Ответы на кроссворды и сканворды
южной америке южных цепей южных предгорьях южном направлении южной африки южном междуречье
выберите длину слова
4 5 6 7 18 Все
выберите первую букву слова
Все
Ответы на вопрос Южных славян 21 букв
- Капелле-ан-ден-Эйссел — Город в Нидерландах, Южная Голландия 21 букв
Обозначь орфограмму, на которую нужно обратить внимание в каждом из данных слов. Образуй от этих слов наречия. Придумай и запиши сними словосочетания. Укажи главные и зависимые слова. Легкий- Дерзкий- Меткий- Жуткий —
Ответы (2)
Укажите, твердый или мягкий согласный произносится перед Е: Кашне, кларнет, компетентный, кузен, кюре, менеджер, модернизм, нейтрон, партер, протекция, реглан, рейд, сессия, синтез, террор, федеральный, форель, шинель, экспресс, альтернатива,
Ответы (1)
если имеется в виду сторона света, то с большой, а если направление, то с маленькой
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 21 июня 2020 года; проверки требуют 4 правки.
Перейти к навигации
Перейти к поиску
Ю́жные славя́не — современная группа славянских народов, а также племён, говорящих на южнославянских языках и живущих преимущественно на Балканах.
Юго-восточная группа[править | править код]
- болгары
- македонцы
Юго-западная группа[править | править код]
- сербы
- хорваты
- боснийцы (босняки)
- черногорцы
- словенцы
Исторически, особенно во времена единой Югославии, существовала попытка к национальному объединению южных славян юго-западной подгруппы в единый супранациональный элемент — югославы.
Славяне-мусульмане[править | править код]
В группе южных славян, испытавших сильное турецкое влияние в эпоху Османской империи, особо выделяются славяне-мусульмане.
Историческая справка[править | править код]
Исторические племена, относящиеся к южным славянам:
- захумляне
Комментарии[править | править код]
Страны[править | править код]
Есть семь стран, в которых южные славяне являются основным населением[1]:
Болгария (84 % болгары)
Сербия (82 % сербы, 2 % босняки, 1 % югославы, 1 % хорваты, 1 % черногорцы)
Сравнение численности восточных, западных и южных славян
Хорватия (90 % хорваты, 4 % сербы, 1,7 % босняки)
Босния и Герцеговина (48 % босняки, 37 % сербы, 14 % хорваты)
Северная Македония (65 % македонцы, 2 % сербы, 1 % босняки)
Словения (83 % словенцы, 2 % сербы, 2 % хорваты 1 % босняки)
Черногория (44,98 % черногорцы, 28,73 % сербы, 8,65 % босняки, 3,31 % славяне-мусульмане, 0,97 % хорваты, 0,34 % сербы-черногорцы, 0,19 % югославы, 0,15 % македонцы, 0,07 % босняки, 0,06 % словенцы, 0,04 % черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03 % горанцы, 0,03 % черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03 % босняки-мусульмане)
Вдобавок, есть традиционные значительные южнославянские меньшинства в неславянских соседних странах, таких как:
- Италия: (словенцы, хорваты)
- Австрия: (словенцы и хорваты, которые признаются как меньшинства. 4 % граждан Австрии составляют боснийцы, сербы, хорваты)
- Венгрия: (сербы, хорваты, словенцы)
- Румыния: (хорваты, болгары, сербы),
- Греция: (славяне в Греции)
- Турция: (босняки, болгары, македонцы)
- Албания: (болгары, македонцы, сербы, черногорцы)
См. также[править | править код]
- Переселение славян на Балканы
- Славянская колонизация Восточных Альп
Примечания[править | править код]
Литература[править | править код]
- Юго-Славяне // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
Ответы на кроссворды и сканворды
южных славян на букву И. Не нашли своего ответа? Уточните вопрос в поле поиска
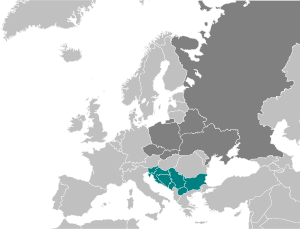
Countries where a South Slavic language is the national language Countries where other Slavic languages are the national language |
| Total population |
|---|
| c. 30 million |
| Regions with significant populations |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovenia |
| Languages |
| Eastern South Slavic: Bulgarian Macedonian Western South Slavic: Serbo-Croatian (Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, Serbian) Slovene |
| Religion |
(Bulgarians, Macedonians, Montenegrins and Serbs)[citation needed]
|
| Related ethnic groups |
| Other Slavs |
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs, and Slovenes, respectively the main populations of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia.
In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning «South Slavia» or «South Slavdom») united majority of South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of Yugoslavia emerged in the late 17th century Croatia, at the time party of Habsburg monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, was proclaimed on 1 December 1918, following the unification of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs with the kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro. With the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, several independent sovereign states were formed. The term «Yugoslavs» was and sometimes still is used as a synonym for «South Slavs», but frequently excludes Bulgarians, and sometimes only refers to the citizens or inhabitants of former Yugoslavia, or only to those who officially registered themselves as ethnic Yugoslavs.
Terminology[edit]
The South Slavs are known in Serbian, Macedonian and Montenegrin as Južni Sloveni (Cyrillic: Јужни Словени); in Bulgarian as Yuzhni Slavyani (Cyrillic: Южни славяни); in Croatian and Bosnian as Južni Slaveni; in Slovene as Južni Slovani. The Slavic root *jugъ means «south». The Slavic ethnonym itself was used by 6th-century writers to describe the southern group of Early Slavs (the Sclaveni); West Slavs were called Veneti and East Slavs Antes.[1] The South Slavs are also called «Balkan Slavs»,[2]
Another name popular in the early modern period was «Illyrians», the name of a pre-Slavic Balkan people, a name first adopted by Dalmatian intellectuals in the late 15th century to refer to South Slavic lands and population.[3] It was then used by the Habsburg monarchy, France, and notably adopted by the 19th-century Croatian Illyrian movement.[4] Eventually, the idea of Yugoslavism appeared, aimed at uniting all South Slav-populated territories into a common state. From this idea emerged Yugoslavia, which however did not include Bulgaria.[citation needed]
History[edit]
Early South Slavs[edit]
The Proto-Slavic homeland is the area of Slavic settlement in Central and Eastern Europe during the first millennium AD, with its precise location debated by archaeologists, ethnographers and historians.[5] None of the proposed homelands reaches the Volga River in the east, over the Dinaric Alps in the southwest or the Balkan Mountains in the south, or past Bohemia in the west.[6] Traditionally, scholars put it in the marshes of Ukraine, or alternatively between the Bug and the Dnieper;[7] however, according to F. Curta, the homeland of the southern Slavs mentioned by 6th-century writers was just north of the Lower Danube.[8] Little is known about the Slavs before the 5th century, when they began to spread out in all directions.[citation needed]
Jordanes, Procopius and other late Roman authors provide the probable earliest references to southern Slavs in the second half of the 6th century.[9] Procopius described the Sclaveni and Antes as two barbarian peoples with the same institutions and customs since ancient times, not ruled by a single leader but living under democracy,[10] while Pseudo-Maurice called them a numerous people, undisciplined, unorganized and leaderless, who did not allow enslavement and conquest, and resistant to hardship, bearing all weathers.[11] They were portrayed by Procopius as unusually tall and strong, of dark skin and «reddish» hair (neither blond nor black), leading a primitive life and living in scattered huts, often changing their residence.[12] Procopius said they were henotheistic, believing in the god of lightning (Perun), the ruler of all, to whom they sacrificed cattle.[12] They went into battle on foot, charging straight at their enemy, armed with spears and small shields, but they did not wear armour.[12]
While archaeological evidence for a large-scale migration is lacking, most present-day historians claim that Slavs invaded and settled the Balkans in the 6th and 7th centuries.[13] According to this dominant narrative, up until the late 560s their main activity across the Danube was raiding, though with limited Slavic settlement mainly through Byzantine colonies of foederati.[14] The Danube and Sava frontier was overwhelmed by large-scale Slavic settlement in the late 6th and early 7th century.[15] What is today central Serbia was an important geo-strategical province, through which the Via Militaris crossed.[16] This area was frequently intruded upon by barbarians in the 5th and 6th centuries.[16] From the Danube, the Slavs commenced raiding the Byzantine Empire on an annual basis from the 520s, spreading destruction, taking loot and herds of cattle, seizing prisoners and taking fortresses. Often, the Byzantine Empire was stretched, defending its rich Asian provinces from Arabs, Persians and others. This meant that even numerically small, disorganised early Slavic raids were capable of causing much disruption, but could not capture the larger, fortified cities.[14] The first Slavic raid south of the Danube was recorded by Procopius, who mentions an attack of the Antes, «who dwell close to the Sclaveni», probably in 518.[17] Sclaveni are first mentioned in the context of the military policy on the Danube frontier of Byzantine Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565).[18] Throughout the century, Slavs raided and plundered deep into the Balkans, from Dalmatia to Greece and Thrace, and were also at times recruited as mercenaries, fighting the Ostrogoths.[19] Justinian seems to have used the strategy of ‘divide and conquer’, and the Sclaveni and Antes are mentioned as fighting each other.[20] The Antes are last mentioned as anti-Byzantine belligerents in 545, and the Sclaveni continued to raid the Balkans.[21] In 558 the Avars arrived at the Black Sea steppe, and defeated the Antes between the Dnieper and Dniester.[22] The Avars subsequently allied themselves with the Sclaveni,[23] although there was an episode in which the Sclavene Daurentius (fl. 577–579), the first Slavic chieftain recorded by name, dismissed Avar suzerainty and retorted that «Others do not conquer our land, we conquer theirs […] so it shall always be for us», and had the Avar envoys slain.[24] By the 580s, as the Slav communities on the Danube became larger and more organized, and as the Avars exerted their influence, raids became larger and resulted in permanent settlement. Most scholars consider the period of 581–584 as the beginning of large-scale Slavic settlement in the Balkans.[25] F. Curta points out that evidence of substantial Slavic presence does not appear before the 7th century and remains qualitatively different from the «Slavic culture» found north of the Danube.[26] In the mid-6th century, the Byzantines re-asserted their control of the Danube frontier, thereby reducing the economic value of Slavic raiding. This growing economic isolation, combined with external threats from the Avars and Byzantines, led to political and military mobilisation. Meanwhile, the itinerant form of agriculture (lacking crop rotation) may have encouraged micro-regional mobility. Seventh-century archaeological sites show earlier hamlet collections evolving into larger communities with differentiated zones for public feasts, craftmanship, etc.[27] It has been suggested that the Sclaveni were the ancestors of the Serbo-Croatian group while the Antes were that of the Bulgarian Slavs, with much mixture in the contact zones.[28][29] The diminished pre-Slavic inhabitants, also including Romanized native peoples,[a] fled from the barbarian invasions and sought refuge inside fortified cities and islands, whilst others fled to remote mountains and forests and adopted a transhumant lifestyle.[30] The Romance speakers within the fortified Dalmatian city-states managed to retain their culture and language for a long time.[31] Meanwhile, the numerous Slavs mixed with and assimilated the descendants of the indigenous population.[32]
Subsequent information about Slavs’ interaction with the Greeks and early Slavic states comes from the 10th-century De Administrando Imperio (DAI) by Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus, the 7th-century compilations of the Miracles of Saint Demetrius (MSD) and the History by Theophylact Simocatta. DAI mentions the beginnings of the Croatian, Serbian and Bulgarian states from the early 7th to the mid-10th century. MSD and Theophylact Simocatta mention the Slavic tribes in Thessaly and Macedonia at the beginning of the 7th century. The 9th-century Royal Frankish Annals (RFA) also mention Slavic tribes in contact with the Franks.[citation needed]
Middle Ages[edit]
By 700 AD, Slavs had settled in most of Central and Southeast Europe, from Austria even down to the Peloponnese of Greece, and from the Adriatic to the Black Sea, with the exception of the coastal areas and certain mountainous regions of the Greek peninsula.[33] The Avars, who arrived in Europe in the late 550s and had a great impact in the Balkans, had from their base in the Carpathian plain, west of main Slavic settlements, asserted control over Slavic tribes with whom they besieged Roman cities. Their influence in the Balkans however diminished by the early 7th century and they were finally defeated and disappeared as a power at the turn of the 9th century by Bulgaria and the Frankish Empire.[34] The first South Slavic polity and regional power was Bulgaria, a state formed in 681 as a union between the much numerous Slavic tribes and the bulgars of Khan Asparuh. The scattered Slavs in Greece, the Sklavinia, were Hellenized.[35] Romance-speakers lived within the fortified Dalmatian city-states.[31] Traditional historiography, based on DAI, holds that the migration of Serbs and Croats to the Balkans was part of a second Slavic wave, placed during Heraclius’ reign.[36]
Inhabiting the territory between the Franks in the north and Byzantium in the south, the Slavs were exposed to competing influences.[37] In 863 to Christianized Great Moravia were sent two Byzantine brothers monks Saints Cyril and Methodius, Slavs from Thessaloniki on missionary work. They created the Glagolitic script and the first Slavic written language, Old Church Slavonic, which they used to translate Biblical works. At the time, the West and South Slavs still spoke a similar language. The script used, Glagolitic, was capable of representing all Slavic sounds, however, it was gradually replaced in Bulgaria in the 9th century, in Russia by the 11th century[38] Glagolitic survived into the 16th century in Croatia, used by Benedictines and Franciscans, but lost importance during the Counter-Reformation when Latin replaced it on the Dalmatian coast.[39] Cyril and Methodius’ disciples found refuge in already Christian Bulgaria, where the Old Church Slavonic became the ecclesiastical language.[39] Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in Bulgaria.[40][41][42] The earliest Slavic literary works were composed in Bulgaria, Duklja and Dalmatia. The religious works were almost exclusively translations, from Latin (Croatia, Slovenia) and especially Greek (Bulgaria, Serbia).[39] In the 10th and 11th centuries the Old Church Slavonic led to the creation of various regional forms like Serbo-Croatian and Slovenian[39] Economic, religious and political centres of Ohrid and Preslav contributed to the important literary production in the Bulgarian Empire.[43] The Bogomil sect, derived from Manichaeism, was deemed heretical, but managed to spread from Bulgaria to Bosnia (where it gained a foothold),[44] and France (Cathars).[citation needed]
Carinthia came under Germanic rule in the 10th century and came permanently under Western (Roman) Christian sphere of influence.[45] What is today Croatia came under Eastern Roman (Byzantine) rule after the Barbarian age, and while most of the territory was Slavicized, a handful of fortified towns, with mixed population, remained under Byzantine authority and continued to use Latin.[45] Dalmatia, now applied to the narrow strip with Byzantine towns, came under the Patriarchate of Constantinople, while the Croatian state remained pagan until Christianization during the reign of Charlemagne, after which religious allegiance was to Rome.[45] Croats threw off Frankish rule in the 9th century and took over the Byzantine Dalmatian towns, after which Hungarian conquest led to Hungarian suzerainty, although retaining an army and institutions.[46] Croatia lost much of Dalmatia to the Republic of Venice which held it until the 18th century.[47] Hungary governed Croatia through a duke, and the coastal towns through a ban.[47] A feudal class emerged in the Croatian hinterland in the late 13th century, among whom were the Kurjaković, Kačić and most notably the Šubić.[48] Dalmatian fortified towns meanwhile maintained autonomy, with a Roman patrician class and Slavic lower class, first under Hungary and then Venice after centuries of struggle.[49]
Ibn al-Faqih described two kinds of South Slavic people, the first of swarthy complexion and dark hair, living near the Adriatic coast, and the other as light, living in the hinterland.[citation needed]
Early modern period[edit]
Through Islamization, communities of Slavic Muslims emerged, which survive until today in Bosnia, south Serbia, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria.[citation needed]
While Pan-Slavism has its origins in the 17th-century Slavic Catholic clergymen in the Republic of Venice and Republic of Ragusa, it crystallized only in the mid-19th century amidst rise of nationalism in the Ottoman and Habsburg empires.[citation needed]
Population[edit]
Languages[edit]
The South Slavic languages, one of three branches of the Slavic languages family (the other being West Slavic and East Slavic), form a dialect continuum. It comprises, from west to east, the official languages of Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria. The South Slavic languages are geographically divided from the rest of the Slavic languages by areas where Germanic (Austria), Hungarian and Romanian languages prevail.
South Slavic standard languages are:
The Serbo-Croatian varieties have strong structural unity and are regarded by most linguists as constituting one language.[50] Today, language secessionism has led to the codification of several distinct standards: Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin. These Serbo-Croatian standards are all based on the Shtokavian dialect group. Other dialect groups, which have lower intelligibility with Shtokavian, are Chakavian in Dalmatia and Kajkavian in Croatia proper. The dominance of Shtokavian across Serbo-Croatian speaking lands is due to historical westward migration during the Ottoman period. Slovene is South Slavic but has many features shared with West Slavic languages. The Prekmurje Slovene and Kajkavian are especially close, and there is no sharp delineation between them. In southeastern Serbia, dialects enter a transitional zone with Bulgarian and Macedonian, with features of both groups, and are commonly called Torlakian. The Eastern South Slavic languages are Bulgarian and Macedonian. Bulgarian has retained more archaic Slavic features in relation to the other languages. Bulgarian has two main yat splits. Macedonian was codified in Communist Yugoslavia in 1945. The Macedonian dialects, divided into three main groups, are regarded overall as being transitional to Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian. The westernmost Bulgarian dialects (called Shopi) share features with Serbo-Croatian. Furthermore, in Greece there is a notable Slavic-speaking population in Greek Macedonia and western Thrace. Balkan Slavic languages are part of a «Balkan sprachbund» with areal features shared with other non-Slavic languages in the Balkans.[citation needed]
Genetics[edit]
Admixture analysis of autosomal SNPs of the Balkan region in a global context on the resolution level of 7 assumed ancestral populations: the African (brown), South/West European (light blue), Asian (yellow), Middle Eastern (orange), South Asian (green), North/East European (dark blue) and beige Caucasus component.[51]
Autosomal analysis presenting the historical contribution of different donor groups in some European populations. Polish sample was selected to represent the Slavic influence, and it is suggesting a strong and early impact in Greece (30-37%), Romania (48-57%), Bulgaria (55-59%), and Hungary (54-84%).[52]
According to the 2013 autosomal IBD survey «of recent genealogical ancestry over the past 3,000 years at a continental scale», the speakers of Serbo-Croatian language share a very high number of common ancestors dated to the migration period approximately 1,500 years ago with Poland and Romania-Bulgaria cluster among others in Eastern Europe. It is concluded to be caused by the Hunnic and Slavic expansion, which was a «relatively small population that expanded over a large geographic area», particularly «the expansion of the Slavic populations into regions of low population density beginning in the sixth century» and that it is «highly coincident with the modern distribution of Slavic languages».[53] According to Kushniarevich et al. 2015, the Hellenthal et al. 2014 IBD analysis also found «multi-directional admixture events among East Europeans (both Slavic and non-Slavic), dated to around 1,000–1,600 YBP» which coincides with «the proposed time-frame for the Slavic expansion».[54] The Slavic influence is «dated to 500-900 CE or a bit later with over 40-50% among Bulgarians, Romanians, and Hungarians».[53] The 2015 IBD analysis found that the South Slavs have lower proximity to Greeks than with East and West Slavs and that there’s an «even patterns of IBD sharing among East-West Slavs–’inter-Slavic’ populations (Hungarians, Romanians and Gagauz)–and South Slavs, i.e. across an area of assumed historic movements of people including Slavs». The slight peak of shared IBD segments between South and East-West Slavs suggests a shared «Slavonic-time ancestry».[54] The 2014 IBD analysis comparison of Western Balkan and Middle Eastern populations also found negligible gene flow between 16th and 19th century during the Islamization of the Balkans.[51]
According to a 2014 admixture analysis of Western Balkan, the South Slavs show a genetic uniformity. The Bosnians and Croatians were more close to East European populations and largely overlapped with Hungarians from Central Europe.[51] In the 2015 analysis, they formed a western South Slavic cluster with the Bosnians and Slovenians in comparison to eastern cluster formed by Macedonians and Bulgarians with Serbians in the middle. The western cluster has an inclination toward Hungarians, Czechs, and Slovaks, while the eastern cluster toward Romanians and some extent Greeks.[54] The modeled ancestral genetic component of Balto-Slavs among South Slavs was between 55 and 70%.[54] In the 2018 analysis of Slovenian population, the Slovenian population clustered with Croatians, Hungarians and was close to Czech.[55]
The 2006 Y-DNA study results «suggest that the Slavic expansion started from the territory of present-day Ukraine, thus supporting the hypothesis that places the earliest known homeland of Slavs in the basin of the middle Dnieper».[56] According to genetic studies until 2020, the distribution, variance and frequency of the Y-DNA haplogroups R1a and I2 and their subclades R-M558, R-M458 and I-CTS10228 among South Slavs are in correlation with the spreading of Slavic languages during the medieval Slavic expansion from Eastern Europe, most probably from the territory of present-day Ukraine and Southeastern Poland.[57][58][59][60][61][62][63]
See also[edit]
- Yugoslavs
- East Slavs
- West Slavs
- List of Slavic studies journals
- Outline of Slavic history and culture
Annotations[edit]
- ^
Prior to the advent of Roman rule, a number of native or autochthonous populations had lived in the Balkans since ancient times. South of the Jireček line were the Greeks. To the north, there were Illyrians, Thracians and Dacians. They were mainly tribalistic and generally lacked awareness of any ethno-political affiliation. Over the classical ages, they were at times invaded, conquered and influenced by Celts, ancient Greeks and ancient Romans. Roman influence, however, was initially limited to cities concentrated along the Dalmatian coast, later spreading to a few scattered cities inside the Balkan interior, particularly along the river Danube (Sirmium, Belgrade, Niš). Roman citizens from throughout the empire settled in these cities and in the adjacent countryside. Following the fall of Rome and numerous barbarian raids, the population in the Balkans dropped, as did commerce and general standards of living. Many people were killed or taken prisoner by invaders. This demographic decline was particularly attributed to a drop in the number of indigenous peasants living in rural areas. They were the most vulnerable to raids and were also hardest hit by the financial crises that plagued the falling empire. However, the Balkans were not desolate, and considerable numbers of indigenous people remained. Only certain areas tended to be affected by the raids (e.g. lands around major land routes, such as the Morava corridor).[64] In addition to the autochthons, there were remnants of previous invaders such as «Huns» and various Germanic peoples when the Slavs arrived. Sarmatian tribes such as the Iazyges were still recorded as living in the Banat region of the Danube.[65] The mixing of Slavs and other peoples is evident in genetic studies included in the article.
- ^
The political status of Kosovo is disputed. Having unilaterally declared independence from Serbia in 2008, Kosovo is formally recognised as an independent state by 101 out of 193 (52.3%) UN member states (with another 13 recognising it at some point but then withdrawing their recognition), while Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own territory.
References[edit]
- ^ Kmietowicz 1976.
- ^ Kmietowicz 1976, Vlasto 1970
- ^ URI 2000, p. 104.
- ^ Hupchick 2004, p. 199.
- ^ Kobyliński 2005, pp. 525–526, Barford 2001, p. 37
- ^ Kobyliński 2005, p. 526, Barford 2001, p. 332
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 25.
- ^ Curta 2006, p. 56.
- ^ Curta 2001, pp. 71–73.
- ^ James 2014, p. 95, Kobyliński 1995, p. 524
- ^ Kobyliński 1995, pp. 524–525.
- ^ a b c Kobyliński 1995, p. 524.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 26–41.
- ^ a b Fine 1991, p. 29.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 33.
- ^ a b Živković 2002, p. 187.
- ^ James 2014, p. 95, Curta 2001, p. 75
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 76.
- ^ Curta 2001, pp. 78–86.
- ^ James 2014, p. 97.
- ^ Byzantinoslavica. Vol. 61–62. Academia. 2003. pp. 78–79.
- ^ Kobyliński 1995, p. 536.
- ^ Kobyliński 1995, p. 537–539.
- ^ Curta 2001, pp. 47, 91.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 31.
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 308.
- ^ Curta 2007, p. 61.
- ^ Hupchick 2004.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 26.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 37.
- ^ a b Fine 1991, p. 35.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 38, 41.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 36.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 29–43.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 41.
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 66.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 90.
- ^ Portal 1969, pp. 90–92.
- ^ a b c d Portal 1969, p. 92.
- ^ Dvornik, Francis (1956). The Slavs: Their Early History and Civilization. Boston: American Academy of Arts and Sciences. p. 179.
The Psalter and the Book of Prophets were adapted or «modernized» with special regard to their use in Bulgarian churches, and it was in this school that glagolitic writing was replaced by the so-called Cyrillic writing, which was more akin to the Greek uncial, simplified matters considerably and is still used by the Orthodox Slavs.
- ^ Florin Curta (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge Medieval Textbooks. Cambridge University Press. pp. 221–222. ISBN 978-0521815390.
Cyrillic preslav.
- ^ J. M. Hussey, Andrew Louth (2010). «The Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire». Oxford History of the Christian Church. Oxford University Press. p. 100. ISBN 978-0191614880.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 93.
- ^ Portal 1969, pp. 93–95.
- ^ a b c Portal 1969, p. 96.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 96–97.
- ^ a b Portal 1969, p. 97.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 97–98.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 98.
- ^ Comrie, Bernard & Corbett, Greville G., eds. (2002) [1st. Pub. 1993]. The Slavonic Languages. London & New York: Routledge. OCLC 49550401.
- ^ a b c L. Kovačević; et al. (2014). «Standing at the Gateway to Europe — The Genetic Structure of Western Balkan Populations Based on Autosomal and Haploid Markers». PLOS One. 9 (8): e105090. Bibcode:2014PLoSO…9j5090K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105090. PMC 4141785. PMID 25148043.
- ^ «Companion website for «A genetic atlas of human admixture history», Hellenthal et al, Science (2014)». A genetic atlas of human admixture history.
Hellenthal, Garrett; Busby, George B.J.; Band, Gavin; Wilson, James F.; Capelli, Cristian; Falush, Daniel; Myers, Simon (14 February 2014). «A Genetic Atlas of Human Admixture History». Science. 343 (6172): 747–751. Bibcode:2014Sci…343..747H. doi:10.1126/science.1243518. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 4209567. PMID 24531965.
Hellenthal, G.; Busby, G. B.; Band, G.; Wilson, J. F.; Capelli, C.; Falush, D.; Myers, S. (2014). «Supplementary Material for «A genetic atlas of human admixture history»«. Science. 343 (6172): 747–751. Bibcode:2014Sci…343..747H. doi:10.1126/science.1243518. PMC 4209567. PMID 24531965.S7.6 «East Europe»: The difference between the ‘East Europe I’ and ‘East Europe II’ analyses is that the latter analysis included the Polish as a potential donor population. The Polish were included in this analysis to reflect a Slavic language speaking source group.» «We speculate that the second event seen in our six Eastern Europe populations between northern European and southern European ancestral sources may correspond to the expansion of Slavic language speaking groups (commonly referred to as the Slavic expansion) across this region at a similar time, perhaps related to displacement caused by the Eurasian steppe invaders (38; 58). Under this scenario, the northerly source in the second event might represent DNA from Slavic-speaking migrants (sampled Slavic-speaking groups are excluded from being donors in the EastEurope I analysis). To test consistency with this, we repainted these populations adding the Polish as a single Slavic-speaking donor group («East Europe II» analysis; see Note S7.6) and, in doing so, they largely replaced the original North European component (Figure S21), although we note that two nearby populations, Belarus and Lithuania, are equally often inferred as sources in our original analysis (Table S12). Outside these six populations, an admixture event at the same time (910CE, 95% CI:720-1140CE) is seen in the southerly neighboring Greeks, between sources represented by multiple neighboring Mediterranean peoples (63%) and the Polish (37%), suggesting a strong and early impact of the Slavic expansions in Greece, a subject of recent debate (37). These shared signals we find across East European groups could explain a recent observation of an excess of IBD sharing among similar groups, including Greece, that was dated to a wide range between 1,000 and 2,000 years ago (37)
- ^ a b P. Ralph; et al. (2013). «The Geography of Recent Genetic Ancestry across Europe». PLOS Biology. 11 (5): e105090. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001555. PMC 3646727. PMID 23667324.
- ^ a b c d A. Kushniarevich; et al. (2015). «Genetic Heritage of the Balto-Slavic Speaking Populations: A Synthesis of Autosomal, Mitochondrial and Y-Chromosomal Data». PLOS One. 10 (9): e0135820. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1035820K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135820. PMC 4558026. PMID 26332464.
- ^ P. M. Delser; et al. (2018). «Genetic Landscape of Slovenians: Past Admixture and Natural Selection Pattern». Frontiers in Genetics. 9: 551. doi:10.3389/fgene.2018.00551. PMC 6252347. PMID 30510563.
- ^ Rebała, K; Mikulich, AI; Tsybovsky, IS; Siváková, D; Dzupinková, Z; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A; Szczerkowska, Z (2007). «Y-STR variation among Slavs: Evidence for the Slavic homeland in the middle Dnieper basin». Journal of Human Genetics. 52 (5): 406–14. doi:10.1007/s10038-007-0125-6. PMID 17364156.
- ^ A. Zupan; et al. (2013). «The paternal perspective of the Slovenian population and its relationship with other populations». Annals of Human Biology. 40 (6): 515–526. doi:10.3109/03014460.2013.813584. PMID 23879710. S2CID 34621779.
However, a study by Battaglia et al. (2009) showed a variance peak for I2a1 in the Ukraine and, based on the observed pattern of variation, it could be suggested that at least part of the I2a1 haplogroup could have arrived in the Balkans and Slovenia with the Slavic migrations from a homeland in present-day Ukraine… The calculated age of this specific haplogroup together with the variation peak detected in the suggested Slavic homeland could represent a signal of Slavic migration arising from medieval Slavic expansions. However, the strong genetic barrier around the area of Bosnia and Herzegovina, associated with the high frequency of the I2a1b-M423 haplogroup, could also be a consequence of a Paleolithic genetic signal of a Balkan refuge area, followed by mixing with a medieval Slavic signal from modern-day Ukraine.
- ^ Underhill, Peter A. (2015), «The phylogenetic and geographic structure of Y-chromosome haplogroup R1a», European Journal of Human Genetics, 23 (1): 124–131, doi:10.1038/ejhg.2014.50, PMC 4266736, PMID 24667786,
R1a-M458 exceeds 20% in the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, and Western Belarus. The lineage averages 11–15% across Russia and Ukraine and occurs at 7% or less elsewhere (Figure 2d). Unlike hg R1a-M458, the R1a-M558 clade is also common in the Volga-Uralic populations. R1a-M558 occurs at 10–33% in parts of Russia, exceeds 26% in Poland and Western Belarus, and varies between 10 and 23% in the Ukraine, whereas it drops 10-fold lower in Western Europe. In general, both R1a-M458 and R1a-M558 occur at low but informative frequencies in Balkan populations with known Slavonic heritage.
- ^ O.M. Utevska (2017). Генофонд українців за різними системами генетичних маркерів: походження і місце на європейському генетичному просторі [The gene pool of Ukrainians revealed by different systems of genetic markers: the origin and statement in Europe] (PhD) (in Ukrainian). National Research Center for Radiation Medicine of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. pp. 219–226, 302.
- ^ Neparáczki, Endre; et al. (2019). «Y-chromosome haplogroups from Hun, Avar and conquering Hungarian period nomadic people of the Carpathian Basin». Scientific Reports. Nature Research. 9 (16569): 16569. Bibcode:2019NatSR…916569N. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53105-5. PMC 6851379. PMID 31719606.
Hg I2a1a2b-L621 was present in 5 Conqueror samples, and a 6th sample form Magyarhomorog (MH/9) most likely also belongs here, as MH/9 is a likely kin of MH/16 (see below). This Hg of European origin is most prominent in the Balkans and Eastern Europe, especially among Slavic speaking groups.
- ^ Pamjav, Horolma; Fehér, Tibor; Németh, Endre; Koppány Csáji, László (2019). Genetika és őstörténet (in Hungarian). Napkút Kiadó. p. 58. ISBN 978-963-263-855-3.
Az I2-CTS10228 (köznevén „dinári-kárpáti») alcsoport legkorábbi közös őse 2200 évvel ezelőttre tehető, így esetében nem arról van szó, hogy a mezolit népesség Kelet-Európában ilyen mértékben fennmaradt volna, hanem arról, hogy egy, a mezolit csoportoktól származó szűk család az európai vaskorban sikeresen integrálódott egy olyan társadalomba, amely hamarosan erőteljes demográfiai expanzióba kezdett. Ez is mutatja, hogy nem feltétlenül népek, mintsem családok sikerével, nemzetségek elterjedésével is számolnunk kell, és ezt a jelenlegi etnikai identitással összefüggésbe hozni lehetetlen. A csoport elterjedése alapján valószínűsíthető, hogy a szláv népek migrációjában vett részt, így válva az R1a-t követően a második legdominánsabb csoporttá a mai Kelet-Európában. Nyugat-Európából viszont teljes mértékben hiányzik, kivéve a kora középkorban szláv nyelvet beszélő keletnémet területeket.
- ^ Fóthi, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Fehér, T.; et al. (2020), «Genetic analysis of male Hungarian Conquerors: European and Asian paternal lineages of the conquering Hungarian tribes», Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 12 (1), doi:10.1007/s12520-019-00996-0,
Based on SNP analysis, the CTS10228 group is 2200 ± 300 years old. The group’s demographic expansion may have begun in Southeast Poland around that time, as carriers of the oldest subgroup are found there today. The group cannot solely be tied to the Slavs, because the proto-Slavic period was later, around 300–500 CE… The SNP-based age of the Eastern European CTS10228 branch is 2200 ± 300 years old. The carriers of the most ancient subgroup live in Southeast Poland, and it is likely that the rapid demographic expansion which brought the marker to other regions in Europe began there. The largest demographic explosion occurred in the Balkans, where the subgroup is dominant in 50.5% of Croatians, 30.1% of Serbs, 31.4% of Montenegrins, and in about 20% of Albanians and Greeks. As a result, this subgroup is often called Dinaric. It is interesting that while it is dominant among modern Balkan peoples, this subgroup has not been present yet during the Roman period, as it is almost absent in Italy as well (see Online Resource 5; ESM_5).
- ^ Kushniarevich, Alena; Kassian, Alexei (2020), «Genetics and Slavic languages», in Marc L. Greenberg (ed.), Encyclopedia of Slavic Languages and Linguistics Online, Brill, doi:10.1163/2589-6229_ESLO_COM_032367, retrieved 10 December 2020,
The geographic distributions of the major eastern European NRY haplogroups (R1a-Z282, I2a-P37) overlap with the area occupied by the present-day Slavs to a great extent, and it might be tempting to consider both haplogroups as Slavic-specic patrilineal lineages
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 9–12, 37.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 57.
Sources[edit]
- Primary sources
- Moravcsik, Gyula, ed. (1967) [1949]. Constantine Porphyrogenitus: De Administrando Imperio (2nd revised ed.). Washington D.C.: Dumbarton Oaks Center for Byzantine Studies. ISBN 9780884020219.
- Scholz, Bernhard Walter, ed. (1970). Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard’s Histories. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472061860.
- Books
- Barford, Paul M. (2001). The Early Slavs: Culture and Society in Early Medieval Eastern Europe. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0801439779.
- Castellan, Georges (1992). History of the Balkans: From Mohammed the Conqueror to Stalin. East European Monographs. ISBN 978-0-88033-222-4.
- Curta, Florin (2001). The Making of the Slavs: History and Archaeology of the Lower Danube Region, c. 500–700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139428880.
- Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81539-0.
- Dvornik, Francis (1962). The Slavs in European History and Civilization. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813507996.
- Fine, John V. A. Jr. (1991) [1983]. The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
- Fine, John V. A. Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (2005). When Ethnicity Did Not Matter in the Balkans: A Study of Identity in Pre-Nationalist Croatia, Dalmatia, and Slavonia in the Medieval and Early-Modern Periods. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472025600.
- Hupchick, Dennis P. (2004) [2002]. The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-6417-5.
- James, Edward (2014). Europe’s Barbarians AD 200-600. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-86825-5.
- Janković, Đorđe (2004). «The Slavs in the 6th Century North Illyricum». Гласник Српског археолошког друштва. 20: 39–61.
- Jelavich, Barbara (1983a). History of the Balkans: Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521274586.
- Jelavich, Barbara (1983b). History of the Balkans: Twentieth Century. Vol. 2. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521274593.
- Kaimakamova, Miliana; Salamon, Maciej (2007). Byzantium, new peoples, new powers: the Byzantino-Slav contact zone, from the ninth to the fifteenth century. Towarzystwo Wydawnicze «Historia Iagellonica». ISBN 978-83-88737-83-1.
- Kmietowicz, Frank A. (1976). Ancient Slavs. Worzalla Publishing Company.
- Kobyliński, Zbigniew (1995). The Slavs. The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 1, C.500-c.700. Cambridge University Press. p. 524. ISBN 978-0-521-36291-7.
- Kobyliński, Zbigniew (2005). «The Slavs». In Fouracre, Paul (ed.). The New Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 1: c.500–c.700. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-36291-7.
- Obolensky, Dimitri (1974) [1971]. The Byzantine Commonwealth: Eastern Europe, 500-1453. London: Cardinal. ISBN 9780351176449.
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of the Byzantine State. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Portal, Roger (1969) [1965]. The Slavs. Translated by Evans, Patrick (Translated from French ed.). Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 9780297763130.
- Runciman, Steven (1930). A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. London: G. Bell & Sons. ISBN 9780598749222.
- Samardžić, Radovan; Duškov, Milan, eds. (1993). Serbs in European Civilization. Belgrade: Nova, Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Institute for Balkan Studies. ISBN 9788675830153.
- Singleton, Fred (1985). A Short History of the Yugoslav Peoples. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27485-2.
- Stavrianos, Leften Stavros (2000). The Balkans Since 1453. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. ISBN 978-1-85065-551-0.
- Vlasto, Alexis P. (1970). The Entry of the Slavs into Christendom: An Introduction to the Medieval History of the Slavs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521074599.
- Živković, Tibor (2002). Јужни Словени под византијском влашћу 600-1025 [South Slavs under the Byzantine Rule (600–1025)]. Belgrade: Историјски институт САНУ. ISBN 9788677430276.
- Živković, Tibor (2008). Forging unity: The South Slavs between East and West 550–1150. Belgrade: The Institute of History, Čigoja štampa. ISBN 9788675585732.
- Journals
- Gitelman, Zvi; Hajda, Lubomyr A.; Himka, John-Paul; Solchanyk, Roman, eds. (2000). Cultures and Nations of Central and Eastern Europe: Essays in Honor of Roman Szporluk. Ukrainian Research Institute, Harvard University. ISBN 978-0-916458-93-5.
Further reading[edit]
Media related to South Slavs at Wikimedia Commons
- Jelavich, C., 1990. South Slav nationalisms—textbooks and Yugoslav Union before 1914. Ohio State Univ Pr.
- Petkov, K., 1997. Infidels, Turks, and women: the South Slavs in the German mind; ca. 1400–1600. Lang.
- Ferjančić, B., 2009. Vizantija i južni Sloveni. Ethos.
- Kovacevic, M.G.J., 1950. Pregled materijalne kulture Juznih Slovena.
- Filipovic, M.S., 1963. Forms and functions of ritual kinship among South Slavs. In V Congres international des sciences anthropologiques et ethnologiques (pp. 77–80).
- Šarić, L., 2004. Balkan identity: Changing self-images of the South Slavs. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural development, 25(5–6), pp. 389–407.
- Ostrogorsky, G., 1963. Byzantium and the South Slavs. The Slavonic and East European Review, 42(98), pp. 1–14.

Countries where a South Slavic language is the national language Countries where other Slavic languages are the national language |
| Total population |
|---|
| c. 30 million |
| Regions with significant populations |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovenia |
| Languages |
| Eastern South Slavic: Bulgarian Macedonian Western South Slavic: Serbo-Croatian (Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, Serbian) Slovene |
| Religion |
(Bulgarians, Macedonians, Montenegrins and Serbs)[citation needed]
|
| Related ethnic groups |
| Other Slavs |
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs, and Slovenes, respectively the main populations of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia.
In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning «South Slavia» or «South Slavdom») united majority of South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of Yugoslavia emerged in the late 17th century Croatia, at the time party of Habsburg monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, was proclaimed on 1 December 1918, following the unification of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs with the kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro. With the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, several independent sovereign states were formed. The term «Yugoslavs» was and sometimes still is used as a synonym for «South Slavs», but frequently excludes Bulgarians, and sometimes only refers to the citizens or inhabitants of former Yugoslavia, or only to those who officially registered themselves as ethnic Yugoslavs.
Terminology[edit]
The South Slavs are known in Serbian, Macedonian and Montenegrin as Južni Sloveni (Cyrillic: Јужни Словени); in Bulgarian as Yuzhni Slavyani (Cyrillic: Южни славяни); in Croatian and Bosnian as Južni Slaveni; in Slovene as Južni Slovani. The Slavic root *jugъ means «south». The Slavic ethnonym itself was used by 6th-century writers to describe the southern group of Early Slavs (the Sclaveni); West Slavs were called Veneti and East Slavs Antes.[1] The South Slavs are also called «Balkan Slavs»,[2]
Another name popular in the early modern period was «Illyrians», the name of a pre-Slavic Balkan people, a name first adopted by Dalmatian intellectuals in the late 15th century to refer to South Slavic lands and population.[3] It was then used by the Habsburg monarchy, France, and notably adopted by the 19th-century Croatian Illyrian movement.[4] Eventually, the idea of Yugoslavism appeared, aimed at uniting all South Slav-populated territories into a common state. From this idea emerged Yugoslavia, which however did not include Bulgaria.[citation needed]
History[edit]
Early South Slavs[edit]
The Proto-Slavic homeland is the area of Slavic settlement in Central and Eastern Europe during the first millennium AD, with its precise location debated by archaeologists, ethnographers and historians.[5] None of the proposed homelands reaches the Volga River in the east, over the Dinaric Alps in the southwest or the Balkan Mountains in the south, or past Bohemia in the west.[6] Traditionally, scholars put it in the marshes of Ukraine, or alternatively between the Bug and the Dnieper;[7] however, according to F. Curta, the homeland of the southern Slavs mentioned by 6th-century writers was just north of the Lower Danube.[8] Little is known about the Slavs before the 5th century, when they began to spread out in all directions.[citation needed]
Jordanes, Procopius and other late Roman authors provide the probable earliest references to southern Slavs in the second half of the 6th century.[9] Procopius described the Sclaveni and Antes as two barbarian peoples with the same institutions and customs since ancient times, not ruled by a single leader but living under democracy,[10] while Pseudo-Maurice called them a numerous people, undisciplined, unorganized and leaderless, who did not allow enslavement and conquest, and resistant to hardship, bearing all weathers.[11] They were portrayed by Procopius as unusually tall and strong, of dark skin and «reddish» hair (neither blond nor black), leading a primitive life and living in scattered huts, often changing their residence.[12] Procopius said they were henotheistic, believing in the god of lightning (Perun), the ruler of all, to whom they sacrificed cattle.[12] They went into battle on foot, charging straight at their enemy, armed with spears and small shields, but they did not wear armour.[12]
While archaeological evidence for a large-scale migration is lacking, most present-day historians claim that Slavs invaded and settled the Balkans in the 6th and 7th centuries.[13] According to this dominant narrative, up until the late 560s their main activity across the Danube was raiding, though with limited Slavic settlement mainly through Byzantine colonies of foederati.[14] The Danube and Sava frontier was overwhelmed by large-scale Slavic settlement in the late 6th and early 7th century.[15] What is today central Serbia was an important geo-strategical province, through which the Via Militaris crossed.[16] This area was frequently intruded upon by barbarians in the 5th and 6th centuries.[16] From the Danube, the Slavs commenced raiding the Byzantine Empire on an annual basis from the 520s, spreading destruction, taking loot and herds of cattle, seizing prisoners and taking fortresses. Often, the Byzantine Empire was stretched, defending its rich Asian provinces from Arabs, Persians and others. This meant that even numerically small, disorganised early Slavic raids were capable of causing much disruption, but could not capture the larger, fortified cities.[14] The first Slavic raid south of the Danube was recorded by Procopius, who mentions an attack of the Antes, «who dwell close to the Sclaveni», probably in 518.[17] Sclaveni are first mentioned in the context of the military policy on the Danube frontier of Byzantine Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565).[18] Throughout the century, Slavs raided and plundered deep into the Balkans, from Dalmatia to Greece and Thrace, and were also at times recruited as mercenaries, fighting the Ostrogoths.[19] Justinian seems to have used the strategy of ‘divide and conquer’, and the Sclaveni and Antes are mentioned as fighting each other.[20] The Antes are last mentioned as anti-Byzantine belligerents in 545, and the Sclaveni continued to raid the Balkans.[21] In 558 the Avars arrived at the Black Sea steppe, and defeated the Antes between the Dnieper and Dniester.[22] The Avars subsequently allied themselves with the Sclaveni,[23] although there was an episode in which the Sclavene Daurentius (fl. 577–579), the first Slavic chieftain recorded by name, dismissed Avar suzerainty and retorted that «Others do not conquer our land, we conquer theirs […] so it shall always be for us», and had the Avar envoys slain.[24] By the 580s, as the Slav communities on the Danube became larger and more organized, and as the Avars exerted their influence, raids became larger and resulted in permanent settlement. Most scholars consider the period of 581–584 as the beginning of large-scale Slavic settlement in the Balkans.[25] F. Curta points out that evidence of substantial Slavic presence does not appear before the 7th century and remains qualitatively different from the «Slavic culture» found north of the Danube.[26] In the mid-6th century, the Byzantines re-asserted their control of the Danube frontier, thereby reducing the economic value of Slavic raiding. This growing economic isolation, combined with external threats from the Avars and Byzantines, led to political and military mobilisation. Meanwhile, the itinerant form of agriculture (lacking crop rotation) may have encouraged micro-regional mobility. Seventh-century archaeological sites show earlier hamlet collections evolving into larger communities with differentiated zones for public feasts, craftmanship, etc.[27] It has been suggested that the Sclaveni were the ancestors of the Serbo-Croatian group while the Antes were that of the Bulgarian Slavs, with much mixture in the contact zones.[28][29] The diminished pre-Slavic inhabitants, also including Romanized native peoples,[a] fled from the barbarian invasions and sought refuge inside fortified cities and islands, whilst others fled to remote mountains and forests and adopted a transhumant lifestyle.[30] The Romance speakers within the fortified Dalmatian city-states managed to retain their culture and language for a long time.[31] Meanwhile, the numerous Slavs mixed with and assimilated the descendants of the indigenous population.[32]
Subsequent information about Slavs’ interaction with the Greeks and early Slavic states comes from the 10th-century De Administrando Imperio (DAI) by Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus, the 7th-century compilations of the Miracles of Saint Demetrius (MSD) and the History by Theophylact Simocatta. DAI mentions the beginnings of the Croatian, Serbian and Bulgarian states from the early 7th to the mid-10th century. MSD and Theophylact Simocatta mention the Slavic tribes in Thessaly and Macedonia at the beginning of the 7th century. The 9th-century Royal Frankish Annals (RFA) also mention Slavic tribes in contact with the Franks.[citation needed]
Middle Ages[edit]
By 700 AD, Slavs had settled in most of Central and Southeast Europe, from Austria even down to the Peloponnese of Greece, and from the Adriatic to the Black Sea, with the exception of the coastal areas and certain mountainous regions of the Greek peninsula.[33] The Avars, who arrived in Europe in the late 550s and had a great impact in the Balkans, had from their base in the Carpathian plain, west of main Slavic settlements, asserted control over Slavic tribes with whom they besieged Roman cities. Their influence in the Balkans however diminished by the early 7th century and they were finally defeated and disappeared as a power at the turn of the 9th century by Bulgaria and the Frankish Empire.[34] The first South Slavic polity and regional power was Bulgaria, a state formed in 681 as a union between the much numerous Slavic tribes and the bulgars of Khan Asparuh. The scattered Slavs in Greece, the Sklavinia, were Hellenized.[35] Romance-speakers lived within the fortified Dalmatian city-states.[31] Traditional historiography, based on DAI, holds that the migration of Serbs and Croats to the Balkans was part of a second Slavic wave, placed during Heraclius’ reign.[36]
Inhabiting the territory between the Franks in the north and Byzantium in the south, the Slavs were exposed to competing influences.[37] In 863 to Christianized Great Moravia were sent two Byzantine brothers monks Saints Cyril and Methodius, Slavs from Thessaloniki on missionary work. They created the Glagolitic script and the first Slavic written language, Old Church Slavonic, which they used to translate Biblical works. At the time, the West and South Slavs still spoke a similar language. The script used, Glagolitic, was capable of representing all Slavic sounds, however, it was gradually replaced in Bulgaria in the 9th century, in Russia by the 11th century[38] Glagolitic survived into the 16th century in Croatia, used by Benedictines and Franciscans, but lost importance during the Counter-Reformation when Latin replaced it on the Dalmatian coast.[39] Cyril and Methodius’ disciples found refuge in already Christian Bulgaria, where the Old Church Slavonic became the ecclesiastical language.[39] Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in Bulgaria.[40][41][42] The earliest Slavic literary works were composed in Bulgaria, Duklja and Dalmatia. The religious works were almost exclusively translations, from Latin (Croatia, Slovenia) and especially Greek (Bulgaria, Serbia).[39] In the 10th and 11th centuries the Old Church Slavonic led to the creation of various regional forms like Serbo-Croatian and Slovenian[39] Economic, religious and political centres of Ohrid and Preslav contributed to the important literary production in the Bulgarian Empire.[43] The Bogomil sect, derived from Manichaeism, was deemed heretical, but managed to spread from Bulgaria to Bosnia (where it gained a foothold),[44] and France (Cathars).[citation needed]
Carinthia came under Germanic rule in the 10th century and came permanently under Western (Roman) Christian sphere of influence.[45] What is today Croatia came under Eastern Roman (Byzantine) rule after the Barbarian age, and while most of the territory was Slavicized, a handful of fortified towns, with mixed population, remained under Byzantine authority and continued to use Latin.[45] Dalmatia, now applied to the narrow strip with Byzantine towns, came under the Patriarchate of Constantinople, while the Croatian state remained pagan until Christianization during the reign of Charlemagne, after which religious allegiance was to Rome.[45] Croats threw off Frankish rule in the 9th century and took over the Byzantine Dalmatian towns, after which Hungarian conquest led to Hungarian suzerainty, although retaining an army and institutions.[46] Croatia lost much of Dalmatia to the Republic of Venice which held it until the 18th century.[47] Hungary governed Croatia through a duke, and the coastal towns through a ban.[47] A feudal class emerged in the Croatian hinterland in the late 13th century, among whom were the Kurjaković, Kačić and most notably the Šubić.[48] Dalmatian fortified towns meanwhile maintained autonomy, with a Roman patrician class and Slavic lower class, first under Hungary and then Venice after centuries of struggle.[49]
Ibn al-Faqih described two kinds of South Slavic people, the first of swarthy complexion and dark hair, living near the Adriatic coast, and the other as light, living in the hinterland.[citation needed]
Early modern period[edit]
Through Islamization, communities of Slavic Muslims emerged, which survive until today in Bosnia, south Serbia, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria.[citation needed]
While Pan-Slavism has its origins in the 17th-century Slavic Catholic clergymen in the Republic of Venice and Republic of Ragusa, it crystallized only in the mid-19th century amidst rise of nationalism in the Ottoman and Habsburg empires.[citation needed]
Population[edit]
Languages[edit]
The South Slavic languages, one of three branches of the Slavic languages family (the other being West Slavic and East Slavic), form a dialect continuum. It comprises, from west to east, the official languages of Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Serbia, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria. The South Slavic languages are geographically divided from the rest of the Slavic languages by areas where Germanic (Austria), Hungarian and Romanian languages prevail.
South Slavic standard languages are:
The Serbo-Croatian varieties have strong structural unity and are regarded by most linguists as constituting one language.[50] Today, language secessionism has led to the codification of several distinct standards: Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin. These Serbo-Croatian standards are all based on the Shtokavian dialect group. Other dialect groups, which have lower intelligibility with Shtokavian, are Chakavian in Dalmatia and Kajkavian in Croatia proper. The dominance of Shtokavian across Serbo-Croatian speaking lands is due to historical westward migration during the Ottoman period. Slovene is South Slavic but has many features shared with West Slavic languages. The Prekmurje Slovene and Kajkavian are especially close, and there is no sharp delineation between them. In southeastern Serbia, dialects enter a transitional zone with Bulgarian and Macedonian, with features of both groups, and are commonly called Torlakian. The Eastern South Slavic languages are Bulgarian and Macedonian. Bulgarian has retained more archaic Slavic features in relation to the other languages. Bulgarian has two main yat splits. Macedonian was codified in Communist Yugoslavia in 1945. The Macedonian dialects, divided into three main groups, are regarded overall as being transitional to Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian. The westernmost Bulgarian dialects (called Shopi) share features with Serbo-Croatian. Furthermore, in Greece there is a notable Slavic-speaking population in Greek Macedonia and western Thrace. Balkan Slavic languages are part of a «Balkan sprachbund» with areal features shared with other non-Slavic languages in the Balkans.[citation needed]
Genetics[edit]
Admixture analysis of autosomal SNPs of the Balkan region in a global context on the resolution level of 7 assumed ancestral populations: the African (brown), South/West European (light blue), Asian (yellow), Middle Eastern (orange), South Asian (green), North/East European (dark blue) and beige Caucasus component.[51]
Autosomal analysis presenting the historical contribution of different donor groups in some European populations. Polish sample was selected to represent the Slavic influence, and it is suggesting a strong and early impact in Greece (30-37%), Romania (48-57%), Bulgaria (55-59%), and Hungary (54-84%).[52]
According to the 2013 autosomal IBD survey «of recent genealogical ancestry over the past 3,000 years at a continental scale», the speakers of Serbo-Croatian language share a very high number of common ancestors dated to the migration period approximately 1,500 years ago with Poland and Romania-Bulgaria cluster among others in Eastern Europe. It is concluded to be caused by the Hunnic and Slavic expansion, which was a «relatively small population that expanded over a large geographic area», particularly «the expansion of the Slavic populations into regions of low population density beginning in the sixth century» and that it is «highly coincident with the modern distribution of Slavic languages».[53] According to Kushniarevich et al. 2015, the Hellenthal et al. 2014 IBD analysis also found «multi-directional admixture events among East Europeans (both Slavic and non-Slavic), dated to around 1,000–1,600 YBP» which coincides with «the proposed time-frame for the Slavic expansion».[54] The Slavic influence is «dated to 500-900 CE or a bit later with over 40-50% among Bulgarians, Romanians, and Hungarians».[53] The 2015 IBD analysis found that the South Slavs have lower proximity to Greeks than with East and West Slavs and that there’s an «even patterns of IBD sharing among East-West Slavs–’inter-Slavic’ populations (Hungarians, Romanians and Gagauz)–and South Slavs, i.e. across an area of assumed historic movements of people including Slavs». The slight peak of shared IBD segments between South and East-West Slavs suggests a shared «Slavonic-time ancestry».[54] The 2014 IBD analysis comparison of Western Balkan and Middle Eastern populations also found negligible gene flow between 16th and 19th century during the Islamization of the Balkans.[51]
According to a 2014 admixture analysis of Western Balkan, the South Slavs show a genetic uniformity. The Bosnians and Croatians were more close to East European populations and largely overlapped with Hungarians from Central Europe.[51] In the 2015 analysis, they formed a western South Slavic cluster with the Bosnians and Slovenians in comparison to eastern cluster formed by Macedonians and Bulgarians with Serbians in the middle. The western cluster has an inclination toward Hungarians, Czechs, and Slovaks, while the eastern cluster toward Romanians and some extent Greeks.[54] The modeled ancestral genetic component of Balto-Slavs among South Slavs was between 55 and 70%.[54] In the 2018 analysis of Slovenian population, the Slovenian population clustered with Croatians, Hungarians and was close to Czech.[55]
The 2006 Y-DNA study results «suggest that the Slavic expansion started from the territory of present-day Ukraine, thus supporting the hypothesis that places the earliest known homeland of Slavs in the basin of the middle Dnieper».[56] According to genetic studies until 2020, the distribution, variance and frequency of the Y-DNA haplogroups R1a and I2 and their subclades R-M558, R-M458 and I-CTS10228 among South Slavs are in correlation with the spreading of Slavic languages during the medieval Slavic expansion from Eastern Europe, most probably from the territory of present-day Ukraine and Southeastern Poland.[57][58][59][60][61][62][63]
See also[edit]
- Yugoslavs
- East Slavs
- West Slavs
- List of Slavic studies journals
- Outline of Slavic history and culture
Annotations[edit]
- ^
Prior to the advent of Roman rule, a number of native or autochthonous populations had lived in the Balkans since ancient times. South of the Jireček line were the Greeks. To the north, there were Illyrians, Thracians and Dacians. They were mainly tribalistic and generally lacked awareness of any ethno-political affiliation. Over the classical ages, they were at times invaded, conquered and influenced by Celts, ancient Greeks and ancient Romans. Roman influence, however, was initially limited to cities concentrated along the Dalmatian coast, later spreading to a few scattered cities inside the Balkan interior, particularly along the river Danube (Sirmium, Belgrade, Niš). Roman citizens from throughout the empire settled in these cities and in the adjacent countryside. Following the fall of Rome and numerous barbarian raids, the population in the Balkans dropped, as did commerce and general standards of living. Many people were killed or taken prisoner by invaders. This demographic decline was particularly attributed to a drop in the number of indigenous peasants living in rural areas. They were the most vulnerable to raids and were also hardest hit by the financial crises that plagued the falling empire. However, the Balkans were not desolate, and considerable numbers of indigenous people remained. Only certain areas tended to be affected by the raids (e.g. lands around major land routes, such as the Morava corridor).[64] In addition to the autochthons, there were remnants of previous invaders such as «Huns» and various Germanic peoples when the Slavs arrived. Sarmatian tribes such as the Iazyges were still recorded as living in the Banat region of the Danube.[65] The mixing of Slavs and other peoples is evident in genetic studies included in the article.
- ^
The political status of Kosovo is disputed. Having unilaterally declared independence from Serbia in 2008, Kosovo is formally recognised as an independent state by 101 out of 193 (52.3%) UN member states (with another 13 recognising it at some point but then withdrawing their recognition), while Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own territory.
References[edit]
- ^ Kmietowicz 1976.
- ^ Kmietowicz 1976, Vlasto 1970
- ^ URI 2000, p. 104.
- ^ Hupchick 2004, p. 199.
- ^ Kobyliński 2005, pp. 525–526, Barford 2001, p. 37
- ^ Kobyliński 2005, p. 526, Barford 2001, p. 332
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 25.
- ^ Curta 2006, p. 56.
- ^ Curta 2001, pp. 71–73.
- ^ James 2014, p. 95, Kobyliński 1995, p. 524
- ^ Kobyliński 1995, pp. 524–525.
- ^ a b c Kobyliński 1995, p. 524.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 26–41.
- ^ a b Fine 1991, p. 29.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 33.
- ^ a b Živković 2002, p. 187.
- ^ James 2014, p. 95, Curta 2001, p. 75
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 76.
- ^ Curta 2001, pp. 78–86.
- ^ James 2014, p. 97.
- ^ Byzantinoslavica. Vol. 61–62. Academia. 2003. pp. 78–79.
- ^ Kobyliński 1995, p. 536.
- ^ Kobyliński 1995, p. 537–539.
- ^ Curta 2001, pp. 47, 91.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 31.
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 308.
- ^ Curta 2007, p. 61.
- ^ Hupchick 2004.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 26.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 37.
- ^ a b Fine 1991, p. 35.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 38, 41.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 36.
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 29–43.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 41.
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 66.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 90.
- ^ Portal 1969, pp. 90–92.
- ^ a b c d Portal 1969, p. 92.
- ^ Dvornik, Francis (1956). The Slavs: Their Early History and Civilization. Boston: American Academy of Arts and Sciences. p. 179.
The Psalter and the Book of Prophets were adapted or «modernized» with special regard to their use in Bulgarian churches, and it was in this school that glagolitic writing was replaced by the so-called Cyrillic writing, which was more akin to the Greek uncial, simplified matters considerably and is still used by the Orthodox Slavs.
- ^ Florin Curta (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge Medieval Textbooks. Cambridge University Press. pp. 221–222. ISBN 978-0521815390.
Cyrillic preslav.
- ^ J. M. Hussey, Andrew Louth (2010). «The Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire». Oxford History of the Christian Church. Oxford University Press. p. 100. ISBN 978-0191614880.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 93.
- ^ Portal 1969, pp. 93–95.
- ^ a b c Portal 1969, p. 96.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 96–97.
- ^ a b Portal 1969, p. 97.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 97–98.
- ^ Portal 1969, p. 98.
- ^ Comrie, Bernard & Corbett, Greville G., eds. (2002) [1st. Pub. 1993]. The Slavonic Languages. London & New York: Routledge. OCLC 49550401.
- ^ a b c L. Kovačević; et al. (2014). «Standing at the Gateway to Europe — The Genetic Structure of Western Balkan Populations Based on Autosomal and Haploid Markers». PLOS One. 9 (8): e105090. Bibcode:2014PLoSO…9j5090K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105090. PMC 4141785. PMID 25148043.
- ^ «Companion website for «A genetic atlas of human admixture history», Hellenthal et al, Science (2014)». A genetic atlas of human admixture history.
Hellenthal, Garrett; Busby, George B.J.; Band, Gavin; Wilson, James F.; Capelli, Cristian; Falush, Daniel; Myers, Simon (14 February 2014). «A Genetic Atlas of Human Admixture History». Science. 343 (6172): 747–751. Bibcode:2014Sci…343..747H. doi:10.1126/science.1243518. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 4209567. PMID 24531965.
Hellenthal, G.; Busby, G. B.; Band, G.; Wilson, J. F.; Capelli, C.; Falush, D.; Myers, S. (2014). «Supplementary Material for «A genetic atlas of human admixture history»«. Science. 343 (6172): 747–751. Bibcode:2014Sci…343..747H. doi:10.1126/science.1243518. PMC 4209567. PMID 24531965.S7.6 «East Europe»: The difference between the ‘East Europe I’ and ‘East Europe II’ analyses is that the latter analysis included the Polish as a potential donor population. The Polish were included in this analysis to reflect a Slavic language speaking source group.» «We speculate that the second event seen in our six Eastern Europe populations between northern European and southern European ancestral sources may correspond to the expansion of Slavic language speaking groups (commonly referred to as the Slavic expansion) across this region at a similar time, perhaps related to displacement caused by the Eurasian steppe invaders (38; 58). Under this scenario, the northerly source in the second event might represent DNA from Slavic-speaking migrants (sampled Slavic-speaking groups are excluded from being donors in the EastEurope I analysis). To test consistency with this, we repainted these populations adding the Polish as a single Slavic-speaking donor group («East Europe II» analysis; see Note S7.6) and, in doing so, they largely replaced the original North European component (Figure S21), although we note that two nearby populations, Belarus and Lithuania, are equally often inferred as sources in our original analysis (Table S12). Outside these six populations, an admixture event at the same time (910CE, 95% CI:720-1140CE) is seen in the southerly neighboring Greeks, between sources represented by multiple neighboring Mediterranean peoples (63%) and the Polish (37%), suggesting a strong and early impact of the Slavic expansions in Greece, a subject of recent debate (37). These shared signals we find across East European groups could explain a recent observation of an excess of IBD sharing among similar groups, including Greece, that was dated to a wide range between 1,000 and 2,000 years ago (37)
- ^ a b P. Ralph; et al. (2013). «The Geography of Recent Genetic Ancestry across Europe». PLOS Biology. 11 (5): e105090. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001555. PMC 3646727. PMID 23667324.
- ^ a b c d A. Kushniarevich; et al. (2015). «Genetic Heritage of the Balto-Slavic Speaking Populations: A Synthesis of Autosomal, Mitochondrial and Y-Chromosomal Data». PLOS One. 10 (9): e0135820. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1035820K. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135820. PMC 4558026. PMID 26332464.
- ^ P. M. Delser; et al. (2018). «Genetic Landscape of Slovenians: Past Admixture and Natural Selection Pattern». Frontiers in Genetics. 9: 551. doi:10.3389/fgene.2018.00551. PMC 6252347. PMID 30510563.
- ^ Rebała, K; Mikulich, AI; Tsybovsky, IS; Siváková, D; Dzupinková, Z; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A; Szczerkowska, Z (2007). «Y-STR variation among Slavs: Evidence for the Slavic homeland in the middle Dnieper basin». Journal of Human Genetics. 52 (5): 406–14. doi:10.1007/s10038-007-0125-6. PMID 17364156.
- ^ A. Zupan; et al. (2013). «The paternal perspective of the Slovenian population and its relationship with other populations». Annals of Human Biology. 40 (6): 515–526. doi:10.3109/03014460.2013.813584. PMID 23879710. S2CID 34621779.
However, a study by Battaglia et al. (2009) showed a variance peak for I2a1 in the Ukraine and, based on the observed pattern of variation, it could be suggested that at least part of the I2a1 haplogroup could have arrived in the Balkans and Slovenia with the Slavic migrations from a homeland in present-day Ukraine… The calculated age of this specific haplogroup together with the variation peak detected in the suggested Slavic homeland could represent a signal of Slavic migration arising from medieval Slavic expansions. However, the strong genetic barrier around the area of Bosnia and Herzegovina, associated with the high frequency of the I2a1b-M423 haplogroup, could also be a consequence of a Paleolithic genetic signal of a Balkan refuge area, followed by mixing with a medieval Slavic signal from modern-day Ukraine.
- ^ Underhill, Peter A. (2015), «The phylogenetic and geographic structure of Y-chromosome haplogroup R1a», European Journal of Human Genetics, 23 (1): 124–131, doi:10.1038/ejhg.2014.50, PMC 4266736, PMID 24667786,
R1a-M458 exceeds 20% in the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, and Western Belarus. The lineage averages 11–15% across Russia and Ukraine and occurs at 7% or less elsewhere (Figure 2d). Unlike hg R1a-M458, the R1a-M558 clade is also common in the Volga-Uralic populations. R1a-M558 occurs at 10–33% in parts of Russia, exceeds 26% in Poland and Western Belarus, and varies between 10 and 23% in the Ukraine, whereas it drops 10-fold lower in Western Europe. In general, both R1a-M458 and R1a-M558 occur at low but informative frequencies in Balkan populations with known Slavonic heritage.
- ^ O.M. Utevska (2017). Генофонд українців за різними системами генетичних маркерів: походження і місце на європейському генетичному просторі [The gene pool of Ukrainians revealed by different systems of genetic markers: the origin and statement in Europe] (PhD) (in Ukrainian). National Research Center for Radiation Medicine of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. pp. 219–226, 302.
- ^ Neparáczki, Endre; et al. (2019). «Y-chromosome haplogroups from Hun, Avar and conquering Hungarian period nomadic people of the Carpathian Basin». Scientific Reports. Nature Research. 9 (16569): 16569. Bibcode:2019NatSR…916569N. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53105-5. PMC 6851379. PMID 31719606.
Hg I2a1a2b-L621 was present in 5 Conqueror samples, and a 6th sample form Magyarhomorog (MH/9) most likely also belongs here, as MH/9 is a likely kin of MH/16 (see below). This Hg of European origin is most prominent in the Balkans and Eastern Europe, especially among Slavic speaking groups.
- ^ Pamjav, Horolma; Fehér, Tibor; Németh, Endre; Koppány Csáji, László (2019). Genetika és őstörténet (in Hungarian). Napkút Kiadó. p. 58. ISBN 978-963-263-855-3.
Az I2-CTS10228 (köznevén „dinári-kárpáti») alcsoport legkorábbi közös őse 2200 évvel ezelőttre tehető, így esetében nem arról van szó, hogy a mezolit népesség Kelet-Európában ilyen mértékben fennmaradt volna, hanem arról, hogy egy, a mezolit csoportoktól származó szűk család az európai vaskorban sikeresen integrálódott egy olyan társadalomba, amely hamarosan erőteljes demográfiai expanzióba kezdett. Ez is mutatja, hogy nem feltétlenül népek, mintsem családok sikerével, nemzetségek elterjedésével is számolnunk kell, és ezt a jelenlegi etnikai identitással összefüggésbe hozni lehetetlen. A csoport elterjedése alapján valószínűsíthető, hogy a szláv népek migrációjában vett részt, így válva az R1a-t követően a második legdominánsabb csoporttá a mai Kelet-Európában. Nyugat-Európából viszont teljes mértékben hiányzik, kivéve a kora középkorban szláv nyelvet beszélő keletnémet területeket.
- ^ Fóthi, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Fehér, T.; et al. (2020), «Genetic analysis of male Hungarian Conquerors: European and Asian paternal lineages of the conquering Hungarian tribes», Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 12 (1), doi:10.1007/s12520-019-00996-0,
Based on SNP analysis, the CTS10228 group is 2200 ± 300 years old. The group’s demographic expansion may have begun in Southeast Poland around that time, as carriers of the oldest subgroup are found there today. The group cannot solely be tied to the Slavs, because the proto-Slavic period was later, around 300–500 CE… The SNP-based age of the Eastern European CTS10228 branch is 2200 ± 300 years old. The carriers of the most ancient subgroup live in Southeast Poland, and it is likely that the rapid demographic expansion which brought the marker to other regions in Europe began there. The largest demographic explosion occurred in the Balkans, where the subgroup is dominant in 50.5% of Croatians, 30.1% of Serbs, 31.4% of Montenegrins, and in about 20% of Albanians and Greeks. As a result, this subgroup is often called Dinaric. It is interesting that while it is dominant among modern Balkan peoples, this subgroup has not been present yet during the Roman period, as it is almost absent in Italy as well (see Online Resource 5; ESM_5).
- ^ Kushniarevich, Alena; Kassian, Alexei (2020), «Genetics and Slavic languages», in Marc L. Greenberg (ed.), Encyclopedia of Slavic Languages and Linguistics Online, Brill, doi:10.1163/2589-6229_ESLO_COM_032367, retrieved 10 December 2020,
The geographic distributions of the major eastern European NRY haplogroups (R1a-Z282, I2a-P37) overlap with the area occupied by the present-day Slavs to a great extent, and it might be tempting to consider both haplogroups as Slavic-specic patrilineal lineages
- ^ Fine 1991, pp. 9–12, 37.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 57.
Sources[edit]
- Primary sources
- Moravcsik, Gyula, ed. (1967) [1949]. Constantine Porphyrogenitus: De Administrando Imperio (2nd revised ed.). Washington D.C.: Dumbarton Oaks Center for Byzantine Studies. ISBN 9780884020219.
- Scholz, Bernhard Walter, ed. (1970). Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard’s Histories. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472061860.
- Books
- Barford, Paul M. (2001). The Early Slavs: Culture and Society in Early Medieval Eastern Europe. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0801439779.
- Castellan, Georges (1992). History of the Balkans: From Mohammed the Conqueror to Stalin. East European Monographs. ISBN 978-0-88033-222-4.
- Curta, Florin (2001). The Making of the Slavs: History and Archaeology of the Lower Danube Region, c. 500–700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139428880.
- Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81539-0.
- Dvornik, Francis (1962). The Slavs in European History and Civilization. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press. ISBN 9780813507996.
- Fine, John V. A. Jr. (1991) [1983]. The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
- Fine, John V. A. Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (2005). When Ethnicity Did Not Matter in the Balkans: A Study of Identity in Pre-Nationalist Croatia, Dalmatia, and Slavonia in the Medieval and Early-Modern Periods. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472025600.
- Hupchick, Dennis P. (2004) [2002]. The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-6417-5.
- James, Edward (2014). Europe’s Barbarians AD 200-600. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-86825-5.
- Janković, Đorđe (2004). «The Slavs in the 6th Century North Illyricum». Гласник Српског археолошког друштва. 20: 39–61.
- Jelavich, Barbara (1983a). History of the Balkans: Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521274586.
- Jelavich, Barbara (1983b). History of the Balkans: Twentieth Century. Vol. 2. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521274593.
- Kaimakamova, Miliana; Salamon, Maciej (2007). Byzantium, new peoples, new powers: the Byzantino-Slav contact zone, from the ninth to the fifteenth century. Towarzystwo Wydawnicze «Historia Iagellonica». ISBN 978-83-88737-83-1.
- Kmietowicz, Frank A. (1976). Ancient Slavs. Worzalla Publishing Company.
- Kobyliński, Zbigniew (1995). The Slavs. The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 1, C.500-c.700. Cambridge University Press. p. 524. ISBN 978-0-521-36291-7.
- Kobyliński, Zbigniew (2005). «The Slavs». In Fouracre, Paul (ed.). The New Cambridge Medieval History, Volume 1: c.500–c.700. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-36291-7.
- Obolensky, Dimitri (1974) [1971]. The Byzantine Commonwealth: Eastern Europe, 500-1453. London: Cardinal. ISBN 9780351176449.
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of the Byzantine State. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Portal, Roger (1969) [1965]. The Slavs. Translated by Evans, Patrick (Translated from French ed.). Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 9780297763130.
- Runciman, Steven (1930). A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. London: G. Bell & Sons. ISBN 9780598749222.
- Samardžić, Radovan; Duškov, Milan, eds. (1993). Serbs in European Civilization. Belgrade: Nova, Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Institute for Balkan Studies. ISBN 9788675830153.
- Singleton, Fred (1985). A Short History of the Yugoslav Peoples. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27485-2.
- Stavrianos, Leften Stavros (2000). The Balkans Since 1453. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. ISBN 978-1-85065-551-0.
- Vlasto, Alexis P. (1970). The Entry of the Slavs into Christendom: An Introduction to the Medieval History of the Slavs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521074599.
- Živković, Tibor (2002). Јужни Словени под византијском влашћу 600-1025 [South Slavs under the Byzantine Rule (600–1025)]. Belgrade: Историјски институт САНУ. ISBN 9788677430276.
- Živković, Tibor (2008). Forging unity: The South Slavs between East and West 550–1150. Belgrade: The Institute of History, Čigoja štampa. ISBN 9788675585732.
- Journals
- Gitelman, Zvi; Hajda, Lubomyr A.; Himka, John-Paul; Solchanyk, Roman, eds. (2000). Cultures and Nations of Central and Eastern Europe: Essays in Honor of Roman Szporluk. Ukrainian Research Institute, Harvard University. ISBN 978-0-916458-93-5.
Further reading[edit]
Media related to South Slavs at Wikimedia Commons
- Jelavich, C., 1990. South Slav nationalisms—textbooks and Yugoslav Union before 1914. Ohio State Univ Pr.
- Petkov, K., 1997. Infidels, Turks, and women: the South Slavs in the German mind; ca. 1400–1600. Lang.
- Ferjančić, B., 2009. Vizantija i južni Sloveni. Ethos.
- Kovacevic, M.G.J., 1950. Pregled materijalne kulture Juznih Slovena.
- Filipovic, M.S., 1963. Forms and functions of ritual kinship among South Slavs. In V Congres international des sciences anthropologiques et ethnologiques (pp. 77–80).
- Šarić, L., 2004. Balkan identity: Changing self-images of the South Slavs. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural development, 25(5–6), pp. 389–407.
- Ostrogorsky, G., 1963. Byzantium and the South Slavs. The Slavonic and East European Review, 42(98), pp. 1–14.
|
|
Ю́жные славя́не — группа славянских народов и племён, говорящих на южнославянских языках и живущих преимущественно на Балканах.
Содержание
- 1 Юго-восточная группа
- 2 Юго-западная группа
- 2.1 Славяне-мусульмане
- 2.2 Историческая справка
- 3 Страны
- 4 Примечания
Юго-восточная группа
- болгары
- македонцы
Юго-западная группа
- сербы
- хорваты
- боснийцы (бошняки)
- черногорцы
- словенцы
Исторически, особенно во времена единой Югославии, существовала попытка к национальному объединению южных славян юго-западной подгруппы в единый супранациональный элемент — югославы.
Славяне-мусульмане
В группе южных славян, испытавших сильное турецкое влияние в эпоху Османской империи, особо выделяются славяне-мусульмане.
Историческая справка
Исторические племена, относящиеся к южным славянам:
- захлумляне
Страны
Есть семь стран, в которых южные славяне являются основным населением:[1]
Болгария (84 % болгары)
Сербия (82 % сербы, 2 % босняки, 1 % югославы, 1 % хорваты, 1 % черногорцы)
Хорватия (90 % хорваты, 4 % сербы, 1,7 % босняки)
Босния и Герцеговина (48 % босняки, 37 % сербы, 14 % хорваты)
Македония (65 % македонцы, 2 % сербы, 1 % босняки)
Словения (83 % словенцы, 2 % сербы, 2 % хорваты 1 % босняки)
Черногория (44,48 % черногорцы, 28,73 % сербы, 8,65 % бошняки, 3,31 % славяне-мусульмане, 0,97% хорваты, 0,34% сербы-черногорцы, 0,3% черногорцы-сербы, 0,19% югославы, 0,15% македонцы, 0,15% русские, 0,07% боснийцы, 0,06% словенцы, 0,04% мусульмане-черногорцы, 0,03% горанцы, 0,03% черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03% бошняки-мусульмане, 0,03% мусульмане-бошняки)
Вдобавок, есть традиционные значительные южнославянские меньшинства в неславянских соседних странах, таких как:
- Италия: (словенцы, хорваты)
- Австрия: (словенцы и хорваты которые признаются как меньшинства. 4 % граждан Австрии составляют босняки, сербы, хорваты и словенцы[источник не указан 270 дней].)
- Венгрия: (сербы, хорваты, словенцы)
- Румыния: (хорваты, болгары, сербы),
- Греция: (славяне в Греции)
- Турция: (босняки, болгары, македонцы)
- Албания: (болгары, македонцы, сербы, черногорцы)
Примечания
- ↑ CIA — The World Factbook
| |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Восточные славяне |
?Болоховцы? • Бужане • Волыняне • Вятичи • Древляне • Дреговичи • Дулебы • Кривичи • Полочане • Поляне • Радимичи • Северяне • Словене • Тиверцы • Уличи • Белые хорваты |
||||||||
| Западные славяне |
|
||||||||
| Южные славяне |
|
Ю́жные славя́не — современная группа славянских народов, а также племён, говорящих на южнославянских языках и живущих преимущественно на Балканах.
Юго-восточная группа
- болгары
- македонцы
Юго-западная группа
- сербы
- хорваты
- боснийцы (босняки)
- черногорцы
- словенцы
Исторически, особенно во времена единой Югославии, существовала попытка к национальному объединению южных славян юго-западной подгруппы в единый супранациональный элемент — югославы.
Славяне-мусульмане
В группе южных славян, испытавших сильное турецкое влияние в эпоху Османской империи, особо выделяются славяне-мусульмане.
Историческая справка
Исторические племена, относящиеся к южным славянам:
- захумляне
Комментарии
Страны
Есть семь стран, в которых южные славяне являются основным населением[1]:
Болгария (84 % болгары)
Сербия (82 % сербы, 2 % босняки, 1 % югославы, 1 % хорваты, 1 % черногорцы)
Хорватия (90 % хорваты, 4 % сербы, 1,7 % босняки)
Босния и Герцеговина (48 % босняки, 37 % сербы, 14 % хорваты)
Северная Македония (65 % македонцы, 2 % сербы, 1 % босняки)
Словения (83 % словенцы, 2 % сербы, 2 % хорваты 1 % босняки)
Черногория (44,98 % черногорцы, 28,73 % сербы, 8,65 % босняки, 3,31 % славяне-мусульмане, 0,97 % хорваты, 0,34 % сербы-черногорцы, 0,19 % югославы, 0,15 % македонцы, 0,07 % босняки, 0,06 % словенцы, 0,04 % черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03 % горанцы, 0,03 % черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03 % босняки-мусульмане)
Вдобавок, есть традиционные значительные южнославянские меньшинства в неславянских соседних странах, таких как:
- Италия: (словенцы, хорваты)
- Австрия: (словенцы и хорваты, которые признаются как меньшинства. 4 % граждан Австрии составляют боснийцы, сербы, хорваты)
- Венгрия: (сербы, хорваты, словенцы)
- Румыния: (хорваты, болгары, сербы),
- Греция: (славяне в Греции)
- Турция: (босняки, болгары, македонцы)
- Албания: (болгары, македонцы, сербы, черногорцы)
См. также
- Переселение славян на Балканы
- Славянская колонизация Восточных Альп
Примечания
- ↑ Этнические группы по странам (англ.) во Всемирной книге фактов ЦРУ
Литература
- Юго-Славяне // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.
Эта страница в последний раз была отредактирована 25 декабря 2022 в 13:28.
Как только страница обновилась в Википедии она обновляется в Вики 2.
Обычно почти сразу, изредка в течении часа.
Южными славянами называют сегодня группу народов, которые говорят на южнославянских языках. По географическому положению они занимают: Балканский полуостров, Альпы. К ним относятся: боснийцы, болгары, хорваты, македонцы, черногорцы, сербы, словенцы. Соответственно, проживающие в одноименных государствах.
История южных славян
В пятом веке нашей эры венеды (предки древних славян) распались на антов и склавинов. Обе этнические группы в шестом веке воевали с Византией. Причинами войн были противостояние племен из Европы с регионами (Черного и Средиземного морей), где сохранялось рабовладение. Около века длились эти войны. И в итоге славяне обосновались на территории реки Дунай и части Балкан. Так и образовалась группа южных славян.
Они пришли на Балканский полуостров примерно в пятом-седьмом веке нашей эры. Было их около сотни тысяч. По сравнению с другими народами и государствами это было очень маленькое количество. Славяне заселяли Альпы со стороны Австрии вплоть до Черного моря. Уже к концу шестого века появилось первое южнославянское государство – Склавиния. Но вскоре оно было разгромлено византийцами. В первой половине седьмого века славяне образовали Союз семи дунайских племен.
Почти одновременно со славянами на Балканы пришли тюркско-булгарские племена, основавшие Болгарское ханство. Оно достигло расцвета в девятом веке, завоевала почти весь Балканский полуостров. В десятом веке крестьяне восстали против феодального строя. Все это значительно подкосило власти Болгарского государства. Оно распалось в 1018 году с помощью Византии.
В девятом веке из появилось еще одно государство, сербское – Рашка. Тремя веками позже Рашка ассимилировала все сербские земли, став важнейшим на Балканах. Но сербские государства быстро приходили к концу. Причиной этого были внутренние проблемы, а также нападение Византии в одиннадцатом веке.
Когда начался упадок Византии, Болгария и Сербия стали набирать обороты. Но в 14 веке эти государства не смогли совладать с турками и были порабощены.
В период Средневековья существовала Австро-Венгрия, в которую входили Хорватия и Словения. Болгария же принадлежала Османии, позже – Турции.
Образ жизни и политическое устройство
- Основным занятием южнославянских племен было сельское хозяйство. Земледелие носило тип перелога. Так как земли были плодородны, то на одной площади можно было выращивать культуры два-три года подряд. Но когда земля «беднела», засевали другие участки.
- Также южнославянские народы занимались садоводством, выращивали виноград, оливковые деревья. Разумеется, широко было распространено скотоводство, особенно в горах и лесах. Разводили славяне и пчел.
- Известно, что они изготавливали оружие из металла, предметы домашнего обихода, украшения, изделия из кожи.
Ячейкой общества была патриархальная семья – задруг. Совокупность нескольких семей составляла соседскую общину. В результате появления государств появлялись князья, знать. На смену племенам приходили княжества.
Постепенно у южных славян зарождаются феодальные отношения, особенно это проявилось в Болгарском ханстве. Но нельзя недооценивать факт, что они появились на Балканах еще до заселения южных славян. Большая часть крестьян попадала в феодальную зависимость. Помимо этого они обязаны были платить налоги.
Феодальный строй приводи к росту посевных участков. Интенсивно происходила вырубка лесов для освоения земель.
- Развивались шелководческое, виноградное хозяйство.
- По данным археологов, в Болгарии были многочисленны гончарные и кузнечные мастерские.
Культура южных славян
Больше всего похвастаться культурным развитием могла Болгария. Входившие в ее состав племена объединились, сплотились. И это создание единого народа стало главной причиной культурного прогресса.
Во-первых, сформировался болгарский язык. Во-вторых, как следствие, возникла письменность. В-третьих, литература. Написанная на своеобразном болгарском языке, она резко отличалась от литературы других европейских стран, написанной на латыни. В книгах звучали патриотические нотки. В-четвертых, архитектура. Все постройки как бы показывали единство и силу Болгарского государства. В-пятых, музыка и живопись.
Конечно, и другие южнославянские государства происходили эти ступени. Просто немного медленнее и позже.
История славян в документах. Загадки происхождения.
Южные славяне
Ю́жные славя́не — современная группа славянских народов, а также племён, говорящих на южнославянских языках и живущих преимущественно на Балканах.
Юго-восточная группа
- болгары
- македонцы
Юго-западная группа
- сербы
- хорваты
- боснийцы (босняки)
- черногорцы
- словенцы
Исторически, особенно во времена единой Югославии, существовала попытка к национальному объединению южных славян юго-западной подгруппы в единый супранациональный элемент — югославы.
Славяне-мусульмане
В группе южных славян, испытавших сильное турецкое влияние в эпоху Османской империи, особо выделяются славяне-мусульмане.
Историческая справка
Исторические племена, относящиеся к южным славянам:
- захумляне
Комментарии
Страны
Есть семь стран, в которых южные славяне являются основным населением[1]:
Болгария (84 % болгары)
Сербия (82 % сербы, 2 % босняки, 1 % югославы, 1 % хорваты, 1 % черногорцы)
Хорватия (90 % хорваты, 4 % сербы, 1,7 % босняки)
Босния и Герцеговина (48 % босняки, 37 % сербы, 14 % хорваты)
Северная Македония (65 % македонцы, 2 % сербы, 1 % босняки)
Словения (83 % словенцы, 2 % сербы, 2 % хорваты 1 % босняки)
Черногория (44,98 % черногорцы, 28,73 % сербы, 8,65 % босняки, 3,31 % славяне-мусульмане, 0,97 % хорваты, 0,34 % сербы-черногорцы, 0,19 % югославы, 0,15 % македонцы, 0,07 % босняки, 0,06 % словенцы, 0,04 % черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03 % горанцы, 0,03 % черногорцы-мусульмане, 0,03 % босняки-мусульмане)
Вдобавок, есть традиционные значительные южнославянские меньшинства в неславянских соседних странах, таких как:
- Италия: (словенцы, хорваты)
- Австрия: (словенцы и хорваты, которые признаются как меньшинства. 4 % граждан Австрии составляют боснийцы, сербы, хорваты)
- Венгрия: (сербы, хорваты, словенцы)
- Румыния: (хорваты, болгары, сербы),
- Греция: (славяне в Греции)
- Турция: (босняки, болгары, македонцы)
- Албания: (болгары, македонцы, сербы, черногорцы)
См. также
- Переселение славян на Балканы
- Славянская колонизация Восточных Альп
Примечания
- ↑ Этнические группы по странам (англ.) во Всемирной книге фактов ЦРУ
Литература
- Юго-Славяне // Энциклопедический словарь Брокгауза и Ефрона : в 86 т. (82 т. и 4 доп.). — СПб., 1890—1907.





