Бесплатный переводчик онлайн с русского на английский
Вам нужно переводить на английский сообщения в чатах, письма бизнес-партнерам и в службы поддержки онлайн-магазинов или домашнее задание? PROMT.One мгновенно переведет с русского на английский и еще на 20+ языков.
Точный переводчик
С помощью PROMT.One наслаждайтесь точным переводом с русского на английский, а также смотрите английскую транскрипцию, произношение и варианты переводов слов с примерами употребления в предложениях. Бесплатный онлайн-переводчик PROMT.One — достойная альтернатива Google Translate и другим сервисам, предоставляющим перевод с английского на русский и с русского на английский. Переводите в браузере на персональных компьютерах, ноутбуках, на мобильных устройствах или установите мобильное приложение Переводчик PROMT.One для iOS и Android.
Нужно больше языков?
PROMT.One бесплатно переводит онлайн с русского на азербайджанский, арабский, греческий, иврит, испанский, итальянский, казахский, китайский, корейский, немецкий, португальский, татарский, турецкий, туркменский, узбекский, украинский, финский, французский, эстонский и японский.
This article is about the Japanese prefecture and its city. For other uses, see Tokyo (disambiguation).
|
Tokyo 東京都 |
|
|---|---|
|
Metropolis |
|
| Tokyo Metropolis | |
|
Clockwise from top:
|
|
|
Flag Seal Emblem |
|
| Anthem: «Tokyo Metropolitan Song» (東京都歌, Tōkyō-to Ka) |
|

Interactive map outlining Tokyo |
|

Location within Japan |
|
| Coordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′32″E / 35.68972°N 139.69222°ECoordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′32″E / 35.68972°N 139.69222°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Kantō |
| Island | Honshu |
| Capital | Tokyo[1] |
| Divisions | 23 special wards, 26 cities, 1 district, and 4 subprefectures |
| Government | |
| • Body | Tokyo Metropolitan Government |
| • Governor | Yuriko Koike (Indp.) |
| • Representatives | 42 |
| • Councilors | 11 |
| Area
[2] |
|
| • Total | 2,194.07 km2 (847.14 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 13,452 km2 (5,194 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 45th in Japan |
| Highest elevation
[3] |
2,017 m (6,617 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population
(2022)[4] |
|
| • Total | 13,988,129 |
| • Rank | 1st in Japan |
| • Density | 6,363/km2 (16,480/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 39,105,000 |
| • Metro
[5] |
40,700,000 |
| • Metro density | 3,000/km2 (7,800/sq mi) |
| • Dialects |
|
| Demonym | Tokyoite |
| Gross Regional Product
(2018)[6] |
|
| • Total, nominal | ¥107 trillion |
| • Per capita | ¥7.7 million |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (Japan Standard Time) |
| ISO 3166-2 |
JP-13 |
| Flower | Yoshino cherry |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Bird | Black-headed gull |
| Website | www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp |
Tokyo (;[7] Japanese: 東京, Tōkyō, [toːkʲoː] (listen)), officially the Tokyo Metropolis (東京都, Tōkyō-to), is the capital and most populous city of Japan.[8] Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area (13,452 square kilometers or 5,194 square miles) is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents as of 2018;[9] the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people.[4] Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan’s largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan’s economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan.
Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed «Tokyo» (lit. ‘Eastern Capital’). Tokyo was devastated by the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, and again by Allied bombing raids during World War II. Beginning in the 1950s, the city underwent rapid reconstruction and expansion efforts, going on to lead the Japanese economic miracle. Since 1943, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government has administered the prefecture’s 23 special wards (formerly Tokyo City), various commuter towns and suburbs in its western area, and two outlying island chains known as the Tokyo Islands.
Tokyo is the second-largest urban economy worldwide by gross domestic product after New York City, and is categorized as an Alpha+ city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. It is also Japan’s leading business hub as part of an industrial region that includes the cities of Yokohama, Kawasaki, and Chiba. As of 2021, Tokyo is home to 37 companies of the Fortune Global 500.[10] In 2020, the city ranked fourth on the Global Financial Centres Index, behind only New York City, London, and Shanghai.[11] Tokyo is home to the world’s tallest tower, Tokyo Skytree,[12] and the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility, the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel (located in Kasukabe, Saitama, a suburb of Tokyo).[13] The Tokyo Metro Ginza Line, opened in 1927, is the oldest underground metro line in East Asia.[14] Recognized as one of the most livable cities in the world, Tokyo was tied fourth with Wellington in the 2021 Global Livability Ranking.[15]
The city has hosted multiple international events, including the 1964 Summer Olympics and 1964 Summer Paralympics, the 2020 Summer Olympics and 2020 Summer Paralympics (postponed; held in 2021), and three summits of the G7 (in 1979, 1986, and 1993). Tokyo is an international research and development hub and is likewise represented by several major universities, most notably the University of Tokyo. Tokyo Station is the central hub for Japan’s high-speed railway network, the Shinkansen; Shinjuku Station in Tokyo is also the world’s busiest train station. Notable special wards of Tokyo include: Chiyoda, the site of the National Diet Building and the Tokyo Imperial Palace; Shinjuku, the city’s administrative center; and Shibuya, a commercial, cultural, and business hub.
Etymology[edit]
| Tokyo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tōkyō in kanji |
|||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 東京 | ||||
| Hiragana | とうきょう | ||||
| Katakana | トウキョウ | ||||
| Kyūjitai | 東亰 | ||||
|
Tokyo was originally known as Edo (江戸), a kanji compound of 江 (e, «cove, inlet») and 戸 (to, «entrance, gate, door»).[16] The name, which can be translated as «estuary», is a reference to the original settlement’s location at the meeting of the Sumida River and Tokyo Bay. During the Meiji Restoration in 1868, the name of the city was changed to Tokyo (東京, from 東 tō «east», and 京 kyō «capital»), when it became the new imperial capital,[17] in line with the East Asian tradition of including the word capital (京) in the name of the capital city (for example, Kyoto (京都), Keijō (京城), Beijing (北京), Nanjing (南京), and Xijing (西京)).[16] During the early Meiji period, the city was sometimes called «Tōkei», an alternative pronunciation for the same characters representing «Tokyo», making it a kanji homograph. Some surviving official English documents use the spelling «Tokei»;[18] however, this pronunciation is now obsolete.[19]
History[edit]
Pre-1869 (Edo period)[edit]
Main article: Edo
Tokyo was originally a village called Edo, in what was formerly part of the old Musashi Province. Edo was first fortified by the Edo clan, in the late twelfth century. In 1457, Ōta Dōkan built Edo Castle. In 1590, Tokugawa Ieyasu moved from Mikawa Province (his lifelong base) to the Kantō region. When he became shōgun in 1603, Edo became the center of his ruling. During the subsequent Edo period, Edo grew into one of the largest cities in the world with a population topping one million by the 18th century.[20]
Edo was still the home of the Tokugawa shogunate and not the capital of Japan (the Emperor himself lived in Kyoto almost continuously from 794 to 1868).[21] During the Edo era, the city enjoyed a prolonged period of peace known as the Pax Tokugawa, and in the presence of such peace, the shogunate adopted a stringent policy of seclusion, which helped to perpetuate the lack of any serious military threat to the city.[22] The absence of war-inflicted devastation allowed Edo to devote the majority of its resources to rebuilding in the wake of the consistent fires, earthquakes, and other devastating natural disasters that plagued the city.
This prolonged period of seclusion however came to an end with the arrival of American Commodore Matthew C. Perry in 1853. Commodore Perry forced the opening of the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate, leading to an increase in the demand for new foreign goods and subsequently a severe rise in inflation.[23] Social unrest mounted in the wake of these higher prices and culminated in widespread rebellions and demonstrations, especially in the form of the «smashing» of rice establishments.[24] Meanwhile, supporters of the Emperor leveraged the disruption that these widespread rebellious demonstrations were causing to further consolidate power by overthrowing the last Tokugawa shōgun, Yoshinobu, in 1867.[25] After 265 years, the Pax Tokugawa came to an end.
- Gallery
-
-
Famous Edo Places. Yamanote (above), Nihonbashi (center) and Shitamachi (below), c. 1858.
-
Suruga street with Mount Fuji by Hiroshige (1856)
1869–1943[edit]
Edo was renamed Tokyo (Eastern Capital) on September 3, 1868, as the new government was consolidating its power after the fall of the Edo shogunate. The young Emperor Meiji visited once at the end of that year and eventually moved in in 1869. Tokyo was already the nation’s political center,[26] and the emperor’s residence made it a de facto imperial capital as well, with the former Edo Castle becoming the Imperial Palace. The city of Tokyo was officially established on May 1, 1889.
The Tokyo Metro Ginza Line portion between Ueno and Asakusa was the first subway line built in Japan and East Asia completed on December 30, 1927.[14] Central Tokyo, like Osaka, has been designed since about 1900 to be centered on major railway stations in a high-density fashion, so suburban railways were built relatively cheaply at street level and with their own right-of-way. Though expressways have been built in Tokyo, the basic design has not changed.[citation needed]
Tokyo went on to suffer two major catastrophes in the 20th century: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, which left 140,000 dead or missing; and World War II.[27]
- Gallery
-
The 1870s Chuo-dori terraces in Ginza, Tokyo
-
-
The Ginza area in 1933
-
«The first underground railway in the Orient», Tokyo Underground, opened on December 30, 1927
1943–1945[edit]
In 1943, the city of Tokyo merged with the prefecture of Tokyo to form the «Metropolitan Prefecture» of Tokyo. Since then, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government served as both the prefecture government for Tokyo, as well as administering the special wards of Tokyo, for what had previously been Tokyo City. World War II wreaked widespread destruction of most of the city due to the persistent Allied air raids on Japan and the use of incendiary bombs. The bombing of Tokyo in 1944 and 1945 is estimated to have killed between 75,000 and 200,000 civilians and left more than half of the city destroyed.[28]
The deadliest night of the war came on March 9–10, 1945, the night of the American «Operation Meetinghouse» raid;[29] as nearly 700,000 incendiary bombs rained on the eastern half of the city, mainly in heavily residential wards. Two-fifths of the city were completely burned, more than 276,000 buildings were demolished, 100,000 civilians were killed, and 110,000 more were injured.[30][31] Between 1940 and 1945, the population of Japan’s capital city dwindled from 6,700,000 to less than 2,800,000, with the majority of those who lost their homes living in «ramshackle, makeshift huts».[32]
- Gallery
-
-
The aftermath of the bombing of Tokyo, March 1945
-
Nihonbashi in 1946
1945–present[edit]
After the war, Tokyo became the base from which the United States under Douglas MacArthur administered Japan for six years. Tokyo struggled to rebuild as occupation authorities stepped in and drastically cut back on Japanese government rebuilding programs, focusing instead on simply improving roads and transportation. Tokyo did not experience fast economic growth until the 1950s.[33]
After the occupation of Japan ended in 1952, Tokyo was completely rebuilt and was showcased to the world during the 1964 Summer Olympics. The 1970s and the 1980s brought new high-rise developments. In 1978, Sunshine 60 – the tallest skyscraper in Asia until 1985, and in Japan until 1991 – and Narita International Airport were constructed, and the population increased to about 11 million in the metropolitan area.[35] The Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum has historic Japanese buildings that existed in the urban landscape of pre-war Tokyo.
Tokyo’s subway and commuter rail network became one of the busiest in the world[36] as more and more people moved to the area. In the 1980s, real estate prices skyrocketed during a real estate and debt bubble. The bubble burst in the early 1990s, and many companies, banks, and individuals were caught with mortgage-backed debts while real estate was shrinking in value. A major recession followed, making the 1990s Japan’s «Lost Decade»,[37] from which it is now slowly recovering.
Tokyo still sees new urban developments on large lots of less profitable land. Recent projects include Ebisu Garden Place, Tennōzu Isle, Shiodome, Roppongi Hills, Shinagawa (now also a Shinkansen station), and the Marunouchi side of Tokyo Station. Buildings of significance have been demolished for more up-to-date shopping facilities such as Omotesando Hills.[38]
Land reclamation projects in Tokyo have also been going on for centuries. The most prominent is the Odaiba area, now a major shopping and entertainment center. Various plans have been proposed[39] for transferring national government functions from Tokyo to secondary capitals in other regions of Japan, to slow down rapid development in Tokyo and revitalize economically lagging areas of the country. These plans have been controversial[40] within Japan and have yet to be realized.
The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami that devastated much of the northeastern coast of Honshu was felt in Tokyo. However, due to Tokyo’s earthquake-resistant infrastructure, damage in Tokyo was very minor compared to areas directly hit by the tsunami,[41] although activity in the city was largely halted.[42] The subsequent nuclear crisis caused by the tsunami has also largely left Tokyo unaffected, despite occasional spikes in radiation levels.[43][44]
On September 7, 2013, the IOC selected Tokyo to host the 2020 Summer Olympics. Tokyo thus became the first Asian city to host the Olympic Games twice.[45] However, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the 2020 Olympic Games took place from July 23, 2021, to August 8, 2021. It is also unclear how the city will deal with an increasing number of issues, urging scholars to offer possible alternatives approaches to tackle the most urgent problems.[46] Although, COVID-19 has impeded the growth of many industries, the real estate market in Japan is yet to be negatively impacted. Japanese real estate has become one of the safest investments for foreign investors around the world.[47]
As of 2020, the Greater Tokyo Area is the world’s largest urban area with over 38 million residents, making it as its largest metro area.
- Gallery
-
Sunshine 60, at 239.7 m (786 ft), the tallest building in Asia until 1985, and in Japan until 1991
Geography and government[edit]
A satellite photo of Tokyo in 2018 taken by ESA Sentinel-2
The mainland portion of Tokyo lies northwest of Tokyo Bay and measures about 90 km (56 mi) east to west and 25 km (16 mi) north to south. The average elevation in Tokyo is 40 m (131 ft).[48] Chiba Prefecture borders it to the east, Yamanashi to the west, Kanagawa to the south, and Saitama to the north. Mainland Tokyo is further subdivided into the special wards (occupying the eastern half) and the Tama area (多摩地域) stretching westwards. Tokyo has a latitude of 35.65 (near the 36th parallel north), which makes it more southern than Rome (41.90), Madrid (40.41), New York City (40.71) and Beijing (39.91).[49]
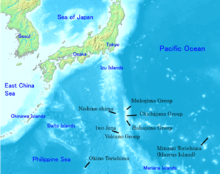
Within the administrative boundaries of Tokyo Metropolis are two island chains in the Pacific Ocean directly south: the Izu Islands, and the Ogasawara Islands, which stretch more than 1,000 km (620 mi) away from the mainland. Because of these islands and the mountainous regions to the west, Tokyo’s overall population density figures far under-represent the real figures for the urban and suburban regions of Tokyo.[50]
Under Japanese law, the prefecture of Tokyo is designated as a to (都), translated as metropolis.[51] Tokyo Prefecture is the most populous prefecture and the densest, with 6,100 inhabitants per square kilometer (16,000/sq mi); by geographic area it is the third-smallest, above only Osaka and Kagawa. Its administrative structure is similar to that of Japan’s other prefectures. The 23 special wards (特別区, tokubetsu-ku), which until 1943 constituted the city of Tokyo, are self-governing municipalities, each having a mayor, a council, and the status of a city.
In addition to these 23 special wards, Tokyo also includes 26 more cities (市 -shi), five towns (町 -chō or machi), and eight villages (村 -son or -mura), each of which has a local government. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers the whole metropolis including the 23 special wards and the cities and towns that constitute the prefecture. It is headed by a publicly elected governor and metropolitan assembly. Its headquarters is in Shinjuku Ward.
Municipalities[edit]
A map with Nishi-Tama District in green
Since 2001, Tokyo consists of 62 municipalities: 23 special wards, 26 cities, 5 towns and 8 villages. Any municipality of Japan has a directly elected mayor and a directly elected assembly, each elected on independent four-year cycles. 23 of Tokyo’s municipalities cover the area that had been Tokyo City until WWII, 30 remain today in the Tama area (former North Tama, West Tama and South Tama districts), 9 on Tokyo’s outlying islands.
- The special wards (特別区, tokubetsu-ku) of Tokyo comprise the area formerly incorporated as Tokyo City. The special wards use the word «city» in their official English name (e.g. Chiyoda City). The wards differ from other cities in having a unique administrative relationship with the prefectural government. Certain municipal functions, such as waterworks, sewerage, and fire-fighting, are handled by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. To pay for the added administrative costs, the prefecture collects municipal taxes, which would usually be levied by the city.[52] The «three central wards» of Tokyo – Chiyoda, Chūō and Minato – are the business core of the city, with a daytime population more than seven times higher than their nighttime population.[53] Chiyoda Ward is unique in that it is in the very heart of the former Tokyo City, yet is one of the least populated wards. It is occupied by many major Japanese companies and is also the seat of the national government, and the Japanese emperor. It is often called the «political center» of the country.[54] Akihabara, known for being an otaku cultural center and a shopping district for computer goods, is also in Chiyoda.
- To the west of the special wards, Tokyo Metropolis consists of cities, towns, and villages that enjoy the same legal status as those elsewhere in Japan. While serving as «bed towns» for those working in central Tokyo, some of them also have a local commercial and industrial base, such as Tachikawa. Collectively, these are often known as the Tama area or Western Tokyo. The far west of the Tama area is occupied by the district (gun) of Nishi-Tama. Much of this area is mountainous and unsuitable for urbanization. The highest mountain in Tokyo, Mount Kumotori, is 2,017 m (6,617 ft) high; other mountains in Tokyo include Takanosu (1,737 m (5,699 ft)), Odake (1,266 m (4,154 ft)), and Mitake (929 m (3,048 ft)). Lake Okutama, on the Tama River near Yamanashi Prefecture, is Tokyo’s largest lake. The district is composed of three towns (Hinode, Mizuho and Okutama) and one village (Hinohara). The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has designated Hachiōji, Tachikawa, Machida, Ōme and Tama New Town as regional centers of the Tama area,[55] as part of its plans to relocate urban functions away from central Tokyo.
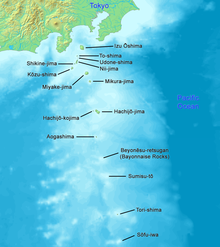
- Tokyo has numerous outlying islands, which extend as far as 1,850 km (1,150 mi) from central Tokyo. Because of the islands’ distance from the administrative headquarters of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government in Shinjuku, local subprefectural branch offices administer them. The Izu Islands are a group of volcanic islands and form part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. The islands in order from closest to Tokyo are Izu Ōshima, Toshima, Nii-jima, Shikine-jima, Kōzu-shima, Miyake-jima, Mikurajima, Hachijō-jima, and Aogashima. The Izu Islands are grouped into three subprefectures. Izu Ōshima and Hachijojima are towns. The remaining islands are six villages, with Niijima and Shikinejima forming one village. The Ogasawara Islands include, from north to south, Chichi-jima, Nishinoshima, Haha-jima, Kita Iwo Jima, Iwo Jima, and Minami Iwo Jima. Ogasawara also administers two tiny outlying islands: Minami Torishima, the easternmost point in Japan and at 1,850 km (1,150 mi) the most distant island from central Tokyo, and Okinotorishima, the southernmost point in Japan.[56] Japan’s claim on an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) surrounding Okinotorishima is contested by China and South Korea as they regard Okinotorishima as uninhabitable rocks which have no EEZ.[57] The Iwo chain and the outlying islands have no permanent population, but hosts Japan Self-Defense Forces personnel. Local populations are only found on Chichi-Jima and Haha-Jima. The islands form both Ogasawara Subprefecture and the village of Ogasawara, Tokyo.
| Flag, name w/o suffix | Full name | District or Subprefecture |
Population | LPE code (w/o checksum) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese | Transcription | Translation | ||||
| 足立区 | Adachi-ku | Adachi Ward | — | 674,067 | 13121 | |
| 荒川区 | Arakawa-ku | Arakawa Ward | 213,648 | 13118 | ||
| 文京区 | Bunkyō-ku | Bunkyō Ward | 223,389 | 13105 | ||
| 千代田区 | Chiyoda-ku | Chiyoda Ward | 59,441 | 13101 | ||
| 中央区 | Chūō-ku | Chūō Ward (Central Ward) |
147,620 | 13102 | ||
| 江戸川区 | Edogawa-ku | Edogawa Ward (Edo River Ward) |
685,899 | 13123 | ||
| 板橋区 | Itabashi-ku | Itabashi Ward | 569,225 | 13119 | ||
| 葛飾区 | Katsushika-ku | Katsushika Ward (after Katsushika District) |
447,140 | 13122 | ||
| 北区 | Kita-ku | Kita Ward (North Ward) |
345,063 | 13117 | ||
| 江東区 | Kōtō-ku | Kōtō Ward | 502,579 | 13108 | ||
| 目黒区 | Meguro-ku | Meguro Ward | 280,283 | 13110 | ||
| 港区 | Minato-ku | Minato Ward (Harbor/Port District) |
248,071 | 13103 | ||
| 中野区 | Nakano-ku | Nakano Ward | 332,902 | 13114 | ||
| 練馬区 | Nerima-ku | Nerima Ward | 726,748 | 13120 | ||
| 大田区 | Ōta-ku | Ōta Ward | 722,608 | 13111 | ||
| 世田谷区 | Setagaya-ku | Setagaya Ward | 910,868 | 13112 | ||
| 渋谷区 | Shibuya-ku | Shibuya Ward | 227,850 | 13113 | ||
| 品川区 | Shinagawa-ku | Shinagawa Ward | 392,492 | 13109 | ||
| 新宿区 | Shinjuku-ku | Shinjuku Ward | 339,211 | 13104 | ||
| 杉並区 | Suginami-ku | Suginami Ward | 570,483 | 13115 | ||
| 墨田区 | Sumida-ku | Sumida Ward | 260,358 | 13107 | ||
| 台東区 | Taitō-ku | Taitō Ward | 200,486 | 13106 | ||
| 豊島区 | Toshima-ku | Toshima Ward (after Toshima District) |
294,673 | 13116 | ||
| あきる野市 | Akiruno-shi | Akiruno City | 80,464 | 13228 | ||
| 昭島市 | Akishima-shi | Akishima City | 111,449 | 13207 | ||
| 調布市 | Chōfu-shi | Chōfu City | 240,668 | 13208 | ||
| 府中市 | Fuchū-shi | Fuchū City (provincial capital city) |
260,891 | 13206 | ||
| 福生市 | Fussa-shi | Fussa City | 58,393 | 13218 | ||
| 八王子市 | Hachiōji-shi | Hachiōji City | 579,330 | 13201 | ||
| 羽村市 | Hamura-shi | Hamura City | 55,596 | 13227 | ||
| 東久留米市 | Higashi-Kurume-shi | Higashi-Kurume City East Kurume City (as opposed to Kurume City, Western Japan) |
116,869 | 13222 | ||
| 東村山市 | Higashi-Murayama-shi | Higashi-Murayama City East Murayama City (after Murayama Region) |
150,984 | 13213 | ||
| 東大和市 | Higashi-Yamato-shi | Higashi-Yamato City (here: Tokyo’s Yamato City)[58] (as opposed to Kanagawa’s Yamato City) |
85,229 | 13220 | ||
| 日野市 | Hino-shi | Hino City | 185,133 | 13212 | ||
| 稲城市 | Inagi-shi | Inagi City | 87,927 | 13225 | ||
| 清瀬市 | Kiyose-shi | Kiyose City | 74,495 | 13221 | ||
| 小平市 | Kodaira-shi | Kodaira City | 194,757 | 13211 | ||
| 小金井市 | Koganei-shi | Koganei City | 121,516 | 13210 | ||
| 国分寺市 | Kokubunji-shi | Kokubunji City (provincial temple city) |
122,787 | 13214 | ||
| 狛江市 | Komae-shi | Komae City | 81,671 | 13219 | ||
| 国立市 | Kunitachi-shi | Kunitachi City | 75,867 | 13215 | ||
| 町田市 | Machida-shi | Machida City | 429,040 | 13209 | ||
| 三鷹市 | Mitaka-shi | Mitaka City | 189,168 | 13204 | ||
| 武蔵村山市 | Musashi-Murayama-shi | Musashi-Murayama City (as opposed to Murayama City, Dewa Province) |
70,649 | 13223 | ||
| 武蔵野市 | Musashino-shi | Musashino City (after Musashino Region) |
143,686 | 13203 | ||
| 西東京市 | Nishi-Tōkyō-shi | Nishi-Tokyo City (Western Tokyo City) |
200,102 | 13229 | ||
| 青梅市 | Ōme-shi | Ōme City | 136,071 | 13205 | ||
| 立川市 | Tachikawa-shi | Tachikawa City | 184,183 | 13202 | ||
| 多摩市 | Tama-shi | Tama City (after Tama district/area/river) |
147,953 | 13224 | ||
| 日の出町 | Hinode-machi | Hinode Town | Nishi-Tama (Western Tama [ja]) |
17,141 | 13305 | |
| 檜原村 | Hinohara-mura | Hinohara Village | 2,194 | 13307 | ||
| 瑞穂町 | Mizuho-machi | Mizuho Town | 33,117 | 13303 | ||
| 奥多摩町 | Okutama-machi | Okutama Town (Rear/Outer Tama Town) |
5,177 | 13308 | ||
| 八丈町 | Hachijō-machi | Hachijō Town (on Hachijō Island) |
Hachijō | 7,516 | 13401 | |
| 青ヶ島村 | Aogashima-mura | Aogashima Village (on Aogashima) |
169 | 13402 | ||
| 三宅村 | Miyake-mura | Miyake Village (on Miyake Island) |
Miyake | 2,451 | 13381 | |
| 御蔵島村 | Mikurajima-mura | Mikurajima Village (Mikura Island Village) |
328 | 13382 | ||
| 大島町 | Ōshima-machi | Ōshima Town ([Izu] Grand Island Town) |
Ōshima | 7,762 | 13361 | |
| 利島村 | Toshima-mura | To-shima Village (on homonymous island) |
309 | 13362 | ||
| 新島村 | Niijima-mura | Niijima Village (on homonymous island) |
2,697 | 13363 | ||
| 神津島村 | Kōzushima-mura | Kōzushima Village (on homonymous island) |
1,856 | 13364 | ||
| 小笠原村 | Ogasawara-mura | Ogasawara Village (on homonymous islands) |
Ogasawara | 3,029 | 13421 | |
| 東京都 | Tōkyō-to | Tokyo «Metropolis» functionally: ~ Prefecture literally/etymologically: ~ Capital |
– | 13,960,236 | 13000 ISO: JP-13 |
-
Tama
-
-
Municipal mergers[edit]
When Tokyo reached its current extent except for smaller border changes in 1893, it consisted of over 170 municipalities, 1 (by definition: district-independent) city, nine districts with their towns and villages, plus the island communities that had never part of ritsuryō[clarification needed] districts. By 1953, the number of municipalities had dropped to 97. The current total of 62 was reached in 2001.
National parks[edit]
Ogasawara National Park, a UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site
As of March 31, 2008, 36% of the total land area of the prefecture was designated as Natural Parks (second only to Shiga Prefecture), namely the Chichibu Tama Kai, Fuji-Hakone-Izu, and Ogasawara National Parks (the last a UNESCO World Heritage Site); Meiji no Mori Takao Quasi-National Park; and Akikawa Kyūryō, Hamura Kusabana Kyūryō, Sayama, Takao Jinba, Takiyama, and Tama Kyūryō Prefectural Natural Parks.[59]
A number of museums are located in Ueno Park: Tokyo National Museum, National Museum of Nature and Science, Shitamachi Museum and National Museum for Western Art, among others. There are also artworks and statues at several places in the park. There is also a zoo in the park, and the park is a popular destination to view cherry blossoms.
Earthquakes[edit]
Minor quakes[edit]
A bilingual sign in Shibuya with instructions (in Japanese and English) in case of an earthquake
Tokyo is near the boundary of three plates, making it an extremely active region for smaller quakes and slippage which frequently affect the urban area with swaying as if in a boat, although epicenters within mainland Tokyo (excluding Tokyo’s 2,000 km (1,243 mi)–long island jurisdiction) are quite rare. It is not uncommon in the metro area to have hundreds of these minor quakes (magnitudes 4–6) that can be felt in a single year, something local residents merely brush off but can be a source of anxiety not only for foreign visitors but for Japanese from elsewhere as well. They rarely cause much damage (sometimes a few injuries) as they are either too small or far away as quakes tend to dance around the region. Particularly active are offshore regions and to a lesser extent Chiba and Ibaraki.[60]
Infrequent powerful quakes[edit]
Tokyo has been hit by powerful megathrust earthquakes in 1703, 1782, 1812, 1855, 1923, and much more indirectly (with some liquefaction in landfill zones) in 2011;[61][62] the frequency of direct and large quakes is a relative rarity. The 1923 earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 8.3, killed 142,000 people, the last time the urban area was directly hit.
Volcanic eruptions[edit]
Mount Fuji is about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Tokyo. There is a low risk of eruption. The last recorded was the Hōei eruption which started on December 16, 1707, and ended about January 1, 1708 (16 days).[63] During the Hōei eruption, the ash amount was 4 cm in southern Tokyo (bay area) and 2 cm to 0.5 cm in central Tokyo.[64] Kanagawa had 16 cm to 8 cm ash and Saitama 0.5 to 0 cm.[64] If the wind blows north-east it could send volcanic ash to Tokyo metropolis.[65] According to the government, less than a millimeter of the volcanic ash from a Mount Fuji eruption could cause power grid problems such as blackouts and stop trains in the Tokyo metropolitan area.[65] A mixture of ash with rain could stick to cellphone antennas, power lines and cause temporary power outages.[65] The affected areas would need to be evacuated.[65]
Water management[edit]
The MAOUDC is the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility.
Tokyo is located on the Kantō Plain with five river systems and dozens of rivers that expand during each season.[66] Important rivers are Edogawa, Nakagawa, Arakawa, Kandagawa, Megurogawa and Tamagawa.[67] In 1947, Typhoon Kathleen struck Tokyo, destroying 31,000 homes and killing 1,100 people.[66] In 1958, Typhoon Ida dropped 400 mm (16 in) of rain in a single week, causing streets to flood.[66] In the 1950s and 1960s, the government invested 6–7% of the national budget on disaster and risk reduction.[66] A huge system of dams, levees and tunnels was constructed.[66] The purpose is to manage heavy rain, typhonic rain, and river floods.[66]
Tokyo has currently the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility called the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel (MAOUDC).[13][66] It took 13 years to build and was completed in 2006. The MAOUDC is a 6.3 km (3.9 mi) long system of tunnels, 22 meters (72 ft) underground, with 70-meter (230 ft) tall cylindrical tanks, each tank being large enough to fit a space shuttle or the Statue of Liberty.[66] During floods, excess water is collected from rivers and drained to the Edo River.[67] Low-lying areas of Kōtō, Edogawa, Sumida, Katsushika, Taitō and Arakawa near the Arakawa River are most at risk of flooding.[67]
Climate[edit]
The former city of Tokyo and the majority of Tokyo prefecture lie in the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen climate classification: Cfa),[68] with hot, humid summers and mild to cool winters with occasional cold spells. The region, like much of Japan, experiences a one-month seasonal lag. The warmest month is August, which averages 26.9 °C (80.4 °F). The coolest month is January, averaging 5.4 °C (41.7 °F). The record low temperature was −9.2 °C (15.4 °F) on January 13, 1876. The record high was 39.5 °C (103.1 °F) on July 20, 2004.
The record highest low temperature is 30.3 °C (86.5 °F), on August 12, 2013, making Tokyo one of only seven observation sites in Japan that have recorded a low temperature over 30 °C (86.0 °F).[69]
Annual rainfall averages nearly 1,600 millimeters (63.0 in), with a wetter summer and a drier winter. The growing season in Tokyo lasts for about 322 days from around mid-February to early January.[70] Snowfall is sporadic, and occurs almost annually.[71] Tokyo often sees typhoons every year, though few are strong. The wettest month since records began in 1876 was October 2004, with 780 millimeters (30 in) of rain,[72] including 270.5 mm (10.65 in) on the ninth of that month.[73] The most recent of four months on record to observe no precipitation is December 1995.[69] Annual precipitation has ranged from 879.5 mm (34.63 in) in 1984 to 2,229.6 mm (87.78 in) in 1938.[69]
| Climate data for Kitanomaru Park, Chiyoda ward, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present[74] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.6 (72.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
39.5 (103.1) |
39.1 (102.4) |
38.1 (100.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.3 (81.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
39.5 (103.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.2 (57.6) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.9 (85.8) |
31.3 (88.3) |
27.5 (81.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
12.0 (53.6) |
20.3 (68.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
23.3 (73.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.7 (45.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
2.1 (35.8) |
5.0 (41.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.5 (74.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
14.8 (58.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.8 (38.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.2 (15.4) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
2.2 (36.0) |
8.5 (47.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 59.7 (2.35) |
56.5 (2.22) |
116.0 (4.57) |
133.7 (5.26) |
139.7 (5.50) |
167.8 (6.61) |
156.2 (6.15) |
154.7 (6.09) |
224.9 (8.85) |
234.8 (9.24) |
96.3 (3.79) |
57.9 (2.28) |
1,598.2 (62.92) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
8 (3.1) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.3 | 6.1 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.1 | 12.8 | 12.0 | 9.4 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 116.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 51 | 52 | 57 | 62 | 68 | 75 | 76 | 74 | 75 | 71 | 64 | 56 | 65 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | −5 (23) |
−4 (25) |
1 (34) |
8 (46) |
13 (55) |
18 (64) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
19 (66) |
12 (54) |
6 (43) |
−1 (30) |
9 (49) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.6 | 170.4 | 175.3 | 178.8 | 179.6 | 124.2 | 151.4 | 174.2 | 126.7 | 129.4 | 149.8 | 174.4 | 1,926.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 61 | 56 | 47 | 45 | 41 | 30 | 34 | 42 | 34 | 37 | 48 | 57 | 44 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source 1: Japan Meteorological Agency[75][76][69] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV),[77] Time and Date (dewpoints, 1985-2015)[78] |
See or edit raw graph data.
Tokyo has experienced significant warming of its climate since temperature records began in 1876.
| Climate data for Tokyo (Tokyo, Japan), 1876–1905 normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.1 (82.6) |
29.8 (85.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.0 (51.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
15.9 (60.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
5.3 (41.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.8 (62.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
18.6 (65.5) |
11.9 (53.4) |
5.4 (41.7) |
0.4 (32.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 55.2 (2.17) |
72.4 (2.85) |
111.0 (4.37) |
129.1 (5.08) |
151.9 (5.98) |
166.3 (6.55) |
139.7 (5.50) |
114.7 (4.52) |
203.3 (8.00) |
184.1 (7.25) |
104.7 (4.12) |
58.7 (2.31) |
1,491.1 (58.7) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 186.7 | 178.5 | 174.1 | 183.1 | 204.8 | 158.5 | 183.9 | 207.0 | 142.8 | 144.0 | 167.4 | 190.8 | 2,121.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[79] |
The western mountainous area of mainland Tokyo, Okutama also lies in the humid subtropical climate (Köppen classification: Cfa).
| Climate data for Ogouchi, Okutama town, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.8 (64.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.3 (97.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
35.0 (95.0) |
30.2 (86.4) |
23.8 (74.8) |
22.8 (73.0) |
36.4 (97.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.6 (45.7) |
10.9 (51.6) |
16.5 (61.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.5 (83.3) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
14.0 (57.2) |
9.3 (48.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
2.2 (36.0) |
5.5 (41.9) |
10.8 (51.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.6 (72.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.3 (57.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.9 (39.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.3 (59.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.1 (68.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.3 (15.3) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
0.7 (33.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
13.2 (55.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49.5 (1.95) |
45.9 (1.81) |
88.5 (3.48) |
106.3 (4.19) |
118.7 (4.67) |
163.2 (6.43) |
205.6 (8.09) |
217.4 (8.56) |
270.2 (10.64) |
215.4 (8.48) |
68.9 (2.71) |
43.7 (1.72) |
1,608 (63.31) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 206.5 | 187.7 | 173.0 | 178.4 | 172.2 | 104.2 | 124.8 | 144.6 | 104.5 | 128.7 | 164.5 | 186.5 | 1,874.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[80][81] |
The climates of Tokyo’s offshore territories vary significantly from those of the city. The climate of Chichijima in Ogasawara village is on the boundary between the tropical savanna climate (Köppen classification: Aw) and the tropical rainforest climate (Köppen classification: Af). It is approximately 1,000 km (621 mi) south of the Greater Tokyo Area, resulting in much different climatic conditions.
| Climate data for Chichijima, Ogasawara, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1896–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
30.1 (86.2) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
33.7 (92.7) |
33.1 (91.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
30.2 (86.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
34.1 (93.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
28.5 (83.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.3 (86.5) |
29.9 (85.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.5 (65.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
26.2 (79.2) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.4 (79.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
20.6 (69.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 15.8 (60.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.4 (70.5) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.1 (79.0) |
25.7 (78.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
21.6 (70.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.2 (70.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.9 (57.0) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.2 (72.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.8 (46.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 63.6 (2.50) |
51.6 (2.03) |
75.8 (2.98) |
113.3 (4.46) |
151.9 (5.98) |
111.8 (4.40) |
79.5 (3.13) |
123.3 (4.85) |
144.2 (5.68) |
141.7 (5.58) |
136.1 (5.36) |
103.3 (4.07) |
1,296.1 (51.02) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 11.0 | 8.5 | 9.8 | 10.0 | 11.8 | 8.8 | 8.6 | 11.3 | 13.4 | 13.7 | 12.0 | 11.2 | 130.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66 | 68 | 72 | 79 | 84 | 86 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 81 | 76 | 70 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 131.3 | 138.3 | 159.2 | 148.3 | 151.8 | 205.6 | 246.8 | 213.7 | 197.7 | 173.2 | 139.1 | 125.3 | 2,030.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[82]
[83] |
Tokyo’s easternmost territory, the island of Minamitorishima in Ogasawara village, is in the tropical savanna climate zone (Köppen classification: Aw). Tokyo’s Izu and Ogasawara islands are affected by an average of 5.4 typhoons a year, compared to 3.1 in mainland Kantō.[84]
Cityscape[edit]
Architecture in Tokyo has largely been shaped by Tokyo’s history. Twice in recent history has the metropolis been left in ruins: first in the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake and later after extensive firebombing in World War II.[85] Because of this, Tokyo’s urban landscape consists mainly of modern and contemporary architecture, and older buildings are scarce.[85] Tokyo features many internationally famous forms of modern architecture including Tokyo International Forum, Asahi Beer Hall, Mode Gakuen Cocoon Tower, NTT Docomo Yoyogi Building and Rainbow Bridge. Tokyo features two distinctive towers: Tokyo Tower and Tokyo Skytree, the latter of which is the tallest tower in both Japan and the world, and the second tallest structure in the world after the Burj Khalifa in Dubai.[12] Mori Building Co started work on Tokyo’s new tallest building which is set to be finished in March 2023. The project will cost 580 billion yen ($5.5 billion).[86]
Tokyo contains numerous parks and gardens. There are four national parks in Tokyo Prefecture, including the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, which includes all of the Izu Islands.
Environment[edit]
Tokyo has enacted a measure to cut greenhouse gases. Governor Shintaro Ishihara created Japan’s first emissions cap system, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emission by a total of 25% by 2020 from the 2000 level.[87] Tokyo is an example of an urban heat island, and the phenomenon is especially serious in its special wards.[88][89] According to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government,[90] the annual mean temperature has increased by about 3 °C (5.4 °F) over the past 100 years. Tokyo has been cited as a «convincing example of the relationship between urban growth and climate».[91]
In 2006, Tokyo enacted the «10 Year Project for Green Tokyo» to be realized by 2016. It set a goal of increasing roadside trees in Tokyo to 1 million (from 480,000), and adding 1,000 ha (2,500 acres) of green space, 88 ha (220 acres) of which will be a new park named «Umi no Mori» (Sea Forest) which will be on a reclaimed island in Tokyo Bay which used to be a landfill.[92] From 2007 to 2010, 436 ha (1,080 acres) of the planned 1,000 ha of green space was created and 220,000 trees were planted, bringing the total to 700,000. As of 2014, roadside trees in Tokyo have increased to 950,000, and a further 300 ha (740 acres) of green space has been added.[93]
Demographics[edit]
Tokyo prefecture population pyramid in 2020
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 590,268 | — |
| 1880 | 712,259 | +20.7% |
| 1890 | 1,389,684 | +95.1% |
| 1900 | 1,580,124 | +13.7% |
| 1910 | 2,202,079 | +39.4% |
| 1920 | 3,699,428 | +68.0% |
| 1925 | 4,485,144 | +21.2% |
| 1930 | 5,408,678 | +20.6% |
| 1935 | 6,369,919 | +17.8% |
| 1940 | 7,354,971 | +15.5% |
| 1945 | 3,488,284 | −52.6% |
| 1950 | 6,277,500 | +80.0% |
| 1955 | 8,037,084 | +28.0% |
| 1960 | 9,683,802 | +20.5% |
| 1965 | 10,869,244 | +12.2% |
| 1970 | 11,408,071 | +5.0% |
| 1975 | 11,673,554 | +2.3% |
| 1980 | 11,618,281 | −0.5% |
| 1985 | 11,829,363 | +1.8% |
| 1990 | 11,855,563 | +0.2% |
| 1995 | 11,773,605 | −0.7% |
| 2000 | 12,064,101 | +2.5% |
| 2005 | 12,576,601 | +4.2% |
| 2010 | 13,159,388 | +4.6% |
| 2015 | 13,515,271 | +2.7% |
| 2020 | 13,982,112 | +3.5% |
As of October 2012, the official intercensal estimate showed 13.506 million people in Tokyo, with 9.214 million living within Tokyo’s 23 wards.[94] During the daytime, the population swells by over 2.5 million as workers and students commute from adjacent areas. This effect is even more pronounced in the three central wards of Chiyoda, Chūō, and Minato, whose collective population as of the 2005 National Census was 326,000 at night, but 2.4 million during the day.[95]
In 1889, the Home Ministry recorded 1,375,937 people in Tokyo City and a total of 1,694,292 people in Tokyo-fu.[96] In the same year, a total of 779 foreign nationals were recorded as residing in Tokyo. The most common nationality was English (209 residents), followed by American (182) and Chinese nationals (137).[97]
|
Tokyo historical population since 1920 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This chart is growth rate of municipalities of Tokyo, Japan. It is estimated by census carried out in 2005 and 2010. Increase 10.0% and over 7.5–9.9% 5.0–7.4% 2.5–4.9% 0.0–2.4% Decrease 0.0–2.4% 2.5–4.9% 5.0–7.4% 7.5–9.9% 10.0% and over |
|
Economy[edit]
Ginza is a popular upscale shopping area in Tokyo.
Tokyo has the largest metropolitan economy in the world. According to a study conducted by PricewaterhouseCoopers, the Greater Tokyo Area (Tokyo–Yokohama, TYO) of 38 million people had a total GDP of $2 trillion in 2012 (at purchasing power parity), which topped that list.
Tokyo is a major international finance center;[99] it houses the headquarters of several of the world’s largest investment banks and insurance companies, and serves as a hub for Japan’s transportation, publishing, electronics and broadcasting industries. During the centralized growth of Japan’s economy following World War II, many large firms moved their headquarters from cities such as Osaka (the historical commercial capital) to Tokyo, in an attempt to take advantage of better access to the government. This trend has begun to slow due to ongoing population growth in Tokyo and the high cost of living there.
Tokyo was rated by the Economist Intelligence Unit as the most expensive (highest cost-of-living) city in the world for 14 years in a row ending in 2006, when it was replaced by Oslo, and later Paris.[100][101]
Tokyo emerged as a leading international financial center (IFC) in the 1960s and has been described as one of the three «command centers» for the world economy, along with New York City and London.[102] In the 2020 Global Financial Centers Index, Tokyo was ranked as having the fourth most competitive financial center in the world (alongside cities such as New York City, London, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, Beijing, San Francisco, Shenzhen and Zurich in the top 10), and second most competitive in Asia (after Shanghai).[11] The Japanese financial market opened up slowly in 1984 and accelerated its internationalization with the «Japanese Big Bang» in 1998.[103] Despite the emergence of Singapore and Hong Kong as competing financial centers, the Tokyo IFC manages to keep a prominent position in Asia. The Tokyo Stock Exchange is Japan’s largest stock exchange, and third largest in the world by market capitalization and fourth largest by share turnover. In 1990 at the end of the Japanese asset price bubble, it accounted for more than 60% of the world stock market value.[104] Tokyo had 8,460 ha (20,900 acres) of agricultural land as of 2003,[105] according to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, placing it last among the nation’s prefectures. The farmland is concentrated in Western Tokyo. Perishables such as vegetables, fruits, and flowers can be conveniently shipped to the markets in the eastern part of the prefecture. Komatsuna and spinach are the most important vegetables; as of 2000, Tokyo supplied 32.5% of the komatsuna sold at its central produce market.[citation needed]
With 36% of its area covered by forest, Tokyo has extensive growths of cryptomeria and Japanese cypress, especially in the mountainous western communities of Akiruno, Ōme, Okutama, Hachiōji, Hinode, and Hinohara. Decreases in the price of timber, increases in the cost of production, and advancing old age among the forestry population have resulted in a decline in Tokyo’s output. In addition, pollen, especially from cryptomeria, is a major allergen for the nearby population centers. Tokyo Bay was once a major source of fish. Most of Tokyo’s fish production comes from the outer islands, such as Izu Ōshima and Hachijō-Jima. Skipjack tuna, nori, and aji are among the ocean products.[106]
Tourism in Tokyo is also a contributor to the economy. In 2006, 4.81 million foreigners and 420 million Japanese visits to Tokyo were made; the economic value of these visits totaled 9.4 trillion yen according to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Many tourists visit the various downtowns, stores, and entertainment districts throughout the neighborhoods of the special wards of Tokyo. Cultural offerings include both omnipresent Japanese pop culture and associated districts such as Shibuya and Harajuku, subcultural attractions such as Studio Ghibli anime center, as well as museums like the Tokyo National Museum, which houses 37% of the country’s artwork national treasures (87/233).
The Toyosu Market in Tokyo is the largest wholesale fish and seafood market in the world since it opened on October 11, 2018.[107] It is also one of the largest wholesale food markets of any kind. It is located in the Toyosu area of Kōtō ward. The Toyosu Market holds strong to the traditions of its predecessor, the Tsukiji Fish Market and Nihonbashi fish market, and serves some 50,000 buyers and sellers every day. Retailers, whole-sellers, auctioneers, and public citizens alike frequent the market, creating a unique microcosm of organized chaos that still continues to fuel the city and its food supply after over four centuries.[108]
Transportation[edit]
Tokyo, which is the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, is Japan’s largest domestic and international hub for rail and ground transportation. However, its airspace has been under the US military’s exclusive control after World War II. Public transportation within Tokyo is dominated by an extensive network of «clean and efficient»[109] trains and subways run by a variety of operators, with buses, monorails and trams playing a secondary feeder role. There are up to 62 electric train lines and more than 900 train stations in Tokyo.[110] Shibuya Crossing is the «world’s busiest pedestrian crossing», with around 3,000 people crossing at a time.[111][112][113]
As a result of World War II, Japanese planes are generally forbidden to fly over Tokyo.[114] Therefore, Japan constructed airports outside Tokyo. Narita International Airport in Chiba Prefecture is the major gateway for international travelers to Japan. Japan’s flag carrier Japan Airlines, as well as All Nippon Airways, have a hub at this airport. Haneda Airport on the reclaimed land at Ōta, offers domestic and international flights. As of 2018, some flight routes into Haneda are permitted through Tokyo airspace.[115]
Various islands governed by Tokyo have their own airports. Hachijō-jima (Hachijojima Airport), Miyakejima (Miyakejima Airport), and Izu Ōshima (Oshima Airport) have services to Tokyo International and other airports.
Rail is the primary mode of transportation in Tokyo,[116] which has the most extensive urban railway network in the world and an equally extensive network of surface lines. JR East operates Tokyo’s largest railway network, including the Yamanote Line loop that circles the center of downtown Tokyo. It operates rail lines in the entire metropolitan area of Tokyo and in the rest of the northeastern part of Honshu. JR East is also responsible for Shinkansen high-speed rail lines.
Two different organizations operate the subway network: the private Tokyo Metro and the governmental Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation. The Metropolitan Government and private carriers operate bus routes and one tram route. Local, regional, and national services are available, with major terminals at the giant railroad stations, including Tokyo, Shinagawa, and Shinjuku.
Expressways link the capital to other points in the Greater Tokyo Area, the Kantō region, and the islands of Kyushu and Shikoku. To build them quickly before the 1964 Summer Olympics, most were constructed above existing roads.[117] Other transportation includes taxis operating in the special wards and the cities and towns. Also, long-distance ferries serve the islands of Tokyo and carry passengers and cargo to domestic and foreign ports.
Education[edit]
Tokyo has many universities, junior colleges, and vocational schools. Many of Japan’s most prestigious universities are in Tokyo, including University of Tokyo, Hitotsubashi University, Meiji University, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Waseda University, Tokyo University of Science, Sophia University, and Keio University.[118] Some of the biggest national universities in Tokyo are:
- Hitotsubashi University
- National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies
- Ochanomizu University
- Tokyo Gakugei University
- Tokyo Institute of Technology
- Tokyo Medical and Dental University
- Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
- Tokyo University of Foreign Studies
- Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology
- Tokyo University of the Arts
- University of Electro-Communications
- University of Tokyo
There is only one non-national public university: Tokyo Metropolitan University. There are also a few universities well known for classes conducted in English and for the teaching of the Japanese language, including the Globis University Graduate School of Management, International Christian University, Sophia University, and Waseda University
Tokyo is also the headquarters of the United Nations University.
Most publicly run kindergartens, elementary schools (years 1 through 6), and junior high (lower secondary) schools (7 through 9) are operated by local wards or municipal offices. Most public senior high (upper secondary) schools in Tokyo are run by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education and are called «Metropolitan High Schools». Tokyo also has many private schools from kindergarten through high school:
Culture[edit]
Tokyo has many museums. In Ueno Park, there is the Tokyo National Museum, the country’s largest museum and specializing in traditional Japanese art; the National Museum of Western Art and Ueno Zoo. Other museums include the National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation in Odaiba; the Edo-Tokyo Museum in Sumida, across the Sumida River from the center of Tokyo; the Nezu Museum in Aoyama; and the National Diet Library, National Archives, and the National Museum of Modern Art, which are near the Imperial Palace.
Tokyo has many theaters for performing arts. These include national and private theaters for traditional forms of Japanese drama. Noteworthy are the National Noh Theatre for noh and the Kabuki-za for Kabuki.[119] Symphony orchestras and other musical organizations perform modern and traditional music. The New National Theater Tokyo in Shibuya is the national center for the performing arts, including opera, ballet, contemporary dance and drama.[120] Tokyo also hosts modern Japanese and international pop, and rock music at venues ranging in size from intimate clubs to internationally known areas such as the Nippon Budokan.
Many different festivals occur throughout Tokyo. Major events include the Sannō at Hie Shrine, the Sanja at Asakusa Shrine, and the biennial Kanda Festivals. The last features a parade with elaborately decorated floats and thousands of people. Annually on the last Saturday of July, an enormous fireworks display over the Sumida River attracts over a million viewers. Once cherry blossoms bloom in spring, many residents gather in Ueno Park, Inokashira Park, and the Shinjuku Gyoen National Garden for picnics under the blossoms.
Harajuku, a neighborhood in Shibuya, is known internationally for its youth style, fashion[121] and cosplay.
Cuisine in Tokyo is internationally acclaimed. In November 2007, Michelin released their first guide for fine dining in Tokyo, awarding 191 stars in total, or about twice as many as Tokyo’s nearest competitor, Paris. As of 2017, 227 restaurants in Tokyo have been awarded (92 in Paris). Twelve establishments were awarded the maximum of three stars (Paris has 10), 54 received two stars, and 161 earned one star.[122]
Sports[edit]
Tokyo, with a diverse array of sports, is home to two professional baseball clubs, the Yomiuri Giants who play at the Tokyo Dome and Tokyo Yakult Swallows at Meiji-Jingu Stadium. The Japan Sumo Association is also headquartered in Tokyo at the Ryōgoku Kokugikan sumo arena where three official sumo tournaments are held annually (in January, May, and September). Soccer clubs in Tokyo include F.C. Tokyo and Tokyo Verdy 1969, both of which play at Ajinomoto Stadium in Chōfu, and FC Machida Zelvia at Nozuta Stadium in Machida. Rugby Union is also played in Tokyo, with multiple Japan Rugby League One clubs based in the city including: Black Rams Tokyo (Setagaya), Tokyo Sungoliath (Fuchū) and Toshiba Brave Lupus Tokyo (Fuchū).
Basketball clubs include the Hitachi SunRockers, Toyota Alvark Tokyo and Tokyo Excellence.
Tokyo hosted the 1964 Summer Olympics, thus becoming the first Asian city to host the Summer Games. The National Stadium, also known as the Olympic Stadium, was host to a number of international sporting events. In 2016, it was to be replaced by the New National Stadium. With a number of world-class sports venues, Tokyo often hosts national and international sporting events such as basketball tournaments, women’s volleyball tournaments, tennis tournaments, swim meets, marathons, rugby union and sevens rugby games, soccer exhibition games, judo, and karate. Tokyo Metropolitan Gymnasium, in Sendagaya, Shibuya, is a large sports complex that includes swimming pools, training rooms, and a large indoor arena. According to Around the Rings, the gymnasium has played host to the October 2011 artistic gymnastics world championships, despite the International Gymnastics Federation’s initial doubt in Tokyo’s ability to host the championships following the March 11 tsunami.[123] Tokyo was also selected to host a number of games for the 2019 Rugby World Cup, and to host the 2020 Summer Olympics and the Paralympics which had to be rescheduled to the summer of 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan.
In popular culture[edit]
Akihabara is the most popular area for fans of anime, manga, and games.
As the largest population center in Japan and the site of the country’s largest broadcasters and studios, Tokyo is frequently the setting for many Japanese movies, television shows, animated series (anime), web comics, light novels, video games, and comic books (manga). In the kaiju (monster movie) genre, landmarks of Tokyo are usually destroyed by giant monsters such as Godzilla and Gamera.
Some Hollywood directors have turned to Tokyo as a backdrop for movies set in Japan. Postwar examples include Tokyo Joe, My Geisha, Tokyo Story and the James Bond film You Only Live Twice; recent examples include Kill Bill, The Fast and the Furious: Tokyo Drift, Lost in Translation, Babel, Inception, The Wolverine and Avengers: Endgame.
Japanese author Haruki Murakami has based some of his novels in Tokyo (including Norwegian Wood), and David Mitchell’s first two novels (number9dream and Ghostwritten) featured the city. Contemporary British painter Carl Randall spent 10 years living in Tokyo as an artist, creating a body of work depicting the city’s crowded streets and public spaces.[124][125][126][127][128]
International relations[edit]
Tokyo is the founding member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21 and is a member of the Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. Tokyo was also a founding member of the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group.
Sister cities and states[edit]
As of 2022, Tokyo has twinning or friendship agreements with the following twelve cities and states:[129]
- New York City, United States (since February 1960)
- Beijing, China (since March 1979)
- Paris, France (since July 1982)[130]
- New South Wales, Australia (since May 1984)
- Seoul, South Korea (since September 1988)
- Jakarta, Indonesia (since October 1989)
- São Paulo State, Brazil (since June 1990)
- Cairo, Egypt (since October 1990)
- Moscow, Russia (since July 1991)
- Berlin, Germany (since May 1994)
- Rome, Italy (since July 1996)
- London, United Kingdom (since October 2015)
Friendship and cooperation agreements[edit]
- Tomsk Oblast, Russia (since May 2015)[131]
- Brussels, Belgium (since October 2016)
- Mumbai, India (since November 2016)
- Los Angeles County, United States (since August 2021)[132]
International academic and scientific research[edit]
Research and development in Japan and the Japanese space program are globally represented by several of Tokyo’s medical and scientific facilities, including the University of Tokyo and other universities in Tokyo, which work in collaboration with many international institutions. Especially with the United States, including NASA and the many private spaceflight companies,[133] Tokyo universities have working relationships with all of the Ivy League institutions (including Harvard and Yale University),[134] along with other research universities and development laboratories, such as Stanford, MIT, and the UC campuses throughout California,[135][136] as well as UNM and Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico.[137][138][139] Other partners worldwide include Oxford University in the United Kingdom,[140] the National University of Singapore in Singapore,[141] the University of Toronto in Canada,[142] and Tsinghua University in China.[143]
See also[edit]
- List of cities proper by population
- List of cities with the most skyscrapers
- List of tallest structures in Tokyo
- List of development projects in Tokyo
- List of largest cities
- List of metropolitan areas in Asia
- List of most expensive cities for expatriate employees
- List of urban agglomerations in Asia
- List of urban areas by population
- Megacity
- Tokyo dialect
- Yamanote and Shitamachi
References[edit]
- ^ 都庁は長野市. Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 12, 2014. Shinjuku is the location of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Office. But Tokyo is not a «municipality». Therefore, for the sake of convenience, the notation of prefectural is «Tokyo».
- ^ «Reiwa 1 nationwide prefectures, cities and towns area statistics (October 1)» (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. December 26, 2019. Archived from the original on April 15, 2020. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- ^ «Mountains of Tokyo Metropolis» (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- ^ a b «Tokyo Loses Population for First Time in 26 Years Amid Pandemic». Bloomberg.com. January 31, 2022. Retrieved May 17, 2022.
- ^ «Major Agglomerations of the World — Population Statistics and Maps».
- ^
«Population economics statistics (Tokyo inner production etc.)» (in Japanese). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Retrieved April 28, 2020. - ^ «Tokyo». Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d. Retrieved January 7, 2022.
- ^ Ōshima, Tadamori (February 23, 2018). 衆議院議員逢坂誠二君提出日本の首都に関する質問に対する答弁書. The House of Representatives, Japan. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
There is no law or regulation that expressly defines Tokyo as the capital. However, we are of the opinion that Tokyo is generally accepted in society to be the capital of Japan.
- ^ Nations, United. «The World’s Cities in 2018» (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ «Global 500». Fortune.
- ^ a b «The Global Financial Centres Index 28» (PDF). Long Finance. September 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ a b «Tokyo – GoJapanGo». Tokyo Attractions – Japanese Lifestyle. Mi Marketing Pty Ltd. Archived from the original on April 26, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ a b «Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel». Archived from the original on September 14, 2018. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ a b Hornyak, Tim (December 16, 2017). «Heart of gold: The Ginza Line celebrates its 90th birthday». Japan Times. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ «The Global Liveability Index 2021» (PDF). The Economist. Retrieved February 5, 2023.
- ^ a b Room, Adrian. Placenames of the World. McFarland & Company (1996), p. 360 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-7864-1814-1.
- ^ US Department of State. (1906). A digest of international law as in diplomatic discussions, treaties and other international agreements (John Bassett Moore, ed.), Volume 5, p. 759 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine; excerpt, «The Mikado, on assuming the exercise of power at Yedo, changed the name of the city to Tokio».
- ^ Fiévé, Nicolas & Paul Waley (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. p. 253.
- ^ 明治東京異聞~トウケイかトウキョウか~東京の読み方 (in Japanese). Tokyo Metropolitan Archives. 2004. Archived from the original on October 6, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ McClain, James, James; et al. (1994). Edo and Paris: Urban Life and the State in the Early Modern Era. p. 13.
- ^ Sorensen, Andre (2004). The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty-First Century. p. 16.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. pp. 33, 55.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. pp. 182–183.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. p. 186.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. p. 188.
- ^ «History of Tokyo». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 12, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ «Tokyo-Yokohama earthquake of 1923». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on June 26, 2015. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ Tipton, Elise K. (2002). Modern Japan: A Social and Political History. Routledge. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-585-45322-4.
- ^ «9 March 1945: Burning the Heart Out of the Enemy». Wired. March 9, 2011. Archived from the original on March 15, 2014. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «1945 Tokyo Firebombing Left Legacy of Terror, Pain». Common Dreams. Archived from the original on January 3, 2015. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- ^ Cybriwsky, Roman (1997). Historical Dictionary of Tokyo. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow. p. 22.
- ^ Hewitt, Kenneth (1983). «Place Annihilation: Area Bombing and the Fate of Urban Places». Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 73 (2): 257–284. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1983.tb01412.x.
- ^ Andre Sorensen. The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty First Century RoutledgeCurzon, 2004. ISBN 0-415-35422-6.
- ^ «Tokyo Narita International Airport (NRT) Airport Information (Tokyo, Japan)». Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ «Rail Transport in The World’s Major Cities» (PDF). Japan Railway and Transport Review. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ Saxonhouse, Gary R.; Stern, Robert M., eds. (2004). Japan’s Lost Decade: Origins, Consequences and Prospects for Recovery. Blackwell Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4051-1917-7.
- ^ Worrall, Julian. «The view from the Hills: Minoru Mori defends the Omotesando Hills development and reveals big plans for Tokyo». Metropolis. Archived from the original on November 19, 2006.
- ^ «Shift of Capital from Tokyo Committee». Japan Productivity Center for Socio-Economic Development. Archived from the original on August 25, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ «Policy Speech by Governor of Tokyo, Shintaro Ishihara at the First Regular Session of the Metropolitan Assembly, 2003». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on November 3, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ «Despite Major Earthquake Zero Tokyo Buildings Collapsed Thanks to Stringent Building Codes». March 11, 2011. Archived from the original on September 12, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^ Williams, Carol J. (March 11, 2011). «Japan earthquake disrupts Tokyo, leaves capital only lightly damaged». Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on December 13, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^
«Tokyo Radiation Levels». Metropolis Magazine. Archived from the original on May 20, 2012. Retrieved April 25, 2012. - ^ «Tokyo radiation levels – daily updates – April». Archived from the original on August 19, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^ «IOC selects Tokyo as host of 2020 Summer Olympic Games». Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ Imai, Heide; Matjaz Ursic (2020). Creativity in Tokyo: Revitalizing a Mature City. Palgrave. ISBN 978-9811566868.
- ^ «Hot Market: Tokyo Residential Real Estate sees Strong Demand in a Tight Market, Prices Surge! – Housing Japan». Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ «Population of Tokyo, Japan». Mongabay. Archived from the original on January 21, 2012. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Tokyo, Japan Geographic Information». Latlong.net. September 2020. Archived from the original on September 14, 2017. Retrieved September 16, 2020.
- ^ «Population of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp. October 2015. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ «Local Government in Japan» (PDF). Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. p. 8. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 23, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^
The Structure of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Archived December 8, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (Tokyo government webpage) - ^ The Population of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government Archived December 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine (Retrieved on July 4, 2009)
- ^ «Pray For Tokyo: Chiyoda». Karis Japan. Archived from the original on July 20, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2015.
- ^ «Development of the Metropolitan Center, Subcenters and New Base». Bureau of Urban Development, Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 23, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ «Ogasawara Islands: World Natural Heritage». Ogasawara Village Industry and Tourist Board. Archived from the original (Adobe Flash) on March 31, 2017. Retrieved June 29, 2018.
- ^ Yoshikawa, Yukie (2005). «Okinotorishima: Just the Tip of the Iceberg». Harvard Asian Quarterly. 9 (4). Archived from the original on November 4, 2013.
- ^ Literally, 東/Higashi- means East; but when Yamato Town was renamed to Higashi-Yamato City in 1970, 東 was meant to represent the 東/Tō- in Tokyo, see Higashi-Yamato City: 市の名称 「東大和」の名称について (Japanese: On the city name «Higashi-Yamato»), retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ «General overview of area figures for Natural Parks by prefecture» (PDF). Ministry of the Environment. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved February 8, 2012.
- ^ Matsu’ura, Ritsuko S. (January 28, 2017). «A short history of Japanese historical seismology: past and the present». Geoscience Letters. 4 (1): 3. Bibcode:2017GSL…..4….3M. doi:10.1186/s40562-017-0069-4 – via BioMed Central.
- ^ Grunewald, Elliot D.; Stein, Ross S. (2006). «A New 1649–1884 Catalog of Destructive Earthquakes near Tokyo and Implications for the Long-term Seismic Process». Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 111 (B12): B12306. Bibcode:2006JGRB..11112306G. doi:10.1029/2005JB004059.
- ^ «A new probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for greater Tokyo» (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ Masato Oyama (March 2007). 宝永四年(1707)噴火 (1707 Eruption). 富士山歴史噴火総解説 (Database of eruptions and other activities of Fuji Volcano, Japan, based on historical records since AD 781) (in Japanese). Shizuoka University. Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- ^ a b https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volcanic-ash-downfall_map_of_Mt.Fuji_Hoei-eruption01.jpg Ashfall distribution map for examining disaster prevention measures (Mt. Fuji Hoei eruption)
- ^ a b c d «Mt Fuji eruption could cripple Tokyo». Nippon TV News 24 Japan. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «The underground cathedral protecting Tokyo from floods». BBC. November 29, 2018. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c «Floods in Tokyo and Safety Tips and Preparation». Plaza Homes. February 28, 2020. Archived from the original on August 14, 2020.
- ^ Peel, M.C., Finlayson, B.L., and McMahon, T.A.: Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification Archived February 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 11, 1633–1644, 2007.
- ^ a b c d 観測史上1~10位の値( 年間を通じての値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 19, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ «Average Weather in Tokyo, Japan, Year Round — Weather Spark».
- ^ «Tokyo observes latest ever 1st snowfall». Archived from the original on March 19, 2007. Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(10月としての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ^ The JMA Tokyo, Tokyo (東京都 東京) station is at 35°41.4′N 139°45.6′E, JMA: 気象統計情報 過去の気象データ検索>都道府県の選択>地点の選択. Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 1, 2018. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ^
気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 18, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2021. - ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on November 2, 2014. Retrieved December 16, 2014.
- ^ «Tokyo, Japan — Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast». Weather Atlas. Yu Media Group. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Climate & Weather Averages in Tokyo». Time and Date. Retrieved August 7, 2022.
- ^ «Station Name: TOKYO WMO Station ID: 47662». Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 7, 2020.
- ^ 気象庁 / 気象統計情報 / 過去の気象データ検索 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値-小河内(東京都). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値-父島(東京都). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 気象統計情報 / 天気予報・台風 / 過去の台風資料 / 台風の統計資料 / 台風の平年値. Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on June 7, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
- ^ a b Hidenobu Jinnai. Tokyo: A Spatial Anthropology. University of California Press (1995), pp. 1–3 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-520-07135-2.
- ^ «Tokyo skyline reaches for new heights with $5.5 billion Mori project». Reuters. August 2, 2019. Archived from the original on August 22, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2019.
- ^ «World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD)». Wbcsd.org. Archived from the original on January 4, 2009. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ Barry, Roger Graham & Richard J. Chorley. Atmosphere, Weather and Climate. Routledge (2003), p. 344 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-415-27170-3.
- ^ Toshiaki Ichinose, Kazuhiro Shimodozono, and Keisuke Hanaki. Impact of anthropogenic heat on urban climate in Tokyo. Atmospheric Environment 33 (1999): 3897–3909.
- ^ «Heat Island Control Measures». kankyo.metro.tokyo.jp. January 6, 2007. Archived from the original on May 24, 2008. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Barry, Roger Graham; Chorley, Richard J. (1987). Atmosphere, Weather and Climate. London: Methuen Publishing. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-416-07152-8.
- ^ «Cool ocean breezes flowing through Tokyo» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 16, 2013. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- ^ «2012 Action Program for Tokyo Vision 2020 – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». Metro.tokyo.jp. Archived from the original on December 9, 2012. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ^ 東京都の人口(推計). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 2, 2018. Retrieved January 17, 2015.
- ^ a b «Population of Tokyo». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on December 23, 2008. Retrieved January 1, 2009.
- ^ 東京府 編 (1890). 東京府統計書. 明治22年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1889)] (in Japanese). Vol. 1. 東京府. pp. 40–41. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) Archived September 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (digital page number 32)
- ^ 東京府 編 (1890). 東京府統計書. 明治22年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1889)] (in Japanese). Vol. 1. 東京府. pp. 66–67. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) Archived September 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (digital page number 46)
- ^ «Tokyo Statistical Yearbook 2018» (Excel 97). Bureau of General Affairs, Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on September 5, 2018. Retrieved September 5, 2018.
- ^
«Financial Centres, All shapes and sizes». The Economist. September 13, 2007. Archived from the original on October 31, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007. - ^ «Top 3 Things to See & Do in Shibuya – Tokyo’s Busiest District». April 13, 2017. Archived from the original on February 5, 2019. Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ^ «The expenses of Japan». The Economist. July 7, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- ^ Sassen, Saskia (2001). The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-07063-6.
- ^ Ito, Takatoshi; Melvin, Michael. «NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES – JAPAN’S BIG BANG AND THE TRANSFORMATION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS» (PDF). www.nber.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 2, 2018. Retrieved February 11, 2019.
- ^ «Tokyo Stock Exchange». Stock-market.in. February 25, 2007. Archived from the original on November 27, 2021. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Horticulture Statistics Team, Production Statistics Division, Statistics and Information Department, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (July 15, 2003). «Statistics on Cultivated Land Area» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 24, 2008. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ «Tokyo Economy — Tokyo Travel Guide». www.tokyo-travelguide.com. Retrieved April 23, 2022.
- ^ Kato, Issei (September 29, 2018). «As Tokyo’s historic Tsukiji market closes, fishmongers mourn». Reuters. Archived from the original on October 3, 2018. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ^ Hannerz, Ulf (2005). «The Fish Market at the Center of the World (Review)». The Journal of Japanese Studies. 31 (2): 428–431. doi:10.1353/jjs.2005.0044. S2CID 143762239.
- ^ «A Country Study: Japan». The Library of Congress. Chapter 2, Neighborhood. Archived from the original on May 26, 2012. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
- ^ «Orientation – Tokyo Travel Guide | Planetyze». Planetyze. Archived from the original on September 10, 2017. Retrieved July 18, 2017.
- ^ 井上恵一朗 (April 22, 2016). 【東京はてな】 渋谷交差点、1回で3千人横断?. 朝日新聞. p. 29.
- ^ 渋谷スクランブル交差点——世界で最もワイルドな交差点にようこそ. CNN.co.jp. August 25, 2019. Archived from the original on September 23, 2020. Retrieved September 26, 2019.
- ^ «The World’s Busiest Pedestrian Crossing». WorldAtlas. March 5, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2020. Retrieved April 13, 2020.
- ^ U.S. military’s Yokota Rapcon airspace is set in six different levels at altitudes between 2,450 and 7,000 meters, stretching over Tokyo and eight other prefectures. Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine Japan Times
- ^ Japan gets approval for new flight routes over Haneda airport using U.S. airspace Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine Japan Times
- ^ Chorus, Paul (2016). «Transit oriented development in Tokyo». Transit Oriented Development: Making it Happen. Routledge. pp. 245–258. ISBN 978-1-317-00732-6.
- ^ «Revamping Tokyo’s expressways could give capital a boost». Yomiuri Shimbun. Archived from the original on November 2, 2012. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ «QS University Rankings: Asia 2016». QS Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. Archived from the original on June 16, 2016. Retrieved June 13, 2016.
- ^ Milner, Rebecca (2013). «Pocket Tokyo.» 4th Edition. Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 978-1-74220-581-6
- ^ Ozaki, Motoki (June 22, 2019). «About us. The Heart Of Performing Arts In Japan». New National Theatre, Tokyo. Archived from the original on June 22, 2019. Retrieved December 7, 2019.
- ^ Perry, Chris (April 25, 2007). Rebels on the Bridge: Subversion, Style, and the New Subculture (Flash) (Report). Self-published (Scribd). Archived from the original on October 14, 2007. Retrieved December 4, 2007.
- ^ «Tokyo ‘top city for good eating’«. BBC News. November 20, 2007. Archived from the original on December 17, 2008. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ «Tokyo Keeps Gymnastics Worlds, Bolsters Olympics Ambitions». Aroundtherings.com. May 23, 2011. Archived from the original on June 1, 2012. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ^ «BBC World Service: World Update. ‘Carl Randall – Painting the faces in Japan’s crowded cities’.», BBC World Service, 2016, archived from the original on December 27, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ «‘Painting the faces in Japan’s crowded cities’.», BBC News – Arts & Entertainment, 2016, archived from the original on February 22, 2017, retrieved July 21, 2018
- ^ ‘Tokyo Portraits by Carl Randall’., The Daiwa Anglo Japanese Foundation, London, 2014, archived from the original on December 21, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ ‘The BP Portrait Awards 2013’., The National Portrait Gallery, London, 2012, archived from the original on February 6, 2017, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ ‘Japan Portraits’., Carl Randall – artist website, 2016, archived from the original on December 21, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ «Sister Cities (States) of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». Archived from the original on June 11, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ^ «Friendship and cooperation agreements». Paris: Marie de Paris. Archived from the original on July 1, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ «Governor of Tomsk Region, Russia, visits Governor Masuzoe». Tokyo Metropolitan Government Official Website. June 15, 2015. Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ Houston, Michael (August 27, 2021). «Tokyo Metropolitan Government signs MoU with 2028 Olympic host City of Los Angeles». Inside the Game. Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ The Space Economy in Figures How Space Contributes to the Global Economy: How Space Contributes to the Global Economy. OECD Publishing. 2019. p. 72. ISBN 978-92-64-80595-8. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Six colleges dominate in research stature». Washington Post. March 27, 2012. Archived from the original on December 25, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Radiation-free stem cell transplants, gene therapy may be within reach». News Center. May 29, 2019. Archived from the original on December 11, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «UTokyo-Berkeley». UTokyo-Berkeley. December 23, 2017. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ Asavanant, W.; Shiozawa, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Charoensombutamon, B.; Emura, H.; Alexander, R. N.; Takeda, S.; Yoshikawa, J. I.; Menicucci, N. C.; Yonezawa, H.; Furusawa, A. (2019). «Generation of time-domain-multiplexed two-dimensional cluster state». Science. 366 (6463): 373–376. arXiv:1903.03918. Bibcode:2019Sci…366..373A. doi:10.1126/science.aay2645. PMID 31624214. S2CID 92979929.
- ^ «Rikkyo University». UNM: Global Education Office. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ United States. Department of Energy (1999). Sandia National Laboratories/New Mexico: Environmental Impact Statement. Sandia National Laboratories/New Mexico: Environmental Impact Statement. p. 166–PA54. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «University of Oxford Japan Office» オックスフォード大学日本事務所. November 30, 2019.
- ^ «The University of Tokyo – National University of Singapore – 1st Joint Symposium – The University of Tokyo». The University of Tokyo. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Exchange: University of Tokyo – University of Toronto». University of Toronto – Learning Abroad. May 5, 2018. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Tsinghua University News». Tsinghua University. July 27, 2018. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
Bibliography[edit]
- Fiévé, Nicolas and Paul Waley. (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 978-0-7007-1409-4; OCLC 51527561
- McClain, James, John M Merriman and Kaoru Ugawa. (1994). Edo and Paris: Urban Life and the State in the Early Modern Era. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-2987-3; OCLC 30157716
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5; OCLC 58053128
- Sorensen, Andre. (2002). The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty First Century. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 978-0-415-22651-6; OCLC 48517502
Further reading[edit]
Guides[edit]
- Bender, Andrew, and Timothy N. Hornyak. Tokyo (City Travel Guide) (2010)
- Mansfield, Stephen. Dk Eyewitness Top 10 Travel Guide: Tokyo (2013)
- Waley, Paul. Tokyo Now and Then: An Explorer’s Guide. (1984). 592 pp
- Yanagihara, Wendy. Lonely Planet Tokyo Encounter
Contemporary[edit]
- Allinson, Gary D. Suburban Tokyo: A Comparative Study in Politics and Social Change. (1979). 258 pp.
- Bestor, Theodore. Neighborhood Tokyo (1989). online edition
- Bestor, Theodore. Tsukiji: The Fish Market at the Centre of the World. (2004) online edition
- Fowler, Edward. San’ya Blues: Labouring Life in Contemporary Tokyo. (1996) ISBN 0-8014-8570-3.
- Friedman, Mildred, ed. Tokyo, Form and Spirit. (1986). 256 pp.
- Jinnai, Hidenobu. Tokyo: A Spatial Anthropology. (1995). 236 pp.
- Jones, Sumie et al. eds. A Tokyo Anthology: Literature from Japan’s Modern Metropolis, 1850–1920 (2017); primary sources excerpt
- Perez, Louis G. Tokyo: Geography, History, and Culture (ABC-CLIO, 2019).
- Reynolds, Jonathan M. «Japan’s Imperial Diet Building: Debate over Construction of a National Identity». Art Journal. 55#3 (1996) pp. 38+.
- Sassen, Saskia. The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo. (1991). 397 pp.
- Sorensen, A. Land Readjustment and Metropolitan Growth: An Examination of Suburban Land Development and Urban Sprawl in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area (2000)
- Taira, J. [re]TOKYO. (2018). San Francisco: ORO Editions. ISBN 978-1-940743-66-0
- Waley, Paul. «Tokyo-as-world-city: Reassessing the Role of Capital and the State in Urban Restructuring». Urban Studies 2007 44(8): 1465–1490. ISSN 0042-0980 Fulltext: Ebsco
External links[edit]
- Official website (in Japanese)
- Official website (in English)
- Go Tokyo travel guide
- Tokyo Convention & Visitors Bureau
Токио — перевод на английский
Токио — город культуры и прогресса…
Tokyo… city of culture and progress…
А эта земля сообщается с Токио?
Is that land connected to Tokyo?
ДОМ В ТОКИО
An Inn in Tokyo
А мы вечером едем экспрессом в Токио.
Tonight, let’s go by express to Tokyo.
Я никогда не представляла Токио таким.
I never imagined Tokyo being like that!
Показать ещё примеры для «tokyo»…
Билл оказал своей Японской протеже идеологическую и финансовую поддержку в её кипящей шекспировскими страстями борьбе с другими кланами Якудза за власть над преступным миром Токио.
Shakespearian-in-magnitude power struggle with the other yakuza clans over who would rule vice in the city of Tokio.
Один билет до Токио, пожалуйста.
One ticket to Tokio, please.
Токио.
How’ve you been, Tokio?
Токио Тацукава. Прошел… вместе с Серидзавой сквозь многое.
Tokio Tatsukawa’s been through a lot with Serizawa.
Показать ещё примеры для «tokio»…
Отправить комментарий
токио
-
1
токио
Sokrat personal > токио
-
2
Токио
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > Токио
-
3
Токио
Русско-английский географический словарь > Токио
-
4
Токио
Новый русско-английский словарь > Токио
-
5
Токио
Новый большой русско-английский словарь > Токио
-
6
Токио
Американизмы. Русско-английский словарь. > Токио
-
7
Токио
Русско-английский синонимический словарь > Токио
-
8
токио
Русско-английский большой базовый словарь > токио
-
9
(the axe) ось Берлин — Рим — Токио
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > (the axe) ось Берлин — Рим — Токио
-
10
(г.) Токио
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > (г.) Токио
-
11
вторая секция фондовых бирж Токио Осаки и Нагои
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > вторая секция фондовых бирж Токио Осаки и Нагои
-
12
вторая секция фондовых бирж Токио, Осаки и Нагои
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > вторая секция фондовых бирж Токио, Осаки и Нагои
-
13
г. Токио
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > г. Токио
-
14
первая секция фондовых бирж Токио Нагои Осаки
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > первая секция фондовых бирж Токио Нагои Осаки
-
15
первая секция фондовых бирж Токио, Нагои, Осаки
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > первая секция фондовых бирж Токио, Нагои, Осаки
-
16
район Токио (Inner central)
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > район Токио (Inner central)
-
17
члены бирж Токио Осаки и Нагои, посредничающие в операциях между другими биржевиками
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > члены бирж Токио Осаки и Нагои, посредничающие в операциях между другими биржевиками
-
18
члены бирж Токио, Осаки и Нагои, посредничающие в операциях между другими биржевиками
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > члены бирж Токио, Осаки и Нагои, посредничающие в операциях между другими биржевиками
-
19
члены бирж токио, Осаки и Нагои
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > члены бирж токио, Осаки и Нагои
-
20
ось Берлин — Рим — Токио
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > ось Берлин — Рим — Токио
Страницы
- Следующая →
- 1
- 2
- 3
См. также в других словарях:
-
Токио — столица Японии. Основан в 1457 г. как замок Эдо. В 1869 г. в Эдо перенесена столица гос ва и город переименован в Токе япон. вост. столица (ср. Сайке зап. столица прежнее название города Киото). Русск. традиц. форма Токио. См. также Киото.… … Географическая энциклопедия
-
Токио — нам часто представляется лихорадочным и напряженным суперсовременным городом с забитыми автомобилями эстакады и пробками на улицах,… … Города мира
-
Токио-га — Tokyo Ga Жанр документальный Режиссёр Вим Вендерс … Википедия
-
Токио — (до 1868 Эдо), столица Японии. Расположена в юго восточной части острова Хонсю, на равнине Канто. в месте впадения pp. Эдогава, Аракава, Сумида и Канто в Токийский залив Тихого океана. Основан в середине XV в. в устье р. Сумида (остров… … Художественная энциклопедия
-
ТОКИО — ТОКИО, столица (с 1869) Японии, на юго востоке острова Хонсю, на равнине Канто, у Токийского залива. Свыше 8 млн. жителей. Один из крупнейших городов мира. В так называемый столичный район (Сютокен) входят города и населенные пункты 4 префектур… … Современная энциклопедия
-
ТОКИО — столица Японии, на юго востоке о. Хонсю, на равнине Канто, у Токийского зал. 8,1 млн. жителей. Население т. н. столичного района (Сютокен) в состав которого входят города и населенные пункты четырех префектур, св. 28 млн. человек (1992). Один из… … Большой Энциклопедический словарь
-
токио — Эдо Словарь русских синонимов. токио сущ., кол во синонимов: 5 • астероид (579) • город … Словарь синонимов
-
Токио — или Тоокео (т. е. восточн. столица) столица Японии, наобширной равнине, при впадении р. Сумидогава в залив Т., у вост. берегаглавного японского о ва Нипон (Хондо). Один из портов, открытых дляиностранной торговли; Гавань мелка, большие суда… … Энциклопедия Брокгауза и Ефрона
-
Токио — У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Токио (значения). Префектура Токио 東京都 Префектура Токио на карте Японии … Википедия
-
Токио — столица Японии, главный экономический и культурный центр страны. Один из крупнейших по численности населения и быстро растущих городов мира. Расположен в юго восточной части острова Хонсю, на равнине Канто, в месте впадения рр. Эдогава,… … Большая советская энциклопедия
-
Токио — столица Японии, на юго востоке острова Хонсю, на равнине Канто, у Токийского залива. 11,8 млн. жителей (1995). Население так называемого столичного района (Сютокен), в состав которого входят города и населённые пункты 4 префектур, свыше 28 млн.… … Энциклопедический словарь
This article is about the Japanese prefecture and its city. For other uses, see Tokyo (disambiguation).
|
Tokyo 東京都 |
|
|---|---|
|
Metropolis |
|
| Tokyo Metropolis | |
|
Clockwise from top:
|
|
|
Flag Seal Emblem |
|
| Anthem: «Tokyo Metropolitan Song» (東京都歌, Tōkyō-to Ka) |
|

Interactive map outlining Tokyo |
|

Location within Japan |
|
| Coordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′32″E / 35.68972°N 139.69222°ECoordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′32″E / 35.68972°N 139.69222°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Kantō |
| Island | Honshu |
| Capital | Tokyo[1] |
| Divisions | 23 special wards, 26 cities, 1 district, and 4 subprefectures |
| Government | |
| • Body | Tokyo Metropolitan Government |
| • Governor | Yuriko Koike (Indp.) |
| • Representatives | 42 |
| • Councilors | 11 |
| Area
[2] |
|
| • Total | 2,194.07 km2 (847.14 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 13,452 km2 (5,194 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 45th in Japan |
| Highest elevation
[3] |
2,017 m (6,617 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population
(2022)[4] |
|
| • Total | 13,988,129 |
| • Rank | 1st in Japan |
| • Density | 6,363/km2 (16,480/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 39,105,000 |
| • Metro
[5] |
40,700,000 |
| • Metro density | 3,000/km2 (7,800/sq mi) |
| • Dialects |
|
| Demonym | Tokyoite |
| Gross Regional Product
(2018)[6] |
|
| • Total, nominal | ¥107 trillion |
| • Per capita | ¥7.7 million |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (Japan Standard Time) |
| ISO 3166-2 |
JP-13 |
| Flower | Yoshino cherry |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Bird | Black-headed gull |
| Website | www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp |
Tokyo (;[7] Japanese: 東京, Tōkyō, [toːkʲoː] (listen)), officially the Tokyo Metropolis (東京都, Tōkyō-to), is the capital and most populous city of Japan.[8] Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area (13,452 square kilometers or 5,194 square miles) is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents as of 2018;[9] the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people.[4] Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan’s largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan’s economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan.
Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed «Tokyo» (lit. ‘Eastern Capital’). Tokyo was devastated by the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, and again by Allied bombing raids during World War II. Beginning in the 1950s, the city underwent rapid reconstruction and expansion efforts, going on to lead the Japanese economic miracle. Since 1943, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government has administered the prefecture’s 23 special wards (formerly Tokyo City), various commuter towns and suburbs in its western area, and two outlying island chains known as the Tokyo Islands.
Tokyo is the second-largest urban economy worldwide by gross domestic product after New York City, and is categorized as an Alpha+ city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. It is also Japan’s leading business hub as part of an industrial region that includes the cities of Yokohama, Kawasaki, and Chiba. As of 2021, Tokyo is home to 37 companies of the Fortune Global 500.[10] In 2020, the city ranked fourth on the Global Financial Centres Index, behind only New York City, London, and Shanghai.[11] Tokyo is home to the world’s tallest tower, Tokyo Skytree,[12] and the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility, the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel (located in Kasukabe, Saitama, a suburb of Tokyo).[13] The Tokyo Metro Ginza Line, opened in 1927, is the oldest underground metro line in East Asia.[14] Recognized as one of the most livable cities in the world, Tokyo was tied fourth with Wellington in the 2021 Global Livability Ranking.[15]
The city has hosted multiple international events, including the 1964 Summer Olympics and 1964 Summer Paralympics, the 2020 Summer Olympics and 2020 Summer Paralympics (postponed; held in 2021), and three summits of the G7 (in 1979, 1986, and 1993). Tokyo is an international research and development hub and is likewise represented by several major universities, most notably the University of Tokyo. Tokyo Station is the central hub for Japan’s high-speed railway network, the Shinkansen; Shinjuku Station in Tokyo is also the world’s busiest train station. Notable special wards of Tokyo include: Chiyoda, the site of the National Diet Building and the Tokyo Imperial Palace; Shinjuku, the city’s administrative center; and Shibuya, a commercial, cultural, and business hub.
Etymology[edit]
| Tokyo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tōkyō in kanji |
|||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 東京 | ||||
| Hiragana | とうきょう | ||||
| Katakana | トウキョウ | ||||
| Kyūjitai | 東亰 | ||||
|
Tokyo was originally known as Edo (江戸), a kanji compound of 江 (e, «cove, inlet») and 戸 (to, «entrance, gate, door»).[16] The name, which can be translated as «estuary», is a reference to the original settlement’s location at the meeting of the Sumida River and Tokyo Bay. During the Meiji Restoration in 1868, the name of the city was changed to Tokyo (東京, from 東 tō «east», and 京 kyō «capital»), when it became the new imperial capital,[17] in line with the East Asian tradition of including the word capital (京) in the name of the capital city (for example, Kyoto (京都), Keijō (京城), Beijing (北京), Nanjing (南京), and Xijing (西京)).[16] During the early Meiji period, the city was sometimes called «Tōkei», an alternative pronunciation for the same characters representing «Tokyo», making it a kanji homograph. Some surviving official English documents use the spelling «Tokei»;[18] however, this pronunciation is now obsolete.[19]
History[edit]
Pre-1869 (Edo period)[edit]
Main article: Edo
Tokyo was originally a village called Edo, in what was formerly part of the old Musashi Province. Edo was first fortified by the Edo clan, in the late twelfth century. In 1457, Ōta Dōkan built Edo Castle. In 1590, Tokugawa Ieyasu moved from Mikawa Province (his lifelong base) to the Kantō region. When he became shōgun in 1603, Edo became the center of his ruling. During the subsequent Edo period, Edo grew into one of the largest cities in the world with a population topping one million by the 18th century.[20]
Edo was still the home of the Tokugawa shogunate and not the capital of Japan (the Emperor himself lived in Kyoto almost continuously from 794 to 1868).[21] During the Edo era, the city enjoyed a prolonged period of peace known as the Pax Tokugawa, and in the presence of such peace, the shogunate adopted a stringent policy of seclusion, which helped to perpetuate the lack of any serious military threat to the city.[22] The absence of war-inflicted devastation allowed Edo to devote the majority of its resources to rebuilding in the wake of the consistent fires, earthquakes, and other devastating natural disasters that plagued the city.
This prolonged period of seclusion however came to an end with the arrival of American Commodore Matthew C. Perry in 1853. Commodore Perry forced the opening of the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate, leading to an increase in the demand for new foreign goods and subsequently a severe rise in inflation.[23] Social unrest mounted in the wake of these higher prices and culminated in widespread rebellions and demonstrations, especially in the form of the «smashing» of rice establishments.[24] Meanwhile, supporters of the Emperor leveraged the disruption that these widespread rebellious demonstrations were causing to further consolidate power by overthrowing the last Tokugawa shōgun, Yoshinobu, in 1867.[25] After 265 years, the Pax Tokugawa came to an end.
- Gallery
-
-
Famous Edo Places. Yamanote (above), Nihonbashi (center) and Shitamachi (below), c. 1858.
-
Suruga street with Mount Fuji by Hiroshige (1856)
1869–1943[edit]
Edo was renamed Tokyo (Eastern Capital) on September 3, 1868, as the new government was consolidating its power after the fall of the Edo shogunate. The young Emperor Meiji visited once at the end of that year and eventually moved in in 1869. Tokyo was already the nation’s political center,[26] and the emperor’s residence made it a de facto imperial capital as well, with the former Edo Castle becoming the Imperial Palace. The city of Tokyo was officially established on May 1, 1889.
The Tokyo Metro Ginza Line portion between Ueno and Asakusa was the first subway line built in Japan and East Asia completed on December 30, 1927.[14] Central Tokyo, like Osaka, has been designed since about 1900 to be centered on major railway stations in a high-density fashion, so suburban railways were built relatively cheaply at street level and with their own right-of-way. Though expressways have been built in Tokyo, the basic design has not changed.[citation needed]
Tokyo went on to suffer two major catastrophes in the 20th century: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, which left 140,000 dead or missing; and World War II.[27]
- Gallery
-
The 1870s Chuo-dori terraces in Ginza, Tokyo
-
-
The Ginza area in 1933
-
«The first underground railway in the Orient», Tokyo Underground, opened on December 30, 1927
1943–1945[edit]
In 1943, the city of Tokyo merged with the prefecture of Tokyo to form the «Metropolitan Prefecture» of Tokyo. Since then, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government served as both the prefecture government for Tokyo, as well as administering the special wards of Tokyo, for what had previously been Tokyo City. World War II wreaked widespread destruction of most of the city due to the persistent Allied air raids on Japan and the use of incendiary bombs. The bombing of Tokyo in 1944 and 1945 is estimated to have killed between 75,000 and 200,000 civilians and left more than half of the city destroyed.[28]
The deadliest night of the war came on March 9–10, 1945, the night of the American «Operation Meetinghouse» raid;[29] as nearly 700,000 incendiary bombs rained on the eastern half of the city, mainly in heavily residential wards. Two-fifths of the city were completely burned, more than 276,000 buildings were demolished, 100,000 civilians were killed, and 110,000 more were injured.[30][31] Between 1940 and 1945, the population of Japan’s capital city dwindled from 6,700,000 to less than 2,800,000, with the majority of those who lost their homes living in «ramshackle, makeshift huts».[32]
- Gallery
-
-
The aftermath of the bombing of Tokyo, March 1945
-
Nihonbashi in 1946
1945–present[edit]
After the war, Tokyo became the base from which the United States under Douglas MacArthur administered Japan for six years. Tokyo struggled to rebuild as occupation authorities stepped in and drastically cut back on Japanese government rebuilding programs, focusing instead on simply improving roads and transportation. Tokyo did not experience fast economic growth until the 1950s.[33]
After the occupation of Japan ended in 1952, Tokyo was completely rebuilt and was showcased to the world during the 1964 Summer Olympics. The 1970s and the 1980s brought new high-rise developments. In 1978, Sunshine 60 – the tallest skyscraper in Asia until 1985, and in Japan until 1991 – and Narita International Airport were constructed, and the population increased to about 11 million in the metropolitan area.[35] The Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum has historic Japanese buildings that existed in the urban landscape of pre-war Tokyo.
Tokyo’s subway and commuter rail network became one of the busiest in the world[36] as more and more people moved to the area. In the 1980s, real estate prices skyrocketed during a real estate and debt bubble. The bubble burst in the early 1990s, and many companies, banks, and individuals were caught with mortgage-backed debts while real estate was shrinking in value. A major recession followed, making the 1990s Japan’s «Lost Decade»,[37] from which it is now slowly recovering.
Tokyo still sees new urban developments on large lots of less profitable land. Recent projects include Ebisu Garden Place, Tennōzu Isle, Shiodome, Roppongi Hills, Shinagawa (now also a Shinkansen station), and the Marunouchi side of Tokyo Station. Buildings of significance have been demolished for more up-to-date shopping facilities such as Omotesando Hills.[38]
Land reclamation projects in Tokyo have also been going on for centuries. The most prominent is the Odaiba area, now a major shopping and entertainment center. Various plans have been proposed[39] for transferring national government functions from Tokyo to secondary capitals in other regions of Japan, to slow down rapid development in Tokyo and revitalize economically lagging areas of the country. These plans have been controversial[40] within Japan and have yet to be realized.
The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami that devastated much of the northeastern coast of Honshu was felt in Tokyo. However, due to Tokyo’s earthquake-resistant infrastructure, damage in Tokyo was very minor compared to areas directly hit by the tsunami,[41] although activity in the city was largely halted.[42] The subsequent nuclear crisis caused by the tsunami has also largely left Tokyo unaffected, despite occasional spikes in radiation levels.[43][44]
On September 7, 2013, the IOC selected Tokyo to host the 2020 Summer Olympics. Tokyo thus became the first Asian city to host the Olympic Games twice.[45] However, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the 2020 Olympic Games took place from July 23, 2021, to August 8, 2021. It is also unclear how the city will deal with an increasing number of issues, urging scholars to offer possible alternatives approaches to tackle the most urgent problems.[46] Although, COVID-19 has impeded the growth of many industries, the real estate market in Japan is yet to be negatively impacted. Japanese real estate has become one of the safest investments for foreign investors around the world.[47]
As of 2020, the Greater Tokyo Area is the world’s largest urban area with over 38 million residents, making it as its largest metro area.
- Gallery
-
Sunshine 60, at 239.7 m (786 ft), the tallest building in Asia until 1985, and in Japan until 1991
Geography and government[edit]
A satellite photo of Tokyo in 2018 taken by ESA Sentinel-2
The mainland portion of Tokyo lies northwest of Tokyo Bay and measures about 90 km (56 mi) east to west and 25 km (16 mi) north to south. The average elevation in Tokyo is 40 m (131 ft).[48] Chiba Prefecture borders it to the east, Yamanashi to the west, Kanagawa to the south, and Saitama to the north. Mainland Tokyo is further subdivided into the special wards (occupying the eastern half) and the Tama area (多摩地域) stretching westwards. Tokyo has a latitude of 35.65 (near the 36th parallel north), which makes it more southern than Rome (41.90), Madrid (40.41), New York City (40.71) and Beijing (39.91).[49]
Within the administrative boundaries of Tokyo Metropolis are two island chains in the Pacific Ocean directly south: the Izu Islands, and the Ogasawara Islands, which stretch more than 1,000 km (620 mi) away from the mainland. Because of these islands and the mountainous regions to the west, Tokyo’s overall population density figures far under-represent the real figures for the urban and suburban regions of Tokyo.[50]
Under Japanese law, the prefecture of Tokyo is designated as a to (都), translated as metropolis.[51] Tokyo Prefecture is the most populous prefecture and the densest, with 6,100 inhabitants per square kilometer (16,000/sq mi); by geographic area it is the third-smallest, above only Osaka and Kagawa. Its administrative structure is similar to that of Japan’s other prefectures. The 23 special wards (特別区, tokubetsu-ku), which until 1943 constituted the city of Tokyo, are self-governing municipalities, each having a mayor, a council, and the status of a city.
In addition to these 23 special wards, Tokyo also includes 26 more cities (市 -shi), five towns (町 -chō or machi), and eight villages (村 -son or -mura), each of which has a local government. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers the whole metropolis including the 23 special wards and the cities and towns that constitute the prefecture. It is headed by a publicly elected governor and metropolitan assembly. Its headquarters is in Shinjuku Ward.
Municipalities[edit]
A map with Nishi-Tama District in green
Since 2001, Tokyo consists of 62 municipalities: 23 special wards, 26 cities, 5 towns and 8 villages. Any municipality of Japan has a directly elected mayor and a directly elected assembly, each elected on independent four-year cycles. 23 of Tokyo’s municipalities cover the area that had been Tokyo City until WWII, 30 remain today in the Tama area (former North Tama, West Tama and South Tama districts), 9 on Tokyo’s outlying islands.
- The special wards (特別区, tokubetsu-ku) of Tokyo comprise the area formerly incorporated as Tokyo City. The special wards use the word «city» in their official English name (e.g. Chiyoda City). The wards differ from other cities in having a unique administrative relationship with the prefectural government. Certain municipal functions, such as waterworks, sewerage, and fire-fighting, are handled by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. To pay for the added administrative costs, the prefecture collects municipal taxes, which would usually be levied by the city.[52] The «three central wards» of Tokyo – Chiyoda, Chūō and Minato – are the business core of the city, with a daytime population more than seven times higher than their nighttime population.[53] Chiyoda Ward is unique in that it is in the very heart of the former Tokyo City, yet is one of the least populated wards. It is occupied by many major Japanese companies and is also the seat of the national government, and the Japanese emperor. It is often called the «political center» of the country.[54] Akihabara, known for being an otaku cultural center and a shopping district for computer goods, is also in Chiyoda.
- To the west of the special wards, Tokyo Metropolis consists of cities, towns, and villages that enjoy the same legal status as those elsewhere in Japan. While serving as «bed towns» for those working in central Tokyo, some of them also have a local commercial and industrial base, such as Tachikawa. Collectively, these are often known as the Tama area or Western Tokyo. The far west of the Tama area is occupied by the district (gun) of Nishi-Tama. Much of this area is mountainous and unsuitable for urbanization. The highest mountain in Tokyo, Mount Kumotori, is 2,017 m (6,617 ft) high; other mountains in Tokyo include Takanosu (1,737 m (5,699 ft)), Odake (1,266 m (4,154 ft)), and Mitake (929 m (3,048 ft)). Lake Okutama, on the Tama River near Yamanashi Prefecture, is Tokyo’s largest lake. The district is composed of three towns (Hinode, Mizuho and Okutama) and one village (Hinohara). The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has designated Hachiōji, Tachikawa, Machida, Ōme and Tama New Town as regional centers of the Tama area,[55] as part of its plans to relocate urban functions away from central Tokyo.
- Tokyo has numerous outlying islands, which extend as far as 1,850 km (1,150 mi) from central Tokyo. Because of the islands’ distance from the administrative headquarters of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government in Shinjuku, local subprefectural branch offices administer them. The Izu Islands are a group of volcanic islands and form part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. The islands in order from closest to Tokyo are Izu Ōshima, Toshima, Nii-jima, Shikine-jima, Kōzu-shima, Miyake-jima, Mikurajima, Hachijō-jima, and Aogashima. The Izu Islands are grouped into three subprefectures. Izu Ōshima and Hachijojima are towns. The remaining islands are six villages, with Niijima and Shikinejima forming one village. The Ogasawara Islands include, from north to south, Chichi-jima, Nishinoshima, Haha-jima, Kita Iwo Jima, Iwo Jima, and Minami Iwo Jima. Ogasawara also administers two tiny outlying islands: Minami Torishima, the easternmost point in Japan and at 1,850 km (1,150 mi) the most distant island from central Tokyo, and Okinotorishima, the southernmost point in Japan.[56] Japan’s claim on an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) surrounding Okinotorishima is contested by China and South Korea as they regard Okinotorishima as uninhabitable rocks which have no EEZ.[57] The Iwo chain and the outlying islands have no permanent population, but hosts Japan Self-Defense Forces personnel. Local populations are only found on Chichi-Jima and Haha-Jima. The islands form both Ogasawara Subprefecture and the village of Ogasawara, Tokyo.
| Flag, name w/o suffix | Full name | District or Subprefecture |
Population | LPE code (w/o checksum) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese | Transcription | Translation | ||||
| 足立区 | Adachi-ku | Adachi Ward | — | 674,067 | 13121 | |
| 荒川区 | Arakawa-ku | Arakawa Ward | 213,648 | 13118 | ||
| 文京区 | Bunkyō-ku | Bunkyō Ward | 223,389 | 13105 | ||
| 千代田区 | Chiyoda-ku | Chiyoda Ward | 59,441 | 13101 | ||
| 中央区 | Chūō-ku | Chūō Ward (Central Ward) |
147,620 | 13102 | ||
| 江戸川区 | Edogawa-ku | Edogawa Ward (Edo River Ward) |
685,899 | 13123 | ||
| 板橋区 | Itabashi-ku | Itabashi Ward | 569,225 | 13119 | ||
| 葛飾区 | Katsushika-ku | Katsushika Ward (after Katsushika District) |
447,140 | 13122 | ||
| 北区 | Kita-ku | Kita Ward (North Ward) |
345,063 | 13117 | ||
| 江東区 | Kōtō-ku | Kōtō Ward | 502,579 | 13108 | ||
| 目黒区 | Meguro-ku | Meguro Ward | 280,283 | 13110 | ||
| 港区 | Minato-ku | Minato Ward (Harbor/Port District) |
248,071 | 13103 | ||
| 中野区 | Nakano-ku | Nakano Ward | 332,902 | 13114 | ||
| 練馬区 | Nerima-ku | Nerima Ward | 726,748 | 13120 | ||
| 大田区 | Ōta-ku | Ōta Ward | 722,608 | 13111 | ||
| 世田谷区 | Setagaya-ku | Setagaya Ward | 910,868 | 13112 | ||
| 渋谷区 | Shibuya-ku | Shibuya Ward | 227,850 | 13113 | ||
| 品川区 | Shinagawa-ku | Shinagawa Ward | 392,492 | 13109 | ||
| 新宿区 | Shinjuku-ku | Shinjuku Ward | 339,211 | 13104 | ||
| 杉並区 | Suginami-ku | Suginami Ward | 570,483 | 13115 | ||
| 墨田区 | Sumida-ku | Sumida Ward | 260,358 | 13107 | ||
| 台東区 | Taitō-ku | Taitō Ward | 200,486 | 13106 | ||
| 豊島区 | Toshima-ku | Toshima Ward (after Toshima District) |
294,673 | 13116 | ||
| あきる野市 | Akiruno-shi | Akiruno City | 80,464 | 13228 | ||
| 昭島市 | Akishima-shi | Akishima City | 111,449 | 13207 | ||
| 調布市 | Chōfu-shi | Chōfu City | 240,668 | 13208 | ||
| 府中市 | Fuchū-shi | Fuchū City (provincial capital city) |
260,891 | 13206 | ||
| 福生市 | Fussa-shi | Fussa City | 58,393 | 13218 | ||
| 八王子市 | Hachiōji-shi | Hachiōji City | 579,330 | 13201 | ||
| 羽村市 | Hamura-shi | Hamura City | 55,596 | 13227 | ||
| 東久留米市 | Higashi-Kurume-shi | Higashi-Kurume City East Kurume City (as opposed to Kurume City, Western Japan) |
116,869 | 13222 | ||
| 東村山市 | Higashi-Murayama-shi | Higashi-Murayama City East Murayama City (after Murayama Region) |
150,984 | 13213 | ||
| 東大和市 | Higashi-Yamato-shi | Higashi-Yamato City (here: Tokyo’s Yamato City)[58] (as opposed to Kanagawa’s Yamato City) |
85,229 | 13220 | ||
| 日野市 | Hino-shi | Hino City | 185,133 | 13212 | ||
| 稲城市 | Inagi-shi | Inagi City | 87,927 | 13225 | ||
| 清瀬市 | Kiyose-shi | Kiyose City | 74,495 | 13221 | ||
| 小平市 | Kodaira-shi | Kodaira City | 194,757 | 13211 | ||
| 小金井市 | Koganei-shi | Koganei City | 121,516 | 13210 | ||
| 国分寺市 | Kokubunji-shi | Kokubunji City (provincial temple city) |
122,787 | 13214 | ||
| 狛江市 | Komae-shi | Komae City | 81,671 | 13219 | ||
| 国立市 | Kunitachi-shi | Kunitachi City | 75,867 | 13215 | ||
| 町田市 | Machida-shi | Machida City | 429,040 | 13209 | ||
| 三鷹市 | Mitaka-shi | Mitaka City | 189,168 | 13204 | ||
| 武蔵村山市 | Musashi-Murayama-shi | Musashi-Murayama City (as opposed to Murayama City, Dewa Province) |
70,649 | 13223 | ||
| 武蔵野市 | Musashino-shi | Musashino City (after Musashino Region) |
143,686 | 13203 | ||
| 西東京市 | Nishi-Tōkyō-shi | Nishi-Tokyo City (Western Tokyo City) |
200,102 | 13229 | ||
| 青梅市 | Ōme-shi | Ōme City | 136,071 | 13205 | ||
| 立川市 | Tachikawa-shi | Tachikawa City | 184,183 | 13202 | ||
| 多摩市 | Tama-shi | Tama City (after Tama district/area/river) |
147,953 | 13224 | ||
| 日の出町 | Hinode-machi | Hinode Town | Nishi-Tama (Western Tama [ja]) |
17,141 | 13305 | |
| 檜原村 | Hinohara-mura | Hinohara Village | 2,194 | 13307 | ||
| 瑞穂町 | Mizuho-machi | Mizuho Town | 33,117 | 13303 | ||
| 奥多摩町 | Okutama-machi | Okutama Town (Rear/Outer Tama Town) |
5,177 | 13308 | ||
| 八丈町 | Hachijō-machi | Hachijō Town (on Hachijō Island) |
Hachijō | 7,516 | 13401 | |
| 青ヶ島村 | Aogashima-mura | Aogashima Village (on Aogashima) |
169 | 13402 | ||
| 三宅村 | Miyake-mura | Miyake Village (on Miyake Island) |
Miyake | 2,451 | 13381 | |
| 御蔵島村 | Mikurajima-mura | Mikurajima Village (Mikura Island Village) |
328 | 13382 | ||
| 大島町 | Ōshima-machi | Ōshima Town ([Izu] Grand Island Town) |
Ōshima | 7,762 | 13361 | |
| 利島村 | Toshima-mura | To-shima Village (on homonymous island) |
309 | 13362 | ||
| 新島村 | Niijima-mura | Niijima Village (on homonymous island) |
2,697 | 13363 | ||
| 神津島村 | Kōzushima-mura | Kōzushima Village (on homonymous island) |
1,856 | 13364 | ||
| 小笠原村 | Ogasawara-mura | Ogasawara Village (on homonymous islands) |
Ogasawara | 3,029 | 13421 | |
| 東京都 | Tōkyō-to | Tokyo «Metropolis» functionally: ~ Prefecture literally/etymologically: ~ Capital |
– | 13,960,236 | 13000 ISO: JP-13 |
-
Tama
-
-
Municipal mergers[edit]
When Tokyo reached its current extent except for smaller border changes in 1893, it consisted of over 170 municipalities, 1 (by definition: district-independent) city, nine districts with their towns and villages, plus the island communities that had never part of ritsuryō[clarification needed] districts. By 1953, the number of municipalities had dropped to 97. The current total of 62 was reached in 2001.
National parks[edit]
Ogasawara National Park, a UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site
As of March 31, 2008, 36% of the total land area of the prefecture was designated as Natural Parks (second only to Shiga Prefecture), namely the Chichibu Tama Kai, Fuji-Hakone-Izu, and Ogasawara National Parks (the last a UNESCO World Heritage Site); Meiji no Mori Takao Quasi-National Park; and Akikawa Kyūryō, Hamura Kusabana Kyūryō, Sayama, Takao Jinba, Takiyama, and Tama Kyūryō Prefectural Natural Parks.[59]
A number of museums are located in Ueno Park: Tokyo National Museum, National Museum of Nature and Science, Shitamachi Museum and National Museum for Western Art, among others. There are also artworks and statues at several places in the park. There is also a zoo in the park, and the park is a popular destination to view cherry blossoms.
Earthquakes[edit]
Minor quakes[edit]
A bilingual sign in Shibuya with instructions (in Japanese and English) in case of an earthquake
Tokyo is near the boundary of three plates, making it an extremely active region for smaller quakes and slippage which frequently affect the urban area with swaying as if in a boat, although epicenters within mainland Tokyo (excluding Tokyo’s 2,000 km (1,243 mi)–long island jurisdiction) are quite rare. It is not uncommon in the metro area to have hundreds of these minor quakes (magnitudes 4–6) that can be felt in a single year, something local residents merely brush off but can be a source of anxiety not only for foreign visitors but for Japanese from elsewhere as well. They rarely cause much damage (sometimes a few injuries) as they are either too small or far away as quakes tend to dance around the region. Particularly active are offshore regions and to a lesser extent Chiba and Ibaraki.[60]
Infrequent powerful quakes[edit]
Tokyo has been hit by powerful megathrust earthquakes in 1703, 1782, 1812, 1855, 1923, and much more indirectly (with some liquefaction in landfill zones) in 2011;[61][62] the frequency of direct and large quakes is a relative rarity. The 1923 earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 8.3, killed 142,000 people, the last time the urban area was directly hit.
Volcanic eruptions[edit]
Mount Fuji is about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Tokyo. There is a low risk of eruption. The last recorded was the Hōei eruption which started on December 16, 1707, and ended about January 1, 1708 (16 days).[63] During the Hōei eruption, the ash amount was 4 cm in southern Tokyo (bay area) and 2 cm to 0.5 cm in central Tokyo.[64] Kanagawa had 16 cm to 8 cm ash and Saitama 0.5 to 0 cm.[64] If the wind blows north-east it could send volcanic ash to Tokyo metropolis.[65] According to the government, less than a millimeter of the volcanic ash from a Mount Fuji eruption could cause power grid problems such as blackouts and stop trains in the Tokyo metropolitan area.[65] A mixture of ash with rain could stick to cellphone antennas, power lines and cause temporary power outages.[65] The affected areas would need to be evacuated.[65]
Water management[edit]
The MAOUDC is the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility.
Tokyo is located on the Kantō Plain with five river systems and dozens of rivers that expand during each season.[66] Important rivers are Edogawa, Nakagawa, Arakawa, Kandagawa, Megurogawa and Tamagawa.[67] In 1947, Typhoon Kathleen struck Tokyo, destroying 31,000 homes and killing 1,100 people.[66] In 1958, Typhoon Ida dropped 400 mm (16 in) of rain in a single week, causing streets to flood.[66] In the 1950s and 1960s, the government invested 6–7% of the national budget on disaster and risk reduction.[66] A huge system of dams, levees and tunnels was constructed.[66] The purpose is to manage heavy rain, typhonic rain, and river floods.[66]
Tokyo has currently the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility called the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel (MAOUDC).[13][66] It took 13 years to build and was completed in 2006. The MAOUDC is a 6.3 km (3.9 mi) long system of tunnels, 22 meters (72 ft) underground, with 70-meter (230 ft) tall cylindrical tanks, each tank being large enough to fit a space shuttle or the Statue of Liberty.[66] During floods, excess water is collected from rivers and drained to the Edo River.[67] Low-lying areas of Kōtō, Edogawa, Sumida, Katsushika, Taitō and Arakawa near the Arakawa River are most at risk of flooding.[67]
Climate[edit]
The former city of Tokyo and the majority of Tokyo prefecture lie in the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen climate classification: Cfa),[68] with hot, humid summers and mild to cool winters with occasional cold spells. The region, like much of Japan, experiences a one-month seasonal lag. The warmest month is August, which averages 26.9 °C (80.4 °F). The coolest month is January, averaging 5.4 °C (41.7 °F). The record low temperature was −9.2 °C (15.4 °F) on January 13, 1876. The record high was 39.5 °C (103.1 °F) on July 20, 2004.
The record highest low temperature is 30.3 °C (86.5 °F), on August 12, 2013, making Tokyo one of only seven observation sites in Japan that have recorded a low temperature over 30 °C (86.0 °F).[69]
Annual rainfall averages nearly 1,600 millimeters (63.0 in), with a wetter summer and a drier winter. The growing season in Tokyo lasts for about 322 days from around mid-February to early January.[70] Snowfall is sporadic, and occurs almost annually.[71] Tokyo often sees typhoons every year, though few are strong. The wettest month since records began in 1876 was October 2004, with 780 millimeters (30 in) of rain,[72] including 270.5 mm (10.65 in) on the ninth of that month.[73] The most recent of four months on record to observe no precipitation is December 1995.[69] Annual precipitation has ranged from 879.5 mm (34.63 in) in 1984 to 2,229.6 mm (87.78 in) in 1938.[69]
| Climate data for Kitanomaru Park, Chiyoda ward, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present[74] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.6 (72.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
39.5 (103.1) |
39.1 (102.4) |
38.1 (100.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.3 (81.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
39.5 (103.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.2 (57.6) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.9 (85.8) |
31.3 (88.3) |
27.5 (81.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
12.0 (53.6) |
20.3 (68.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
23.3 (73.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.7 (45.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
2.1 (35.8) |
5.0 (41.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.5 (74.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
14.8 (58.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.8 (38.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.2 (15.4) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
2.2 (36.0) |
8.5 (47.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 59.7 (2.35) |
56.5 (2.22) |
116.0 (4.57) |
133.7 (5.26) |
139.7 (5.50) |
167.8 (6.61) |
156.2 (6.15) |
154.7 (6.09) |
224.9 (8.85) |
234.8 (9.24) |
96.3 (3.79) |
57.9 (2.28) |
1,598.2 (62.92) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
8 (3.1) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.3 | 6.1 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.1 | 12.8 | 12.0 | 9.4 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 116.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 51 | 52 | 57 | 62 | 68 | 75 | 76 | 74 | 75 | 71 | 64 | 56 | 65 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | −5 (23) |
−4 (25) |
1 (34) |
8 (46) |
13 (55) |
18 (64) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
19 (66) |
12 (54) |
6 (43) |
−1 (30) |
9 (49) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.6 | 170.4 | 175.3 | 178.8 | 179.6 | 124.2 | 151.4 | 174.2 | 126.7 | 129.4 | 149.8 | 174.4 | 1,926.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 61 | 56 | 47 | 45 | 41 | 30 | 34 | 42 | 34 | 37 | 48 | 57 | 44 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source 1: Japan Meteorological Agency[75][76][69] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV),[77] Time and Date (dewpoints, 1985-2015)[78] |
See or edit raw graph data.
Tokyo has experienced significant warming of its climate since temperature records began in 1876.
| Climate data for Tokyo (Tokyo, Japan), 1876–1905 normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.1 (82.6) |
29.8 (85.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.0 (51.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
15.9 (60.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
5.3 (41.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.8 (62.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
18.6 (65.5) |
11.9 (53.4) |
5.4 (41.7) |
0.4 (32.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 55.2 (2.17) |
72.4 (2.85) |
111.0 (4.37) |
129.1 (5.08) |
151.9 (5.98) |
166.3 (6.55) |
139.7 (5.50) |
114.7 (4.52) |
203.3 (8.00) |
184.1 (7.25) |
104.7 (4.12) |
58.7 (2.31) |
1,491.1 (58.7) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 186.7 | 178.5 | 174.1 | 183.1 | 204.8 | 158.5 | 183.9 | 207.0 | 142.8 | 144.0 | 167.4 | 190.8 | 2,121.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[79] |
The western mountainous area of mainland Tokyo, Okutama also lies in the humid subtropical climate (Köppen classification: Cfa).
| Climate data for Ogouchi, Okutama town, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.8 (64.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.3 (97.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
35.0 (95.0) |
30.2 (86.4) |
23.8 (74.8) |
22.8 (73.0) |
36.4 (97.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.6 (45.7) |
10.9 (51.6) |
16.5 (61.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.5 (83.3) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
14.0 (57.2) |
9.3 (48.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
2.2 (36.0) |
5.5 (41.9) |
10.8 (51.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.6 (72.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.3 (57.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.9 (39.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.3 (59.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.1 (68.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.3 (15.3) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
0.7 (33.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
13.2 (55.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49.5 (1.95) |
45.9 (1.81) |
88.5 (3.48) |
106.3 (4.19) |
118.7 (4.67) |
163.2 (6.43) |
205.6 (8.09) |
217.4 (8.56) |
270.2 (10.64) |
215.4 (8.48) |
68.9 (2.71) |
43.7 (1.72) |
1,608 (63.31) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 206.5 | 187.7 | 173.0 | 178.4 | 172.2 | 104.2 | 124.8 | 144.6 | 104.5 | 128.7 | 164.5 | 186.5 | 1,874.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[80][81] |
The climates of Tokyo’s offshore territories vary significantly from those of the city. The climate of Chichijima in Ogasawara village is on the boundary between the tropical savanna climate (Köppen classification: Aw) and the tropical rainforest climate (Köppen classification: Af). It is approximately 1,000 km (621 mi) south of the Greater Tokyo Area, resulting in much different climatic conditions.
| Climate data for Chichijima, Ogasawara, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1896–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
30.1 (86.2) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
33.7 (92.7) |
33.1 (91.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
30.2 (86.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
34.1 (93.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
28.5 (83.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.3 (86.5) |
29.9 (85.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.5 (65.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
26.2 (79.2) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.4 (79.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
20.6 (69.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 15.8 (60.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.4 (70.5) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.1 (79.0) |
25.7 (78.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
21.6 (70.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.2 (70.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.9 (57.0) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.2 (72.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.8 (46.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 63.6 (2.50) |
51.6 (2.03) |
75.8 (2.98) |
113.3 (4.46) |
151.9 (5.98) |
111.8 (4.40) |
79.5 (3.13) |
123.3 (4.85) |
144.2 (5.68) |
141.7 (5.58) |
136.1 (5.36) |
103.3 (4.07) |
1,296.1 (51.02) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 11.0 | 8.5 | 9.8 | 10.0 | 11.8 | 8.8 | 8.6 | 11.3 | 13.4 | 13.7 | 12.0 | 11.2 | 130.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66 | 68 | 72 | 79 | 84 | 86 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 81 | 76 | 70 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 131.3 | 138.3 | 159.2 | 148.3 | 151.8 | 205.6 | 246.8 | 213.7 | 197.7 | 173.2 | 139.1 | 125.3 | 2,030.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[82]
[83] |
Tokyo’s easternmost territory, the island of Minamitorishima in Ogasawara village, is in the tropical savanna climate zone (Köppen classification: Aw). Tokyo’s Izu and Ogasawara islands are affected by an average of 5.4 typhoons a year, compared to 3.1 in mainland Kantō.[84]
Cityscape[edit]
Architecture in Tokyo has largely been shaped by Tokyo’s history. Twice in recent history has the metropolis been left in ruins: first in the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake and later after extensive firebombing in World War II.[85] Because of this, Tokyo’s urban landscape consists mainly of modern and contemporary architecture, and older buildings are scarce.[85] Tokyo features many internationally famous forms of modern architecture including Tokyo International Forum, Asahi Beer Hall, Mode Gakuen Cocoon Tower, NTT Docomo Yoyogi Building and Rainbow Bridge. Tokyo features two distinctive towers: Tokyo Tower and Tokyo Skytree, the latter of which is the tallest tower in both Japan and the world, and the second tallest structure in the world after the Burj Khalifa in Dubai.[12] Mori Building Co started work on Tokyo’s new tallest building which is set to be finished in March 2023. The project will cost 580 billion yen ($5.5 billion).[86]
Tokyo contains numerous parks and gardens. There are four national parks in Tokyo Prefecture, including the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, which includes all of the Izu Islands.
Environment[edit]
Tokyo has enacted a measure to cut greenhouse gases. Governor Shintaro Ishihara created Japan’s first emissions cap system, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emission by a total of 25% by 2020 from the 2000 level.[87] Tokyo is an example of an urban heat island, and the phenomenon is especially serious in its special wards.[88][89] According to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government,[90] the annual mean temperature has increased by about 3 °C (5.4 °F) over the past 100 years. Tokyo has been cited as a «convincing example of the relationship between urban growth and climate».[91]
In 2006, Tokyo enacted the «10 Year Project for Green Tokyo» to be realized by 2016. It set a goal of increasing roadside trees in Tokyo to 1 million (from 480,000), and adding 1,000 ha (2,500 acres) of green space, 88 ha (220 acres) of which will be a new park named «Umi no Mori» (Sea Forest) which will be on a reclaimed island in Tokyo Bay which used to be a landfill.[92] From 2007 to 2010, 436 ha (1,080 acres) of the planned 1,000 ha of green space was created and 220,000 trees were planted, bringing the total to 700,000. As of 2014, roadside trees in Tokyo have increased to 950,000, and a further 300 ha (740 acres) of green space has been added.[93]
Demographics[edit]
Tokyo prefecture population pyramid in 2020
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 590,268 | — |
| 1880 | 712,259 | +20.7% |
| 1890 | 1,389,684 | +95.1% |
| 1900 | 1,580,124 | +13.7% |
| 1910 | 2,202,079 | +39.4% |
| 1920 | 3,699,428 | +68.0% |
| 1925 | 4,485,144 | +21.2% |
| 1930 | 5,408,678 | +20.6% |
| 1935 | 6,369,919 | +17.8% |
| 1940 | 7,354,971 | +15.5% |
| 1945 | 3,488,284 | −52.6% |
| 1950 | 6,277,500 | +80.0% |
| 1955 | 8,037,084 | +28.0% |
| 1960 | 9,683,802 | +20.5% |
| 1965 | 10,869,244 | +12.2% |
| 1970 | 11,408,071 | +5.0% |
| 1975 | 11,673,554 | +2.3% |
| 1980 | 11,618,281 | −0.5% |
| 1985 | 11,829,363 | +1.8% |
| 1990 | 11,855,563 | +0.2% |
| 1995 | 11,773,605 | −0.7% |
| 2000 | 12,064,101 | +2.5% |
| 2005 | 12,576,601 | +4.2% |
| 2010 | 13,159,388 | +4.6% |
| 2015 | 13,515,271 | +2.7% |
| 2020 | 13,982,112 | +3.5% |
As of October 2012, the official intercensal estimate showed 13.506 million people in Tokyo, with 9.214 million living within Tokyo’s 23 wards.[94] During the daytime, the population swells by over 2.5 million as workers and students commute from adjacent areas. This effect is even more pronounced in the three central wards of Chiyoda, Chūō, and Minato, whose collective population as of the 2005 National Census was 326,000 at night, but 2.4 million during the day.[95]
In 1889, the Home Ministry recorded 1,375,937 people in Tokyo City and a total of 1,694,292 people in Tokyo-fu.[96] In the same year, a total of 779 foreign nationals were recorded as residing in Tokyo. The most common nationality was English (209 residents), followed by American (182) and Chinese nationals (137).[97]
|
Tokyo historical population since 1920 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This chart is growth rate of municipalities of Tokyo, Japan. It is estimated by census carried out in 2005 and 2010. Increase 10.0% and over 7.5–9.9% 5.0–7.4% 2.5–4.9% 0.0–2.4% Decrease 0.0–2.4% 2.5–4.9% 5.0–7.4% 7.5–9.9% 10.0% and over |
|
Economy[edit]
Ginza is a popular upscale shopping area in Tokyo.
Tokyo has the largest metropolitan economy in the world. According to a study conducted by PricewaterhouseCoopers, the Greater Tokyo Area (Tokyo–Yokohama, TYO) of 38 million people had a total GDP of $2 trillion in 2012 (at purchasing power parity), which topped that list.
Tokyo is a major international finance center;[99] it houses the headquarters of several of the world’s largest investment banks and insurance companies, and serves as a hub for Japan’s transportation, publishing, electronics and broadcasting industries. During the centralized growth of Japan’s economy following World War II, many large firms moved their headquarters from cities such as Osaka (the historical commercial capital) to Tokyo, in an attempt to take advantage of better access to the government. This trend has begun to slow due to ongoing population growth in Tokyo and the high cost of living there.
Tokyo was rated by the Economist Intelligence Unit as the most expensive (highest cost-of-living) city in the world for 14 years in a row ending in 2006, when it was replaced by Oslo, and later Paris.[100][101]
Tokyo emerged as a leading international financial center (IFC) in the 1960s and has been described as one of the three «command centers» for the world economy, along with New York City and London.[102] In the 2020 Global Financial Centers Index, Tokyo was ranked as having the fourth most competitive financial center in the world (alongside cities such as New York City, London, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, Beijing, San Francisco, Shenzhen and Zurich in the top 10), and second most competitive in Asia (after Shanghai).[11] The Japanese financial market opened up slowly in 1984 and accelerated its internationalization with the «Japanese Big Bang» in 1998.[103] Despite the emergence of Singapore and Hong Kong as competing financial centers, the Tokyo IFC manages to keep a prominent position in Asia. The Tokyo Stock Exchange is Japan’s largest stock exchange, and third largest in the world by market capitalization and fourth largest by share turnover. In 1990 at the end of the Japanese asset price bubble, it accounted for more than 60% of the world stock market value.[104] Tokyo had 8,460 ha (20,900 acres) of agricultural land as of 2003,[105] according to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, placing it last among the nation’s prefectures. The farmland is concentrated in Western Tokyo. Perishables such as vegetables, fruits, and flowers can be conveniently shipped to the markets in the eastern part of the prefecture. Komatsuna and spinach are the most important vegetables; as of 2000, Tokyo supplied 32.5% of the komatsuna sold at its central produce market.[citation needed]
With 36% of its area covered by forest, Tokyo has extensive growths of cryptomeria and Japanese cypress, especially in the mountainous western communities of Akiruno, Ōme, Okutama, Hachiōji, Hinode, and Hinohara. Decreases in the price of timber, increases in the cost of production, and advancing old age among the forestry population have resulted in a decline in Tokyo’s output. In addition, pollen, especially from cryptomeria, is a major allergen for the nearby population centers. Tokyo Bay was once a major source of fish. Most of Tokyo’s fish production comes from the outer islands, such as Izu Ōshima and Hachijō-Jima. Skipjack tuna, nori, and aji are among the ocean products.[106]
Tourism in Tokyo is also a contributor to the economy. In 2006, 4.81 million foreigners and 420 million Japanese visits to Tokyo were made; the economic value of these visits totaled 9.4 trillion yen according to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Many tourists visit the various downtowns, stores, and entertainment districts throughout the neighborhoods of the special wards of Tokyo. Cultural offerings include both omnipresent Japanese pop culture and associated districts such as Shibuya and Harajuku, subcultural attractions such as Studio Ghibli anime center, as well as museums like the Tokyo National Museum, which houses 37% of the country’s artwork national treasures (87/233).
The Toyosu Market in Tokyo is the largest wholesale fish and seafood market in the world since it opened on October 11, 2018.[107] It is also one of the largest wholesale food markets of any kind. It is located in the Toyosu area of Kōtō ward. The Toyosu Market holds strong to the traditions of its predecessor, the Tsukiji Fish Market and Nihonbashi fish market, and serves some 50,000 buyers and sellers every day. Retailers, whole-sellers, auctioneers, and public citizens alike frequent the market, creating a unique microcosm of organized chaos that still continues to fuel the city and its food supply after over four centuries.[108]
Transportation[edit]
Tokyo, which is the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, is Japan’s largest domestic and international hub for rail and ground transportation. However, its airspace has been under the US military’s exclusive control after World War II. Public transportation within Tokyo is dominated by an extensive network of «clean and efficient»[109] trains and subways run by a variety of operators, with buses, monorails and trams playing a secondary feeder role. There are up to 62 electric train lines and more than 900 train stations in Tokyo.[110] Shibuya Crossing is the «world’s busiest pedestrian crossing», with around 3,000 people crossing at a time.[111][112][113]
As a result of World War II, Japanese planes are generally forbidden to fly over Tokyo.[114] Therefore, Japan constructed airports outside Tokyo. Narita International Airport in Chiba Prefecture is the major gateway for international travelers to Japan. Japan’s flag carrier Japan Airlines, as well as All Nippon Airways, have a hub at this airport. Haneda Airport on the reclaimed land at Ōta, offers domestic and international flights. As of 2018, some flight routes into Haneda are permitted through Tokyo airspace.[115]
Various islands governed by Tokyo have their own airports. Hachijō-jima (Hachijojima Airport), Miyakejima (Miyakejima Airport), and Izu Ōshima (Oshima Airport) have services to Tokyo International and other airports.
Rail is the primary mode of transportation in Tokyo,[116] which has the most extensive urban railway network in the world and an equally extensive network of surface lines. JR East operates Tokyo’s largest railway network, including the Yamanote Line loop that circles the center of downtown Tokyo. It operates rail lines in the entire metropolitan area of Tokyo and in the rest of the northeastern part of Honshu. JR East is also responsible for Shinkansen high-speed rail lines.
Two different organizations operate the subway network: the private Tokyo Metro and the governmental Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation. The Metropolitan Government and private carriers operate bus routes and one tram route. Local, regional, and national services are available, with major terminals at the giant railroad stations, including Tokyo, Shinagawa, and Shinjuku.
Expressways link the capital to other points in the Greater Tokyo Area, the Kantō region, and the islands of Kyushu and Shikoku. To build them quickly before the 1964 Summer Olympics, most were constructed above existing roads.[117] Other transportation includes taxis operating in the special wards and the cities and towns. Also, long-distance ferries serve the islands of Tokyo and carry passengers and cargo to domestic and foreign ports.
Education[edit]
Tokyo has many universities, junior colleges, and vocational schools. Many of Japan’s most prestigious universities are in Tokyo, including University of Tokyo, Hitotsubashi University, Meiji University, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Waseda University, Tokyo University of Science, Sophia University, and Keio University.[118] Some of the biggest national universities in Tokyo are:
- Hitotsubashi University
- National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies
- Ochanomizu University
- Tokyo Gakugei University
- Tokyo Institute of Technology
- Tokyo Medical and Dental University
- Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
- Tokyo University of Foreign Studies
- Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology
- Tokyo University of the Arts
- University of Electro-Communications
- University of Tokyo
There is only one non-national public university: Tokyo Metropolitan University. There are also a few universities well known for classes conducted in English and for the teaching of the Japanese language, including the Globis University Graduate School of Management, International Christian University, Sophia University, and Waseda University
Tokyo is also the headquarters of the United Nations University.
Most publicly run kindergartens, elementary schools (years 1 through 6), and junior high (lower secondary) schools (7 through 9) are operated by local wards or municipal offices. Most public senior high (upper secondary) schools in Tokyo are run by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education and are called «Metropolitan High Schools». Tokyo also has many private schools from kindergarten through high school:
Culture[edit]
Tokyo has many museums. In Ueno Park, there is the Tokyo National Museum, the country’s largest museum and specializing in traditional Japanese art; the National Museum of Western Art and Ueno Zoo. Other museums include the National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation in Odaiba; the Edo-Tokyo Museum in Sumida, across the Sumida River from the center of Tokyo; the Nezu Museum in Aoyama; and the National Diet Library, National Archives, and the National Museum of Modern Art, which are near the Imperial Palace.
Tokyo has many theaters for performing arts. These include national and private theaters for traditional forms of Japanese drama. Noteworthy are the National Noh Theatre for noh and the Kabuki-za for Kabuki.[119] Symphony orchestras and other musical organizations perform modern and traditional music. The New National Theater Tokyo in Shibuya is the national center for the performing arts, including opera, ballet, contemporary dance and drama.[120] Tokyo also hosts modern Japanese and international pop, and rock music at venues ranging in size from intimate clubs to internationally known areas such as the Nippon Budokan.
Many different festivals occur throughout Tokyo. Major events include the Sannō at Hie Shrine, the Sanja at Asakusa Shrine, and the biennial Kanda Festivals. The last features a parade with elaborately decorated floats and thousands of people. Annually on the last Saturday of July, an enormous fireworks display over the Sumida River attracts over a million viewers. Once cherry blossoms bloom in spring, many residents gather in Ueno Park, Inokashira Park, and the Shinjuku Gyoen National Garden for picnics under the blossoms.
Harajuku, a neighborhood in Shibuya, is known internationally for its youth style, fashion[121] and cosplay.
Cuisine in Tokyo is internationally acclaimed. In November 2007, Michelin released their first guide for fine dining in Tokyo, awarding 191 stars in total, or about twice as many as Tokyo’s nearest competitor, Paris. As of 2017, 227 restaurants in Tokyo have been awarded (92 in Paris). Twelve establishments were awarded the maximum of three stars (Paris has 10), 54 received two stars, and 161 earned one star.[122]
Sports[edit]
Tokyo, with a diverse array of sports, is home to two professional baseball clubs, the Yomiuri Giants who play at the Tokyo Dome and Tokyo Yakult Swallows at Meiji-Jingu Stadium. The Japan Sumo Association is also headquartered in Tokyo at the Ryōgoku Kokugikan sumo arena where three official sumo tournaments are held annually (in January, May, and September). Soccer clubs in Tokyo include F.C. Tokyo and Tokyo Verdy 1969, both of which play at Ajinomoto Stadium in Chōfu, and FC Machida Zelvia at Nozuta Stadium in Machida. Rugby Union is also played in Tokyo, with multiple Japan Rugby League One clubs based in the city including: Black Rams Tokyo (Setagaya), Tokyo Sungoliath (Fuchū) and Toshiba Brave Lupus Tokyo (Fuchū).
Basketball clubs include the Hitachi SunRockers, Toyota Alvark Tokyo and Tokyo Excellence.
Tokyo hosted the 1964 Summer Olympics, thus becoming the first Asian city to host the Summer Games. The National Stadium, also known as the Olympic Stadium, was host to a number of international sporting events. In 2016, it was to be replaced by the New National Stadium. With a number of world-class sports venues, Tokyo often hosts national and international sporting events such as basketball tournaments, women’s volleyball tournaments, tennis tournaments, swim meets, marathons, rugby union and sevens rugby games, soccer exhibition games, judo, and karate. Tokyo Metropolitan Gymnasium, in Sendagaya, Shibuya, is a large sports complex that includes swimming pools, training rooms, and a large indoor arena. According to Around the Rings, the gymnasium has played host to the October 2011 artistic gymnastics world championships, despite the International Gymnastics Federation’s initial doubt in Tokyo’s ability to host the championships following the March 11 tsunami.[123] Tokyo was also selected to host a number of games for the 2019 Rugby World Cup, and to host the 2020 Summer Olympics and the Paralympics which had to be rescheduled to the summer of 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan.
In popular culture[edit]
Akihabara is the most popular area for fans of anime, manga, and games.
As the largest population center in Japan and the site of the country’s largest broadcasters and studios, Tokyo is frequently the setting for many Japanese movies, television shows, animated series (anime), web comics, light novels, video games, and comic books (manga). In the kaiju (monster movie) genre, landmarks of Tokyo are usually destroyed by giant monsters such as Godzilla and Gamera.
Some Hollywood directors have turned to Tokyo as a backdrop for movies set in Japan. Postwar examples include Tokyo Joe, My Geisha, Tokyo Story and the James Bond film You Only Live Twice; recent examples include Kill Bill, The Fast and the Furious: Tokyo Drift, Lost in Translation, Babel, Inception, The Wolverine and Avengers: Endgame.
Japanese author Haruki Murakami has based some of his novels in Tokyo (including Norwegian Wood), and David Mitchell’s first two novels (number9dream and Ghostwritten) featured the city. Contemporary British painter Carl Randall spent 10 years living in Tokyo as an artist, creating a body of work depicting the city’s crowded streets and public spaces.[124][125][126][127][128]
International relations[edit]
Tokyo is the founding member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21 and is a member of the Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. Tokyo was also a founding member of the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group.
Sister cities and states[edit]
As of 2022, Tokyo has twinning or friendship agreements with the following twelve cities and states:[129]
- New York City, United States (since February 1960)
- Beijing, China (since March 1979)
- Paris, France (since July 1982)[130]
- New South Wales, Australia (since May 1984)
- Seoul, South Korea (since September 1988)
- Jakarta, Indonesia (since October 1989)
- São Paulo State, Brazil (since June 1990)
- Cairo, Egypt (since October 1990)
- Moscow, Russia (since July 1991)
- Berlin, Germany (since May 1994)
- Rome, Italy (since July 1996)
- London, United Kingdom (since October 2015)
Friendship and cooperation agreements[edit]
- Tomsk Oblast, Russia (since May 2015)[131]
- Brussels, Belgium (since October 2016)
- Mumbai, India (since November 2016)
- Los Angeles County, United States (since August 2021)[132]
International academic and scientific research[edit]
Research and development in Japan and the Japanese space program are globally represented by several of Tokyo’s medical and scientific facilities, including the University of Tokyo and other universities in Tokyo, which work in collaboration with many international institutions. Especially with the United States, including NASA and the many private spaceflight companies,[133] Tokyo universities have working relationships with all of the Ivy League institutions (including Harvard and Yale University),[134] along with other research universities and development laboratories, such as Stanford, MIT, and the UC campuses throughout California,[135][136] as well as UNM and Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico.[137][138][139] Other partners worldwide include Oxford University in the United Kingdom,[140] the National University of Singapore in Singapore,[141] the University of Toronto in Canada,[142] and Tsinghua University in China.[143]
See also[edit]
- List of cities proper by population
- List of cities with the most skyscrapers
- List of tallest structures in Tokyo
- List of development projects in Tokyo
- List of largest cities
- List of metropolitan areas in Asia
- List of most expensive cities for expatriate employees
- List of urban agglomerations in Asia
- List of urban areas by population
- Megacity
- Tokyo dialect
- Yamanote and Shitamachi
References[edit]
- ^ 都庁は長野市. Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 12, 2014. Shinjuku is the location of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Office. But Tokyo is not a «municipality». Therefore, for the sake of convenience, the notation of prefectural is «Tokyo».
- ^ «Reiwa 1 nationwide prefectures, cities and towns area statistics (October 1)» (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. December 26, 2019. Archived from the original on April 15, 2020. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- ^ «Mountains of Tokyo Metropolis» (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- ^ a b «Tokyo Loses Population for First Time in 26 Years Amid Pandemic». Bloomberg.com. January 31, 2022. Retrieved May 17, 2022.
- ^ «Major Agglomerations of the World — Population Statistics and Maps».
- ^
«Population economics statistics (Tokyo inner production etc.)» (in Japanese). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Retrieved April 28, 2020. - ^ «Tokyo». Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d. Retrieved January 7, 2022.
- ^ Ōshima, Tadamori (February 23, 2018). 衆議院議員逢坂誠二君提出日本の首都に関する質問に対する答弁書. The House of Representatives, Japan. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
There is no law or regulation that expressly defines Tokyo as the capital. However, we are of the opinion that Tokyo is generally accepted in society to be the capital of Japan.
- ^ Nations, United. «The World’s Cities in 2018» (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ «Global 500». Fortune.
- ^ a b «The Global Financial Centres Index 28» (PDF). Long Finance. September 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ a b «Tokyo – GoJapanGo». Tokyo Attractions – Japanese Lifestyle. Mi Marketing Pty Ltd. Archived from the original on April 26, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ a b «Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel». Archived from the original on September 14, 2018. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ a b Hornyak, Tim (December 16, 2017). «Heart of gold: The Ginza Line celebrates its 90th birthday». Japan Times. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ «The Global Liveability Index 2021» (PDF). The Economist. Retrieved February 5, 2023.
- ^ a b Room, Adrian. Placenames of the World. McFarland & Company (1996), p. 360 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-7864-1814-1.
- ^ US Department of State. (1906). A digest of international law as in diplomatic discussions, treaties and other international agreements (John Bassett Moore, ed.), Volume 5, p. 759 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine; excerpt, «The Mikado, on assuming the exercise of power at Yedo, changed the name of the city to Tokio».
- ^ Fiévé, Nicolas & Paul Waley (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. p. 253.
- ^ 明治東京異聞~トウケイかトウキョウか~東京の読み方 (in Japanese). Tokyo Metropolitan Archives. 2004. Archived from the original on October 6, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ McClain, James, James; et al. (1994). Edo and Paris: Urban Life and the State in the Early Modern Era. p. 13.
- ^ Sorensen, Andre (2004). The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty-First Century. p. 16.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. pp. 33, 55.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. pp. 182–183.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. p. 186.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. p. 188.
- ^ «History of Tokyo». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 12, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ «Tokyo-Yokohama earthquake of 1923». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on June 26, 2015. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ Tipton, Elise K. (2002). Modern Japan: A Social and Political History. Routledge. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-585-45322-4.
- ^ «9 March 1945: Burning the Heart Out of the Enemy». Wired. March 9, 2011. Archived from the original on March 15, 2014. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «1945 Tokyo Firebombing Left Legacy of Terror, Pain». Common Dreams. Archived from the original on January 3, 2015. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- ^ Cybriwsky, Roman (1997). Historical Dictionary of Tokyo. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow. p. 22.
- ^ Hewitt, Kenneth (1983). «Place Annihilation: Area Bombing and the Fate of Urban Places». Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 73 (2): 257–284. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1983.tb01412.x.
- ^ Andre Sorensen. The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty First Century RoutledgeCurzon, 2004. ISBN 0-415-35422-6.
- ^ «Tokyo Narita International Airport (NRT) Airport Information (Tokyo, Japan)». Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ «Rail Transport in The World’s Major Cities» (PDF). Japan Railway and Transport Review. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ Saxonhouse, Gary R.; Stern, Robert M., eds. (2004). Japan’s Lost Decade: Origins, Consequences and Prospects for Recovery. Blackwell Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4051-1917-7.
- ^ Worrall, Julian. «The view from the Hills: Minoru Mori defends the Omotesando Hills development and reveals big plans for Tokyo». Metropolis. Archived from the original on November 19, 2006.
- ^ «Shift of Capital from Tokyo Committee». Japan Productivity Center for Socio-Economic Development. Archived from the original on August 25, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ «Policy Speech by Governor of Tokyo, Shintaro Ishihara at the First Regular Session of the Metropolitan Assembly, 2003». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on November 3, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ «Despite Major Earthquake Zero Tokyo Buildings Collapsed Thanks to Stringent Building Codes». March 11, 2011. Archived from the original on September 12, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^ Williams, Carol J. (March 11, 2011). «Japan earthquake disrupts Tokyo, leaves capital only lightly damaged». Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on December 13, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^
«Tokyo Radiation Levels». Metropolis Magazine. Archived from the original on May 20, 2012. Retrieved April 25, 2012. - ^ «Tokyo radiation levels – daily updates – April». Archived from the original on August 19, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^ «IOC selects Tokyo as host of 2020 Summer Olympic Games». Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ Imai, Heide; Matjaz Ursic (2020). Creativity in Tokyo: Revitalizing a Mature City. Palgrave. ISBN 978-9811566868.
- ^ «Hot Market: Tokyo Residential Real Estate sees Strong Demand in a Tight Market, Prices Surge! – Housing Japan». Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ «Population of Tokyo, Japan». Mongabay. Archived from the original on January 21, 2012. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Tokyo, Japan Geographic Information». Latlong.net. September 2020. Archived from the original on September 14, 2017. Retrieved September 16, 2020.
- ^ «Population of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp. October 2015. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ «Local Government in Japan» (PDF). Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. p. 8. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 23, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^
The Structure of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Archived December 8, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (Tokyo government webpage) - ^ The Population of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government Archived December 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine (Retrieved on July 4, 2009)
- ^ «Pray For Tokyo: Chiyoda». Karis Japan. Archived from the original on July 20, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2015.
- ^ «Development of the Metropolitan Center, Subcenters and New Base». Bureau of Urban Development, Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 23, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ «Ogasawara Islands: World Natural Heritage». Ogasawara Village Industry and Tourist Board. Archived from the original (Adobe Flash) on March 31, 2017. Retrieved June 29, 2018.
- ^ Yoshikawa, Yukie (2005). «Okinotorishima: Just the Tip of the Iceberg». Harvard Asian Quarterly. 9 (4). Archived from the original on November 4, 2013.
- ^ Literally, 東/Higashi- means East; but when Yamato Town was renamed to Higashi-Yamato City in 1970, 東 was meant to represent the 東/Tō- in Tokyo, see Higashi-Yamato City: 市の名称 「東大和」の名称について (Japanese: On the city name «Higashi-Yamato»), retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ «General overview of area figures for Natural Parks by prefecture» (PDF). Ministry of the Environment. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved February 8, 2012.
- ^ Matsu’ura, Ritsuko S. (January 28, 2017). «A short history of Japanese historical seismology: past and the present». Geoscience Letters. 4 (1): 3. Bibcode:2017GSL…..4….3M. doi:10.1186/s40562-017-0069-4 – via BioMed Central.
- ^ Grunewald, Elliot D.; Stein, Ross S. (2006). «A New 1649–1884 Catalog of Destructive Earthquakes near Tokyo and Implications for the Long-term Seismic Process». Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 111 (B12): B12306. Bibcode:2006JGRB..11112306G. doi:10.1029/2005JB004059.
- ^ «A new probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for greater Tokyo» (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ Masato Oyama (March 2007). 宝永四年(1707)噴火 (1707 Eruption). 富士山歴史噴火総解説 (Database of eruptions and other activities of Fuji Volcano, Japan, based on historical records since AD 781) (in Japanese). Shizuoka University. Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- ^ a b https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volcanic-ash-downfall_map_of_Mt.Fuji_Hoei-eruption01.jpg Ashfall distribution map for examining disaster prevention measures (Mt. Fuji Hoei eruption)
- ^ a b c d «Mt Fuji eruption could cripple Tokyo». Nippon TV News 24 Japan. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «The underground cathedral protecting Tokyo from floods». BBC. November 29, 2018. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c «Floods in Tokyo and Safety Tips and Preparation». Plaza Homes. February 28, 2020. Archived from the original on August 14, 2020.
- ^ Peel, M.C., Finlayson, B.L., and McMahon, T.A.: Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification Archived February 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 11, 1633–1644, 2007.
- ^ a b c d 観測史上1~10位の値( 年間を通じての値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 19, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ «Average Weather in Tokyo, Japan, Year Round — Weather Spark».
- ^ «Tokyo observes latest ever 1st snowfall». Archived from the original on March 19, 2007. Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(10月としての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ^ The JMA Tokyo, Tokyo (東京都 東京) station is at 35°41.4′N 139°45.6′E, JMA: 気象統計情報 過去の気象データ検索>都道府県の選択>地点の選択. Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 1, 2018. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ^
気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 18, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2021. - ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on November 2, 2014. Retrieved December 16, 2014.
- ^ «Tokyo, Japan — Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast». Weather Atlas. Yu Media Group. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Climate & Weather Averages in Tokyo». Time and Date. Retrieved August 7, 2022.
- ^ «Station Name: TOKYO WMO Station ID: 47662». Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 7, 2020.
- ^ 気象庁 / 気象統計情報 / 過去の気象データ検索 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値-小河内(東京都). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値-父島(東京都). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 気象統計情報 / 天気予報・台風 / 過去の台風資料 / 台風の統計資料 / 台風の平年値. Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on June 7, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
- ^ a b Hidenobu Jinnai. Tokyo: A Spatial Anthropology. University of California Press (1995), pp. 1–3 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-520-07135-2.
- ^ «Tokyo skyline reaches for new heights with $5.5 billion Mori project». Reuters. August 2, 2019. Archived from the original on August 22, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2019.
- ^ «World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD)». Wbcsd.org. Archived from the original on January 4, 2009. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ Barry, Roger Graham & Richard J. Chorley. Atmosphere, Weather and Climate. Routledge (2003), p. 344 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-415-27170-3.
- ^ Toshiaki Ichinose, Kazuhiro Shimodozono, and Keisuke Hanaki. Impact of anthropogenic heat on urban climate in Tokyo. Atmospheric Environment 33 (1999): 3897–3909.
- ^ «Heat Island Control Measures». kankyo.metro.tokyo.jp. January 6, 2007. Archived from the original on May 24, 2008. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Barry, Roger Graham; Chorley, Richard J. (1987). Atmosphere, Weather and Climate. London: Methuen Publishing. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-416-07152-8.
- ^ «Cool ocean breezes flowing through Tokyo» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 16, 2013. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- ^ «2012 Action Program for Tokyo Vision 2020 – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». Metro.tokyo.jp. Archived from the original on December 9, 2012. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ^ 東京都の人口(推計). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 2, 2018. Retrieved January 17, 2015.
- ^ a b «Population of Tokyo». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on December 23, 2008. Retrieved January 1, 2009.
- ^ 東京府 編 (1890). 東京府統計書. 明治22年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1889)] (in Japanese). Vol. 1. 東京府. pp. 40–41. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) Archived September 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (digital page number 32)
- ^ 東京府 編 (1890). 東京府統計書. 明治22年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1889)] (in Japanese). Vol. 1. 東京府. pp. 66–67. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) Archived September 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (digital page number 46)
- ^ «Tokyo Statistical Yearbook 2018» (Excel 97). Bureau of General Affairs, Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on September 5, 2018. Retrieved September 5, 2018.
- ^
«Financial Centres, All shapes and sizes». The Economist. September 13, 2007. Archived from the original on October 31, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007. - ^ «Top 3 Things to See & Do in Shibuya – Tokyo’s Busiest District». April 13, 2017. Archived from the original on February 5, 2019. Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ^ «The expenses of Japan». The Economist. July 7, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- ^ Sassen, Saskia (2001). The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-07063-6.
- ^ Ito, Takatoshi; Melvin, Michael. «NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES – JAPAN’S BIG BANG AND THE TRANSFORMATION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS» (PDF). www.nber.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 2, 2018. Retrieved February 11, 2019.
- ^ «Tokyo Stock Exchange». Stock-market.in. February 25, 2007. Archived from the original on November 27, 2021. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Horticulture Statistics Team, Production Statistics Division, Statistics and Information Department, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (July 15, 2003). «Statistics on Cultivated Land Area» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 24, 2008. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ «Tokyo Economy — Tokyo Travel Guide». www.tokyo-travelguide.com. Retrieved April 23, 2022.
- ^ Kato, Issei (September 29, 2018). «As Tokyo’s historic Tsukiji market closes, fishmongers mourn». Reuters. Archived from the original on October 3, 2018. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ^ Hannerz, Ulf (2005). «The Fish Market at the Center of the World (Review)». The Journal of Japanese Studies. 31 (2): 428–431. doi:10.1353/jjs.2005.0044. S2CID 143762239.
- ^ «A Country Study: Japan». The Library of Congress. Chapter 2, Neighborhood. Archived from the original on May 26, 2012. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
- ^ «Orientation – Tokyo Travel Guide | Planetyze». Planetyze. Archived from the original on September 10, 2017. Retrieved July 18, 2017.
- ^ 井上恵一朗 (April 22, 2016). 【東京はてな】 渋谷交差点、1回で3千人横断?. 朝日新聞. p. 29.
- ^ 渋谷スクランブル交差点——世界で最もワイルドな交差点にようこそ. CNN.co.jp. August 25, 2019. Archived from the original on September 23, 2020. Retrieved September 26, 2019.
- ^ «The World’s Busiest Pedestrian Crossing». WorldAtlas. March 5, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2020. Retrieved April 13, 2020.
- ^ U.S. military’s Yokota Rapcon airspace is set in six different levels at altitudes between 2,450 and 7,000 meters, stretching over Tokyo and eight other prefectures. Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine Japan Times
- ^ Japan gets approval for new flight routes over Haneda airport using U.S. airspace Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine Japan Times
- ^ Chorus, Paul (2016). «Transit oriented development in Tokyo». Transit Oriented Development: Making it Happen. Routledge. pp. 245–258. ISBN 978-1-317-00732-6.
- ^ «Revamping Tokyo’s expressways could give capital a boost». Yomiuri Shimbun. Archived from the original on November 2, 2012. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ «QS University Rankings: Asia 2016». QS Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. Archived from the original on June 16, 2016. Retrieved June 13, 2016.
- ^ Milner, Rebecca (2013). «Pocket Tokyo.» 4th Edition. Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 978-1-74220-581-6
- ^ Ozaki, Motoki (June 22, 2019). «About us. The Heart Of Performing Arts In Japan». New National Theatre, Tokyo. Archived from the original on June 22, 2019. Retrieved December 7, 2019.
- ^ Perry, Chris (April 25, 2007). Rebels on the Bridge: Subversion, Style, and the New Subculture (Flash) (Report). Self-published (Scribd). Archived from the original on October 14, 2007. Retrieved December 4, 2007.
- ^ «Tokyo ‘top city for good eating’«. BBC News. November 20, 2007. Archived from the original on December 17, 2008. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ «Tokyo Keeps Gymnastics Worlds, Bolsters Olympics Ambitions». Aroundtherings.com. May 23, 2011. Archived from the original on June 1, 2012. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ^ «BBC World Service: World Update. ‘Carl Randall – Painting the faces in Japan’s crowded cities’.», BBC World Service, 2016, archived from the original on December 27, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ «‘Painting the faces in Japan’s crowded cities’.», BBC News – Arts & Entertainment, 2016, archived from the original on February 22, 2017, retrieved July 21, 2018
- ^ ‘Tokyo Portraits by Carl Randall’., The Daiwa Anglo Japanese Foundation, London, 2014, archived from the original on December 21, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ ‘The BP Portrait Awards 2013’., The National Portrait Gallery, London, 2012, archived from the original on February 6, 2017, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ ‘Japan Portraits’., Carl Randall – artist website, 2016, archived from the original on December 21, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ «Sister Cities (States) of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». Archived from the original on June 11, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ^ «Friendship and cooperation agreements». Paris: Marie de Paris. Archived from the original on July 1, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ «Governor of Tomsk Region, Russia, visits Governor Masuzoe». Tokyo Metropolitan Government Official Website. June 15, 2015. Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ Houston, Michael (August 27, 2021). «Tokyo Metropolitan Government signs MoU with 2028 Olympic host City of Los Angeles». Inside the Game. Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ The Space Economy in Figures How Space Contributes to the Global Economy: How Space Contributes to the Global Economy. OECD Publishing. 2019. p. 72. ISBN 978-92-64-80595-8. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Six colleges dominate in research stature». Washington Post. March 27, 2012. Archived from the original on December 25, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Radiation-free stem cell transplants, gene therapy may be within reach». News Center. May 29, 2019. Archived from the original on December 11, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «UTokyo-Berkeley». UTokyo-Berkeley. December 23, 2017. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ Asavanant, W.; Shiozawa, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Charoensombutamon, B.; Emura, H.; Alexander, R. N.; Takeda, S.; Yoshikawa, J. I.; Menicucci, N. C.; Yonezawa, H.; Furusawa, A. (2019). «Generation of time-domain-multiplexed two-dimensional cluster state». Science. 366 (6463): 373–376. arXiv:1903.03918. Bibcode:2019Sci…366..373A. doi:10.1126/science.aay2645. PMID 31624214. S2CID 92979929.
- ^ «Rikkyo University». UNM: Global Education Office. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ United States. Department of Energy (1999). Sandia National Laboratories/New Mexico: Environmental Impact Statement. Sandia National Laboratories/New Mexico: Environmental Impact Statement. p. 166–PA54. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «University of Oxford Japan Office» オックスフォード大学日本事務所. November 30, 2019.
- ^ «The University of Tokyo – National University of Singapore – 1st Joint Symposium – The University of Tokyo». The University of Tokyo. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Exchange: University of Tokyo – University of Toronto». University of Toronto – Learning Abroad. May 5, 2018. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Tsinghua University News». Tsinghua University. July 27, 2018. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
Bibliography[edit]
- Fiévé, Nicolas and Paul Waley. (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 978-0-7007-1409-4; OCLC 51527561
- McClain, James, John M Merriman and Kaoru Ugawa. (1994). Edo and Paris: Urban Life and the State in the Early Modern Era. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-2987-3; OCLC 30157716
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5; OCLC 58053128
- Sorensen, Andre. (2002). The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty First Century. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 978-0-415-22651-6; OCLC 48517502
Further reading[edit]
Guides[edit]
- Bender, Andrew, and Timothy N. Hornyak. Tokyo (City Travel Guide) (2010)
- Mansfield, Stephen. Dk Eyewitness Top 10 Travel Guide: Tokyo (2013)
- Waley, Paul. Tokyo Now and Then: An Explorer’s Guide. (1984). 592 pp
- Yanagihara, Wendy. Lonely Planet Tokyo Encounter
Contemporary[edit]
- Allinson, Gary D. Suburban Tokyo: A Comparative Study in Politics and Social Change. (1979). 258 pp.
- Bestor, Theodore. Neighborhood Tokyo (1989). online edition
- Bestor, Theodore. Tsukiji: The Fish Market at the Centre of the World. (2004) online edition
- Fowler, Edward. San’ya Blues: Labouring Life in Contemporary Tokyo. (1996) ISBN 0-8014-8570-3.
- Friedman, Mildred, ed. Tokyo, Form and Spirit. (1986). 256 pp.
- Jinnai, Hidenobu. Tokyo: A Spatial Anthropology. (1995). 236 pp.
- Jones, Sumie et al. eds. A Tokyo Anthology: Literature from Japan’s Modern Metropolis, 1850–1920 (2017); primary sources excerpt
- Perez, Louis G. Tokyo: Geography, History, and Culture (ABC-CLIO, 2019).
- Reynolds, Jonathan M. «Japan’s Imperial Diet Building: Debate over Construction of a National Identity». Art Journal. 55#3 (1996) pp. 38+.
- Sassen, Saskia. The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo. (1991). 397 pp.
- Sorensen, A. Land Readjustment and Metropolitan Growth: An Examination of Suburban Land Development and Urban Sprawl in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area (2000)
- Taira, J. [re]TOKYO. (2018). San Francisco: ORO Editions. ISBN 978-1-940743-66-0
- Waley, Paul. «Tokyo-as-world-city: Reassessing the Role of Capital and the State in Urban Restructuring». Urban Studies 2007 44(8): 1465–1490. ISSN 0042-0980 Fulltext: Ebsco
External links[edit]
- Official website (in Japanese)
- Official website (in English)
- Go Tokyo travel guide
- Tokyo Convention & Visitors Bureau
This article is about the Japanese prefecture and its city. For other uses, see Tokyo (disambiguation).
|
Tokyo 東京都 |
|
|---|---|
|
Metropolis |
|
| Tokyo Metropolis | |
|
Clockwise from top:
|
|
|
Flag Seal Emblem |
|
| Anthem: «Tokyo Metropolitan Song» (東京都歌, Tōkyō-to Ka) |
|

Interactive map outlining Tokyo |
|

Location within Japan |
|
| Coordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′32″E / 35.68972°N 139.69222°ECoordinates: 35°41′23″N 139°41′32″E / 35.68972°N 139.69222°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Kantō |
| Island | Honshu |
| Capital | Tokyo[1] |
| Divisions | 23 special wards, 26 cities, 1 district, and 4 subprefectures |
| Government | |
| • Body | Tokyo Metropolitan Government |
| • Governor | Yuriko Koike (Indp.) |
| • Representatives | 42 |
| • Councilors | 11 |
| Area
[2] |
|
| • Total | 2,194.07 km2 (847.14 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 13,452 km2 (5,194 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 45th in Japan |
| Highest elevation
[3] |
2,017 m (6,617 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population
(2022)[4] |
|
| • Total | 13,988,129 |
| • Rank | 1st in Japan |
| • Density | 6,363/km2 (16,480/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 39,105,000 |
| • Metro
[5] |
40,700,000 |
| • Metro density | 3,000/km2 (7,800/sq mi) |
| • Dialects |
|
| Demonym | Tokyoite |
| Gross Regional Product
(2018)[6] |
|
| • Total, nominal | ¥107 trillion |
| • Per capita | ¥7.7 million |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (Japan Standard Time) |
| ISO 3166-2 |
JP-13 |
| Flower | Yoshino cherry |
| Tree | Ginkgo |
| Bird | Black-headed gull |
| Website | www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp |
Tokyo (;[7] Japanese: 東京, Tōkyō, [toːkʲoː] (listen)), officially the Tokyo Metropolis (東京都, Tōkyō-to), is the capital and most populous city of Japan.[8] Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area (13,452 square kilometers or 5,194 square miles) is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents as of 2018;[9] the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people.[4] Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan’s largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan’s economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan.
Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed «Tokyo» (lit. ‘Eastern Capital’). Tokyo was devastated by the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, and again by Allied bombing raids during World War II. Beginning in the 1950s, the city underwent rapid reconstruction and expansion efforts, going on to lead the Japanese economic miracle. Since 1943, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government has administered the prefecture’s 23 special wards (formerly Tokyo City), various commuter towns and suburbs in its western area, and two outlying island chains known as the Tokyo Islands.
Tokyo is the second-largest urban economy worldwide by gross domestic product after New York City, and is categorized as an Alpha+ city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. It is also Japan’s leading business hub as part of an industrial region that includes the cities of Yokohama, Kawasaki, and Chiba. As of 2021, Tokyo is home to 37 companies of the Fortune Global 500.[10] In 2020, the city ranked fourth on the Global Financial Centres Index, behind only New York City, London, and Shanghai.[11] Tokyo is home to the world’s tallest tower, Tokyo Skytree,[12] and the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility, the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel (located in Kasukabe, Saitama, a suburb of Tokyo).[13] The Tokyo Metro Ginza Line, opened in 1927, is the oldest underground metro line in East Asia.[14] Recognized as one of the most livable cities in the world, Tokyo was tied fourth with Wellington in the 2021 Global Livability Ranking.[15]
The city has hosted multiple international events, including the 1964 Summer Olympics and 1964 Summer Paralympics, the 2020 Summer Olympics and 2020 Summer Paralympics (postponed; held in 2021), and three summits of the G7 (in 1979, 1986, and 1993). Tokyo is an international research and development hub and is likewise represented by several major universities, most notably the University of Tokyo. Tokyo Station is the central hub for Japan’s high-speed railway network, the Shinkansen; Shinjuku Station in Tokyo is also the world’s busiest train station. Notable special wards of Tokyo include: Chiyoda, the site of the National Diet Building and the Tokyo Imperial Palace; Shinjuku, the city’s administrative center; and Shibuya, a commercial, cultural, and business hub.
Etymology[edit]
| Tokyo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tōkyō in kanji |
|||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | 東京 | ||||
| Hiragana | とうきょう | ||||
| Katakana | トウキョウ | ||||
| Kyūjitai | 東亰 | ||||
|
Tokyo was originally known as Edo (江戸), a kanji compound of 江 (e, «cove, inlet») and 戸 (to, «entrance, gate, door»).[16] The name, which can be translated as «estuary», is a reference to the original settlement’s location at the meeting of the Sumida River and Tokyo Bay. During the Meiji Restoration in 1868, the name of the city was changed to Tokyo (東京, from 東 tō «east», and 京 kyō «capital»), when it became the new imperial capital,[17] in line with the East Asian tradition of including the word capital (京) in the name of the capital city (for example, Kyoto (京都), Keijō (京城), Beijing (北京), Nanjing (南京), and Xijing (西京)).[16] During the early Meiji period, the city was sometimes called «Tōkei», an alternative pronunciation for the same characters representing «Tokyo», making it a kanji homograph. Some surviving official English documents use the spelling «Tokei»;[18] however, this pronunciation is now obsolete.[19]
History[edit]
Pre-1869 (Edo period)[edit]
Main article: Edo
Tokyo was originally a village called Edo, in what was formerly part of the old Musashi Province. Edo was first fortified by the Edo clan, in the late twelfth century. In 1457, Ōta Dōkan built Edo Castle. In 1590, Tokugawa Ieyasu moved from Mikawa Province (his lifelong base) to the Kantō region. When he became shōgun in 1603, Edo became the center of his ruling. During the subsequent Edo period, Edo grew into one of the largest cities in the world with a population topping one million by the 18th century.[20]
Edo was still the home of the Tokugawa shogunate and not the capital of Japan (the Emperor himself lived in Kyoto almost continuously from 794 to 1868).[21] During the Edo era, the city enjoyed a prolonged period of peace known as the Pax Tokugawa, and in the presence of such peace, the shogunate adopted a stringent policy of seclusion, which helped to perpetuate the lack of any serious military threat to the city.[22] The absence of war-inflicted devastation allowed Edo to devote the majority of its resources to rebuilding in the wake of the consistent fires, earthquakes, and other devastating natural disasters that plagued the city.
This prolonged period of seclusion however came to an end with the arrival of American Commodore Matthew C. Perry in 1853. Commodore Perry forced the opening of the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate, leading to an increase in the demand for new foreign goods and subsequently a severe rise in inflation.[23] Social unrest mounted in the wake of these higher prices and culminated in widespread rebellions and demonstrations, especially in the form of the «smashing» of rice establishments.[24] Meanwhile, supporters of the Emperor leveraged the disruption that these widespread rebellious demonstrations were causing to further consolidate power by overthrowing the last Tokugawa shōgun, Yoshinobu, in 1867.[25] After 265 years, the Pax Tokugawa came to an end.
- Gallery
-
-
Famous Edo Places. Yamanote (above), Nihonbashi (center) and Shitamachi (below), c. 1858.
-
Suruga street with Mount Fuji by Hiroshige (1856)
1869–1943[edit]
Edo was renamed Tokyo (Eastern Capital) on September 3, 1868, as the new government was consolidating its power after the fall of the Edo shogunate. The young Emperor Meiji visited once at the end of that year and eventually moved in in 1869. Tokyo was already the nation’s political center,[26] and the emperor’s residence made it a de facto imperial capital as well, with the former Edo Castle becoming the Imperial Palace. The city of Tokyo was officially established on May 1, 1889.
The Tokyo Metro Ginza Line portion between Ueno and Asakusa was the first subway line built in Japan and East Asia completed on December 30, 1927.[14] Central Tokyo, like Osaka, has been designed since about 1900 to be centered on major railway stations in a high-density fashion, so suburban railways were built relatively cheaply at street level and with their own right-of-way. Though expressways have been built in Tokyo, the basic design has not changed.[citation needed]
Tokyo went on to suffer two major catastrophes in the 20th century: the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, which left 140,000 dead or missing; and World War II.[27]
- Gallery
-
The 1870s Chuo-dori terraces in Ginza, Tokyo
-
-
The Ginza area in 1933
-
«The first underground railway in the Orient», Tokyo Underground, opened on December 30, 1927
1943–1945[edit]
In 1943, the city of Tokyo merged with the prefecture of Tokyo to form the «Metropolitan Prefecture» of Tokyo. Since then, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government served as both the prefecture government for Tokyo, as well as administering the special wards of Tokyo, for what had previously been Tokyo City. World War II wreaked widespread destruction of most of the city due to the persistent Allied air raids on Japan and the use of incendiary bombs. The bombing of Tokyo in 1944 and 1945 is estimated to have killed between 75,000 and 200,000 civilians and left more than half of the city destroyed.[28]
The deadliest night of the war came on March 9–10, 1945, the night of the American «Operation Meetinghouse» raid;[29] as nearly 700,000 incendiary bombs rained on the eastern half of the city, mainly in heavily residential wards. Two-fifths of the city were completely burned, more than 276,000 buildings were demolished, 100,000 civilians were killed, and 110,000 more were injured.[30][31] Between 1940 and 1945, the population of Japan’s capital city dwindled from 6,700,000 to less than 2,800,000, with the majority of those who lost their homes living in «ramshackle, makeshift huts».[32]
- Gallery
-
-
The aftermath of the bombing of Tokyo, March 1945
-
Nihonbashi in 1946
1945–present[edit]
After the war, Tokyo became the base from which the United States under Douglas MacArthur administered Japan for six years. Tokyo struggled to rebuild as occupation authorities stepped in and drastically cut back on Japanese government rebuilding programs, focusing instead on simply improving roads and transportation. Tokyo did not experience fast economic growth until the 1950s.[33]
After the occupation of Japan ended in 1952, Tokyo was completely rebuilt and was showcased to the world during the 1964 Summer Olympics. The 1970s and the 1980s brought new high-rise developments. In 1978, Sunshine 60 – the tallest skyscraper in Asia until 1985, and in Japan until 1991 – and Narita International Airport were constructed, and the population increased to about 11 million in the metropolitan area.[35] The Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum has historic Japanese buildings that existed in the urban landscape of pre-war Tokyo.
Tokyo’s subway and commuter rail network became one of the busiest in the world[36] as more and more people moved to the area. In the 1980s, real estate prices skyrocketed during a real estate and debt bubble. The bubble burst in the early 1990s, and many companies, banks, and individuals were caught with mortgage-backed debts while real estate was shrinking in value. A major recession followed, making the 1990s Japan’s «Lost Decade»,[37] from which it is now slowly recovering.
Tokyo still sees new urban developments on large lots of less profitable land. Recent projects include Ebisu Garden Place, Tennōzu Isle, Shiodome, Roppongi Hills, Shinagawa (now also a Shinkansen station), and the Marunouchi side of Tokyo Station. Buildings of significance have been demolished for more up-to-date shopping facilities such as Omotesando Hills.[38]
Land reclamation projects in Tokyo have also been going on for centuries. The most prominent is the Odaiba area, now a major shopping and entertainment center. Various plans have been proposed[39] for transferring national government functions from Tokyo to secondary capitals in other regions of Japan, to slow down rapid development in Tokyo and revitalize economically lagging areas of the country. These plans have been controversial[40] within Japan and have yet to be realized.
The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami that devastated much of the northeastern coast of Honshu was felt in Tokyo. However, due to Tokyo’s earthquake-resistant infrastructure, damage in Tokyo was very minor compared to areas directly hit by the tsunami,[41] although activity in the city was largely halted.[42] The subsequent nuclear crisis caused by the tsunami has also largely left Tokyo unaffected, despite occasional spikes in radiation levels.[43][44]
On September 7, 2013, the IOC selected Tokyo to host the 2020 Summer Olympics. Tokyo thus became the first Asian city to host the Olympic Games twice.[45] However, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the 2020 Olympic Games took place from July 23, 2021, to August 8, 2021. It is also unclear how the city will deal with an increasing number of issues, urging scholars to offer possible alternatives approaches to tackle the most urgent problems.[46] Although, COVID-19 has impeded the growth of many industries, the real estate market in Japan is yet to be negatively impacted. Japanese real estate has become one of the safest investments for foreign investors around the world.[47]
As of 2020, the Greater Tokyo Area is the world’s largest urban area with over 38 million residents, making it as its largest metro area.
- Gallery
-
Sunshine 60, at 239.7 m (786 ft), the tallest building in Asia until 1985, and in Japan until 1991
Geography and government[edit]
A satellite photo of Tokyo in 2018 taken by ESA Sentinel-2
The mainland portion of Tokyo lies northwest of Tokyo Bay and measures about 90 km (56 mi) east to west and 25 km (16 mi) north to south. The average elevation in Tokyo is 40 m (131 ft).[48] Chiba Prefecture borders it to the east, Yamanashi to the west, Kanagawa to the south, and Saitama to the north. Mainland Tokyo is further subdivided into the special wards (occupying the eastern half) and the Tama area (多摩地域) stretching westwards. Tokyo has a latitude of 35.65 (near the 36th parallel north), which makes it more southern than Rome (41.90), Madrid (40.41), New York City (40.71) and Beijing (39.91).[49]
Within the administrative boundaries of Tokyo Metropolis are two island chains in the Pacific Ocean directly south: the Izu Islands, and the Ogasawara Islands, which stretch more than 1,000 km (620 mi) away from the mainland. Because of these islands and the mountainous regions to the west, Tokyo’s overall population density figures far under-represent the real figures for the urban and suburban regions of Tokyo.[50]
Under Japanese law, the prefecture of Tokyo is designated as a to (都), translated as metropolis.[51] Tokyo Prefecture is the most populous prefecture and the densest, with 6,100 inhabitants per square kilometer (16,000/sq mi); by geographic area it is the third-smallest, above only Osaka and Kagawa. Its administrative structure is similar to that of Japan’s other prefectures. The 23 special wards (特別区, tokubetsu-ku), which until 1943 constituted the city of Tokyo, are self-governing municipalities, each having a mayor, a council, and the status of a city.
In addition to these 23 special wards, Tokyo also includes 26 more cities (市 -shi), five towns (町 -chō or machi), and eight villages (村 -son or -mura), each of which has a local government. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers the whole metropolis including the 23 special wards and the cities and towns that constitute the prefecture. It is headed by a publicly elected governor and metropolitan assembly. Its headquarters is in Shinjuku Ward.
Municipalities[edit]
A map with Nishi-Tama District in green
Since 2001, Tokyo consists of 62 municipalities: 23 special wards, 26 cities, 5 towns and 8 villages. Any municipality of Japan has a directly elected mayor and a directly elected assembly, each elected on independent four-year cycles. 23 of Tokyo’s municipalities cover the area that had been Tokyo City until WWII, 30 remain today in the Tama area (former North Tama, West Tama and South Tama districts), 9 on Tokyo’s outlying islands.
- The special wards (特別区, tokubetsu-ku) of Tokyo comprise the area formerly incorporated as Tokyo City. The special wards use the word «city» in their official English name (e.g. Chiyoda City). The wards differ from other cities in having a unique administrative relationship with the prefectural government. Certain municipal functions, such as waterworks, sewerage, and fire-fighting, are handled by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. To pay for the added administrative costs, the prefecture collects municipal taxes, which would usually be levied by the city.[52] The «three central wards» of Tokyo – Chiyoda, Chūō and Minato – are the business core of the city, with a daytime population more than seven times higher than their nighttime population.[53] Chiyoda Ward is unique in that it is in the very heart of the former Tokyo City, yet is one of the least populated wards. It is occupied by many major Japanese companies and is also the seat of the national government, and the Japanese emperor. It is often called the «political center» of the country.[54] Akihabara, known for being an otaku cultural center and a shopping district for computer goods, is also in Chiyoda.
- To the west of the special wards, Tokyo Metropolis consists of cities, towns, and villages that enjoy the same legal status as those elsewhere in Japan. While serving as «bed towns» for those working in central Tokyo, some of them also have a local commercial and industrial base, such as Tachikawa. Collectively, these are often known as the Tama area or Western Tokyo. The far west of the Tama area is occupied by the district (gun) of Nishi-Tama. Much of this area is mountainous and unsuitable for urbanization. The highest mountain in Tokyo, Mount Kumotori, is 2,017 m (6,617 ft) high; other mountains in Tokyo include Takanosu (1,737 m (5,699 ft)), Odake (1,266 m (4,154 ft)), and Mitake (929 m (3,048 ft)). Lake Okutama, on the Tama River near Yamanashi Prefecture, is Tokyo’s largest lake. The district is composed of three towns (Hinode, Mizuho and Okutama) and one village (Hinohara). The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has designated Hachiōji, Tachikawa, Machida, Ōme and Tama New Town as regional centers of the Tama area,[55] as part of its plans to relocate urban functions away from central Tokyo.
- Tokyo has numerous outlying islands, which extend as far as 1,850 km (1,150 mi) from central Tokyo. Because of the islands’ distance from the administrative headquarters of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government in Shinjuku, local subprefectural branch offices administer them. The Izu Islands are a group of volcanic islands and form part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. The islands in order from closest to Tokyo are Izu Ōshima, Toshima, Nii-jima, Shikine-jima, Kōzu-shima, Miyake-jima, Mikurajima, Hachijō-jima, and Aogashima. The Izu Islands are grouped into three subprefectures. Izu Ōshima and Hachijojima are towns. The remaining islands are six villages, with Niijima and Shikinejima forming one village. The Ogasawara Islands include, from north to south, Chichi-jima, Nishinoshima, Haha-jima, Kita Iwo Jima, Iwo Jima, and Minami Iwo Jima. Ogasawara also administers two tiny outlying islands: Minami Torishima, the easternmost point in Japan and at 1,850 km (1,150 mi) the most distant island from central Tokyo, and Okinotorishima, the southernmost point in Japan.[56] Japan’s claim on an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) surrounding Okinotorishima is contested by China and South Korea as they regard Okinotorishima as uninhabitable rocks which have no EEZ.[57] The Iwo chain and the outlying islands have no permanent population, but hosts Japan Self-Defense Forces personnel. Local populations are only found on Chichi-Jima and Haha-Jima. The islands form both Ogasawara Subprefecture and the village of Ogasawara, Tokyo.
| Flag, name w/o suffix | Full name | District or Subprefecture |
Population | LPE code (w/o checksum) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese | Transcription | Translation | ||||
| 足立区 | Adachi-ku | Adachi Ward | — | 674,067 | 13121 | |
| 荒川区 | Arakawa-ku | Arakawa Ward | 213,648 | 13118 | ||
| 文京区 | Bunkyō-ku | Bunkyō Ward | 223,389 | 13105 | ||
| 千代田区 | Chiyoda-ku | Chiyoda Ward | 59,441 | 13101 | ||
| 中央区 | Chūō-ku | Chūō Ward (Central Ward) |
147,620 | 13102 | ||
| 江戸川区 | Edogawa-ku | Edogawa Ward (Edo River Ward) |
685,899 | 13123 | ||
| 板橋区 | Itabashi-ku | Itabashi Ward | 569,225 | 13119 | ||
| 葛飾区 | Katsushika-ku | Katsushika Ward (after Katsushika District) |
447,140 | 13122 | ||
| 北区 | Kita-ku | Kita Ward (North Ward) |
345,063 | 13117 | ||
| 江東区 | Kōtō-ku | Kōtō Ward | 502,579 | 13108 | ||
| 目黒区 | Meguro-ku | Meguro Ward | 280,283 | 13110 | ||
| 港区 | Minato-ku | Minato Ward (Harbor/Port District) |
248,071 | 13103 | ||
| 中野区 | Nakano-ku | Nakano Ward | 332,902 | 13114 | ||
| 練馬区 | Nerima-ku | Nerima Ward | 726,748 | 13120 | ||
| 大田区 | Ōta-ku | Ōta Ward | 722,608 | 13111 | ||
| 世田谷区 | Setagaya-ku | Setagaya Ward | 910,868 | 13112 | ||
| 渋谷区 | Shibuya-ku | Shibuya Ward | 227,850 | 13113 | ||
| 品川区 | Shinagawa-ku | Shinagawa Ward | 392,492 | 13109 | ||
| 新宿区 | Shinjuku-ku | Shinjuku Ward | 339,211 | 13104 | ||
| 杉並区 | Suginami-ku | Suginami Ward | 570,483 | 13115 | ||
| 墨田区 | Sumida-ku | Sumida Ward | 260,358 | 13107 | ||
| 台東区 | Taitō-ku | Taitō Ward | 200,486 | 13106 | ||
| 豊島区 | Toshima-ku | Toshima Ward (after Toshima District) |
294,673 | 13116 | ||
| あきる野市 | Akiruno-shi | Akiruno City | 80,464 | 13228 | ||
| 昭島市 | Akishima-shi | Akishima City | 111,449 | 13207 | ||
| 調布市 | Chōfu-shi | Chōfu City | 240,668 | 13208 | ||
| 府中市 | Fuchū-shi | Fuchū City (provincial capital city) |
260,891 | 13206 | ||
| 福生市 | Fussa-shi | Fussa City | 58,393 | 13218 | ||
| 八王子市 | Hachiōji-shi | Hachiōji City | 579,330 | 13201 | ||
| 羽村市 | Hamura-shi | Hamura City | 55,596 | 13227 | ||
| 東久留米市 | Higashi-Kurume-shi | Higashi-Kurume City East Kurume City (as opposed to Kurume City, Western Japan) |
116,869 | 13222 | ||
| 東村山市 | Higashi-Murayama-shi | Higashi-Murayama City East Murayama City (after Murayama Region) |
150,984 | 13213 | ||
| 東大和市 | Higashi-Yamato-shi | Higashi-Yamato City (here: Tokyo’s Yamato City)[58] (as opposed to Kanagawa’s Yamato City) |
85,229 | 13220 | ||
| 日野市 | Hino-shi | Hino City | 185,133 | 13212 | ||
| 稲城市 | Inagi-shi | Inagi City | 87,927 | 13225 | ||
| 清瀬市 | Kiyose-shi | Kiyose City | 74,495 | 13221 | ||
| 小平市 | Kodaira-shi | Kodaira City | 194,757 | 13211 | ||
| 小金井市 | Koganei-shi | Koganei City | 121,516 | 13210 | ||
| 国分寺市 | Kokubunji-shi | Kokubunji City (provincial temple city) |
122,787 | 13214 | ||
| 狛江市 | Komae-shi | Komae City | 81,671 | 13219 | ||
| 国立市 | Kunitachi-shi | Kunitachi City | 75,867 | 13215 | ||
| 町田市 | Machida-shi | Machida City | 429,040 | 13209 | ||
| 三鷹市 | Mitaka-shi | Mitaka City | 189,168 | 13204 | ||
| 武蔵村山市 | Musashi-Murayama-shi | Musashi-Murayama City (as opposed to Murayama City, Dewa Province) |
70,649 | 13223 | ||
| 武蔵野市 | Musashino-shi | Musashino City (after Musashino Region) |
143,686 | 13203 | ||
| 西東京市 | Nishi-Tōkyō-shi | Nishi-Tokyo City (Western Tokyo City) |
200,102 | 13229 | ||
| 青梅市 | Ōme-shi | Ōme City | 136,071 | 13205 | ||
| 立川市 | Tachikawa-shi | Tachikawa City | 184,183 | 13202 | ||
| 多摩市 | Tama-shi | Tama City (after Tama district/area/river) |
147,953 | 13224 | ||
| 日の出町 | Hinode-machi | Hinode Town | Nishi-Tama (Western Tama [ja]) |
17,141 | 13305 | |
| 檜原村 | Hinohara-mura | Hinohara Village | 2,194 | 13307 | ||
| 瑞穂町 | Mizuho-machi | Mizuho Town | 33,117 | 13303 | ||
| 奥多摩町 | Okutama-machi | Okutama Town (Rear/Outer Tama Town) |
5,177 | 13308 | ||
| 八丈町 | Hachijō-machi | Hachijō Town (on Hachijō Island) |
Hachijō | 7,516 | 13401 | |
| 青ヶ島村 | Aogashima-mura | Aogashima Village (on Aogashima) |
169 | 13402 | ||
| 三宅村 | Miyake-mura | Miyake Village (on Miyake Island) |
Miyake | 2,451 | 13381 | |
| 御蔵島村 | Mikurajima-mura | Mikurajima Village (Mikura Island Village) |
328 | 13382 | ||
| 大島町 | Ōshima-machi | Ōshima Town ([Izu] Grand Island Town) |
Ōshima | 7,762 | 13361 | |
| 利島村 | Toshima-mura | To-shima Village (on homonymous island) |
309 | 13362 | ||
| 新島村 | Niijima-mura | Niijima Village (on homonymous island) |
2,697 | 13363 | ||
| 神津島村 | Kōzushima-mura | Kōzushima Village (on homonymous island) |
1,856 | 13364 | ||
| 小笠原村 | Ogasawara-mura | Ogasawara Village (on homonymous islands) |
Ogasawara | 3,029 | 13421 | |
| 東京都 | Tōkyō-to | Tokyo «Metropolis» functionally: ~ Prefecture literally/etymologically: ~ Capital |
– | 13,960,236 | 13000 ISO: JP-13 |
-
Tama
-
-
Municipal mergers[edit]
When Tokyo reached its current extent except for smaller border changes in 1893, it consisted of over 170 municipalities, 1 (by definition: district-independent) city, nine districts with their towns and villages, plus the island communities that had never part of ritsuryō[clarification needed] districts. By 1953, the number of municipalities had dropped to 97. The current total of 62 was reached in 2001.
National parks[edit]
Ogasawara National Park, a UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site
As of March 31, 2008, 36% of the total land area of the prefecture was designated as Natural Parks (second only to Shiga Prefecture), namely the Chichibu Tama Kai, Fuji-Hakone-Izu, and Ogasawara National Parks (the last a UNESCO World Heritage Site); Meiji no Mori Takao Quasi-National Park; and Akikawa Kyūryō, Hamura Kusabana Kyūryō, Sayama, Takao Jinba, Takiyama, and Tama Kyūryō Prefectural Natural Parks.[59]
A number of museums are located in Ueno Park: Tokyo National Museum, National Museum of Nature and Science, Shitamachi Museum and National Museum for Western Art, among others. There are also artworks and statues at several places in the park. There is also a zoo in the park, and the park is a popular destination to view cherry blossoms.
Earthquakes[edit]
Minor quakes[edit]
A bilingual sign in Shibuya with instructions (in Japanese and English) in case of an earthquake
Tokyo is near the boundary of three plates, making it an extremely active region for smaller quakes and slippage which frequently affect the urban area with swaying as if in a boat, although epicenters within mainland Tokyo (excluding Tokyo’s 2,000 km (1,243 mi)–long island jurisdiction) are quite rare. It is not uncommon in the metro area to have hundreds of these minor quakes (magnitudes 4–6) that can be felt in a single year, something local residents merely brush off but can be a source of anxiety not only for foreign visitors but for Japanese from elsewhere as well. They rarely cause much damage (sometimes a few injuries) as they are either too small or far away as quakes tend to dance around the region. Particularly active are offshore regions and to a lesser extent Chiba and Ibaraki.[60]
Infrequent powerful quakes[edit]
Tokyo has been hit by powerful megathrust earthquakes in 1703, 1782, 1812, 1855, 1923, and much more indirectly (with some liquefaction in landfill zones) in 2011;[61][62] the frequency of direct and large quakes is a relative rarity. The 1923 earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 8.3, killed 142,000 people, the last time the urban area was directly hit.
Volcanic eruptions[edit]
Mount Fuji is about 100 km (62 mi) southwest of Tokyo. There is a low risk of eruption. The last recorded was the Hōei eruption which started on December 16, 1707, and ended about January 1, 1708 (16 days).[63] During the Hōei eruption, the ash amount was 4 cm in southern Tokyo (bay area) and 2 cm to 0.5 cm in central Tokyo.[64] Kanagawa had 16 cm to 8 cm ash and Saitama 0.5 to 0 cm.[64] If the wind blows north-east it could send volcanic ash to Tokyo metropolis.[65] According to the government, less than a millimeter of the volcanic ash from a Mount Fuji eruption could cause power grid problems such as blackouts and stop trains in the Tokyo metropolitan area.[65] A mixture of ash with rain could stick to cellphone antennas, power lines and cause temporary power outages.[65] The affected areas would need to be evacuated.[65]
Water management[edit]
The MAOUDC is the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility.
Tokyo is located on the Kantō Plain with five river systems and dozens of rivers that expand during each season.[66] Important rivers are Edogawa, Nakagawa, Arakawa, Kandagawa, Megurogawa and Tamagawa.[67] In 1947, Typhoon Kathleen struck Tokyo, destroying 31,000 homes and killing 1,100 people.[66] In 1958, Typhoon Ida dropped 400 mm (16 in) of rain in a single week, causing streets to flood.[66] In the 1950s and 1960s, the government invested 6–7% of the national budget on disaster and risk reduction.[66] A huge system of dams, levees and tunnels was constructed.[66] The purpose is to manage heavy rain, typhonic rain, and river floods.[66]
Tokyo has currently the world’s largest underground floodwater diversion facility called the Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel (MAOUDC).[13][66] It took 13 years to build and was completed in 2006. The MAOUDC is a 6.3 km (3.9 mi) long system of tunnels, 22 meters (72 ft) underground, with 70-meter (230 ft) tall cylindrical tanks, each tank being large enough to fit a space shuttle or the Statue of Liberty.[66] During floods, excess water is collected from rivers and drained to the Edo River.[67] Low-lying areas of Kōtō, Edogawa, Sumida, Katsushika, Taitō and Arakawa near the Arakawa River are most at risk of flooding.[67]
Climate[edit]
The former city of Tokyo and the majority of Tokyo prefecture lie in the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen climate classification: Cfa),[68] with hot, humid summers and mild to cool winters with occasional cold spells. The region, like much of Japan, experiences a one-month seasonal lag. The warmest month is August, which averages 26.9 °C (80.4 °F). The coolest month is January, averaging 5.4 °C (41.7 °F). The record low temperature was −9.2 °C (15.4 °F) on January 13, 1876. The record high was 39.5 °C (103.1 °F) on July 20, 2004.
The record highest low temperature is 30.3 °C (86.5 °F), on August 12, 2013, making Tokyo one of only seven observation sites in Japan that have recorded a low temperature over 30 °C (86.0 °F).[69]
Annual rainfall averages nearly 1,600 millimeters (63.0 in), with a wetter summer and a drier winter. The growing season in Tokyo lasts for about 322 days from around mid-February to early January.[70] Snowfall is sporadic, and occurs almost annually.[71] Tokyo often sees typhoons every year, though few are strong. The wettest month since records began in 1876 was October 2004, with 780 millimeters (30 in) of rain,[72] including 270.5 mm (10.65 in) on the ninth of that month.[73] The most recent of four months on record to observe no precipitation is December 1995.[69] Annual precipitation has ranged from 879.5 mm (34.63 in) in 1984 to 2,229.6 mm (87.78 in) in 1938.[69]
| Climate data for Kitanomaru Park, Chiyoda ward, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present[74] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.6 (72.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
39.5 (103.1) |
39.1 (102.4) |
38.1 (100.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.3 (81.1) |
24.8 (76.6) |
39.5 (103.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.2 (57.6) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.9 (85.8) |
31.3 (88.3) |
27.5 (81.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
12.0 (53.6) |
20.3 (68.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
23.3 (73.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.7 (45.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
2.1 (35.8) |
5.0 (41.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.5 (74.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
14.8 (58.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.8 (38.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.2 (15.4) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
2.2 (36.0) |
8.5 (47.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 59.7 (2.35) |
56.5 (2.22) |
116.0 (4.57) |
133.7 (5.26) |
139.7 (5.50) |
167.8 (6.61) |
156.2 (6.15) |
154.7 (6.09) |
224.9 (8.85) |
234.8 (9.24) |
96.3 (3.79) |
57.9 (2.28) |
1,598.2 (62.92) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) |
4 (1.6) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
8 (3.1) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.3 | 6.1 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.1 | 12.8 | 12.0 | 9.4 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 116.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 51 | 52 | 57 | 62 | 68 | 75 | 76 | 74 | 75 | 71 | 64 | 56 | 65 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | −5 (23) |
−4 (25) |
1 (34) |
8 (46) |
13 (55) |
18 (64) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
19 (66) |
12 (54) |
6 (43) |
−1 (30) |
9 (49) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.6 | 170.4 | 175.3 | 178.8 | 179.6 | 124.2 | 151.4 | 174.2 | 126.7 | 129.4 | 149.8 | 174.4 | 1,926.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 61 | 56 | 47 | 45 | 41 | 30 | 34 | 42 | 34 | 37 | 48 | 57 | 44 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Source 1: Japan Meteorological Agency[75][76][69] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV),[77] Time and Date (dewpoints, 1985-2015)[78] |
See or edit raw graph data.
Tokyo has experienced significant warming of its climate since temperature records began in 1876.
| Climate data for Tokyo (Tokyo, Japan), 1876–1905 normals | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.1 (82.6) |
29.8 (85.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
11.0 (51.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
20.5 (68.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
15.9 (60.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
5.3 (41.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.8 (62.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
18.6 (65.5) |
11.9 (53.4) |
5.4 (41.7) |
0.4 (32.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 55.2 (2.17) |
72.4 (2.85) |
111.0 (4.37) |
129.1 (5.08) |
151.9 (5.98) |
166.3 (6.55) |
139.7 (5.50) |
114.7 (4.52) |
203.3 (8.00) |
184.1 (7.25) |
104.7 (4.12) |
58.7 (2.31) |
1,491.1 (58.7) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 186.7 | 178.5 | 174.1 | 183.1 | 204.8 | 158.5 | 183.9 | 207.0 | 142.8 | 144.0 | 167.4 | 190.8 | 2,121.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[79] |
The western mountainous area of mainland Tokyo, Okutama also lies in the humid subtropical climate (Köppen classification: Cfa).
| Climate data for Ogouchi, Okutama town, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1875–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.8 (64.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.3 (97.3) |
36.4 (97.5) |
35.0 (95.0) |
30.2 (86.4) |
23.8 (74.8) |
22.8 (73.0) |
36.4 (97.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.6 (45.7) |
10.9 (51.6) |
16.5 (61.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.5 (83.3) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.8 (65.8) |
14.0 (57.2) |
9.3 (48.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
2.2 (36.0) |
5.5 (41.9) |
10.8 (51.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.6 (72.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.3 (57.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.9 (39.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.3 (59.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.1 (68.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.3 (15.3) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
0.7 (33.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
13.2 (55.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49.5 (1.95) |
45.9 (1.81) |
88.5 (3.48) |
106.3 (4.19) |
118.7 (4.67) |
163.2 (6.43) |
205.6 (8.09) |
217.4 (8.56) |
270.2 (10.64) |
215.4 (8.48) |
68.9 (2.71) |
43.7 (1.72) |
1,608 (63.31) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 206.5 | 187.7 | 173.0 | 178.4 | 172.2 | 104.2 | 124.8 | 144.6 | 104.5 | 128.7 | 164.5 | 186.5 | 1,874.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[80][81] |
The climates of Tokyo’s offshore territories vary significantly from those of the city. The climate of Chichijima in Ogasawara village is on the boundary between the tropical savanna climate (Köppen classification: Aw) and the tropical rainforest climate (Köppen classification: Af). It is approximately 1,000 km (621 mi) south of the Greater Tokyo Area, resulting in much different climatic conditions.
| Climate data for Chichijima, Ogasawara, Tokyo, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1896–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
26.7 (80.1) |
28.4 (83.1) |
30.1 (86.2) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
33.7 (92.7) |
33.1 (91.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
30.2 (86.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
34.1 (93.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
28.5 (83.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.3 (86.5) |
29.9 (85.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.5 (65.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
26.2 (79.2) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
26.4 (79.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
20.6 (69.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 15.8 (60.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
16.8 (62.2) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.4 (70.5) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.1 (79.0) |
25.7 (78.3) |
24.4 (75.9) |
21.6 (70.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.2 (70.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
7.8 (46.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.9 (57.0) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.2 (72.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.8 (46.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 63.6 (2.50) |
51.6 (2.03) |
75.8 (2.98) |
113.3 (4.46) |
151.9 (5.98) |
111.8 (4.40) |
79.5 (3.13) |
123.3 (4.85) |
144.2 (5.68) |
141.7 (5.58) |
136.1 (5.36) |
103.3 (4.07) |
1,296.1 (51.02) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 11.0 | 8.5 | 9.8 | 10.0 | 11.8 | 8.8 | 8.6 | 11.3 | 13.4 | 13.7 | 12.0 | 11.2 | 130.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66 | 68 | 72 | 79 | 84 | 86 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 81 | 76 | 70 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 131.3 | 138.3 | 159.2 | 148.3 | 151.8 | 205.6 | 246.8 | 213.7 | 197.7 | 173.2 | 139.1 | 125.3 | 2,030.3 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[82]
[83] |
Tokyo’s easternmost territory, the island of Minamitorishima in Ogasawara village, is in the tropical savanna climate zone (Köppen classification: Aw). Tokyo’s Izu and Ogasawara islands are affected by an average of 5.4 typhoons a year, compared to 3.1 in mainland Kantō.[84]
Cityscape[edit]
Architecture in Tokyo has largely been shaped by Tokyo’s history. Twice in recent history has the metropolis been left in ruins: first in the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake and later after extensive firebombing in World War II.[85] Because of this, Tokyo’s urban landscape consists mainly of modern and contemporary architecture, and older buildings are scarce.[85] Tokyo features many internationally famous forms of modern architecture including Tokyo International Forum, Asahi Beer Hall, Mode Gakuen Cocoon Tower, NTT Docomo Yoyogi Building and Rainbow Bridge. Tokyo features two distinctive towers: Tokyo Tower and Tokyo Skytree, the latter of which is the tallest tower in both Japan and the world, and the second tallest structure in the world after the Burj Khalifa in Dubai.[12] Mori Building Co started work on Tokyo’s new tallest building which is set to be finished in March 2023. The project will cost 580 billion yen ($5.5 billion).[86]
Tokyo contains numerous parks and gardens. There are four national parks in Tokyo Prefecture, including the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, which includes all of the Izu Islands.
Environment[edit]
Tokyo has enacted a measure to cut greenhouse gases. Governor Shintaro Ishihara created Japan’s first emissions cap system, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emission by a total of 25% by 2020 from the 2000 level.[87] Tokyo is an example of an urban heat island, and the phenomenon is especially serious in its special wards.[88][89] According to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government,[90] the annual mean temperature has increased by about 3 °C (5.4 °F) over the past 100 years. Tokyo has been cited as a «convincing example of the relationship between urban growth and climate».[91]
In 2006, Tokyo enacted the «10 Year Project for Green Tokyo» to be realized by 2016. It set a goal of increasing roadside trees in Tokyo to 1 million (from 480,000), and adding 1,000 ha (2,500 acres) of green space, 88 ha (220 acres) of which will be a new park named «Umi no Mori» (Sea Forest) which will be on a reclaimed island in Tokyo Bay which used to be a landfill.[92] From 2007 to 2010, 436 ha (1,080 acres) of the planned 1,000 ha of green space was created and 220,000 trees were planted, bringing the total to 700,000. As of 2014, roadside trees in Tokyo have increased to 950,000, and a further 300 ha (740 acres) of green space has been added.[93]
Demographics[edit]
Tokyo prefecture population pyramid in 2020
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | 590,268 | — |
| 1880 | 712,259 | +20.7% |
| 1890 | 1,389,684 | +95.1% |
| 1900 | 1,580,124 | +13.7% |
| 1910 | 2,202,079 | +39.4% |
| 1920 | 3,699,428 | +68.0% |
| 1925 | 4,485,144 | +21.2% |
| 1930 | 5,408,678 | +20.6% |
| 1935 | 6,369,919 | +17.8% |
| 1940 | 7,354,971 | +15.5% |
| 1945 | 3,488,284 | −52.6% |
| 1950 | 6,277,500 | +80.0% |
| 1955 | 8,037,084 | +28.0% |
| 1960 | 9,683,802 | +20.5% |
| 1965 | 10,869,244 | +12.2% |
| 1970 | 11,408,071 | +5.0% |
| 1975 | 11,673,554 | +2.3% |
| 1980 | 11,618,281 | −0.5% |
| 1985 | 11,829,363 | +1.8% |
| 1990 | 11,855,563 | +0.2% |
| 1995 | 11,773,605 | −0.7% |
| 2000 | 12,064,101 | +2.5% |
| 2005 | 12,576,601 | +4.2% |
| 2010 | 13,159,388 | +4.6% |
| 2015 | 13,515,271 | +2.7% |
| 2020 | 13,982,112 | +3.5% |
As of October 2012, the official intercensal estimate showed 13.506 million people in Tokyo, with 9.214 million living within Tokyo’s 23 wards.[94] During the daytime, the population swells by over 2.5 million as workers and students commute from adjacent areas. This effect is even more pronounced in the three central wards of Chiyoda, Chūō, and Minato, whose collective population as of the 2005 National Census was 326,000 at night, but 2.4 million during the day.[95]
In 1889, the Home Ministry recorded 1,375,937 people in Tokyo City and a total of 1,694,292 people in Tokyo-fu.[96] In the same year, a total of 779 foreign nationals were recorded as residing in Tokyo. The most common nationality was English (209 residents), followed by American (182) and Chinese nationals (137).[97]
|
Tokyo historical population since 1920 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This chart is growth rate of municipalities of Tokyo, Japan. It is estimated by census carried out in 2005 and 2010. Increase 10.0% and over 7.5–9.9% 5.0–7.4% 2.5–4.9% 0.0–2.4% Decrease 0.0–2.4% 2.5–4.9% 5.0–7.4% 7.5–9.9% 10.0% and over |
|
Economy[edit]
Ginza is a popular upscale shopping area in Tokyo.
Tokyo has the largest metropolitan economy in the world. According to a study conducted by PricewaterhouseCoopers, the Greater Tokyo Area (Tokyo–Yokohama, TYO) of 38 million people had a total GDP of $2 trillion in 2012 (at purchasing power parity), which topped that list.
Tokyo is a major international finance center;[99] it houses the headquarters of several of the world’s largest investment banks and insurance companies, and serves as a hub for Japan’s transportation, publishing, electronics and broadcasting industries. During the centralized growth of Japan’s economy following World War II, many large firms moved their headquarters from cities such as Osaka (the historical commercial capital) to Tokyo, in an attempt to take advantage of better access to the government. This trend has begun to slow due to ongoing population growth in Tokyo and the high cost of living there.
Tokyo was rated by the Economist Intelligence Unit as the most expensive (highest cost-of-living) city in the world for 14 years in a row ending in 2006, when it was replaced by Oslo, and later Paris.[100][101]
Tokyo emerged as a leading international financial center (IFC) in the 1960s and has been described as one of the three «command centers» for the world economy, along with New York City and London.[102] In the 2020 Global Financial Centers Index, Tokyo was ranked as having the fourth most competitive financial center in the world (alongside cities such as New York City, London, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Singapore, Beijing, San Francisco, Shenzhen and Zurich in the top 10), and second most competitive in Asia (after Shanghai).[11] The Japanese financial market opened up slowly in 1984 and accelerated its internationalization with the «Japanese Big Bang» in 1998.[103] Despite the emergence of Singapore and Hong Kong as competing financial centers, the Tokyo IFC manages to keep a prominent position in Asia. The Tokyo Stock Exchange is Japan’s largest stock exchange, and third largest in the world by market capitalization and fourth largest by share turnover. In 1990 at the end of the Japanese asset price bubble, it accounted for more than 60% of the world stock market value.[104] Tokyo had 8,460 ha (20,900 acres) of agricultural land as of 2003,[105] according to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, placing it last among the nation’s prefectures. The farmland is concentrated in Western Tokyo. Perishables such as vegetables, fruits, and flowers can be conveniently shipped to the markets in the eastern part of the prefecture. Komatsuna and spinach are the most important vegetables; as of 2000, Tokyo supplied 32.5% of the komatsuna sold at its central produce market.[citation needed]
With 36% of its area covered by forest, Tokyo has extensive growths of cryptomeria and Japanese cypress, especially in the mountainous western communities of Akiruno, Ōme, Okutama, Hachiōji, Hinode, and Hinohara. Decreases in the price of timber, increases in the cost of production, and advancing old age among the forestry population have resulted in a decline in Tokyo’s output. In addition, pollen, especially from cryptomeria, is a major allergen for the nearby population centers. Tokyo Bay was once a major source of fish. Most of Tokyo’s fish production comes from the outer islands, such as Izu Ōshima and Hachijō-Jima. Skipjack tuna, nori, and aji are among the ocean products.[106]
Tourism in Tokyo is also a contributor to the economy. In 2006, 4.81 million foreigners and 420 million Japanese visits to Tokyo were made; the economic value of these visits totaled 9.4 trillion yen according to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Many tourists visit the various downtowns, stores, and entertainment districts throughout the neighborhoods of the special wards of Tokyo. Cultural offerings include both omnipresent Japanese pop culture and associated districts such as Shibuya and Harajuku, subcultural attractions such as Studio Ghibli anime center, as well as museums like the Tokyo National Museum, which houses 37% of the country’s artwork national treasures (87/233).
The Toyosu Market in Tokyo is the largest wholesale fish and seafood market in the world since it opened on October 11, 2018.[107] It is also one of the largest wholesale food markets of any kind. It is located in the Toyosu area of Kōtō ward. The Toyosu Market holds strong to the traditions of its predecessor, the Tsukiji Fish Market and Nihonbashi fish market, and serves some 50,000 buyers and sellers every day. Retailers, whole-sellers, auctioneers, and public citizens alike frequent the market, creating a unique microcosm of organized chaos that still continues to fuel the city and its food supply after over four centuries.[108]
Transportation[edit]
Tokyo, which is the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, is Japan’s largest domestic and international hub for rail and ground transportation. However, its airspace has been under the US military’s exclusive control after World War II. Public transportation within Tokyo is dominated by an extensive network of «clean and efficient»[109] trains and subways run by a variety of operators, with buses, monorails and trams playing a secondary feeder role. There are up to 62 electric train lines and more than 900 train stations in Tokyo.[110] Shibuya Crossing is the «world’s busiest pedestrian crossing», with around 3,000 people crossing at a time.[111][112][113]
As a result of World War II, Japanese planes are generally forbidden to fly over Tokyo.[114] Therefore, Japan constructed airports outside Tokyo. Narita International Airport in Chiba Prefecture is the major gateway for international travelers to Japan. Japan’s flag carrier Japan Airlines, as well as All Nippon Airways, have a hub at this airport. Haneda Airport on the reclaimed land at Ōta, offers domestic and international flights. As of 2018, some flight routes into Haneda are permitted through Tokyo airspace.[115]
Various islands governed by Tokyo have their own airports. Hachijō-jima (Hachijojima Airport), Miyakejima (Miyakejima Airport), and Izu Ōshima (Oshima Airport) have services to Tokyo International and other airports.
Rail is the primary mode of transportation in Tokyo,[116] which has the most extensive urban railway network in the world and an equally extensive network of surface lines. JR East operates Tokyo’s largest railway network, including the Yamanote Line loop that circles the center of downtown Tokyo. It operates rail lines in the entire metropolitan area of Tokyo and in the rest of the northeastern part of Honshu. JR East is also responsible for Shinkansen high-speed rail lines.
Two different organizations operate the subway network: the private Tokyo Metro and the governmental Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation. The Metropolitan Government and private carriers operate bus routes and one tram route. Local, regional, and national services are available, with major terminals at the giant railroad stations, including Tokyo, Shinagawa, and Shinjuku.
Expressways link the capital to other points in the Greater Tokyo Area, the Kantō region, and the islands of Kyushu and Shikoku. To build them quickly before the 1964 Summer Olympics, most were constructed above existing roads.[117] Other transportation includes taxis operating in the special wards and the cities and towns. Also, long-distance ferries serve the islands of Tokyo and carry passengers and cargo to domestic and foreign ports.
Education[edit]
Tokyo has many universities, junior colleges, and vocational schools. Many of Japan’s most prestigious universities are in Tokyo, including University of Tokyo, Hitotsubashi University, Meiji University, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Waseda University, Tokyo University of Science, Sophia University, and Keio University.[118] Some of the biggest national universities in Tokyo are:
- Hitotsubashi University
- National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies
- Ochanomizu University
- Tokyo Gakugei University
- Tokyo Institute of Technology
- Tokyo Medical and Dental University
- Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
- Tokyo University of Foreign Studies
- Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology
- Tokyo University of the Arts
- University of Electro-Communications
- University of Tokyo
There is only one non-national public university: Tokyo Metropolitan University. There are also a few universities well known for classes conducted in English and for the teaching of the Japanese language, including the Globis University Graduate School of Management, International Christian University, Sophia University, and Waseda University
Tokyo is also the headquarters of the United Nations University.
Most publicly run kindergartens, elementary schools (years 1 through 6), and junior high (lower secondary) schools (7 through 9) are operated by local wards or municipal offices. Most public senior high (upper secondary) schools in Tokyo are run by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education and are called «Metropolitan High Schools». Tokyo also has many private schools from kindergarten through high school:
Culture[edit]
Tokyo has many museums. In Ueno Park, there is the Tokyo National Museum, the country’s largest museum and specializing in traditional Japanese art; the National Museum of Western Art and Ueno Zoo. Other museums include the National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation in Odaiba; the Edo-Tokyo Museum in Sumida, across the Sumida River from the center of Tokyo; the Nezu Museum in Aoyama; and the National Diet Library, National Archives, and the National Museum of Modern Art, which are near the Imperial Palace.
Tokyo has many theaters for performing arts. These include national and private theaters for traditional forms of Japanese drama. Noteworthy are the National Noh Theatre for noh and the Kabuki-za for Kabuki.[119] Symphony orchestras and other musical organizations perform modern and traditional music. The New National Theater Tokyo in Shibuya is the national center for the performing arts, including opera, ballet, contemporary dance and drama.[120] Tokyo also hosts modern Japanese and international pop, and rock music at venues ranging in size from intimate clubs to internationally known areas such as the Nippon Budokan.
Many different festivals occur throughout Tokyo. Major events include the Sannō at Hie Shrine, the Sanja at Asakusa Shrine, and the biennial Kanda Festivals. The last features a parade with elaborately decorated floats and thousands of people. Annually on the last Saturday of July, an enormous fireworks display over the Sumida River attracts over a million viewers. Once cherry blossoms bloom in spring, many residents gather in Ueno Park, Inokashira Park, and the Shinjuku Gyoen National Garden for picnics under the blossoms.
Harajuku, a neighborhood in Shibuya, is known internationally for its youth style, fashion[121] and cosplay.
Cuisine in Tokyo is internationally acclaimed. In November 2007, Michelin released their first guide for fine dining in Tokyo, awarding 191 stars in total, or about twice as many as Tokyo’s nearest competitor, Paris. As of 2017, 227 restaurants in Tokyo have been awarded (92 in Paris). Twelve establishments were awarded the maximum of three stars (Paris has 10), 54 received two stars, and 161 earned one star.[122]
Sports[edit]
Tokyo, with a diverse array of sports, is home to two professional baseball clubs, the Yomiuri Giants who play at the Tokyo Dome and Tokyo Yakult Swallows at Meiji-Jingu Stadium. The Japan Sumo Association is also headquartered in Tokyo at the Ryōgoku Kokugikan sumo arena where three official sumo tournaments are held annually (in January, May, and September). Soccer clubs in Tokyo include F.C. Tokyo and Tokyo Verdy 1969, both of which play at Ajinomoto Stadium in Chōfu, and FC Machida Zelvia at Nozuta Stadium in Machida. Rugby Union is also played in Tokyo, with multiple Japan Rugby League One clubs based in the city including: Black Rams Tokyo (Setagaya), Tokyo Sungoliath (Fuchū) and Toshiba Brave Lupus Tokyo (Fuchū).
Basketball clubs include the Hitachi SunRockers, Toyota Alvark Tokyo and Tokyo Excellence.
Tokyo hosted the 1964 Summer Olympics, thus becoming the first Asian city to host the Summer Games. The National Stadium, also known as the Olympic Stadium, was host to a number of international sporting events. In 2016, it was to be replaced by the New National Stadium. With a number of world-class sports venues, Tokyo often hosts national and international sporting events such as basketball tournaments, women’s volleyball tournaments, tennis tournaments, swim meets, marathons, rugby union and sevens rugby games, soccer exhibition games, judo, and karate. Tokyo Metropolitan Gymnasium, in Sendagaya, Shibuya, is a large sports complex that includes swimming pools, training rooms, and a large indoor arena. According to Around the Rings, the gymnasium has played host to the October 2011 artistic gymnastics world championships, despite the International Gymnastics Federation’s initial doubt in Tokyo’s ability to host the championships following the March 11 tsunami.[123] Tokyo was also selected to host a number of games for the 2019 Rugby World Cup, and to host the 2020 Summer Olympics and the Paralympics which had to be rescheduled to the summer of 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan.
In popular culture[edit]
Akihabara is the most popular area for fans of anime, manga, and games.
As the largest population center in Japan and the site of the country’s largest broadcasters and studios, Tokyo is frequently the setting for many Japanese movies, television shows, animated series (anime), web comics, light novels, video games, and comic books (manga). In the kaiju (monster movie) genre, landmarks of Tokyo are usually destroyed by giant monsters such as Godzilla and Gamera.
Some Hollywood directors have turned to Tokyo as a backdrop for movies set in Japan. Postwar examples include Tokyo Joe, My Geisha, Tokyo Story and the James Bond film You Only Live Twice; recent examples include Kill Bill, The Fast and the Furious: Tokyo Drift, Lost in Translation, Babel, Inception, The Wolverine and Avengers: Endgame.
Japanese author Haruki Murakami has based some of his novels in Tokyo (including Norwegian Wood), and David Mitchell’s first two novels (number9dream and Ghostwritten) featured the city. Contemporary British painter Carl Randall spent 10 years living in Tokyo as an artist, creating a body of work depicting the city’s crowded streets and public spaces.[124][125][126][127][128]
International relations[edit]
Tokyo is the founding member of the Asian Network of Major Cities 21 and is a member of the Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. Tokyo was also a founding member of the C40 Cities Climate Leadership Group.
Sister cities and states[edit]
As of 2022, Tokyo has twinning or friendship agreements with the following twelve cities and states:[129]
- New York City, United States (since February 1960)
- Beijing, China (since March 1979)
- Paris, France (since July 1982)[130]
- New South Wales, Australia (since May 1984)
- Seoul, South Korea (since September 1988)
- Jakarta, Indonesia (since October 1989)
- São Paulo State, Brazil (since June 1990)
- Cairo, Egypt (since October 1990)
- Moscow, Russia (since July 1991)
- Berlin, Germany (since May 1994)
- Rome, Italy (since July 1996)
- London, United Kingdom (since October 2015)
Friendship and cooperation agreements[edit]
- Tomsk Oblast, Russia (since May 2015)[131]
- Brussels, Belgium (since October 2016)
- Mumbai, India (since November 2016)
- Los Angeles County, United States (since August 2021)[132]
International academic and scientific research[edit]
Research and development in Japan and the Japanese space program are globally represented by several of Tokyo’s medical and scientific facilities, including the University of Tokyo and other universities in Tokyo, which work in collaboration with many international institutions. Especially with the United States, including NASA and the many private spaceflight companies,[133] Tokyo universities have working relationships with all of the Ivy League institutions (including Harvard and Yale University),[134] along with other research universities and development laboratories, such as Stanford, MIT, and the UC campuses throughout California,[135][136] as well as UNM and Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico.[137][138][139] Other partners worldwide include Oxford University in the United Kingdom,[140] the National University of Singapore in Singapore,[141] the University of Toronto in Canada,[142] and Tsinghua University in China.[143]
See also[edit]
- List of cities proper by population
- List of cities with the most skyscrapers
- List of tallest structures in Tokyo
- List of development projects in Tokyo
- List of largest cities
- List of metropolitan areas in Asia
- List of most expensive cities for expatriate employees
- List of urban agglomerations in Asia
- List of urban areas by population
- Megacity
- Tokyo dialect
- Yamanote and Shitamachi
References[edit]
- ^ 都庁は長野市. Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on April 19, 2014. Retrieved April 12, 2014. Shinjuku is the location of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Office. But Tokyo is not a «municipality». Therefore, for the sake of convenience, the notation of prefectural is «Tokyo».
- ^ «Reiwa 1 nationwide prefectures, cities and towns area statistics (October 1)» (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. December 26, 2019. Archived from the original on April 15, 2020. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- ^ «Mountains of Tokyo Metropolis» (in Japanese). Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- ^ a b «Tokyo Loses Population for First Time in 26 Years Amid Pandemic». Bloomberg.com. January 31, 2022. Retrieved May 17, 2022.
- ^ «Major Agglomerations of the World — Population Statistics and Maps».
- ^
«Population economics statistics (Tokyo inner production etc.)» (in Japanese). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Retrieved April 28, 2020. - ^ «Tokyo». Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d. Retrieved January 7, 2022.
- ^ Ōshima, Tadamori (February 23, 2018). 衆議院議員逢坂誠二君提出日本の首都に関する質問に対する答弁書. The House of Representatives, Japan. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
There is no law or regulation that expressly defines Tokyo as the capital. However, we are of the opinion that Tokyo is generally accepted in society to be the capital of Japan.
- ^ Nations, United. «The World’s Cities in 2018» (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved May 5, 2020.
- ^ «Global 500». Fortune.
- ^ a b «The Global Financial Centres Index 28» (PDF). Long Finance. September 2020. Retrieved October 4, 2020.
- ^ a b «Tokyo – GoJapanGo». Tokyo Attractions – Japanese Lifestyle. Mi Marketing Pty Ltd. Archived from the original on April 26, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ a b «Metropolitan Area Outer Underground Discharge Channel». Archived from the original on September 14, 2018. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ a b Hornyak, Tim (December 16, 2017). «Heart of gold: The Ginza Line celebrates its 90th birthday». Japan Times. Archived from the original on December 9, 2020. Retrieved December 29, 2017.
- ^ «The Global Liveability Index 2021» (PDF). The Economist. Retrieved February 5, 2023.
- ^ a b Room, Adrian. Placenames of the World. McFarland & Company (1996), p. 360 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-7864-1814-1.
- ^ US Department of State. (1906). A digest of international law as in diplomatic discussions, treaties and other international agreements (John Bassett Moore, ed.), Volume 5, p. 759 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine; excerpt, «The Mikado, on assuming the exercise of power at Yedo, changed the name of the city to Tokio».
- ^ Fiévé, Nicolas & Paul Waley (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. p. 253.
- ^ 明治東京異聞~トウケイかトウキョウか~東京の読み方 (in Japanese). Tokyo Metropolitan Archives. 2004. Archived from the original on October 6, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ McClain, James, James; et al. (1994). Edo and Paris: Urban Life and the State in the Early Modern Era. p. 13.
- ^ Sorensen, Andre (2004). The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty-First Century. p. 16.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. pp. 33, 55.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. pp. 182–183.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. p. 186.
- ^ Naitō, Akira (2003). Edo, the City That Became Tokyo: An Illustrated History. p. 188.
- ^ «History of Tokyo». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 12, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ «Tokyo-Yokohama earthquake of 1923». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on June 26, 2015. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ Tipton, Elise K. (2002). Modern Japan: A Social and Political History. Routledge. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-585-45322-4.
- ^ «9 March 1945: Burning the Heart Out of the Enemy». Wired. March 9, 2011. Archived from the original on March 15, 2014. Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- ^ «1945 Tokyo Firebombing Left Legacy of Terror, Pain». Common Dreams. Archived from the original on January 3, 2015. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- ^ Cybriwsky, Roman (1997). Historical Dictionary of Tokyo. Lanham, MD: Scarecrow. p. 22.
- ^ Hewitt, Kenneth (1983). «Place Annihilation: Area Bombing and the Fate of Urban Places». Annals of the Association of American Geographers. 73 (2): 257–284. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1983.tb01412.x.
- ^ Andre Sorensen. The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty First Century RoutledgeCurzon, 2004. ISBN 0-415-35422-6.
- ^ «Tokyo Narita International Airport (NRT) Airport Information (Tokyo, Japan)». Archived from the original on October 17, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ «Rail Transport in The World’s Major Cities» (PDF). Japan Railway and Transport Review. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ Saxonhouse, Gary R.; Stern, Robert M., eds. (2004). Japan’s Lost Decade: Origins, Consequences and Prospects for Recovery. Blackwell Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4051-1917-7.
- ^ Worrall, Julian. «The view from the Hills: Minoru Mori defends the Omotesando Hills development and reveals big plans for Tokyo». Metropolis. Archived from the original on November 19, 2006.
- ^ «Shift of Capital from Tokyo Committee». Japan Productivity Center for Socio-Economic Development. Archived from the original on August 25, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ «Policy Speech by Governor of Tokyo, Shintaro Ishihara at the First Regular Session of the Metropolitan Assembly, 2003». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on November 3, 2007. Retrieved October 17, 2007.
- ^ «Despite Major Earthquake Zero Tokyo Buildings Collapsed Thanks to Stringent Building Codes». March 11, 2011. Archived from the original on September 12, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^ Williams, Carol J. (March 11, 2011). «Japan earthquake disrupts Tokyo, leaves capital only lightly damaged». Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on December 13, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^
«Tokyo Radiation Levels». Metropolis Magazine. Archived from the original on May 20, 2012. Retrieved April 25, 2012. - ^ «Tokyo radiation levels – daily updates – April». Archived from the original on August 19, 2011. Retrieved October 11, 2011.
- ^ «IOC selects Tokyo as host of 2020 Summer Olympic Games». Archived from the original on October 10, 2014. Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- ^ Imai, Heide; Matjaz Ursic (2020). Creativity in Tokyo: Revitalizing a Mature City. Palgrave. ISBN 978-9811566868.
- ^ «Hot Market: Tokyo Residential Real Estate sees Strong Demand in a Tight Market, Prices Surge! – Housing Japan». Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ «Population of Tokyo, Japan». Mongabay. Archived from the original on January 21, 2012. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ^ «Tokyo, Japan Geographic Information». Latlong.net. September 2020. Archived from the original on September 14, 2017. Retrieved September 16, 2020.
- ^ «Population of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp. October 2015. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ «Local Government in Japan» (PDF). Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. p. 8. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 23, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^
The Structure of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Archived December 8, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (Tokyo government webpage) - ^ The Population of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government Archived December 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine (Retrieved on July 4, 2009)
- ^ «Pray For Tokyo: Chiyoda». Karis Japan. Archived from the original on July 20, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2015.
- ^ «Development of the Metropolitan Center, Subcenters and New Base». Bureau of Urban Development, Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 23, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ «Ogasawara Islands: World Natural Heritage». Ogasawara Village Industry and Tourist Board. Archived from the original (Adobe Flash) on March 31, 2017. Retrieved June 29, 2018.
- ^ Yoshikawa, Yukie (2005). «Okinotorishima: Just the Tip of the Iceberg». Harvard Asian Quarterly. 9 (4). Archived from the original on November 4, 2013.
- ^ Literally, 東/Higashi- means East; but when Yamato Town was renamed to Higashi-Yamato City in 1970, 東 was meant to represent the 東/Tō- in Tokyo, see Higashi-Yamato City: 市の名称 「東大和」の名称について (Japanese: On the city name «Higashi-Yamato»), retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ «General overview of area figures for Natural Parks by prefecture» (PDF). Ministry of the Environment. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 21, 2012. Retrieved February 8, 2012.
- ^ Matsu’ura, Ritsuko S. (January 28, 2017). «A short history of Japanese historical seismology: past and the present». Geoscience Letters. 4 (1): 3. Bibcode:2017GSL…..4….3M. doi:10.1186/s40562-017-0069-4 – via BioMed Central.
- ^ Grunewald, Elliot D.; Stein, Ross S. (2006). «A New 1649–1884 Catalog of Destructive Earthquakes near Tokyo and Implications for the Long-term Seismic Process». Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 111 (B12): B12306. Bibcode:2006JGRB..11112306G. doi:10.1029/2005JB004059.
- ^ «A new probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for greater Tokyo» (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ Masato Oyama (March 2007). 宝永四年(1707)噴火 (1707 Eruption). 富士山歴史噴火総解説 (Database of eruptions and other activities of Fuji Volcano, Japan, based on historical records since AD 781) (in Japanese). Shizuoka University. Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- ^ a b https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Volcanic-ash-downfall_map_of_Mt.Fuji_Hoei-eruption01.jpg Ashfall distribution map for examining disaster prevention measures (Mt. Fuji Hoei eruption)
- ^ a b c d «Mt Fuji eruption could cripple Tokyo». Nippon TV News 24 Japan. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020 – via YouTube.
- ^ a b c d e f g h «The underground cathedral protecting Tokyo from floods». BBC. November 29, 2018. Archived from the original on November 8, 2020.
- ^ a b c «Floods in Tokyo and Safety Tips and Preparation». Plaza Homes. February 28, 2020. Archived from the original on August 14, 2020.
- ^ Peel, M.C., Finlayson, B.L., and McMahon, T.A.: Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification Archived February 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 11, 1633–1644, 2007.
- ^ a b c d 観測史上1~10位の値( 年間を通じての値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 19, 2021. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ «Average Weather in Tokyo, Japan, Year Round — Weather Spark».
- ^ «Tokyo observes latest ever 1st snowfall». Archived from the original on March 19, 2007. Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(10月としての値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ^ The JMA Tokyo, Tokyo (東京都 東京) station is at 35°41.4′N 139°45.6′E, JMA: 気象統計情報 過去の気象データ検索>都道府県の選択>地点の選択. Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 1, 2018. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ^
気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 18, 2016. Retrieved May 19, 2021. - ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on November 2, 2014. Retrieved December 16, 2014.
- ^ «Tokyo, Japan — Detailed climate information and monthly weather forecast». Weather Atlas. Yu Media Group. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Climate & Weather Averages in Tokyo». Time and Date. Retrieved August 7, 2022.
- ^ «Station Name: TOKYO WMO Station ID: 47662». Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved July 7, 2020.
- ^ 気象庁 / 気象統計情報 / 過去の気象データ検索 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値-小河内(東京都). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 平年値(年・月ごとの値) (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値-父島(東京都). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved September 7, 2021.
- ^ 気象統計情報 / 天気予報・台風 / 過去の台風資料 / 台風の統計資料 / 台風の平年値. Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on June 7, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
- ^ a b Hidenobu Jinnai. Tokyo: A Spatial Anthropology. University of California Press (1995), pp. 1–3 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-520-07135-2.
- ^ «Tokyo skyline reaches for new heights with $5.5 billion Mori project». Reuters. August 2, 2019. Archived from the original on August 22, 2019. Retrieved August 22, 2019.
- ^ «World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD)». Wbcsd.org. Archived from the original on January 4, 2009. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ Barry, Roger Graham & Richard J. Chorley. Atmosphere, Weather and Climate. Routledge (2003), p. 344 Archived January 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 0-415-27170-3.
- ^ Toshiaki Ichinose, Kazuhiro Shimodozono, and Keisuke Hanaki. Impact of anthropogenic heat on urban climate in Tokyo. Atmospheric Environment 33 (1999): 3897–3909.
- ^ «Heat Island Control Measures». kankyo.metro.tokyo.jp. January 6, 2007. Archived from the original on May 24, 2008. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Barry, Roger Graham; Chorley, Richard J. (1987). Atmosphere, Weather and Climate. London: Methuen Publishing. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-416-07152-8.
- ^ «Cool ocean breezes flowing through Tokyo» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 16, 2013. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- ^ «2012 Action Program for Tokyo Vision 2020 – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». Metro.tokyo.jp. Archived from the original on December 9, 2012. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ^ 東京都の人口(推計). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on October 2, 2018. Retrieved January 17, 2015.
- ^ a b «Population of Tokyo». Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on December 23, 2008. Retrieved January 1, 2009.
- ^ 東京府 編 (1890). 東京府統計書. 明治22年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1889)] (in Japanese). Vol. 1. 東京府. pp. 40–41. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) Archived September 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (digital page number 32)
- ^ 東京府 編 (1890). 東京府統計書. 明治22年 [Tōkyō-Fu Statistics Book (1889)] (in Japanese). Vol. 1. 東京府. pp. 66–67. (National Diet Library Digital Archive) Archived September 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (digital page number 46)
- ^ «Tokyo Statistical Yearbook 2018» (Excel 97). Bureau of General Affairs, Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Archived from the original on September 5, 2018. Retrieved September 5, 2018.
- ^
«Financial Centres, All shapes and sizes». The Economist. September 13, 2007. Archived from the original on October 31, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2007. - ^ «Top 3 Things to See & Do in Shibuya – Tokyo’s Busiest District». April 13, 2017. Archived from the original on February 5, 2019. Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ^ «The expenses of Japan». The Economist. July 7, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- ^ Sassen, Saskia (2001). The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-07063-6.
- ^ Ito, Takatoshi; Melvin, Michael. «NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES – JAPAN’S BIG BANG AND THE TRANSFORMATION OF FINANCIAL MARKETS» (PDF). www.nber.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 2, 2018. Retrieved February 11, 2019.
- ^ «Tokyo Stock Exchange». Stock-market.in. February 25, 2007. Archived from the original on November 27, 2021. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Horticulture Statistics Team, Production Statistics Division, Statistics and Information Department, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (July 15, 2003). «Statistics on Cultivated Land Area» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 24, 2008. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ «Tokyo Economy — Tokyo Travel Guide». www.tokyo-travelguide.com. Retrieved April 23, 2022.
- ^ Kato, Issei (September 29, 2018). «As Tokyo’s historic Tsukiji market closes, fishmongers mourn». Reuters. Archived from the original on October 3, 2018. Retrieved October 4, 2018.
- ^ Hannerz, Ulf (2005). «The Fish Market at the Center of the World (Review)». The Journal of Japanese Studies. 31 (2): 428–431. doi:10.1353/jjs.2005.0044. S2CID 143762239.
- ^ «A Country Study: Japan». The Library of Congress. Chapter 2, Neighborhood. Archived from the original on May 26, 2012. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
- ^ «Orientation – Tokyo Travel Guide | Planetyze». Planetyze. Archived from the original on September 10, 2017. Retrieved July 18, 2017.
- ^ 井上恵一朗 (April 22, 2016). 【東京はてな】 渋谷交差点、1回で3千人横断?. 朝日新聞. p. 29.
- ^ 渋谷スクランブル交差点——世界で最もワイルドな交差点にようこそ. CNN.co.jp. August 25, 2019. Archived from the original on September 23, 2020. Retrieved September 26, 2019.
- ^ «The World’s Busiest Pedestrian Crossing». WorldAtlas. March 5, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2020. Retrieved April 13, 2020.
- ^ U.S. military’s Yokota Rapcon airspace is set in six different levels at altitudes between 2,450 and 7,000 meters, stretching over Tokyo and eight other prefectures. Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine Japan Times
- ^ Japan gets approval for new flight routes over Haneda airport using U.S. airspace Archived June 12, 2018, at the Wayback Machine Japan Times
- ^ Chorus, Paul (2016). «Transit oriented development in Tokyo». Transit Oriented Development: Making it Happen. Routledge. pp. 245–258. ISBN 978-1-317-00732-6.
- ^ «Revamping Tokyo’s expressways could give capital a boost». Yomiuri Shimbun. Archived from the original on November 2, 2012. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ «QS University Rankings: Asia 2016». QS Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. Archived from the original on June 16, 2016. Retrieved June 13, 2016.
- ^ Milner, Rebecca (2013). «Pocket Tokyo.» 4th Edition. Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 978-1-74220-581-6
- ^ Ozaki, Motoki (June 22, 2019). «About us. The Heart Of Performing Arts In Japan». New National Theatre, Tokyo. Archived from the original on June 22, 2019. Retrieved December 7, 2019.
- ^ Perry, Chris (April 25, 2007). Rebels on the Bridge: Subversion, Style, and the New Subculture (Flash) (Report). Self-published (Scribd). Archived from the original on October 14, 2007. Retrieved December 4, 2007.
- ^ «Tokyo ‘top city for good eating’«. BBC News. November 20, 2007. Archived from the original on December 17, 2008. Retrieved October 18, 2008.
- ^ «Tokyo Keeps Gymnastics Worlds, Bolsters Olympics Ambitions». Aroundtherings.com. May 23, 2011. Archived from the original on June 1, 2012. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- ^ «BBC World Service: World Update. ‘Carl Randall – Painting the faces in Japan’s crowded cities’.», BBC World Service, 2016, archived from the original on December 27, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ «‘Painting the faces in Japan’s crowded cities’.», BBC News – Arts & Entertainment, 2016, archived from the original on February 22, 2017, retrieved July 21, 2018
- ^ ‘Tokyo Portraits by Carl Randall’., The Daiwa Anglo Japanese Foundation, London, 2014, archived from the original on December 21, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ ‘The BP Portrait Awards 2013’., The National Portrait Gallery, London, 2012, archived from the original on February 6, 2017, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ ‘Japan Portraits’., Carl Randall – artist website, 2016, archived from the original on December 21, 2016, retrieved December 21, 2016
- ^ «Sister Cities (States) of Tokyo – Tokyo Metropolitan Government». Archived from the original on June 11, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ^ «Friendship and cooperation agreements». Paris: Marie de Paris. Archived from the original on July 1, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2016.
- ^ «Governor of Tomsk Region, Russia, visits Governor Masuzoe». Tokyo Metropolitan Government Official Website. June 15, 2015. Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ Houston, Michael (August 27, 2021). «Tokyo Metropolitan Government signs MoU with 2028 Olympic host City of Los Angeles». Inside the Game. Retrieved September 6, 2022.
- ^ The Space Economy in Figures How Space Contributes to the Global Economy: How Space Contributes to the Global Economy. OECD Publishing. 2019. p. 72. ISBN 978-92-64-80595-8. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Six colleges dominate in research stature». Washington Post. March 27, 2012. Archived from the original on December 25, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Radiation-free stem cell transplants, gene therapy may be within reach». News Center. May 29, 2019. Archived from the original on December 11, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «UTokyo-Berkeley». UTokyo-Berkeley. December 23, 2017. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ Asavanant, W.; Shiozawa, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Charoensombutamon, B.; Emura, H.; Alexander, R. N.; Takeda, S.; Yoshikawa, J. I.; Menicucci, N. C.; Yonezawa, H.; Furusawa, A. (2019). «Generation of time-domain-multiplexed two-dimensional cluster state». Science. 366 (6463): 373–376. arXiv:1903.03918. Bibcode:2019Sci…366..373A. doi:10.1126/science.aay2645. PMID 31624214. S2CID 92979929.
- ^ «Rikkyo University». UNM: Global Education Office. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ United States. Department of Energy (1999). Sandia National Laboratories/New Mexico: Environmental Impact Statement. Sandia National Laboratories/New Mexico: Environmental Impact Statement. p. 166–PA54. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «University of Oxford Japan Office» オックスフォード大学日本事務所. November 30, 2019.
- ^ «The University of Tokyo – National University of Singapore – 1st Joint Symposium – The University of Tokyo». The University of Tokyo. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Exchange: University of Tokyo – University of Toronto». University of Toronto – Learning Abroad. May 5, 2018. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- ^ «Tsinghua University News». Tsinghua University. July 27, 2018. Archived from the original on December 24, 2019. Retrieved December 24, 2019.
Bibliography[edit]
- Fiévé, Nicolas and Paul Waley. (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 978-0-7007-1409-4; OCLC 51527561
- McClain, James, John M Merriman and Kaoru Ugawa. (1994). Edo and Paris: Urban Life and the State in the Early Modern Era. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-2987-3; OCLC 30157716
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5; OCLC 58053128
- Sorensen, Andre. (2002). The Making of Urban Japan: Cities and Planning from Edo to the Twenty First Century. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 978-0-415-22651-6; OCLC 48517502
Further reading[edit]
Guides[edit]
- Bender, Andrew, and Timothy N. Hornyak. Tokyo (City Travel Guide) (2010)
- Mansfield, Stephen. Dk Eyewitness Top 10 Travel Guide: Tokyo (2013)
- Waley, Paul. Tokyo Now and Then: An Explorer’s Guide. (1984). 592 pp
- Yanagihara, Wendy. Lonely Planet Tokyo Encounter
Contemporary[edit]
- Allinson, Gary D. Suburban Tokyo: A Comparative Study in Politics and Social Change. (1979). 258 pp.
- Bestor, Theodore. Neighborhood Tokyo (1989). online edition
- Bestor, Theodore. Tsukiji: The Fish Market at the Centre of the World. (2004) online edition
- Fowler, Edward. San’ya Blues: Labouring Life in Contemporary Tokyo. (1996) ISBN 0-8014-8570-3.
- Friedman, Mildred, ed. Tokyo, Form and Spirit. (1986). 256 pp.
- Jinnai, Hidenobu. Tokyo: A Spatial Anthropology. (1995). 236 pp.
- Jones, Sumie et al. eds. A Tokyo Anthology: Literature from Japan’s Modern Metropolis, 1850–1920 (2017); primary sources excerpt
- Perez, Louis G. Tokyo: Geography, History, and Culture (ABC-CLIO, 2019).
- Reynolds, Jonathan M. «Japan’s Imperial Diet Building: Debate over Construction of a National Identity». Art Journal. 55#3 (1996) pp. 38+.
- Sassen, Saskia. The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo. (1991). 397 pp.
- Sorensen, A. Land Readjustment and Metropolitan Growth: An Examination of Suburban Land Development and Urban Sprawl in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area (2000)
- Taira, J. [re]TOKYO. (2018). San Francisco: ORO Editions. ISBN 978-1-940743-66-0
- Waley, Paul. «Tokyo-as-world-city: Reassessing the Role of Capital and the State in Urban Restructuring». Urban Studies 2007 44(8): 1465–1490. ISSN 0042-0980 Fulltext: Ebsco
External links[edit]
- Official website (in Japanese)
- Official website (in English)
- Go Tokyo travel guide
- Tokyo Convention & Visitors Bureau