Речь Посполитая
- Речь Посполитая
-
Р’ечь Поспол’итая (ист.)
Русский орфографический словарь. / Российская академия наук. Ин-т рус. яз. им. В. В. Виноградова. — М.: «Азбуковник».
.
1999.
Синонимы:
Смотреть что такое «Речь Посполитая» в других словарях:
-
Речь Посполитая — ← … Википедия
-
РЕЧЬ ПОСПОЛИТАЯ — (Речь Посполита; польск. Rzeczpospolita республика), традиционное название польского государства с конца 15 века, представлявшего собой сословную монархию (см. СОСЛОВНАЯ МОНАРХИЯ) во главе с избираемым сеймом (см. СЕЙМ (орган власти)) королем. С… … Энциклопедический словарь
-
Речь Посполитая — (Речь Посполита; польск. Rzeczpospolita республика) традиционное название польского государства с конца 15 века, представлявшего собой сословную монархию во главе с избираемым сеймом королем. С момента заключения Люблинской унии 1569 года и до… … Политология. Словарь.
-
речь посполитая — сущ., кол во синонимов: 1 • польша (4) Словарь синонимов ASIS. В.Н. Тришин. 2013 … Словарь синонимов
-
Речь Посполитая, образование государства — В конце XV начале XVI в. Польша являлась одной из сильнейших держав в Центральной и Восточной Европе. Политическое укрепление Польши было обусловлено экономическим подъёмом XIV XV вв. и стояло в тесной связи с успешным исходом борьбы с основным… … Всемирная история. Энциклопедия
-
Речь Посполитая Трёх Народов — Герб предлагавшийся для Республики Трёх Народов. Речь Посполитая Трёх Народов (польск. Rzeczpospolita Trojga Narodów) политический проект превращения конфедерации … Википедия
-
Речь Посполитая — Интересующимся историей будет, вероятно, любопытно узнать, что это название (существовавшее с 1569 до 1759 года) нашего ближайшего славянского соседа – польского государства, было образовано как калька с латинского res publica (см. республика):… … Этимологический словарь русского языка Крылова
-
Речь Посполитая — (ист.) … Орфографический словарь русского языка
-
Новогрудское воеводство (I Речь Посполитая) — У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Новогрудское воеводство. Новогрудское воеводство лат. Palatinatus Novogrodensis старобел. … Герб … Википедия
-
Волынское воеводство (I Речь Посполитая) — Волыньское воеводство Волынское воеводство (польск. Województwo wołyńskie) воеводство Речи Посполитой, которое существовало в 1569 1795 годах в составе провинции Ма … Википедия
Толковый словарь русского языка. Поиск по слову, типу, синониму, антониму и описанию. Словарь ударений.
речь посполита
ТОЛКОВЫЙ СЛОВАРЬ
ж.
Официальное наименование объединенного польско-литовского государства со времени Люблинской унии (1569 — 1795 гг.).
ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
Речь Посполи́та (польск. Rzeczpospolita — республика), официальное название объединённого польско-литовского государства со времени Люблинской унии 1569 до 1795. В 1772-95 в результате разделов большая часть Речи Посполитой вошла в состав Российской империи.
БОЛЬШОЙ ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
РЕЧЬ ПОСПОЛИТА (польск. Rzeczpospolita — республика) — официальное название объединенного польско-литовского государства со времени Люблинской унии 1569 до 1795.
ИЛЛЮСТРИРОВАННЫЙ ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
РЕЧЬ ПОСПОЛИТА (польское Rzeczpospolita — республика), официальное название объединенного польско-литовского государства в 1569 — 1795.
ПОЛЕЗНЫЕ СЕРВИСЫ
речь посполитая
ЭНЦИКЛОПЕДИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
РЕЧЬ ПОСПОЛИТАЯ — РЕЧЬ ПОСПОЛИ́ТАЯ (Речь Посполита; польск. Rzeczpospolita — республика), традиционное название польского государства с конца 15 века, представлявшего собой сословную монархию (см. СОСЛОВНАЯ МОНАРХИЯ) во главе с избираемым сеймом (см. СЕЙМ (орган власти)) королем. С момента заключения Люблинской унии (см. ЛЮБЛИНСКАЯ УНИЯ) 1569 года и до 1795 года Речь Посполитая была официальным наименованием объединенного польско-литовского государства.
ОРФОГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ СЛОВАРЬ
СИНОНИМЫ
сущ., кол-во синонимов: 1
ЭТИМОЛОГИЯ
Интересующимся историей будет, вероятно, любопытно узнать, что это название (существовавшее с 1569 до 1759 года) нашего ближайшего славянского соседа — польского государства, было образовано как калька с латинского res publica (см. республика): Rzecz pospolita по-польски, как и по-латински, означает «общественное дело».
ПОЛЕЗНЫЕ СЕРВИСЫ
|
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1569–1795[1] | ||||||||||||||
|
Royal Banner Royal Coat of arms |
||||||||||||||
Motto:
|
||||||||||||||
| Anthem: Gaude Mater Polonia | ||||||||||||||

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (green) with vassal states (light green) at their peak in 1619 |
||||||||||||||
| Capital |
de jure:
de facto:
|
|||||||||||||
| Common languages | Official: Polish and Latin Regional:
|
|||||||||||||
| Religion | Official: Roman Catholicism[3] Minority:
|
|||||||||||||
| Government |
|
|||||||||||||
| King / Grand Duke | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1569–1572 (first) |
Sigismund II Augustus | |||||||||||||
|
• 1764–1795 (last) |
Stanislaw II Augustus | |||||||||||||
| Legislature | General sejm | |||||||||||||
|
• Upper house |
Senate | |||||||||||||
|
• Lower house |
Chamber of Deputies | |||||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period | |||||||||||||
|
• Union established |
1 July 1569 | |||||||||||||
|
• 1st Partition |
5 August 1772 | |||||||||||||
|
• 3 May Constitution |
3 May 1791 | |||||||||||||
|
• 2nd Partition |
23 January 1793[1] | |||||||||||||
|
• 3rd Partition |
24 October 1795[1] | |||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||
| 1582[8] | 815,000 km2 (315,000 sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| 1618[9][10] | 1,000,000 km2 (390,000 sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1582[8] |
~8,000,000 | |||||||||||||
|
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth,[b] formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania,[c] was a bi-confederal[11] state, sometimes called a federation,[12] of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest[13][14] and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi)[15][16] and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million.[17][18] Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages.
The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a de facto personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish queen Jadwiga (Hedwig) and Lithuania’s Grand Duke Jogaila, who was crowned King jure uxoris Władysław II Jagiełło of Poland. The First Partition in 1772 and the Second Partition in 1793 greatly reduced the state’s size. The Commonwealth was partitioned out of existence in the Third Partition of 1795.
The Union possessed many features unique among contemporary states. Its political system was characterized by strict checks upon monarchical power. These checks were enacted by a legislature (sejm) controlled by the nobility (szlachta). This idiosyncratic system was a precursor to modern concepts of democracy,[19] as of 1791 constitutional monarchy,[20][21][22] and federation.[23] Although the two component states of the Commonwealth were formally equal, Poland was the dominant partner in the union.[24]
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was marked by high levels of ethnic diversity and by relative religious tolerance, guaranteed by the Warsaw Confederation Act 1573;[25][26][d] however, the degree of religious freedom varied over time.[27] The Constitution of 1791 acknowledged Catholicism as the «dominant religion», unlike the Warsaw Confederation, but freedom of religion was still granted with it.[22]
After several decades of prosperity,[28][29][30] it entered a period of protracted political,[22][31] military, and economic decline.[32] Its growing weakness led to its partitioning among its neighbors (Austria, Prussia, and Russia) during the late 18th century. Shortly before its demise, the Commonwealth adopted a massive reform effort and enacted the 3 May Constitution, which was the first codified constitution in modern European history and the second in modern world history after the United States Constitution.[33][34][35][36][37]
Name
The official name of the state was the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (Polish: Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie, Lithuanian: Lenkijos Karalystė ir Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė, Latin: Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae) and the Latin term was usually employed in international treaties and diplomacy.[38]
In the 17th century and later it was also known as the ‘Most Serene Commonwealth of Poland’ (Polish: Najjaśniejsza Rzeczpospolita Polska, Latin: Serenissima Res Publica Poloniae),[39] the Commonwealth of the Polish Kingdom,[40] or the Commonwealth of Poland.[41]
Western Europeans often simplified the name to ‘Poland’ and in most past and modern sources it is referred to as the Kingdom of Poland, or just Poland.[38][42][43] The terms ‘Commonwealth of Poland’ and ‘Commonwealth of Two Nations’ (Polish: Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów, Latin: Res Publica Utriusque Nationis) were used in the Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations.[44] The English term Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and German Polen-Litauen are seen as renderings of the ‘Commonwealth of Two Nations’ variant.[38]
Other informal names include the ‘Republic of Nobles’ (Polish: Rzeczpospolita szlachecka) and the ‘First Commonwealth’ (Polish: I Rzeczpospolita), the latter relatively common in historiography to distinguish it from the Second Polish Republic.
History
Prelude (1370–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania underwent an alternating series of wars and alliances across the 13th and 14th centuries.[45] The relations between the two states differed at times as each strived and competed for political, economic or military dominance of the region.[46] In turn, Poland had remained a staunch ally of its southern neighbour, Hungary. The last Polish monarch from the native Piast dynasty, Casimir the Great, died on 5 November 1370 without fathering a legitimate male heir.[47] Consequently, the crown passed onto his Hungarian nephew, Louis of Anjou, who ruled the Kingdom of Hungary in a personal union with Poland.[47] A fundamental step in developing extensive ties with Lithuania was a succession crisis arising in the 1380s.[48] Louis died on 10 September 1382 and, like his uncle, did not produce a son to succeed him. His two daughters, Mary and Jadwiga (Hedwig), held claims to the vast dual realm.[47]
The Polish lords rejected Mary in favour of her younger sister Jadwiga, partly due to Mary’s association with Sigismund of Luxembourg.[49] The future queen regnant was betrothed to young William Habsburg, Duke of Austria, but certain factions of the nobility remained apprehensive believing that William would not secure domestic interests.[50] Instead, they turned to Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania. Jogaila was a lifelong pagan and vowed to adopt Catholicism upon marriage by signing the Union of Krewo on 14 August 1385.[51] The Act imposed Christianity in Lithuania and transformed Poland into a diarchy, a kingdom ruled over by two sovereigns; their descendants and successive monarchs held the titles of king and grand duke respectively.[52] The ultimate clause dictated that Lithuania was to be merged in perpetuity (perpetuo applicare) with the Polish Kingdom; however, this did not take effect until 1569.[53] Jogaila was crowned as Władysław II Jagiełło at Wawel Cathedral on 4 March 1386.[54]
Union of Lublin (1569)
Several minor agreements were struck before unification, notably the Union of Kraków and Vilnius, the Union of Vilnius and Radom and the Union of Grodno. Lithuania’s vulnerable position and rising tensions on its eastern flank persuaded the nobles to seek a closer bond with Poland.[55] The idea of a federation presented better economic opportunities, whilst securing Lithuania’s borders from hostile states to the north, south and east.[56] Lesser Lithuanian nobility were eager to share the personal privileges and political liberties enjoyed by the Polish szlachta, but did not accept Polish demands for the incorporation of the Grand Duchy into Poland as a mere province, with no sense of autonomy.[57] Mikołaj «the Red» Radziwiłł (Radvila Rudasis) and his cousin Mikołaj «the Black» Radziwiłł, two prominent nobles and military commanders in Lithuania, vocally opposed the union.[58]
A fierce proponent of a single unified Commonwealth was Sigismund II Augustus, who was childless and ailing. According to historians, it was his active involvement which hastened the process and made the union possible.[59] A parliament (sejm) convened on 10 January 1569 in the city of Lublin, attended by envoys from both nations. It was agreed that the merger will take place the same year and both parliaments will be fused into a joint assembly.[60] No independent parliamentary convocation or diet was henceforth permitted.[60] Subjects of the Polish Crown were no longer restricted in purchasing land on Lithuanian territory and a single currency was established.[61] Whilst the military remained separate, a unified foreign policy meant that Lithuanian troops were obliged to contribute during a conflict not to their advantage.[62] As a result, several Lithuanian magnates deplored the accords and left the assembly in protest.[63] Sigismund II used his authority as grand duke and enforced the Act of Union in contumaciam. In fear, the absent nobles promptly returned to the negotiations.[64] The Union of Lublin was passed by the gathered deputies and signed by attendees on 1 July, thus creating the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.[63]
Sigismund’s death in 1572 was followed by an interregnum during which adjustments were made to the constitutional system; these adjustments significantly increased the power of the Polish nobility and established a truly elective monarchy.[65]
Apex and the Golden Age (1573–1648)
The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at its greatest extent in 1619.
On 11 May 1573, Henry de Valois, son of Henry II of France and Catherine de’ Medici, was proclaimed King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania in the first royal election outside Warsaw. Approximately 40,000 nobles cast a vote in what was to become a centuries-long tradition of a nobles’ democracy (Golden Liberty). Henry already posed as a candidate before Sigismund’s death and received widespread support from the pro-French factions. The choice was a political move aimed at curtailing Habsburg hegemony, ending skirmishes with the French-allied Ottomans, and profiting from the lucrative trade with France. Upon ascending the throne, Henry signed the contractual agreement known as the Pacta conventa and approbated the Henrician Articles.[66] The Act stated the fundamental principles of governance and constitutional law in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.[67] In June 1574, Henry abandoned Poland and headed back to claim the French crown following the death of his brother and predecessor, Charles IX.[68] The throne was subsequently declared vacant.
The interregnum concluded on 12 December 1575 when primate Jakub Uchański declared Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor, as the next king.[69] The decision was condemned by the anti-Habsburg coalition, which demanded a «native» candidate.[70] As a compromise, on 13 December 1575 Anna Jagiellon – sister of Sigismund Augustus and a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty – became the new monarch.[71] The nobles simultaneously elected Stephen Báthory as co-regent, who ruled jure uxoris.[70] Báthory’s election proved controversial – Lithuania and Ducal Prussia initially refused to recognize the Transylvanian as their ruler.[72] The wealthy port city of Gdańsk (Danzig) staged a revolt, and, with the help of Denmark, blockaded maritime trade to neutral Elbląg (Elbing).[73] Báthory, unable to penetrate the city’s extensive fortifications, succumbed to the demands for greater privileges and freedoms.[73] However, his successful Livonian campaign ended in the annexation of Livonia and the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (modern-day Estonia and Latvia, respectively), thus expanding the Commonwealth’s influence into the Baltics.[74] Most importantly, Poland gained the Hanseatic city of Riga on the Baltic Sea.
Sigismund III Vasa, who reigned between 1587 – 1632, presided over an era of prosperity and territorial expansion of the Commonwealth.
In 1587, Sigismund Vasa – the son of John III of Sweden and Catherine Jagiellon – won the election, but his claim was overtly contested by Maximilian III of Austria, who launched a military expedition to challenge the new king.[75] His defeat in 1588 at the hands of Jan Zamoyski sealed Sigismund’s right to the throne of Poland and Sweden.[76] Sigismund’s long reign marked an end to the Polish Golden Age and the beginning of the Silver Age.[77] A devout Catholic, he hoped to restore absolutism and imposed Roman Catholicism during the height of the Counter-Reformation.[78] His intolerance towards the Protestants in Sweden sparked a war of independence, which ended the Polish–Swedish union.[79] As a consequence, he was deposed in Sweden by his uncle Charles IX Vasa.[80] In Poland, the Zebrzydowski rebellion was brutally suppressed.[81]
Sigismund III then initiated a policy of expansionism, and invaded Russia in 1609 when that country was plagued by a civil war known as the Time of Troubles. In July 1610, the outnumbered Polish force comprising winged hussars defeated the Russians at the Battle of Klushino, which enabled the Poles to take and occupy Moscow for the next two years.[82] The disgraced Vasili IV of Russia was transported in a cage to Warsaw where he paid a tribute to Sigismund; Vasili was later murdered in captivity.[83] The Commonwealth forces were eventually driven out on 4 November 1612 (celebrated as Unity Day in Russia). The war concluded with a truce that granted Poland–Lithuania extensive territories in the east and marked its largest territorial expansion.[84] At least five million Russians died between 1598 and 1613, the result of continuous conflict, famine and Sigismund’s invasion.[85]
Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the early 17th century
The Polish–Ottoman War (1620–21) forced Poland to withdraw from Moldavia in southeastern Europe, but Sigismund’s victory over the Turks at Khotyn diminished the supremacy of the Sultanate and eventually led to the murder of Osman II.[86] This secured the Turkish frontier for the duration of Sigismund’s rule. In spite of the victories in the Polish–Swedish War (1626–1629), the exhausted Commonwealth army signed the Treaty of Altmark which ceded much of Livonia to Sweden under Gustavus Adolphus.[87] At the same time, the country’s powerful parliament was dominated by nobles (Pic. 2) who were reluctant to get involved in the Thirty Years’ War; this neutrality spared the country from the ravages of a political-religious conflict that devastated most of contemporary Europe.[88]
During this period, Poland was experiencing a cultural awakening and extensive developments in arts and architecture; the first Vasa king openly sponsored foreign painters, craftsmen, musicians and engineers, who settled in the Commonwealth at his request.[89]
Sigismund’s eldest son, Ladislaus succeeded him as Władysław IV in 1632 with no major opposition.[90] A skilled tactician, he invested in artillery, modernised the army and fiercely defended the Commonwealth’s eastern borders.[91] Under the Treaty of Stuhmsdorf, he reclaimed regions of Livonia and the Baltics which were lost during the Polish-Swedish wars.[92] Unlike his father who worshipped the Habsburgs, Władysław sought closer ties with France and married Marie Louise Gonzaga, daughter of Charles I Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, in 1646.[93]
Deluge, rebellions and Vienna (1648–1696)
The Commonwealth’s power and stability began waning after a series of blows during the following decades. Władysław’s brother, John II Casimir, proved to be weak and impotent. The multicultural and mega-diverse federation already suffered domestic problems. As persecution of religious and ethnic minorities strengthened, several groups started to rebel.[citation needed]
A major rebellion of self-governed Ukrainian Cossacks inhabiting south-eastern borderlands of the Commonwealth rioted against Polish and Catholic oppression of Orthodox Ukraine in 1648, in what came to be known as the Khmelnytsky Uprising. It resulted in a Ukrainian request, under the terms of the Treaty of Pereyaslav, for protection by the Russian Tsar. In 1651, in the face of a growing threat from Poland, and forsaken by his Tatar allies, Khmelnytsky asked the Tsar to incorporate Ukraine as an autonomous duchy under Russian protection. Russian annexation of Zaporizhian Ukraine gradually supplanted Polish influence in that part of Europe. In the years following, Polish settlers, nobles, Catholics and Jews became the victims of retaliation massacres instigated by the Cossacks in their dominions. The other blow to the Commonwealth was a Swedish invasion in 1655, known as the Deluge, which was supported by troops of Transylvanian Duke George II Rákóczi and Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg. Under the Treaty of Bromberg in 1657, Catholic Poland was forced to renounce its suzerainty over Protestant Prussia; in 1701 the once-insignificant duchy was transformed into the Kingdom of Prussia, which became a major European power in the 18th century and proved to be Poland’s most enduring foe.[citation needed]
In the late 17th century, the king of the weakened Commonwealth, John III Sobieski, allied with Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I to deal crushing defeats to the Ottoman Empire. In 1683, the Battle of Vienna marked the final turning point in the 250-year struggle between the forces of Christian Europe and the Islamic Ottomans. For its centuries-long opposition to Muslim advances, the Commonwealth would gain the name of Antemurale Christianitatis (bulwark of Christianity).[23][94] During the next 16 years, the Great Turkish War would drive the Turks permanently south of the Danube River, never again to threaten central Europe.[95]
Political turmoil and the enlightenment (1697–1771)
John Sobieski’s death in 1696 arguably ended the period of national sovereignty, and Poland’s relative authority over the region dwindled swiftly. By the 18th century, destabilization of its political system brought the Commonwealth to the brink of civil war and the state became increasingly susceptible to foreign influence.[96] The remaining European powers perpetually meddled in the country’s affairs.[97] Upon the death of a king, several royal houses actively intruded in the hope of securing votes for their desired candidates.[98] The practice was common and apparent, and the selection was often the result of hefty bribes directed at corrupt nobles.[99] Louis XIV of France heavily invested in François Louis, Prince of Conti, in opposition to James Louis Sobieski, Maximilian Emanuel of Bavaria and Frederick Augustus of Saxony.[100] The latter’s conversion from Lutheranism to Catholicism awed the conservative magnates and Pope Innocent XII, who in turn voiced their endorsement.[101] Imperial Russia and Habsburg Austria also contributed by financing Frederick, whose election took place in June 1697. Many questioned the legality of his elevation to the throne; it was speculated that the Prince of Conti had received more votes and was the rightful heir. Frederick hurried with his armies to Poland to quell any opposition. He was crowned as Augustus II in September and Conti’s brief military engagement near Gdańsk in November of the same year proved fruitless.[102]
The House of Wettin ruled Poland–Lithuania and Saxony simultaneously, dividing power between the two states. In spite of his controversial means of attaining power, Augustus II lavishly spent on the arts and left an extensive cultural and architectural (Baroque) legacy in both countries. In Poland, he expanded Wilanów and facilitated the refurbishment of the Warsaw Royal Castle into a modern palatial residence.[103] Countless landmarks and monuments in the city bear a name referencing the Saxon kings, notably Saxon Garden, Saxon Axis and the former Saxon Palace.[104] The period saw the development of urban planning, street allocation, hospitals, schools (Collegium Nobilium), public parks and libraries (Załuski Library). First manufactories producing on a mass scale were opened to satisfy the demands of the nobility as consumers.[105]
At the height of the Great Northern War a coalition (Warsaw Confederation) against Augustus II was formed by Stanisław Leszczyński and other magnates sponsored by Sweden. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was formally neutral at this point, as Augustus entered the war as Elector of Saxony. Disregarding Polish negotiation proposals supported by the Swedish parliament, Charles crossed into the Commonwealth and vanquished the Saxe-Polish forces at the Battle of Klissow in 1702 and at the Battle of Pultusk in 1703.[106] Charles then succeeded in dethroning Augustus and coercing the Sejm (parliament) to replace him with Stanisław in 1704.[107] Augustus regained the throne in 1709,[108] but his own death in 1733 sparked the War of the Polish Succession in which Stanisław once more attempted to seize the crown, this time with the support of France.[109] The Pacification Sejm (1736) culminated in Augustus III succeeding his father.[110]
The relative peace and inactivity that followed only weakened Poland’s reputation on the world stage.[111] Aleksander Brückner noted that Polish customs and traditions were abandoned in favour of everything foreign, and neighbouring states continued to exploit Poland to their advantage.[111] Moreover, Western Europe’s increasing exploitation of resources in the Americas rendered the Commonwealth’s supplies less crucial which resulted in financial losses.[112] Augustus III spent little time in the Commonwealth, instead preferring the Saxon city of Dresden. He appointed Heinrich von Brühl as viceroy and minister of Polish affairs who in turn left the politics to Polish magnate families, such as the Czartoryskis and the Radziwills.[113] It was also during this period that the Polish Enlightenment began to sprout.
Partitions (1772–1795)
In 1764, aristocrat Stanisław August Poniatowski was elected monarch with the connivance and support of his former lover Catherine the Great, a German noblewoman who became Empress of Russia.[114]
Poniatowski’s attempts at reform were met with staunch resistance both internally and externally. Any goal of stabilizing the Commonwealth was dangerous for its ambitious and aggressive neighbours. Like his predecessors, he sponsored artists and architects. In 1765 he founded the Warsaw Corps of Cadets, the first state school in Poland for all classes of society.[115] In 1773 the king and parliament formed the Commission of National Education, the first Ministry of Education in European history.[116][117] In 1792, the king ordered the creation of Virtuti Militari, the oldest military decoration still in use.[118] Stanisław August also admired the culture of Ancient kingdoms, particularly Rome and Greece; Neoclassicism became the dominant form of architectural and cultural expression.
Politically, however, the vast Commonwealth was in steady decline and by 1768, it started to be considered by Russians as a protectorate of the Russian Empire despite the fact that it was still an independent state.[119][120] A majority of control over Poland was central to Catherine’s diplomatic and military strategies.[121] Attempts at reform, such as the Four-Year Sejm’s May Constitution, came too late. The country was partitioned in three stages by the Russian Empire, the German Kingdom of Prussia, and the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy. By 1795, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had been completely erased from the map of Europe. Poland and Lithuania were not re-established as independent countries until 1918.[122]
State organization and politics
Golden Liberty
The political doctrine of the Commonwealth was our state is a republic under the presidency of the King. Chancellor Jan Zamoyski summed up this doctrine when he said that Rex regnat et non-gubernat («The King reigns but [lit. ‘and’] does not govern»).[123] The Commonwealth had a parliament, the Sejm, as well as a Senat and an elected king (Pic. 1). The king was obliged to respect citizens’ rights specified in King Henry’s Articles as well as in pacta conventa, negotiated at the time of his election.[67]
The monarch’s power was limited in favour of a sizable noble class. Each new king had to pledge to uphold the Henrician Articles, which were the basis of Poland’s political system (and included near-unprecedented guarantees of religious tolerance). Over time, the Henrician Articles were merged with the pacta conventa, specific pledges agreed to by the king-elect. From that point onwards, the king was effectively a partner with the noble class and was constantly supervised by a group of senators. The Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislation (the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones).[67]
The foundation of the Commonwealth’s political system, the «Golden Liberty» (Latin: Aurea Libertas or Polish: Złota Wolność, a term used from 1573 on), included:
- election of the king by all nobles wishing to participate, known as wolna elekcja (free election);
- Sejm, the Commonwealth parliament which the king was required to hold every two years;
- pacta conventa (Latin), «agreed-to agreements» negotiated with the king-elect, including a bill of rights, binding on the king, derived from the earlier Henrician Articles.
- religious freedom guaranteed by Warsaw Confederation Act 1573,[25][page needed]
- rokosz (insurrection), the right of szlachta to form a legal rebellion against a king who violated their guaranteed freedoms;
- liberum veto (Latin), the right of an individual Sejm deputy to oppose a decision by the majority in a Sejm session; the voicing of such a «free veto» nullified all the legislation that had been passed at that session; during the crisis of the second half of the 17th century, Polish nobles could also use the liberum veto in provincial sejmiks;
- konfederacja (from the Latin confederatio), the right to form an organization to force through a common political aim.
The three regions (see below) of the Commonwealth enjoyed a degree of autonomy.[124][page needed] Each voivodship had its own parliament (sejmik), which exercised serious political power, including choice of poseł (deputy) to the national Sejm and charging of the deputy with specific voting instructions. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania had its own separate army, treasury and most other official institutions.[125][126]
Golden Liberty created a state that was unusual for its time, although somewhat similar political systems existed in the contemporary city-states like the Republic of Venice.[127][page needed] Both states were styled «Serenissima Respublica» or the «Most Serene Republic».[128] At a time when most European countries were headed toward centralization, absolute monarchy and religious and dynastic warfare, the Commonwealth experimented with decentralization,[23] confederation and federation, democracy and religious tolerance.[129]
This political system unusual for its time stemmed from the ascendance of the szlachta noble class over other social classes and over the political system of monarchy. In time, the szlachta accumulated enough privileges (such as those established by the Nihil novi Act of 1505) that no monarch could hope to break the szlachta’s grip on power. The Commonwealth’s political system is difficult to fit into a simple category, but it can be tentatively described as a mixture of:
- confederation and federation, with regard to the broad autonomy of its regions. It is, however, difficult to decisively call the Commonwealth either confederation or federation, as it had some qualities of both;
- oligarchy, as only the szlachta (nobility) – around 15% of the population – had political rights;[23]
- democracy, since all the szlachta were equal in rights and privileges, and the Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislation (the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones). Also, the 15% of Commonwealth population who enjoyed those political rights (the szlachta)[130] was a substantially larger percentage than in majority European countries even in the nineteenth century;[131] note that in 1820 in France only about 1.5% of the male adult population had the right to vote, and in 1840 in Belgium, only about 5%.[130][131]
- elective monarchy, since the monarch, elected by the szlachta, was Head of State;
- constitutional monarchy, since the monarch was bound by pacta conventa and other laws, and the szlachta could disobey any king’s decrees they deemed illegal.
Magnate oligarchy
The end of the Jagiellonian dynasty in 1572 – after nearly two centuries – disrupted the fragile equilibrium of the Commonwealth’s government. Power increasingly slipped away from the central government to the nobility.[67]
When presented with periodic opportunities to fill the throne, the szlachta exhibited a preference for foreign candidates who would not establish a strong and long-lasting dynasty. This policy often produced monarchs who were either totally ineffective or in constant debilitating conflict with the nobility.[citation needed] Furthermore, aside from notable exceptions such as the able Stefan Batory from Transylvania (1576–86), the kings of foreign origin were inclined to subordinate the interests of the Commonwealth to those of their own country and ruling house. This was especially visible in the policies and actions of the first two elected kings from the Swedish House of Vasa, whose politics brought the Commonwealth into conflict with Sweden, culminating in the war known as the Deluge (1655), one of the events that mark the end of the Commonwealth’s Golden Age and the beginning of the Commonwealth’s decline.[132]
The Zebrzydowski Rebellion (1606–1607) marked a substantial increase in the power of the Polish magnates, and the transformation of szlachta democracy into magnate oligarchy. The Commonwealth’s political system was vulnerable to outside interference, as Sejm deputies bribed[133][134] by foreign powers might use their liberum veto to block attempted reforms. This sapped the Commonwealth and plunged it into political paralysis and anarchy for over a century, from the mid-17th century to the end of the 18th, while its neighbours stabilized their internal affairs and increased their military might.[citation needed]
Late reforms
The Commonwealth did eventually make a serious effort to reform its political system, adopting in 1791 the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which historian Norman Davies calls the first of its kind in Europe.[37] The revolutionary Constitution recast the erstwhile Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as a Polish–Lithuanian federal state with a hereditary monarchy and abolished many of the deleterious features of the old system.
The new constitution:
- abolished the liberum veto and banned the szlachta’s confederations;
- provided for a separation of powers among legislative, executive and judicial branches of government;
- established «popular sovereignty» and extended political rights to include not only the nobility but the bourgeoisie;
- increased the rights of the peasantry;
- preserved religious tolerance (but with a condemnation of apostasy from the Catholic faith).
These reforms came too late, however, as the Commonwealth was immediately invaded from all sides by its neighbors, which had been content to leave the Commonwealth alone as a weak buffer state, but reacted strongly to attempts by king Stanisław August Poniatowski and other reformers to strengthen the country.[124][page needed] Russia feared the revolutionary implications of the 3 May Constitution’s political reforms and the prospect of the Commonwealth regaining its position as a European power. Catherine the Great regarded the May constitution as fatal to her influence[135] and declared the Polish constitution Jacobinical.[136] Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin drafted the act for the Targowica Confederation, referring to the constitution as the «contagion of democratic ideas».[137] Meanwhile, Prussia and Austria used it as a pretext for further territorial expansion.[136] Prussian minister Ewald Friedrich von Hertzberg called the constitution «a blow to the Prussian monarchy»,[138] fearing that a strengthened Poland would once again dominate Prussia.[135][139] In the end, the 3 May Constitution was never fully implemented, and the Commonwealth entirely ceased to exist only four years after its adoption.[140]
Economy
Gdańsk (Danzig), the Commonwealth’s chief seaport and trading centre from which goods would be transported along the Vistula River to Warsaw, Kraków and other towns in the country.
Cereals exports in the years 1619–1799. Agriculture, once extremely profitable to the nobility, became much less so after the mid-17th century.
The economy of the Commonwealth was predominantly based on agricultural output and trade, though there was an abundance of artisan workshops and manufactories — notably paper mills, leather tanneries, ironworks, glassworks and brickyards.[141] Some major cities were home to craftsmen, jewellers and clockmakers.[141] The majority of industries and trades were concentrated in the Kingdom of Poland; the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was more rural and its economy was driven by farming and clothmaking.[141] Mining developed in the south-west region of Poland which was rich in natural resources such as lead, coal, copper and salt.[142] The currency used in Poland–Lithuania was the złoty (meaning «the golden») and its subunit, the grosz. Foreign coins in the form of ducats, thalers and shillings were widely accepted and exchanged.[143] The city of Gdańsk had the privilege of minting its own coinage.[144] In 1794, Tadeusz Kościuszko began issuing the first Polish banknotes.[145]
The country played a significant role in the supply of Western Europe by the export of grain (rye), cattle (oxen), furs, timber, linen, cannabis, ash, tar, carminic acid and amber.[146][147][148][149] Cereals, cattle and fur amounted to nearly 90% of the country’s exports to European markets by overland and maritime trade in the 16th century.[148] From Gdańsk, ships carried cargo to the major ports of the Low Countries, such as Antwerp and Amsterdam.[150][151] The land routes, mostly to the German provinces of the Holy Roman Empire such as the cities of Leipzig and Nuremberg, were used for the export of live cattle (herds of around 50,000 head) hides, salt, tobacco, hemp and cotton from the Greater Poland region.[152][153] In turn, the Commonwealth imported wine, beer, fruit, exotic spices, luxury goods (e.g. tapestries, Pic. 5), furniture, fabrics as well as industrial products like steel and tools.[154]
The agricultural sector was dominated by feudalism based on the plantation system (serfs).[32] Slavery was forbidden in Poland in the 15th century, and formally abolished in Lithuania in 1588,[155] replaced by the second enserfment. Typically a nobleman’s landholding comprised a folwark, a large farmstead worked by serfs to produce surpluses for internal and external trade. This economic arrangement worked well for the ruling classes and nobles in the early years of the Commonwealth, which was one of the most prosperous eras of the grain trade.[156] The economic strength of Commonwealth grain trade waned from the late 17th century on. Trade relationships were disrupted by the wars, and the Commonwealth proved unable to improve its transport infrastructure or its agricultural practices.[157] Serfs in the region were increasingly tempted to flee.[158] The Commonwealth’s major attempts at countering this problem and improving productivity consisted of increasing serfs’ workload and further restricting their freedoms in a process known as export-led serfdom.[157][158]
The owner of a folwark usually signed a contract with merchants of Gdańsk, who controlled 80% of this inland trade, to ship the grain north to that seaport on the Baltic Sea.[159] Countless rivers and waterways in the Commonwealth were used for shipping purposes, including the Vistula, Pilica, Bug, San, Nida, Wieprz, Neman. The rivers had relatively developed infrastructure, with river ports and granaries. Most of the river shipping moved north, southward transport being less profitable, and barges and rafts were often sold off in Gdańsk for lumber. Grodno become an important site after formation of a customs post at Augustów in 1569, which became a checkpoint for merchants travelling to the Crown lands from the Grand Duchy.[160]
Coat of arms of the Commonwealth on a 15 ducat coin, 1617
5-złoty banknote issued in 1794
Urban population of the Commonwealth was low compared to Western Europe. Exact numbers depend on calculation methods. According to one source, the urban population of the Commonwealth was about 20% of the total in the 17th century, compared to approximately 50% in the Netherlands and Italy (Pic. 7).[149] Another source suggests much lower figures: 4–8% urban population in Poland, 34–39% in the Netherlands and 22–23% in Italy.[161] The Commonwealth’s preoccupation with agriculture, coupled with the nobles’ privileged position when compared to the bourgeoisie, resulted in a fairly slow process of urbanization and thus a rather slow development of industries.[149] The nobility could also regulate the price of grain for their advantage, thus acquiring much wealth. Some of the largest trade fairs in the Commonwealth were held at Lublin.[162]
Several ancient trading routes such as the Amber Road (Pic. 4)[163] extended across Poland–Lithuania, which was situated in the heart of Europe and attracted foreign merchants or settlers.[164] Countless goods and cultural artefacts continued to pass from one region to another via the Commonwealth, particularly that the country was a link between the Middle East, the Ottoman Empire and Western Europe.[165] For instance, Isfahan rugs imported from Persia to the Commonwealth were incorrectly known as «Polish rugs» (French: Polonaise) in Western Europe.[166]
Military
Kraków Militia, a local guard formation in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth during the 16th and 17th centuries
The military in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth evolved from the merger of the armies from the Polish Kingdom and from the Grand Lithuanian Duchy, though each state maintained its own division.[167] The united armed forces comprised the Crown Army (armia koronna), recruited in Poland, and the Lithuanian Army (armia litewska) in the Grand Duchy.[167] The military was headed by the Hetman, a rank equivalent to that of a general or supreme commander in other countries. Monarchs could not declare war or summon an army without the consent of the Sejm parliament or the Senate.[168] The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Navy never played a major role in the military structure from the mid-17th century onwards.[169]
The most prestigious formation of the two respective armes were their 16th- and 17th-century heavy cavalry in the form of Winged Hussars (husaria), whereas the Polish Royal Guards and Lithuanian Guards [pl] were the elite of the infantry; the regiments were supervised by the king and his family.[170] In 1788, the Great Sejm approved landslide reforms and defined future structures of the military; the Crown Army was to be split into four divisions, with seventeen field infantry regiments and eight cavalry brigades excluding special units; the Lithuanian Army was to be subdivided into two divisions, eight field regiments and two cavalry brigades excluding special units.[171] If implemented, the reform predicted an army of almost 100,000 men.[172]
The armies of those states differed from the organization common in other parts of Europe; according to Bardach, the mercenary formations (wojsko najemne), common in Western Europe, never gained widespread popularity in Poland.[173] Brzezinski, however, notes that foreign mercenaries did form a significant portion of the more elite infantry units, at least until the early 17th century.[174] In 16th-century Poland, several other formations formed the core of the military.[175] There was a small standing army, obrona potoczna («continuous defense») about 1,500–3,000 strong, paid for by the king, and primarily stationed at the troubled southern and eastern borders.[175][176] It was supplemented by two formations mobilized in case of war — the pospolite ruszenie (Polish for levée en masse – feudal levy of mostly noble knights-landholders), and the wojsko zaciężne, recruited by the Polish commanders for the conflict. It differed from other European mercenary formations in that it was commanded by Polish officers, and dissolved after the conflict has ended.[175]
A historical re-enactor dressed in the Polish Winged Hussars armour
Several years before the Union of Lublin, the Polish obrona potoczna was reformed, as the Sejm (national parliament of Poland) legislated in 1562–1563 the creation of wojsko kwarciane, named after kwarta tax levied on the royal lands for the purpose of maintaining this formation.[175] This formation was also paid for by the king, and in the peacetime, numbered about 3,500–4,000 men according to Bardach;[175] Brzezinski gives the range of 3,000–5,000.[176] It was composed mostly of the light cavalry units manned by nobility (szlachta) and commanded by hetmans.[175][177] Often, in wartime, the Sejm would legislate a temporary increase in the size of the wojsko kwarciane.[175]
Following the end of the Commonwealth, the Polish-Lithuanian military tradition would be continued by the Napoleonic Polish Legions and the Army of the Duchy of Warsaw.[178]
Culture
Science and literature
The Commonwealth was an important European center for the development of modern social and political ideas. It was famous for its rare quasi-democratic political system, praised by philosophers, and during the Counter-Reformation was known for near-unparalleled religious tolerance, with peacefully coexisting Roman Catholic, Jewish, Orthodox Christian, Protestant and Muslim (Sufi) communities. In the 18th century, the French Catholic Rulhiere wrote of 16th century Poland: «This country, which in our day we have seen divided on the pretext of religion, is the first state in Europe that exemplified tolerance. In this state, mosques arose between churches and synagogues.»[33] The Commonwealth gave rise to the famous Christian sect of the Polish Brethren, antecedents of British and American Unitarianism.[179]
With its political system, the Commonwealth gave birth to political philosophers such as Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski (1503–1572) (Pic. 9), Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki (1530–1607) and Piotr Skarga (1536–1612). Later, works by Stanisław Staszic (1755–1826) and Hugo Kołłątaj (1750–1812) helped pave the way for the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which Norman Davies calls the first of its kind in Europe.[37]
Kraków’s Jagiellonian University is one of the oldest universities in the world (established in 1364),[180] together with the Jesuit Academy of Wilno (established in 1579) they were the major scholarly and scientific centers in the Commonwealth. The Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, Polish for Commission for National Education, formed in 1773, was the world’s first national Ministry of Education.[181] Commonwealth scientists included: Martin Kromer (1512–1589), historian and cartographer; Michael Sendivogius (1566–1636), alchemist and chemist; Jan Brożek (Ioannes Broscius in Latin) (1585–1652), polymath: a mathematician, physician and astronomer; Krzysztof Arciszewski (Crestofle d’Artischau Arciszewski in Portuguese) (1592–1656), engineer, ethnographer, general and admiral of the Dutch West Indies Company army in the war with the Spanish Empire for control of Brazil;[182] Kazimierz Siemienowicz (1600–1651), military engineer, artillery specialist and a founder of rocketry; Johannes Hevelius (1611–1687), astronomer, founder of lunar topography; Michał Boym (1612–1659), orientalist, cartographer, naturalist and diplomat in Ming Dynasty’s service (Pic. 11); Adam Adamandy Kochański (1631–1700), mathematician and engineer; Baal Shem Tov (הבעל שם טוב in Hebrew) (1698–1760), considered to be the founder of Hasidic Judaism; Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt (1728–1810), astronomer and mathematician (Pic. 12); Jan Krzysztof Kluk (1739–1796), naturalist, agronomist and entomologist, John Jonston (1603–1675) scholar and physician, descended from Scottish nobility. In 1628 the Czech teacher, scientist, educator, and writer John Amos Comenius took refuge in the Commonwealth, when the Protestants were persecuted under the Counter Reformation.[179][183]
The works of many Commonwealth authors are considered classics, including those of Jan Kochanowski (Pic. 10), Wacław Potocki, Ignacy Krasicki, and Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz. Many szlachta members wrote memoirs and diaries. Perhaps the most famous are the Memoirs of Polish History by Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł (1595–1656) and the Memoirs of Jan Chryzostom Pasek (ca. 1636–ca. 1701). Jakub Sobieski (1590–1646) (father of John III Sobieski) wrote notable diaries. During the Khotyn expedition in 1621 he wrote a diary called Commentariorum chotinensis belli libri tres (Diary of the Chocim War), which was published in 1646 in Gdańsk. It was used by Wacław Potocki as a basis for his epic poem, Transakcja wojny chocimskiej (The Progress of the War of Chocim). He also authored instructions for the journey of his sons to Kraków (1640) and France (1645), a good example of liberal education of the era.[184]
Art and music
The art and music of the Commonwealth was largely shaped by prevailing European trends, though the country’s minorities, foreigners as well as native folk cultures also contributed to its versatile nature. A common art form of the Sarmatian period were coffin portraits (portrety trumienne) used in funerals and other important ceremonies.[185] As a rule, such portraits were nailed to sheet metal, six- or eight- sided in shape, fixed to the front of a coffin placed on a high, ornate catafalque.[186] These were a unique and distinguishable feature of the Commonwealth’s high culture, not found elsewhere in Europe.[187] A similar tradition was only practiced in Roman Egypt.[187] Polish monarchs and nobles frequently invited and sponsored foreign painters and artisans, notably from the Low Countries (the Netherlands, Flanders and Belgium), Germany or Italy.[188] The interiors of upper-class residences, palaces and manors were adorned by wall tapestries (arrasy or tapiseria) imported from Western Europe; the most renowned collection are the Jagiellonian tapestries exhibited at Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków.[189]
The economic, cultural and political ties between France and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth gave rise to the term à la polonaise, French for «Polish-styled».[190] With the marriage of Marie Leszczyńska to Louis XV of France in 1725, Polish culture began to flourish at the Palace of Versailles.[191] Polish beds (lit à la polonaise) draped with baldachins became a centrepiece of Louis XV furniture in French chateaus.[192] Folk flower motifs as well as Polish fashion were popularized in the form of a back-draped polonaise dress (robe à la polonaise) worn by aristocrats at Versailles.[193]
The religious cultures of Poland–Lithuania coexisted and penetrated each other for the entirety of the Commonwealth’s history – the Jews adopted elements of the national dress,[194] loanwords and calques became commonplace and Roman Catholic churches in regions with significant Protestant populations were much simpler in décor than those in other parts of Poland–Lithuania.[195] Mutual influence was further reflected in the great popularity of Byzantine icons (Pic. 13) and the icons resembling effigies of Mary in the predominantly Latin territories of today’s Poland (Black Madonna) and Lithuania (Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn).[196] Conversely, Latin infiltration into Ruthenian Orthodox and Protestant art was also conventional (Pic. 3).[197]
Music was a common feature of religious and secular events. To that end many noblemen founded church and school choirs, and employed their own ensembles of musicians. Some, like Stanisław Lubomirski built their own opera houses (in Nowy Wiśnicz). Others, like Janusz Skumin Tyszkiewicz and Krzysztof Radziwiłł were known for their sponsorship of arts which manifested itself in their permanently retained orchestras, at their courts in Wilno (Vilnius).[198] Musical life further flourished under the House of Vasa. Both foreign and domestic composers were active in the Commonwealth. Sigismund III brought in Italian composers and conductors, such as Luca Marenzio, Annibale Stabile, Asprilio Pacelli, Marco Scacchi and Diomedes Cato for the royal orchestra. Notable home grown musicians, who also composed and played for the King’s court, included Bartłomiej Pękiel, Jacek Różycki, Adam Jarzębski, Marcin Mielczewski, Stanisław Sylwester Szarzyński, Damian Stachowicz, Mikołaj Zieleński and Grzegorz Gorczycki.[198]
Architecture
The architecture of the cities in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth reflected a combination of Polish, German and Italian trends. Italian Mannerism or the Late Renaissance had a profound impact on traditional burgher architecture which can be observed to this day – castles and tenements were fitted with central Italianate courtyards composed of arched loggias, colonnades, bay windows, balconies, portals and ornamental balustrades.[199] Ceiling frescos, sgraffito, plafonds and coffering (patterned ceilings; Polish kaseton; from Italian cassettone) were widespread.[200] Rooftops were generally covered with terracotta rooftiles. The most distinguishable feature of Polish Mannerism are decorative «attics» above the cornice on the façade.[201] Cities in northern Poland–Lithuania and in Livonia adopted the Hanseatic (or «Dutch») style as their primary form of architectural expression, comparable to that of the Netherlands, Belgium, northern Germany and Scandinavia.[202]
Wilanów Palace, completed in 1696, exemplifies the opulence of royal and noble residences in the Commonwealth.
The introduction of Baroque architecture was marked by construction of several Jesuit and Roman Catholic churches across Poland and Lithuania, notably the Peter and Paul Church in Kraków, the Corpus Christi Church in Nesvizh, Lublin Cathedral and UNESCO-enlisted sanctuary at Kalwaria Zebrzydowska. Fine examples of decorative Baroque and Rococo include Saint Anne’s in Kraków and the Fara Church in Poznań. Another characteristic is the common usage of black marble.[203] Altars, fonts, portals, balustrades, columns, monuments, tombstones, headstones and whole rooms (e.g. Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, St. Casimir Chapel of the Vilnius Cathedral and Vasa Chapel at Wawel Cathedral) were extensively decorated with black marble, which became popular after the mid-17th century.[204]
Magnates often undertook construction projects as monuments to themselves: churches, cathedrals, monasteries (Pic. 14), and palaces like the present-day Presidential Palace in Warsaw and Pidhirtsi Castle built by Grand Hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski. The largest projects involved entire towns, although in time many of them would lapse into obscurity or were abandoned. These towns were generally named after the sponsoring magnate. Among the most prominent is Zamość, founded by Jan Zamoyski and designed by the Italian architect Bernardo Morando as an ideal city. The magnates throughout Poland competed with the kings. The monumental castle Krzyżtopór, built in the style palazzo in fortezza between 1627 and 1644, had several courtyards surrounded by fortifications. Similar fortified complexes include castles in Łańcut and Krasiczyn.[citation needed]
The fascination with the culture and art of the Orient in the late Baroque period is reflected by Queen Marie’s Chinese Palace in Zolochiv (Złoczów).[205] 18th-century magnate palaces represents the characteristic type of Baroque suburban residence built entre cour et jardin (between the entrance court and the garden). Its architecture – a merger of European art with old Commonwealth building traditions are visible in Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (Pic. 15), Branicki Palace in Białystok, Potocki Palace in Radzyń Podlaski, Raczyński Palace in Rogalin, Nieborów Palace and Kozłówka Palace near Lubartów. Lesser nobility resided in country manor houses known as dworek. Neoclassicism replaced Baroque by the second half of the 18th century – the last ruler of the Poland–Lithuania, Stanisław August Poniatowski, greatly admired the classical architecture of Ancient Rome and promoted it as a symbol of the Polish Enlightenment.[206] The Palace on the Isle and the exterior of St. Anne’s Church in Warsaw are part of the neoclassical legacy of the former Commonwealth.
Szlachta and Sarmatism
The prevalent ideology of the szlachta became «Sarmatism», named after the Sarmatians, alleged ancestors of the Poles.[139] This belief system was an important part of szlachta culture, penetrating all aspects of its life. Sarmatism enshrined equality among szlachta, horseback riding, tradition, provincial quaint life in manor houses, peace and pacifism; championed oriental-inspired souvenirs or attire for men (żupan, kontusz, sukmana, pas kontuszowy, delia, szabla); favoured European Baroque architecture; endorsed Latin as a language of thought or expression; and served to integrate the multi-ethnic nobility by creating an almost nationalistic sense of unity and of pride in Golden Liberty.[139]
In its early, idealistic form, Sarmatism represented a positive cultural movement: it supported religious belief, honesty, national pride, courage, equality and freedom. In time, however, it became distorted. Late extreme Sarmatism turned belief into bigotry, honesty into political naïveté, pride into arrogance, courage into stubbornness and freedom into anarchy.[208] The faults of Sarmatism were blamed for the demise of the country from the late 18th century onwards. Criticism, often one-sided and exaggerated, was used by the Polish reformists to push for radical changes. This self-deprecation was accompanied by works of German, Russian and Austrian historians, who tried to prove that it was Poland itself that was to blame for its fall.[209]
Demographics
Social strata in the Commonwealth’s society in 1655. From left: Jew, barber surgeon, painter, butcher, musician, tailor, barmaid, pharmacist, shoemaker, goldsmith, merchant and Armenian
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was immensely multicultural throughout its existence — it comprised countless religious identities and ethnic minorities inhabiting the country’s vast territory.[210] The precise number of minority groups and their populations can only be hypothesized.[211] Statistically, the most prominent groups were the Poles, Lithuanians, Germans, Ruthenians and Jews.[212] There were also considerable numbers of Czechs, Hungarians, Livonians, Romanis, Vlachs, Armenians, Italians, Scots and the Dutch (Olędrzy), who were either categorized as merchants, settlers or refugees fleeing religious persecution.[212]
Prior to the union with Lithuania, the Kingdom of Poland was much more homogenous; approximately 70% of the population was Polish and Roman Catholic.[213] With the creation of the Commonwealth, the number of Poles in comparison to the total population decreased to 50%.[214] In 1569, the population stood at 7 million, with roughly 4.5 million Poles, 750,000 Lithuanians, 700,000 Jews and 2 million Ruthenians.[215] Historians Michał Kopczyński and Wojciech Tygielski suggest that with the territorial expansion after the Truce of Deulino in 1618, the Commonwealth’s population reached 12 million people, of which Poles constituted only 40%.[214][17] At that time the nobility made up 10% of the entire population and the burghers around 15%.[17] The average population density per square kilometer was: 24 in Mazovia, 23 in Lesser Poland, 19 in Greater Poland, 12 in Lublin palatinate, 10 in the Lwów area, 7 in Podolia and Volhynia, and 3 in the Kiev Voivodeship. There was a tendency for the people from the more densely inhabited western territories to migrate eastwards.[216]
Density of urban network of the Commonwealth per each voivodeship in 1650
A sudden change in the country’s demographics occurred in the mid-17th century.[17] The Second Northern War and the Deluge followed by famine in the period from 1648 to 1657 were accountable for at least 4 million deaths.[17] Coupled with further territorial losses, by 1717 the population had fallen to 9 million.[17] The population slowly recovered throughout the 18th century; just before the first partition of Poland in 1772, the Commonwealth’s population was 14 million, including around 1 million nobles.[217] In 1792, the population of Poland was around 11 million and included 750,000 nobles.[217]
The most multicultural and robust city in the country was Gdańsk, a major Hanseatic seaport on the Baltic and Poland’s wealthiest region. Gdańsk at the time was inhabited by a German-speaking majority[218] and further hosted large numbers of foreign merchants, particularly of Scottish, Dutch or Scandinavian extraction.[219] Historically, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was more diverse than the Kingdom of Poland, and was deemed a melting pot of many cultures and religions.[220] Hence, the inhabitants of the Grand Duchy were collectively known as Litvins regardless of their nationality, with the exception of Jews residing in Lithuania who were called Litvaks.
Despite guaranteed religious tolerance, gradual Polonization and Counter-Reformation sought to minimize the Commonwealth’s diversity; the aim was to root out some minorities by imposing the Polish language, Latin, Polish culture and the Roman Catholic religion where possible.[221] By the late 18th century, the Lithuanian language, culture and identity became vulnerable;[221] the country’s name was changed to «Commonwealth of Poland» in 1791.
Religion
The Warsaw Confederation signed on 28 January 1573 secured the rights of minorities and religions;[222] it allowed all persons to practice any faith freely, though religious tolerance varied at times. As outlined by Norman Davies, «the wording and substance of the declaration of the Confederation of Warsaw of were extraordinary with regards to prevailing conditions elsewhere in Europe; and they governed the principles of religious life in the Republic for over two hundred years.»[223] Subsequently, the Catholic church initiated a counter-reformation in Poland, relying heavily on methods of persuasion and legal means. As a result, compared to many other European countries, the conflict between the Catholics and the Protestants in Poland was relatively peaceful.[224][225]
Poland retained religious freedom laws during an era when religious persecution was an everyday occurrence in the rest of Europe.[226] The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a place where the most radical religious sects, trying to escape persecution in other countries of the Christian world, sought refuge.[227] In 1561 Giovanni Bernardino Bonifacio d’Oria, a religious exile living in Poland, wrote of his adopted country’s virtues to a colleague back in Italy: «You could live here in accordance with your ideas and preferences, in great, even the greatest freedoms, including writing and publishing. No one is a censor here.»[33] Others, particularly the leaders of the Roman Catholic church, the Jesuits and papal legates, were less optimistic about Poland’s religious frivolity.
«This country became a place of shelter for heretics» – Cardinal Stanislaus Hosius, papal legate to Poland.[227]
To be Polish, in remote and multi-ethnic parts of the Commonwealth, was then much less an index of ethnicity than of religion and rank; it was a designation largely reserved for the landed noble class (szlachta), which included Poles, but also many members of non-Polish origin who converted to Catholicism in increasing numbers with each following generation. For the non-Polish noble such conversion meant a final step of Polonization that followed the adoption of the Polish language and culture.[228] Poland, as the culturally most advanced part of the Commonwealth, with the royal court, the capital, the largest cities, the second-oldest university in Central Europe (after Prague), and the more liberal and democratic social institutions had proven an irresistible magnet for the non-Polish nobility in the Commonwealth.[23] Many referred to themselves as «gente Ruthenus, natione Polonus» (Ruthenian by blood, Polish by nationality) since the 16th century onwards.[229]
The church in Kamieniec Podolski was converted into a mosque during the Turkish occupation between 1672 and 1699, with the 33-meter minaret being added at that time.[231]
As a result, in the eastern territories a Polish (or Polonized) aristocracy dominated a peasantry whose great majority was neither Polish nor Catholic. Moreover, the decades of peace brought huge colonization efforts to the eastern territories (nowadays roughly western and central Ukraine),[232] heightening the tensions among nobles, Jews, Cossacks (traditionally Orthodox), Polish and Ruthenian peasants. When the latter, deprived of their native protectors among the Ruthenian nobility, turned for protection to cossacks that facilitated violence which in the end broke the Commonwealth. The tensions were aggravated by conflicts between Eastern Orthodoxy and the Greek Catholic Church following the Union of Brest, overall discrimination of Orthodox religions by dominant Catholicism,[233] and several Cossack uprisings. In the west and north, many cities had sizable German minorities, often belonging to Lutheran or Reformed churches. The Commonwealth had also one of the largest Jewish diasporas in the world – by the mid-16th century 80% of the world’s Jews lived in Poland (Pic. 16).[234]
Until the Reformation, the szlachta were mostly Catholics (Pic. 13). However, many noble families quickly adopted the Reformed religion. After the Counter-Reformation, when the Catholic Church regained power in Poland, the szlachta became almost exclusively Catholic.[235]
The Crown had about double the population of Lithuania and five times the income of the latter’s treasury. As with other countries, the borders, area and population of the Commonwealth varied over time. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski (1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km2 area and a population of 7.5 million.[236] After the Truce of Deulino (1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 990,000 km2 and a population of 11–12 million (including some 4 million Poles and close to a million Lithuanians).[237]
Languages
- Polish – officially recognized;[238] dominant language, used by most of the Commonwealth’s nobility[238][239][240][241] and by the peasantry in the Crown province;[242] official language in the Crown chancellery and since 1697 in the Grand Duchy chancellery.[243] Dominant language in the towns.[242]
- Latin – officially recognized;[238][244] commonly used in foreign relations[243] and popular as a second language among some of the nobility.[245]
- French – not officially recognized; replaced Latin at the royal court in Warsaw in the beginning of the 18th century as a language used in foreign relations and as genuine spoken language.[246][247] It was commonly used as a language of science and literature and as a second language among some of the nobility.[248]
- Ruthenian – also known as Chancellery Slavonic;[243] officially recognized;[238] official language in the Grand Duchy chancellery until 1697 (when replaced by Polish) and in Bratslav, Chernihiv, Kiev and Volhynian voivodeships until 1673;[249][250] used in some foreign relations[243][244][251] its dialects (modern Belarusian and Ukrainian) were widely used in the Grand Duchy and eastern parts of the Crown as spoken language.
- Lithuanian – not officially recognized;[238][252] but used in some official documents in the Grand Duchy[253][254][255] and, mostly, used as a spoken language in the northernmost part of the country (in Lithuania Proper)[256] and the northern part of Ducal Prussia (Polish fief).
- German – officially recognized;[238] used in some foreign relations,[243] in Ducal Prussia and by German minorities especially in the Royal Prussia and Greater Poland.[242][257]
- Hebrew – officially recognized;[238] and Aramaic used by Jews for religious, scholarly, and legal matters.
- Yiddish – not officially recognized;[258][259] used by Jews in their daily life[242]
- Italian – not officially recognized; used in some foreign relations and by Italian minorities in cities.[260]
- Armenian – officially recognized;[238] used by the Armenian minority.[259][261]
- Arabic – not officially recognized; used in some foreign relations[262] and by Tatars in their religious matters, they also wrote Ruthenian in the Arabic script.[263]
Legacy
The Duchy of Warsaw, established in 1807 by Napoleon Bonaparte, traced its origins to the Commonwealth. Other revival movements appeared during the November Uprising (1830–31), the January Uprising (1863–64) and in the 1920s, with Józef Piłsudski’s failed attempt to create a Polish-led Intermarium (Międzymorze) federation that, at its largest extent, would span from Finland in the north to the Balkans in the south.[264] The contemporary Republic of Poland considers itself a successor to the Commonwealth,[265] whereas the Republic of Lithuania, re-established at the end of World War I, saw the participation of the Lithuanian state in the old Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth mostly in a negative light at the early stages of regaining its independence,[266] although this attitude has been changing in recent years.[267]
Administrative divisions
While the term «Poland» was also commonly used to denote this whole polity, Poland was in fact only part of a greater whole – the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which comprised primarily two parts:
- the Crown of the Polish Kingdom (Poland proper), colloquially «the Crown»
- the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, colloquially «Lithuania»
The Commonwealth was further divided into smaller administrative units known as voivodeships (województwa). Each voivodeship was governed by a Voivode (wojewoda, governor). Voivodeships were further divided into starostwa, each starostwo being governed by a starosta. Cities were governed by castellans. There were frequent exceptions to these rules, often involving the ziemia subunit of administration.[citation needed]
The lands that once belonged to the Commonwealth are now largely distributed among several Central and East European countries: Poland, Ukraine, Moldova (Transnistria), Belarus, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia.[268][269] Also some small towns in Upper Hungary (today mostly Slovakia), became a part of Poland in the Treaty of Lubowla (Spiš towns).
Other notable parts of the Commonwealth, without respect to region or voivodeship divisions, include:
- Lesser Poland Province (Polish: Małopolska), southern Poland, with two largest cities, its capital at Kraków and Lublin in the north-east;
- Greater Poland Province (Polish: Wielkopolska), west–central Poland around Poznań and the Warta River system;
- Mazovia (Polish: Mazowsze), central Poland, with its capital at Warsaw;
- Lithuania Proper (Lithuanian: Didžioji Lietuva), northwest Grand Duchy, its most Catholic and ethnically Lithuanian part, capital Vilnius;
- Duchy of Samogitia (Lithuanian: Žemaitija; Polish: Żmudź), westernmost and most autonomous part of Grand Duchy of Lithuania, also the western part of Lithuania Proper, capital Raseiniai;
- Royal Prussia (Polish: Prusy Królewskie), at the southern shore of the Baltic Sea, was an autonomous area since the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), incorporated into the Crown in 1569 with the Commonwealth’s formation;
- Pomerelia (Polish: Pomorze Gdańskie), Pomerania around Gdańsk, western part of Royal Prussia;
- Ruthenia (Polish: Ruś), the eastern Commonwealth, adjoining Russia;
- Duchy of Livonia (Inflanty), a joint domain of the Crown and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Parts lost to Sweden in the 1620s and in 1660;
- Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (Lithuanian: Kuršas ir Žiemgala; Polish: Kurlandia i Semigalia), a northern fief of the Commonwealth. It established a colony in Tobago in 1637 and on St. Andrews Island at the Gambia River in 1651 (see Couronian colonization);
- Silesia (Polish: Śląsk) was not within the Commonwealth, but small parts belonged to various Commonwealth kings; in particular, the Vasa kings were dukes of Opole (Oppeln), Prudnik (Neustadt) and Racibórz (Ratibor) from 1645 to 1666.[270]
Topographical map of the Commonwealth in 1764
Commonwealth borders shifted with wars and treaties, sometimes several times in a decade, especially in the eastern and southern parts. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski (1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km2 area and a population of 7.5 million.[236] After the Truce of Deulino (1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 1 million km2 (990,000 km2) and a population of about 11 million.[237]
Geography
In the 16th century, the Polish bishop and cartographer Martin Kromer, who studied in Bologna, published a Latin atlas, entitled Poland: about Its Location, People, Culture, Offices and the Polish Commonwealth, which was regarded as one of the most comprehensive guides to the country.[271]
Kromer’s works and other contemporary maps, such as those of Gerardus Mercator, show the Commonwealth as mostly plains. The Commonwealth’s southeastern part, the Kresy, was famous for its steppes. The Carpathian Mountains formed part of the southern border, with the Tatra Mountain chain the highest, and the Baltic Sea formed the Commonwealth’s northern border. As with most European countries at the time, the Commonwealth had extensive forest cover, especially in the east. Today, what remains of the Białowieża Forest constitutes the last largely intact primeval forest in Europe.[272]
Image gallery
- Politics and economy
-
Statuta Regni Poloniae in ordinem alphabeti digesta (Statutes of the Polish Kingdom, Arranged in Alphabetical Order), 1563
-
-
18th century amber casket. Gdańsk patronized by the Polish court flourished as the center for amber working in the 17th century.[273]
-
-
Silver tankard by Józef Ceypler, Kraków, 1739–1745
-
Example of the merchant architecture: Konopnica’s tenement house in Lublin, 1575
-
Hussars’ armours, first half of the 17th century
- Science, art and architecture
-
De republica emendanda (1554) by Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski, proposed a deep programme of reforms of the state, society and church.
-
Title page of Treny (1580) by Jan Kochanowski, a series of elegies upon the death of his beloved daughter, is an acknowledged masterpiece.
-
-
-
-
See also
- History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1648)
- History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1648–1764)
- History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1764–1795)
- List of medieval great powers
- Armorial of Polish nobility
- List of szlachta
- Polish heraldry
- Lithuanian nobility
- Armenians in Poland
- History of the Germans in Poland
- History of the Jews in Poland
- History of Poland
- History of Lithuania
- Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth
- Polish–Lithuanian–Muscovite Commonwealth
Notes
- ^ Pro Fide, Lege et Rege was the motto since the 18th century.
a. ^ Name in native and official languages:
- Latin: Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae / Serenissima Res Publica Poloniae[39]
- French: Royaume de Pologne et Grand-duché de Lituanie / Sérénissime République de Pologne et Grand-duché de Lituanie[278]
- Polish: Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie
- Lithuanian: Lenkijos Karalystė ir Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė
- Belarusian: Каралеўства Польскае і Вялікае Княства Літоўскае (Karaleŭstva Polskaje і Vialikaje Kniastva Litoŭskaje)
- Ukrainian: Королівство Польське і Велике князівство Литовське
- German: Königreich Polen und Großfürstentum Litauen
b. ^ Some historians date the change of the Polish capital from Kraków to Warsaw between 1595 and 1611, although Warsaw was not officially designated capital until 1793.[279] The Commonwealth Sejm began meeting in Warsaw soon after the Union of Lublin and its rulers generally maintained their courts there, although coronations continued to take place in Kraków.[279] The modern concept of a single capital city was to some extent inapplicable in the feudal and decentralized Commonwealth.[279] Warsaw is described by some historians as the capital of the entire Commonwealth.[280][281] Wilno, the capital of the Grand Duchy,[282][283][284] is sometimes called the second capital of the entity.[285][286]
Notes
- ^ Royal Banner used by the Vasa dynasty
- ^
- Polish: Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów;
- Latin: Res Publica Utriusque Nationis;
- Lithuanian: Abiejų Tautų Respublika, Žečpospolita;
- German: Republik beider Nationen, Republik beider Völker, Republik Polen-Litauen;
- Ukrainian: Річ Посполита;
- Belarusian: Рэч Паспалітая;
- Ruthenian: Рѣчъ Посполита
- ^
- Polish: Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie;
- Latin: Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae;
- Lithuanian: Lenkijos Karalystė ir Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė;
- German: Königreich Polen und des Großfürstentums Litauen
- Ukrainian: Королівство Польське і Велике князівство Литовське;
- Belarusian: Польскае Каралеўства і Вялікае Княства Літоўскае
- ^ This quality of the Commonwealth was recognized by its contemporaries. Robert Burton, in his The Anatomy of Melancholy, first published in 1621, writes of Poland: «Poland is a receptacle of all religions, where Samosetans, Socinians, Photinians …, Arians, Anabaptists are to be found»; «In Europe, Poland and Amsterdam are the common sanctuaries [for Jews]».
References
- ^ a b Partitions of Poland at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ a b c d Jagiellonian University Centre for European studies, «A Very Short History of Kraków», see: «1596 administrative capital, the tiny village of Warsaw». Archived from the original on 12 March 2009. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- ^ Richters, Katja (2012). The Post-Soviet Russian Orthodox Church: Politics, Culture and Greater Russia. Routledge. p. 133. ISBN 9781136296369.
formed part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth which was ruled by Catholic monarchs who made Roman Catholicism the state religio…
- ^ a b Janusz Sykała: Od Polan mieszkających w lasach – historia Polski – aż do króla Stasia, Gdansk, 2010.
- ^ a b Georg Ziaja: Lexikon des polnischen Adels im Goldenen Zeitalter 1500–1600, p. 9.
- ^ «Artykuły henrykowskie — szlachecka prekonstytucja — Historia — polskieradio24.pl». polskieradio24.pl.
- ^ «Poland — The First Partition | Britannica». www.britannica.com.
- ^ a b Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 14, ISBN 83-7000-016-9.
- ^ Bertram Benedict (1919): A history of the great war. Bureau of national literature, inc. p. 21.
- ^ According to Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 16, ~ 990.000 km2
- ^ Hahn, Gordon M. (9 November 2021). The Russian Dilemma: Security, Vigilance and Relations with the West from Ivan III to Putin. McFarland. p. 35. ISBN 978-1-4766-8187-0.
- ^ Zbigniew Pucek: Państwo i społeczeństwo 2012/1, Krakow, 2012, p. 17.
- ^ Norman Davies, Europe: A History, Pimlico 1997, p. 554: «Poland–Lithuania was another country which experienced its ‘Golden Age’ during the sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries. The realm of the last Jagiellons was absolutely the largest state in Europe»
- ^ Piotr Wandycz (2001). The price of freedom (p.66). p. 66. ISBN 978-0-415-25491-5. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ^ Bertram Benedict (1919). A history of the great war. Bureau of national literature, inc. p. 21. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ^ According to Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 16, 990.000 km2
- ^ a b c d e f Based on 1618 population map Archived 17 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine (p. 115), 1618 languages map (p119), 1657–67 losses map (p. 128) and 1717 map Archived 17 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine (p. 141) from Iwo Cyprian Pogonowski, Poland a Historical Atlas, Hippocrene Books, 1987, ISBN 0-88029-394-2
- ^ According to Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 16, just over 9 million in 1618.
- ^ Maciej Janowski, Polish Liberal Thought, Central European University Press, 2001, ISBN 963-9241-18-0, Google Print: p. 3, p. 12
- ^ Paul W. Schroeder, The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848, Oxford University Press, 1996, ISBN 0-19-820654-2, Google print p. 84
- ^ Rett R. Ludwikowski, Constitution-Making in the Region of Former Soviet Dominance, Duke University Press, 1997, ISBN 0-8223-1802-4, Google Print, p. 34
- ^ a b c George Sanford, Democratic Government in Poland: Constitutional Politics Since 1989, Palgrave, 2002, ISBN 0-333-77475-2, Google print p. 11 – constitutional monarchy, p. 3 – anarchy
- ^ a b c d e Aleksander Gella, Development of Class Structure in Eastern Europe: Poland and Her Southern Neighbors, SUNY Press, 1998, ISBN 0-88706-833-2, Google Print, p. 13
- ^ «Formally, Poland and Lithuania were to be distinct, equal components of the federation … But Poland, which retained possession of the Lithuanian lands it had seized, had greater representation in the diet and became the dominant partner.»«Lublin, Union of». Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006.[1]
- ^ a b # Norman Davies, God’s Playground. A History of Poland, Vol. 1: The Origins to 1795, Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-925339-0 / ISBN 0-19-925340-4
- ^ Halina Stephan, Living in Translation: Polish Writers in America, Rodopi, 2003, ISBN 90-420-1016-9, Google Print p. 373. Quoting from Sarmatian Review academic journal mission statement: «Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was … characterized by religious tolerance unusual in premodern Europe»
- ^ Gross, Feliks (1999). Citizenship and Ethnicity: The Growth and Development of a Democratic Multiethnic Institution (notes). Greenwood Press. p. 122. ISBN 0-313-30932-9.
- ^ «In the mid-1500s, united Poland was the largest state in Europe and perhaps the continent’s most powerful state politically and militarily». «Poland». Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
- ^ Francis Dvornik (1992). The Slavs in European History and Civilization. Rutgers University Press. p. 300. ISBN 0-8135-0799-5.
- ^ Salo Wittmayer Baron (1976). A social and religious history of the Jews. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-08853-1.
- ^ Martin Van Gelderen, Quentin Skinner, Republicanism: A Shared European Heritage, Cambridge University Press, 2002, ISBN 0-521-80756-5 p. 54.
- ^ a b «The Causes of Slavery or Serfdom: A Hypothesis» Archived 15 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine (discussion and full online text) of Evsey Domar (1970). Economic History Review 30:1 (March), pp. 18–32.
- ^ a b c «Page Not Found: Error: IU Robert H. McKinney School of Law: IUPUI». IU Robert H. McKinney School of Law.
- ^ Blaustein, Albert (1993). Constitutions of the World. Fred B. Rothman & Company. ISBN 9780837703626.
- ^ Isaac Kramnick, Introduction, Madison, James (1987). The Federalist Papers. Penguin Classics. p. 13. ISBN 0-14-044495-5.
May second oldest constitution.
- ^ John Markoff describes the advent of modern codified national constitutions as one of the milestones of democracy, and states that «The first European country to follow the U.S. example was Poland in 1791.» John Markoff, Waves of Democracy, 1996, ISBN 0-8039-9019-7, p. 121.
- ^ a b c Davies, Norman (1996). Europe: A History. Oxford University Press. p. 699. ISBN 0-19-820171-0.
- ^ a b c «Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae – definicja, synonimy, przykłady użycia». sjp.pwn.pl. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- ^ a b Ex quo serenissima respublica Poloniae in corpore ad exempluin omnium aliarnm potentiarum, lilulum regiuin Borussiae recognoscere decrevit (…)
Antoine-François-Claude Ferrand (1820). «Volume 1». Histoire des trois démembremens de la Pologne: pour faire suite à l’histoire de l’Anarchie de Pologne par Rulhière (in French). Deterville. p. 182. - ^ the name given by Marcin Kromer in his work Polonia sive de situ, populis, moribus, magistratibus et re publica regni Polonici libri duo, 1577.
- ^ the therm used for instance in Zbior Deklaracyi, Not I Czynnosci Głownieyszych, Ktore Poprzedziły I Zaszły Pod Czas Seymu Pod Węzłem Konfederacyi Odprawuiącego Się Od Dnia 18. Wrzesnia 1772. Do 14 Maia 1773
- ^ Name used for the common state, Henryk Rutkowski, Terytorium, w: Encyklopedia historii gospodarczej Polski do 1945 roku, t. II, Warszawa 1981, s. 398.
- ^ Richard Buterwick. The Polish Revolution and the Catholic Church, 1788–1792: A Political History. Oxford University Press. 2012. pp. 5, xvii.
- ^ 1791 document signed by the King Stanislaw August «Zareczenie wzaiemne Oboyga Narodow» pp. 1, 5 [2]
- ^ Jasienica, Paweł (1997). Polska Jagiellonów. Polska: Prószyński i Spółka. pp. 30–32. ISBN 9788381238816.
- ^ Jasienica 1997, pp. 30–32
- ^ a b c Halecki 1991, p. 52
- ^ Halecki 1991, p. 71
- ^ Engel, Pál (2001). The Realm of St Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526. I.B. Tauris Publishers. p. 170. ISBN 1-86064-061-3.
- ^ Halecki, Oscar (1991). Jadwiga of Anjou and the Rise of East Central Europe. Polish Institute of Arts and Sciences of America. pp. 116–117. ISBN 0-88033-206-9.
- ^ Jasienica 1997, p. 63
- ^ Halecki 1991, p. 155
- ^ Manikowska, Halina (2005). Historia dla Maturzysty. Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Szkolne PWN. p. 141. ISBN 83-7195-853-6.
- ^ Bojtár, Endre (1999), Foreword to the Past: A Cultural History of the Baltic People, translated by Walter J. Renfroe, Budapest: Central European University Press, p. 182, ISBN 978-963-9116-42-9
- ^ Butterwick 2021, pp. 12–14
- ^ Butterwick 2021
- ^ Butterwick, Richard (2021). The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1733–1795. Yale University Press. p. 14. ISBN 9780300252200.
- ^ Borucki, Marek (2009). Historia Polski do 2009 roku. Polska: Mada. p. 57. ISBN 9788389624598.
- ^ Gierowski, Józef (1986a). Historia Polski 1505–1764. Warsaw: PWN. pp. 92–109. ISBN 83-01-03732-6.
- ^ a b Butterwick 2021, p. 21
- ^ Pernal, Andrew Boleslaw (2010). Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów a Ukraina. Polska: Księgarnia Akademicka. p. 10. ISBN 9788371889738.
- ^ Pernal 2010, p. 10
- ^ a b Maniecky & Szajnocha 1869, p. 504
- ^ Maniecky, Wojciech; Szajnocha, Karol (1869). Dziennik Literacki (in Polish). Ossoliński. p. 504.
- ^ The death of Sigismund II Augustus in 1572 was followed by a three-year Interregnum during which adjustments were made in the constitutional system. The lower nobility was now included in the selection process, and the power of the monarch was further circumscribed in favor of the expanded noble class. From that point, the king was effectively a partner with the noble class and constantly supervised by a group of senators.
«The Elective Monarchy». Poland – The Historical Setting. Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. 1992. Archived from the original on June 4, 2011. Retrieved July 15, 2011. - ^ Bardach, Juliusz (1987). Historia państwa i prawa polskiego (in Polish). Warszawa: PWN. pp. 216–217.
- ^ a b c d Bardach 1987, pp. 216–217
- ^ Stone, Daniel (2001). The Polish-Lithuanian state, 1386–1795 [A History of East Central Europe, Volume IV.] Seattle: University of Washington Press. p. 118. ISBN 0-295-98093-1.
- ^ Besala, Jerzy; Biedrzycka, Agnieszka (2005). Stefan Batory: Polski Słownik Biograficzny (in Polish). Vol. XLIII. p. 116.
- ^ a b Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, p. 116
- ^ Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, p. 117
- ^ Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, pp. 116–117
- ^ a b Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, pp. 118–119
- ^ Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, pp. 121
- ^ Szujski, Józef (1894). Dzieła Józefa Szujskiego. Dzieje Polski (in Polish). Vol. 3. Kraków: Szujski-Kluczycki. p. 139. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ pisze, Przemek (3 July 2013). «Bitwa pod Byczyną. Zamoyski upokarza Habsburgów i gwarantuje tron Zygmuntowi III – HISTORIA.org.pl – historia, kultura, muzea, matura, rekonstrukcje i recenzje historyczne». Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ^ Kizwalter, Tomasz (1987). Kryzys Oświecenia a początki konserwatyzmu polskiego (in Polish). Warszawa (Warsaw): Uniwersytet Warszawski. p. 21. Retrieved 3 May 2021.
- ^ Szujski 1894, p. 161
- ^ Peterson, Gary Dean (2014). Warrior Kings of Sweden. The Rise of an Empire in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries. McFarland, Incorporated, Publishers. ISBN 9781476604114. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Peterson 2014, p. 107
- ^ Jędruch, Jacek (1982). Constitutions, Elections, and Legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977. University Press of America. p. 89. ISBN 9780819125095. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ Dabrowski, Patrice M. (2014). Poland. The First Thousand Years. US: Cornell University Press. p. 168. ISBN 9781501757402. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Shubin, Daniel H. (2009). Tsars and Imposters. Russia’s Time of Troubles. New York: Algora. p. 201. ISBN 9780875866871. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ Cooper, J. P. (1979). The New Cambridge Modern History: Volume 4, The Decline of Spain and the Thirty Years War, 1609-48/49. CUP Archive. ISBN 9780521297134. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ Gillespie, Alexander (2017). The Causes of War. Vol. III: 1400 CE to 1650 CE. Portland: Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 194. ISBN 9781509917662. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Dyer, Thomas Henry (1861). The History of Modern Europe. Vol. From the Fall of Constantinople, in 1453, to the War in the Crimea, in 1857. Volume 2. London: J. Murray. p. 504. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ^ Podhorodecki, Leszek (1985). Rapier i koncerz: z dziejów wojen polsko-szwedzkich. Warsaw: Książka i Wiedza. pp. 191–200. ISBN 83-05-11452-X.
- ^ Gillespie 2017, p. 141
- ^ Miłobędzki, Adam (1980). Dzieje sztuki polskiej: Architektura polska XVII wieku (in Polish). Polska: Panstwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe. p. 115. ISBN 9788301013639. Retrieved 8 January 2021.
- ^ Czapliński, Władysław (1976). Władysław IV i jego czasy [Władysław IV and His Times] (in Polish). Warsaw: PW «Wiedza Poweszechna». pp. 102–118.
- ^ Czapliński 1976, p. 170
- ^ Czapliński 1976, p. 202
- ^ Czapliński 1976, pp. 353–356
- ^ Poland, the knight among nations, Louis Edwin Van Norman, New York: 1907, p. 18.
- ^ William J. Duiker, Jackson J. Spielvogel (2006). The Essential World History: Volume II: Since 1500. Cengage Learning. p. 336. ISBN 0-495-09766-7.
- ^ Gintel, Jan (1971). Wiek XVIII-XIX. Polska: Wydawnictwo Literackie. p. 143.
- ^ Gintel 1971, p. 143
- ^ Instytut Badań Literackich (1969). Studia staropolskie. Vol. 24, 25. Polska: Zakład Ossolińskich. p. 172.
- ^ Instytut Badań Literackich 1969, p. 172
- ^ Borucki, Marek (1976). Jak w dawnej Polsce królów obierano. Polska: Ludowa Spółdzielnia Wydawnicza. pp. 138–143.
- ^ Spórna (2003). Słownik władców Polski i pretendentów do tronu polskiego. Polska: Zielona Sowa. p. 30. ISBN 9788372205605.
- ^ Borucki 1976, pp. 138–143
- ^ Dobrowolski (1962). Historia sztuki polskiej w zarysie: Sztuka nowożytna. Polska: Wydawnictwo Literackie.
- ^ Davies, Norman (1992). Boże igrzysko. Historia Polski. Od początków do roku 1795. Polska: Znak. p. 412. ISBN 9788370063849.
- ^ Brückner, Aleksander (1931). Dzieje kultury polskiej. Czasy nowsze do roku 1831. Polska: Wiedza Powszechna. p. 27. ISBN 9788321408613.
- ^ Frost, Robert I (2000). The Northern Wars. War, State and Society in Northeastern Europe 1558–1721. Harlow: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-06429-4.
- ^ Tucker, S.C. (2010). A Global Chronology of Conflict, Vol. Two. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, LLC. p. 694. ISBN 9781851096671.
- ^ Tucker 2010, p. 710
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). «Polish Succession War» . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 21 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 981–982.
- ^ Lindsey, J. O. (ed). The Cambridge New Modern History, Volume 7.
- ^ a b Brückner 1931, p. 157
- ^ Rey Koslowski (2000). Migrants and citizens: demographic change in the European state system. Cornell University Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-8014-3714-4.
polish lithuanian commonwealth americas western europe.
- ^ Spórna 2003
- ^ Bartłomiej Szyndler (2009). Racławice 1794. Bellona Publishing. pp. 64–65. ISBN 9788311116061. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ^ Bartłomiej Kaczorowski (2004). Nowa encyklopedia powszechna PWN: Sud-żyz. Polska: PWN. p. 75. ISBN 9788301141875.
- ^ Norman Davies (28 February 2005). God’s Playground: 1795 to the present. Columbia University Press. p. 167. ISBN 978-0-231-12819-3.
- ^ Ted Tapper; David Palfreyman (2005). Understanding Mass Higher Education: Comparative Perspectives On Access. RoutledgeFalmer. p. 140. ISBN 978-0-415-35491-2.
- ^ Kitowicz, Jędrzej (2019). Customs and Culture in Poland Under the Last Saxon King. Central European University Press. p. 262. ISBN 9789633862766.
- ^ Sužiedėlis 2011, p. xxv.
- ^ Andrzej Jezierski, Cecylia Leszczyńska, Historia gospodarcza Polski, 2003, s. 68.
- ^ Russia’s Rise as a European Power, 1650–1750 Archived 5 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine, Jeremy Black, History Today, Vol. 36 Issue: 8, August 1986.
- ^ Roman, Wanda Krystyna (2003). Działalność niepodległościowa żołnierzy polskich na Litwie i Wileńszczyźnie. Polska: Naukowe Wydawn. Piotrkowskie. p. 23. ISBN 9788388865084. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Jan Zamoyski’s speech in the Parliament, 1605 Harbottle Thomas Benfield (2009). Dictionary of Quotations (Classical). BiblioBazaar, LLC. p. 254. ISBN 978-1-113-14791-2.
- ^ a b Pacy, James S.; James T. McHugh (2001). Diplomats without a Country: Baltic Diplomacy, International Law, and the Cold War (1st ed.). Post Road West, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-31878-6. Retrieved 3 September 2006.
- ^ Josef Macha (1974). Ecclesiastical Unification. Pont. Institutum Orientalium Studiorum. p. 154.
- ^ Andrej Kotljarchuk (2006). In the Shadows of Poland and Russia: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Sweden in the European Crisis of the Mid-17th Century. Stockholm University. pp. 37, 87. ISBN 978-91-89-31563-1.
- ^ Joanna Olkiewicz, Najaśniejsza Republika Wenecka (Most Serene Republic of Venice), Książka i Wiedza, 1972, Warszawa
- ^ Joseph Conrad, Notes on Life and Letters: Notes on Life and Letters, Cambridge University Press, 2004, ISBN 0-521-56163-9, Google Print, p. 422 (notes)
- ^ Frost, Robert I. The Northern Wars: War, State and Society in northeastern Europe, 1558–1721. Harlow, England; New York: Longman’s. 2000. Especially pp. 9–11, 114, 181, 323.
- ^ a b David Sneath (2007). The headless state: aristocratic orders, kinship society, & misrepresentations of nomadic inner Asia. Columbia University Press. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-231-14054-6.
- ^ a b M. L. Bush (1988). Rich noble, poor noble. Manchester University Press ND. pp. 8–9. ISBN 0-7190-2381-5.
- ^ Frost, Robert I. (2004). After the Deluge; Poland-Lithuania and the Second Northern War, 1655–1660. Cambridge: University Press. ISBN 9780521544023.
- ^ William Christian Bullitt, Jr., The Great Globe Itself: A Preface to World Affairs, Transaction Publishers, 2005, ISBN 1-4128-0490-6, Google Print, pp. 42–43
- ^ John Adams, The Political Writings of John Adams, Regnery Gateway, 2001, ISBN 0-89526-292-4, Google Print, p. 242
- ^ a b Henry Eldridge Bourne, The Revolutionary Period in Europe 1763 to 1815, Kessinger Publishing, 2005, ISBN 1-4179-3418-2, Google Print p. 161
- ^ a b Wolfgang Menzel, Germany from the Earliest Period Vol. 4, Kessinger Publishing, 2004, ISBN 1-4191-2171-5, Google Print, p. 33
- ^ Isabel de Madariaga, Russia in the Age of Catherine the Great, Sterling Publishing Company, Inc., 2002, ISBN 1-84212-511-7, Google Print p. 431
- ^ Carl L. Bucki, The Constitution of May 3, 1791 Archived 5 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Text of a presentation made at the Polish Arts Club of Buffalo on the occasion of the celebrations of Poland’s Constitution Day on 3 May 1996. Retrieved 20 March 2006.
- ^ a b c Piotr Stefan Wandycz. The Price of Freedom: A History of East Central Europe from the Middle Ages to the Present, Routledge (UK), 2001, ISBN 0-415-25491-4, Google Print p. 131.
- ^ Niepodległość. Vol. 6. Polska: Fundacja «Polonia Restituta,». 1991. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Sobiech, Marcin (2018). «Jak powstawała i co zawiera mapa Rzeczpospolitej Obojga Narodów». Exgeo (in Polish). Marcin Sobiech. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Kucharczuk 2011, p. 64
- ^ «shillings – Polish translation – Linguee». Linguee.com. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
- ^ Flisowski, Zbigniew (1985). Bastion u wrót Gdańska. Polska: Nasza Księgarnia. p. 11. ISBN 9788310087799.
- ^ «Pierwsze polskie banknoty». Skarbnica Narodowa (in Polish). Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Gdańskie Towarzystwo Naukowe (1991). Seria popularno-naukowa «Pomorze Gdańskie» (in Polish). Vol. 19. Gdańsk: Towarzystwo Naukowe. p. 149. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Kucharczuk, Katarzyna (2011). Polska samorządna; ilustrowane dzieje administracji i samorządu terytorialnego na tle historii Polski. Carta Blanca. p. 66. ISBN 9788377051207. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ a b Zsigmond Pál Pach, Zs. P. Pach (1970). The role of East-Central Europe in international trade, 16th and 17th centuries. Akadémiai Kiadó. p. 220.
- ^ a b c Institute of History (Polish Academy of Sciences) (1991). «Volumes 63–66». Acta Poloniae historica. National Ossoliński Institute. p. 42. ISBN 0-88033-186-0.
- ^ Krzysztof Olszewski (2007). The Rise and Decline of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth due to Grain Trade. pp. 6–7.
- ^ Maciej Kobyliński. «Rzeczpospolita spichlerzem Europy». www.polinow.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ Nicholas L. Chirovsky (1984). The Lithuanian-Rus’commonwealth, the Polish domination, and the Cossack-Hetman state. Philosophical Library. p. 367. ISBN 0-8022-2407-5.
- ^ Sven-Olof Lindquist, Birgitta Radhe (1989). Economy and culture in the Baltic, 1650–1700: papers of the VIIIth Visby Symposium held at Gotland’s Historical Museum, Visby, August 18th–22th [sic], 1986. Gotlands Fornsal. p. 367. ISBN 91-971048-8-4.
- ^ Sowa, Jan (2015). Inna Rzeczpospolita jest możliwa! Widma przeszłości, wizje przyszłości (in Polish). Polska: WAB. ISBN 9788328022034. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ «Welcome to Encyclopædia Britannica’s Guide to History». Britannica.com. 31 January 1910. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ PPerry Anderson (1979). Lineages of the absolutist state. Verso. p. 285. ISBN 0-86091-710-X.
- ^ a b Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries (2007). A history of Eastern Europe: crisis and change. Taylor & Francis. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-415-36627-4.
- ^ a b Yves-Marie Bercé (1987). Revolt and revolution in early modern Europe: an essay on the history of political violence. Manchester University Press. p. 151.
- ^ Krzysztof Olszewski (2007). The Rise and Decline of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth due to Grain Trade (PDF). p. 7. Retrieved 22 April 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Jarmo Kotilaine (2005). Russia’s foreign trade and economic expansion in the seventeenth century: windows on the world. BRILL. p. 47. ISBN 90-04-13896-X.
- ^ Allen, Robert. «Economic Structure and agricultural productivity in Europe, 1300–1800» (PDF). Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ kurkowski, Jan (2010). «Jarmarki w województwie lubelskim w XVI w.» Pasaż Wiedzy. Muzeum Pałacu Króla Jana III w Wilanowie. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Billock, Jennifer (2019). «Follow the Ancient Amber Road». Smithsonian Magazine. Smithsonian. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ «Drogi handlowe w dawnej Polsce». PWN. Encyklopedia PWN. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Polskie Towarzystwo Historyczne (1989). Kwartalnik historyczny. Vol. 3–4. Polskie Towarzystwo Historyczne. p. 214. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ ««Polonaise» carpet». www.museu.gulbenkian.pt. Archived from the original on February 28, 2003. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- ^ a b Stachowicz 1894, p. 279
- ^ Tomaszewska, A. «Wolna elekcja i zasady jej funkcjonowania» (PDF). Tomaszewska. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Juliusz Bardach, Zdzisław Kaczmarczyk, Bogusław Leśnodorski (1957). Historia państwa i prawa Polski do roku 1795 (in Polish). Vol. 2. Polska: Państwowe Wydawn. Naukowe. pp. 306–308. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Richard Brzezinski (1988). Polish Armies 1569–1696 (2). Osprey Publishing. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-85045-744-5.
- ^ Stachowicz, Michał (1894). Wojsko polskie Kościuszki w roku 1794 (in Polish). Poznań: Księgarnia Katolicka. pp. 23–25. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ Stachowicz 1894, pp. 23–25
- ^ Juliusz Bardach, Boguslaw Lesnodorski, and Michal Pietrzak, Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego (Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe), 1987, p. 229.
- ^ Brzezinski (1988), p. 6.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bardach et al. (1987), pp. 229–230.
- ^ a b Brzezinski (1987), p. 10.
- ^ Bardach et al. (1987), pp. 227–228.
- ^ Zwoliński, Stefan (1995). Naczelni wodzowie i wyżsi dowódcy Polskich Sił Zbrojnych na Zachodzie (in Polish). Polska: Wojskowy Instytut Historyczny. p. 12. ISBN 9788386268276. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ a b J. K. Fedorowicz; Maria Bogucka; Henryk Samsonowicz (1982). A Republic of nobles: studies in Polish history to 1864. CUP Archive. p. 209. ISBN 0-521-24093-X.
- ^ Jacek F. Gieras (1994). «Volume 30 of Monographs in electrical and electronic engineering, Oxford science publications». Linear induction drives. Oxford University Press. p. V. ISBN 0-19-859381-3.
- ^ Norman Davies (2005). God’s Playground: A History of Poland. Columbia University Press. p. 167. ISBN 0-231-12819-3.
- ^ «Setting Sail». www.warsawvoice.pl. 29 May 2003. Retrieved 21 May 2009.
- ^ Paul Peucker. «Jan Amos Comenius (1592–1670)» (PDF). www.moravian.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 2, 2009. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- ^ Jacek Jędruch (1982). Constitutions, Elections, and Legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977: A Guide to Their History. University Press of America. p. 125. ISBN 978-08-19-12509-5.
- ^ «Portraits collection». www.muzeum.leszno.pl. Retrieved 18 May 2009.
- ^ Mariusz Karpowicz (1991). Baroque in Poland. Arkady. p. 68. ISBN 83-213-3412-1.
- ^ a b Łyczak, Bartłomiej (1 January 2011). «The Coffin Portrait and Celebration of Death in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the Modern Period». IKON. 4: 233–242. doi:10.1484/J.IKON.5.100699.
- ^ Szablowski, Jerzy (1975). Arrasy flamandzkie w zamku królewskim na Wawelu (in Polish). Polska: Arkady. p. 15. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Szablowski, Jerzy (1975). Arrasy flamandzkie w zamku królewskim na Wawelu (in Polish). Polska: Arkady. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Orlińska-Mianowska, Ewa (2008). Fashion world of the 18th and early 19th century. Polska: Bosz. ISBN 9788387730727. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Singleton, Esther (12 December 2019). «French and English furniture distinctive styles and periods described and illustrated». Good Press – via Google Books.
- ^ Dialog. Miesiȩcznik poświȩcony dramaturgii współczesnej, teatralnej, filmowej, radiowej, telewizyjnej. Vol. 11. Polska: RSW «Prasa». 1966. p. 6. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Waugh, Norah (1968). The Cut of Women’s Clothes. London: Routledge. pp. 72–73. ISBN 0-87830-026-0.
- ^ Lubliner, Ludwig (1858). Obrona Żydów zamieszkałych w krajach polskich od niesłusznych zarzutów i fałszywych oskarzeń. Brussels: C. Vanderauwer. p. 7. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Muthesius, Stefan (1994). Polska; art, architecture, design 966–1990. Langewiesche Köster. p. 34. ISBN 9783784576121. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Państwowy Instytut Badania Sztuki Ludowej (1974). «Volumes 28–29». Polska sztuka ludowa (Polish Folk Art). Państwowy Instytut Sztuki. p. 259.
- ^ Paul Robert Magocsi (1996). A history of Ukraine. University of Toronto Press. pp. 286–287. ISBN 0-8020-7820-6.
- ^ a b Michael J. Mikoś. «Baroque». www.staropolska.pl. Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ^ Rolska-Boruch, Irena (2003). «Domy pańskie» na Lubelszczyźnie od późnego gotyku do wczesnego baroku. Polska: Wydawnictwo KUL. ISBN 9788373630291. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Kowalczyk, Jerzy (1973). Sebastiano Serlio a sztuka polska. Polska: Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich. p. 119. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Miłobędzki, Adam (1994). The architecture of Poland: a chapter of the European heritage. Kraków: International Cultural Centre. p. 110. ISBN 9788385739142.
- ^ Zdzisław Klimczuk, Józef Garliński (1996). Most Holandia – Polska (in Polish). Polska: Bis Press. p. 32. ISBN 9788390149424. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Karpowicz, Mariusz (1994). Sztuki polskiej drogi dziwne (in Polish). Excalibur. p. 47. ISBN 9788390015286. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Feliks Gryglewicz, Romuald Łukaszyk, Wincenty Granat, Zygmunt Sułowski (1973). Encyklopedia katolicka: Kinszasa-Krzymuska. Lublin: Tow. Nauk. Katolickiego Uniwersytetu Lubelskiego. p. 1189. ISBN 9788373060685. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ «Palaces and Castles in a Lion Country». www.lvivtoday.com.ua. 2 June 2008. Retrieved 19 May 2009.
- ^ Snopek, Jerzy (1999). Oświecenie. Polska: Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN. p. 134. ISBN 9788301129170. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Kazimierz Maliszewski (1990). Obraz świata i Rzeczypospolitej w polskich gazetach rękopiśmiennych z okresu późnego baroku: studium z dziejów kształtowania się i rozpowszechniania sarmackich stereotypów wiedzy i informacji o «theatrum mundi» (in Polish). Schr. p. 79. ISBN 83-231-0239-2. W każdym razie «królowa bez korony i pierwsza dama Rzeczypospolitej», jak współcześni określali Sieniawską, zasługuje na biografię naukową.
- ^ Andrzej Wasko, Sarmatism or the Enlightenment: <space>The Dilemma of Polish Culture, Sarmatian Review XVII:2, online
- ^ Dziejochciejstwo, dziejokrętactwo, Janusz Tazbir, Polityka 6 (2591) 10 February 2007 (in Polish)
- ^ Paradowski, Ryszard (2005). Unia Europejska a społeczeństwo obywatelskie (in Polish). Poznań: Wydawn. Nauk. Instytutu Nauk Politycznych i Dziennikarstwa Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza. p. 168. ISBN 9788387704940.
- ^ Kopczyński, Michał; Tygielski, Wojciech (2010). Pod wspólnym niebem. Narody dawnej Rzeczypospolitej (in Polish). Warszawa: Bellona. ISBN 9788311117242.
- ^ a b Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010
- ^ Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, p. 236
- ^ a b Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, p. 237
- ^ Total and Jewish population based on Frazee; others are estimations from Pogonowski (see the following reference). Charles A. Frazee, World History the Easy Way, Barron’s Educational Series, ISBN 0-8120-9766-1, Google Print, 50
- ^ R. B. Wernham, The new Cambridge modern history: The Counter-Reformation and price revolution, 1559–1610, 1968, Cambridge University Press, Google print p. 377
- ^ a b Matthew P. Romaniello, Charles Lipp. Contested Spaces of Nobility in Early Modern Europe. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. 2011. p. 233.
- ^ Polish Sociological Review (in Polish). Polish Sociological Association. 2007. p. 96.
- ^ Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, p. 201
- ^ Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, pp. 25–83
- ^ a b Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, pp. 29–38
- ^ Stone, Daniel, The Polish-Lithuanian State, 1386–1795, Seattle and London: University of Washington Press, 2001.
- ^ Norman Davies, God’s Playground. A History of Poland, Vol. 1: The Origins to 1795, Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Page 126. ISBN 0-19-925339-0 / ISBN 0-19-925340-4
- ^ Paul R. Magocsi (2010). A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples. University of Toronto Press. p. 169. ISBN 978-1-4426-1021-7.
- ^ Jeannie Labno (2011). Commemorating the Polish Renaissance Child: Funeral Monuments and Their European Context. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-7546-6825-1.
- ^ Piekarski, Adam (1979). Freedom of Conscience and Religion in Poland. Interpress Publishers. p. 31.
- ^ a b «Memory of the World Register Nomination Form». portal.unesco.org. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- ^ Linda Gordon, Cossack Rebellions: Social Turmoil in the Sixteenth Century Ukraine, SUNY Press, 1983, ISBN 0-87395-654-0, Google Print, p. 51
- ^ Serhii Plokhy (2006). The origins of the Slavic nations: premodern identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. Cambridge University Press. p. 169. ISBN 0-521-86403-8.
- ^ «Lemberg». Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 3 September 2010.
- ^ Peter Kardash, Brett Lockwood (1988). Ukraine and Ukrainians. Fortuna. p. 134. ISBN 9780731675036.
- ^ Magocsi, Paul R. (2010). A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples. University of Toronto Press. p. 190. ISBN 978-1442610217.
- ^ «Poland, history of», Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [3]. Retrieved 10 February 2006 Archived 1 November 2004 at the Wayback Machine and «Ukraine», Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [4]. Retrieved 14 February 2006. Archived 24 January 2005 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «European Jewish Congress – Poland». Eurojewcong.org. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ Thus, at the time of the first partition in 1772, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth consisted of 43 per cent Latin Catholics, 33 per cent Greek Catholics, 10 per cent Christian Orthodox, 9 per cent Jews and 4 per cent Protestant Willfried Spohn, Anna Triandafyllidou (2003). Europeanisation, national identities, and migration: changes in boundary constructions between Western and Eastern Europe. Routledge. p. 127. ISBN 0-415-29667-6.
- ^ a b Artūras Tereškinas (2005). Imperfect communities: identity, discourse and nation in the seventeenth-century Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Lietuvių literatūros ir tautosakos institutas. p. 31. ISBN 9955-475-94-3.
- ^ a b Aleksander Gieysztor, ed. (1988). Rzeczpospolita w dobie Jana III (Commonwealth during the reign of John III). Royal Castle in Warsaw. p. 45.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Anatol Lieven, The Baltic Revolution: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and the Path to Independence, Yale University Press, 1994, ISBN 0-300-06078-5, Google Print, p. 48
- ^ Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, Language and Nationalism in Europe, Oxford University Press, 2000, ISBN 0-19-925085-5, Google Print p. 184
- ^ Östen Dahl, Maria Koptjevskaja-Tamm], The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact, John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2001, ISBN 90-272-3057-9, Google Print, p. 45
- ^ Glanville Price, Encyclopedia of the Languages of Europe, Blackwell Publishing, 1998, ISBN 0-631-22039-9, Google Print, p. 30
- ^ a b c d Mikulas Teich & Roy Porter, The National Question in Europe in Historical Context, Cambridge University Press, 1993, ISBN 0-521-36713-1, Google Print, p. 295
- ^ a b c d e Kevin O’Connor, Culture And Customs of the Baltic States, Greenwood Press, 2006, ISBN 0-313-33125-1, Google Print, p. 115
- ^ a b Daniel. Z Stone, A History of East Central Europe, p. 46.
- ^ Karin Friedrich et al., The Other Prussia: Royal Prussia, Poland and Liberty, 1569–1772, Cambridge University
Press, 2000, ISBN 0-521-58335-7, Google Print, p. 88 - ^ Tomasz Kamusella (2008). The Politics of Language and Nationalism in Modern Central Europe. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-230-55070-4.
- ^ L’union personnelle polono-saxonne contribua davantage à faire connaître en Pologne le français que l’allemand. Cette fonction de la langue française, devenue l’instrument de communication entre les groupes dirigeants des deux pays. Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of History (1970). «Volume 22». Acta Poloniae historica (in French). National Ossoliński Institute. p. 79.
- ^ They were the first Catholic schools in which one of the main languages of instruction was Polish. […] Although he followed Locke in attaching weight to the native language, in general Latin lost ground to French rather than Polish. Richard Butterwick (1998). Poland’s last king and English culture: Stanisław August Poniatowski, 1732–1798. Oxford University Press. p. 70. ISBN 0-19-820701-8.
- ^ України, ЦДЕА. «Державна архівна служба України». archives.gov.ua.
- ^ Although still sometimes in use by the end of the XVII century and lack of official decree like one for Grand Duchy chancellery, there was no separate Ruthenian Metrica since 1673.
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Jan Owsinski, Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis, M.E. Sharpe, 2003, ISBN 0-7656-0665-8, Google Print, p. 177
- ^ Östen Dahl, Maria Koptjevskaja-Tamm, The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact, John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2001, ISBN 90-272-3057-9, Google Print, p. 41
- ^ Zinkevičius, Z. (1993). Rytų Lietuva praeityje ir dabar. Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidykla. p. 70. ISBN 5-420-01085-2.
Official usage of Lithuanian language in the 16th century Lithuania’s cities proves magistrate’s decree of Wilno city, which was sealed by Žygimantas Augustas’ in 1552…//Courts juratory were written in Lithuanian language. In fact, such [courts juratory written in Lithuanian] survived from the 17th century…
- ^ ««Mes Wladislaus…» a letter from Wladyslaw Vasa issued in 1639 written in Lithuanian language«. Retrieved 3 September 2006.
- ^ Ališauskas, V.; L. Jovaiša; M. Paknys; R. Petrauskas; E. Raila; et al. (2001). Lietuvos Didžiosios Kunigaikštijos kultūra. Tyrinėjimai ir vaizdai. Vilnius. p. 500. ISBN 9955-445-26-2.
In 1794 Government’s declarations were carried out and in Lithuanian.
- ^ Daniel. Z Stone, A History of East Central Europe, p. 4.
- ^ Czesław Miłosz, The History of Polish Literature, University of California Press, 1983, ISBN 0-520-04477-0, Google Print, p. 108
- ^ Jan K. Ostrowski, Land of the Winged Horsemen: Art in Poland, 1572–1764, Yale University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-300-07918-4, Google Print, p. 27
- ^ a b Joanna B. Michlic (2006). Poland’s threatening other: the image of the Jew from 1880 to the present. U of Nebraska Press. p. 42. ISBN 0-8032-3240-3.
- ^ Karol Zierhoffer, Zofia Zierhoffer (2000). Nazwy zachodnioeuropejskie w języku polskim a związki Polski z kulturą Europy (in Polish). Wydawnictwo Poznańskiego Towarzystwa Przyjaciół Nauk. p. 79. ISBN 83-7063-286-6. Podobną opinię przekazał nieco późnej, w 1577 r. Marcin Kromer «Za naszej pamięci weszli […] do głównych miast Polski kupcy i rzemieślnicy włoscy, a język ich jest także częściowo w użyciu, mianowicie wśród wytworniejszych Polaków, którzy chętnie podróżują do Włoch».
- ^ Rosemary A. Chorzempa (1993). Polish roots. Genealogical Pub. ISBN 0-8063-1378-1.
- ^ Jan K. Ostrowski, ed. (1999). Art in Poland, 1572–1764: land of the winged horsemen. Art Services International. p. 32. ISBN 0-88397-131-3. In 1600 the son of the chancellor of Poland was learning four languages: Latin, Greek, Turkish, and Polish. By the time he had completed his studies, he was fluent not only in Turkish but also in Tatar and Arabic.
- ^ Lola Romanucci-Ross; George A. De Vos; Takeyuki Tsuda (2006). Ethnic identity: problems and prospects for the twenty-first century. Rowman Altamira. p. 84. ISBN 0-7591-0973-7.
- ^ Barile, Davide (2019). Historic Power Europe; A Post-Hegelian Interpretation of European Integration. New York: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781000731132.
- ^ A. stated, for instance by the preamble of the Constitution of the Republic of Poland of 1997.
- ^ Alfonsas Eidintas, Vytautas Zalys, Lithuania in European Politics: The Years of the First Republic, 1918–1940, Palgrave, 1999, ISBN 0-312-22458-3. Print, p. 78
- ^ ««Zobaczyć Kresy». Grzegorz Górny. Rzeczpospolita 23 August 2008 (in Polish)» (in Polish). Rp.pl. 23 August 2008. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ Sarah Johnstone (2008). Ukraine. Lonely Planet. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-74104-481-2.
- ^ Stephen K. Batalden, Sandra L. Batalden (1997). The newly independent states of Eurasia: handbook of former Soviet republics. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 45. ISBN 0-89774-940-5.
- ^ Richard M. Golden (2006). «Volume 4». Encyclopedia of witchcraft: the Western tradition. ABC-CLIO. p. 1039. ISBN 1-57607-243-6.
- ^ Girolamo Imbruglia; Rolando Minuti; Luisa Simonutti (2007). Traduzioni e circolazione delle idee nella cultura europea tra ‘500 e ‘700 (in Italian). Bibliopolis. p. 76. ISBN 978-88-70-88537-8.
- ^ Daniel H. Cole (2002). Pollution and property: comparing ownership institutions for environmental protection. Cambridge University Press. p. 106. ISBN 0-521-00109-9.
- ^ Gordon Campbell (2006). The Grove encyclopedia of decorative arts. Oxford University Press US. p. 13. ISBN 01-95189-48-5.
- ^ Gwei-Djen Lu; Joseph Needham; Vivienne Lo (2002). Celestial lancets: a history and rationale of acupuncture and moxa. Routledge. p. 284. ISBN 07-00714-58-8.
- ^ Ian Ridpath. «Taurus Poniatovii — Poniatowski’s bull». www.ianridpath.com. Retrieved 18 May 2009.
- ^ «Old City of Zamość». UNESCO World Heritage Centre. 23 September 2009. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- ^ After a fire had destroyed a wooden synagogue in 1733 Stanislaw Lubomirski decided to found a new bricked synagogue building. Polin Travel. «Lancut». www.jewish-guide.pl. Retrieved 2 September 2010.
- ^ Guillaume de Lamberty (1735). «Volume 3». Mémoires pour servir à l’histoire du XVIIIe siècle, contenant les négociations, traitez, résolutions et autres documents authentiques concernant les affaires d’état: avec le supplément aux années MDCXCVI-MDCCIII (in French). p. 343.
Généreux et Magnifiques Seigneurs les Sénateurs et autres Ordres de la Sérénissime République de Pologne et du grand Duché de Lithuanie
- ^ a b c Francis W. Carter (1994). Trade and urban development in Poland: an economic geography of Cracow, from its origins to 1795 – Volume 20 of Cambridge studies in historical geography. Cambridge University Press. pp. 186, 187. ISBN 978-0-521-41239-1.
- ^ Daniel Stone (2001). The Polish–Lithuanian state, 1386–1795. University of Washington Press. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-295-98093-5.
- ^ Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries (1998). A history of eastern Europe: crisis and change. Routledge. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-415-16111-4.
- ^ Norman Davies (1998). Europe: A History. HarperCollins. pp. 657–660. ISBN 978-0-06-097468-8.
vilnius capital grand duchy.
- ^ Politics and reformations: communities, polities, nations, and empires. 2007 p. 206.
- ^ Zeitschrift für Ostmitteleuropa-Forschung. 2006, Vol. 55; p. 2.
- ^ Thomas A. Brady, Christopher Ocker; entry by David Frick (2007). Politics and reformations: communities, polities, nations, and empires : essays in honor of Thomas A. Brady, Jr. Brill Publishers. p. 206. ISBN 978-90-04-16173-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer; essay by Tomas Venclova (2004). History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th and 20th centuries (Volume 2). John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 11. ISBN 978-90-272-3453-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Bibliography
- Bardach, Juliusz; Lesnodorski, Boguslaw; Pietrzak, Michal (1987). Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego. Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe. ISBN 9788301079192.
- Brzezinski, Richard (1987). Polish Armies (1): 1569–1696. Men-At-Arms Series. Vol. 184. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 0-85045-736-X.
- Brzezinski, Richard (1988). Polish Armies (2): 1569–1696. Men-At-Arms Series. Vol. 188. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 0-85045-744-0.
- Frost, Robert (2015). The Oxford History of Poland–Lithuania. Vol. I: The Making of the Polish–Lithuanian Union, 1385–1569. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0198208693.
- Litwin, Henryk (October 2016). «Central European Superpower». BUM Magazine.
- Norkus, Zenonas (2017). An Unproclaimed Empire: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania: From the Viewpoint of Comparative Historical Sociology of Empires. Routledge. ISBN 978-1138281547.
- Rowell, S. C. (2014). Lithuania Ascending: A Pagan Empire within East-Central Europe, 1295–1345. Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Fourth Series. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107658769.
- Rowell, S. C.; Baronas, Darius (2015). The Conversion of Lithuania. From Pagan Barbarians to Late Medieval Christians. Vilnius: Institute of Lithuanian Literature and Folklore. ISBN 978-6094251528.
- Stone, Daniel Z. (2014). The Polish–Lithuanian State, 1386–1795. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0295803623.
- Sužiedėlis, Saulius A. (2011). Historical Dictionary of Lithuania (2 ed.). Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0810875364.
External links
Media related to Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at Wikimedia Commons
- Commonwealth of Diverse Cultures: Poland’s Heritage Archived 24 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine (in Polish and English)
- Knowledge passage (in Polish)
- The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth–Maps, history of cities in Poland, Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania Archived 17 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine (in Polish)
- The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth on BBC Radio 4 «In Our Time» 14 Oct. 2021, Melvyn Bragg with Robert I. Frost, University of Aberdeen, Katarzyna Kosior, Northumbria University and Norman Davies, University of Oxford
Coordinates: 50°03′14″N 19°56′05″E / 50.05389°N 19.93472°E
|
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1569–1795[1] | ||||||||||||||
|
Royal Banner Royal Coat of arms |
||||||||||||||
Motto:
|
||||||||||||||
| Anthem: Gaude Mater Polonia | ||||||||||||||

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (green) with vassal states (light green) at their peak in 1619 |
||||||||||||||
| Capital |
de jure:
de facto:
|
|||||||||||||
| Common languages | Official: Polish and Latin Regional:
|
|||||||||||||
| Religion | Official: Roman Catholicism[3] Minority:
|
|||||||||||||
| Government |
|
|||||||||||||
| King / Grand Duke | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1569–1572 (first) |
Sigismund II Augustus | |||||||||||||
|
• 1764–1795 (last) |
Stanislaw II Augustus | |||||||||||||
| Legislature | General sejm | |||||||||||||
|
• Upper house |
Senate | |||||||||||||
|
• Lower house |
Chamber of Deputies | |||||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period | |||||||||||||
|
• Union established |
1 July 1569 | |||||||||||||
|
• 1st Partition |
5 August 1772 | |||||||||||||
|
• 3 May Constitution |
3 May 1791 | |||||||||||||
|
• 2nd Partition |
23 January 1793[1] | |||||||||||||
|
• 3rd Partition |
24 October 1795[1] | |||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||
| 1582[8] | 815,000 km2 (315,000 sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| 1618[9][10] | 1,000,000 km2 (390,000 sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||
|
• 1582[8] |
~8,000,000 | |||||||||||||
|
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth,[b] formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania,[c] was a bi-confederal[11] state, sometimes called a federation,[12] of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest[13][14] and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi)[15][16] and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million.[17][18] Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages.
The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a de facto personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish queen Jadwiga (Hedwig) and Lithuania’s Grand Duke Jogaila, who was crowned King jure uxoris Władysław II Jagiełło of Poland. The First Partition in 1772 and the Second Partition in 1793 greatly reduced the state’s size. The Commonwealth was partitioned out of existence in the Third Partition of 1795.
The Union possessed many features unique among contemporary states. Its political system was characterized by strict checks upon monarchical power. These checks were enacted by a legislature (sejm) controlled by the nobility (szlachta). This idiosyncratic system was a precursor to modern concepts of democracy,[19] as of 1791 constitutional monarchy,[20][21][22] and federation.[23] Although the two component states of the Commonwealth were formally equal, Poland was the dominant partner in the union.[24]
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was marked by high levels of ethnic diversity and by relative religious tolerance, guaranteed by the Warsaw Confederation Act 1573;[25][26][d] however, the degree of religious freedom varied over time.[27] The Constitution of 1791 acknowledged Catholicism as the «dominant religion», unlike the Warsaw Confederation, but freedom of religion was still granted with it.[22]
After several decades of prosperity,[28][29][30] it entered a period of protracted political,[22][31] military, and economic decline.[32] Its growing weakness led to its partitioning among its neighbors (Austria, Prussia, and Russia) during the late 18th century. Shortly before its demise, the Commonwealth adopted a massive reform effort and enacted the 3 May Constitution, which was the first codified constitution in modern European history and the second in modern world history after the United States Constitution.[33][34][35][36][37]
Name
The official name of the state was the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (Polish: Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie, Lithuanian: Lenkijos Karalystė ir Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė, Latin: Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae) and the Latin term was usually employed in international treaties and diplomacy.[38]
In the 17th century and later it was also known as the ‘Most Serene Commonwealth of Poland’ (Polish: Najjaśniejsza Rzeczpospolita Polska, Latin: Serenissima Res Publica Poloniae),[39] the Commonwealth of the Polish Kingdom,[40] or the Commonwealth of Poland.[41]
Western Europeans often simplified the name to ‘Poland’ and in most past and modern sources it is referred to as the Kingdom of Poland, or just Poland.[38][42][43] The terms ‘Commonwealth of Poland’ and ‘Commonwealth of Two Nations’ (Polish: Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów, Latin: Res Publica Utriusque Nationis) were used in the Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations.[44] The English term Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and German Polen-Litauen are seen as renderings of the ‘Commonwealth of Two Nations’ variant.[38]
Other informal names include the ‘Republic of Nobles’ (Polish: Rzeczpospolita szlachecka) and the ‘First Commonwealth’ (Polish: I Rzeczpospolita), the latter relatively common in historiography to distinguish it from the Second Polish Republic.
History
Prelude (1370–1569)
The Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania underwent an alternating series of wars and alliances across the 13th and 14th centuries.[45] The relations between the two states differed at times as each strived and competed for political, economic or military dominance of the region.[46] In turn, Poland had remained a staunch ally of its southern neighbour, Hungary. The last Polish monarch from the native Piast dynasty, Casimir the Great, died on 5 November 1370 without fathering a legitimate male heir.[47] Consequently, the crown passed onto his Hungarian nephew, Louis of Anjou, who ruled the Kingdom of Hungary in a personal union with Poland.[47] A fundamental step in developing extensive ties with Lithuania was a succession crisis arising in the 1380s.[48] Louis died on 10 September 1382 and, like his uncle, did not produce a son to succeed him. His two daughters, Mary and Jadwiga (Hedwig), held claims to the vast dual realm.[47]
The Polish lords rejected Mary in favour of her younger sister Jadwiga, partly due to Mary’s association with Sigismund of Luxembourg.[49] The future queen regnant was betrothed to young William Habsburg, Duke of Austria, but certain factions of the nobility remained apprehensive believing that William would not secure domestic interests.[50] Instead, they turned to Jogaila, the Grand Duke of Lithuania. Jogaila was a lifelong pagan and vowed to adopt Catholicism upon marriage by signing the Union of Krewo on 14 August 1385.[51] The Act imposed Christianity in Lithuania and transformed Poland into a diarchy, a kingdom ruled over by two sovereigns; their descendants and successive monarchs held the titles of king and grand duke respectively.[52] The ultimate clause dictated that Lithuania was to be merged in perpetuity (perpetuo applicare) with the Polish Kingdom; however, this did not take effect until 1569.[53] Jogaila was crowned as Władysław II Jagiełło at Wawel Cathedral on 4 March 1386.[54]
Union of Lublin (1569)
Several minor agreements were struck before unification, notably the Union of Kraków and Vilnius, the Union of Vilnius and Radom and the Union of Grodno. Lithuania’s vulnerable position and rising tensions on its eastern flank persuaded the nobles to seek a closer bond with Poland.[55] The idea of a federation presented better economic opportunities, whilst securing Lithuania’s borders from hostile states to the north, south and east.[56] Lesser Lithuanian nobility were eager to share the personal privileges and political liberties enjoyed by the Polish szlachta, but did not accept Polish demands for the incorporation of the Grand Duchy into Poland as a mere province, with no sense of autonomy.[57] Mikołaj «the Red» Radziwiłł (Radvila Rudasis) and his cousin Mikołaj «the Black» Radziwiłł, two prominent nobles and military commanders in Lithuania, vocally opposed the union.[58]
A fierce proponent of a single unified Commonwealth was Sigismund II Augustus, who was childless and ailing. According to historians, it was his active involvement which hastened the process and made the union possible.[59] A parliament (sejm) convened on 10 January 1569 in the city of Lublin, attended by envoys from both nations. It was agreed that the merger will take place the same year and both parliaments will be fused into a joint assembly.[60] No independent parliamentary convocation or diet was henceforth permitted.[60] Subjects of the Polish Crown were no longer restricted in purchasing land on Lithuanian territory and a single currency was established.[61] Whilst the military remained separate, a unified foreign policy meant that Lithuanian troops were obliged to contribute during a conflict not to their advantage.[62] As a result, several Lithuanian magnates deplored the accords and left the assembly in protest.[63] Sigismund II used his authority as grand duke and enforced the Act of Union in contumaciam. In fear, the absent nobles promptly returned to the negotiations.[64] The Union of Lublin was passed by the gathered deputies and signed by attendees on 1 July, thus creating the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.[63]
Sigismund’s death in 1572 was followed by an interregnum during which adjustments were made to the constitutional system; these adjustments significantly increased the power of the Polish nobility and established a truly elective monarchy.[65]
Apex and the Golden Age (1573–1648)
The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at its greatest extent in 1619.
On 11 May 1573, Henry de Valois, son of Henry II of France and Catherine de’ Medici, was proclaimed King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania in the first royal election outside Warsaw. Approximately 40,000 nobles cast a vote in what was to become a centuries-long tradition of a nobles’ democracy (Golden Liberty). Henry already posed as a candidate before Sigismund’s death and received widespread support from the pro-French factions. The choice was a political move aimed at curtailing Habsburg hegemony, ending skirmishes with the French-allied Ottomans, and profiting from the lucrative trade with France. Upon ascending the throne, Henry signed the contractual agreement known as the Pacta conventa and approbated the Henrician Articles.[66] The Act stated the fundamental principles of governance and constitutional law in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.[67] In June 1574, Henry abandoned Poland and headed back to claim the French crown following the death of his brother and predecessor, Charles IX.[68] The throne was subsequently declared vacant.
The interregnum concluded on 12 December 1575 when primate Jakub Uchański declared Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor, as the next king.[69] The decision was condemned by the anti-Habsburg coalition, which demanded a «native» candidate.[70] As a compromise, on 13 December 1575 Anna Jagiellon – sister of Sigismund Augustus and a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty – became the new monarch.[71] The nobles simultaneously elected Stephen Báthory as co-regent, who ruled jure uxoris.[70] Báthory’s election proved controversial – Lithuania and Ducal Prussia initially refused to recognize the Transylvanian as their ruler.[72] The wealthy port city of Gdańsk (Danzig) staged a revolt, and, with the help of Denmark, blockaded maritime trade to neutral Elbląg (Elbing).[73] Báthory, unable to penetrate the city’s extensive fortifications, succumbed to the demands for greater privileges and freedoms.[73] However, his successful Livonian campaign ended in the annexation of Livonia and the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (modern-day Estonia and Latvia, respectively), thus expanding the Commonwealth’s influence into the Baltics.[74] Most importantly, Poland gained the Hanseatic city of Riga on the Baltic Sea.
Sigismund III Vasa, who reigned between 1587 – 1632, presided over an era of prosperity and territorial expansion of the Commonwealth.
In 1587, Sigismund Vasa – the son of John III of Sweden and Catherine Jagiellon – won the election, but his claim was overtly contested by Maximilian III of Austria, who launched a military expedition to challenge the new king.[75] His defeat in 1588 at the hands of Jan Zamoyski sealed Sigismund’s right to the throne of Poland and Sweden.[76] Sigismund’s long reign marked an end to the Polish Golden Age and the beginning of the Silver Age.[77] A devout Catholic, he hoped to restore absolutism and imposed Roman Catholicism during the height of the Counter-Reformation.[78] His intolerance towards the Protestants in Sweden sparked a war of independence, which ended the Polish–Swedish union.[79] As a consequence, he was deposed in Sweden by his uncle Charles IX Vasa.[80] In Poland, the Zebrzydowski rebellion was brutally suppressed.[81]
Sigismund III then initiated a policy of expansionism, and invaded Russia in 1609 when that country was plagued by a civil war known as the Time of Troubles. In July 1610, the outnumbered Polish force comprising winged hussars defeated the Russians at the Battle of Klushino, which enabled the Poles to take and occupy Moscow for the next two years.[82] The disgraced Vasili IV of Russia was transported in a cage to Warsaw where he paid a tribute to Sigismund; Vasili was later murdered in captivity.[83] The Commonwealth forces were eventually driven out on 4 November 1612 (celebrated as Unity Day in Russia). The war concluded with a truce that granted Poland–Lithuania extensive territories in the east and marked its largest territorial expansion.[84] At least five million Russians died between 1598 and 1613, the result of continuous conflict, famine and Sigismund’s invasion.[85]
Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the early 17th century
The Polish–Ottoman War (1620–21) forced Poland to withdraw from Moldavia in southeastern Europe, but Sigismund’s victory over the Turks at Khotyn diminished the supremacy of the Sultanate and eventually led to the murder of Osman II.[86] This secured the Turkish frontier for the duration of Sigismund’s rule. In spite of the victories in the Polish–Swedish War (1626–1629), the exhausted Commonwealth army signed the Treaty of Altmark which ceded much of Livonia to Sweden under Gustavus Adolphus.[87] At the same time, the country’s powerful parliament was dominated by nobles (Pic. 2) who were reluctant to get involved in the Thirty Years’ War; this neutrality spared the country from the ravages of a political-religious conflict that devastated most of contemporary Europe.[88]
During this period, Poland was experiencing a cultural awakening and extensive developments in arts and architecture; the first Vasa king openly sponsored foreign painters, craftsmen, musicians and engineers, who settled in the Commonwealth at his request.[89]
Sigismund’s eldest son, Ladislaus succeeded him as Władysław IV in 1632 with no major opposition.[90] A skilled tactician, he invested in artillery, modernised the army and fiercely defended the Commonwealth’s eastern borders.[91] Under the Treaty of Stuhmsdorf, he reclaimed regions of Livonia and the Baltics which were lost during the Polish-Swedish wars.[92] Unlike his father who worshipped the Habsburgs, Władysław sought closer ties with France and married Marie Louise Gonzaga, daughter of Charles I Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, in 1646.[93]
Deluge, rebellions and Vienna (1648–1696)
The Commonwealth’s power and stability began waning after a series of blows during the following decades. Władysław’s brother, John II Casimir, proved to be weak and impotent. The multicultural and mega-diverse federation already suffered domestic problems. As persecution of religious and ethnic minorities strengthened, several groups started to rebel.[citation needed]
A major rebellion of self-governed Ukrainian Cossacks inhabiting south-eastern borderlands of the Commonwealth rioted against Polish and Catholic oppression of Orthodox Ukraine in 1648, in what came to be known as the Khmelnytsky Uprising. It resulted in a Ukrainian request, under the terms of the Treaty of Pereyaslav, for protection by the Russian Tsar. In 1651, in the face of a growing threat from Poland, and forsaken by his Tatar allies, Khmelnytsky asked the Tsar to incorporate Ukraine as an autonomous duchy under Russian protection. Russian annexation of Zaporizhian Ukraine gradually supplanted Polish influence in that part of Europe. In the years following, Polish settlers, nobles, Catholics and Jews became the victims of retaliation massacres instigated by the Cossacks in their dominions. The other blow to the Commonwealth was a Swedish invasion in 1655, known as the Deluge, which was supported by troops of Transylvanian Duke George II Rákóczi and Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg. Under the Treaty of Bromberg in 1657, Catholic Poland was forced to renounce its suzerainty over Protestant Prussia; in 1701 the once-insignificant duchy was transformed into the Kingdom of Prussia, which became a major European power in the 18th century and proved to be Poland’s most enduring foe.[citation needed]
In the late 17th century, the king of the weakened Commonwealth, John III Sobieski, allied with Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I to deal crushing defeats to the Ottoman Empire. In 1683, the Battle of Vienna marked the final turning point in the 250-year struggle between the forces of Christian Europe and the Islamic Ottomans. For its centuries-long opposition to Muslim advances, the Commonwealth would gain the name of Antemurale Christianitatis (bulwark of Christianity).[23][94] During the next 16 years, the Great Turkish War would drive the Turks permanently south of the Danube River, never again to threaten central Europe.[95]
Political turmoil and the enlightenment (1697–1771)
John Sobieski’s death in 1696 arguably ended the period of national sovereignty, and Poland’s relative authority over the region dwindled swiftly. By the 18th century, destabilization of its political system brought the Commonwealth to the brink of civil war and the state became increasingly susceptible to foreign influence.[96] The remaining European powers perpetually meddled in the country’s affairs.[97] Upon the death of a king, several royal houses actively intruded in the hope of securing votes for their desired candidates.[98] The practice was common and apparent, and the selection was often the result of hefty bribes directed at corrupt nobles.[99] Louis XIV of France heavily invested in François Louis, Prince of Conti, in opposition to James Louis Sobieski, Maximilian Emanuel of Bavaria and Frederick Augustus of Saxony.[100] The latter’s conversion from Lutheranism to Catholicism awed the conservative magnates and Pope Innocent XII, who in turn voiced their endorsement.[101] Imperial Russia and Habsburg Austria also contributed by financing Frederick, whose election took place in June 1697. Many questioned the legality of his elevation to the throne; it was speculated that the Prince of Conti had received more votes and was the rightful heir. Frederick hurried with his armies to Poland to quell any opposition. He was crowned as Augustus II in September and Conti’s brief military engagement near Gdańsk in November of the same year proved fruitless.[102]
The House of Wettin ruled Poland–Lithuania and Saxony simultaneously, dividing power between the two states. In spite of his controversial means of attaining power, Augustus II lavishly spent on the arts and left an extensive cultural and architectural (Baroque) legacy in both countries. In Poland, he expanded Wilanów and facilitated the refurbishment of the Warsaw Royal Castle into a modern palatial residence.[103] Countless landmarks and monuments in the city bear a name referencing the Saxon kings, notably Saxon Garden, Saxon Axis and the former Saxon Palace.[104] The period saw the development of urban planning, street allocation, hospitals, schools (Collegium Nobilium), public parks and libraries (Załuski Library). First manufactories producing on a mass scale were opened to satisfy the demands of the nobility as consumers.[105]
At the height of the Great Northern War a coalition (Warsaw Confederation) against Augustus II was formed by Stanisław Leszczyński and other magnates sponsored by Sweden. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was formally neutral at this point, as Augustus entered the war as Elector of Saxony. Disregarding Polish negotiation proposals supported by the Swedish parliament, Charles crossed into the Commonwealth and vanquished the Saxe-Polish forces at the Battle of Klissow in 1702 and at the Battle of Pultusk in 1703.[106] Charles then succeeded in dethroning Augustus and coercing the Sejm (parliament) to replace him with Stanisław in 1704.[107] Augustus regained the throne in 1709,[108] but his own death in 1733 sparked the War of the Polish Succession in which Stanisław once more attempted to seize the crown, this time with the support of France.[109] The Pacification Sejm (1736) culminated in Augustus III succeeding his father.[110]
The relative peace and inactivity that followed only weakened Poland’s reputation on the world stage.[111] Aleksander Brückner noted that Polish customs and traditions were abandoned in favour of everything foreign, and neighbouring states continued to exploit Poland to their advantage.[111] Moreover, Western Europe’s increasing exploitation of resources in the Americas rendered the Commonwealth’s supplies less crucial which resulted in financial losses.[112] Augustus III spent little time in the Commonwealth, instead preferring the Saxon city of Dresden. He appointed Heinrich von Brühl as viceroy and minister of Polish affairs who in turn left the politics to Polish magnate families, such as the Czartoryskis and the Radziwills.[113] It was also during this period that the Polish Enlightenment began to sprout.
Partitions (1772–1795)
In 1764, aristocrat Stanisław August Poniatowski was elected monarch with the connivance and support of his former lover Catherine the Great, a German noblewoman who became Empress of Russia.[114]
Poniatowski’s attempts at reform were met with staunch resistance both internally and externally. Any goal of stabilizing the Commonwealth was dangerous for its ambitious and aggressive neighbours. Like his predecessors, he sponsored artists and architects. In 1765 he founded the Warsaw Corps of Cadets, the first state school in Poland for all classes of society.[115] In 1773 the king and parliament formed the Commission of National Education, the first Ministry of Education in European history.[116][117] In 1792, the king ordered the creation of Virtuti Militari, the oldest military decoration still in use.[118] Stanisław August also admired the culture of Ancient kingdoms, particularly Rome and Greece; Neoclassicism became the dominant form of architectural and cultural expression.
Politically, however, the vast Commonwealth was in steady decline and by 1768, it started to be considered by Russians as a protectorate of the Russian Empire despite the fact that it was still an independent state.[119][120] A majority of control over Poland was central to Catherine’s diplomatic and military strategies.[121] Attempts at reform, such as the Four-Year Sejm’s May Constitution, came too late. The country was partitioned in three stages by the Russian Empire, the German Kingdom of Prussia, and the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy. By 1795, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had been completely erased from the map of Europe. Poland and Lithuania were not re-established as independent countries until 1918.[122]
State organization and politics
Golden Liberty
The political doctrine of the Commonwealth was our state is a republic under the presidency of the King. Chancellor Jan Zamoyski summed up this doctrine when he said that Rex regnat et non-gubernat («The King reigns but [lit. ‘and’] does not govern»).[123] The Commonwealth had a parliament, the Sejm, as well as a Senat and an elected king (Pic. 1). The king was obliged to respect citizens’ rights specified in King Henry’s Articles as well as in pacta conventa, negotiated at the time of his election.[67]
The monarch’s power was limited in favour of a sizable noble class. Each new king had to pledge to uphold the Henrician Articles, which were the basis of Poland’s political system (and included near-unprecedented guarantees of religious tolerance). Over time, the Henrician Articles were merged with the pacta conventa, specific pledges agreed to by the king-elect. From that point onwards, the king was effectively a partner with the noble class and was constantly supervised by a group of senators. The Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislation (the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones).[67]
The foundation of the Commonwealth’s political system, the «Golden Liberty» (Latin: Aurea Libertas or Polish: Złota Wolność, a term used from 1573 on), included:
- election of the king by all nobles wishing to participate, known as wolna elekcja (free election);
- Sejm, the Commonwealth parliament which the king was required to hold every two years;
- pacta conventa (Latin), «agreed-to agreements» negotiated with the king-elect, including a bill of rights, binding on the king, derived from the earlier Henrician Articles.
- religious freedom guaranteed by Warsaw Confederation Act 1573,[25][page needed]
- rokosz (insurrection), the right of szlachta to form a legal rebellion against a king who violated their guaranteed freedoms;
- liberum veto (Latin), the right of an individual Sejm deputy to oppose a decision by the majority in a Sejm session; the voicing of such a «free veto» nullified all the legislation that had been passed at that session; during the crisis of the second half of the 17th century, Polish nobles could also use the liberum veto in provincial sejmiks;
- konfederacja (from the Latin confederatio), the right to form an organization to force through a common political aim.
The three regions (see below) of the Commonwealth enjoyed a degree of autonomy.[124][page needed] Each voivodship had its own parliament (sejmik), which exercised serious political power, including choice of poseł (deputy) to the national Sejm and charging of the deputy with specific voting instructions. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania had its own separate army, treasury and most other official institutions.[125][126]
Golden Liberty created a state that was unusual for its time, although somewhat similar political systems existed in the contemporary city-states like the Republic of Venice.[127][page needed] Both states were styled «Serenissima Respublica» or the «Most Serene Republic».[128] At a time when most European countries were headed toward centralization, absolute monarchy and religious and dynastic warfare, the Commonwealth experimented with decentralization,[23] confederation and federation, democracy and religious tolerance.[129]
This political system unusual for its time stemmed from the ascendance of the szlachta noble class over other social classes and over the political system of monarchy. In time, the szlachta accumulated enough privileges (such as those established by the Nihil novi Act of 1505) that no monarch could hope to break the szlachta’s grip on power. The Commonwealth’s political system is difficult to fit into a simple category, but it can be tentatively described as a mixture of:
- confederation and federation, with regard to the broad autonomy of its regions. It is, however, difficult to decisively call the Commonwealth either confederation or federation, as it had some qualities of both;
- oligarchy, as only the szlachta (nobility) – around 15% of the population – had political rights;[23]
- democracy, since all the szlachta were equal in rights and privileges, and the Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislation (the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones). Also, the 15% of Commonwealth population who enjoyed those political rights (the szlachta)[130] was a substantially larger percentage than in majority European countries even in the nineteenth century;[131] note that in 1820 in France only about 1.5% of the male adult population had the right to vote, and in 1840 in Belgium, only about 5%.[130][131]
- elective monarchy, since the monarch, elected by the szlachta, was Head of State;
- constitutional monarchy, since the monarch was bound by pacta conventa and other laws, and the szlachta could disobey any king’s decrees they deemed illegal.
Magnate oligarchy
The end of the Jagiellonian dynasty in 1572 – after nearly two centuries – disrupted the fragile equilibrium of the Commonwealth’s government. Power increasingly slipped away from the central government to the nobility.[67]
When presented with periodic opportunities to fill the throne, the szlachta exhibited a preference for foreign candidates who would not establish a strong and long-lasting dynasty. This policy often produced monarchs who were either totally ineffective or in constant debilitating conflict with the nobility.[citation needed] Furthermore, aside from notable exceptions such as the able Stefan Batory from Transylvania (1576–86), the kings of foreign origin were inclined to subordinate the interests of the Commonwealth to those of their own country and ruling house. This was especially visible in the policies and actions of the first two elected kings from the Swedish House of Vasa, whose politics brought the Commonwealth into conflict with Sweden, culminating in the war known as the Deluge (1655), one of the events that mark the end of the Commonwealth’s Golden Age and the beginning of the Commonwealth’s decline.[132]
The Zebrzydowski Rebellion (1606–1607) marked a substantial increase in the power of the Polish magnates, and the transformation of szlachta democracy into magnate oligarchy. The Commonwealth’s political system was vulnerable to outside interference, as Sejm deputies bribed[133][134] by foreign powers might use their liberum veto to block attempted reforms. This sapped the Commonwealth and plunged it into political paralysis and anarchy for over a century, from the mid-17th century to the end of the 18th, while its neighbours stabilized their internal affairs and increased their military might.[citation needed]
Late reforms
The Commonwealth did eventually make a serious effort to reform its political system, adopting in 1791 the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which historian Norman Davies calls the first of its kind in Europe.[37] The revolutionary Constitution recast the erstwhile Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as a Polish–Lithuanian federal state with a hereditary monarchy and abolished many of the deleterious features of the old system.
The new constitution:
- abolished the liberum veto and banned the szlachta’s confederations;
- provided for a separation of powers among legislative, executive and judicial branches of government;
- established «popular sovereignty» and extended political rights to include not only the nobility but the bourgeoisie;
- increased the rights of the peasantry;
- preserved religious tolerance (but with a condemnation of apostasy from the Catholic faith).
These reforms came too late, however, as the Commonwealth was immediately invaded from all sides by its neighbors, which had been content to leave the Commonwealth alone as a weak buffer state, but reacted strongly to attempts by king Stanisław August Poniatowski and other reformers to strengthen the country.[124][page needed] Russia feared the revolutionary implications of the 3 May Constitution’s political reforms and the prospect of the Commonwealth regaining its position as a European power. Catherine the Great regarded the May constitution as fatal to her influence[135] and declared the Polish constitution Jacobinical.[136] Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin drafted the act for the Targowica Confederation, referring to the constitution as the «contagion of democratic ideas».[137] Meanwhile, Prussia and Austria used it as a pretext for further territorial expansion.[136] Prussian minister Ewald Friedrich von Hertzberg called the constitution «a blow to the Prussian monarchy»,[138] fearing that a strengthened Poland would once again dominate Prussia.[135][139] In the end, the 3 May Constitution was never fully implemented, and the Commonwealth entirely ceased to exist only four years after its adoption.[140]
Economy
Gdańsk (Danzig), the Commonwealth’s chief seaport and trading centre from which goods would be transported along the Vistula River to Warsaw, Kraków and other towns in the country.
Cereals exports in the years 1619–1799. Agriculture, once extremely profitable to the nobility, became much less so after the mid-17th century.
The economy of the Commonwealth was predominantly based on agricultural output and trade, though there was an abundance of artisan workshops and manufactories — notably paper mills, leather tanneries, ironworks, glassworks and brickyards.[141] Some major cities were home to craftsmen, jewellers and clockmakers.[141] The majority of industries and trades were concentrated in the Kingdom of Poland; the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was more rural and its economy was driven by farming and clothmaking.[141] Mining developed in the south-west region of Poland which was rich in natural resources such as lead, coal, copper and salt.[142] The currency used in Poland–Lithuania was the złoty (meaning «the golden») and its subunit, the grosz. Foreign coins in the form of ducats, thalers and shillings were widely accepted and exchanged.[143] The city of Gdańsk had the privilege of minting its own coinage.[144] In 1794, Tadeusz Kościuszko began issuing the first Polish banknotes.[145]
The country played a significant role in the supply of Western Europe by the export of grain (rye), cattle (oxen), furs, timber, linen, cannabis, ash, tar, carminic acid and amber.[146][147][148][149] Cereals, cattle and fur amounted to nearly 90% of the country’s exports to European markets by overland and maritime trade in the 16th century.[148] From Gdańsk, ships carried cargo to the major ports of the Low Countries, such as Antwerp and Amsterdam.[150][151] The land routes, mostly to the German provinces of the Holy Roman Empire such as the cities of Leipzig and Nuremberg, were used for the export of live cattle (herds of around 50,000 head) hides, salt, tobacco, hemp and cotton from the Greater Poland region.[152][153] In turn, the Commonwealth imported wine, beer, fruit, exotic spices, luxury goods (e.g. tapestries, Pic. 5), furniture, fabrics as well as industrial products like steel and tools.[154]
The agricultural sector was dominated by feudalism based on the plantation system (serfs).[32] Slavery was forbidden in Poland in the 15th century, and formally abolished in Lithuania in 1588,[155] replaced by the second enserfment. Typically a nobleman’s landholding comprised a folwark, a large farmstead worked by serfs to produce surpluses for internal and external trade. This economic arrangement worked well for the ruling classes and nobles in the early years of the Commonwealth, which was one of the most prosperous eras of the grain trade.[156] The economic strength of Commonwealth grain trade waned from the late 17th century on. Trade relationships were disrupted by the wars, and the Commonwealth proved unable to improve its transport infrastructure or its agricultural practices.[157] Serfs in the region were increasingly tempted to flee.[158] The Commonwealth’s major attempts at countering this problem and improving productivity consisted of increasing serfs’ workload and further restricting their freedoms in a process known as export-led serfdom.[157][158]
The owner of a folwark usually signed a contract with merchants of Gdańsk, who controlled 80% of this inland trade, to ship the grain north to that seaport on the Baltic Sea.[159] Countless rivers and waterways in the Commonwealth were used for shipping purposes, including the Vistula, Pilica, Bug, San, Nida, Wieprz, Neman. The rivers had relatively developed infrastructure, with river ports and granaries. Most of the river shipping moved north, southward transport being less profitable, and barges and rafts were often sold off in Gdańsk for lumber. Grodno become an important site after formation of a customs post at Augustów in 1569, which became a checkpoint for merchants travelling to the Crown lands from the Grand Duchy.[160]
Coat of arms of the Commonwealth on a 15 ducat coin, 1617
5-złoty banknote issued in 1794
Urban population of the Commonwealth was low compared to Western Europe. Exact numbers depend on calculation methods. According to one source, the urban population of the Commonwealth was about 20% of the total in the 17th century, compared to approximately 50% in the Netherlands and Italy (Pic. 7).[149] Another source suggests much lower figures: 4–8% urban population in Poland, 34–39% in the Netherlands and 22–23% in Italy.[161] The Commonwealth’s preoccupation with agriculture, coupled with the nobles’ privileged position when compared to the bourgeoisie, resulted in a fairly slow process of urbanization and thus a rather slow development of industries.[149] The nobility could also regulate the price of grain for their advantage, thus acquiring much wealth. Some of the largest trade fairs in the Commonwealth were held at Lublin.[162]
Several ancient trading routes such as the Amber Road (Pic. 4)[163] extended across Poland–Lithuania, which was situated in the heart of Europe and attracted foreign merchants or settlers.[164] Countless goods and cultural artefacts continued to pass from one region to another via the Commonwealth, particularly that the country was a link between the Middle East, the Ottoman Empire and Western Europe.[165] For instance, Isfahan rugs imported from Persia to the Commonwealth were incorrectly known as «Polish rugs» (French: Polonaise) in Western Europe.[166]
Military
Kraków Militia, a local guard formation in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth during the 16th and 17th centuries
The military in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth evolved from the merger of the armies from the Polish Kingdom and from the Grand Lithuanian Duchy, though each state maintained its own division.[167] The united armed forces comprised the Crown Army (armia koronna), recruited in Poland, and the Lithuanian Army (armia litewska) in the Grand Duchy.[167] The military was headed by the Hetman, a rank equivalent to that of a general or supreme commander in other countries. Monarchs could not declare war or summon an army without the consent of the Sejm parliament or the Senate.[168] The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Navy never played a major role in the military structure from the mid-17th century onwards.[169]
The most prestigious formation of the two respective armes were their 16th- and 17th-century heavy cavalry in the form of Winged Hussars (husaria), whereas the Polish Royal Guards and Lithuanian Guards [pl] were the elite of the infantry; the regiments were supervised by the king and his family.[170] In 1788, the Great Sejm approved landslide reforms and defined future structures of the military; the Crown Army was to be split into four divisions, with seventeen field infantry regiments and eight cavalry brigades excluding special units; the Lithuanian Army was to be subdivided into two divisions, eight field regiments and two cavalry brigades excluding special units.[171] If implemented, the reform predicted an army of almost 100,000 men.[172]
The armies of those states differed from the organization common in other parts of Europe; according to Bardach, the mercenary formations (wojsko najemne), common in Western Europe, never gained widespread popularity in Poland.[173] Brzezinski, however, notes that foreign mercenaries did form a significant portion of the more elite infantry units, at least until the early 17th century.[174] In 16th-century Poland, several other formations formed the core of the military.[175] There was a small standing army, obrona potoczna («continuous defense») about 1,500–3,000 strong, paid for by the king, and primarily stationed at the troubled southern and eastern borders.[175][176] It was supplemented by two formations mobilized in case of war — the pospolite ruszenie (Polish for levée en masse – feudal levy of mostly noble knights-landholders), and the wojsko zaciężne, recruited by the Polish commanders for the conflict. It differed from other European mercenary formations in that it was commanded by Polish officers, and dissolved after the conflict has ended.[175]
A historical re-enactor dressed in the Polish Winged Hussars armour
Several years before the Union of Lublin, the Polish obrona potoczna was reformed, as the Sejm (national parliament of Poland) legislated in 1562–1563 the creation of wojsko kwarciane, named after kwarta tax levied on the royal lands for the purpose of maintaining this formation.[175] This formation was also paid for by the king, and in the peacetime, numbered about 3,500–4,000 men according to Bardach;[175] Brzezinski gives the range of 3,000–5,000.[176] It was composed mostly of the light cavalry units manned by nobility (szlachta) and commanded by hetmans.[175][177] Often, in wartime, the Sejm would legislate a temporary increase in the size of the wojsko kwarciane.[175]
Following the end of the Commonwealth, the Polish-Lithuanian military tradition would be continued by the Napoleonic Polish Legions and the Army of the Duchy of Warsaw.[178]
Culture
Science and literature
The Commonwealth was an important European center for the development of modern social and political ideas. It was famous for its rare quasi-democratic political system, praised by philosophers, and during the Counter-Reformation was known for near-unparalleled religious tolerance, with peacefully coexisting Roman Catholic, Jewish, Orthodox Christian, Protestant and Muslim (Sufi) communities. In the 18th century, the French Catholic Rulhiere wrote of 16th century Poland: «This country, which in our day we have seen divided on the pretext of religion, is the first state in Europe that exemplified tolerance. In this state, mosques arose between churches and synagogues.»[33] The Commonwealth gave rise to the famous Christian sect of the Polish Brethren, antecedents of British and American Unitarianism.[179]
With its political system, the Commonwealth gave birth to political philosophers such as Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski (1503–1572) (Pic. 9), Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki (1530–1607) and Piotr Skarga (1536–1612). Later, works by Stanisław Staszic (1755–1826) and Hugo Kołłątaj (1750–1812) helped pave the way for the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which Norman Davies calls the first of its kind in Europe.[37]
Kraków’s Jagiellonian University is one of the oldest universities in the world (established in 1364),[180] together with the Jesuit Academy of Wilno (established in 1579) they were the major scholarly and scientific centers in the Commonwealth. The Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, Polish for Commission for National Education, formed in 1773, was the world’s first national Ministry of Education.[181] Commonwealth scientists included: Martin Kromer (1512–1589), historian and cartographer; Michael Sendivogius (1566–1636), alchemist and chemist; Jan Brożek (Ioannes Broscius in Latin) (1585–1652), polymath: a mathematician, physician and astronomer; Krzysztof Arciszewski (Crestofle d’Artischau Arciszewski in Portuguese) (1592–1656), engineer, ethnographer, general and admiral of the Dutch West Indies Company army in the war with the Spanish Empire for control of Brazil;[182] Kazimierz Siemienowicz (1600–1651), military engineer, artillery specialist and a founder of rocketry; Johannes Hevelius (1611–1687), astronomer, founder of lunar topography; Michał Boym (1612–1659), orientalist, cartographer, naturalist and diplomat in Ming Dynasty’s service (Pic. 11); Adam Adamandy Kochański (1631–1700), mathematician and engineer; Baal Shem Tov (הבעל שם טוב in Hebrew) (1698–1760), considered to be the founder of Hasidic Judaism; Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt (1728–1810), astronomer and mathematician (Pic. 12); Jan Krzysztof Kluk (1739–1796), naturalist, agronomist and entomologist, John Jonston (1603–1675) scholar and physician, descended from Scottish nobility. In 1628 the Czech teacher, scientist, educator, and writer John Amos Comenius took refuge in the Commonwealth, when the Protestants were persecuted under the Counter Reformation.[179][183]
The works of many Commonwealth authors are considered classics, including those of Jan Kochanowski (Pic. 10), Wacław Potocki, Ignacy Krasicki, and Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz. Many szlachta members wrote memoirs and diaries. Perhaps the most famous are the Memoirs of Polish History by Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł (1595–1656) and the Memoirs of Jan Chryzostom Pasek (ca. 1636–ca. 1701). Jakub Sobieski (1590–1646) (father of John III Sobieski) wrote notable diaries. During the Khotyn expedition in 1621 he wrote a diary called Commentariorum chotinensis belli libri tres (Diary of the Chocim War), which was published in 1646 in Gdańsk. It was used by Wacław Potocki as a basis for his epic poem, Transakcja wojny chocimskiej (The Progress of the War of Chocim). He also authored instructions for the journey of his sons to Kraków (1640) and France (1645), a good example of liberal education of the era.[184]
Art and music
The art and music of the Commonwealth was largely shaped by prevailing European trends, though the country’s minorities, foreigners as well as native folk cultures also contributed to its versatile nature. A common art form of the Sarmatian period were coffin portraits (portrety trumienne) used in funerals and other important ceremonies.[185] As a rule, such portraits were nailed to sheet metal, six- or eight- sided in shape, fixed to the front of a coffin placed on a high, ornate catafalque.[186] These were a unique and distinguishable feature of the Commonwealth’s high culture, not found elsewhere in Europe.[187] A similar tradition was only practiced in Roman Egypt.[187] Polish monarchs and nobles frequently invited and sponsored foreign painters and artisans, notably from the Low Countries (the Netherlands, Flanders and Belgium), Germany or Italy.[188] The interiors of upper-class residences, palaces and manors were adorned by wall tapestries (arrasy or tapiseria) imported from Western Europe; the most renowned collection are the Jagiellonian tapestries exhibited at Wawel Royal Castle in Kraków.[189]
The economic, cultural and political ties between France and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth gave rise to the term à la polonaise, French for «Polish-styled».[190] With the marriage of Marie Leszczyńska to Louis XV of France in 1725, Polish culture began to flourish at the Palace of Versailles.[191] Polish beds (lit à la polonaise) draped with baldachins became a centrepiece of Louis XV furniture in French chateaus.[192] Folk flower motifs as well as Polish fashion were popularized in the form of a back-draped polonaise dress (robe à la polonaise) worn by aristocrats at Versailles.[193]
The religious cultures of Poland–Lithuania coexisted and penetrated each other for the entirety of the Commonwealth’s history – the Jews adopted elements of the national dress,[194] loanwords and calques became commonplace and Roman Catholic churches in regions with significant Protestant populations were much simpler in décor than those in other parts of Poland–Lithuania.[195] Mutual influence was further reflected in the great popularity of Byzantine icons (Pic. 13) and the icons resembling effigies of Mary in the predominantly Latin territories of today’s Poland (Black Madonna) and Lithuania (Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn).[196] Conversely, Latin infiltration into Ruthenian Orthodox and Protestant art was also conventional (Pic. 3).[197]
Music was a common feature of religious and secular events. To that end many noblemen founded church and school choirs, and employed their own ensembles of musicians. Some, like Stanisław Lubomirski built their own opera houses (in Nowy Wiśnicz). Others, like Janusz Skumin Tyszkiewicz and Krzysztof Radziwiłł were known for their sponsorship of arts which manifested itself in their permanently retained orchestras, at their courts in Wilno (Vilnius).[198] Musical life further flourished under the House of Vasa. Both foreign and domestic composers were active in the Commonwealth. Sigismund III brought in Italian composers and conductors, such as Luca Marenzio, Annibale Stabile, Asprilio Pacelli, Marco Scacchi and Diomedes Cato for the royal orchestra. Notable home grown musicians, who also composed and played for the King’s court, included Bartłomiej Pękiel, Jacek Różycki, Adam Jarzębski, Marcin Mielczewski, Stanisław Sylwester Szarzyński, Damian Stachowicz, Mikołaj Zieleński and Grzegorz Gorczycki.[198]
Architecture
The architecture of the cities in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth reflected a combination of Polish, German and Italian trends. Italian Mannerism or the Late Renaissance had a profound impact on traditional burgher architecture which can be observed to this day – castles and tenements were fitted with central Italianate courtyards composed of arched loggias, colonnades, bay windows, balconies, portals and ornamental balustrades.[199] Ceiling frescos, sgraffito, plafonds and coffering (patterned ceilings; Polish kaseton; from Italian cassettone) were widespread.[200] Rooftops were generally covered with terracotta rooftiles. The most distinguishable feature of Polish Mannerism are decorative «attics» above the cornice on the façade.[201] Cities in northern Poland–Lithuania and in Livonia adopted the Hanseatic (or «Dutch») style as their primary form of architectural expression, comparable to that of the Netherlands, Belgium, northern Germany and Scandinavia.[202]
Wilanów Palace, completed in 1696, exemplifies the opulence of royal and noble residences in the Commonwealth.
The introduction of Baroque architecture was marked by construction of several Jesuit and Roman Catholic churches across Poland and Lithuania, notably the Peter and Paul Church in Kraków, the Corpus Christi Church in Nesvizh, Lublin Cathedral and UNESCO-enlisted sanctuary at Kalwaria Zebrzydowska. Fine examples of decorative Baroque and Rococo include Saint Anne’s in Kraków and the Fara Church in Poznań. Another characteristic is the common usage of black marble.[203] Altars, fonts, portals, balustrades, columns, monuments, tombstones, headstones and whole rooms (e.g. Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, St. Casimir Chapel of the Vilnius Cathedral and Vasa Chapel at Wawel Cathedral) were extensively decorated with black marble, which became popular after the mid-17th century.[204]
Magnates often undertook construction projects as monuments to themselves: churches, cathedrals, monasteries (Pic. 14), and palaces like the present-day Presidential Palace in Warsaw and Pidhirtsi Castle built by Grand Hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski. The largest projects involved entire towns, although in time many of them would lapse into obscurity or were abandoned. These towns were generally named after the sponsoring magnate. Among the most prominent is Zamość, founded by Jan Zamoyski and designed by the Italian architect Bernardo Morando as an ideal city. The magnates throughout Poland competed with the kings. The monumental castle Krzyżtopór, built in the style palazzo in fortezza between 1627 and 1644, had several courtyards surrounded by fortifications. Similar fortified complexes include castles in Łańcut and Krasiczyn.[citation needed]
The fascination with the culture and art of the Orient in the late Baroque period is reflected by Queen Marie’s Chinese Palace in Zolochiv (Złoczów).[205] 18th-century magnate palaces represents the characteristic type of Baroque suburban residence built entre cour et jardin (between the entrance court and the garden). Its architecture – a merger of European art with old Commonwealth building traditions are visible in Wilanów Palace in Warsaw (Pic. 15), Branicki Palace in Białystok, Potocki Palace in Radzyń Podlaski, Raczyński Palace in Rogalin, Nieborów Palace and Kozłówka Palace near Lubartów. Lesser nobility resided in country manor houses known as dworek. Neoclassicism replaced Baroque by the second half of the 18th century – the last ruler of the Poland–Lithuania, Stanisław August Poniatowski, greatly admired the classical architecture of Ancient Rome and promoted it as a symbol of the Polish Enlightenment.[206] The Palace on the Isle and the exterior of St. Anne’s Church in Warsaw are part of the neoclassical legacy of the former Commonwealth.
Szlachta and Sarmatism
The prevalent ideology of the szlachta became «Sarmatism», named after the Sarmatians, alleged ancestors of the Poles.[139] This belief system was an important part of szlachta culture, penetrating all aspects of its life. Sarmatism enshrined equality among szlachta, horseback riding, tradition, provincial quaint life in manor houses, peace and pacifism; championed oriental-inspired souvenirs or attire for men (żupan, kontusz, sukmana, pas kontuszowy, delia, szabla); favoured European Baroque architecture; endorsed Latin as a language of thought or expression; and served to integrate the multi-ethnic nobility by creating an almost nationalistic sense of unity and of pride in Golden Liberty.[139]
In its early, idealistic form, Sarmatism represented a positive cultural movement: it supported religious belief, honesty, national pride, courage, equality and freedom. In time, however, it became distorted. Late extreme Sarmatism turned belief into bigotry, honesty into political naïveté, pride into arrogance, courage into stubbornness and freedom into anarchy.[208] The faults of Sarmatism were blamed for the demise of the country from the late 18th century onwards. Criticism, often one-sided and exaggerated, was used by the Polish reformists to push for radical changes. This self-deprecation was accompanied by works of German, Russian and Austrian historians, who tried to prove that it was Poland itself that was to blame for its fall.[209]
Demographics
Social strata in the Commonwealth’s society in 1655. From left: Jew, barber surgeon, painter, butcher, musician, tailor, barmaid, pharmacist, shoemaker, goldsmith, merchant and Armenian
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was immensely multicultural throughout its existence — it comprised countless religious identities and ethnic minorities inhabiting the country’s vast territory.[210] The precise number of minority groups and their populations can only be hypothesized.[211] Statistically, the most prominent groups were the Poles, Lithuanians, Germans, Ruthenians and Jews.[212] There were also considerable numbers of Czechs, Hungarians, Livonians, Romanis, Vlachs, Armenians, Italians, Scots and the Dutch (Olędrzy), who were either categorized as merchants, settlers or refugees fleeing religious persecution.[212]
Prior to the union with Lithuania, the Kingdom of Poland was much more homogenous; approximately 70% of the population was Polish and Roman Catholic.[213] With the creation of the Commonwealth, the number of Poles in comparison to the total population decreased to 50%.[214] In 1569, the population stood at 7 million, with roughly 4.5 million Poles, 750,000 Lithuanians, 700,000 Jews and 2 million Ruthenians.[215] Historians Michał Kopczyński and Wojciech Tygielski suggest that with the territorial expansion after the Truce of Deulino in 1618, the Commonwealth’s population reached 12 million people, of which Poles constituted only 40%.[214][17] At that time the nobility made up 10% of the entire population and the burghers around 15%.[17] The average population density per square kilometer was: 24 in Mazovia, 23 in Lesser Poland, 19 in Greater Poland, 12 in Lublin palatinate, 10 in the Lwów area, 7 in Podolia and Volhynia, and 3 in the Kiev Voivodeship. There was a tendency for the people from the more densely inhabited western territories to migrate eastwards.[216]
Density of urban network of the Commonwealth per each voivodeship in 1650
A sudden change in the country’s demographics occurred in the mid-17th century.[17] The Second Northern War and the Deluge followed by famine in the period from 1648 to 1657 were accountable for at least 4 million deaths.[17] Coupled with further territorial losses, by 1717 the population had fallen to 9 million.[17] The population slowly recovered throughout the 18th century; just before the first partition of Poland in 1772, the Commonwealth’s population was 14 million, including around 1 million nobles.[217] In 1792, the population of Poland was around 11 million and included 750,000 nobles.[217]
The most multicultural and robust city in the country was Gdańsk, a major Hanseatic seaport on the Baltic and Poland’s wealthiest region. Gdańsk at the time was inhabited by a German-speaking majority[218] and further hosted large numbers of foreign merchants, particularly of Scottish, Dutch or Scandinavian extraction.[219] Historically, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was more diverse than the Kingdom of Poland, and was deemed a melting pot of many cultures and religions.[220] Hence, the inhabitants of the Grand Duchy were collectively known as Litvins regardless of their nationality, with the exception of Jews residing in Lithuania who were called Litvaks.
Despite guaranteed religious tolerance, gradual Polonization and Counter-Reformation sought to minimize the Commonwealth’s diversity; the aim was to root out some minorities by imposing the Polish language, Latin, Polish culture and the Roman Catholic religion where possible.[221] By the late 18th century, the Lithuanian language, culture and identity became vulnerable;[221] the country’s name was changed to «Commonwealth of Poland» in 1791.
Religion
The Warsaw Confederation signed on 28 January 1573 secured the rights of minorities and religions;[222] it allowed all persons to practice any faith freely, though religious tolerance varied at times. As outlined by Norman Davies, «the wording and substance of the declaration of the Confederation of Warsaw of were extraordinary with regards to prevailing conditions elsewhere in Europe; and they governed the principles of religious life in the Republic for over two hundred years.»[223] Subsequently, the Catholic church initiated a counter-reformation in Poland, relying heavily on methods of persuasion and legal means. As a result, compared to many other European countries, the conflict between the Catholics and the Protestants in Poland was relatively peaceful.[224][225]
Poland retained religious freedom laws during an era when religious persecution was an everyday occurrence in the rest of Europe.[226] The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a place where the most radical religious sects, trying to escape persecution in other countries of the Christian world, sought refuge.[227] In 1561 Giovanni Bernardino Bonifacio d’Oria, a religious exile living in Poland, wrote of his adopted country’s virtues to a colleague back in Italy: «You could live here in accordance with your ideas and preferences, in great, even the greatest freedoms, including writing and publishing. No one is a censor here.»[33] Others, particularly the leaders of the Roman Catholic church, the Jesuits and papal legates, were less optimistic about Poland’s religious frivolity.
«This country became a place of shelter for heretics» – Cardinal Stanislaus Hosius, papal legate to Poland.[227]
To be Polish, in remote and multi-ethnic parts of the Commonwealth, was then much less an index of ethnicity than of religion and rank; it was a designation largely reserved for the landed noble class (szlachta), which included Poles, but also many members of non-Polish origin who converted to Catholicism in increasing numbers with each following generation. For the non-Polish noble such conversion meant a final step of Polonization that followed the adoption of the Polish language and culture.[228] Poland, as the culturally most advanced part of the Commonwealth, with the royal court, the capital, the largest cities, the second-oldest university in Central Europe (after Prague), and the more liberal and democratic social institutions had proven an irresistible magnet for the non-Polish nobility in the Commonwealth.[23] Many referred to themselves as «gente Ruthenus, natione Polonus» (Ruthenian by blood, Polish by nationality) since the 16th century onwards.[229]
The church in Kamieniec Podolski was converted into a mosque during the Turkish occupation between 1672 and 1699, with the 33-meter minaret being added at that time.[231]
As a result, in the eastern territories a Polish (or Polonized) aristocracy dominated a peasantry whose great majority was neither Polish nor Catholic. Moreover, the decades of peace brought huge colonization efforts to the eastern territories (nowadays roughly western and central Ukraine),[232] heightening the tensions among nobles, Jews, Cossacks (traditionally Orthodox), Polish and Ruthenian peasants. When the latter, deprived of their native protectors among the Ruthenian nobility, turned for protection to cossacks that facilitated violence which in the end broke the Commonwealth. The tensions were aggravated by conflicts between Eastern Orthodoxy and the Greek Catholic Church following the Union of Brest, overall discrimination of Orthodox religions by dominant Catholicism,[233] and several Cossack uprisings. In the west and north, many cities had sizable German minorities, often belonging to Lutheran or Reformed churches. The Commonwealth had also one of the largest Jewish diasporas in the world – by the mid-16th century 80% of the world’s Jews lived in Poland (Pic. 16).[234]
Until the Reformation, the szlachta were mostly Catholics (Pic. 13). However, many noble families quickly adopted the Reformed religion. After the Counter-Reformation, when the Catholic Church regained power in Poland, the szlachta became almost exclusively Catholic.[235]
The Crown had about double the population of Lithuania and five times the income of the latter’s treasury. As with other countries, the borders, area and population of the Commonwealth varied over time. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski (1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km2 area and a population of 7.5 million.[236] After the Truce of Deulino (1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 990,000 km2 and a population of 11–12 million (including some 4 million Poles and close to a million Lithuanians).[237]
Languages
- Polish – officially recognized;[238] dominant language, used by most of the Commonwealth’s nobility[238][239][240][241] and by the peasantry in the Crown province;[242] official language in the Crown chancellery and since 1697 in the Grand Duchy chancellery.[243] Dominant language in the towns.[242]
- Latin – officially recognized;[238][244] commonly used in foreign relations[243] and popular as a second language among some of the nobility.[245]
- French – not officially recognized; replaced Latin at the royal court in Warsaw in the beginning of the 18th century as a language used in foreign relations and as genuine spoken language.[246][247] It was commonly used as a language of science and literature and as a second language among some of the nobility.[248]
- Ruthenian – also known as Chancellery Slavonic;[243] officially recognized;[238] official language in the Grand Duchy chancellery until 1697 (when replaced by Polish) and in Bratslav, Chernihiv, Kiev and Volhynian voivodeships until 1673;[249][250] used in some foreign relations[243][244][251] its dialects (modern Belarusian and Ukrainian) were widely used in the Grand Duchy and eastern parts of the Crown as spoken language.
- Lithuanian – not officially recognized;[238][252] but used in some official documents in the Grand Duchy[253][254][255] and, mostly, used as a spoken language in the northernmost part of the country (in Lithuania Proper)[256] and the northern part of Ducal Prussia (Polish fief).
- German – officially recognized;[238] used in some foreign relations,[243] in Ducal Prussia and by German minorities especially in the Royal Prussia and Greater Poland.[242][257]
- Hebrew – officially recognized;[238] and Aramaic used by Jews for religious, scholarly, and legal matters.
- Yiddish – not officially recognized;[258][259] used by Jews in their daily life[242]
- Italian – not officially recognized; used in some foreign relations and by Italian minorities in cities.[260]
- Armenian – officially recognized;[238] used by the Armenian minority.[259][261]
- Arabic – not officially recognized; used in some foreign relations[262] and by Tatars in their religious matters, they also wrote Ruthenian in the Arabic script.[263]
Legacy
The Duchy of Warsaw, established in 1807 by Napoleon Bonaparte, traced its origins to the Commonwealth. Other revival movements appeared during the November Uprising (1830–31), the January Uprising (1863–64) and in the 1920s, with Józef Piłsudski’s failed attempt to create a Polish-led Intermarium (Międzymorze) federation that, at its largest extent, would span from Finland in the north to the Balkans in the south.[264] The contemporary Republic of Poland considers itself a successor to the Commonwealth,[265] whereas the Republic of Lithuania, re-established at the end of World War I, saw the participation of the Lithuanian state in the old Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth mostly in a negative light at the early stages of regaining its independence,[266] although this attitude has been changing in recent years.[267]
Administrative divisions
While the term «Poland» was also commonly used to denote this whole polity, Poland was in fact only part of a greater whole – the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which comprised primarily two parts:
- the Crown of the Polish Kingdom (Poland proper), colloquially «the Crown»
- the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, colloquially «Lithuania»
The Commonwealth was further divided into smaller administrative units known as voivodeships (województwa). Each voivodeship was governed by a Voivode (wojewoda, governor). Voivodeships were further divided into starostwa, each starostwo being governed by a starosta. Cities were governed by castellans. There were frequent exceptions to these rules, often involving the ziemia subunit of administration.[citation needed]
The lands that once belonged to the Commonwealth are now largely distributed among several Central and East European countries: Poland, Ukraine, Moldova (Transnistria), Belarus, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia.[268][269] Also some small towns in Upper Hungary (today mostly Slovakia), became a part of Poland in the Treaty of Lubowla (Spiš towns).
Other notable parts of the Commonwealth, without respect to region or voivodeship divisions, include:
- Lesser Poland Province (Polish: Małopolska), southern Poland, with two largest cities, its capital at Kraków and Lublin in the north-east;
- Greater Poland Province (Polish: Wielkopolska), west–central Poland around Poznań and the Warta River system;
- Mazovia (Polish: Mazowsze), central Poland, with its capital at Warsaw;
- Lithuania Proper (Lithuanian: Didžioji Lietuva), northwest Grand Duchy, its most Catholic and ethnically Lithuanian part, capital Vilnius;
- Duchy of Samogitia (Lithuanian: Žemaitija; Polish: Żmudź), westernmost and most autonomous part of Grand Duchy of Lithuania, also the western part of Lithuania Proper, capital Raseiniai;
- Royal Prussia (Polish: Prusy Królewskie), at the southern shore of the Baltic Sea, was an autonomous area since the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), incorporated into the Crown in 1569 with the Commonwealth’s formation;
- Pomerelia (Polish: Pomorze Gdańskie), Pomerania around Gdańsk, western part of Royal Prussia;
- Ruthenia (Polish: Ruś), the eastern Commonwealth, adjoining Russia;
- Duchy of Livonia (Inflanty), a joint domain of the Crown and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Parts lost to Sweden in the 1620s and in 1660;
- Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (Lithuanian: Kuršas ir Žiemgala; Polish: Kurlandia i Semigalia), a northern fief of the Commonwealth. It established a colony in Tobago in 1637 and on St. Andrews Island at the Gambia River in 1651 (see Couronian colonization);
- Silesia (Polish: Śląsk) was not within the Commonwealth, but small parts belonged to various Commonwealth kings; in particular, the Vasa kings were dukes of Opole (Oppeln), Prudnik (Neustadt) and Racibórz (Ratibor) from 1645 to 1666.[270]
Topographical map of the Commonwealth in 1764
Commonwealth borders shifted with wars and treaties, sometimes several times in a decade, especially in the eastern and southern parts. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski (1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km2 area and a population of 7.5 million.[236] After the Truce of Deulino (1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 1 million km2 (990,000 km2) and a population of about 11 million.[237]
Geography
In the 16th century, the Polish bishop and cartographer Martin Kromer, who studied in Bologna, published a Latin atlas, entitled Poland: about Its Location, People, Culture, Offices and the Polish Commonwealth, which was regarded as one of the most comprehensive guides to the country.[271]
Kromer’s works and other contemporary maps, such as those of Gerardus Mercator, show the Commonwealth as mostly plains. The Commonwealth’s southeastern part, the Kresy, was famous for its steppes. The Carpathian Mountains formed part of the southern border, with the Tatra Mountain chain the highest, and the Baltic Sea formed the Commonwealth’s northern border. As with most European countries at the time, the Commonwealth had extensive forest cover, especially in the east. Today, what remains of the Białowieża Forest constitutes the last largely intact primeval forest in Europe.[272]
Image gallery
- Politics and economy
-
Statuta Regni Poloniae in ordinem alphabeti digesta (Statutes of the Polish Kingdom, Arranged in Alphabetical Order), 1563
-
-
18th century amber casket. Gdańsk patronized by the Polish court flourished as the center for amber working in the 17th century.[273]
-
-
Silver tankard by Józef Ceypler, Kraków, 1739–1745
-
Example of the merchant architecture: Konopnica’s tenement house in Lublin, 1575
-
Hussars’ armours, first half of the 17th century
- Science, art and architecture
-
De republica emendanda (1554) by Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski, proposed a deep programme of reforms of the state, society and church.
-
Title page of Treny (1580) by Jan Kochanowski, a series of elegies upon the death of his beloved daughter, is an acknowledged masterpiece.
-
-
-
-
See also
- History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1648)
- History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1648–1764)
- History of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1764–1795)
- List of medieval great powers
- Armorial of Polish nobility
- List of szlachta
- Polish heraldry
- Lithuanian nobility
- Armenians in Poland
- History of the Germans in Poland
- History of the Jews in Poland
- History of Poland
- History of Lithuania
- Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth
- Polish–Lithuanian–Muscovite Commonwealth
Notes
- ^ Pro Fide, Lege et Rege was the motto since the 18th century.
a. ^ Name in native and official languages:
- Latin: Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae / Serenissima Res Publica Poloniae[39]
- French: Royaume de Pologne et Grand-duché de Lituanie / Sérénissime République de Pologne et Grand-duché de Lituanie[278]
- Polish: Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie
- Lithuanian: Lenkijos Karalystė ir Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė
- Belarusian: Каралеўства Польскае і Вялікае Княства Літоўскае (Karaleŭstva Polskaje і Vialikaje Kniastva Litoŭskaje)
- Ukrainian: Королівство Польське і Велике князівство Литовське
- German: Königreich Polen und Großfürstentum Litauen
b. ^ Some historians date the change of the Polish capital from Kraków to Warsaw between 1595 and 1611, although Warsaw was not officially designated capital until 1793.[279] The Commonwealth Sejm began meeting in Warsaw soon after the Union of Lublin and its rulers generally maintained their courts there, although coronations continued to take place in Kraków.[279] The modern concept of a single capital city was to some extent inapplicable in the feudal and decentralized Commonwealth.[279] Warsaw is described by some historians as the capital of the entire Commonwealth.[280][281] Wilno, the capital of the Grand Duchy,[282][283][284] is sometimes called the second capital of the entity.[285][286]
Notes
- ^ Royal Banner used by the Vasa dynasty
- ^
- Polish: Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów;
- Latin: Res Publica Utriusque Nationis;
- Lithuanian: Abiejų Tautų Respublika, Žečpospolita;
- German: Republik beider Nationen, Republik beider Völker, Republik Polen-Litauen;
- Ukrainian: Річ Посполита;
- Belarusian: Рэч Паспалітая;
- Ruthenian: Рѣчъ Посполита
- ^
- Polish: Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie;
- Latin: Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae;
- Lithuanian: Lenkijos Karalystė ir Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė;
- German: Königreich Polen und des Großfürstentums Litauen
- Ukrainian: Королівство Польське і Велике князівство Литовське;
- Belarusian: Польскае Каралеўства і Вялікае Княства Літоўскае
- ^ This quality of the Commonwealth was recognized by its contemporaries. Robert Burton, in his The Anatomy of Melancholy, first published in 1621, writes of Poland: «Poland is a receptacle of all religions, where Samosetans, Socinians, Photinians …, Arians, Anabaptists are to be found»; «In Europe, Poland and Amsterdam are the common sanctuaries [for Jews]».
References
- ^ a b Partitions of Poland at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ a b c d Jagiellonian University Centre for European studies, «A Very Short History of Kraków», see: «1596 administrative capital, the tiny village of Warsaw». Archived from the original on 12 March 2009. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- ^ Richters, Katja (2012). The Post-Soviet Russian Orthodox Church: Politics, Culture and Greater Russia. Routledge. p. 133. ISBN 9781136296369.
formed part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth which was ruled by Catholic monarchs who made Roman Catholicism the state religio…
- ^ a b Janusz Sykała: Od Polan mieszkających w lasach – historia Polski – aż do króla Stasia, Gdansk, 2010.
- ^ a b Georg Ziaja: Lexikon des polnischen Adels im Goldenen Zeitalter 1500–1600, p. 9.
- ^ «Artykuły henrykowskie — szlachecka prekonstytucja — Historia — polskieradio24.pl». polskieradio24.pl.
- ^ «Poland — The First Partition | Britannica». www.britannica.com.
- ^ a b Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 14, ISBN 83-7000-016-9.
- ^ Bertram Benedict (1919): A history of the great war. Bureau of national literature, inc. p. 21.
- ^ According to Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 16, ~ 990.000 km2
- ^ Hahn, Gordon M. (9 November 2021). The Russian Dilemma: Security, Vigilance and Relations with the West from Ivan III to Putin. McFarland. p. 35. ISBN 978-1-4766-8187-0.
- ^ Zbigniew Pucek: Państwo i społeczeństwo 2012/1, Krakow, 2012, p. 17.
- ^ Norman Davies, Europe: A History, Pimlico 1997, p. 554: «Poland–Lithuania was another country which experienced its ‘Golden Age’ during the sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries. The realm of the last Jagiellons was absolutely the largest state in Europe»
- ^ Piotr Wandycz (2001). The price of freedom (p.66). p. 66. ISBN 978-0-415-25491-5. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ^ Bertram Benedict (1919). A history of the great war. Bureau of national literature, inc. p. 21. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ^ According to Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 16, 990.000 km2
- ^ a b c d e f Based on 1618 population map Archived 17 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine (p. 115), 1618 languages map (p119), 1657–67 losses map (p. 128) and 1717 map Archived 17 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine (p. 141) from Iwo Cyprian Pogonowski, Poland a Historical Atlas, Hippocrene Books, 1987, ISBN 0-88029-394-2
- ^ According to Panstwowe Przedsiebiorstwo Wydawnictw Kartograficznych: Atlas Historyczny Polski, wydanie X, 1990, p. 16, just over 9 million in 1618.
- ^ Maciej Janowski, Polish Liberal Thought, Central European University Press, 2001, ISBN 963-9241-18-0, Google Print: p. 3, p. 12
- ^ Paul W. Schroeder, The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848, Oxford University Press, 1996, ISBN 0-19-820654-2, Google print p. 84
- ^ Rett R. Ludwikowski, Constitution-Making in the Region of Former Soviet Dominance, Duke University Press, 1997, ISBN 0-8223-1802-4, Google Print, p. 34
- ^ a b c George Sanford, Democratic Government in Poland: Constitutional Politics Since 1989, Palgrave, 2002, ISBN 0-333-77475-2, Google print p. 11 – constitutional monarchy, p. 3 – anarchy
- ^ a b c d e Aleksander Gella, Development of Class Structure in Eastern Europe: Poland and Her Southern Neighbors, SUNY Press, 1998, ISBN 0-88706-833-2, Google Print, p. 13
- ^ «Formally, Poland and Lithuania were to be distinct, equal components of the federation … But Poland, which retained possession of the Lithuanian lands it had seized, had greater representation in the diet and became the dominant partner.»«Lublin, Union of». Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006.[1]
- ^ a b # Norman Davies, God’s Playground. A History of Poland, Vol. 1: The Origins to 1795, Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-925339-0 / ISBN 0-19-925340-4
- ^ Halina Stephan, Living in Translation: Polish Writers in America, Rodopi, 2003, ISBN 90-420-1016-9, Google Print p. 373. Quoting from Sarmatian Review academic journal mission statement: «Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was … characterized by religious tolerance unusual in premodern Europe»
- ^ Gross, Feliks (1999). Citizenship and Ethnicity: The Growth and Development of a Democratic Multiethnic Institution (notes). Greenwood Press. p. 122. ISBN 0-313-30932-9.
- ^ «In the mid-1500s, united Poland was the largest state in Europe and perhaps the continent’s most powerful state politically and militarily». «Poland». Encyclopædia Britannica. 2009. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 26 June 2009.
- ^ Francis Dvornik (1992). The Slavs in European History and Civilization. Rutgers University Press. p. 300. ISBN 0-8135-0799-5.
- ^ Salo Wittmayer Baron (1976). A social and religious history of the Jews. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-08853-1.
- ^ Martin Van Gelderen, Quentin Skinner, Republicanism: A Shared European Heritage, Cambridge University Press, 2002, ISBN 0-521-80756-5 p. 54.
- ^ a b «The Causes of Slavery or Serfdom: A Hypothesis» Archived 15 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine (discussion and full online text) of Evsey Domar (1970). Economic History Review 30:1 (March), pp. 18–32.
- ^ a b c «Page Not Found: Error: IU Robert H. McKinney School of Law: IUPUI». IU Robert H. McKinney School of Law.
- ^ Blaustein, Albert (1993). Constitutions of the World. Fred B. Rothman & Company. ISBN 9780837703626.
- ^ Isaac Kramnick, Introduction, Madison, James (1987). The Federalist Papers. Penguin Classics. p. 13. ISBN 0-14-044495-5.
May second oldest constitution.
- ^ John Markoff describes the advent of modern codified national constitutions as one of the milestones of democracy, and states that «The first European country to follow the U.S. example was Poland in 1791.» John Markoff, Waves of Democracy, 1996, ISBN 0-8039-9019-7, p. 121.
- ^ a b c Davies, Norman (1996). Europe: A History. Oxford University Press. p. 699. ISBN 0-19-820171-0.
- ^ a b c «Regnum Poloniae Magnusque Ducatus Lithuaniae – definicja, synonimy, przykłady użycia». sjp.pwn.pl. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- ^ a b Ex quo serenissima respublica Poloniae in corpore ad exempluin omnium aliarnm potentiarum, lilulum regiuin Borussiae recognoscere decrevit (…)
Antoine-François-Claude Ferrand (1820). «Volume 1». Histoire des trois démembremens de la Pologne: pour faire suite à l’histoire de l’Anarchie de Pologne par Rulhière (in French). Deterville. p. 182. - ^ the name given by Marcin Kromer in his work Polonia sive de situ, populis, moribus, magistratibus et re publica regni Polonici libri duo, 1577.
- ^ the therm used for instance in Zbior Deklaracyi, Not I Czynnosci Głownieyszych, Ktore Poprzedziły I Zaszły Pod Czas Seymu Pod Węzłem Konfederacyi Odprawuiącego Się Od Dnia 18. Wrzesnia 1772. Do 14 Maia 1773
- ^ Name used for the common state, Henryk Rutkowski, Terytorium, w: Encyklopedia historii gospodarczej Polski do 1945 roku, t. II, Warszawa 1981, s. 398.
- ^ Richard Buterwick. The Polish Revolution and the Catholic Church, 1788–1792: A Political History. Oxford University Press. 2012. pp. 5, xvii.
- ^ 1791 document signed by the King Stanislaw August «Zareczenie wzaiemne Oboyga Narodow» pp. 1, 5 [2]
- ^ Jasienica, Paweł (1997). Polska Jagiellonów. Polska: Prószyński i Spółka. pp. 30–32. ISBN 9788381238816.
- ^ Jasienica 1997, pp. 30–32
- ^ a b c Halecki 1991, p. 52
- ^ Halecki 1991, p. 71
- ^ Engel, Pál (2001). The Realm of St Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526. I.B. Tauris Publishers. p. 170. ISBN 1-86064-061-3.
- ^ Halecki, Oscar (1991). Jadwiga of Anjou and the Rise of East Central Europe. Polish Institute of Arts and Sciences of America. pp. 116–117. ISBN 0-88033-206-9.
- ^ Jasienica 1997, p. 63
- ^ Halecki 1991, p. 155
- ^ Manikowska, Halina (2005). Historia dla Maturzysty. Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Szkolne PWN. p. 141. ISBN 83-7195-853-6.
- ^ Bojtár, Endre (1999), Foreword to the Past: A Cultural History of the Baltic People, translated by Walter J. Renfroe, Budapest: Central European University Press, p. 182, ISBN 978-963-9116-42-9
- ^ Butterwick 2021, pp. 12–14
- ^ Butterwick 2021
- ^ Butterwick, Richard (2021). The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1733–1795. Yale University Press. p. 14. ISBN 9780300252200.
- ^ Borucki, Marek (2009). Historia Polski do 2009 roku. Polska: Mada. p. 57. ISBN 9788389624598.
- ^ Gierowski, Józef (1986a). Historia Polski 1505–1764. Warsaw: PWN. pp. 92–109. ISBN 83-01-03732-6.
- ^ a b Butterwick 2021, p. 21
- ^ Pernal, Andrew Boleslaw (2010). Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów a Ukraina. Polska: Księgarnia Akademicka. p. 10. ISBN 9788371889738.
- ^ Pernal 2010, p. 10
- ^ a b Maniecky & Szajnocha 1869, p. 504
- ^ Maniecky, Wojciech; Szajnocha, Karol (1869). Dziennik Literacki (in Polish). Ossoliński. p. 504.
- ^ The death of Sigismund II Augustus in 1572 was followed by a three-year Interregnum during which adjustments were made in the constitutional system. The lower nobility was now included in the selection process, and the power of the monarch was further circumscribed in favor of the expanded noble class. From that point, the king was effectively a partner with the noble class and constantly supervised by a group of senators.
«The Elective Monarchy». Poland – The Historical Setting. Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. 1992. Archived from the original on June 4, 2011. Retrieved July 15, 2011. - ^ Bardach, Juliusz (1987). Historia państwa i prawa polskiego (in Polish). Warszawa: PWN. pp. 216–217.
- ^ a b c d Bardach 1987, pp. 216–217
- ^ Stone, Daniel (2001). The Polish-Lithuanian state, 1386–1795 [A History of East Central Europe, Volume IV.] Seattle: University of Washington Press. p. 118. ISBN 0-295-98093-1.
- ^ Besala, Jerzy; Biedrzycka, Agnieszka (2005). Stefan Batory: Polski Słownik Biograficzny (in Polish). Vol. XLIII. p. 116.
- ^ a b Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, p. 116
- ^ Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, p. 117
- ^ Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, pp. 116–117
- ^ a b Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, pp. 118–119
- ^ Besala & Biedrzycka 2005, pp. 121
- ^ Szujski, Józef (1894). Dzieła Józefa Szujskiego. Dzieje Polski (in Polish). Vol. 3. Kraków: Szujski-Kluczycki. p. 139. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ pisze, Przemek (3 July 2013). «Bitwa pod Byczyną. Zamoyski upokarza Habsburgów i gwarantuje tron Zygmuntowi III – HISTORIA.org.pl – historia, kultura, muzea, matura, rekonstrukcje i recenzje historyczne». Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ^ Kizwalter, Tomasz (1987). Kryzys Oświecenia a początki konserwatyzmu polskiego (in Polish). Warszawa (Warsaw): Uniwersytet Warszawski. p. 21. Retrieved 3 May 2021.
- ^ Szujski 1894, p. 161
- ^ Peterson, Gary Dean (2014). Warrior Kings of Sweden. The Rise of an Empire in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries. McFarland, Incorporated, Publishers. ISBN 9781476604114. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ^ Peterson 2014, p. 107
- ^ Jędruch, Jacek (1982). Constitutions, Elections, and Legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977. University Press of America. p. 89. ISBN 9780819125095. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ Dabrowski, Patrice M. (2014). Poland. The First Thousand Years. US: Cornell University Press. p. 168. ISBN 9781501757402. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Shubin, Daniel H. (2009). Tsars and Imposters. Russia’s Time of Troubles. New York: Algora. p. 201. ISBN 9780875866871. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ Cooper, J. P. (1979). The New Cambridge Modern History: Volume 4, The Decline of Spain and the Thirty Years War, 1609-48/49. CUP Archive. ISBN 9780521297134. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ Gillespie, Alexander (2017). The Causes of War. Vol. III: 1400 CE to 1650 CE. Portland: Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 194. ISBN 9781509917662. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Dyer, Thomas Henry (1861). The History of Modern Europe. Vol. From the Fall of Constantinople, in 1453, to the War in the Crimea, in 1857. Volume 2. London: J. Murray. p. 504. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ^ Podhorodecki, Leszek (1985). Rapier i koncerz: z dziejów wojen polsko-szwedzkich. Warsaw: Książka i Wiedza. pp. 191–200. ISBN 83-05-11452-X.
- ^ Gillespie 2017, p. 141
- ^ Miłobędzki, Adam (1980). Dzieje sztuki polskiej: Architektura polska XVII wieku (in Polish). Polska: Panstwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe. p. 115. ISBN 9788301013639. Retrieved 8 January 2021.
- ^ Czapliński, Władysław (1976). Władysław IV i jego czasy [Władysław IV and His Times] (in Polish). Warsaw: PW «Wiedza Poweszechna». pp. 102–118.
- ^ Czapliński 1976, p. 170
- ^ Czapliński 1976, p. 202
- ^ Czapliński 1976, pp. 353–356
- ^ Poland, the knight among nations, Louis Edwin Van Norman, New York: 1907, p. 18.
- ^ William J. Duiker, Jackson J. Spielvogel (2006). The Essential World History: Volume II: Since 1500. Cengage Learning. p. 336. ISBN 0-495-09766-7.
- ^ Gintel, Jan (1971). Wiek XVIII-XIX. Polska: Wydawnictwo Literackie. p. 143.
- ^ Gintel 1971, p. 143
- ^ Instytut Badań Literackich (1969). Studia staropolskie. Vol. 24, 25. Polska: Zakład Ossolińskich. p. 172.
- ^ Instytut Badań Literackich 1969, p. 172
- ^ Borucki, Marek (1976). Jak w dawnej Polsce królów obierano. Polska: Ludowa Spółdzielnia Wydawnicza. pp. 138–143.
- ^ Spórna (2003). Słownik władców Polski i pretendentów do tronu polskiego. Polska: Zielona Sowa. p. 30. ISBN 9788372205605.
- ^ Borucki 1976, pp. 138–143
- ^ Dobrowolski (1962). Historia sztuki polskiej w zarysie: Sztuka nowożytna. Polska: Wydawnictwo Literackie.
- ^ Davies, Norman (1992). Boże igrzysko. Historia Polski. Od początków do roku 1795. Polska: Znak. p. 412. ISBN 9788370063849.
- ^ Brückner, Aleksander (1931). Dzieje kultury polskiej. Czasy nowsze do roku 1831. Polska: Wiedza Powszechna. p. 27. ISBN 9788321408613.
- ^ Frost, Robert I (2000). The Northern Wars. War, State and Society in Northeastern Europe 1558–1721. Harlow: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-06429-4.
- ^ Tucker, S.C. (2010). A Global Chronology of Conflict, Vol. Two. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, LLC. p. 694. ISBN 9781851096671.
- ^ Tucker 2010, p. 710
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). «Polish Succession War» . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 21 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 981–982.
- ^ Lindsey, J. O. (ed). The Cambridge New Modern History, Volume 7.
- ^ a b Brückner 1931, p. 157
- ^ Rey Koslowski (2000). Migrants and citizens: demographic change in the European state system. Cornell University Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-8014-3714-4.
polish lithuanian commonwealth americas western europe.
- ^ Spórna 2003
- ^ Bartłomiej Szyndler (2009). Racławice 1794. Bellona Publishing. pp. 64–65. ISBN 9788311116061. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ^ Bartłomiej Kaczorowski (2004). Nowa encyklopedia powszechna PWN: Sud-żyz. Polska: PWN. p. 75. ISBN 9788301141875.
- ^ Norman Davies (28 February 2005). God’s Playground: 1795 to the present. Columbia University Press. p. 167. ISBN 978-0-231-12819-3.
- ^ Ted Tapper; David Palfreyman (2005). Understanding Mass Higher Education: Comparative Perspectives On Access. RoutledgeFalmer. p. 140. ISBN 978-0-415-35491-2.
- ^ Kitowicz, Jędrzej (2019). Customs and Culture in Poland Under the Last Saxon King. Central European University Press. p. 262. ISBN 9789633862766.
- ^ Sužiedėlis 2011, p. xxv.
- ^ Andrzej Jezierski, Cecylia Leszczyńska, Historia gospodarcza Polski, 2003, s. 68.
- ^ Russia’s Rise as a European Power, 1650–1750 Archived 5 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine, Jeremy Black, History Today, Vol. 36 Issue: 8, August 1986.
- ^ Roman, Wanda Krystyna (2003). Działalność niepodległościowa żołnierzy polskich na Litwie i Wileńszczyźnie. Polska: Naukowe Wydawn. Piotrkowskie. p. 23. ISBN 9788388865084. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Jan Zamoyski’s speech in the Parliament, 1605 Harbottle Thomas Benfield (2009). Dictionary of Quotations (Classical). BiblioBazaar, LLC. p. 254. ISBN 978-1-113-14791-2.
- ^ a b Pacy, James S.; James T. McHugh (2001). Diplomats without a Country: Baltic Diplomacy, International Law, and the Cold War (1st ed.). Post Road West, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-31878-6. Retrieved 3 September 2006.
- ^ Josef Macha (1974). Ecclesiastical Unification. Pont. Institutum Orientalium Studiorum. p. 154.
- ^ Andrej Kotljarchuk (2006). In the Shadows of Poland and Russia: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Sweden in the European Crisis of the Mid-17th Century. Stockholm University. pp. 37, 87. ISBN 978-91-89-31563-1.
- ^ Joanna Olkiewicz, Najaśniejsza Republika Wenecka (Most Serene Republic of Venice), Książka i Wiedza, 1972, Warszawa
- ^ Joseph Conrad, Notes on Life and Letters: Notes on Life and Letters, Cambridge University Press, 2004, ISBN 0-521-56163-9, Google Print, p. 422 (notes)
- ^ Frost, Robert I. The Northern Wars: War, State and Society in northeastern Europe, 1558–1721. Harlow, England; New York: Longman’s. 2000. Especially pp. 9–11, 114, 181, 323.
- ^ a b David Sneath (2007). The headless state: aristocratic orders, kinship society, & misrepresentations of nomadic inner Asia. Columbia University Press. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-231-14054-6.
- ^ a b M. L. Bush (1988). Rich noble, poor noble. Manchester University Press ND. pp. 8–9. ISBN 0-7190-2381-5.
- ^ Frost, Robert I. (2004). After the Deluge; Poland-Lithuania and the Second Northern War, 1655–1660. Cambridge: University Press. ISBN 9780521544023.
- ^ William Christian Bullitt, Jr., The Great Globe Itself: A Preface to World Affairs, Transaction Publishers, 2005, ISBN 1-4128-0490-6, Google Print, pp. 42–43
- ^ John Adams, The Political Writings of John Adams, Regnery Gateway, 2001, ISBN 0-89526-292-4, Google Print, p. 242
- ^ a b Henry Eldridge Bourne, The Revolutionary Period in Europe 1763 to 1815, Kessinger Publishing, 2005, ISBN 1-4179-3418-2, Google Print p. 161
- ^ a b Wolfgang Menzel, Germany from the Earliest Period Vol. 4, Kessinger Publishing, 2004, ISBN 1-4191-2171-5, Google Print, p. 33
- ^ Isabel de Madariaga, Russia in the Age of Catherine the Great, Sterling Publishing Company, Inc., 2002, ISBN 1-84212-511-7, Google Print p. 431
- ^ Carl L. Bucki, The Constitution of May 3, 1791 Archived 5 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine, Text of a presentation made at the Polish Arts Club of Buffalo on the occasion of the celebrations of Poland’s Constitution Day on 3 May 1996. Retrieved 20 March 2006.
- ^ a b c Piotr Stefan Wandycz. The Price of Freedom: A History of East Central Europe from the Middle Ages to the Present, Routledge (UK), 2001, ISBN 0-415-25491-4, Google Print p. 131.
- ^ Niepodległość. Vol. 6. Polska: Fundacja «Polonia Restituta,». 1991. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Sobiech, Marcin (2018). «Jak powstawała i co zawiera mapa Rzeczpospolitej Obojga Narodów». Exgeo (in Polish). Marcin Sobiech. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Kucharczuk 2011, p. 64
- ^ «shillings – Polish translation – Linguee». Linguee.com. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
- ^ Flisowski, Zbigniew (1985). Bastion u wrót Gdańska. Polska: Nasza Księgarnia. p. 11. ISBN 9788310087799.
- ^ «Pierwsze polskie banknoty». Skarbnica Narodowa (in Polish). Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Gdańskie Towarzystwo Naukowe (1991). Seria popularno-naukowa «Pomorze Gdańskie» (in Polish). Vol. 19. Gdańsk: Towarzystwo Naukowe. p. 149. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Kucharczuk, Katarzyna (2011). Polska samorządna; ilustrowane dzieje administracji i samorządu terytorialnego na tle historii Polski. Carta Blanca. p. 66. ISBN 9788377051207. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ a b Zsigmond Pál Pach, Zs. P. Pach (1970). The role of East-Central Europe in international trade, 16th and 17th centuries. Akadémiai Kiadó. p. 220.
- ^ a b c Institute of History (Polish Academy of Sciences) (1991). «Volumes 63–66». Acta Poloniae historica. National Ossoliński Institute. p. 42. ISBN 0-88033-186-0.
- ^ Krzysztof Olszewski (2007). The Rise and Decline of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth due to Grain Trade. pp. 6–7.
- ^ Maciej Kobyliński. «Rzeczpospolita spichlerzem Europy». www.polinow.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- ^ Nicholas L. Chirovsky (1984). The Lithuanian-Rus’commonwealth, the Polish domination, and the Cossack-Hetman state. Philosophical Library. p. 367. ISBN 0-8022-2407-5.
- ^ Sven-Olof Lindquist, Birgitta Radhe (1989). Economy and culture in the Baltic, 1650–1700: papers of the VIIIth Visby Symposium held at Gotland’s Historical Museum, Visby, August 18th–22th [sic], 1986. Gotlands Fornsal. p. 367. ISBN 91-971048-8-4.
- ^ Sowa, Jan (2015). Inna Rzeczpospolita jest możliwa! Widma przeszłości, wizje przyszłości (in Polish). Polska: WAB. ISBN 9788328022034. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ «Welcome to Encyclopædia Britannica’s Guide to History». Britannica.com. 31 January 1910. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ PPerry Anderson (1979). Lineages of the absolutist state. Verso. p. 285. ISBN 0-86091-710-X.
- ^ a b Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries (2007). A history of Eastern Europe: crisis and change. Taylor & Francis. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-415-36627-4.
- ^ a b Yves-Marie Bercé (1987). Revolt and revolution in early modern Europe: an essay on the history of political violence. Manchester University Press. p. 151.
- ^ Krzysztof Olszewski (2007). The Rise and Decline of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth due to Grain Trade (PDF). p. 7. Retrieved 22 April 2009.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Jarmo Kotilaine (2005). Russia’s foreign trade and economic expansion in the seventeenth century: windows on the world. BRILL. p. 47. ISBN 90-04-13896-X.
- ^ Allen, Robert. «Economic Structure and agricultural productivity in Europe, 1300–1800» (PDF). Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ kurkowski, Jan (2010). «Jarmarki w województwie lubelskim w XVI w.» Pasaż Wiedzy. Muzeum Pałacu Króla Jana III w Wilanowie. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Billock, Jennifer (2019). «Follow the Ancient Amber Road». Smithsonian Magazine. Smithsonian. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ «Drogi handlowe w dawnej Polsce». PWN. Encyklopedia PWN. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Polskie Towarzystwo Historyczne (1989). Kwartalnik historyczny. Vol. 3–4. Polskie Towarzystwo Historyczne. p. 214. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ ««Polonaise» carpet». www.museu.gulbenkian.pt. Archived from the original on February 28, 2003. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- ^ a b Stachowicz 1894, p. 279
- ^ Tomaszewska, A. «Wolna elekcja i zasady jej funkcjonowania» (PDF). Tomaszewska. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ^ Juliusz Bardach, Zdzisław Kaczmarczyk, Bogusław Leśnodorski (1957). Historia państwa i prawa Polski do roku 1795 (in Polish). Vol. 2. Polska: Państwowe Wydawn. Naukowe. pp. 306–308. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Richard Brzezinski (1988). Polish Armies 1569–1696 (2). Osprey Publishing. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-85045-744-5.
- ^ Stachowicz, Michał (1894). Wojsko polskie Kościuszki w roku 1794 (in Polish). Poznań: Księgarnia Katolicka. pp. 23–25. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ Stachowicz 1894, pp. 23–25
- ^ Juliusz Bardach, Boguslaw Lesnodorski, and Michal Pietrzak, Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego (Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe), 1987, p. 229.
- ^ Brzezinski (1988), p. 6.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bardach et al. (1987), pp. 229–230.
- ^ a b Brzezinski (1987), p. 10.
- ^ Bardach et al. (1987), pp. 227–228.
- ^ Zwoliński, Stefan (1995). Naczelni wodzowie i wyżsi dowódcy Polskich Sił Zbrojnych na Zachodzie (in Polish). Polska: Wojskowy Instytut Historyczny. p. 12. ISBN 9788386268276. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ a b J. K. Fedorowicz; Maria Bogucka; Henryk Samsonowicz (1982). A Republic of nobles: studies in Polish history to 1864. CUP Archive. p. 209. ISBN 0-521-24093-X.
- ^ Jacek F. Gieras (1994). «Volume 30 of Monographs in electrical and electronic engineering, Oxford science publications». Linear induction drives. Oxford University Press. p. V. ISBN 0-19-859381-3.
- ^ Norman Davies (2005). God’s Playground: A History of Poland. Columbia University Press. p. 167. ISBN 0-231-12819-3.
- ^ «Setting Sail». www.warsawvoice.pl. 29 May 2003. Retrieved 21 May 2009.
- ^ Paul Peucker. «Jan Amos Comenius (1592–1670)» (PDF). www.moravian.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 2, 2009. Retrieved May 18, 2009.
- ^ Jacek Jędruch (1982). Constitutions, Elections, and Legislatures of Poland, 1493–1977: A Guide to Their History. University Press of America. p. 125. ISBN 978-08-19-12509-5.
- ^ «Portraits collection». www.muzeum.leszno.pl. Retrieved 18 May 2009.
- ^ Mariusz Karpowicz (1991). Baroque in Poland. Arkady. p. 68. ISBN 83-213-3412-1.
- ^ a b Łyczak, Bartłomiej (1 January 2011). «The Coffin Portrait and Celebration of Death in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the Modern Period». IKON. 4: 233–242. doi:10.1484/J.IKON.5.100699.
- ^ Szablowski, Jerzy (1975). Arrasy flamandzkie w zamku królewskim na Wawelu (in Polish). Polska: Arkady. p. 15. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Szablowski, Jerzy (1975). Arrasy flamandzkie w zamku królewskim na Wawelu (in Polish). Polska: Arkady. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Orlińska-Mianowska, Ewa (2008). Fashion world of the 18th and early 19th century. Polska: Bosz. ISBN 9788387730727. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Singleton, Esther (12 December 2019). «French and English furniture distinctive styles and periods described and illustrated». Good Press – via Google Books.
- ^ Dialog. Miesiȩcznik poświȩcony dramaturgii współczesnej, teatralnej, filmowej, radiowej, telewizyjnej. Vol. 11. Polska: RSW «Prasa». 1966. p. 6. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Waugh, Norah (1968). The Cut of Women’s Clothes. London: Routledge. pp. 72–73. ISBN 0-87830-026-0.
- ^ Lubliner, Ludwig (1858). Obrona Żydów zamieszkałych w krajach polskich od niesłusznych zarzutów i fałszywych oskarzeń. Brussels: C. Vanderauwer. p. 7. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Muthesius, Stefan (1994). Polska; art, architecture, design 966–1990. Langewiesche Köster. p. 34. ISBN 9783784576121. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Państwowy Instytut Badania Sztuki Ludowej (1974). «Volumes 28–29». Polska sztuka ludowa (Polish Folk Art). Państwowy Instytut Sztuki. p. 259.
- ^ Paul Robert Magocsi (1996). A history of Ukraine. University of Toronto Press. pp. 286–287. ISBN 0-8020-7820-6.
- ^ a b Michael J. Mikoś. «Baroque». www.staropolska.pl. Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ^ Rolska-Boruch, Irena (2003). «Domy pańskie» na Lubelszczyźnie od późnego gotyku do wczesnego baroku. Polska: Wydawnictwo KUL. ISBN 9788373630291. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Kowalczyk, Jerzy (1973). Sebastiano Serlio a sztuka polska. Polska: Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich. p. 119. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Miłobędzki, Adam (1994). The architecture of Poland: a chapter of the European heritage. Kraków: International Cultural Centre. p. 110. ISBN 9788385739142.
- ^ Zdzisław Klimczuk, Józef Garliński (1996). Most Holandia – Polska (in Polish). Polska: Bis Press. p. 32. ISBN 9788390149424. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Karpowicz, Mariusz (1994). Sztuki polskiej drogi dziwne (in Polish). Excalibur. p. 47. ISBN 9788390015286. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Feliks Gryglewicz, Romuald Łukaszyk, Wincenty Granat, Zygmunt Sułowski (1973). Encyklopedia katolicka: Kinszasa-Krzymuska. Lublin: Tow. Nauk. Katolickiego Uniwersytetu Lubelskiego. p. 1189. ISBN 9788373060685. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ «Palaces and Castles in a Lion Country». www.lvivtoday.com.ua. 2 June 2008. Retrieved 19 May 2009.
- ^ Snopek, Jerzy (1999). Oświecenie. Polska: Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN. p. 134. ISBN 9788301129170. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Kazimierz Maliszewski (1990). Obraz świata i Rzeczypospolitej w polskich gazetach rękopiśmiennych z okresu późnego baroku: studium z dziejów kształtowania się i rozpowszechniania sarmackich stereotypów wiedzy i informacji o «theatrum mundi» (in Polish). Schr. p. 79. ISBN 83-231-0239-2. W każdym razie «królowa bez korony i pierwsza dama Rzeczypospolitej», jak współcześni określali Sieniawską, zasługuje na biografię naukową.
- ^ Andrzej Wasko, Sarmatism or the Enlightenment: <space>The Dilemma of Polish Culture, Sarmatian Review XVII:2, online
- ^ Dziejochciejstwo, dziejokrętactwo, Janusz Tazbir, Polityka 6 (2591) 10 February 2007 (in Polish)
- ^ Paradowski, Ryszard (2005). Unia Europejska a społeczeństwo obywatelskie (in Polish). Poznań: Wydawn. Nauk. Instytutu Nauk Politycznych i Dziennikarstwa Uniwersytetu im. Adama Mickiewicza. p. 168. ISBN 9788387704940.
- ^ Kopczyński, Michał; Tygielski, Wojciech (2010). Pod wspólnym niebem. Narody dawnej Rzeczypospolitej (in Polish). Warszawa: Bellona. ISBN 9788311117242.
- ^ a b Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010
- ^ Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, p. 236
- ^ a b Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, p. 237
- ^ Total and Jewish population based on Frazee; others are estimations from Pogonowski (see the following reference). Charles A. Frazee, World History the Easy Way, Barron’s Educational Series, ISBN 0-8120-9766-1, Google Print, 50
- ^ R. B. Wernham, The new Cambridge modern history: The Counter-Reformation and price revolution, 1559–1610, 1968, Cambridge University Press, Google print p. 377
- ^ a b Matthew P. Romaniello, Charles Lipp. Contested Spaces of Nobility in Early Modern Europe. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. 2011. p. 233.
- ^ Polish Sociological Review (in Polish). Polish Sociological Association. 2007. p. 96.
- ^ Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, p. 201
- ^ Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, pp. 25–83
- ^ a b Kopczyński & Tygielski 2010, pp. 29–38
- ^ Stone, Daniel, The Polish-Lithuanian State, 1386–1795, Seattle and London: University of Washington Press, 2001.
- ^ Norman Davies, God’s Playground. A History of Poland, Vol. 1: The Origins to 1795, Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Page 126. ISBN 0-19-925339-0 / ISBN 0-19-925340-4
- ^ Paul R. Magocsi (2010). A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples. University of Toronto Press. p. 169. ISBN 978-1-4426-1021-7.
- ^ Jeannie Labno (2011). Commemorating the Polish Renaissance Child: Funeral Monuments and Their European Context. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-7546-6825-1.
- ^ Piekarski, Adam (1979). Freedom of Conscience and Religion in Poland. Interpress Publishers. p. 31.
- ^ a b «Memory of the World Register Nomination Form». portal.unesco.org. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- ^ Linda Gordon, Cossack Rebellions: Social Turmoil in the Sixteenth Century Ukraine, SUNY Press, 1983, ISBN 0-87395-654-0, Google Print, p. 51
- ^ Serhii Plokhy (2006). The origins of the Slavic nations: premodern identities in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. Cambridge University Press. p. 169. ISBN 0-521-86403-8.
- ^ «Lemberg». Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 3 September 2010.
- ^ Peter Kardash, Brett Lockwood (1988). Ukraine and Ukrainians. Fortuna. p. 134. ISBN 9780731675036.
- ^ Magocsi, Paul R. (2010). A History of Ukraine: The Land and Its Peoples. University of Toronto Press. p. 190. ISBN 978-1442610217.
- ^ «Poland, history of», Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [3]. Retrieved 10 February 2006 Archived 1 November 2004 at the Wayback Machine and «Ukraine», Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica Premium Service. [4]. Retrieved 14 February 2006. Archived 24 January 2005 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «European Jewish Congress – Poland». Eurojewcong.org. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ Thus, at the time of the first partition in 1772, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth consisted of 43 per cent Latin Catholics, 33 per cent Greek Catholics, 10 per cent Christian Orthodox, 9 per cent Jews and 4 per cent Protestant Willfried Spohn, Anna Triandafyllidou (2003). Europeanisation, national identities, and migration: changes in boundary constructions between Western and Eastern Europe. Routledge. p. 127. ISBN 0-415-29667-6.
- ^ a b Artūras Tereškinas (2005). Imperfect communities: identity, discourse and nation in the seventeenth-century Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Lietuvių literatūros ir tautosakos institutas. p. 31. ISBN 9955-475-94-3.
- ^ a b Aleksander Gieysztor, ed. (1988). Rzeczpospolita w dobie Jana III (Commonwealth during the reign of John III). Royal Castle in Warsaw. p. 45.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Anatol Lieven, The Baltic Revolution: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and the Path to Independence, Yale University Press, 1994, ISBN 0-300-06078-5, Google Print, p. 48
- ^ Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, Language and Nationalism in Europe, Oxford University Press, 2000, ISBN 0-19-925085-5, Google Print p. 184
- ^ Östen Dahl, Maria Koptjevskaja-Tamm], The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact, John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2001, ISBN 90-272-3057-9, Google Print, p. 45
- ^ Glanville Price, Encyclopedia of the Languages of Europe, Blackwell Publishing, 1998, ISBN 0-631-22039-9, Google Print, p. 30
- ^ a b c d Mikulas Teich & Roy Porter, The National Question in Europe in Historical Context, Cambridge University Press, 1993, ISBN 0-521-36713-1, Google Print, p. 295
- ^ a b c d e Kevin O’Connor, Culture And Customs of the Baltic States, Greenwood Press, 2006, ISBN 0-313-33125-1, Google Print, p. 115
- ^ a b Daniel. Z Stone, A History of East Central Europe, p. 46.
- ^ Karin Friedrich et al., The Other Prussia: Royal Prussia, Poland and Liberty, 1569–1772, Cambridge University
Press, 2000, ISBN 0-521-58335-7, Google Print, p. 88 - ^ Tomasz Kamusella (2008). The Politics of Language and Nationalism in Modern Central Europe. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-230-55070-4.
- ^ L’union personnelle polono-saxonne contribua davantage à faire connaître en Pologne le français que l’allemand. Cette fonction de la langue française, devenue l’instrument de communication entre les groupes dirigeants des deux pays. Polish Academy of Sciences Institute of History (1970). «Volume 22». Acta Poloniae historica (in French). National Ossoliński Institute. p. 79.
- ^ They were the first Catholic schools in which one of the main languages of instruction was Polish. […] Although he followed Locke in attaching weight to the native language, in general Latin lost ground to French rather than Polish. Richard Butterwick (1998). Poland’s last king and English culture: Stanisław August Poniatowski, 1732–1798. Oxford University Press. p. 70. ISBN 0-19-820701-8.
- ^ України, ЦДЕА. «Державна архівна служба України». archives.gov.ua.
- ^ Although still sometimes in use by the end of the XVII century and lack of official decree like one for Grand Duchy chancellery, there was no separate Ruthenian Metrica since 1673.
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Jan Owsinski, Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis, M.E. Sharpe, 2003, ISBN 0-7656-0665-8, Google Print, p. 177
- ^ Östen Dahl, Maria Koptjevskaja-Tamm, The Circum-Baltic Languages: Typology and Contact, John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2001, ISBN 90-272-3057-9, Google Print, p. 41
- ^ Zinkevičius, Z. (1993). Rytų Lietuva praeityje ir dabar. Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidykla. p. 70. ISBN 5-420-01085-2.
Official usage of Lithuanian language in the 16th century Lithuania’s cities proves magistrate’s decree of Wilno city, which was sealed by Žygimantas Augustas’ in 1552…//Courts juratory were written in Lithuanian language. In fact, such [courts juratory written in Lithuanian] survived from the 17th century…
- ^ ««Mes Wladislaus…» a letter from Wladyslaw Vasa issued in 1639 written in Lithuanian language«. Retrieved 3 September 2006.
- ^ Ališauskas, V.; L. Jovaiša; M. Paknys; R. Petrauskas; E. Raila; et al. (2001). Lietuvos Didžiosios Kunigaikštijos kultūra. Tyrinėjimai ir vaizdai. Vilnius. p. 500. ISBN 9955-445-26-2.
In 1794 Government’s declarations were carried out and in Lithuanian.
- ^ Daniel. Z Stone, A History of East Central Europe, p. 4.
- ^ Czesław Miłosz, The History of Polish Literature, University of California Press, 1983, ISBN 0-520-04477-0, Google Print, p. 108
- ^ Jan K. Ostrowski, Land of the Winged Horsemen: Art in Poland, 1572–1764, Yale University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-300-07918-4, Google Print, p. 27
- ^ a b Joanna B. Michlic (2006). Poland’s threatening other: the image of the Jew from 1880 to the present. U of Nebraska Press. p. 42. ISBN 0-8032-3240-3.
- ^ Karol Zierhoffer, Zofia Zierhoffer (2000). Nazwy zachodnioeuropejskie w języku polskim a związki Polski z kulturą Europy (in Polish). Wydawnictwo Poznańskiego Towarzystwa Przyjaciół Nauk. p. 79. ISBN 83-7063-286-6. Podobną opinię przekazał nieco późnej, w 1577 r. Marcin Kromer «Za naszej pamięci weszli […] do głównych miast Polski kupcy i rzemieślnicy włoscy, a język ich jest także częściowo w użyciu, mianowicie wśród wytworniejszych Polaków, którzy chętnie podróżują do Włoch».
- ^ Rosemary A. Chorzempa (1993). Polish roots. Genealogical Pub. ISBN 0-8063-1378-1.
- ^ Jan K. Ostrowski, ed. (1999). Art in Poland, 1572–1764: land of the winged horsemen. Art Services International. p. 32. ISBN 0-88397-131-3. In 1600 the son of the chancellor of Poland was learning four languages: Latin, Greek, Turkish, and Polish. By the time he had completed his studies, he was fluent not only in Turkish but also in Tatar and Arabic.
- ^ Lola Romanucci-Ross; George A. De Vos; Takeyuki Tsuda (2006). Ethnic identity: problems and prospects for the twenty-first century. Rowman Altamira. p. 84. ISBN 0-7591-0973-7.
- ^ Barile, Davide (2019). Historic Power Europe; A Post-Hegelian Interpretation of European Integration. New York: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781000731132.
- ^ A. stated, for instance by the preamble of the Constitution of the Republic of Poland of 1997.
- ^ Alfonsas Eidintas, Vytautas Zalys, Lithuania in European Politics: The Years of the First Republic, 1918–1940, Palgrave, 1999, ISBN 0-312-22458-3. Print, p. 78
- ^ ««Zobaczyć Kresy». Grzegorz Górny. Rzeczpospolita 23 August 2008 (in Polish)» (in Polish). Rp.pl. 23 August 2008. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
- ^ Sarah Johnstone (2008). Ukraine. Lonely Planet. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-74104-481-2.
- ^ Stephen K. Batalden, Sandra L. Batalden (1997). The newly independent states of Eurasia: handbook of former Soviet republics. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 45. ISBN 0-89774-940-5.
- ^ Richard M. Golden (2006). «Volume 4». Encyclopedia of witchcraft: the Western tradition. ABC-CLIO. p. 1039. ISBN 1-57607-243-6.
- ^ Girolamo Imbruglia; Rolando Minuti; Luisa Simonutti (2007). Traduzioni e circolazione delle idee nella cultura europea tra ‘500 e ‘700 (in Italian). Bibliopolis. p. 76. ISBN 978-88-70-88537-8.
- ^ Daniel H. Cole (2002). Pollution and property: comparing ownership institutions for environmental protection. Cambridge University Press. p. 106. ISBN 0-521-00109-9.
- ^ Gordon Campbell (2006). The Grove encyclopedia of decorative arts. Oxford University Press US. p. 13. ISBN 01-95189-48-5.
- ^ Gwei-Djen Lu; Joseph Needham; Vivienne Lo (2002). Celestial lancets: a history and rationale of acupuncture and moxa. Routledge. p. 284. ISBN 07-00714-58-8.
- ^ Ian Ridpath. «Taurus Poniatovii — Poniatowski’s bull». www.ianridpath.com. Retrieved 18 May 2009.
- ^ «Old City of Zamość». UNESCO World Heritage Centre. 23 September 2009. Retrieved 15 September 2011.
- ^ After a fire had destroyed a wooden synagogue in 1733 Stanislaw Lubomirski decided to found a new bricked synagogue building. Polin Travel. «Lancut». www.jewish-guide.pl. Retrieved 2 September 2010.
- ^ Guillaume de Lamberty (1735). «Volume 3». Mémoires pour servir à l’histoire du XVIIIe siècle, contenant les négociations, traitez, résolutions et autres documents authentiques concernant les affaires d’état: avec le supplément aux années MDCXCVI-MDCCIII (in French). p. 343.
Généreux et Magnifiques Seigneurs les Sénateurs et autres Ordres de la Sérénissime République de Pologne et du grand Duché de Lithuanie
- ^ a b c Francis W. Carter (1994). Trade and urban development in Poland: an economic geography of Cracow, from its origins to 1795 – Volume 20 of Cambridge studies in historical geography. Cambridge University Press. pp. 186, 187. ISBN 978-0-521-41239-1.
- ^ Daniel Stone (2001). The Polish–Lithuanian state, 1386–1795. University of Washington Press. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-295-98093-5.
- ^ Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries (1998). A history of eastern Europe: crisis and change. Routledge. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-415-16111-4.
- ^ Norman Davies (1998). Europe: A History. HarperCollins. pp. 657–660. ISBN 978-0-06-097468-8.
vilnius capital grand duchy.
- ^ Politics and reformations: communities, polities, nations, and empires. 2007 p. 206.
- ^ Zeitschrift für Ostmitteleuropa-Forschung. 2006, Vol. 55; p. 2.
- ^ Thomas A. Brady, Christopher Ocker; entry by David Frick (2007). Politics and reformations: communities, polities, nations, and empires : essays in honor of Thomas A. Brady, Jr. Brill Publishers. p. 206. ISBN 978-90-04-16173-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer; essay by Tomas Venclova (2004). History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th and 20th centuries (Volume 2). John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 11. ISBN 978-90-272-3453-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Bibliography
- Bardach, Juliusz; Lesnodorski, Boguslaw; Pietrzak, Michal (1987). Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego. Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe. ISBN 9788301079192.
- Brzezinski, Richard (1987). Polish Armies (1): 1569–1696. Men-At-Arms Series. Vol. 184. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 0-85045-736-X.
- Brzezinski, Richard (1988). Polish Armies (2): 1569–1696. Men-At-Arms Series. Vol. 188. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 0-85045-744-0.
- Frost, Robert (2015). The Oxford History of Poland–Lithuania. Vol. I: The Making of the Polish–Lithuanian Union, 1385–1569. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0198208693.
- Litwin, Henryk (October 2016). «Central European Superpower». BUM Magazine.
- Norkus, Zenonas (2017). An Unproclaimed Empire: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania: From the Viewpoint of Comparative Historical Sociology of Empires. Routledge. ISBN 978-1138281547.
- Rowell, S. C. (2014). Lithuania Ascending: A Pagan Empire within East-Central Europe, 1295–1345. Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Fourth Series. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107658769.
- Rowell, S. C.; Baronas, Darius (2015). The Conversion of Lithuania. From Pagan Barbarians to Late Medieval Christians. Vilnius: Institute of Lithuanian Literature and Folklore. ISBN 978-6094251528.
- Stone, Daniel Z. (2014). The Polish–Lithuanian State, 1386–1795. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0295803623.
- Sužiedėlis, Saulius A. (2011). Historical Dictionary of Lithuania (2 ed.). Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0810875364.
External links
Media related to Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth at Wikimedia Commons
- Commonwealth of Diverse Cultures: Poland’s Heritage Archived 24 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine (in Polish and English)
- Knowledge passage (in Polish)
- The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth–Maps, history of cities in Poland, Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania Archived 17 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine (in Polish)
- The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth on BBC Radio 4 «In Our Time» 14 Oct. 2021, Melvyn Bragg with Robert I. Frost, University of Aberdeen, Katarzyna Kosior, Northumbria University and Norman Davies, University of Oxford
Coordinates: 50°03′14″N 19°56′05″E / 50.05389°N 19.93472°E
Эта статья — об историческом государстве 1569—1795 гг. О других значениях термина см. Речь Посполитая (значения).
| Историческое государство | ||||
| Речь Посполитая | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| польск. Rzeczpospolita Korony Polskiej i Wielkiego Księstwa Litewskiego лит. Lenkijos ir Lietuvos sandraugos bei Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė |
||||
|
||||
|
Девиз: « (лат.) Si Deus Nobiscum quis contra nos (Если с нами Бог, то кто против нас?) в XVIII веке: (лат.) Pro Fide, Lege et Rege (За веру, закон и короля)» |
||||
| Гимн: Gaude Mater Polonia[d] | ||||
 Речь Посполитая в границах 1700 года |
||||
|
←
1 июля 1569 — 24 октября 1795 |
||||
| Столица |
Краков (до 1795, формально) Варшава (с 1596, фактически) |
|||
| Язык(и) | польский, латинский, западнорусский (официально в Великом княжестве Литовском до 1696 года; на территории Брацлавского, Волынского, Киевского и Черниговского воеводств Польши — до 1653 года[1]), армянский (языки меньшинств)[2] | |||
| Официальный язык | польский, западнорусский язык и латынь | |||
| Религия | католическая церковь и Русская униатская церковь | |||
| Денежная единица | польский злотый | |||
| Площадь |
865 000 км² (1580 год) 878 000 км² (1650 год) 718 000 км² (1771 год) |
|||
| Население |
7,5 млн чел. (1580 год) 12,3 млн чел. (1771 год) |
|||
| Форма правления |
наследственная монархия (1569–1573) выборная монархия (1573–1791, 1792–1795) конституционная монархия (1791–1792) |
|||
| Политический режим | шляхетская демократия | |||
| Король польский и великий князь литовский | ||||
| • 1569—1572 | Сигизмунд II Август (первый) | |||
| • 1764—1795 | Станислав II Август Понятовский (последний) | |||
| История | ||||
| • 1569 | Люблинская уния | |||
| • 1596 | Брестская уния | |||
| • 1772 | Первый раздел | |||
| • 1793 | Второй раздел | |||
| • 1795 | Третий раздел | |||
Речь Посполи́тая (польск. Rzeczpospolita) — федерация[3][4] Королевства Польского и Великого княжества Литовского, возникшая в результате Люблинской унии в 1569 году и ликвидированная в 1795 году с разделом государства между Россией, Пруссией и Австрией. Располагалась преимущественно на территориях современных Польши, Украины, Белоруссии и Литвы, а также частично на территории современных России, Латвии и Молдавии.
При наличии единого государственного устройства Королевство Польское и Великое княжество Литовское имели каждое свой собственный административный аппарат, казну, войско и законы. Главой государства являлся пожизненно избираемый сеймом монарх, носивший титул короля польского и великого князя литовского. Существовавший в Речи Посполитой специфический политический режим принято называть шляхетской демократией[5].
Название[править | править код]
Традиционное название государства — «Речь Посполитая» — является дословным переводом на польский язык латинского термина Res Publica (польск. rzecz — вещь, дело; pospolita — общая)[6]. На русский язык этот термин дословно переводится как «общее дело» или «общая вещь»[7]. Официальное название государства — Королевство Польское и Великое княжество Литовское (польск. Królestwo Polskie i Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie). Местными жителями государство обычно называлось просто Речь Посполитая (польск. Rzeczpospolita; зап.-русск. Рѣч Посполита). Собственно Королевство Польское местные жители кратко называли Короной, а Великое княжество Литовское — Литвой, а иногда — Великим княжеством.
С XVII века в дипломатической переписке использовалось название Светлейшая Речь Посполитая Польская (польск. Najjaśniejsza Rzeczpospolita Polska; лат. Serenissima Res Publica Poloniae)[8].
Ныне широко употребляемое название Речь Посполитая Обоих Народов (польск. Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów) не является аутентичным и, вероятно, получило распространение после выхода в свет в 1967 году одноимённой исторической трилогии польского писателя Павла Ясеницы.
В современной польской историографии период в истории Польши с 1569 по 1795 именуется «I Речь Посполитая», с 1918 по 1939 — «II Речь Посполитая», с 1989 года — «III Речь Посполитая». Период существования Польской Народной Республики (1944—1989) в этой нумерации не учитывается или называется термином Rzeczpospolita Ludowa (народная республика), чтобы подчеркнуть её отличие от других Речей Посполитых[9].
Государственное устройство[править | править код]
Речь Посполитая считалась общим государством «обоих народов» — польского и литовского, под которыми понималась совокупность представителей шляхетского сословия Королевства Польского и Великого княжества Литовского. Верховная власть, сильно ограниченная со стороны шляхты, принадлежала пожизненно избираемому монарху, носившему единый титул короля польского и великого князя литовского (в его краткой версии). Законодательная, а также частично судебная власть находилась в руках Сейма, состоявшего из двух палат: Сената и Посольской избы. В состав Сената входили высшие государственные сановники и католическое духовенство, Посольская изба состояла из депутатов, называемых послами. Выборы депутатов происходили на поветовых сеймиках, представлявших собой специально созываемые перед началом работы Сейма собрания местной шляхты. Каждый повет отправлял на сейм двух делегатов, которым вручались составленные на сеймике инструкции, отражающие позицию шляхты повета по обсуждаемым на Сейме вопросам[10].
Будучи парламентским институтом, сеймики также исполняли функцию органов местного самоуправления, представлявшими собой основную форму реализации политических интересов шляхты, постоянно добивавшейся расширения их полномочий. С формальной и идеологической точки зрения все представители шляхты были равны, хотя на практике решающую роль в управлении государством играла немногочисленная группа крупнейших землевладельцев — магнатов. Особенно сильно влияние магнатерии было в Великом княжестве Литовском, однако с течением времени подобная ситуация сложилась и в Королевстве Польском. Постепенно мелкая и даже средняя шляхта оказалась зависима от магнатов, так как без их поддержки не могла добиться назначения на должности и улучшения своего экономического положения. По мере расширения влияния магнатов сеймиковая политическая культура приходила в упадок, виной чему была слабость государственного аппарата и особенно отсутствие влияния центральной власти на регионы[11].
Избрание монарха происходило на проводившемся в окрестностях Варшавы элекционном сейме, принять участие в котором могли все шляхтичи. Право быть избранным также имел каждый шляхтич, при этом в большинстве случаев кандидатами на престол становились представители иностранных династий. Избираемый пожизненно монарх не имел права передачи трона по наследству, издания декретов (привилеев), противоречащих законам, а также ареста шляхтича без суда. Дополнительные ограничения на королевскую власть накладывали так называемые генриковы артикулы, принимаемые монархом перед вступлением на престол. Политические и финансовые обязанности монарха определялись ещё одним обязательным соглашением, известным как Pacta conventa. Подписанием этого договора король и великий князь отказывался от передачи трона по наследству, обязывался править в согласии с королевским советом из 18 сенаторов, не реже раза в два года созывать Сейм, без разрешения которого не объявлять войны и мира и не вводить новые налоги. На территории Великого княжества Литовского условия правления великого князя определялись также положениями Статута Великого княжества Литовского[10].
История[править | править код]
Создание[править | править код]
Речь Посполитая явилась своего рода продолжением государства Ягеллонов — личной унии Королевства Польского и Великого княжества Литовского, существовавшей с перерывами с 1385 года. В 1569 году между Королевством Польским и Великим княжеством Литовским была заключена Люблинская уния, по которой оба государства объединялись в одно — с избираемым общим монархом с двойным титулом короля польского и великого князя литовского, общим сеймом, единой внешней политикой и монетной системой. При этом обе части сохраняли свою администрацию, казну (включая денежную эмиссию), войско, суды, оставалась и граница между государствами с взиманием таможенных сборов. Великое княжество Литовское, несмотря на протесты магнатерии, утратило при этом значительные территории на юге, Волынь, Подолье и Киевщину.
Политическая история[править | править код]
Для Речи Посполитой было характерно уникальное государственное устройство. Первое столетие её существования польские историографы называют «Золотым веком», каким он был для нобилитированного меньшинства страны — шляхты, а также для многих горожан, пользовавшихся выгодами самоуправления по Магдебургскому праву. Однако в дальнейшем в политической жизни страны всё более нарастала анархия, а катастрофические демографические потери в ходе войн второй половины XVII — начала XVIII веков предопределили экономический упадок. В последние годы существования страны были проведены масштабные реформы как в экономической, так и в политической сферах, с помощью которых планировалось обеспечить Речи Посполитой устойчивое развитие, однако в этот момент объединённые силы трёх соседних держав уничтожили и разделили государство между собой.
В момент образования Речь Посполитая находилась в состоянии тяжёлой войны с Россией, ставшей одной из главных причин заключения Люблинской унии. Несмотря на крайне неудачное начало, война была завершена умеренно выгодным для Речи Посполитой Ям-Запольским миром. Разногласия по поводу выборов нового короля после смерти Стефана привели к вторжению австрийской армии, которая была разбита, а возглавлявший её эрцгерцог Максимилиан взят в плен. Восстания Косинского и Наливайко в конце XVI века, несмотря на их неудачу, ознаменовали становление украинского казачества как важной политической силы.
В начале XVII века внешняя политика страны становится более экспансионистской; король Сигизмунд III ведёт войны с Россией, Швецией, Османской империей. Также шляхта, иногда с позволения короля, а иногда вопреки его воле, принимала участие в Молдавских войнах магнатов с целью установления контроля над Молдавией. В то же время некоторые польские подразделения приняли участие в Тридцатилетней войне на территории Священной Римской империи. Благодаря мастерству полководцев, таких как Ян Ходкевич, Речь Посполитая одержала немало побед, тем не менее эти войны не привели к кардинальному изменению геополитической ситуации в её пользу.
Речь Посполитая в 1635 году
Середина XVII века оказалась для Речи Посполитой катастрофической: восстание Богдана Хмельницкого, Русско-польская война (1654—1667) и война со Швецией поставили государство на грань гибели. Тем не менее король Ян II Казимир сумел удержать страну от распада и поглощения соседями. Следующий период роста политического могущества Речи Посполитой связывается с правлением Яна III Собеского; наиболее известна его победа в битве под стенами Вены, положившая конец экспансии Османской империи в Европе.
Участие в Северной войне на стороне России привело к превращению территории Речи Посполитой в арену боевых действий, вызвало разорение населения и экономическое ослабление страны. Принцип Liberum veto, мешая проведению любых реформ, приводил также и к отставанию в организации вооружённых сил по сравнению с соседними странами, что поставило дальнейшее существование Речи Посполитой под угрозу. Возрастающее вмешательство иностранных держав в её внутренние дела не встречало достойного сопротивления большую часть XVIII века. В 1768 году по итогам так называемого Сейма Репнина, на котором русский посол под угрозой русских войск в Варшаве навязал сейму невыгодные для страны законы, Речь Посполитая фактически превратилась в протекторат Российской империи[12][13].
Лишь в правление последнего короля Станислава Августа были проведены масштабные реформы, кардинально изменившие государственный строй Речи Посполитой и увенчавшиеся принятием Конституции 3 мая 1791 года[14][15][16].
Реформы принесли свои плоды; благодаря участию в них видных экономистов того времени, таких как Антоний Тизенгауз, наблюдался экономический подъём. Однако Россия в ходе Русско-польской войны (1792), опираясь на Тарговицкую конфедерацию, уничтожила результаты реформ. После Гродненского сейма 1793 года, по которому был утверждён второй раздел Польши, Речь Посполитая снова попала в политическую зависимость от России[17]. Последней попыткой спасти Речь Посполитую было Восстание Костюшко, которое было подавлено русскими и прусскими войсками, и в результате Третьего раздела в 1795 году Речь Посполитая прекратила своё существование.
Религиозная история[править | править код]
Население Речи Посполитой было многоконфессиональным: в этнических Польше и Литве проживали в основном римо-католики, на русских землях — православные, а затем униаты, по всей территории государства проживали протестанты различных направлений, иудеи (среди еврейского меньшинства) и мусульмане (среди татарского меньшинства). В первые годы существования государства господствовала веротерпимость: равноправие католиков и православных гарантировалось привилеем от 7 июня 1563 года, а в 1573 году Варшавская конфедерация провозгласила свободу вероисповедания, закрепив за Речью Посполитой статус самой веротерпимой страны в Европе[источник не указан 333 дня].
Однако в правление Сигизмунда III религиозная обстановка в стране изменилась; среди многих причин этого называют победу Контрреформации; взгляды ряда влиятельных иерархов католической и православной церквей, включая Петра Скаргу и Ипатия Поцея, по различным религиозным вопросам, таким, например, как вопрос о единстве веры и полезности этого для страны и общества; ослабление православной церкви в XVI веке в ходе Реформации и Ливонской войны (разорение Полоцка и взятие в плен российскими войсками православного архиепископа Арсения) и др[18]. В 1596 году на церковном соборе была принята Брестская уния, приведшая к возникновению униатской церкви. Первым следствием этого события явился резкий рост религиозной конфронтации, доходящей до восстаний и убийств (таких, например, как восстания, связанные с деятельностью архиепископа Иосафата, и его убийство). Уния также вызвала рост самоорганизации общества в форме братств и бурное распространение полемической литературы.
Сейм 1632 года, приведший к власти Владислава IV, сделал ряд шагов в сторону возвращения веротерпимости, приняв законы, обеспечивавшие права протестантов, православных и униатов. К 1647 году в Речи Посполитой насчитывалось около 4 тысяч униатских и более 13,5 тысяч православных приходов[19].
К середине XVII века уровень религиозных свобод в Речи Посполитой стал уступать уровню передовых европейских стран. К этому времени большинство протестантских общин прекратили своё существование, оставаясь заметным религиозным меньшинством только на немногих приграничных территориях. Часть протестантов эмигрировала в Западную Европу. Сделавшись господствующей религиозной организацией, католическая церковь стала преследовать атеизм; одного из приверженцев этого учения — Казимира Лыщинского — казнили в 1689 году. С другой стороны, в Речь Посполитую переселялись верующие из стран, где уровень религиозных свобод стоял ещё ниже; таковыми были, например, преследуемые в России староверы[20][21].
Подчинение Киевской православной митрополии Московскому патриархату в 1688 году означало потерю самостоятельности православной церкви в Речи Посполитой; число её прихожан продолжало уменьшаться. Ко времени разделов Речи Посполитой православные стали небольшим религиозным меньшинством, в то время как униатская церковь вышла на второе место в стране после католичества, насчитывая 8 епархий с 9300 приходами, 172 монастырями, 10 300 священниками и 4,5 миллионами прихожан (36 % населения Речи Посполитой)[22].
В XVIII веке религиозный вопрос широко использовался соседями Речи Посполитой для вмешательства в её внутренние дела.
Разделы Речи Посполитой[править | править код]
Карта разделов Речи Посполитой
| Раздел | Дата | Участники | Территории |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 5 августа 1772 года | Эрцгерцогство Австрия | Часть Западной Украины и южная часть Польши |
| Королевство Пруссия | Северо-западная часть Польши | ||
| Российская империя | Восточная Белоруссия, часть Прибалтики (Инфлянты) | ||
| II | 23 января 1793 года | Королевство Пруссия | Гданьск, Познань и Торунь с частью северных польских земель |
| Российская империя | Центральная часть Белоруссии с городами Минск, Несвиж, Слуцк,
Пинск и часть Правобережной Украины |
||
| III | 24 октября 1795 года | Эрцгерцогство Австрия | Малая Польша с Краковом и Люблином, южная часть Подляшья
и западная часть Брестского воеводства |
| Королевство Пруссия | Большая часть Мазовецкого воеводства вместе с Варшавой,
части Подляшского, Гродненского, Трокского воеводств и Жемайтии |
||
| Российская империя | Западная Белоруссия, часть Литвы, Курляндия, Западная Волынь,
часть Холмской земли |
Попытки восстановления государства[править | править код]
Попыткой возродить Речь Посполитую можно назвать создание Наполеоном Варшавского герцогства в 1807 году. Аналогичные попытки предпринимались во время Ноябрьского восстания (1830—1831), Январского восстания (1863—1864) и в 1920-е, когда Юзеф Пилсудский выдвинул идею создания Междуморья — конфедерации Польши, Литвы, Белоруссии и Украины. Современная Польша называет себя наследницей Речи Посполитой.
Территория и население[править | править код]
Речь Посполитая располагалась преимущественно на территориях современных Польши, Украины, Белоруссии и Литвы, а также на части территории России, Латвии, Эстонии, Молдавии и Словакии. В северо-западной части государства, омывавшейся Балтийским морем, на протяжении всего её существования располагалось германской герцогство, а затем и королевство Пруссия.
| Год | Население, млн. чел. | Площадь, тыс. км² | Плотность, чел. на км² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1580 | 7,5 | 865 | 9 |
| 1650 | 11 | 878 | 12 |
| 1771 | 12,3 | 718 | 17 |
| Источник: Cezary Kuklo. Demografia Rzeczypospolitej Przedrozbiorowej. — Warsawa: Wydawnictwo DiG, 2009. — P. 211. — 518 p. |
На протяжении двух веков Речь Посполитая была одним из крупнейших государств Европы. После подписания в 1618 году Деулинского перемирия её территория достигла максимальной площади в 990 тыс. км² и оставалась таковой до перехода основной части Ливонии к Швеции по Митавскому перемирию в 1622 году[23].
Численность населения примерно с 7 миллионов в 1569 году достигла 12,3 миллионов человек в 1771 году[23]. До Люблинской унии Королевство Польское было заселено гораздо плотнее Великого княжества Литовского, где при примерно троекратном преимуществе в площади территории плотность населения была в 3—4 раза ниже. Значительная часть земель Великого княжества была практически безлюдна (см. Дикое Поле). Подобная ситуация сохранялась и позднее. Наиболее значительно население государства сокращалось в годы военных лихолетий и массовых эпидемий второй половины XVII — начала XVIII веков[23].
Столица[править | править код]
Официальной столицей Речи Посполитой был Краков. В 1596 замок Вавель подвергся пожару, поэтому король Сигизмунд III временно перенёс резиденцию в Варшаву. С тех пор Варшава стала фактической столицей, хотя столичное положение города не было зафиксировано ни в одном документе, а польские короли и великие князья литовские продолжали короноваться в Кракове. Варшава была провозглашена официальной столицей только по принятии Майской конституции 1791 года.
Административное деление[править | править код]
Административно-территориальное деление Речи Посполитой в 1619 году
Административно-территориальное деление Речи Посполитой в 1619 году (при нажатии на область осуществляется переход на соответствующую статью)
Провинции Речи Посполитой в 1629 году
Речь Посполитая состояла из трёх провинций. Великое княжество Литовское составляло отдельную провинцию, а Королевство Польское делилось на Великопольскую[pl]* и Малопольскую провинции[pl]*. Провинции делились на воеводства, а те, в свою очередь, — на поветы (уезды).
Великопольская провинция[править | править код]
| Герб | Воеводство | Воеводский город | Образование | Число поветов | Территория, км² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Брест-Куявское воеводство | Брест-Куявский | XIV век | 5 | 3000 | |
| Варминское епископство | Лидзбарк-Варминьски | 1466 | 10 | 4249 | |
| Гнезненское воеводство | Гнезно | 1768 | 3 | 7500 | |
| Иновроцлавское воеводство | Иновроцлав | XIV век | 5 | 2900 | |
| Калишское воеводство | Калиш | 1314 | 6 | 15 000 | |
| Ленчицкое воеводство | Ленчица | 1772 | 3 | 4000 | |
| Мальборкское воеводство | Мальборк | 1466 | 4 | 2000 | |
| Мазовецкое воеводство | Варшава | 1526 | 23 | 23 000 | |
| Плоцкое воеводство | Плоцк | 1495 | 8 | 3500 | |
| Познанское воеводство | Познань | XIV век | 4 | 15 500 | |
| Поморское воеводство | Скаршевы | 1454 | 8 | 12 907 | |
| Равское воеводство | Рава | 1462 | 6 | 6000 | |
| Серадзское воеводство | Серадз | 1339 | 4 | 10 000 | |
| Хелмненское воеводство | Хелмно | 1466 | 2 | 4654 |
Малопольская провинция[править | править код]
| Герб | Воеводство | Воеводский город | Образование | Число поветов | Территория, км² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Белзское воеводство | Белз | 1462 | 4 | 9000 | |
| Брацлавское воеводство | Брацлав | 1569 | 2 | 31 500 | |
| Волынское воеводство | Луцк | 1569 | 3 | 38 000 | |
| Киевское воеводство | Киев | 1471 | 3 | 200 000 | |
| Краковское воеводство | Краков | XIV век | 4 | 17 500 | |
| Люблинское воеводство | Люблин | 1474 | 3 | 10 000 | |
| Подляское воеводство | Дрогичин | 1513 | 3 | ||
| Подольское воеводство | Каменец-Подольский | 1434 | 3 | 17 750 | |
| Русское воеводство | Львов | 1434 | 13 | 83 000 | |
| Сандомирское воеводство | Сандомир | XIV век | 6 | 24 000 | |
| Черниговское воеводство | Чернигов | 1635 | 2 |
Великое княжество Литовское[править | править код]
| Воеводство | Воеводский город | Образование[24] | Число поветов | Территория, км²[25] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Берестейское воеводство | Брест | 1566 | 2 | 40 600 |
| Виленское воеводство | Вильна | 1413 | 5 | 44 200 |
| Витебское воеводство | Витебск | 1511 | 2 | 24 600 |
| Жемайтское староство | Россиены | 1411 | 1 | 23 300 |
| Минское воеводство | Минск | 1566 | 3 | 55 500 |
| Мстиславское воеводство | Мстиславль | 1566 | 1 | 22 600 |
| Новогрудское воеводство | Новогродок | 1507 | 3 | 33 200 |
| Полоцкое воеводство | Полоцк | 1504 | 1 | 21 800 |
| Смоленское воеводство | Смоленск | 1514 | 2 | 53 000 |
| Трокское воеводство | Троки | 1413 | 4 | 31 100 |
Особое положение было закреплено за Задвинским герцогством (Ливонским княжеством), провинцией Великого княжества Литовского с ноября 1561 года. После подписания Люблинской унии герцогство стало совместным владением (кондоминиумом) Польской Короны и Княжества Литовского. В 1582 году герцогство было поделено на три части, преобразованные в 1598 году в Венденское, Дерптское и Перновское воеводства. В результате войны со Швецией 1600—1627 годов основная часть герцогства отошла последней, а оставшаяся часть Венденского воеводства была преобразована в Инфлянтское воеводство (формально создано в 1667 году).
Кроме перечисленного, в состав Королевства Польского входили обладавшие особым статусом автономные Княжество Севежское и Княжество-епископство Варминское. Также в состав Короны входило несколько анклавов в Спише.
Экономика[править | править код]
Финансовая система[править | править код]
Как и везде в Европе того времени, в основу финансов Речи Посполитой были положены монеты, чья ценность обеспечивалась содержанием в них драгоценных металлов. Однако обе части страны, Польша и Литва, несмотря на объединение, сохранили свои монетные системы. Основой денежной системы в Королевстве Польском был польский грош, или осьмак. Один грош делился на 8 денариев, а 30 польских грошей составляли злотый. Основой денежной системы Великого Княжества Литовского был литовский грош, причём 8 литовских грошей были равны 10 польским. Один литовский грош делился на 10 пенязей, а 60 грошей составляли копу. Копа и злотый были счётными денежными единицами, остальные выпускались в виде реальных серебряных и биллонных монет. Реже использовались другие счётные единицы, такие как вярдунок, рубль и гривна. В разные годы чеканились монеты достоинством в 1/2, 1, 2, 3 пенязя, 1/2, 1, полтора, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 польских и литовских грошей. Кроме того, в Речи Посполитой выпускалась крупная серебряная монета — талер и крупная золотая — дукат, а также дробные и кратные им единицы, такие как 1/2, 1/4, 1/6 талера; 1/2 дуката, 2 дуката. Поскольку талер чеканился из серебра высокой пробы, а содержание серебра в гроше постепенно понижалось в связи с инфляцией, его курс не был постоянным, изменившись за время существования Речи Посполитой от 30 до 240 польских грошей за 1 талер. Стоимость дуката составляла от 1,5 до 2,5 талеров.
К середине XVII века пенязи-денарии вышли из употребления, им на смену пришла мелкая медная монета — солид, или шэляг (нынче обычно называемый боратинкой), курс которого составлял 1/3 польского гроша, иногда падая до 1/5 гроша. Реформой 1766 г. устаревшие монеты XVII—XVIII веков были изъяты из обращения, содержание серебра в монетах было повышено, а низшие грошовые номиналы становятся медными.
Подобно большинству стран Европы тех времён, в Речи Посполитой выплаты могли осуществляться монетами любых государств в соответствии с содержанием в них драгоценных металлов, причём в целях упрощения и единообразия расчётов суммы обычно пересчитывались в национальные денежные единицы. В связи с этим рынки Речи Посполитой свободно принимали талеры и дукаты других стран Европы, равные по номиналу и стоимости отечественным. Также на рынках обращалось значительное количество мелких серебряных монет соседней Пруссии и других германских княжеств, Ливонского ордена (во 2-й пол. XVI в.), Швеции (с 1621 г.) и других государств[26].
Культура и религия[править | править код]
Немалую роль в жизни Речи Посполитой, особенно в её образовательной системе, играл орден иезуитов. Вступавшие в орден поляки работали как в пределах Речи Посполитой, так и по всему миру. Среди наиболее знаменитых польских иезуитов XVII века — Андрей Боболя, замученный казаками в Полесье в 1657 году, и Михал Бойм, умерший в 1659 году в джунглях на вьетнамско-китайской границе, пытаясь найти последнего южноминского императора и доставить ему ответ папы римского на просьбу о помощи от первой (и последней) китайской императрицы-католички[27].
Архивы[править | править код]
Примечания[править | править код]
- ↑ «Руськая» серия Коронной метрик (недоступная ссылка). Дата обращения 2 октября 2017. Архивировано 3 октября 2017 года.
- ↑ С. Захаркевич. Армяне Речи Посполитой: анализ модели культурной адаптации // Художественная культура армянских общин на землях Речи Посполитой: Материалы Международной научной конференции / Сост. и отв. ред. И. Н. Скворцова. — Минск: Арт. Дизайн, 2013. — С. 23.
- ↑ Вялікае Княства Літоўскае. Энцыклапедыя у 3 т. — Мн.: БелЭн, 2005. — Т. 1: Абаленскі — Кадэнцыя. — С. 18. — 684 с. — ISBN 985-11-0314-4.
- ↑ Речь Посполита // Большая российская энциклопедия : [в 35 т.] / гл. ред. Ю. С. Осипов. — М. : Большая российская энциклопедия, 2004—2017.
- ↑ Голенченко Г. «Шляхетская демократия» в Великом княжестве Литовском XVI–XVIІІ вв // Беларусь и Россия: общество и государство. — Мн.. — Вып. 2. Архивировано 10 сентября 2011 года.
- ↑ Pietrzyk-Reeves D. The foundations of Rzeczpospolita in the 16th century and the influence of humanism and republicanism (польск.) = Pietrzyk-Reeves D. Podstawy wspólnotowego ładu Rzeczypospolitej w XVI wieku a wpływ humanizmu i republikanizmu // Polska czyli… Idee wspólnoty politycznej i tożsamości narodowej w polskiej tradycji intelektualnej. — Kraków: Ośrodek Myśli Politycznej, 2011. — S. 15—50.
- ↑ Хархордин О. В. Была ли res publica вещью? // Неприкосновенный запас. — 2007. — № 5 (55).
- ↑ См., например, текст договора Яна III Собеского с Фридрихом Августом (1677) [1] (недоступная ссылка) (лат.) или текст союзного договора Речи Посполитой с Прусским королевством (1790) [2] (польск.).
- ↑ Дмитрук, Е. П. Название польского государства и особенности его политико-государственного устройства в XX в. согласно конституционным актам: историко-юридический анализ // Право.by. — 2014. — 1 (27). — c. 13-18.
- ↑ 1 2 Грыцкевіч А. Дзяржаны і палітычны лад // Вялікае Княства Літоўскае. Энцыклапедыя у 3 т. — Мн.: БелЭн, 2005. — Т. 1: Абаленскі — Кадэнцыя. — С. 43—44. — 684 с. — ISBN 985-11-0314-4.
- ↑ Радаман А. Соймік // Вялікае Княства Літоўскае. Энцыклапедыя у 3 т. — Мн.: БелЭн, 2005. — Т. 2: Кадэцкі корпус — Яцкевіч. — С. 617. — 788 с. — ISBN 985-11-0378-0.
- ↑ Andrzej Jezierski, Cecylia Leszczyńska, Historia gospodarcza Polski, 2003, s. 68.
- ↑ Historical dictionary of Lithuania. Saulius Suziedelis. 2011
- ↑ James Madison. The Federalist Papers Penguin Classics. — 1987. — ISBN 0-14-044495-5.
- ↑ Albert Blaustein. Constitutions of the World. — Fred B. Rothman & Company, 1993. — ISBN 0-8377-0362-X.
- ↑ Bill Moyers. Moyers on Democracy 2009. — Random House Digital, Inc.. — P. 68. — ISBN 978-0-307-38773-8.
- ↑ Jeremy Black. Russia’s Rise as a European Power, 1650—1750, History Today, Vol. 36 Issue: 8, August 1986.
- ↑ Нарысы гісторыі Беларусі. — Мн.: Беларусь, 1994. — Т. 1. — С. 177. — 528 с.
- ↑ Вялікае Княства Літоўскае. Энцыклапедыя у 3 т. — Мн.: Беларуская Энцыклапедыя імя П. Броўкі, 2005. — Т. 1: Абаленскі — Кадэнцыя. — С. 114—116. — 684 с. — ISBN 985-11-0314-4
- ↑ Вольные люди из московских владений. Когда была основана Ветка? (недоступная ссылка). Сайт города Ветка и Ветковского района Гомельской области. Дата обращения 24 марта 2018. Архивировано 24 марта 2018 года.
- ↑ Ветковская школа иконописи, ветковская резьба… Чем ещё знаменит город Ветка в Гомельской области? (рус.), Столичное телевидение — СТВ. Дата обращения 24 марта 2018.
- ↑ Kuklo C. Demografia Rzeczypospolitej Przedrozbiorowej. — Warsawa: Wydawnictwo DiG, 2009. — P. 211. — 518 p.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Cezary Kuklo. Demografia Rzeczypospolitej Przedrozbiorowej. — Warsawa: Wydawnictwo DiG, 2009. — P. 211. — 518 p. — ISBN 978-83-7181-590-4.
- ↑ Administration // Encyclopedia Lituanica / Simas Sužiedėlis, Juozas Kapočius. — Boston, Massachusetts, 1970—1978. — Т. I. — С. 17—21.
- ↑ Stasys Vaitiekūnas. Lietuvos gyventojai: Per du tūkstantmečius. — Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidybos institutas, 2006. — P. 53. — ISBN 5-420-01585-4.
- ↑ Рябцевич В. Н. Нумизматика Беларуси. — Мн.: Полымя, 1995.
- ↑ Mungello David E. Curious Land: Jesuit Accommodation and the Origins of Sinology. — Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press, 1989. — P. 139. — 405 p. — ISBN 0824812190. — ISBN 9780824812195.
Литература[править | править код]
- Bardach, Juliusz; Lesnodorski, Boguslaw; Pietrzak, Michal. Historia panstwa i prawa polskiego (неопр.). — Warsaw: Paristwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe, 1987.
- Brzezinski, Richard. Polish Armies (1): 1569–1696 (Men-At-Arms Series, 184) (неопр.). — Osprey Publishing, 1987. — ISBN 0-85045-736-X.
- Brzezinski, Richard. Polish Armies (2): 1569–1696 (Men-At-Arms Series, 188) (неопр.). — Osprey Publishing, 1988. — ISBN 0-85045-744-0.
- Sužiedėlis, Saulius A. Historical Dictionary of Lithuania (неопр.). — 2. — Scarecrow Press (англ.)русск., 2011. — ISBN 978-0810875364.
Ссылки[править | править код]
- Польша, история // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
- Commonwealth of Diverse Cultures: Poland’s Heritage (польск.) (англ.)
- The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth-Maps, history of cities in Poland, Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania (польск.)
Русский[править]
Тип и синтаксические свойства сочетания[править]
Речь Пос—по—ли́—та·я
Устойчивое сочетание (имя собственное). Используется в качестве именной группы.
Имя собственное, топоним.
Произношение[править]
- МФА: [ˈrʲet͡ɕ pəspɐˈlʲitəɪ̯ə]
Семантические свойства[править]
Значение[править]
- истор. федерация Королевства Польского и Великого княжества Литовского, возникшая в результате Люблинской унии в 1569 году и ликвидированная в 1795 году с разделом государства между Россией, Пруссией и Австрией ◆ Отсутствует пример употребления (см. рекомендации).
Синонимы[править]
Антонимы[править]
- —
Гиперонимы[править]
- федерация
Гипонимы[править]
Этимология[править]
Перевод[править]
| Список переводов | |
|
Библиография[править]
Фразеологизмы и устойчивые сочетания[править]
- Вторая Речь Посполитая (Польская Республика, польск. Rzeczpospolita Polska, II Rzeczpospolita) — польское государство, восстановленное в 1918 году. Название подчеркивает непрерывную связь с Речью Посполитой (1569–1795), ликвидированной в результате её разделов между Российской империей, Пруссией и Австрией в конце XVIII века
- Третья Речь Посполитая (польск. III Rzeczpospolita — буквально Третья Республика) — употреблённое в Конституции определение польского государства, появившееся после основных политических изменений, происшедших в 1989–1990 годах. Официальное название государства — Республика Польша (польск. Rzeczpospolita Polska)





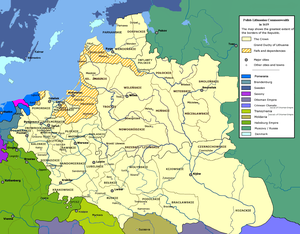





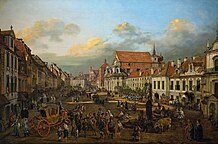








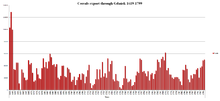













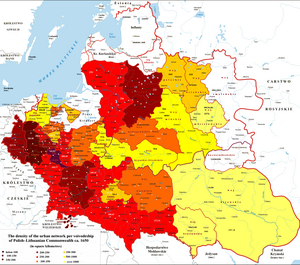





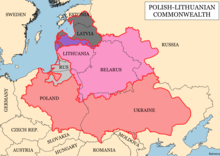



![18th century amber casket. Gdańsk patronized by the Polish court flourished as the center for amber working in the 17th century.[273]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/09/Malbork_%28DerHexer%29_2010-07-14_067.jpg/150px-Malbork_%28DerHexer%29_2010-07-14_067.jpg)






![Taurus Poniatovii, constellation originated by Marcin Poczobutt in 1777 to honor the king Stanisław II Augustus[275]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7a/Taurus_Poniatovii.PNG/150px-Taurus_Poniatovii.PNG)


![Łańcut Synagogue was established by Stanisław Lubomirski, 1733.[277]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9a/%C5%81a%C5%84cut_synagoga_06.jpg/100px-%C5%81a%C5%84cut_synagoga_06.jpg)









