Сеу́л (кор. 서울 Соуль — «столица») — столица и крупнейший город Республики Корея. Население более 10 млн человек.
Содержание
- 1 Название
- 1.1 Китайская транскрипция
- 2 География и климат
- 3 История
- 4 Административное деление
- 5 Население
- 6 Экономика
- 6.1 Финансы
- 7 Транспорт
- 7.1 Воздушный транспорт
- 7.2 Метрополитен
- 7.3 Городской транспорт
- 8 Досуг
- 9 Туризм и достопримечательности
- 10 Высшее образование
- 11 Спорт
- 12 Международные отношения
- 12.1 Города-побратимы
- 12.2 Города-партнёры
- 13 Известные личности
- 14 Галерея
- 15 См. также
- 16 Примечания
- 17 Ссылки
- 17.1 Карты
Название
Слово Соуль происходит от древнекорейского соболь или сораболь («столица») периода Силла. Тогда это слово относили к городу Кёнджу, бывшей столице Силла. В ханчче кён (京) означает «столица»; этот слог встречается, например, в официальном названии административной единицы на территории Сеула в годы японского колониального правления (Кёнсон/Кэйдзё) и в названиях железных и автомобильных дорог (Кёнбусон, 경부선 — железнодорожная линия Сеул-Пусан; Кёнъи н косокторо, 경인고속도로 — скоростная автодорога Сеул-Инчхон).
Китайская транскрипция
В отличие от большинства корейских географических названий, слово «Сеул» не имеет аналога на ханче, и по-китайски город называют его прежним именем (漢城/汉城, китайское чтение Ханьчэн, корейское Хансон; значение — «крепость на реке Ханган», но при желании можно трактовать и как «китайская крепость», «крепость ханьцев»). В январе 2005 года правительство города запросило изменение китайского названия города на 首爾/首尔 (Shǒu’ěr, Шоу-эр), что является приблизительным воспроизведением корейского произношения в китайском языке (в самом корейском, однако, 首爾 читается 수이 , Су-и). При этом 首 (шоу) значит «первый» и «столица». Китайцы приняли это название. Это изменение касается только носителей китайского языка и не оказывает влияние на корейское название города.
География и климат
Климат Сеула определяется как муссонный. Сеул находится на одной широте с югом Турции (Анталья, Аланья), Грецией, Испанией и другими тёплыми странами, тем не менее в городе, несмотря на то, что он окружён морем, отмечается устойчивая, хотя и непродолжительная мягкая зима. Средний минимум в январе достигает −6 °C.
Лето в городе не только очень жаркое (средняя температура августа 25,4 °C), но и очень влажное. Однако сильная жара в городе бывает редко, и температура крайне редко достигает 35 °C и выше. Этим Сеул отличается от городов с тропическим пустынным и степным климатом (Каир, Ташкент, Астрахань и другие), в которых схожа среднеиюльская температура. Летом в город приходит муссон (май-сентябрь), и среднемесячное количество осадков превышает 300 мм. За сутки иногда может выпасть более 100 мм осадков, а при прохождении тайфуна — более 250 мм осадков (для сравнения: годовая норма осадков в Москве составляет примерно 705 мм).
В остальные времена года преобладают ветры с материка, а зимой преобладает антициклониальный тип погоды. Сеул не защищён от северных ветров горами, иногда в городе температура может опускаться до температур в −15 °C и ниже.
| Климат Сеула | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Показатель | Янв. | Фев. | Март | Апр. | Май | Июнь | Июль | Авг. | Сен. | Окт. | Нояб. | Дек. | Год |
| Абсолютный максимум, °C | 13,5 | 18,7 | 23,0 | 29,8 | 32,4 | 37,4 | 38,4 | 38,1 | 36,0 | 29,6 | 25,9 | 19,6 | 38,4 |
| Средний максимум, °C | 1,6 | 4,1 | 10,2 | 17,6 | 22,8 | 26,9 | 28,8 | 29,5 | 25,6 | 19,7 | 11,5 | 4,2 | 16,9 |
| Средняя температура, °C | −2,7 | −0,1 | 5,5 | 12,2 | 17,4 | 21,9 | 24,9 | 25,4 | 20,8 | 14,4 | 6,8 | 0,2 | 12,2 |
| Средний минимум, °C | −6,1 | −4,1 | 1,1 | 7,3 | 12,6 | 17,8 | 21,8 | 22,1 | 16,7 | 9,8 | 2,9 | −3,4 | 8,2 |
| Абсолютный минимум, °C | −22 | −19,8 | −15,3 | −4,6 | 4,6 | 7,0 | 11,9 | 12,5 | 3,9 | −2,6 | −11,5 | −18,1 | −22 |
| Норма осадков, мм | 22 | 24 | 46 | 77 | 102 | 133 | 328 | 348 | 138 | 49 | 53 | 25 | 1345 |
| Источник: worldweather.org, Погода и Климат,[1] |
История
Классическая корейская архитектура
Первое название города — Виресон, был столицей государства Пэкче начиная с 370 год н. э. Во времена Корё был известен как Хансон (漢城, «крепость на берегу реки Ханган»). Во времена династии Чосон, начавшейся в 1394 году, был столицей государства и назывался Ханян (漢陽)). В годы японского колониального правления на территории города располагалась административная единица Кёнсон (яп. 京城, Кэйдзё), название Сеул было окончательно утверждено в независимой Корее в 1946 году.
Пэкче, одно из трёх корейских королевств, было основано в 18 году до н. э., со столицей в городе Виресон в районе современного Сеула. С тех пор сохранились развалины городских стен. Управление городом вскоре перешло от Пэкче к Корё в V веке, а затем к Силла в VI веке.
В XI веке правительство Корё, завоевавшее Силла, построило крепость, известную как «Южная Столица».
Когда Чосон сменила Корё, столица была перенесена в Сеул (Хансон, позднее Ханян), где оставалась до конца правления династии.
Изначально город был полностью окружен крепостной стеной высотой до семи метров для защиты населения от диких животных, разбойников и вражеских армий. Затем город разросся за стены и, хотя они сейчас не существуют (кроме небольшого участка к северу от центра города), крепостные ворота существуют по сей день, самые известные из них: Намдэмун и Тондэмун. Во времена Чосон ворота открывались и закрывались каждый день под звуки больших колоколов.
11 февраля 2008 года ворота Намдэмун, построенные в 1398-м году, были почти полностью уничтожены огнем — поджог устроил пожилой горожанин, обращения о рассмотрении жилищной проблемы которого городские власти систематически игнорировали (компания-застройщик выплатила этому горожанину заниженную сумму компенсации за земельный участок, который располагался на территории намечаемой застройки). Позднее, после поимки поджигателя полицией, он раскаялся в содеянном и попросил у нации прощения за свой проступок. Ранее этот же человек устроил поджог в сеульском дворце Чхангёнгун.
Ворота не имели охраны, возможно, потому, что никому в голову прийти не могло покушаться на национальное достояние № 1.
Основная причина практически полной неспособности пожарных справиться с огнём состояла в том, что ворота были деревянными, и вся их конструкция была пропитана водоотталкивающим средством для защиты от осадков. В итоге это же средство отталкивало воду, которой пожарные расчёты в течение нескольких часов поливали горящие ворота.
Правительство Республики Корея пообещало нации в течение трёх лет восстановить ворота, для чего были выделены финансовые средства в размере 21 миллиона долларов США. По информации некоторых сеульских газет, часть компаний-подрядчиков по восстановлению ворот вызвалась производить работы бесплатно.
Во время войны в Корее Сеул дважды переходил в руки северокорейских и китайских войск (в июне—сентябре 1950 и январе—марте 1951 годов). В результате боевых действий город был сильно разрушен. По крайней мере 191 000 построек, 55 000 жилых домов и 1000 предприятий лежало в руинах. Вдобавок, поток беженцев заполнил город, увеличив численность населения до 2,5 миллионов, большей частью бездомных.
После войны Сеул был быстро восстановлен и снова стал политическим и экономическим центром страны. Сегодня население города — это четверть населения Южной Кореи, Сеул занимает седьмое место среди городов мира по количеству штаб-квартир корпораций, входящих в список пятисот крупнейших транснациональных корпораций по версии журнала Fortune[2].
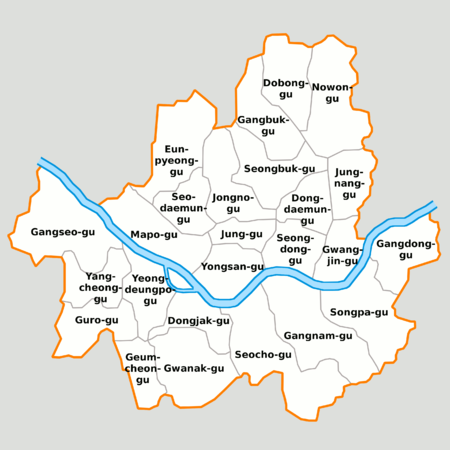
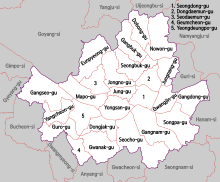
Административное деление
Районы Сеула
Сеул разделен на 25 ку (구 — муниципальный округ, имеющий статус самоуправления), которые в свою очередь разделены на 522 тон (동 — административный район), 13 787 тхон и 102 796 пан.
- Каннамгу (강남구; 江南區)
- Кандонгу (강동구; 江東區)
- Канбукку (강북구; 江北區)
- Кансогу (강서구; 江西區)
- Кванакку (관악구; 冠岳區)
- Кванджингу (광진구; 廣津區)
- Курогу (구로구; 九老區)
- Кымчхонгу (금천구; 衿川區)
- Новонгу (노원구; 蘆原區)
- Тобонгу (도봉구; 道峰區)
- Тондэмунгу (동대문구; 東大門區)
- Тонджакку (동작구; 銅雀區)
- Мапхогу (마포구; 麻浦區)
- Содэмунгу (서대문구; 西大門區)
- Сочхогу (서초구; 瑞草區)
- Сондонгу (성동구; 城東區)
- Сонбукку (성북구; 城北區)
- Сонпхагу (송파구; 松坡區)
- Янчхонгу (양천구; 陽川區)
- Йондынпхогу (영등포구; 永登浦區)
- Йонсангу (용산구; 龍山區)
- Ынпхёнгу (은평구; 恩平區)
- Чонногу (종로구; 鍾路區)
- Чунгу (중구; 中區)
- Чуннангу (중랑구; 中浪區)
Население
|
|
Экономика
Сеул — один из крупнейших промышленных и финансовых центров мира. Здесь располагаются штаб-квартиры корпораций Samsung, LG, Hyundai, Kia и SK. В Сеуле работают около 20 000 предприятий. Хотя Сеул занимает всего 0,6% территории Республики Корея, город производит 21% ВВП страны[3]. Главные отрасли промышленности: торговля, машиностроение, телекоммуникации, электроника, строительство.
Финансы
В Сеуле находятся штаб-квартиры многих международных компаний[4]. Интернациональные банки Citigroup, Deutsche Bank, HSBC, Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, Barclays, Grupo Santander, UBS, Credit Suisse, UniCredit, Société Générale, Calyon, BBVA, Macquarie Group, ING Bank, State Street и Standard Chartered имеют свои филиалы в городе.
-
Всемирный Торговый Центр
-
Дорога Тегеранно
-
Вид на часть Сеула
-
Комплекс корпорации Самсунг
-
Панорама Сеула
Транспорт
Воздушный транспорт
Город обслуживается двумя аэропортами. Аэропорт Кимпхо (англ.) долгое время был единственным в стране международным аэропортом. В марте 2001 года открылся Международный аэропорт Инчхон в городе Инчхон. После этого аэропорт Кимпхо стал осуществлять только внутренние рейсы (за исключением рейсов в Токио и Шанхай). Инчхонский аэропорт входит в число крупнейших в Восточной Азии, наряду с аэропортами Гонконга и Сингапура. Оба аэропорта связаны с Сеулом скоростными автомагистралями. В 2008 году открыто железнодорожное сообщение между аэропортами Кимпхо и Инчхон, а с 2011 года оба аэропорта связаны с Центральным вокзалом Сеула.
Метрополитен
В городе действует метрополитен, по объёмам пассажироперевозок занимающий одно из первых мест в Азии. Девять линий метро имеют номера от 1 до 9, есть линия Чунъансон (кор. 중앙선), являющаяся железной дорогой, но имеющая общие станции пересадок с линиями метрополитена, и линия Пундансон (кор. 분당선), тоже относящаяся скорее к железной дороге, нежели к линии метрополитена. Эта линия состоит из 20 станций, но на территории города имеет лишь 8 станций.
Определение количества станций метро, принадлежащих городу, является очень сложным ввиду тесного взаимодействия государственного и частного капиталов при строительстве линий метрополитена, а также в связи с тем, что сеульское метро изначально появилось как часть пригородных железных дорог (первая линия метро была всего лишь соединительным участком двух пригородных железных дорог).
Девятая линия метро введена в эксплуатацию в 2009 году. Она протянулась вдоль южного берега реки Ханган и состоит из 36 станций.
На схемах метрополитена линии и станции пронумерованы, что позволяет иностранцам довольно легко ориентироваться при назначении встреч на определённых станциях. Названия всех станций и вообще все указатели в метрополитене продублированы на английском языке (а названия станций имеют аналоги ханча).
Городской транспорт
Сеульский автобус
Транспортный бум в Сеуле берет свое начало в эпоху Корейской империи, когда были проложены первые автодороги и первая железная дорога до Синыйджу. С тех пор транспортная система города сильно разрослась, сделав его одним из крупнейших транспортных узлов Азии. В городе проложен метрополитен с девятью линиями, действует около 200 автобусных маршрутов, и шесть больших автострад (хайвеев), соединяющих районы города и пригороды. Сеул соединяется с другими городами страны посредством скоростной железной дороги KTX, являющейся одной из самых быстрых в мире.
До середины 1970-х гг. в деловом центре Сеула существовал и трамвайный транспорт, однако в связи с началом ввода в эксплуатацию метрополитена, а также с тем обстоятельством, что трамвайные пути занимали слишком много места на узких улочках Сеула в условиях постоянного увеличения численности автотранспорта, было принято решение ликвидировать трамвай как вид транспорта.
В городе и на междугородних маршрутах очень развит автобусный транспорт. Автобусы имеют преимущество перед частным автотранспортом и это правило соблюдается в абсолютном большинстве случаев (основные нарушители этого правила — таксисты, с которыми у водителей автобусов идёт непримиримая вражда — это замечают многие гости Сеула). Однако в связи с неуклонным ростом личного автотранспорта несколько лет назад серьёзно встала проблема пробок на дорогах. Проблему пробок для автобусов отчасти удалось решить благодаря инициативе нынешнего президента, а в то время (2007 год) ещё мэра Сеула Ли Мён Бака — на одной из центральных дорог Ханганно (кор. 한강로) от моста Ханган (кор. 한강대교) до площади сеульского вокзала были проложены специальные автобусные линии. В результате нововведения время поездки горожан из южных районов Сеула в центр города утром и из центра города вечером по этому маршруту сократилось примерно в 2,5-3 раза. Сразу же вслед за этим нововведением в других районах Сеула последовали аналогичные изменения.
Досуг
Вход в развлекательный центр COEX
Перестроенный Чхонгечхон
Исторический центр города — это город династии Чосон, находящийся теперь в деловом квартале. Там соседствуют древние дворцы, штаб-квартиры корпораций, современные офисные здания и гостиницы. Эта часть города находится в долине Чхонгечхон (청계천). К северу от делового центра находится гора Пукхансан, а к югу — небольшая гора Намсан.
Далее на юг находятся бывшие окраины Ёнсангу и Мапогу и протекает река Ханган. На другой стороне реки, в юго-восточной части Сеула находится современный район Каннамгу и его окрестности. Здесь располагается корейский Международный Торговый Центр. Большой популярностью пользуется развлекательный комплекс COEX, в котором сосредоточено огромное количество всевозможных закусочных и ресторанчиков, кинотеатров и магазинов, а также — большой подземный океанариум.
В соседнем районе Сонпхагу расположен парк развлечений Lotte World, который также является очень популярным местом в городе.
На Ёыйдо, небольшом острове посреди реки Ханган, на котором в древние времена была переправа на северный берег реки, и который некогда использовался в качестве военного аэродрома, располагаются Национальная Ассамблея Республики Корея, главные теле- и радиовещательные студии и большое количество офисных зданий.
Аккуратная планировка города была ключевой концепцией при его застройке начиная с XIV века. Королевские дворцы династии Чосон по сей день находятся в Сеуле. Главный императорский дворец (Кёнбоккун) восстановлен в прежнем облике.
В связи с большим объёмом работы, проделанным правительством города для снижения загрязнения окружающей среды, воздух в городе по чистоте равен токийскому, и намного чище, чем в Пекине. В Сеуле и окружающих районах располагается шесть больших парков, включая Сеульский лес, открытый в 2005 году. Зона вокруг Сеула засажена лесополосой для защиты от загрязнения предприятиями, находящимися в провинции Кёнгидо. Кроме того, в Сеуле находятся три больших парка развлечений: Lotte World, Seoul Land и Everland, расположенный в пригороде Йонъин. Самый посещаемый из них — Lotte World. Другие центры отдыха — это, прежде всего, олимпийский стадион и стадион чемпионата мира 2002-го года, а также публичный парк в центре города.
Берег острова Йоидо — пожалуй, самая развитая часть городского парка реки Ханган (кор. 한강시민공원), который протянулся по обоим берегам и проходит через весь город: у берега работают корабли-рестораны, по трём маршрутам курсируют речные трамвайчики, помимо этого есть станция речного такси (перевозка осуществляется небольшими катерами, довольно быстрыми), также на берегу острова расположено большое количество коммерческих палаток, торгующих продуктами быстрого приготовления и напитками (вплоть до алкогольных), есть несколько пунктов аренды велосипедов, спортивные площадки (со штангами, турниками и т. д.), туалеты. Эта часть парка реки Ханган пользуется у горожан огромной популярностью, поскольку далеко не у всех есть время выехать с семьёй/друзьями за город или к морю даже на выходных. Огромные скопления народа наблюдаются в основном ближе к концу недели, на выходных и по праздникам. В будние дни по вечерам у берега можно встретить немало офисных работников, которые приходят отдохнуть с коллегами после окончания трудового дня. Основной контингент приезжающих сюда — молодёжь, однако часто встречаются и люди пожилого возраста.
Специально для любителей велосипедного спорта вдоль обоих берегов реки Ханган протянулись велосипедные трассы. Территория парка в данный момент (март 2009 г.) активно перестраивается городскими властями. Окончание реконструкции намечено на конец 2009 года.
Практически на всём протяжении в пределах города реку Ханган (а также велосипедные дорожки и спортивные площадки) от жилых районов отгораживают скоростные автомагистрали. Для того, чтобы горожанам было удобнее добираться до берегов реки, через автомагистрали в некоторых местах уже построены, а местами ещё строятся пешеходные и велосипедные мостики.
Туризм и достопримечательности
Династия Чосон построила в Сеуле «Пять больших дворцов»:
- Чхандоккун (창덕궁; 昌德宮)
- Чхангёнгун (창경궁; 昌慶宮)
- Токсугун (덕수궁; 德壽宮)
- Кёнбоккун (경복궁; 景福宮)
- Кёнхигун (경희궁; 慶熙宮)
Кроме того, есть один менее значимый дворец:
- Унхёнгун (운현궁; 雲峴宮)
Известные храмы и гробницы:
- Чонмё
- Тонмё
- Мунмё
- Чогеса
- Хвагеса
- Наксондэ
Музеи и галереи:
- Национальный исторический музей
- Военный мемориал
В пригородах:
- Монумент Самджондо
- Намхансон
- Пукхансон
- Парк Намсан
- Парк Сунджюн
Другие:
- Юксам Билдинг
- Фонтан радуги
- Чхонвадэ
-
Здание «Юксам», второе в Корее по высоте
-
Также в Сеуле и в его пригорадах находится множество тематических парков (парков развлечений) и аквапарков:
- Everland
- Lotte World
- Seoul Land
- Ocean World
- Carribean Bay
- Tiger World
- Большой сеульский парк
Высшее образование
В Сеуле располагаются самые престижные университеты страны, включая Сеульский национальный университет, Университет Корё, и Университет Ёнсэ.
Другие университеты:
|
|
Спорт
В 1988 году Сеул стал столицей XX летних Олимпийских игр, а в 2002 году — одним из мест проведения чемпионата мира по футболу.
-
-
Стадион Сеул Уорлд Кап
-
Бейсбольный стадион
Международные отношения
Города-побратимыСписок городов-побратимов в соответствии с официальным сайтом[5]:
|
Города-партнёрыСписок городов-партнёров в соответствии с официальным сайтом[5]:
|
Известные личности
- Ли Мин Хо — южнокорейский актёр.
- Пэ Ён Джун — южнокорейский актёр.
- Чон Мён Хун — южнокорейский пианист и дирижёр.
- Ли Чхон Ён — южнокорейский футболист.
- Ли, Джим — американско-корейский художник и издатель комиксов.
- Пэк Намджун — американо-корейский художник.
- Пак Чэ Сан — южнокорейский рэпер.
- Пак Чи Сон — южнокорейский футболист.
- Пак, Линда — американская телевизионная актриса.
- Чон Джи Хун — южнокорейский певец, танцор, актёр.
- Юн Сон До — корейский поэт.
- Ли Сын Хун — южнокорейский конькобежец.
- Хон Мён Бо — южнокорейский футболист и тренер.
- Чхве Чин-силь — южнокорейская актриса.
- Ким Хён А — южнокорейская танцовщица и певица.
Галерея
-
Аэрофотосъёмка города
-
-
Вокзал Сеула
-
Поезд скоростной железной дороги KTX
-
Башня Намсан
-
Фестиваль Hi! Seoul
См. также
- Особые города Кореи
Примечания
- ↑ Temperatures in Seoul rise to record high at 25.9 degrees for Nov.. The Korean Times. Архивировано из первоисточника 27 июня 2012. Проверено 13 января 2012.
- ↑ GLOBAL CITIES & DEVELOPMENTAL STATES. New York, Tokyo, Seoul
- ↑ Welcome to KTC. Lmg.go.kr. Архивировано из первоисточника 6 августа 2012.
- ↑ Global : Cities, CNN.
- ↑ 1 2 http://english.seoul.go.kr/gover/cooper/coo_02sis.html
Ссылки
| Сеул на Викискладе? |
- Информация о Сеуле Организация Туризма Кореи
- Сайт правительства города
- Фотографии города
- Путеводитель «Сеул» в Викигиде
Карты
- Карта Сеула (кор.)
- Схема сеульского метро
- Карта делового центра Сеула
- Карта Сеула и окраин
|
|
| |
|
|---|---|
|
Герб • Флаг • Гимн • Государственный строй • Конституция • Парламент • Административное деление • География • Города • Столица • Население • Языки • История • Экономика • Валюта • Культура • Религия • Кинематограф • Литература • Музыка • Праздники • Спорт • Образование • Наука • Транспорт • Туризм • Почта (история и марки) • Интернет • Вооружённые силы • Внешняя политика |
|
Административное деление Республики Корея |
|
|---|---|
|
Город особого статуса: Сеул |
|
Столицы Азии |
|---|
|
Страны-члены ООН: Абу-Даби | Амман | Анкара | Астана | Ашхабад | Багдад | Баку | Бандар-Сери-Бегаван | Бангкок | Бейрут | Бишкек | Вьентьян | Дакка | Дамаск | Дили | Доха | Душанбе | Джакарта | Ереван | Иерусалим | Исламабад | Кабул | Катманду | Куала-Лумпур | Мале | Манама | Манила | Маскат | Москва | Нейпьидо | Никосия | Нью-Дели | Пекин | Пномпень | Путраджая | Пхеньян | Сана | Сеул | Сингапур | Ташкент | Тбилиси | Тхимпху | Тегеран | Токио | Улан-Батор | Ханой | Шри-Джаяварденепура-Котте | Эль-Кувейт | Эр-Рияд |
|
Столицы летних Олимпийских игр |
|
|---|---|
|
1896: Афины • 1900: Париж • 1904: Сент-Луис • 1908: Лондон • 1912: Стокгольм • 1916: Берлин • 1920: Антверпен • 1924: Париж • 1928: Амстердам • 1932: Лос-Анджелес • 1936: Берлин • 1940: Токио • 1944: Лондон • 1948: Лондон • 1952: Хельсинки • 1956: Мельбурн • 1960: Рим • 1964: Токио • 1968: Мехико • 1972: Мюнхен • 1976: Монреаль • 1980: Москва • 1984: Лос-Анджелес • 1988: Сеул • 1992: Барселона • 1996: Атланта • 2000: Сидней • 2004: Афины • 2008: Пекин • 2012: Лондон • 2016: Рио-де-Жанейро |
| |
||
|---|---|---|
| Литосфера | Острова (Чеджудо) • Горы (Халласан) • Вулканы • Пещеры • Крайние точки • Равнины • Корейский архипелаг |  |
| Гидросфера | Моря • Заливы и бухты • Реки (Нактонган) • Озёра • Водохранилища • Каналы • Водопады | |
| Атмосфера | Климат Южной Кореи | |
| Биосфера | Заповедники Южной Кореи • Национальные парки Южной Кореи • Заказники Южной Кореи | |
| Антропосфера | Экология • Административное деление • Столица Южной Кореи • Города • Время |
Home
About
Blog
Contact Us
Log In
Sign Up
Home>Слова, начинающиеся на букву С>Сеул>Перевод на корейский язык
Как будет Сеул по-корейски
Здесь Вы найдете слово Сеул на корейском языке. Надеемся, это поможет Вам улучшить свой корейский язык.
Вот как будет Сеул по-корейски:
서울
[править]
Сеул на всех языках
Другие слова рядом со словом Сеул
- сетка
- сетчатка
- сеть
- Сеул
- сечение
- сечь
- сеять
Цитирование
«Сеул по-корейски.» In Different Languages, https://www.indifferentlanguages.com/ru/%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE/%D1%81%D0%B5%D1%83%D0%BB/%D0%BF%D0%BE-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%B9%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8.
Копировать
Скопировано
Посмотрите другие переводы русских слов на корейский язык:
- буран
- взрываться
- взрывной
- двинуться
- живой интерес
- когда-то
- прилегать
Слова по Алфавиту
| Город особого подчинения | ||||
| Сеул | ||||
| 서울 | ||||
|
|
||||
|
||||
| 37°35′ с. ш. 127°00′ в. д.HGЯO | ||||
| Страна |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Статус | Особый город Кореи | |||
| Регион | Сеульский национальный столичный регион | |||
| Внутреннее деление | 25 районов | |||
| Мэр | Пак Вонсун | |||
| История и география | ||||
| Основан | 1394 год | |||
| Первое упоминание | IV век до н. э. | |||
| Прежние названия | Виресон, Ханян, Хансон, Кёнсон, Кэйдзё | |||
| Площадь |
605,25[источник не указан 1139 дней] км² |
|||
| Высота центра | 38 м | |||
| Часовой пояс | UTC+9:00 | |||
| Население | ||||
| Население | 10 063 197[1] человек (2015) | |||
| Плотность | 16 626,5 чел./км² | |||
| Агломерация | 23 480 000[2] человек (2015) | |||
| Цифровые идентификаторы | ||||
| Телефонный код | +82-2 | |||
| seoul.go.kr | ||||
|
Сеул |
||||
Сеу́л (кор. 서울 [sʰʌ.ul], Соуль — букв.: «столица») — город, столица Республики Корея. Образует единственный в стране город особого подчинения, разделённый на 25 самоуправляемых районов. Официальное название города — Город особого подчинения Сеул (кор. 서울특별시 Соуль-тхыкпёльси)
Население — 10,1 млн человек (2015), или 19,5 % населения страны. Образует агломерацию Сеул-Инчхон с населением 23,5 млн человек (2015), четвёртую по величине в мире. Расположен на северо-западе Республики Корея вблизи Жёлтого моря, на равнине в окружении гор, на берегах реки Ханган, в 24 км от границы с КНДР.
Главный политический, экономический и культурный центр Республики Корея. Один из ведущих финансовых центров Восточной Азии.
С 1394 года под названием Ханян — столица Кореи, с 1948 года под названием Сеул — столица Республики Корея. Во время Корейской войны город был сильно разрушен. Сохранились остатки крепостной стены с воротами, восстановлен дворцовый комплекс Кёнбоккун XIV века. Имеются объекты Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
Содержание
- 1 Название города
- 1.1 Китайская транскрипция
- 2 История
- 3 Физико-географическая характеристика
- 3.1 Климат
- 4 Административное деление
- 5 Население
- 6 Экономика
- 7 Транспорт
- 7.1 Городской
- 7.2 Междугородный
- 8 Вузы
- 9 Культура
- 10 Архитектура
- 11 Международные отношения
- 11.1 Угроза обстрела Сеула артиллерией КНДР
- 12 Примечания
- 13 Ссылки
Название города
Слово Соуль происходит от древнекорейского соболь или сораболь («столица») периода Силла. Тогда это слово относили к городу Кёнджу, бывшей столице Силла. В ханчче кён (京) означает «столица»; этот слог встречается, например, в официальном названии административной единицы на территории Сеула в годы японского колониального правления (Кёнсон/Кэйдзё) и в названиях железных и автомобильных дорог (Кёнбусон, 경부선 — железнодорожная линия Сеул-Пусан; Кёнъин косокторо, 경인고속도로 — скоростная автодорога Сеул-Инчхон)[источник не указан 1139 дней].
Китайская транскрипция
В отличие от большинства корейских географических названий, слово «Сеул» не имеет аналога на ханче, и по-китайски город называют его прежним именем (漢城/汉城, китайское чтение — Ханьчэн, корейское — Хансон; значение — «крепость на реке Ханган», но при желании можно трактовать и как «китайская крепость», «крепость ханьцев»). В январе 2005 года правительство города запросило изменение китайского названия города на 首爾/首尔 (Shǒu’ěr, Шоу-эр), что является приблизительным воспроизведением корейского произношения в китайском языке (в самом корейском, однако, 首爾 читается 수이 , Су-и). При этом 首 (шоу) значит «первый» и «столица». Китайцы приняли это название. Это изменение касается только носителей китайского языка и не оказывает влияние на корейское название города[3][4][5].
История
Основная статья: История Сеула[en]
Сеул на картине 1898 года
Первое название города — Виресон, он был столицей государства Пэкче, начиная с 370 года до н. э. Во времена Корё был известен как Хансон (漢城, «крепость на берегу реки Ханган»). Во времена династии Чосон, начавшейся в 1394 году, был столицей государства и назывался Ханян (漢陽)). В годы японского колониального правления на территории города располагалась административная единица Кёнсон (яп. 京城, Кэйдзё), название Сеул было окончательно утверждено в независимой Корее в 1946 году.
Пэкче, одно из трёх корейских королевств, было основано в 18 году до н. э., со столицей в городе Виресон в районе современного Сеула. С тех пор сохранились развалины городских стен. Управление городом вскоре перешло от Пэкче к Корё в V веке, а затем к Силла в VI веке. В XI веке правительство Корё, завоевавшее Силла, построило крепость, известную как «Южная Столица». Когда Чосон сменила Корё, столица была перенесена в Сеул (Хансон, позднее Ханян), где оставалась до конца правления династии.
Изначально город был полностью окружен крепостной стеной высотой до семи метров для защиты населения от диких животных, разбойников и вражеских армий. Затем город разросся за стены и, хотя они сейчас не существуют (кроме небольшого участка к северу от центра города), крепостные ворота существуют по сей день, самые известные из них: Намдэмун и Тондэмун. Во времена Чосон ворота открывались и закрывались каждый день под звуки больших колоколов.
Во время Корейской войны Сеул дважды переходил в руки северокорейских и китайских войск (в июне—сентябре 1950 и январе—марте 1951 годов). В результате боевых действий город был сильно разрушен. По крайней мере 191 000 построек, 55 000 жилых домов и 1000 предприятий лежало в руинах. Вдобавок, поток беженцев заполнил город, увеличив численность населения до 2,5 миллионов, большей частью бездомных. После войны Сеул был быстро восстановлен и снова стал политическим и экономическим центром страны.
По старой конституции КНДР 1948 года Сеул являлся столицей Северной Кореи[6]. В 1988 году Сеул стал столицей XX летних Олимпийских игр, а в 2002 году — одним из мест проведения чемпионата мира по футболу[7].
Физико-географическая характеристика
Сеул расположен на северо-западе Республики Корея, на равнинной местности, на берегах судоходной реки Ханган.
Северная от реки часть города называется Канбук («к северу от реки») и Каннам («к югу от реки»). К Каннаму прилегает остров Ёыйдо. Среди притоков Хангана — Танчон, Чхонгечхон и другие. Исторический центр окружён горами «Нэсасан» (Четыре горы с внутренней стороны крепостной стены): Пугаксан с севера, Наксан с востока, Намсан с юга и Инвансан с запада. На расположенной вблизи исторического центра лесистой горе Намсан (Южная гора) возвышается Сеульская телевизионная башня, к которой ведёт канатная дорога. Город целиком окружают горы «Весасан» (Четыре горы с внешней стороны крепостной стены): Пукхансан (высотою до 836,5 м) с севера, Ёнмасан с востока, Кванаксан с юга и Тогянсан с запада[8].
В административно-территориальном отношении Сеул с четырёх сторон граничит с провинцией Кёнгидо, а также с городом-метрополией Инчхоном на западе. Расстояние до Жёлтого моря по прямой составляет 15 км, до границы с КНДР — 24 км, до Пхеньяна — 193 км[комм. 1].
Климат
Климат муссонный. Сеул находится на одной широте с югом Турции (Анталья, Аланья), Грецией, Испанией и другими тёплыми странами, тем не менее в городе отмечается устойчивая, хотя и непродолжительная мягкая зима. Средний температурный минимум января: −6,8 °C.
Лето жаркое (средняя температура августа — +25,5 °C) и очень влажное, из-за чего пот хуже испаряется и меньше охлаждает организм, поэтому жара переносится гораздо тяжелее, чем, например, в Астрахани, где схожая среднеиюльская температура, но из-за полупустынного климата воздух сухой и пот с кожи быстро испаряется. Однако сильная жара в городе бывает редко, и температура крайне редко достигает 35 °C. Этим Сеул отличается от городов с тропическим пустынным и степным климатом (Каир, Ташкент, Астрахань и другие), в которых схожа среднеиюльская температура. Летом в город приходит муссон (май-сентябрь), и среднемесячное количество осадков превышает 300 мм. За сутки иногда может выпасть более 100 мм осадков, а при прохождении тайфуна — более 250 мм осадков (для сравнения: годовая норма осадков в Москве составляет примерно 705 мм).
В остальные времена года преобладают ветры с материка, а зимой преобладает антициклониальный тип погоды. Сеул не защищён от северных ветров горами, иногда в городе температура может опускаться до −15 °C и ниже.
| Климат Сеула | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Показатель | Янв. | Фев. | Март | Апр. | Май | Июнь | Июль | Авг. | Сен. | Окт. | Нояб. | Дек. | Год |
| Абсолютный максимум, °C | 14 | 18,7 | 23,8 | 29,8 | 33 | 36 | 38,3 | 39,6 | 32,4 | 30 | 25,9 | 16,2 | 39,6 |
| Средний максимум, °C | 1,5 | 4,9 | 10,4 | 18 | 23,1 | 27,1 | 28,8 | 29,8 | 25,8 | 19,7 | 11,4 | 4,5 | 17,1 |
| Средняя температура, °C | −2,5 | 0,4 | 5,4 | 12,1 | 17,5 | 22,1 | 25 | 25,5 | 20,7 | 13,9 | 6,6 | 0,2 | 12,2 |
| Средний минимум, °C | −6,8 | −4 | 0,8 | 6,9 | 12,4 | 17,7 | 21,7 | 22,1 | 16,3 | 9,1 | 2,2 | −3,9 | 7,9 |
| Абсолютный минимум, °C | −23 | −18 | −10 | −3 | 3 | 9 | 13 | 14 | 5 | −4 | −11 | −20 | −23 |
| Норма осадков, мм | 21 | 25 | 47 | 65 | 107 | 136 | 396 | 365 | 170 | 53 | 51 | 21 | 1455 |
| Средняя влажность, % | 60 | 58 | 58 | 56 | 63 | 68 | 78 | 76 | 69 | 64 | 62 | 61 | 64 |
| Источник: Погода и Климат |
Административное деление
Сеул разделен на 25 ку (구 — муниципальный округ, имеющий статус самоуправления), которые, в свою очередь, разделены на 522 тон (동 — административный район), 13 787 тхон и 102 796 пан.

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
|
|
|
Население
Художественная галерея Ильмин
|
|
Экономика
Сегодня население города — это четверть населения Южной Кореи, Сеул занимает (на 2001 год) седьмое место среди городов мира по количеству штаб-квартир корпораций, входящих в список пятисот крупнейших транснациональных корпораций по версии журнала Fortune[9].
Сеул — один из крупнейших промышленных и финансовых центров мира. Здесь располагаются штаб-квартиры корпораций Samsung, LG, Hyundai, Kia и SK. В Сеуле работают около 20 000 предприятий. Хотя Сеул занимает всего 0,6 % территории Республики Корея, город производит 21 % ВВП страны[10]. Главные отрасли промышленности: торговля, машиностроение, телекоммуникации, электроника, строительство.
В Сеуле находятся штаб-квартиры многих международных компаний[11]. Интернациональные банки Citigroup, Deutsche Bank, HSBC, Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, Barclays, Grupo Santander, UBS, Credit Suisse, UniCredit, Société Générale, Calyon, BBVA, Macquarie Group, ING Bank, State Street и Standard Chartered имеют свои филиалы в городе.
Сеул по данным The Economist Intelligence Unit в 2015 году вошёл в десятку самых дорогих городов мира[12].
Транспорт
Городской
Центральный железнодорожный вокзал Сеула
Наземный вестибюль станции Йонсан
Сеульский метрополитен по объёмам пассажироперевозок занимает одно из первых мест в Азии. Девять линий метро имеют номера от 1 до 9, есть линия Чунъансон (кор. 중앙선), являющаяся железной дорогой, но имеющая общие станции пересадок с линиями метрополитена, и линия Пундансон (кор. 분당선), тоже относящаяся скорее к железной дороге, нежели к линии метрополитена. Эта линия состоит из 20 станций, но на территории города имеет лишь 8 станций. Определение количества станций метро, принадлежащих городу, является очень сложным ввиду тесного взаимодействия государственного и частного капиталов при строительстве линий метрополитена, а также в связи с тем, что сеульское метро изначально появилось как часть пригородных железных дорог (первая линия метро была всего лишь соединительным участком двух пригородных железных дорог). Девятая линия метро введена в эксплуатацию в 2009 году. Она протянулась вдоль южного берега реки Ханган и состоит из 36 станций. На схемах метрополитена линии и станции пронумерованы, что позволяет иностранцам довольно легко ориентироваться при назначении встреч на определённых станциях. Названия всех станций и вообще все указатели в метрополитене продублированы на английском языке (а названия станций имеют аналоги ханча).
До середины 1970-х гг. в деловом центре Сеула существовал и трамвайный транспорт, однако в связи с началом ввода в эксплуатацию метрополитена, а также с тем обстоятельством, что трамвайные пути занимали слишком много места на узких улочках Сеула в условиях постоянного увеличения численности автотранспорта, было принято решение ликвидировать трамвай как вид транспорта.
В городе и на междугородних маршрутах очень развит автобусный транспорт. Автобусы имеют преимущество перед частным автотранспортом и это правило соблюдается в абсолютном большинстве случаев (основные нарушители этого правила — таксисты, с которыми у водителей автобусов идёт непримиримая вражда — это замечают многие гости Сеула). Однако в связи с неуклонным ростом количества личного автотранспорта несколько лет назад серьёзно встала проблема пробок на дорогах. Проблему пробок для автобусов отчасти удалось решить благодаря инициативе будущего президента, а в то время (2007 год) ещё мэра Сеула Ли Мён Бака — на одной из центральных дорог Ханганно (кор. 한강로) от моста Ханган (кор. 한강대교) до площади сеульского вокзала были проложены специальные автобусные линии. В результате нововведения время поездки горожан из южных районов Сеула в центр города утром и из центра города вечером по этому маршруту сократилось примерно в 2,5-3 раза. Сразу же вслед за этим нововведением в других районах Сеула последовали аналогичные изменения.
Междугородный
Транспортный бум в Сеуле берёт начало в эпоху Корейской империи, когда были проложены первые автодороги и первая железная дорога до Синыйджу. С тех пор транспортная система города сильно разрослась, сделав его одним из крупнейших транспортных узлов Азии. В городе проложен метрополитен с девятью линиями, действует около 200 автобусных маршрутов и шесть больших автострад (хайвеев), соединяющих районы города и пригороды. Сеул соединяется с другими городами страны посредством Корейской скоростной железной дороги, являющейся одной из самых быстрых в мире.
Город обслуживается двумя аэропортами. Аэропорт Кимпхо (англ.) долгое время был единственным в стране международным аэропортом. В марте 2001 года открылся Международный аэропорт Инчхон в городе Инчхон. После этого аэропорт Кимпхо стал осуществлять только внутренние рейсы (за исключением рейсов в Токио и Шанхай). Инчхонский аэропорт входит в число крупнейших в Восточной Азии, наряду с аэропортами Гонконга и Сингапура. Оба аэропорта связаны с Сеулом скоростными автомагистралями. В 2008 году открыто железнодорожное сообщение между аэропортами Кимпхо и Инчхон, а с 2011 года оба аэропорта связаны с сеульским вокзалом.
Вузы
В Сеуле располагаются самые престижные университеты страны, включая Сеульский национальный университет, университет Корё, и университет Ёнсе. Среди прочих: Университет Чунан, Университет искусств Чхуге, Университет Тонгук, Женский университет Тондок, Женский университет Токсон, Женский университет Ихва, Университет иностранных языков Хангук, Университет Хансон, Университет Ханян, Теологический университет Ханён, Университет Хоник, Университет Индок, Университет Канвун, Университет Конгук, Университет Кунмин, Корейский государственный открытый университет, Корейский государственный спортивный университет, Государственный университет искусств, Университет Кёнги, Университет Кёнхи, Университет Мёнджи, Университет Самюк, Университет Санмён, Университет Седжон, Университет Согён, Сеульский женский университет,
Университет Соган, Женский университет Сонсин, Женский университет Сунмён, Университет Сунсиль, Университет Сонгюнгван, Сеульский муниципальный университет.
Культура
Большой популярностью пользуется развлекательный комплекс COEX, в котором сосредоточено огромное количество всевозможных закусочных и ресторанчиков, кинотеатров и магазинов, а также — большой подземный океанариум. В соседнем районе Сонпхагу расположен парк развлечений Lotte World, который также является очень популярным местом в городе. В связи с большим объёмом работы, проделанным правительством города для снижения загрязнения окружающей среды, воздух в городе по чистоте равен токийскому, и намного чище, чем в Пекине. В Сеуле и окружающих районах располагается шесть больших парков, включая Сеульский лес, открытый в 2005 году. Зона вокруг Сеула засажена лесополосой для защиты от загрязнения предприятиями, находящимися в провинции Кёнгидо. Кроме того, в Сеуле находятся три больших парка развлечений: Lotte World, Seoul Land и Everland, расположенный в пригороде Йонъин. Самый посещаемый из них — Lotte World. Другие центры отдыха — это, прежде всего, олимпийский стадион и стадион чемпионата мира 2002-го года, а также публичный парк в центре города. Берег острова Йоыйдо — пожалуй, самая развитая часть городского парка реки Ханган (кор. 한강시민공원), который протянулся по обоим берегам и проходит через весь город: у берега работают корабли-рестораны, по трём маршрутам курсируют речные трамвайчики, помимо этого есть станция речного такси (перевозка осуществляется небольшими катерами, довольно быстрыми), также на берегу острова расположено большое количество коммерческих палаток, торгующих продуктами быстрого приготовления и напитками (вплоть до алкогольных), есть несколько пунктов аренды велосипедов, спортивные площадки (со штангами, турниками и т. д.), туалеты. Эта часть парка реки Ханган пользуется у горожан огромной популярностью, поскольку далеко не у всех есть время выехать с семьёй/друзьями за город или к морю даже на выходных. Огромные скопления народа наблюдаются в основном ближе к концу недели, на выходных и по праздникам. В будние дни по вечерам у берега можно встретить немало офисных работников, которые приходят отдохнуть с коллегами после окончания трудового дня. Основной контингент приезжающих сюда — молодёжь, однако часто встречаются и люди пожилого возраста.
Специально для любителей велосипедного спорта вдоль обоих берегов реки Ханган протянулись велосипедные трассы. Территория парка в данный момент (март 2009 г.) активно перестраивается городскими властями. Окончание реконструкции намечено на конец 2009 года. Почти на всём протяжении в пределах города реку Ханган (а также велосипедные дорожки и спортивные площадки) от жилых районов отгораживают скоростные автомагистрали. Для того, чтобы горожанам было удобнее добираться до берегов реки, через автомагистрали в некоторых местах уже построены, а местами ещё строятся пешеходные и велосипедные мостики.
Музеи и галереи: Национальный исторический музей, Военный мемориал, Национальный музей современного искусства, Музей оптических иллюзий (Trick Eye Museum) на Хондэ. В пригородах: Монумент Самджондо, Намхансон, Пукхансон, Парк Намсан, Парк Сунджюн. Другие: Юксам Билдинг, Фонтан радуги, Чхонвадэ. Также в Сеуле и в его пригородах находится множество тематических парков (парков развлечений) и аквапарков: Everland, Lotte World, Seoul Land, Ocean World, Carribean Bay, Tiger World, Большой сеульский парк.
Архитектура
Согласно действующему генеральному плану Сеула до 2030 года, город имеет три главных центра: исторический центр города имеет границы Ханяна времён династии Чосон (проспект Чонно и площадь Кванхвамун), деловой центр Каннам и финансовый Ёндынпхо-Ёыйдо[13].
Там соседствуют древние дворцы, штаб-квартиры корпораций, современные офисные здания и гостиницы. Эта часть города находится в долине Чхонгечхон (청계천). К северу от делового центра находится гора Пукхансан, а к югу — небольшая гора Намсан. Далее на юг находятся бывшие окраины Ёнсангу и Мапогу и протекает река Ханган. На другой стороне реки, в юго-восточной части Сеула находится современный район Каннамгу и его окрестности. Здесь располагается корейский Международный Торговый Центр. На Йоыйдо, небольшом острове посреди реки Ханган, на котором в древние времена была переправа на северный берег реки, и который некогда использовался в качестве военного аэродрома, располагаются Национальная Ассамблея Республики Корея, главные теле- и радиовещательные студии и большое количество офисных зданий. Аккуратная планировка города была ключевой концепцией при его застройке начиная с XIV века. Королевские дворцы династии Чосон по сей день находятся в Сеуле. Главный императорский дворец (Кёнбоккун) восстановлен в прежнем облике. Династия Чосон построила в Сеуле «Пять больших дворцов»: Чхандоккун, Чхангёнгун, Токсугун, Кёнбоккун, Кёнхигун. Кроме того, есть один менее значимый дворец Унхёнгун. Известные храмы и гробницы: Чонмё, Тонмё, Мунмё, Чогеса, Хвагеса, Наксондэ.
Международные отношения
Сеул (на 2015 год) поддерживает отношения, установленные в период с 1997 по 2012 год, с японским островом Хоккайдо, китайскими провинциями Провинция Цзянсу и Провинция Чжэцзян, городами: Оттавой, Будапештом, Миланом, Шэньчжэнем, Мапуту, Барселоной, Берлином, Стамбулом, Минском, Гуанчжоу, Аддис-Абебой, Бухарестом, Амстердамом, Лос-Анджелесом, Шицзячжуаном, Чжэцзяном и Буэнос-Айресом. Установлены побратимские связи с австралийским штатом Новый Южный Уэльс (в 1991 году) и 23 городами Европы, Азии, Африки, Северной и Южной Америки[14]:
|
|
|
|
|
Угроза обстрела Сеула артиллерией КНДР
Руководство Северной Кореи неоднократно угрожало уничтожением Сеула в случае войны с Южной Кореей и США[15][16][17]. Вследствие близости к границе вся территория сеульской агломерации может быть обстреляна северокорейской тяжелой артиллерией (по северным окраинам города могут работать и артиллерийские системы средних калибров). На территории КНДР вдоль ДМЗ, в непосредственной близости от сеульской агломерации, располагается несколько тысяч орудий, в том числе РСЗО и тяжелые артиллерийские системы калибром 170 и 240 миллиметров[18].
Примечания
- Комментарии
- ↑ Расчёт расстояний по сервису Карты Google до Жёлтого моря и границы с КНДР — от городской черты Сеула, расстояние между городами указано как расстояние между площадью Кванхвамун в Сеуле и площадью имени Ким Ир Сена в Пхеньяне.
- Источники
- ↑ 연령별 인구현황. 서울특별시. // rcps.egov.go.kr. Проверено 10 сентября 2015.
- ↑ См. стр. 20: Demographia World Urban Areas. // demographia.com. Проверено 10 сентября 2015.
- ↑ “서울, 중국어표기 ‘首尔’”. 한국일보. 2005년 1월 19일.
- ↑ 汉城中文名称改为“首尔”.
- ↑ 汉城变“首尔” 何以让人有些费解?.
- ↑ Савельев, Р. В. Проблемы Корейского полуострова и интересы России. — Институт Дальнего Востока РАН, 1998. — С. 65.
- ↑ ЧЕМПИОНАТ МИРА — 2002 СТАРТУЕТ В СЕУЛЕ. ФУТБОЛЬНЫЙ АЖИОТАЖ ДОСТИГ ПИКА
- ↑ Корея: цифры и факты. Южная Корея, прошлое и настоящее. — Министерство культуры, спорта и туризма Центр культуры и информации Кореи, 2013. — С. 142.
- ↑ Global cities & developmental states. New York, Tokyo, Seoul. // msu.edu. Проверено 10 сентября 2015.
- ↑ Welcome to KTC. Lmg.go.kr. Архивировано 6 августа 2012 года.
- ↑ Global : Cities, CNN.
- ↑ Worldwide Cost of Living 2015. Which city is the most expensive to live in? Which city is the cheapest?. — Лондон, 2015. — С. 1.
- ↑ Утверждён «Генеральный план Сеула-2030». // k-window.com. Проверено 10 сентября 2015.
- ↑ Sister Cities. // english.seoul.go.kr. Проверено 10 сентября 2015.
- ↑ Regnum: Пхеньян заявил о готовности нанести удар по Сеулу в любой момент
- ↑ Ведомости: Северная Корея отрабатывает артиллерийские удары по Сеулу
- ↑ Korrespondent.net: Северная Корея показала, как уничтожит Сеул
- ↑ Лента.ру: Как армии КНДР с устаревшим вооружением удается обеспечивать безопасность страны
Ссылки
| Сеул в Викисловаре | |
| Сеул на Викискладе | |
| Сеул в Викиновостях | |
| Сеул в Викигиде |
- Официальный сайт столичной администрации Сеула (кор.), (англ.)
- Сеул На сайте Национальной организации туризма Кореи (кор.), (рус.)
- Фотопрогулки по районам города На сайте globalphotos.org
Сеул — краткий видеообзор/ Timelapse: South Korea’s Stunning Seoul
This article is about the capital city of South Korea. For other uses, see Seoul (disambiguation).
|
Seoul 서울 |
|
|---|---|
|
Special city |
|
| Seoul Special City 서울특별시 |
|
|
From top, left to right: |
|
|
Flag Seal Coat of arms Wordmark |
|
| Motto:
«I • Seoul • U»[1] |
|
| Anthem: none[2] | |
 |
|
|
Seoul Seoul (South Korea) Seoul Seoul (Asia) Seoul Seoul (Earth) |
|
| Coordinates: 37°33′36″N 126°59′24″E / 37.56000°N 126.99000°ECoordinates: 37°33′36″N 126°59′24″E / 37.56000°N 126.99000°E | |
| Country | |
| Area | Seoul Capital |
| Founded by | Gen. Yi Sŏng-gye |
| Districts | 25 districts |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Body | Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul Metropolitan Council |
| • Mayor | Oh Se-hoon (People Power) |
| • National Assembly | 49 |
| Area
[3] |
|
| • Special city | 605.21 km2 (233.67 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 12,685 km2 (4,898 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 38 m (125 ft) |
| Highest elevation
(Bukhan Mountain) |
836.5 m (2,744.4 ft) |
| Lowest elevation
(Yellow Sea) |
0 m (0 ft) |
| Population
(October 2022)[5] |
|
| • Special city | 9,443,722 |
| • Rank | 1st |
| • Density | 16,000/km2 (40,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 26,037,000[4] |
| • Metro density | 2,053/km2 (5,320/sq mi) |
| • Demonym | Seoulite |
| • Dialect | Gyeonggi |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Korean Standard Time) |
| Bird | Korean magpie |
| Color | Seoul Red[6] |
| Flower | Forsythia |
| Font | Seoul fonts (Seoul Hangang and Seoul Namsan)[7] |
| Mascot | Haechi |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Nominal GDP (Special City) |
US$384 billion[8] |
| Nominal GDP per capita (Special City) |
US$39,558[8] |
| Website | seoul.go.kr |
Seoul (; Korean: [sʰʌul] (listen); lit. ‘Capital’), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.[9] According to the 2020 census, Seoul has a population of 9.9 million people, and forms the heart of the Seoul Capital Area with the surrounding Incheon metropolis and Gyeonggi province. Considered to be a global city and rated as an Alpha – City by Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC),[10] Seoul was the world’s fourth largest metropolitan economy in 2014, following Tokyo, New York City and Los Angeles.
Seoul was rated Asia’s most livable city with the second highest quality of life globally by Arcadis in 2015, with a GDP per capita (PPP) of around $40,000. With major technology hubs centered in Gangnam and Digital Media City,[11] the Seoul Capital Area is home to the headquarters of 15 Fortune Global 500 companies, including Samsung,[12] LG, and Hyundai. Ranked seventh in the Global Power City Index and Global Financial Centres Index, the metropolis exerts a major influence in global affairs as one of the five leading hosts of global conferences.[13] Seoul has hosted the 1986 Asian Games, 1988 Summer Olympics, and the 2010 G20 Seoul summit.
Seoul was the capital of various Korean states, including Baekje, Joseon, the Korean Empire, Goryeo (as a secondary capital), and presently South Korea. It is strategically located along the Han River. Seoul’s history stretches back over two thousand years, when it was founded in 18 BC by the people of Baekje, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. The city was later designated the capital of Korea under the Joseon dynasty. Seoul is surrounded by a mountainous and hilly landscape, with Bukhan Mountain located on the northern edge of the city. The Seoul Capital Area contains five UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Changdeok Palace, Hwaseong Fortress, Jongmyo Shrine, Namhansanseong and the Royal Tombs of the Joseon Dynasty.[14] More recently, Seoul has been a major site of modern architectural construction – major modern landmarks include the N Seoul Tower, the 63 Building, the Lotte World Tower, the Dongdaemun Design Plaza, Lotte World, Trade Tower, COEX, IFC Seoul, and the Parc1. Seoul was named the 2010 World Design Capital. It is the birthplace of K-pop and the Korean wave, as it is the heart of Korean culture and massive medias, entertainment firms, and broadcasters.
Etymology
The city has been known in the past by the names Wiryeseong (위례성; 慰禮城, during the Baekje era), Namcheon (남천; 南川,[15] during the Silla era), Hanyang (한양; 漢陽, during the Goryeo era), Hanseong (한성; 漢城, during the Joseon era), and Keijō (京城) or Gyeongseong (경성; 京城) during Japanese rule.[16]
During Japan’s annexation of Korea, Hanseong (漢城) was renamed Keijō (京城) by the Imperial authorities to prevent confusion with the hanja ‘漢‘ (a transliteration of an ancient Korean word Han (한) meaning «great»), which also refers to Han people or the Han dynasty in Chinese and in Japanese is a term for «China».[17]
After World War II and Korea’s liberation, the city took its present name, which originated from the Korean word meaning «capital city», which is believed to have descended from an ancient word, Seorabeol (Korean: 서라벌; Hanja: 徐羅伐), which originally referred to Gyeongju, the capital of Silla.[18] Ancient Gyeongju was also known in documents by the Chinese-style name Geumseong (金城, literally «Gold Castle or City» or «Metal Castle or City»), but it is unclear whether the native Korean-style name Seorabeol had the same meaning as Geumseong.[citation needed]
Unlike most place names in Korea, «Seoul» has no corresponding hanja (Chinese characters used in the Korean language). On January 18, 2005, the Seoul government changed its official name in Chinese characters from the historic Hancheng (simplified Chinese: 汉城; traditional Chinese: 漢城; pinyin: Hànchéng) to Shou’er (simplified Chinese: 首尔; traditional Chinese: 首爾; pinyin: Shǒu’ěr).[19][20]
History
Settlement of the Han River area, where present-day Seoul is located, began around 4000 BC.[21]
Seoul is first recorded as Wiryeseong, the capital of Baekje (founded in 18 BC) in the northeastern area of modern Seoul.[21] There are several city walls remaining in the area that date from this time. Pungnaptoseong, an earthen wall located southeast Seoul, is widely believed to have been at the main Wiryeseong site.[22] As the Three Kingdoms competed for this strategic region, control passed from Baekje to Goguryeo in the 5th century.[23]
However, according to Samguk Sagi, both Baekje and Silla described the land as frontier border of Baekje, not as the capital region.[24][25] Moreover, Jinheung Taewang Stele found at current day Bukhansan tells that the place was underdeveloped as of 6th century AD,[15] suggesting that the first capital Wiryeseong was not located in or nearby Seoul.
In July or August 553, Silla took the control of the region from Baekje, and the city became a part of newly established Sin Province (신주; 新州).[24][25] Sin (新) has both meaning of «New» and «Silla», thus literally means New Silla Province.
In November 555, Jinheung Taewang made royal visit to Bukhansan, and inspected the borderline.[26] In 557, Silla abolished Sin Province, and established Bukhansan Province (북한산주; 北漢山州).[27] The word Hanseong (한성; 漢城; Han Fortress) appears on the stone wall of «Pyongyang Fortress», which was presumably built in the mid to late 6th century AD over period of 42 years, located in Pyongyang, while there is no evidence that Seoul had name Hanseong dating the three kingdoms and earlier period.[28][29][30][31][32]
In 568, Jinheung Taewang made another royal visit to the northern border, visited Hanseong, and stayed in Namcheon on his way back to the capital. During his stay, he set Jinheung Taewang Stele, abolished Bukhansan Province, and established Namcheon Province (남천주; 南川州; South River Province), appointing the city as the provincial capital.[15][33] Based on the naming system, the actual name of Han River during this time was likely Namcheon (Nam River) itself or should have the word ending with «cheon» (천; 川) not «gang» (강; 江) nor «su» (수; 水). In addition, «Bukhansan» Jinheung Stele clearly states that Silla had possession of Hanseong (modern day Pyongyang), thus Bukhansan has to be located north of Hanseong. Modern day Pyongyang was not Pyongyang, Taedong River was likely Han River, and Bukhansan was not Bukhansan during the three kingdoms period.[15][34] Moreover, Pyongyang was a common noun meaning capital used by Goguryeo and Goryeo dynasties, similar to Seoul.[35]
In 603, Goguryeo attacked Bukhansanseong (북한산성; 北漢山城; Bukhan Mountain Fortress), which Silla ended up winning.[36][37] In 604, Silla abolished Namcheon Province, and reestablished Bukhansan Province in order to strengthen the northern border. The city lost its provincial capital position and was put under Bukhansan Province once again.[38] This further proves that Bukhansan was located in the North of modern day Pyongyang as changing the provincial name and objective would not be required if Bukhansan was located within Seoul.
In the 11th century Goryeo, which succeeded Unified Silla, built a summer palace in Seoul, which was referred to as the «Southern Capital». It was only from this period that Seoul became a larger settlement.[21] When Joseon replaced Goryeo, the capital was moved to Seoul (also known as Hanyang or Hanseong), where it remained until the fall of the dynasty. The Gyeongbok Palace, built in the 14th century, served as the royal residence until 1592. The other large palace, Changdeokgung, constructed in 1405, served as the main royal palace from 1611 to 1872.[21] After Joseon changed its name to the Korean Empire in 1897, Hwangseong also designated Seoul.[clarification needed]
Originally, the city was entirely surrounded by a massive circular stone wall to provide its citizens security from wild animals, thieves and attacks. The city has grown beyond those walls and although the wall no longer stands (except along Bugaksan Mountain (Korean: 북악산; Hanja: 北岳山), north of the downtown area[39]), the gates remain near the downtown district of Seoul, including most notably Sungnyemun (commonly known as Namdaemun) and Heunginjimun (commonly known as Dongdaemun).[40] During the Joseon dynasty, the gates were opened and closed each day, accompanied by the ringing of large bells at the Bosingak belfry.[41] In the late 19th century, after hundreds of years of isolation, Seoul opened its gates to foreigners and began to modernize. Seoul became the first city in East Asia to introduce electricity in the royal palace, built by the Edison Illuminating Company[42] and a decade later Seoul also implemented electrical street lights.[43]
Much of the development was due to trade with foreign countries like France and the United States. For example, the Seoul Electric Company, Seoul Electric Trolley Company, and Seoul Fresh Spring Water Company were all joint Korean–U.S. owned enterprises.[44] In 1904, an American by the name of Angus Hamilton visited the city and said, «The streets of Seoul are magnificent, spacious, clean, admirably made and well-drained. The narrow, dirty lanes have been widened, gutters have been covered, roadways broadened. Seoul is within measurable distance of becoming the highest, most interesting and cleanest city in the East.»[45]
After the annexation treaty in 1910, Japan annexed Korea and renamed the city Gyeongseong («Kyongsong» in Korean and «Keijo» in Japanese). Japanese technology was imported, the city walls were removed, some of the gates demolished. Roads became paved and Western-style buildings were constructed. The city was liberated by U.S. forces at the end of World War II.[21]
In 1945, the city was officially named Seoul, and was designated as a special city in 1949.[21]
During the Korean War, Seoul changed hands between the Soviet/Chinese-backed North Korean forces and the American-backed South Korean forces several times, leaving the city heavily damaged after the war. The capital was temporarily relocated to Busan.[21] One estimate of the extensive damage states that after the war, at least 191,000 buildings, 55,000 houses, and 1,000 factories lay in ruins. In addition, a flood of refugees had entered Seoul during the war, swelling the population of the city and its metropolitan area to an estimated 1.5 million by 1955.[46]
Following the war, Seoul began to focus on reconstruction and modernization. As South Korea’s economy started to grow rapidly from the 1960s, urbanization also accelerated and workers began to move to Seoul and other larger cities.[46] From the 1970s, the size of Seoul administrative area greatly expanded as it annexed a number of towns and villages from several surrounding counties.[47]
Until 1972, Seoul was claimed by North Korea as its de jure capital, being specified as such in Article 103 of the 1948 North Korean constitution.[48]
South Korea’s 2019 population was estimated at 51.71 million, and according to the 2018 Population and Housing Census, 49.8% of the population resided in the Seoul metropolitan area. This was up by 0.7% from 49.1% in 2010, showing a distinct trend toward the concentration of the population in the capital.[49] Seoul has become the economic, political and cultural hub of the country,[21] with several Fortune Global 500 companies, including Samsung, SK Holdings, Hyundai, POSCO and LG Group headquartered there.[50]
Seoul was the host city of the 1986 Asian Games and 1988 Summer Olympics as well as one of the venues of the 2002 FIFA World Cup.
On 29 October 2022, at least 153 people were crushed to death when a crowd surged in an alleyway during Halloween festivities in Seoul’s Itaewon district. President Yoon declared a state of official national mourning.[51]
Various views of Seoul from the 63 Building in July, 2019
Geography
Seoul is in the northwest of South Korea. Seoul proper comprises 605.25 km2 (233.69 sq mi),[3] with a radius of approximately 15 km (9 mi), roughly bisected into northern and southern halves by the Han River. The Han River and its surrounding area played an important role in Korean history. The Three Kingdoms of Korea strove to take control of this land, where the river was used as a trade route to China (via the Yellow Sea).[52] The river is no longer actively used for navigation, because its estuary is located at the borders of the two Koreas, with civilian entry barred. Historically, the city was during the Joseon dynasty bounded by the Seoul Fortress Wall, which stretched between the four main mountains in central Seoul: Bugaksan, Inwangsan, Naksan and Namsan. The city is bordered by eight mountains, as well as the more level lands of the Han River plain and western areas. Due to its geography and to economic development policies, Seoul is a very polycentric city. The area that was the old capital in the Joseon dynasty, and mostly comprises Jongno District and Jung District, constitutes the historical and political center of the city. However, for example, the city’s financial capital is widely considered to be in Yeouido, while its economic capital is Gangnam District.[citation needed]
Climate
| Seoul | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Seoul has a humid continental climate influenced by the monsoons (Köppen: Dwa). Being in the extreme East Asia, the climate can be described as humid subtropical (Cwa, by -3 °C isotherm) with great variation in temperature and precipitation throughout the year.[53][54] The suburbs of Seoul are generally cooler than the center of Seoul because of the urban heat island effect.[55] Summers are hot and humid, with the East Asian monsoon taking place from June until September. August, the hottest month, has average high and low temperatures of 32.6 and 23.4 °C (91 and 74 °F) with higher temperatures possible. Heat index values can surpass 40 °C (104.0 °F) at the height of summer.
Winters are usually cold to freezing with average January high and low temperatures of 1.5 and −5.9 °C (34.7 and 21.4 °F), and are generally much drier than summers, with an average of 24.9 days of snow annually. Sometimes, temperatures drop dramatically to below −10 °C (14 °F), and on some occasions as low as −15 °C (5 °F) in the mid winter period of January and February. Temperatures below −20 °C (−4 °F) have been recorded.
| Climate data for Seoul (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1907–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
29.8 (85.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.2 (99.0) |
38.4 (101.1) |
39.6 (103.3) |
35.1 (95.2) |
30.1 (86.2) |
25.9 (78.6) |
17.7 (63.9) |
39.6 (103.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.0 (51.8) |
17.9 (64.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
20.2 (68.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.9 (28.6) |
0.7 (33.3) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.6 (54.7) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
21.6 (70.9) |
15.0 (59.0) |
7.5 (45.5) |
0.2 (32.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.5 (22.1) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
18.7 (65.7) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.5 (−8.5) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−14.1 (6.6) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
2.4 (36.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
12.9 (55.2) |
13.5 (56.3) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 16.8 (0.66) |
28.2 (1.11) |
36.9 (1.45) |
72.9 (2.87) |
103.6 (4.08) |
129.5 (5.10) |
414.4 (16.31) |
348.2 (13.71) |
141.5 (5.57) |
52.2 (2.06) |
51.1 (2.01) |
22.6 (0.89) |
1,417.9 (55.82) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.1 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 9.9 | 16.3 | 14.7 | 9.1 | 6.1 | 8.8 | 7.8 | 108.6 |
| Average snowy days | 7.1 | 5.1 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 6.4 | 23.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 56.2 | 54.6 | 54.6 | 54.8 | 59.7 | 65.7 | 76.2 | 73.5 | 66.4 | 61.8 | 60.4 | 57.8 | 61.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 169.6 | 170.8 | 198.2 | 206.3 | 223.0 | 189.1 | 123.6 | 156.1 | 179.7 | 206.5 | 157.3 | 162.9 | 2,143.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 52.3 | 53.6 | 51.0 | 51.9 | 48.4 | 41.2 | 26.8 | 36.2 | 47.2 | 57.1 | 50.2 | 51.1 | 46.4 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source 1: Korea Meteorological Administration (percent sunshine 1981–2010)[56][57][58][59][60] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV)[61] |
| Climate data for Namsan Park, Jung District, Seoul (1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) |
4.1 (39.4) |
10.5 (50.9) |
17.8 (64.0) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.6 (81.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.6 (85.3) |
25.3 (77.5) |
19.1 (66.4) |
10.7 (51.3) |
2.6 (36.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.7 (53.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −6.5 (20.3) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
1.1 (34.0) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
21.8 (71.2) |
17.1 (62.8) |
10.5 (50.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
8.2 (46.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.9 (0.43) |
21.5 (0.85) |
30.3 (1.19) |
59.7 (2.35) |
84.6 (3.33) |
114.3 (4.50) |
333.8 (13.14) |
263.4 (10.37) |
103.6 (4.08) |
39.1 (1.54) |
40.9 (1.61) |
15.2 (0.60) |
1,117.3 (43.99) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.4 | 3.8 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 12.9 | 12.1 | 7.0 | 4.8 | 7.0 | 4.4 | 82.2 |
| Source: Korea Meteorological Administration[56] |
| Climate data for Seoul–Gimpo International Airport (1981–2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 1.4 (34.5) |
4.5 (40.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
17.6 (63.7) |
22.7 (72.9) |
26.6 (79.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.7 (85.5) |
25.6 (78.1) |
19.7 (67.5) |
11.4 (52.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.8 (25.2) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
4.5 (40.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.5 (70.7) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
20.1 (68.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
5.8 (42.4) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
11.5 (52.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −9.1 (15.6) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.8 (62.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.4 (70.5) |
15.1 (59.2) |
7.3 (45.1) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 18.1 (0.71) |
20.0 (0.79) |
40.7 (1.60) |
58.0 (2.28) |
96.2 (3.79) |
119.4 (4.70) |
357.2 (14.06) |
307.5 (12.11) |
155.4 (6.12) |
49.7 (1.96) |
47.6 (1.87) |
19.0 (0.75) |
1,288.7 (50.74) |
| Source: Aviation Meteorological Office[62] |
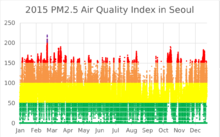
Air quality
Very Unhealthy
Unhealthy
Unhealthy for sensitive groups
According to the Environmental Performance Index 2016, South Korea ranked 173rd out of 180 countries in terms of air quality. More than 50 percent of the populations in South Korea are exposed to dangerous levels of fine dust.[63][64]
Air pollution is a major issue in Seoul.[65][66][67][68] According to the 2016 World Health Organization Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database,[69] the annual average PM2.5 concentration in 2014 was 24 micrograms per cubic meter (1.0×10−5 gr/cu ft), which is 2.4 times higher than that recommended by the WHO Air Quality Guidelines[70] for the annual mean PM2.5. The Seoul Metropolitan Government monitors and publicly shares real-time air quality data.[71]
Since the early 1960s, the Ministry of Environment has implemented a range of policies and air pollutant standards to improve and manage air quality for its people.[72] The «Special Act on the Improvement of Air Quality in the Seoul Metropolitan Area» was passed in December 2003. Its 1st Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan (2005–2014) focused on improving the concentrations of PM10 and nitrogen dioxide by reducing emissions.[73] As a result, the annual average PM10 concentrations decreased from 70.0 μg/m3 in 2001 to 44.4 μg/m3 in 2011[74] and 46 μg/m3 in 2014.[69] As of 2014, the annual average PM10 concentration was still at least twice than that recommended by the WHO Air Quality Guidelines.[70] The 2nd Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan (2015–2024) added PM2.5 and ozone to its list of managed pollutants.[75]
Asian dust, emissions from Seoul and in general from the rest of South Korea, as well as emissions from China, all contribute to Seoul’s air quality.[66][76] A partnership between researchers in South Korea and the United States is conducting an international air quality field study in Korea (KORUS-AQ) to determine how much each source contributes.[77]
Besides air quality, greenhouse gas emissions represent hot issues in South Korea since the country is among top-10 strongest emitters in the world. Seoul is the strongest hotspot of greenhouse gas emissions in the country and according to satellite data, the persistent carbon dioxide anomaly over the city is one of the strongest in the world.[78]
Government
The Seoul Metropolitan Government is the local government for Seoul, and is responsible for the administration and provision of various services to the city, including correctional institutions, education, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services. It is headed by a mayor and three vice mayors, and is divided into 25 autonomous districts and 522 administrative neighborhoods.[79][80]
Administrative districts
Seoul is divided into 25 gu (Korean: 구; Hanja: 區) (district).[81] The gu vary greatly in area (from 10 to 47 km2 or 3.9 to 18.1 sq mi) and population (from fewer than 140,000 to 630,000). Songpa has the most people, while Seocho has the largest area. The government of each gu handles many of the functions that are handled by city governments in other jurisdictions. Each gu is divided into «dong» (동; 洞) or neighborhoods. Some gu have only a few dong while others like Jongno District have a very large number of distinct neighborhoods. Gu of Seoul consist of 423 administrative dongs (행정동) in total.[81] Dong are also sub-divided into 13,787 tong (통; 統), which are further divided into 102,796 ban in total.
- Dobong District (도봉구; 道峰區)
- Dongdaemun District (동대문구; 東大門區)
- Dongjak District (동작구; 銅雀區)
- Eunpyeong District (은평구; 恩平區)
- Gangbuk District (강북구; 江北區)
- Gangdong District (강동구; 江東區)
- Gangnam District (강남구; 江南區)
- Gangseo District (강서구; 江西區)
- Geumcheon District (금천구; 衿川區)
- Guro District (구로구; 九老區)
- Gwanak District (관악구; 冠岳區)
- Gwangjin District (광진구; 廣津區)
- Jongno District (종로구; 鍾路區)
- Jung District (중구; 中區)
- Jungnang District (중랑구; 中浪區)
- Mapo District (마포구; 麻浦區)
- Nowon District (노원구; 蘆原區)
- Seocho District (서초구; 瑞草區)
- Seodaemun District (서대문구; 西大門區)
- Seongbuk District (성북구; 城北區)
- Seongdong District (성동구; 城東區)
- Songpa District (송파구; 松坡區)
- Yangcheon District (양천구; 陽川區)
- Yeongdeungpo District (영등포구; 永登浦區)
- Yongsan District (용산구; 龍山區)
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1,021,000 | — |
| 1960 | 2,361,000 | +8.74% |
| 1970 | 5,312,000 | +8.45% |
| 1980 | 8,244,000 | +4.49% |
| 1990 | 10,518,000 | +2.47% |
| 2000 | 9,879,000 | −0.62% |
| 2010 | 9,796,000 | −0.08% |
| 2020 | 9,963,000 | +0.17% |
| source:[82] |
Seoul proper is noted for its population density, which is almost twice that of New York City and eight times greater than Rome. Its metropolitan area was the most densely populated among OECD countries in Asia in 2012, and second worldwide after that of Paris.[83] As of 2015, the population was 9.86 million,[84] in 2012, it was 10.44 million. As of 2021, the population is 9.59 million.[85][86] As of the end of June 2011, 10.29 million Republic of Korea citizens lived in the city. This was a 0.24% decrease from the end of 2010. The population of Seoul has been dropping since the early 1990s, the reasons being the high costs of living, urban sprawling to Gyeonggi region’s satellite bed cities and an aging population.[84]
As of 2016, the number of foreigners living in Seoul was 404,037, 22.9% of the total foreign population in South Korea.[87] As of June 2011, 186,631 foreigners were Chinese citizens of Korean ancestry. This was an 8.84% increase from the end of 2010 and a 12.85% increase from June 2010. The next largest group was Chinese citizens who are not of Korean ethnicity; 29,901 of them resided in Seoul. The next highest group consisted of the 9,999 United States citizens who were not of Korean ancestry. The next highest group were Taiwanese citizens, at 8,717.[88]
The two major religions in Seoul are Christianity and Buddhism. Other religions include Muism (indigenous religion) and Confucianism. Seoul is home to one of the world’s largest Christian congregations, Yoido Full Gospel Church, which has around 830,000 members.[89] According to the 2015 census, 10.8% of the population follows Buddhism and 35% follows Christianity (24.3% Protestantism and 10.7% Catholicism). 53.6% of the population is irreligious.[90]
Religion in Seoul (2015)[90]
Not religious (53.6%)
Other (0.6%)
Seoul is home to the world’s largest modern university founded by a Buddhist Order, Dongguk University.[91] Native Seoulites tend to speak the Gyeonggi dialect of Korean.[citation needed]
Economy
Seoul is the business and financial hub of South Korea. Although it accounts for only 0.6 percent of the nation’s land area, 48.3 percent of South Korea’s bank deposits were held in Seoul in 2003,[92] and the city generated 23 percent of the country’s GDP overall in 2012.[93] In 2008 the Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index ranked Seoul No.9.[94] The Global Financial Centres Index in 2015 listed Seoul as the 6th financially most competitive city in the world.[95] The Economist Intelligence Unit ranked Seoul 15th in the list of «Overall 2025 City Competitiveness» regarding future competitiveness of cities.[96]
Manufacturing
The traditional, labor-intensive manufacturing industries have been continuously replaced by information technology, electronics and assembly-type of industries;[97][98] however, food and beverage production, as well as printing and publishing remained among the core industries.[97] Major manufacturers are headquartered in the city, including Samsung, LG, Hyundai, Kia and SK. Notable food and beverage companies include Jinro, whose soju is the most sold alcoholic drink in the world, beating out Smirnoff vodka;[99] top selling beer producers Hite (merged with Jinro) and Oriental Brewery.[100] It also hosts food giants like Seoul Dairy Cooperative, Nongshim Group, Ottogi, CJ, Orion, Maeil Holdings, Namyang Dairy Products and Lotte.
Finance
Yeouido, the main financial district of Seoul
Seoul hosts large concentration of headquarters of International companies and banks, including 15 companies on Fortune 500 list such as Samsung, LG and Hyundai.[101] Most bank headquarters and the Korea Exchange are located in Yeouido (Yeoui island),[97] which is often called «South Korea’s Wall Street» and has been serving as the financial center of the city since the 1980s.[102] The Seoul international finance center & SIFC MALL, Hanhwa 63 building, the Hanhwa insurance company head office. Hanhwa is one of the three largest South Korean insurance companies, along with Samsung Life and Gangnam & Kyobo life insurance group.
Commerce
Myeong-dong is one of the most popular destinations in Seoul.
The largest wholesale and retail market in South Korea, the Dongdaemun Market, is located in Seoul.[103] Myeongdong is a shopping and entertainment area in downtown Seoul with mid- to high-end stores, fashion boutiques and international brand outlets.[104] The nearby Namdaemun Market, named after the Namdaemun Gate, is the oldest continually running market in Seoul.[105]
Insadong is the cultural art market of Seoul, where traditional and modern Korean artworks, such as paintings, sculptures and calligraphy are sold.[106] Hwanghak-dong Flea Market and Janganpyeong Antique Market also offer antique products.[107][108] Some shops for local designers have opened in Samcheong-dong, where numerous small art galleries are located. While Itaewon had catered mainly to foreign tourists and American soldiers based in the city, Koreans now comprise the majority of visitors to the area.[109] The Gangnam district is one of the most affluent areas in Seoul[109] and is noted for the fashionable and upscale Apgujeong-dong and Cheongdam-dong areas and the COEX Mall. Wholesale markets include Noryangjin Fisheries Wholesale Market and Garak Market.
The Yongsan Electronics Market is the largest electronics market in Asia. Electronics markets are Gangbyeon station metro line 2 Techno mart, ENTER6 MALL & Shindorim station Technomart mall complex.[110]
Times Square is one of Seoul’s largest shopping malls featuring the CGV Starium, the world’s largest permanent 35 mm cinema screen.[111]
Korea World Trade Center Complex, which comprises COEX mall, congress center, 3 Inter-continental hotels, Business tower (Asem tower), Residence hotel, Casino and City airport terminal was established in 1988 in time for the Seoul Olympics. The 2nd World trade trade center is being planned at Seoul Olympic stadium complex as MICE HUB by Seoul city. Ex-Kepco head office building was purchased by Hyundai motor group with 9billion USD to build 115-storey Hyundai GBC & hotel complex until 2021. Now ex-kepco 25-storey building is under demolition.
Technology
Seoul has been described as the world’s «most wired city»,[112] ranked first in technology readiness by PwC’s Cities of Opportunity report.[113] Seoul has a very technologically advanced infrastructure.[114][115]
Seoul is among the world leaders in Internet connectivity, being the capital of South Korea, which has the world’s highest fiber-optic broadband penetration and highest global average internet speeds of 26.1 Mbit/s.[116][117] Since 2015, Seoul has provided free Wi-Fi access in outdoor spaces through a 47.7 billion won ($44 million) project with Internet access at 10,430 parks, streets and other public places.[118] Internet speeds in some apartment buildings reach up to 52.5Gbit/s with assistance from Nokia, and though the average standard consists of 100 Mbit/s services, providers nationwide are rapidly rolling out 1Gbit/s connections at the equivalent of US$20 per month.[119] In addition, the city is served by the KTX high-speed rail and the Seoul Subway, which provides 4G LTE, WiFi and DMB inside subway cars. 5G will be introduced commercially in March 2019 in Seoul.
Architecture
The traditional heart of Seoul is the old Joseon dynasty city, now the downtown area, where most palaces, government offices, corporate headquarters, hotels, and traditional markets are located. Cheonggyecheon, a stream that runs from west to east through the valley before emptying into the Han River, was for many years covered with concrete, but was recently restored by an urban revival project in 2005.[120] Jongno street, meaning «Bell Street», has been a principal street and one of the earliest commercial streets of the city,[121][122] on which one can find Bosingak, a pavilion containing a large bell. The bell signaled the different times of the day and controlled the four major gates to the city. North of downtown is Bukhan Mountain, and to the south is the smaller Namsan. Further south are the old suburbs, Yongsan District and Mapo District. Across the Han River are the newer and wealthier areas of Gangnam District, Seocho District and surrounding neighborhoods.
Historical architecture
Seoul has many historical and cultural landmarks. In Amsa-dong Prehistoric Settlement Site, Gangdong District, neolithic remains were excavated and accidentally discovered by a flood in 1925.[123]
Urban and civil planning was a key concept when Seoul was first designed to serve as a capital in the late 14th century. The Joseon dynasty built the «Five Grand Palaces» in Seoul – Changdeokgung, Changgyeonggung, Deoksugung, Gyeongbokgung and Gyeonghuigung – all of which are located in Jongno and Jung Districts. Among them, Changdeokgung was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1997 as an «outstanding example of Far Eastern palace architecture and garden design». The main palace, Gyeongbokgung, underwent a large-scale restoration project.[124] The palaces are considered exemplary architecture of the Joseon period. Beside the palaces, Unhyeongung is known for being the royal residence of Regent Daewongun, the father of Emperor Gojong at the end of the Joseon Dynasty.
Seoul has been surrounded by walls that were built to regulate visitors from other regions and protect the city in case of an invasion. Pungnap Toseong is a flat earthen wall built at the edge of the Han River, which is widely believed to be the site of Wiryeseong. Mongchon Toseong (Korean: 몽촌토성; Hanja: 蒙村土城) is another earthen wall built during the Baekje period that is now located inside the Olympic Park.[22] The Fortress Wall of Seoul was built early in the Joseon dynasty for protection of the city. After many centuries of destruction and rebuilding, about 2⁄3 of the wall remains, as well as six of the original eight gates. These gates include Sungnyemun and Heunginjimun, commonly known as Namdaemun (South Great Gate) and Dongdaemun (East Great Gate). Namdaemun was the oldest wooden gate until a 2008 arson attack, and was re-opened after complete restoration in 2013.[125] Located near the gates are the traditional markets and largest shopping center, Namdaemun Market and Dongdaemun Market.
There are also many buildings constructed with international styles in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Independence Gate was built in 1897 to inspire an independent spirit. Seoul Station was opened in 1900 as Gyeongseong Station.
Modern architecture
Various high-rise office buildings and residential buildings, like the Gangnam Finance Center, the Tower Palace, Namsan Seoul Tower, and the Lotte World Tower, dominate the city’s skyline. The tallest building is Lotte World Tower, reaching a height of 555m. It opened to the public in April 2017. It is also the 4th highest building in the world.
The World Trade Center Seoul, located in Gangnam District, hosts various expositions and conferences. Also in Gangnam District is the COEX Mall, a large indoor shopping and entertainment complex. Downstream from Gangnam District is Yeouido, an island that is home to the National Assembly, major broadcasting studios, and a number of large office buildings, as well as the Korea Finance Building and the Yoido Full Gospel Church. The Olympic Stadium, Olympic Park, and Lotte World are located in Songpa District, on the south side of the Han River, upstream from Gangnam District. Three new modern landmarks of Seoul are Dongdaemun Design Plaza & Park, designed by Zaha Hadid, the new wave-shaped Seoul City Hall, by Yoo Kerl of iArc, and the Lotte World Tower, the 5th tallest building in the world designed by Kohn Pedersen Fox.
In 2010 Seoul was designated the World Design Capital for the year.[126]
Culture
Museums
Seoul is home to 115 museums,[127] including four national and nine official municipal museums. Among the city’s national museum, The National Museum of Korea[128] is the most representative of museums in not only Seoul but all of South Korea. Since its establishment in 1945, the museum has built a collection of 220,000 artifacts.[129] In October 2005, the museum moved to a new building in Yongsan Family Park.
The National Folk Museum is located on the grounds of the Gyeongbokgung Palace in the district of Jongno District and uses replicas of historical objects to illustrate the folk history of the Korean people.[130] The National Palace Museum of Korea is also located on the grounds of the Gyeongbokgung Palace. Finally, the Seoul branch of the National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art, whose main museum is located in Gwacheon, opened in 2013, in Sogyeok-dong.
Bukchon Hanok Village and Namsangol Hanok Village are old residential districts consisting of hanok Korean traditional houses, parks, and museums that allows visitors to experience traditional Korean culture.[131][132]
The War Memorial, one of nine municipal museums in Seoul, offers visitors an educational and emotional experience of various wars in which Korea was involved, including Korean War themes.[133][134] The Seodaemun Prison is a former prison built during the Japanese occupation, and is used as a historic museum.[135]
The Seoul Museum of Art and Ilmin Museum of Art have preserved the appearance of the old building that is visually unique from the neighboring tall, modern buildings. The former is operated by Seoul City Council and sits adjacent to Gyeonghuigung Palace, a Joseon dynasty royal palace. Leeum, Samsung Museum of Art, is widely regarded as one of Seoul’s largest private museum. For many Korean film lovers from all over the world, the Korean Film Archive is running the Korean Film Museum and Cinematheque KOFA in its main center located in Digital Media City(DMC), Sangam-dong. The Tteok & Kitchen Utensil Museum and Kimchi Field Museum provide information regarding Korean culinary history.
Religious monuments
There are also religious buildings that take important roles in Korean society and politics. The Wongudan altar was a sacrificial place where Korean rulers held heavenly rituals since the Three Kingdoms period. Since the Joseon dynasty adopted Confucianism as its national ideology in the 14th century, the state built many Confucian shrines. The descendants of the Joseon royal family still continue to hold ceremonies to commemorate ancestors at Jongmyo. It is the oldest royal Confucian shrine preserved and the ritual ceremonies continue a tradition established in the 14th century. Sajikdan, Munmyo and Dongmyo were built during the same period. Although Buddhism was suppressed by the Joseon state, it has continued its existence. Jogyesa is the headquarters of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism. Hwagyesa and Bongeunsa are also major Buddhist temples in Seoul.
The Myeongdong Cathedral is a landmark of the Myeongdong, Jung District and the biggest Catholic church in Seoul established in 1883. It is a symbol of Catholicism in Korea. It was also a focus for political dissent in the 1980s. In this way the Roman Catholic Church has a very strong influence in Korean society. And Yakhyeon Catholic Church in Jungnim-dong, Jung District is first Catholic parish in Korea. It has been the first Gothic church ever built in Korea.
There are many Protestant churches in Seoul. The most numerous are Presbyterian, but there are also many Methodist and Baptist churches. Yoido Full Gospel Church is a Pentecostal church affiliated with the Assemblies of God on Yeouido in Seoul. With approximately 830,000 members (2007), it is the largest Pentecostal Christian congregation in the world, which has been recognized by the Guinness Book of World Records.[citation needed]
The St. Nicholas Cathedral, but sometimes called bald church, is the only Byzantine-style church in Seoul. It is located in Ahyeon-dong, Mapo District, and is cathedral of the Orthodox Metropolis of Korea. In 2015, it was designated as a Seoul Future Heritage.
Festivals
In October 2012, KBS Hall in Seoul hosted major international music festivals – First ABU TV and Radio Song Festivals within frameworks of Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union 49th General Assembly.[136][better source needed][137]
Hi! Seoul Festival is a seasonal cultural festival held four times a year every spring, summer, autumn, and winter in Seoul, South Korea since 2003. It is based on the «Seoul Citizens’ Day» held on every October since 1994 to commemorate the 600 years history of Seoul as the capital of the country. The festival is arranged under the Seoul Metropolitan Government. As of 2012, Seoul has hosted Ultra Music Festival Korea, an annual dance music festival that takes place on the 2nd weekend of June.[138]
Parks
Despite the city’s population density, Seoul has a large quantity of parks. One of the most famous parks is Namsan Park, which offers recreational hiking and views of the downtown Seoul skyline. The N Seoul Tower is located at Namsan Park. Seoul Olympic Park, located in Songpa District and built to host the 1988 Summer Olympics is Seoul’s largest park. Among the other largest parks in the city are Seoul Forest, Dream Forest, Children’s Grand Park and Haneul Park. The Wongaksa Pagoda 10 tier pagoda is located In Tapgol Park, a small public park with an area of 19,599 m2 (210,962 sq ft). Areas around streams serve as public places for relaxation and recreation. Tancheon stream and the nearby area serve as a large park with paths for both walkers and cyclists.
Cheonggyecheon, a stream that runs nearly 6 km (4 mi) through downtown Seoul, is popular among both Seoul residents and tourists. In 2017 the Seoullo 7017 Skypark opened, spanning diagonally overtop Seoul Station.
There are also many parks along the Han River, such as Ichon Hangang Park, Yeouido Hangang Park, Mangwon Hangang Park, Nanji Hangang Park, Banpo Hangang Park, Ttukseom Hangang Park and Jamsil Hangang Park.
The Seoul National Capital Area also contains a green belt aimed at preventing the city from sprawling out into neighboring Gyeonggi Province. These areas are frequently sought after by people looking to escape from urban life on weekends and during vacations.
There are also various parks under construction or in project, such as the Gyeongui Line Forest Trail, Seoul Station 7017, Seosomun Memorial Park and Yongsan Park.
Seoul is also home to the world’s largest indoor amusement park, Lotte World. Other recreation centers include the former Olympic and World Cup stadiums and the City Hall public lawn.
Media
Seoul is home of the major South Korean networks KBS, SBS, and MBC. The city is also home to the major South Korean newspapers Chosun Ilbo, Donga Ilbo, Joongang Ilbo, and Hankook Ilbo.
Sports
Fireworks at the closing ceremonies of the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul
Seoul is a major center of South Korean sports, and has the largest number of professional sports teams and facilities in the country.
In the history of South Korea’s major professional sports league championships, which include the K League, KBO League, KBL, and V-League, Seoul had multiple championship winners during the same season twice; in 1990, when Lucky-Goldstar FC (currently FC Seoul) won the 1990 K League and the LG Twins won the 1990 KBO League, and in 2016, when FC Seoul won the 2016 K League Classic and the Doosan Bears won the 2016 KBO League.[139]
International competition
Seoul hosted the 1986 Asian Games, also known as Asiad, 1988 Olympic Games, and Paralympic Games. It also served as one of the host cities of the 2002 FIFA World Cup. Seoul World Cup Stadium hosted the opening ceremony and first game of the tournament.
Taekwondo is South Korea’s national sport and Seoul is the location of the Kukkiwon, the world headquarters of taekwondo, as well as the World Taekwondo Federation.
Domestic sports clubs
Football
Seoul’s most well-known football club is FC Seoul.
- Men’s football
| Tier | League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | K League 1 | FC Seoul | Seoul World Cup Stadium |
| 2nd | K League 2 | Seoul E-Land | Mokdong Stadium |
| 4th | K4 League | Seoul Jungnang FC | Jungnang Public Ground |
| Seoul Nowon United | Nowon Madeul Stadium |
- Women’s football
| Tier | League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | WK League | Seoul City WFC | Seoul World Cup Auxiliary Stadium |
Baseball
| League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|
| KBO League | ||
| LG Twins | Jamsil Baseball Stadium | |
| Doosan Bears | ||
| Kiwoom Heroes | Gocheok Sky Dome |
Basketball
| League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|
| KBL | ||
| Seoul SK Knights | Jamsil Students’ Gymnasium | |
| Seoul Samsung Thunders | Jamsil Arena |
Volleyball
| League | Division | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-League | |||
| Men | Seoul Woori Card WooriWON | Jangchung Arena | |
| Women | GS Caltex Seoul KIXX |
Handball
- Seoul City
Transportation
Seoul has a well developed transportation network. Its system dates back to the era of the Korean Empire, when the first streetcar lines were laid and a railroad linking Seoul and Incheon was completed.[140] Seoul’s most important streetcar line ran along Jongno until it was replaced by Line 1 of the subway system in the early 1970s. Other notable streets in downtown Seoul include Euljiro, Teheranno, Sejongno, Chungmuro, Yulgongno, and Toegyero. There are nine major subway lines stretching for more than 250 km (155 mi), with one additional line planned. As of 2010, 25% of the population has a commute time of an hour or longer.
Bus
Seoul’s bus system is operated by the Seoul Metropolitan Government (S.M.G.), with four primary bus configurations available servicing most of the city. Seoul has many large intercity/express bus terminals. These buses connect Seoul with cities throughout South Korea. The Seoul Express Bus Terminal, Central City Terminal and Seoul Nambu Terminal are located in the district of Seocho District. In addition, East Seoul Bus Terminal in Gwangjin District and Sangbong Terminal in Jungnang District handles traffics mainly from Gangwon and Chungcheong provinces.
Urban rail
Seoul has a comprehensive urban railway network of 21 rapid transit, light metro and commuter lines that interconnects every district of the city and the surrounding areas of Incheon, Gyeonggi province, western Gangwon province, and northern Chungnam province. With more than 8 million passengers per day, the subway is one of the busiest subway systems in the world and the largest in the world, with a total track length of 940 km (580 mi). In addition, in order to cope with the various modes of transport, Seoul’s metropolitan government employs several mathematicians to coordinate the subway, bus, and traffic schedules into one timetable. The various lines are run by Korail, Seoul Metro, NeoTrans Co. Ltd., AREX, and Seoul Metro Line 9 Corporation.
Train
Seoul is connected to every major city in South Korea by rail. Most major South Korean cities are linked via the KTX high-speed train, which has a normal operation speed of more than 300 km/h (186 mph). The Mugunghwa and Saemaeul trains also stop at all major stations. Major railroad stations include:
- Seoul Station, Yongsan District: Gyeongbu line (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa-ho)
- Yongsan station, Yongsan District: Honam line (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa), Jeolla/Janghang lines (Saemaul/Mugunghwa)
- Yeongdeungpo station, Yeongdeungpo District: Gyeongbu/Honam/Janghang lines (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Saemaul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa)
- Cheongnyangni station, Dongdaemun District: Gyeongchun/Jungang/Yeongdong/Taebaek lines (ITX-Cheongchun/ITX-Saemaeul/Mugunghwa)
- Suseo station (HSR), Gangnam District: Suseo HSR (SRT)
Airports
Seoul is served by two international airports, Incheon International Airport and Gimpo International Airport.
Gimpo International Airport opened in 1939 as an airfield for the Japanese Imperial Army and opened for civil aircraft in 1957. Since the opening of Incheon International, Gimpo International handles domestic flights along with some short haul international flights to Tokyo Haneda, Osaka Kansai, Taipei Songshan, Shanghai Hongqiao, and Beijing Capital although flights to Osaka Kansai and Beijing Capital also operate from Incheon International.
Incheon International Airport opened in March 2001 in Yeongjong island. It is now responsible for major international flights. Incheon International Airport is Asia’s eighth busiest airport in terms of passengers, the world’s fourth busiest airport by cargo traffic, and the world’s eighth busiest airport in terms of international passengers in 2014. In 2016, 57,765,397 passengers used the airport. Incheon International Airport opened terminal 2 on January 18, 2018.
Incheon and Gimpo are linked to Seoul by expressway, and to each other by the AREX to Seoul Station. Intercity bus services are available to various destinations around the country.
Cycling
Cycling is becoming increasingly popular in Seoul and in the entire country. Both banks of the Han River have cycling paths that run all the way across the city along the river. In addition, Seoul introduced in 2015 a bicycle-sharing system named Ddareungi (and named Seoul Bike in English).[141]
Education
Universities
Seoul is home to the majority of South Korea’s most prestigious universities, including Seoul National University, Yonsei University, Korea University.
Seoul ranked 2nd on the QS Best Student Cities 2023.[142]
Secondary education
Compulsory education lasts from grade 1–9 (six years of elementary school and 3 years of middle school).[143] Students spend six years in elementary school, three years in middle school, and three years in high school. Secondary schools generally require students to wear uniforms. There is an exit exam for graduating from high school and many students proceeding to the university level are required to take the College Scholastic Ability Test that is held every November. Although there is a test for non-high school graduates, called school qualification exam, most Koreans take the test.
Seoul is home to various specialized schools, including three science high schools, and six foreign language High Schools. Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education comprises 235 College-Preparatory High Schools, 80 Vocational Schools, 377 Middle Schools, and 33 Special Education Schools as of 2009.
International relations
Seoul is a member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21 and the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group. In addition, Seoul hosts many embassies of countries it has diplomatic ties with.
Sister cities
Seoul has 23 sister cities:[144]
[145]
Taipei, Taiwan (1968)
Ankara, Turkey (1971)
Honolulu, United States (1976)
San Francisco, United States (1976)
São Paulo, Brazil (1977)
Bogotá, Colombia (1982)
Jakarta, Indonesia (1984)
Tokyo, Japan (1988)
Moscow, Russia (1991)
New South Wales, Australia (1991)
Paris, France (1991)
Mexico City, Mexico (1992)
Beijing, China (1993)
Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia (1995)
Hanoi, Vietnam (1996)
Warsaw, Poland (1996)
Cairo, Egypt (1997)
Rome, Italy (2000)
Astana, Kazakhstan (2004)
Washington, D.C., United States (2006)
Athens, Greece (2006)
Bangkok, Thailand (2006)
Tashkent, Uzbekistan (2010)
See also
- Geography of South Korea
- List of cities in South Korea
- List of most populous cities
References
- ^ 논란 겪은 ‘I·SEOUL·U’ 서울 공식브랜드로 확정. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
- ^ «서울시 사이트에 서울 시가인 서울의 찬가가 없습니다». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ^ a b «Seoul Statistics (Land Area)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 24 March 2010.
- ^ Seoul Capital Area
- ^ «City Overview (Population)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ «Color». Archived from the original on 11 May 2012. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- ^ «Seoul’s symbols». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- ^ a b «2018년 지역소득(잠정)». Archived from the original on 21 June 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Before 1972, Seoul was the de jure capital of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) as stated in Article 103 Archived 14 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine of the 1948 constitution.
- ^ «The World According to GaWC 2020». GaWC — Research Network. Globalization and World Cities. Archived from the original on 24 August 2020. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ «Tech capitals of the world». The Age. Melbourne. 15 June 2009. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ «Samsung Electronics». Fortune. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ Union of International Associations (UIA) International Meetings Statistics for the Year 2011 Archived 3 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Joel Fischer.
- ^ «Lists: Republic of Korea». UNESCO. Archived from the original on 25 December 2019. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Monument on Bukhansan Mountain Commemorating the Border Inspection by King Jinheung of Silla». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ Yu, Woo-ik; Lee, Chan (6 November 2019). «Seoul». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 9 June 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
The city was popularly called Seoul in Korean during both the Chosŏn (Yi) dynasty (1392–1910) and the period of Japanese rule (1910–45), although the official names in those periods were Hansŏng (Hanseong) and Kyŏngsŏng (Gyeongseong), respectively.
- ^ Kim, Dong Hoon (22 March 2017). Eclipsed Cinema: The Film Culture of Colonial Korea. ISBN 9781474421829. Archived from the original on 14 July 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ^ «Yahoo holiday travel guide». Uk.holidaysguide.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2007.
- ^ 서울특별시표기 首爾로…중국, 곧 정식 사용키로 :: 네이버 뉴스 (in Korean). News.naver.com. 23 October 2005. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- ^ Characters, Good. «Chinese Naming Crisis Danger Opportunity Summer 2006 – Good Characters». goodcharacters.com. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «Seoul». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ a b «Pungnap-toseong (Earthen Ramparts)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ Tennant (12 November 2012). History Of Korea. ISBN 9781136166983. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020.
- ^ a b «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 19». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ a b «Samguk Sagi Baekje Seong 19». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 24». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 28». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 1». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 2». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 3». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 4». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 6». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 45». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ ««고구려 수도 평양은 북한땅에 없었다»«. 신동아 (in Korean). 22 January 2013. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ «고대 평양은 지금의 평양이 아니다». K스피릿 (in Korean). 11 July 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinpyeong 30». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Goguryeo Yeongyang 15». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinpyeong 32». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Bugaksan Mountain». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Seoul City Wall». UNESCO. Archived from the original on 31 December 2019. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Bosingak Belfry». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ Nam Moon Hyon. «Early History of Electrical Engineering in Korea: Edison and First Electric Lighting in the Kingdom of Corea» (PDF). Promoting the History of EE Jan 23–26, 2000. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ Kyung Moon Hwang (2010). A History of Korea. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 142. ISBN 9780230364523. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Young-Iob Chung (2006). Korea under Siege, 1876–1945 : Capital Formation and Economic Transformation. Oxford University Press. p. 70. ISBN 9780198039662.
- ^ Bruce Cumings (2005). Korea’s Place in the Sun: A Modern History. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 9780393347531. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ^ a b Stephen Hamnett, Dean Forbes, ed. (2012). Planning Asian Cities: Risks and Resilience. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 9781136639272. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ «Urban Planning of Seoul» (PDF). Seoul Metropolitan Government. 2009. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Archived copy» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ «Korean Cultural Centre India New Delhi». Korean Cultural Centre India New Delhi. Archived from the original on 20 July 2020. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ^ «GLOBAL 500». CNNMoney. 23 July 2012. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «At least 153 killed in crowd crush during Halloween festivities in Seoul». The Guardian. 30 October 2022.
- ^ «Brief History of Hangang (River)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 31 October 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Seoul, South Korea Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)». Weatherbase. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2019.
- ^ Peterson, Adam (31 October 2018), English: Data sources: Köppen types calculated from data from WorldClim.org, archived from the original on 10 October 2020, retrieved 9 June 2019
- ^ Lee, Sang-Hyun; Baik, Jong-Jin (1 March 2010). «Statistical and dynamical characteristics of the urban heat island intensity in Seoul». Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 100 (1–2): 227–237. Bibcode:2010ThApC.100..227L. doi:10.1007/s00704-009-0247-1. S2CID 120641921. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- ^ a b
«Climatological Normals of Korea (1991 ~ 2020)» (PDF) (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. pp. II-27, II-28, II-465. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 31 January 2022. - ^
우리나라 기후평년값 — 파일셋 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021. - ^
우리나라 기후평년값 — 그래프 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021. - ^
순위값 — 구역별조회 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021. - ^
«Climatological Normals of Korea» (PDF). Korea Meteorological Administration. 2011. p. 499 and 649. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016. - ^ «Seoul, South Korea — Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast». Weather Atlas. Yu Media Group. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- ^
저고도 항공기상정보 포털 (in Korean). Aviation Meteorological Office. - ^ «South Korea near bottom of world survey of air quality». The Korea Herald. 16 May 2016. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
South Korea ranked 173rd out of 180 countries in terms of air quality, the Environmental Performance Index 2016 rankings showed Monday. … A report said that 1.3 billion people exposed to poor air quality lived in East Asian countries, with more than 50 percent of the populations in South Korea and China exposed to dangerous levels of fine dust.
- ^ «South Korea | Environmental Performance Index – Development». epi.yale.edu. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ^ Lee, Hyun-jeong. «Korea Wrestles with Growing Health Threat from Fined Dust» Archived 9 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Korea Herald. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ a b Hu, Elise. «Korea’s Air Is Dirty, But It’s Not All Close-Neighbor China’s Fault» Archived 9 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine. NPR. 3 June 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ «Seoul’s smelly gingko problem». BBC News. 12 October 2015. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
- ^ «[Feature] South Korea’s odor pollution problem». 3 October 2018. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
- ^ a b Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database. Archived 19 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine World Health Organization. May 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ a b WHO Air Quality Guidelines. Archived 23 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine World Health Organization. September 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ Air Quality Information. Archived 10 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Seoul Metropolitan Government. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ Yu-Jin Choi; Woon-Soo Kim (25 June 2015). «Changes in Seoul’s Air Quality Control Policy». Seoul Solution. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ 1st Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan. Archived 27 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- ^ Kim, Honghyok; Kim, Hyomi; Lee, Jong-Tae (2015). «Effects of ambient air particles on mortality in Seoul: Have the effects changed over time?». Environmental Research. 140: 684–690. Bibcode:2015ER….140..684K. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2015.05.029. PMID 26079317.
- ^ 2nd Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan. Archived 26 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- ^ Chung, Anna. «Korea’s policy towards pollution and fine particle: a sense of urgency» Archived 2017-04-27 at the Wayback Machine. Korea Analysis. v2. June 2014. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- ^ Zastrow, Mark (6 May 2016). «NASA jet gets a sniff of pollution over South Korea». Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2016.19875. S2CID 130657973. Archived from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ Labzovskii, Lev; Jeong, Su-Jong; Parazoo, Nicholas C. (2019). «Working towards confident spaceborne monitoring of carbon emissions from cities using Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2». Remote Sensing of Environment. 233. 111359. Bibcode:2019RSEnv.233k1359L. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2019.111359. S2CID 202176909.
- ^ «서울특별시청 Seoul Metropolitan Government» (in Korean). Doosan Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 22 January 2013. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ «Organization Chart». Official site of Seoul Metropolitan Government. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ a b «Administrative Districts». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ «World Urbanization Prospects». Archived from the original on 19 January 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ «Regional population density: Asia and Oceania, 2012: Inhabitants per square kilometre, TL3 regions». OECD Regions at a Glance 2013. 2013. doi:10.1787/reg_glance-2013-graph37-en. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ a b «Seoul’s Population Drops Below 10 Million for First Time in 25 Years». Chosun Ilbo. 14 February 2014. Archived from the original on 4 March 2014. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ^ «32년 만에 ‘1000만 서울 시대’ 막 내렸다…» 한국일보 (in Korean). 3 March 2021. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ «Seoul Statistics (Population)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ «1.76 million foreigners live in South Korea; 3.4% of population». 17 November 2017. Archived from the original on 21 December 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- ^ «Korean Chinese account for nearly 70% of foreigners in Seoul». The Korea Times. 11 September 2011. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «South Korean mega-churches. For God and country». Economist. 15 October 2011. Archived from the original on 15 January 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ a b «2015 Census – Religion Results» (in Korean). KOSIS KOrean Statistical Information Service. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- ^ «Dongguk University». Archived from the original on 15 September 2018.
- ^ Yim, Seok-hui. «Geographical Features of Social Polarization in Seoul, South Korea» (PDF). In Mizuuchi, Toshio (ed.). Representing Local Places and Raising Voices from Below. Osaka City University. p. 34. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ^ Industrial Policy and Territorial Development: Lessons from Korea. OECD Development Center. 16 May 2012. p. 58. ISBN 9789264173897.
- ^ «Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index» (PDF). MasterCard. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 June 2008. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «The Global Financial Centres Index 12» (PDF). Z/Yen Group. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 March 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «Hot Spots 2025: Benchmarking the Future Competitiveness of Cities» (PDF). The Economist Intelligence Unit. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ a b c «Seoul: Economy». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «The primacy of Seoul and the capital region». United Nations University. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «It’s official: Jinro soju is the world’s best-selling liquor». CNNTravel. 12 June 2012. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ «Fiery food, boring beer». The Economist. 24 November 2012. Archived from the original on 1 July 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- ^ «Global : Cities». CNN. Archived from the original on 29 May 2010. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ «Neon shines brightly during the bustle on Yeouido stock street». Korea JoongAng Daily. 5 January 2010. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «Dongdaemun Market». Visit Seoul. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «Myeong-dong». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 15 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ 서울공식여행가이드. Visit Seoul Net. Archived from the original on 14 February 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
- ^ «Insa-dong». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «Hwanghak-dong Flea Market». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 12, 2014.
- ^ «Antique Markets». Seoul Matropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 8 October 2010. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ a b «Itaewon: Going Gangnam Style?». The Korea Times. 14 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Yongsan Electronics Market, Asia’s largest IT shopping mall». KBS World. 1 March 2011. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Largest Permanent 35mm Cinema Screen». Guinnessworldrecords.com. 18 August 2009. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ «50 reasons why Seoul is world’s greatest city». 12 July 2017. Archived from the original on 22 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ PricewaterhouseCoopers. «Cities of Opportunity» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 May 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ «KOREA: Future is now for Korean info-tech». AsiaMedia. Regents of the University of California. 14 June 2005. Archived from the original on 16 December 2008.
- ^ «Tech capitals of the world – Technology». The Age. Melbourne, Australia. 18 June 2007. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ akamai’s [state of the internet] Q4 2016 report (PDF) (Report). Akamai Technologies. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 May 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ^ «Hi Seoul, SOUL OF ASIA – Seoul Located In the Center of Asian Metropolises». English.seoul.go.kr. Archived from the original on 10 July 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ Wifi in All Public Areas Archived June 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CJ헬로비전-에러페이지. Archived from the original on 20 December 2017. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ^ «Seoul’s Cheonggyecheon Stream symbolizes Korea’s past, present and tomorrow». Korea.net. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ Vinayak Bharne, ed. (2013). The Emerging Asian City: Concomitant Urbanities and Urbanisms. Routledge. p. 59. ISBN 9780415525978. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Andrei Lankov (24 June 2010). «Jongno walk». The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Amsa-dong Prehistoric Settlement Site». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «About the Palace». Gyeongbokgung Palace. Archived from the original on 14 June 2008. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Sungnyemun to open to great fanfare after more than five years of renovation». The Korea Herald. 30 April 2013. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 1 May 2013.
- ^ «The Seoul of World Design». Bloomberg Businessweek. 27 February 2008. Archived from the original on 18 April 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Status of Museum». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «국립중앙박물관». www.museum.go.kr. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ «Seoul’s best museums». CNN. 27 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 September 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- ^ «National Folk Museum of Korea». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «Namsangol Hanok Village». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 12 October 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «Bukchon Hanok Village». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ Veale, Jennifer. «Seoul: 10 Things to Do». Time. Time magazine. Archived from the original on 27 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «The War Memorial of Korea». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «Seodaemun Prison History Museum». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 4 June 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «ABU TV and Radio Song Festivals 2012». ESCKAZ.com. Archived from the original on 10 April 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ «ABU GA Seoul 2012». Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union. Archived from the original on 3 March 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ «Ultra Korea – June 8, 9, 10 2018». Ultra Korea. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ 2016 프로야구와 프로축구는 모두’서울의 봄’ (in Korean). Medeaus Ilbo. 7 November 2016. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ^ «The subway’s past and present».[dead link]
- ^ «Expanded Operation of Seoul Bike «Ddareungi»«. 18 March 2016. Archived from the original on 5 April 2019.
- ^ «QS Best Student Cities 2023». Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. 29 June 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- ^ 의무교육(무상의무교육). Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ^ «Sister & Friendship Cities -«. Official Website of the Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ «Exchange Cities of Seoul Metropolitan Council». Seoul Metropolitan Council. Archived from the original on 7 September 2022. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
External links
Official sites
- Official website (in English)
- Seoul Information & Communication Plaza website (in Korean)
Tourism and living information
- i Tour Seoul – The Official Seoul Tourism Guide Site
This article is about the capital city of South Korea. For other uses, see Seoul (disambiguation).
|
Seoul 서울 |
|
|---|---|
|
Special city |
|
| Seoul Special City 서울특별시 |
|
|
From top, left to right: |
|
|
Flag Seal Coat of arms Wordmark |
|
| Motto:
«I • Seoul • U»[1] |
|
| Anthem: none[2] | |
 |
|
|
Seoul Seoul (South Korea) Seoul Seoul (Asia) Seoul Seoul (Earth) |
|
| Coordinates: 37°33′36″N 126°59′24″E / 37.56000°N 126.99000°ECoordinates: 37°33′36″N 126°59′24″E / 37.56000°N 126.99000°E | |
| Country | |
| Area | Seoul Capital |
| Founded by | Gen. Yi Sŏng-gye |
| Districts | 25 districts |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Body | Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul Metropolitan Council |
| • Mayor | Oh Se-hoon (People Power) |
| • National Assembly | 49 |
| Area
[3] |
|
| • Special city | 605.21 km2 (233.67 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 12,685 km2 (4,898 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 38 m (125 ft) |
| Highest elevation
(Bukhan Mountain) |
836.5 m (2,744.4 ft) |
| Lowest elevation
(Yellow Sea) |
0 m (0 ft) |
| Population
(October 2022)[5] |
|
| • Special city | 9,443,722 |
| • Rank | 1st |
| • Density | 16,000/km2 (40,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 26,037,000[4] |
| • Metro density | 2,053/km2 (5,320/sq mi) |
| • Demonym | Seoulite |
| • Dialect | Gyeonggi |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Korean Standard Time) |
| Bird | Korean magpie |
| Color | Seoul Red[6] |
| Flower | Forsythia |
| Font | Seoul fonts (Seoul Hangang and Seoul Namsan)[7] |
| Mascot | Haechi |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Nominal GDP (Special City) |
US$384 billion[8] |
| Nominal GDP per capita (Special City) |
US$39,558[8] |
| Website | seoul.go.kr |
Seoul (; Korean: [sʰʌul] (listen); lit. ‘Capital’), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.[9] According to the 2020 census, Seoul has a population of 9.9 million people, and forms the heart of the Seoul Capital Area with the surrounding Incheon metropolis and Gyeonggi province. Considered to be a global city and rated as an Alpha – City by Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC),[10] Seoul was the world’s fourth largest metropolitan economy in 2014, following Tokyo, New York City and Los Angeles.
Seoul was rated Asia’s most livable city with the second highest quality of life globally by Arcadis in 2015, with a GDP per capita (PPP) of around $40,000. With major technology hubs centered in Gangnam and Digital Media City,[11] the Seoul Capital Area is home to the headquarters of 15 Fortune Global 500 companies, including Samsung,[12] LG, and Hyundai. Ranked seventh in the Global Power City Index and Global Financial Centres Index, the metropolis exerts a major influence in global affairs as one of the five leading hosts of global conferences.[13] Seoul has hosted the 1986 Asian Games, 1988 Summer Olympics, and the 2010 G20 Seoul summit.
Seoul was the capital of various Korean states, including Baekje, Joseon, the Korean Empire, Goryeo (as a secondary capital), and presently South Korea. It is strategically located along the Han River. Seoul’s history stretches back over two thousand years, when it was founded in 18 BC by the people of Baekje, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. The city was later designated the capital of Korea under the Joseon dynasty. Seoul is surrounded by a mountainous and hilly landscape, with Bukhan Mountain located on the northern edge of the city. The Seoul Capital Area contains five UNESCO World Heritage Sites: Changdeok Palace, Hwaseong Fortress, Jongmyo Shrine, Namhansanseong and the Royal Tombs of the Joseon Dynasty.[14] More recently, Seoul has been a major site of modern architectural construction – major modern landmarks include the N Seoul Tower, the 63 Building, the Lotte World Tower, the Dongdaemun Design Plaza, Lotte World, Trade Tower, COEX, IFC Seoul, and the Parc1. Seoul was named the 2010 World Design Capital. It is the birthplace of K-pop and the Korean wave, as it is the heart of Korean culture and massive medias, entertainment firms, and broadcasters.
Etymology
The city has been known in the past by the names Wiryeseong (위례성; 慰禮城, during the Baekje era), Namcheon (남천; 南川,[15] during the Silla era), Hanyang (한양; 漢陽, during the Goryeo era), Hanseong (한성; 漢城, during the Joseon era), and Keijō (京城) or Gyeongseong (경성; 京城) during Japanese rule.[16]
During Japan’s annexation of Korea, Hanseong (漢城) was renamed Keijō (京城) by the Imperial authorities to prevent confusion with the hanja ‘漢‘ (a transliteration of an ancient Korean word Han (한) meaning «great»), which also refers to Han people or the Han dynasty in Chinese and in Japanese is a term for «China».[17]
After World War II and Korea’s liberation, the city took its present name, which originated from the Korean word meaning «capital city», which is believed to have descended from an ancient word, Seorabeol (Korean: 서라벌; Hanja: 徐羅伐), which originally referred to Gyeongju, the capital of Silla.[18] Ancient Gyeongju was also known in documents by the Chinese-style name Geumseong (金城, literally «Gold Castle or City» or «Metal Castle or City»), but it is unclear whether the native Korean-style name Seorabeol had the same meaning as Geumseong.[citation needed]
Unlike most place names in Korea, «Seoul» has no corresponding hanja (Chinese characters used in the Korean language). On January 18, 2005, the Seoul government changed its official name in Chinese characters from the historic Hancheng (simplified Chinese: 汉城; traditional Chinese: 漢城; pinyin: Hànchéng) to Shou’er (simplified Chinese: 首尔; traditional Chinese: 首爾; pinyin: Shǒu’ěr).[19][20]
History
Settlement of the Han River area, where present-day Seoul is located, began around 4000 BC.[21]
Seoul is first recorded as Wiryeseong, the capital of Baekje (founded in 18 BC) in the northeastern area of modern Seoul.[21] There are several city walls remaining in the area that date from this time. Pungnaptoseong, an earthen wall located southeast Seoul, is widely believed to have been at the main Wiryeseong site.[22] As the Three Kingdoms competed for this strategic region, control passed from Baekje to Goguryeo in the 5th century.[23]
However, according to Samguk Sagi, both Baekje and Silla described the land as frontier border of Baekje, not as the capital region.[24][25] Moreover, Jinheung Taewang Stele found at current day Bukhansan tells that the place was underdeveloped as of 6th century AD,[15] suggesting that the first capital Wiryeseong was not located in or nearby Seoul.
In July or August 553, Silla took the control of the region from Baekje, and the city became a part of newly established Sin Province (신주; 新州).[24][25] Sin (新) has both meaning of «New» and «Silla», thus literally means New Silla Province.
In November 555, Jinheung Taewang made royal visit to Bukhansan, and inspected the borderline.[26] In 557, Silla abolished Sin Province, and established Bukhansan Province (북한산주; 北漢山州).[27] The word Hanseong (한성; 漢城; Han Fortress) appears on the stone wall of «Pyongyang Fortress», which was presumably built in the mid to late 6th century AD over period of 42 years, located in Pyongyang, while there is no evidence that Seoul had name Hanseong dating the three kingdoms and earlier period.[28][29][30][31][32]
In 568, Jinheung Taewang made another royal visit to the northern border, visited Hanseong, and stayed in Namcheon on his way back to the capital. During his stay, he set Jinheung Taewang Stele, abolished Bukhansan Province, and established Namcheon Province (남천주; 南川州; South River Province), appointing the city as the provincial capital.[15][33] Based on the naming system, the actual name of Han River during this time was likely Namcheon (Nam River) itself or should have the word ending with «cheon» (천; 川) not «gang» (강; 江) nor «su» (수; 水). In addition, «Bukhansan» Jinheung Stele clearly states that Silla had possession of Hanseong (modern day Pyongyang), thus Bukhansan has to be located north of Hanseong. Modern day Pyongyang was not Pyongyang, Taedong River was likely Han River, and Bukhansan was not Bukhansan during the three kingdoms period.[15][34] Moreover, Pyongyang was a common noun meaning capital used by Goguryeo and Goryeo dynasties, similar to Seoul.[35]
In 603, Goguryeo attacked Bukhansanseong (북한산성; 北漢山城; Bukhan Mountain Fortress), which Silla ended up winning.[36][37] In 604, Silla abolished Namcheon Province, and reestablished Bukhansan Province in order to strengthen the northern border. The city lost its provincial capital position and was put under Bukhansan Province once again.[38] This further proves that Bukhansan was located in the North of modern day Pyongyang as changing the provincial name and objective would not be required if Bukhansan was located within Seoul.
In the 11th century Goryeo, which succeeded Unified Silla, built a summer palace in Seoul, which was referred to as the «Southern Capital». It was only from this period that Seoul became a larger settlement.[21] When Joseon replaced Goryeo, the capital was moved to Seoul (also known as Hanyang or Hanseong), where it remained until the fall of the dynasty. The Gyeongbok Palace, built in the 14th century, served as the royal residence until 1592. The other large palace, Changdeokgung, constructed in 1405, served as the main royal palace from 1611 to 1872.[21] After Joseon changed its name to the Korean Empire in 1897, Hwangseong also designated Seoul.[clarification needed]
Originally, the city was entirely surrounded by a massive circular stone wall to provide its citizens security from wild animals, thieves and attacks. The city has grown beyond those walls and although the wall no longer stands (except along Bugaksan Mountain (Korean: 북악산; Hanja: 北岳山), north of the downtown area[39]), the gates remain near the downtown district of Seoul, including most notably Sungnyemun (commonly known as Namdaemun) and Heunginjimun (commonly known as Dongdaemun).[40] During the Joseon dynasty, the gates were opened and closed each day, accompanied by the ringing of large bells at the Bosingak belfry.[41] In the late 19th century, after hundreds of years of isolation, Seoul opened its gates to foreigners and began to modernize. Seoul became the first city in East Asia to introduce electricity in the royal palace, built by the Edison Illuminating Company[42] and a decade later Seoul also implemented electrical street lights.[43]
Much of the development was due to trade with foreign countries like France and the United States. For example, the Seoul Electric Company, Seoul Electric Trolley Company, and Seoul Fresh Spring Water Company were all joint Korean–U.S. owned enterprises.[44] In 1904, an American by the name of Angus Hamilton visited the city and said, «The streets of Seoul are magnificent, spacious, clean, admirably made and well-drained. The narrow, dirty lanes have been widened, gutters have been covered, roadways broadened. Seoul is within measurable distance of becoming the highest, most interesting and cleanest city in the East.»[45]
After the annexation treaty in 1910, Japan annexed Korea and renamed the city Gyeongseong («Kyongsong» in Korean and «Keijo» in Japanese). Japanese technology was imported, the city walls were removed, some of the gates demolished. Roads became paved and Western-style buildings were constructed. The city was liberated by U.S. forces at the end of World War II.[21]
In 1945, the city was officially named Seoul, and was designated as a special city in 1949.[21]
During the Korean War, Seoul changed hands between the Soviet/Chinese-backed North Korean forces and the American-backed South Korean forces several times, leaving the city heavily damaged after the war. The capital was temporarily relocated to Busan.[21] One estimate of the extensive damage states that after the war, at least 191,000 buildings, 55,000 houses, and 1,000 factories lay in ruins. In addition, a flood of refugees had entered Seoul during the war, swelling the population of the city and its metropolitan area to an estimated 1.5 million by 1955.[46]
Following the war, Seoul began to focus on reconstruction and modernization. As South Korea’s economy started to grow rapidly from the 1960s, urbanization also accelerated and workers began to move to Seoul and other larger cities.[46] From the 1970s, the size of Seoul administrative area greatly expanded as it annexed a number of towns and villages from several surrounding counties.[47]
Until 1972, Seoul was claimed by North Korea as its de jure capital, being specified as such in Article 103 of the 1948 North Korean constitution.[48]
South Korea’s 2019 population was estimated at 51.71 million, and according to the 2018 Population and Housing Census, 49.8% of the population resided in the Seoul metropolitan area. This was up by 0.7% from 49.1% in 2010, showing a distinct trend toward the concentration of the population in the capital.[49] Seoul has become the economic, political and cultural hub of the country,[21] with several Fortune Global 500 companies, including Samsung, SK Holdings, Hyundai, POSCO and LG Group headquartered there.[50]
Seoul was the host city of the 1986 Asian Games and 1988 Summer Olympics as well as one of the venues of the 2002 FIFA World Cup.
On 29 October 2022, at least 153 people were crushed to death when a crowd surged in an alleyway during Halloween festivities in Seoul’s Itaewon district. President Yoon declared a state of official national mourning.[51]
Various views of Seoul from the 63 Building in July, 2019
Geography
Seoul is in the northwest of South Korea. Seoul proper comprises 605.25 km2 (233.69 sq mi),[3] with a radius of approximately 15 km (9 mi), roughly bisected into northern and southern halves by the Han River. The Han River and its surrounding area played an important role in Korean history. The Three Kingdoms of Korea strove to take control of this land, where the river was used as a trade route to China (via the Yellow Sea).[52] The river is no longer actively used for navigation, because its estuary is located at the borders of the two Koreas, with civilian entry barred. Historically, the city was during the Joseon dynasty bounded by the Seoul Fortress Wall, which stretched between the four main mountains in central Seoul: Bugaksan, Inwangsan, Naksan and Namsan. The city is bordered by eight mountains, as well as the more level lands of the Han River plain and western areas. Due to its geography and to economic development policies, Seoul is a very polycentric city. The area that was the old capital in the Joseon dynasty, and mostly comprises Jongno District and Jung District, constitutes the historical and political center of the city. However, for example, the city’s financial capital is widely considered to be in Yeouido, while its economic capital is Gangnam District.[citation needed]
Climate
| Seoul | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Seoul has a humid continental climate influenced by the monsoons (Köppen: Dwa). Being in the extreme East Asia, the climate can be described as humid subtropical (Cwa, by -3 °C isotherm) with great variation in temperature and precipitation throughout the year.[53][54] The suburbs of Seoul are generally cooler than the center of Seoul because of the urban heat island effect.[55] Summers are hot and humid, with the East Asian monsoon taking place from June until September. August, the hottest month, has average high and low temperatures of 32.6 and 23.4 °C (91 and 74 °F) with higher temperatures possible. Heat index values can surpass 40 °C (104.0 °F) at the height of summer.
Winters are usually cold to freezing with average January high and low temperatures of 1.5 and −5.9 °C (34.7 and 21.4 °F), and are generally much drier than summers, with an average of 24.9 days of snow annually. Sometimes, temperatures drop dramatically to below −10 °C (14 °F), and on some occasions as low as −15 °C (5 °F) in the mid winter period of January and February. Temperatures below −20 °C (−4 °F) have been recorded.
| Climate data for Seoul (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1907–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.4 (57.9) |
18.7 (65.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
29.8 (85.6) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.2 (99.0) |
38.4 (101.1) |
39.6 (103.3) |
35.1 (95.2) |
30.1 (86.2) |
25.9 (78.6) |
17.7 (63.9) |
39.6 (103.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.0 (51.8) |
17.9 (64.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
20.2 (68.4) |
11.9 (53.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.9 (28.6) |
0.7 (33.3) |
6.1 (43.0) |
12.6 (54.7) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
21.6 (70.9) |
15.0 (59.0) |
7.5 (45.5) |
0.2 (32.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.5 (22.1) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
1.9 (35.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
18.7 (65.7) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.5 (−8.5) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−14.1 (6.6) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
2.4 (36.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
12.9 (55.2) |
13.5 (56.3) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 16.8 (0.66) |
28.2 (1.11) |
36.9 (1.45) |
72.9 (2.87) |
103.6 (4.08) |
129.5 (5.10) |
414.4 (16.31) |
348.2 (13.71) |
141.5 (5.57) |
52.2 (2.06) |
51.1 (2.01) |
22.6 (0.89) |
1,417.9 (55.82) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.1 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 9.9 | 16.3 | 14.7 | 9.1 | 6.1 | 8.8 | 7.8 | 108.6 |
| Average snowy days | 7.1 | 5.1 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 6.4 | 23.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 56.2 | 54.6 | 54.6 | 54.8 | 59.7 | 65.7 | 76.2 | 73.5 | 66.4 | 61.8 | 60.4 | 57.8 | 61.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 169.6 | 170.8 | 198.2 | 206.3 | 223.0 | 189.1 | 123.6 | 156.1 | 179.7 | 206.5 | 157.3 | 162.9 | 2,143.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 52.3 | 53.6 | 51.0 | 51.9 | 48.4 | 41.2 | 26.8 | 36.2 | 47.2 | 57.1 | 50.2 | 51.1 | 46.4 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source 1: Korea Meteorological Administration (percent sunshine 1981–2010)[56][57][58][59][60] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV)[61] |
| Climate data for Namsan Park, Jung District, Seoul (1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) |
4.1 (39.4) |
10.5 (50.9) |
17.8 (64.0) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.6 (81.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.6 (85.3) |
25.3 (77.5) |
19.1 (66.4) |
10.7 (51.3) |
2.6 (36.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.7 (53.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −6.5 (20.3) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
1.1 (34.0) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
21.8 (71.2) |
17.1 (62.8) |
10.5 (50.9) |
3.0 (37.4) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
8.2 (46.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.9 (0.43) |
21.5 (0.85) |
30.3 (1.19) |
59.7 (2.35) |
84.6 (3.33) |
114.3 (4.50) |
333.8 (13.14) |
263.4 (10.37) |
103.6 (4.08) |
39.1 (1.54) |
40.9 (1.61) |
15.2 (0.60) |
1,117.3 (43.99) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.4 | 3.8 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 12.9 | 12.1 | 7.0 | 4.8 | 7.0 | 4.4 | 82.2 |
| Source: Korea Meteorological Administration[56] |
| Climate data for Seoul–Gimpo International Airport (1981–2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 1.4 (34.5) |
4.5 (40.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
17.6 (63.7) |
22.7 (72.9) |
26.6 (79.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.7 (85.5) |
25.6 (78.1) |
19.7 (67.5) |
11.4 (52.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.8 (25.2) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
4.5 (40.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.5 (70.7) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
20.1 (68.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
5.8 (42.4) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
11.5 (52.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −9.1 (15.6) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.8 (62.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.4 (70.5) |
15.1 (59.2) |
7.3 (45.1) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 18.1 (0.71) |
20.0 (0.79) |
40.7 (1.60) |
58.0 (2.28) |
96.2 (3.79) |
119.4 (4.70) |
357.2 (14.06) |
307.5 (12.11) |
155.4 (6.12) |
49.7 (1.96) |
47.6 (1.87) |
19.0 (0.75) |
1,288.7 (50.74) |
| Source: Aviation Meteorological Office[62] |
Air quality
Very Unhealthy
Unhealthy
Unhealthy for sensitive groups
According to the Environmental Performance Index 2016, South Korea ranked 173rd out of 180 countries in terms of air quality. More than 50 percent of the populations in South Korea are exposed to dangerous levels of fine dust.[63][64]
Air pollution is a major issue in Seoul.[65][66][67][68] According to the 2016 World Health Organization Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database,[69] the annual average PM2.5 concentration in 2014 was 24 micrograms per cubic meter (1.0×10−5 gr/cu ft), which is 2.4 times higher than that recommended by the WHO Air Quality Guidelines[70] for the annual mean PM2.5. The Seoul Metropolitan Government monitors and publicly shares real-time air quality data.[71]
Since the early 1960s, the Ministry of Environment has implemented a range of policies and air pollutant standards to improve and manage air quality for its people.[72] The «Special Act on the Improvement of Air Quality in the Seoul Metropolitan Area» was passed in December 2003. Its 1st Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan (2005–2014) focused on improving the concentrations of PM10 and nitrogen dioxide by reducing emissions.[73] As a result, the annual average PM10 concentrations decreased from 70.0 μg/m3 in 2001 to 44.4 μg/m3 in 2011[74] and 46 μg/m3 in 2014.[69] As of 2014, the annual average PM10 concentration was still at least twice than that recommended by the WHO Air Quality Guidelines.[70] The 2nd Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan (2015–2024) added PM2.5 and ozone to its list of managed pollutants.[75]
Asian dust, emissions from Seoul and in general from the rest of South Korea, as well as emissions from China, all contribute to Seoul’s air quality.[66][76] A partnership between researchers in South Korea and the United States is conducting an international air quality field study in Korea (KORUS-AQ) to determine how much each source contributes.[77]
Besides air quality, greenhouse gas emissions represent hot issues in South Korea since the country is among top-10 strongest emitters in the world. Seoul is the strongest hotspot of greenhouse gas emissions in the country and according to satellite data, the persistent carbon dioxide anomaly over the city is one of the strongest in the world.[78]
Government
The Seoul Metropolitan Government is the local government for Seoul, and is responsible for the administration and provision of various services to the city, including correctional institutions, education, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services. It is headed by a mayor and three vice mayors, and is divided into 25 autonomous districts and 522 administrative neighborhoods.[79][80]
Administrative districts
Seoul is divided into 25 gu (Korean: 구; Hanja: 區) (district).[81] The gu vary greatly in area (from 10 to 47 km2 or 3.9 to 18.1 sq mi) and population (from fewer than 140,000 to 630,000). Songpa has the most people, while Seocho has the largest area. The government of each gu handles many of the functions that are handled by city governments in other jurisdictions. Each gu is divided into «dong» (동; 洞) or neighborhoods. Some gu have only a few dong while others like Jongno District have a very large number of distinct neighborhoods. Gu of Seoul consist of 423 administrative dongs (행정동) in total.[81] Dong are also sub-divided into 13,787 tong (통; 統), which are further divided into 102,796 ban in total.
- Dobong District (도봉구; 道峰區)
- Dongdaemun District (동대문구; 東大門區)
- Dongjak District (동작구; 銅雀區)
- Eunpyeong District (은평구; 恩平區)
- Gangbuk District (강북구; 江北區)
- Gangdong District (강동구; 江東區)
- Gangnam District (강남구; 江南區)
- Gangseo District (강서구; 江西區)
- Geumcheon District (금천구; 衿川區)
- Guro District (구로구; 九老區)
- Gwanak District (관악구; 冠岳區)
- Gwangjin District (광진구; 廣津區)
- Jongno District (종로구; 鍾路區)
- Jung District (중구; 中區)
- Jungnang District (중랑구; 中浪區)
- Mapo District (마포구; 麻浦區)
- Nowon District (노원구; 蘆原區)
- Seocho District (서초구; 瑞草區)
- Seodaemun District (서대문구; 西大門區)
- Seongbuk District (성북구; 城北區)
- Seongdong District (성동구; 城東區)
- Songpa District (송파구; 松坡區)
- Yangcheon District (양천구; 陽川區)
- Yeongdeungpo District (영등포구; 永登浦區)
- Yongsan District (용산구; 龍山區)
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 1,021,000 | — |
| 1960 | 2,361,000 | +8.74% |
| 1970 | 5,312,000 | +8.45% |
| 1980 | 8,244,000 | +4.49% |
| 1990 | 10,518,000 | +2.47% |
| 2000 | 9,879,000 | −0.62% |
| 2010 | 9,796,000 | −0.08% |
| 2020 | 9,963,000 | +0.17% |
| source:[82] |
Seoul proper is noted for its population density, which is almost twice that of New York City and eight times greater than Rome. Its metropolitan area was the most densely populated among OECD countries in Asia in 2012, and second worldwide after that of Paris.[83] As of 2015, the population was 9.86 million,[84] in 2012, it was 10.44 million. As of 2021, the population is 9.59 million.[85][86] As of the end of June 2011, 10.29 million Republic of Korea citizens lived in the city. This was a 0.24% decrease from the end of 2010. The population of Seoul has been dropping since the early 1990s, the reasons being the high costs of living, urban sprawling to Gyeonggi region’s satellite bed cities and an aging population.[84]
As of 2016, the number of foreigners living in Seoul was 404,037, 22.9% of the total foreign population in South Korea.[87] As of June 2011, 186,631 foreigners were Chinese citizens of Korean ancestry. This was an 8.84% increase from the end of 2010 and a 12.85% increase from June 2010. The next largest group was Chinese citizens who are not of Korean ethnicity; 29,901 of them resided in Seoul. The next highest group consisted of the 9,999 United States citizens who were not of Korean ancestry. The next highest group were Taiwanese citizens, at 8,717.[88]
The two major religions in Seoul are Christianity and Buddhism. Other religions include Muism (indigenous religion) and Confucianism. Seoul is home to one of the world’s largest Christian congregations, Yoido Full Gospel Church, which has around 830,000 members.[89] According to the 2015 census, 10.8% of the population follows Buddhism and 35% follows Christianity (24.3% Protestantism and 10.7% Catholicism). 53.6% of the population is irreligious.[90]
Religion in Seoul (2015)[90]
Not religious (53.6%)
Other (0.6%)
Seoul is home to the world’s largest modern university founded by a Buddhist Order, Dongguk University.[91] Native Seoulites tend to speak the Gyeonggi dialect of Korean.[citation needed]
Economy
Seoul is the business and financial hub of South Korea. Although it accounts for only 0.6 percent of the nation’s land area, 48.3 percent of South Korea’s bank deposits were held in Seoul in 2003,[92] and the city generated 23 percent of the country’s GDP overall in 2012.[93] In 2008 the Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index ranked Seoul No.9.[94] The Global Financial Centres Index in 2015 listed Seoul as the 6th financially most competitive city in the world.[95] The Economist Intelligence Unit ranked Seoul 15th in the list of «Overall 2025 City Competitiveness» regarding future competitiveness of cities.[96]
Manufacturing
The traditional, labor-intensive manufacturing industries have been continuously replaced by information technology, electronics and assembly-type of industries;[97][98] however, food and beverage production, as well as printing and publishing remained among the core industries.[97] Major manufacturers are headquartered in the city, including Samsung, LG, Hyundai, Kia and SK. Notable food and beverage companies include Jinro, whose soju is the most sold alcoholic drink in the world, beating out Smirnoff vodka;[99] top selling beer producers Hite (merged with Jinro) and Oriental Brewery.[100] It also hosts food giants like Seoul Dairy Cooperative, Nongshim Group, Ottogi, CJ, Orion, Maeil Holdings, Namyang Dairy Products and Lotte.
Finance
Yeouido, the main financial district of Seoul
Seoul hosts large concentration of headquarters of International companies and banks, including 15 companies on Fortune 500 list such as Samsung, LG and Hyundai.[101] Most bank headquarters and the Korea Exchange are located in Yeouido (Yeoui island),[97] which is often called «South Korea’s Wall Street» and has been serving as the financial center of the city since the 1980s.[102] The Seoul international finance center & SIFC MALL, Hanhwa 63 building, the Hanhwa insurance company head office. Hanhwa is one of the three largest South Korean insurance companies, along with Samsung Life and Gangnam & Kyobo life insurance group.
Commerce
Myeong-dong is one of the most popular destinations in Seoul.
The largest wholesale and retail market in South Korea, the Dongdaemun Market, is located in Seoul.[103] Myeongdong is a shopping and entertainment area in downtown Seoul with mid- to high-end stores, fashion boutiques and international brand outlets.[104] The nearby Namdaemun Market, named after the Namdaemun Gate, is the oldest continually running market in Seoul.[105]
Insadong is the cultural art market of Seoul, where traditional and modern Korean artworks, such as paintings, sculptures and calligraphy are sold.[106] Hwanghak-dong Flea Market and Janganpyeong Antique Market also offer antique products.[107][108] Some shops for local designers have opened in Samcheong-dong, where numerous small art galleries are located. While Itaewon had catered mainly to foreign tourists and American soldiers based in the city, Koreans now comprise the majority of visitors to the area.[109] The Gangnam district is one of the most affluent areas in Seoul[109] and is noted for the fashionable and upscale Apgujeong-dong and Cheongdam-dong areas and the COEX Mall. Wholesale markets include Noryangjin Fisheries Wholesale Market and Garak Market.
The Yongsan Electronics Market is the largest electronics market in Asia. Electronics markets are Gangbyeon station metro line 2 Techno mart, ENTER6 MALL & Shindorim station Technomart mall complex.[110]
Times Square is one of Seoul’s largest shopping malls featuring the CGV Starium, the world’s largest permanent 35 mm cinema screen.[111]
Korea World Trade Center Complex, which comprises COEX mall, congress center, 3 Inter-continental hotels, Business tower (Asem tower), Residence hotel, Casino and City airport terminal was established in 1988 in time for the Seoul Olympics. The 2nd World trade trade center is being planned at Seoul Olympic stadium complex as MICE HUB by Seoul city. Ex-Kepco head office building was purchased by Hyundai motor group with 9billion USD to build 115-storey Hyundai GBC & hotel complex until 2021. Now ex-kepco 25-storey building is under demolition.
Technology
Seoul has been described as the world’s «most wired city»,[112] ranked first in technology readiness by PwC’s Cities of Opportunity report.[113] Seoul has a very technologically advanced infrastructure.[114][115]
Seoul is among the world leaders in Internet connectivity, being the capital of South Korea, which has the world’s highest fiber-optic broadband penetration and highest global average internet speeds of 26.1 Mbit/s.[116][117] Since 2015, Seoul has provided free Wi-Fi access in outdoor spaces through a 47.7 billion won ($44 million) project with Internet access at 10,430 parks, streets and other public places.[118] Internet speeds in some apartment buildings reach up to 52.5Gbit/s with assistance from Nokia, and though the average standard consists of 100 Mbit/s services, providers nationwide are rapidly rolling out 1Gbit/s connections at the equivalent of US$20 per month.[119] In addition, the city is served by the KTX high-speed rail and the Seoul Subway, which provides 4G LTE, WiFi and DMB inside subway cars. 5G will be introduced commercially in March 2019 in Seoul.
Architecture
The traditional heart of Seoul is the old Joseon dynasty city, now the downtown area, where most palaces, government offices, corporate headquarters, hotels, and traditional markets are located. Cheonggyecheon, a stream that runs from west to east through the valley before emptying into the Han River, was for many years covered with concrete, but was recently restored by an urban revival project in 2005.[120] Jongno street, meaning «Bell Street», has been a principal street and one of the earliest commercial streets of the city,[121][122] on which one can find Bosingak, a pavilion containing a large bell. The bell signaled the different times of the day and controlled the four major gates to the city. North of downtown is Bukhan Mountain, and to the south is the smaller Namsan. Further south are the old suburbs, Yongsan District and Mapo District. Across the Han River are the newer and wealthier areas of Gangnam District, Seocho District and surrounding neighborhoods.
Historical architecture
Seoul has many historical and cultural landmarks. In Amsa-dong Prehistoric Settlement Site, Gangdong District, neolithic remains were excavated and accidentally discovered by a flood in 1925.[123]
Urban and civil planning was a key concept when Seoul was first designed to serve as a capital in the late 14th century. The Joseon dynasty built the «Five Grand Palaces» in Seoul – Changdeokgung, Changgyeonggung, Deoksugung, Gyeongbokgung and Gyeonghuigung – all of which are located in Jongno and Jung Districts. Among them, Changdeokgung was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1997 as an «outstanding example of Far Eastern palace architecture and garden design». The main palace, Gyeongbokgung, underwent a large-scale restoration project.[124] The palaces are considered exemplary architecture of the Joseon period. Beside the palaces, Unhyeongung is known for being the royal residence of Regent Daewongun, the father of Emperor Gojong at the end of the Joseon Dynasty.
Seoul has been surrounded by walls that were built to regulate visitors from other regions and protect the city in case of an invasion. Pungnap Toseong is a flat earthen wall built at the edge of the Han River, which is widely believed to be the site of Wiryeseong. Mongchon Toseong (Korean: 몽촌토성; Hanja: 蒙村土城) is another earthen wall built during the Baekje period that is now located inside the Olympic Park.[22] The Fortress Wall of Seoul was built early in the Joseon dynasty for protection of the city. After many centuries of destruction and rebuilding, about 2⁄3 of the wall remains, as well as six of the original eight gates. These gates include Sungnyemun and Heunginjimun, commonly known as Namdaemun (South Great Gate) and Dongdaemun (East Great Gate). Namdaemun was the oldest wooden gate until a 2008 arson attack, and was re-opened after complete restoration in 2013.[125] Located near the gates are the traditional markets and largest shopping center, Namdaemun Market and Dongdaemun Market.
There are also many buildings constructed with international styles in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Independence Gate was built in 1897 to inspire an independent spirit. Seoul Station was opened in 1900 as Gyeongseong Station.
Modern architecture
Various high-rise office buildings and residential buildings, like the Gangnam Finance Center, the Tower Palace, Namsan Seoul Tower, and the Lotte World Tower, dominate the city’s skyline. The tallest building is Lotte World Tower, reaching a height of 555m. It opened to the public in April 2017. It is also the 4th highest building in the world.
The World Trade Center Seoul, located in Gangnam District, hosts various expositions and conferences. Also in Gangnam District is the COEX Mall, a large indoor shopping and entertainment complex. Downstream from Gangnam District is Yeouido, an island that is home to the National Assembly, major broadcasting studios, and a number of large office buildings, as well as the Korea Finance Building and the Yoido Full Gospel Church. The Olympic Stadium, Olympic Park, and Lotte World are located in Songpa District, on the south side of the Han River, upstream from Gangnam District. Three new modern landmarks of Seoul are Dongdaemun Design Plaza & Park, designed by Zaha Hadid, the new wave-shaped Seoul City Hall, by Yoo Kerl of iArc, and the Lotte World Tower, the 5th tallest building in the world designed by Kohn Pedersen Fox.
In 2010 Seoul was designated the World Design Capital for the year.[126]
Culture
Museums
Seoul is home to 115 museums,[127] including four national and nine official municipal museums. Among the city’s national museum, The National Museum of Korea[128] is the most representative of museums in not only Seoul but all of South Korea. Since its establishment in 1945, the museum has built a collection of 220,000 artifacts.[129] In October 2005, the museum moved to a new building in Yongsan Family Park.
The National Folk Museum is located on the grounds of the Gyeongbokgung Palace in the district of Jongno District and uses replicas of historical objects to illustrate the folk history of the Korean people.[130] The National Palace Museum of Korea is also located on the grounds of the Gyeongbokgung Palace. Finally, the Seoul branch of the National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art, whose main museum is located in Gwacheon, opened in 2013, in Sogyeok-dong.
Bukchon Hanok Village and Namsangol Hanok Village are old residential districts consisting of hanok Korean traditional houses, parks, and museums that allows visitors to experience traditional Korean culture.[131][132]
The War Memorial, one of nine municipal museums in Seoul, offers visitors an educational and emotional experience of various wars in which Korea was involved, including Korean War themes.[133][134] The Seodaemun Prison is a former prison built during the Japanese occupation, and is used as a historic museum.[135]
The Seoul Museum of Art and Ilmin Museum of Art have preserved the appearance of the old building that is visually unique from the neighboring tall, modern buildings. The former is operated by Seoul City Council and sits adjacent to Gyeonghuigung Palace, a Joseon dynasty royal palace. Leeum, Samsung Museum of Art, is widely regarded as one of Seoul’s largest private museum. For many Korean film lovers from all over the world, the Korean Film Archive is running the Korean Film Museum and Cinematheque KOFA in its main center located in Digital Media City(DMC), Sangam-dong. The Tteok & Kitchen Utensil Museum and Kimchi Field Museum provide information regarding Korean culinary history.
Religious monuments
There are also religious buildings that take important roles in Korean society and politics. The Wongudan altar was a sacrificial place where Korean rulers held heavenly rituals since the Three Kingdoms period. Since the Joseon dynasty adopted Confucianism as its national ideology in the 14th century, the state built many Confucian shrines. The descendants of the Joseon royal family still continue to hold ceremonies to commemorate ancestors at Jongmyo. It is the oldest royal Confucian shrine preserved and the ritual ceremonies continue a tradition established in the 14th century. Sajikdan, Munmyo and Dongmyo were built during the same period. Although Buddhism was suppressed by the Joseon state, it has continued its existence. Jogyesa is the headquarters of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism. Hwagyesa and Bongeunsa are also major Buddhist temples in Seoul.
The Myeongdong Cathedral is a landmark of the Myeongdong, Jung District and the biggest Catholic church in Seoul established in 1883. It is a symbol of Catholicism in Korea. It was also a focus for political dissent in the 1980s. In this way the Roman Catholic Church has a very strong influence in Korean society. And Yakhyeon Catholic Church in Jungnim-dong, Jung District is first Catholic parish in Korea. It has been the first Gothic church ever built in Korea.
There are many Protestant churches in Seoul. The most numerous are Presbyterian, but there are also many Methodist and Baptist churches. Yoido Full Gospel Church is a Pentecostal church affiliated with the Assemblies of God on Yeouido in Seoul. With approximately 830,000 members (2007), it is the largest Pentecostal Christian congregation in the world, which has been recognized by the Guinness Book of World Records.[citation needed]
The St. Nicholas Cathedral, but sometimes called bald church, is the only Byzantine-style church in Seoul. It is located in Ahyeon-dong, Mapo District, and is cathedral of the Orthodox Metropolis of Korea. In 2015, it was designated as a Seoul Future Heritage.
Festivals
In October 2012, KBS Hall in Seoul hosted major international music festivals – First ABU TV and Radio Song Festivals within frameworks of Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union 49th General Assembly.[136][better source needed][137]
Hi! Seoul Festival is a seasonal cultural festival held four times a year every spring, summer, autumn, and winter in Seoul, South Korea since 2003. It is based on the «Seoul Citizens’ Day» held on every October since 1994 to commemorate the 600 years history of Seoul as the capital of the country. The festival is arranged under the Seoul Metropolitan Government. As of 2012, Seoul has hosted Ultra Music Festival Korea, an annual dance music festival that takes place on the 2nd weekend of June.[138]
Parks
Despite the city’s population density, Seoul has a large quantity of parks. One of the most famous parks is Namsan Park, which offers recreational hiking and views of the downtown Seoul skyline. The N Seoul Tower is located at Namsan Park. Seoul Olympic Park, located in Songpa District and built to host the 1988 Summer Olympics is Seoul’s largest park. Among the other largest parks in the city are Seoul Forest, Dream Forest, Children’s Grand Park and Haneul Park. The Wongaksa Pagoda 10 tier pagoda is located In Tapgol Park, a small public park with an area of 19,599 m2 (210,962 sq ft). Areas around streams serve as public places for relaxation and recreation. Tancheon stream and the nearby area serve as a large park with paths for both walkers and cyclists.
Cheonggyecheon, a stream that runs nearly 6 km (4 mi) through downtown Seoul, is popular among both Seoul residents and tourists. In 2017 the Seoullo 7017 Skypark opened, spanning diagonally overtop Seoul Station.
There are also many parks along the Han River, such as Ichon Hangang Park, Yeouido Hangang Park, Mangwon Hangang Park, Nanji Hangang Park, Banpo Hangang Park, Ttukseom Hangang Park and Jamsil Hangang Park.
The Seoul National Capital Area also contains a green belt aimed at preventing the city from sprawling out into neighboring Gyeonggi Province. These areas are frequently sought after by people looking to escape from urban life on weekends and during vacations.
There are also various parks under construction or in project, such as the Gyeongui Line Forest Trail, Seoul Station 7017, Seosomun Memorial Park and Yongsan Park.
Seoul is also home to the world’s largest indoor amusement park, Lotte World. Other recreation centers include the former Olympic and World Cup stadiums and the City Hall public lawn.
Media
Seoul is home of the major South Korean networks KBS, SBS, and MBC. The city is also home to the major South Korean newspapers Chosun Ilbo, Donga Ilbo, Joongang Ilbo, and Hankook Ilbo.
Sports
Fireworks at the closing ceremonies of the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul
Seoul is a major center of South Korean sports, and has the largest number of professional sports teams and facilities in the country.
In the history of South Korea’s major professional sports league championships, which include the K League, KBO League, KBL, and V-League, Seoul had multiple championship winners during the same season twice; in 1990, when Lucky-Goldstar FC (currently FC Seoul) won the 1990 K League and the LG Twins won the 1990 KBO League, and in 2016, when FC Seoul won the 2016 K League Classic and the Doosan Bears won the 2016 KBO League.[139]
International competition
Seoul hosted the 1986 Asian Games, also known as Asiad, 1988 Olympic Games, and Paralympic Games. It also served as one of the host cities of the 2002 FIFA World Cup. Seoul World Cup Stadium hosted the opening ceremony and first game of the tournament.
Taekwondo is South Korea’s national sport and Seoul is the location of the Kukkiwon, the world headquarters of taekwondo, as well as the World Taekwondo Federation.
Domestic sports clubs
Football
Seoul’s most well-known football club is FC Seoul.
- Men’s football
| Tier | League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | K League 1 | FC Seoul | Seoul World Cup Stadium |
| 2nd | K League 2 | Seoul E-Land | Mokdong Stadium |
| 4th | K4 League | Seoul Jungnang FC | Jungnang Public Ground |
| Seoul Nowon United | Nowon Madeul Stadium |
- Women’s football
| Tier | League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top | WK League | Seoul City WFC | Seoul World Cup Auxiliary Stadium |
Baseball
| League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|
| KBO League | ||
| LG Twins | Jamsil Baseball Stadium | |
| Doosan Bears | ||
| Kiwoom Heroes | Gocheok Sky Dome |
Basketball
| League | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|
| KBL | ||
| Seoul SK Knights | Jamsil Students’ Gymnasium | |
| Seoul Samsung Thunders | Jamsil Arena |
Volleyball
| League | Division | Club | Home stadium |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-League | |||
| Men | Seoul Woori Card WooriWON | Jangchung Arena | |
| Women | GS Caltex Seoul KIXX |
Handball
- Seoul City
Transportation
Seoul has a well developed transportation network. Its system dates back to the era of the Korean Empire, when the first streetcar lines were laid and a railroad linking Seoul and Incheon was completed.[140] Seoul’s most important streetcar line ran along Jongno until it was replaced by Line 1 of the subway system in the early 1970s. Other notable streets in downtown Seoul include Euljiro, Teheranno, Sejongno, Chungmuro, Yulgongno, and Toegyero. There are nine major subway lines stretching for more than 250 km (155 mi), with one additional line planned. As of 2010, 25% of the population has a commute time of an hour or longer.
Bus
Seoul’s bus system is operated by the Seoul Metropolitan Government (S.M.G.), with four primary bus configurations available servicing most of the city. Seoul has many large intercity/express bus terminals. These buses connect Seoul with cities throughout South Korea. The Seoul Express Bus Terminal, Central City Terminal and Seoul Nambu Terminal are located in the district of Seocho District. In addition, East Seoul Bus Terminal in Gwangjin District and Sangbong Terminal in Jungnang District handles traffics mainly from Gangwon and Chungcheong provinces.
Urban rail
Seoul has a comprehensive urban railway network of 21 rapid transit, light metro and commuter lines that interconnects every district of the city and the surrounding areas of Incheon, Gyeonggi province, western Gangwon province, and northern Chungnam province. With more than 8 million passengers per day, the subway is one of the busiest subway systems in the world and the largest in the world, with a total track length of 940 km (580 mi). In addition, in order to cope with the various modes of transport, Seoul’s metropolitan government employs several mathematicians to coordinate the subway, bus, and traffic schedules into one timetable. The various lines are run by Korail, Seoul Metro, NeoTrans Co. Ltd., AREX, and Seoul Metro Line 9 Corporation.
Train
Seoul is connected to every major city in South Korea by rail. Most major South Korean cities are linked via the KTX high-speed train, which has a normal operation speed of more than 300 km/h (186 mph). The Mugunghwa and Saemaeul trains also stop at all major stations. Major railroad stations include:
- Seoul Station, Yongsan District: Gyeongbu line (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa-ho)
- Yongsan station, Yongsan District: Honam line (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa), Jeolla/Janghang lines (Saemaul/Mugunghwa)
- Yeongdeungpo station, Yeongdeungpo District: Gyeongbu/Honam/Janghang lines (KTX/ITX-Saemaeul/Saemaul/Nuriro/Mugunghwa)
- Cheongnyangni station, Dongdaemun District: Gyeongchun/Jungang/Yeongdong/Taebaek lines (ITX-Cheongchun/ITX-Saemaeul/Mugunghwa)
- Suseo station (HSR), Gangnam District: Suseo HSR (SRT)
Airports
Seoul is served by two international airports, Incheon International Airport and Gimpo International Airport.
Gimpo International Airport opened in 1939 as an airfield for the Japanese Imperial Army and opened for civil aircraft in 1957. Since the opening of Incheon International, Gimpo International handles domestic flights along with some short haul international flights to Tokyo Haneda, Osaka Kansai, Taipei Songshan, Shanghai Hongqiao, and Beijing Capital although flights to Osaka Kansai and Beijing Capital also operate from Incheon International.
Incheon International Airport opened in March 2001 in Yeongjong island. It is now responsible for major international flights. Incheon International Airport is Asia’s eighth busiest airport in terms of passengers, the world’s fourth busiest airport by cargo traffic, and the world’s eighth busiest airport in terms of international passengers in 2014. In 2016, 57,765,397 passengers used the airport. Incheon International Airport opened terminal 2 on January 18, 2018.
Incheon and Gimpo are linked to Seoul by expressway, and to each other by the AREX to Seoul Station. Intercity bus services are available to various destinations around the country.
Cycling
Cycling is becoming increasingly popular in Seoul and in the entire country. Both banks of the Han River have cycling paths that run all the way across the city along the river. In addition, Seoul introduced in 2015 a bicycle-sharing system named Ddareungi (and named Seoul Bike in English).[141]
Education
Universities
Seoul is home to the majority of South Korea’s most prestigious universities, including Seoul National University, Yonsei University, Korea University.
Seoul ranked 2nd on the QS Best Student Cities 2023.[142]
Secondary education
Compulsory education lasts from grade 1–9 (six years of elementary school and 3 years of middle school).[143] Students spend six years in elementary school, three years in middle school, and three years in high school. Secondary schools generally require students to wear uniforms. There is an exit exam for graduating from high school and many students proceeding to the university level are required to take the College Scholastic Ability Test that is held every November. Although there is a test for non-high school graduates, called school qualification exam, most Koreans take the test.
Seoul is home to various specialized schools, including three science high schools, and six foreign language High Schools. Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education comprises 235 College-Preparatory High Schools, 80 Vocational Schools, 377 Middle Schools, and 33 Special Education Schools as of 2009.
International relations
Seoul is a member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21 and the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group. In addition, Seoul hosts many embassies of countries it has diplomatic ties with.
Sister cities
Seoul has 23 sister cities:[144]
[145]
Taipei, Taiwan (1968)
Ankara, Turkey (1971)
Honolulu, United States (1976)
San Francisco, United States (1976)
São Paulo, Brazil (1977)
Bogotá, Colombia (1982)
Jakarta, Indonesia (1984)
Tokyo, Japan (1988)
Moscow, Russia (1991)
New South Wales, Australia (1991)
Paris, France (1991)
Mexico City, Mexico (1992)
Beijing, China (1993)
Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia (1995)
Hanoi, Vietnam (1996)
Warsaw, Poland (1996)
Cairo, Egypt (1997)
Rome, Italy (2000)
Astana, Kazakhstan (2004)
Washington, D.C., United States (2006)
Athens, Greece (2006)
Bangkok, Thailand (2006)
Tashkent, Uzbekistan (2010)
See also
- Geography of South Korea
- List of cities in South Korea
- List of most populous cities
References
- ^ 논란 겪은 ‘I·SEOUL·U’ 서울 공식브랜드로 확정. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
- ^ «서울시 사이트에 서울 시가인 서울의 찬가가 없습니다». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ^ a b «Seoul Statistics (Land Area)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 24 March 2010.
- ^ Seoul Capital Area
- ^ «City Overview (Population)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021. Retrieved 26 November 2021.
- ^ «Color». Archived from the original on 11 May 2012. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- ^ «Seoul’s symbols». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2016.
- ^ a b «2018년 지역소득(잠정)». Archived from the original on 21 June 2020. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ Before 1972, Seoul was the de jure capital of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) as stated in Article 103 Archived 14 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine of the 1948 constitution.
- ^ «The World According to GaWC 2020». GaWC — Research Network. Globalization and World Cities. Archived from the original on 24 August 2020. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ «Tech capitals of the world». The Age. Melbourne. 15 June 2009. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ «Samsung Electronics». Fortune. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ Union of International Associations (UIA) International Meetings Statistics for the Year 2011 Archived 3 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Joel Fischer.
- ^ «Lists: Republic of Korea». UNESCO. Archived from the original on 25 December 2019. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- ^ a b c d «Monument on Bukhansan Mountain Commemorating the Border Inspection by King Jinheung of Silla». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ Yu, Woo-ik; Lee, Chan (6 November 2019). «Seoul». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 9 June 2015. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
The city was popularly called Seoul in Korean during both the Chosŏn (Yi) dynasty (1392–1910) and the period of Japanese rule (1910–45), although the official names in those periods were Hansŏng (Hanseong) and Kyŏngsŏng (Gyeongseong), respectively.
- ^ Kim, Dong Hoon (22 March 2017). Eclipsed Cinema: The Film Culture of Colonial Korea. ISBN 9781474421829. Archived from the original on 14 July 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ^ «Yahoo holiday travel guide». Uk.holidaysguide.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2007.
- ^ 서울특별시표기 首爾로…중국, 곧 정식 사용키로 :: 네이버 뉴스 (in Korean). News.naver.com. 23 October 2005. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2012.
- ^ Characters, Good. «Chinese Naming Crisis Danger Opportunity Summer 2006 – Good Characters». goodcharacters.com. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «Seoul». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ a b «Pungnap-toseong (Earthen Ramparts)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ Tennant (12 November 2012). History Of Korea. ISBN 9781136166983. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020.
- ^ a b «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 19». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ a b «Samguk Sagi Baekje Seong 19». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 24». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 28». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 1». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 2». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 3». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 4». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Pyongyang Fortress Stone 6». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinheung 45». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ ««고구려 수도 평양은 북한땅에 없었다»«. 신동아 (in Korean). 22 January 2013. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ «고대 평양은 지금의 평양이 아니다». K스피릿 (in Korean). 11 July 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinpyeong 30». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Goguryeo Yeongyang 15». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Samguk Sagi Silla Jinpyeong 32». National Institute of Korean History.
- ^ «Bugaksan Mountain». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Seoul City Wall». UNESCO. Archived from the original on 31 December 2019. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Bosingak Belfry». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ Nam Moon Hyon. «Early History of Electrical Engineering in Korea: Edison and First Electric Lighting in the Kingdom of Corea» (PDF). Promoting the History of EE Jan 23–26, 2000. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ Kyung Moon Hwang (2010). A History of Korea. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 142. ISBN 9780230364523. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Young-Iob Chung (2006). Korea under Siege, 1876–1945 : Capital Formation and Economic Transformation. Oxford University Press. p. 70. ISBN 9780198039662.
- ^ Bruce Cumings (2005). Korea’s Place in the Sun: A Modern History. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 9780393347531. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ^ a b Stephen Hamnett, Dean Forbes, ed. (2012). Planning Asian Cities: Risks and Resilience. Routledge. p. 159. ISBN 9781136639272. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ «Urban Planning of Seoul» (PDF). Seoul Metropolitan Government. 2009. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Archived copy» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ «Korean Cultural Centre India New Delhi». Korean Cultural Centre India New Delhi. Archived from the original on 20 July 2020. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ^ «GLOBAL 500». CNNMoney. 23 July 2012. Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «At least 153 killed in crowd crush during Halloween festivities in Seoul». The Guardian. 30 October 2022.
- ^ «Brief History of Hangang (River)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 31 October 2016. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Seoul, South Korea Köppen Climate Classification (Weatherbase)». Weatherbase. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2019.
- ^ Peterson, Adam (31 October 2018), English: Data sources: Köppen types calculated from data from WorldClim.org, archived from the original on 10 October 2020, retrieved 9 June 2019
- ^ Lee, Sang-Hyun; Baik, Jong-Jin (1 March 2010). «Statistical and dynamical characteristics of the urban heat island intensity in Seoul». Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 100 (1–2): 227–237. Bibcode:2010ThApC.100..227L. doi:10.1007/s00704-009-0247-1. S2CID 120641921. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2018.
- ^ a b
«Climatological Normals of Korea (1991 ~ 2020)» (PDF) (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. pp. II-27, II-28, II-465. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 31 January 2022. - ^
우리나라 기후평년값 — 파일셋 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021. - ^
우리나라 기후평년값 — 그래프 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021. - ^
순위값 — 구역별조회 (in Korean). Korea Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2 October 2021. - ^
«Climatological Normals of Korea» (PDF). Korea Meteorological Administration. 2011. p. 499 and 649. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016. - ^ «Seoul, South Korea — Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast». Weather Atlas. Yu Media Group. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- ^
저고도 항공기상정보 포털 (in Korean). Aviation Meteorological Office. - ^ «South Korea near bottom of world survey of air quality». The Korea Herald. 16 May 2016. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
South Korea ranked 173rd out of 180 countries in terms of air quality, the Environmental Performance Index 2016 rankings showed Monday. … A report said that 1.3 billion people exposed to poor air quality lived in East Asian countries, with more than 50 percent of the populations in South Korea and China exposed to dangerous levels of fine dust.
- ^ «South Korea | Environmental Performance Index – Development». epi.yale.edu. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ^ Lee, Hyun-jeong. «Korea Wrestles with Growing Health Threat from Fined Dust» Archived 9 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Korea Herald. 23 March 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ a b Hu, Elise. «Korea’s Air Is Dirty, But It’s Not All Close-Neighbor China’s Fault» Archived 9 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine. NPR. 3 June 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ «Seoul’s smelly gingko problem». BBC News. 12 October 2015. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
- ^ «[Feature] South Korea’s odor pollution problem». 3 October 2018. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 16 February 2019.
- ^ a b Global Urban Ambient Air Pollution Database. Archived 19 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine World Health Organization. May 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ a b WHO Air Quality Guidelines. Archived 23 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine World Health Organization. September 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ Air Quality Information. Archived 10 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Seoul Metropolitan Government. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ Yu-Jin Choi; Woon-Soo Kim (25 June 2015). «Changes in Seoul’s Air Quality Control Policy». Seoul Solution. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ 1st Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan. Archived 27 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- ^ Kim, Honghyok; Kim, Hyomi; Lee, Jong-Tae (2015). «Effects of ambient air particles on mortality in Seoul: Have the effects changed over time?». Environmental Research. 140: 684–690. Bibcode:2015ER….140..684K. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2015.05.029. PMID 26079317.
- ^ 2nd Seoul Metropolitan Air Quality Improvement Plan. Archived 26 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- ^ Chung, Anna. «Korea’s policy towards pollution and fine particle: a sense of urgency» Archived 2017-04-27 at the Wayback Machine. Korea Analysis. v2. June 2014. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- ^ Zastrow, Mark (6 May 2016). «NASA jet gets a sniff of pollution over South Korea». Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2016.19875. S2CID 130657973. Archived from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 26 April 2017.
- ^ Labzovskii, Lev; Jeong, Su-Jong; Parazoo, Nicholas C. (2019). «Working towards confident spaceborne monitoring of carbon emissions from cities using Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2». Remote Sensing of Environment. 233. 111359. Bibcode:2019RSEnv.233k1359L. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2019.111359. S2CID 202176909.
- ^ «서울특별시청 Seoul Metropolitan Government» (in Korean). Doosan Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 22 January 2013. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ «Organization Chart». Official site of Seoul Metropolitan Government. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- ^ a b «Administrative Districts». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ «World Urbanization Prospects». Archived from the original on 19 January 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ «Regional population density: Asia and Oceania, 2012: Inhabitants per square kilometre, TL3 regions». OECD Regions at a Glance 2013. 2013. doi:10.1787/reg_glance-2013-graph37-en. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ a b «Seoul’s Population Drops Below 10 Million for First Time in 25 Years». Chosun Ilbo. 14 February 2014. Archived from the original on 4 March 2014. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- ^ «32년 만에 ‘1000만 서울 시대’ 막 내렸다…» 한국일보 (in Korean). 3 March 2021. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ «Seoul Statistics (Population)». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ «1.76 million foreigners live in South Korea; 3.4% of population». 17 November 2017. Archived from the original on 21 December 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- ^ «Korean Chinese account for nearly 70% of foreigners in Seoul». The Korea Times. 11 September 2011. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «South Korean mega-churches. For God and country». Economist. 15 October 2011. Archived from the original on 15 January 2018. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ a b «2015 Census – Religion Results» (in Korean). KOSIS KOrean Statistical Information Service. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- ^ «Dongguk University». Archived from the original on 15 September 2018.
- ^ Yim, Seok-hui. «Geographical Features of Social Polarization in Seoul, South Korea» (PDF). In Mizuuchi, Toshio (ed.). Representing Local Places and Raising Voices from Below. Osaka City University. p. 34. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ^ Industrial Policy and Territorial Development: Lessons from Korea. OECD Development Center. 16 May 2012. p. 58. ISBN 9789264173897.
- ^ «Worldwide Centers of Commerce Index» (PDF). MasterCard. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 June 2008. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «The Global Financial Centres Index 12» (PDF). Z/Yen Group. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 March 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «Hot Spots 2025: Benchmarking the Future Competitiveness of Cities» (PDF). The Economist Intelligence Unit. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 January 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ a b c «Seoul: Economy». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «The primacy of Seoul and the capital region». United Nations University. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «It’s official: Jinro soju is the world’s best-selling liquor». CNNTravel. 12 June 2012. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ «Fiery food, boring beer». The Economist. 24 November 2012. Archived from the original on 1 July 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- ^ «Global : Cities». CNN. Archived from the original on 29 May 2010. Retrieved 3 August 2020.
- ^ «Neon shines brightly during the bustle on Yeouido stock street». Korea JoongAng Daily. 5 January 2010. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ «Dongdaemun Market». Visit Seoul. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «Myeong-dong». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 15 February 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ 서울공식여행가이드. Visit Seoul Net. Archived from the original on 14 February 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
- ^ «Insa-dong». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ «Hwanghak-dong Flea Market». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 12, 2014.
- ^ «Antique Markets». Seoul Matropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 8 October 2010. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ a b «Itaewon: Going Gangnam Style?». The Korea Times. 14 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Yongsan Electronics Market, Asia’s largest IT shopping mall». KBS World. 1 March 2011. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Largest Permanent 35mm Cinema Screen». Guinnessworldrecords.com. 18 August 2009. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ «50 reasons why Seoul is world’s greatest city». 12 July 2017. Archived from the original on 22 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ PricewaterhouseCoopers. «Cities of Opportunity» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 May 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ «KOREA: Future is now for Korean info-tech». AsiaMedia. Regents of the University of California. 14 June 2005. Archived from the original on 16 December 2008.
- ^ «Tech capitals of the world – Technology». The Age. Melbourne, Australia. 18 June 2007. Archived from the original on 12 September 2009. Retrieved 18 June 2009.
- ^ akamai’s [state of the internet] Q4 2016 report (PDF) (Report). Akamai Technologies. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 May 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ^ «Hi Seoul, SOUL OF ASIA – Seoul Located In the Center of Asian Metropolises». English.seoul.go.kr. Archived from the original on 10 July 2012. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ^ Wifi in All Public Areas Archived June 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CJ헬로비전-에러페이지. Archived from the original on 20 December 2017. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ^ «Seoul’s Cheonggyecheon Stream symbolizes Korea’s past, present and tomorrow». Korea.net. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ Vinayak Bharne, ed. (2013). The Emerging Asian City: Concomitant Urbanities and Urbanisms. Routledge. p. 59. ISBN 9780415525978. Archived from the original on 25 January 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ Andrei Lankov (24 June 2010). «Jongno walk». The Korea Times. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Amsa-dong Prehistoric Settlement Site». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «About the Palace». Gyeongbokgung Palace. Archived from the original on 14 June 2008. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Sungnyemun to open to great fanfare after more than five years of renovation». The Korea Herald. 30 April 2013. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 1 May 2013.
- ^ «The Seoul of World Design». Bloomberg Businessweek. 27 February 2008. Archived from the original on 18 April 2014. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ «Status of Museum». Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 11 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «국립중앙박물관». www.museum.go.kr. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ^ «Seoul’s best museums». CNN. 27 October 2011. Archived from the original on 16 September 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- ^ «National Folk Museum of Korea». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 16 July 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «Namsangol Hanok Village». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 12 October 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «Bukchon Hanok Village». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 15 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ Veale, Jennifer. «Seoul: 10 Things to Do». Time. Time magazine. Archived from the original on 27 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «The War Memorial of Korea». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 14 February 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «Seodaemun Prison History Museum». Korea Tourism Organization. Archived from the original on 4 June 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ «ABU TV and Radio Song Festivals 2012». ESCKAZ.com. Archived from the original on 10 April 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ «ABU GA Seoul 2012». Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union. Archived from the original on 3 March 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ «Ultra Korea – June 8, 9, 10 2018». Ultra Korea. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ 2016 프로야구와 프로축구는 모두’서울의 봄’ (in Korean). Medeaus Ilbo. 7 November 2016. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ^ «The subway’s past and present».[dead link]
- ^ «Expanded Operation of Seoul Bike «Ddareungi»«. 18 March 2016. Archived from the original on 5 April 2019.
- ^ «QS Best Student Cities 2023». Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. 29 June 2022. Archived from the original on 7 July 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- ^ 의무교육(무상의무교육). Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ^ «Sister & Friendship Cities -«. Official Website of the Seoul Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ «Exchange Cities of Seoul Metropolitan Council». Seoul Metropolitan Council. Archived from the original on 7 September 2022. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
External links
Official sites
- Official website (in English)
- Seoul Information & Communication Plaza website (in Korean)
Tourism and living information
- i Tour Seoul – The Official Seoul Tourism Guide Site
Население — 10,1 млн человек (2015), или 19,5 % населения страны. Образует агломерацию Сеул-Инчхон с населением 23,5 млн человек (2015), четвертую по величине в мире. Расположен на северо-западе Республики Корея вблизи Жёлтого моря, на равнине в окружении гор, на берегах реки Хан, в 24 км от границы с КНДР.
Главный политический, экономический и культурный центр Республики Корея. Один из ведущих финансовых центров Восточной Азии.
С 1394 года под названием Ханян — столица Кореи, с 1948 года под названием Сеул — столица Республики Корея. Во время Корейской войны город был сильно разрушен. Сохранились остатки крепостной стены с воротами, восстановлен дворцовый комплекс Кёнбоккун XIV века. Имеются объекты Всемирного наследия ЮНЕСКО.
Название населенного пункта (город): Сеул
Международное название: Saeul
Код ISO, IATA города: 11
Размер населенного пункта: Областной центр или город с населением более 1лн.человек
Район: 🔍 Сеул, Seul
Районный центр: Mia-dong
Регион (область,штат): Столичный, Stolichnij
Областной центр:
Округ:
Страна: 
Столица Сеул
Часть света: Азия
Код страны (2): KR
Код страны (3): KOR
☎ Телефонный код города Сеул: +82-2
[как звонить в Сеул]
Длина номера телефона в стране: 12
Как звонить? Как набирать?
Порядок набора со стационарного телефона:
8-гудок-10-82-2-Номер телефона в городе Saeul
Чтобы позвонить с мобильного телефона набирайте:
+82-2-Номер телефона в городе
Как набрать «+» на мобильном телефоне?
Для ввода символа «плюс» на клавиатуре мобильного телефона нужно несколько секунд удерживать клавишу «0».
✉ Почтовый индекс(zip-код): 480-071
🚘 Автомобильный код региона:
⌚ Временная зона (Time Zone, UTC, GMT): +9 Asia/Seoul, сейчас в Сеул 17 часов 41 минут
Язык: Корейский
Широта (latitude): 37.5833 N
Долгота (longitude): 127 E
Wikipedia:
Сеул на русском,
Saeul на английском
Альтернативные названия: 의정부시 (Корейский), Ийджонбу (Украинский), Uijeongbu (Немецкий), Uijeongbu (Французский), Ŭijŏngbu (Польский), 議政府市 (Японский), 議政府市 (Китайский), Uijeongbu (Шведский), सियोल (Хинди), Seoul (Немецкий), Séoul (Французский), Seúl (Испанский), Seoul (Итальянский), Seul (Польский), ソウル特別市 (Японский), 首爾 (Китайский), 서울특별시 (Корейский), Սեուլ (Армянский), سيول (Арабский), Σεούλ (Греческий (новогреческий)), სეული (Грузинский), סיאול (Иврит), โซล (Тайский), சியோல் (Тамильский), সিউল (Бенгальский), སེ་ཨུལ། (Тибетский), सोल (Маратхи), Seul (Турецкий), Сөүл (Монгольский), Seul (Азербайджанский), Seul (Узбекский), Seoul (Датский), Seoel (Нидерландский (Голландский)), Seoul (Шведский), Soul (Финский (Suomi)), Soul (Чешский), Szöul (Венгерский), Seul (Румынский), Seoul (Эсперанто), Seoul (Яванский), Seoul (Вьетнамский), سیول (Урду), Seulum (Латинский), Seulas (Литовский), Seula (Латышский), Seul (Словенский), Sŏul (Эстонский), Seul (Хорватский), Seoul (Норвежский), Seoul (Индонезийский), سئول (Персидский), സോൾ (Малаялам), ಸೌಲ್ (Каннада), សេអ៊ូល (Кхмерский), Soul (Словацкий), Kuri (Французский), Kuri (Испанский), 구리 (Корейский), Saeul, Seoul (Корейский), Ыйджонбу (Белорусский), Кури
Сеул на картах:
Google
OpenStreet
Яндекс
Земля
Ближайшие города
Для загрузки карты выберите соответствующую вкладку.
(карты сразу не загружаются для экономии Вашего трафика и ускорения загрузки)
Ссылки на карты для открытия в новом окне:
Google,
OpenStreet,
Яндекс.
Сеул на карте Республика Корея
Перед вами подробная карта населенного пункта Сеул с указанием названий улиц на русском языке и номерами домов.
Вы легко сможете проложить маршрут, передвигая карту во всех направлениях с помощью мышки.
Вы можете изменить масштаб, воспользовавшись шкалой со значками «+» и «-», расположенной на карте справа. Проще всего регулировать масштаб изображения, вращая колесико мышки.
В какой стране находится Сеул
Сеул расположен в Южная Корея, регион Столичный. Этот город имеет свою историю и традиции.
Географические координаты Сеул: 37.5833 градусов северной широты и 127 градусов восточной долготы.
Виртуальная прогулка
Интерактивная карта Сеул с достопримечательностями и другими туристическими объектами — незаменимый помощник в подготовке самостоятельного путешествия.
В режиме «Карта», значок которой находится в левом верхнем углу, вы можете увидеть план города, а также подробную карту автомобильных дорог с номерами трасс.
Также вы можете увидеть отмеченные на карте ж/д вокзалы и аэропорты города. Рядом вы располагается кнопка «Спутник».
Включив спутниковый режим, Вы рассмотрите рельеф местности, а увеличив изображение, сможете очень подробно изучить город.
Перенесите «человечка» из правого нижнего угла карты на любую улицу города, и вы сможете совершить виртуальную прогулку по Сеул.
Направление движения регулируйте с помощью стрелочек, которые появятся в центре экрана.
Поворачивая колесико мышки, вы сможете приблизить или отдалить изображение.
_
_
_
_
Быстрый переход:
- Все страны.
- Все гео-сервисы.
- Поиск страны, региона, района, города.
- Найти город по названию.
- Купить базу данных городов и скрипты.
- Описание API страны, регионы, города.