which enjoyed great success in the Orientalism of the fin de siècle.
Life[edit]
Omar Khayyam was born, of Khorasani Persian ancestry, in Nishapur in 1048.[10][11][12][13][14] In medieval Persian texts he is usually simply called Omar Khayyam.[15] Although open to doubt, it has often been assumed that his forebears followed the trade of tent-making, since Khayyam means tent-maker in Arabic.[16]: 30 The historian Bayhaqi, who was personally acquainted with Omar, provides the full details of his horoscope: «he was Gemini, the sun and Mercury being in the ascendant[…]».[17]: 471 This was used by modern scholars to establish his date of birth as 18 May 1048.[9]: 658
Khayyam’s boyhood was spent in Nishapur,[9]: 659 a leading metropolis under the Great Seljuq Empire,[18]: 15 [19] and it had been a major center of the Zoroastrian religion.[10]: 68 His full name, as it appears in the Arabic sources, was Abu’l Fath Omar ibn Ibrahim al-Khayyam.[20] His gifts were recognized by his early tutors who sent him to study under Imam Muwaffaq Nishaburi, the greatest teacher of the Khorasan region who tutored the children of the highest nobility. Omar made a great friendship with him through the years.[10]: 20 Khayyam was also taught by the Zoroastrian mathematician, Abu Hassan Bahmanyar bin Marzban.[21] After studying science, philosophy, mathematics and astronomy at Nishapur, about the year 1068 he traveled to the province of Bukhara, where he frequented the renowned library of the Ark. In about 1070 he moved to Samarkand, where he started to compose his famous treatise on algebra under the patronage of Abu Tahir Abd al-Rahman ibn ʿAlaq, the governor and chief judge of the city.[22] Omar Khayyam was kindly received by the Karakhanid ruler Shams al-Mulk Nasr, who according to Bayhaqi, would «show him the greatest honour, so much so that he would seat [Omar] beside him on his throne».[16]: 34 [10]: 47
In 1073–4 peace was concluded with Sultan Malik-Shah I who had made incursions into Karakhanid dominions. Khayyam entered the service of Malik-Shah in 1074–5 when he was invited by the Grand Vizier Nizam al-Mulk to meet Malik-Shah in the city of Marv. Khayyam was subsequently commissioned to set up an observatory in Isfahan and lead a group of scientists in carrying out precise astronomical observations aimed at the revision of the Persian calendar. The undertaking began probably in 1076 and ended in 1079[10]: 28 when Omar Khayyam and his colleagues concluded their measurements of the length of the year, reporting it as 365.24219858156 days.[23] Given that the length of the year is changing in the sixth decimal place over a person’s lifetime, this is outstandingly accurate. For comparison the length of the year at the end of the 19th century was 365.242196 days, while today it is 365.242190 days.
After the death of Malik-Shah and his vizier (murdered, it is thought, by the Ismaili order of Assassins), Omar fell from favor at court, and as a result, he soon set out on his pilgrimage to Mecca. A possible ulterior motive for his pilgrimage reported by Al-Qifti, was a public demonstration of his faith with a view to allaying suspicions of skepticism and confuting the allegations of unorthodoxy (including possible sympathy or adherence to Zoroastrianism) levelled at him by a hostile clergy.[24][10]: 29 He was then invited by the new Sultan Sanjar to Marv, possibly to work as a court astrologer.[1] He was later allowed to return to Nishapur owing to his declining health. Upon his return, he seems to have lived the life of a recluse.[25]: 99
Omar Khayyam died at the age of 83 in his hometown of Nishapur on 4 December 1131, and he is buried in what is now the Mausoleum of Omar Khayyam. One of his disciples Nizami Aruzi relates the story that sometime during 1112–3 Khayyam was in Balkh in the company of Al-Isfizari (one of the scientists who had collaborated with him on the Jalali calendar) when he made a prophecy that «my tomb shall be in a spot where the north wind may scatter roses over it».[16]: 36 [19] Four years after his death, Aruzi located his tomb in a cemetery in a then large and well-known quarter of Nishapur on the road to Marv. As it had been foreseen by Khayyam, Aruzi found the tomb situated at the foot of a garden-wall over which pear trees and peach trees had thrust their heads and dropped their flowers so that his tombstone was hidden beneath them.[16]
Mathematics[edit]
Khayyam was famous during his life as a mathematician. His surviving mathematical works include: A commentary on the difficulties concerning the postulates of Euclid’s Elements (Risāla fī šarḥ mā aškala min muṣādarāt kitāb Uqlīdis, completed in December 1077),[citation needed] On the division of a quadrant of a circle (Risālah fī qismah rub‘ al-dā’irah, undated but completed prior to the treatise on algebra),[citation needed] and On proofs for problems concerning Algebra (Maqāla fi l-jabr wa l-muqābala, most likely completed in 1079[7]: 281 ). He furthermore wrote a treatise on the binomial theorem and extracting the nth root of natural numbers, which has been lost.[10]: 197
Theory of parallels[edit]
A part of Khayyam’s commentary on Euclid’s Elements deals with the parallel axiom.[7]: 282 The treatise of Khayyam can be considered the first treatment of the axiom not based on petitio principii, but on a more intuitive postulate. Khayyam refutes the previous attempts by other mathematicians to prove the proposition, mainly on grounds that each of them had postulated something that was by no means easier to admit than the Fifth Postulate itself.[citation needed] Drawing upon Aristotle’s views, he rejects the usage of movement in geometry and therefore dismisses the different attempt by Al-Haytham.[26][27] Unsatisfied with the failure of mathematicians to prove Euclid’s statement from his other postulates, Omar tried to connect the axiom with the Fourth Postulate, which states that all right angles are equal to one another.[7]: 282
Khayyam was the first to consider the three distinct cases of acute, obtuse, and right angle for the summit angles of a Khayyam-Saccheri quadrilateral.[7]: 283 After proving a number of theorems about them, he showed that Postulate V follows from the right angle hypothesis, and refuted the obtuse and acute cases as self-contradictory.[citation needed] His elaborate attempt to prove the parallel postulate was significant for the further development of geometry, as it clearly shows the possibility of non-Euclidean geometries. The hypotheses of acute, obtuse, and right angles are now known to lead respectively to the non-Euclidean hyperbolic geometry of Gauss-Bolyai-Lobachevsky, to that of Riemannian geometry, and to Euclidean geometry.[28]
«Cubic equation and intersection of conic sections» the first page of a two-chaptered manuscript kept in Tehran University.
Tusi’s commentaries on Khayyam’s treatment of parallels made its way to Europe. John Wallis, professor of geometry at Oxford, translated Tusi’s commentary into Latin. Jesuit geometer Girolamo Saccheri, whose work (euclides ab omni naevo vindicatus, 1733) is generally considered the first step in the eventual development of non-Euclidean geometry, was familiar with the work of Wallis. The American historian of mathematics David Eugene Smith mentions that Saccheri «used the same lemma as the one of Tusi, even lettering the figure in precisely the same way and using the lemma for the same purpose». He further says that «Tusi distinctly states that it is due to Omar Khayyam, and from the text, it seems clear that the latter was his inspirer.»[25]: 104 [29][10]: 195
The real number concept[edit]
This treatise on Euclid contains another contribution dealing with the theory of proportions and with the compounding of ratios. Khayyam discusses the relationship between the concept of ratio and the concept of number and explicitly raises various theoretical difficulties. In particular, he contributes to the theoretical study of the concept of irrational number.[citation needed] Displeased with Euclid’s definition of equal ratios, he redefined the concept of a number by the use of a continuous fraction as the means of expressing a ratio. Rosenfeld and Youschkevitch (1973) argue that «by placing irrational quantities and numbers on the same operational scale, [Khayyam] began a true revolution in the doctrine of number.» Likewise, it was noted by D. J. Struik that Omar was «on the road to that extension of the number concept which leads to the notion of the real number.»[7]: 284
Geometric algebra[edit]
Omar Khayyam’s construction of a solution to the cubic x3 + 2x = 2x2 + 2. The intersection point produced by the circle and the hyperbola determine the desired segment.
Rashed and Vahabzadeh (2000) have argued that because of his thoroughgoing geometrical approach to algebraic equations, Khayyam can be considered the precursor of Descartes in the invention of analytic geometry.[30]: 248 In The Treatise on the Division of a Quadrant of a Circle Khayyam applied algebra to geometry. In this work, he devoted himself mainly to investigating whether it is possible to divide a circular quadrant into two parts such that the line segments projected from the dividing point to the perpendicular diameters of the circle form a specific ratio. His solution, in turn, employed several curve constructions that led to equations containing cubic and quadratic terms.[30]: 248
The solution of cubic equations[edit]
Khayyam seems to have been the first to conceive a general theory of cubic equations[31] and the first to geometrically solve every type of cubic equation, so far as positive roots are concerned.[32] The treatise on algebra contains his work on cubic equations.[33] It is divided into three parts: (i) equations which can be solved with compass and straight edge, (ii) equations which can be solved by means of conic sections, and (iii) equations which involve the inverse of the unknown.[34]
Khayyam produced an exhaustive list of all possible equations involving lines, squares, and cubes.[35]: 43 He considered three binomial equations, nine trinomial equations, and seven tetranomial equations.[7]: 281 For the first and second degree polynomials, he provided numerical solutions by geometric construction. He concluded that there are fourteen different types of cubics that cannot be reduced to an equation of a lesser degree.[citation needed] For these he could not accomplish the construction of his unknown segment with compass and straight edge. He proceeded to present geometric solutions to all types of cubic equations using the properties of conic sections.[36]: 157 [7]: 281 The prerequisite lemmas for Khayyam’s geometrical proof include Euclid VI, Prop 13, and Apollonius II, Prop 12.[36]: 155 The positive root of a cubic equation was determined as the abscissa of a point of intersection of two conics, for instance, the intersection of two parabolas, or the intersection of a parabola and a circle, etc.[37]: 141 However, he acknowledged that the arithmetic problem of these cubics was still unsolved, adding that «possibly someone else will come to know it after us».[36]: 158 This task remained open until the sixteenth century, where algebraic solution of the cubic equation was found in its generality by Cardano, Del Ferro, and Tartaglia in Renaissance Italy.[7]: 282
Whoever thinks algebra is a trick in obtaining unknowns has thought it in vain. No attention should be paid to the fact that algebra and geometry are different in appearance. Algebras are geometric facts which are proved by propositions five and six of Book two of Elements.
Omar Khayyam[38]
In effect, Khayyam’s work is an effort to unify algebra and geometry.[39]: 241 This particular geometric solution of cubic equations has been further investigated by M. Hachtroudi and extended to solving fourth-degree equations.[40] Although similar methods had appeared sporadically since Menaechmus, and further developed by the 10th-century mathematician Abu al-Jud,[41][42] Khayyam’s work can be considered the first systematic study and the first exact method of solving cubic equations.[43] The mathematician Woepcke (1851) who offered translations of Khayyam’s algebra into French praised him for his «power of generalization and his rigorously systematic procedure.»[44]: 10
Binomial theorem and extraction of roots[edit]
From the Indians one has methods for obtaining square and cube roots, methods based on knowledge of individual cases – namely the knowledge of the squares of the nine digits 12, 22, 32 (etc.) and their respective products, i.e. 2 × 3 etc. We have written a treatise on the proof of the validity of those methods and that they satisfy the conditions. In addition we have increased their types, namely in the form of the determination of the fourth, fifth, sixth roots up to any desired degree. No one preceded us in this and those proofs are purely arithmetic, founded on the arithmetic of The Elements.
Omar Khayyam, Treatise on Demonstration of Problems of Algebra[45]
In his algebraic treatise, Khayyam alludes to a book he had written on the extraction of the 

Astronomy[edit]
Representation of the intercalation scheme of the Jalali calendar
In 1074–5, Omar Khayyam was commissioned by Sultan Malik-Shah to build an observatory at Isfahan and reform the Persian calendar. There was a panel of eight scholars working under the direction of Khayyam to make large-scale astronomical observations and revise the astronomical tables.[37]: 141 Recalibrating the calendar fixed the first day of the year at the exact moment of the passing of the Sun’s center across vernal equinox. This marks the beginning of spring or Nowrūz, a day in which the Sun enters the first degree of Aries before noon.[48]
[49] The resultant calendar was named in Malik-Shah’s honor as the Jalālī calendar, and was inaugurated on 15 March 1079.[50] The observatory itself was disused after the death of Malik-Shah in 1092.[9]: 659
The Jalālī calendar was a true solar calendar where the duration of each month is equal to the time of the passage of the Sun across the corresponding sign of the Zodiac. The calendar reform introduced a unique 33-year intercalation cycle. As indicated by the works of Khazini, Khayyam’s group implemented an intercalation system based on quadrennial and quinquennial leap years. Therefore, the calendar consisted of 25 ordinary years that included 365 days, and 8 leap years that included 366 days.[51] The calendar remained in use across Greater Iran from the 11th to the 20th centuries. In 1911 the Jalali calendar became the official national calendar of Qajar Iran. In 1925 this calendar was simplified and the names of the months were modernized, resulting in the modern Iranian calendar. The Jalali calendar is more accurate than the Gregorian calendar of 1582,[9]: 659 with an error of one day accumulating over 5,000 years, compared to one day every 3,330 years in the Gregorian calendar.[10]: 200
Moritz Cantor considered it the most perfect calendar ever devised.[25]: 101
One of his pupils Nizami Aruzi of Samarcand relates that Khayyam apparently did not have a belief in astrology and divination: «I did not observe that he (scil. Omar Khayyam) had any great belief in astrological predictions, nor have I seen or heard of any of the great [scientists] who had such belief.»[44]: 11 While working for Sultan Sanjar as an astrologer he was asked to predict the weather – a job that he apparently did not do well.[10]: 30 George Saliba (2002) explains that the term ‘ilm al-nujūm, used in various sources in which references to Omar’s life and work could be found, has sometimes been incorrectly translated to mean astrology. He adds: «from at least the middle of the tenth century, according to Farabi’s enumeration of the sciences, that this science, ‘ilm al-nujūm, was already split into two parts, one dealing with astrology and the other with theoretical mathematical astronomy.»[52]: 224
Other works[edit]
He has a short treatise devoted to Archimedes’ principle (in full title, On the Deception of Knowing the Two Quantities of Gold and Silver in a Compound Made of the Two). For a compound of gold adulterated with silver, he describes a method to measure more exactly the weight per capacity of each element. It involves weighing the compound both in air and in water, since weights are easier to measure exactly than volumes. By repeating the same with both gold and silver one finds exactly how much heavier than water gold, silver and the compound were. This treatise was extensively examined by Eilhard Wiedemann who believed that Khayyam’s solution was more accurate and sophisticated than that of Khazini and Al-Nayrizi who also dealt with the subject elsewhere.[10]: 198
Another short treatise is concerned with music theory in which he discusses the connection between music and arithmetic. Khayyam’s contribution was in providing a systematic classification of musical scales, and discussing the mathematical relationship among notes, minor, major and tetrachords.[10]: 198
Poetry[edit]
Rendition of a ruba’i from the Bodleian manuscript, rendered in Shekasteh calligraphy.
The earliest allusion to Omar Khayyam’s poetry is from the historian Imad ad-Din al-Isfahani, a younger contemporary of Khayyam, who explicitly identifies him as both a poet and a scientist (Kharidat al-qasr, 1174).[10]: 49 [53]: 35 One of the earliest specimens of Omar Khayyam’s Rubiyat is from Fakhr al-Din Razi. In his work Al-tanbih ‘ala ba‘d asrar al-maw‘dat fi’l-Qur’an (ca. 1160), he quotes one of his poems (corresponding to quatrain LXII of FitzGerald’s first edition). Daya in his writings (Mirsad al-‘Ibad, ca. 1230) quotes two quatrains, one of which is the same as the one already reported by Razi. An additional quatrain is quoted by the historian Juvayni (Tarikh-i Jahangushay, ca. 1226–1283).[53]: 36–37 [10]: 92 In 1340 Jajarmi includes thirteen quatrains of Khayyam in his work containing an anthology of the works of famous Persian poets (Munis al-ahrār), two of which have hitherto been known from the older sources.[54] A comparatively late manuscript is the Bodleian MS. Ouseley 140, written in Shiraz in 1460, which contains 158 quatrains on 47 folia. The manuscript belonged to William Ouseley (1767–1842) and was purchased by the Bodleian Library in 1844.
There are occasional quotes of verses attributed to Omar in texts attributed to authors of the 13th and 14th centuries, but these are of doubtful authenticity, so that skeptical scholars point out that the entire tradition may be pseudepigraphic.[53]: 11
Hans Heinrich Schaeder in 1934 commented that the name of Omar Khayyam «is to be struck out from the history of Persian literature» due to the lack of any material that could confidently be attributed to him.
De Blois (2004) presents a bibliography of the manuscript tradition, concluding pessimistically that the situation has not changed significantly since Schaeder’s time.[55]
Five of the quatrains later attributed to Omar are found as early as 30 years after his death, quoted in Sindbad-Nameh. While this establishes that these specific verses were in circulation in Omar’s time or shortly later, it doesn’t imply that the verses must be his. De Blois concludes that at the least the process of attributing poetry to Omar Khayyam appears to have begun already in the 13th century.[56] Edward Granville Browne (1906) notes the difficulty of disentangling authentic from spurious quatrains: «while it is certain that Khayyam wrote many quatrains, it is hardly possible, save in a few exceptional cases, to assert positively that he wrote any of those ascribed to him».[9]: 663
In addition to the Persian quatrains, there are twenty-five Arabic poems attributed to Khayyam which are attested by historians such as al-Isfahani, Shahrazuri (Nuzhat al-Arwah, ca. 1201–1211), Qifti (Tārikh al-hukamā, 1255), and Hamdallah Mustawfi (Tarikh-i guzida, 1339).[10]: 39
Boyle and Frye (1975) emphasize that there are a number of other Persian scholars who occasionally wrote quatrains, including Avicenna, Ghazzali, and Tusi. They conclude that it is also possible that for Khayyam poetry was an amusement of his leisure hours: «these brief poems seem often to have been the work of scholars and scientists who composed them, perhaps, in moments of relaxation to edify or amuse the inner circle of their disciples».[9]: 662
The poetry attributed to Omar Khayyam has contributed greatly to his popular fame in the modern period as a direct result of the extreme popularity of the translation of such verses into English by Edward FitzGerald (1859). FitzGerald’s Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam contains loose translations of quatrains from the Bodleian manuscript. It enjoyed such success in the fin de siècle period that a bibliography compiled in 1929 listed more than 300 separate editions,[57] and many more have been published since.[58]
Philosophy[edit]
Khayyam considered himself intellectually to be a student of Avicenna.[59] According to Al-Bayhaqi, he was reading the metaphysics in Avicenna’s the Book of Healing before he died.[9]: 661 There are six philosophical papers believed to have been written by Khayyam. One of them, On existence (Fi’l-wujūd), was written originally in Persian and deals with the subject of existence and its relationship to universals. Another paper, titled The necessity of contradiction in the world, determinism and subsistence (Darurat al-tadād fi’l-‘ālam wa’l-jabr wa’l-baqā’), is written in Arabic and deals with free will and determinism.[59]: 475 The titles of his other works are On being and necessity (Risālah fī’l-kawn wa’l-taklīf), The Treatise on Transcendence in Existence (Al-Risālah al-ulā fi’l-wujūd), On the knowledge of the universal principles of existence (Risālah dar ‘ilm kulliyāt-i wujūd), and Abridgement concerning natural phenomena (Mukhtasar fi’l-Tabi‘iyyāt).
Religious views[edit]
A literal reading of Khayyam’s quatrains leads to the interpretation of his philosophic attitude toward life as a combination of pessimism, nihilism, Epicureanism, fatalism, and agnosticism.[10]: 6 [60] This view is taken by Iranologists such as Arthur Christensen, H. Schaeder, Richard N. Frye, E. D. Ross,[61]: 365 E. H. Whinfield[44]: 40 and George Sarton.[18]: 18 Conversely, the Khayyamic quatrains have also been described as mystical Sufi poetry.[62] In addition to his Persian quatrains, J. C. E. Bowen (1973) mentions that Khayyam’s Arabic poems also «express a pessimistic viewpoint which is entirely consonant with the outlook of the deeply thoughtful rationalist philosopher that Khayyam is known historically to have been.»[63]: 69 Edward FitzGerald emphasized the religious skepticism he found in Khayyam.[64] In his preface to the Rubáiyát he claimed that he «was hated and dreaded by the Sufis»,[65] and denied any pretense at divine allegory: «his Wine is the veritable Juice of the Grape: his Tavern, where it was to be had: his Saki, the Flesh and Blood that poured it out for him.»[66]: 62 Sadegh Hedayat is one of the most notable proponents of Khayyam’s philosophy as agnostic skepticism, and according to Jan Rypka (1934), he even considered Khayyam an atheist.[67] Hedayat (1923) states that «while Khayyam believes in the transmutation and transformation of the human body, he does not believe in a separate soul; if we are lucky, our bodily particles would be used in the making of a jug of wine.»[68] Omar Khayyam’s poetry has been cited in the context of New Atheism, such as in The Portable Atheist by Christopher Hitchens.[69]
Al-Qifti (ca. 1172–1248) appears to confirm this view of Omar’s philosophy.[9]: 663 In his work The History of Learned Men he reports that Omar’s poems were only outwardly in the Sufi style, but were written with an anti-religious agenda.[61]: 365 He also mentions that he was at one point indicted for impiety, but went on a pilgrimage to prove he was pious.[10]: 29 The report has it that upon returning to his native city he concealed his deepest convictions and practised a strictly religious life, going morning and evening to the place of worship.[61]: 355
In the context of a piece entitled On the Knowledge of the Principles of Existence, Khayyam endorses the Sufi path.[10]: 8 Csillik (1960) suggests the possibility that Omar Khayyam could see in Sufism an ally against orthodox religiosity.[70]: 75 Other commentators do not accept that Omar’s poetry has an anti-religious agenda and interpret his references to wine and drunkenness in the conventional metaphorical sense common in Sufism. The French translator J. B. Nicolas held that Omar’s constant exhortations to drink wine should not be taken literally, but should be regarded rather in the light of Sufi thought where rapturous intoxication by «wine» is to be understood as a metaphor for the enlightened state or divine rapture of baqaa.[71] The view of Omar Khayyam as a Sufi was defended by Bjerregaard (1915),[72] Idries Shah (1999),[73] and Dougan (1991) who attributes the reputation of hedonism to the failings of FitzGerald’s translation, arguing that Omar’s poetry is to be understood as «deeply esoteric».[74] On the other hand, Iranian experts such as Mohammad Ali Foroughi and Mojtaba Minovi rejected the hypothesis that Omar Khayyam was a Sufi.[63]: 72 Foroughi stated that Khayyam’s ideas may have been consistent with that of Sufis at times but there is no evidence that he was formally a Sufi. Aminrazavi (2007) states that «Sufi interpretation of Khayyam is possible only by reading into his Rubāʿīyyāt extensively and by stretching the content to fit the classical Sufi doctrine.»[10]: 128 Furthermore, Frye (1975) emphasizes that Khayyam was intensely disliked by a number of celebrated Sufi mystics who belonged to the same century. This includes Shams Tabrizi (spiritual guide of Rumi),[10]: 58 Najm al-Din Daya who described Omar Khayyam as «an unhappy philosopher, atheist, and materialist»,[63]: 71 and Attar who regarded him not as a fellow-mystic but a free-thinking scientist who awaited punishments hereafter.[9]: 663
Seyyed Hossein Nasr argues that it is «reductive» to use a literal interpretation of his verses (many of which are of uncertain authenticity to begin with) to establish Omar Khayyam’s philosophy. Instead, he adduces Khayyam’s interpretive translation of Avicenna’s treatise Discourse on Unity (Al-Khutbat al-Tawhīd), where he expresses orthodox views on Divine Unity in agreement with the author.[75] The prose works believed to be Omar’s are written in the Peripatetic style and are explicitly theistic, dealing with subjects such as the existence of God and theodicy.[10]: 160 As noted by Bowen these works indicate his involvement in the problems of metaphysics rather than in the subtleties of Sufism.[63]: 71 As evidence of Khayyam’s faith and/or conformity to Islamic customs, Aminrazavi mentions that in his treatises he offers salutations and prayers, praising God and Muhammad. In most biographical extracts, he is referred to with religious honorifics such as Imām, The Patron of Faith (Ghīyāth al-Dīn), and The Evidence of Truth (Hujjat al-Haqq).[10] He also notes that biographers who praise his religiosity generally avoid making reference to his poetry, while the ones who mention his poetry often do not praise his religious character.[10]: 48 For instance, Al-Bayhaqi’s account, which antedates by some years other biographical notices, speaks of Omar as a very pious man who professed orthodox views down to his last hour.[76]: 174
On the basis of all the existing textual and biographical evidence, the question remains somewhat open,[10]: 11 and as a result Khayyam has received sharply conflicting appreciations and criticisms.[61]: 350
Reception[edit]
The various biographical extracts referring to Omar Khayyam describe him as unequalled in scientific knowledge and achievement during his time.[77] Many called him by the epithet King of the Wise (Arabic: ملك الحکماء).[54]: 436 [37]: 141 Shahrazuri (d. 1300) esteems him highly as a mathematician, and claims that he may be regarded as «the successor of Avicenna in the various branches of philosophic learning».[61]: 352 Al-Qifti (d. 1248), even though disagreeing with his views, concedes he was «unrivalled in his knowledge of natural philosophy and astronomy».[61]: 355 Despite being hailed as a poet by a number of biographers, according to Richard N. Frye «it is still possible to argue that Khayyam’s status as a poet of the first rank is a comparatively late development.»[9]: 663
Thomas Hyde was the first European to call attention to Omar and to translate one of his quatrains into Latin (Historia religionis veterum Persarum eorumque magorum, 1700).[78]: 525 Western interest in Persia grew with the Orientalism movement in the 19th century. Joseph von Hammer-Purgstall (1774–1856) translated some of Khayyam’s poems into German in 1818, and Gore Ouseley (1770–1844) into English in 1846, but Khayyam remained relatively unknown in the West until after the publication of Edward FitzGerald’s Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam in 1859. FitzGerald’s work at first was unsuccessful but was popularised by Whitley Stokes from 1861 onward, and the work came to be greatly admired by the Pre-Raphaelites. In 1872 FitzGerald had a third edition printed which increased interest in the work in America. By the 1880s, the book was extremely well known throughout the English-speaking world, to the extent of the formation of numerous «Omar Khayyam Clubs» and a «fin de siècle cult of the Rubaiyat».[79] Khayyam’s poems have been translated into many languages; many of the more recent ones are more literal than that of FitzGerald.[80]
FitzGerald’s translation was a factor in rekindling interest in Khayyam as a poet even in his native Iran.[81] Sadegh Hedayat in his Songs of Khayyam (Taranehha-ye Khayyam, 1934) reintroduced Omar’s poetic legacy to modern Iran. Under the Pahlavi dynasty, a new monument of white marble, designed by the architect Houshang Seyhoun, was erected over his tomb. A statue by Abolhassan Sadighi was erected in Laleh Park, Tehran in the 1960s, and a bust by the same sculptor was placed near Khayyam’s mausoleum in Nishapur. In 2009, the state of Iran donated a pavilion to the United Nations Office in Vienna, inaugurated at Vienna International Center.[82] In 2016, three statues of Khayyam were unveiled: one at the University of Oklahoma, one in Nishapur and one in Florence, Italy.[83] Over 150 composers have used the Rubaiyat as their source of inspiration. The earliest such composer was Liza Lehmann.[citation needed]
FitzGerald rendered Omar’s name as «Tentmaker», and the anglicized name of «Omar the Tentmaker» resonated in English-speaking popular culture for a while. Thus, Nathan Haskell Dole published a novel called Omar, the Tentmaker: A Romance of Old Persia in 1898. Omar the Tentmaker of Naishapur is a historical novel by John Smith Clarke, published in 1910. «Omar the Tentmaker» is also the title of a 1914 play by Richard Walton Tully in an oriental setting, adapted as a silent film in 1922. US General Omar Bradley was given the nickname «Omar the Tent-Maker» in World War II.[84]
The Moving Finger quatrain[edit]
The quatrain by Omar Khayyam known as «The Moving Finger», in the form of its translation by the English poet Edward Fitzgerald is one of the most popular quatrains in the Anglosphere.[85] It reads:
The Moving Finger writes; and having writ,
Moves on: nor all your Piety nor Wit
Shall lure it back to cancel half a Line,
Nor all your Tears wash out a Word of it.[86][b]
The title of the novel «The Moving Finger» written by Agatha Christie and published in 1942 was inspired by this quatrain of the translation of Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam by Edward Fitzgerald.[85] Martin Luther King also cites this quatrain of Omar Khayyam in one of his speeches «Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence»:[85][87]
“We may cry out desperately for time to pause in her passage, but time is adamant to every plea and rushes on. Over the bleached bones and jumbled residues of numerous civilizations are written the pathetic words, ‘Too late.’ There is an invisible book of life that faithfully records our vigilance or our neglect. Omar Khayyam is right: ‘The moving finger writes, and having writ moves on.’”
In one of his apologetic speeches about the Clinton–Lewinsky scandal, Bill Clinton, the 42nd president of the US, also cites this quatrain.[85][88]
Other popular culture references[edit]
The French-Lebanese writer Amin Maalouf based the first half of his historical fiction novel Samarkand on Khayyam’s life and the creation of his Rubaiyat. The sculptor Eduardo Chillida produced four massive iron pieces titled Mesa de Omar Khayyam (Omar Khayyam’s Table) in the 1980s.[89][90]
The lunar crater Omar Khayyam was named in his honour in 1970, as was the minor planet 3095 Omarkhayyam discovered by Soviet astronomer Lyudmila Zhuravlyova in 1980.[91]
Google has released two Google Doodles commemorating him. The first was on his 964th birthday on 18 May 2012. The second was on his 971st birthday on 18 May 2019.[92]
Gallery[edit]
-
-
Monument to Omar Khayyam in Ciudad Universitaria of Madrid
See also[edit]
- The Keeper: The Legend of Omar Khayyam
- Nozhat al-Majales
- Omar Khayyam (film)
- Noted Khayyamologists:
- Badiozzaman Forouzanfar
- Abdolhossein Zarrinkoob
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ [oˈmæɾ xæjˈjɒːm];
- ^ … بر لوح نشان بودنیها بودهاست
… پیوسته قلم ز نیک و بد فرسودهاست
… در روز ازل هر آنچه بایست بداد
غم خوردن و کوشیدن ما بیهودهاست
Citations[edit]
- ^ a b c «Omar Khayyam (Persian poet and astronomer)». Britannica.com. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ^ a b Seyyed Hossein Nasr and Mehdi Aminrazavi. An Anthology of Philosophy in Iran, Vol. 1: From Zoroaster to ‘Umar Khayyam, I.B. Tauris in association with The Institute of Ismaili Studies, 2007.
- ^ Dehkhoda, Ali-Akbar. Dehkhoda Dictionary (in Persian). Tehran.
- ^ «Omar Khayyam | Persian poet and astronomer | Britannica». www.britannica.com. Retrieved 15 April 2022.
- ^ Levy, Reuben (2011). The Persian Language (RLE Iran B). Taylor & Francis Group. p. 94. ISBN 9780415608558.
- ^ O’Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., «Omar Khayyam», MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Struik, D. (1958). «Omar Khayyam, mathematician». The Mathematics Teacher, 51(4), 280–285.
- ^ With an error of one day accumulating over 5,000 years, it was more precise than the Gregorian calendar of 1582, which has an error of one day in 3,330 years in the Gregorian calendar (Aminrazavi 2007:200).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4. Cambridge University Press (1975): Richard Nelson Frye
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Mehdi Aminrazavi, The Wine of Wisdom: The Life, Poetry and Philosophy of Omar Khayyam, Oneworld Publications (2007)
- ^ Arberry 2008, p. 16. «Omar composed his shafts of wit and shapes of beauty in his native Persian, which by the tenth century had recovered from the stunning blow dealt it by Arabic.»
- ^ Al-Khalili, Jim (30 September 2010). Pathfinders: The Golden Age of Arabic Science. Penguin UK. ISBN 978-0-14-196501-7.
Later, al-Karkhi, Ibn-Tahir and the great Ibn al-Haytham in the tenth/eleventh century took it further by considering cubic and quartic equations, followed by the Persian mathematician and poet Omar Khayyam in the eleventh century
- ^ Rosenfeld, B. A.; Fouchécour, Ch-H. De (24 April 2012). «ʿUmar K̲h̲ayyam». Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition.
- ^ Peter Avery and John Heath-Stubbs, The Ruba’iyat of Omar Khayyam, (Penguin Group, 1981), 14; «These dates, 1048–1031, tell us that Khayyam lived when the Seljuq Turkish Sultans were extending and consolidating their power over Persia and when the effects of this power were particularly felt in Nishapur, Khayyam’s birthplace.»
- ^ Frye (1975:658); e.g. in Rashid-al-Din Hamadani (Browne 1899:409f) or in Munis al-ahrar (Ross 1927:436).
- ^ a b c d Boyle, J. A., Omar Khayyam: astronomer, mathematician, and poet, Bulletin of the John Rylands Library. 1969; 52(1):30–45.
- ^ E. D. R., & H. A. R. G. (1929). The Earliest Account of ‘Umar Khayyam. Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies, University of London, 5(3), 467–473.
- ^ a b «The Tomb of Omar Khayyâm», George Sarton, Isis, Vol. 29, No. 1 (Jul. 1938), 15.
- ^ a b Edward FitzGerald, Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, Ed. Christopher Decker, (University of Virginia Press, 1997), xv; «The Seljuq Turks had invaded the province of Khorasan in the 1030s, and the city of Nishapur surrendered to them voluntarily in 1038. Thus Omar Khayyam grew to maturity during the first of the several alien dynasties that would rule Iran until the twentieth century.».
- ^ in e.g. Al-Qifti (Aminrazavi 2007:55) or Abu’l-Hasan Bayhaqi. (E. D. R., & H. A. R. G. (1929:436).
- ^ «His own man». The Spectator. 21 November 2007. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- ^ Boris A. Rosenfeld «Umar al-Khayyam» in Helaine Selin, Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures, Springer-Verlag, 2008, p. 2175-2176
- ^ «Omar Khayyam — Biography». Maths History. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ Aminrazavi, Mehdi (2010). «Review of Omar Khayyam: Poet, Rebel, Astronomer». Iranian Studies. 43 (4): 569–571. doi:10.1080/00210862.2010.495592. ISSN 0021-0862. JSTOR 23033230. S2CID 162241136.
- ^ a b c Great Muslim Mathematicians. Penerbit UTM (July 2000): Mohini Mohamed
- ^ (Rozenfeld 1988, pp. 64–65)
- ^ (Katz 1998, p. 270). Excerpt: In some sense, his treatment was better than ibn al-Haytham’s because he explicitly formulated a new postulate to replace Euclid’s rather than have the latter hidden in a new definition.
- ^ Rolwing, R. & Levine, M. (1969). «The Parallel Postulate». The Mathematics Teacher, 62(8), 665–669.
- ^ Smith, David (1935). «Euclid, Omar Khayyam and Saccheri,» Scripta Mathematica.
- ^ a b Cooper, G. (2003). Journal of the American Oriental Society, 123(1), 248–249.
- ^ «Khayyam biography». www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk. Retrieved 13 July 2018.
However, Khayyam himself seems to have been the first to conceive a general theory of cubic equations.
- ^ Howard Eves (1958). «Omar Khayyam’s Solution of Cubic Equations», The Mathematics Teacher (1958), pp. 302–303.
- ^ «Omar Al Hay of Chorassan, about 1079 AD did most to elevate to a method the solution of the algebraic equations by intersecting conics.»
Guilbeau, Lucye (1930), «The History of the Solution of the Cubic Equation», Mathematics News Letter, 5 (4): 8–12, doi:10.2307/3027812, JSTOR 3027812, S2CID 125245433 - ^ Bijan Vahabzadeh,
«Khayyam, Omar xv. As Mathematician», Encyclopædia Iranica. - ^ Netz, R. (1999). «Archimedes Transformed: The Case of a Result Stating a Maximum for a Cubic Equation». Archive for History of Exact Sciences, 54(1), 1–47.
- ^ a b c Deborah A. Kent, & David J. Muraki (2016). «A Geometric Solution of a Cubic by Omar Khayyam … in Which Colored Diagrams Are Used Instead of Letters for the Greater Ease of Learners». The American Mathematical Monthly, 123(2), 149–160.
- ^ a b c d e Kennedy, E. (1958). «Omar Khayyam». The Mathematics Teacher, Vol. 59, No. 2 (1966), pp. 140–142.
- ^ A. R. Amir-Moez, «A Paper of Omar Khayyám», Scripta Mathematica 26 (1963), pp. 323–437
- ^ The Mathematics Teacher, 25(4), 238–241. (1932).
- ^ A. R. Amir-Moez, Khayyam’s Solution of Cubic Equations, Mathematics Magazine, Vol. 35, No. 5 (November 1962), pp. 269–271. This paper contains an extension by the late Mohsen Hashtroodi of Khayyam’s method to degree four equations.
- ^ Waerden, Bartel L. van der (2013). A History of Algebra: From al-Khwārizmī to Emmy Noether. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 29. ISBN 978-3-642-51599-6.
- ^ Sidoli, Nathan; Brummelen, Glen Van (30 October 2013). From Alexandria, Through Baghdad: Surveys and Studies in the Ancient Greek and Medieval Islamic Mathematical Sciences in Honor of J.L. Berggren. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 110. ISBN 978-3-642-36736-6.
- ^ Mathematical Masterpieces: Further Chronicles by the Explorers, p. 92
- ^ a b c E. H. Whinfield, The Quatrains of Omar Khayyam, Psychology Press (2000)
- ^ «Muslim extraction of roots». Mactutor History of Mathematics.
- ^ J. L. Coolidge, The Story of the Binomial Theorem, Amer. Math. Monthly, Vol. 56, No. 3 (Mar. 1949), pp. 147–157
- ^ Susan Nichols, Al-Karaji: Tenth-Century Mathematician and Engineer, 2017. Rosen Publishing. p. 60
- ^ Akrami, Musa (2011). «The development of Iranian calendar: historical and astronomical foundations». arXiv:1111.4926 [physics.hist-ph].
- ^ Panaino, A; Abdollahy, R; Balland, D. «Calendars (In the Islamic period)». Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^ Farrell, Charlotte (1996), «The ninth-century renaissance in astronomy», The Physics Teacher, 34 (5): 268–272, Bibcode:1996PhTea..34..268F, doi:10.1119/1.2344432.
- ^ Heydari-Malayeri, M (2004). «concise review of the Iranian calendar». arXiv:astro-ph/0409620.
- ^ Saliba, G. (2002). Iranian Studies, 35(1/3), 220–225.
- ^ a b c Ali Dashti (translated by L. P. Elwell-Sutton), In Search of Omar Khayyam, Routledge Library Editions: Iran (2012)
- ^ a b Edward Denison Ross, Omar Khayyam, Bulletin of the School Of Oriental Studies London Institution (1927)
- ^ Francois De Blois, Persian Literature – A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (2004), p. 307.
- ^ François De Blois, Persian Literature – A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (2004), p. 305.
- ^ Ambrose George Potter, A Bibliography of the Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam (1929).
- ^ François De Blois, Persian Literature – A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (2004), p. 312.
- ^ a b Nasr, S. H., & Aminrazavi, M. (2007). Anthology of philosophy in Persia: from Zoroaster to Omar Khayyam.[ISBN missing]
- ^ Boscaglia, F. (2015). Pessoa, Borges and Khayyam. Variaciones Borges
- ^ a b c d e f Ross, E. (1898). Al-Musaffariyé: Containing a Recent Contribution to the Study of ‘Omar Khayyām. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 349–366.
- ^ Aminrazavi, Mehdi. «Umar Khayyam». Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ^ a b c d J. C. E. Bowen. (1973). The Rubāՙiyyāt of Omar Khayyam: A Critical Assessment of Robert Graves’ and Omar Ali Shah’s Translation. Iran, 11, 63–73.
- ^ Davis, Dick. «FitzGerald, Edward». Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
- ^ FitzGerald, E. (2010). Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam (p. 12). Champaign, Ill.: Project Gutenberg
- ^ Schenker, D. (1981). Fugitive Articulation: An Introduction to «The Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyam». Victorian Poetry, 19(1), 49–64.
- ^ Hedayat’s «Blind Owl» as a Western Novel. Princeton Legacy Library: Michael Beard
- ^ Katouzian, H. (1991). Sadeq Hedayat: The life and literature of an Iranian writer (p. 138). London: I.B. Tauris
- ^ Hitchens, C. (2007). The portable atheist: Essential readings for the nonbeliever (p. 7). Philadelphia, PA: Da Capo.
- ^ Csillik, B. (1960). «The Real ‘Omar Khayyām'». Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, 10(1), 59–77. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/23682646
- ^ Albano, G. (2008). The Benefits of Reading the «Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám» as Pastoral. Victorian Poetry, 46(1), 55–67.
- ^ C. H. A. Bjerregaard, Sufism: Omar Khayyam and E. Fitzgerald, The Sufi Publishing Society (1915), p. 3
- ^ Idries Shah, The Sufis, Octagon Press (1999), pp. 165–166
- ^ «Every line of the Rubaiyat has more meaning than almost anything you could read in Sufi literature» Abdullah Dougan Who is the Potter? Gnostic Press 1991 ISBN 0-473-01064-X
- ^ S. H. Nasr, 2006, Islamic Philosophy from Its Origin to the Present, Chapter 9., pp. 165–183
- ^ Meyerhof, M. (1948). ‘Alī al-Bayhaqī’s Tatimmat Siwān al-Hikma: A Biographical Work on Learned Men of the Islam. Osiris, 8, 122–217.
- ^ e.g. by the author of Firdaws al-tawārikh (Ross 1898:356), author of Tārikh alfī (Ross 1898:358), and al-Isfahani (Aminrazavi 2007:49).
- ^ Beveridge, H. (1905). XVIII. Omar Khayyam. Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, 37(3), 521–526.
- ^ J. D. Yohannan, Persian Poetry in England and America, 1977. p. 202.
- ^ The Great Umar Khayyam: A Global Reception of the Rubaiyat (AUP – Leiden University Press) by A. A. Seyed-Gohrab, 2012.
- ^ Simidchieva, M. (2011). FitzGerald’s Rubáiyát and Agnosticism. In A. Poole, C. Van Ruymbeke, & W. Martin (Eds.), FitzGerald’s Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám: Popularity and Neglect (pp. 55–72). Anthem Press.
- ^ UNIS. «Monument to Be Inaugurated at the Vienna International Centre, ‘Scholars Pavilion’ donated to International Organizations in Vienna by Iran».
- ^ «Khayyam statue finally set up at University of Oklahoma». Tehran Times. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- ^ Jeffrey D. Lavoie, The Private Life of General Omar N. Bradley (2015), p. 13.
- ^ a b c d «The Moving Finger: Glimpses into the Life of a Persian Quatrain». www.leidenmedievalistsblog.nl. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ FitzGerald, Stanza LXXI, 4th ed.
- ^ «17. MLK Beyond Vietnam.pdf (hawaii.edu)» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2022.
- ^ «Quatrain 36». exploring khayyaam. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ Omar Khayyam’s Table II Retrieved 8 August 2021.
- ^ Omar Khayyam’s Table III Retrieved 8 August 2021.
- ^ Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. 1979. p. 255. Retrieved 8 September 2012 – via Google Books.
- ^ «How Omar Khayyam changed the way people measure time». The Independent. 17 May 2019. Archived from the original on 24 May 2022. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
Further reading[edit]
- Arberry, Arthur John (2008). Aspects of Islamic Civilization: As Depicted in the Original Texts. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-42600-8.
- Biegstraaten, Jos (2008). «Omar Khayyam (Impact On Literature And Society In The West)». Encyclopaedia Iranica. Vol. 15. Encyclopaedia Iranica Foundation.
- Boyle, J. A., ed. (1968). The Cambridge History of Iran (5): The Saljug and Mongol Periods. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-06936-X.
- Browne, E. (1899). «Yet More Light on ‘Umar-i-Khayyām». Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, 409–420. JSTOR 25208104.
- Katz, Victor (1998). A History of Mathematics: An Introduction (2nd ed.). Addison-Wesley. p. 879. ISBN 0-321-01618-1.
- Knoebel, Art; Laubenbacher, Reinhard; Lodder, Jerry (2007). Mathematical Masterpieces: Further Chronicles by the Explorers. Springer. ISBN 978-0387330617.
- Nasr, S. H. (2006). Islamic Philosophy from Its Origin to the Present: Philosophy in the Land of Prophecy. SUNY Press. ISBN 0-7914-6799-6.
- Ross, E. (1927). «Omar Khayyam». Bulletin of the School of Oriental Studies, University of London, 4(3), 433–439. JSTOR 606948.
- Rozenfeld, Boris A. (1988). A History of Non-Euclidean Geometry: Evolution of the Concept of a Geometric Space. Springer Verlag. pp. 65, 471. ISBN 0-387-96458-4.
- Rypka, Jan (1968). History of Iranian Literature. Reidel Publishing Company. OCLC 460598. ISBN 90-277-0143-1
- Smith, David Eugene (1935). «Euclid, Omar Khayyâm, and Saccheri». Scripta Mathematica. III (1): 5–10. OCLC 14156259.
- Turner, Howard R. (1997). Science in Medieval Islam: An Illustrated Introduction. University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-78149-0.
External links[edit]
- Works by or about Omar Khayyam at Internet Archive
- Works by Omar Khayyam at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
- Hashemipour, Behnaz (2007). «Khayyām: Ghiyāth al‐Dīn Abū al‐Fatḥ ʿUmar ibn Ibrāhīm al‐Khayyāmī al‐Nīshāpūrī». In Thomas Hockey; et al. (eds.). The Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers. New York: Springer. pp. 627–8. ISBN 978-0-387-31022-0. (PDF version)
- Umar Khayyam, in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
- The illustrated Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám at Internet Archive.
| Омар Хайям | |
| перс.عُمَر خَیّام نیشابوری | |
 Памятник Омару Хайяму в Бухаресте, Румыния |
|
| руководитель исфаханской обсерватории 1076 — 1092 |
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Личная информация | |
| Имя при рождении: |
Омар ибн Ибрахим Нишапури |
| Прозвище: |
Гиясаддин |
| Профессия, род деятельности: |
математик, астроном, поэт, писатель, философ, музыкант, астролог |
| Дата рождения: |
18 мая 1048 |
| Место рождения: |
Нишапур, Центральный бакхш[d], Нишапур[d], Хорасан-Резави, Иран |
| Дата смерти: |
4 декабря 1131 (83 года) |
| Место смерти: |
Нишапур, Центральный бакхш[d], Нишапур[d], Хорасан-Резави, Иран |
| Страна: |
Сельджукская империя |
| Вероисповедание: |
ислам и суннизм |
| Отец: |
Ибрахим Нишапури |
|
Научная деятельность |
|
| Направление деятельности: |
поэзия, математика и астрономия |
| Работодатель: |
Нишапур |
| Ученики: |
Музаффар аль-Асфизари и Абдуррахман аль-Хазини |
|
Дополнительная информация |
|
| Родственные проекты: |
|
Ома́р Хайя́м Нишапури́ (перс. عُمَر خَیّام نیشابوری; 18 мая 1048, Нишапур — 4 декабря 1131[1], там же) — персидский философ, математик, астроном и поэт[2].
Внёс вклад в алгебру построением классификации кубических уравнений и их решением с помощью конических сечений. Известен во всём мире как выдающийся философ и поэт. В Иране и Афганистане Омар Хайям также известен созданием самого точного из ныне используемых календарей[3]. Учениками Хайяма были такие учёные, как Музаффар аль-Асфизари и Абдуррахман аль-Хазини.
Содержание
- 1 Имя
- 2 Биография
- 3 Научная деятельность
- 3.1 Математика
- 3.2 Астрономия
- 4 Рубаи
- 5 Высказывания Хайяма
- 6 Память о Хайяме
- 7 Издания рубаи
- 8 См. также
- 9 Примечания
- 10 Литература
- 10.1 Математические, естественнонаучные и философские трактаты
- 10.2 О нём
- 11 Ссылки
Имя[править | править вики-текст]
Гийясадди́н Абу-ль-Фатх Ома́р ибн Ибрахим аль-Хайя́м Нишапури́
- غیاث الدین Гийяс ад-Дин — хитаб, «Помощь религии».
- ابوالفتح Абу-ль-Фатх — кунья, «отец Фатха» (у него не было сына по имени «Фатх»).
- عمر Омар — исм (личное имя).
- بن ابراهیم ибн Ибрахим — насаб, «сын Ибрахима».
- خیام Хайям — тахаллус, «палаточный мастер» (предположительно, указание на ремесло отца; от слова «хайма» — палатка, от этого же слова предположительно происходит старорусское «хамовник» — текстильщик).
- نیشابورﻯ Нишапури — нисба, «из Нишапура».
Биография[править | править вики-текст]
Родился в городе Нишапур, который находится в Хорасане (ныне иранская провинция Хорасан-Резави). Омар был сыном палаточника, также у него была младшая сестра по имени Аиша. В 8 лет начал глубоко заниматься математикой, астрономией, философией. В 12 лет Омар стал учеником Нишапурского медресе. Позднее обучался в медресе Балха, Самарканда и Бухары. Там он с отличием закончил курс по мусульманскому праву и медицине, получив квалификацию хаки́ма, то есть врача[4]. Но медицинская практика его мало интересовала. Изучал сочинения известного математика и астронома Сабита ибн Курры, труды греческих математиков.
Детство Хайяма пришлось на жестокий период сельджукского завоевания Центральной Азии. Погибло множество людей, в том числе значительная часть учёных. Позже в предисловии к своей «Алгебре» Хайям напишет горькие слова:
Мы были свидетелями гибели учёных, от которых осталась небольшая многострадальная кучка людей. Суровость судьбы в эти времена препятствует им всецело отдаться совершенствованию и углублению своей науки. Большая часть тех, которые в настоящее время имеют вид учёных, одевают истину ложью, не выходя в науке за пределы подделки и лицемерия. И если они встречают человека, отличающегося тем, что он ищет истину и любит правду, старается отвергнуть ложь и лицемерие и отказаться от хвастовства и обмана, они делают его предметом своего презрения и насмешек.
Картина «На могиле Омара Хайяма»
В возрасте шестнадцати лет Хайям пережил первую в своей жизни утрату: во время эпидемии умер его отец, а потом и мать. Омар продал отцовский дом и мастерскую и отправился в Самарканд. В то время это был признанный на Востоке научный и культурный центр. В Самарканде Хайям становится вначале учеником одного из медресе, но после нескольких выступлений на диспутах он настолько поразил всех своей учёностью, что его сразу же сделали наставником.
Как и другие крупные учёные того времени, Омар не задерживался подолгу в каком-то городе. Всего через четыре года он покинул Самарканд и переехал в Бухару, где начал работать в хранилищах книг. За десять лет, что учёный прожил в Бухаре, он написал четыре фундаментальных трактата по математике.
В 1074 году его пригласили в Исфахан, центр государства Санджаров, ко двору сельджукского султана Мелик-шаха I. По инициативе и при покровительстве главного шахского визиря Низам аль-Мулька Омар становится духовным наставником султана. Через два года Мелик-шах назначил его руководителем дворцовой обсерватории, одной из крупнейших в мире[5]. Работая на этой должности, Омар Хайям не только продолжал занятия математикой, но и стал известным астрономом. С группой учёных он разработал солнечный календарь, более точный, чем григорианский. Составил «Маликшахские астрономические таблицы», включавшие небольшой звездный каталог[6]. Здесь же написал «Комментарии к трудностям во введениях книги Евклида» (1077 г.) из трёх книг; во второй и третьей книгах исследовал теорию отношений и учение о числе[2]. Однако в 1092 году, со смертью покровительствовавшего ему султана Мелик-шаха и визиря Низам ал-Мулька, исфаханский период его жизни заканчивается. Обвинённый в безбожном вольнодумстве, поэт вынужден покинуть сельджукскую столицу.
О последних часах жизни Хайяма известно со слов его младшего современника — Бейхаки, ссылающегося на слова зятя поэта.
Однажды во время чтения «Книги об исцелении» Абу Али ибн Сины Хайям почувствовал приближение смерти (а было тогда ему уже за восемьдесят). Остановился он в чтении на разделе, посвященном труднейшему метафизическому вопросу и озаглавленному «Единое во множественном», заложил между листов золотую зубочистку, которую держал в руке, и закрыл фолиант. Затем он позвал своих близких и учеников, составил завещание и после этого уже не принимал ни пищи, ни питья. Исполнив молитву на сон грядущий, он положил земной поклон и, стоя на коленях, произнёс: «Боже! По мере своих сил я старался познать Тебя. Прости меня! Поскольку я познал Тебя, постольку я к Тебе приблизился». С этими словами на устах Хайям и умер.
Свидетельство о последних годах жизни поэта, оставленное автором «Четырёх бесед»
В году 1113 в Балхе, на улице Работорговцев, в доме Абу Саида Джарре остановились ходжа имам Омар Хайям и ходжа имам Музаффар Исфизари, а я присоединился к услужению им. Во время пира я услышал, как Доказательство Истины Омар сказал: «Могила моя будет расположена в таком месте, где каждую весну ветерок будет осыпать меня цветами». Меня эти слова удивили, но я знал, что такой человек не станет говорить пустых слов. Когда в 1136 я приехал в Нишапур, прошло уже четыре года с тех пор, как тот великий закрыл своё лицо покрывалом земли, и низкий мир осиротел без него. И для меня он был наставником. В пятницу я пошел поклониться его праху взял с собой одного человека, чтобы он указал мне его могилу. Он привел меня на кладбище Хайре, повернул налево у подножия стены, огораживающей сад, и я увидел его могилу. Грушевые и абрикосовые деревья свесились из этого сада и, распростерши над могилой цветущие ветви, всю могилу его скрывали под цветами. И пришли мне на память те слова, что я слышал от него в Балхе, и я разрыдался, ибо на всей поверхности земли и в странах Обитаемой четверти я не увидел бы для него более подходящего места. Бог, Святой и Всевышний, да уготовит ему место в райских кущах милостью своей и щедростью!
Научная деятельность[править | править вики-текст]
Математика[править | править вики-текст]
Хайяму принадлежит «Трактат о доказательствах задач алгебры и алмукабалы», в котором даётся классификация уравнений и излагается решение уравнений 1-й, 2-й и 3-й степени[7]. В первых главах трактата Хайям излагает алгебраический метод решения квадратных уравнений, описанный ещё ал-Хорезми. В следующих главах он развивает геометрический метод решения кубических уравнений, восходящий к Архимеду: корни данных уравнений в этом методе определялись как общие точки пересечения двух подходящих конических сечений[8]. Хайям привёл обоснование этого метода, классификацию типов уравнений, алгоритм выбора типа конического сечения, оценку числа (положительных) корней и их величины. К сожалению, Хайям не заметил, что кубическое уравнение может иметь три положительных действительных корня. До явных алгебраических формул Кардано Хайяму дойти не удалось, но он высказал надежду, что явное решение будет найдено в будущем.
Во введении к данному трактату Омар Хайям даёт первое дошедшее до нас определение алгебры как науки, утверждая: алгебра — это наука об определении неизвестных величин, состоящих в некоторых отношениях с величинами известными, причём такое определение осуществляется с помощью составления и решения уравнений[7].
В 1077 г. Хайям закончил работу над важным математическим трудом — «Комментарии к трудностям во введениях книги Евклида». Трактат состоял из трёх книг; первая содержала оригинальную теорию параллельных прямых, вторая и третья посвящены усовершенствованию теории отношений и пропорций[5]. В первой книге Хайям пытается доказать V постулат Евклида и заменяет его более простым и очевидным эквивалентом: Две сходящиеся прямые должны пересечься; по сути, в ходе этих попыток Омар Хайям доказал первые теоремы геометрий Лобачевского и Римана[2].
Далее Хайям рассматривает в своём трактате иррациональные числа как вполне законные, определяя равенство двух отношений как последовательное равенство всех подходящих частных в алгоритме Евклида. Евклидову теорию пропорций он заменил численной теорией[8].
При этом в третьей книге «Комментариев», посвящённой составлению (то есть умножению) отношений, Хайям по-новому трактует связь понятий отношения и числа. Рассматривая отношение двух непрерывных геометрических величин A и B, он рассуждает так: «Выберем единицу и сделаем её отношение к величине G равным отношению A к B, и будем смотреть на величину G как на линию, поверхность, тело или время; но будем смотреть на неё как на величину, отвлечённую разумом от всего этого и принадлежащую к числам, но не к числам абсолютным и настоящим[9], так как отношение A к B часто может не быть числовым… Следует, что бы ты знал, что эта единица является делимой и величина G, являющаяся произвольной величиной, рассматривается как число в указанном выше смысле»[10]. Высказавшись за введение в математику делимой единицы и нового рода чисел, Хайям теоретически обосновал расширение понятия числа до положительного действительного числа[11][8].
Ещё одна математическая работа Хайяма — «Об искусстве определения количества золота и серебра в состоящем из них теле»[2] — посвящена классической задаче на смешение, впервые решённой ещё Архимедом[12].
Астрономия[править | править вики-текст]
Хайям возглавлял группу астрономов Исфахана, которая в правление сельджукского султана Джалал ад-Дина Малик-шаха разработала принципиально новый солнечный календарь. Он был принят официально в 1079 г. Основным предназначением этого календаря была как можно более строгая привязка Новруза (то есть начала года) к весеннему равноденствию, понимаемому как вхождение солнца в зодиакальное созвездие Овна[13]. Так, 1 фарвардина (Новруз) 468 солнечного года хиджры, в которое был принят календарь, соответствовало пятнице, 9 рамазана 417 лунного года хиджры, и 19 фарвардина 448 года эры Йездигерда (15 марта 1079 г.). Для отличия от зороастрийского солнечного года, называвшегося «древним»[14] или «персидским»[15] , новый календарь стали называть по имени султана — «Джалали»[16] или «Малеки»[17]. Количество дней в месяцах календаря «Джалали» варьировало в зависимости от сроков вступления солнца в тот или иной зодиакальный знак и могло колебаться от 29 до 32 дней[18]. Были предложены и новые названия месяцев, а также дней каждого месяца по образцу зороастрийского календаря. Однако они не прижились, и месяцы стали именоваться в общем случае именем соответствующего знака зодиака[19].
С чисто астрономической точки зрения календарь «Джалали» был точнее, чем древнеримский юлианский календарь, применявшийся в современной Хайяму Европе, и точнее, чем позднейший европейский григорианский календарь. Вместо цикла «1 високосный на 4 года» (юлианский календарь) или «97 високосных на 400 лет» (григорианский календарь) Хайямом принято было соотношение «8 високосных на 33 года». Другими словами, из каждых 33-х лет 8 были високосными и 25 обычными. Этот календарь точнее всех других известных соответствует году весенних равноденствий. Проект Омара Хайяма был утверждён и лёг в основу иранского календаря, который вплоть до настоящего времени действует в Иране в качестве официального с 1079 года[20][18].
Хайям составил «Маликшахов зидж», включающий звёздный каталог 100 ярких звёзд и посвященный сельджукскому султану Маликшаху ибн Алп Арслану. Наблюдения зиджа датированы 1079 годом («на начало [первого] года високоса малики»); рукопись не сохранилась, но существуют списки с неё. [21]
Рубаи[править | править вики-текст]
Основная статья: Рубаи
При жизни Хайям был известен исключительно как выдающийся учёный. На протяжении всей жизни он писал стихотворные афоризмы (рубаи), в которых высказывал свои сокровенные мысли о жизни, о человеке, о его знании. С годами количество приписываемых Хайяму четверостиший росло в геометрической прогрессии и к XX веку превысило 5000. Очевидно, свои сочинения приписывали Хайяму все те, кто опасался преследований за вольнодумство и богохульство. Точно установить, какие из них действительно принадлежат Хайяму (если он вообще сочинял стихи), практически невозможно. Некоторые исследователи считают возможным авторство Хайяма в отношении 300—500 рубаи[22].
Долгое время Омар Хайям был забыт. По счастливой случайности тетрадь с его стихами попала в викторианскую эпоху в руки английского поэта Эдварда Фицджеральда, который перевёл многие рубаи сначала на латынь, а потом на английский. В начале XX века рубаи в весьма вольном и оригинальном переложении Фицджеральда стали едва ли не самым популярным произведением викторианской поэзии[23]. Всемирная известность Омара Хайяма как глашатая гедонизма, отрицающего посмертное воздаяние, пробудила интерес и к его научным достижениям, которые были открыты заново и переосознаны.
Высказывания Хайяма[править | править вики-текст]
«О небо, к подлецам щедра твоя рука: / Им — бани, мельницы и воды арыка́; / А кто душою чист, тому лишь корка хлеба. / Такое небо — тьфу! — не стоит и плевка».
Память о Хайяме[править | править вики-текст]
Хотя прижизненных изображений Омара Хайяма не сохранилось и его облик неизвестен, памятники поэту были установлены во многих персоязычных странах и за их пределами (например, в Душанбе, Ашхабаде, Бухаресте). В 1935 году азербайджанский писатель Гусейн Джавид написал пьесу «Хайям», посвящённую Омару Хайяму.
-
Рубаи Омара Хайяма на Моричу Хани в Сараево
-
Рубаи Омара Хайяма
-
Изображение Омара Хайяма
-
Памятник в Иране
-
Планетарий имени Омара Хайяма в Нишапуре
- В 1970 г. Международный астрономический союз присвоил имя Омара Хайяма кратеру на обратной стороне Луны.
Издания рубаи[править | править вики-текст]
Первым стал переводить Омара Хайяма на русский язык В. Л. Величко (1891)[24]. Хрестоматийный перевод рубаи на русский язык (1910) выполнил Константин Бальмонт. Некоторые русскоязычные издания рубаи:
- Омар Хайям. Рубайят. Перевёл с таджикского-фарси: Владимир Державин. Издательство «ИРФОН», Душанбе, 1965 г.
- Омар Хайям. Рубаи. — Ташкент, изд. ЦК КП Узбекистана, 1978. — 104 с., 200 000 экз.
- Омар Хайям. Рубаи: Пер. с перс.-тадж. / Вступ. ст. З. Н. Ворожейкиной и А. Ш. Шахвердова; Сост. и примеч. А. Ш. Шахвердова. — Л.: Сов. писатель, 1986. — 320 с. Тираж 100 000 экз. (Библиотека поэта. Большая серия. Издание третье).
- Омар Хайям. Рубаи. Перевод С. Северцева — в: Великое Древо. Поэты Востока. М., 1984, с. 282—284.
- Омар Хайям: Рубайят. Сопоставление переводов. / Малкович Р.Ш.. — СПб.: Издательство РХГА, 2012. — 696 с. — 500 экз. — ISBN 978-5-88812-542-7.
См. также[править | править вики-текст]
- Хамрийят
Примечания[править | править вики-текст]
- ↑ Amin Maalouf, «Samarkand.». Иногда указываются и другие даты.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Боголюбов, 1983, с. 501.
- ↑ Климишин И. А. Календарь и хронология. — Изд. 3. — М.: Наука, 1990. — С. 38—39. — 478 с. — ISBN 5-02-014354-5.
- ↑ НЭУ, 2000—2005, Умар Ҳайём.
- ↑ 1 2 Глезер, 1982, с. 121.
- ↑ Звездный каталог ал-Бируни с приложением каталогов Хайама и ат-Туси. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.. // Историко-астрономические исследования. Вып. VIII. 1962. С.83-192.
- ↑ 1 2 Глезер, 1982, с. 120.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Стройк, 1984, с. 97.
- ↑ То есть к натуральным числам.
- ↑ Омар Хайям. Математические трактаты / Пер. Б. А. Розенфельда // Историко-математические исследования. Вып. VI. 1952. — С. 105—106.
- ↑ Глезер, 1982, с. 124.
- ↑ Глезер, 1982, с. 121—122.
- ↑ согласно Naṣīr-al-Dīn Ṭūsī. Zīj-e īl-ḵānī
- ↑ qadīmī (перс. قديمى — «древний»)
- ↑ fārsī (перс. فارسى — «персидский»)
- ↑ jalālī (перс. جلالی)
- ↑ malekī (перс. ملکی)
- ↑ 1 2 Климишин И. А. Календарь и хронология. — М.: Наука, 1981. — 192 с.
- ↑ В фарси имена знаков Зодиака представляют собой заимствования из арабского языка
- ↑ Heydari-Malayeri M. A concise review of the Iranian calendar. Paris Observatory, 2006.
- ↑ Хаййам Омар. Трактаты. Перевод Б. А. Розенфельда. Редакция В. С. Сегаля и А. П. Юшкевича. Статья и комментарии Б. А. Розенфельда и А. П. Юшкевича. М., 1962.
- ↑ http://books.google.ru/books?id=nKUqLLDtz_cC&pg=PP6
- ↑ BBC Radio 4 — In Our Time, The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam
- ↑ Знакомство с творческим наследием Омара Хайяма в России | ИноСМИ — Все, что достойно перевода
Литература[править | править вики-текст]
- Умар Ҳайём — Национальная энциклопедия Узбекистана. — Ташкент, 2000—2005. (узб.)
Математические, естественнонаучные и философские трактаты[править | править вики-текст]
- Хайям Омар. О доказательстве задач алгебры и алмукабалы. Историко-математические исследования, 6, 1953, с. 15—66.
- Хайям Омар. Комментарии к трудным постулатам книги Евклида. Историко-математические исследования, 6, 1953, с. 67-107.
- Хайям Омар. Об искусстве определения золота и серебра в состоящем из них теле. Историко-математические исследования, 6, 1953, с. 108—112.
- Хайям Омар. Трактаты.. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012. Перевод А. П. Юшкевича. Статья и комментарии Б. А. Розенфельда и А. П. Юшкевича. М.: Изд. вост. лит., 1961.
- Хаййам Омар. Трактаты. Перевод Б. А. Розенфельда. Редакция В. С. Сегаля и А. П. Юшкевича. Статья и комментарии Б. А. Розенфельда и А. П. Юшкевича. М., 1962.
- Хайям Омар. Первый алгебраический трактат. Историко-математические исследования, 15, 1963, с. 445—472.
- Хайям Омар. О прямом кустасе. Историко-математические исследования, 19, 1974, с. 274—278.
- Хайям Омар. Речь о родах, которые образуются квартой. Историко-математические исследования, 19, 1974, с. 279—284.
О нём[править | править вики-текст]
- М.-Н. О. Османов. Омар Хайям // Большая советская энциклопедия. — М.: Советская энциклопедия, 1969—1978.
- М.-Н. Османов. Омар Хайям // Краткая литературная энциклопедия: В 9 т. / Гл. ред. А. А. Сурков. — М.: Сов. энцикл., 1968. — Т. 5: Мурари — Припев.
- Омар Хайям // Литература и язык. Современная иллюстрированная энциклопедия / Под редакцией проф. Горкина А.П.. — М.: Росмэн, 2006.
- История математики. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012. с древнейших времён до начала XIX столетия (под ред. А. П. Юшкевича). — Т. I. — М.: Наука, 1972.
- Боголюбов А. Н. Математики. Механики. Биографический справочник. — Киев: Наукова думка, 1983. — 639 с.
- Глезер Г. И. История математики в школе. VII – VIII классы. — М.: Просвещение, 1982. — 240 с.
- Крамар Ф. Д. Об исследованиях Омара Хайяма и Насирэддина Туси по теории параллельных линий. — Алма-Ата, 1964.
- Крымский А. Е.,. Хейям, Омар // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
- Розенфельд Б. А., Юшкевич А. П. Омар Хайям. — М.: Наука, 1965. — 194 с.
- Розенфельд Б. А., Юшкевич А. П. Теория параллельных линий на средневековом Востоке. IX — XIV вв. — М.: Наука, 1983. — 128 с.
- Стройк Д. Я. Краткий очерк истории математики. 4-е изд. — М.: Наука, 1984. — 284 с.
- Султанов Ш. З., Султанов К. З. Омар Хайям. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.. — М.: Мол. гвардия, 1987. — 320 с. — (Жизнь замечательных людей. Вып. 679).
- Шамсиддинов Д. Проблема общих понятий и научной абстракции в творчестве Омара Хайяма // Философские науки. — 1987. — № 7. — С. 101—105.
- Ильясов Я. Заклинатель змей; Башня молчания: Повести. — Ташкент: Изд-во лит. и искусства, 1986. — 496 с.
- Гулиа Г. Д. Сказание об Омаре Хайяме». — М.: Художественная литература, 1980. — 432 с.
Ссылки[править | править вики-текст]
| Омар Хайям в Викицитатнике? | |
| Омар Хайям в Викитеке? | |
| Омар Хайям на Викискладе? |
- ОМАР ХАЙЯМ — рубаи, стихи афоризмы — лучшие переводы.
- Русские стихотворные переводы рубаи Омара Хайяма (1891—1997). Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
- Биография и рубаи Омара Хайяма. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
- Изречения Омара Хайяма. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
- Афоризмы Омара Хайяма. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
- Омар Хайям. «Рубаи». Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
- Омар Хайям в библиотеке Максима Мошкова
- Певец жизни
- Хайам в «Визуальном словаре». Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
- «Японский городовой» — самая полная коллекция поэзии Омара Хайама. Составитель: Андрей Андриенко(недоступная ссылка — история). Архивировано из первоисточника 22 января 2000.(недоступная ссылка с 20-09-2015 (331 день))
- Полный перевод рубаи Омара Хайяма. Переводчик: Игорь Голубев. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.(недоступная ссылка с 20-09-2015 (331 день))
- Омар Ибн-Ибрахим Нишапури Хайям — Литература Ирана X—XV в. Восток. ACADEMIA, Москва Ленинград, 1935.(недоступная ссылка с 20-09-2015 (331 день))
- Омар Хайям на Притчи.ру. Архивировано из первоисточника 28 ноября 2012.
Поэты и поэтессы, писавшие на персидском языке |
|
|---|---|
| Поэты |
Унсури • Дакики • Рудаки • Насир Хосров • Ибн Сина • Фирдоуси • Омар Хайям • Низами Гянджеви • Манучехри • Анвари • Саади • Аттар • Хафиз Ширази • Камол Худжанди • Джалаладдин Руми • Джами • Бедиль • Амир Хосров Дехлеви • Хагани Ширвани |
| Поэтессы |
Робиаи Балхи • Зебунниса • Мехсети Гянджеви • Куррат-уль-Айн |
|
Тематические сайты |
Notable Names Database · Internet Movie Database · MusicBrainz |
|---|---|
| Словари и энциклопедии |
Большая российская · Britannica (онлайн) |
| Нормативный контроль |
BNF: 119181488 · GND: 118736302 · ICCU: ITICCUCFIV96900 · ISNI: 0000 0001 2283 6122 · LCCN: n79105787 · NDL: 00451778 · NKC: jn20010601215 · NTA: 069041024 · SUDOC: 027053008 · VIAF: 100210377 · ULAN: 500245123 |
Вопрос написания имени Омар Хайяма
Автор Brillioni, августа 3, 2017, 11:49
0 Пользователи и 1 гость просматривают эту тему.
Добрый день!
Подскажите, как правильно написать фразу:
1. Мудрость Омар Хайяма
2. Мудрость Омара Хайяма
В интернете пишут и так и так. Мы планируем запустить в серию его работы и нам нужно на коробке написать заголовок. Боюсь ошибиться.
zwh
-
- Сообщения: 27,313
- Записан
Из Вики:
Цитировать
Проект Омара Хайяма был утверждён и лёг в основу иранского календаря, который вплоть до настоящего времени действует в Иране в качестве официального с 1079 года.
zazsa
-
- Сообщения: 1,428
- Occupation: Вождь мирового офисного планктоната.
- Записан
Меня больше интересует, почему он не Хаям/Хайам.
Привет участникам международного лингвистического форума!
У всякого народа есть родина, но только у нас – Гондурас.
Переписываю историю. Разжигаю национальную, религиозную рознь и ненависть к социальным группам. Недорого.
Bhudh
-
- Сообщения: 68,695
- aka 蝎
-
- Записан
Пиши, что думаешь, но думай, что пишешь.
MONEŌ ERGŌ MANEŌ.
Waheeba dokin ʔebi naha.
«каждый пост в интернете имеет коэффициент бреда» © Невский чукчо
Виоленсия
-
- Сообщения: 7,893
- К тебе приходит песец
- Записан
«Мудрость Омар Хайяма» отдаёт разговорностью. Как «мудрость Иван Иваныча». 
bvs
-
- Сообщения: 14,232
- Записан
По норме, в именах, состоящих из нескольких частей, разделенных пробелом, склоняются все части, за исключением дальневосточных (китайских, корейских, вьетнамских и т.д.). Но есть и отклонения, ср. разговорное «Жюль Верна», «Майн Рида».
bvs
-
- Сообщения: 14,232
- Записан
Цитата: zazsa от августа 3, 2017, 17:01
Меня больше интересует, почему он не Хаям/Хайам.
В оригинале j удвоенное, но вообще в русском любое иностранное -Vjа традиционно транскрибируется в -йя, ср. фр. Boyard/рус. Бойяр.
zwh
-
- Сообщения: 27,313
- Записан
bvs
-
- Сообщения: 14,232
- Записан
zwh
-
- Сообщения: 27,313
- Записан
Цитата: bvs от августа 5, 2017, 22:48
Цитата: zwh от августа 5, 2017, 22:36
Цитата: bvs от августа 5, 2017, 20:42
Цитата: zazsa от августа 3, 2017, 17:01
Меня больше интересует, почему он не Хаям/Хайам.В оригинале j удвоенное, но вообще в русском любое иностранное -Vjа традиционно транскрибируется в -йя, ср. фр. Boyard/рус. Бойяр.
Майами?
Там нет йота в написании: Miami.
А у Хайяма есть?
bvs
-
- Сообщения: 14,232
- Записан
zwh
-
- Сообщения: 27,313
- Записан
zazsa
-
- Сообщения: 1,428
- Occupation: Вождь мирового офисного планктоната.
- Записан
Iskandar, bvs, спасибо за разъяснения. Но всё равно как-то некошерно выглядит. Ну да ладно, в таких случаях ещё терпимо, а вот за «паранойю» вообще убивать на месте нужно. Наверно, самое уродливое слово в русском языке.
Привет участникам международного лингвистического форума!
У всякого народа есть родина, но только у нас – Гондурас.
Переписываю историю. Разжигаю национальную, религиозную рознь и ненависть к социальным группам. Недорого.
Bhudh
-
- Сообщения: 68,695
- aka 蝎
-
- Записан
И как παράνοια передавать? Пара́ноя или пара́нэа?
Пиши, что думаешь, но думай, что пишешь.
MONEŌ ERGŌ MANEŌ.
Waheeba dokin ʔebi naha.
«каждый пост в интернете имеет коэффициент бреда» © Невский чукчо
Драгана
-
- Сообщения: 17,257
- Записан
Цитата: Виоленсия от августа 5, 2017, 20:19
«Мудрость Омар Хайяма» отдаёт разговорностью. Как «мудрость Иван Иваныча».
Или как «прочитал Жюль Верна». Тоже порой встречается.
Литературно все имена подобного типа — мужского рода, оканчивающиеся на согласный — в русском языке склоняются. Омара Хайяма, Жюля Верна, Ивана Ивановича.
zwh
-
- Сообщения: 27,313
- Записан
Текст: Аполлинария Аврутина *
Пожалуй, ни один современный ближневосточный автор, даже самый модный, не может похвастаться в наши дни такими тиражами, как Хайям. Стоит зайти в любой книжный магазин, будь то Россия, Европа, Америка, и в отделе литературы о Востоке вам непременно встретится три-четыре разных издания Хайяма.
Вообще говоря, весь мир совершенно неверно произносит и пишет его имя. Писать его имя следует «Умар Хаййам», именно так оно передается в арабской графике. Правильно произносить имя этого персидского поэта следует как «Омар-е Хаййам», что переводится как «Омар Палаточник». Персидское слово «Хайям» буквально значит «палатка», и к этому слову этимологически восходит старорусское «хамовник», то есть «текстильщик», а от него уже — район в Москве, где, в частности, купил себе усадьбу Лев Толстой. Иными словами, на русский язык имя Омара Хайяма можно переводить как «Омар-хамовник», «Омар-текстильщик». Полное имя Хайяма — Гиййас ад-Дин Абу-л-Фатх Омар ибн Ибрахим аль-Хайям, имя сообщает нам, что поэт родом из семьи потомственных ремесленников, сын Ибрагима-палаточника.
О жизненном пути Омара-палаточника известно немногое, факты его биографии в некоторой степени легендарны. Точных, документальных свидетельств его жизни немного. О его поэтическом творчестве источники стали упоминать вообще спустя долгое время после его смерти (в XIII—XIV вв.), а
среди специалистов бытует мнение, что те рубаи (букв. «четверостишия»), где упоминается имя Хайяма, вообще написаны не им, а поздними поклонниками его творчества.
В знаменитой энциклопедии Брокгауза и Ефрона Хайяму посвящены две статьи. В сорок втором томе есть статья «Омар Аль-Каями» об ученом-математике, а в семьдесят третьем томе статья «Хейям, или Омар Хейям» — о поэте.
Если верить источникам, в 70-х годах Хайям был приглашен Малик-шахом для строительства дворцовой обсерватории и реформирования солнечного календаря. В итоге этот календарь был разработан группой ведущих ученых-астрономов того времени, среди которых был и Хайям, и оказался на 7 минут точнее григорианского календаря, который ввели в Европе в XVI в., — то есть намного точнее того календаря, которым мы пользуемся сейчас. Если бы обсерватория, которую планировал построить Малик-шах по проекту Омара Хайяма, была достроена, возможно, она бы стала более известной и более крупной, нежели самаркандская обсерватория знаменитого внука Тамерлана, правителя династии Тимуридов, Улугбека, правившего в XV в. и составившего многочисленные карты звездного неба, которыми в Европе пользовались едва ли не до XIX в.
Более того, список математических открытий, совершенных Хайямом-математиком, позволяет говорить о том, что он, пользуясь наработками индийских ученых, смог сделать то, что впоследствии удалось повторить только Исааку Ньютону.
Однако научная карьера гениального математика, астронома и астролога прервалась после убийства его покровителя-шаха. Начался период скитаний.
Чтобы избежать нападок и даже репрессий, Омар Хайям удалился от дел и науки и отправился странствовать. По всей вероятности, именно на этот период, если речь все же идет об одном человеке, приходится расцвет его поэтического творчества — ироничные рубаи являют читателю всю неприкрытую правду жизни.
Однако и с рубаи-четверостишиями все непросто. Специалистам хорошо известно, что в мире переведено и издано намного больше четверостиший, приписываемых Хайяму, чем Хайям мог написать и написал. Иными словами, как это нередко случалось в средневековой ближневосточной мусульманской литературе, имя легендарного автора со временем превратилось в коллективный псевдоним. Таких случаев в истории литературы Востока немало, а кроме того, довольно долго бытовала традиция приписывать тому или иному автору все, где упоминалось его имя. Поэтому до сих пор точное количество четверостиший, написанных Омаром Хайямом, совершенно неизвестно, как и неизвестно, какие именно рубаи он написал.
Существует легенда, что в момент гибели «Титаника» на его борту находилась подлинная рукопись Хайяма, которая, разумеется, в катастрофе была утрачена.
Этой легенде вряд ли стоит верить: за много веков рукописи Омара Хайяма подделывали так много раз, что нередко с их атрибуцией ошибались даже крупные специалисты. Например, у многих иранистов на слуху история, когда знаменитый американский иранист Ричард Фрай купил за большую сумму поддельную рукопись Омара Хайяма для библиотеки Гарвардского университета. Однако впоследствии университет провел экспертизу, подделка была обнаружена, хотя качество поддельного манускрипта вызывало изумление знатоков — степень подделки некоторых элементов рукописи было невозможно уточнить, ситуацию спасла голубая краска, которая никак не могла быть в обращении во времена Хайяма. Другие подделки в разное время были приобретены библиотеками Кембриджа, Честера Битти, Национальной библиотекой и рядом частных коллекционеров.
Поэт и ученый, намного опередивший свое время, сотворивший своей жизнью немало тайн, продолжает творить эти тайны и спустя много веков после смерти. Смелый настолько, что отважился в свое время в поэзии хулить Аллаха, Омар Хайям продолжает удивлять мир своими речами…
Автор статьи выражает благодарность за помощь в подготовке материала старшему научному сотруднику ИВР РАН, кандидату исторических наук Алексею Александровичу Хисматуллину. Также при подготовке материала было использовано интервью с О. Ф. Акимушкиным от 2007 г.: М. С. Баконина. «Любимый поэт президента» на сайте и Предисловие к серии «Назидательная литература эпохи Салджукидов на персидском языке: оригиналы и подделки» (А. А. Хисматуллин, Амир Му‘Иззи Нишапури Сийасат-Нама/Сийар Ал-Мулук: подделка, приписанная Низам ал-Мулку. Петербургское Востоковедение, СПб. — М.: 2018).
*Аполлинария Аврутина — лауреат Яснополянской премии (как переводчица Орхана Памука), доцент Восточного факультета СПбГУ.
Хорхе Луис Борхес о Хайяме и его английском переводчике Эдварде Фицджеральде:
…Около 1854 года ему дают посмотреть рукописный свод сочинений Омара, составленный по одному лишь принципу, алфавитному порядку рифм; Фицджеральд пробует одну рифму по-латыни и усматривает возможность соткать из них целостную и органическую книгу, открывающуюся образами утра, розы и соловья и завершающуюся ночью и могилой. Столь неимоверной и даже неправдоподобной цели Фицджеральд посвящает свою жизнь — жизнь человека беззаботного, одинокого и фанатичного. В 1859 году он публикует первый перевод «Рубайят», за которым следуют другие, богатые разнообразием и отделкой. Происходит чудо: из плодотворного симбиоза персидского астронома, снизошедшего к поэзии, и эксцентричного англичанина, читающего восточные и испанские книги, не особо вникая в смысл, рождается выдающийся поэт, не похожий ни на того, ни на другого. Суинберн пишет, что Фицджеральд «уступил Омару Хайяму звание одного из крупнейших поэтов Англии», а Честертон, восприимчивый к романтичности и классичности этой превосходной книги, замечает, что в ней одновременно «мелодия ускользает, а текст длится». Некоторые критики считают Фицджеральдова Омара английской поэзией с персидскими аллюзиями; Фицджеральд — составитель, шлифовальщик и сочинитель — требует, однако, чтобы мы читали его «Рубайят» как древнеперсидскую поэзию.
Случай вызывает догадки метафизического толка. Омар (как известно) исповедовал платоновско-пифагорейскую доктрину многократного воплощения души; через века его душа, видимо, перевоплотилась в Англии, дабы на далеком германском языке с вкраплениями латыни исполнилась литературная судьба, подавленная в Нишапуре математикой. Исаак Лурия эль Леон учил, что душа умершего может войти в душу-неудачницу, дабы поддержать и наставить ее; быть может, в 1857 году душа Омара поселилась в душе Фицджеральда. В «Рубайят» сказано, что всемирная история — это спектакль, задуманный, поставленный и созерцаемый Богом; такое наблюдение (терминологически именуемое «пантеизм») позволяет предположить, что англичанину удалось воссоздать перса, поскольку оба, по сути, были Богом или случайным взглядом Бога. Более правдоподобна и не менее чудесна, чем эти сверхъестественные предположения, гипотеза благотворного совпадения. Иногда облака принимают форму гор или львов; аналогичным образом печаль Эдварда Фицджеральда и пожелтевший манускрипт с лиловыми литерами, забытый на полке оксфордской Bodleyana, приняли, к нашему блату, форму поэзии. Всякое соавторство загадочно. А соавторство нашего англичанина и перса — как никакое другое, ибо слишком они разные, и, вероятно, в жизни бы не стали друзьями, а смерть, перипетии и время понадобились только лишь для того, дабы последний узнал о первом, что оба они — один и тот же поэт.
Хорхе Луис Борхес. «Загадка Эдварда Фицджеральда». Пер. с исп. И. Петровского.
Толковый словарь русского языка. Поиск по слову, типу, синониму, антониму и описанию. Словарь ударений.
омар хайям
ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
Ома́р Хайя́м — настоящее имя Гиясаддин Абу-ль-Фатх Омар ибн Ибрахим (около 1048 — после 1112), персидский поэт, философ, учёный. Писал также на арабском языке. Всемирно известные философские четверостишия — рубаи проникнуты гедоническими мотивами, пафосом свободной личности, антиклерикальным вольнодумством. Автор не утративших и в XX в. значения математических трактатов, философского трактата «О всеобщности бытия» и др. Возглавлял в 1074-92 астрономическую обсерваторию в Исфахане.
* * *
ОМАР ХАЙЯМ — ОМА́Р ХАЙЯ́М (ок. 1048 — после 1122), персидский поэт, математик и философ. Всемирно известные философские четверостишия — рубаи (см. РУБАИ) проникнуты гедоническими мотивами, пафосом свободы личности, антиклерикальным вольнодумством. В математических трудах дал изложение решения уравнений до 3-й степени включительно.
БОЛЬШОЙ ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
ОМАР ХАЙЯМ (ок. 1048 — после 1122) — персидский и таджикский поэт, математик и философ. Всемирно известные философские четверостишия — рубаи проникнуты гедоническими мотивами, пафосом свободы личности, антиклерикальным вольнодумством. В математических трудах дал изложение решения уравнений до 3-й степени включительно.
ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЯ КОЛЬЕРА
ОМАР ХАЙЯМ (ок. 1048 — после 1122), персидский поэт, полное имя — Гиясаддин Абу-ль-Фатх Омар ибн Ибрахим. Родился в Нишапуре. Прозвище Хайям (Палаточник) связано с профессией его отца или кого-то еще из предков. При жизни и до сравнительно недавнего времени Хайям был известен главным образом как выдающийся математик, физик и астроном. Его Алгебра, написанная на арабском языке, была впервые опубликована и переведена на французский Ф.Вепке в 1851. Выполненный Э.Фицджералдом (1809-1883) перевод избранных четверостиший Омара Хайяма (рубайят), впервые появившийся в 1859, и затем издание самого текста и французский перевод Никола 1867 принесли Омару Хайяму славу певца разочарования и скептицизма. Восточные и западные ученые издавна спорят о том, понимать ли стихотворения Омара Хайяма буквально или в них символически представлено устремление мистической души к единству с Богом. Более того, существует серьезная проблема авторства четверостиший Хайяма: оригинальные рукописи, среди которых нет старше 14 в., значительно отличаются по числу и порядку включенных в них стихотворений; Хайяму приписывается не менее 1391 четверостишия (большинство изданий ограничивается 101 четверостишием, выбранным Фицджералдом); многие из них можно найти у других поэтов. Тщательно анализируя сохранившийся материал, некоторые ученые пытались устранить неподлинные элементы и восстановить «истинного» Хайяма. Однако результаты этой работы весьма противоречивы.
ЛИТЕРАТУРА
Розенфельд Б.А., Юшкевич А.П. Омар Хайям. М., 1965 Омар Хайям. Рубайат (2 изд.). М., 1975 Омар Хайям. Рубаи. Ташкент, 1983
ИЛЛЮСТРИРОВАННЫЙ ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
Омар Хайям.
ОМАР ХАЙЯМ (настоящее имя Гиясаддин Абу-ль-Фатх Омар ибн Ибрахим) (1048 — 1122), персидский поэт, философ, учёный. Писал также на арабском языке. Автор не утративших и в 20 в. значения математических трактатов, философского трактата «О всеобщности бытия» и др. Возглавлял в 1074 — 92 астрономическую обсерваторию в Исфахане, в 1079 ввёл календарь, более точный, чем современный григорианский. Непреходящую мировую славу принесли ему стихи — философские, гедонические и вольнодумные рубаи, вызывавшие ожесточённые нападки духовенства.
ГРАММАТИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
ПОЛЕЗНЫЕ СЕРВИСЫ
Имя Омара Хайяма известно всему миру благодаря написанным им четверостишиям «рубаи». Однако, этим его роль в истории не ограничена. В алгебре он построил классификацию кубических уравнений и дал их решения с помощью конических сечений. А в Иране Омар Хайям известен созданием более точного, по сравнению с европейским, календаря, который официально используется с 11 века.
Омар Хайям (Omar Khayyam, Гиясаддин Абу-ль-Фатх Омар ибн Ибрахим аль-Хайям Нишапури) родился 18 мая 1048 года в Нишапуре, в семье палаточника.
Уже в возрасте 8 лет Омар знал Коран по памяти, занимался изучением математики, астрономии и философии. В 12 лет он стал учеником Нишапурского медресе. Хаяйм блестяще закончил курс по мусульманскому праву и медицине, получив квалификацию хакима (врача). Медицина его интересовала мало, он посвятил свое время изучению сочинения известного математика и астронома Сабита ибн Курры, а также трудов греческих математиков.
Когда ему исполнилось 16 лет, от эпидемии умирают его родители. Омар продает отцовский дом и мастерскую и отправляется в Самарканд – на тот момент признанный на Востоке научный и культурный центр.
В Самарканде Хайям становится сначала учеником одного из медресе, но после нескольких выступлений на диспутах он настолько поразил всех своей ученостью, что его сразу же сделали наставником.
Как и другие крупные учёные того времени, Омар не задерживался подолгу в каком-то городе. Всего через четыре года он покинул Самарканд и переехал в Бухару, где начал работать в хранилищах книг. За десять лет, что учёный прожил в Бухаре, он написал четыре фундаментальных трактата по математике.
В 1074 году его пригласили в Исфахан, центр государства Санджаров, ко двору сельджукского султана Мелик-шаха I. Он становится духовным наставником султана. Однако в 1092 году, со смертью покровительствовавшего ему султана Мелик-шаха и визиря Низам ал-Мулка, исфаханский период его жизни заканчивается.
К славе Хайяма как выдающегося математика и астронома прибавилась в эти годы и крамольная слава вероотступника. Его философские взгляды вызывали ярое недовольство ревнителей ислама, его отношения с высшим духовенством резко ухудшились. Они приняли столь опасный для Омара характер, что, обвинённый в безбожном вольнодумстве, поэт вынужден был покинуть сельджукскую столицу.
О позднем периоде жизни Хайяма известно очень мало. Историки указывают, что некоторое время он пребывал в Мерве, а в какой-то момент вернулся в родной Нишапур, где и прожил до последних дней жизни, лишь иногда покидая его для посещения Бухары или Балха.
В эти годы Омар вел преподавание в Нишапурском медресе, имел небольшой круг близких учеников, изредка принимал искавших встречи с ним ученых и философов, участвовал в научных диспутах.
Умер выдающийся поэт, философ и ученый Омар Хайям 4 декабря 1131 года в Нишапуре. Он остался в веках благодаря своим четверостишиям – мудрым, полным юмора, лукавства и дерзости рубаи. Долгое время был забыт, но его творчество стало известным европейцам в новое время благодаря переводам Эдварда Фитцджеральда.
Материалы к празднику в Журнале Calend.ru:
Статья ко дню рождения: «Что знает об Омаре Хайяме современная молодежь, и кем он был на самом деле?»